User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Vaccination regimen effective in preventing pneumonia in MM patients
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
Patients with hematological malignancies are at high risk of invasive Staphylococcus pneumoniae. Multiple myeloma (MM) patients, in particular, have been found to have one of the highest incidences of invasive pneumococcal disease. However, researchers found that a full three-dose vaccination regimen by 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine was protective in MM patients when provided between treatment courses, according to a study reported in Vaccine.
The researchers performed a prospective study of 18 adult patients who were vaccinated with PCV13, compared with 18 control-matched patients from 2017 to 2020. The three-dose vaccination regimen was provided between treatment courses with novel target agents (bortezomib, lenalidomide, ixazomib) with a minimum of a 1-month interval. They used the incidence of pneumonias during the one-year observation period as the primary outcome.
Totally there were 12 cases (33.3%) of clinically and radiologically confirmed pneumonias in the entire study group (n = 36), with a distribution between the vaccinated and nonvaccinated groups of 3 (16.7%) and 9 (50%). respectively (P = .037).
The absolute risk reduction seen with vaccination was 33.3%, and the number needed to treat with PCV13 vaccination in MM patients receiving novel agents was 3.0; (95% confidence interval 1.61-22.1). In addition, there were no adverse effects seen from vaccination, according to the authors.
“Despite the expected decrease in immunological response to vaccination during the chemotherapy, we have shown the clinical effectiveness of a PCV13 vaccination schedule based on 3 doses given with a minimum 1 month interval between the courses of novel agents,” the investigators concluded.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Stoma I et al. Vaccine. 2020 May 14; doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.024.
FROM VACCINE
COVID-19: Delirium first, depression, anxiety, insomnia later?
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chilblain-like lesions reported in children thought to have COVID-19
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Pulmonology, critical care earnings on the upswing before pandemic
As the COVID spring progresses, the days before the pandemic may seem like a dream: Practices were open, waiting rooms were full of unmasked people, and PPE was plentiful.
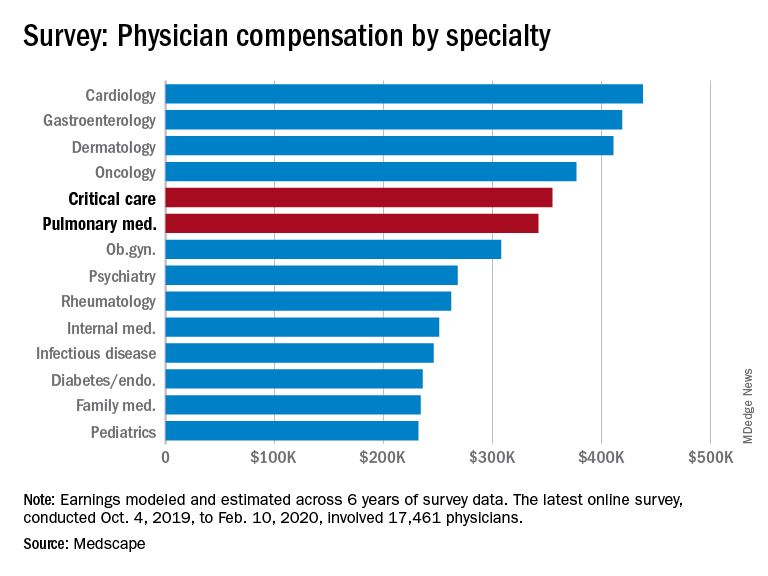
Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, shows what pulmonology and critical care looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
Back then, earnings were up. Average compensation reported by pulmonologists was up from $331,000 in 2019 to $342,000 this year, a 3.3% increase. For intensivists, earnings rose from $349,000 to $355,000, or 1.7%. Average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey – 1.5% higher than the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for the next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
One problem area for intensivists, even before the pandemic, was paperwork and administration. Of the 26 specialties for which data are available, critical care was highest for amount of time spent on paperwork, at 19.1 hours per week. Those in pulmonary medicine spent 15.6 hours per week, which also happened to be the average for all specialists, the survey data show.
Both specialties also ranked high in denied/resubmitted claims: Intensivists were fourth among the 27 types of specialists with reliable data, with 20% of claims denied, and pulmonologists were tied for eighth at 18%, Medscape said.
Only 50% of pulmonologists surveyed said that they were being fairly compensated, putting them 26th among the 29 specialties on that list. Those in critical care medicine were 13th, with a 59% positive response, Medscape reported.
In the end, though, it looks like you can’t keep a good pulmonologist or intensivist down. When asked if they would choose medicine again, 83% of pulmonologists said yes, just one percentage point behind a three-way tie for first. Intensivists were just a little further down the list at 81%, according to the survey.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
As the COVID spring progresses, the days before the pandemic may seem like a dream: Practices were open, waiting rooms were full of unmasked people, and PPE was plentiful.

Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, shows what pulmonology and critical care looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
Back then, earnings were up. Average compensation reported by pulmonologists was up from $331,000 in 2019 to $342,000 this year, a 3.3% increase. For intensivists, earnings rose from $349,000 to $355,000, or 1.7%. Average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey – 1.5% higher than the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for the next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
One problem area for intensivists, even before the pandemic, was paperwork and administration. Of the 26 specialties for which data are available, critical care was highest for amount of time spent on paperwork, at 19.1 hours per week. Those in pulmonary medicine spent 15.6 hours per week, which also happened to be the average for all specialists, the survey data show.
Both specialties also ranked high in denied/resubmitted claims: Intensivists were fourth among the 27 types of specialists with reliable data, with 20% of claims denied, and pulmonologists were tied for eighth at 18%, Medscape said.
Only 50% of pulmonologists surveyed said that they were being fairly compensated, putting them 26th among the 29 specialties on that list. Those in critical care medicine were 13th, with a 59% positive response, Medscape reported.
In the end, though, it looks like you can’t keep a good pulmonologist or intensivist down. When asked if they would choose medicine again, 83% of pulmonologists said yes, just one percentage point behind a three-way tie for first. Intensivists were just a little further down the list at 81%, according to the survey.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
As the COVID spring progresses, the days before the pandemic may seem like a dream: Practices were open, waiting rooms were full of unmasked people, and PPE was plentiful.

Medscape’s latest physician survey, conducted from Oct. 4, 2019, to Feb. 10, 2020, shows what pulmonology and critical care looked like just before the coronavirus arrived.
Back then, earnings were up. Average compensation reported by pulmonologists was up from $331,000 in 2019 to $342,000 this year, a 3.3% increase. For intensivists, earnings rose from $349,000 to $355,000, or 1.7%. Average income for all specialists was $346,000 in this year’s survey – 1.5% higher than the $341,000 earned in 2019, Medscape reported.
Prospects for the next year, however, are grim. “We found out that we have a 10% salary decrease effective May 2 to Dec. 25. Our bonus will be based on clinical productivity, and since our numbers are down, that is likely to go away,” a pediatric emergency physician told Medscape.
One problem area for intensivists, even before the pandemic, was paperwork and administration. Of the 26 specialties for which data are available, critical care was highest for amount of time spent on paperwork, at 19.1 hours per week. Those in pulmonary medicine spent 15.6 hours per week, which also happened to be the average for all specialists, the survey data show.
Both specialties also ranked high in denied/resubmitted claims: Intensivists were fourth among the 27 types of specialists with reliable data, with 20% of claims denied, and pulmonologists were tied for eighth at 18%, Medscape said.
Only 50% of pulmonologists surveyed said that they were being fairly compensated, putting them 26th among the 29 specialties on that list. Those in critical care medicine were 13th, with a 59% positive response, Medscape reported.
In the end, though, it looks like you can’t keep a good pulmonologist or intensivist down. When asked if they would choose medicine again, 83% of pulmonologists said yes, just one percentage point behind a three-way tie for first. Intensivists were just a little further down the list at 81%, according to the survey.
The respondents were Medscape members who had been invited to participate. The sample size was 17,461 physicians, and compensation was modeled and estimated based on a range of variables across 6 years of survey data. The sampling error was ±0.74%.
FDA expands approval of atezolizumab in NSCLC
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the approved indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Atezolizumab is now approved as first-line monotherapy for adults with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors are EGFR and ALK wild-type but have high PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥50% of tumor cells or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells covering ≥10% of the tumor area).
The FDA also approved the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay as a companion diagnostic to identify patients with NSCLC who are eligible for treatment with atezolizumab.
The drug was evaluated in the IMpower110 trial (NCT02409342), which enrolled patients with stage IV, PD-L1–positive (tumor cells [TC] ≥1% or immune cells [IC] ≥1%) NSCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
The patients were randomized to receive atezolizumab at 1,200 mg every 3 weeks (n = 286) or platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 263), which consisted of carboplatin or cisplatin with either pemetrexed or gemcitabine, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Overall survival was superior in the atezolizumab arm, but only among patients with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥50% or IC ≥10%). The median overall survival was 20.2 months among PD-L1–high patients in the atezolizumab arm and 13.1 months among PD-L1–high patients in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.59; P = .0106). There was no significant difference in overall survival between the treatment arms for patients in the other two PD-L1 subgroups – TC ≥5% or IC ≥5% and TC ≥1% or IC ≥1%.
Serious adverse events occurred in 28% of patients receiving atezolizumab. The most frequent of these were pneumonia (2.8%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2.1%), and pneumonitis (2.1%). Fatal adverse events in the atezolizumab arm included unexplained death, aspiration, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, mechanical ileus, sepsis, cerebral infraction, and device occlusion (one patient each).
For more details on atezolizumab, see the full prescribing information.
The FDA has granted the approval of atezolizumab to Genentech and the approval of the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay to Ventana Medical Systems.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the approved indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Atezolizumab is now approved as first-line monotherapy for adults with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors are EGFR and ALK wild-type but have high PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥50% of tumor cells or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells covering ≥10% of the tumor area).
The FDA also approved the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay as a companion diagnostic to identify patients with NSCLC who are eligible for treatment with atezolizumab.
The drug was evaluated in the IMpower110 trial (NCT02409342), which enrolled patients with stage IV, PD-L1–positive (tumor cells [TC] ≥1% or immune cells [IC] ≥1%) NSCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
The patients were randomized to receive atezolizumab at 1,200 mg every 3 weeks (n = 286) or platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 263), which consisted of carboplatin or cisplatin with either pemetrexed or gemcitabine, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Overall survival was superior in the atezolizumab arm, but only among patients with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥50% or IC ≥10%). The median overall survival was 20.2 months among PD-L1–high patients in the atezolizumab arm and 13.1 months among PD-L1–high patients in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.59; P = .0106). There was no significant difference in overall survival between the treatment arms for patients in the other two PD-L1 subgroups – TC ≥5% or IC ≥5% and TC ≥1% or IC ≥1%.
Serious adverse events occurred in 28% of patients receiving atezolizumab. The most frequent of these were pneumonia (2.8%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2.1%), and pneumonitis (2.1%). Fatal adverse events in the atezolizumab arm included unexplained death, aspiration, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, mechanical ileus, sepsis, cerebral infraction, and device occlusion (one patient each).
For more details on atezolizumab, see the full prescribing information.
The FDA has granted the approval of atezolizumab to Genentech and the approval of the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay to Ventana Medical Systems.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the approved indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Atezolizumab is now approved as first-line monotherapy for adults with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors are EGFR and ALK wild-type but have high PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥50% of tumor cells or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells covering ≥10% of the tumor area).
The FDA also approved the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay as a companion diagnostic to identify patients with NSCLC who are eligible for treatment with atezolizumab.
The drug was evaluated in the IMpower110 trial (NCT02409342), which enrolled patients with stage IV, PD-L1–positive (tumor cells [TC] ≥1% or immune cells [IC] ≥1%) NSCLC who had received no prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
The patients were randomized to receive atezolizumab at 1,200 mg every 3 weeks (n = 286) or platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 263), which consisted of carboplatin or cisplatin with either pemetrexed or gemcitabine, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Overall survival was superior in the atezolizumab arm, but only among patients with high PD-L1 expression (TC ≥50% or IC ≥10%). The median overall survival was 20.2 months among PD-L1–high patients in the atezolizumab arm and 13.1 months among PD-L1–high patients in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.59; P = .0106). There was no significant difference in overall survival between the treatment arms for patients in the other two PD-L1 subgroups – TC ≥5% or IC ≥5% and TC ≥1% or IC ≥1%.
Serious adverse events occurred in 28% of patients receiving atezolizumab. The most frequent of these were pneumonia (2.8%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2.1%), and pneumonitis (2.1%). Fatal adverse events in the atezolizumab arm included unexplained death, aspiration, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism, acute myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, mechanical ileus, sepsis, cerebral infraction, and device occlusion (one patient each).
For more details on atezolizumab, see the full prescribing information.
The FDA has granted the approval of atezolizumab to Genentech and the approval of the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) Assay to Ventana Medical Systems.
Today’s top news highlights: Risks & benefits of universal masking, prostate cancer rising
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Large COVID-19 dataset: Kidney injury in >35% of those in hospital
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AAN publishes ethical guidance on patient care during the pandemic
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
FROM NEUROLOGY
New diagnostic CT scan model predicts pulmonary hypertension
A new CT scan pulmonary angiography model may help optimize the diagnostic work-up process for patients with suspected pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a recent study.
The diagnostic and prognostic utility of the model was validated in a tertiary referral population of treatment-naive patients who had a high pretest probability of PH.
“The aim of this study was to (a) build a diagnostic CT model in patients with suspected PH using the current guideline definition of PH (mPAP [mean pulmonary arterial pressure] ≥25 mm Hg) and the recent proposed definition of >20 mm Hg and (b) test its prognostic significance,” wrote Andrew J. Swift, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Sheffield (England) and colleagues in European Radiology.
The study cohort included 491 patients with suspected PH who underwent routine CT pulmonary angiography and right-heart catheterization between April 2012 and March 2016. CT metrics for patients with PH were developed using axial and reconstructed images.
The researchers identified the derivation (n = 247) and validation (n = 244) cohorts using random patient selection. In the derivation cohort, multivariate regression analysis was conducted to develop a model with the ability to predict mPAP ≥25 mm Hg and >20 mm Hg.
In the validation cohort, receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed to establish compromise CT thresholds, as well as sensitivity and specificity. The prognostic utility of the model was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Derivation cohort
Among the 247 patients in the derivation cohort, a CT regression model was identified, which included right-ventricle outflow tract thickness, main pulmonary artery diameter, and left ventricular area and interventricular septal angle; the area under the curve (AUC) in this cohort was 0.92.
Validation cohort
Among the 244 patients in the validation cohort, the model demonstrated strong diagnostic utility for the detection of PH, with an AUC of 0.91 and 0.94 for mPAP >20 mm Hg and ≥25 mm Hg, respectively.
With respect to the prognostic utility of the model, the researchers found that the diagnostic thresholds were prognostic in the CT model (all P < .01).
“The diagnostic CT thresholds are also of prognostic value; patients found not to have PH on CT have an excellent outcome,” they explained.
Dr. Swift and colleagues acknowledged that positive and negative predictive values will change based on the diagnostic setting. As a result, the findings from the current study may only be applicable to tertiary referral patient populations.
“This data may be particularly helpful when triaging patients with suspected severe PH for consideration of targeted pulmonary vascular therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Wellcome Trust, the National Institute for Health Research, MRC POLARIS, and Bayer. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest with any companies related to the publication.
SOURCE: Swift AJ et al. Eur Radiol. 2020 Apr 27. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06846-1.
A new CT scan pulmonary angiography model may help optimize the diagnostic work-up process for patients with suspected pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a recent study.
The diagnostic and prognostic utility of the model was validated in a tertiary referral population of treatment-naive patients who had a high pretest probability of PH.
“The aim of this study was to (a) build a diagnostic CT model in patients with suspected PH using the current guideline definition of PH (mPAP [mean pulmonary arterial pressure] ≥25 mm Hg) and the recent proposed definition of >20 mm Hg and (b) test its prognostic significance,” wrote Andrew J. Swift, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Sheffield (England) and colleagues in European Radiology.
The study cohort included 491 patients with suspected PH who underwent routine CT pulmonary angiography and right-heart catheterization between April 2012 and March 2016. CT metrics for patients with PH were developed using axial and reconstructed images.
The researchers identified the derivation (n = 247) and validation (n = 244) cohorts using random patient selection. In the derivation cohort, multivariate regression analysis was conducted to develop a model with the ability to predict mPAP ≥25 mm Hg and >20 mm Hg.
In the validation cohort, receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed to establish compromise CT thresholds, as well as sensitivity and specificity. The prognostic utility of the model was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Derivation cohort
Among the 247 patients in the derivation cohort, a CT regression model was identified, which included right-ventricle outflow tract thickness, main pulmonary artery diameter, and left ventricular area and interventricular septal angle; the area under the curve (AUC) in this cohort was 0.92.
Validation cohort
Among the 244 patients in the validation cohort, the model demonstrated strong diagnostic utility for the detection of PH, with an AUC of 0.91 and 0.94 for mPAP >20 mm Hg and ≥25 mm Hg, respectively.
With respect to the prognostic utility of the model, the researchers found that the diagnostic thresholds were prognostic in the CT model (all P < .01).
“The diagnostic CT thresholds are also of prognostic value; patients found not to have PH on CT have an excellent outcome,” they explained.
Dr. Swift and colleagues acknowledged that positive and negative predictive values will change based on the diagnostic setting. As a result, the findings from the current study may only be applicable to tertiary referral patient populations.
“This data may be particularly helpful when triaging patients with suspected severe PH for consideration of targeted pulmonary vascular therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Wellcome Trust, the National Institute for Health Research, MRC POLARIS, and Bayer. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest with any companies related to the publication.
SOURCE: Swift AJ et al. Eur Radiol. 2020 Apr 27. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06846-1.
A new CT scan pulmonary angiography model may help optimize the diagnostic work-up process for patients with suspected pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a recent study.
The diagnostic and prognostic utility of the model was validated in a tertiary referral population of treatment-naive patients who had a high pretest probability of PH.
“The aim of this study was to (a) build a diagnostic CT model in patients with suspected PH using the current guideline definition of PH (mPAP [mean pulmonary arterial pressure] ≥25 mm Hg) and the recent proposed definition of >20 mm Hg and (b) test its prognostic significance,” wrote Andrew J. Swift, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Sheffield (England) and colleagues in European Radiology.
The study cohort included 491 patients with suspected PH who underwent routine CT pulmonary angiography and right-heart catheterization between April 2012 and March 2016. CT metrics for patients with PH were developed using axial and reconstructed images.
The researchers identified the derivation (n = 247) and validation (n = 244) cohorts using random patient selection. In the derivation cohort, multivariate regression analysis was conducted to develop a model with the ability to predict mPAP ≥25 mm Hg and >20 mm Hg.
In the validation cohort, receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed to establish compromise CT thresholds, as well as sensitivity and specificity. The prognostic utility of the model was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Derivation cohort
Among the 247 patients in the derivation cohort, a CT regression model was identified, which included right-ventricle outflow tract thickness, main pulmonary artery diameter, and left ventricular area and interventricular septal angle; the area under the curve (AUC) in this cohort was 0.92.
Validation cohort
Among the 244 patients in the validation cohort, the model demonstrated strong diagnostic utility for the detection of PH, with an AUC of 0.91 and 0.94 for mPAP >20 mm Hg and ≥25 mm Hg, respectively.
With respect to the prognostic utility of the model, the researchers found that the diagnostic thresholds were prognostic in the CT model (all P < .01).
“The diagnostic CT thresholds are also of prognostic value; patients found not to have PH on CT have an excellent outcome,” they explained.
Dr. Swift and colleagues acknowledged that positive and negative predictive values will change based on the diagnostic setting. As a result, the findings from the current study may only be applicable to tertiary referral patient populations.
“This data may be particularly helpful when triaging patients with suspected severe PH for consideration of targeted pulmonary vascular therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Wellcome Trust, the National Institute for Health Research, MRC POLARIS, and Bayer. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest with any companies related to the publication.
SOURCE: Swift AJ et al. Eur Radiol. 2020 Apr 27. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06846-1.
FROM EUROPEAN RADIOLOGY
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.