User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Vitamin D deficiency clearly linked to inflammation
Vitamin D deficiency has a causative role in the systemic inflammation that commonly accompanies it, with inflammation declining, reflected by reductions in elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), as vitamin D levels increase to normal levels, new research shows.
However, there is no reverse effect between the two: Changes in CRP levels did not appear to affect vitamin D levels.
first author Elina Hypponen, PhD, a professor in nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Centre for Precision Health, Adelaide, said in an interview.
“Given that the serum CRP level is a widely used biomarker for chronic inflammation, these results suggest that improving vitamin D status may reduce chronic inflammation, but only for people with vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen and coauthors reported in their study, published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Vitamin D associated with CRP in ‘L-shaped’ manner
Nutritional factors are known to influence systemic inflammation in a variety of ways. However, there has been debate over the association between vitamin D – specifically, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D), an indicator of vitamin D status – and CRP, with some reports of observational associations between the two disputed in more robust randomized trials.
To further evaluate the relationship, the authors performed a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis, using a cohort of 294,970 unrelated participants of White/British ancestry in the UK Biobank, the largest cohort to date with measured serum 25(OH)D concentrations, they noted.
Overall, the average 25(OH)D concentration was 50.0 nmol/L (range, 10-340 nmol/L), with 11.7% (n = 34,403) of participants having concentrations of less than 25 nmol/L, considered deficient.
The analysis showed that genetically predicted serum 25(OH)D was associated with serum CRP in an L-shaped manner, with CRP levels, and hence inflammation, sharply decreasing in relation to increasing 25(OH)D concentration to normal levels.
However, the relationship was only significant among participants with 25(OH)D levels in the deficiency range (< 25 nmol/L), with the association leveling off at about 50 nmol/L of 25(OH)D, which is generally considered a normal level.
The association was supported in further stratified Mendelian randomization analyses, which confirmed an inverse association between serum 25(OH)D in the deficiency range and CRP, but not with higher concentrations of serum vitamin D.
Conversely, neither linear nor nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses showed a causal effect of serum CRP level on 25(OH)D concentrations.
The findings suggest that “improving vitamin D status in the deficiency range could reduce systemic low-grade inflammation and potentially mitigate the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component,” the authors noted.
Dr. Hypponen added that the greatest reductions in CRP are observed with correction of the most severe vitamin D deficiency.
“The strongest benefits of improving concentrations will be seen for people with severe deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen said in an interview.
“In our study, much of the benefit was achieved when people reached the National Academy of Sciences endorsed cutoff of 50 nmol/L [for vitamin D sufficiency].”
Prohormone effects?
The anti-inflammatory effects observed with serum vitamin D could be related to its role as a prohormone that can impact vitamin D receptor–expressing immune cells, such as monocytes, B cells, T cells, and antigen-presenting cells, the authors noted.
“Indeed, cell experiments have shown that active vitamin D can inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including [tumor necrosis factor]–alpha, interleukin-1b, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12, and promote the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine,” they explained.
In that regard, adequate vitamin D concentrations could be important in preventing inflammation-related complications from obesity and reduce the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, and others, the authors noted.
Previous studies unable to assess effect of deficiency
While the current findings contradict other studies that have used Mendelian randomization and showed no causal effect of 25(OH)D on CRP, those previous studies only used a standard linear Mendelian randomization method that could not rule out the possibility of a ‘threshold effect’ restricted to vitamin D deficiency, the authors noted.
“Indeed, it is logical to expect that improving vitamin D status would be relevant only in the presence of vitamin D deficiency, whereas any further additions may be redundant and, in the ... extreme of supplementation, might become toxic,” they wrote.
However, the nonlinear Mendelian randomization approach used in the current study allows for better detection of the association, and the authors point out that the method has also been recently used in research showing an adverse effect of vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular disease risk and mortality, which would not be visible using the standard linear Mendelian randomization approach.
Meanwhile, the current findings add to broader research showing benefits of increases in vitamin D to be mainly limited to those who are deficient, with limited benefit of supplementation for those who are not, Dr. Hypponen emphasized.
“We have repeatedly seen evidence for health benefits for increasing vitamin D concentrations in individuals with very low levels, while for others, there appears to be little to no benefit,” Dr. Hypponen said in a press statement.
“These findings highlight the importance of avoiding clinical vitamin D deficiency and provide further evidence for the wide-ranging effects of hormonal vitamin D,” she added.
The study was financially supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D deficiency has a causative role in the systemic inflammation that commonly accompanies it, with inflammation declining, reflected by reductions in elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), as vitamin D levels increase to normal levels, new research shows.
However, there is no reverse effect between the two: Changes in CRP levels did not appear to affect vitamin D levels.
first author Elina Hypponen, PhD, a professor in nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Centre for Precision Health, Adelaide, said in an interview.
“Given that the serum CRP level is a widely used biomarker for chronic inflammation, these results suggest that improving vitamin D status may reduce chronic inflammation, but only for people with vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen and coauthors reported in their study, published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Vitamin D associated with CRP in ‘L-shaped’ manner
Nutritional factors are known to influence systemic inflammation in a variety of ways. However, there has been debate over the association between vitamin D – specifically, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D), an indicator of vitamin D status – and CRP, with some reports of observational associations between the two disputed in more robust randomized trials.
To further evaluate the relationship, the authors performed a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis, using a cohort of 294,970 unrelated participants of White/British ancestry in the UK Biobank, the largest cohort to date with measured serum 25(OH)D concentrations, they noted.
Overall, the average 25(OH)D concentration was 50.0 nmol/L (range, 10-340 nmol/L), with 11.7% (n = 34,403) of participants having concentrations of less than 25 nmol/L, considered deficient.
The analysis showed that genetically predicted serum 25(OH)D was associated with serum CRP in an L-shaped manner, with CRP levels, and hence inflammation, sharply decreasing in relation to increasing 25(OH)D concentration to normal levels.
However, the relationship was only significant among participants with 25(OH)D levels in the deficiency range (< 25 nmol/L), with the association leveling off at about 50 nmol/L of 25(OH)D, which is generally considered a normal level.
The association was supported in further stratified Mendelian randomization analyses, which confirmed an inverse association between serum 25(OH)D in the deficiency range and CRP, but not with higher concentrations of serum vitamin D.
Conversely, neither linear nor nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses showed a causal effect of serum CRP level on 25(OH)D concentrations.
The findings suggest that “improving vitamin D status in the deficiency range could reduce systemic low-grade inflammation and potentially mitigate the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component,” the authors noted.
Dr. Hypponen added that the greatest reductions in CRP are observed with correction of the most severe vitamin D deficiency.
“The strongest benefits of improving concentrations will be seen for people with severe deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen said in an interview.
“In our study, much of the benefit was achieved when people reached the National Academy of Sciences endorsed cutoff of 50 nmol/L [for vitamin D sufficiency].”
Prohormone effects?
The anti-inflammatory effects observed with serum vitamin D could be related to its role as a prohormone that can impact vitamin D receptor–expressing immune cells, such as monocytes, B cells, T cells, and antigen-presenting cells, the authors noted.
“Indeed, cell experiments have shown that active vitamin D can inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including [tumor necrosis factor]–alpha, interleukin-1b, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12, and promote the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine,” they explained.
In that regard, adequate vitamin D concentrations could be important in preventing inflammation-related complications from obesity and reduce the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, and others, the authors noted.
Previous studies unable to assess effect of deficiency
While the current findings contradict other studies that have used Mendelian randomization and showed no causal effect of 25(OH)D on CRP, those previous studies only used a standard linear Mendelian randomization method that could not rule out the possibility of a ‘threshold effect’ restricted to vitamin D deficiency, the authors noted.
“Indeed, it is logical to expect that improving vitamin D status would be relevant only in the presence of vitamin D deficiency, whereas any further additions may be redundant and, in the ... extreme of supplementation, might become toxic,” they wrote.
However, the nonlinear Mendelian randomization approach used in the current study allows for better detection of the association, and the authors point out that the method has also been recently used in research showing an adverse effect of vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular disease risk and mortality, which would not be visible using the standard linear Mendelian randomization approach.
Meanwhile, the current findings add to broader research showing benefits of increases in vitamin D to be mainly limited to those who are deficient, with limited benefit of supplementation for those who are not, Dr. Hypponen emphasized.
“We have repeatedly seen evidence for health benefits for increasing vitamin D concentrations in individuals with very low levels, while for others, there appears to be little to no benefit,” Dr. Hypponen said in a press statement.
“These findings highlight the importance of avoiding clinical vitamin D deficiency and provide further evidence for the wide-ranging effects of hormonal vitamin D,” she added.
The study was financially supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D deficiency has a causative role in the systemic inflammation that commonly accompanies it, with inflammation declining, reflected by reductions in elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), as vitamin D levels increase to normal levels, new research shows.
However, there is no reverse effect between the two: Changes in CRP levels did not appear to affect vitamin D levels.
first author Elina Hypponen, PhD, a professor in nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Centre for Precision Health, Adelaide, said in an interview.
“Given that the serum CRP level is a widely used biomarker for chronic inflammation, these results suggest that improving vitamin D status may reduce chronic inflammation, but only for people with vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen and coauthors reported in their study, published in the International Journal of Epidemiology.
Vitamin D associated with CRP in ‘L-shaped’ manner
Nutritional factors are known to influence systemic inflammation in a variety of ways. However, there has been debate over the association between vitamin D – specifically, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D), an indicator of vitamin D status – and CRP, with some reports of observational associations between the two disputed in more robust randomized trials.
To further evaluate the relationship, the authors performed a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis, using a cohort of 294,970 unrelated participants of White/British ancestry in the UK Biobank, the largest cohort to date with measured serum 25(OH)D concentrations, they noted.
Overall, the average 25(OH)D concentration was 50.0 nmol/L (range, 10-340 nmol/L), with 11.7% (n = 34,403) of participants having concentrations of less than 25 nmol/L, considered deficient.
The analysis showed that genetically predicted serum 25(OH)D was associated with serum CRP in an L-shaped manner, with CRP levels, and hence inflammation, sharply decreasing in relation to increasing 25(OH)D concentration to normal levels.
However, the relationship was only significant among participants with 25(OH)D levels in the deficiency range (< 25 nmol/L), with the association leveling off at about 50 nmol/L of 25(OH)D, which is generally considered a normal level.
The association was supported in further stratified Mendelian randomization analyses, which confirmed an inverse association between serum 25(OH)D in the deficiency range and CRP, but not with higher concentrations of serum vitamin D.
Conversely, neither linear nor nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses showed a causal effect of serum CRP level on 25(OH)D concentrations.
The findings suggest that “improving vitamin D status in the deficiency range could reduce systemic low-grade inflammation and potentially mitigate the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component,” the authors noted.
Dr. Hypponen added that the greatest reductions in CRP are observed with correction of the most severe vitamin D deficiency.
“The strongest benefits of improving concentrations will be seen for people with severe deficiency,” Dr. Hypponen said in an interview.
“In our study, much of the benefit was achieved when people reached the National Academy of Sciences endorsed cutoff of 50 nmol/L [for vitamin D sufficiency].”
Prohormone effects?
The anti-inflammatory effects observed with serum vitamin D could be related to its role as a prohormone that can impact vitamin D receptor–expressing immune cells, such as monocytes, B cells, T cells, and antigen-presenting cells, the authors noted.
“Indeed, cell experiments have shown that active vitamin D can inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including [tumor necrosis factor]–alpha, interleukin-1b, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12, and promote the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine,” they explained.
In that regard, adequate vitamin D concentrations could be important in preventing inflammation-related complications from obesity and reduce the risk or severity of chronic illnesses with an inflammatory component, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, and others, the authors noted.
Previous studies unable to assess effect of deficiency
While the current findings contradict other studies that have used Mendelian randomization and showed no causal effect of 25(OH)D on CRP, those previous studies only used a standard linear Mendelian randomization method that could not rule out the possibility of a ‘threshold effect’ restricted to vitamin D deficiency, the authors noted.
“Indeed, it is logical to expect that improving vitamin D status would be relevant only in the presence of vitamin D deficiency, whereas any further additions may be redundant and, in the ... extreme of supplementation, might become toxic,” they wrote.
However, the nonlinear Mendelian randomization approach used in the current study allows for better detection of the association, and the authors point out that the method has also been recently used in research showing an adverse effect of vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular disease risk and mortality, which would not be visible using the standard linear Mendelian randomization approach.
Meanwhile, the current findings add to broader research showing benefits of increases in vitamin D to be mainly limited to those who are deficient, with limited benefit of supplementation for those who are not, Dr. Hypponen emphasized.
“We have repeatedly seen evidence for health benefits for increasing vitamin D concentrations in individuals with very low levels, while for others, there appears to be little to no benefit,” Dr. Hypponen said in a press statement.
“These findings highlight the importance of avoiding clinical vitamin D deficiency and provide further evidence for the wide-ranging effects of hormonal vitamin D,” she added.
The study was financially supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY
Long COVID case study: persistent hormone deficiencies
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Stop pretending’ there’s a magic formula to weight loss
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care now offering physicians the 26.7-hour day
Taking ‘not enough hours in the day’ to new heights
It’s no secret that there’s a big doctor shortage in the United States. Going through medical school is long, expensive, and stressful, and it’s not like those long, stressful hours stop once you finally do get that degree. There is, however, an excellent reason to take that dive into doctorhood: You’ll gain mastery over time itself.
A study from the University of Chicago, Johns Hopkins University, and Imperial College London has revealed the truth. By using data pulled from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the researchers found that primary care physicians who see an average number of patients and follow all the current national guidelines for preventive care, chronic disease care, and acute care – plus administrative tasks – must work 26.7 hours a day. That works out to 14.1 hours of preventive care, 7.2 hours of chronic disease care, 2.2 hours of acute care, and 3.2 hours of documentation and inbox management.
Astute readers may note that this is a bit more than the traditional 8-hour workday. It is, in fact, more hours than there actually are in a day. As it turns out, Doctor Strange is more of a documentary than …
Hang on, we’re receiving word that doctors are not in fact wizards who can bend time and space to their will, nor are they sitting on a stash of Time-Turners they saved from the Ministry of Magic before Voldemort destroyed them all. They are, according to the study, overworked and overburdened with too many things and too little time. This is why outcomes haven’t improved despite technological advances and why burnout is so common. We’d be burned out too, having to work temporally impossible hours.
The study authors suggested a team-based approach to medicine that would spread the workload out to nurses, physician assistants, dietitians, etc., estimating that about two-thirds of what a primary care physician does can be handled by someone else. A team-based approach would reduce the physician’s required hours down to 9.3 hours a day, which is at least physically possible. It’s either that or we make the day longer, which sounds like the plot of an episode of Futurama. Swap overwork for global warming and a longer day for a longer year and it is actually the plot of an episode of Futurama.
After a hard day of thinking, brains need their rest
Do you ever feel like you have no more capacity to think or make any more decisions after a long day at work? Do you need a few extra cups of coffee to even make it through the day, even though you’re mostly just sitting around talking and typing? Have we got the research for you: Mental exhaustion is an actual thing. Imagine that double whammy of having a job that’s physically and mentally demanding.
A recent study in Current Biology explained why we feel so exhausted after doing something mentally demanding for several hours. Over that time, glutamate builds up in synapses of the prefrontal cortex, which affects our decision making and leads to cognitive lethargy. Your brain eventually becomes more interested in tasks that are less mentally fatiguing, and that’s probably why you’re reading this LOTME right now instead of getting back to work.
“Our findings show that cognitive work results in a true functional alteration – accumulation of noxious substances – so fatigue would indeed be a signal that makes us stop working but for a different purpose: to preserve the integrity of brain functioning,” senior author Mathias Pessiglione of Pitié-Salpêtrière University, Paris, said in a written statement.
The group of researchers conducted studies by using magnetic resonance spectroscopy to look at two groups of people over the course of a workday: One group had mentally tasking jobs and one didn’t. Those who had to think harder for their jobs had more signs of fatigue, such as reduced pupil dilation and glutamate in synapses of the prefrontal cortex. They also looked for more rewards that required less thinking.
For those whose mentally exhausting jobs probably won’t get better or change, the researchers suggest getting as much rest as possible. Those who don’t have that option will have to continue drinking those 7 cups of coffee a day. ... and reading LOTME.
Hmm, might be a new tagline for us in there somewhere. LOTME: Tired brains love us? When you’re too tired to think, think of LOTME? You can’t spell mental exhaustion without L-O-T-M-E?
Testosterone shows its warm and fuzzy side
Stereotypically, men are loud, knuckle-dragging Neanderthals. The hair coming out of our faces is kind of a dead giveaway, right? We grunt, we scratch, we start wars, we watch sports on TV. But why? It’s the testosterone. Everyone knows that. Testosterone makes men aggressive … or does it?
Since this sort of research generally isn’t done with actual men, investigators at Emory University used Mongolian gerbils. The advantage being that males exhibit cuddling behavior after females become pregnant and they don’t watch a lot of sports on TV. They introduced a male and female gerbil, who then formed a pair bond and the female became pregnant. When the male started displaying cuddling behaviors, the researchers injected him with testosterone, expecting to see his antisocial side.
“Instead, we were surprised that a male gerbil became even more cuddly and prosocial with his partner. He became like ‘super partner,’ ” lead author Aubrey Kelly, PhD, said in a written statement from the university.
For the next experiment, the female was removed and another male was introduced to a male who had already received a testosterone injection. That male was surprisingly unaggressive toward the intruder, at least initially. Then he received a second injection of testosterone. “It was like they suddenly woke up and realized they weren’t supposed to be friendly in that context,” Dr. Kelly said.
The testosterone seemed to influence the activity of oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” the investigators suggested. “It’s surprising because normally we think of testosterone as increasing sexual behaviors and aggression. But we’ve shown that it can have more nuanced effects, depending on the social context.”
The researchers were not as surprised when their use of the phrase “super partner” led to a bidding war between DC and Marvel. Then came the contact from the Department of Defense, wondering about weaponized testosterone: Would it be possible for some sort of bomb to turn Vlad “the Impaler” Putin into Vlad “the Cuddler” Putin?
Are instruments spreading the sounds of COVID?
COVID restrictions are practically a thing of the past now. With more people laxed on being in close proximity to each other and the CDC not even recommending social distancing anymore, live concerts and events are back in full swing. But with new variants on the rise and people being a little more cautious, should we be worried about musical instruments spreading COVID?
Yes and no.
A study published in Physics of Fluids looked at wind instruments specifically and how much aerosol is produced and dispersed when playing them. For the study, the investigators measured fog particles with a laser and aerosol concentration with a particle counter to see how fast these particles decay in the air from the distance of the instrument.
Musicians in an orchestra typically would sit close together to produce the best sound, but with COVID that became an issue, senior author Paulo Arratia of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in a separate written statement. By looking at the distance traveled by the particles coming from a single instrument and how quickly they decayed, they could determine if sitting in close proximity is an actual threat.
Well, the threat was no greater than talking to someone face to face. Particle exit speeds were lower than for a cough or a sneeze, and the maximum decay length was 2 meters from the instrument’s opening.
But that’s just one instrument: What kind of impact does a whole orchestra have on a space? The researchers are looking into that too, but for now they suggest that musicians continue to stay 6 feet away from each other.
So, yeah, there is a threat, but it’s probably safer for you to see that orchestra than have someone sneeze on you.
Music to our ears.
Taking ‘not enough hours in the day’ to new heights
It’s no secret that there’s a big doctor shortage in the United States. Going through medical school is long, expensive, and stressful, and it’s not like those long, stressful hours stop once you finally do get that degree. There is, however, an excellent reason to take that dive into doctorhood: You’ll gain mastery over time itself.
A study from the University of Chicago, Johns Hopkins University, and Imperial College London has revealed the truth. By using data pulled from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the researchers found that primary care physicians who see an average number of patients and follow all the current national guidelines for preventive care, chronic disease care, and acute care – plus administrative tasks – must work 26.7 hours a day. That works out to 14.1 hours of preventive care, 7.2 hours of chronic disease care, 2.2 hours of acute care, and 3.2 hours of documentation and inbox management.
Astute readers may note that this is a bit more than the traditional 8-hour workday. It is, in fact, more hours than there actually are in a day. As it turns out, Doctor Strange is more of a documentary than …
Hang on, we’re receiving word that doctors are not in fact wizards who can bend time and space to their will, nor are they sitting on a stash of Time-Turners they saved from the Ministry of Magic before Voldemort destroyed them all. They are, according to the study, overworked and overburdened with too many things and too little time. This is why outcomes haven’t improved despite technological advances and why burnout is so common. We’d be burned out too, having to work temporally impossible hours.
The study authors suggested a team-based approach to medicine that would spread the workload out to nurses, physician assistants, dietitians, etc., estimating that about two-thirds of what a primary care physician does can be handled by someone else. A team-based approach would reduce the physician’s required hours down to 9.3 hours a day, which is at least physically possible. It’s either that or we make the day longer, which sounds like the plot of an episode of Futurama. Swap overwork for global warming and a longer day for a longer year and it is actually the plot of an episode of Futurama.
After a hard day of thinking, brains need their rest
Do you ever feel like you have no more capacity to think or make any more decisions after a long day at work? Do you need a few extra cups of coffee to even make it through the day, even though you’re mostly just sitting around talking and typing? Have we got the research for you: Mental exhaustion is an actual thing. Imagine that double whammy of having a job that’s physically and mentally demanding.
A recent study in Current Biology explained why we feel so exhausted after doing something mentally demanding for several hours. Over that time, glutamate builds up in synapses of the prefrontal cortex, which affects our decision making and leads to cognitive lethargy. Your brain eventually becomes more interested in tasks that are less mentally fatiguing, and that’s probably why you’re reading this LOTME right now instead of getting back to work.
“Our findings show that cognitive work results in a true functional alteration – accumulation of noxious substances – so fatigue would indeed be a signal that makes us stop working but for a different purpose: to preserve the integrity of brain functioning,” senior author Mathias Pessiglione of Pitié-Salpêtrière University, Paris, said in a written statement.
The group of researchers conducted studies by using magnetic resonance spectroscopy to look at two groups of people over the course of a workday: One group had mentally tasking jobs and one didn’t. Those who had to think harder for their jobs had more signs of fatigue, such as reduced pupil dilation and glutamate in synapses of the prefrontal cortex. They also looked for more rewards that required less thinking.
For those whose mentally exhausting jobs probably won’t get better or change, the researchers suggest getting as much rest as possible. Those who don’t have that option will have to continue drinking those 7 cups of coffee a day. ... and reading LOTME.
Hmm, might be a new tagline for us in there somewhere. LOTME: Tired brains love us? When you’re too tired to think, think of LOTME? You can’t spell mental exhaustion without L-O-T-M-E?
Testosterone shows its warm and fuzzy side
Stereotypically, men are loud, knuckle-dragging Neanderthals. The hair coming out of our faces is kind of a dead giveaway, right? We grunt, we scratch, we start wars, we watch sports on TV. But why? It’s the testosterone. Everyone knows that. Testosterone makes men aggressive … or does it?
Since this sort of research generally isn’t done with actual men, investigators at Emory University used Mongolian gerbils. The advantage being that males exhibit cuddling behavior after females become pregnant and they don’t watch a lot of sports on TV. They introduced a male and female gerbil, who then formed a pair bond and the female became pregnant. When the male started displaying cuddling behaviors, the researchers injected him with testosterone, expecting to see his antisocial side.
“Instead, we were surprised that a male gerbil became even more cuddly and prosocial with his partner. He became like ‘super partner,’ ” lead author Aubrey Kelly, PhD, said in a written statement from the university.
For the next experiment, the female was removed and another male was introduced to a male who had already received a testosterone injection. That male was surprisingly unaggressive toward the intruder, at least initially. Then he received a second injection of testosterone. “It was like they suddenly woke up and realized they weren’t supposed to be friendly in that context,” Dr. Kelly said.
The testosterone seemed to influence the activity of oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” the investigators suggested. “It’s surprising because normally we think of testosterone as increasing sexual behaviors and aggression. But we’ve shown that it can have more nuanced effects, depending on the social context.”
The researchers were not as surprised when their use of the phrase “super partner” led to a bidding war between DC and Marvel. Then came the contact from the Department of Defense, wondering about weaponized testosterone: Would it be possible for some sort of bomb to turn Vlad “the Impaler” Putin into Vlad “the Cuddler” Putin?
Are instruments spreading the sounds of COVID?
COVID restrictions are practically a thing of the past now. With more people laxed on being in close proximity to each other and the CDC not even recommending social distancing anymore, live concerts and events are back in full swing. But with new variants on the rise and people being a little more cautious, should we be worried about musical instruments spreading COVID?
Yes and no.
A study published in Physics of Fluids looked at wind instruments specifically and how much aerosol is produced and dispersed when playing them. For the study, the investigators measured fog particles with a laser and aerosol concentration with a particle counter to see how fast these particles decay in the air from the distance of the instrument.
Musicians in an orchestra typically would sit close together to produce the best sound, but with COVID that became an issue, senior author Paulo Arratia of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in a separate written statement. By looking at the distance traveled by the particles coming from a single instrument and how quickly they decayed, they could determine if sitting in close proximity is an actual threat.
Well, the threat was no greater than talking to someone face to face. Particle exit speeds were lower than for a cough or a sneeze, and the maximum decay length was 2 meters from the instrument’s opening.
But that’s just one instrument: What kind of impact does a whole orchestra have on a space? The researchers are looking into that too, but for now they suggest that musicians continue to stay 6 feet away from each other.
So, yeah, there is a threat, but it’s probably safer for you to see that orchestra than have someone sneeze on you.
Music to our ears.
Taking ‘not enough hours in the day’ to new heights
It’s no secret that there’s a big doctor shortage in the United States. Going through medical school is long, expensive, and stressful, and it’s not like those long, stressful hours stop once you finally do get that degree. There is, however, an excellent reason to take that dive into doctorhood: You’ll gain mastery over time itself.
A study from the University of Chicago, Johns Hopkins University, and Imperial College London has revealed the truth. By using data pulled from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the researchers found that primary care physicians who see an average number of patients and follow all the current national guidelines for preventive care, chronic disease care, and acute care – plus administrative tasks – must work 26.7 hours a day. That works out to 14.1 hours of preventive care, 7.2 hours of chronic disease care, 2.2 hours of acute care, and 3.2 hours of documentation and inbox management.
Astute readers may note that this is a bit more than the traditional 8-hour workday. It is, in fact, more hours than there actually are in a day. As it turns out, Doctor Strange is more of a documentary than …
Hang on, we’re receiving word that doctors are not in fact wizards who can bend time and space to their will, nor are they sitting on a stash of Time-Turners they saved from the Ministry of Magic before Voldemort destroyed them all. They are, according to the study, overworked and overburdened with too many things and too little time. This is why outcomes haven’t improved despite technological advances and why burnout is so common. We’d be burned out too, having to work temporally impossible hours.
The study authors suggested a team-based approach to medicine that would spread the workload out to nurses, physician assistants, dietitians, etc., estimating that about two-thirds of what a primary care physician does can be handled by someone else. A team-based approach would reduce the physician’s required hours down to 9.3 hours a day, which is at least physically possible. It’s either that or we make the day longer, which sounds like the plot of an episode of Futurama. Swap overwork for global warming and a longer day for a longer year and it is actually the plot of an episode of Futurama.
After a hard day of thinking, brains need their rest
Do you ever feel like you have no more capacity to think or make any more decisions after a long day at work? Do you need a few extra cups of coffee to even make it through the day, even though you’re mostly just sitting around talking and typing? Have we got the research for you: Mental exhaustion is an actual thing. Imagine that double whammy of having a job that’s physically and mentally demanding.
A recent study in Current Biology explained why we feel so exhausted after doing something mentally demanding for several hours. Over that time, glutamate builds up in synapses of the prefrontal cortex, which affects our decision making and leads to cognitive lethargy. Your brain eventually becomes more interested in tasks that are less mentally fatiguing, and that’s probably why you’re reading this LOTME right now instead of getting back to work.
“Our findings show that cognitive work results in a true functional alteration – accumulation of noxious substances – so fatigue would indeed be a signal that makes us stop working but for a different purpose: to preserve the integrity of brain functioning,” senior author Mathias Pessiglione of Pitié-Salpêtrière University, Paris, said in a written statement.
The group of researchers conducted studies by using magnetic resonance spectroscopy to look at two groups of people over the course of a workday: One group had mentally tasking jobs and one didn’t. Those who had to think harder for their jobs had more signs of fatigue, such as reduced pupil dilation and glutamate in synapses of the prefrontal cortex. They also looked for more rewards that required less thinking.
For those whose mentally exhausting jobs probably won’t get better or change, the researchers suggest getting as much rest as possible. Those who don’t have that option will have to continue drinking those 7 cups of coffee a day. ... and reading LOTME.
Hmm, might be a new tagline for us in there somewhere. LOTME: Tired brains love us? When you’re too tired to think, think of LOTME? You can’t spell mental exhaustion without L-O-T-M-E?
Testosterone shows its warm and fuzzy side
Stereotypically, men are loud, knuckle-dragging Neanderthals. The hair coming out of our faces is kind of a dead giveaway, right? We grunt, we scratch, we start wars, we watch sports on TV. But why? It’s the testosterone. Everyone knows that. Testosterone makes men aggressive … or does it?
Since this sort of research generally isn’t done with actual men, investigators at Emory University used Mongolian gerbils. The advantage being that males exhibit cuddling behavior after females become pregnant and they don’t watch a lot of sports on TV. They introduced a male and female gerbil, who then formed a pair bond and the female became pregnant. When the male started displaying cuddling behaviors, the researchers injected him with testosterone, expecting to see his antisocial side.
“Instead, we were surprised that a male gerbil became even more cuddly and prosocial with his partner. He became like ‘super partner,’ ” lead author Aubrey Kelly, PhD, said in a written statement from the university.
For the next experiment, the female was removed and another male was introduced to a male who had already received a testosterone injection. That male was surprisingly unaggressive toward the intruder, at least initially. Then he received a second injection of testosterone. “It was like they suddenly woke up and realized they weren’t supposed to be friendly in that context,” Dr. Kelly said.
The testosterone seemed to influence the activity of oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” the investigators suggested. “It’s surprising because normally we think of testosterone as increasing sexual behaviors and aggression. But we’ve shown that it can have more nuanced effects, depending on the social context.”
The researchers were not as surprised when their use of the phrase “super partner” led to a bidding war between DC and Marvel. Then came the contact from the Department of Defense, wondering about weaponized testosterone: Would it be possible for some sort of bomb to turn Vlad “the Impaler” Putin into Vlad “the Cuddler” Putin?
Are instruments spreading the sounds of COVID?
COVID restrictions are practically a thing of the past now. With more people laxed on being in close proximity to each other and the CDC not even recommending social distancing anymore, live concerts and events are back in full swing. But with new variants on the rise and people being a little more cautious, should we be worried about musical instruments spreading COVID?
Yes and no.
A study published in Physics of Fluids looked at wind instruments specifically and how much aerosol is produced and dispersed when playing them. For the study, the investigators measured fog particles with a laser and aerosol concentration with a particle counter to see how fast these particles decay in the air from the distance of the instrument.
Musicians in an orchestra typically would sit close together to produce the best sound, but with COVID that became an issue, senior author Paulo Arratia of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in a separate written statement. By looking at the distance traveled by the particles coming from a single instrument and how quickly they decayed, they could determine if sitting in close proximity is an actual threat.
Well, the threat was no greater than talking to someone face to face. Particle exit speeds were lower than for a cough or a sneeze, and the maximum decay length was 2 meters from the instrument’s opening.
But that’s just one instrument: What kind of impact does a whole orchestra have on a space? The researchers are looking into that too, but for now they suggest that musicians continue to stay 6 feet away from each other.
So, yeah, there is a threat, but it’s probably safer for you to see that orchestra than have someone sneeze on you.
Music to our ears.
Asking patients about their gender identity: ‘Normalize’ the discussion and other recommendations
PORTLAND, ORE. –
“From the patient perspective, there’s nothing more awkward than having an awkward provider asking awkward questions,” Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
In 2014, Sean Cahill, PhD, and Harvey Makadon, MD, published an article recommending the inclusion of sexual orientation and gender identity questions in electronic medical records, a practice that Dr. Yeung characterized as “the most patient-centered way to collect sexual orientation and gender identity information. The most important thing is to ask routinely on an intake form where they fill it out themselves. All electronic medical records have the capacity to do so.”
On the other hand, when asking new patients about their sexual orientation and gender identity in person, it’s important to normalize the discussion and ask in an inclusive way, said Dr. Yeung, who was the lead author on published recommendations on dermatologic care for LGBTQ persons published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “For example, I always say, ‘I’m Howa Yeung. I use him pronouns,’ ” he said. “ ‘How should I address you?’ Then they will tell you. Allow people to lead the way.”
Other suggested tips in the JAAD article include to avoid using terms such as “sir” or “miss” until the patient’s gender identify is ascertained. Instead, use gender-neutral terms such as “they” or “the patient” when referring to new patients. Do not use the pronoun “it.” If a patient’s name does not match a name in the medical record, ask, “What is the name on your insurance/records?” and avoid assuming gender(s) of a patient’s partner or parents. Instead, consider asking, “Who did you bring with you today?” “Are you in a relationship?” “What are the names of your parents?”
Normalizing questions about the patient’s sexual history is also key. “I tell patients that I routinely ask about sexual history for patients with similar skin issues because it helps me provide the best care for them,” Dr. Yeung said. “I also discuss confidentiality and documentation.”
Dr. Yeung reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. –
“From the patient perspective, there’s nothing more awkward than having an awkward provider asking awkward questions,” Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
In 2014, Sean Cahill, PhD, and Harvey Makadon, MD, published an article recommending the inclusion of sexual orientation and gender identity questions in electronic medical records, a practice that Dr. Yeung characterized as “the most patient-centered way to collect sexual orientation and gender identity information. The most important thing is to ask routinely on an intake form where they fill it out themselves. All electronic medical records have the capacity to do so.”
On the other hand, when asking new patients about their sexual orientation and gender identity in person, it’s important to normalize the discussion and ask in an inclusive way, said Dr. Yeung, who was the lead author on published recommendations on dermatologic care for LGBTQ persons published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “For example, I always say, ‘I’m Howa Yeung. I use him pronouns,’ ” he said. “ ‘How should I address you?’ Then they will tell you. Allow people to lead the way.”
Other suggested tips in the JAAD article include to avoid using terms such as “sir” or “miss” until the patient’s gender identify is ascertained. Instead, use gender-neutral terms such as “they” or “the patient” when referring to new patients. Do not use the pronoun “it.” If a patient’s name does not match a name in the medical record, ask, “What is the name on your insurance/records?” and avoid assuming gender(s) of a patient’s partner or parents. Instead, consider asking, “Who did you bring with you today?” “Are you in a relationship?” “What are the names of your parents?”
Normalizing questions about the patient’s sexual history is also key. “I tell patients that I routinely ask about sexual history for patients with similar skin issues because it helps me provide the best care for them,” Dr. Yeung said. “I also discuss confidentiality and documentation.”
Dr. Yeung reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. –
“From the patient perspective, there’s nothing more awkward than having an awkward provider asking awkward questions,” Howa Yeung, MD, MSc, assistant professor of dermatology at Emory University, Atlanta, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
In 2014, Sean Cahill, PhD, and Harvey Makadon, MD, published an article recommending the inclusion of sexual orientation and gender identity questions in electronic medical records, a practice that Dr. Yeung characterized as “the most patient-centered way to collect sexual orientation and gender identity information. The most important thing is to ask routinely on an intake form where they fill it out themselves. All electronic medical records have the capacity to do so.”
On the other hand, when asking new patients about their sexual orientation and gender identity in person, it’s important to normalize the discussion and ask in an inclusive way, said Dr. Yeung, who was the lead author on published recommendations on dermatologic care for LGBTQ persons published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “For example, I always say, ‘I’m Howa Yeung. I use him pronouns,’ ” he said. “ ‘How should I address you?’ Then they will tell you. Allow people to lead the way.”
Other suggested tips in the JAAD article include to avoid using terms such as “sir” or “miss” until the patient’s gender identify is ascertained. Instead, use gender-neutral terms such as “they” or “the patient” when referring to new patients. Do not use the pronoun “it.” If a patient’s name does not match a name in the medical record, ask, “What is the name on your insurance/records?” and avoid assuming gender(s) of a patient’s partner or parents. Instead, consider asking, “Who did you bring with you today?” “Are you in a relationship?” “What are the names of your parents?”
Normalizing questions about the patient’s sexual history is also key. “I tell patients that I routinely ask about sexual history for patients with similar skin issues because it helps me provide the best care for them,” Dr. Yeung said. “I also discuss confidentiality and documentation.”
Dr. Yeung reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT PDA 2022
Pediatricians at odds over gender-affirming care for trans kids
Some members of the American Academy of Pediatrics say its association leadership is blocking discussion about a resolution asking for a “rigorous systematic review” of gender-affirming care guidelines.
At issue is 2018 guidance that states children can undergo hormonal therapy after they are deemed appropriate candidates following a thorough mental health evaluation.
Critics say minors under age 18 may be getting “fast-tracked” to hormonal treatment too quickly or inappropriately and can end up regretting the decision and facing medical conditions like sterility.
Five AAP members, which has a total membership of around 67,000 pediatricians in the United States and Canada, this year penned Resolution 27, calling for a possible update of the guidelines following consultation with stakeholders that include mental health and medical clinicians, parents, and patients “with diverse views and experiences.”
Those members and others in written comments on a members-only website accuse the AAP of deliberately silencing debate on the issue and changing resolution rules. Any AAP member can submit a resolution for consideration by the group’s leadership at its annual policy meeting.
This year, the AAP sent an email to members stating it would not allow comments on resolutions that had not been “sponsored” by one of the group’s 66 chapters or 88 internal committees, councils, or sections.
That’s why comments were not allowed on Resolution 27, said Mark Del Monte, the AAP’s CEO. A second attempt to get sponsorship during the annual leadership forum, held earlier this month in Chicago, also failed, he noted. Mr. Del Monte told this news organization that changes to the resolution process are made every year and that no rule changes were directly associated with Resolution 27.
But one of the resolution’s authors said there was sponsorship when members first drafted the suggestion. Julia Mason, MD, a board member for the Society for Evidence-based Gender Medicine and a pediatrician in private practice in Gresham, Ore., says an AAP chapter president agreed to second Resolution 27 but backed off after attending a different AAP meeting. Dr. Mason did not name the member.
On Aug. 10, AAP President Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, wrote in a blog on the AAP website – after the AAP leadership meeting in Chicago – that the lack of sponsorship “meant no one was willing to support their proposal.”
The AAP Leadership Council’s 154 voting entities approved 48 resolutions at the meeting, all of which will be referred to the AAP Board of Directors for potential, but not definite, action as the Board only takes resolutions under advisement, Mr. Del Monte notes.
In an email allowing members to comment on a resolution (number 28) regarding education support for caring for transgender patients, 23 chose to support Resolution 27 instead.
“I am wholeheartedly in support of Resolution 27, which interestingly has been removed from the list of resolutions for member comment,” one comment read. “I can no longer trust the AAP to provide medical evidence-based education with regard to care for transgender individuals.”
“We don’t need a formal resolution to look at the evidence around the care of transgender young people. Evaluating the evidence behind our recommendations, which the unsponsored resolution called for, is a routine part of the Academy’s policy-writing process,” wrote Dr. Szilagyi in her blog.
Mr. Del Monte says that “the 2018 policy is under review now.”
So far, “the evidence that we have seen reinforces our policy that gender-affirming care is the correct approach,” Mr. Del Monte stresses. “It is supported by every mainstream medical society in the world and is the standard of care,” he maintains.
Among those societies is the World Professional Association for Transgender Health, which in the draft of its latest Standards of Care (SOC8) – the first new guidance on the issue for 10 years – reportedly lowers the age for “top surgery” to 15 years.
The final SOC8 will most likely be published to coincide with WPATH’s annual meeting in September in Montreal.
Opponents plan to protest outside the AAP’s annual meeting, in Anaheim in October, Dr. Mason says.
“I’m concerned that kids with a transient gender identity are being funneled into medicalization that does not serve them,” Dr. Mason says. “I am worried that the trans identity is valued over the possibility of desistance,” she adds, admitting that her goal is to have fewer children transition gender.
Last summer, AAP found itself in hot water on the same topic when it barred SEGM from having a booth at the AAP annual meeting in 2021, as reported by this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some members of the American Academy of Pediatrics say its association leadership is blocking discussion about a resolution asking for a “rigorous systematic review” of gender-affirming care guidelines.
At issue is 2018 guidance that states children can undergo hormonal therapy after they are deemed appropriate candidates following a thorough mental health evaluation.
Critics say minors under age 18 may be getting “fast-tracked” to hormonal treatment too quickly or inappropriately and can end up regretting the decision and facing medical conditions like sterility.
Five AAP members, which has a total membership of around 67,000 pediatricians in the United States and Canada, this year penned Resolution 27, calling for a possible update of the guidelines following consultation with stakeholders that include mental health and medical clinicians, parents, and patients “with diverse views and experiences.”
Those members and others in written comments on a members-only website accuse the AAP of deliberately silencing debate on the issue and changing resolution rules. Any AAP member can submit a resolution for consideration by the group’s leadership at its annual policy meeting.
This year, the AAP sent an email to members stating it would not allow comments on resolutions that had not been “sponsored” by one of the group’s 66 chapters or 88 internal committees, councils, or sections.
That’s why comments were not allowed on Resolution 27, said Mark Del Monte, the AAP’s CEO. A second attempt to get sponsorship during the annual leadership forum, held earlier this month in Chicago, also failed, he noted. Mr. Del Monte told this news organization that changes to the resolution process are made every year and that no rule changes were directly associated with Resolution 27.
But one of the resolution’s authors said there was sponsorship when members first drafted the suggestion. Julia Mason, MD, a board member for the Society for Evidence-based Gender Medicine and a pediatrician in private practice in Gresham, Ore., says an AAP chapter president agreed to second Resolution 27 but backed off after attending a different AAP meeting. Dr. Mason did not name the member.
On Aug. 10, AAP President Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, wrote in a blog on the AAP website – after the AAP leadership meeting in Chicago – that the lack of sponsorship “meant no one was willing to support their proposal.”
The AAP Leadership Council’s 154 voting entities approved 48 resolutions at the meeting, all of which will be referred to the AAP Board of Directors for potential, but not definite, action as the Board only takes resolutions under advisement, Mr. Del Monte notes.
In an email allowing members to comment on a resolution (number 28) regarding education support for caring for transgender patients, 23 chose to support Resolution 27 instead.
“I am wholeheartedly in support of Resolution 27, which interestingly has been removed from the list of resolutions for member comment,” one comment read. “I can no longer trust the AAP to provide medical evidence-based education with regard to care for transgender individuals.”
“We don’t need a formal resolution to look at the evidence around the care of transgender young people. Evaluating the evidence behind our recommendations, which the unsponsored resolution called for, is a routine part of the Academy’s policy-writing process,” wrote Dr. Szilagyi in her blog.
Mr. Del Monte says that “the 2018 policy is under review now.”
So far, “the evidence that we have seen reinforces our policy that gender-affirming care is the correct approach,” Mr. Del Monte stresses. “It is supported by every mainstream medical society in the world and is the standard of care,” he maintains.
Among those societies is the World Professional Association for Transgender Health, which in the draft of its latest Standards of Care (SOC8) – the first new guidance on the issue for 10 years – reportedly lowers the age for “top surgery” to 15 years.
The final SOC8 will most likely be published to coincide with WPATH’s annual meeting in September in Montreal.
Opponents plan to protest outside the AAP’s annual meeting, in Anaheim in October, Dr. Mason says.
“I’m concerned that kids with a transient gender identity are being funneled into medicalization that does not serve them,” Dr. Mason says. “I am worried that the trans identity is valued over the possibility of desistance,” she adds, admitting that her goal is to have fewer children transition gender.
Last summer, AAP found itself in hot water on the same topic when it barred SEGM from having a booth at the AAP annual meeting in 2021, as reported by this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some members of the American Academy of Pediatrics say its association leadership is blocking discussion about a resolution asking for a “rigorous systematic review” of gender-affirming care guidelines.
At issue is 2018 guidance that states children can undergo hormonal therapy after they are deemed appropriate candidates following a thorough mental health evaluation.
Critics say minors under age 18 may be getting “fast-tracked” to hormonal treatment too quickly or inappropriately and can end up regretting the decision and facing medical conditions like sterility.
Five AAP members, which has a total membership of around 67,000 pediatricians in the United States and Canada, this year penned Resolution 27, calling for a possible update of the guidelines following consultation with stakeholders that include mental health and medical clinicians, parents, and patients “with diverse views and experiences.”
Those members and others in written comments on a members-only website accuse the AAP of deliberately silencing debate on the issue and changing resolution rules. Any AAP member can submit a resolution for consideration by the group’s leadership at its annual policy meeting.
This year, the AAP sent an email to members stating it would not allow comments on resolutions that had not been “sponsored” by one of the group’s 66 chapters or 88 internal committees, councils, or sections.
That’s why comments were not allowed on Resolution 27, said Mark Del Monte, the AAP’s CEO. A second attempt to get sponsorship during the annual leadership forum, held earlier this month in Chicago, also failed, he noted. Mr. Del Monte told this news organization that changes to the resolution process are made every year and that no rule changes were directly associated with Resolution 27.
But one of the resolution’s authors said there was sponsorship when members first drafted the suggestion. Julia Mason, MD, a board member for the Society for Evidence-based Gender Medicine and a pediatrician in private practice in Gresham, Ore., says an AAP chapter president agreed to second Resolution 27 but backed off after attending a different AAP meeting. Dr. Mason did not name the member.
On Aug. 10, AAP President Moira Szilagyi, MD, PhD, wrote in a blog on the AAP website – after the AAP leadership meeting in Chicago – that the lack of sponsorship “meant no one was willing to support their proposal.”
The AAP Leadership Council’s 154 voting entities approved 48 resolutions at the meeting, all of which will be referred to the AAP Board of Directors for potential, but not definite, action as the Board only takes resolutions under advisement, Mr. Del Monte notes.
In an email allowing members to comment on a resolution (number 28) regarding education support for caring for transgender patients, 23 chose to support Resolution 27 instead.
“I am wholeheartedly in support of Resolution 27, which interestingly has been removed from the list of resolutions for member comment,” one comment read. “I can no longer trust the AAP to provide medical evidence-based education with regard to care for transgender individuals.”
“We don’t need a formal resolution to look at the evidence around the care of transgender young people. Evaluating the evidence behind our recommendations, which the unsponsored resolution called for, is a routine part of the Academy’s policy-writing process,” wrote Dr. Szilagyi in her blog.
Mr. Del Monte says that “the 2018 policy is under review now.”
So far, “the evidence that we have seen reinforces our policy that gender-affirming care is the correct approach,” Mr. Del Monte stresses. “It is supported by every mainstream medical society in the world and is the standard of care,” he maintains.
Among those societies is the World Professional Association for Transgender Health, which in the draft of its latest Standards of Care (SOC8) – the first new guidance on the issue for 10 years – reportedly lowers the age for “top surgery” to 15 years.
The final SOC8 will most likely be published to coincide with WPATH’s annual meeting in September in Montreal.
Opponents plan to protest outside the AAP’s annual meeting, in Anaheim in October, Dr. Mason says.
“I’m concerned that kids with a transient gender identity are being funneled into medicalization that does not serve them,” Dr. Mason says. “I am worried that the trans identity is valued over the possibility of desistance,” she adds, admitting that her goal is to have fewer children transition gender.
Last summer, AAP found itself in hot water on the same topic when it barred SEGM from having a booth at the AAP annual meeting in 2021, as reported by this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors using fake positive reviews to boost business
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five years ago, Kay Dean relied upon Yelp! and Google reviews in her search for a doctor in her area. After finding a physician with fairly high reviews, Ms. Dean was shocked when her personal experience was significantly worse than patients on the review platforms.
Following her experience, Ms. Dean, a former federal government investigator, became skeptical and used her skills to investigate the practice on all review platforms. She uncovered that the practice had a review from an individual who was involved in a review trading group on Facebook, where organizations openly barter their services in exchange for positive reviews fraud.
“I discovered that the online review world was just saturated with fake reviews, much more so than I think most people are aware ... and law enforcement regulators aren’t doing anything to address the problem,” said Ms. Dean. “In this online space, it’s the Wild West; cheating is rewarded.”
Ms. Dean decided to take matters into her own hands. She created a YouTube channel called Fake Review Watch, where she exposes real businesses and their attempts to dupe potential consumers with fake positive reviews.
For example, one video analyzes an orthopedic surgeon in Manhattan with an abundance of five-star reviews. Through her detailed analysis, Ms. Dean created a spreadsheet of the 26 alleged patients of the orthopedic surgeon that had submitted glowing reviews. She looked into other businesses that the individuals had left reviews for and found a significant amount of overlap.
According to the video, 19 of the doctor’s reviewers had left high reviews for the same moving company in Las Vegas, and 18 of them reviewed the same locksmith in Texas. Overall, eight of the patients reviewed the same mover, locksmith, and hotel in New Zealand.
A matter of trust
Ms. Dean expressed the gravity of this phenomenon, especially in health care, as patients often head online first when searching for care options. Based on a survey by Software Advice, about 84% of patients use online reviews to assess a physician, and 77% use review sites as the first step in finding a doctor.
Patient trust has continued to diminish in recent years, particularly following the pandemic. In a 2021 global ranking of trust levels towards health care by country, the U.S. health care system ranked 19th, far below those of several developing countries.
Owing to the rise of fake patient reviews and their inscrutable nature, Ms. Dean advises staying away from online review platforms. Instead, she suggests sticking to the old-fashioned method of getting recommendations from friends and relatives, not virtual people.
Ms. Dean explained a few indicators that she looks for when trying to identify a fake review.
“The business has all five-star reviews, negative reviews are followed by five-star reviews, or the business has an abnormal number of positive reviews in a short period of time,” she noted. “Some businesses try to bury legitimate negative reviews by obtaining more recent, fake, positive ones. The recent reviews will contradict the specific criticisms in the negative review.”
She warned that consumers should not give credibility to reviews simply because the reviewer is dubbed “Elite” or a Google Local Guide, because she has seen plenty of these individuals posting fake reviews.
Unfortunately, review platforms haven’t been doing much self-policing. Google and Healthgrades have a series of policies against fake engagement, impersonation, misinformation, and misrepresentation, according to their websites. However, the only consequence of these violations is review removal.
Both Yelp! and Google say they have automated software that distinguishes real versus fake reviews. When Yelp! uncovers users engaging in compensation review activity, it removes their reviews, closes their account, and blocks those users from creating future Yelp! accounts.
Physicians’ basis
Moreover,
“I think there’s an erosion of business ethics because cheating is rewarded. You can’t compete in an environment where your competition is allowed to accumulate numerous fake reviews while you’re still trying to fill chairs in your business,” said Ms. Dean. “Your competition is then getting the business because the tech companies are allowing this fraud.”
Family physician and practice owner Mike Woo-Ming, MD, MPH, provides career coaching for physicians, including maintaining a good reputation – in-person and online. He has seen physicians bumping up their own five-star reviews personally as well as posting negative reviews for their competition.
“I’ve seen where they’re going to lose business, as many practices were affected through COVID,” he said. “Business owners can become desperate and may decide to start posting or buying reviews because they know people will choose certain services these days based upon reviews.”
Dr. Woo-Ming expressed his frustration with fellow physicians who give in to purchasing fake reviews, because the patients have no idea whether reviews are genuine or not.
To encourage genuine positive reviews, Dr. Woo-Ming’s practice uses a third-party app system that sends patients a follow-up email or text asking about their experience with a link to review sites.
“Honest reviews are a reflection of what I can do to improve my business. At the end of the day, if you’re truly providing great service and you’re helping people by providing great medical care, those are going to win out,” he said. “I would rather, as a responsible practice owner, improve the experience and outcome for the patient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dig like an archaeologist
You can observe a lot by watching. – Yogi Berra
He was a fit man in his 40s. Thick legs. Maybe he was a long-distance walker? The bones of his right arm were more developed than his left – a right-handed thrower. His lower left fibula was fractured from a severely rolled ankle. He carried a walking stick that was glossy in the middle from where he gripped it with his left hand, dragging his bad left foot along. Dental cavities tell the story of his diet: honey, carobs, dates. Carbon 14 dating confirms that he lived during the Chalcolithic period, approximately 6,000 years ago. He was likely a shepherd in the Judean Desert.
Isn’t it amazing how much we can know about another human even across such an enormous chasm of time? If you’d asked me when I was 11 what I wanted to be, I’d have said archaeologist. .
A 64-year-old woman with a 4-cm red, brown shiny plaque on her right calf. She burned it on her boyfriend’s Harley Davidson nearly 40 years ago. She wonders where he is now.
A 58-year-old man with a 3-inch scar on his right wrist. He fell off his 6-year-old’s skimboard. ORIF.
A 40-year-old woman with bilateral mastectomy scars.
A 66-year-old with a lichenified nodule on his left forearm. When I shaved it off, a quarter inch spicule of glass came out. It was from a car accident in his first car, a Chevy Impala. He saved the piece of glass as a souvenir.
A fit 50-year-old with extensive scars on his feet and ankles. “Yeah, I went ‘whistling-in’ on a training jump,” he said. He was a retired Navy Seal and raconteur with quite a tale about the day his parachute malfunctioned. Some well placed live oak trees is why he’s around for his skin screening.
A classic, rope-like open-heart scar on the chest of a thin, young, healthy, flaxen-haired woman. Dissected aorta.
A 30-something woman dressed in a pants suit with razor-thin parallel scars on her volar forearms and proximal thighs. She asks if any laser could remove them.
A rotund, hard-living, bearded man with chest and upper-arm tattoos of flames and nudie girls now mixed with the striking face of an old woman and three little kids: His mom and grandkids. He shows me where the fourth grandkid will go and gives me a bear hug to thank me for the care when he leaves.
Attending to these details shifts us from autopilot to present. It keeps us involved, holding our attention even if it’s the 20th skin screening or diabetic foot exam of the day. And what a gift to share in the intimate details of another’s life.
Like examining the minute details of an ancient bone, dig for the history with curiosity, pity, humility. The perfect moment for asking might be when you stand with your #15 blade ready to introduce a new scar and become part of this human’s story forever.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
You can observe a lot by watching. – Yogi Berra
He was a fit man in his 40s. Thick legs. Maybe he was a long-distance walker? The bones of his right arm were more developed than his left – a right-handed thrower. His lower left fibula was fractured from a severely rolled ankle. He carried a walking stick that was glossy in the middle from where he gripped it with his left hand, dragging his bad left foot along. Dental cavities tell the story of his diet: honey, carobs, dates. Carbon 14 dating confirms that he lived during the Chalcolithic period, approximately 6,000 years ago. He was likely a shepherd in the Judean Desert.
Isn’t it amazing how much we can know about another human even across such an enormous chasm of time? If you’d asked me when I was 11 what I wanted to be, I’d have said archaeologist. .
A 64-year-old woman with a 4-cm red, brown shiny plaque on her right calf. She burned it on her boyfriend’s Harley Davidson nearly 40 years ago. She wonders where he is now.
A 58-year-old man with a 3-inch scar on his right wrist. He fell off his 6-year-old’s skimboard. ORIF.
A 40-year-old woman with bilateral mastectomy scars.
A 66-year-old with a lichenified nodule on his left forearm. When I shaved it off, a quarter inch spicule of glass came out. It was from a car accident in his first car, a Chevy Impala. He saved the piece of glass as a souvenir.
A fit 50-year-old with extensive scars on his feet and ankles. “Yeah, I went ‘whistling-in’ on a training jump,” he said. He was a retired Navy Seal and raconteur with quite a tale about the day his parachute malfunctioned. Some well placed live oak trees is why he’s around for his skin screening.
A classic, rope-like open-heart scar on the chest of a thin, young, healthy, flaxen-haired woman. Dissected aorta.
A 30-something woman dressed in a pants suit with razor-thin parallel scars on her volar forearms and proximal thighs. She asks if any laser could remove them.
A rotund, hard-living, bearded man with chest and upper-arm tattoos of flames and nudie girls now mixed with the striking face of an old woman and three little kids: His mom and grandkids. He shows me where the fourth grandkid will go and gives me a bear hug to thank me for the care when he leaves.
Attending to these details shifts us from autopilot to present. It keeps us involved, holding our attention even if it’s the 20th skin screening or diabetic foot exam of the day. And what a gift to share in the intimate details of another’s life.
Like examining the minute details of an ancient bone, dig for the history with curiosity, pity, humility. The perfect moment for asking might be when you stand with your #15 blade ready to introduce a new scar and become part of this human’s story forever.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
You can observe a lot by watching. – Yogi Berra
He was a fit man in his 40s. Thick legs. Maybe he was a long-distance walker? The bones of his right arm were more developed than his left – a right-handed thrower. His lower left fibula was fractured from a severely rolled ankle. He carried a walking stick that was glossy in the middle from where he gripped it with his left hand, dragging his bad left foot along. Dental cavities tell the story of his diet: honey, carobs, dates. Carbon 14 dating confirms that he lived during the Chalcolithic period, approximately 6,000 years ago. He was likely a shepherd in the Judean Desert.
Isn’t it amazing how much we can know about another human even across such an enormous chasm of time? If you’d asked me when I was 11 what I wanted to be, I’d have said archaeologist. .
A 64-year-old woman with a 4-cm red, brown shiny plaque on her right calf. She burned it on her boyfriend’s Harley Davidson nearly 40 years ago. She wonders where he is now.
A 58-year-old man with a 3-inch scar on his right wrist. He fell off his 6-year-old’s skimboard. ORIF.
A 40-year-old woman with bilateral mastectomy scars.
A 66-year-old with a lichenified nodule on his left forearm. When I shaved it off, a quarter inch spicule of glass came out. It was from a car accident in his first car, a Chevy Impala. He saved the piece of glass as a souvenir.
A fit 50-year-old with extensive scars on his feet and ankles. “Yeah, I went ‘whistling-in’ on a training jump,” he said. He was a retired Navy Seal and raconteur with quite a tale about the day his parachute malfunctioned. Some well placed live oak trees is why he’s around for his skin screening.
A classic, rope-like open-heart scar on the chest of a thin, young, healthy, flaxen-haired woman. Dissected aorta.
A 30-something woman dressed in a pants suit with razor-thin parallel scars on her volar forearms and proximal thighs. She asks if any laser could remove them.
A rotund, hard-living, bearded man with chest and upper-arm tattoos of flames and nudie girls now mixed with the striking face of an old woman and three little kids: His mom and grandkids. He shows me where the fourth grandkid will go and gives me a bear hug to thank me for the care when he leaves.
Attending to these details shifts us from autopilot to present. It keeps us involved, holding our attention even if it’s the 20th skin screening or diabetic foot exam of the day. And what a gift to share in the intimate details of another’s life.
Like examining the minute details of an ancient bone, dig for the history with curiosity, pity, humility. The perfect moment for asking might be when you stand with your #15 blade ready to introduce a new scar and become part of this human’s story forever.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Does PREDICT accurately estimate breast cancer survival?
The PREDICT score does not seem to be particularly accurate when it comes to estimating overall survival (OS) in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. This is the conclusion of an international study published in the journal npj Breast Cancer. The work was supervised by Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, an oncologist at the IRCCS San Martino Polyclinic Hospital in Genoa, Italy.
As the authors explain, “PREDICT is a publicly available online tool that helps to predict the individual prognosis of patients with early breast cancer and to show the impact of adjuvant treatments administered after breast cancer surgery.” The tool uses traditional clinical-pathological factors. The authors also point out that the original version of this tool was validated in several datasets of patients with breast cancer. In 2011, it was updated to include HER2 status.
The investigators noted that, although the use of PREDICT is recommended to aid decision-making in the adjuvant setting, its prognostic role in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapies – even trastuzumab-based ones – remains unclear.
Therefore, they decided to analyze PREDICT’s prognostic performance using data extracted from the ALTTO trial, the largest adjuvant study ever conducted in the field of HER2-positive early breast cancer. That trial “represented a unique opportunity to investigate the reliability and prognostic performance of PREDICT in women with HER2-positive disease,” according to the investigators. They went on to specify that ALTTO evaluated adjuvant lapatinib plus trastuzumab vs. trastuzumab alone in 8,381 patients – 2,794 of whom were included in their own analysis.
What the analysis found was that, overall, PREDICT underestimated 5-year OS by 6.7%. The observed 5-year OS was 94.7%, and the predicted 5-year OS was 88.0%.
The highest absolute differences were observed for patients with hormone receptor–negative disease, nodal involvement, and large tumor size (13.0%, 15.8%, and 15.3%, respectively),” they wrote. Furthermore, they reported that “the suboptimal performance of this prognostic tool was observed irrespective of type of anti-HER2 treatment, type of chemotherapy regimen, age of the patients at the time of diagnosis, central hormone receptor status, pathological nodal status, and pathological tumor size.”
To potentially explain the reasons for the underestimation of patients’ OS, the authors questioned whether the population used to validate PREDICT accurately mirrored the real-world population of patients with HER2-positive disease treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. “Moreover, the current standard of care for early breast cancer is even superior to the treatment received by many patients in the ALTTO study. … As such, the discordance between OS estimated by PREDICT and the current real-world OS is expected to be even higher. Therefore,” the researchers concluded, “our results suggest that the current version of PREDICT should be used with caution for prognostication in HER2-positive early breast cancer patients treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
The PREDICT score does not seem to be particularly accurate when it comes to estimating overall survival (OS) in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. This is the conclusion of an international study published in the journal npj Breast Cancer. The work was supervised by Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, an oncologist at the IRCCS San Martino Polyclinic Hospital in Genoa, Italy.
As the authors explain, “PREDICT is a publicly available online tool that helps to predict the individual prognosis of patients with early breast cancer and to show the impact of adjuvant treatments administered after breast cancer surgery.” The tool uses traditional clinical-pathological factors. The authors also point out that the original version of this tool was validated in several datasets of patients with breast cancer. In 2011, it was updated to include HER2 status.
The investigators noted that, although the use of PREDICT is recommended to aid decision-making in the adjuvant setting, its prognostic role in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapies – even trastuzumab-based ones – remains unclear.
Therefore, they decided to analyze PREDICT’s prognostic performance using data extracted from the ALTTO trial, the largest adjuvant study ever conducted in the field of HER2-positive early breast cancer. That trial “represented a unique opportunity to investigate the reliability and prognostic performance of PREDICT in women with HER2-positive disease,” according to the investigators. They went on to specify that ALTTO evaluated adjuvant lapatinib plus trastuzumab vs. trastuzumab alone in 8,381 patients – 2,794 of whom were included in their own analysis.
What the analysis found was that, overall, PREDICT underestimated 5-year OS by 6.7%. The observed 5-year OS was 94.7%, and the predicted 5-year OS was 88.0%.
The highest absolute differences were observed for patients with hormone receptor–negative disease, nodal involvement, and large tumor size (13.0%, 15.8%, and 15.3%, respectively),” they wrote. Furthermore, they reported that “the suboptimal performance of this prognostic tool was observed irrespective of type of anti-HER2 treatment, type of chemotherapy regimen, age of the patients at the time of diagnosis, central hormone receptor status, pathological nodal status, and pathological tumor size.”
To potentially explain the reasons for the underestimation of patients’ OS, the authors questioned whether the population used to validate PREDICT accurately mirrored the real-world population of patients with HER2-positive disease treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. “Moreover, the current standard of care for early breast cancer is even superior to the treatment received by many patients in the ALTTO study. … As such, the discordance between OS estimated by PREDICT and the current real-world OS is expected to be even higher. Therefore,” the researchers concluded, “our results suggest that the current version of PREDICT should be used with caution for prognostication in HER2-positive early breast cancer patients treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
The PREDICT score does not seem to be particularly accurate when it comes to estimating overall survival (OS) in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. This is the conclusion of an international study published in the journal npj Breast Cancer. The work was supervised by Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, an oncologist at the IRCCS San Martino Polyclinic Hospital in Genoa, Italy.
As the authors explain, “PREDICT is a publicly available online tool that helps to predict the individual prognosis of patients with early breast cancer and to show the impact of adjuvant treatments administered after breast cancer surgery.” The tool uses traditional clinical-pathological factors. The authors also point out that the original version of this tool was validated in several datasets of patients with breast cancer. In 2011, it was updated to include HER2 status.
The investigators noted that, although the use of PREDICT is recommended to aid decision-making in the adjuvant setting, its prognostic role in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who are treated with modern chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapies – even trastuzumab-based ones – remains unclear.
Therefore, they decided to analyze PREDICT’s prognostic performance using data extracted from the ALTTO trial, the largest adjuvant study ever conducted in the field of HER2-positive early breast cancer. That trial “represented a unique opportunity to investigate the reliability and prognostic performance of PREDICT in women with HER2-positive disease,” according to the investigators. They went on to specify that ALTTO evaluated adjuvant lapatinib plus trastuzumab vs. trastuzumab alone in 8,381 patients – 2,794 of whom were included in their own analysis.
What the analysis found was that, overall, PREDICT underestimated 5-year OS by 6.7%. The observed 5-year OS was 94.7%, and the predicted 5-year OS was 88.0%.
The highest absolute differences were observed for patients with hormone receptor–negative disease, nodal involvement, and large tumor size (13.0%, 15.8%, and 15.3%, respectively),” they wrote. Furthermore, they reported that “the suboptimal performance of this prognostic tool was observed irrespective of type of anti-HER2 treatment, type of chemotherapy regimen, age of the patients at the time of diagnosis, central hormone receptor status, pathological nodal status, and pathological tumor size.”
To potentially explain the reasons for the underestimation of patients’ OS, the authors questioned whether the population used to validate PREDICT accurately mirrored the real-world population of patients with HER2-positive disease treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies. “Moreover, the current standard of care for early breast cancer is even superior to the treatment received by many patients in the ALTTO study. … As such, the discordance between OS estimated by PREDICT and the current real-world OS is expected to be even higher. Therefore,” the researchers concluded, “our results suggest that the current version of PREDICT should be used with caution for prognostication in HER2-positive early breast cancer patients treated in the modern era with effective chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted therapies.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
FROM NPJ BREAST CANCER
‘Obesity paradox’ in AFib challenged as mortality climbs with BMI
The relationship between body mass index (BMI) and all-cause mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) is U-shaped, with the risk highest in those who are underweight or severely obese and lowest in patients defined simply as obese, a registry analysis suggests. It also showed a similar relationship between BMI and risk for new or worsening heart failure (HF).
Mortality bottomed out at a BMI of about 30-35 kg/m2, which suggests that mild obesity was protective, compared even with “normal-weight” or “overweight” BMI. Still, mortality went up sharply from there with rising BMI.
But higher BMI, a surrogate for obesity, apparently didn’t worsen outcomes by itself. The risk for death from any cause at higher obesity levels was found to depend a lot on related risk factors and comorbidities when the analysis controlled for conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
The findings suggest an inverse relationship between BMI and all-cause mortality in AFib only for patients with BMI less than about 30. They therefore argue against any “obesity paradox” in AFib that posits consistently better survival with increasing levels of obesity, say researchers, based on their analysis of patients with new-onset AFib in the GARFIELD-AF registry.
“It’s common practice now for clinicians to discuss weight within a clinic setting when they’re talking to their AFib patients,” observed Christian Fielder Camm, BM, BCh, University of Oxford (England), and Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust, Reading, England. So studies suggesting an inverse association between BMI and AFib-related risk can be a concern.
Such studies “seem to suggest that once you’ve got AFib, maintaining a high or very high BMI may in some way be protective – which is contrary to what would seem to make sense and certainly contrary to what our results have shown,” Dr. Camm told this news organization.
“I think that having further evidence now to suggest, actually, that greater BMI is associated with a greater risk of all-cause mortality and heart failure helps reframe that discussion at the physician-patient interaction level more clearly, and ensures that we’re able to talk to our patients appropriately about risks associated with BMI and atrial fibrillation,” said Dr. Camm, who is lead author on the analysis published in Open Heart.
“Obesity is a cause of most cardiovascular diseases, but [these] data would support that being overweight or having mild obesity does not increase the risk,” observed Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the John Ochsner Heart and Vascular Institute, New Orleans, La., and the Ochsner Clinical School at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
“At a BMI of 40, it’s very important for them to lose weight for their long-term prognosis,” Dr. Lavie noted, but “at a BMI of 30, the important thing would be to prevent further weight gain. And if they could keep their BMI of 30, they should have a good prognosis. Their prognosis would be particularly good if they didn’t gain weight and put themselves in a more extreme obesity class that is associated with worse risk.”
The current analysis, Dr. Lavie said, “is way better than the AFFIRM study,” which yielded an obesity-paradox report on its patients with AFib about a dozen years ago. “It’s got more data, more numbers, more statistical power,” and breaks BMI into more categories.
That previous analysis based on the influential AFFIRM randomized trial separated its 4,060 patients with AFib into normal (BMI, 18.5-25), overweight (BMI, 25-30), and obese (BMI, > 30) categories, per the convention at the time. It concluded that “obese patients with atrial fibrillation appear to have better long-term outcomes than nonobese patients.”
Bleeding risk on oral anticoagulants
Also noteworthy in the current analysis, variation in BMI didn’t seem to affect mortality or risk for major bleeding or nonhemorrhagic stroke according to choice of oral anticoagulant – whether a new oral anticoagulant (NOAC) or a vitamin K antagonist (VKA).
“We saw that even in the obese and extremely obese group, all-cause mortality was lower in the group taking NOACs, compared with taking warfarin,” Dr. Camm observed, “which goes against the idea that we would need any kind of dose adjustments for increased BMI.”
Indeed, the report notes, use of NOACs, compared with VKA, was associated with a 23% drop in risk for death among patients who were either normal weight or overweight and also in those who were obese or extremely obese.
Those findings “are basically saying that the NOACs look better than warfarin regardless of weight,” agreed Dr. Lavie. “The problem is that the study is not very powered.”
Whereas the benefits of NOACs, compared to VKA, seem similar for patients with a BMI of 30 or 34, compared with a BMI of 23, for example, “none of the studies has many people with 50 BMI.” Many clinicians “feel uncomfortable giving the same dose of NOAC to somebody who has a 60 BMI,” he said. At least with warfarin, “you can check the INR [international normalized ratio].”
The current analysis included 40,482 patients with recently diagnosed AFib and at least one other stroke risk factor from among the registry’s more than 50,000 patients from 35 countries, enrolled from 2010 to 2016. They were followed for 2 years.
The 703 patients with BMI under 18.5 at AFib diagnosis were classified per World Health Organization definitions as underweight; the 13,095 with BMI 18.5-25 as normal weight; the 15,043 with BMI 25-30 as overweight; the 7,560 with BMI 30-35 as obese; and the 4,081 with BMI above 35 as extremely obese. Their ages averaged 71 years, and 55.6% were men.
BMI effects on different outcomes
Relationships between BMI and all-cause mortality and between BMI and new or worsening HF emerged as U-shaped, the risk climbing with both increasing and decreasing BMI. The nadir BMI for risk was about 30 in the case of mortality and about 25 for new or worsening HF.
The all-cause mortality risk rose by 32% for every 5 BMI points lower than a BMI of 30, and by 16% for every 5 BMI points higher than 30, in a partially adjusted analysis. The risk for new or worsening HF rose significantly with increasing but not decreasing BMI, and the reverse was observed for the endpoint of major bleeding.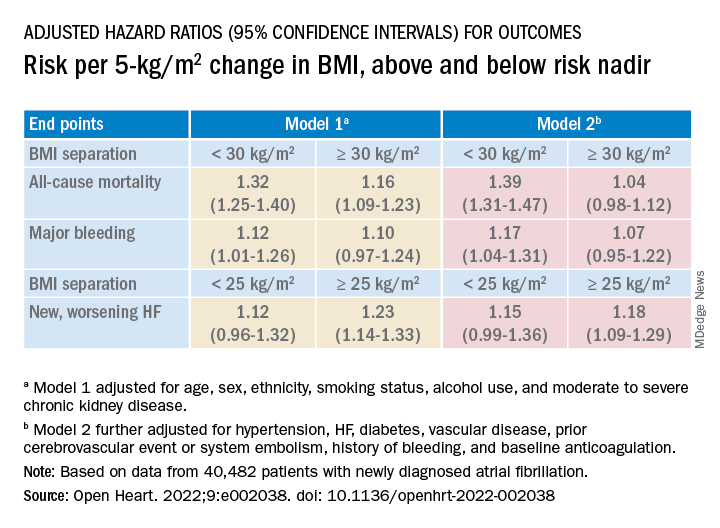
The effect of BMI on all-cause mortality was “substantially attenuated” when the analysis was further adjusted with “likely mediators of any association between BMI and outcomes,” including hypertension, diabetes, HF, cerebrovascular events, and history of bleeding, Dr. Camm said.
That blunted BMI-mortality relationship, he said, “suggests that a lot of the effect is mediated through relatively traditional risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.”
The 2010 AFFIRM analysis by BMI, Dr. Lavie noted, “didn’t even look at the underweight; they actually threw them out.” Yet, such patients with AFib, who tend to be extremely frail or have chronic diseases or conditions other than the arrhythmia, are common. A take-home of the current study is that “the underweight with atrial fibrillation have a really bad prognosis.”
That message isn’t heard as much, he observed, “but is as important as saying that BMI 30 has the best prognosis. The worst prognosis is with the underweight or the really extreme obese.”
Dr. Camm discloses research funding from the British Heart Foundation. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Lavie has previously disclosed serving as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health and DSM Nutritional Products and is the author of “The Obesity Paradox: When Thinner Means Sicker and Heavier Means Healthier” (Avery, 2014).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The relationship between body mass index (BMI) and all-cause mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) is U-shaped, with the risk highest in those who are underweight or severely obese and lowest in patients defined simply as obese, a registry analysis suggests. It also showed a similar relationship between BMI and risk for new or worsening heart failure (HF).
Mortality bottomed out at a BMI of about 30-35 kg/m2, which suggests that mild obesity was protective, compared even with “normal-weight” or “overweight” BMI. Still, mortality went up sharply from there with rising BMI.
But higher BMI, a surrogate for obesity, apparently didn’t worsen outcomes by itself. The risk for death from any cause at higher obesity levels was found to depend a lot on related risk factors and comorbidities when the analysis controlled for conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
The findings suggest an inverse relationship between BMI and all-cause mortality in AFib only for patients with BMI less than about 30. They therefore argue against any “obesity paradox” in AFib that posits consistently better survival with increasing levels of obesity, say researchers, based on their analysis of patients with new-onset AFib in the GARFIELD-AF registry.
“It’s common practice now for clinicians to discuss weight within a clinic setting when they’re talking to their AFib patients,” observed Christian Fielder Camm, BM, BCh, University of Oxford (England), and Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust, Reading, England. So studies suggesting an inverse association between BMI and AFib-related risk can be a concern.
Such studies “seem to suggest that once you’ve got AFib, maintaining a high or very high BMI may in some way be protective – which is contrary to what would seem to make sense and certainly contrary to what our results have shown,” Dr. Camm told this news organization.
“I think that having further evidence now to suggest, actually, that greater BMI is associated with a greater risk of all-cause mortality and heart failure helps reframe that discussion at the physician-patient interaction level more clearly, and ensures that we’re able to talk to our patients appropriately about risks associated with BMI and atrial fibrillation,” said Dr. Camm, who is lead author on the analysis published in Open Heart.
“Obesity is a cause of most cardiovascular diseases, but [these] data would support that being overweight or having mild obesity does not increase the risk,” observed Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the John Ochsner Heart and Vascular Institute, New Orleans, La., and the Ochsner Clinical School at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
“At a BMI of 40, it’s very important for them to lose weight for their long-term prognosis,” Dr. Lavie noted, but “at a BMI of 30, the important thing would be to prevent further weight gain. And if they could keep their BMI of 30, they should have a good prognosis. Their prognosis would be particularly good if they didn’t gain weight and put themselves in a more extreme obesity class that is associated with worse risk.”
The current analysis, Dr. Lavie said, “is way better than the AFFIRM study,” which yielded an obesity-paradox report on its patients with AFib about a dozen years ago. “It’s got more data, more numbers, more statistical power,” and breaks BMI into more categories.
That previous analysis based on the influential AFFIRM randomized trial separated its 4,060 patients with AFib into normal (BMI, 18.5-25), overweight (BMI, 25-30), and obese (BMI, > 30) categories, per the convention at the time. It concluded that “obese patients with atrial fibrillation appear to have better long-term outcomes than nonobese patients.”
Bleeding risk on oral anticoagulants
Also noteworthy in the current analysis, variation in BMI didn’t seem to affect mortality or risk for major bleeding or nonhemorrhagic stroke according to choice of oral anticoagulant – whether a new oral anticoagulant (NOAC) or a vitamin K antagonist (VKA).
“We saw that even in the obese and extremely obese group, all-cause mortality was lower in the group taking NOACs, compared with taking warfarin,” Dr. Camm observed, “which goes against the idea that we would need any kind of dose adjustments for increased BMI.”
Indeed, the report notes, use of NOACs, compared with VKA, was associated with a 23% drop in risk for death among patients who were either normal weight or overweight and also in those who were obese or extremely obese.
Those findings “are basically saying that the NOACs look better than warfarin regardless of weight,” agreed Dr. Lavie. “The problem is that the study is not very powered.”
Whereas the benefits of NOACs, compared to VKA, seem similar for patients with a BMI of 30 or 34, compared with a BMI of 23, for example, “none of the studies has many people with 50 BMI.” Many clinicians “feel uncomfortable giving the same dose of NOAC to somebody who has a 60 BMI,” he said. At least with warfarin, “you can check the INR [international normalized ratio].”
The current analysis included 40,482 patients with recently diagnosed AFib and at least one other stroke risk factor from among the registry’s more than 50,000 patients from 35 countries, enrolled from 2010 to 2016. They were followed for 2 years.
The 703 patients with BMI under 18.5 at AFib diagnosis were classified per World Health Organization definitions as underweight; the 13,095 with BMI 18.5-25 as normal weight; the 15,043 with BMI 25-30 as overweight; the 7,560 with BMI 30-35 as obese; and the 4,081 with BMI above 35 as extremely obese. Their ages averaged 71 years, and 55.6% were men.
BMI effects on different outcomes
Relationships between BMI and all-cause mortality and between BMI and new or worsening HF emerged as U-shaped, the risk climbing with both increasing and decreasing BMI. The nadir BMI for risk was about 30 in the case of mortality and about 25 for new or worsening HF.
The all-cause mortality risk rose by 32% for every 5 BMI points lower than a BMI of 30, and by 16% for every 5 BMI points higher than 30, in a partially adjusted analysis. The risk for new or worsening HF rose significantly with increasing but not decreasing BMI, and the reverse was observed for the endpoint of major bleeding.
The effect of BMI on all-cause mortality was “substantially attenuated” when the analysis was further adjusted with “likely mediators of any association between BMI and outcomes,” including hypertension, diabetes, HF, cerebrovascular events, and history of bleeding, Dr. Camm said.
That blunted BMI-mortality relationship, he said, “suggests that a lot of the effect is mediated through relatively traditional risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.”
The 2010 AFFIRM analysis by BMI, Dr. Lavie noted, “didn’t even look at the underweight; they actually threw them out.” Yet, such patients with AFib, who tend to be extremely frail or have chronic diseases or conditions other than the arrhythmia, are common. A take-home of the current study is that “the underweight with atrial fibrillation have a really bad prognosis.”
That message isn’t heard as much, he observed, “but is as important as saying that BMI 30 has the best prognosis. The worst prognosis is with the underweight or the really extreme obese.”
Dr. Camm discloses research funding from the British Heart Foundation. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Lavie has previously disclosed serving as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health and DSM Nutritional Products and is the author of “The Obesity Paradox: When Thinner Means Sicker and Heavier Means Healthier” (Avery, 2014).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The relationship between body mass index (BMI) and all-cause mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) is U-shaped, with the risk highest in those who are underweight or severely obese and lowest in patients defined simply as obese, a registry analysis suggests. It also showed a similar relationship between BMI and risk for new or worsening heart failure (HF).
Mortality bottomed out at a BMI of about 30-35 kg/m2, which suggests that mild obesity was protective, compared even with “normal-weight” or “overweight” BMI. Still, mortality went up sharply from there with rising BMI.
But higher BMI, a surrogate for obesity, apparently didn’t worsen outcomes by itself. The risk for death from any cause at higher obesity levels was found to depend a lot on related risk factors and comorbidities when the analysis controlled for conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
The findings suggest an inverse relationship between BMI and all-cause mortality in AFib only for patients with BMI less than about 30. They therefore argue against any “obesity paradox” in AFib that posits consistently better survival with increasing levels of obesity, say researchers, based on their analysis of patients with new-onset AFib in the GARFIELD-AF registry.
“It’s common practice now for clinicians to discuss weight within a clinic setting when they’re talking to their AFib patients,” observed Christian Fielder Camm, BM, BCh, University of Oxford (England), and Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust, Reading, England. So studies suggesting an inverse association between BMI and AFib-related risk can be a concern.
Such studies “seem to suggest that once you’ve got AFib, maintaining a high or very high BMI may in some way be protective – which is contrary to what would seem to make sense and certainly contrary to what our results have shown,” Dr. Camm told this news organization.
“I think that having further evidence now to suggest, actually, that greater BMI is associated with a greater risk of all-cause mortality and heart failure helps reframe that discussion at the physician-patient interaction level more clearly, and ensures that we’re able to talk to our patients appropriately about risks associated with BMI and atrial fibrillation,” said Dr. Camm, who is lead author on the analysis published in Open Heart.
“Obesity is a cause of most cardiovascular diseases, but [these] data would support that being overweight or having mild obesity does not increase the risk,” observed Carl J. Lavie, MD, of the John Ochsner Heart and Vascular Institute, New Orleans, La., and the Ochsner Clinical School at the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
“At a BMI of 40, it’s very important for them to lose weight for their long-term prognosis,” Dr. Lavie noted, but “at a BMI of 30, the important thing would be to prevent further weight gain. And if they could keep their BMI of 30, they should have a good prognosis. Their prognosis would be particularly good if they didn’t gain weight and put themselves in a more extreme obesity class that is associated with worse risk.”
The current analysis, Dr. Lavie said, “is way better than the AFFIRM study,” which yielded an obesity-paradox report on its patients with AFib about a dozen years ago. “It’s got more data, more numbers, more statistical power,” and breaks BMI into more categories.
That previous analysis based on the influential AFFIRM randomized trial separated its 4,060 patients with AFib into normal (BMI, 18.5-25), overweight (BMI, 25-30), and obese (BMI, > 30) categories, per the convention at the time. It concluded that “obese patients with atrial fibrillation appear to have better long-term outcomes than nonobese patients.”
Bleeding risk on oral anticoagulants
Also noteworthy in the current analysis, variation in BMI didn’t seem to affect mortality or risk for major bleeding or nonhemorrhagic stroke according to choice of oral anticoagulant – whether a new oral anticoagulant (NOAC) or a vitamin K antagonist (VKA).
“We saw that even in the obese and extremely obese group, all-cause mortality was lower in the group taking NOACs, compared with taking warfarin,” Dr. Camm observed, “which goes against the idea that we would need any kind of dose adjustments for increased BMI.”
Indeed, the report notes, use of NOACs, compared with VKA, was associated with a 23% drop in risk for death among patients who were either normal weight or overweight and also in those who were obese or extremely obese.
Those findings “are basically saying that the NOACs look better than warfarin regardless of weight,” agreed Dr. Lavie. “The problem is that the study is not very powered.”
Whereas the benefits of NOACs, compared to VKA, seem similar for patients with a BMI of 30 or 34, compared with a BMI of 23, for example, “none of the studies has many people with 50 BMI.” Many clinicians “feel uncomfortable giving the same dose of NOAC to somebody who has a 60 BMI,” he said. At least with warfarin, “you can check the INR [international normalized ratio].”
The current analysis included 40,482 patients with recently diagnosed AFib and at least one other stroke risk factor from among the registry’s more than 50,000 patients from 35 countries, enrolled from 2010 to 2016. They were followed for 2 years.
The 703 patients with BMI under 18.5 at AFib diagnosis were classified per World Health Organization definitions as underweight; the 13,095 with BMI 18.5-25 as normal weight; the 15,043 with BMI 25-30 as overweight; the 7,560 with BMI 30-35 as obese; and the 4,081 with BMI above 35 as extremely obese. Their ages averaged 71 years, and 55.6% were men.
BMI effects on different outcomes
Relationships between BMI and all-cause mortality and between BMI and new or worsening HF emerged as U-shaped, the risk climbing with both increasing and decreasing BMI. The nadir BMI for risk was about 30 in the case of mortality and about 25 for new or worsening HF.
The all-cause mortality risk rose by 32% for every 5 BMI points lower than a BMI of 30, and by 16% for every 5 BMI points higher than 30, in a partially adjusted analysis. The risk for new or worsening HF rose significantly with increasing but not decreasing BMI, and the reverse was observed for the endpoint of major bleeding.
The effect of BMI on all-cause mortality was “substantially attenuated” when the analysis was further adjusted with “likely mediators of any association between BMI and outcomes,” including hypertension, diabetes, HF, cerebrovascular events, and history of bleeding, Dr. Camm said.
That blunted BMI-mortality relationship, he said, “suggests that a lot of the effect is mediated through relatively traditional risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.”
The 2010 AFFIRM analysis by BMI, Dr. Lavie noted, “didn’t even look at the underweight; they actually threw them out.” Yet, such patients with AFib, who tend to be extremely frail or have chronic diseases or conditions other than the arrhythmia, are common. A take-home of the current study is that “the underweight with atrial fibrillation have a really bad prognosis.”
That message isn’t heard as much, he observed, “but is as important as saying that BMI 30 has the best prognosis. The worst prognosis is with the underweight or the really extreme obese.”
Dr. Camm discloses research funding from the British Heart Foundation. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Lavie has previously disclosed serving as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health and DSM Nutritional Products and is the author of “The Obesity Paradox: When Thinner Means Sicker and Heavier Means Healthier” (Avery, 2014).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OPEN HEART










