User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Kids with food allergies the newest victims of COVID-19?
Food insecurity is not knowing how you will get your next meal. This pandemic has led to a lot of it, especially as a result of massive unemployment. Now imagine being in that situation with a food-allergic child. It would be frightening.
There is always a level of anxiety for parents of food-allergic children, but the Food and Drug Administration–mandated labeling of food allergens has helped to allay some of those concerns. Shopping can feel safer, even if it’s not foolproof.
Now, that fear for the safety of food-allergic children is going to be compounded by the FDA’s latest announcement, made at the behest of the food industry.
Disruptions in the food supply chain caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have created some problems for the food industry. The industry sought – and received – relief from the FDA; they are now allowing some ingredient substitutions without mandating a change in labeling. These changes were made without opportunity for public comment, according to the FDA, because of the exigency of the situation. Furthermore, the changes may stay in effect for an indeterminate period of time after the pandemic is deemed under control.
Labeling of gluten and the major eight allergens (peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and crustacean shellfish) cannot change under the new guidelines. The FDA also advised “consideration” of major food allergens recognized in other countries (sesame, celery, lupin, buckwheat, molluscan shellfish, and mustard). Of these, lupin is known to cross-react with peanut, and sesame seed allergy is increasingly prevalent. In fact, the FDA has considered adding it to the list of major allergens.
Meanwhile, according to this temporary FDA policy, substitutions should be limited to no more than 2% of the weight of the final product unless it is a variety of the same ingredient. The example provided is substitution of one type of mushroom for another, but even that could be an issue for the rare patient. And what if this is misinterpreted – as will surely happen somewhere – and one seed is substituted for another?
A friend of mine is a pediatrician and mother of a child who is allergic to sesame, peanuts, tree nuts, and garbanzo beans. Naturally, she had grave concerns about these changes. She also wondered what the liability would be for the food manufacturing company in the current situation despite the FDA notice, which seems like a valid point. It is worth noting that, at the very top of this FDA notice, are the words “contains nonbinding recommendations,” so manufacturers may want to think twice about how they approach this. A minority of companies have pledged to relabel foods if necessary. Meanwhile, without any alert in advance, it is now up to patients and their physicians to sort out the attendant risks.
The FDA should have advised or mandated that food manufacturers give notice to online and physical retailers of ingredient changes. A simple sign in front of a display or alert online would be a very reasonable solution and pose no burden to those involved. It should be self-evident that mistakes always happen, especially under duress, and that the loosening of these regulations will have unintended consequences. To the severe problem of food insecurity, we can add one more concern for the parents of allergic children: food-allergen insecurity.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Food insecurity is not knowing how you will get your next meal. This pandemic has led to a lot of it, especially as a result of massive unemployment. Now imagine being in that situation with a food-allergic child. It would be frightening.
There is always a level of anxiety for parents of food-allergic children, but the Food and Drug Administration–mandated labeling of food allergens has helped to allay some of those concerns. Shopping can feel safer, even if it’s not foolproof.
Now, that fear for the safety of food-allergic children is going to be compounded by the FDA’s latest announcement, made at the behest of the food industry.
Disruptions in the food supply chain caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have created some problems for the food industry. The industry sought – and received – relief from the FDA; they are now allowing some ingredient substitutions without mandating a change in labeling. These changes were made without opportunity for public comment, according to the FDA, because of the exigency of the situation. Furthermore, the changes may stay in effect for an indeterminate period of time after the pandemic is deemed under control.
Labeling of gluten and the major eight allergens (peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and crustacean shellfish) cannot change under the new guidelines. The FDA also advised “consideration” of major food allergens recognized in other countries (sesame, celery, lupin, buckwheat, molluscan shellfish, and mustard). Of these, lupin is known to cross-react with peanut, and sesame seed allergy is increasingly prevalent. In fact, the FDA has considered adding it to the list of major allergens.
Meanwhile, according to this temporary FDA policy, substitutions should be limited to no more than 2% of the weight of the final product unless it is a variety of the same ingredient. The example provided is substitution of one type of mushroom for another, but even that could be an issue for the rare patient. And what if this is misinterpreted – as will surely happen somewhere – and one seed is substituted for another?
A friend of mine is a pediatrician and mother of a child who is allergic to sesame, peanuts, tree nuts, and garbanzo beans. Naturally, she had grave concerns about these changes. She also wondered what the liability would be for the food manufacturing company in the current situation despite the FDA notice, which seems like a valid point. It is worth noting that, at the very top of this FDA notice, are the words “contains nonbinding recommendations,” so manufacturers may want to think twice about how they approach this. A minority of companies have pledged to relabel foods if necessary. Meanwhile, without any alert in advance, it is now up to patients and their physicians to sort out the attendant risks.
The FDA should have advised or mandated that food manufacturers give notice to online and physical retailers of ingredient changes. A simple sign in front of a display or alert online would be a very reasonable solution and pose no burden to those involved. It should be self-evident that mistakes always happen, especially under duress, and that the loosening of these regulations will have unintended consequences. To the severe problem of food insecurity, we can add one more concern for the parents of allergic children: food-allergen insecurity.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Food insecurity is not knowing how you will get your next meal. This pandemic has led to a lot of it, especially as a result of massive unemployment. Now imagine being in that situation with a food-allergic child. It would be frightening.
There is always a level of anxiety for parents of food-allergic children, but the Food and Drug Administration–mandated labeling of food allergens has helped to allay some of those concerns. Shopping can feel safer, even if it’s not foolproof.
Now, that fear for the safety of food-allergic children is going to be compounded by the FDA’s latest announcement, made at the behest of the food industry.
Disruptions in the food supply chain caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have created some problems for the food industry. The industry sought – and received – relief from the FDA; they are now allowing some ingredient substitutions without mandating a change in labeling. These changes were made without opportunity for public comment, according to the FDA, because of the exigency of the situation. Furthermore, the changes may stay in effect for an indeterminate period of time after the pandemic is deemed under control.
Labeling of gluten and the major eight allergens (peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and crustacean shellfish) cannot change under the new guidelines. The FDA also advised “consideration” of major food allergens recognized in other countries (sesame, celery, lupin, buckwheat, molluscan shellfish, and mustard). Of these, lupin is known to cross-react with peanut, and sesame seed allergy is increasingly prevalent. In fact, the FDA has considered adding it to the list of major allergens.
Meanwhile, according to this temporary FDA policy, substitutions should be limited to no more than 2% of the weight of the final product unless it is a variety of the same ingredient. The example provided is substitution of one type of mushroom for another, but even that could be an issue for the rare patient. And what if this is misinterpreted – as will surely happen somewhere – and one seed is substituted for another?
A friend of mine is a pediatrician and mother of a child who is allergic to sesame, peanuts, tree nuts, and garbanzo beans. Naturally, she had grave concerns about these changes. She also wondered what the liability would be for the food manufacturing company in the current situation despite the FDA notice, which seems like a valid point. It is worth noting that, at the very top of this FDA notice, are the words “contains nonbinding recommendations,” so manufacturers may want to think twice about how they approach this. A minority of companies have pledged to relabel foods if necessary. Meanwhile, without any alert in advance, it is now up to patients and their physicians to sort out the attendant risks.
The FDA should have advised or mandated that food manufacturers give notice to online and physical retailers of ingredient changes. A simple sign in front of a display or alert online would be a very reasonable solution and pose no burden to those involved. It should be self-evident that mistakes always happen, especially under duress, and that the loosening of these regulations will have unintended consequences. To the severe problem of food insecurity, we can add one more concern for the parents of allergic children: food-allergen insecurity.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
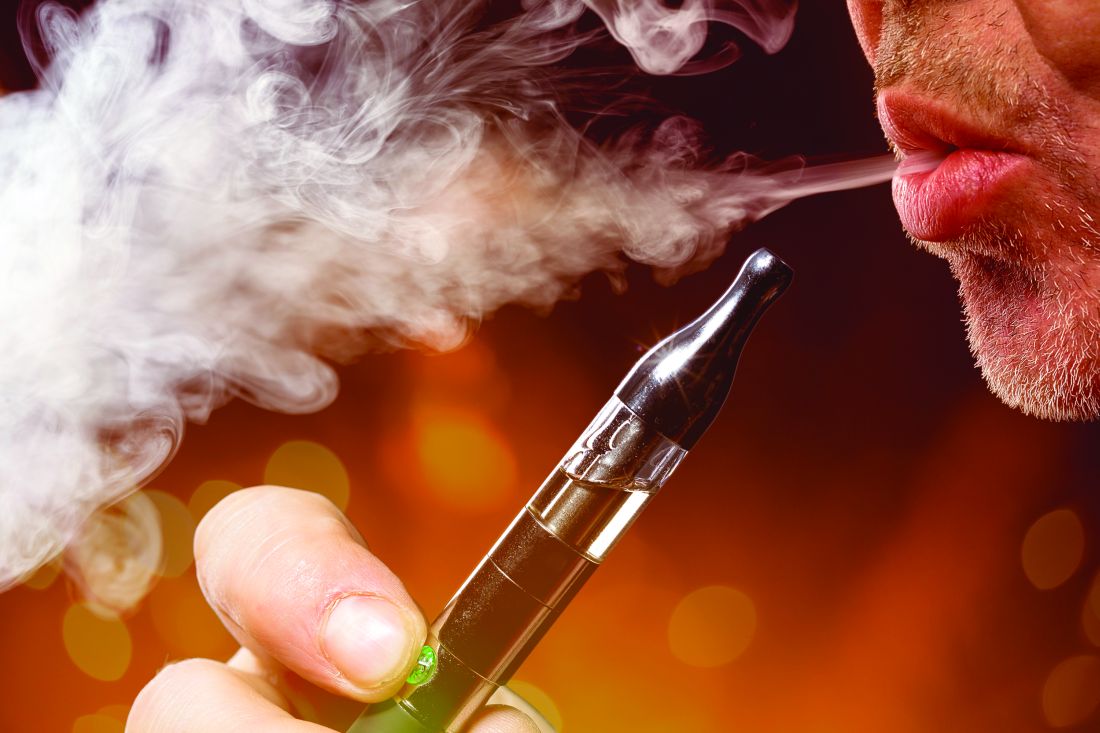
Former smokers using e-cigarettes at risk for cigarette smoking relapse
The use of , results from a large longitudinal cohort study demonstrated.
“For the many clinicians treating former smokers who have successfully quit all nicotine products, the implications are that use of [electronic nicotine delivery systems] should be discouraged, just as use of all other tobacco products is discouraged,” researchers led by Colm D. Everard, PhD, reported in a study published in JAMA Network Open (2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.4813).
Dr. Everard, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues based their comments on results from a survey of adult former smokers who participated in Waves 1-4 of the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study (2013-2018). They limited the analysis to 2,273 former cigarette smokers who self-reported reported no tobacco product use at Wave 1, and categorized them as recent former smokers (defined as having last smoked within the past 12 previous months) or as long-term former smokers (defined as having last smoked for longer ago than in the previous 12 months). The main outcome of interest was the self-reported current use of cigarettes at follow-up interviews, which was defined as every day or some days. Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) comprised e-cigarettes, e-cigars, e-pipes, and e-hookahs. Other tobacco products included cigars, pipe tobacco, hookahs, snus tobacco, other smokeless tobacco, and dissolvable tobacco.
Of the 2,273 adult former smokers, 52% were women, 60% were older than age 50, and 80% were non-Hispanic white. Adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) analysis revealed that the use of ENDS was associated with significant risk of cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.63) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.79). The use of other tobacco products was associated with significant risk for cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.97) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.82).
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it did not assess different ENDS devices, different e-liquid nicotine levels, or frequency of ENDS use and their associations with cigarette smoking relapse. It also did not explore the mechanism by which ENDS use may lead to reestablishing or reinforcing nicotine-seeking behavior among former cigarette users. “Determining pharmacologic, behavioral, or some other explanation for these findings may require laboratory-based research,” they wrote.
The PATH Study is supported with federal funds from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One of the study authors, Wilson M. Compton, MD, reported having long-term stock holdings in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer. The other authors reported having no financial disclosures.
The use of , results from a large longitudinal cohort study demonstrated.
“For the many clinicians treating former smokers who have successfully quit all nicotine products, the implications are that use of [electronic nicotine delivery systems] should be discouraged, just as use of all other tobacco products is discouraged,” researchers led by Colm D. Everard, PhD, reported in a study published in JAMA Network Open (2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.4813).
Dr. Everard, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues based their comments on results from a survey of adult former smokers who participated in Waves 1-4 of the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study (2013-2018). They limited the analysis to 2,273 former cigarette smokers who self-reported reported no tobacco product use at Wave 1, and categorized them as recent former smokers (defined as having last smoked within the past 12 previous months) or as long-term former smokers (defined as having last smoked for longer ago than in the previous 12 months). The main outcome of interest was the self-reported current use of cigarettes at follow-up interviews, which was defined as every day or some days. Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) comprised e-cigarettes, e-cigars, e-pipes, and e-hookahs. Other tobacco products included cigars, pipe tobacco, hookahs, snus tobacco, other smokeless tobacco, and dissolvable tobacco.
Of the 2,273 adult former smokers, 52% were women, 60% were older than age 50, and 80% were non-Hispanic white. Adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) analysis revealed that the use of ENDS was associated with significant risk of cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.63) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.79). The use of other tobacco products was associated with significant risk for cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.97) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.82).
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it did not assess different ENDS devices, different e-liquid nicotine levels, or frequency of ENDS use and their associations with cigarette smoking relapse. It also did not explore the mechanism by which ENDS use may lead to reestablishing or reinforcing nicotine-seeking behavior among former cigarette users. “Determining pharmacologic, behavioral, or some other explanation for these findings may require laboratory-based research,” they wrote.
The PATH Study is supported with federal funds from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One of the study authors, Wilson M. Compton, MD, reported having long-term stock holdings in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer. The other authors reported having no financial disclosures.
The use of , results from a large longitudinal cohort study demonstrated.
“For the many clinicians treating former smokers who have successfully quit all nicotine products, the implications are that use of [electronic nicotine delivery systems] should be discouraged, just as use of all other tobacco products is discouraged,” researchers led by Colm D. Everard, PhD, reported in a study published in JAMA Network Open (2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.4813).
Dr. Everard, of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and colleagues based their comments on results from a survey of adult former smokers who participated in Waves 1-4 of the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study (2013-2018). They limited the analysis to 2,273 former cigarette smokers who self-reported reported no tobacco product use at Wave 1, and categorized them as recent former smokers (defined as having last smoked within the past 12 previous months) or as long-term former smokers (defined as having last smoked for longer ago than in the previous 12 months). The main outcome of interest was the self-reported current use of cigarettes at follow-up interviews, which was defined as every day or some days. Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) comprised e-cigarettes, e-cigars, e-pipes, and e-hookahs. Other tobacco products included cigars, pipe tobacco, hookahs, snus tobacco, other smokeless tobacco, and dissolvable tobacco.
Of the 2,273 adult former smokers, 52% were women, 60% were older than age 50, and 80% were non-Hispanic white. Adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) analysis revealed that the use of ENDS was associated with significant risk of cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.63) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.79). The use of other tobacco products was associated with significant risk for cigarette smoking relapse among recent former smokers (AHR 1.97) and among long-term former smokers (AHR 3.82).
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it did not assess different ENDS devices, different e-liquid nicotine levels, or frequency of ENDS use and their associations with cigarette smoking relapse. It also did not explore the mechanism by which ENDS use may lead to reestablishing or reinforcing nicotine-seeking behavior among former cigarette users. “Determining pharmacologic, behavioral, or some other explanation for these findings may require laboratory-based research,” they wrote.
The PATH Study is supported with federal funds from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One of the study authors, Wilson M. Compton, MD, reported having long-term stock holdings in General Electric, 3M, and Pfizer. The other authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
WHO clarifies comments on asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2
A World Health Organization (WHO) official is walking back her comments characterizing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 by asymptomatic individuals as “rare.”
Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, caused a stir June 8 when she said that countries are reporting that many of their asymptomatic cases develop into cases of mild disease. For patients with truly asymptomatic disease, countries are “not finding secondary transmission onward. It’s very rare,” she said.
Suppressing symptomatic cases, on the other hand, would result in a “drastic reduction” in transmission, she noted. “But from the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” she said.
But on June 9 – following a day of confusion and criticism – Dr. Van Kerkhove sought to clarify her comments on asymptomatic transmission during a live social media Q&A. She noted that while “the majority of transmission that we know about” is through individuals with symptoms, “there are a subset of people who don’t develop symptoms, and to truly understand how many people don’t have symptoms – we don’t actually have that answer yet.”
Between 6% and 41% of individuals may be asymptomatic based on estimates, she acknowledged.“What we need to better understand is how many of the people in the population don’t have symptoms, and separately, how many of those individuals go on to transmit to others,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also emphasized that her initial comments were made in response to a question raised at the press conference, and called it a misunderstanding. “I wasn’t stating a policy of WHO or anything like that,” she said. “I was just trying to articulate what we know.”
The phrase “very rare” referred to a subset of studies and reports WHO had received from its member states following asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19. “I was referring to some detailed investigations, cluster investigations, case contact tracing, where we had reports from member states saying that, when we follow asymptomatic cases, it’s very rare – and I used the phrase very rare – that we found a secondary transmission,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove’s initial comments drew criticism from medical and public health professionals, who said the statement was “confusing” and communicated poorly.
Eric J. Topol, MD, tweeted that WHO had “engendered considerable confusion” with the comments about asymptomatic individuals rarely transmitting SARS-CoV-2. Dr. Topol, the author of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine that suggested as many as 40%-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic, said that it was not possible to determine whether asymptomatic individuals in the cohorts he studied were capable of spread like pre-symptomatic individuals. “We only know the viral loads are similar from multiple reports. And we do know some spread occurs from [asymptomatic] people,” he said.
Andy Slavitt, former acting administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, said in a tweet that he believed WHO made “an irresponsible statement even though it was based on legitimate observations.” Reports by Member States do not reach a “bar of rigor,” he said.
Natalie E. Dean, PhD, assistant professor of biostatistics at the University of Florida, tweeted that the initial comments by the WHO seemed to be trying to draw a distinction between asymptomatic individuals who never develop symptoms, and presymptomatic individuals who present as asymptomatic, but later develop symptoms. Finding that asymptomatic cases rarely transmit the virus could change how people exposed to those asymptomatic individuals are monitored, but “it seems more of scientific than practical interest,” she noted. “People without current symptoms could be infectious. Act accordingly.”
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, also weighed in on the controversial WHO comments, telling Good Morning America on June 10 that Dr. Van Kerkhove's initial statement that asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 transmission is a rare event is "not correct."
This article was updated 6/10/20.
A World Health Organization (WHO) official is walking back her comments characterizing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 by asymptomatic individuals as “rare.”
Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, caused a stir June 8 when she said that countries are reporting that many of their asymptomatic cases develop into cases of mild disease. For patients with truly asymptomatic disease, countries are “not finding secondary transmission onward. It’s very rare,” she said.
Suppressing symptomatic cases, on the other hand, would result in a “drastic reduction” in transmission, she noted. “But from the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” she said.
But on June 9 – following a day of confusion and criticism – Dr. Van Kerkhove sought to clarify her comments on asymptomatic transmission during a live social media Q&A. She noted that while “the majority of transmission that we know about” is through individuals with symptoms, “there are a subset of people who don’t develop symptoms, and to truly understand how many people don’t have symptoms – we don’t actually have that answer yet.”
Between 6% and 41% of individuals may be asymptomatic based on estimates, she acknowledged.“What we need to better understand is how many of the people in the population don’t have symptoms, and separately, how many of those individuals go on to transmit to others,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also emphasized that her initial comments were made in response to a question raised at the press conference, and called it a misunderstanding. “I wasn’t stating a policy of WHO or anything like that,” she said. “I was just trying to articulate what we know.”
The phrase “very rare” referred to a subset of studies and reports WHO had received from its member states following asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19. “I was referring to some detailed investigations, cluster investigations, case contact tracing, where we had reports from member states saying that, when we follow asymptomatic cases, it’s very rare – and I used the phrase very rare – that we found a secondary transmission,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove’s initial comments drew criticism from medical and public health professionals, who said the statement was “confusing” and communicated poorly.
Eric J. Topol, MD, tweeted that WHO had “engendered considerable confusion” with the comments about asymptomatic individuals rarely transmitting SARS-CoV-2. Dr. Topol, the author of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine that suggested as many as 40%-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic, said that it was not possible to determine whether asymptomatic individuals in the cohorts he studied were capable of spread like pre-symptomatic individuals. “We only know the viral loads are similar from multiple reports. And we do know some spread occurs from [asymptomatic] people,” he said.
Andy Slavitt, former acting administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, said in a tweet that he believed WHO made “an irresponsible statement even though it was based on legitimate observations.” Reports by Member States do not reach a “bar of rigor,” he said.
Natalie E. Dean, PhD, assistant professor of biostatistics at the University of Florida, tweeted that the initial comments by the WHO seemed to be trying to draw a distinction between asymptomatic individuals who never develop symptoms, and presymptomatic individuals who present as asymptomatic, but later develop symptoms. Finding that asymptomatic cases rarely transmit the virus could change how people exposed to those asymptomatic individuals are monitored, but “it seems more of scientific than practical interest,” she noted. “People without current symptoms could be infectious. Act accordingly.”
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, also weighed in on the controversial WHO comments, telling Good Morning America on June 10 that Dr. Van Kerkhove's initial statement that asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 transmission is a rare event is "not correct."
This article was updated 6/10/20.
A World Health Organization (WHO) official is walking back her comments characterizing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 by asymptomatic individuals as “rare.”
Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, caused a stir June 8 when she said that countries are reporting that many of their asymptomatic cases develop into cases of mild disease. For patients with truly asymptomatic disease, countries are “not finding secondary transmission onward. It’s very rare,” she said.
Suppressing symptomatic cases, on the other hand, would result in a “drastic reduction” in transmission, she noted. “But from the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” she said.
But on June 9 – following a day of confusion and criticism – Dr. Van Kerkhove sought to clarify her comments on asymptomatic transmission during a live social media Q&A. She noted that while “the majority of transmission that we know about” is through individuals with symptoms, “there are a subset of people who don’t develop symptoms, and to truly understand how many people don’t have symptoms – we don’t actually have that answer yet.”
Between 6% and 41% of individuals may be asymptomatic based on estimates, she acknowledged.“What we need to better understand is how many of the people in the population don’t have symptoms, and separately, how many of those individuals go on to transmit to others,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also emphasized that her initial comments were made in response to a question raised at the press conference, and called it a misunderstanding. “I wasn’t stating a policy of WHO or anything like that,” she said. “I was just trying to articulate what we know.”
The phrase “very rare” referred to a subset of studies and reports WHO had received from its member states following asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19. “I was referring to some detailed investigations, cluster investigations, case contact tracing, where we had reports from member states saying that, when we follow asymptomatic cases, it’s very rare – and I used the phrase very rare – that we found a secondary transmission,” she said.
Dr. Van Kerkhove’s initial comments drew criticism from medical and public health professionals, who said the statement was “confusing” and communicated poorly.
Eric J. Topol, MD, tweeted that WHO had “engendered considerable confusion” with the comments about asymptomatic individuals rarely transmitting SARS-CoV-2. Dr. Topol, the author of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine that suggested as many as 40%-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic, said that it was not possible to determine whether asymptomatic individuals in the cohorts he studied were capable of spread like pre-symptomatic individuals. “We only know the viral loads are similar from multiple reports. And we do know some spread occurs from [asymptomatic] people,” he said.
Andy Slavitt, former acting administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, said in a tweet that he believed WHO made “an irresponsible statement even though it was based on legitimate observations.” Reports by Member States do not reach a “bar of rigor,” he said.
Natalie E. Dean, PhD, assistant professor of biostatistics at the University of Florida, tweeted that the initial comments by the WHO seemed to be trying to draw a distinction between asymptomatic individuals who never develop symptoms, and presymptomatic individuals who present as asymptomatic, but later develop symptoms. Finding that asymptomatic cases rarely transmit the virus could change how people exposed to those asymptomatic individuals are monitored, but “it seems more of scientific than practical interest,” she noted. “People without current symptoms could be infectious. Act accordingly.”
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, also weighed in on the controversial WHO comments, telling Good Morning America on June 10 that Dr. Van Kerkhove's initial statement that asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 transmission is a rare event is "not correct."
This article was updated 6/10/20.
Age leads COVID-19 hospitalization risk factors in RMDs
Being aged older than 65 years was associated with the highest risk of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) needing hospital treatment for COVID-19, according to the first results to be reported from ReCoVery, the German national COVID-19 registry.
Older patients with RMDs were five times more likely than younger patients to be hospitalized if they tested positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and developed COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.3-11.4).
The likelihood of hospitalization was also significantly increased by the current or prior use of glucocorticoids (OR, 2.59; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4) and by the presence of cardiovascular disease (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4).
“The register is a joint initiative of the German Society for Rheumatology and the Justus Liebig University in Giessen,” explained Anne Regierer, MD, during a live session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“The current pandemic has changed all of our lives. For patients it brought a lot of uncertainty and fears,” said Dr. Regierer, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin.
“The risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRD] is still largely unknown. We still don’t know whether they have a high risk of getting the infection or whether they have a higher risk of a severer case ... therefore there’s an urgent need to have data to generate evidence for the management of our patients.”
Launched at the end of March 2020, the German registry now includes data on 251 patients – 194 of whom have recovered – provided by more than 200 registered rheumatologists. The registry data have now been integrated into the EULAR COVID-19 Database, which is itself part of a global effort to better understand and optimally manage RMD patients during the pandemic.
“The data presented by Dr. Regierer looked at similar outcomes and found quite similar results, which is reassuring,” Kimme Hyrich, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Manchester (England) and a consultant rheumatologist in the Kellgren Centre for Rheumatology at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, said in an interview.
“We are very grateful for this collaboration [with the German society and others]. Our first publication has looked at hospitalization, but with more data we may have the opportunity to look at less-common outcomes [e.g. death, other COVID complications] or within individual diseases or treatments. So far I don’t think we will come to a different conclusion,” observed Dr. Hyrich, who is on the steering committee for the EULAR COVID-19 Database.
“These initial data are reassuring in that the majority of cases of COVID reported to our database have recovered, including those who were hospitalized,” she said.
Current EULAR advice is to continue treatment with glucocorticoids in patients who are being chronically treated, but to use them at the lowest possible dose.
The objectives of this first analysis of the German registry was to provide a description of the patients who did and did not require hospitalization and those who needed ventilation, as well as look at possible risk factors for hospitalization.
Dr. Regierer reported that, of 192 patients they included – all with a positive lab test for SARS-CoV-2 – 128 (67%) did not require hospital admission. Of those that did (n = 64), 43 (22%) did not need ventilation and 21 (11%) did. Fifteen patients died, all of whom had been hospitalized, and all but one of them had needed ventilation.
Concerning the characteristics of the patients, those who needed hospital treatment with and without ventilation were older than those who were not admitted (70 vs. 65 vs. 54 years, respectively).
“Looking at the sexes, the gender distribution is also interesting. We see 69% females in the nonhospitalized patients, 65% of the inpatients without ventilation, but only 43% females in the ventilated patients. So in this group, the male patients are the majority,” Dr. Regierer observed.
Just over half of all patients in the nonhospitalized and the hospitalized without ventilation groups had IRD in remission, but those in the hospitalized with ventilation group less than one-fifth had their IRD under control.
“Of course we have to keep in mind the small sample sizes,” Dr. Regierer said, but the distribution of patients by disease type was “what you’d expect in clinical care.” The majority of patients in each of the three groups had RA (47%, 56%, and 57%), followed by psoriatic arthritis (19%, 7%, and 14%), axial spondyloarthritis (11%, 5%, and 0%), systemic lupus erythematosus (6%, 2%, and 0%), and vasculitis (1%, 5%, and 5%).
Patients who were hospitalized with and without ventilation were more likely to have more than one comorbidity than those who were not hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The most frequent comorbidity was cardiovascular disease with 58% and 76% in the inpatient groups,” Dr. Regierer reported. One-third of the nonhospitalized patients had a cardiovascular comorbidity.
“If we look at pulmonary disease, we see that 38% of the ventilator patients had an underlying pulmonary disease,” she added. This was in comparison with 19% of the hospitalized without ventilation and 13% of the nonhospitalized patients. Diabetes was another common comorbidity in hospitalized patients with (16%) and without (19%) ventilation versus just 2% of nonhospitalized patients. While these and other comorbidities such as chronic renal insufficiency were associated with higher odds ratios in the multivariate risk factor analysis, they did not reach statistical significance.
With regard to RMD treatments, more than 60% of patients in the hospitalized group had received treatment with glucocorticoids versus 37% of those who did not get admitted. No differences were seen for the other treatments.
Interestingly, “female sex, remission, and use of NSAIDs have an odds ratio smaller than 1. So there might be a lower risk of hospitalization associated with these factors,” Dr. Regierer said.
Dr. Regierer has received grant support and is part of speaker’s bureaus for a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hyrich disclosed grant income from Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, and Pfizer, and receiving speaker fees from AbbVie.
Being aged older than 65 years was associated with the highest risk of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) needing hospital treatment for COVID-19, according to the first results to be reported from ReCoVery, the German national COVID-19 registry.
Older patients with RMDs were five times more likely than younger patients to be hospitalized if they tested positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and developed COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.3-11.4).
The likelihood of hospitalization was also significantly increased by the current or prior use of glucocorticoids (OR, 2.59; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4) and by the presence of cardiovascular disease (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4).
“The register is a joint initiative of the German Society for Rheumatology and the Justus Liebig University in Giessen,” explained Anne Regierer, MD, during a live session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“The current pandemic has changed all of our lives. For patients it brought a lot of uncertainty and fears,” said Dr. Regierer, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin.
“The risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRD] is still largely unknown. We still don’t know whether they have a high risk of getting the infection or whether they have a higher risk of a severer case ... therefore there’s an urgent need to have data to generate evidence for the management of our patients.”
Launched at the end of March 2020, the German registry now includes data on 251 patients – 194 of whom have recovered – provided by more than 200 registered rheumatologists. The registry data have now been integrated into the EULAR COVID-19 Database, which is itself part of a global effort to better understand and optimally manage RMD patients during the pandemic.
“The data presented by Dr. Regierer looked at similar outcomes and found quite similar results, which is reassuring,” Kimme Hyrich, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Manchester (England) and a consultant rheumatologist in the Kellgren Centre for Rheumatology at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, said in an interview.
“We are very grateful for this collaboration [with the German society and others]. Our first publication has looked at hospitalization, but with more data we may have the opportunity to look at less-common outcomes [e.g. death, other COVID complications] or within individual diseases or treatments. So far I don’t think we will come to a different conclusion,” observed Dr. Hyrich, who is on the steering committee for the EULAR COVID-19 Database.
“These initial data are reassuring in that the majority of cases of COVID reported to our database have recovered, including those who were hospitalized,” she said.
Current EULAR advice is to continue treatment with glucocorticoids in patients who are being chronically treated, but to use them at the lowest possible dose.
The objectives of this first analysis of the German registry was to provide a description of the patients who did and did not require hospitalization and those who needed ventilation, as well as look at possible risk factors for hospitalization.
Dr. Regierer reported that, of 192 patients they included – all with a positive lab test for SARS-CoV-2 – 128 (67%) did not require hospital admission. Of those that did (n = 64), 43 (22%) did not need ventilation and 21 (11%) did. Fifteen patients died, all of whom had been hospitalized, and all but one of them had needed ventilation.
Concerning the characteristics of the patients, those who needed hospital treatment with and without ventilation were older than those who were not admitted (70 vs. 65 vs. 54 years, respectively).
“Looking at the sexes, the gender distribution is also interesting. We see 69% females in the nonhospitalized patients, 65% of the inpatients without ventilation, but only 43% females in the ventilated patients. So in this group, the male patients are the majority,” Dr. Regierer observed.
Just over half of all patients in the nonhospitalized and the hospitalized without ventilation groups had IRD in remission, but those in the hospitalized with ventilation group less than one-fifth had their IRD under control.
“Of course we have to keep in mind the small sample sizes,” Dr. Regierer said, but the distribution of patients by disease type was “what you’d expect in clinical care.” The majority of patients in each of the three groups had RA (47%, 56%, and 57%), followed by psoriatic arthritis (19%, 7%, and 14%), axial spondyloarthritis (11%, 5%, and 0%), systemic lupus erythematosus (6%, 2%, and 0%), and vasculitis (1%, 5%, and 5%).
Patients who were hospitalized with and without ventilation were more likely to have more than one comorbidity than those who were not hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The most frequent comorbidity was cardiovascular disease with 58% and 76% in the inpatient groups,” Dr. Regierer reported. One-third of the nonhospitalized patients had a cardiovascular comorbidity.
“If we look at pulmonary disease, we see that 38% of the ventilator patients had an underlying pulmonary disease,” she added. This was in comparison with 19% of the hospitalized without ventilation and 13% of the nonhospitalized patients. Diabetes was another common comorbidity in hospitalized patients with (16%) and without (19%) ventilation versus just 2% of nonhospitalized patients. While these and other comorbidities such as chronic renal insufficiency were associated with higher odds ratios in the multivariate risk factor analysis, they did not reach statistical significance.
With regard to RMD treatments, more than 60% of patients in the hospitalized group had received treatment with glucocorticoids versus 37% of those who did not get admitted. No differences were seen for the other treatments.
Interestingly, “female sex, remission, and use of NSAIDs have an odds ratio smaller than 1. So there might be a lower risk of hospitalization associated with these factors,” Dr. Regierer said.
Dr. Regierer has received grant support and is part of speaker’s bureaus for a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hyrich disclosed grant income from Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, and Pfizer, and receiving speaker fees from AbbVie.
Being aged older than 65 years was associated with the highest risk of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) needing hospital treatment for COVID-19, according to the first results to be reported from ReCoVery, the German national COVID-19 registry.
Older patients with RMDs were five times more likely than younger patients to be hospitalized if they tested positive for SARS‑CoV‑2 and developed COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.3-11.4).
The likelihood of hospitalization was also significantly increased by the current or prior use of glucocorticoids (OR, 2.59; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4) and by the presence of cardiovascular disease (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.2-5.4).
“The register is a joint initiative of the German Society for Rheumatology and the Justus Liebig University in Giessen,” explained Anne Regierer, MD, during a live session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“The current pandemic has changed all of our lives. For patients it brought a lot of uncertainty and fears,” said Dr. Regierer, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin.
“The risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRD] is still largely unknown. We still don’t know whether they have a high risk of getting the infection or whether they have a higher risk of a severer case ... therefore there’s an urgent need to have data to generate evidence for the management of our patients.”
Launched at the end of March 2020, the German registry now includes data on 251 patients – 194 of whom have recovered – provided by more than 200 registered rheumatologists. The registry data have now been integrated into the EULAR COVID-19 Database, which is itself part of a global effort to better understand and optimally manage RMD patients during the pandemic.
“The data presented by Dr. Regierer looked at similar outcomes and found quite similar results, which is reassuring,” Kimme Hyrich, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Manchester (England) and a consultant rheumatologist in the Kellgren Centre for Rheumatology at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, said in an interview.
“We are very grateful for this collaboration [with the German society and others]. Our first publication has looked at hospitalization, but with more data we may have the opportunity to look at less-common outcomes [e.g. death, other COVID complications] or within individual diseases or treatments. So far I don’t think we will come to a different conclusion,” observed Dr. Hyrich, who is on the steering committee for the EULAR COVID-19 Database.
“These initial data are reassuring in that the majority of cases of COVID reported to our database have recovered, including those who were hospitalized,” she said.
Current EULAR advice is to continue treatment with glucocorticoids in patients who are being chronically treated, but to use them at the lowest possible dose.
The objectives of this first analysis of the German registry was to provide a description of the patients who did and did not require hospitalization and those who needed ventilation, as well as look at possible risk factors for hospitalization.
Dr. Regierer reported that, of 192 patients they included – all with a positive lab test for SARS-CoV-2 – 128 (67%) did not require hospital admission. Of those that did (n = 64), 43 (22%) did not need ventilation and 21 (11%) did. Fifteen patients died, all of whom had been hospitalized, and all but one of them had needed ventilation.
Concerning the characteristics of the patients, those who needed hospital treatment with and without ventilation were older than those who were not admitted (70 vs. 65 vs. 54 years, respectively).
“Looking at the sexes, the gender distribution is also interesting. We see 69% females in the nonhospitalized patients, 65% of the inpatients without ventilation, but only 43% females in the ventilated patients. So in this group, the male patients are the majority,” Dr. Regierer observed.
Just over half of all patients in the nonhospitalized and the hospitalized without ventilation groups had IRD in remission, but those in the hospitalized with ventilation group less than one-fifth had their IRD under control.
“Of course we have to keep in mind the small sample sizes,” Dr. Regierer said, but the distribution of patients by disease type was “what you’d expect in clinical care.” The majority of patients in each of the three groups had RA (47%, 56%, and 57%), followed by psoriatic arthritis (19%, 7%, and 14%), axial spondyloarthritis (11%, 5%, and 0%), systemic lupus erythematosus (6%, 2%, and 0%), and vasculitis (1%, 5%, and 5%).
Patients who were hospitalized with and without ventilation were more likely to have more than one comorbidity than those who were not hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The most frequent comorbidity was cardiovascular disease with 58% and 76% in the inpatient groups,” Dr. Regierer reported. One-third of the nonhospitalized patients had a cardiovascular comorbidity.
“If we look at pulmonary disease, we see that 38% of the ventilator patients had an underlying pulmonary disease,” she added. This was in comparison with 19% of the hospitalized without ventilation and 13% of the nonhospitalized patients. Diabetes was another common comorbidity in hospitalized patients with (16%) and without (19%) ventilation versus just 2% of nonhospitalized patients. While these and other comorbidities such as chronic renal insufficiency were associated with higher odds ratios in the multivariate risk factor analysis, they did not reach statistical significance.
With regard to RMD treatments, more than 60% of patients in the hospitalized group had received treatment with glucocorticoids versus 37% of those who did not get admitted. No differences were seen for the other treatments.
Interestingly, “female sex, remission, and use of NSAIDs have an odds ratio smaller than 1. So there might be a lower risk of hospitalization associated with these factors,” Dr. Regierer said.
Dr. Regierer has received grant support and is part of speaker’s bureaus for a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hyrich disclosed grant income from Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, and Pfizer, and receiving speaker fees from AbbVie.
FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
COVID-19 drives nursing homes to overhaul infection control efforts
The toll that COVID-19 has taken on nursing homes and their postacute and long-term care residents has a multilayered backstory involving underresourced organizational structures, inherent susceptibilities, minimally trained infection prevention staff, variable abilities to isolate and quarantine large numbers of patients and residents, and a lack of governmental support.
“Nursing homes have been trying their best to combat this pandemic using the best infection control procedures they have, but blindfolded and with their hands tied behind their backs,” said Joseph G. Ouslander, MD, professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, which has teaching affiliations with three senior communities.
Nursing home leaders are debating how to best use testing to guide transmission-based precautions and isolation strategies and how to keep residents safe while allowing some socialization after months of conflicting guidance from public health officials (on testing and on sites of care for patients discharged from the hospital, for instance), with a lack of adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies, and with nursing home resident deaths estimated to account for at least one-quarter of the total COVID-19–related mortality in the United States.
“COVID is not going away [over the next couple of years],” said Michael Wasserman, MD, medical director of the Eisenberg Village at the Los Angeles Jewish Home and president of the California Association of Long-Term Care Medicine.
Dr. Wasserman and other experts in both long-term care and infectious disease said in interviews that, through the rest of the pandemic and beyond, nursing homes need the following:
- Full-time, well-trained “infection preventionists” – infection prevention managers, in essence – who can lead improvements in emergency preparedness and infection prevention and control (IPC)
- Medical directors who are well qualified and engaged
- A survey/inspection process that is educational and not solely punitive
- More resources and attention to structural reform
“If this pandemic doesn’t create significant change in the nursing home industry, nothing ever will,” Dr. Wasserman said.
Prepandemic experience
When Ghinwa Dumyati, MD, began working with nursing homes in early March to prevent and contain COVID-19 outbreaks, her focus was on PPE.
Nursing home staff were intimately familiar with standard precautions, and many had used contact precautions to prevent transmission of infections like Clostridioides difficile and Candida auris, as well as droplet precautions for influenza. With the threat of COVID-19, nursing homes “had a brand-new requirement to do both contact and droplet precautions – with a new need for eye protection – and in some situations, respiratory precautions with N95 masks,” said Dr. Dumyati, professor of medicine and director of communicable disease surveillance and prevention at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. “And on top of that, [staff] had to learn to conserve and reuse PPE.”
Staff had not been fit-tested for use of N95 respirators, she noted. “The only time an N95 was used in the nursing home prior to COVID-19,” she said, “was for a suspected tuberculosis patient [before hospital admission].”
Similarly, nursing homes had experience in quarantining units to prevent transmission of illnesses like influenza or norovirus – keeping residents in their rooms with no visitations or social activity, for instance – but never did they have to arrange “massive movements of residents to completely new units or parts of a unit,” said Dr. Dumyati, who also has led hospital and nursing home collaborative programs in Rochester to beat back C. difficile, and is now helping to formulate COVID-19 recommendations and guidance for members of AMDA – The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care.
As the SARS-CoV-2 virus began its spread through the United States, efforts to strengthen IPC programs in nursing homes in Rochester and elsewhere had been focused largely on multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and antibiotic stewardship – not on pandemic preparedness.
Reducing antibiotic use had become a national priority, and a 2016 rule by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services required nursing homes to develop, over a 3-year period, an IPC program that included an antibiotic stewardship component and employment of a trained infection preventionist on at least a half-time basis. Emergency preparedness (e.g., having alternate energy sources for a facility) was also included in the rule, but it was only in 2019 when CMS updated its “Requirements for Participation” rule to stipulate that emergency preparedness include planning for “emerging infectious diseases.”
“The 2016 regulations came about because infections were so problematic in nursing homes,” especially urinary tract infections, C. difficile, and drug-resistant infections, said Patricia Stone, PhD, RN, of the Center for Health Policy at the Columbia University School of Nursing, New York, who has published widely on infection prevention and control in nursing homes.
An analysis of IPC practices in 2014 and in 2018 suggests that the IPC-focused rules were helping, mainly with antibiotic stewardship programs but also with respect to some of the practices aimed at outbreak control, such as having policies in place for grouping infected residents together, instructing infected staff to stay home, and quarantining units on which outbreaks occur, Dr. Stone said. Policies for confining residents to rooms were reported by approximately 74% of nursing homes in 2014, and by approximately 87% in 2018, for instance. Overall, nursing homes were “getting better policies in place,” she said. The analysis compared data from two cross-sectional surveys of nursing homes conducted in 2014 and 2018 (945 and 888 facilities, respectively).
Nursing homes “have a long way to go,” however, with respect to the training of infection preventionists, Dr. Stone said. In 2014, her analysis shows, almost 65% of infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training and less than 3% were Certified in Infection Control (CIC) – a credential awarded by the Certification Board of Infection Control & Epidemiology. Of the 35% who had some form of official training, most completed state or local training courses.
The numbers improved slightly in 2018, with 7% of nursing homes reporting their infection preventionists had the highest-level certification, and 44% reporting that their infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training. Research has shown that infection-control training of any kind has a “strong effect” on IPC-related outcomes. While not demonstrated in research thus far, it seems plausible that “facilities with certified [infection preventionists] will have better processes in place,” said Dr. Stone, whose research has documented the need for more monitoring of staff compliance with hand-washing and other IPC procedures.
Infection preventionists in nursing homes typically have been directors of nursing or assistant directors of nursing who fold IPC responsibilities into a multitude of other responsibilities. Before the 2016 rules, some smaller facilities hired off-site consultants to do the job.
CMS upped the ante after several months of COVID-19, recommending in mid-May that nursing homes assign at least one individual with training in infection control “to provide on-site management of the IPC program.” The infection preventionists should be a “full-time role” in facilities that have more than 100 residents, the CMS guidance said. (Prior to the pandemic, CMS issued proposed regulations in 2019 that would modify the time an infection preventionist must devote to a facility from “part time” to “sufficient time.”)
However, neither the 2016 rule nor the most recent guidance on infection preventionists define the length or content of training.
Swati Gaur, MD, chair of the Infection Advisory Committee of AMDA and a certified medical director of two skilled nursing facilities in Gainesville, Ga., said that the pandemic “has really started to crystallize some of the limitations of having a very vague role, not just in terms of what an [infection preventionists] does [in the nursing home] but also the training,”
Fortunately, Dr. Gaur said, when SARS-CoV-2 struck, she had just transitioned her facilities’ designated infection preventionist to work full-time on the role. She had worked closely with her infection preventionist on IPC issues but wishes she had arranged for more rigorous independent training. “The role of the [infection preventionist] is huge and complicated,” now involving employee health, contract tracing, cohorting, isolation, and compliance with precautions and use of PPE, in addition to surveillance, data reporting, and communication with public health officials, she said.
“Facilities are finding out now that [the infection preventionist] cannot be an afterthought. And it won’t end with COVID. We have other respiratory illnesses like flu and other viruses that we struggle with all the time,” said Dr. Gaur, who is working alongside Dr. Dumyati and two other long-term care experts on AMDA’s COVID-19 guidance. The nursing homes that Dr. Gaur directs are part of the Northeast Georgia Health Care System and together include 271 beds.
Moving forward
IPC practices often collide with facilities’ role as a home, especially to those receiving long-term care. “We always have to measure what we do [to prevent and control infections] against patient autonomy and residents’ rights,” said Dr. Gaur. “We have struggled with these issues, prior to the pandemic. If patients are positive for multidrug resistant organisms [for instance], how long can they be isolated in their own rooms? You can’t for days and months put someone in a single room and create isolation. That’s where the science of infection prevention can collide with residents’ rights.”
Over the years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has acknowledged this discordance, leaving it to facilities to decide, for instance, whether to actively screen for colonization with MDROs. In 2019, to help nursing homes prevent the transmission of MDROs from residents who are colonized but not actively infected, the CDC introduced new “enhanced barrier precautions” that require the use of gowns and gloves for specific resident activities identified as having a high risk of MDRO transmission. The new category of precautions is less restrictive than traditional contact precautions, which keep residents in their rooms.
Infection control in nursing homes “isn’t where it needs to be ... but we’re always going to have in nursing homes a situation where there’s a high potential for rapid transmission of infectious disease,” said Christopher Crnich, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who chairs the long-term care special interest group of the Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America and has offered COVID-19 advice to his state’s department of public health.
“Anytime you have a congregative community, particularly one that involves susceptible hosts, there will be an intrinsically susceptible environment ... I’m a bit disturbed by the emphasis on saying, ‘This nursing home had a COVID-19 outbreak, therefore this nursing home did something wrong,’ ” Dr. Crnich said.
“How we mitigate the size of the outbreaks is where we need to focus our attention,” he said. The goal with SARS-CoV-2, he said, is to recognize its introduction “as rapidly as possible” and stop its spread through empiric symptom- and exposure-based isolation, multiple waves of targeted testing, widespread use of contact and droplet precautions, and isolating staff as necessary.
As awareness grew this year among long-term care leaders that relying too heavily on symptom-based strategies may not be effective to prevent introduction and transmission of SARS-CoV-2, a study published in April in the New England Journal of Medicine cemented the need for a testing strategy not limited to symptomatic individuals.
The study documented that more than half of residents in a nursing home who had positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and that most went on to develop symptoms. The study was conducted after one case of COVID-19 had been identified.
Some states issued calls this spring for “universal testing” of all nursing home patients and staff, and the CMS recommendations issued to state and local officials in mid-May for phased nursing home “reopening” call for baseline testing of all residents and staff, followed by retesting all residents weekly until all residents test negative and by retesting all staff continuing every week.
However, the experts contacted for this story said that, without a highly accurate and accessible point-of-care test (and even with one, considering the virus’ incubation period), a universal approach that includes all nursing home residents may have more limited value than is being touted. In many scenarios, they said, it is most meaningful to focus still-limited testing supplies on the staff, many of whom work at more than one facility and are believed to be primary vectors of SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Ouslander, Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders have been discussing testing at length, trying to reach consensus on best policies. “I don’t think there’s any uniform approach or uniform agreement,” said Dr. Ouslander. “For me, under ideal circumstances what needs to be done to protect older people in nursing homes is to get access to as many accurate viral tests as possible and test staff at least once a week or every 10 days.”
In some facilities, there may be an unspoken barrier to the frequent testing of staff: Fear that staff who test positive will need to be quarantined, with no one to take their place on the front line. Dr. Ouslander said he knows of one county health department that has discouraged nursing homes from testing asymptomatic staff. “It’s insane and truly shocking,” he said.
At the University of Rochester Medical Center, Dr. Dumyati said, staffing agencies are running short of nurse aide substitutes, and staffing issues have become the “biggest challenge” facing a regional multidisciplinary group of medical directors, hospital leaders, and health department officials who are working to troubleshoot COVID-19 issues. “Some of our nursing homes have ended up sending some of their residents to other nursing homes or to the hospital [because of the loss of staff],” she said.
Currently in the state of New York, she noted, COVID-19 patients may not be discharged to nursing homes until they test negative for the virus through PCR testing. “And some people don’t clear by PCR for 4-6 weeks.”
The barriers
Staffing shortages – real in some locales, and anticipated in others as economic reopening grows – are reflective of underlying structural and financial factors that work against optimal IPC, experts said. It’s not uncommon for certified nurse assistants (CNAs) to be assigned to 10-15 residents. And according to AMDA, 30%-46% of CNAs are reported to receive some form of public assistance. Low wages force many CNAs to work other jobs, including shifts at other nursing homes.
Turnover of nursing home leadership also creates problems. Dr. Crnich calls it “one of the biggest barriers” to effective IPC in nursing homes. “Facilities can tolerate some turnover in their front line staff,” he said, “as long as their leadership structure remains relatively stable.” Dr. Stone and her coinvestigators have documented at least yearly turnover in top positions: They found that, in 2018, approximately one-quarter of facilities reported employing three or more infection preventionists, three or more administrators, and three or more directors of nursing during the prior 3 years.
Medical directors, moreover, are not uniformly qualified, engaged with their facilities, or supported by nursing home administrators. “It’s an open secret, I think, that a lot of facilities want a medical director who is a good referral source,” said Dr. Gaur. “A medical director needs to be completely engaged in [quality improvement and] infection control practices.”
Some nursing home chains, she noted, “have realized the value of the medical director, and have changed the way they’re paying them. They’re actually holding them accountable [for quality and outcomes].”
Medical directors such as Dr. Wasserman, who previously oversaw a 74-facility nursing home chain in California as chief medical officer and then chief executive officer and has worked on nursing home quality improvement processes for his state, said there is much that can be done clinically to prevent the spread of infections, such as more frequent use of telemedicine, more attention to “deprescribing” unnecessary medications (which reduces the number of medication passes and, thus, the number of “transmission opportunities”), and the use of continuous remote monitoring. He has been trying to secure Bluetooth-enabled pulse oximetry and temperature monitoring for the Los Angeles Jewish Home and other facilities.
Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders believe that a more educational inspection process would also lead to improvements in IPC. “The punitive nature of the survey process is morally deflating to frontline staff [and] penalties take money away from operations,” Dr. Wasserman said. “It’s not a productive approach to quality improvement.”
Dr. Stone agreed. Infection control is now the primary focus of CMS’s inspection process, and she said that increased regulatory scrutiny of IPC beyond COVID-19 is a “good thing.” Her research has shown that most deficiencies identified by inspectors are infection control deficiencies, and that in 2014 and 2018, approximately one-third of nursing homes had infection control citations. (CMS recently increased penalties and fines for identified deficiencies.)
“But my hope would be that the survey process would be more educational [as it is for hospitals],” she said. “We need to be supporting nursing homes to do a better job.”
A silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic, as Dr. Stone sees it, is that nursing homes may be more engaged with data reporting and infection surveillance going forward. Nursing homes are now required to report their COVID-19 cases to the CDC through its hospital-dominant National Healthcare Safety Network, and the CDC has made technical changes that now make it “easier [than it was in the past] for nursing homes to join and participate,” she said. “Now that all nursing homes are engaged, will they be engaged post-COVID, too? I hope so. Surveillance [of infections] is a first step toward better outcomes.”
For now, said Dr. Crnich, the intensive prevention and mitigation efforts that are being required of nursing homes to minimize COVID-19’s impact is “a big deal and will tax the resources of most nursing homes and exceed the resources of many” without outside support, Dr. Crnich said. “This has been the most illuminating part of all this, and will probably require us to reconsider how we’re resourcing our nursing homes moving forward into the future.”
The toll that COVID-19 has taken on nursing homes and their postacute and long-term care residents has a multilayered backstory involving underresourced organizational structures, inherent susceptibilities, minimally trained infection prevention staff, variable abilities to isolate and quarantine large numbers of patients and residents, and a lack of governmental support.
“Nursing homes have been trying their best to combat this pandemic using the best infection control procedures they have, but blindfolded and with their hands tied behind their backs,” said Joseph G. Ouslander, MD, professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, which has teaching affiliations with three senior communities.
Nursing home leaders are debating how to best use testing to guide transmission-based precautions and isolation strategies and how to keep residents safe while allowing some socialization after months of conflicting guidance from public health officials (on testing and on sites of care for patients discharged from the hospital, for instance), with a lack of adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies, and with nursing home resident deaths estimated to account for at least one-quarter of the total COVID-19–related mortality in the United States.
“COVID is not going away [over the next couple of years],” said Michael Wasserman, MD, medical director of the Eisenberg Village at the Los Angeles Jewish Home and president of the California Association of Long-Term Care Medicine.
Dr. Wasserman and other experts in both long-term care and infectious disease said in interviews that, through the rest of the pandemic and beyond, nursing homes need the following:
- Full-time, well-trained “infection preventionists” – infection prevention managers, in essence – who can lead improvements in emergency preparedness and infection prevention and control (IPC)
- Medical directors who are well qualified and engaged
- A survey/inspection process that is educational and not solely punitive
- More resources and attention to structural reform
“If this pandemic doesn’t create significant change in the nursing home industry, nothing ever will,” Dr. Wasserman said.
Prepandemic experience
When Ghinwa Dumyati, MD, began working with nursing homes in early March to prevent and contain COVID-19 outbreaks, her focus was on PPE.
Nursing home staff were intimately familiar with standard precautions, and many had used contact precautions to prevent transmission of infections like Clostridioides difficile and Candida auris, as well as droplet precautions for influenza. With the threat of COVID-19, nursing homes “had a brand-new requirement to do both contact and droplet precautions – with a new need for eye protection – and in some situations, respiratory precautions with N95 masks,” said Dr. Dumyati, professor of medicine and director of communicable disease surveillance and prevention at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. “And on top of that, [staff] had to learn to conserve and reuse PPE.”
Staff had not been fit-tested for use of N95 respirators, she noted. “The only time an N95 was used in the nursing home prior to COVID-19,” she said, “was for a suspected tuberculosis patient [before hospital admission].”
Similarly, nursing homes had experience in quarantining units to prevent transmission of illnesses like influenza or norovirus – keeping residents in their rooms with no visitations or social activity, for instance – but never did they have to arrange “massive movements of residents to completely new units or parts of a unit,” said Dr. Dumyati, who also has led hospital and nursing home collaborative programs in Rochester to beat back C. difficile, and is now helping to formulate COVID-19 recommendations and guidance for members of AMDA – The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care.
As the SARS-CoV-2 virus began its spread through the United States, efforts to strengthen IPC programs in nursing homes in Rochester and elsewhere had been focused largely on multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and antibiotic stewardship – not on pandemic preparedness.
Reducing antibiotic use had become a national priority, and a 2016 rule by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services required nursing homes to develop, over a 3-year period, an IPC program that included an antibiotic stewardship component and employment of a trained infection preventionist on at least a half-time basis. Emergency preparedness (e.g., having alternate energy sources for a facility) was also included in the rule, but it was only in 2019 when CMS updated its “Requirements for Participation” rule to stipulate that emergency preparedness include planning for “emerging infectious diseases.”
“The 2016 regulations came about because infections were so problematic in nursing homes,” especially urinary tract infections, C. difficile, and drug-resistant infections, said Patricia Stone, PhD, RN, of the Center for Health Policy at the Columbia University School of Nursing, New York, who has published widely on infection prevention and control in nursing homes.
An analysis of IPC practices in 2014 and in 2018 suggests that the IPC-focused rules were helping, mainly with antibiotic stewardship programs but also with respect to some of the practices aimed at outbreak control, such as having policies in place for grouping infected residents together, instructing infected staff to stay home, and quarantining units on which outbreaks occur, Dr. Stone said. Policies for confining residents to rooms were reported by approximately 74% of nursing homes in 2014, and by approximately 87% in 2018, for instance. Overall, nursing homes were “getting better policies in place,” she said. The analysis compared data from two cross-sectional surveys of nursing homes conducted in 2014 and 2018 (945 and 888 facilities, respectively).
Nursing homes “have a long way to go,” however, with respect to the training of infection preventionists, Dr. Stone said. In 2014, her analysis shows, almost 65% of infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training and less than 3% were Certified in Infection Control (CIC) – a credential awarded by the Certification Board of Infection Control & Epidemiology. Of the 35% who had some form of official training, most completed state or local training courses.
The numbers improved slightly in 2018, with 7% of nursing homes reporting their infection preventionists had the highest-level certification, and 44% reporting that their infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training. Research has shown that infection-control training of any kind has a “strong effect” on IPC-related outcomes. While not demonstrated in research thus far, it seems plausible that “facilities with certified [infection preventionists] will have better processes in place,” said Dr. Stone, whose research has documented the need for more monitoring of staff compliance with hand-washing and other IPC procedures.
Infection preventionists in nursing homes typically have been directors of nursing or assistant directors of nursing who fold IPC responsibilities into a multitude of other responsibilities. Before the 2016 rules, some smaller facilities hired off-site consultants to do the job.
CMS upped the ante after several months of COVID-19, recommending in mid-May that nursing homes assign at least one individual with training in infection control “to provide on-site management of the IPC program.” The infection preventionists should be a “full-time role” in facilities that have more than 100 residents, the CMS guidance said. (Prior to the pandemic, CMS issued proposed regulations in 2019 that would modify the time an infection preventionist must devote to a facility from “part time” to “sufficient time.”)
However, neither the 2016 rule nor the most recent guidance on infection preventionists define the length or content of training.
Swati Gaur, MD, chair of the Infection Advisory Committee of AMDA and a certified medical director of two skilled nursing facilities in Gainesville, Ga., said that the pandemic “has really started to crystallize some of the limitations of having a very vague role, not just in terms of what an [infection preventionists] does [in the nursing home] but also the training,”
Fortunately, Dr. Gaur said, when SARS-CoV-2 struck, she had just transitioned her facilities’ designated infection preventionist to work full-time on the role. She had worked closely with her infection preventionist on IPC issues but wishes she had arranged for more rigorous independent training. “The role of the [infection preventionist] is huge and complicated,” now involving employee health, contract tracing, cohorting, isolation, and compliance with precautions and use of PPE, in addition to surveillance, data reporting, and communication with public health officials, she said.
“Facilities are finding out now that [the infection preventionist] cannot be an afterthought. And it won’t end with COVID. We have other respiratory illnesses like flu and other viruses that we struggle with all the time,” said Dr. Gaur, who is working alongside Dr. Dumyati and two other long-term care experts on AMDA’s COVID-19 guidance. The nursing homes that Dr. Gaur directs are part of the Northeast Georgia Health Care System and together include 271 beds.
Moving forward
IPC practices often collide with facilities’ role as a home, especially to those receiving long-term care. “We always have to measure what we do [to prevent and control infections] against patient autonomy and residents’ rights,” said Dr. Gaur. “We have struggled with these issues, prior to the pandemic. If patients are positive for multidrug resistant organisms [for instance], how long can they be isolated in their own rooms? You can’t for days and months put someone in a single room and create isolation. That’s where the science of infection prevention can collide with residents’ rights.”
Over the years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has acknowledged this discordance, leaving it to facilities to decide, for instance, whether to actively screen for colonization with MDROs. In 2019, to help nursing homes prevent the transmission of MDROs from residents who are colonized but not actively infected, the CDC introduced new “enhanced barrier precautions” that require the use of gowns and gloves for specific resident activities identified as having a high risk of MDRO transmission. The new category of precautions is less restrictive than traditional contact precautions, which keep residents in their rooms.
Infection control in nursing homes “isn’t where it needs to be ... but we’re always going to have in nursing homes a situation where there’s a high potential for rapid transmission of infectious disease,” said Christopher Crnich, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who chairs the long-term care special interest group of the Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America and has offered COVID-19 advice to his state’s department of public health.
“Anytime you have a congregative community, particularly one that involves susceptible hosts, there will be an intrinsically susceptible environment ... I’m a bit disturbed by the emphasis on saying, ‘This nursing home had a COVID-19 outbreak, therefore this nursing home did something wrong,’ ” Dr. Crnich said.
“How we mitigate the size of the outbreaks is where we need to focus our attention,” he said. The goal with SARS-CoV-2, he said, is to recognize its introduction “as rapidly as possible” and stop its spread through empiric symptom- and exposure-based isolation, multiple waves of targeted testing, widespread use of contact and droplet precautions, and isolating staff as necessary.
As awareness grew this year among long-term care leaders that relying too heavily on symptom-based strategies may not be effective to prevent introduction and transmission of SARS-CoV-2, a study published in April in the New England Journal of Medicine cemented the need for a testing strategy not limited to symptomatic individuals.
The study documented that more than half of residents in a nursing home who had positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and that most went on to develop symptoms. The study was conducted after one case of COVID-19 had been identified.
Some states issued calls this spring for “universal testing” of all nursing home patients and staff, and the CMS recommendations issued to state and local officials in mid-May for phased nursing home “reopening” call for baseline testing of all residents and staff, followed by retesting all residents weekly until all residents test negative and by retesting all staff continuing every week.
However, the experts contacted for this story said that, without a highly accurate and accessible point-of-care test (and even with one, considering the virus’ incubation period), a universal approach that includes all nursing home residents may have more limited value than is being touted. In many scenarios, they said, it is most meaningful to focus still-limited testing supplies on the staff, many of whom work at more than one facility and are believed to be primary vectors of SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Ouslander, Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders have been discussing testing at length, trying to reach consensus on best policies. “I don’t think there’s any uniform approach or uniform agreement,” said Dr. Ouslander. “For me, under ideal circumstances what needs to be done to protect older people in nursing homes is to get access to as many accurate viral tests as possible and test staff at least once a week or every 10 days.”
In some facilities, there may be an unspoken barrier to the frequent testing of staff: Fear that staff who test positive will need to be quarantined, with no one to take their place on the front line. Dr. Ouslander said he knows of one county health department that has discouraged nursing homes from testing asymptomatic staff. “It’s insane and truly shocking,” he said.
At the University of Rochester Medical Center, Dr. Dumyati said, staffing agencies are running short of nurse aide substitutes, and staffing issues have become the “biggest challenge” facing a regional multidisciplinary group of medical directors, hospital leaders, and health department officials who are working to troubleshoot COVID-19 issues. “Some of our nursing homes have ended up sending some of their residents to other nursing homes or to the hospital [because of the loss of staff],” she said.
Currently in the state of New York, she noted, COVID-19 patients may not be discharged to nursing homes until they test negative for the virus through PCR testing. “And some people don’t clear by PCR for 4-6 weeks.”
The barriers
Staffing shortages – real in some locales, and anticipated in others as economic reopening grows – are reflective of underlying structural and financial factors that work against optimal IPC, experts said. It’s not uncommon for certified nurse assistants (CNAs) to be assigned to 10-15 residents. And according to AMDA, 30%-46% of CNAs are reported to receive some form of public assistance. Low wages force many CNAs to work other jobs, including shifts at other nursing homes.
Turnover of nursing home leadership also creates problems. Dr. Crnich calls it “one of the biggest barriers” to effective IPC in nursing homes. “Facilities can tolerate some turnover in their front line staff,” he said, “as long as their leadership structure remains relatively stable.” Dr. Stone and her coinvestigators have documented at least yearly turnover in top positions: They found that, in 2018, approximately one-quarter of facilities reported employing three or more infection preventionists, three or more administrators, and three or more directors of nursing during the prior 3 years.
Medical directors, moreover, are not uniformly qualified, engaged with their facilities, or supported by nursing home administrators. “It’s an open secret, I think, that a lot of facilities want a medical director who is a good referral source,” said Dr. Gaur. “A medical director needs to be completely engaged in [quality improvement and] infection control practices.”
Some nursing home chains, she noted, “have realized the value of the medical director, and have changed the way they’re paying them. They’re actually holding them accountable [for quality and outcomes].”
Medical directors such as Dr. Wasserman, who previously oversaw a 74-facility nursing home chain in California as chief medical officer and then chief executive officer and has worked on nursing home quality improvement processes for his state, said there is much that can be done clinically to prevent the spread of infections, such as more frequent use of telemedicine, more attention to “deprescribing” unnecessary medications (which reduces the number of medication passes and, thus, the number of “transmission opportunities”), and the use of continuous remote monitoring. He has been trying to secure Bluetooth-enabled pulse oximetry and temperature monitoring for the Los Angeles Jewish Home and other facilities.
Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders believe that a more educational inspection process would also lead to improvements in IPC. “The punitive nature of the survey process is morally deflating to frontline staff [and] penalties take money away from operations,” Dr. Wasserman said. “It’s not a productive approach to quality improvement.”
Dr. Stone agreed. Infection control is now the primary focus of CMS’s inspection process, and she said that increased regulatory scrutiny of IPC beyond COVID-19 is a “good thing.” Her research has shown that most deficiencies identified by inspectors are infection control deficiencies, and that in 2014 and 2018, approximately one-third of nursing homes had infection control citations. (CMS recently increased penalties and fines for identified deficiencies.)
“But my hope would be that the survey process would be more educational [as it is for hospitals],” she said. “We need to be supporting nursing homes to do a better job.”
A silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic, as Dr. Stone sees it, is that nursing homes may be more engaged with data reporting and infection surveillance going forward. Nursing homes are now required to report their COVID-19 cases to the CDC through its hospital-dominant National Healthcare Safety Network, and the CDC has made technical changes that now make it “easier [than it was in the past] for nursing homes to join and participate,” she said. “Now that all nursing homes are engaged, will they be engaged post-COVID, too? I hope so. Surveillance [of infections] is a first step toward better outcomes.”
For now, said Dr. Crnich, the intensive prevention and mitigation efforts that are being required of nursing homes to minimize COVID-19’s impact is “a big deal and will tax the resources of most nursing homes and exceed the resources of many” without outside support, Dr. Crnich said. “This has been the most illuminating part of all this, and will probably require us to reconsider how we’re resourcing our nursing homes moving forward into the future.”
The toll that COVID-19 has taken on nursing homes and their postacute and long-term care residents has a multilayered backstory involving underresourced organizational structures, inherent susceptibilities, minimally trained infection prevention staff, variable abilities to isolate and quarantine large numbers of patients and residents, and a lack of governmental support.
“Nursing homes have been trying their best to combat this pandemic using the best infection control procedures they have, but blindfolded and with their hands tied behind their backs,” said Joseph G. Ouslander, MD, professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, which has teaching affiliations with three senior communities.
Nursing home leaders are debating how to best use testing to guide transmission-based precautions and isolation strategies and how to keep residents safe while allowing some socialization after months of conflicting guidance from public health officials (on testing and on sites of care for patients discharged from the hospital, for instance), with a lack of adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies, and with nursing home resident deaths estimated to account for at least one-quarter of the total COVID-19–related mortality in the United States.
“COVID is not going away [over the next couple of years],” said Michael Wasserman, MD, medical director of the Eisenberg Village at the Los Angeles Jewish Home and president of the California Association of Long-Term Care Medicine.
Dr. Wasserman and other experts in both long-term care and infectious disease said in interviews that, through the rest of the pandemic and beyond, nursing homes need the following:
- Full-time, well-trained “infection preventionists” – infection prevention managers, in essence – who can lead improvements in emergency preparedness and infection prevention and control (IPC)
- Medical directors who are well qualified and engaged
- A survey/inspection process that is educational and not solely punitive
- More resources and attention to structural reform
“If this pandemic doesn’t create significant change in the nursing home industry, nothing ever will,” Dr. Wasserman said.
Prepandemic experience
When Ghinwa Dumyati, MD, began working with nursing homes in early March to prevent and contain COVID-19 outbreaks, her focus was on PPE.
Nursing home staff were intimately familiar with standard precautions, and many had used contact precautions to prevent transmission of infections like Clostridioides difficile and Candida auris, as well as droplet precautions for influenza. With the threat of COVID-19, nursing homes “had a brand-new requirement to do both contact and droplet precautions – with a new need for eye protection – and in some situations, respiratory precautions with N95 masks,” said Dr. Dumyati, professor of medicine and director of communicable disease surveillance and prevention at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. “And on top of that, [staff] had to learn to conserve and reuse PPE.”
Staff had not been fit-tested for use of N95 respirators, she noted. “The only time an N95 was used in the nursing home prior to COVID-19,” she said, “was for a suspected tuberculosis patient [before hospital admission].”
Similarly, nursing homes had experience in quarantining units to prevent transmission of illnesses like influenza or norovirus – keeping residents in their rooms with no visitations or social activity, for instance – but never did they have to arrange “massive movements of residents to completely new units or parts of a unit,” said Dr. Dumyati, who also has led hospital and nursing home collaborative programs in Rochester to beat back C. difficile, and is now helping to formulate COVID-19 recommendations and guidance for members of AMDA – The Society for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care.
As the SARS-CoV-2 virus began its spread through the United States, efforts to strengthen IPC programs in nursing homes in Rochester and elsewhere had been focused largely on multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) and antibiotic stewardship – not on pandemic preparedness.
Reducing antibiotic use had become a national priority, and a 2016 rule by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services required nursing homes to develop, over a 3-year period, an IPC program that included an antibiotic stewardship component and employment of a trained infection preventionist on at least a half-time basis. Emergency preparedness (e.g., having alternate energy sources for a facility) was also included in the rule, but it was only in 2019 when CMS updated its “Requirements for Participation” rule to stipulate that emergency preparedness include planning for “emerging infectious diseases.”
“The 2016 regulations came about because infections were so problematic in nursing homes,” especially urinary tract infections, C. difficile, and drug-resistant infections, said Patricia Stone, PhD, RN, of the Center for Health Policy at the Columbia University School of Nursing, New York, who has published widely on infection prevention and control in nursing homes.
An analysis of IPC practices in 2014 and in 2018 suggests that the IPC-focused rules were helping, mainly with antibiotic stewardship programs but also with respect to some of the practices aimed at outbreak control, such as having policies in place for grouping infected residents together, instructing infected staff to stay home, and quarantining units on which outbreaks occur, Dr. Stone said. Policies for confining residents to rooms were reported by approximately 74% of nursing homes in 2014, and by approximately 87% in 2018, for instance. Overall, nursing homes were “getting better policies in place,” she said. The analysis compared data from two cross-sectional surveys of nursing homes conducted in 2014 and 2018 (945 and 888 facilities, respectively).
Nursing homes “have a long way to go,” however, with respect to the training of infection preventionists, Dr. Stone said. In 2014, her analysis shows, almost 65% of infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training and less than 3% were Certified in Infection Control (CIC) – a credential awarded by the Certification Board of Infection Control & Epidemiology. Of the 35% who had some form of official training, most completed state or local training courses.
The numbers improved slightly in 2018, with 7% of nursing homes reporting their infection preventionists had the highest-level certification, and 44% reporting that their infection preventionists had no specific infection-control training. Research has shown that infection-control training of any kind has a “strong effect” on IPC-related outcomes. While not demonstrated in research thus far, it seems plausible that “facilities with certified [infection preventionists] will have better processes in place,” said Dr. Stone, whose research has documented the need for more monitoring of staff compliance with hand-washing and other IPC procedures.
Infection preventionists in nursing homes typically have been directors of nursing or assistant directors of nursing who fold IPC responsibilities into a multitude of other responsibilities. Before the 2016 rules, some smaller facilities hired off-site consultants to do the job.
CMS upped the ante after several months of COVID-19, recommending in mid-May that nursing homes assign at least one individual with training in infection control “to provide on-site management of the IPC program.” The infection preventionists should be a “full-time role” in facilities that have more than 100 residents, the CMS guidance said. (Prior to the pandemic, CMS issued proposed regulations in 2019 that would modify the time an infection preventionist must devote to a facility from “part time” to “sufficient time.”)
However, neither the 2016 rule nor the most recent guidance on infection preventionists define the length or content of training.
Swati Gaur, MD, chair of the Infection Advisory Committee of AMDA and a certified medical director of two skilled nursing facilities in Gainesville, Ga., said that the pandemic “has really started to crystallize some of the limitations of having a very vague role, not just in terms of what an [infection preventionists] does [in the nursing home] but also the training,”
Fortunately, Dr. Gaur said, when SARS-CoV-2 struck, she had just transitioned her facilities’ designated infection preventionist to work full-time on the role. She had worked closely with her infection preventionist on IPC issues but wishes she had arranged for more rigorous independent training. “The role of the [infection preventionist] is huge and complicated,” now involving employee health, contract tracing, cohorting, isolation, and compliance with precautions and use of PPE, in addition to surveillance, data reporting, and communication with public health officials, she said.
“Facilities are finding out now that [the infection preventionist] cannot be an afterthought. And it won’t end with COVID. We have other respiratory illnesses like flu and other viruses that we struggle with all the time,” said Dr. Gaur, who is working alongside Dr. Dumyati and two other long-term care experts on AMDA’s COVID-19 guidance. The nursing homes that Dr. Gaur directs are part of the Northeast Georgia Health Care System and together include 271 beds.
Moving forward
IPC practices often collide with facilities’ role as a home, especially to those receiving long-term care. “We always have to measure what we do [to prevent and control infections] against patient autonomy and residents’ rights,” said Dr. Gaur. “We have struggled with these issues, prior to the pandemic. If patients are positive for multidrug resistant organisms [for instance], how long can they be isolated in their own rooms? You can’t for days and months put someone in a single room and create isolation. That’s where the science of infection prevention can collide with residents’ rights.”
Over the years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has acknowledged this discordance, leaving it to facilities to decide, for instance, whether to actively screen for colonization with MDROs. In 2019, to help nursing homes prevent the transmission of MDROs from residents who are colonized but not actively infected, the CDC introduced new “enhanced barrier precautions” that require the use of gowns and gloves for specific resident activities identified as having a high risk of MDRO transmission. The new category of precautions is less restrictive than traditional contact precautions, which keep residents in their rooms.
Infection control in nursing homes “isn’t where it needs to be ... but we’re always going to have in nursing homes a situation where there’s a high potential for rapid transmission of infectious disease,” said Christopher Crnich, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who chairs the long-term care special interest group of the Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America and has offered COVID-19 advice to his state’s department of public health.
“Anytime you have a congregative community, particularly one that involves susceptible hosts, there will be an intrinsically susceptible environment ... I’m a bit disturbed by the emphasis on saying, ‘This nursing home had a COVID-19 outbreak, therefore this nursing home did something wrong,’ ” Dr. Crnich said.
“How we mitigate the size of the outbreaks is where we need to focus our attention,” he said. The goal with SARS-CoV-2, he said, is to recognize its introduction “as rapidly as possible” and stop its spread through empiric symptom- and exposure-based isolation, multiple waves of targeted testing, widespread use of contact and droplet precautions, and isolating staff as necessary.
As awareness grew this year among long-term care leaders that relying too heavily on symptom-based strategies may not be effective to prevent introduction and transmission of SARS-CoV-2, a study published in April in the New England Journal of Medicine cemented the need for a testing strategy not limited to symptomatic individuals.
The study documented that more than half of residents in a nursing home who had positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and that most went on to develop symptoms. The study was conducted after one case of COVID-19 had been identified.
Some states issued calls this spring for “universal testing” of all nursing home patients and staff, and the CMS recommendations issued to state and local officials in mid-May for phased nursing home “reopening” call for baseline testing of all residents and staff, followed by retesting all residents weekly until all residents test negative and by retesting all staff continuing every week.
However, the experts contacted for this story said that, without a highly accurate and accessible point-of-care test (and even with one, considering the virus’ incubation period), a universal approach that includes all nursing home residents may have more limited value than is being touted. In many scenarios, they said, it is most meaningful to focus still-limited testing supplies on the staff, many of whom work at more than one facility and are believed to be primary vectors of SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Ouslander, Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders have been discussing testing at length, trying to reach consensus on best policies. “I don’t think there’s any uniform approach or uniform agreement,” said Dr. Ouslander. “For me, under ideal circumstances what needs to be done to protect older people in nursing homes is to get access to as many accurate viral tests as possible and test staff at least once a week or every 10 days.”
In some facilities, there may be an unspoken barrier to the frequent testing of staff: Fear that staff who test positive will need to be quarantined, with no one to take their place on the front line. Dr. Ouslander said he knows of one county health department that has discouraged nursing homes from testing asymptomatic staff. “It’s insane and truly shocking,” he said.
At the University of Rochester Medical Center, Dr. Dumyati said, staffing agencies are running short of nurse aide substitutes, and staffing issues have become the “biggest challenge” facing a regional multidisciplinary group of medical directors, hospital leaders, and health department officials who are working to troubleshoot COVID-19 issues. “Some of our nursing homes have ended up sending some of their residents to other nursing homes or to the hospital [because of the loss of staff],” she said.
Currently in the state of New York, she noted, COVID-19 patients may not be discharged to nursing homes until they test negative for the virus through PCR testing. “And some people don’t clear by PCR for 4-6 weeks.”
The barriers
Staffing shortages – real in some locales, and anticipated in others as economic reopening grows – are reflective of underlying structural and financial factors that work against optimal IPC, experts said. It’s not uncommon for certified nurse assistants (CNAs) to be assigned to 10-15 residents. And according to AMDA, 30%-46% of CNAs are reported to receive some form of public assistance. Low wages force many CNAs to work other jobs, including shifts at other nursing homes.
Turnover of nursing home leadership also creates problems. Dr. Crnich calls it “one of the biggest barriers” to effective IPC in nursing homes. “Facilities can tolerate some turnover in their front line staff,” he said, “as long as their leadership structure remains relatively stable.” Dr. Stone and her coinvestigators have documented at least yearly turnover in top positions: They found that, in 2018, approximately one-quarter of facilities reported employing three or more infection preventionists, three or more administrators, and three or more directors of nursing during the prior 3 years.
Medical directors, moreover, are not uniformly qualified, engaged with their facilities, or supported by nursing home administrators. “It’s an open secret, I think, that a lot of facilities want a medical director who is a good referral source,” said Dr. Gaur. “A medical director needs to be completely engaged in [quality improvement and] infection control practices.”
Some nursing home chains, she noted, “have realized the value of the medical director, and have changed the way they’re paying them. They’re actually holding them accountable [for quality and outcomes].”
Medical directors such as Dr. Wasserman, who previously oversaw a 74-facility nursing home chain in California as chief medical officer and then chief executive officer and has worked on nursing home quality improvement processes for his state, said there is much that can be done clinically to prevent the spread of infections, such as more frequent use of telemedicine, more attention to “deprescribing” unnecessary medications (which reduces the number of medication passes and, thus, the number of “transmission opportunities”), and the use of continuous remote monitoring. He has been trying to secure Bluetooth-enabled pulse oximetry and temperature monitoring for the Los Angeles Jewish Home and other facilities.
Dr. Wasserman and other long-term care leaders believe that a more educational inspection process would also lead to improvements in IPC. “The punitive nature of the survey process is morally deflating to frontline staff [and] penalties take money away from operations,” Dr. Wasserman said. “It’s not a productive approach to quality improvement.”
Dr. Stone agreed. Infection control is now the primary focus of CMS’s inspection process, and she said that increased regulatory scrutiny of IPC beyond COVID-19 is a “good thing.” Her research has shown that most deficiencies identified by inspectors are infection control deficiencies, and that in 2014 and 2018, approximately one-third of nursing homes had infection control citations. (CMS recently increased penalties and fines for identified deficiencies.)
“But my hope would be that the survey process would be more educational [as it is for hospitals],” she said. “We need to be supporting nursing homes to do a better job.”
A silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic, as Dr. Stone sees it, is that nursing homes may be more engaged with data reporting and infection surveillance going forward. Nursing homes are now required to report their COVID-19 cases to the CDC through its hospital-dominant National Healthcare Safety Network, and the CDC has made technical changes that now make it “easier [than it was in the past] for nursing homes to join and participate,” she said. “Now that all nursing homes are engaged, will they be engaged post-COVID, too? I hope so. Surveillance [of infections] is a first step toward better outcomes.”
For now, said Dr. Crnich, the intensive prevention and mitigation efforts that are being required of nursing homes to minimize COVID-19’s impact is “a big deal and will tax the resources of most nursing homes and exceed the resources of many” without outside support, Dr. Crnich said. “This has been the most illuminating part of all this, and will probably require us to reconsider how we’re resourcing our nursing homes moving forward into the future.”
One-fifth of stem cell transplantation patients develop PTSD
Approximately one-fifth of patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), based on a retrospective analysis.
Patient factors at time of transplantation, such as low quality of life and high anxiety, predicted PTSD 6 months later, reported lead author Sarah Griffith, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“We know that patients admitted for HSCT are often isolated in the hospital for a prolonged period of time, usually about 3-4 weeks, and that they endure substantial toxicities that impact both their physical and psychological well-being,” Dr. Griffith said. “We also know from the literature that HSCT can be considered a traumatic event and that it may lead to clinically significant PTSD symptoms.” But studies evaluating the prevalence and characteristics of PTSD in this patient population have been lacking, she noted.
Dr. Griffith and her colleagues therefore conducted a retrospective analysis involving 250 adults with hematologic malignancies who underwent autologous or allogeneic HSCT during clinical trials conducted from 2014 to 2016. Median patient age was 56 years.
The first objective of the study was to measure the prevalence of PTSD. The second was to characterize features of PTSD such as intrusion, which entails reliving experiences in the form of nightmares or flashbacks, and hypervigilance, which encompasses insomnia, irritability, and hyperarousal for threat. The third objective was to determine risk factors at baseline.
At time of admission for HSCT, after 2 weeks of hospitalization, and again 6 months after transplantation, patients were evaluated using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Bone Marrow Transplant (FACT-BMT), and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), which measured of quality of life, anxiety, and depression. Six months after HSCT, patients also underwent screening for PTSD with the Post-Traumatic Stress Checklist (PTSD-CL). Multivariate regression models were used to determine predictive risk factors.
Six months after HSCT, 18.9% of patients had clinically significant PTSD symptoms; most common were symptoms of avoidance (92.3%), hypervigilance (92.3%), and intrusion (76.9%). Among those who did not have clinically significant PTSD, almost one-quarter (24.5%) demonstrated significant hypervigilance, while 13.7% showed symptoms of avoidance.
“Clinically significant PTSD symptoms are common in the transplant population,” Dr. Griffith said.
Baseline predictors of PTSD included single status and lower quality of life. More severe PTSD was predicted by single status, younger age, higher baseline scores for anxiety or depression, and increased anxiety during hospitalization.
Concluding her presentation, Dr. Griffith said that the findings, while correlative and not causative, should prompt concern and intervention.
“It is very important to be aware of and to manage PTSD symptoms in these patients,” she said. “There are several baseline factors that can be identified prior to HSCT that may illuminate patients at risk for developing worse PTSD symptoms down the road, and these patients may benefit from tailored supportive care interventions.”
Specifically, Dr. Griffith recommended integrating palliative care into hospitalization, as this has been shown to reduce anxiety.
In a virtual presentation, invited discussant Nirali N. Shah, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., highlighted the importance of the findings, while also noting that the impact of palliative care on risk of PTSD has yet to be demonstrated.
Dr. Shah suggested that future research may be improved through use of a formal diagnosis for PTSD, instead of a PTSD checklist, as was used in the present study.
“And certainly long-term follow-up would be important to evaluate the utility of this tool looking at symptoms beyond 6 months,” she said.
Dr. Shah went on to discuss the relevance of the findings for pediatric populations, as children may face unique risk factors and consequences related to PTSD.
“[PTSD in children] may be impacted by family dynamics and structure,” Dr. Shah said. “Children may also have significant neurocognitive implications as a result of their underlying disease or prior therapy. They may experience chronic pain as they go out into adulthood and long-term survivorship, and may also struggle with symptoms of anxiety and depression.”
According to Dr. Shah, one previous study involving more than 6,000 adult survivors of childhood cancer found that PTSD was relatively common, with prevalence rate of 9%, suggesting that interventional work is necessary.
“Applying the data in the study from Griffith et al. suggests that evaluation in the more proximal posttransplant period for children is needed to specifically evaluate PTSD and symptoms thereof, and to try to use this to identify an opportunity for intervention,” Dr. Shah said.
“Pediatric-specific assessments are essential to optimally capture disease and/or age-specific considerations,” she added.
The study was funded by the Lymphoma and Leukemia Society. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Vector Oncology, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Gaido Health/BCG Digital Ventures.
SOURCE: Griffith et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract # 7505.
Approximately one-fifth of patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), based on a retrospective analysis.
Patient factors at time of transplantation, such as low quality of life and high anxiety, predicted PTSD 6 months later, reported lead author Sarah Griffith, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“We know that patients admitted for HSCT are often isolated in the hospital for a prolonged period of time, usually about 3-4 weeks, and that they endure substantial toxicities that impact both their physical and psychological well-being,” Dr. Griffith said. “We also know from the literature that HSCT can be considered a traumatic event and that it may lead to clinically significant PTSD symptoms.” But studies evaluating the prevalence and characteristics of PTSD in this patient population have been lacking, she noted.
Dr. Griffith and her colleagues therefore conducted a retrospective analysis involving 250 adults with hematologic malignancies who underwent autologous or allogeneic HSCT during clinical trials conducted from 2014 to 2016. Median patient age was 56 years.
The first objective of the study was to measure the prevalence of PTSD. The second was to characterize features of PTSD such as intrusion, which entails reliving experiences in the form of nightmares or flashbacks, and hypervigilance, which encompasses insomnia, irritability, and hyperarousal for threat. The third objective was to determine risk factors at baseline.
At time of admission for HSCT, after 2 weeks of hospitalization, and again 6 months after transplantation, patients were evaluated using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Bone Marrow Transplant (FACT-BMT), and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), which measured of quality of life, anxiety, and depression. Six months after HSCT, patients also underwent screening for PTSD with the Post-Traumatic Stress Checklist (PTSD-CL). Multivariate regression models were used to determine predictive risk factors.
Six months after HSCT, 18.9% of patients had clinically significant PTSD symptoms; most common were symptoms of avoidance (92.3%), hypervigilance (92.3%), and intrusion (76.9%). Among those who did not have clinically significant PTSD, almost one-quarter (24.5%) demonstrated significant hypervigilance, while 13.7% showed symptoms of avoidance.
“Clinically significant PTSD symptoms are common in the transplant population,” Dr. Griffith said.
Baseline predictors of PTSD included single status and lower quality of life. More severe PTSD was predicted by single status, younger age, higher baseline scores for anxiety or depression, and increased anxiety during hospitalization.
Concluding her presentation, Dr. Griffith said that the findings, while correlative and not causative, should prompt concern and intervention.
“It is very important to be aware of and to manage PTSD symptoms in these patients,” she said. “There are several baseline factors that can be identified prior to HSCT that may illuminate patients at risk for developing worse PTSD symptoms down the road, and these patients may benefit from tailored supportive care interventions.”
Specifically, Dr. Griffith recommended integrating palliative care into hospitalization, as this has been shown to reduce anxiety.
In a virtual presentation, invited discussant Nirali N. Shah, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., highlighted the importance of the findings, while also noting that the impact of palliative care on risk of PTSD has yet to be demonstrated.
Dr. Shah suggested that future research may be improved through use of a formal diagnosis for PTSD, instead of a PTSD checklist, as was used in the present study.
“And certainly long-term follow-up would be important to evaluate the utility of this tool looking at symptoms beyond 6 months,” she said.
Dr. Shah went on to discuss the relevance of the findings for pediatric populations, as children may face unique risk factors and consequences related to PTSD.
“[PTSD in children] may be impacted by family dynamics and structure,” Dr. Shah said. “Children may also have significant neurocognitive implications as a result of their underlying disease or prior therapy. They may experience chronic pain as they go out into adulthood and long-term survivorship, and may also struggle with symptoms of anxiety and depression.”
According to Dr. Shah, one previous study involving more than 6,000 adult survivors of childhood cancer found that PTSD was relatively common, with prevalence rate of 9%, suggesting that interventional work is necessary.
“Applying the data in the study from Griffith et al. suggests that evaluation in the more proximal posttransplant period for children is needed to specifically evaluate PTSD and symptoms thereof, and to try to use this to identify an opportunity for intervention,” Dr. Shah said.
“Pediatric-specific assessments are essential to optimally capture disease and/or age-specific considerations,” she added.
The study was funded by the Lymphoma and Leukemia Society. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Vector Oncology, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Gaido Health/BCG Digital Ventures.
SOURCE: Griffith et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract # 7505.
Approximately one-fifth of patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), based on a retrospective analysis.
Patient factors at time of transplantation, such as low quality of life and high anxiety, predicted PTSD 6 months later, reported lead author Sarah Griffith, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
“We know that patients admitted for HSCT are often isolated in the hospital for a prolonged period of time, usually about 3-4 weeks, and that they endure substantial toxicities that impact both their physical and psychological well-being,” Dr. Griffith said. “We also know from the literature that HSCT can be considered a traumatic event and that it may lead to clinically significant PTSD symptoms.” But studies evaluating the prevalence and characteristics of PTSD in this patient population have been lacking, she noted.
Dr. Griffith and her colleagues therefore conducted a retrospective analysis involving 250 adults with hematologic malignancies who underwent autologous or allogeneic HSCT during clinical trials conducted from 2014 to 2016. Median patient age was 56 years.
The first objective of the study was to measure the prevalence of PTSD. The second was to characterize features of PTSD such as intrusion, which entails reliving experiences in the form of nightmares or flashbacks, and hypervigilance, which encompasses insomnia, irritability, and hyperarousal for threat. The third objective was to determine risk factors at baseline.
At time of admission for HSCT, after 2 weeks of hospitalization, and again 6 months after transplantation, patients were evaluated using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Bone Marrow Transplant (FACT-BMT), and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), which measured of quality of life, anxiety, and depression. Six months after HSCT, patients also underwent screening for PTSD with the Post-Traumatic Stress Checklist (PTSD-CL). Multivariate regression models were used to determine predictive risk factors.
Six months after HSCT, 18.9% of patients had clinically significant PTSD symptoms; most common were symptoms of avoidance (92.3%), hypervigilance (92.3%), and intrusion (76.9%). Among those who did not have clinically significant PTSD, almost one-quarter (24.5%) demonstrated significant hypervigilance, while 13.7% showed symptoms of avoidance.
“Clinically significant PTSD symptoms are common in the transplant population,” Dr. Griffith said.
Baseline predictors of PTSD included single status and lower quality of life. More severe PTSD was predicted by single status, younger age, higher baseline scores for anxiety or depression, and increased anxiety during hospitalization.
Concluding her presentation, Dr. Griffith said that the findings, while correlative and not causative, should prompt concern and intervention.
“It is very important to be aware of and to manage PTSD symptoms in these patients,” she said. “There are several baseline factors that can be identified prior to HSCT that may illuminate patients at risk for developing worse PTSD symptoms down the road, and these patients may benefit from tailored supportive care interventions.”
Specifically, Dr. Griffith recommended integrating palliative care into hospitalization, as this has been shown to reduce anxiety.
In a virtual presentation, invited discussant Nirali N. Shah, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., highlighted the importance of the findings, while also noting that the impact of palliative care on risk of PTSD has yet to be demonstrated.
Dr. Shah suggested that future research may be improved through use of a formal diagnosis for PTSD, instead of a PTSD checklist, as was used in the present study.
“And certainly long-term follow-up would be important to evaluate the utility of this tool looking at symptoms beyond 6 months,” she said.
Dr. Shah went on to discuss the relevance of the findings for pediatric populations, as children may face unique risk factors and consequences related to PTSD.
“[PTSD in children] may be impacted by family dynamics and structure,” Dr. Shah said. “Children may also have significant neurocognitive implications as a result of their underlying disease or prior therapy. They may experience chronic pain as they go out into adulthood and long-term survivorship, and may also struggle with symptoms of anxiety and depression.”
According to Dr. Shah, one previous study involving more than 6,000 adult survivors of childhood cancer found that PTSD was relatively common, with prevalence rate of 9%, suggesting that interventional work is necessary.
“Applying the data in the study from Griffith et al. suggests that evaluation in the more proximal posttransplant period for children is needed to specifically evaluate PTSD and symptoms thereof, and to try to use this to identify an opportunity for intervention,” Dr. Shah said.
“Pediatric-specific assessments are essential to optimally capture disease and/or age-specific considerations,” she added.
The study was funded by the Lymphoma and Leukemia Society. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Vector Oncology, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Gaido Health/BCG Digital Ventures.
SOURCE: Griffith et al. ASCO 2020. Abstract # 7505.
FROM ASCO 2020
Daily Recap: Avoid alcohol to reduce cancer risk, COVID’s lasting health system impact
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
ACS Update: ‘It is best not to drink alcohol’
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is taking its strongest stance yet against drinking. In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the ACS now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.” Previously, the organizations had suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive. The guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. Read more.
COVID health system changes may be here to stay
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced sudden major changes to the nation’s health care system that are unlikely to be reversed. While there’s some good news, there are also some alarming trends. Experts said there are three trends that are likely to stick around: telehealth for all, an exodus of primary care physicians, and less emphasis on hospital care. “I’ve been trying to raise the alarm about the kind of perilous future of primary care,” said Farzad Mostashari, MD, a top Department of Health & Human Services official in the Obama administration. Dr. Mostashari runs Aledade, a company that helps primary care doctors make the transition from fee-for-service medicine to new payment models. The American Academy of Family Physicians reports that 70% of primary care physicians are reporting declines in patient volume of 50% or more since March, and 40% have laid off or furloughed staff. The AAFP has joined other primary care and insurance groups in asking HHS for an infusion of cash. “This is absolutely essential to effectively treat patients today and to maintain their ongoing operations until we overcome this public health emergency,” the groups wrote. Read more.
Asthma-COPD overlap deaths
Death rates for combined asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease declined during 1999-2016, but the risk remains higher among women, compared with men, and in certain occupations, according to a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There is also an association between mortality and nonworking status among adults aged 25-64 years, which “suggests that asthma-COPD overlap might be associated with substantial morbidity,” Katelynn E. Dodd, MPH, and associates at the CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “These patients have been reported to have worse health outcomes than do those with asthma or COPD alone.” Read more.
Cancer triage in a pandemic: There’s an app for that
Deciding which cancer patients need immediate treatment and who can safely wait is an uncomfortable assessment for cancer clinicians during the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, a new tool, which appears to be the first of its kind, quantifies that risk-benefit analysis. But its presence immediately raises the question: can it help? OncCOVID is a free tool that was launched in May by the University of Michigan. It allows physicians to individualize risk estimates for delaying treatment of up to 25 early- to late-stage cancers. It includes more than 45 patient characteristics, such as age, location, cancer type, cancer stage, treatment plan, underlying medical conditions, and proposed length of delay in care. “We thought, isn’t it better to at least provide some evidence-based quantification, rather than a back-of-the-envelope three-tier system that is just sort of ‘made up’?“ explained one of the developers, Daniel Spratt, MD, associate professor of radiation oncology at Michigan Medicine. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center . All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com .
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
ACS Update: ‘It is best not to drink alcohol’
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is taking its strongest stance yet against drinking. In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the ACS now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.” Previously, the organizations had suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive. The guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. Read more.
COVID health system changes may be here to stay
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced sudden major changes to the nation’s health care system that are unlikely to be reversed. While there’s some good news, there are also some alarming trends. Experts said there are three trends that are likely to stick around: telehealth for all, an exodus of primary care physicians, and less emphasis on hospital care. “I’ve been trying to raise the alarm about the kind of perilous future of primary care,” said Farzad Mostashari, MD, a top Department of Health & Human Services official in the Obama administration. Dr. Mostashari runs Aledade, a company that helps primary care doctors make the transition from fee-for-service medicine to new payment models. The American Academy of Family Physicians reports that 70% of primary care physicians are reporting declines in patient volume of 50% or more since March, and 40% have laid off or furloughed staff. The AAFP has joined other primary care and insurance groups in asking HHS for an infusion of cash. “This is absolutely essential to effectively treat patients today and to maintain their ongoing operations until we overcome this public health emergency,” the groups wrote. Read more.
Asthma-COPD overlap deaths
Death rates for combined asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease declined during 1999-2016, but the risk remains higher among women, compared with men, and in certain occupations, according to a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There is also an association between mortality and nonworking status among adults aged 25-64 years, which “suggests that asthma-COPD overlap might be associated with substantial morbidity,” Katelynn E. Dodd, MPH, and associates at the CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “These patients have been reported to have worse health outcomes than do those with asthma or COPD alone.” Read more.
Cancer triage in a pandemic: There’s an app for that
Deciding which cancer patients need immediate treatment and who can safely wait is an uncomfortable assessment for cancer clinicians during the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, a new tool, which appears to be the first of its kind, quantifies that risk-benefit analysis. But its presence immediately raises the question: can it help? OncCOVID is a free tool that was launched in May by the University of Michigan. It allows physicians to individualize risk estimates for delaying treatment of up to 25 early- to late-stage cancers. It includes more than 45 patient characteristics, such as age, location, cancer type, cancer stage, treatment plan, underlying medical conditions, and proposed length of delay in care. “We thought, isn’t it better to at least provide some evidence-based quantification, rather than a back-of-the-envelope three-tier system that is just sort of ‘made up’?“ explained one of the developers, Daniel Spratt, MD, associate professor of radiation oncology at Michigan Medicine. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center . All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com .
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
ACS Update: ‘It is best not to drink alcohol’
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is taking its strongest stance yet against drinking. In its updated cancer prevention guidelines, the ACS now recommends that “it is best not to drink alcohol.” Previously, the organizations had suggested that, for those who consume alcoholic beverages, intake should be no more than one drink per day for women or two per day for men. That recommendation is still in place, but is now accompanied by this new, stronger directive. The guidelines also place more emphasis on reducing the consumption of processed and red meat and highly processed foods, and on increasing physical activity. “Individual choice is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but having the right policies and environmental factors to break down these barriers is also important, and that is something that clinicians can support,” said Laura Makaroff, DO, American Cancer Society senior vice president. The guidelines were published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. Read more.
COVID health system changes may be here to stay
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced sudden major changes to the nation’s health care system that are unlikely to be reversed. While there’s some good news, there are also some alarming trends. Experts said there are three trends that are likely to stick around: telehealth for all, an exodus of primary care physicians, and less emphasis on hospital care. “I’ve been trying to raise the alarm about the kind of perilous future of primary care,” said Farzad Mostashari, MD, a top Department of Health & Human Services official in the Obama administration. Dr. Mostashari runs Aledade, a company that helps primary care doctors make the transition from fee-for-service medicine to new payment models. The American Academy of Family Physicians reports that 70% of primary care physicians are reporting declines in patient volume of 50% or more since March, and 40% have laid off or furloughed staff. The AAFP has joined other primary care and insurance groups in asking HHS for an infusion of cash. “This is absolutely essential to effectively treat patients today and to maintain their ongoing operations until we overcome this public health emergency,” the groups wrote. Read more.
Asthma-COPD overlap deaths
Death rates for combined asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease declined during 1999-2016, but the risk remains higher among women, compared with men, and in certain occupations, according to a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There is also an association between mortality and nonworking status among adults aged 25-64 years, which “suggests that asthma-COPD overlap might be associated with substantial morbidity,” Katelynn E. Dodd, MPH, and associates at the CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. “These patients have been reported to have worse health outcomes than do those with asthma or COPD alone.” Read more.
Cancer triage in a pandemic: There’s an app for that
Deciding which cancer patients need immediate treatment and who can safely wait is an uncomfortable assessment for cancer clinicians during the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, a new tool, which appears to be the first of its kind, quantifies that risk-benefit analysis. But its presence immediately raises the question: can it help? OncCOVID is a free tool that was launched in May by the University of Michigan. It allows physicians to individualize risk estimates for delaying treatment of up to 25 early- to late-stage cancers. It includes more than 45 patient characteristics, such as age, location, cancer type, cancer stage, treatment plan, underlying medical conditions, and proposed length of delay in care. “We thought, isn’t it better to at least provide some evidence-based quantification, rather than a back-of-the-envelope three-tier system that is just sort of ‘made up’?“ explained one of the developers, Daniel Spratt, MD, associate professor of radiation oncology at Michigan Medicine. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center . All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com .
Irritability strongly linked to suicidal behavior in major depression
Irritability in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and stimulant use disorder (SUD) is strongly linked to suicidality and should be assessed by clinicians.
Three clinical trials of adults with MDD and one trial of adults with SUD showed that the link between irritability and suicidality was stronger than the association between depression severity and suicidal behaviors.
“Irritability is an important construct that is not often studied in adults with major depressive disorder,” Manish K. Jha, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“If you look at current diagnostic convention, irritability is not considered a symptom of major depressive episodes in adults, but below age 18, it is considered one of the two main symptoms,” Dr. Jha said.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2020 annual Meeting.
Clinically useful
Irritability is assessed using age-related norms of behavior, Dr. Jha said.
“The best way to conceptualize it is that it is the propensity to get angry easily or more frequently as compared to peers in response to frustration. I have a 2½-year old, and if he throws a tantrum, that is perfectly age appropriate. But if I do the same thing, it would be extreme irritability. The pediatric literature uses the word ‘grouchiness,’ but it is a little bit difficult to define, in part because it hasn’t been studied extensively,” he said.
To better understand the potential association between irritability and suicidality, the investigators reviewed results of three trials involving adults with MDD. These trials were CO-MED (Combining Medications to Enhance Depression Outcomes), which included 665 patients; EMBARC (Establishing Moderators and Biosignatures of Antidepressant Response in Clinical Care), which included 296 patients; and SAMS (Suicide Assessment Methodology Study), which included 266 patients.
They also examined the STRIDE (Stimulant Reduction Intervention Using Dosed Exercise) study, which was conducted in 302 adults with SUD.
All studies assessed irritability using the Concise Associated Symptom Tracking scale, a 5-point Likert scale. The trials also assessed suicidality with the Concise Health Risk Tracking Suicidal Thoughts.
The investigators found that irritability and suicidality were positively correlated. The association between irritability and suicidality was 2-11 times stronger than the link to overall depression.
Higher irritability at baseline predicted higher levels of suicidality at week 9 in CO-MED (P = .011), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P = .007), but not in SAMS (P = .21).
Greater reduction in irritability from baseline to week 4 predicted lower levels of suicidality at week 8 in CO-MED (P = .007), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P < .0001), but not in SAMS (P = .065).
Similarly, lower baseline levels and greater reductions in irritability were associated with lower levels of suicidality at week 28 of CO-MED, week 16 of EMBARC, and week 36 of STRIDE.
, and he believes that measuring irritability in MDD “has clinical utility.”
A common and disabling symptom
Commenting on the study, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the findings provide further support that irritability is a relatively common and disabling symptom associated with major depression.
“The presence of significant irritability was associated with higher levels of suicidal ideation and is therefore highly relevant for clinicians to assess,” said Dr. Mathew, who was not part of the study.
“Early improvements in irritability are associated with better longer-term outcomes with antidepressant treatments, and this highlights the need for careful clinical evaluation early on in the course of antidepressant therapy, ideally within the first 2 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Jha reports financial relationships with Acadia Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Mathew reports financial relationships with Allergan, Vistagen, Janssen, Clexio, and Biohaven.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Irritability in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and stimulant use disorder (SUD) is strongly linked to suicidality and should be assessed by clinicians.
Three clinical trials of adults with MDD and one trial of adults with SUD showed that the link between irritability and suicidality was stronger than the association between depression severity and suicidal behaviors.
“Irritability is an important construct that is not often studied in adults with major depressive disorder,” Manish K. Jha, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“If you look at current diagnostic convention, irritability is not considered a symptom of major depressive episodes in adults, but below age 18, it is considered one of the two main symptoms,” Dr. Jha said.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2020 annual Meeting.
Clinically useful
Irritability is assessed using age-related norms of behavior, Dr. Jha said.
“The best way to conceptualize it is that it is the propensity to get angry easily or more frequently as compared to peers in response to frustration. I have a 2½-year old, and if he throws a tantrum, that is perfectly age appropriate. But if I do the same thing, it would be extreme irritability. The pediatric literature uses the word ‘grouchiness,’ but it is a little bit difficult to define, in part because it hasn’t been studied extensively,” he said.
To better understand the potential association between irritability and suicidality, the investigators reviewed results of three trials involving adults with MDD. These trials were CO-MED (Combining Medications to Enhance Depression Outcomes), which included 665 patients; EMBARC (Establishing Moderators and Biosignatures of Antidepressant Response in Clinical Care), which included 296 patients; and SAMS (Suicide Assessment Methodology Study), which included 266 patients.
They also examined the STRIDE (Stimulant Reduction Intervention Using Dosed Exercise) study, which was conducted in 302 adults with SUD.
All studies assessed irritability using the Concise Associated Symptom Tracking scale, a 5-point Likert scale. The trials also assessed suicidality with the Concise Health Risk Tracking Suicidal Thoughts.
The investigators found that irritability and suicidality were positively correlated. The association between irritability and suicidality was 2-11 times stronger than the link to overall depression.
Higher irritability at baseline predicted higher levels of suicidality at week 9 in CO-MED (P = .011), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P = .007), but not in SAMS (P = .21).
Greater reduction in irritability from baseline to week 4 predicted lower levels of suicidality at week 8 in CO-MED (P = .007), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P < .0001), but not in SAMS (P = .065).
Similarly, lower baseline levels and greater reductions in irritability were associated with lower levels of suicidality at week 28 of CO-MED, week 16 of EMBARC, and week 36 of STRIDE.
, and he believes that measuring irritability in MDD “has clinical utility.”
A common and disabling symptom
Commenting on the study, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the findings provide further support that irritability is a relatively common and disabling symptom associated with major depression.
“The presence of significant irritability was associated with higher levels of suicidal ideation and is therefore highly relevant for clinicians to assess,” said Dr. Mathew, who was not part of the study.
“Early improvements in irritability are associated with better longer-term outcomes with antidepressant treatments, and this highlights the need for careful clinical evaluation early on in the course of antidepressant therapy, ideally within the first 2 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Jha reports financial relationships with Acadia Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Mathew reports financial relationships with Allergan, Vistagen, Janssen, Clexio, and Biohaven.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Irritability in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and stimulant use disorder (SUD) is strongly linked to suicidality and should be assessed by clinicians.
Three clinical trials of adults with MDD and one trial of adults with SUD showed that the link between irritability and suicidality was stronger than the association between depression severity and suicidal behaviors.
“Irritability is an important construct that is not often studied in adults with major depressive disorder,” Manish K. Jha, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“If you look at current diagnostic convention, irritability is not considered a symptom of major depressive episodes in adults, but below age 18, it is considered one of the two main symptoms,” Dr. Jha said.
The findings were presented at the virtual American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2020 annual Meeting.
Clinically useful
Irritability is assessed using age-related norms of behavior, Dr. Jha said.
“The best way to conceptualize it is that it is the propensity to get angry easily or more frequently as compared to peers in response to frustration. I have a 2½-year old, and if he throws a tantrum, that is perfectly age appropriate. But if I do the same thing, it would be extreme irritability. The pediatric literature uses the word ‘grouchiness,’ but it is a little bit difficult to define, in part because it hasn’t been studied extensively,” he said.
To better understand the potential association between irritability and suicidality, the investigators reviewed results of three trials involving adults with MDD. These trials were CO-MED (Combining Medications to Enhance Depression Outcomes), which included 665 patients; EMBARC (Establishing Moderators and Biosignatures of Antidepressant Response in Clinical Care), which included 296 patients; and SAMS (Suicide Assessment Methodology Study), which included 266 patients.
They also examined the STRIDE (Stimulant Reduction Intervention Using Dosed Exercise) study, which was conducted in 302 adults with SUD.
All studies assessed irritability using the Concise Associated Symptom Tracking scale, a 5-point Likert scale. The trials also assessed suicidality with the Concise Health Risk Tracking Suicidal Thoughts.
The investigators found that irritability and suicidality were positively correlated. The association between irritability and suicidality was 2-11 times stronger than the link to overall depression.
Higher irritability at baseline predicted higher levels of suicidality at week 9 in CO-MED (P = .011), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P = .007), but not in SAMS (P = .21).
Greater reduction in irritability from baseline to week 4 predicted lower levels of suicidality at week 8 in CO-MED (P = .007), EMBARC (P < .0001), and STRIDE (P < .0001), but not in SAMS (P = .065).
Similarly, lower baseline levels and greater reductions in irritability were associated with lower levels of suicidality at week 28 of CO-MED, week 16 of EMBARC, and week 36 of STRIDE.
, and he believes that measuring irritability in MDD “has clinical utility.”
A common and disabling symptom
Commenting on the study, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said the findings provide further support that irritability is a relatively common and disabling symptom associated with major depression.
“The presence of significant irritability was associated with higher levels of suicidal ideation and is therefore highly relevant for clinicians to assess,” said Dr. Mathew, who was not part of the study.
“Early improvements in irritability are associated with better longer-term outcomes with antidepressant treatments, and this highlights the need for careful clinical evaluation early on in the course of antidepressant therapy, ideally within the first 2 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Jha reports financial relationships with Acadia Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Mathew reports financial relationships with Allergan, Vistagen, Janssen, Clexio, and Biohaven.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Human sitters in the COVID era
Data collection needed for care of suicidal hospitalized patients
I am writing this commentary to bring to readers’ attention a medical and ethical complexity related to human sitters for presumably suicidal, COVID-19–positive hospitalized patients.
To shape and bundle the ethics issues addressed here into a single question, I offer the following: Should policies and practices requiring that patients in presumed need of a sitter because of assessed suicidality change when the patient is COVID-19–positive? Although the analysis might be similar when a sitter is monitoring a Patient Under Investigation (PUI), here I focus only on COVID-19–positive patients. Similarly, there are other reasons for sitters, of course, such as to prevent elopement, or, if a patient is in restraints, to prevent the patient from pulling out lines or tubes. Again, discussion of some of these ethical complications is beyond the scope of this piece. Just considering the matter of potential suicidality and sitters is complex enough. And so, to start, I sought out existing sources for guidance.
In looking for such sources, I first turned to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services before COVID-19. CMS has required that there be a sitter for a patient who is suicidal and that the sitter remain in the room so that the sitter can intervene expeditiously if the patient tries to hurt himself or herself. There has been no change in this guidance since the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. To the best of my knowledge, there is no substantive guidance for protecting sitters from contagion other than PPE. Given this, it begs the question:
In my hospital, I already have begun discussing the potential risks of harm and potential benefits to our suicidal patients of having a sitter directly outside the patient’s room. I also have considered whether to have one sitter watching several room cameras at once, commonly referred to as “telehealth strategies.”
To be sure, sitting for hours in the room of a COVID-19–positive patient is onerous. The sitter is required to be in full PPE (N-95 mask, gown, and gloves), which is hot and uncomfortable. Current practice is resource intensive in other ways. It requires changing out the sitter every 2 hours, which uses substantial amounts of PPE and multiple sitters.
Regardless, however, there are really no data upon which to base any sound ethics judgment about what should or should not be tried. We just have no information on how to attempt to balance potential risks and prospects for the benefit of whom and when. And, given that good clinical ethics always begin with the facts, I write this piece to see whether readers have thought about these issues before – and whether any of clinicians have started collecting the valuable data needed to begin making sound ethical judgments about how to care for our presumably suicidal COVID-19–positive patients and the sitters who watch over them.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center and professor of psychiatry at Georgetown University, Washington. She has no disclosures and can be reached at [email protected].
This column is an outcome of a discussion that occurred during Psych/Ethics rounds on June 5, and does not represent any official statements of Medstar Washington Hospital Center or any entity of the MedStar Corp. Dr. Ritchie would like to thank Evan G. DeRenzo, PhD, of the John J. Lynch Center for Ethics, for her thoughtful review of a previous draft of this commentary.
Data collection needed for care of suicidal hospitalized patients
Data collection needed for care of suicidal hospitalized patients
I am writing this commentary to bring to readers’ attention a medical and ethical complexity related to human sitters for presumably suicidal, COVID-19–positive hospitalized patients.
To shape and bundle the ethics issues addressed here into a single question, I offer the following: Should policies and practices requiring that patients in presumed need of a sitter because of assessed suicidality change when the patient is COVID-19–positive? Although the analysis might be similar when a sitter is monitoring a Patient Under Investigation (PUI), here I focus only on COVID-19–positive patients. Similarly, there are other reasons for sitters, of course, such as to prevent elopement, or, if a patient is in restraints, to prevent the patient from pulling out lines or tubes. Again, discussion of some of these ethical complications is beyond the scope of this piece. Just considering the matter of potential suicidality and sitters is complex enough. And so, to start, I sought out existing sources for guidance.
In looking for such sources, I first turned to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services before COVID-19. CMS has required that there be a sitter for a patient who is suicidal and that the sitter remain in the room so that the sitter can intervene expeditiously if the patient tries to hurt himself or herself. There has been no change in this guidance since the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. To the best of my knowledge, there is no substantive guidance for protecting sitters from contagion other than PPE. Given this, it begs the question:
In my hospital, I already have begun discussing the potential risks of harm and potential benefits to our suicidal patients of having a sitter directly outside the patient’s room. I also have considered whether to have one sitter watching several room cameras at once, commonly referred to as “telehealth strategies.”
To be sure, sitting for hours in the room of a COVID-19–positive patient is onerous. The sitter is required to be in full PPE (N-95 mask, gown, and gloves), which is hot and uncomfortable. Current practice is resource intensive in other ways. It requires changing out the sitter every 2 hours, which uses substantial amounts of PPE and multiple sitters.
Regardless, however, there are really no data upon which to base any sound ethics judgment about what should or should not be tried. We just have no information on how to attempt to balance potential risks and prospects for the benefit of whom and when. And, given that good clinical ethics always begin with the facts, I write this piece to see whether readers have thought about these issues before – and whether any of clinicians have started collecting the valuable data needed to begin making sound ethical judgments about how to care for our presumably suicidal COVID-19–positive patients and the sitters who watch over them.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center and professor of psychiatry at Georgetown University, Washington. She has no disclosures and can be reached at [email protected].
This column is an outcome of a discussion that occurred during Psych/Ethics rounds on June 5, and does not represent any official statements of Medstar Washington Hospital Center or any entity of the MedStar Corp. Dr. Ritchie would like to thank Evan G. DeRenzo, PhD, of the John J. Lynch Center for Ethics, for her thoughtful review of a previous draft of this commentary.
I am writing this commentary to bring to readers’ attention a medical and ethical complexity related to human sitters for presumably suicidal, COVID-19–positive hospitalized patients.
To shape and bundle the ethics issues addressed here into a single question, I offer the following: Should policies and practices requiring that patients in presumed need of a sitter because of assessed suicidality change when the patient is COVID-19–positive? Although the analysis might be similar when a sitter is monitoring a Patient Under Investigation (PUI), here I focus only on COVID-19–positive patients. Similarly, there are other reasons for sitters, of course, such as to prevent elopement, or, if a patient is in restraints, to prevent the patient from pulling out lines or tubes. Again, discussion of some of these ethical complications is beyond the scope of this piece. Just considering the matter of potential suicidality and sitters is complex enough. And so, to start, I sought out existing sources for guidance.
In looking for such sources, I first turned to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services before COVID-19. CMS has required that there be a sitter for a patient who is suicidal and that the sitter remain in the room so that the sitter can intervene expeditiously if the patient tries to hurt himself or herself. There has been no change in this guidance since the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. To the best of my knowledge, there is no substantive guidance for protecting sitters from contagion other than PPE. Given this, it begs the question:
In my hospital, I already have begun discussing the potential risks of harm and potential benefits to our suicidal patients of having a sitter directly outside the patient’s room. I also have considered whether to have one sitter watching several room cameras at once, commonly referred to as “telehealth strategies.”
To be sure, sitting for hours in the room of a COVID-19–positive patient is onerous. The sitter is required to be in full PPE (N-95 mask, gown, and gloves), which is hot and uncomfortable. Current practice is resource intensive in other ways. It requires changing out the sitter every 2 hours, which uses substantial amounts of PPE and multiple sitters.
Regardless, however, there are really no data upon which to base any sound ethics judgment about what should or should not be tried. We just have no information on how to attempt to balance potential risks and prospects for the benefit of whom and when. And, given that good clinical ethics always begin with the facts, I write this piece to see whether readers have thought about these issues before – and whether any of clinicians have started collecting the valuable data needed to begin making sound ethical judgments about how to care for our presumably suicidal COVID-19–positive patients and the sitters who watch over them.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center and professor of psychiatry at Georgetown University, Washington. She has no disclosures and can be reached at [email protected].
This column is an outcome of a discussion that occurred during Psych/Ethics rounds on June 5, and does not represent any official statements of Medstar Washington Hospital Center or any entity of the MedStar Corp. Dr. Ritchie would like to thank Evan G. DeRenzo, PhD, of the John J. Lynch Center for Ethics, for her thoughtful review of a previous draft of this commentary.
Elevated inflammation common in children’s severe COVID-19 disease
according to data from 50 patients at a single tertiary care center.
“Risk factors for severe disease in pediatric populations have not been clearly identified and the high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in NYC offers an opportunity to describe severe pediatric disease in more detail,” wrote Philip Zachariah, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and colleagues.
In a retrospective case series published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 50 patients: 41 classified as severe and 9 classified as nonsevere. Among the patients, 27 were male and 25 were Hispanic. The patient population had a median of 2 days from symptom onset to hospital admission. The most common symptoms were fever (80%) and respiratory symptoms (64%). Seventy-six percent of patients had a median length of stay of 3 days (range 1-30 days).
At hospital admission, children with severe disease had significantly higher levels of several inflammatory markers compared with those without severe disease, notably C-reactive protein (median 8.978 mg/dL vs. 0.64 mg/dL) and procalcitonin (median 0.31 ng/mL vs. 0.17 ng/mL, (P < .001 for both). High mean peak levels of C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin 6, ferritin, and D-dimer were seen among the nine children (16%) who required mechanical ventilation, Dr. Zachariah and associates said.
None of the 14 infants and 1 of the 8 immunocompromised children in the study had severe disease, the researchers wrote.
Bacterial coinfections detected while patients were hospitalized were bacteremia in 6%, suspected bacterial pneumonia in 18%, urinary tract infections in 10%, skin and soft tissue infections in 6%, and streptococcus pharyngitis in 2%, Dr. Zachariah and associates reported.
Overall, 61% of the children had comorbidities identified in previous COVID-19 studies, of which obesity was the most common (22%); other comorbidities included asthma, sickle cell disease, cardiac disease, and diabetes. Obesity also was significantly associated with the need for mechanical ventilation in children aged 2 years and older (67%). A total of 16 patients required respiratory support, 9 of these were placed on mechanical ventilation; 6 of these 9 children were obese.
Fifteen patients (30%) who met criteria for increased oxygen requirements and respiratory distress received hydroxychloroquine, but the small sample size did not allow for assessment of treatment efficacy, the researchers said.
“Expanding our knowledge of COVID-19 [disease] in children will potentially permit early recognition of SARS-CoV-2 infection, understanding of the natural history of disease, and potential complications, said Stephen I. Pelton, MD, professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. This review of 50 SARS-CoV-2 infected children (less than 21 years of age) “provides insight into the short period of symptoms prior to hospitalization, challenges the concept that infants less than 1 year are at greatest risk of severe disease (as from the experience in China), and suggests rapid recovery in many children, as median length of stay was 3 days.
“The review revealed two findings that were surprising to me. First, the median length of stay of 3 days. As nearly 20% of the children required mechanical ventilation, it suggests many of the children were discharged quickly after evaluation, suggesting that we need to identify markers of severity to predict those children likely to have progressive disease and require respiratory support,” Dr. Pelton noted.
“The second observation suggests high rates of bacterial infection (bacteremia, pneumonia, UTI, and skin and soft tissue infection). I do not think this has been widely reported in adults, and may represent a difference between child and adult disease. More studies such as this will be required to identify how common coinfection with bacteria is,” he said.
“The take-home message is that although most children with COVID-19 have a mild or even asymptomatic course, some become severely ill requiring ventilator support and potentially ECMO [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation]. Potential predictors of severity include high C-reactive protein, obesity, and older age [adolescence], said Dr. Pelton, who was not involved in the study.
What additional research is needed? Dr. Pelton said that better markers of severe disease are needed, as well as an understanding of why obesity is a risk factor for severe disease in both children and adults. Are these prediabetic patients? he asked.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and high proportion of Hispanic patients, which may limit generalizability, and some symptoms and comorbidities may have been missed because of the retrospective nature of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results support the need for hospitals to remain vigilant to the variable presentations of COVID-19 infections in children.
“Therapeutic considerations need to [include] the risk of toxicity, control of antiviral replication, and early recognition and management of immune dysregulation,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Zachariah had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Zachariah P et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 June 3. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.2430.
according to data from 50 patients at a single tertiary care center.
“Risk factors for severe disease in pediatric populations have not been clearly identified and the high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in NYC offers an opportunity to describe severe pediatric disease in more detail,” wrote Philip Zachariah, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and colleagues.
In a retrospective case series published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 50 patients: 41 classified as severe and 9 classified as nonsevere. Among the patients, 27 were male and 25 were Hispanic. The patient population had a median of 2 days from symptom onset to hospital admission. The most common symptoms were fever (80%) and respiratory symptoms (64%). Seventy-six percent of patients had a median length of stay of 3 days (range 1-30 days).
At hospital admission, children with severe disease had significantly higher levels of several inflammatory markers compared with those without severe disease, notably C-reactive protein (median 8.978 mg/dL vs. 0.64 mg/dL) and procalcitonin (median 0.31 ng/mL vs. 0.17 ng/mL, (P < .001 for both). High mean peak levels of C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin 6, ferritin, and D-dimer were seen among the nine children (16%) who required mechanical ventilation, Dr. Zachariah and associates said.
None of the 14 infants and 1 of the 8 immunocompromised children in the study had severe disease, the researchers wrote.
Bacterial coinfections detected while patients were hospitalized were bacteremia in 6%, suspected bacterial pneumonia in 18%, urinary tract infections in 10%, skin and soft tissue infections in 6%, and streptococcus pharyngitis in 2%, Dr. Zachariah and associates reported.
Overall, 61% of the children had comorbidities identified in previous COVID-19 studies, of which obesity was the most common (22%); other comorbidities included asthma, sickle cell disease, cardiac disease, and diabetes. Obesity also was significantly associated with the need for mechanical ventilation in children aged 2 years and older (67%). A total of 16 patients required respiratory support, 9 of these were placed on mechanical ventilation; 6 of these 9 children were obese.
Fifteen patients (30%) who met criteria for increased oxygen requirements and respiratory distress received hydroxychloroquine, but the small sample size did not allow for assessment of treatment efficacy, the researchers said.
“Expanding our knowledge of COVID-19 [disease] in children will potentially permit early recognition of SARS-CoV-2 infection, understanding of the natural history of disease, and potential complications, said Stephen I. Pelton, MD, professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. This review of 50 SARS-CoV-2 infected children (less than 21 years of age) “provides insight into the short period of symptoms prior to hospitalization, challenges the concept that infants less than 1 year are at greatest risk of severe disease (as from the experience in China), and suggests rapid recovery in many children, as median length of stay was 3 days.
“The review revealed two findings that were surprising to me. First, the median length of stay of 3 days. As nearly 20% of the children required mechanical ventilation, it suggests many of the children were discharged quickly after evaluation, suggesting that we need to identify markers of severity to predict those children likely to have progressive disease and require respiratory support,” Dr. Pelton noted.
“The second observation suggests high rates of bacterial infection (bacteremia, pneumonia, UTI, and skin and soft tissue infection). I do not think this has been widely reported in adults, and may represent a difference between child and adult disease. More studies such as this will be required to identify how common coinfection with bacteria is,” he said.
“The take-home message is that although most children with COVID-19 have a mild or even asymptomatic course, some become severely ill requiring ventilator support and potentially ECMO [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation]. Potential predictors of severity include high C-reactive protein, obesity, and older age [adolescence], said Dr. Pelton, who was not involved in the study.
What additional research is needed? Dr. Pelton said that better markers of severe disease are needed, as well as an understanding of why obesity is a risk factor for severe disease in both children and adults. Are these prediabetic patients? he asked.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and high proportion of Hispanic patients, which may limit generalizability, and some symptoms and comorbidities may have been missed because of the retrospective nature of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results support the need for hospitals to remain vigilant to the variable presentations of COVID-19 infections in children.
“Therapeutic considerations need to [include] the risk of toxicity, control of antiviral replication, and early recognition and management of immune dysregulation,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Zachariah had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Zachariah P et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 June 3. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.2430.
according to data from 50 patients at a single tertiary care center.
“Risk factors for severe disease in pediatric populations have not been clearly identified and the high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in NYC offers an opportunity to describe severe pediatric disease in more detail,” wrote Philip Zachariah, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital, New York, and colleagues.
In a retrospective case series published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 50 patients: 41 classified as severe and 9 classified as nonsevere. Among the patients, 27 were male and 25 were Hispanic. The patient population had a median of 2 days from symptom onset to hospital admission. The most common symptoms were fever (80%) and respiratory symptoms (64%). Seventy-six percent of patients had a median length of stay of 3 days (range 1-30 days).
At hospital admission, children with severe disease had significantly higher levels of several inflammatory markers compared with those without severe disease, notably C-reactive protein (median 8.978 mg/dL vs. 0.64 mg/dL) and procalcitonin (median 0.31 ng/mL vs. 0.17 ng/mL, (P < .001 for both). High mean peak levels of C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukin 6, ferritin, and D-dimer were seen among the nine children (16%) who required mechanical ventilation, Dr. Zachariah and associates said.
None of the 14 infants and 1 of the 8 immunocompromised children in the study had severe disease, the researchers wrote.
Bacterial coinfections detected while patients were hospitalized were bacteremia in 6%, suspected bacterial pneumonia in 18%, urinary tract infections in 10%, skin and soft tissue infections in 6%, and streptococcus pharyngitis in 2%, Dr. Zachariah and associates reported.
Overall, 61% of the children had comorbidities identified in previous COVID-19 studies, of which obesity was the most common (22%); other comorbidities included asthma, sickle cell disease, cardiac disease, and diabetes. Obesity also was significantly associated with the need for mechanical ventilation in children aged 2 years and older (67%). A total of 16 patients required respiratory support, 9 of these were placed on mechanical ventilation; 6 of these 9 children were obese.
Fifteen patients (30%) who met criteria for increased oxygen requirements and respiratory distress received hydroxychloroquine, but the small sample size did not allow for assessment of treatment efficacy, the researchers said.
“Expanding our knowledge of COVID-19 [disease] in children will potentially permit early recognition of SARS-CoV-2 infection, understanding of the natural history of disease, and potential complications, said Stephen I. Pelton, MD, professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. This review of 50 SARS-CoV-2 infected children (less than 21 years of age) “provides insight into the short period of symptoms prior to hospitalization, challenges the concept that infants less than 1 year are at greatest risk of severe disease (as from the experience in China), and suggests rapid recovery in many children, as median length of stay was 3 days.
“The review revealed two findings that were surprising to me. First, the median length of stay of 3 days. As nearly 20% of the children required mechanical ventilation, it suggests many of the children were discharged quickly after evaluation, suggesting that we need to identify markers of severity to predict those children likely to have progressive disease and require respiratory support,” Dr. Pelton noted.
“The second observation suggests high rates of bacterial infection (bacteremia, pneumonia, UTI, and skin and soft tissue infection). I do not think this has been widely reported in adults, and may represent a difference between child and adult disease. More studies such as this will be required to identify how common coinfection with bacteria is,” he said.
“The take-home message is that although most children with COVID-19 have a mild or even asymptomatic course, some become severely ill requiring ventilator support and potentially ECMO [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation]. Potential predictors of severity include high C-reactive protein, obesity, and older age [adolescence], said Dr. Pelton, who was not involved in the study.
What additional research is needed? Dr. Pelton said that better markers of severe disease are needed, as well as an understanding of why obesity is a risk factor for severe disease in both children and adults. Are these prediabetic patients? he asked.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and high proportion of Hispanic patients, which may limit generalizability, and some symptoms and comorbidities may have been missed because of the retrospective nature of the study, the researchers noted. However, the results support the need for hospitals to remain vigilant to the variable presentations of COVID-19 infections in children.
“Therapeutic considerations need to [include] the risk of toxicity, control of antiviral replication, and early recognition and management of immune dysregulation,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Zachariah had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies and organizations. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Zachariah P et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 June 3. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.2430.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS