User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Pulmonary artery denervation eases PAH after endarterectomy
Pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) provides persistent and clinically significant hemodynamic improvements in patients with persistent chronic thromboembolic hypertension (CTEPH) after pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), according to a randomized, sham-controlled trial.
“PADN in patients with CTEPH after PEA was safe and effective,” according to an investigating team led by Alexander Romanov, MD, PhD.
The mean reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) was 258 dyn/sec per cm–5 for those randomized to PADN versus 149 dyn/sec per cm–5 (P = .001) for those randomized to the sham procedure, according to the newly published findings.
For the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), the mean distance was 470 m for the experimental group versus 399 m (P = .03) for the controls.
Several secondary endpoints measuring hemodynamics also favored PADN relative to the sham procedure at 12 months. This included the relative increase in tricuspid annular systolic excursion (P = .03) and the increase in the right ventricular fraction area (P < .001).
A total of 50 patients with residual CTEPH for at least 6 months after PEA despite medical therapy were enrolled and randomized. Entry criteria included a mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) of 25 mm Hg or greater or PVR greater than 400 dyn/sec per cm–5 on right heart catheterization. Patients with comorbidities associated with a life expectancy of less than 1 year were excluded.
Those randomized to the sham group were treated with riociguat over the course of follow-up. This therapy was not offered to patients in the PADN group, but all patients were blinded to the procedure and told that riociguat might or might not be administered.
Following the procedure, participating clinicians, who were also blinded to the procedure, were instructed to provide standard therapies for heart failure, such beta-blockers, diuretics, or digoxin, as needed. All patients were placed on an oral anticoagulant.
At 12 months the mean PAP (26 vs. 35 mm Hg; P < .001) and the mean systolic PAP (46 vs. 54 mm Hg; P = .01) were significantly lower in the PADN group versus those who underwent a sham procedure.
About 52% of the PADN group versus 12% of the sham group were classified as responders by the definition of a PVR reduction of at least 150 dyn/sec per cm–5 and 6MWT improvement of at least 20%, compared with baseline, reported Dr. Romanov, of the E. Meshalkin National Medical Research Center, ministry of health, Novosibirsk, Russia, and coinvestigators.
Of the three deaths caused by heart failure over the course of follow-up, two occurred in the sham group. Of the eight hospitalizations for heart failure, seven (29% of the sham group) occurred among controls versus one in those treated with PADN (4% of this group; P = .049).
There was one groin hematoma at the puncture site in each group. Both resolved without any consequences prior to hospital discharge. There were no other significant procedure-related complications in either group.
Larger multicenter trials are needed to confirm these findings, according to both the trial investigators and Marius M. Hoeper, MD, who is charge of the pulmonary hypertension program at the Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
In an editorial that accompanied publication of these findings, Dr. Hoeper identified the small sample size of this study as one of its limitations, but he said the results are consistent with several other small studies associating pulmonary artery denervation with benefit in pulmonary hypertension.
“It appears as if we are currently witnessing the emergence of a new treatment option for various forms of pulmonary hypertension,” Dr. Hoeper wrote. In his critique of the study, he suggested that it would have been “more informative” if both groups were on background riociguat, but the data from this and other studies so far indicates that ablation to achieve denervation “is safe and feasible.”
The PADN technique used in this study might be relevant to the results. Dr. Hoeper noted that the investigators employed catheter tip–based electroanatomic mapping with a novel remote navigation system with three-dimensional imaging of the right ventricle and central pulmonary arteries.
“Apparently, this approach minimizes radiation exposure and provides precise location of ablation sites,” Dr. Hoeper observed. However, he called for direct comparisons of this tool to the guidance systems used in other studies.
In an interview, Dr. Hoeper acknowledged that it is not yet clear that a large-scale trial of pulmonary artery denervation for the indication evaluated in this study is coming. He noted several strategies in CTEPH are widely used without trials confirming a reduction in clinical events.
“Balloon pulmonary angioplasty for CTEPH has become an established treatment around the world without any randomized, controlled trial and without demonstration of improved outcomes. A couple of well-conducted observational trials might be sufficient to convince physicians to introduce PADN as well,” he said. If such studies associated PADN with “improvements in hemodynamics, exercise capacity, and patient-reported outcomes, it might be sufficient.”
Currently, Dr. Hoeper is most concerned about obtaining further evidence of safety, which he characterized as a “major issue.”
If a multicenter trial is conducted “the primary endpoint should be focused on clinical events,” according to Dr. Romanov, who was asked to comment on the next steps in validating PADN for the treatment of CTEPH-associated pulmonary hypertension persisting after endarterectomy.
“The mortality rate during 1-year long-term follow-up is not so high, but heart failure progression is a problem. So in my view, the primary endpoint should be a composite of death and heart failure hospitalization,” he said. He called for follow-up duration of 2-3 years.
Jonathan Steinberg, MD, director of cardiac clinical trials and education, Summit Medical Group, Montclair, N.J., also called a trial with hard endpoints, such as death, the ideal.
In the meantime, hemodynamic and functional measures “are still quite valuable and move the ball forward for this intervention,” he said in an interview. Senior author of this trial and principle investigator of the recent ERADICATE-AF trial, which evaluated renal denervation in preventing recurrence of atrial fibrillation (JAMA. 2020;323:248-55), Dr. Steinberg predicted, “I do indeed suspect we will see trials that are more accomplishable [than a large-scale, randomized, controlled trial] in the not too distant future.”
Dr. Romanov received funding from Biosense Webster. Dr. Hoeper has received fees for lectures and/or consultations from Acceleron, Actelion, Bayer, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Romanov A et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Aug 17;76:916-26.
Pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) provides persistent and clinically significant hemodynamic improvements in patients with persistent chronic thromboembolic hypertension (CTEPH) after pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), according to a randomized, sham-controlled trial.
“PADN in patients with CTEPH after PEA was safe and effective,” according to an investigating team led by Alexander Romanov, MD, PhD.
The mean reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) was 258 dyn/sec per cm–5 for those randomized to PADN versus 149 dyn/sec per cm–5 (P = .001) for those randomized to the sham procedure, according to the newly published findings.
For the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), the mean distance was 470 m for the experimental group versus 399 m (P = .03) for the controls.
Several secondary endpoints measuring hemodynamics also favored PADN relative to the sham procedure at 12 months. This included the relative increase in tricuspid annular systolic excursion (P = .03) and the increase in the right ventricular fraction area (P < .001).
A total of 50 patients with residual CTEPH for at least 6 months after PEA despite medical therapy were enrolled and randomized. Entry criteria included a mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) of 25 mm Hg or greater or PVR greater than 400 dyn/sec per cm–5 on right heart catheterization. Patients with comorbidities associated with a life expectancy of less than 1 year were excluded.
Those randomized to the sham group were treated with riociguat over the course of follow-up. This therapy was not offered to patients in the PADN group, but all patients were blinded to the procedure and told that riociguat might or might not be administered.
Following the procedure, participating clinicians, who were also blinded to the procedure, were instructed to provide standard therapies for heart failure, such beta-blockers, diuretics, or digoxin, as needed. All patients were placed on an oral anticoagulant.
At 12 months the mean PAP (26 vs. 35 mm Hg; P < .001) and the mean systolic PAP (46 vs. 54 mm Hg; P = .01) were significantly lower in the PADN group versus those who underwent a sham procedure.
About 52% of the PADN group versus 12% of the sham group were classified as responders by the definition of a PVR reduction of at least 150 dyn/sec per cm–5 and 6MWT improvement of at least 20%, compared with baseline, reported Dr. Romanov, of the E. Meshalkin National Medical Research Center, ministry of health, Novosibirsk, Russia, and coinvestigators.
Of the three deaths caused by heart failure over the course of follow-up, two occurred in the sham group. Of the eight hospitalizations for heart failure, seven (29% of the sham group) occurred among controls versus one in those treated with PADN (4% of this group; P = .049).
There was one groin hematoma at the puncture site in each group. Both resolved without any consequences prior to hospital discharge. There were no other significant procedure-related complications in either group.
Larger multicenter trials are needed to confirm these findings, according to both the trial investigators and Marius M. Hoeper, MD, who is charge of the pulmonary hypertension program at the Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
In an editorial that accompanied publication of these findings, Dr. Hoeper identified the small sample size of this study as one of its limitations, but he said the results are consistent with several other small studies associating pulmonary artery denervation with benefit in pulmonary hypertension.
“It appears as if we are currently witnessing the emergence of a new treatment option for various forms of pulmonary hypertension,” Dr. Hoeper wrote. In his critique of the study, he suggested that it would have been “more informative” if both groups were on background riociguat, but the data from this and other studies so far indicates that ablation to achieve denervation “is safe and feasible.”
The PADN technique used in this study might be relevant to the results. Dr. Hoeper noted that the investigators employed catheter tip–based electroanatomic mapping with a novel remote navigation system with three-dimensional imaging of the right ventricle and central pulmonary arteries.
“Apparently, this approach minimizes radiation exposure and provides precise location of ablation sites,” Dr. Hoeper observed. However, he called for direct comparisons of this tool to the guidance systems used in other studies.
In an interview, Dr. Hoeper acknowledged that it is not yet clear that a large-scale trial of pulmonary artery denervation for the indication evaluated in this study is coming. He noted several strategies in CTEPH are widely used without trials confirming a reduction in clinical events.
“Balloon pulmonary angioplasty for CTEPH has become an established treatment around the world without any randomized, controlled trial and without demonstration of improved outcomes. A couple of well-conducted observational trials might be sufficient to convince physicians to introduce PADN as well,” he said. If such studies associated PADN with “improvements in hemodynamics, exercise capacity, and patient-reported outcomes, it might be sufficient.”
Currently, Dr. Hoeper is most concerned about obtaining further evidence of safety, which he characterized as a “major issue.”
If a multicenter trial is conducted “the primary endpoint should be focused on clinical events,” according to Dr. Romanov, who was asked to comment on the next steps in validating PADN for the treatment of CTEPH-associated pulmonary hypertension persisting after endarterectomy.
“The mortality rate during 1-year long-term follow-up is not so high, but heart failure progression is a problem. So in my view, the primary endpoint should be a composite of death and heart failure hospitalization,” he said. He called for follow-up duration of 2-3 years.
Jonathan Steinberg, MD, director of cardiac clinical trials and education, Summit Medical Group, Montclair, N.J., also called a trial with hard endpoints, such as death, the ideal.
In the meantime, hemodynamic and functional measures “are still quite valuable and move the ball forward for this intervention,” he said in an interview. Senior author of this trial and principle investigator of the recent ERADICATE-AF trial, which evaluated renal denervation in preventing recurrence of atrial fibrillation (JAMA. 2020;323:248-55), Dr. Steinberg predicted, “I do indeed suspect we will see trials that are more accomplishable [than a large-scale, randomized, controlled trial] in the not too distant future.”
Dr. Romanov received funding from Biosense Webster. Dr. Hoeper has received fees for lectures and/or consultations from Acceleron, Actelion, Bayer, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Romanov A et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Aug 17;76:916-26.
Pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) provides persistent and clinically significant hemodynamic improvements in patients with persistent chronic thromboembolic hypertension (CTEPH) after pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), according to a randomized, sham-controlled trial.
“PADN in patients with CTEPH after PEA was safe and effective,” according to an investigating team led by Alexander Romanov, MD, PhD.
The mean reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) was 258 dyn/sec per cm–5 for those randomized to PADN versus 149 dyn/sec per cm–5 (P = .001) for those randomized to the sham procedure, according to the newly published findings.
For the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), the mean distance was 470 m for the experimental group versus 399 m (P = .03) for the controls.
Several secondary endpoints measuring hemodynamics also favored PADN relative to the sham procedure at 12 months. This included the relative increase in tricuspid annular systolic excursion (P = .03) and the increase in the right ventricular fraction area (P < .001).
A total of 50 patients with residual CTEPH for at least 6 months after PEA despite medical therapy were enrolled and randomized. Entry criteria included a mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) of 25 mm Hg or greater or PVR greater than 400 dyn/sec per cm–5 on right heart catheterization. Patients with comorbidities associated with a life expectancy of less than 1 year were excluded.
Those randomized to the sham group were treated with riociguat over the course of follow-up. This therapy was not offered to patients in the PADN group, but all patients were blinded to the procedure and told that riociguat might or might not be administered.
Following the procedure, participating clinicians, who were also blinded to the procedure, were instructed to provide standard therapies for heart failure, such beta-blockers, diuretics, or digoxin, as needed. All patients were placed on an oral anticoagulant.
At 12 months the mean PAP (26 vs. 35 mm Hg; P < .001) and the mean systolic PAP (46 vs. 54 mm Hg; P = .01) were significantly lower in the PADN group versus those who underwent a sham procedure.
About 52% of the PADN group versus 12% of the sham group were classified as responders by the definition of a PVR reduction of at least 150 dyn/sec per cm–5 and 6MWT improvement of at least 20%, compared with baseline, reported Dr. Romanov, of the E. Meshalkin National Medical Research Center, ministry of health, Novosibirsk, Russia, and coinvestigators.
Of the three deaths caused by heart failure over the course of follow-up, two occurred in the sham group. Of the eight hospitalizations for heart failure, seven (29% of the sham group) occurred among controls versus one in those treated with PADN (4% of this group; P = .049).
There was one groin hematoma at the puncture site in each group. Both resolved without any consequences prior to hospital discharge. There were no other significant procedure-related complications in either group.
Larger multicenter trials are needed to confirm these findings, according to both the trial investigators and Marius M. Hoeper, MD, who is charge of the pulmonary hypertension program at the Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
In an editorial that accompanied publication of these findings, Dr. Hoeper identified the small sample size of this study as one of its limitations, but he said the results are consistent with several other small studies associating pulmonary artery denervation with benefit in pulmonary hypertension.
“It appears as if we are currently witnessing the emergence of a new treatment option for various forms of pulmonary hypertension,” Dr. Hoeper wrote. In his critique of the study, he suggested that it would have been “more informative” if both groups were on background riociguat, but the data from this and other studies so far indicates that ablation to achieve denervation “is safe and feasible.”
The PADN technique used in this study might be relevant to the results. Dr. Hoeper noted that the investigators employed catheter tip–based electroanatomic mapping with a novel remote navigation system with three-dimensional imaging of the right ventricle and central pulmonary arteries.
“Apparently, this approach minimizes radiation exposure and provides precise location of ablation sites,” Dr. Hoeper observed. However, he called for direct comparisons of this tool to the guidance systems used in other studies.
In an interview, Dr. Hoeper acknowledged that it is not yet clear that a large-scale trial of pulmonary artery denervation for the indication evaluated in this study is coming. He noted several strategies in CTEPH are widely used without trials confirming a reduction in clinical events.
“Balloon pulmonary angioplasty for CTEPH has become an established treatment around the world without any randomized, controlled trial and without demonstration of improved outcomes. A couple of well-conducted observational trials might be sufficient to convince physicians to introduce PADN as well,” he said. If such studies associated PADN with “improvements in hemodynamics, exercise capacity, and patient-reported outcomes, it might be sufficient.”
Currently, Dr. Hoeper is most concerned about obtaining further evidence of safety, which he characterized as a “major issue.”
If a multicenter trial is conducted “the primary endpoint should be focused on clinical events,” according to Dr. Romanov, who was asked to comment on the next steps in validating PADN for the treatment of CTEPH-associated pulmonary hypertension persisting after endarterectomy.
“The mortality rate during 1-year long-term follow-up is not so high, but heart failure progression is a problem. So in my view, the primary endpoint should be a composite of death and heart failure hospitalization,” he said. He called for follow-up duration of 2-3 years.
Jonathan Steinberg, MD, director of cardiac clinical trials and education, Summit Medical Group, Montclair, N.J., also called a trial with hard endpoints, such as death, the ideal.
In the meantime, hemodynamic and functional measures “are still quite valuable and move the ball forward for this intervention,” he said in an interview. Senior author of this trial and principle investigator of the recent ERADICATE-AF trial, which evaluated renal denervation in preventing recurrence of atrial fibrillation (JAMA. 2020;323:248-55), Dr. Steinberg predicted, “I do indeed suspect we will see trials that are more accomplishable [than a large-scale, randomized, controlled trial] in the not too distant future.”
Dr. Romanov received funding from Biosense Webster. Dr. Hoeper has received fees for lectures and/or consultations from Acceleron, Actelion, Bayer, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer.
SOURCE: Romanov A et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Aug 17;76:916-26.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Pulmonary rehab reduces COPD readmissions
Pulmonary rehabilitation reduces the likelihood that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will be readmitted to the hospital in the year after discharge by 33%, new research shows, but few patients participate in those programs.
In fact, in a retrospective cohort of 197,376 patients from 4446 hospitals, only 1.5% of patients initiated pulmonary rehabilitation in the 90 days after hospital discharge.
“This is a striking finding,” said Mihaela Stefan, PhD, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School–Baystate in Springfield. “Our study demonstrates that we need to increase access to rehabilitation to reduce the risk of readmissions.”
Not enough patients are initiating rehabilitation, but the onus is not only on them; the system is failing them. “We wanted to understand how much pulmonary rehabilitation lowers the readmission rate,” Stefan told Medscape Medical News.
So she and her colleagues examined the records of patients who were hospitalized for COPD in 2014 to see whether they had begun rehabilitation in the 90 days after discharge and whether they were readmitted to the hospital in the subsequent 12 months.
Patients who were unlikely to initiate pulmonary rehabilitation — such as those with dementia or metastatic cancer and those discharged to hospice care or a nursing home — were excluded from the analysis, Stefan said during her presentation at the study results at the virtual American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2020 International Conference.
The risk analysis was complex because many patients died before the year was out, and “a patient who dies has no risk of being readmitted,” she explained. Selection bias was also a factor because patients who do pulmonary rehab tend to be in better shape.
The researchers used propensity score matching and Anderson–Gill models of cumulative rehospitalizations or death at 1 year with time-varying exposure to pulmonary rehabilitation to account for clustering of individual events and adjust for covariates. “It was a complicated risk analysis,” she said.
In the year after discharge, 130,660 patients (66%) were readmitted to the hospital. The rate of rehospitalization was lower for those who initiated rehabilitation than for those who did not (59% vs 66%), as was the mean number of readmissions per patient (1.4 vs 1.8).
Rehabilitation was associated with a lower risk for readmission or death (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.66 - 0.69).
“We know the referral rates are low and that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective in clinical trials,” said Stefan, and now “we see that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective when you look at patients in real life.”
From a provider perspective, “we need to make sure that hospitals get more money for pulmonary rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation is paid for,” she explained. "But pulmonary rehab is not a lucrative business. I don›t know why the CMS pays more for cardiac."
A rehabilitation program generally consists of 36 sessions, held two or three times a week, and many patients can’t afford that on their own, she noted. Transportation is another huge issue.
A recent study in which semi-structured interviews were conducted with 15 COPD patients showed that the main barriers to enrollment in a pulmonary rehabilitation program are lack of awareness, family obligations, transportation, and lack of motivation, said Stefan, who was involved in that research.
Telehealth rehabilitation programs might become more available in the near future, given the COVID pandemic. But “currently, Medicare doesn’t pay for telerehab,” she said. Virtual sessions might attract more patients, but lack of computer access and training could present another barrier for some.
PAH rehab
Uptake for pulmonary rehabilitation is as low for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) as it is for those with COPD, according to another study presented at the virtual ATS meeting.
An examination of the electronic health records of 111,356 veterans who experienced incident PAH from 2010 to 2016 showed that only 1,737 (1.6%) followed through on pulmonary rehabilitation.
“Exercise therapy is safe and effective at improving outcomes,” lead author Thomas Cascino, MD, from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, said in an ATS press release. “Recognizing that it is being underutilized is a necessary first step in working toward increasing patient access to rehab.
His group is currently working on a trial for home-based rehabilitation “using wearable technology as a means to expand access for people unable to come to center-based rehab for a variety of reasons,” he explained.
“The goal of all our treatments is to help people feel better and live longer,” Cascino added.
Stefan and Cascino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pulmonary rehabilitation reduces the likelihood that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will be readmitted to the hospital in the year after discharge by 33%, new research shows, but few patients participate in those programs.
In fact, in a retrospective cohort of 197,376 patients from 4446 hospitals, only 1.5% of patients initiated pulmonary rehabilitation in the 90 days after hospital discharge.
“This is a striking finding,” said Mihaela Stefan, PhD, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School–Baystate in Springfield. “Our study demonstrates that we need to increase access to rehabilitation to reduce the risk of readmissions.”
Not enough patients are initiating rehabilitation, but the onus is not only on them; the system is failing them. “We wanted to understand how much pulmonary rehabilitation lowers the readmission rate,” Stefan told Medscape Medical News.
So she and her colleagues examined the records of patients who were hospitalized for COPD in 2014 to see whether they had begun rehabilitation in the 90 days after discharge and whether they were readmitted to the hospital in the subsequent 12 months.
Patients who were unlikely to initiate pulmonary rehabilitation — such as those with dementia or metastatic cancer and those discharged to hospice care or a nursing home — were excluded from the analysis, Stefan said during her presentation at the study results at the virtual American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2020 International Conference.
The risk analysis was complex because many patients died before the year was out, and “a patient who dies has no risk of being readmitted,” she explained. Selection bias was also a factor because patients who do pulmonary rehab tend to be in better shape.
The researchers used propensity score matching and Anderson–Gill models of cumulative rehospitalizations or death at 1 year with time-varying exposure to pulmonary rehabilitation to account for clustering of individual events and adjust for covariates. “It was a complicated risk analysis,” she said.
In the year after discharge, 130,660 patients (66%) were readmitted to the hospital. The rate of rehospitalization was lower for those who initiated rehabilitation than for those who did not (59% vs 66%), as was the mean number of readmissions per patient (1.4 vs 1.8).
Rehabilitation was associated with a lower risk for readmission or death (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.66 - 0.69).
“We know the referral rates are low and that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective in clinical trials,” said Stefan, and now “we see that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective when you look at patients in real life.”
From a provider perspective, “we need to make sure that hospitals get more money for pulmonary rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation is paid for,” she explained. "But pulmonary rehab is not a lucrative business. I don›t know why the CMS pays more for cardiac."
A rehabilitation program generally consists of 36 sessions, held two or three times a week, and many patients can’t afford that on their own, she noted. Transportation is another huge issue.
A recent study in which semi-structured interviews were conducted with 15 COPD patients showed that the main barriers to enrollment in a pulmonary rehabilitation program are lack of awareness, family obligations, transportation, and lack of motivation, said Stefan, who was involved in that research.
Telehealth rehabilitation programs might become more available in the near future, given the COVID pandemic. But “currently, Medicare doesn’t pay for telerehab,” she said. Virtual sessions might attract more patients, but lack of computer access and training could present another barrier for some.
PAH rehab
Uptake for pulmonary rehabilitation is as low for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) as it is for those with COPD, according to another study presented at the virtual ATS meeting.
An examination of the electronic health records of 111,356 veterans who experienced incident PAH from 2010 to 2016 showed that only 1,737 (1.6%) followed through on pulmonary rehabilitation.
“Exercise therapy is safe and effective at improving outcomes,” lead author Thomas Cascino, MD, from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, said in an ATS press release. “Recognizing that it is being underutilized is a necessary first step in working toward increasing patient access to rehab.
His group is currently working on a trial for home-based rehabilitation “using wearable technology as a means to expand access for people unable to come to center-based rehab for a variety of reasons,” he explained.
“The goal of all our treatments is to help people feel better and live longer,” Cascino added.
Stefan and Cascino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pulmonary rehabilitation reduces the likelihood that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will be readmitted to the hospital in the year after discharge by 33%, new research shows, but few patients participate in those programs.
In fact, in a retrospective cohort of 197,376 patients from 4446 hospitals, only 1.5% of patients initiated pulmonary rehabilitation in the 90 days after hospital discharge.
“This is a striking finding,” said Mihaela Stefan, PhD, from the University of Massachusetts Medical School–Baystate in Springfield. “Our study demonstrates that we need to increase access to rehabilitation to reduce the risk of readmissions.”
Not enough patients are initiating rehabilitation, but the onus is not only on them; the system is failing them. “We wanted to understand how much pulmonary rehabilitation lowers the readmission rate,” Stefan told Medscape Medical News.
So she and her colleagues examined the records of patients who were hospitalized for COPD in 2014 to see whether they had begun rehabilitation in the 90 days after discharge and whether they were readmitted to the hospital in the subsequent 12 months.
Patients who were unlikely to initiate pulmonary rehabilitation — such as those with dementia or metastatic cancer and those discharged to hospice care or a nursing home — were excluded from the analysis, Stefan said during her presentation at the study results at the virtual American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2020 International Conference.
The risk analysis was complex because many patients died before the year was out, and “a patient who dies has no risk of being readmitted,” she explained. Selection bias was also a factor because patients who do pulmonary rehab tend to be in better shape.
The researchers used propensity score matching and Anderson–Gill models of cumulative rehospitalizations or death at 1 year with time-varying exposure to pulmonary rehabilitation to account for clustering of individual events and adjust for covariates. “It was a complicated risk analysis,” she said.
In the year after discharge, 130,660 patients (66%) were readmitted to the hospital. The rate of rehospitalization was lower for those who initiated rehabilitation than for those who did not (59% vs 66%), as was the mean number of readmissions per patient (1.4 vs 1.8).
Rehabilitation was associated with a lower risk for readmission or death (hazard ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.66 - 0.69).
“We know the referral rates are low and that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective in clinical trials,” said Stefan, and now “we see that pulmonary rehabilitation is effective when you look at patients in real life.”
From a provider perspective, “we need to make sure that hospitals get more money for pulmonary rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation is paid for,” she explained. "But pulmonary rehab is not a lucrative business. I don›t know why the CMS pays more for cardiac."
A rehabilitation program generally consists of 36 sessions, held two or three times a week, and many patients can’t afford that on their own, she noted. Transportation is another huge issue.
A recent study in which semi-structured interviews were conducted with 15 COPD patients showed that the main barriers to enrollment in a pulmonary rehabilitation program are lack of awareness, family obligations, transportation, and lack of motivation, said Stefan, who was involved in that research.
Telehealth rehabilitation programs might become more available in the near future, given the COVID pandemic. But “currently, Medicare doesn’t pay for telerehab,” she said. Virtual sessions might attract more patients, but lack of computer access and training could present another barrier for some.
PAH rehab
Uptake for pulmonary rehabilitation is as low for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) as it is for those with COPD, according to another study presented at the virtual ATS meeting.
An examination of the electronic health records of 111,356 veterans who experienced incident PAH from 2010 to 2016 showed that only 1,737 (1.6%) followed through on pulmonary rehabilitation.
“Exercise therapy is safe and effective at improving outcomes,” lead author Thomas Cascino, MD, from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, said in an ATS press release. “Recognizing that it is being underutilized is a necessary first step in working toward increasing patient access to rehab.
His group is currently working on a trial for home-based rehabilitation “using wearable technology as a means to expand access for people unable to come to center-based rehab for a variety of reasons,” he explained.
“The goal of all our treatments is to help people feel better and live longer,” Cascino added.
Stefan and Cascino have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 child case count now over 400,000
according to a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
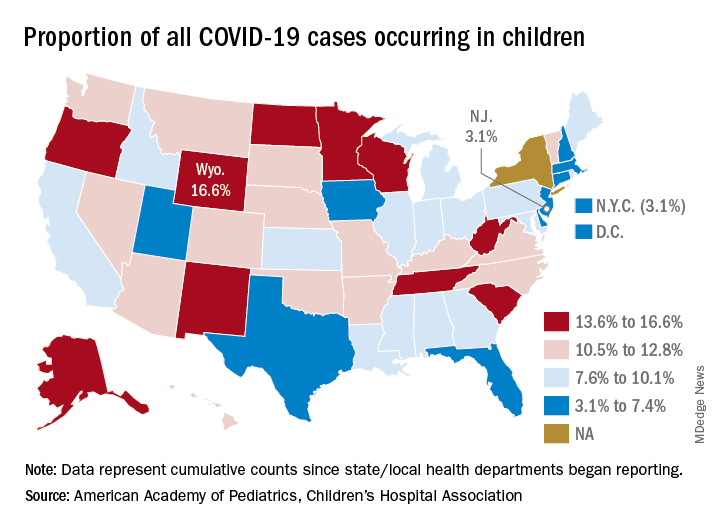
The 406,000 children who have tested positive for COVID-19 represent 9.1% of all cases reported so far by 49 states (New York does not provide age distribution), New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Since the proportion of child cases also was 9.1% on Aug. 6, the most recent week is the first without an increase since tracking began in mid-April, the report shows.
State-level data show that Wyoming has the highest percentage of child cases (16.6%) after Alabama changed its “definition of child case from 0-24 to 0-17 years, resulting in a downward revision of cumulative child cases,” the AAP and the CHA said. Alabama’s proportion of such cases dropped from 22.5% to 9.0%.
New Jersey had the lowest rate (3.1%) again this week, along with New York City, but both were up slightly from the week before, when New Jersey was at 2.9% and N.Y.C. was 3.0%. The only states, other than Alabama, that saw declines over the last week were Arkansas, Massachusetts, Mississippi, South Dakota, Texas, and West Virginia. Texas, however, has reported age for only 8% of its confirmed cases, the report noted.
The overall rate of child COVID-19 cases as of Aug. 13 was 538 per 100,000 children, up from 500.7 per 100,000 a week earlier. Arizona was again highest among the states with a rate of 1,254 per 100,000 (up from 1,206) and Vermont was lowest at 121, although Puerto Rico (114) and Guam (88) were lower still, the AAP/CHA data indicate.
For the nine states that report testing information for children, Arizona has the highest positivity rate at 18.3% and West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%. Data on hospitalizations – available from 21 states and N.Y.C. – show that 3,849 children have been admitted, with rates varying from 0.2% of children in Hawaii to 8.8% in the Big Apple, according to the report.
More specific information on child cases, such as symptoms or underlying conditions, is not being provided by states at this time, the AAP and CHA pointed out.
according to a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The 406,000 children who have tested positive for COVID-19 represent 9.1% of all cases reported so far by 49 states (New York does not provide age distribution), New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Since the proportion of child cases also was 9.1% on Aug. 6, the most recent week is the first without an increase since tracking began in mid-April, the report shows.
State-level data show that Wyoming has the highest percentage of child cases (16.6%) after Alabama changed its “definition of child case from 0-24 to 0-17 years, resulting in a downward revision of cumulative child cases,” the AAP and the CHA said. Alabama’s proportion of such cases dropped from 22.5% to 9.0%.
New Jersey had the lowest rate (3.1%) again this week, along with New York City, but both were up slightly from the week before, when New Jersey was at 2.9% and N.Y.C. was 3.0%. The only states, other than Alabama, that saw declines over the last week were Arkansas, Massachusetts, Mississippi, South Dakota, Texas, and West Virginia. Texas, however, has reported age for only 8% of its confirmed cases, the report noted.
The overall rate of child COVID-19 cases as of Aug. 13 was 538 per 100,000 children, up from 500.7 per 100,000 a week earlier. Arizona was again highest among the states with a rate of 1,254 per 100,000 (up from 1,206) and Vermont was lowest at 121, although Puerto Rico (114) and Guam (88) were lower still, the AAP/CHA data indicate.
For the nine states that report testing information for children, Arizona has the highest positivity rate at 18.3% and West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%. Data on hospitalizations – available from 21 states and N.Y.C. – show that 3,849 children have been admitted, with rates varying from 0.2% of children in Hawaii to 8.8% in the Big Apple, according to the report.
More specific information on child cases, such as symptoms or underlying conditions, is not being provided by states at this time, the AAP and CHA pointed out.
according to a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The 406,000 children who have tested positive for COVID-19 represent 9.1% of all cases reported so far by 49 states (New York does not provide age distribution), New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Since the proportion of child cases also was 9.1% on Aug. 6, the most recent week is the first without an increase since tracking began in mid-April, the report shows.
State-level data show that Wyoming has the highest percentage of child cases (16.6%) after Alabama changed its “definition of child case from 0-24 to 0-17 years, resulting in a downward revision of cumulative child cases,” the AAP and the CHA said. Alabama’s proportion of such cases dropped from 22.5% to 9.0%.
New Jersey had the lowest rate (3.1%) again this week, along with New York City, but both were up slightly from the week before, when New Jersey was at 2.9% and N.Y.C. was 3.0%. The only states, other than Alabama, that saw declines over the last week were Arkansas, Massachusetts, Mississippi, South Dakota, Texas, and West Virginia. Texas, however, has reported age for only 8% of its confirmed cases, the report noted.
The overall rate of child COVID-19 cases as of Aug. 13 was 538 per 100,000 children, up from 500.7 per 100,000 a week earlier. Arizona was again highest among the states with a rate of 1,254 per 100,000 (up from 1,206) and Vermont was lowest at 121, although Puerto Rico (114) and Guam (88) were lower still, the AAP/CHA data indicate.
For the nine states that report testing information for children, Arizona has the highest positivity rate at 18.3% and West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%. Data on hospitalizations – available from 21 states and N.Y.C. – show that 3,849 children have been admitted, with rates varying from 0.2% of children in Hawaii to 8.8% in the Big Apple, according to the report.
More specific information on child cases, such as symptoms or underlying conditions, is not being provided by states at this time, the AAP and CHA pointed out.
HFNC more comfortable for posthypercapnic patients with COPD
Following invasive ventilation for severe hypercapnic respiratory failure, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease had similar levels of treatment failure if they received high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy or noninvasive ventilation, recent research in Critical Care has suggested.
However, for patients with COPD weaned off invasive ventilation, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen therapy was “more comfortable and better tolerated,” compared with noninvasive ventilation (NIV). In addition, “airway care interventions and the incidence of nasofacial skin breakdown associated with HFNC were significantly lower than in NIV,” according to Dingyu Tan of the Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou (China) University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, and colleagues. “HFNC appears to be an effective means of respiratory support for COPD patients extubated after severe hypercapnic respiratory failure,” they said.
The investigators screened patients with COPD and hypercapnic respiratory failure for enrollment, including those who met Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) criteria, were 85 years old or younger and caring for themselves, had bronchopulmonary infection–induced respiratory failure, and had achieved pulmonary infection control criteria. Exclusion criteria were:
- Patients under age 18 years.
- Presence of oral or facial trauma.
- Poor sputum excretion ability.
- Hemodynamic instability that would contraindicate use of NIV.
- Poor cough during PIC window.
- Poor short-term prognosis.
- Failure of the heart, brain, liver or kidney.
- Patients who could not consent to treatment.
Patients were determined to have failed treatment if they returned to invasive mechanical ventilation or switched from one treatment to another (HFNC to NIV or NIV to HFNC). Investigators also performed an arterial blood gas analysis, recorded the number of duration of airway care interventions, and monitored vital signs at 1 hour, 24 hours, and 48 hours after extubation as secondary analyses.
Overall, 44 patients randomized to receive HFNC and 42 patients randomized for NIV were available for analysis. The investigators found 22.7% of patients in the HFNC group and 28.6% in the NIV group experienced treatment failure (risk difference, –5.8%; 95% confidence interval, −23.8 to 12.4%; P = .535), with patients in the HFNC group experiencing a significantly lower level of treatment intolerance, compared with patients in the NIV group (risk difference, –50.0%; 95% CI, −74.6 to −12.9%; P = .015). There were no significant differences between either group regarding intubation (−0.65%; 95% CI, −16.01 to 14.46%), while rate of switching treatments was lower in the HFNC group but not significant (−5.2%; 95% CI, −19.82 to 9.05%).
Patients in both the HFNC and NIV groups had faster mean respiratory rates 1 hour after extubation (P < .050). After 24 hours, the NIV group had higher-than-baseline respiratory rates, compared with the HFNC group, which had returned to normal (20 vs. 24.5 breaths per minute; P < .050). Both groups had returned to baseline by 48 hours after extubation. At 1 hour after extubation, patients in the HFNC group had lower PaO2/FiO2 (P < .050) and pH values (P < .050), and higher PaCO2 values (P less than .050), compared with baseline. There were no statistically significant differences in PaO2/FiO2, pH, and PaCO2 values in either group at 24 hours or 48 hours after extubation.
Daily airway care interventions were significantly higher on average in the NIV group, compared with the HFNC group (7 vs. 6; P = .0006), and the HFNC group also had significantly better comfort scores (7 vs. 5; P < .001) as measured by a modified visual analog scale, as well as incidence of nasal and facial skin breakdown (0 vs. 9.6%; P = .027), compared with the NIV group.
Results difficult to apply to North American patients
David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, a professor specializing in critical care at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview the results of this trial may not be applicable for patients with infection-related respiratory failure and COPD in North America “due to the differences in common weaning practices between North America and China.”
For example, the trial used the pulmonary infection control (PIC) window criteria for extubation, which requires a significant decrease in radiographic infiltrates, improvement in quality and quantity of sputum, normalizing of leukocyte count, a synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) rate of 10-12 breaths per minute, and pressure support less than 10-12 cm/H2O (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1255-67).
“The process used to achieve these measures is not standardized. In North America, daily awakening and screening for spontaneous breathing trials would be usual, but this was not reported in the current trial,” he explained.
Differences in patient population also make the application of the results difficult, Dr. Bowton said. “Only 60% of the patients had spirometrically confirmed COPD and fewer than half were on at least dual inhaled therapy prior to hospitalization with only one-third taking beta agonists or anticholinergic agents,” he noted. “The cause of respiratory failure was infectious, requiring an infiltrate on chest radiograph; thus, patients with hypercarbic respiratory failure without a new infiltrate were excluded from the study. On average, patients were hypercarbic, yet alkalemic at the time of extubation; the PaCO2 and pH at the time of intubation were not reported.
“This study suggests that in some patients with COPD and respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, HFO [high-flow oxygen] may be better tolerated and equally effective as NIPPV [noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation] at mitigating the need for reintubation following extubation. In this patient population where hypoxemia prior to extubation was not severe, the mechanisms by which HFO is beneficial remain speculative,” he said.
This study was funded by the Rui E special fund for emergency medicine research and the Yangzhou Science and Technology Development Plan. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bowton reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tan D et al. Crit Care. 2020 Aug 6. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03214-9.
Following invasive ventilation for severe hypercapnic respiratory failure, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease had similar levels of treatment failure if they received high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy or noninvasive ventilation, recent research in Critical Care has suggested.
However, for patients with COPD weaned off invasive ventilation, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen therapy was “more comfortable and better tolerated,” compared with noninvasive ventilation (NIV). In addition, “airway care interventions and the incidence of nasofacial skin breakdown associated with HFNC were significantly lower than in NIV,” according to Dingyu Tan of the Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou (China) University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, and colleagues. “HFNC appears to be an effective means of respiratory support for COPD patients extubated after severe hypercapnic respiratory failure,” they said.
The investigators screened patients with COPD and hypercapnic respiratory failure for enrollment, including those who met Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) criteria, were 85 years old or younger and caring for themselves, had bronchopulmonary infection–induced respiratory failure, and had achieved pulmonary infection control criteria. Exclusion criteria were:
- Patients under age 18 years.
- Presence of oral or facial trauma.
- Poor sputum excretion ability.
- Hemodynamic instability that would contraindicate use of NIV.
- Poor cough during PIC window.
- Poor short-term prognosis.
- Failure of the heart, brain, liver or kidney.
- Patients who could not consent to treatment.
Patients were determined to have failed treatment if they returned to invasive mechanical ventilation or switched from one treatment to another (HFNC to NIV or NIV to HFNC). Investigators also performed an arterial blood gas analysis, recorded the number of duration of airway care interventions, and monitored vital signs at 1 hour, 24 hours, and 48 hours after extubation as secondary analyses.
Overall, 44 patients randomized to receive HFNC and 42 patients randomized for NIV were available for analysis. The investigators found 22.7% of patients in the HFNC group and 28.6% in the NIV group experienced treatment failure (risk difference, –5.8%; 95% confidence interval, −23.8 to 12.4%; P = .535), with patients in the HFNC group experiencing a significantly lower level of treatment intolerance, compared with patients in the NIV group (risk difference, –50.0%; 95% CI, −74.6 to −12.9%; P = .015). There were no significant differences between either group regarding intubation (−0.65%; 95% CI, −16.01 to 14.46%), while rate of switching treatments was lower in the HFNC group but not significant (−5.2%; 95% CI, −19.82 to 9.05%).
Patients in both the HFNC and NIV groups had faster mean respiratory rates 1 hour after extubation (P < .050). After 24 hours, the NIV group had higher-than-baseline respiratory rates, compared with the HFNC group, which had returned to normal (20 vs. 24.5 breaths per minute; P < .050). Both groups had returned to baseline by 48 hours after extubation. At 1 hour after extubation, patients in the HFNC group had lower PaO2/FiO2 (P < .050) and pH values (P < .050), and higher PaCO2 values (P less than .050), compared with baseline. There were no statistically significant differences in PaO2/FiO2, pH, and PaCO2 values in either group at 24 hours or 48 hours after extubation.
Daily airway care interventions were significantly higher on average in the NIV group, compared with the HFNC group (7 vs. 6; P = .0006), and the HFNC group also had significantly better comfort scores (7 vs. 5; P < .001) as measured by a modified visual analog scale, as well as incidence of nasal and facial skin breakdown (0 vs. 9.6%; P = .027), compared with the NIV group.
Results difficult to apply to North American patients
David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, a professor specializing in critical care at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview the results of this trial may not be applicable for patients with infection-related respiratory failure and COPD in North America “due to the differences in common weaning practices between North America and China.”
For example, the trial used the pulmonary infection control (PIC) window criteria for extubation, which requires a significant decrease in radiographic infiltrates, improvement in quality and quantity of sputum, normalizing of leukocyte count, a synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) rate of 10-12 breaths per minute, and pressure support less than 10-12 cm/H2O (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1255-67).
“The process used to achieve these measures is not standardized. In North America, daily awakening and screening for spontaneous breathing trials would be usual, but this was not reported in the current trial,” he explained.
Differences in patient population also make the application of the results difficult, Dr. Bowton said. “Only 60% of the patients had spirometrically confirmed COPD and fewer than half were on at least dual inhaled therapy prior to hospitalization with only one-third taking beta agonists or anticholinergic agents,” he noted. “The cause of respiratory failure was infectious, requiring an infiltrate on chest radiograph; thus, patients with hypercarbic respiratory failure without a new infiltrate were excluded from the study. On average, patients were hypercarbic, yet alkalemic at the time of extubation; the PaCO2 and pH at the time of intubation were not reported.
“This study suggests that in some patients with COPD and respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, HFO [high-flow oxygen] may be better tolerated and equally effective as NIPPV [noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation] at mitigating the need for reintubation following extubation. In this patient population where hypoxemia prior to extubation was not severe, the mechanisms by which HFO is beneficial remain speculative,” he said.
This study was funded by the Rui E special fund for emergency medicine research and the Yangzhou Science and Technology Development Plan. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bowton reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tan D et al. Crit Care. 2020 Aug 6. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03214-9.
Following invasive ventilation for severe hypercapnic respiratory failure, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease had similar levels of treatment failure if they received high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy or noninvasive ventilation, recent research in Critical Care has suggested.
However, for patients with COPD weaned off invasive ventilation, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen therapy was “more comfortable and better tolerated,” compared with noninvasive ventilation (NIV). In addition, “airway care interventions and the incidence of nasofacial skin breakdown associated with HFNC were significantly lower than in NIV,” according to Dingyu Tan of the Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou (China) University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, and colleagues. “HFNC appears to be an effective means of respiratory support for COPD patients extubated after severe hypercapnic respiratory failure,” they said.
The investigators screened patients with COPD and hypercapnic respiratory failure for enrollment, including those who met Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) criteria, were 85 years old or younger and caring for themselves, had bronchopulmonary infection–induced respiratory failure, and had achieved pulmonary infection control criteria. Exclusion criteria were:
- Patients under age 18 years.
- Presence of oral or facial trauma.
- Poor sputum excretion ability.
- Hemodynamic instability that would contraindicate use of NIV.
- Poor cough during PIC window.
- Poor short-term prognosis.
- Failure of the heart, brain, liver or kidney.
- Patients who could not consent to treatment.
Patients were determined to have failed treatment if they returned to invasive mechanical ventilation or switched from one treatment to another (HFNC to NIV or NIV to HFNC). Investigators also performed an arterial blood gas analysis, recorded the number of duration of airway care interventions, and monitored vital signs at 1 hour, 24 hours, and 48 hours after extubation as secondary analyses.
Overall, 44 patients randomized to receive HFNC and 42 patients randomized for NIV were available for analysis. The investigators found 22.7% of patients in the HFNC group and 28.6% in the NIV group experienced treatment failure (risk difference, –5.8%; 95% confidence interval, −23.8 to 12.4%; P = .535), with patients in the HFNC group experiencing a significantly lower level of treatment intolerance, compared with patients in the NIV group (risk difference, –50.0%; 95% CI, −74.6 to −12.9%; P = .015). There were no significant differences between either group regarding intubation (−0.65%; 95% CI, −16.01 to 14.46%), while rate of switching treatments was lower in the HFNC group but not significant (−5.2%; 95% CI, −19.82 to 9.05%).
Patients in both the HFNC and NIV groups had faster mean respiratory rates 1 hour after extubation (P < .050). After 24 hours, the NIV group had higher-than-baseline respiratory rates, compared with the HFNC group, which had returned to normal (20 vs. 24.5 breaths per minute; P < .050). Both groups had returned to baseline by 48 hours after extubation. At 1 hour after extubation, patients in the HFNC group had lower PaO2/FiO2 (P < .050) and pH values (P < .050), and higher PaCO2 values (P less than .050), compared with baseline. There were no statistically significant differences in PaO2/FiO2, pH, and PaCO2 values in either group at 24 hours or 48 hours after extubation.
Daily airway care interventions were significantly higher on average in the NIV group, compared with the HFNC group (7 vs. 6; P = .0006), and the HFNC group also had significantly better comfort scores (7 vs. 5; P < .001) as measured by a modified visual analog scale, as well as incidence of nasal and facial skin breakdown (0 vs. 9.6%; P = .027), compared with the NIV group.
Results difficult to apply to North American patients
David L. Bowton, MD, FCCP, a professor specializing in critical care at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in an interview the results of this trial may not be applicable for patients with infection-related respiratory failure and COPD in North America “due to the differences in common weaning practices between North America and China.”
For example, the trial used the pulmonary infection control (PIC) window criteria for extubation, which requires a significant decrease in radiographic infiltrates, improvement in quality and quantity of sputum, normalizing of leukocyte count, a synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) rate of 10-12 breaths per minute, and pressure support less than 10-12 cm/H2O (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1255-67).
“The process used to achieve these measures is not standardized. In North America, daily awakening and screening for spontaneous breathing trials would be usual, but this was not reported in the current trial,” he explained.
Differences in patient population also make the application of the results difficult, Dr. Bowton said. “Only 60% of the patients had spirometrically confirmed COPD and fewer than half were on at least dual inhaled therapy prior to hospitalization with only one-third taking beta agonists or anticholinergic agents,” he noted. “The cause of respiratory failure was infectious, requiring an infiltrate on chest radiograph; thus, patients with hypercarbic respiratory failure without a new infiltrate were excluded from the study. On average, patients were hypercarbic, yet alkalemic at the time of extubation; the PaCO2 and pH at the time of intubation were not reported.
“This study suggests that in some patients with COPD and respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, HFO [high-flow oxygen] may be better tolerated and equally effective as NIPPV [noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation] at mitigating the need for reintubation following extubation. In this patient population where hypoxemia prior to extubation was not severe, the mechanisms by which HFO is beneficial remain speculative,” he said.
This study was funded by the Rui E special fund for emergency medicine research and the Yangzhou Science and Technology Development Plan. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Bowton reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tan D et al. Crit Care. 2020 Aug 6. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03214-9.
FROM CRITICAL CARE
Evidence mounts for COVID-19 effects on thyroid gland
Rates of thyrotoxicosis are significantly higher among patients who are critically ill with COVID-19 than among patients who are critically ill but who do not not have COVID-19, suggesting an atypical form of thyroiditis related to the novel coronavirus infection, according to new research.
“We suggest routine assessment of thyroid function in patients with COVID-19 requiring high-intensity care because they frequently present with thyrotoxicosis due to a form of subacute thyroiditis related to SARS-CoV-2,” the authors wrote in correspondence published online in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology.
However, notably, the study – which compared critically ill ICU patients who had COVID-19 with those who did not have COVID-19 or who had milder cases of COVID-19 – indicates that thyroid disorders do not appear to increase the risk of developing COVID-19, first author Ilaria Muller, MD, PhD, of the department of endocrinology, IRCCS Fondazione Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, said in an interview.
“It is important to highlight that we did not find an increased prevalence of preexisting thyroid disorders in COVID-19 patients (contrary to early media reports),” she said. “So far, clinical observations do not support this fear, and we need to reassure people with thyroid disorders, since such disorders are very common among the general population.”
Yet the findings add to emerging evidence of a COVID-19/thyroid relationship, Angela M. Leung, MD, said in an interview.
“Given the health care impacts of the current COVID-19 pandemic worldwide, this study provides some insight on the potential systemic inflammation, as well as thyroid-specific inflammation, of the SARS-Cov-2 virus that is described in some emerging reports,” she said.
“This study joins at least six others that have reported a clinical presentation resembling subacute thyroiditis in critically ill patients with COVID-19,” noted Dr. Leung, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Thyroid function analysis in those with severe COVID-19
Dr. Muller explained that preliminary data from her institution showed thyroid abnormalities in patients who were severely ill with COVID-19. She and her team extended the evaluation to include thyroid data and other data on 93 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to high-intensity care units (HICUs) in Italy during the 2020 pandemic.
Those data were compared with data on 101 critically ill patients admitted to the same HICUs in 2019 who did not have COVID-19. A third group of 52 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to low-intensity care units (LICUs) in Italy in 2020 were also included in the analysis.
The mean age of the patients in the HICU 2020 group was 65.3 years; in the HICU 2019 group, it was 73 years; and in the LICU group, it was 70 years (P = .001). In addition, the HICU 2020 group included more men than the other two groups (69% vs. 56% and 48%; P = .03).
Of note, only 9% of patients in the HICU 2020 group had preexisting thyroid disorders, compared with 21% in the LICU group and 23% in the HICU 2019 group (P = .017).
These findings suggest that “such conditions are not a risk factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection or severity of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
The patients with the preexisting thyroid conditions were excluded from the thyroid function analysis.
A significantly higher proportion of patients in the HICU 2020 group (13; 15%) were thyrotoxic upon admission, compared with just 1 (1%) of 78 patients in the HICU 2019 group (P = .002) and one (2%) of 41 patients in the LICU group (P = .025).
Among the 14 patients in the two COVID-19 groups who had thyrotoxicosis, the majority were male (9; 64%)
Among those in the HICU 2020 group, serum thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations were lower than in either of the other two groups (P = .018), and serum free thyroxine (free T4) concentrations were higher than in the LICU group (P = .016) but not the HICU 2019 group.
Differences compared with other infection-related thyroiditis
Although thyrotoxicosis relating to subacute viral thyroiditis can result from a wide variety of viral infections, there are some key differences with COVID-19, Dr. Muller said.
“Thyroid dysfunction related to SARS-CoV-2 seems to be milder than that of classic subacute thyroiditis due to other viruses,” she explained. Furthermore, thyroid dysfunction associated with other viral infections is more common in women, whereas there were more male patients with the COVID-19–related atypical thyroiditis.
In addition, the thyroid effects developed early with COVID-19, whereas they usually emerge after the infections by other viruses.
Patients did not demonstrate the neck pain that is common with classic viral thyroiditis, and the thyroid abnormalities appear to correlate with the severity of COVID-19, whereas they are seen even in patients with mild symptoms when other viral infections are the cause.
In addition to the risk for subacute viral thyroiditis, critically ill patients in general are at risk of developing nonthyroidal illness syndrome, with alterations in thyroid function. However, thyroid hormone measures in the patients severely ill with COVID-19 were not consistent with that syndrome.
A subanalysis of eight HICU 2020 patients with thyroid dysfunction who were followed for 55 days after discharge showed that two experienced hyperthyroidism but likely not from COVID-19; in the remaining six, thyroid function normalized.
Muller speculated that, when ill with COVID-19, the patients likely had a combination of SARS-CoV-2–related atypical thyroiditis and nonthyroidal illness syndrome, known as T4 toxicosis.
Will there be any long-term effects?
Importantly, it remains unknown whether the novel coronavirus has longer-term effects on the thyroid, Dr. Muller said.
“We cannot predict what will be the long-lasting thyroid effects after COVID-19,” she said.
With classic subacute viral thyroiditis, “After a few years ... 5%-20% of patients develop permanent hypothyroidism, [and] the same might happen in COVID-19 patients,” she hypothesized. “We will follow our patients long term to answer this question – this study is already ongoing.”
In the meantime, diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 is important, inasmuch as it could worsen the already critical conditions of patients, Muller stressed.
“The gold-standard treatment for thyroiditis is steroids, so the presence of thyroid dysfunction might represent an additional indication to such treatment in COVID-19 patients, to be verified in properly designed clinical trials,” she advised.
ACE2 cell receptors highly expressed in thyroid
Dr. Muller and colleagues also noted recent research showing that ACE2 – demonstrated to be a key host-cell entry receptor for both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 – is expressed in even higher levels in the thyroid than the lungs, where it causes COVID-19’s notorious pulmonary effects.
Dr. Muller said the implications of ACE2 expression in the thyroid remain to be elucidated.
“If ACE2 is confirmed to be expressed at higher levels, compared with the lungs in the thyroid gland and other tissues, i.e., small intestine, testis, kidney, heart, etc, dedicated studies will be needed to correlate ACE2 expression with the organs’ susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 reflected by clinical presentation,” she said.
Dr. Leung added that, as a take-home message from these and the other thyroid/COVID-19 studies, “data are starting to show us that COVID-19 infection may cause thyrotoxicosis that is possibly related to thyroid and systemic inflammation. However, the serum thyroid function test abnormalities seen in COVID-19 patients with subacute thyroiditis are also likely exacerbated to a substantial extent by nonthyroidal illness physiology.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leung is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes and Endocrinology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of thyrotoxicosis are significantly higher among patients who are critically ill with COVID-19 than among patients who are critically ill but who do not not have COVID-19, suggesting an atypical form of thyroiditis related to the novel coronavirus infection, according to new research.
“We suggest routine assessment of thyroid function in patients with COVID-19 requiring high-intensity care because they frequently present with thyrotoxicosis due to a form of subacute thyroiditis related to SARS-CoV-2,” the authors wrote in correspondence published online in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology.
However, notably, the study – which compared critically ill ICU patients who had COVID-19 with those who did not have COVID-19 or who had milder cases of COVID-19 – indicates that thyroid disorders do not appear to increase the risk of developing COVID-19, first author Ilaria Muller, MD, PhD, of the department of endocrinology, IRCCS Fondazione Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, said in an interview.
“It is important to highlight that we did not find an increased prevalence of preexisting thyroid disorders in COVID-19 patients (contrary to early media reports),” she said. “So far, clinical observations do not support this fear, and we need to reassure people with thyroid disorders, since such disorders are very common among the general population.”
Yet the findings add to emerging evidence of a COVID-19/thyroid relationship, Angela M. Leung, MD, said in an interview.
“Given the health care impacts of the current COVID-19 pandemic worldwide, this study provides some insight on the potential systemic inflammation, as well as thyroid-specific inflammation, of the SARS-Cov-2 virus that is described in some emerging reports,” she said.
“This study joins at least six others that have reported a clinical presentation resembling subacute thyroiditis in critically ill patients with COVID-19,” noted Dr. Leung, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Thyroid function analysis in those with severe COVID-19
Dr. Muller explained that preliminary data from her institution showed thyroid abnormalities in patients who were severely ill with COVID-19. She and her team extended the evaluation to include thyroid data and other data on 93 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to high-intensity care units (HICUs) in Italy during the 2020 pandemic.
Those data were compared with data on 101 critically ill patients admitted to the same HICUs in 2019 who did not have COVID-19. A third group of 52 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to low-intensity care units (LICUs) in Italy in 2020 were also included in the analysis.
The mean age of the patients in the HICU 2020 group was 65.3 years; in the HICU 2019 group, it was 73 years; and in the LICU group, it was 70 years (P = .001). In addition, the HICU 2020 group included more men than the other two groups (69% vs. 56% and 48%; P = .03).
Of note, only 9% of patients in the HICU 2020 group had preexisting thyroid disorders, compared with 21% in the LICU group and 23% in the HICU 2019 group (P = .017).
These findings suggest that “such conditions are not a risk factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection or severity of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
The patients with the preexisting thyroid conditions were excluded from the thyroid function analysis.
A significantly higher proportion of patients in the HICU 2020 group (13; 15%) were thyrotoxic upon admission, compared with just 1 (1%) of 78 patients in the HICU 2019 group (P = .002) and one (2%) of 41 patients in the LICU group (P = .025).
Among the 14 patients in the two COVID-19 groups who had thyrotoxicosis, the majority were male (9; 64%)
Among those in the HICU 2020 group, serum thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations were lower than in either of the other two groups (P = .018), and serum free thyroxine (free T4) concentrations were higher than in the LICU group (P = .016) but not the HICU 2019 group.
Differences compared with other infection-related thyroiditis
Although thyrotoxicosis relating to subacute viral thyroiditis can result from a wide variety of viral infections, there are some key differences with COVID-19, Dr. Muller said.
“Thyroid dysfunction related to SARS-CoV-2 seems to be milder than that of classic subacute thyroiditis due to other viruses,” she explained. Furthermore, thyroid dysfunction associated with other viral infections is more common in women, whereas there were more male patients with the COVID-19–related atypical thyroiditis.
In addition, the thyroid effects developed early with COVID-19, whereas they usually emerge after the infections by other viruses.
Patients did not demonstrate the neck pain that is common with classic viral thyroiditis, and the thyroid abnormalities appear to correlate with the severity of COVID-19, whereas they are seen even in patients with mild symptoms when other viral infections are the cause.
In addition to the risk for subacute viral thyroiditis, critically ill patients in general are at risk of developing nonthyroidal illness syndrome, with alterations in thyroid function. However, thyroid hormone measures in the patients severely ill with COVID-19 were not consistent with that syndrome.
A subanalysis of eight HICU 2020 patients with thyroid dysfunction who were followed for 55 days after discharge showed that two experienced hyperthyroidism but likely not from COVID-19; in the remaining six, thyroid function normalized.
Muller speculated that, when ill with COVID-19, the patients likely had a combination of SARS-CoV-2–related atypical thyroiditis and nonthyroidal illness syndrome, known as T4 toxicosis.
Will there be any long-term effects?
Importantly, it remains unknown whether the novel coronavirus has longer-term effects on the thyroid, Dr. Muller said.
“We cannot predict what will be the long-lasting thyroid effects after COVID-19,” she said.
With classic subacute viral thyroiditis, “After a few years ... 5%-20% of patients develop permanent hypothyroidism, [and] the same might happen in COVID-19 patients,” she hypothesized. “We will follow our patients long term to answer this question – this study is already ongoing.”
In the meantime, diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 is important, inasmuch as it could worsen the already critical conditions of patients, Muller stressed.
“The gold-standard treatment for thyroiditis is steroids, so the presence of thyroid dysfunction might represent an additional indication to such treatment in COVID-19 patients, to be verified in properly designed clinical trials,” she advised.
ACE2 cell receptors highly expressed in thyroid
Dr. Muller and colleagues also noted recent research showing that ACE2 – demonstrated to be a key host-cell entry receptor for both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 – is expressed in even higher levels in the thyroid than the lungs, where it causes COVID-19’s notorious pulmonary effects.
Dr. Muller said the implications of ACE2 expression in the thyroid remain to be elucidated.
“If ACE2 is confirmed to be expressed at higher levels, compared with the lungs in the thyroid gland and other tissues, i.e., small intestine, testis, kidney, heart, etc, dedicated studies will be needed to correlate ACE2 expression with the organs’ susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 reflected by clinical presentation,” she said.
Dr. Leung added that, as a take-home message from these and the other thyroid/COVID-19 studies, “data are starting to show us that COVID-19 infection may cause thyrotoxicosis that is possibly related to thyroid and systemic inflammation. However, the serum thyroid function test abnormalities seen in COVID-19 patients with subacute thyroiditis are also likely exacerbated to a substantial extent by nonthyroidal illness physiology.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leung is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes and Endocrinology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of thyrotoxicosis are significantly higher among patients who are critically ill with COVID-19 than among patients who are critically ill but who do not not have COVID-19, suggesting an atypical form of thyroiditis related to the novel coronavirus infection, according to new research.
“We suggest routine assessment of thyroid function in patients with COVID-19 requiring high-intensity care because they frequently present with thyrotoxicosis due to a form of subacute thyroiditis related to SARS-CoV-2,” the authors wrote in correspondence published online in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology.
However, notably, the study – which compared critically ill ICU patients who had COVID-19 with those who did not have COVID-19 or who had milder cases of COVID-19 – indicates that thyroid disorders do not appear to increase the risk of developing COVID-19, first author Ilaria Muller, MD, PhD, of the department of endocrinology, IRCCS Fondazione Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, said in an interview.
“It is important to highlight that we did not find an increased prevalence of preexisting thyroid disorders in COVID-19 patients (contrary to early media reports),” she said. “So far, clinical observations do not support this fear, and we need to reassure people with thyroid disorders, since such disorders are very common among the general population.”
Yet the findings add to emerging evidence of a COVID-19/thyroid relationship, Angela M. Leung, MD, said in an interview.
“Given the health care impacts of the current COVID-19 pandemic worldwide, this study provides some insight on the potential systemic inflammation, as well as thyroid-specific inflammation, of the SARS-Cov-2 virus that is described in some emerging reports,” she said.
“This study joins at least six others that have reported a clinical presentation resembling subacute thyroiditis in critically ill patients with COVID-19,” noted Dr. Leung, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Thyroid function analysis in those with severe COVID-19
Dr. Muller explained that preliminary data from her institution showed thyroid abnormalities in patients who were severely ill with COVID-19. She and her team extended the evaluation to include thyroid data and other data on 93 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to high-intensity care units (HICUs) in Italy during the 2020 pandemic.
Those data were compared with data on 101 critically ill patients admitted to the same HICUs in 2019 who did not have COVID-19. A third group of 52 patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to low-intensity care units (LICUs) in Italy in 2020 were also included in the analysis.
The mean age of the patients in the HICU 2020 group was 65.3 years; in the HICU 2019 group, it was 73 years; and in the LICU group, it was 70 years (P = .001). In addition, the HICU 2020 group included more men than the other two groups (69% vs. 56% and 48%; P = .03).
Of note, only 9% of patients in the HICU 2020 group had preexisting thyroid disorders, compared with 21% in the LICU group and 23% in the HICU 2019 group (P = .017).
These findings suggest that “such conditions are not a risk factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection or severity of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
The patients with the preexisting thyroid conditions were excluded from the thyroid function analysis.
A significantly higher proportion of patients in the HICU 2020 group (13; 15%) were thyrotoxic upon admission, compared with just 1 (1%) of 78 patients in the HICU 2019 group (P = .002) and one (2%) of 41 patients in the LICU group (P = .025).
Among the 14 patients in the two COVID-19 groups who had thyrotoxicosis, the majority were male (9; 64%)
Among those in the HICU 2020 group, serum thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations were lower than in either of the other two groups (P = .018), and serum free thyroxine (free T4) concentrations were higher than in the LICU group (P = .016) but not the HICU 2019 group.
Differences compared with other infection-related thyroiditis
Although thyrotoxicosis relating to subacute viral thyroiditis can result from a wide variety of viral infections, there are some key differences with COVID-19, Dr. Muller said.
“Thyroid dysfunction related to SARS-CoV-2 seems to be milder than that of classic subacute thyroiditis due to other viruses,” she explained. Furthermore, thyroid dysfunction associated with other viral infections is more common in women, whereas there were more male patients with the COVID-19–related atypical thyroiditis.
In addition, the thyroid effects developed early with COVID-19, whereas they usually emerge after the infections by other viruses.
Patients did not demonstrate the neck pain that is common with classic viral thyroiditis, and the thyroid abnormalities appear to correlate with the severity of COVID-19, whereas they are seen even in patients with mild symptoms when other viral infections are the cause.
In addition to the risk for subacute viral thyroiditis, critically ill patients in general are at risk of developing nonthyroidal illness syndrome, with alterations in thyroid function. However, thyroid hormone measures in the patients severely ill with COVID-19 were not consistent with that syndrome.
A subanalysis of eight HICU 2020 patients with thyroid dysfunction who were followed for 55 days after discharge showed that two experienced hyperthyroidism but likely not from COVID-19; in the remaining six, thyroid function normalized.
Muller speculated that, when ill with COVID-19, the patients likely had a combination of SARS-CoV-2–related atypical thyroiditis and nonthyroidal illness syndrome, known as T4 toxicosis.
Will there be any long-term effects?
Importantly, it remains unknown whether the novel coronavirus has longer-term effects on the thyroid, Dr. Muller said.
“We cannot predict what will be the long-lasting thyroid effects after COVID-19,” she said.
With classic subacute viral thyroiditis, “After a few years ... 5%-20% of patients develop permanent hypothyroidism, [and] the same might happen in COVID-19 patients,” she hypothesized. “We will follow our patients long term to answer this question – this study is already ongoing.”
In the meantime, diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 is important, inasmuch as it could worsen the already critical conditions of patients, Muller stressed.
“The gold-standard treatment for thyroiditis is steroids, so the presence of thyroid dysfunction might represent an additional indication to such treatment in COVID-19 patients, to be verified in properly designed clinical trials,” she advised.
ACE2 cell receptors highly expressed in thyroid
Dr. Muller and colleagues also noted recent research showing that ACE2 – demonstrated to be a key host-cell entry receptor for both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 – is expressed in even higher levels in the thyroid than the lungs, where it causes COVID-19’s notorious pulmonary effects.
Dr. Muller said the implications of ACE2 expression in the thyroid remain to be elucidated.
“If ACE2 is confirmed to be expressed at higher levels, compared with the lungs in the thyroid gland and other tissues, i.e., small intestine, testis, kidney, heart, etc, dedicated studies will be needed to correlate ACE2 expression with the organs’ susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 reflected by clinical presentation,” she said.
Dr. Leung added that, as a take-home message from these and the other thyroid/COVID-19 studies, “data are starting to show us that COVID-19 infection may cause thyrotoxicosis that is possibly related to thyroid and systemic inflammation. However, the serum thyroid function test abnormalities seen in COVID-19 patients with subacute thyroiditis are also likely exacerbated to a substantial extent by nonthyroidal illness physiology.”
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leung is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes and Endocrinology.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Non-COVID-19 clinical trials grind to a halt during pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unique and unprecedented challenges for the clinical research world, with potentially long-lasting consequences.
A new analysis of the extent of disruption shows that the average rate of stopped trials nearly doubled during the first 5 months of 2020, compared with the 2 previous years.
“Typically, clinical research precedes clinical practice by several years, so this disruption we’re seeing now will be felt for many years to come,” said Mario Guadino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
The analysis was published online July 31 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The researchers used Python software to query meta-data from all trials reported on ClinicalTrials.gov. Of 321,218 non-COVID-19 trials queried, 28,672 (8.9%) were reported as stopped, defined as a switch in trial status from “recruiting” to “active and not recruiting,” “completed,” “suspended,” “terminated,” or “withdrawn.”
The average rate of discontinuation was 638 trials/month from January 2017 to December 2019, rising to 1,147 trials/month between January 2020 and May 2020 (P < .001 for trend).
Once stopped (as opposed to paused), restarting a trial is a tricky prospect, said Dr. Guadino. “You can’t stop and restart a trial because it creates a lot of issues, so we should expect many of these stopped trials to never be completed.”
He said these figures likely represent an underestimate of the true impact of the pandemic because there is typically a delay in the updating of the status of a trial on ClinicalTrials.gov.
“We are likely looking only at the tip of the iceberg,” he added. “My impression is that the number of trials that will be affected and even canceled will be very high.”
As for cardiology trials, one of the report’s authors, Deepak Bhatt, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, without naming specific trials, had this to say: “Several cardiovascular trials were paused, and some were permanently discontinued. It may be a while before we fully appreciate just how much information was lost and how much might be salvaged.”
He’s not worried, however, that upcoming cardiology meetings, which have moved online for the foreseeable future, might get a bit boring. “Fortunately, there is enough good work going on in the cardiovascular and cardiometabolic space that I believe there will still be ample randomized and observational data of high quality to present at the major meetings,” Dr. Bhatt said in an email.
The researchers found a weak correlation between the national population-adjusted numbers of COVID-19 cases and the proportion of non-COVID-19 trials stopped by country.
Even for trials that stopped recruiting for a period of time but are continuing, there are myriad issues involving compliance, data integrity, statistical interpretability, etc.
“Even if there is just a temporary disruption, that will most likely lead to reduced enrollment, missing follow-up visits, and protocol deviations, all things that would be red flags during normal times and impact the quality of the clinical trial,” said Dr. Guadino.
“And if your outcome of interest is mortality, well, how exactly do you measure that during a pandemic?” he added.
Stopped for lack of funding
Besides the logistical issues, another reason trials may be in jeopardy is funding. A warning early in the pandemic from the research community in Canada that funding was quickly drying up, leaving both jobs and data at risk, led to an aid package from the government to keep the lights on.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and similar groups “have devoted large sums of money to research in COVID, which is of course very appropriate, but that clearly reduces the amount of funding that is available for other researchers,” said Dr. Guadino.
Some funding agencies around the world have canceled or put on hold all non-COVID-19 clinical trials still at the design state, Dr. Guadino said in an interview.
The NIH, he stressed, has not canceled funding and has been “extremely open and cooperative” in trying to help trialists navigate the many COVID-generated issues. They’ve even issued guidance on how to manage trials during COVID-19.
Of note, in the survey, the majority of the trials stopped (95.4%) had nongovernmental funding.
“The data are not very granular, so we’re only able to make some very simple, descriptive comments, but it does seem like the more fragile trials – those that are smaller and industry-funded – are the ones more likely to be disrupted,” said Dr. Guadino.
In some cases, he said, priorities have shifted to COVID-19. “If a small company is sponsoring a trial and they decide they want to sponsor something related to COVID, or they realize that because of the slow enrollment, the trial becomes too expensive to complete, they may opt to just abandon it,” said Dr. Guadino.
At what cost? It will take years to sort that out, he said.
This study received no funding. Dr. Guadino and Dr. Bhatt are both active trialists, participating in both industry- and government-sponsored clinical research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unique and unprecedented challenges for the clinical research world, with potentially long-lasting consequences.
A new analysis of the extent of disruption shows that the average rate of stopped trials nearly doubled during the first 5 months of 2020, compared with the 2 previous years.
“Typically, clinical research precedes clinical practice by several years, so this disruption we’re seeing now will be felt for many years to come,” said Mario Guadino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
The analysis was published online July 31 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The researchers used Python software to query meta-data from all trials reported on ClinicalTrials.gov. Of 321,218 non-COVID-19 trials queried, 28,672 (8.9%) were reported as stopped, defined as a switch in trial status from “recruiting” to “active and not recruiting,” “completed,” “suspended,” “terminated,” or “withdrawn.”
The average rate of discontinuation was 638 trials/month from January 2017 to December 2019, rising to 1,147 trials/month between January 2020 and May 2020 (P < .001 for trend).
Once stopped (as opposed to paused), restarting a trial is a tricky prospect, said Dr. Guadino. “You can’t stop and restart a trial because it creates a lot of issues, so we should expect many of these stopped trials to never be completed.”
He said these figures likely represent an underestimate of the true impact of the pandemic because there is typically a delay in the updating of the status of a trial on ClinicalTrials.gov.
“We are likely looking only at the tip of the iceberg,” he added. “My impression is that the number of trials that will be affected and even canceled will be very high.”
As for cardiology trials, one of the report’s authors, Deepak Bhatt, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, without naming specific trials, had this to say: “Several cardiovascular trials were paused, and some were permanently discontinued. It may be a while before we fully appreciate just how much information was lost and how much might be salvaged.”
He’s not worried, however, that upcoming cardiology meetings, which have moved online for the foreseeable future, might get a bit boring. “Fortunately, there is enough good work going on in the cardiovascular and cardiometabolic space that I believe there will still be ample randomized and observational data of high quality to present at the major meetings,” Dr. Bhatt said in an email.
The researchers found a weak correlation between the national population-adjusted numbers of COVID-19 cases and the proportion of non-COVID-19 trials stopped by country.
Even for trials that stopped recruiting for a period of time but are continuing, there are myriad issues involving compliance, data integrity, statistical interpretability, etc.
“Even if there is just a temporary disruption, that will most likely lead to reduced enrollment, missing follow-up visits, and protocol deviations, all things that would be red flags during normal times and impact the quality of the clinical trial,” said Dr. Guadino.
“And if your outcome of interest is mortality, well, how exactly do you measure that during a pandemic?” he added.
Stopped for lack of funding
Besides the logistical issues, another reason trials may be in jeopardy is funding. A warning early in the pandemic from the research community in Canada that funding was quickly drying up, leaving both jobs and data at risk, led to an aid package from the government to keep the lights on.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and similar groups “have devoted large sums of money to research in COVID, which is of course very appropriate, but that clearly reduces the amount of funding that is available for other researchers,” said Dr. Guadino.
Some funding agencies around the world have canceled or put on hold all non-COVID-19 clinical trials still at the design state, Dr. Guadino said in an interview.
The NIH, he stressed, has not canceled funding and has been “extremely open and cooperative” in trying to help trialists navigate the many COVID-generated issues. They’ve even issued guidance on how to manage trials during COVID-19.
Of note, in the survey, the majority of the trials stopped (95.4%) had nongovernmental funding.
“The data are not very granular, so we’re only able to make some very simple, descriptive comments, but it does seem like the more fragile trials – those that are smaller and industry-funded – are the ones more likely to be disrupted,” said Dr. Guadino.
In some cases, he said, priorities have shifted to COVID-19. “If a small company is sponsoring a trial and they decide they want to sponsor something related to COVID, or they realize that because of the slow enrollment, the trial becomes too expensive to complete, they may opt to just abandon it,” said Dr. Guadino.
At what cost? It will take years to sort that out, he said.
This study received no funding. Dr. Guadino and Dr. Bhatt are both active trialists, participating in both industry- and government-sponsored clinical research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unique and unprecedented challenges for the clinical research world, with potentially long-lasting consequences.
A new analysis of the extent of disruption shows that the average rate of stopped trials nearly doubled during the first 5 months of 2020, compared with the 2 previous years.
“Typically, clinical research precedes clinical practice by several years, so this disruption we’re seeing now will be felt for many years to come,” said Mario Guadino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
The analysis was published online July 31 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The researchers used Python software to query meta-data from all trials reported on ClinicalTrials.gov. Of 321,218 non-COVID-19 trials queried, 28,672 (8.9%) were reported as stopped, defined as a switch in trial status from “recruiting” to “active and not recruiting,” “completed,” “suspended,” “terminated,” or “withdrawn.”
The average rate of discontinuation was 638 trials/month from January 2017 to December 2019, rising to 1,147 trials/month between January 2020 and May 2020 (P < .001 for trend).
Once stopped (as opposed to paused), restarting a trial is a tricky prospect, said Dr. Guadino. “You can’t stop and restart a trial because it creates a lot of issues, so we should expect many of these stopped trials to never be completed.”
He said these figures likely represent an underestimate of the true impact of the pandemic because there is typically a delay in the updating of the status of a trial on ClinicalTrials.gov.
“We are likely looking only at the tip of the iceberg,” he added. “My impression is that the number of trials that will be affected and even canceled will be very high.”
As for cardiology trials, one of the report’s authors, Deepak Bhatt, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, without naming specific trials, had this to say: “Several cardiovascular trials were paused, and some were permanently discontinued. It may be a while before we fully appreciate just how much information was lost and how much might be salvaged.”
He’s not worried, however, that upcoming cardiology meetings, which have moved online for the foreseeable future, might get a bit boring. “Fortunately, there is enough good work going on in the cardiovascular and cardiometabolic space that I believe there will still be ample randomized and observational data of high quality to present at the major meetings,” Dr. Bhatt said in an email.
The researchers found a weak correlation between the national population-adjusted numbers of COVID-19 cases and the proportion of non-COVID-19 trials stopped by country.
Even for trials that stopped recruiting for a period of time but are continuing, there are myriad issues involving compliance, data integrity, statistical interpretability, etc.
“Even if there is just a temporary disruption, that will most likely lead to reduced enrollment, missing follow-up visits, and protocol deviations, all things that would be red flags during normal times and impact the quality of the clinical trial,” said Dr. Guadino.
“And if your outcome of interest is mortality, well, how exactly do you measure that during a pandemic?” he added.
Stopped for lack of funding
Besides the logistical issues, another reason trials may be in jeopardy is funding. A warning early in the pandemic from the research community in Canada that funding was quickly drying up, leaving both jobs and data at risk, led to an aid package from the government to keep the lights on.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and similar groups “have devoted large sums of money to research in COVID, which is of course very appropriate, but that clearly reduces the amount of funding that is available for other researchers,” said Dr. Guadino.
Some funding agencies around the world have canceled or put on hold all non-COVID-19 clinical trials still at the design state, Dr. Guadino said in an interview.
The NIH, he stressed, has not canceled funding and has been “extremely open and cooperative” in trying to help trialists navigate the many COVID-generated issues. They’ve even issued guidance on how to manage trials during COVID-19.
Of note, in the survey, the majority of the trials stopped (95.4%) had nongovernmental funding.
“The data are not very granular, so we’re only able to make some very simple, descriptive comments, but it does seem like the more fragile trials – those that are smaller and industry-funded – are the ones more likely to be disrupted,” said Dr. Guadino.
In some cases, he said, priorities have shifted to COVID-19. “If a small company is sponsoring a trial and they decide they want to sponsor something related to COVID, or they realize that because of the slow enrollment, the trial becomes too expensive to complete, they may opt to just abandon it,” said Dr. Guadino.
At what cost? It will take years to sort that out, he said.
This study received no funding. Dr. Guadino and Dr. Bhatt are both active trialists, participating in both industry- and government-sponsored clinical research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Send kids to school safely if possible, supplement virtually
The abrupt transition to online learning for American children in kindergarten through 12th grade has left educators and parents unprepared, but virtual learning can be a successful part of education going forward, according to a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics. However, schools also can reopen safely if precautions are taken, and students would benefit in many ways, according to a second viewpoint.
“As policy makers, health care professionals, and parents prepare for the fall semester and as public and private schools grapple with how to make that possible, a better understanding of K-12 virtual learning options and outcomes may facilitate those difficult decisions,” wrote Erik Black, PhD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville; Richard Ferdig, PhD, of Kent State University, Ohio; and Lindsay A. Thompson, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Importantly, K-12 virtual schooling is not suited for all students or all families.”
In a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics, the authors noted that virtual schooling has existed in the United States in various forms for some time. “Just like the myriad options that are available for face-to-face schooling in the U.S., virtual schooling exists in a complex landscape of for-profit, charter, and public options.”
Not all virtual schools are equal
Consequently, not all virtual schools are created equal, they emphasized. Virtual education can be successful for many students when presented by trained online instructors using a curriculum designed to be effective in an online venue.
“Parents need to seek reviews and ask for educational outcomes from each virtual school system to assess the quality of the provided education,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson emphasized.
Key questions for parents to consider when faced with online learning include the type of technology needed to participate; whether their child can maintain a study schedule and complete assignments with limited supervision; whether their child could ask for help and communicate with teachers through technology including phone, text, email, or video; and whether their child has the basic reading, math, and computer literacy skills to engage in online learning, the authors said. Other questions include the school’s expectations for parents and caregivers, how student information may be shared, and how the virtual school lines up with state standards for K-12 educators (in the case of options outside the public school system).
“The COVID-19 pandemic offers a unique challenge for educators, policymakers, and health care professionals to partner with parents to make the best local and individual decisions for children,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson concluded.
Schools may be able to open safely
Children continue to make up a low percentage of COVID-19 cases and appear less likely to experience illness, wrote C. Jason Wang, MD, PhD, and Henry Bair, BS, of Stanford (Calif.) University in a second viewpoint also published in JAMA Pediatrics. The impact of long-term school closures extends beyond education and can “exacerbate socioeconomic disparities, amplify existing educational inequalities, and aggravate food insecurity, domestic violence, and mental health disorders,” they wrote.
Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair proposed that school districts “engage key stakeholders to establish a COVID-19 task force, composed of the superintendent, members of the school board, teachers, parents, and health care professionals to develop policies and procedures,” that would allow schools to open safely.
The authors outlined strategies including adapting teaching spaces to accommodate physical distance, with the addition of temporary modular buildings if needed. They advised assigned seating on school buses, and acknowledged the need for the availability of protective equipment, including hand sanitizer and masks, as well as the possible use of transparent barriers on the sides of student desks.
“As the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] guidance suggests, teachers who must work closely with students with special needs or with students who are unable to wear masks should wear N95 masks if possible or wear face shields in addition to surgical masks,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair noted. Other elements of the AAP guidance include the creation of fixed cohorts of students and teachers to limit virus exposure.
“Even with all the precautions in place, COVID-19 outbreaks within schools are still likely,” they said. “Therefore, schools will need to remain flexible and consider temporary closures if there is an outbreak involving multiple students and/or staff and be ready to transition to online education.”
The AAP guidance does not address operational approaches to identifying signs and symptoms of COVID-19, the authors noted. “To address this, we recommend that schools implement multilevel screening for students and staff.”
“In summary, to maximize health and educational outcomes, school districts should adopt some or all of the measures of the AAP guidance and prioritize them after considering local COVID-19 incidence, key stakeholder input, and budgetary constraints,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair concluded.
Schools opening is a regional decision
“The mission of the AAP is to attain optimal physical, mental, and social health and well-being for all infants, children, adolescents, and young adults,” Howard Smart, MD, said in an interview. The question of school reopening “is of national importance, and the AAP has a national role in making recommendations regarding national policy affecting the health of the children.”
“The decision to open schools will be made regionally, but it is important for a nonpolitical national voice to make expert recommendations,” he emphasized.
“Many of the recommendations are ideal goals,” noted Dr. Smart, chairman of the department of pediatrics at the Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. “It will be difficult, for example, to implement symptom screening every day before school, no matter where it is performed. Some of the measures may be quite costly, and take time to implement, or require expansion of school staff, for which there may be no budget.”
In addition, “[n]ot all students are likely to comply with masking, distance, and hand-washing recommendations. One student who is noncompliant will be able to infect many other students and staff, as has been seen in other countries.” Also, parental attitudes toward control measures are likely to affect student attitudes, he noted.
“I have interviewed many families at recent checkups, and most have felt that the rush to remote learning that occurred at the end of the last school year resulted in fairly disorganized instruction,” Dr. Smart said. “They are hoping that, having had the summer to plan ahead, the remote teaching will be handled better. Remote learning will certainly work best for self-motivated, organized students with good family support, as noted in the Black, Ferdig, and Thompson article,” he said.
Pediatricians can support the schools by being a source of evidence-based information for parents, Dr. Smart said. “Pediatricians with time and energy might want to volunteer to hold informational video conferences for parents and/or school personnel if they feel they are up to date on current COVID-19 science and want to handle potentially contentious questions.”
The decision parents make to send their children back to school comes down to a risk-benefit calculation. “In some communities this may be left to parents, while in other communities this will a public health decision,” he said. “It is still not clear whether having students attend school in person will result in increased spread of COVID-19 among the students, or in their communities. Although some evidence from early in the pandemic suggests that children may not spread the virus as much as adults, more recent evidence suggests that children 10 years and older do transmit the virus at least as much as adults.”
“The risk to the students and the community, therefore, is unknown,” and difficult to compare with the benefit of in-person schooling, Dr. Smart noted.
“We will learn quite a bit from communities where students do go back to in-person class, as we follow the progression of COVID-19 over the weeks following the resumption of instruction.” Ultimately, advice to parents will need to be tailored to the current conditions of COVID-19 transmission in the community, he concluded.
It’s not just about education
“The AAP released its guidance to ensure that as school districts were contemplating reopening they were considering the full array of risks for children and adolescents. These risks included not only those related to COVID-19, but also those related to the impact of not reopening in-person,” Nathaniel Beers, MD, president of the HSC Health Care System in Washington, said in an interview.
“Students and families are dependent on schools for much more than just an education, and those [elements] need to be factored into the decisions to reopen,” the pediatrician said.
However, “[t]he major barrier for schools is resources to safely reopen,” said Dr. Beers. “The additional staffing and supplies will require additional funding. There are increased demands regardless of whether students are learning in-person or virtually or through hybrid models.”
“Another significant barrier is ensuring that parents and staff are actively engaged in planning for the type of model being used,” he said.
“All of the models require buy-in by staff and parents. This will require significant outreach and strong communication plans. Schools also need to ensure they are planning not just for how to return students to schools, but what will happen when staff or students test positive for COVID-19. Students, families, and staff all will need to know what these plans are up front to feel confident in returning to school,” he emphasized.
“There are students who can thrive in a virtual learning environment,” Dr. Beers said. “There are also students who benefit from the virtual learning environment because of their own risk, or because of a family member’s risk for COVID-19 or the complications from it.”
“However, many children with disabilities have struggled in a virtual environment,” he said. “These students struggle to access the educational services without the adequate supports at home. They often receive additional services in school, such as speech, occupational therapy or physical therapy, or nursing services, that may not have transitioned to home but are critical for their health and development. Many students with disabilities are dependent on family members to successfully access the educational services they need.”
“Pediatricians can play a role in providing feedback on recommendations related to physical distancing and face coverings in particular,” said Dr. Beers. “In addition, they can be helpful in developing plans for children with disabilities as well as what the response plan should be for students who become sick during the school day.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a decision tool for parents who are considering whether to send their child to in-person school, and pediatricians can help parents walk through these questions, Dr. Beers noted. “In addition, pediatricians play an important role in helping patients and families think about the risks of COVID for the patient and other family members, and this can be helpful in addressing the anxiety that parents and patients may be experiencing.”
Further information can be found in Return to School During COVID-19, which can be located at HealthyChildren.org, by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The authors of the viewpoints had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smart, a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board, had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Beers has served on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News in the past, but had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCES: Black E, Ferdig R, Thompson LA. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3800. Wang CJ and Bair H. JAMA Pediatr. Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3871.
The abrupt transition to online learning for American children in kindergarten through 12th grade has left educators and parents unprepared, but virtual learning can be a successful part of education going forward, according to a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics. However, schools also can reopen safely if precautions are taken, and students would benefit in many ways, according to a second viewpoint.
“As policy makers, health care professionals, and parents prepare for the fall semester and as public and private schools grapple with how to make that possible, a better understanding of K-12 virtual learning options and outcomes may facilitate those difficult decisions,” wrote Erik Black, PhD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville; Richard Ferdig, PhD, of Kent State University, Ohio; and Lindsay A. Thompson, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Importantly, K-12 virtual schooling is not suited for all students or all families.”
In a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics, the authors noted that virtual schooling has existed in the United States in various forms for some time. “Just like the myriad options that are available for face-to-face schooling in the U.S., virtual schooling exists in a complex landscape of for-profit, charter, and public options.”
Not all virtual schools are equal
Consequently, not all virtual schools are created equal, they emphasized. Virtual education can be successful for many students when presented by trained online instructors using a curriculum designed to be effective in an online venue.
“Parents need to seek reviews and ask for educational outcomes from each virtual school system to assess the quality of the provided education,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson emphasized.
Key questions for parents to consider when faced with online learning include the type of technology needed to participate; whether their child can maintain a study schedule and complete assignments with limited supervision; whether their child could ask for help and communicate with teachers through technology including phone, text, email, or video; and whether their child has the basic reading, math, and computer literacy skills to engage in online learning, the authors said. Other questions include the school’s expectations for parents and caregivers, how student information may be shared, and how the virtual school lines up with state standards for K-12 educators (in the case of options outside the public school system).
“The COVID-19 pandemic offers a unique challenge for educators, policymakers, and health care professionals to partner with parents to make the best local and individual decisions for children,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson concluded.
Schools may be able to open safely
Children continue to make up a low percentage of COVID-19 cases and appear less likely to experience illness, wrote C. Jason Wang, MD, PhD, and Henry Bair, BS, of Stanford (Calif.) University in a second viewpoint also published in JAMA Pediatrics. The impact of long-term school closures extends beyond education and can “exacerbate socioeconomic disparities, amplify existing educational inequalities, and aggravate food insecurity, domestic violence, and mental health disorders,” they wrote.
Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair proposed that school districts “engage key stakeholders to establish a COVID-19 task force, composed of the superintendent, members of the school board, teachers, parents, and health care professionals to develop policies and procedures,” that would allow schools to open safely.
The authors outlined strategies including adapting teaching spaces to accommodate physical distance, with the addition of temporary modular buildings if needed. They advised assigned seating on school buses, and acknowledged the need for the availability of protective equipment, including hand sanitizer and masks, as well as the possible use of transparent barriers on the sides of student desks.
“As the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] guidance suggests, teachers who must work closely with students with special needs or with students who are unable to wear masks should wear N95 masks if possible or wear face shields in addition to surgical masks,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair noted. Other elements of the AAP guidance include the creation of fixed cohorts of students and teachers to limit virus exposure.
“Even with all the precautions in place, COVID-19 outbreaks within schools are still likely,” they said. “Therefore, schools will need to remain flexible and consider temporary closures if there is an outbreak involving multiple students and/or staff and be ready to transition to online education.”
The AAP guidance does not address operational approaches to identifying signs and symptoms of COVID-19, the authors noted. “To address this, we recommend that schools implement multilevel screening for students and staff.”
“In summary, to maximize health and educational outcomes, school districts should adopt some or all of the measures of the AAP guidance and prioritize them after considering local COVID-19 incidence, key stakeholder input, and budgetary constraints,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair concluded.
Schools opening is a regional decision
“The mission of the AAP is to attain optimal physical, mental, and social health and well-being for all infants, children, adolescents, and young adults,” Howard Smart, MD, said in an interview. The question of school reopening “is of national importance, and the AAP has a national role in making recommendations regarding national policy affecting the health of the children.”
“The decision to open schools will be made regionally, but it is important for a nonpolitical national voice to make expert recommendations,” he emphasized.
“Many of the recommendations are ideal goals,” noted Dr. Smart, chairman of the department of pediatrics at the Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. “It will be difficult, for example, to implement symptom screening every day before school, no matter where it is performed. Some of the measures may be quite costly, and take time to implement, or require expansion of school staff, for which there may be no budget.”
In addition, “[n]ot all students are likely to comply with masking, distance, and hand-washing recommendations. One student who is noncompliant will be able to infect many other students and staff, as has been seen in other countries.” Also, parental attitudes toward control measures are likely to affect student attitudes, he noted.
“I have interviewed many families at recent checkups, and most have felt that the rush to remote learning that occurred at the end of the last school year resulted in fairly disorganized instruction,” Dr. Smart said. “They are hoping that, having had the summer to plan ahead, the remote teaching will be handled better. Remote learning will certainly work best for self-motivated, organized students with good family support, as noted in the Black, Ferdig, and Thompson article,” he said.
Pediatricians can support the schools by being a source of evidence-based information for parents, Dr. Smart said. “Pediatricians with time and energy might want to volunteer to hold informational video conferences for parents and/or school personnel if they feel they are up to date on current COVID-19 science and want to handle potentially contentious questions.”
The decision parents make to send their children back to school comes down to a risk-benefit calculation. “In some communities this may be left to parents, while in other communities this will a public health decision,” he said. “It is still not clear whether having students attend school in person will result in increased spread of COVID-19 among the students, or in their communities. Although some evidence from early in the pandemic suggests that children may not spread the virus as much as adults, more recent evidence suggests that children 10 years and older do transmit the virus at least as much as adults.”
“The risk to the students and the community, therefore, is unknown,” and difficult to compare with the benefit of in-person schooling, Dr. Smart noted.
“We will learn quite a bit from communities where students do go back to in-person class, as we follow the progression of COVID-19 over the weeks following the resumption of instruction.” Ultimately, advice to parents will need to be tailored to the current conditions of COVID-19 transmission in the community, he concluded.
It’s not just about education
“The AAP released its guidance to ensure that as school districts were contemplating reopening they were considering the full array of risks for children and adolescents. These risks included not only those related to COVID-19, but also those related to the impact of not reopening in-person,” Nathaniel Beers, MD, president of the HSC Health Care System in Washington, said in an interview.
“Students and families are dependent on schools for much more than just an education, and those [elements] need to be factored into the decisions to reopen,” the pediatrician said.
However, “[t]he major barrier for schools is resources to safely reopen,” said Dr. Beers. “The additional staffing and supplies will require additional funding. There are increased demands regardless of whether students are learning in-person or virtually or through hybrid models.”
“Another significant barrier is ensuring that parents and staff are actively engaged in planning for the type of model being used,” he said.
“All of the models require buy-in by staff and parents. This will require significant outreach and strong communication plans. Schools also need to ensure they are planning not just for how to return students to schools, but what will happen when staff or students test positive for COVID-19. Students, families, and staff all will need to know what these plans are up front to feel confident in returning to school,” he emphasized.
“There are students who can thrive in a virtual learning environment,” Dr. Beers said. “There are also students who benefit from the virtual learning environment because of their own risk, or because of a family member’s risk for COVID-19 or the complications from it.”
“However, many children with disabilities have struggled in a virtual environment,” he said. “These students struggle to access the educational services without the adequate supports at home. They often receive additional services in school, such as speech, occupational therapy or physical therapy, or nursing services, that may not have transitioned to home but are critical for their health and development. Many students with disabilities are dependent on family members to successfully access the educational services they need.”
“Pediatricians can play a role in providing feedback on recommendations related to physical distancing and face coverings in particular,” said Dr. Beers. “In addition, they can be helpful in developing plans for children with disabilities as well as what the response plan should be for students who become sick during the school day.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a decision tool for parents who are considering whether to send their child to in-person school, and pediatricians can help parents walk through these questions, Dr. Beers noted. “In addition, pediatricians play an important role in helping patients and families think about the risks of COVID for the patient and other family members, and this can be helpful in addressing the anxiety that parents and patients may be experiencing.”
Further information can be found in Return to School During COVID-19, which can be located at HealthyChildren.org, by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The authors of the viewpoints had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smart, a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board, had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Beers has served on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News in the past, but had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCES: Black E, Ferdig R, Thompson LA. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3800. Wang CJ and Bair H. JAMA Pediatr. Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3871.
The abrupt transition to online learning for American children in kindergarten through 12th grade has left educators and parents unprepared, but virtual learning can be a successful part of education going forward, according to a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics. However, schools also can reopen safely if precautions are taken, and students would benefit in many ways, according to a second viewpoint.
“As policy makers, health care professionals, and parents prepare for the fall semester and as public and private schools grapple with how to make that possible, a better understanding of K-12 virtual learning options and outcomes may facilitate those difficult decisions,” wrote Erik Black, PhD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville; Richard Ferdig, PhD, of Kent State University, Ohio; and Lindsay A. Thompson, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“Importantly, K-12 virtual schooling is not suited for all students or all families.”
In a viewpoint published in JAMA Pediatrics, the authors noted that virtual schooling has existed in the United States in various forms for some time. “Just like the myriad options that are available for face-to-face schooling in the U.S., virtual schooling exists in a complex landscape of for-profit, charter, and public options.”
Not all virtual schools are equal
Consequently, not all virtual schools are created equal, they emphasized. Virtual education can be successful for many students when presented by trained online instructors using a curriculum designed to be effective in an online venue.
“Parents need to seek reviews and ask for educational outcomes from each virtual school system to assess the quality of the provided education,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson emphasized.
Key questions for parents to consider when faced with online learning include the type of technology needed to participate; whether their child can maintain a study schedule and complete assignments with limited supervision; whether their child could ask for help and communicate with teachers through technology including phone, text, email, or video; and whether their child has the basic reading, math, and computer literacy skills to engage in online learning, the authors said. Other questions include the school’s expectations for parents and caregivers, how student information may be shared, and how the virtual school lines up with state standards for K-12 educators (in the case of options outside the public school system).
“The COVID-19 pandemic offers a unique challenge for educators, policymakers, and health care professionals to partner with parents to make the best local and individual decisions for children,” Dr. Black, Dr. Ferdig, and Dr. Thompson concluded.
Schools may be able to open safely
Children continue to make up a low percentage of COVID-19 cases and appear less likely to experience illness, wrote C. Jason Wang, MD, PhD, and Henry Bair, BS, of Stanford (Calif.) University in a second viewpoint also published in JAMA Pediatrics. The impact of long-term school closures extends beyond education and can “exacerbate socioeconomic disparities, amplify existing educational inequalities, and aggravate food insecurity, domestic violence, and mental health disorders,” they wrote.
Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair proposed that school districts “engage key stakeholders to establish a COVID-19 task force, composed of the superintendent, members of the school board, teachers, parents, and health care professionals to develop policies and procedures,” that would allow schools to open safely.
The authors outlined strategies including adapting teaching spaces to accommodate physical distance, with the addition of temporary modular buildings if needed. They advised assigned seating on school buses, and acknowledged the need for the availability of protective equipment, including hand sanitizer and masks, as well as the possible use of transparent barriers on the sides of student desks.
“As the AAP [American Academy of Pediatrics] guidance suggests, teachers who must work closely with students with special needs or with students who are unable to wear masks should wear N95 masks if possible or wear face shields in addition to surgical masks,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair noted. Other elements of the AAP guidance include the creation of fixed cohorts of students and teachers to limit virus exposure.
“Even with all the precautions in place, COVID-19 outbreaks within schools are still likely,” they said. “Therefore, schools will need to remain flexible and consider temporary closures if there is an outbreak involving multiple students and/or staff and be ready to transition to online education.”
The AAP guidance does not address operational approaches to identifying signs and symptoms of COVID-19, the authors noted. “To address this, we recommend that schools implement multilevel screening for students and staff.”
“In summary, to maximize health and educational outcomes, school districts should adopt some or all of the measures of the AAP guidance and prioritize them after considering local COVID-19 incidence, key stakeholder input, and budgetary constraints,” Dr. Wang and Mr. Bair concluded.
Schools opening is a regional decision
“The mission of the AAP is to attain optimal physical, mental, and social health and well-being for all infants, children, adolescents, and young adults,” Howard Smart, MD, said in an interview. The question of school reopening “is of national importance, and the AAP has a national role in making recommendations regarding national policy affecting the health of the children.”
“The decision to open schools will be made regionally, but it is important for a nonpolitical national voice to make expert recommendations,” he emphasized.
“Many of the recommendations are ideal goals,” noted Dr. Smart, chairman of the department of pediatrics at the Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. “It will be difficult, for example, to implement symptom screening every day before school, no matter where it is performed. Some of the measures may be quite costly, and take time to implement, or require expansion of school staff, for which there may be no budget.”
In addition, “[n]ot all students are likely to comply with masking, distance, and hand-washing recommendations. One student who is noncompliant will be able to infect many other students and staff, as has been seen in other countries.” Also, parental attitudes toward control measures are likely to affect student attitudes, he noted.
“I have interviewed many families at recent checkups, and most have felt that the rush to remote learning that occurred at the end of the last school year resulted in fairly disorganized instruction,” Dr. Smart said. “They are hoping that, having had the summer to plan ahead, the remote teaching will be handled better. Remote learning will certainly work best for self-motivated, organized students with good family support, as noted in the Black, Ferdig, and Thompson article,” he said.
Pediatricians can support the schools by being a source of evidence-based information for parents, Dr. Smart said. “Pediatricians with time and energy might want to volunteer to hold informational video conferences for parents and/or school personnel if they feel they are up to date on current COVID-19 science and want to handle potentially contentious questions.”
The decision parents make to send their children back to school comes down to a risk-benefit calculation. “In some communities this may be left to parents, while in other communities this will a public health decision,” he said. “It is still not clear whether having students attend school in person will result in increased spread of COVID-19 among the students, or in their communities. Although some evidence from early in the pandemic suggests that children may not spread the virus as much as adults, more recent evidence suggests that children 10 years and older do transmit the virus at least as much as adults.”
“The risk to the students and the community, therefore, is unknown,” and difficult to compare with the benefit of in-person schooling, Dr. Smart noted.
“We will learn quite a bit from communities where students do go back to in-person class, as we follow the progression of COVID-19 over the weeks following the resumption of instruction.” Ultimately, advice to parents will need to be tailored to the current conditions of COVID-19 transmission in the community, he concluded.
It’s not just about education
“The AAP released its guidance to ensure that as school districts were contemplating reopening they were considering the full array of risks for children and adolescents. These risks included not only those related to COVID-19, but also those related to the impact of not reopening in-person,” Nathaniel Beers, MD, president of the HSC Health Care System in Washington, said in an interview.
“Students and families are dependent on schools for much more than just an education, and those [elements] need to be factored into the decisions to reopen,” the pediatrician said.
However, “[t]he major barrier for schools is resources to safely reopen,” said Dr. Beers. “The additional staffing and supplies will require additional funding. There are increased demands regardless of whether students are learning in-person or virtually or through hybrid models.”
“Another significant barrier is ensuring that parents and staff are actively engaged in planning for the type of model being used,” he said.
“All of the models require buy-in by staff and parents. This will require significant outreach and strong communication plans. Schools also need to ensure they are planning not just for how to return students to schools, but what will happen when staff or students test positive for COVID-19. Students, families, and staff all will need to know what these plans are up front to feel confident in returning to school,” he emphasized.
“There are students who can thrive in a virtual learning environment,” Dr. Beers said. “There are also students who benefit from the virtual learning environment because of their own risk, or because of a family member’s risk for COVID-19 or the complications from it.”
“However, many children with disabilities have struggled in a virtual environment,” he said. “These students struggle to access the educational services without the adequate supports at home. They often receive additional services in school, such as speech, occupational therapy or physical therapy, or nursing services, that may not have transitioned to home but are critical for their health and development. Many students with disabilities are dependent on family members to successfully access the educational services they need.”
“Pediatricians can play a role in providing feedback on recommendations related to physical distancing and face coverings in particular,” said Dr. Beers. “In addition, they can be helpful in developing plans for children with disabilities as well as what the response plan should be for students who become sick during the school day.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a decision tool for parents who are considering whether to send their child to in-person school, and pediatricians can help parents walk through these questions, Dr. Beers noted. “In addition, pediatricians play an important role in helping patients and families think about the risks of COVID for the patient and other family members, and this can be helpful in addressing the anxiety that parents and patients may be experiencing.”
Further information can be found in Return to School During COVID-19, which can be located at HealthyChildren.org, by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
The authors of the viewpoints had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Smart, a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board, had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Beers has served on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News in the past, but had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCES: Black E, Ferdig R, Thompson LA. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3800. Wang CJ and Bair H. JAMA Pediatr. Aug 11. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3871.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Incidence, prognosis of second lung cancers support long-term surveillance
Second lung cancers occurring up to a decade after the first are on the rise, but their prognosis is similar – especially when detected early – which supports long-term surveillance in survivors, finds a large population-based study.
Although guidelines recommend continued annual low-dose CT scan surveillance extending beyond 4 years for this population based on expert consensus, long-term evidence of benefit is lacking.
Investigators led by John M. Varlotto, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, analyzed Surveillance, Epidemiology & End Results (SEER) data for more than 58,000 patients with first and sometimes second non–small cell lung cancers initially treated by surgical resection.
Study results reported in Lung Cancer showed that the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers occurring 4-10 years after the first lung cancer rose sharply during the 1985-2014 study period, driven by a large uptick in women patients.
Among all patients, second lung cancers had similar overall survival as first lung cancers, but poorer lung cancer–specific survival. However, among the subset of patients having early-stage resectable disease (tumors measuring less than 4 cm with negative nodes), both outcomes were statistically indistinguishable.
“Because our investigation noted that the overall survival of patients undergoing a second lung cancer operation was similar to those patients undergoing a first operation, and because there is a rising rate of second lung cancer in lung cancer survivors, we feel that continued surveillance beyond the 4-year interval as recommended by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery as well as the [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines would be beneficial to long-term survivors of early-stage lung cancer,” Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators wrote.
“The recent results from recent lung cancer screening studies demonstrate that females may benefit preferentially from screening … and our study suggests that these preferential benefits of increased CT scan surveillance may extend to females who are long-term survivors of lung cancer as well,” they added.
Findings in context
“As this is an observational study, it is challenging to understand what is driving the rise in prevalence of second lung cancers,” Mara Antonoff, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston commented in an interview.
“Overall, the findings are very important, as they suggest that we should continue to perform surveillance imaging for patients beyond recommended guidelines, which may allow us to achieve better survival outcomes for those individuals who develop a second lung cancer years after the first lung cancer,” she agreed.
“Just as lung cancer screening is important to identifying lung cancers at an earlier stage when they are more easily treatable and more likely to be cured, surveillance after an initial treatment for lung cancer would allow a diagnosis of second lung cancers at an earlier stage, so the patients can again achieve durable cure,” Dr. Antonoff concluded.
Study details
For the study, Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators used data from SEER-13 and SEER-18 to identify patients with a lung cancer diagnosis during 1998-2013, and data from SEER-9, covering the years 1985-2014, to calculate rates of second cancers occurring 4-10 years after a first lung cancer.
Analyses were based on 58,758 patients with a surgically resected first primary lung cancer (55.9% with early-stage disease) and 384 patients with a surgically resected second primary lung cancer (77.6% with early-stage disease). Median follow-up was 76 months for the former and 46 months for the latter.
Results showed that in the 4-10 years after a first lung cancer diagnosis, the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers rose by study year but remained less than that of all other second cancers combined until the mid-2000s. Among women, incidence started rising sharply in 2001 and significantly exceeded that of all other second cancers starting in 2005.
In the entire population of study patients, propensity-adjusted analyses showed that second lung cancers were similar to first lung cancers on overall survival (P = .1726) but had worse lung cancer–specific survival (P = .0143). However, in the subset of patients with early-stage resectable disease, second and first lung cancers were similar on both overall survival (P = .3872) and lung cancer–specific survival (P = .1276).
Dr. Varlotto disclosed that he had no conflicts of interest. The study was funded by the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Massachusetts. Dr. Antonoff disclosed that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Varlotto JM et al. Lung Cancer. 2020;147:115-122.
Second lung cancers occurring up to a decade after the first are on the rise, but their prognosis is similar – especially when detected early – which supports long-term surveillance in survivors, finds a large population-based study.
Although guidelines recommend continued annual low-dose CT scan surveillance extending beyond 4 years for this population based on expert consensus, long-term evidence of benefit is lacking.
Investigators led by John M. Varlotto, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, analyzed Surveillance, Epidemiology & End Results (SEER) data for more than 58,000 patients with first and sometimes second non–small cell lung cancers initially treated by surgical resection.
Study results reported in Lung Cancer showed that the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers occurring 4-10 years after the first lung cancer rose sharply during the 1985-2014 study period, driven by a large uptick in women patients.
Among all patients, second lung cancers had similar overall survival as first lung cancers, but poorer lung cancer–specific survival. However, among the subset of patients having early-stage resectable disease (tumors measuring less than 4 cm with negative nodes), both outcomes were statistically indistinguishable.
“Because our investigation noted that the overall survival of patients undergoing a second lung cancer operation was similar to those patients undergoing a first operation, and because there is a rising rate of second lung cancer in lung cancer survivors, we feel that continued surveillance beyond the 4-year interval as recommended by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery as well as the [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines would be beneficial to long-term survivors of early-stage lung cancer,” Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators wrote.
“The recent results from recent lung cancer screening studies demonstrate that females may benefit preferentially from screening … and our study suggests that these preferential benefits of increased CT scan surveillance may extend to females who are long-term survivors of lung cancer as well,” they added.
Findings in context
“As this is an observational study, it is challenging to understand what is driving the rise in prevalence of second lung cancers,” Mara Antonoff, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston commented in an interview.
“Overall, the findings are very important, as they suggest that we should continue to perform surveillance imaging for patients beyond recommended guidelines, which may allow us to achieve better survival outcomes for those individuals who develop a second lung cancer years after the first lung cancer,” she agreed.
“Just as lung cancer screening is important to identifying lung cancers at an earlier stage when they are more easily treatable and more likely to be cured, surveillance after an initial treatment for lung cancer would allow a diagnosis of second lung cancers at an earlier stage, so the patients can again achieve durable cure,” Dr. Antonoff concluded.
Study details
For the study, Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators used data from SEER-13 and SEER-18 to identify patients with a lung cancer diagnosis during 1998-2013, and data from SEER-9, covering the years 1985-2014, to calculate rates of second cancers occurring 4-10 years after a first lung cancer.
Analyses were based on 58,758 patients with a surgically resected first primary lung cancer (55.9% with early-stage disease) and 384 patients with a surgically resected second primary lung cancer (77.6% with early-stage disease). Median follow-up was 76 months for the former and 46 months for the latter.
Results showed that in the 4-10 years after a first lung cancer diagnosis, the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers rose by study year but remained less than that of all other second cancers combined until the mid-2000s. Among women, incidence started rising sharply in 2001 and significantly exceeded that of all other second cancers starting in 2005.
In the entire population of study patients, propensity-adjusted analyses showed that second lung cancers were similar to first lung cancers on overall survival (P = .1726) but had worse lung cancer–specific survival (P = .0143). However, in the subset of patients with early-stage resectable disease, second and first lung cancers were similar on both overall survival (P = .3872) and lung cancer–specific survival (P = .1276).
Dr. Varlotto disclosed that he had no conflicts of interest. The study was funded by the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Massachusetts. Dr. Antonoff disclosed that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Varlotto JM et al. Lung Cancer. 2020;147:115-122.
Second lung cancers occurring up to a decade after the first are on the rise, but their prognosis is similar – especially when detected early – which supports long-term surveillance in survivors, finds a large population-based study.
Although guidelines recommend continued annual low-dose CT scan surveillance extending beyond 4 years for this population based on expert consensus, long-term evidence of benefit is lacking.
Investigators led by John M. Varlotto, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worcester, analyzed Surveillance, Epidemiology & End Results (SEER) data for more than 58,000 patients with first and sometimes second non–small cell lung cancers initially treated by surgical resection.
Study results reported in Lung Cancer showed that the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers occurring 4-10 years after the first lung cancer rose sharply during the 1985-2014 study period, driven by a large uptick in women patients.
Among all patients, second lung cancers had similar overall survival as first lung cancers, but poorer lung cancer–specific survival. However, among the subset of patients having early-stage resectable disease (tumors measuring less than 4 cm with negative nodes), both outcomes were statistically indistinguishable.
“Because our investigation noted that the overall survival of patients undergoing a second lung cancer operation was similar to those patients undergoing a first operation, and because there is a rising rate of second lung cancer in lung cancer survivors, we feel that continued surveillance beyond the 4-year interval as recommended by the American Association for Thoracic Surgery as well as the [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines would be beneficial to long-term survivors of early-stage lung cancer,” Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators wrote.
“The recent results from recent lung cancer screening studies demonstrate that females may benefit preferentially from screening … and our study suggests that these preferential benefits of increased CT scan surveillance may extend to females who are long-term survivors of lung cancer as well,” they added.
Findings in context
“As this is an observational study, it is challenging to understand what is driving the rise in prevalence of second lung cancers,” Mara Antonoff, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston commented in an interview.
“Overall, the findings are very important, as they suggest that we should continue to perform surveillance imaging for patients beyond recommended guidelines, which may allow us to achieve better survival outcomes for those individuals who develop a second lung cancer years after the first lung cancer,” she agreed.
“Just as lung cancer screening is important to identifying lung cancers at an earlier stage when they are more easily treatable and more likely to be cured, surveillance after an initial treatment for lung cancer would allow a diagnosis of second lung cancers at an earlier stage, so the patients can again achieve durable cure,” Dr. Antonoff concluded.
Study details
For the study, Dr. Varlotto and coinvestigators used data from SEER-13 and SEER-18 to identify patients with a lung cancer diagnosis during 1998-2013, and data from SEER-9, covering the years 1985-2014, to calculate rates of second cancers occurring 4-10 years after a first lung cancer.
Analyses were based on 58,758 patients with a surgically resected first primary lung cancer (55.9% with early-stage disease) and 384 patients with a surgically resected second primary lung cancer (77.6% with early-stage disease). Median follow-up was 76 months for the former and 46 months for the latter.
Results showed that in the 4-10 years after a first lung cancer diagnosis, the age-adjusted incidence of second lung cancers rose by study year but remained less than that of all other second cancers combined until the mid-2000s. Among women, incidence started rising sharply in 2001 and significantly exceeded that of all other second cancers starting in 2005.
In the entire population of study patients, propensity-adjusted analyses showed that second lung cancers were similar to first lung cancers on overall survival (P = .1726) but had worse lung cancer–specific survival (P = .0143). However, in the subset of patients with early-stage resectable disease, second and first lung cancers were similar on both overall survival (P = .3872) and lung cancer–specific survival (P = .1276).
Dr. Varlotto disclosed that he had no conflicts of interest. The study was funded by the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Massachusetts. Dr. Antonoff disclosed that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Varlotto JM et al. Lung Cancer. 2020;147:115-122.
FROM LUNG CANCER
Severe obesity ups risk for death in younger men with COVID-19
In a large California health care plan, among patients with COVID-19, men aged 60 years and younger had a much higher risk of dying within 3 weeks of diagnosis if they had severe obesity as opposed to being of normal weight, independently of other risk factors.
reported Sara Y. Tartof, PhD, MPH, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Pasadena, Calif., and coauthors.
The data “highlight the leading role of severe obesity over correlated risk factors, providing a target for early intervention,” they concluded in an article published online Aug. 12 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This work adds to nearly 300 articles that have shown that severe obesity is associated with an increased risk for morbidity and mortality from COVID-19.
In an accompanying editorial, David A. Kass, MD, said: “Consistency of this new study and prior research should put to rest the contention that obesity is common in severe COVID-19 because it is common in the population.”
Rather, these findings show that “obesity is an important independent risk factor for serious COVID-19 disease,” he pointed out.
On the basis of this evidence, “arguably the hardest question to answer is: What is to be done?” wondered Kass, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Although data consistently show that a body mass index >35 kg/m2 is predictive of major health risks, “weight reduction at that level of obesity is difficult and certainly is not achieved rapidly,” Dr. Kass stressed.
“Therefore ... social distancing; altering behaviors to reduce viral exposure and transmission, such as wearing masks; and instituting policies and health care approaches that recognize the potential effects of obesity should be implemented,” he emphasized. “These actions should help and are certainly doable.”
Similarly, Dr. Tartof and colleagues said their “findings also reveal the distressing collision of two pandemics: COVID-19 and obesity.
“As COVID-19 continues to spread unabated, we must focus our immediate efforts on containing the crisis at hand,” they urged.
However, the findings also “underscore the need for future collective efforts to combat the equally devastating, and potentially synergistic, force of the obesity epidemic.”
COVID-19 pandemic collides with obesity epidemic
Previous studies of obesity and COVID-19 were small, did not adjust for multiple confounders, or did not include nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Tartof and coauthors wrote.
Their study included 6,916 members of the Kaiser Permanente Southern California health care plan who were diagnosed with COVID-19 from Feb. 13 to May 2, 2020.
The researchers calculated the risk for death at 21 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis; findings were corrected for age, sex, race/ethnicity, smoking, myocardial infarction, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, renal disease, metastatic tumor or malignancy, other immune disease, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, asthma, organ transplant, and diabetes status.
On the basis of BMI, the patients were classified as being underweight, of normal weight, overweight, or as having class 1, 2, or 3 obesity. BMI of 18.5 to 24 kg/m2 is defined as normal weight.
Class 3 obesity, also called severe obesity, included moderately severe obesity (BMI, 40-44 kg/m2) and extremely severe obesity (≥45 kg/m2).
A little more than half of the patients were women (55%), and more than 50% were Hispanic (54%).
A total of 206 patients (3%) died within 21 days of being diagnosed with COVID-19; of these, 67% had been hospitalized, and 43% had been intubated.
Overall, the COVID-19 patients with moderately severe or extremely severe obesity had a 2.7-fold and 4.2-fold increased risk for death, respectively, within 3 weeks compared with patients of normal weight.
Patients in the other BMI categories did not have a significantly higher risk of dying during follow-up.
However, each decade of increasing age after age 40 was associated with a stepwise increased risk for death within 3 weeks of the COVID-19 diagnosis.
Risk stratified by age and sex
Further analysis showed that, “most strikingly,” among patients aged 60 and younger, those with moderately severe obesity and extremely severe obesity had significant 17-fold and 12-fold higher risks of dying during follow-up, respectively, compared with patients of normal weight, the researchers reported.
In patients older than 60, moderately severe obesity did not confer a significant increased risk for imminent death from COVID-19; extremely severe obesity conferred a smaller, threefold increased risk for this.
“Our finding that severe obesity, particularly among younger patients, eclipses the mortality risk posed by other obesity-related conditions, such as history of myocardial infarction (MI), diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia, suggests a significant pathophysiologic link between excess adiposity and severe COVID-19 illness,” the researchers noted.
This independent increased risk for death with severe obesity was seen in men but not in women.
Men with moderately severe and extremely severe obesity had significant 4.8-fold and 10-fold higher risks of dying within 3 weeks, respectively, compared with men of normal weight.
“That the risks are higher in younger patients is probably not because obesity is particularly damaging in this age group; it is more likely that other serious comorbidities that evolve later in life take over as dominant risk factors,” Dr. Kass suggested in his editorial.
“That males are particularly affected may reflect their greater visceral adiposity over females, given that this fat is notably proinflammatory and contributes to metabolic and vascular disease,” he added.
“As a cardiologist who studies heart failure,” Dr. Kass wrote, “I am struck by how many of the mechanisms that are mentioned in reviews of obesity risk and heart disease are also mentioned in reviews of obesity and COVID-19.”
The study was funded by Roche-Genentech. Kass has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures of the authors are listed in the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a large California health care plan, among patients with COVID-19, men aged 60 years and younger had a much higher risk of dying within 3 weeks of diagnosis if they had severe obesity as opposed to being of normal weight, independently of other risk factors.
reported Sara Y. Tartof, PhD, MPH, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Pasadena, Calif., and coauthors.
The data “highlight the leading role of severe obesity over correlated risk factors, providing a target for early intervention,” they concluded in an article published online Aug. 12 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This work adds to nearly 300 articles that have shown that severe obesity is associated with an increased risk for morbidity and mortality from COVID-19.
In an accompanying editorial, David A. Kass, MD, said: “Consistency of this new study and prior research should put to rest the contention that obesity is common in severe COVID-19 because it is common in the population.”
Rather, these findings show that “obesity is an important independent risk factor for serious COVID-19 disease,” he pointed out.
On the basis of this evidence, “arguably the hardest question to answer is: What is to be done?” wondered Kass, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Although data consistently show that a body mass index >35 kg/m2 is predictive of major health risks, “weight reduction at that level of obesity is difficult and certainly is not achieved rapidly,” Dr. Kass stressed.
“Therefore ... social distancing; altering behaviors to reduce viral exposure and transmission, such as wearing masks; and instituting policies and health care approaches that recognize the potential effects of obesity should be implemented,” he emphasized. “These actions should help and are certainly doable.”
Similarly, Dr. Tartof and colleagues said their “findings also reveal the distressing collision of two pandemics: COVID-19 and obesity.
“As COVID-19 continues to spread unabated, we must focus our immediate efforts on containing the crisis at hand,” they urged.
However, the findings also “underscore the need for future collective efforts to combat the equally devastating, and potentially synergistic, force of the obesity epidemic.”
COVID-19 pandemic collides with obesity epidemic
Previous studies of obesity and COVID-19 were small, did not adjust for multiple confounders, or did not include nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Tartof and coauthors wrote.
Their study included 6,916 members of the Kaiser Permanente Southern California health care plan who were diagnosed with COVID-19 from Feb. 13 to May 2, 2020.
The researchers calculated the risk for death at 21 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis; findings were corrected for age, sex, race/ethnicity, smoking, myocardial infarction, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, renal disease, metastatic tumor or malignancy, other immune disease, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, asthma, organ transplant, and diabetes status.
On the basis of BMI, the patients were classified as being underweight, of normal weight, overweight, or as having class 1, 2, or 3 obesity. BMI of 18.5 to 24 kg/m2 is defined as normal weight.
Class 3 obesity, also called severe obesity, included moderately severe obesity (BMI, 40-44 kg/m2) and extremely severe obesity (≥45 kg/m2).
A little more than half of the patients were women (55%), and more than 50% were Hispanic (54%).
A total of 206 patients (3%) died within 21 days of being diagnosed with COVID-19; of these, 67% had been hospitalized, and 43% had been intubated.
Overall, the COVID-19 patients with moderately severe or extremely severe obesity had a 2.7-fold and 4.2-fold increased risk for death, respectively, within 3 weeks compared with patients of normal weight.
Patients in the other BMI categories did not have a significantly higher risk of dying during follow-up.
However, each decade of increasing age after age 40 was associated with a stepwise increased risk for death within 3 weeks of the COVID-19 diagnosis.
Risk stratified by age and sex
Further analysis showed that, “most strikingly,” among patients aged 60 and younger, those with moderately severe obesity and extremely severe obesity had significant 17-fold and 12-fold higher risks of dying during follow-up, respectively, compared with patients of normal weight, the researchers reported.
In patients older than 60, moderately severe obesity did not confer a significant increased risk for imminent death from COVID-19; extremely severe obesity conferred a smaller, threefold increased risk for this.
“Our finding that severe obesity, particularly among younger patients, eclipses the mortality risk posed by other obesity-related conditions, such as history of myocardial infarction (MI), diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia, suggests a significant pathophysiologic link between excess adiposity and severe COVID-19 illness,” the researchers noted.
This independent increased risk for death with severe obesity was seen in men but not in women.
Men with moderately severe and extremely severe obesity had significant 4.8-fold and 10-fold higher risks of dying within 3 weeks, respectively, compared with men of normal weight.
“That the risks are higher in younger patients is probably not because obesity is particularly damaging in this age group; it is more likely that other serious comorbidities that evolve later in life take over as dominant risk factors,” Dr. Kass suggested in his editorial.
“That males are particularly affected may reflect their greater visceral adiposity over females, given that this fat is notably proinflammatory and contributes to metabolic and vascular disease,” he added.
“As a cardiologist who studies heart failure,” Dr. Kass wrote, “I am struck by how many of the mechanisms that are mentioned in reviews of obesity risk and heart disease are also mentioned in reviews of obesity and COVID-19.”
The study was funded by Roche-Genentech. Kass has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures of the authors are listed in the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a large California health care plan, among patients with COVID-19, men aged 60 years and younger had a much higher risk of dying within 3 weeks of diagnosis if they had severe obesity as opposed to being of normal weight, independently of other risk factors.
reported Sara Y. Tartof, PhD, MPH, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Pasadena, Calif., and coauthors.
The data “highlight the leading role of severe obesity over correlated risk factors, providing a target for early intervention,” they concluded in an article published online Aug. 12 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This work adds to nearly 300 articles that have shown that severe obesity is associated with an increased risk for morbidity and mortality from COVID-19.
In an accompanying editorial, David A. Kass, MD, said: “Consistency of this new study and prior research should put to rest the contention that obesity is common in severe COVID-19 because it is common in the population.”
Rather, these findings show that “obesity is an important independent risk factor for serious COVID-19 disease,” he pointed out.
On the basis of this evidence, “arguably the hardest question to answer is: What is to be done?” wondered Kass, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Although data consistently show that a body mass index >35 kg/m2 is predictive of major health risks, “weight reduction at that level of obesity is difficult and certainly is not achieved rapidly,” Dr. Kass stressed.
“Therefore ... social distancing; altering behaviors to reduce viral exposure and transmission, such as wearing masks; and instituting policies and health care approaches that recognize the potential effects of obesity should be implemented,” he emphasized. “These actions should help and are certainly doable.”
Similarly, Dr. Tartof and colleagues said their “findings also reveal the distressing collision of two pandemics: COVID-19 and obesity.
“As COVID-19 continues to spread unabated, we must focus our immediate efforts on containing the crisis at hand,” they urged.
However, the findings also “underscore the need for future collective efforts to combat the equally devastating, and potentially synergistic, force of the obesity epidemic.”
COVID-19 pandemic collides with obesity epidemic
Previous studies of obesity and COVID-19 were small, did not adjust for multiple confounders, or did not include nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Tartof and coauthors wrote.
Their study included 6,916 members of the Kaiser Permanente Southern California health care plan who were diagnosed with COVID-19 from Feb. 13 to May 2, 2020.
The researchers calculated the risk for death at 21 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis; findings were corrected for age, sex, race/ethnicity, smoking, myocardial infarction, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, renal disease, metastatic tumor or malignancy, other immune disease, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, asthma, organ transplant, and diabetes status.
On the basis of BMI, the patients were classified as being underweight, of normal weight, overweight, or as having class 1, 2, or 3 obesity. BMI of 18.5 to 24 kg/m2 is defined as normal weight.
Class 3 obesity, also called severe obesity, included moderately severe obesity (BMI, 40-44 kg/m2) and extremely severe obesity (≥45 kg/m2).
A little more than half of the patients were women (55%), and more than 50% were Hispanic (54%).
A total of 206 patients (3%) died within 21 days of being diagnosed with COVID-19; of these, 67% had been hospitalized, and 43% had been intubated.
Overall, the COVID-19 patients with moderately severe or extremely severe obesity had a 2.7-fold and 4.2-fold increased risk for death, respectively, within 3 weeks compared with patients of normal weight.
Patients in the other BMI categories did not have a significantly higher risk of dying during follow-up.
However, each decade of increasing age after age 40 was associated with a stepwise increased risk for death within 3 weeks of the COVID-19 diagnosis.
Risk stratified by age and sex
Further analysis showed that, “most strikingly,” among patients aged 60 and younger, those with moderately severe obesity and extremely severe obesity had significant 17-fold and 12-fold higher risks of dying during follow-up, respectively, compared with patients of normal weight, the researchers reported.
In patients older than 60, moderately severe obesity did not confer a significant increased risk for imminent death from COVID-19; extremely severe obesity conferred a smaller, threefold increased risk for this.
“Our finding that severe obesity, particularly among younger patients, eclipses the mortality risk posed by other obesity-related conditions, such as history of myocardial infarction (MI), diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia, suggests a significant pathophysiologic link between excess adiposity and severe COVID-19 illness,” the researchers noted.
This independent increased risk for death with severe obesity was seen in men but not in women.
Men with moderately severe and extremely severe obesity had significant 4.8-fold and 10-fold higher risks of dying within 3 weeks, respectively, compared with men of normal weight.
“That the risks are higher in younger patients is probably not because obesity is particularly damaging in this age group; it is more likely that other serious comorbidities that evolve later in life take over as dominant risk factors,” Dr. Kass suggested in his editorial.
“That males are particularly affected may reflect their greater visceral adiposity over females, given that this fat is notably proinflammatory and contributes to metabolic and vascular disease,” he added.
“As a cardiologist who studies heart failure,” Dr. Kass wrote, “I am struck by how many of the mechanisms that are mentioned in reviews of obesity risk and heart disease are also mentioned in reviews of obesity and COVID-19.”
The study was funded by Roche-Genentech. Kass has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures of the authors are listed in the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 40% of residents said training prepped them for COVID-19
Most residents who were asked whether their training prepared them for COVID-19 in a Medscape survey said it had not or they weren’t sure.
Whereas 40% said they felt prepared, 30% said they did not feel prepared and 31% answered they were unsure. (Numbers were rounded, so some answers pushed above 100%.)
One quarter have $300,000 or more in student debt
The Medscape Residents Salary & Debt Report 2020, with data collected April 3 to June 1, found that nearly one in four residents (24%) had medical school debt of more than $300,000. Half (49%) had more than $200,000.
The data include answers from 1,659 U.S. medical residents.
For the sixth straight year, female residents were more satisfied with their pay than were their male colleagues. This year the satisfaction gap was 45% female compared with 42% male. That imbalance came despite their making nearly the same pay overall ($63,700 for men and $63,000 for women).
Among practicing physicians, the pay gap is much wider: Men make 25% more in primary care and 31% more in specialties.
Ten percent thought they should earn 76%-100% more.
For those not satisfied with pay, the top reasons were feeling the pay was too low for the hours worked (81%) or too low compared with other medical staff, such as physician assistants (PAs) or nurses (77% chose that answer).
As for hours worked, 31% of residents reported they spend more than 60 hours/week seeing patients.
The top-paying specialties, averaging $69,500, were allergy and immunology, hematology, plastic surgery, aesthetic medicine, rheumatology, and specialized surgery. The lowest paid were family medicine residents at $58,500.
In primary care, overall, most residents said they planned to specialize. Only 47% planned to continue to work in primary care. Male residents were much more likely to say they will subspecialize than were their female colleagues (52% vs. 35%).
More than 90% of residents say future pay has influenced their choice of specialty, though more men than women felt that way (93% vs. 86%).
Good relationships with others
Overall, residents reported good relationships with attending physicians and nurses.
Most (88%) said they had good or very good relationships with attending physicians, 10% said the relationships were fair, and 2% said they were poor.
In addition, 89% of residents said the amount of supervision was appropriate, 4% said there was too much, and 7% said there was too little.
Relationships with nurses/PAs were slightly less positive overall: Eighty-two percent reported good or very good relationships with nurses/PAs, 15% said those relationships were fair, and 3% said they were poor.
One respondent said: “Our relationships could be better, but I think everyone is just overwhelmed with COVID-19, so emotions are heightened.”
Another said: “It takes time to earn the respect from nurses.”
Seventy-seven percent said they were satisfied with their learning experience overall, 12% were neutral on the question, and 11% said they were dissatisfied or very dissatisfied.
Work-life balance is the top concern
Work-life balance continues to be the top concern for residents. More than one-quarter (27%) in residency years 1 through 4 listed that as the top concern, and even more (32%) of those in years 5 through 8 agreed.
That was followed by demands on time and fear of failure or making a serious mistake.
The survey indicates that benefit packages for residents have stayed much the same over the past 2 years with health insurance and paid time off for sick leave, vacation, and personal time most commonly reported at 89% and 87%, respectively.
Much less common were benefits including commuter assistance (parking, public transportation) at 24%, housing allowance (8%), and child care (4%).
The vast majority of residents reported doing scut work (unskilled tasks): More than half (54%) reported doing 1-10 hours/week and 22% did 11-20 hours/week. Regardless of the number of hours, however, 62% said the time spent performing these tasks was appropriate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Most residents who were asked whether their training prepared them for COVID-19 in a Medscape survey said it had not or they weren’t sure.
Whereas 40% said they felt prepared, 30% said they did not feel prepared and 31% answered they were unsure. (Numbers were rounded, so some answers pushed above 100%.)
One quarter have $300,000 or more in student debt
The Medscape Residents Salary & Debt Report 2020, with data collected April 3 to June 1, found that nearly one in four residents (24%) had medical school debt of more than $300,000. Half (49%) had more than $200,000.
The data include answers from 1,659 U.S. medical residents.
For the sixth straight year, female residents were more satisfied with their pay than were their male colleagues. This year the satisfaction gap was 45% female compared with 42% male. That imbalance came despite their making nearly the same pay overall ($63,700 for men and $63,000 for women).
Among practicing physicians, the pay gap is much wider: Men make 25% more in primary care and 31% more in specialties.
Ten percent thought they should earn 76%-100% more.
For those not satisfied with pay, the top reasons were feeling the pay was too low for the hours worked (81%) or too low compared with other medical staff, such as physician assistants (PAs) or nurses (77% chose that answer).
As for hours worked, 31% of residents reported they spend more than 60 hours/week seeing patients.
The top-paying specialties, averaging $69,500, were allergy and immunology, hematology, plastic surgery, aesthetic medicine, rheumatology, and specialized surgery. The lowest paid were family medicine residents at $58,500.
In primary care, overall, most residents said they planned to specialize. Only 47% planned to continue to work in primary care. Male residents were much more likely to say they will subspecialize than were their female colleagues (52% vs. 35%).
More than 90% of residents say future pay has influenced their choice of specialty, though more men than women felt that way (93% vs. 86%).
Good relationships with others
Overall, residents reported good relationships with attending physicians and nurses.
Most (88%) said they had good or very good relationships with attending physicians, 10% said the relationships were fair, and 2% said they were poor.
In addition, 89% of residents said the amount of supervision was appropriate, 4% said there was too much, and 7% said there was too little.
Relationships with nurses/PAs were slightly less positive overall: Eighty-two percent reported good or very good relationships with nurses/PAs, 15% said those relationships were fair, and 3% said they were poor.
One respondent said: “Our relationships could be better, but I think everyone is just overwhelmed with COVID-19, so emotions are heightened.”
Another said: “It takes time to earn the respect from nurses.”
Seventy-seven percent said they were satisfied with their learning experience overall, 12% were neutral on the question, and 11% said they were dissatisfied or very dissatisfied.
Work-life balance is the top concern
Work-life balance continues to be the top concern for residents. More than one-quarter (27%) in residency years 1 through 4 listed that as the top concern, and even more (32%) of those in years 5 through 8 agreed.
That was followed by demands on time and fear of failure or making a serious mistake.
The survey indicates that benefit packages for residents have stayed much the same over the past 2 years with health insurance and paid time off for sick leave, vacation, and personal time most commonly reported at 89% and 87%, respectively.
Much less common were benefits including commuter assistance (parking, public transportation) at 24%, housing allowance (8%), and child care (4%).
The vast majority of residents reported doing scut work (unskilled tasks): More than half (54%) reported doing 1-10 hours/week and 22% did 11-20 hours/week. Regardless of the number of hours, however, 62% said the time spent performing these tasks was appropriate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Most residents who were asked whether their training prepared them for COVID-19 in a Medscape survey said it had not or they weren’t sure.
Whereas 40% said they felt prepared, 30% said they did not feel prepared and 31% answered they were unsure. (Numbers were rounded, so some answers pushed above 100%.)
One quarter have $300,000 or more in student debt
The Medscape Residents Salary & Debt Report 2020, with data collected April 3 to June 1, found that nearly one in four residents (24%) had medical school debt of more than $300,000. Half (49%) had more than $200,000.
The data include answers from 1,659 U.S. medical residents.
For the sixth straight year, female residents were more satisfied with their pay than were their male colleagues. This year the satisfaction gap was 45% female compared with 42% male. That imbalance came despite their making nearly the same pay overall ($63,700 for men and $63,000 for women).
Among practicing physicians, the pay gap is much wider: Men make 25% more in primary care and 31% more in specialties.
Ten percent thought they should earn 76%-100% more.
For those not satisfied with pay, the top reasons were feeling the pay was too low for the hours worked (81%) or too low compared with other medical staff, such as physician assistants (PAs) or nurses (77% chose that answer).
As for hours worked, 31% of residents reported they spend more than 60 hours/week seeing patients.
The top-paying specialties, averaging $69,500, were allergy and immunology, hematology, plastic surgery, aesthetic medicine, rheumatology, and specialized surgery. The lowest paid were family medicine residents at $58,500.
In primary care, overall, most residents said they planned to specialize. Only 47% planned to continue to work in primary care. Male residents were much more likely to say they will subspecialize than were their female colleagues (52% vs. 35%).
More than 90% of residents say future pay has influenced their choice of specialty, though more men than women felt that way (93% vs. 86%).
Good relationships with others
Overall, residents reported good relationships with attending physicians and nurses.
Most (88%) said they had good or very good relationships with attending physicians, 10% said the relationships were fair, and 2% said they were poor.
In addition, 89% of residents said the amount of supervision was appropriate, 4% said there was too much, and 7% said there was too little.
Relationships with nurses/PAs were slightly less positive overall: Eighty-two percent reported good or very good relationships with nurses/PAs, 15% said those relationships were fair, and 3% said they were poor.
One respondent said: “Our relationships could be better, but I think everyone is just overwhelmed with COVID-19, so emotions are heightened.”
Another said: “It takes time to earn the respect from nurses.”
Seventy-seven percent said they were satisfied with their learning experience overall, 12% were neutral on the question, and 11% said they were dissatisfied or very dissatisfied.
Work-life balance is the top concern
Work-life balance continues to be the top concern for residents. More than one-quarter (27%) in residency years 1 through 4 listed that as the top concern, and even more (32%) of those in years 5 through 8 agreed.
That was followed by demands on time and fear of failure or making a serious mistake.
The survey indicates that benefit packages for residents have stayed much the same over the past 2 years with health insurance and paid time off for sick leave, vacation, and personal time most commonly reported at 89% and 87%, respectively.
Much less common were benefits including commuter assistance (parking, public transportation) at 24%, housing allowance (8%), and child care (4%).
The vast majority of residents reported doing scut work (unskilled tasks): More than half (54%) reported doing 1-10 hours/week and 22% did 11-20 hours/week. Regardless of the number of hours, however, 62% said the time spent performing these tasks was appropriate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.








