User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Excess deaths jump 23% in U.S. in 2020, mostly because of COVID-19
The United States saw nearly 23% more deaths than expected during the first 9 months of the pandemic, and almost three-quarters of those deaths involved COVID-19.
For comparison, the death rate increased by 2.5% or less annually in recent years.
At the same time, rates of deaths from heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, and diabetes also increased from March 1, 2020, to Jan. 2, 2021, especially during COVID-19 surges.
“Excess deaths surged in the east in April, followed by extended summer and early winter surges concentrated in Southern and Western states, respectively. Many of these states weakly embraced, or discouraged, pandemic control measures and lifted restrictions earlier than other states,” lead author Steven H. Woolf, MD, MPH, from the Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online April 2, 2021, in JAMA.
COVID-19 mortality included all deaths for which it was cited as an underlying or contributing cause in records from the District of Columbia and 49 states. North Carolina was excluded for insufficient data.
More than half a million excess deaths
Between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, the United States experienced 2,801,439 deaths, or 522,368 excess deaths. A total 72.4% of these events were attributed to COVID-19.
Not all racial and ethnic groups were equally represented. For example, the rate of excess deaths was higher among non-Hispanic Black populations, at 208.4 deaths per 100,000. Non-Hispanic White populations experienced 157 deaths per 100,000, and Hispanic populations experienced 139.8 deaths per 100,000.
Further, non-Hispanic Black individuals accounted for 16.9% of the excess deaths but only 12.5% of the U.S. population, which reflects “racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality,” the authors noted.
Not adjusting for population aging is a potential limitation, as was reliance on provisional data and the likelihood that some death certificates were inaccurate.
In February, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden, stated that political divisions likely played a role in the 500,000-plus COVID-19–related deaths in the United States.
Then a report came out on March 26 indicating that a different U.S. response to the pandemic could have avoided almost 400,000 COVID-19 deaths. In addition, an April 1 study in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report revealed that COVID-19 is now the third leading cause of death in the United States, after heart disease and cancer.
‘Massive’ excessive mortality
“There is no more visible or alarming manifestation of the toll of the COVID-19 pandemic than the deaths it has caused. In this issue of JAMA, Dr. Woolf and colleagues provide updated analyses that demonstrate that the excess mortality in the U.S. between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, has been massive,” Alan Garber, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“It seems likely that COVID-19 will have contributed to nearly as many deaths in the U.S. as the great influenza pandemic of 1918, and more than in any influenza outbreak in the U.S. since then,” added Dr. Garber, provost of Harvard University in Cambridge, Mass.
This study of excess mortality illustrates what is at stake, he added. “Despite the scientific, medical and public health progress of recent decades, the loss of life attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic exceeds the mortality of major wars. No nation should squander this opportunity to do what it takes to prepare for the next one.”
Dr. Woolf and Dr. Garber disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The National Institutes of Health supported the research through its National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute on Aging.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States saw nearly 23% more deaths than expected during the first 9 months of the pandemic, and almost three-quarters of those deaths involved COVID-19.
For comparison, the death rate increased by 2.5% or less annually in recent years.
At the same time, rates of deaths from heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, and diabetes also increased from March 1, 2020, to Jan. 2, 2021, especially during COVID-19 surges.
“Excess deaths surged in the east in April, followed by extended summer and early winter surges concentrated in Southern and Western states, respectively. Many of these states weakly embraced, or discouraged, pandemic control measures and lifted restrictions earlier than other states,” lead author Steven H. Woolf, MD, MPH, from the Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online April 2, 2021, in JAMA.
COVID-19 mortality included all deaths for which it was cited as an underlying or contributing cause in records from the District of Columbia and 49 states. North Carolina was excluded for insufficient data.
More than half a million excess deaths
Between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, the United States experienced 2,801,439 deaths, or 522,368 excess deaths. A total 72.4% of these events were attributed to COVID-19.
Not all racial and ethnic groups were equally represented. For example, the rate of excess deaths was higher among non-Hispanic Black populations, at 208.4 deaths per 100,000. Non-Hispanic White populations experienced 157 deaths per 100,000, and Hispanic populations experienced 139.8 deaths per 100,000.
Further, non-Hispanic Black individuals accounted for 16.9% of the excess deaths but only 12.5% of the U.S. population, which reflects “racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality,” the authors noted.
Not adjusting for population aging is a potential limitation, as was reliance on provisional data and the likelihood that some death certificates were inaccurate.
In February, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden, stated that political divisions likely played a role in the 500,000-plus COVID-19–related deaths in the United States.
Then a report came out on March 26 indicating that a different U.S. response to the pandemic could have avoided almost 400,000 COVID-19 deaths. In addition, an April 1 study in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report revealed that COVID-19 is now the third leading cause of death in the United States, after heart disease and cancer.
‘Massive’ excessive mortality
“There is no more visible or alarming manifestation of the toll of the COVID-19 pandemic than the deaths it has caused. In this issue of JAMA, Dr. Woolf and colleagues provide updated analyses that demonstrate that the excess mortality in the U.S. between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, has been massive,” Alan Garber, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“It seems likely that COVID-19 will have contributed to nearly as many deaths in the U.S. as the great influenza pandemic of 1918, and more than in any influenza outbreak in the U.S. since then,” added Dr. Garber, provost of Harvard University in Cambridge, Mass.
This study of excess mortality illustrates what is at stake, he added. “Despite the scientific, medical and public health progress of recent decades, the loss of life attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic exceeds the mortality of major wars. No nation should squander this opportunity to do what it takes to prepare for the next one.”
Dr. Woolf and Dr. Garber disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The National Institutes of Health supported the research through its National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute on Aging.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States saw nearly 23% more deaths than expected during the first 9 months of the pandemic, and almost three-quarters of those deaths involved COVID-19.
For comparison, the death rate increased by 2.5% or less annually in recent years.
At the same time, rates of deaths from heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, and diabetes also increased from March 1, 2020, to Jan. 2, 2021, especially during COVID-19 surges.
“Excess deaths surged in the east in April, followed by extended summer and early winter surges concentrated in Southern and Western states, respectively. Many of these states weakly embraced, or discouraged, pandemic control measures and lifted restrictions earlier than other states,” lead author Steven H. Woolf, MD, MPH, from the Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online April 2, 2021, in JAMA.
COVID-19 mortality included all deaths for which it was cited as an underlying or contributing cause in records from the District of Columbia and 49 states. North Carolina was excluded for insufficient data.
More than half a million excess deaths
Between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, the United States experienced 2,801,439 deaths, or 522,368 excess deaths. A total 72.4% of these events were attributed to COVID-19.
Not all racial and ethnic groups were equally represented. For example, the rate of excess deaths was higher among non-Hispanic Black populations, at 208.4 deaths per 100,000. Non-Hispanic White populations experienced 157 deaths per 100,000, and Hispanic populations experienced 139.8 deaths per 100,000.
Further, non-Hispanic Black individuals accounted for 16.9% of the excess deaths but only 12.5% of the U.S. population, which reflects “racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality,” the authors noted.
Not adjusting for population aging is a potential limitation, as was reliance on provisional data and the likelihood that some death certificates were inaccurate.
In February, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, chief medical adviser to President Joe Biden, stated that political divisions likely played a role in the 500,000-plus COVID-19–related deaths in the United States.
Then a report came out on March 26 indicating that a different U.S. response to the pandemic could have avoided almost 400,000 COVID-19 deaths. In addition, an April 1 study in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report revealed that COVID-19 is now the third leading cause of death in the United States, after heart disease and cancer.
‘Massive’ excessive mortality
“There is no more visible or alarming manifestation of the toll of the COVID-19 pandemic than the deaths it has caused. In this issue of JAMA, Dr. Woolf and colleagues provide updated analyses that demonstrate that the excess mortality in the U.S. between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 2, 2021, has been massive,” Alan Garber, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“It seems likely that COVID-19 will have contributed to nearly as many deaths in the U.S. as the great influenza pandemic of 1918, and more than in any influenza outbreak in the U.S. since then,” added Dr. Garber, provost of Harvard University in Cambridge, Mass.
This study of excess mortality illustrates what is at stake, he added. “Despite the scientific, medical and public health progress of recent decades, the loss of life attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic exceeds the mortality of major wars. No nation should squander this opportunity to do what it takes to prepare for the next one.”
Dr. Woolf and Dr. Garber disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The National Institutes of Health supported the research through its National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute on Aging.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinically important deterioration predicts poor future outcomes in COPD
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
Patients with COPD may benefit from stepped-up treatment of short-term disease progression with triple therapy to stave off longer-term exacerbations and all-cause mortality.
, a study based on data from more than 10,000 patients has shown.
For this study, clinically important deterioration (CID) as a measure of COPD is defined as a combination of change in lung function and/or health status, or a first acute moderate to severe COPD exacerbation, wrote MeiLan K. Han, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
The study was published in ERJ Open Research The investigators analyzed data from the IMPACT trial, a phase III, double-blind, multicenter, 52-week study of symptomatic COPD patients aged 40 years and older.
In the intent-to-treat population, patients with symptomatic COPD and at least one moderate or severe exacerbation in the past year were randomized to a once-daily dose of fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) 100/62.5/25 mcg (4,151 patients); FF/VI 100/25 mcg (4,134 patients); or UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mcg using a single dry-power inhaler (2,070 patients).
The researchers explored both the prognostic value of a CID event on future clinical outcomes and the impact of single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy on reducing CID risk. CID was defined as any of the following: moderate/severe exacerbation; deterioration in lung function (defined as a decrease of 100 mL or more from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume per second); or deterioration in health status based on increases of 4.0 units or more on the St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score or 2.0 units or more on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score.
Overall, patients with a CID by 28 weeks had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, as well as smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52 (P < .001 for all). In addition, CID patients had an increased risk of all-cause mortality after 28 weeks, compared with patients without CID. However, FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk, compared with dual therapies, the researchers noted.
Based on the CID SGRQ definition, patients with CID had a 75% increase in moderate to severe exacerbations by week 28 and a 96% in severe exacerbations over weeks 29-52. The increases were similar using the CID CAT definition (72% and 91%, respectively).
Patients with CID also showed significantly reduced improvements in both lung function and health status after 1 year, and a significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to patients without CID.
In comparing triple vs. double therapies, FF/UMEC/VI patients showed significant reductions in CID risk by 52 weeks, compared with patients treated with FF/VI and UMEC/VI. This difference was true across all subgroups, except for the subgroup of patients who were on long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) therapy prior to screening, the researchers said.
In addition, “treatment effect was greater at higher blood eosinophil counts for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of CID as a primary endpoint, the relatively short 5-month follow-up period, and the use of a symptomatic patient population with an established risk of exacerbation, which could limit generalizability, the researchers noted. However, the findings support the value of preventing short-term CID and adding inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) or bronchodilation for patients in this study population, they said.
Data may help drive tailored treatments
“This study is a post hoc analysis of data from the IMPACT trial, an RCT examining triple therapy vs ICS/LABA vs LABA/LAMA,” Dr. Han, lead and corresponding author, said in an interview. “In this particular paper, we conducted a treatment independent analysis examining individuals who experienced clinically important deteriorations at week 28 and then compared outcomes at week 52 based on CID status at week 28. Patients with a CID by week 28 had significantly increased exacerbation rates after week 28, smaller improvements in lung function and health status at week 52, and increased risk of all-cause mortality after week 28 versus patients who were CID free,” she emphasized. “We also saw that FF/UMEC/VI significantly reduced CID risk versus dual therapies.” These data suggest that shorter-term changes are associated with longer term outcomes, and provide important information both for the purposes of clinical trials design as well as patient clinical assessments, she added.
Dr. Han said she was not surprised by the findings. “I think these results are consistent with prior analyses but suggest that short-term outcomes relate to longer-term ones,” she said. However, she stressed the need for individualized treatment.
“While there are relationships between symptoms, lung function, and exacerbations as demonstrated by these analyses, in any individual patient sometimes these three disease axes do not perfectly align,” she explained. Dr. Han’s main message for clinicians in practice is that optimization of triple therapy in patients with severe disease and high risk for exacerbations was associated not only with short-term improvements in symptoms and lung function, but also with longer-term reductions in exacerbations and mortality.
As for additional research, prospective studies using CID as a primary or secondary outcome would help validate the composite outcome in this study, as regulatory agencies have been slow to adopt composite outcomes, Dr. Han said.
Dr. Han disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, which funded the study, as well as AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sunovion, Mylan, Merck, and Verona.
FROM ERJ OPEN RESEARCH
Technique combines ‘best of both worlds’ to target lung nodules
The technique – bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation – had a 100% technical success rate and produced low rates of complications in a single-center study.
“We combined the best of both worlds [for this] technique,” said investigator Joyce Chan, MBBS, of Prince of Wales Hospital in Hong Kong, when describing the method at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 64MO).
Dr. Chan explained that microwave ablation of lung nodules is faster and produces larger ablation zones, compared with radiofrequency ablation, and bronchoscopic ablation is thought to produce fewer pleural-based complications than percutaneous ablation.
Bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation is performed in a hybrid operating room. First, the patient is intubated and anesthetized. Then, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy is used to zero in on the lung nodule, which is punctured by a microwave catheter. Cone-beam CT is used to confirm the location of the catheter.
“Next, we connect the system externally to a console, and then we just press the button to microwave it, just like what you do to food,” Dr. Chan explained.
Ablation takes about 10 minutes, and another CT is done to assess success. Ground-glass opacities are seen in the ablated area.
Study results
Dr. Chan and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of 36 patients who underwent bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation between March 2019 and December 2020.
The patients were unfit for or unwilling to undergo surgical resection. They had to have stage 1a lung cancers, isolated lung oligometastases, or radiologically suspicious lesions. The nodules had to be less than 3 cm in size, preferably with a bronchus leading directly to the lesion.
The patients had a mean age of 68 years. Their lesions had a mean maximal diameter of 15.2 mm, and 68% were in the peripheral one-third of the lung.
In all, 44 nodules were treated with bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation. The technical success rate was 100%, although eight nodules required double ablation.
The majority of patients (95%) were discharged within 3 days, with 77% discharged on day 1. Complications included mild pain (15.9%), pneumothorax (9.1%), fever/ablation reaction (4.5%), self-limiting hemoptysis (2.3%), and bronchopleural fistula (2.3%).
The ablation zone volume decreased “rapidly” in the first 6-9 months, then leveled off, Dr. Chan noted.
In the 16 nodules with 1 year of follow-up, there were 2 complete responses, 13 partial responses, and no progressions.
It’s too soon to know if the recurrence rate will be lower than the up to 30% recurrence rate with percutaneous microwave ablation, and it’s too soon to know if, without transpleural puncture, the risk of tumor seeding is lower, Dr. Chan said.
“This presentation ... is extremely important,” said invited discussant John Edwards, MBChB, PhD, of Sheffield (England) Teaching Hospitals National Health Service Foundation Trust. “There is a great novelty value in the combination. The complications and the radiologic response rates were quite acceptable.”
The research was funded by the University Grants Committee in Hong Kong. Dr. Chan reported having no disclosures. Her colleagues disclosed relationships with Medtronic, Siemens Healthineers, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Edwards disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Zimmer Biomet, Stryker Leibinger, Pacific Biosciences, BioNano Genomics, Argenx, and Moderna.
The technique – bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation – had a 100% technical success rate and produced low rates of complications in a single-center study.
“We combined the best of both worlds [for this] technique,” said investigator Joyce Chan, MBBS, of Prince of Wales Hospital in Hong Kong, when describing the method at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 64MO).
Dr. Chan explained that microwave ablation of lung nodules is faster and produces larger ablation zones, compared with radiofrequency ablation, and bronchoscopic ablation is thought to produce fewer pleural-based complications than percutaneous ablation.
Bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation is performed in a hybrid operating room. First, the patient is intubated and anesthetized. Then, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy is used to zero in on the lung nodule, which is punctured by a microwave catheter. Cone-beam CT is used to confirm the location of the catheter.
“Next, we connect the system externally to a console, and then we just press the button to microwave it, just like what you do to food,” Dr. Chan explained.
Ablation takes about 10 minutes, and another CT is done to assess success. Ground-glass opacities are seen in the ablated area.
Study results
Dr. Chan and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of 36 patients who underwent bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation between March 2019 and December 2020.
The patients were unfit for or unwilling to undergo surgical resection. They had to have stage 1a lung cancers, isolated lung oligometastases, or radiologically suspicious lesions. The nodules had to be less than 3 cm in size, preferably with a bronchus leading directly to the lesion.
The patients had a mean age of 68 years. Their lesions had a mean maximal diameter of 15.2 mm, and 68% were in the peripheral one-third of the lung.
In all, 44 nodules were treated with bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation. The technical success rate was 100%, although eight nodules required double ablation.
The majority of patients (95%) were discharged within 3 days, with 77% discharged on day 1. Complications included mild pain (15.9%), pneumothorax (9.1%), fever/ablation reaction (4.5%), self-limiting hemoptysis (2.3%), and bronchopleural fistula (2.3%).
The ablation zone volume decreased “rapidly” in the first 6-9 months, then leveled off, Dr. Chan noted.
In the 16 nodules with 1 year of follow-up, there were 2 complete responses, 13 partial responses, and no progressions.
It’s too soon to know if the recurrence rate will be lower than the up to 30% recurrence rate with percutaneous microwave ablation, and it’s too soon to know if, without transpleural puncture, the risk of tumor seeding is lower, Dr. Chan said.
“This presentation ... is extremely important,” said invited discussant John Edwards, MBChB, PhD, of Sheffield (England) Teaching Hospitals National Health Service Foundation Trust. “There is a great novelty value in the combination. The complications and the radiologic response rates were quite acceptable.”
The research was funded by the University Grants Committee in Hong Kong. Dr. Chan reported having no disclosures. Her colleagues disclosed relationships with Medtronic, Siemens Healthineers, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Edwards disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Zimmer Biomet, Stryker Leibinger, Pacific Biosciences, BioNano Genomics, Argenx, and Moderna.
The technique – bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation – had a 100% technical success rate and produced low rates of complications in a single-center study.
“We combined the best of both worlds [for this] technique,” said investigator Joyce Chan, MBBS, of Prince of Wales Hospital in Hong Kong, when describing the method at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 64MO).
Dr. Chan explained that microwave ablation of lung nodules is faster and produces larger ablation zones, compared with radiofrequency ablation, and bronchoscopic ablation is thought to produce fewer pleural-based complications than percutaneous ablation.
Bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation is performed in a hybrid operating room. First, the patient is intubated and anesthetized. Then, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy is used to zero in on the lung nodule, which is punctured by a microwave catheter. Cone-beam CT is used to confirm the location of the catheter.
“Next, we connect the system externally to a console, and then we just press the button to microwave it, just like what you do to food,” Dr. Chan explained.
Ablation takes about 10 minutes, and another CT is done to assess success. Ground-glass opacities are seen in the ablated area.
Study results
Dr. Chan and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of 36 patients who underwent bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation between March 2019 and December 2020.
The patients were unfit for or unwilling to undergo surgical resection. They had to have stage 1a lung cancers, isolated lung oligometastases, or radiologically suspicious lesions. The nodules had to be less than 3 cm in size, preferably with a bronchus leading directly to the lesion.
The patients had a mean age of 68 years. Their lesions had a mean maximal diameter of 15.2 mm, and 68% were in the peripheral one-third of the lung.
In all, 44 nodules were treated with bronchoscopic transbronchial microwave ablation. The technical success rate was 100%, although eight nodules required double ablation.
The majority of patients (95%) were discharged within 3 days, with 77% discharged on day 1. Complications included mild pain (15.9%), pneumothorax (9.1%), fever/ablation reaction (4.5%), self-limiting hemoptysis (2.3%), and bronchopleural fistula (2.3%).
The ablation zone volume decreased “rapidly” in the first 6-9 months, then leveled off, Dr. Chan noted.
In the 16 nodules with 1 year of follow-up, there were 2 complete responses, 13 partial responses, and no progressions.
It’s too soon to know if the recurrence rate will be lower than the up to 30% recurrence rate with percutaneous microwave ablation, and it’s too soon to know if, without transpleural puncture, the risk of tumor seeding is lower, Dr. Chan said.
“This presentation ... is extremely important,” said invited discussant John Edwards, MBChB, PhD, of Sheffield (England) Teaching Hospitals National Health Service Foundation Trust. “There is a great novelty value in the combination. The complications and the radiologic response rates were quite acceptable.”
The research was funded by the University Grants Committee in Hong Kong. Dr. Chan reported having no disclosures. Her colleagues disclosed relationships with Medtronic, Siemens Healthineers, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Edwards disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Zimmer Biomet, Stryker Leibinger, Pacific Biosciences, BioNano Genomics, Argenx, and Moderna.
FROM ELCC 2021
Children likely the ‘leading edge’ in spread of COVID-19 variants
Public health officials in the Midwest and Northeast are sounding the alarm about steep new increases in COVID-19 cases in children.
The increases seem to be driven by greater circulation of more contagious variants, just as children and teens have returned to in-person activities such as sports, parties, and classes.
“I can just tell you from my 46 years in the business, I’ve never seen dynamic transmission in kids like we’re seeing right now, younger kids,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, who directs the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
In earlier surges, children – especially younger children – played only minor roles in transmitting the infection. When they were diagnosed with COVID-19, their symptoms tended to be mild or even absent, and for reasons that aren’t well understood, they haven’t usually been the first cases in households or clusters.
Now, as more SARS-CoV-2 variants have begun to dominate, and seniors gain protection from vaccines, that pattern may be changing. Infectious disease experts are watching to see if COVID-19 will start to spread in a pattern more similar to influenza, with children becoming infected first and bringing the infection home to their parents.
Michigan sees jump in cases
Governors in some hard-hit states are pleading with a pandemic-weary public to keep up mask-wearing and social distancing and avoid unnecessary travel and large gatherings in order to protect in-person classes.
In Michigan, many schools reopened and youth sports resumed just as the more contagious B.1.1.7 variant spread widely. There, cases are rising among all age groups, but the largest number of new COVID-19 cases is among children aged 10-19, the first time that’s happened since the start of the pandemic.
Over the month of March, incidence in this age group had more than doubled in the state. Cases among younger children – infants through 9-year-olds – are also going up, increasing by more than 230% since Feb. 19, according to data from the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
The increases have prompted some schools to pause in-person learning for a time after spring break to slow transmission, according to Natasha Bagdasarian, MD, senior public health physician with the Michigan health department in Ann Arbor.
In Minnesota, on a recent call with reporters, Ruth Lynfield, MD, state epidemiologist, said the B.1.1.7 variant, which has rapidly risen in the state, has a higher attack rate among children than that of earlier versions of the virus, meaning they’re more likely to be infected when exposed.
“We certainly get the sense that youth are what we might refer to as the leading edge of the spread of variants,” she said.
Dr. Lynfield said they were tracking cases spreading through youth sports, classrooms, and daycare centers.
In Massachusetts, the largest number of new COVID-19 infections in the last 2 weeks of March was among children and teens. Massachusetts has the fifth-highest number of recorded B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, according to CDC data.
Although most COVID-19 cases in children and teens are mild, the disease can be severe for those who have underlying medical conditions. Even in healthy children, it can trigger a serious postviral syndrome called MIS-C that requires hospitalization.
Emerging studies show that children, like adults, can develop the lingering symptoms of long COVID-19. Recent data from the United Kingdom show 10%-15% of children younger than 16 infected with COVID-19 still had at least one symptom 5 weeks later.
Dr. Osterholm said it remains to be seen whether more cases in children will also mean a rise in more serious outcomes for children, as it has in Europe and Israel.
In Israel, the B.1.1.7 variant arrived at the end of December and became dominant in January. By the end of January, Hadassah Ein Kerem Medical Center in Jerusalem had four patients in its newly opened pediatric COVID-19 ICU unit. They ranged in age from 13 days to 2 years.
By early February, the Ministry of Health warned the country’s doctors to prepare for an “imminent upward trend” in pediatric COVID-19 cases. They notified hospitals to be ready to open more ICU beds for children with COVID-19, according to Cyrille Cohen, PhD, head of the laboratory of immunotherapy at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel.
On March 31, French President Emmanuel Macron ordered France into its third national lockdown and closed schools for 3 weeks to try to hold off a third wave of COVID-19. President Macron had been a staunch defender of keeping schools open, but said the closure was necessary.
“It is the best solution to slow down the virus,” he said, according to Reuters.
German Chancellor Angela Merkel recently announced a new lockdown for Germany as the spread of the variants has led to rising cases there.
“I think what we’re seeing here is this is going to play out over the country,” said Dr. Osterholm. “Before this time, we didn’t see major transmission in younger kids particularly K through eighth grade, and now we’re seeing that happening with many school outbreaks, particularly in the Northeast and in the Midwest.” He added that it will spread through southern states as well.
Fall surge all over again
“It’s starting to feel an awful lot like déjà vu, where the hospitalization numbers, the positivity rate, all of the metrics that we track are trending up significantly, and it’s feeling like the fall surge,” said Brian Peters, CEO of the Michigan Hospital Association. “It’s feeling in many ways like the initial surge a year ago.”
Mr. Peters said that in January and February, COVID-19 hospitalizations in Michigan were less than 1,000 a day. Recently, he said, there were 2,558 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in Michigan.
About half of adults aged 65 and older have been fully vaccinated in Michigan. That’s led to a dramatic drop in cases and hospitalizations among seniors, who are at highest risk of death. At the same time, Gov. Gretchen Whitmer and health officials with the Biden administration have encouraged schools to reopen for in-person learning, and extracurricular activities have largely resumed.
The same circumstances – students in classrooms, combined with the arrival of the variants – resulted in COVID-19 cases caused by the B.1.1.7 variant increasing among younger age groups in the United Kingdom.
When schools were locked down again, however, cases caused by variant and wild type viruses both dropped in children, suggesting that there wasn’t anything that made B.1.1.7 extra risky for children, but that the strain is more contagious for everyone. Sports, extracurricular activities, and classrooms offered the virus plenty of opportunities to spread.
In Michigan, Dr. Bagdasarian said the outbreaks in children started with winter sports.
“Not necessarily transmission on the field, but we’re really talking about social gatherings that were happening in and around sports,” like the pizza party to celebrate a team win, she said, “and I think those social gatherings were a big driver.”
“Outbreaks are trickling over into teams and trickling over into schools, which is exactly what we want to avoid,” she added.
Thus far, Michigan has been reserving vaccine doses for older adults but will open eligibility to anyone age 16 and older starting on April 6.
Until younger age groups can be vaccinated, Mr. Peters said people need to continue to be careful.
“We see people letting their guard down and it’s to be expected,” Mr. Peters said. “People have COVID fatigue, and they are eager to get together with their friends. We’re not out of the woods yet.”
Children ‘heavily impacted’
In Nebraska, Alice Sato, MD, PhD, hospital epidemiologist at Children’s Hospital and Medical Center in Omaha, said they saw an increase in MIS-C cases after the winter surges, and she’s watching the data carefully as COVID-19 cases tick up in other midwestern states.
Dr. Sato got so tired of hearing people compare COVID-19 to the flu that she pulled some numbers on pediatric deaths.
While COVID-19 fatality rates in children are much lower than they are for adults, at least 279 children have died across the United States since the start of the pandemic. The highest number of confirmed pediatric deaths recorded during any of the previous 10 flu seasons was 188, according to the CDC.
“So while children are relatively spared, they’re still heavily impacted,” said Dr. Sato.
She was thrilled to hear the recent news that the Pfizer vaccine works well in children aged 12-15, but because Pfizer’s cold-chain requirements make it one the trickiest to store, the Food and Drug Administration hasn’t given the go-ahead yet. She said it will be months before she has any to offer to teens in her state.
In the meantime, genetic testing has shown that the variants are already circulating there.
“We really want parents and family members who are eligible to be vaccinated because that is a great way to protect children that I cannot vaccinate yet,” Dr. Sato said. “The best way for me to protect children is to prevent the adults around them from being infected.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Public health officials in the Midwest and Northeast are sounding the alarm about steep new increases in COVID-19 cases in children.
The increases seem to be driven by greater circulation of more contagious variants, just as children and teens have returned to in-person activities such as sports, parties, and classes.
“I can just tell you from my 46 years in the business, I’ve never seen dynamic transmission in kids like we’re seeing right now, younger kids,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, who directs the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
In earlier surges, children – especially younger children – played only minor roles in transmitting the infection. When they were diagnosed with COVID-19, their symptoms tended to be mild or even absent, and for reasons that aren’t well understood, they haven’t usually been the first cases in households or clusters.
Now, as more SARS-CoV-2 variants have begun to dominate, and seniors gain protection from vaccines, that pattern may be changing. Infectious disease experts are watching to see if COVID-19 will start to spread in a pattern more similar to influenza, with children becoming infected first and bringing the infection home to their parents.
Michigan sees jump in cases
Governors in some hard-hit states are pleading with a pandemic-weary public to keep up mask-wearing and social distancing and avoid unnecessary travel and large gatherings in order to protect in-person classes.
In Michigan, many schools reopened and youth sports resumed just as the more contagious B.1.1.7 variant spread widely. There, cases are rising among all age groups, but the largest number of new COVID-19 cases is among children aged 10-19, the first time that’s happened since the start of the pandemic.
Over the month of March, incidence in this age group had more than doubled in the state. Cases among younger children – infants through 9-year-olds – are also going up, increasing by more than 230% since Feb. 19, according to data from the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
The increases have prompted some schools to pause in-person learning for a time after spring break to slow transmission, according to Natasha Bagdasarian, MD, senior public health physician with the Michigan health department in Ann Arbor.
In Minnesota, on a recent call with reporters, Ruth Lynfield, MD, state epidemiologist, said the B.1.1.7 variant, which has rapidly risen in the state, has a higher attack rate among children than that of earlier versions of the virus, meaning they’re more likely to be infected when exposed.
“We certainly get the sense that youth are what we might refer to as the leading edge of the spread of variants,” she said.
Dr. Lynfield said they were tracking cases spreading through youth sports, classrooms, and daycare centers.
In Massachusetts, the largest number of new COVID-19 infections in the last 2 weeks of March was among children and teens. Massachusetts has the fifth-highest number of recorded B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, according to CDC data.
Although most COVID-19 cases in children and teens are mild, the disease can be severe for those who have underlying medical conditions. Even in healthy children, it can trigger a serious postviral syndrome called MIS-C that requires hospitalization.
Emerging studies show that children, like adults, can develop the lingering symptoms of long COVID-19. Recent data from the United Kingdom show 10%-15% of children younger than 16 infected with COVID-19 still had at least one symptom 5 weeks later.
Dr. Osterholm said it remains to be seen whether more cases in children will also mean a rise in more serious outcomes for children, as it has in Europe and Israel.
In Israel, the B.1.1.7 variant arrived at the end of December and became dominant in January. By the end of January, Hadassah Ein Kerem Medical Center in Jerusalem had four patients in its newly opened pediatric COVID-19 ICU unit. They ranged in age from 13 days to 2 years.
By early February, the Ministry of Health warned the country’s doctors to prepare for an “imminent upward trend” in pediatric COVID-19 cases. They notified hospitals to be ready to open more ICU beds for children with COVID-19, according to Cyrille Cohen, PhD, head of the laboratory of immunotherapy at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel.
On March 31, French President Emmanuel Macron ordered France into its third national lockdown and closed schools for 3 weeks to try to hold off a third wave of COVID-19. President Macron had been a staunch defender of keeping schools open, but said the closure was necessary.
“It is the best solution to slow down the virus,” he said, according to Reuters.
German Chancellor Angela Merkel recently announced a new lockdown for Germany as the spread of the variants has led to rising cases there.
“I think what we’re seeing here is this is going to play out over the country,” said Dr. Osterholm. “Before this time, we didn’t see major transmission in younger kids particularly K through eighth grade, and now we’re seeing that happening with many school outbreaks, particularly in the Northeast and in the Midwest.” He added that it will spread through southern states as well.
Fall surge all over again
“It’s starting to feel an awful lot like déjà vu, where the hospitalization numbers, the positivity rate, all of the metrics that we track are trending up significantly, and it’s feeling like the fall surge,” said Brian Peters, CEO of the Michigan Hospital Association. “It’s feeling in many ways like the initial surge a year ago.”
Mr. Peters said that in January and February, COVID-19 hospitalizations in Michigan were less than 1,000 a day. Recently, he said, there were 2,558 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in Michigan.
About half of adults aged 65 and older have been fully vaccinated in Michigan. That’s led to a dramatic drop in cases and hospitalizations among seniors, who are at highest risk of death. At the same time, Gov. Gretchen Whitmer and health officials with the Biden administration have encouraged schools to reopen for in-person learning, and extracurricular activities have largely resumed.
The same circumstances – students in classrooms, combined with the arrival of the variants – resulted in COVID-19 cases caused by the B.1.1.7 variant increasing among younger age groups in the United Kingdom.
When schools were locked down again, however, cases caused by variant and wild type viruses both dropped in children, suggesting that there wasn’t anything that made B.1.1.7 extra risky for children, but that the strain is more contagious for everyone. Sports, extracurricular activities, and classrooms offered the virus plenty of opportunities to spread.
In Michigan, Dr. Bagdasarian said the outbreaks in children started with winter sports.
“Not necessarily transmission on the field, but we’re really talking about social gatherings that were happening in and around sports,” like the pizza party to celebrate a team win, she said, “and I think those social gatherings were a big driver.”
“Outbreaks are trickling over into teams and trickling over into schools, which is exactly what we want to avoid,” she added.
Thus far, Michigan has been reserving vaccine doses for older adults but will open eligibility to anyone age 16 and older starting on April 6.
Until younger age groups can be vaccinated, Mr. Peters said people need to continue to be careful.
“We see people letting their guard down and it’s to be expected,” Mr. Peters said. “People have COVID fatigue, and they are eager to get together with their friends. We’re not out of the woods yet.”
Children ‘heavily impacted’
In Nebraska, Alice Sato, MD, PhD, hospital epidemiologist at Children’s Hospital and Medical Center in Omaha, said they saw an increase in MIS-C cases after the winter surges, and she’s watching the data carefully as COVID-19 cases tick up in other midwestern states.
Dr. Sato got so tired of hearing people compare COVID-19 to the flu that she pulled some numbers on pediatric deaths.
While COVID-19 fatality rates in children are much lower than they are for adults, at least 279 children have died across the United States since the start of the pandemic. The highest number of confirmed pediatric deaths recorded during any of the previous 10 flu seasons was 188, according to the CDC.
“So while children are relatively spared, they’re still heavily impacted,” said Dr. Sato.
She was thrilled to hear the recent news that the Pfizer vaccine works well in children aged 12-15, but because Pfizer’s cold-chain requirements make it one the trickiest to store, the Food and Drug Administration hasn’t given the go-ahead yet. She said it will be months before she has any to offer to teens in her state.
In the meantime, genetic testing has shown that the variants are already circulating there.
“We really want parents and family members who are eligible to be vaccinated because that is a great way to protect children that I cannot vaccinate yet,” Dr. Sato said. “The best way for me to protect children is to prevent the adults around them from being infected.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Public health officials in the Midwest and Northeast are sounding the alarm about steep new increases in COVID-19 cases in children.
The increases seem to be driven by greater circulation of more contagious variants, just as children and teens have returned to in-person activities such as sports, parties, and classes.
“I can just tell you from my 46 years in the business, I’ve never seen dynamic transmission in kids like we’re seeing right now, younger kids,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, who directs the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
In earlier surges, children – especially younger children – played only minor roles in transmitting the infection. When they were diagnosed with COVID-19, their symptoms tended to be mild or even absent, and for reasons that aren’t well understood, they haven’t usually been the first cases in households or clusters.
Now, as more SARS-CoV-2 variants have begun to dominate, and seniors gain protection from vaccines, that pattern may be changing. Infectious disease experts are watching to see if COVID-19 will start to spread in a pattern more similar to influenza, with children becoming infected first and bringing the infection home to their parents.
Michigan sees jump in cases
Governors in some hard-hit states are pleading with a pandemic-weary public to keep up mask-wearing and social distancing and avoid unnecessary travel and large gatherings in order to protect in-person classes.
In Michigan, many schools reopened and youth sports resumed just as the more contagious B.1.1.7 variant spread widely. There, cases are rising among all age groups, but the largest number of new COVID-19 cases is among children aged 10-19, the first time that’s happened since the start of the pandemic.
Over the month of March, incidence in this age group had more than doubled in the state. Cases among younger children – infants through 9-year-olds – are also going up, increasing by more than 230% since Feb. 19, according to data from the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
The increases have prompted some schools to pause in-person learning for a time after spring break to slow transmission, according to Natasha Bagdasarian, MD, senior public health physician with the Michigan health department in Ann Arbor.
In Minnesota, on a recent call with reporters, Ruth Lynfield, MD, state epidemiologist, said the B.1.1.7 variant, which has rapidly risen in the state, has a higher attack rate among children than that of earlier versions of the virus, meaning they’re more likely to be infected when exposed.
“We certainly get the sense that youth are what we might refer to as the leading edge of the spread of variants,” she said.
Dr. Lynfield said they were tracking cases spreading through youth sports, classrooms, and daycare centers.
In Massachusetts, the largest number of new COVID-19 infections in the last 2 weeks of March was among children and teens. Massachusetts has the fifth-highest number of recorded B.1.1.7 cases in the United States, according to CDC data.
Although most COVID-19 cases in children and teens are mild, the disease can be severe for those who have underlying medical conditions. Even in healthy children, it can trigger a serious postviral syndrome called MIS-C that requires hospitalization.
Emerging studies show that children, like adults, can develop the lingering symptoms of long COVID-19. Recent data from the United Kingdom show 10%-15% of children younger than 16 infected with COVID-19 still had at least one symptom 5 weeks later.
Dr. Osterholm said it remains to be seen whether more cases in children will also mean a rise in more serious outcomes for children, as it has in Europe and Israel.
In Israel, the B.1.1.7 variant arrived at the end of December and became dominant in January. By the end of January, Hadassah Ein Kerem Medical Center in Jerusalem had four patients in its newly opened pediatric COVID-19 ICU unit. They ranged in age from 13 days to 2 years.
By early February, the Ministry of Health warned the country’s doctors to prepare for an “imminent upward trend” in pediatric COVID-19 cases. They notified hospitals to be ready to open more ICU beds for children with COVID-19, according to Cyrille Cohen, PhD, head of the laboratory of immunotherapy at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel.
On March 31, French President Emmanuel Macron ordered France into its third national lockdown and closed schools for 3 weeks to try to hold off a third wave of COVID-19. President Macron had been a staunch defender of keeping schools open, but said the closure was necessary.
“It is the best solution to slow down the virus,” he said, according to Reuters.
German Chancellor Angela Merkel recently announced a new lockdown for Germany as the spread of the variants has led to rising cases there.
“I think what we’re seeing here is this is going to play out over the country,” said Dr. Osterholm. “Before this time, we didn’t see major transmission in younger kids particularly K through eighth grade, and now we’re seeing that happening with many school outbreaks, particularly in the Northeast and in the Midwest.” He added that it will spread through southern states as well.
Fall surge all over again
“It’s starting to feel an awful lot like déjà vu, where the hospitalization numbers, the positivity rate, all of the metrics that we track are trending up significantly, and it’s feeling like the fall surge,” said Brian Peters, CEO of the Michigan Hospital Association. “It’s feeling in many ways like the initial surge a year ago.”
Mr. Peters said that in January and February, COVID-19 hospitalizations in Michigan were less than 1,000 a day. Recently, he said, there were 2,558 people hospitalized with COVID-19 in Michigan.
About half of adults aged 65 and older have been fully vaccinated in Michigan. That’s led to a dramatic drop in cases and hospitalizations among seniors, who are at highest risk of death. At the same time, Gov. Gretchen Whitmer and health officials with the Biden administration have encouraged schools to reopen for in-person learning, and extracurricular activities have largely resumed.
The same circumstances – students in classrooms, combined with the arrival of the variants – resulted in COVID-19 cases caused by the B.1.1.7 variant increasing among younger age groups in the United Kingdom.
When schools were locked down again, however, cases caused by variant and wild type viruses both dropped in children, suggesting that there wasn’t anything that made B.1.1.7 extra risky for children, but that the strain is more contagious for everyone. Sports, extracurricular activities, and classrooms offered the virus plenty of opportunities to spread.
In Michigan, Dr. Bagdasarian said the outbreaks in children started with winter sports.
“Not necessarily transmission on the field, but we’re really talking about social gatherings that were happening in and around sports,” like the pizza party to celebrate a team win, she said, “and I think those social gatherings were a big driver.”
“Outbreaks are trickling over into teams and trickling over into schools, which is exactly what we want to avoid,” she added.
Thus far, Michigan has been reserving vaccine doses for older adults but will open eligibility to anyone age 16 and older starting on April 6.
Until younger age groups can be vaccinated, Mr. Peters said people need to continue to be careful.
“We see people letting their guard down and it’s to be expected,” Mr. Peters said. “People have COVID fatigue, and they are eager to get together with their friends. We’re not out of the woods yet.”
Children ‘heavily impacted’
In Nebraska, Alice Sato, MD, PhD, hospital epidemiologist at Children’s Hospital and Medical Center in Omaha, said they saw an increase in MIS-C cases after the winter surges, and she’s watching the data carefully as COVID-19 cases tick up in other midwestern states.
Dr. Sato got so tired of hearing people compare COVID-19 to the flu that she pulled some numbers on pediatric deaths.
While COVID-19 fatality rates in children are much lower than they are for adults, at least 279 children have died across the United States since the start of the pandemic. The highest number of confirmed pediatric deaths recorded during any of the previous 10 flu seasons was 188, according to the CDC.
“So while children are relatively spared, they’re still heavily impacted,” said Dr. Sato.
She was thrilled to hear the recent news that the Pfizer vaccine works well in children aged 12-15, but because Pfizer’s cold-chain requirements make it one the trickiest to store, the Food and Drug Administration hasn’t given the go-ahead yet. She said it will be months before she has any to offer to teens in her state.
In the meantime, genetic testing has shown that the variants are already circulating there.
“We really want parents and family members who are eligible to be vaccinated because that is a great way to protect children that I cannot vaccinate yet,” Dr. Sato said. “The best way for me to protect children is to prevent the adults around them from being infected.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AstraZeneca COVID vaccine: Clotting disorder mechanism revealed?
The European Medicines Agency continues to reassure the public about the safety of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, although several countries have imposed new restrictions on the product, owing to its link to a rare clotting disorder.
Use of the vaccine has been suspended for individuals younger than 55 or 60 years in several European countries and in Canada after reports of a prothrombotic disorder and thrombocytopenia, mainly in younger individuals.
Now, more information on the prothrombotic disorder has become available. The vaccine appears to be linked to a condition that clinically resembles heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and that occurs mainly in younger women.
Researchers have described clinical and laboratory details of nine patients from Germany and Austria who developed this condition 4-16 days after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine in a preprint article published March 28, 2021, on Research Square.
They found that serum from four patients who were tested showed platelet-activating antibodies directed against platelet factor 4 (PF4), similar to what is seen in HIT.
They are proposing naming the condition “vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT)” to avoid confusion with HIT.
At a press conference March 31, the EMA said its ongoing review of the situation “has not identified any specific risk factors, such as age, gender, or a previous medical history of clotting disorders, for these very rare events. A causal link with the vaccine is not proven but is possible, and further analysis is continuing.”
A statement from the agency noted: “EMA is of the view that the benefits of the AstraZeneca vaccine in preventing COVID-19, with its associated risk of hospitalization and death, outweigh the risks of side effects.”
But it added: “Vaccinated people should be aware of the remote possibility of these very rare types of blood clots occurring. If they have symptoms suggestive of clotting problems as described in the product information, they should seek immediate medical attention and inform health care professionals of their recent vaccination.”
VIPIT study
In the Research Square preprint article, a group led by Andreas Greinacher, MD, professor of transfusion medicine at the Greifswald (Germany) University Clinic, reported on clinical and laboratory features of nine patients (eight of whom were women) in Germany and Austria who developed thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after they received the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The researchers explained that they investigated whether these patients could have a prothrombotic disorder caused by platelet-activating antibodies directed against PF4, which is known to be caused by heparin and sometimes environmental triggers.
The nine patients were aged 22-49 years and presented with thrombosis beginning 4-16 days post vaccination. Seven patients had cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), one had pulmonary embolism, and one had splanchnic vein thrombosis and CVT. Four patients died. None had received heparin prior to symptom onset.
Serum from four patients was tested for anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, and all four tested strongly positive. All four also tested strongly positive on platelet activation assay for the presence of PF4 independently of heparin.
The authors noted that it has been recognized that triggers other than heparin, including some infections, can rarely cause a disorder that strongly resembles HIT. These cases have been referred to as spontaneous HIT syndrome.
They said that their current findings have several important clinical implications.
“Clinicians should be aware that onset of (venous or arterial) thrombosis particularly at unusual sites such as in the brain or abdomen and thrombocytopenia beginning approximately 5-14 days after vaccination can represent a rare adverse effect of preceding COVID-19 vaccination,” they wrote. To date, this has only been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They pointed out that enzyme immunoassays for HIT are widely available and can be used to investigate for potential postvaccination anti-PF4 antibody–associated thrombocytopenia/thrombosis. For such patients, referral should be made to a laboratory that performs platelet-activation assays.
Although this syndrome differs from typical HIT, the researchers noted that at least one patient showed strong platelet activation in the presence of heparin. They thus recommended therapy with nonheparin anticoagulants, such as the direct oral anticoagulants.
They also wrote that high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to be effective for treating severe HIT and could also be an important treatment adjunct for patients who develop life-threatening thrombotic events, such as cerebral vein sinus thrombosis (CVST), after being vaccinated.
EMA data to date
Updated data, reported at the EMA press briefing on March 31, indicate that 62 cases of CVST have been reported worldwide (44 from the European Union). These data may not yet include all the German cases.
Peter Arlett, MD, head of pharmacovigilance and epidemiology at the EMA, said there were more cases than expected in the 2-week window after vaccination among patients younger than 60 and that health care professionals should be alert to features of this condition, including headache and blurred vision.
He suggested that the higher rate of the condition among younger women may reflect the population that received this vaccine, because initially, the vaccine was not recommended for older people in many countries and was targeted toward younger health care workers, who were mainly women.
The German regulatory agency, the Paul Ehrlich Institute, reported this week that it has now registered 31 cases of CVST among nearly 2.7 million people who had received the vaccine in Germany. Of these patients, 19 also were found to have a deficiency of blood platelets or thrombocytopenia. Nine of the affected patients died. All but two of the cases occurred in women aged 20-63 years. The two men were aged 36 and 57 years.
These data have prompted the German authorities to limit use of the AstraZeneca vaccine to those aged 60 years and older. Even before this decision, senior clinicians in Germany had been urging a change in the vaccination recommendations.
For example, Bernd Salzberger, MD, head of infectious diseases, University Hospital Regensburg (Germany), told the Science Media Center: “In women, a complicated course of COVID disease is less common from the start and is so rare in younger women that the chance of avoiding a fatal course through vaccination in women without comorbidities is of the same order of magnitude as the risk of this rare side effect.”
Sandra Ciesek, MD, a virologist at Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany, told the journal Science: “The argument I keep hearing is that the risk-benefit ratio is still positive. But we do not have just one vaccine, we have several. So, restricting the AstraZeneca vaccine to older people makes sense to me, and it does not waste any doses.”
Concerns put in perspective
Commenting of the latest developments, thrombosis expert Saskia Middeldorp, MD, head of internal medicine at Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said it was vitally important that these concerns be put in perspective and that the vaccination program with the AstraZeneca product continue.
“There are some concerning reports about very rare blood clotting disorders and low platelet counts possibly associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine. Groups from Germany and Norway have identified a syndrome similar to HIT, which seems to explain the cause of this very rare side effect,” Dr. Middeldorp noted.
“But with such a high pressure from the virus and many countries now going into a third wave of infection, anything that might slow down vaccination rates will cause much more harm than good,” she warned.
Dr. Middeldorp believes the incidence of this HIT-type syndrome linked to the vaccine is about 1-2 per million. “These are estimates based on the number of reports of this side effect and denominators from the U.K. and EU populations,” she explained. However, Germany has restricted the vaccine on the basis of German data, which appear to show higher rates of the condition. It is not known why the rates are higher in Germany.
“The European Medicines Agency is looking at this very closely. Their statement is quite clear. There is no foundation for changing policy on vaccination,” Dr. Middeldorp stated.
She cautioned that these reports were reducing confidence in the AstraZeneca vaccine, particularly among young people, which she said was causing “a major setback” for the vaccination program.
Noting that everything must be viewed in the context of this severe pandemic, Dr. Middeldorp emphasized that the benefit of the vaccine outweighed any risk, even among young people.
“To those who may be hesitating to have the vaccine as they don’t think they are at high risk of severe COVID infection, I would say there are a lot of young people in the ICU at present with COVID, and your chance of a severe COVID illness is far higher than the 1 or 2 in a million risk of a severe reaction to the vaccine,” she stated.
Dr. Greinacher has received grants and nonfinancial support from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Paringenix, Bayer Healthcare, Gore, Rovi, Sagent, and Biomarin/Prosensa; personal fees from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Macopharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chromatec, and Instrumentation Laboratory; and nonfinancial support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Portola, Ergomed, and GTH outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The European Medicines Agency continues to reassure the public about the safety of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, although several countries have imposed new restrictions on the product, owing to its link to a rare clotting disorder.
Use of the vaccine has been suspended for individuals younger than 55 or 60 years in several European countries and in Canada after reports of a prothrombotic disorder and thrombocytopenia, mainly in younger individuals.
Now, more information on the prothrombotic disorder has become available. The vaccine appears to be linked to a condition that clinically resembles heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and that occurs mainly in younger women.
Researchers have described clinical and laboratory details of nine patients from Germany and Austria who developed this condition 4-16 days after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine in a preprint article published March 28, 2021, on Research Square.
They found that serum from four patients who were tested showed platelet-activating antibodies directed against platelet factor 4 (PF4), similar to what is seen in HIT.
They are proposing naming the condition “vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT)” to avoid confusion with HIT.
At a press conference March 31, the EMA said its ongoing review of the situation “has not identified any specific risk factors, such as age, gender, or a previous medical history of clotting disorders, for these very rare events. A causal link with the vaccine is not proven but is possible, and further analysis is continuing.”
A statement from the agency noted: “EMA is of the view that the benefits of the AstraZeneca vaccine in preventing COVID-19, with its associated risk of hospitalization and death, outweigh the risks of side effects.”
But it added: “Vaccinated people should be aware of the remote possibility of these very rare types of blood clots occurring. If they have symptoms suggestive of clotting problems as described in the product information, they should seek immediate medical attention and inform health care professionals of their recent vaccination.”
VIPIT study
In the Research Square preprint article, a group led by Andreas Greinacher, MD, professor of transfusion medicine at the Greifswald (Germany) University Clinic, reported on clinical and laboratory features of nine patients (eight of whom were women) in Germany and Austria who developed thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after they received the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The researchers explained that they investigated whether these patients could have a prothrombotic disorder caused by platelet-activating antibodies directed against PF4, which is known to be caused by heparin and sometimes environmental triggers.
The nine patients were aged 22-49 years and presented with thrombosis beginning 4-16 days post vaccination. Seven patients had cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), one had pulmonary embolism, and one had splanchnic vein thrombosis and CVT. Four patients died. None had received heparin prior to symptom onset.
Serum from four patients was tested for anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, and all four tested strongly positive. All four also tested strongly positive on platelet activation assay for the presence of PF4 independently of heparin.
The authors noted that it has been recognized that triggers other than heparin, including some infections, can rarely cause a disorder that strongly resembles HIT. These cases have been referred to as spontaneous HIT syndrome.
They said that their current findings have several important clinical implications.
“Clinicians should be aware that onset of (venous or arterial) thrombosis particularly at unusual sites such as in the brain or abdomen and thrombocytopenia beginning approximately 5-14 days after vaccination can represent a rare adverse effect of preceding COVID-19 vaccination,” they wrote. To date, this has only been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They pointed out that enzyme immunoassays for HIT are widely available and can be used to investigate for potential postvaccination anti-PF4 antibody–associated thrombocytopenia/thrombosis. For such patients, referral should be made to a laboratory that performs platelet-activation assays.
Although this syndrome differs from typical HIT, the researchers noted that at least one patient showed strong platelet activation in the presence of heparin. They thus recommended therapy with nonheparin anticoagulants, such as the direct oral anticoagulants.
They also wrote that high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to be effective for treating severe HIT and could also be an important treatment adjunct for patients who develop life-threatening thrombotic events, such as cerebral vein sinus thrombosis (CVST), after being vaccinated.
EMA data to date
Updated data, reported at the EMA press briefing on March 31, indicate that 62 cases of CVST have been reported worldwide (44 from the European Union). These data may not yet include all the German cases.
Peter Arlett, MD, head of pharmacovigilance and epidemiology at the EMA, said there were more cases than expected in the 2-week window after vaccination among patients younger than 60 and that health care professionals should be alert to features of this condition, including headache and blurred vision.
He suggested that the higher rate of the condition among younger women may reflect the population that received this vaccine, because initially, the vaccine was not recommended for older people in many countries and was targeted toward younger health care workers, who were mainly women.
The German regulatory agency, the Paul Ehrlich Institute, reported this week that it has now registered 31 cases of CVST among nearly 2.7 million people who had received the vaccine in Germany. Of these patients, 19 also were found to have a deficiency of blood platelets or thrombocytopenia. Nine of the affected patients died. All but two of the cases occurred in women aged 20-63 years. The two men were aged 36 and 57 years.
These data have prompted the German authorities to limit use of the AstraZeneca vaccine to those aged 60 years and older. Even before this decision, senior clinicians in Germany had been urging a change in the vaccination recommendations.
For example, Bernd Salzberger, MD, head of infectious diseases, University Hospital Regensburg (Germany), told the Science Media Center: “In women, a complicated course of COVID disease is less common from the start and is so rare in younger women that the chance of avoiding a fatal course through vaccination in women without comorbidities is of the same order of magnitude as the risk of this rare side effect.”
Sandra Ciesek, MD, a virologist at Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany, told the journal Science: “The argument I keep hearing is that the risk-benefit ratio is still positive. But we do not have just one vaccine, we have several. So, restricting the AstraZeneca vaccine to older people makes sense to me, and it does not waste any doses.”
Concerns put in perspective
Commenting of the latest developments, thrombosis expert Saskia Middeldorp, MD, head of internal medicine at Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said it was vitally important that these concerns be put in perspective and that the vaccination program with the AstraZeneca product continue.
“There are some concerning reports about very rare blood clotting disorders and low platelet counts possibly associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine. Groups from Germany and Norway have identified a syndrome similar to HIT, which seems to explain the cause of this very rare side effect,” Dr. Middeldorp noted.
“But with such a high pressure from the virus and many countries now going into a third wave of infection, anything that might slow down vaccination rates will cause much more harm than good,” she warned.
Dr. Middeldorp believes the incidence of this HIT-type syndrome linked to the vaccine is about 1-2 per million. “These are estimates based on the number of reports of this side effect and denominators from the U.K. and EU populations,” she explained. However, Germany has restricted the vaccine on the basis of German data, which appear to show higher rates of the condition. It is not known why the rates are higher in Germany.
“The European Medicines Agency is looking at this very closely. Their statement is quite clear. There is no foundation for changing policy on vaccination,” Dr. Middeldorp stated.
She cautioned that these reports were reducing confidence in the AstraZeneca vaccine, particularly among young people, which she said was causing “a major setback” for the vaccination program.
Noting that everything must be viewed in the context of this severe pandemic, Dr. Middeldorp emphasized that the benefit of the vaccine outweighed any risk, even among young people.
“To those who may be hesitating to have the vaccine as they don’t think they are at high risk of severe COVID infection, I would say there are a lot of young people in the ICU at present with COVID, and your chance of a severe COVID illness is far higher than the 1 or 2 in a million risk of a severe reaction to the vaccine,” she stated.
Dr. Greinacher has received grants and nonfinancial support from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Paringenix, Bayer Healthcare, Gore, Rovi, Sagent, and Biomarin/Prosensa; personal fees from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Macopharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chromatec, and Instrumentation Laboratory; and nonfinancial support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Portola, Ergomed, and GTH outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The European Medicines Agency continues to reassure the public about the safety of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, although several countries have imposed new restrictions on the product, owing to its link to a rare clotting disorder.
Use of the vaccine has been suspended for individuals younger than 55 or 60 years in several European countries and in Canada after reports of a prothrombotic disorder and thrombocytopenia, mainly in younger individuals.
Now, more information on the prothrombotic disorder has become available. The vaccine appears to be linked to a condition that clinically resembles heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and that occurs mainly in younger women.
Researchers have described clinical and laboratory details of nine patients from Germany and Austria who developed this condition 4-16 days after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine in a preprint article published March 28, 2021, on Research Square.
They found that serum from four patients who were tested showed platelet-activating antibodies directed against platelet factor 4 (PF4), similar to what is seen in HIT.
They are proposing naming the condition “vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT)” to avoid confusion with HIT.
At a press conference March 31, the EMA said its ongoing review of the situation “has not identified any specific risk factors, such as age, gender, or a previous medical history of clotting disorders, for these very rare events. A causal link with the vaccine is not proven but is possible, and further analysis is continuing.”
A statement from the agency noted: “EMA is of the view that the benefits of the AstraZeneca vaccine in preventing COVID-19, with its associated risk of hospitalization and death, outweigh the risks of side effects.”
But it added: “Vaccinated people should be aware of the remote possibility of these very rare types of blood clots occurring. If they have symptoms suggestive of clotting problems as described in the product information, they should seek immediate medical attention and inform health care professionals of their recent vaccination.”
VIPIT study
In the Research Square preprint article, a group led by Andreas Greinacher, MD, professor of transfusion medicine at the Greifswald (Germany) University Clinic, reported on clinical and laboratory features of nine patients (eight of whom were women) in Germany and Austria who developed thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after they received the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The researchers explained that they investigated whether these patients could have a prothrombotic disorder caused by platelet-activating antibodies directed against PF4, which is known to be caused by heparin and sometimes environmental triggers.
The nine patients were aged 22-49 years and presented with thrombosis beginning 4-16 days post vaccination. Seven patients had cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), one had pulmonary embolism, and one had splanchnic vein thrombosis and CVT. Four patients died. None had received heparin prior to symptom onset.
Serum from four patients was tested for anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, and all four tested strongly positive. All four also tested strongly positive on platelet activation assay for the presence of PF4 independently of heparin.
The authors noted that it has been recognized that triggers other than heparin, including some infections, can rarely cause a disorder that strongly resembles HIT. These cases have been referred to as spontaneous HIT syndrome.
They said that their current findings have several important clinical implications.
“Clinicians should be aware that onset of (venous or arterial) thrombosis particularly at unusual sites such as in the brain or abdomen and thrombocytopenia beginning approximately 5-14 days after vaccination can represent a rare adverse effect of preceding COVID-19 vaccination,” they wrote. To date, this has only been reported with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They pointed out that enzyme immunoassays for HIT are widely available and can be used to investigate for potential postvaccination anti-PF4 antibody–associated thrombocytopenia/thrombosis. For such patients, referral should be made to a laboratory that performs platelet-activation assays.
Although this syndrome differs from typical HIT, the researchers noted that at least one patient showed strong platelet activation in the presence of heparin. They thus recommended therapy with nonheparin anticoagulants, such as the direct oral anticoagulants.
They also wrote that high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to be effective for treating severe HIT and could also be an important treatment adjunct for patients who develop life-threatening thrombotic events, such as cerebral vein sinus thrombosis (CVST), after being vaccinated.
EMA data to date
Updated data, reported at the EMA press briefing on March 31, indicate that 62 cases of CVST have been reported worldwide (44 from the European Union). These data may not yet include all the German cases.
Peter Arlett, MD, head of pharmacovigilance and epidemiology at the EMA, said there were more cases than expected in the 2-week window after vaccination among patients younger than 60 and that health care professionals should be alert to features of this condition, including headache and blurred vision.
He suggested that the higher rate of the condition among younger women may reflect the population that received this vaccine, because initially, the vaccine was not recommended for older people in many countries and was targeted toward younger health care workers, who were mainly women.
The German regulatory agency, the Paul Ehrlich Institute, reported this week that it has now registered 31 cases of CVST among nearly 2.7 million people who had received the vaccine in Germany. Of these patients, 19 also were found to have a deficiency of blood platelets or thrombocytopenia. Nine of the affected patients died. All but two of the cases occurred in women aged 20-63 years. The two men were aged 36 and 57 years.
These data have prompted the German authorities to limit use of the AstraZeneca vaccine to those aged 60 years and older. Even before this decision, senior clinicians in Germany had been urging a change in the vaccination recommendations.
For example, Bernd Salzberger, MD, head of infectious diseases, University Hospital Regensburg (Germany), told the Science Media Center: “In women, a complicated course of COVID disease is less common from the start and is so rare in younger women that the chance of avoiding a fatal course through vaccination in women without comorbidities is of the same order of magnitude as the risk of this rare side effect.”
Sandra Ciesek, MD, a virologist at Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany, told the journal Science: “The argument I keep hearing is that the risk-benefit ratio is still positive. But we do not have just one vaccine, we have several. So, restricting the AstraZeneca vaccine to older people makes sense to me, and it does not waste any doses.”
Concerns put in perspective
Commenting of the latest developments, thrombosis expert Saskia Middeldorp, MD, head of internal medicine at Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said it was vitally important that these concerns be put in perspective and that the vaccination program with the AstraZeneca product continue.
“There are some concerning reports about very rare blood clotting disorders and low platelet counts possibly associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine. Groups from Germany and Norway have identified a syndrome similar to HIT, which seems to explain the cause of this very rare side effect,” Dr. Middeldorp noted.
“But with such a high pressure from the virus and many countries now going into a third wave of infection, anything that might slow down vaccination rates will cause much more harm than good,” she warned.
Dr. Middeldorp believes the incidence of this HIT-type syndrome linked to the vaccine is about 1-2 per million. “These are estimates based on the number of reports of this side effect and denominators from the U.K. and EU populations,” she explained. However, Germany has restricted the vaccine on the basis of German data, which appear to show higher rates of the condition. It is not known why the rates are higher in Germany.
“The European Medicines Agency is looking at this very closely. Their statement is quite clear. There is no foundation for changing policy on vaccination,” Dr. Middeldorp stated.
She cautioned that these reports were reducing confidence in the AstraZeneca vaccine, particularly among young people, which she said was causing “a major setback” for the vaccination program.
Noting that everything must be viewed in the context of this severe pandemic, Dr. Middeldorp emphasized that the benefit of the vaccine outweighed any risk, even among young people.
“To those who may be hesitating to have the vaccine as they don’t think they are at high risk of severe COVID infection, I would say there are a lot of young people in the ICU at present with COVID, and your chance of a severe COVID illness is far higher than the 1 or 2 in a million risk of a severe reaction to the vaccine,” she stated.
Dr. Greinacher has received grants and nonfinancial support from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Paringenix, Bayer Healthcare, Gore, Rovi, Sagent, and Biomarin/Prosensa; personal fees from Aspen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Macopharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chromatec, and Instrumentation Laboratory; and nonfinancial support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Portola, Ergomed, and GTH outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Starting April 5, patients can read your notes: 5 things to consider
Change in writing style is not mandated
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Change in writing style is not mandated
Change in writing style is not mandated
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Camrelizumab ‘another brick in the wall’ against squamous NSCLC
.
Results of the CAMEL-sq trial showed a progression-free survival (PFS) advantage of 3.6 months with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo (P < .0001). The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in the camrelizumab arm, but it was significantly better than in the placebo arm (P < .0001).
Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy is already a standard of care in China for patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC who are negative for EGFR and ALK mutations, study investigator Caicun Zhou, MD, PhD, said when presenting the CAMEL-sq results at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 96O).
The CAMEL-sq findings now support the combination as a “standard first-line treatment for advanced squamous NSCLC,” said Dr. Zhou of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital and Tongji University.
“The study has kind of changed our daily practice,” he said. “I do think we will have the label, camrelizumab plus chemo as first-line treatment for squamous [NSCLC] in China, maybe in a couple of months.”
“Camrelizumab will most likely be another brick in the wall for our Chinese patients and colleagues to use for patients with squamous histology, non–small cell lung cancer in addition to pembrolizumab,” said Julie Renee Brahmer, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, who was the invited discussant for the trial.
Dr. Brahmer noted that the PFS hazard ratio in this trial – 0.37 – was “impressive.”
Patients and treatment
CAMEL-sq is a phase 3, double-blind, multicenter trial. The 390 patients enrolled had pathologically-confirmed stage IIIB or IV squamous NSCLC, and they had not received any prior treatment.
Patients received four to six cycles of chemotherapy, consisting of carboplatin and paclitaxel given every 3 weeks. Camrelizumab was added to one arm at a dose of 200 mg, and placebo was added to the other.
This was followed by a maintenance phase in which patients remained on active treatment with camrelizumab or placebo for up to 2 years. Patients in the placebo arm could cross over to camrelizumab at progression.
The median age of patients was similar in the camrelizumab and placebo arms (64 years and 62 years, respectively). The majority of study subjects in both arms were men (more than 90%), had a history of smoking (more than 80%), and had stage IV disease (more than 70%).
Efficacy and safety
The median PFS was 8.5 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.9 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.37; P < .0001). The median OS was not reached in the camrelizumab arm and was 14.5 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.55, P < .0001).
The survival benefits were observed in spite of a crossover rate of 46.9%, Dr. Zhou noted.
Furthermore, survival benefits were consistent across all the subgroups tested. Regardless of age, sex, performance status, smoking history, disease stage, presence of liver or brain metastases, or PD-L1 expression, there was an apparent advantage of camrelizumab over placebo.
The objective response rate was higher in the camrelizumab arm than in the placebo arm, at 64.8% and 36.7%, respectively (P < .0001).
The clinical response seen with camrelizumab was “robust and durable,” Dr. Zhou said. Indeed, the duration of response was 13.1 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.4 months in the placebo arm.
Grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were reported in a similar percentage of camrelizumab- or placebo-treated patients (73.6% and 71.4%, respectively). However, “the majority of treatment-related adverse effects were chemotherapy related,” Dr. Zhou pointed out. This included decreased total white blood cell, neutrophil, red blood cell, and platelet counts as well as alopecia and increased liver enzymes.
Immune-related AEs occurred in 76.7% of patients in the camrelizumab arm and 20.4% of those in the placebo arm.
“The majority of immune-related adverse events were grade 1 or grade 2; easily manageable in our daily practice,” Dr. Zhou noted.
Putting CAMEL-sq into perspective
Data from other trials of immunotherapy-chemotherapy combinations in squamous NSCLC have been presented recently but with less impressive results, Dr. Brahmer said.
In one trial – ORIENT-12 – sintilimab was combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin (ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA56). The median PFS, per investigators, was 5.5 months with sintilimab and 4.9 months without it, both of which are lower than the 8.5 months seen with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in the CAMEL-sq trial.
Another trial is KEYNOTE-407, in which patients received pembrolizumab or placebo plus a carboplatin-paclitaxel (or nab-paclitaxel) regimen. Three-year follow-up data from the trial were presented at ELCC 2021 (Abstract 97O). Continued improvements in second PFS (HR, 0.59) and OS (HR, 0.71) were observed with pembrolizumab-chemotherapy versus placebo-chemotherapy.
“We have to remember the high PD-L1-negative disease rate in the CAMEL-sq study, compared to the KEYNOTE-407 rate,” before stacking the two studies against each other, Dr. Brahmer noted. In KEYNOTE-407, almost 35% of patients had PD-L1 expression of less than 1%, compared with nearly 50% in the CAMEL-sq study.
That aside, “very similar impressive 1-year progression-free survival rates are seen on both studies,” Dr. Brahmer said. “I hope that camrelizumab has continued follow-up so we can see how these patients will do long-term.
“My eyebrows were raised a little bit at the camrelizumab immune-related AE rate of almost 76%, compared to the immune-related AE rate of about 36% in the KEYNOTE-407 study,” Dr. Brahmer said.
She noted, however, that almost two-thirds of the immune-related AEs in CAMEL-sq were due to reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation, which doesn’t appear to have been previously reported with PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors. This is a side effect seen in studies of liver cancer and may be linked to PFS, Dr. Brahmer said.
CAMEL-sq is funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co. Ltd. Dr. Zhou disclosed honoraria from multiple pharmaceutical companies, including the study sponsor. Two of Dr. Zhou’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Brahmer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lily, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Easi, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Regeneron, and RAPT Therapeutics Inc.
.
Results of the CAMEL-sq trial showed a progression-free survival (PFS) advantage of 3.6 months with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo (P < .0001). The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in the camrelizumab arm, but it was significantly better than in the placebo arm (P < .0001).
Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy is already a standard of care in China for patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC who are negative for EGFR and ALK mutations, study investigator Caicun Zhou, MD, PhD, said when presenting the CAMEL-sq results at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 96O).
The CAMEL-sq findings now support the combination as a “standard first-line treatment for advanced squamous NSCLC,” said Dr. Zhou of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital and Tongji University.
“The study has kind of changed our daily practice,” he said. “I do think we will have the label, camrelizumab plus chemo as first-line treatment for squamous [NSCLC] in China, maybe in a couple of months.”
“Camrelizumab will most likely be another brick in the wall for our Chinese patients and colleagues to use for patients with squamous histology, non–small cell lung cancer in addition to pembrolizumab,” said Julie Renee Brahmer, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, who was the invited discussant for the trial.
Dr. Brahmer noted that the PFS hazard ratio in this trial – 0.37 – was “impressive.”
Patients and treatment
CAMEL-sq is a phase 3, double-blind, multicenter trial. The 390 patients enrolled had pathologically-confirmed stage IIIB or IV squamous NSCLC, and they had not received any prior treatment.
Patients received four to six cycles of chemotherapy, consisting of carboplatin and paclitaxel given every 3 weeks. Camrelizumab was added to one arm at a dose of 200 mg, and placebo was added to the other.
This was followed by a maintenance phase in which patients remained on active treatment with camrelizumab or placebo for up to 2 years. Patients in the placebo arm could cross over to camrelizumab at progression.
The median age of patients was similar in the camrelizumab and placebo arms (64 years and 62 years, respectively). The majority of study subjects in both arms were men (more than 90%), had a history of smoking (more than 80%), and had stage IV disease (more than 70%).
Efficacy and safety
The median PFS was 8.5 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.9 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.37; P < .0001). The median OS was not reached in the camrelizumab arm and was 14.5 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.55, P < .0001).
The survival benefits were observed in spite of a crossover rate of 46.9%, Dr. Zhou noted.
Furthermore, survival benefits were consistent across all the subgroups tested. Regardless of age, sex, performance status, smoking history, disease stage, presence of liver or brain metastases, or PD-L1 expression, there was an apparent advantage of camrelizumab over placebo.
The objective response rate was higher in the camrelizumab arm than in the placebo arm, at 64.8% and 36.7%, respectively (P < .0001).
The clinical response seen with camrelizumab was “robust and durable,” Dr. Zhou said. Indeed, the duration of response was 13.1 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.4 months in the placebo arm.
Grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were reported in a similar percentage of camrelizumab- or placebo-treated patients (73.6% and 71.4%, respectively). However, “the majority of treatment-related adverse effects were chemotherapy related,” Dr. Zhou pointed out. This included decreased total white blood cell, neutrophil, red blood cell, and platelet counts as well as alopecia and increased liver enzymes.
Immune-related AEs occurred in 76.7% of patients in the camrelizumab arm and 20.4% of those in the placebo arm.
“The majority of immune-related adverse events were grade 1 or grade 2; easily manageable in our daily practice,” Dr. Zhou noted.
Putting CAMEL-sq into perspective
Data from other trials of immunotherapy-chemotherapy combinations in squamous NSCLC have been presented recently but with less impressive results, Dr. Brahmer said.
In one trial – ORIENT-12 – sintilimab was combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin (ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA56). The median PFS, per investigators, was 5.5 months with sintilimab and 4.9 months without it, both of which are lower than the 8.5 months seen with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in the CAMEL-sq trial.
Another trial is KEYNOTE-407, in which patients received pembrolizumab or placebo plus a carboplatin-paclitaxel (or nab-paclitaxel) regimen. Three-year follow-up data from the trial were presented at ELCC 2021 (Abstract 97O). Continued improvements in second PFS (HR, 0.59) and OS (HR, 0.71) were observed with pembrolizumab-chemotherapy versus placebo-chemotherapy.
“We have to remember the high PD-L1-negative disease rate in the CAMEL-sq study, compared to the KEYNOTE-407 rate,” before stacking the two studies against each other, Dr. Brahmer noted. In KEYNOTE-407, almost 35% of patients had PD-L1 expression of less than 1%, compared with nearly 50% in the CAMEL-sq study.
That aside, “very similar impressive 1-year progression-free survival rates are seen on both studies,” Dr. Brahmer said. “I hope that camrelizumab has continued follow-up so we can see how these patients will do long-term.
“My eyebrows were raised a little bit at the camrelizumab immune-related AE rate of almost 76%, compared to the immune-related AE rate of about 36% in the KEYNOTE-407 study,” Dr. Brahmer said.
She noted, however, that almost two-thirds of the immune-related AEs in CAMEL-sq were due to reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation, which doesn’t appear to have been previously reported with PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors. This is a side effect seen in studies of liver cancer and may be linked to PFS, Dr. Brahmer said.
CAMEL-sq is funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co. Ltd. Dr. Zhou disclosed honoraria from multiple pharmaceutical companies, including the study sponsor. Two of Dr. Zhou’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Brahmer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lily, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Easi, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Regeneron, and RAPT Therapeutics Inc.
.
Results of the CAMEL-sq trial showed a progression-free survival (PFS) advantage of 3.6 months with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo (P < .0001). The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in the camrelizumab arm, but it was significantly better than in the placebo arm (P < .0001).
Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy is already a standard of care in China for patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC who are negative for EGFR and ALK mutations, study investigator Caicun Zhou, MD, PhD, said when presenting the CAMEL-sq results at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 96O).
The CAMEL-sq findings now support the combination as a “standard first-line treatment for advanced squamous NSCLC,” said Dr. Zhou of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital and Tongji University.
“The study has kind of changed our daily practice,” he said. “I do think we will have the label, camrelizumab plus chemo as first-line treatment for squamous [NSCLC] in China, maybe in a couple of months.”
“Camrelizumab will most likely be another brick in the wall for our Chinese patients and colleagues to use for patients with squamous histology, non–small cell lung cancer in addition to pembrolizumab,” said Julie Renee Brahmer, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, who was the invited discussant for the trial.
Dr. Brahmer noted that the PFS hazard ratio in this trial – 0.37 – was “impressive.”
Patients and treatment
CAMEL-sq is a phase 3, double-blind, multicenter trial. The 390 patients enrolled had pathologically-confirmed stage IIIB or IV squamous NSCLC, and they had not received any prior treatment.
Patients received four to six cycles of chemotherapy, consisting of carboplatin and paclitaxel given every 3 weeks. Camrelizumab was added to one arm at a dose of 200 mg, and placebo was added to the other.
This was followed by a maintenance phase in which patients remained on active treatment with camrelizumab or placebo for up to 2 years. Patients in the placebo arm could cross over to camrelizumab at progression.
The median age of patients was similar in the camrelizumab and placebo arms (64 years and 62 years, respectively). The majority of study subjects in both arms were men (more than 90%), had a history of smoking (more than 80%), and had stage IV disease (more than 70%).
Efficacy and safety
The median PFS was 8.5 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.9 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.37; P < .0001). The median OS was not reached in the camrelizumab arm and was 14.5 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.55, P < .0001).
The survival benefits were observed in spite of a crossover rate of 46.9%, Dr. Zhou noted.
Furthermore, survival benefits were consistent across all the subgroups tested. Regardless of age, sex, performance status, smoking history, disease stage, presence of liver or brain metastases, or PD-L1 expression, there was an apparent advantage of camrelizumab over placebo.
The objective response rate was higher in the camrelizumab arm than in the placebo arm, at 64.8% and 36.7%, respectively (P < .0001).
The clinical response seen with camrelizumab was “robust and durable,” Dr. Zhou said. Indeed, the duration of response was 13.1 months in the camrelizumab arm and 4.4 months in the placebo arm.
Grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were reported in a similar percentage of camrelizumab- or placebo-treated patients (73.6% and 71.4%, respectively). However, “the majority of treatment-related adverse effects were chemotherapy related,” Dr. Zhou pointed out. This included decreased total white blood cell, neutrophil, red blood cell, and platelet counts as well as alopecia and increased liver enzymes.
Immune-related AEs occurred in 76.7% of patients in the camrelizumab arm and 20.4% of those in the placebo arm.
“The majority of immune-related adverse events were grade 1 or grade 2; easily manageable in our daily practice,” Dr. Zhou noted.
Putting CAMEL-sq into perspective
Data from other trials of immunotherapy-chemotherapy combinations in squamous NSCLC have been presented recently but with less impressive results, Dr. Brahmer said.
In one trial – ORIENT-12 – sintilimab was combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin (ESMO 2020, Abstract LBA56). The median PFS, per investigators, was 5.5 months with sintilimab and 4.9 months without it, both of which are lower than the 8.5 months seen with camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in the CAMEL-sq trial.
Another trial is KEYNOTE-407, in which patients received pembrolizumab or placebo plus a carboplatin-paclitaxel (or nab-paclitaxel) regimen. Three-year follow-up data from the trial were presented at ELCC 2021 (Abstract 97O). Continued improvements in second PFS (HR, 0.59) and OS (HR, 0.71) were observed with pembrolizumab-chemotherapy versus placebo-chemotherapy.
“We have to remember the high PD-L1-negative disease rate in the CAMEL-sq study, compared to the KEYNOTE-407 rate,” before stacking the two studies against each other, Dr. Brahmer noted. In KEYNOTE-407, almost 35% of patients had PD-L1 expression of less than 1%, compared with nearly 50% in the CAMEL-sq study.
That aside, “very similar impressive 1-year progression-free survival rates are seen on both studies,” Dr. Brahmer said. “I hope that camrelizumab has continued follow-up so we can see how these patients will do long-term.
“My eyebrows were raised a little bit at the camrelizumab immune-related AE rate of almost 76%, compared to the immune-related AE rate of about 36% in the KEYNOTE-407 study,” Dr. Brahmer said.
She noted, however, that almost two-thirds of the immune-related AEs in CAMEL-sq were due to reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation, which doesn’t appear to have been previously reported with PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors. This is a side effect seen in studies of liver cancer and may be linked to PFS, Dr. Brahmer said.
CAMEL-sq is funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co. Ltd. Dr. Zhou disclosed honoraria from multiple pharmaceutical companies, including the study sponsor. Two of Dr. Zhou’s coauthors are employees of the company. Dr. Brahmer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lily, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Sanofi, Easi, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Regeneron, and RAPT Therapeutics Inc.
FROM ELCC 2021
COVID-19 in 2020: Deaths and disparities
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
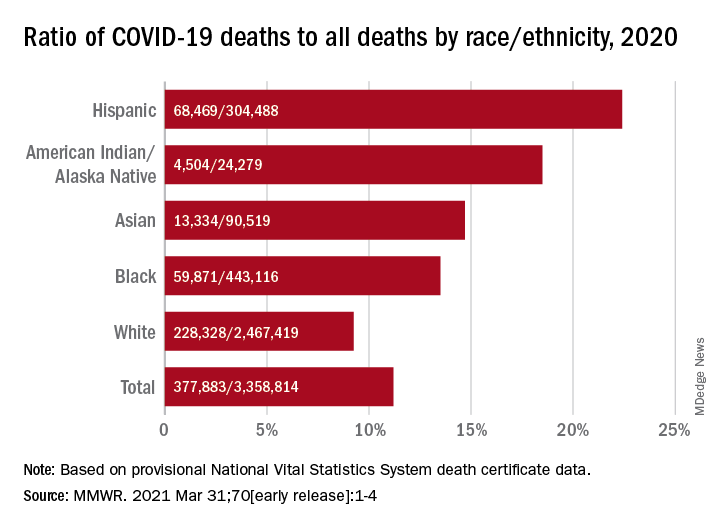
Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
FROM MMWR
Pfizer: Vaccine shown 100% effective in children aged 12-15
The study enrolled 2,260 adolescents aged 12-15. No infections were reported in the group given the vaccine produced by Pfizer and its European partner, BioNTech, the release said. The placebo group reported 18 cases of COVID-19.
The vaccinated children showed a strong antibody response with no serious side effects.
Albert Bourla, PhD, chairman and CEO of Pfizer, said the company plans to seek Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, which could allow this age group to be vaccinated before the start of the next school year. Pfizer will also seek authorization from the European Medicines Agency.
“We share the urgency to expand the authorization of our vaccine to use in younger populations and are encouraged by the clinical trial data from adolescents between the ages of 12 and 15,” Dr. Bourla said in the release.
The clinical trials showed a stronger response in children aged 12-15 than the 95% effectiveness reported in clinical trials in adults. The Pfizer vaccine is now authorized to be given to people aged 16 and up in the United States.
Health experts said the clinical trials – while not peer-reviewed – amounted to very good news.
“The sooner that we can get vaccines into as many people as possible, regardless of their age, the sooner we will be able to really feel like we’re ending this pandemic for good,” Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist affiliated with Georgetown University in Washington, told The New York Times.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently said that getting children vaccinated is an important step toward achieving herd immunity.
“We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape,” he said earlier in March during a hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee. “We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer said it started clinical trials during the week of March 23 with children aged 5-11 and will next start trials with children aged 2-5, followed by children aged 6 months to 2 years. Vaccine makers Moderna and AstraZeneca also have started clinical trials in younger children.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The study enrolled 2,260 adolescents aged 12-15. No infections were reported in the group given the vaccine produced by Pfizer and its European partner, BioNTech, the release said. The placebo group reported 18 cases of COVID-19.
The vaccinated children showed a strong antibody response with no serious side effects.
Albert Bourla, PhD, chairman and CEO of Pfizer, said the company plans to seek Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, which could allow this age group to be vaccinated before the start of the next school year. Pfizer will also seek authorization from the European Medicines Agency.
“We share the urgency to expand the authorization of our vaccine to use in younger populations and are encouraged by the clinical trial data from adolescents between the ages of 12 and 15,” Dr. Bourla said in the release.
The clinical trials showed a stronger response in children aged 12-15 than the 95% effectiveness reported in clinical trials in adults. The Pfizer vaccine is now authorized to be given to people aged 16 and up in the United States.
Health experts said the clinical trials – while not peer-reviewed – amounted to very good news.
“The sooner that we can get vaccines into as many people as possible, regardless of their age, the sooner we will be able to really feel like we’re ending this pandemic for good,” Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist affiliated with Georgetown University in Washington, told The New York Times.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently said that getting children vaccinated is an important step toward achieving herd immunity.
“We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape,” he said earlier in March during a hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee. “We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer said it started clinical trials during the week of March 23 with children aged 5-11 and will next start trials with children aged 2-5, followed by children aged 6 months to 2 years. Vaccine makers Moderna and AstraZeneca also have started clinical trials in younger children.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The study enrolled 2,260 adolescents aged 12-15. No infections were reported in the group given the vaccine produced by Pfizer and its European partner, BioNTech, the release said. The placebo group reported 18 cases of COVID-19.
The vaccinated children showed a strong antibody response with no serious side effects.
Albert Bourla, PhD, chairman and CEO of Pfizer, said the company plans to seek Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, which could allow this age group to be vaccinated before the start of the next school year. Pfizer will also seek authorization from the European Medicines Agency.
“We share the urgency to expand the authorization of our vaccine to use in younger populations and are encouraged by the clinical trial data from adolescents between the ages of 12 and 15,” Dr. Bourla said in the release.
The clinical trials showed a stronger response in children aged 12-15 than the 95% effectiveness reported in clinical trials in adults. The Pfizer vaccine is now authorized to be given to people aged 16 and up in the United States.
Health experts said the clinical trials – while not peer-reviewed – amounted to very good news.
“The sooner that we can get vaccines into as many people as possible, regardless of their age, the sooner we will be able to really feel like we’re ending this pandemic for good,” Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist affiliated with Georgetown University in Washington, told The New York Times.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, recently said that getting children vaccinated is an important step toward achieving herd immunity.
“We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape,” he said earlier in March during a hearing of the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee. “We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer said it started clinical trials during the week of March 23 with children aged 5-11 and will next start trials with children aged 2-5, followed by children aged 6 months to 2 years. Vaccine makers Moderna and AstraZeneca also have started clinical trials in younger children.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC adds new medical conditions to COVID-19 high-risk list
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



