User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


NFL’s only physician player opts out of 2020 season over COVID
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Canadian-born Duvernay-Tardif, right guard for the Kansas City Chiefs, announced on Twitter on July 24 what he called “one of the most difficult decisions I have had to make in my life.”
“There is no doubt in my mind the Chiefs’ medical staff have put together a strong plan to minimize the health risks associated with COVID-19, but some risks will remain,” he posted.
“Being at the frontline during this offseason has given me a different perspective on this pandemic and the stress it puts on individuals and our healthcare system. I cannot allow myself to potentially transmit the virus in our communities simply to play the sport that I love. If I am to take risks, I will do it caring for patients.”
According to CNN, Duvernay-Tardif, less than 3 months after helping the Chiefs win the Super Bowl in February, began working at a long-term care facility near Montreal in what he described as a “nursing role.”
Duvernay-Tardif wrote recently in an article for Sports Illustrated that he has not completed his residency and is not yet licensed to practice.
“My first day back in the hospital was April 24,” Duvernay-Tardif wrote. “I felt nervous the night before, but a good nervous, like before a game.”
Duvernay-Tardif has also served on the NFL Players’ Association COVID-19 task force, according to Yahoo News .
A spokesperson for Duvernay-Tardif told Medscape Medical News he was unavailable to comment about the announcement.
Starting His Dual Career
Duvernay-Tardif, 29, was drafted in the sixth round by the Chiefs in 2014.
According to Forbes , he spent 8 years (2010-2018) pursuing his medical degree while still playing college football for McGill University in Montreal. Duvernay-Tardif played offensive tackle for the Redmen and in his senior year (2013) won the Metras Trophy as most outstanding lineman in Canadian college football.
He explained in a previous Medscape interview how he managed his dual career; as a doctor he said he would like to focus on emergency medicine:
“I would say that at around 16-17 years of age, I was pretty convinced that medicine was for me,” he told Medscape.
“I was lucky that I didn’t have to do an undergrad program,” he continued. “In Canada, they have a fast-track program where instead of doing a full undergrad before getting into medical school, you can do a 1-year program where you can do all your physiology and biology classes all together.
“I had the chance to get into that program, and that’s how I was able to manage football and medicine at the same time. There’s no way I could have finished my med school doing part-time med school like I did for the past 4 years.”
ESPN explained the opt-out option: “According to an agreement approved by both the league and the union on [July 24], players considered high risk for COVID-19 can earn $350,000 and an accrued NFL season if they choose to opt out of the 2020 season. Players without risk can earn $150,000 for opting out. Duvernay-Tardif was scheduled to make $2.75 million this season.”
The danger of COVID-19 in professional sports has already been seen in Major League Baseball.
According to USA Today, the Miami Marlins have at least 14 players and staff who have tested positive for COVID-19, and major league baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred must decide whether to further delay the shortened season, cancel it, or allow it to continue.
MLB postponed the Marlins’ home opener July 27 against the Baltimore Orioles as well as the New York Yankees game in Philadelphia against the Phillies.
COVID-19 also shut down professional, college, high school, and recreational sports throughout much of the country beginning in March.
Medicine, Football Intersect
In the previous Medscape interview, Duvernay-Tardif talked about how medicine influenced his football career.
“For me, medicine was really helpful in the sense that I was better able to build a routine and question what works for me and what doesn’t. It gave me the ability to structure my work in order to optimize my time and to make sure that it’s pertinent.
“Another thing is the psychology and the sports psychology. I think there’s a little bit of a stigma around mental health issues in professional sports and everywhere, actually. I think because of medicine, I was more willing to question myself and more willing to use different tools in order to be a better football player.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diary of a rheumatologist who briefly became a COVID hospitalist
When the coronavirus pandemic hit New York City in early March, the Hospital for Special Surgery leadership decided that the best way to serve the city was to stop elective orthopedic procedures temporarily and use the facility to take on patients from its sister institution, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital.
As in other institutions, it was all hands on deck. , other internal medicine subspecialists were asked to volunteer, including rheumatologists and primary care sports medicine doctors.
As a rheumatologist, it had been well over 10 years since I had last done any inpatient work. I was filled with trepidation, but I was also excited to dive in.
April 4:
Feeling very unmoored. I am in unfamiliar territory, and it’s terrifying. There are so many things that I no longer know how to do. Thankfully, the hospitalists are gracious, extremely supportive, and helpful.
My N95 doesn’t fit well. It’s never fit — not during residency or fellowship, not in any job I’ve had, and not today. The lady fit-testing me said she was sorry, but the look on her face said, “I’m sorry, but you’re going to die.”
April 7:
We don’t know how to treat coronavirus. I’ve sent some patients home, others I’ve sent to the ICU. Thank goodness for treatment algorithms from leadership, but we are sorely lacking good-quality data.
Our infectious disease doctor doesn’t think hydroxychloroquine works at all; I suspect he is right. The guidance right now is to give hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to everyone who is sick enough to be admitted, but there are methodologic flaws in the early enthusiastic preprints, and so far, I’ve not noticed any demonstrable benefit.
The only thing that seems to be happening is that I am seeing more QT prolongation — not something I previously counseled my rheumatology patients on.
April 9:
The patients have been, with a few exceptions, alone in the room. They’re not allowed to have visitors and are required to wear masks all the time. Anyone who enters their rooms is fully covered up so you can barely see them. It’s anonymous and dehumanizing.
We’re instructed to take histories by phone in order to limit the time spent in each room. I buck this instruction; I still take histories in person because human contact seems more important now than ever.
Except maybe I should be smarter about this. One of my patients refuses any treatment, including oxygen support. She firmly believes this is a result of 5G networks — something I later discovered was a common conspiracy theory. She refused to wear a mask despite having a very bad cough. She coughed in my face a lot when we were chatting. My face with my ill-fitting N95 mask. Maybe the fit-testing lady’s eyes weren’t lying and I will die after all.
April 15:
On the days when I’m not working as a hospitalist, I am still doing remote visits with my rheumatology patients. It feels good to be doing something familiar and something I’m actually good at. But it is surreal to be faced with the quotidian on one hand and life and death on the other.
I recently saw a fairly new patient, and I still haven’t figured out if she has a rheumatic condition or if her symptoms all stem from an alcohol use disorder. In our previous visits, she could barely acknowledge that her drinking was an issue. On today’s visit, she told me she was 1½ months sober.
I don’t know her very well, but it was the happiest news I’d heard in a long time. I was so beside myself with joy that I cried, which says more about my current emotional state than anything else, really.
April 21:
On my panel of patients, I have three women with COVID-19 — all of whom lost their husbands to COVID-19, and none of whom were able to say their goodbyes. I cannot even begin to imagine what it must be like to survive this period of illness, isolation, and fear, only to be met on the other side by grief.
Rheumatology doesn’t lend itself too well to such existential concerns; I am not equipped for this. Perhaps my only advantage as a rheumatologist is that I know how to use IVIG, anakinra, and tocilizumab.
Someone on my panel was started on anakinra, and it turned his case around. Would he have gotten better without it anyway? We’ll never know for sure.
April 28:
Patients seem to be requiring prolonged intubation. We have now reached the stage where patients are alive but trached and PEGed. One of my patients had been intubated for close to 3 weeks. She was one of four people in her family who contracted the illness (they had had a dinner party before New York’s state of emergency was declared). We thought she might die once she was extubated, but she is still fighting. Unconscious, unarousable, but breathing on her own.
Will she ever wake up? We don’t know. We put the onus on her family to make decisions about placing a PEG tube in. They can only do so from a distance with imperfect information gleaned from periodic, brief FaceTime interactions — where no interaction happens at all.
May 4:
It’s my last day as a “COVID hospitalist.” When I first started, I felt like I was being helpful. Walking home in the middle of the 7 PM cheers for healthcare workers frequently left me teary eyed. As horrible as the situation was, I was proud of myself for volunteering to help and appreciative of a broken city’s gratitude toward all healthcare workers in general. Maybe I bought into the idea that, like many others around me, I am a hero.
I don’t feel like a hero, though. The stuff I saw was easy compared with the stuff that my colleagues in critical care saw. Our hospital accepted the more stable patient transfers from our sister hospitals. Patients who remained in the NewYork–Presbyterian system were sicker, with encephalitis, thrombotic complications, multiorgan failure, and cytokine release syndrome. It’s the doctors who took care of those patients who deserve to be called heroes.
No, I am no hero. But did my volunteering make a difference? It made a difference to me. The overwhelming feeling I am left with isn’t pride; it’s humility. I feel humbled that I could feel so unexpectedly touched by the lives of people that I had no idea I could feel touched by.
Postscript:
My patient Esther [name changed to hide her identity] died from COVID-19. She was MY patient — not a patient I met as a COVID hospitalist, but a patient with rheumatoid arthritis whom I cared for for years.
She had scleromalacia and multiple failed scleral grafts, which made her profoundly sad. She fought her anxiety fiercely and always with poise and panache. One way she dealt with her anxiety was that she constantly messaged me via our EHR portal. She ran everything by me and trusted me to be her rock.
The past month has been so busy that I just now noticed it had been a month since I last heard from her. I tried to call her but got her voicemail. It wasn’t until I exchanged messages with her ophthalmologist that I found out she had passed away from complications of COVID-19.
She was taking rituximab and mycophenolate. I wonder if these drugs made her sicker than she would have been otherwise; it fills me with sadness. I wonder if she was alone like my other COVID-19 patients. I wonder if she was afraid. I am sorry that I wasn’t able to say goodbye.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for this rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com. This article is part of a partnership between Medscape and Hospital for Special Surgery.
When the coronavirus pandemic hit New York City in early March, the Hospital for Special Surgery leadership decided that the best way to serve the city was to stop elective orthopedic procedures temporarily and use the facility to take on patients from its sister institution, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital.
As in other institutions, it was all hands on deck. , other internal medicine subspecialists were asked to volunteer, including rheumatologists and primary care sports medicine doctors.
As a rheumatologist, it had been well over 10 years since I had last done any inpatient work. I was filled with trepidation, but I was also excited to dive in.
April 4:
Feeling very unmoored. I am in unfamiliar territory, and it’s terrifying. There are so many things that I no longer know how to do. Thankfully, the hospitalists are gracious, extremely supportive, and helpful.
My N95 doesn’t fit well. It’s never fit — not during residency or fellowship, not in any job I’ve had, and not today. The lady fit-testing me said she was sorry, but the look on her face said, “I’m sorry, but you’re going to die.”
April 7:
We don’t know how to treat coronavirus. I’ve sent some patients home, others I’ve sent to the ICU. Thank goodness for treatment algorithms from leadership, but we are sorely lacking good-quality data.
Our infectious disease doctor doesn’t think hydroxychloroquine works at all; I suspect he is right. The guidance right now is to give hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to everyone who is sick enough to be admitted, but there are methodologic flaws in the early enthusiastic preprints, and so far, I’ve not noticed any demonstrable benefit.
The only thing that seems to be happening is that I am seeing more QT prolongation — not something I previously counseled my rheumatology patients on.
April 9:
The patients have been, with a few exceptions, alone in the room. They’re not allowed to have visitors and are required to wear masks all the time. Anyone who enters their rooms is fully covered up so you can barely see them. It’s anonymous and dehumanizing.
We’re instructed to take histories by phone in order to limit the time spent in each room. I buck this instruction; I still take histories in person because human contact seems more important now than ever.
Except maybe I should be smarter about this. One of my patients refuses any treatment, including oxygen support. She firmly believes this is a result of 5G networks — something I later discovered was a common conspiracy theory. She refused to wear a mask despite having a very bad cough. She coughed in my face a lot when we were chatting. My face with my ill-fitting N95 mask. Maybe the fit-testing lady’s eyes weren’t lying and I will die after all.
April 15:
On the days when I’m not working as a hospitalist, I am still doing remote visits with my rheumatology patients. It feels good to be doing something familiar and something I’m actually good at. But it is surreal to be faced with the quotidian on one hand and life and death on the other.
I recently saw a fairly new patient, and I still haven’t figured out if she has a rheumatic condition or if her symptoms all stem from an alcohol use disorder. In our previous visits, she could barely acknowledge that her drinking was an issue. On today’s visit, she told me she was 1½ months sober.
I don’t know her very well, but it was the happiest news I’d heard in a long time. I was so beside myself with joy that I cried, which says more about my current emotional state than anything else, really.
April 21:
On my panel of patients, I have three women with COVID-19 — all of whom lost their husbands to COVID-19, and none of whom were able to say their goodbyes. I cannot even begin to imagine what it must be like to survive this period of illness, isolation, and fear, only to be met on the other side by grief.
Rheumatology doesn’t lend itself too well to such existential concerns; I am not equipped for this. Perhaps my only advantage as a rheumatologist is that I know how to use IVIG, anakinra, and tocilizumab.
Someone on my panel was started on anakinra, and it turned his case around. Would he have gotten better without it anyway? We’ll never know for sure.
April 28:
Patients seem to be requiring prolonged intubation. We have now reached the stage where patients are alive but trached and PEGed. One of my patients had been intubated for close to 3 weeks. She was one of four people in her family who contracted the illness (they had had a dinner party before New York’s state of emergency was declared). We thought she might die once she was extubated, but she is still fighting. Unconscious, unarousable, but breathing on her own.
Will she ever wake up? We don’t know. We put the onus on her family to make decisions about placing a PEG tube in. They can only do so from a distance with imperfect information gleaned from periodic, brief FaceTime interactions — where no interaction happens at all.
May 4:
It’s my last day as a “COVID hospitalist.” When I first started, I felt like I was being helpful. Walking home in the middle of the 7 PM cheers for healthcare workers frequently left me teary eyed. As horrible as the situation was, I was proud of myself for volunteering to help and appreciative of a broken city’s gratitude toward all healthcare workers in general. Maybe I bought into the idea that, like many others around me, I am a hero.
I don’t feel like a hero, though. The stuff I saw was easy compared with the stuff that my colleagues in critical care saw. Our hospital accepted the more stable patient transfers from our sister hospitals. Patients who remained in the NewYork–Presbyterian system were sicker, with encephalitis, thrombotic complications, multiorgan failure, and cytokine release syndrome. It’s the doctors who took care of those patients who deserve to be called heroes.
No, I am no hero. But did my volunteering make a difference? It made a difference to me. The overwhelming feeling I am left with isn’t pride; it’s humility. I feel humbled that I could feel so unexpectedly touched by the lives of people that I had no idea I could feel touched by.
Postscript:
My patient Esther [name changed to hide her identity] died from COVID-19. She was MY patient — not a patient I met as a COVID hospitalist, but a patient with rheumatoid arthritis whom I cared for for years.
She had scleromalacia and multiple failed scleral grafts, which made her profoundly sad. She fought her anxiety fiercely and always with poise and panache. One way she dealt with her anxiety was that she constantly messaged me via our EHR portal. She ran everything by me and trusted me to be her rock.
The past month has been so busy that I just now noticed it had been a month since I last heard from her. I tried to call her but got her voicemail. It wasn’t until I exchanged messages with her ophthalmologist that I found out she had passed away from complications of COVID-19.
She was taking rituximab and mycophenolate. I wonder if these drugs made her sicker than she would have been otherwise; it fills me with sadness. I wonder if she was alone like my other COVID-19 patients. I wonder if she was afraid. I am sorry that I wasn’t able to say goodbye.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for this rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com. This article is part of a partnership between Medscape and Hospital for Special Surgery.
When the coronavirus pandemic hit New York City in early March, the Hospital for Special Surgery leadership decided that the best way to serve the city was to stop elective orthopedic procedures temporarily and use the facility to take on patients from its sister institution, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital.
As in other institutions, it was all hands on deck. , other internal medicine subspecialists were asked to volunteer, including rheumatologists and primary care sports medicine doctors.
As a rheumatologist, it had been well over 10 years since I had last done any inpatient work. I was filled with trepidation, but I was also excited to dive in.
April 4:
Feeling very unmoored. I am in unfamiliar territory, and it’s terrifying. There are so many things that I no longer know how to do. Thankfully, the hospitalists are gracious, extremely supportive, and helpful.
My N95 doesn’t fit well. It’s never fit — not during residency or fellowship, not in any job I’ve had, and not today. The lady fit-testing me said she was sorry, but the look on her face said, “I’m sorry, but you’re going to die.”
April 7:
We don’t know how to treat coronavirus. I’ve sent some patients home, others I’ve sent to the ICU. Thank goodness for treatment algorithms from leadership, but we are sorely lacking good-quality data.
Our infectious disease doctor doesn’t think hydroxychloroquine works at all; I suspect he is right. The guidance right now is to give hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to everyone who is sick enough to be admitted, but there are methodologic flaws in the early enthusiastic preprints, and so far, I’ve not noticed any demonstrable benefit.
The only thing that seems to be happening is that I am seeing more QT prolongation — not something I previously counseled my rheumatology patients on.
April 9:
The patients have been, with a few exceptions, alone in the room. They’re not allowed to have visitors and are required to wear masks all the time. Anyone who enters their rooms is fully covered up so you can barely see them. It’s anonymous and dehumanizing.
We’re instructed to take histories by phone in order to limit the time spent in each room. I buck this instruction; I still take histories in person because human contact seems more important now than ever.
Except maybe I should be smarter about this. One of my patients refuses any treatment, including oxygen support. She firmly believes this is a result of 5G networks — something I later discovered was a common conspiracy theory. She refused to wear a mask despite having a very bad cough. She coughed in my face a lot when we were chatting. My face with my ill-fitting N95 mask. Maybe the fit-testing lady’s eyes weren’t lying and I will die after all.
April 15:
On the days when I’m not working as a hospitalist, I am still doing remote visits with my rheumatology patients. It feels good to be doing something familiar and something I’m actually good at. But it is surreal to be faced with the quotidian on one hand and life and death on the other.
I recently saw a fairly new patient, and I still haven’t figured out if she has a rheumatic condition or if her symptoms all stem from an alcohol use disorder. In our previous visits, she could barely acknowledge that her drinking was an issue. On today’s visit, she told me she was 1½ months sober.
I don’t know her very well, but it was the happiest news I’d heard in a long time. I was so beside myself with joy that I cried, which says more about my current emotional state than anything else, really.
April 21:
On my panel of patients, I have three women with COVID-19 — all of whom lost their husbands to COVID-19, and none of whom were able to say their goodbyes. I cannot even begin to imagine what it must be like to survive this period of illness, isolation, and fear, only to be met on the other side by grief.
Rheumatology doesn’t lend itself too well to such existential concerns; I am not equipped for this. Perhaps my only advantage as a rheumatologist is that I know how to use IVIG, anakinra, and tocilizumab.
Someone on my panel was started on anakinra, and it turned his case around. Would he have gotten better without it anyway? We’ll never know for sure.
April 28:
Patients seem to be requiring prolonged intubation. We have now reached the stage where patients are alive but trached and PEGed. One of my patients had been intubated for close to 3 weeks. She was one of four people in her family who contracted the illness (they had had a dinner party before New York’s state of emergency was declared). We thought she might die once she was extubated, but she is still fighting. Unconscious, unarousable, but breathing on her own.
Will she ever wake up? We don’t know. We put the onus on her family to make decisions about placing a PEG tube in. They can only do so from a distance with imperfect information gleaned from periodic, brief FaceTime interactions — where no interaction happens at all.
May 4:
It’s my last day as a “COVID hospitalist.” When I first started, I felt like I was being helpful. Walking home in the middle of the 7 PM cheers for healthcare workers frequently left me teary eyed. As horrible as the situation was, I was proud of myself for volunteering to help and appreciative of a broken city’s gratitude toward all healthcare workers in general. Maybe I bought into the idea that, like many others around me, I am a hero.
I don’t feel like a hero, though. The stuff I saw was easy compared with the stuff that my colleagues in critical care saw. Our hospital accepted the more stable patient transfers from our sister hospitals. Patients who remained in the NewYork–Presbyterian system were sicker, with encephalitis, thrombotic complications, multiorgan failure, and cytokine release syndrome. It’s the doctors who took care of those patients who deserve to be called heroes.
No, I am no hero. But did my volunteering make a difference? It made a difference to me. The overwhelming feeling I am left with isn’t pride; it’s humility. I feel humbled that I could feel so unexpectedly touched by the lives of people that I had no idea I could feel touched by.
Postscript:
My patient Esther [name changed to hide her identity] died from COVID-19. She was MY patient — not a patient I met as a COVID hospitalist, but a patient with rheumatoid arthritis whom I cared for for years.
She had scleromalacia and multiple failed scleral grafts, which made her profoundly sad. She fought her anxiety fiercely and always with poise and panache. One way she dealt with her anxiety was that she constantly messaged me via our EHR portal. She ran everything by me and trusted me to be her rock.
The past month has been so busy that I just now noticed it had been a month since I last heard from her. I tried to call her but got her voicemail. It wasn’t until I exchanged messages with her ophthalmologist that I found out she had passed away from complications of COVID-19.
She was taking rituximab and mycophenolate. I wonder if these drugs made her sicker than she would have been otherwise; it fills me with sadness. I wonder if she was alone like my other COVID-19 patients. I wonder if she was afraid. I am sorry that I wasn’t able to say goodbye.
Karmela Kim Chan, MD, is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for this rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com. This article is part of a partnership between Medscape and Hospital for Special Surgery.
COVID-19 fears would keep most Hispanics with stroke, MI symptoms home
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.
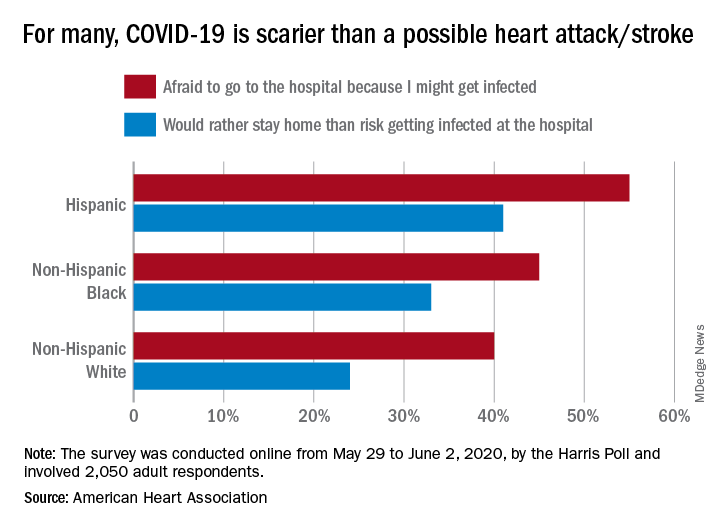
Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.

Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.

Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
Cleaner data confirm severe COVID-19 link to diabetes, hypertension
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY
Ultrasound, cardiac CT valuable in COVID-19 assessment
As if the management of patients with severe COVID-19 infections is not complicated enough, an estimated 50%-60% of patients admitted to an ICU with the disease will have some form of cardiovascular involvement, which further increases their already high risk for morbidity and mortality.
Multimodality cardiovascular imaging, chosen wisely, can both help to direct management of cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19 and lessen risk of exposure of health care workers to SARS-CoV-2, said members of an expert panel from the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Imaging Leadership Council.
“When we face a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, it’s not like any other disease because we face potential exposure risk to personnel doing imaging studies and also to other patients,” corresponding author Marcelo F. Di Carli, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Boston said in an interview.
“Any imaging study that is being considered should be performed only if we think it will help us make a change in the way that we’re going to treat that particular patient. This is true for imaging in any disease – why would you do an imaging study that will make no difference in treatment? – but the stakes are even higher in COVID-19,” he said.
The panel’s recommendations for cardiovascular imaging in patients with COVID-19 are outlined in a guidance document published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Testing and biomarkers
The guidance begins by highlighting the importance of diagnostic testing for COVID-19 infection and the use of universal precautions for health care personnel performing imaging studies, as well as disinfection of imaging equipment and rooms after each use.
Circulating biomarkers that measure end-organ stress or injury, inflammation, hypoperfusion, and activation of thrombosis/hemostasis pathways may be prognostically useful, but “almost none of the widely measured biomarkers represent a specific trigger for imaging outside of that supported by clinical judgment,” the guidance states.
In contrast, low to moderate, nonrising concentrations of markers for myocardial stress, such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP), or of myocardial injury, such as cardiac troponins (cTn), may be helpful for excluding the need for imaging.
“Importantly, clinicians should be aware that most patients with abnormal BNP/NT-proBNP or cTn do not have acute heart failure or myocardial infarction; and rise in concentration of either class of biomarker presumably reflects complex processes including direct myocardial stress/injury related to systemic illness,” the panel members wrote.
Oldies but goodies
“One thing that we found out in our review of the literature and in our experiences in our own work settings is that cardiac ultrasound plays a huge role in this disease – like in any disease – but this one in particular,” Dr. Di Carli said. “One of the most feared complications in COVID-19 leads to inflammation of the heart muscle, which then leads to heart dysfunction. And of course cardiac ultrasound, because of its portability, can be performed at bedside to help clinicians ascertain an abnormality in the heart.”
Cardiac CT is also extremely helpful for determining whether patients with ECG findings suggestive of infarction have suffered an actual thrombotic event.
“These patients may best be served by a noninvasive study as compared to an invasive coronary angiogram,” he said.
Clinical scenarios
Cardiologists may be called in to consult on the evaluation of possible cardiogenic components of pulmonary abnormalities in patients who present with dyspnea and chest x-rays showing airspace or interstitial infiltrates suggestive of pneumonia, the authors noted.
“Clinicians will rely on history, physical exam, ECG [electrocardiogram] and biomarkers, and recent cardiac imaging tests if available. Underlying cardiac history including [coronary artery disease], cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmia should be sought, and frequent contributors to decompensation should be eliminated,” they wrote.
For patients with suspected cardiac injury, either point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiography can be used for the initial evaluation, with additional, more advanced technologies called into play for specific clinical scenarios outlined in the guidance.
For example, the guidance recommends that patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG readings with clinical concern for ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome or high clinical risk for in-hospital mortality from conditions such as cardiogenic shock, dynamic ST-segment changes, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 40% thought to be caused by non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction be referred for emergent coronary angiography and reperfusion.
In contrast, in patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG but equivocal symptoms, atypical or equivocal ECG abnormalities, or late presentations, point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiogram could be used to look for regional wall motion abnormalities and left ventricular ejection fraction, whereas in patients with chest pain and ST-elevation without clear evidence of ST-elevation myocardial infarction, coronary CT angiography can help to rule out ACS and point to alternate diagnoses, the authors said.
The guidance also offers recommendations for imaging in patients with hemodynamic instability (shock or hypotension), patients with new left ventricular dysfunction in the absence of shock or hypotension, and patients with subacute and chronic-phase disease.
Development of the guidance document was supported by the ACC. Dr. Di Carli disclosed institutional grant support from Gilead Sciences and Spectrum Dynamics, and consulting income from Janssen and Bayer.
SOURCE: Rudski L et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.080.
As if the management of patients with severe COVID-19 infections is not complicated enough, an estimated 50%-60% of patients admitted to an ICU with the disease will have some form of cardiovascular involvement, which further increases their already high risk for morbidity and mortality.
Multimodality cardiovascular imaging, chosen wisely, can both help to direct management of cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19 and lessen risk of exposure of health care workers to SARS-CoV-2, said members of an expert panel from the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Imaging Leadership Council.
“When we face a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, it’s not like any other disease because we face potential exposure risk to personnel doing imaging studies and also to other patients,” corresponding author Marcelo F. Di Carli, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Boston said in an interview.
“Any imaging study that is being considered should be performed only if we think it will help us make a change in the way that we’re going to treat that particular patient. This is true for imaging in any disease – why would you do an imaging study that will make no difference in treatment? – but the stakes are even higher in COVID-19,” he said.
The panel’s recommendations for cardiovascular imaging in patients with COVID-19 are outlined in a guidance document published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Testing and biomarkers
The guidance begins by highlighting the importance of diagnostic testing for COVID-19 infection and the use of universal precautions for health care personnel performing imaging studies, as well as disinfection of imaging equipment and rooms after each use.
Circulating biomarkers that measure end-organ stress or injury, inflammation, hypoperfusion, and activation of thrombosis/hemostasis pathways may be prognostically useful, but “almost none of the widely measured biomarkers represent a specific trigger for imaging outside of that supported by clinical judgment,” the guidance states.
In contrast, low to moderate, nonrising concentrations of markers for myocardial stress, such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP), or of myocardial injury, such as cardiac troponins (cTn), may be helpful for excluding the need for imaging.
“Importantly, clinicians should be aware that most patients with abnormal BNP/NT-proBNP or cTn do not have acute heart failure or myocardial infarction; and rise in concentration of either class of biomarker presumably reflects complex processes including direct myocardial stress/injury related to systemic illness,” the panel members wrote.
Oldies but goodies
“One thing that we found out in our review of the literature and in our experiences in our own work settings is that cardiac ultrasound plays a huge role in this disease – like in any disease – but this one in particular,” Dr. Di Carli said. “One of the most feared complications in COVID-19 leads to inflammation of the heart muscle, which then leads to heart dysfunction. And of course cardiac ultrasound, because of its portability, can be performed at bedside to help clinicians ascertain an abnormality in the heart.”
Cardiac CT is also extremely helpful for determining whether patients with ECG findings suggestive of infarction have suffered an actual thrombotic event.
“These patients may best be served by a noninvasive study as compared to an invasive coronary angiogram,” he said.
Clinical scenarios
Cardiologists may be called in to consult on the evaluation of possible cardiogenic components of pulmonary abnormalities in patients who present with dyspnea and chest x-rays showing airspace or interstitial infiltrates suggestive of pneumonia, the authors noted.
“Clinicians will rely on history, physical exam, ECG [electrocardiogram] and biomarkers, and recent cardiac imaging tests if available. Underlying cardiac history including [coronary artery disease], cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmia should be sought, and frequent contributors to decompensation should be eliminated,” they wrote.
For patients with suspected cardiac injury, either point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiography can be used for the initial evaluation, with additional, more advanced technologies called into play for specific clinical scenarios outlined in the guidance.
For example, the guidance recommends that patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG readings with clinical concern for ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome or high clinical risk for in-hospital mortality from conditions such as cardiogenic shock, dynamic ST-segment changes, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 40% thought to be caused by non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction be referred for emergent coronary angiography and reperfusion.
In contrast, in patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG but equivocal symptoms, atypical or equivocal ECG abnormalities, or late presentations, point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiogram could be used to look for regional wall motion abnormalities and left ventricular ejection fraction, whereas in patients with chest pain and ST-elevation without clear evidence of ST-elevation myocardial infarction, coronary CT angiography can help to rule out ACS and point to alternate diagnoses, the authors said.
The guidance also offers recommendations for imaging in patients with hemodynamic instability (shock or hypotension), patients with new left ventricular dysfunction in the absence of shock or hypotension, and patients with subacute and chronic-phase disease.
Development of the guidance document was supported by the ACC. Dr. Di Carli disclosed institutional grant support from Gilead Sciences and Spectrum Dynamics, and consulting income from Janssen and Bayer.
SOURCE: Rudski L et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.080.
As if the management of patients with severe COVID-19 infections is not complicated enough, an estimated 50%-60% of patients admitted to an ICU with the disease will have some form of cardiovascular involvement, which further increases their already high risk for morbidity and mortality.
Multimodality cardiovascular imaging, chosen wisely, can both help to direct management of cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19 and lessen risk of exposure of health care workers to SARS-CoV-2, said members of an expert panel from the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Imaging Leadership Council.
“When we face a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, it’s not like any other disease because we face potential exposure risk to personnel doing imaging studies and also to other patients,” corresponding author Marcelo F. Di Carli, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Boston said in an interview.
“Any imaging study that is being considered should be performed only if we think it will help us make a change in the way that we’re going to treat that particular patient. This is true for imaging in any disease – why would you do an imaging study that will make no difference in treatment? – but the stakes are even higher in COVID-19,” he said.
The panel’s recommendations for cardiovascular imaging in patients with COVID-19 are outlined in a guidance document published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Testing and biomarkers
The guidance begins by highlighting the importance of diagnostic testing for COVID-19 infection and the use of universal precautions for health care personnel performing imaging studies, as well as disinfection of imaging equipment and rooms after each use.
Circulating biomarkers that measure end-organ stress or injury, inflammation, hypoperfusion, and activation of thrombosis/hemostasis pathways may be prognostically useful, but “almost none of the widely measured biomarkers represent a specific trigger for imaging outside of that supported by clinical judgment,” the guidance states.
In contrast, low to moderate, nonrising concentrations of markers for myocardial stress, such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP), or of myocardial injury, such as cardiac troponins (cTn), may be helpful for excluding the need for imaging.
“Importantly, clinicians should be aware that most patients with abnormal BNP/NT-proBNP or cTn do not have acute heart failure or myocardial infarction; and rise in concentration of either class of biomarker presumably reflects complex processes including direct myocardial stress/injury related to systemic illness,” the panel members wrote.
Oldies but goodies
“One thing that we found out in our review of the literature and in our experiences in our own work settings is that cardiac ultrasound plays a huge role in this disease – like in any disease – but this one in particular,” Dr. Di Carli said. “One of the most feared complications in COVID-19 leads to inflammation of the heart muscle, which then leads to heart dysfunction. And of course cardiac ultrasound, because of its portability, can be performed at bedside to help clinicians ascertain an abnormality in the heart.”
Cardiac CT is also extremely helpful for determining whether patients with ECG findings suggestive of infarction have suffered an actual thrombotic event.
“These patients may best be served by a noninvasive study as compared to an invasive coronary angiogram,” he said.
Clinical scenarios
Cardiologists may be called in to consult on the evaluation of possible cardiogenic components of pulmonary abnormalities in patients who present with dyspnea and chest x-rays showing airspace or interstitial infiltrates suggestive of pneumonia, the authors noted.
“Clinicians will rely on history, physical exam, ECG [electrocardiogram] and biomarkers, and recent cardiac imaging tests if available. Underlying cardiac history including [coronary artery disease], cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmia should be sought, and frequent contributors to decompensation should be eliminated,” they wrote.
For patients with suspected cardiac injury, either point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiography can be used for the initial evaluation, with additional, more advanced technologies called into play for specific clinical scenarios outlined in the guidance.
For example, the guidance recommends that patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG readings with clinical concern for ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome or high clinical risk for in-hospital mortality from conditions such as cardiogenic shock, dynamic ST-segment changes, or left ventricular ejection fraction less than 40% thought to be caused by non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction be referred for emergent coronary angiography and reperfusion.
In contrast, in patients with chest pain and abnormal ECG but equivocal symptoms, atypical or equivocal ECG abnormalities, or late presentations, point-of-care ultrasound or limited echocardiogram could be used to look for regional wall motion abnormalities and left ventricular ejection fraction, whereas in patients with chest pain and ST-elevation without clear evidence of ST-elevation myocardial infarction, coronary CT angiography can help to rule out ACS and point to alternate diagnoses, the authors said.
The guidance also offers recommendations for imaging in patients with hemodynamic instability (shock or hypotension), patients with new left ventricular dysfunction in the absence of shock or hypotension, and patients with subacute and chronic-phase disease.
Development of the guidance document was supported by the ACC. Dr. Di Carli disclosed institutional grant support from Gilead Sciences and Spectrum Dynamics, and consulting income from Janssen and Bayer.
SOURCE: Rudski L et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.080.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Combination therapy quells COVID-19 cytokine storm
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
One-third of outpatients with COVID-19 are unwell weeks later
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Small NY study: Mother-baby transmission of COVID-19 not seen
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Men occupy most leadership roles in medicine
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
FROM PHM20
Rapid drop of antibodies seen in those with mild COVID-19
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.