User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Delirium risk factors identified in ICU cancer patients
Hematology-oncology patients who receive treatment in the intensive care unit often develop delirium, and according to new findings, mechanical ventilation, high-dose corticosteroid use, and brain metastases were identified as independent risk factors.
Roughly half of all hematology-oncology patients who were admitted to the ICU experienced delirium, explained lead author Rachel Klosko, PharmD, PGY-2 cardiology pharmacy resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
“Delirium was associated with increased mortality, an increase in hospital length of stay, and increased length of stay in the ICU,” she said.
Dr. Klosko presented the study results at the at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), which was held virtually this year.
Delirium is an acute and fluctuating disturbance of consciousness and cognition and fluctuates in severity. Critically ill patients are subject to numerous risk factors for delirium. “It can occur in independently of any known neurological disorder,” said Dr. Klosko, adding that its occurrence has been associated with poorer outcomes in ICU patients.
In this study, Dr. Klosko and colleagues sought to determine the incidence of delirium in cancer patients who were admitted to the ICU, as well as identify the associated risk factors and recognize potential consequences of the development of delirium in this patient population.
They conducted a single center, retrospective, cohort study that evaluated patients between the ages of 18 and 89 years who were admitted to the hematology-oncology medical or surgical ICU between July 1, 2018, and June 30, 2019.
The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of delirium within 7 days of ICU admission, defined as two positive Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) assessments within 24 hours. Patients identified with delirium were compared to those without it, for the evaluation of secondary endpoints that included hospital mortality and ICU and hospital length of stay. The researchers also sought to identify independent risk factors for delirium in this population.
A total of 244 patients were included in the final analysis. Of this group, 125 (51.2%) experienced delirium during their stay in the ICU, and 119 (48.8%) did not.
Mortality in the delirium group was significantly higher at 32.8% vs. 15.1% (P = .001). In addition, the delirium group was associated with significantly higher ICU length of stay (6 days vs. 3 days, P < .001) and hospital length of stay (21 days vs. 12 days, P < .001).
“When comparing the baseline characteristics between the two groups, the delirium group had a longer hospital length prior to ICU admission, a higher SOFA score, a higher rate of brain metastases, a higher rate of shock, and higher receipt of high-dose steroids, benzodiazepines, and immunotherapy,” said Dr. Klosko.
After multivariable regression, four variables were included in the final model. Among patients with delirium, the SOFA score increased by 25% (odds ratio[OR] 1.25, P < .001), while the odds of delirium were almost four times higher among those treated with high-dose corticosteroids (OR 3.79, P = .004). Delirium was also eight times higher (OR 8.48, P < .001) among those who received mechanical ventilation and five times higher in (OR 5.38, P = .015) in patients with brain metastases.
Dr. Klosko noted that the main limitations for this study were that it was a single center retrospective analysis, and that patients were reviewed within the first 7 days of ICU admission. “This potentially missed patients who developed delirium outside of this time frame,” she said. In addition, “too few patients received high-dose benzodiazepines,” and “none of the patients received continuous neuromuscular blockade.”
However, in “contrast to these limitations, this is the largest study to date that has analyzed delirium in this population,” Dr. Klosko said.
Commenting on the study, Brenda Pun, DNP, RN, director of data quality at the Vanderbilt Critical Illness, Brain Dysfunction, and Survivorship Center, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the goal of this study was to describe delirium in this specific population. “But I will take a step backward and say that they are just confirming that these patients look like other ICU patients in many regards,” she said.
She explained that the sicker patients are, the higher the rates of delirium. “We have implemented strategies to lower these rates, and they have improved,” Dr. Pun said. “Ten years ago, I would say that 80% of patients who were on a ventilator would have delirium but now the rates are around 50% and that’s what we are typically seeing now.”
Dr. Pun emphasized that this study shows that delirium is like the “canary in the coal mine” or a red flag. “It’s a sign that something is wrong and that we need to pay attention, because the patient’s outcome may be worse,” she said. “So this is saying that we need to see if there is something that can be changed or modified to decrease the incidence of delirium—these are important questions.”
There was no outside sponsor. The authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pun has no disclosures.
Hematology-oncology patients who receive treatment in the intensive care unit often develop delirium, and according to new findings, mechanical ventilation, high-dose corticosteroid use, and brain metastases were identified as independent risk factors.
Roughly half of all hematology-oncology patients who were admitted to the ICU experienced delirium, explained lead author Rachel Klosko, PharmD, PGY-2 cardiology pharmacy resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
“Delirium was associated with increased mortality, an increase in hospital length of stay, and increased length of stay in the ICU,” she said.
Dr. Klosko presented the study results at the at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), which was held virtually this year.
Delirium is an acute and fluctuating disturbance of consciousness and cognition and fluctuates in severity. Critically ill patients are subject to numerous risk factors for delirium. “It can occur in independently of any known neurological disorder,” said Dr. Klosko, adding that its occurrence has been associated with poorer outcomes in ICU patients.
In this study, Dr. Klosko and colleagues sought to determine the incidence of delirium in cancer patients who were admitted to the ICU, as well as identify the associated risk factors and recognize potential consequences of the development of delirium in this patient population.
They conducted a single center, retrospective, cohort study that evaluated patients between the ages of 18 and 89 years who were admitted to the hematology-oncology medical or surgical ICU between July 1, 2018, and June 30, 2019.
The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of delirium within 7 days of ICU admission, defined as two positive Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) assessments within 24 hours. Patients identified with delirium were compared to those without it, for the evaluation of secondary endpoints that included hospital mortality and ICU and hospital length of stay. The researchers also sought to identify independent risk factors for delirium in this population.
A total of 244 patients were included in the final analysis. Of this group, 125 (51.2%) experienced delirium during their stay in the ICU, and 119 (48.8%) did not.
Mortality in the delirium group was significantly higher at 32.8% vs. 15.1% (P = .001). In addition, the delirium group was associated with significantly higher ICU length of stay (6 days vs. 3 days, P < .001) and hospital length of stay (21 days vs. 12 days, P < .001).
“When comparing the baseline characteristics between the two groups, the delirium group had a longer hospital length prior to ICU admission, a higher SOFA score, a higher rate of brain metastases, a higher rate of shock, and higher receipt of high-dose steroids, benzodiazepines, and immunotherapy,” said Dr. Klosko.
After multivariable regression, four variables were included in the final model. Among patients with delirium, the SOFA score increased by 25% (odds ratio[OR] 1.25, P < .001), while the odds of delirium were almost four times higher among those treated with high-dose corticosteroids (OR 3.79, P = .004). Delirium was also eight times higher (OR 8.48, P < .001) among those who received mechanical ventilation and five times higher in (OR 5.38, P = .015) in patients with brain metastases.
Dr. Klosko noted that the main limitations for this study were that it was a single center retrospective analysis, and that patients were reviewed within the first 7 days of ICU admission. “This potentially missed patients who developed delirium outside of this time frame,” she said. In addition, “too few patients received high-dose benzodiazepines,” and “none of the patients received continuous neuromuscular blockade.”
However, in “contrast to these limitations, this is the largest study to date that has analyzed delirium in this population,” Dr. Klosko said.
Commenting on the study, Brenda Pun, DNP, RN, director of data quality at the Vanderbilt Critical Illness, Brain Dysfunction, and Survivorship Center, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the goal of this study was to describe delirium in this specific population. “But I will take a step backward and say that they are just confirming that these patients look like other ICU patients in many regards,” she said.
She explained that the sicker patients are, the higher the rates of delirium. “We have implemented strategies to lower these rates, and they have improved,” Dr. Pun said. “Ten years ago, I would say that 80% of patients who were on a ventilator would have delirium but now the rates are around 50% and that’s what we are typically seeing now.”
Dr. Pun emphasized that this study shows that delirium is like the “canary in the coal mine” or a red flag. “It’s a sign that something is wrong and that we need to pay attention, because the patient’s outcome may be worse,” she said. “So this is saying that we need to see if there is something that can be changed or modified to decrease the incidence of delirium—these are important questions.”
There was no outside sponsor. The authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pun has no disclosures.
Hematology-oncology patients who receive treatment in the intensive care unit often develop delirium, and according to new findings, mechanical ventilation, high-dose corticosteroid use, and brain metastases were identified as independent risk factors.
Roughly half of all hematology-oncology patients who were admitted to the ICU experienced delirium, explained lead author Rachel Klosko, PharmD, PGY-2 cardiology pharmacy resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
“Delirium was associated with increased mortality, an increase in hospital length of stay, and increased length of stay in the ICU,” she said.
Dr. Klosko presented the study results at the at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), which was held virtually this year.
Delirium is an acute and fluctuating disturbance of consciousness and cognition and fluctuates in severity. Critically ill patients are subject to numerous risk factors for delirium. “It can occur in independently of any known neurological disorder,” said Dr. Klosko, adding that its occurrence has been associated with poorer outcomes in ICU patients.
In this study, Dr. Klosko and colleagues sought to determine the incidence of delirium in cancer patients who were admitted to the ICU, as well as identify the associated risk factors and recognize potential consequences of the development of delirium in this patient population.
They conducted a single center, retrospective, cohort study that evaluated patients between the ages of 18 and 89 years who were admitted to the hematology-oncology medical or surgical ICU between July 1, 2018, and June 30, 2019.
The study’s primary endpoint was the incidence of delirium within 7 days of ICU admission, defined as two positive Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) assessments within 24 hours. Patients identified with delirium were compared to those without it, for the evaluation of secondary endpoints that included hospital mortality and ICU and hospital length of stay. The researchers also sought to identify independent risk factors for delirium in this population.
A total of 244 patients were included in the final analysis. Of this group, 125 (51.2%) experienced delirium during their stay in the ICU, and 119 (48.8%) did not.
Mortality in the delirium group was significantly higher at 32.8% vs. 15.1% (P = .001). In addition, the delirium group was associated with significantly higher ICU length of stay (6 days vs. 3 days, P < .001) and hospital length of stay (21 days vs. 12 days, P < .001).
“When comparing the baseline characteristics between the two groups, the delirium group had a longer hospital length prior to ICU admission, a higher SOFA score, a higher rate of brain metastases, a higher rate of shock, and higher receipt of high-dose steroids, benzodiazepines, and immunotherapy,” said Dr. Klosko.
After multivariable regression, four variables were included in the final model. Among patients with delirium, the SOFA score increased by 25% (odds ratio[OR] 1.25, P < .001), while the odds of delirium were almost four times higher among those treated with high-dose corticosteroids (OR 3.79, P = .004). Delirium was also eight times higher (OR 8.48, P < .001) among those who received mechanical ventilation and five times higher in (OR 5.38, P = .015) in patients with brain metastases.
Dr. Klosko noted that the main limitations for this study were that it was a single center retrospective analysis, and that patients were reviewed within the first 7 days of ICU admission. “This potentially missed patients who developed delirium outside of this time frame,” she said. In addition, “too few patients received high-dose benzodiazepines,” and “none of the patients received continuous neuromuscular blockade.”
However, in “contrast to these limitations, this is the largest study to date that has analyzed delirium in this population,” Dr. Klosko said.
Commenting on the study, Brenda Pun, DNP, RN, director of data quality at the Vanderbilt Critical Illness, Brain Dysfunction, and Survivorship Center, Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that the goal of this study was to describe delirium in this specific population. “But I will take a step backward and say that they are just confirming that these patients look like other ICU patients in many regards,” she said.
She explained that the sicker patients are, the higher the rates of delirium. “We have implemented strategies to lower these rates, and they have improved,” Dr. Pun said. “Ten years ago, I would say that 80% of patients who were on a ventilator would have delirium but now the rates are around 50% and that’s what we are typically seeing now.”
Dr. Pun emphasized that this study shows that delirium is like the “canary in the coal mine” or a red flag. “It’s a sign that something is wrong and that we need to pay attention, because the patient’s outcome may be worse,” she said. “So this is saying that we need to see if there is something that can be changed or modified to decrease the incidence of delirium—these are important questions.”
There was no outside sponsor. The authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pun has no disclosures.
FROM CCC50
Vaccine mismatch: What to do after dose 1 when plans change
Ideally, Americans receiving their Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccines will get both doses from the same manufacturer, said Gregory Poland, MD, a vaccinologist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
After all, that’s how they were tested for efficacy and safety, and it was results from those studies that led to emergency use authorization (EUA) being granted by the Food and Drug Administration.
But states and countries have struggled to keep up with the demand for vaccine, and more flexible vaccination schedules could help.
So researchers are exploring whether it is safe and effective to get the first and second doses from different manufacturers. And they are even wondering whether mixing doses from different manufacturers could increase effectiveness, particularly in light of emerging variants.
It’s called the “interchangeability issue,” said Dr. Poland, who has gotten a steady stream of questions about it.
For example, a patient recently asked about options for his father, who had gotten his first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine in Ecuador, but had since moved to the United States, where that product has not been approved for use.
Dr. Poland said in an interview that he prefaces each answer with: “I’ve got no science for what I’m about to tell you.”
In this particular case, he recommended that the man’s father talk with his doctor about his level of COVID-19 risk and consider whether he should gamble on the AstraZeneca vaccine getting approved in the United States soon, or whether he should ask for a second dose from one of the three vaccines currently approved.
On March 22, 2021, AstraZeneca released positive results from its phase 3 trial, which will likely speed its path toward use in the United States.
Although clinical trials have started to test combinations and boosters, there’s currently no definitive evidence from human trials on mixing COVID vaccines, Dr. Poland pointed out.
But a study of a mixed-vaccine regimen is currently underway in the United Kingdom.
Participants in that 13-month trial will be given the Oxford/AstraZeneca and Pfizer/BioNTech vaccines in different combinations and at different intervals. The first results from that trial are expected this summer.
And interim results from a trial combining Russia’s Sputnik V and the AstraZeneca vaccines are expected in 2 months, according to a Reuters report.
Mix only in ‘exceptional situations’
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been hesitant to open the door to mixing Pfizer and Moderna vaccinations, noting that the two “are not interchangeable.” But CDC guidance has changed slightly. Now, instead of saying the two vaccines should not be mixed, CDC guidance says they can be mixed in “exceptional situations,” and that the second dose can be administered up to 6 weeks after the first dose.
It is reasonable to assume that mixing COVID-19 vaccines that use the same platform – such as the mRNA platform used by both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines – will be acceptable, Dr. Poland said, although human trials have not proven that.
However, it is unclear whether vaccines that use different platforms can be mixed. Can the first dose of an mRNA vaccine be followed by an adenovirus-based vaccine, like the Johnson & Johnson product or Novavax, if that vaccine is granted an EUA?
Ross Kedl, PhD, a vaccine researcher and professor of immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said matching vaccine platforms might not be the preferred vaccination strategy.
He disagreed that there’s a lack of science surrounding the issue, and said all signs point to mixing as not only a good option, but probably a better one.
Researcher says science backs mixing
A mix of two different vaccine platforms likely enhances immunity, Dr. Kedl said. The heterologous prime-boost strategy has been used in animal studies for decades, “and it is well known that this promotes a much better immune response than when immunizing with the same vaccine twice.
“If you think about it in a Venn diagram sort of way, it makes sense,” he said in an interview. “Each vaccine has a number of components in it that influence immunity in various ways, but between the two of them, they only have one component that is similar. In the case of the coronavirus vaccines, the one thing both have in common is the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2. In essence, this gives you two shots at generating immunity against the one thing in each vaccine you care most about, but only one shot for the other vaccine components in each platform, resulting in an amplified response against the common target.”
In fact, the heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategy has proven to be effective in humans in early studies.
For example, an Ebola regimen that consisted of an adenovirus vector, similar to the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, and a modified vaccinia virus vector showed promise in a phase 1 study. And an HIV regimen that consisted of the combination of a DNA vaccine, similar to the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, and another viral vector showed encouraging results in a proof-of-concept study.
In both these cases, the heterologous prime-boost strategy was far better than single-vaccine prime-boost regimens, Dr. Kedl pointed out. And neither study reported any safety issues with the combinations.
For now, it’s best to stick with the same manufacturer for both shots, as the CDC guidance suggests, he said, agreeing with Dr. Poland.
But “I would be very surprised if we didn’t move to a mixing of vaccine platforms for the population,” Dr. Kedl said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ideally, Americans receiving their Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccines will get both doses from the same manufacturer, said Gregory Poland, MD, a vaccinologist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
After all, that’s how they were tested for efficacy and safety, and it was results from those studies that led to emergency use authorization (EUA) being granted by the Food and Drug Administration.
But states and countries have struggled to keep up with the demand for vaccine, and more flexible vaccination schedules could help.
So researchers are exploring whether it is safe and effective to get the first and second doses from different manufacturers. And they are even wondering whether mixing doses from different manufacturers could increase effectiveness, particularly in light of emerging variants.
It’s called the “interchangeability issue,” said Dr. Poland, who has gotten a steady stream of questions about it.
For example, a patient recently asked about options for his father, who had gotten his first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine in Ecuador, but had since moved to the United States, where that product has not been approved for use.
Dr. Poland said in an interview that he prefaces each answer with: “I’ve got no science for what I’m about to tell you.”
In this particular case, he recommended that the man’s father talk with his doctor about his level of COVID-19 risk and consider whether he should gamble on the AstraZeneca vaccine getting approved in the United States soon, or whether he should ask for a second dose from one of the three vaccines currently approved.
On March 22, 2021, AstraZeneca released positive results from its phase 3 trial, which will likely speed its path toward use in the United States.
Although clinical trials have started to test combinations and boosters, there’s currently no definitive evidence from human trials on mixing COVID vaccines, Dr. Poland pointed out.
But a study of a mixed-vaccine regimen is currently underway in the United Kingdom.
Participants in that 13-month trial will be given the Oxford/AstraZeneca and Pfizer/BioNTech vaccines in different combinations and at different intervals. The first results from that trial are expected this summer.
And interim results from a trial combining Russia’s Sputnik V and the AstraZeneca vaccines are expected in 2 months, according to a Reuters report.
Mix only in ‘exceptional situations’
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been hesitant to open the door to mixing Pfizer and Moderna vaccinations, noting that the two “are not interchangeable.” But CDC guidance has changed slightly. Now, instead of saying the two vaccines should not be mixed, CDC guidance says they can be mixed in “exceptional situations,” and that the second dose can be administered up to 6 weeks after the first dose.
It is reasonable to assume that mixing COVID-19 vaccines that use the same platform – such as the mRNA platform used by both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines – will be acceptable, Dr. Poland said, although human trials have not proven that.
However, it is unclear whether vaccines that use different platforms can be mixed. Can the first dose of an mRNA vaccine be followed by an adenovirus-based vaccine, like the Johnson & Johnson product or Novavax, if that vaccine is granted an EUA?
Ross Kedl, PhD, a vaccine researcher and professor of immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said matching vaccine platforms might not be the preferred vaccination strategy.
He disagreed that there’s a lack of science surrounding the issue, and said all signs point to mixing as not only a good option, but probably a better one.
Researcher says science backs mixing
A mix of two different vaccine platforms likely enhances immunity, Dr. Kedl said. The heterologous prime-boost strategy has been used in animal studies for decades, “and it is well known that this promotes a much better immune response than when immunizing with the same vaccine twice.
“If you think about it in a Venn diagram sort of way, it makes sense,” he said in an interview. “Each vaccine has a number of components in it that influence immunity in various ways, but between the two of them, they only have one component that is similar. In the case of the coronavirus vaccines, the one thing both have in common is the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2. In essence, this gives you two shots at generating immunity against the one thing in each vaccine you care most about, but only one shot for the other vaccine components in each platform, resulting in an amplified response against the common target.”
In fact, the heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategy has proven to be effective in humans in early studies.
For example, an Ebola regimen that consisted of an adenovirus vector, similar to the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, and a modified vaccinia virus vector showed promise in a phase 1 study. And an HIV regimen that consisted of the combination of a DNA vaccine, similar to the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, and another viral vector showed encouraging results in a proof-of-concept study.
In both these cases, the heterologous prime-boost strategy was far better than single-vaccine prime-boost regimens, Dr. Kedl pointed out. And neither study reported any safety issues with the combinations.
For now, it’s best to stick with the same manufacturer for both shots, as the CDC guidance suggests, he said, agreeing with Dr. Poland.
But “I would be very surprised if we didn’t move to a mixing of vaccine platforms for the population,” Dr. Kedl said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ideally, Americans receiving their Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccines will get both doses from the same manufacturer, said Gregory Poland, MD, a vaccinologist at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
After all, that’s how they were tested for efficacy and safety, and it was results from those studies that led to emergency use authorization (EUA) being granted by the Food and Drug Administration.
But states and countries have struggled to keep up with the demand for vaccine, and more flexible vaccination schedules could help.
So researchers are exploring whether it is safe and effective to get the first and second doses from different manufacturers. And they are even wondering whether mixing doses from different manufacturers could increase effectiveness, particularly in light of emerging variants.
It’s called the “interchangeability issue,” said Dr. Poland, who has gotten a steady stream of questions about it.
For example, a patient recently asked about options for his father, who had gotten his first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine in Ecuador, but had since moved to the United States, where that product has not been approved for use.
Dr. Poland said in an interview that he prefaces each answer with: “I’ve got no science for what I’m about to tell you.”
In this particular case, he recommended that the man’s father talk with his doctor about his level of COVID-19 risk and consider whether he should gamble on the AstraZeneca vaccine getting approved in the United States soon, or whether he should ask for a second dose from one of the three vaccines currently approved.
On March 22, 2021, AstraZeneca released positive results from its phase 3 trial, which will likely speed its path toward use in the United States.
Although clinical trials have started to test combinations and boosters, there’s currently no definitive evidence from human trials on mixing COVID vaccines, Dr. Poland pointed out.
But a study of a mixed-vaccine regimen is currently underway in the United Kingdom.
Participants in that 13-month trial will be given the Oxford/AstraZeneca and Pfizer/BioNTech vaccines in different combinations and at different intervals. The first results from that trial are expected this summer.
And interim results from a trial combining Russia’s Sputnik V and the AstraZeneca vaccines are expected in 2 months, according to a Reuters report.
Mix only in ‘exceptional situations’
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been hesitant to open the door to mixing Pfizer and Moderna vaccinations, noting that the two “are not interchangeable.” But CDC guidance has changed slightly. Now, instead of saying the two vaccines should not be mixed, CDC guidance says they can be mixed in “exceptional situations,” and that the second dose can be administered up to 6 weeks after the first dose.
It is reasonable to assume that mixing COVID-19 vaccines that use the same platform – such as the mRNA platform used by both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines – will be acceptable, Dr. Poland said, although human trials have not proven that.
However, it is unclear whether vaccines that use different platforms can be mixed. Can the first dose of an mRNA vaccine be followed by an adenovirus-based vaccine, like the Johnson & Johnson product or Novavax, if that vaccine is granted an EUA?
Ross Kedl, PhD, a vaccine researcher and professor of immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said matching vaccine platforms might not be the preferred vaccination strategy.
He disagreed that there’s a lack of science surrounding the issue, and said all signs point to mixing as not only a good option, but probably a better one.
Researcher says science backs mixing
A mix of two different vaccine platforms likely enhances immunity, Dr. Kedl said. The heterologous prime-boost strategy has been used in animal studies for decades, “and it is well known that this promotes a much better immune response than when immunizing with the same vaccine twice.
“If you think about it in a Venn diagram sort of way, it makes sense,” he said in an interview. “Each vaccine has a number of components in it that influence immunity in various ways, but between the two of them, they only have one component that is similar. In the case of the coronavirus vaccines, the one thing both have in common is the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2. In essence, this gives you two shots at generating immunity against the one thing in each vaccine you care most about, but only one shot for the other vaccine components in each platform, resulting in an amplified response against the common target.”
In fact, the heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategy has proven to be effective in humans in early studies.
For example, an Ebola regimen that consisted of an adenovirus vector, similar to the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, and a modified vaccinia virus vector showed promise in a phase 1 study. And an HIV regimen that consisted of the combination of a DNA vaccine, similar to the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, and another viral vector showed encouraging results in a proof-of-concept study.
In both these cases, the heterologous prime-boost strategy was far better than single-vaccine prime-boost regimens, Dr. Kedl pointed out. And neither study reported any safety issues with the combinations.
For now, it’s best to stick with the same manufacturer for both shots, as the CDC guidance suggests, he said, agreeing with Dr. Poland.
But “I would be very surprised if we didn’t move to a mixing of vaccine platforms for the population,” Dr. Kedl said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines could lose their punch within a year, experts say
In a survey of 77 epidemiologists from 28 countries by the People’s Vaccine Alliance, 66.2% predicted that the world has a year or less before variants make current vaccines ineffective. The People’s Vaccine Alliance is a coalition of more than 50 organizations, including the African Alliance, Oxfam, Public Citizen, and UNAIDS (the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS).
Almost a third (32.5%) of those surveyed said ineffectiveness would happen in 9 months or less; 18.2% said 6 months or less.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that, while it’s hard to say whether vaccines could become ineffective in that time frame, “It’s perfectly reasonable to think it could happen.”
The good news, said Dr. Offit, who was not involved with the survey, is that SARS-CoV-2 mutates slowly, compared with other viruses such as influenza.
“To date,” he said, “the mutations that have occurred are not far enough away from the immunity induced by your natural infection or immunization such that one isn’t protected at least against severe and critical disease.”
That’s the goal of vaccines, he noted: “to keep people from suffering mightily.”
A line may be crossed
“And so far that’s happening, even with the variants,” Dr. Offit said. “That line has not been crossed. But I think we should assume that it might be.”
Dr. Offit said it will be critical to monitor anyone who gets hospitalized who is known to have been infected or fully vaccinated. Then countries need to get really good at sequencing those viruses.
The great majority of those surveyed (88%) said that persistently low vaccine coverage in many countries would make it more likely that vaccine-resistant mutations will appear.
Coverage comparisons between countries are stark.
Many countries haven’t given a single vaccine dose
While rich countries are giving COVID-19 vaccinations at the rate of a person a second, many of the poorest countries have given hardly any vaccines, the People’s Vaccine Alliance says.
Additionally, according to researchers at the Global Health Innovation Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., high- and upper-middle–income countries, which represent one-fifth of the world’s population, have bought about 6 billion doses. But low- and lower-middle–income countries, which make up four-fifths of the population, have bought only about 2.6 billion, an article in Nature reports.
“You’re only as strong as your weakest country,” Dr. Offit said. “If we haven’t learned that what happens in other countries can [affect the global population], we haven’t been paying attention.”
Gregg Gonsalves, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., one of the academic centers surveyed, didn’t specify a timeline for when vaccines would become ineffective, but said in a press release that the urgency for widespread global vaccination is real.
“Unless we vaccinate the world,” he said, “we leave the playing field open to more and more mutations, which could churn out variants that could evade our current vaccines and require booster shots to deal with them.”
“Dire, but not surprising”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, a pulmonologist at John Hopkins University, Baltimore, whose research focuses on health care disparities, said the survey findings were “dire, but not surprising.”
Johns Hopkins was another of the centers surveyed, but Dr. Galiatsatos wasn’t personally involved with the survey.
COVID-19, Dr. Galiatsatos pointed out, has laid bare disparities, both in who gets the vaccine and who’s involved in trials to develop the vaccines.
“It’s morally concerning and an ethical reckoning,” he said in an interview.
Recognition of the borderless swath of destruction the virus is exacting is critical, he said.
The United States “has to realize this can’t be a U.S.-centric issue,” he said. “We’re going to be back to the beginning if we don’t make sure that every country is doing well. We haven’t seen that level of uniform approach.”
He noted that scientists have always known that viruses mutate, but now the race is on to find the parts of SARS-CoV-2 that don’t mutate as much.
“My suspicion is we’ll probably need boosters instead of a whole different vaccine,” Dr. Galiatsatos said.
Among the strategies sought by the People’s Vaccine Alliance is for all pharmaceutical companies working on COVID-19 vaccines to openly share technology and intellectual property through the World Health Organization COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, to speed production and rollout of vaccines to all countries.
In the survey, 74% said that open sharing of technology and intellectual property could boost global vaccine coverage; 23% said maybe and 3% said it wouldn’t help.
The survey was carried out between Feb. 17 and March 25, 2021. Respondents included epidemiologists, virologists, and infection disease specialists from the following countries: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Canada, Denmark, Ethiopia, France, Guatemala, India, Italy, Kenya, Lebanon, Norway, Philippines, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Spain, United Arab Emirates, Uganda, United Kingdom, United States, Vietnam, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Dr. Offit and Dr. Galiatsatos reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a survey of 77 epidemiologists from 28 countries by the People’s Vaccine Alliance, 66.2% predicted that the world has a year or less before variants make current vaccines ineffective. The People’s Vaccine Alliance is a coalition of more than 50 organizations, including the African Alliance, Oxfam, Public Citizen, and UNAIDS (the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS).
Almost a third (32.5%) of those surveyed said ineffectiveness would happen in 9 months or less; 18.2% said 6 months or less.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that, while it’s hard to say whether vaccines could become ineffective in that time frame, “It’s perfectly reasonable to think it could happen.”
The good news, said Dr. Offit, who was not involved with the survey, is that SARS-CoV-2 mutates slowly, compared with other viruses such as influenza.
“To date,” he said, “the mutations that have occurred are not far enough away from the immunity induced by your natural infection or immunization such that one isn’t protected at least against severe and critical disease.”
That’s the goal of vaccines, he noted: “to keep people from suffering mightily.”
A line may be crossed
“And so far that’s happening, even with the variants,” Dr. Offit said. “That line has not been crossed. But I think we should assume that it might be.”
Dr. Offit said it will be critical to monitor anyone who gets hospitalized who is known to have been infected or fully vaccinated. Then countries need to get really good at sequencing those viruses.
The great majority of those surveyed (88%) said that persistently low vaccine coverage in many countries would make it more likely that vaccine-resistant mutations will appear.
Coverage comparisons between countries are stark.
Many countries haven’t given a single vaccine dose
While rich countries are giving COVID-19 vaccinations at the rate of a person a second, many of the poorest countries have given hardly any vaccines, the People’s Vaccine Alliance says.
Additionally, according to researchers at the Global Health Innovation Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., high- and upper-middle–income countries, which represent one-fifth of the world’s population, have bought about 6 billion doses. But low- and lower-middle–income countries, which make up four-fifths of the population, have bought only about 2.6 billion, an article in Nature reports.
“You’re only as strong as your weakest country,” Dr. Offit said. “If we haven’t learned that what happens in other countries can [affect the global population], we haven’t been paying attention.”
Gregg Gonsalves, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., one of the academic centers surveyed, didn’t specify a timeline for when vaccines would become ineffective, but said in a press release that the urgency for widespread global vaccination is real.
“Unless we vaccinate the world,” he said, “we leave the playing field open to more and more mutations, which could churn out variants that could evade our current vaccines and require booster shots to deal with them.”
“Dire, but not surprising”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, a pulmonologist at John Hopkins University, Baltimore, whose research focuses on health care disparities, said the survey findings were “dire, but not surprising.”
Johns Hopkins was another of the centers surveyed, but Dr. Galiatsatos wasn’t personally involved with the survey.
COVID-19, Dr. Galiatsatos pointed out, has laid bare disparities, both in who gets the vaccine and who’s involved in trials to develop the vaccines.
“It’s morally concerning and an ethical reckoning,” he said in an interview.
Recognition of the borderless swath of destruction the virus is exacting is critical, he said.
The United States “has to realize this can’t be a U.S.-centric issue,” he said. “We’re going to be back to the beginning if we don’t make sure that every country is doing well. We haven’t seen that level of uniform approach.”
He noted that scientists have always known that viruses mutate, but now the race is on to find the parts of SARS-CoV-2 that don’t mutate as much.
“My suspicion is we’ll probably need boosters instead of a whole different vaccine,” Dr. Galiatsatos said.
Among the strategies sought by the People’s Vaccine Alliance is for all pharmaceutical companies working on COVID-19 vaccines to openly share technology and intellectual property through the World Health Organization COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, to speed production and rollout of vaccines to all countries.
In the survey, 74% said that open sharing of technology and intellectual property could boost global vaccine coverage; 23% said maybe and 3% said it wouldn’t help.
The survey was carried out between Feb. 17 and March 25, 2021. Respondents included epidemiologists, virologists, and infection disease specialists from the following countries: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Canada, Denmark, Ethiopia, France, Guatemala, India, Italy, Kenya, Lebanon, Norway, Philippines, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Spain, United Arab Emirates, Uganda, United Kingdom, United States, Vietnam, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Dr. Offit and Dr. Galiatsatos reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a survey of 77 epidemiologists from 28 countries by the People’s Vaccine Alliance, 66.2% predicted that the world has a year or less before variants make current vaccines ineffective. The People’s Vaccine Alliance is a coalition of more than 50 organizations, including the African Alliance, Oxfam, Public Citizen, and UNAIDS (the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS).
Almost a third (32.5%) of those surveyed said ineffectiveness would happen in 9 months or less; 18.2% said 6 months or less.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that, while it’s hard to say whether vaccines could become ineffective in that time frame, “It’s perfectly reasonable to think it could happen.”
The good news, said Dr. Offit, who was not involved with the survey, is that SARS-CoV-2 mutates slowly, compared with other viruses such as influenza.
“To date,” he said, “the mutations that have occurred are not far enough away from the immunity induced by your natural infection or immunization such that one isn’t protected at least against severe and critical disease.”
That’s the goal of vaccines, he noted: “to keep people from suffering mightily.”
A line may be crossed
“And so far that’s happening, even with the variants,” Dr. Offit said. “That line has not been crossed. But I think we should assume that it might be.”
Dr. Offit said it will be critical to monitor anyone who gets hospitalized who is known to have been infected or fully vaccinated. Then countries need to get really good at sequencing those viruses.
The great majority of those surveyed (88%) said that persistently low vaccine coverage in many countries would make it more likely that vaccine-resistant mutations will appear.
Coverage comparisons between countries are stark.
Many countries haven’t given a single vaccine dose
While rich countries are giving COVID-19 vaccinations at the rate of a person a second, many of the poorest countries have given hardly any vaccines, the People’s Vaccine Alliance says.
Additionally, according to researchers at the Global Health Innovation Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., high- and upper-middle–income countries, which represent one-fifth of the world’s population, have bought about 6 billion doses. But low- and lower-middle–income countries, which make up four-fifths of the population, have bought only about 2.6 billion, an article in Nature reports.
“You’re only as strong as your weakest country,” Dr. Offit said. “If we haven’t learned that what happens in other countries can [affect the global population], we haven’t been paying attention.”
Gregg Gonsalves, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., one of the academic centers surveyed, didn’t specify a timeline for when vaccines would become ineffective, but said in a press release that the urgency for widespread global vaccination is real.
“Unless we vaccinate the world,” he said, “we leave the playing field open to more and more mutations, which could churn out variants that could evade our current vaccines and require booster shots to deal with them.”
“Dire, but not surprising”
Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, MHS, a pulmonologist at John Hopkins University, Baltimore, whose research focuses on health care disparities, said the survey findings were “dire, but not surprising.”
Johns Hopkins was another of the centers surveyed, but Dr. Galiatsatos wasn’t personally involved with the survey.
COVID-19, Dr. Galiatsatos pointed out, has laid bare disparities, both in who gets the vaccine and who’s involved in trials to develop the vaccines.
“It’s morally concerning and an ethical reckoning,” he said in an interview.
Recognition of the borderless swath of destruction the virus is exacting is critical, he said.
The United States “has to realize this can’t be a U.S.-centric issue,” he said. “We’re going to be back to the beginning if we don’t make sure that every country is doing well. We haven’t seen that level of uniform approach.”
He noted that scientists have always known that viruses mutate, but now the race is on to find the parts of SARS-CoV-2 that don’t mutate as much.
“My suspicion is we’ll probably need boosters instead of a whole different vaccine,” Dr. Galiatsatos said.
Among the strategies sought by the People’s Vaccine Alliance is for all pharmaceutical companies working on COVID-19 vaccines to openly share technology and intellectual property through the World Health Organization COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, to speed production and rollout of vaccines to all countries.
In the survey, 74% said that open sharing of technology and intellectual property could boost global vaccine coverage; 23% said maybe and 3% said it wouldn’t help.
The survey was carried out between Feb. 17 and March 25, 2021. Respondents included epidemiologists, virologists, and infection disease specialists from the following countries: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Canada, Denmark, Ethiopia, France, Guatemala, India, Italy, Kenya, Lebanon, Norway, Philippines, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Spain, United Arab Emirates, Uganda, United Kingdom, United States, Vietnam, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Dr. Offit and Dr. Galiatsatos reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
National Psoriasis Foundation recommends some stop methotrexate for 2 weeks after J&J vaccine
The , Joel M. Gelfand, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
The new guidance states: “Patients 60 or older who have at least one comorbidity associated with an increased risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, and who are taking methotrexate with well-controlled psoriatic disease, may, in consultation with their prescriber, consider holding it for 2 weeks after receiving the Ad26.COV2.S [Johnson & Johnson] vaccine in order to potentially improve vaccine response.”
The key word here is “potentially.” There is no hard evidence that a 2-week hold on methotrexate after receiving the killed adenovirus vaccine will actually provide a clinically meaningful benefit. But it’s a hypothetical possibility. The rationale stems from a small randomized trial conducted in South Korea several years ago in which patients with rheumatoid arthritis were assigned to hold or continue their methotrexate for the first 2 weeks after receiving an inactivated-virus influenza vaccine. The antibody response to the vaccine was better in those who temporarily halted their methotrexate, explained Dr. Gelfand, cochair of the NPF COVID-19 Task Force and professor of dermatology and of epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“If you have a patient on methotrexate who’s 60 or older and whose psoriasis is completely controlled and quiescent and the patient is concerned about how well the vaccine is going to work, this is a reasonable thing to consider in someone who’s at higher risk for poor outcomes if they get infected,” he said.
If the informed patient wants to continue on methotrexate without interruption, that’s fine, too, in light of the lack of compelling evidence on this issue, the dermatologist added at the conference, sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The NPF task force does not extend the recommendation to consider holding methotrexate in recipients of the mRNA-based Moderna and Pfizer vaccines because of their very different mechanisms of action. Nor is it recommended to hold biologic agents after receiving any of the available COVID-19 vaccines. Studies have shown no altered immunologic response to influenza or pneumococcal vaccines in patients who continued on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors or interleukin-17 inhibitors. The interleukin-23 inhibitors haven’t been studied in this regard.
The task force recommends that most psoriasis patients should continue on treatment throughout the pandemic, and newly diagnosed patients should commence appropriate therapy as if there was no pandemic.
“We’ve learned that many patients who stopped their treatment for psoriatic disease early in the pandemic came to regret that decision because their psoriasis flared and got worse and required reinstitution of therapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The current data is largely reassuring that if there is an effect of our therapies on the risk of COVID, it must be rather small and therefore unlikely to be clinically meaningful for our patients.”
Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant to and recipient of institutional research grants from Pfizer and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
The , Joel M. Gelfand, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
The new guidance states: “Patients 60 or older who have at least one comorbidity associated with an increased risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, and who are taking methotrexate with well-controlled psoriatic disease, may, in consultation with their prescriber, consider holding it for 2 weeks after receiving the Ad26.COV2.S [Johnson & Johnson] vaccine in order to potentially improve vaccine response.”
The key word here is “potentially.” There is no hard evidence that a 2-week hold on methotrexate after receiving the killed adenovirus vaccine will actually provide a clinically meaningful benefit. But it’s a hypothetical possibility. The rationale stems from a small randomized trial conducted in South Korea several years ago in which patients with rheumatoid arthritis were assigned to hold or continue their methotrexate for the first 2 weeks after receiving an inactivated-virus influenza vaccine. The antibody response to the vaccine was better in those who temporarily halted their methotrexate, explained Dr. Gelfand, cochair of the NPF COVID-19 Task Force and professor of dermatology and of epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“If you have a patient on methotrexate who’s 60 or older and whose psoriasis is completely controlled and quiescent and the patient is concerned about how well the vaccine is going to work, this is a reasonable thing to consider in someone who’s at higher risk for poor outcomes if they get infected,” he said.
If the informed patient wants to continue on methotrexate without interruption, that’s fine, too, in light of the lack of compelling evidence on this issue, the dermatologist added at the conference, sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The NPF task force does not extend the recommendation to consider holding methotrexate in recipients of the mRNA-based Moderna and Pfizer vaccines because of their very different mechanisms of action. Nor is it recommended to hold biologic agents after receiving any of the available COVID-19 vaccines. Studies have shown no altered immunologic response to influenza or pneumococcal vaccines in patients who continued on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors or interleukin-17 inhibitors. The interleukin-23 inhibitors haven’t been studied in this regard.
The task force recommends that most psoriasis patients should continue on treatment throughout the pandemic, and newly diagnosed patients should commence appropriate therapy as if there was no pandemic.
“We’ve learned that many patients who stopped their treatment for psoriatic disease early in the pandemic came to regret that decision because their psoriasis flared and got worse and required reinstitution of therapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The current data is largely reassuring that if there is an effect of our therapies on the risk of COVID, it must be rather small and therefore unlikely to be clinically meaningful for our patients.”
Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant to and recipient of institutional research grants from Pfizer and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
The , Joel M. Gelfand, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
The new guidance states: “Patients 60 or older who have at least one comorbidity associated with an increased risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, and who are taking methotrexate with well-controlled psoriatic disease, may, in consultation with their prescriber, consider holding it for 2 weeks after receiving the Ad26.COV2.S [Johnson & Johnson] vaccine in order to potentially improve vaccine response.”
The key word here is “potentially.” There is no hard evidence that a 2-week hold on methotrexate after receiving the killed adenovirus vaccine will actually provide a clinically meaningful benefit. But it’s a hypothetical possibility. The rationale stems from a small randomized trial conducted in South Korea several years ago in which patients with rheumatoid arthritis were assigned to hold or continue their methotrexate for the first 2 weeks after receiving an inactivated-virus influenza vaccine. The antibody response to the vaccine was better in those who temporarily halted their methotrexate, explained Dr. Gelfand, cochair of the NPF COVID-19 Task Force and professor of dermatology and of epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“If you have a patient on methotrexate who’s 60 or older and whose psoriasis is completely controlled and quiescent and the patient is concerned about how well the vaccine is going to work, this is a reasonable thing to consider in someone who’s at higher risk for poor outcomes if they get infected,” he said.
If the informed patient wants to continue on methotrexate without interruption, that’s fine, too, in light of the lack of compelling evidence on this issue, the dermatologist added at the conference, sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The NPF task force does not extend the recommendation to consider holding methotrexate in recipients of the mRNA-based Moderna and Pfizer vaccines because of their very different mechanisms of action. Nor is it recommended to hold biologic agents after receiving any of the available COVID-19 vaccines. Studies have shown no altered immunologic response to influenza or pneumococcal vaccines in patients who continued on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors or interleukin-17 inhibitors. The interleukin-23 inhibitors haven’t been studied in this regard.
The task force recommends that most psoriasis patients should continue on treatment throughout the pandemic, and newly diagnosed patients should commence appropriate therapy as if there was no pandemic.
“We’ve learned that many patients who stopped their treatment for psoriatic disease early in the pandemic came to regret that decision because their psoriasis flared and got worse and required reinstitution of therapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The current data is largely reassuring that if there is an effect of our therapies on the risk of COVID, it must be rather small and therefore unlikely to be clinically meaningful for our patients.”
Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant to and recipient of institutional research grants from Pfizer and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
New COVID-19 cases rise again in children
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
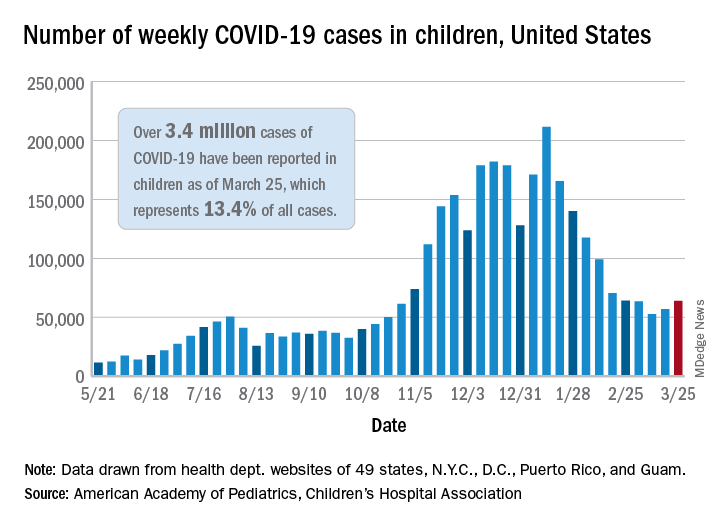
That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
Long-haul COVID-19 brings welcome attention to POTS
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.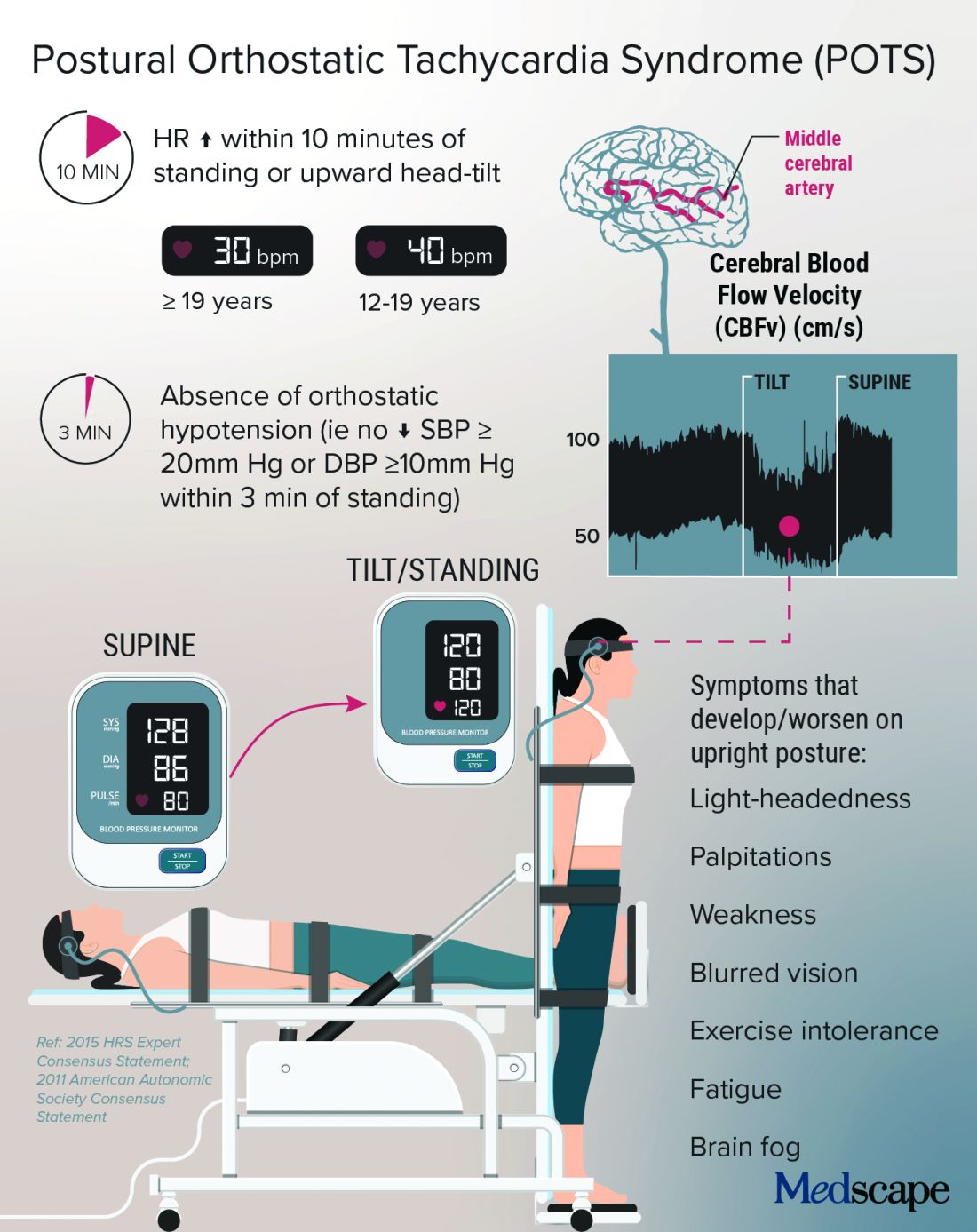
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Febuxostat, allopurinol real-world cardiovascular risk appears equal
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Can benefits of SBRT outweigh risks in ultra-central lung tumors?
Of the 72 patients studied, 15 (21%) experienced grade 3 or higher toxicity and 10 (14%) died of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage.
This doesn’t completely write off the use of SBRT for ultra-central lung tumors, according to Joyce Lodeweges, MD, of University Medical Center (UMC) Utrecht in the Netherlands.
“We have to inform the patient very well that there are some high risks to this treatment,” she said at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 61M0).
Dr. Lodeweges noted that keeping the biologically effective dose of radiation to the main bronchus below a certain threshold (< 90 Gy) could reduce the risk of toxicity significantly, making SBRT a viable option for some patients. In addition, MRI-guided daily adaptation of the radiation treatment to organs at risk may make the treatment safer.
Varying definitions, regimens spur debate
SBRT is standard care in peripherally located, stage I non–small cell lung cancer that is inoperable or if the patient refuses surgery, noted study discussant Yolande Lievens, MD, PhD, of Ghent University Hospital in Belgium.
“[SBRT] has good local control rates with low toxicity even in patients with COPD or being elderly,” Dr. Lievens said.
“In more moderately central tumors, there is quite some evidence that risk-adapted fractionation schemes can be delivered in a safe way and lead to high local control rates,” she added. “For ultra-central legions, there’s still not a recommendation to treat with SBRT because we see a lot of increased toxicity.”
“For ultra-central tumors, SBRT is still under debate,” agreed Dr. Lodeweges. “This is because of the varying definitions in the literature and the varying fractionation schemes used.”
How the location of tumors is defined is important. Central tumors are those that are at least 2 cm away from the main bronchial tree, whereas ultra-central tumors are those that butt onto it or overlap it.
In Dr. Lodeweges’s study, ultra-central tumors were defined as those with a planning target volume (PTV) abutting or overlapping the main bronchi, trachea, and/or esophagus.
Study details
Between 2012 and 2020, there were 72 patients with ultra-central lung tumors treated at UMC Utrecht. Most patients (78%) had a PTV covering the main bronchus, with 21% each having PTVs overlapping the trachea or esophagus.
Patients received a protracted SBRT regimen of 60 Gy given in 12 fractions. The median follow-up was 19 months.
The local failure-free survival rate was 98% at 1 year and 85% at 2 years. Overall survival rates were 77% and 52%, respectively.
Receiving a biologically effective dose of more than 90 Gy to the main bronchus increased the risk of grade 3 or higher toxicity. On the other hand, patient age and tumor histology did not affect the risk of adverse events.
The use of antithrombotic therapy didn’t have any bearing on toxicity either, but it’s a possible risk factor to consider, Dr. Lodeweges said. Peri- or endobronchial tumor location is another consideration.
Findings in context
How do the results of the current study sit with other studies of SBRT in non–small cell lung cancer? Dr. Lievens pointed out that overall survival at 2 years was lower in the current trial (52%) than in patients with central tumors treated in the RTOG 0813 trial (68%-73%) or those with peripheral tumors in the CHISEL trial (77%).
There were, of course, different fractions and doses of radiotherapy used in these trials, with lower doses and more fractions in the UMC Utrecht study, and there was higher toxicity when ultra-central lesions were treated.
“Optimized radiotherapy dose fractionation regimens are investigated quite intensively to improve the clinical benefit. This is an important area of research,” Dr. Lievens said.
The high local control rates but serious risk of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage seen in the current study “calls for further investigation of dose/volume parameters in the context of the location of the tumor but also in the context of other treatment modalities,” she added. “Advanced technologies in radiotherapy, which allow better imaging and daily adaptation, such as the MR-Linac, can optimize clinical benefits.”
The study was supported by UMC Utrecht and received no commercial funding. Dr. Lodeweges and Dr. Lievens had no relevant conflicts of interest.
Of the 72 patients studied, 15 (21%) experienced grade 3 or higher toxicity and 10 (14%) died of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage.
This doesn’t completely write off the use of SBRT for ultra-central lung tumors, according to Joyce Lodeweges, MD, of University Medical Center (UMC) Utrecht in the Netherlands.
“We have to inform the patient very well that there are some high risks to this treatment,” she said at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 61M0).
Dr. Lodeweges noted that keeping the biologically effective dose of radiation to the main bronchus below a certain threshold (< 90 Gy) could reduce the risk of toxicity significantly, making SBRT a viable option for some patients. In addition, MRI-guided daily adaptation of the radiation treatment to organs at risk may make the treatment safer.
Varying definitions, regimens spur debate
SBRT is standard care in peripherally located, stage I non–small cell lung cancer that is inoperable or if the patient refuses surgery, noted study discussant Yolande Lievens, MD, PhD, of Ghent University Hospital in Belgium.
“[SBRT] has good local control rates with low toxicity even in patients with COPD or being elderly,” Dr. Lievens said.
“In more moderately central tumors, there is quite some evidence that risk-adapted fractionation schemes can be delivered in a safe way and lead to high local control rates,” she added. “For ultra-central legions, there’s still not a recommendation to treat with SBRT because we see a lot of increased toxicity.”
“For ultra-central tumors, SBRT is still under debate,” agreed Dr. Lodeweges. “This is because of the varying definitions in the literature and the varying fractionation schemes used.”
How the location of tumors is defined is important. Central tumors are those that are at least 2 cm away from the main bronchial tree, whereas ultra-central tumors are those that butt onto it or overlap it.
In Dr. Lodeweges’s study, ultra-central tumors were defined as those with a planning target volume (PTV) abutting or overlapping the main bronchi, trachea, and/or esophagus.
Study details
Between 2012 and 2020, there were 72 patients with ultra-central lung tumors treated at UMC Utrecht. Most patients (78%) had a PTV covering the main bronchus, with 21% each having PTVs overlapping the trachea or esophagus.
Patients received a protracted SBRT regimen of 60 Gy given in 12 fractions. The median follow-up was 19 months.
The local failure-free survival rate was 98% at 1 year and 85% at 2 years. Overall survival rates were 77% and 52%, respectively.
Receiving a biologically effective dose of more than 90 Gy to the main bronchus increased the risk of grade 3 or higher toxicity. On the other hand, patient age and tumor histology did not affect the risk of adverse events.
The use of antithrombotic therapy didn’t have any bearing on toxicity either, but it’s a possible risk factor to consider, Dr. Lodeweges said. Peri- or endobronchial tumor location is another consideration.
Findings in context
How do the results of the current study sit with other studies of SBRT in non–small cell lung cancer? Dr. Lievens pointed out that overall survival at 2 years was lower in the current trial (52%) than in patients with central tumors treated in the RTOG 0813 trial (68%-73%) or those with peripheral tumors in the CHISEL trial (77%).
There were, of course, different fractions and doses of radiotherapy used in these trials, with lower doses and more fractions in the UMC Utrecht study, and there was higher toxicity when ultra-central lesions were treated.
“Optimized radiotherapy dose fractionation regimens are investigated quite intensively to improve the clinical benefit. This is an important area of research,” Dr. Lievens said.
The high local control rates but serious risk of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage seen in the current study “calls for further investigation of dose/volume parameters in the context of the location of the tumor but also in the context of other treatment modalities,” she added. “Advanced technologies in radiotherapy, which allow better imaging and daily adaptation, such as the MR-Linac, can optimize clinical benefits.”
The study was supported by UMC Utrecht and received no commercial funding. Dr. Lodeweges and Dr. Lievens had no relevant conflicts of interest.
Of the 72 patients studied, 15 (21%) experienced grade 3 or higher toxicity and 10 (14%) died of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage.
This doesn’t completely write off the use of SBRT for ultra-central lung tumors, according to Joyce Lodeweges, MD, of University Medical Center (UMC) Utrecht in the Netherlands.
“We have to inform the patient very well that there are some high risks to this treatment,” she said at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021 (Abstract 61M0).
Dr. Lodeweges noted that keeping the biologically effective dose of radiation to the main bronchus below a certain threshold (< 90 Gy) could reduce the risk of toxicity significantly, making SBRT a viable option for some patients. In addition, MRI-guided daily adaptation of the radiation treatment to organs at risk may make the treatment safer.
Varying definitions, regimens spur debate
SBRT is standard care in peripherally located, stage I non–small cell lung cancer that is inoperable or if the patient refuses surgery, noted study discussant Yolande Lievens, MD, PhD, of Ghent University Hospital in Belgium.
“[SBRT] has good local control rates with low toxicity even in patients with COPD or being elderly,” Dr. Lievens said.
“In more moderately central tumors, there is quite some evidence that risk-adapted fractionation schemes can be delivered in a safe way and lead to high local control rates,” she added. “For ultra-central legions, there’s still not a recommendation to treat with SBRT because we see a lot of increased toxicity.”
“For ultra-central tumors, SBRT is still under debate,” agreed Dr. Lodeweges. “This is because of the varying definitions in the literature and the varying fractionation schemes used.”
How the location of tumors is defined is important. Central tumors are those that are at least 2 cm away from the main bronchial tree, whereas ultra-central tumors are those that butt onto it or overlap it.
In Dr. Lodeweges’s study, ultra-central tumors were defined as those with a planning target volume (PTV) abutting or overlapping the main bronchi, trachea, and/or esophagus.
Study details
Between 2012 and 2020, there were 72 patients with ultra-central lung tumors treated at UMC Utrecht. Most patients (78%) had a PTV covering the main bronchus, with 21% each having PTVs overlapping the trachea or esophagus.
Patients received a protracted SBRT regimen of 60 Gy given in 12 fractions. The median follow-up was 19 months.
The local failure-free survival rate was 98% at 1 year and 85% at 2 years. Overall survival rates were 77% and 52%, respectively.
Receiving a biologically effective dose of more than 90 Gy to the main bronchus increased the risk of grade 3 or higher toxicity. On the other hand, patient age and tumor histology did not affect the risk of adverse events.
The use of antithrombotic therapy didn’t have any bearing on toxicity either, but it’s a possible risk factor to consider, Dr. Lodeweges said. Peri- or endobronchial tumor location is another consideration.
Findings in context
How do the results of the current study sit with other studies of SBRT in non–small cell lung cancer? Dr. Lievens pointed out that overall survival at 2 years was lower in the current trial (52%) than in patients with central tumors treated in the RTOG 0813 trial (68%-73%) or those with peripheral tumors in the CHISEL trial (77%).
There were, of course, different fractions and doses of radiotherapy used in these trials, with lower doses and more fractions in the UMC Utrecht study, and there was higher toxicity when ultra-central lesions were treated.
“Optimized radiotherapy dose fractionation regimens are investigated quite intensively to improve the clinical benefit. This is an important area of research,” Dr. Lievens said.
The high local control rates but serious risk of bronchopulmonary hemorrhage seen in the current study “calls for further investigation of dose/volume parameters in the context of the location of the tumor but also in the context of other treatment modalities,” she added. “Advanced technologies in radiotherapy, which allow better imaging and daily adaptation, such as the MR-Linac, can optimize clinical benefits.”
The study was supported by UMC Utrecht and received no commercial funding. Dr. Lodeweges and Dr. Lievens had no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ELCC 2021
COVID-19 ‘long-haul’ symptoms overlap with ME/CFS
People experiencing long-term symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection are increasingly meeting criteria for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), a phenomenon that highlights the need for unified research and clinical approaches, speakers said at a press briefing March 25 held by the advocacy group MEAction.
“Post-COVID lingering illness was predictable. Similar lingering fatigue syndromes have been reported in the scientific literature for nearly 100 years, following a variety of well-documented infections with viruses, bacteria, fungi, and even protozoa,” said Anthony Komaroff, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Core criteria for ME/CFS established by the Institute of Medicine in 2015 include substantial decrement in functioning for at least 6 months, postexertional malaise (PEM), or a worsening of symptoms following even minor exertion (often described as “crashes”), unrefreshing sleep, and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
Patients with ME/CFS also commonly experience painful headaches, muscle or joint aches, and allergies/other sensitivities. Although many patients can trace their symptoms to an initiating infection, “the cause is often unclear because the diagnosis is often delayed for months or years after symptom onset,” said Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, who leads a clinician coalition that aims to improve ME/CFS management.
In an international survey of 3762 COVID-19 “long-haulers” published in a preprint in December of 2020, the most frequent symptoms reported at least 6 months after illness onset were fatigue in 78%, PEM in 72%, and cognitive dysfunction (“brain fog”) in 55%. At the time of the survey, 45% reported requiring reduced work schedules because of their illness, and 22% reported being unable to work at all.
Dr. Bateman said those findings align with her experience so far with 12 COVID-19 “long haulers” who self-referred to her ME/CFS and fibromyalgia specialty clinic. Nine of the 12 met criteria for postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) based on the 10-minute NASA Lean Test, she said, and half also met the 2016 American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia.
“Some were severely impaired. We suspect a small fiber polyneuropathy in about half, and mast cell activation syndrome in more than half. We look forward to doing more testing,” Dr. Bateman said.
To be sure, Dr. Komaroff noted, there are some differences. “Long COVID” patients will often experience breathlessness and ongoing anosmia (loss of taste and smell), which aren’t typical of ME/CFS.
But, he said, “many of the symptoms are quite similar ... My guess is that ME/CFS is an illness with a final common pathway that can be triggered by different things,” said Dr. Komaroff, a senior physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and editor-in-chief of the Harvard Health Letter.
Based on previous data about CFS suggesting a 10% rate of symptoms persisting at least a year following a variety of infectious agents and the predicted 200 million COVID-19 cases globally by the end of 2021, Dr. Komaroff estimated that about 20 million cases of “long COVID” would be expected in the next year.
‘A huge investment’
On the research side, the National Institutes of Health recently appropriated $1.15 billion dollars over the next 4 years to investigate “the heterogeneity in the recovery process after COVID and to develop treatments for those suffering from [postacute COVID-19 syndrome]” according to a Feb. 5, 2021, blog from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
That same day, another NINDS blog announced “new resources for large-scale ME/CFS research” and emphasized the tie-in with long–COVID-19 syndrome.
“That’s a huge investment. In my opinion, there will be several lingering illnesses following COVID,” Dr. Komaroff said, adding, “It’s my bet that long COVID will prove to be caused by certain kinds of abnormalities in the brain, some of the same abnormalities already identified in ME/CFS. Research will determine whether that’s right or wrong.”
In 2017, NINDS had announced a large increase in funding for ME/CFS research, including the creation of four dedicated research centers. In April 2019, NINDS held a 2-day conference highlighting that ongoing work, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
During the briefing, NINDS clinical director Avindra Nath, MD, described a comprehensive ongoing ME/CFS intramural study he’s been leading since 2016.
He’s now also overseeing two long–COVID-19 studies, one of which has a protocol similar to that of the ME/CFS study and will include individuals who are still experiencing long-term symptoms following confirmed cases of COVID-19. The aim is to screen about 1,300 patients. Several task forces are now examining all of these data together.
“Each aspect is now being analyzed … What we learn from one applies to the other,” Dr. Nath said.
Advice for clinicians
In interviews, Dr. Bateman and Dr. Nath offered clinical advice for managing patients who meet ME/CFS criteria, whether they had confirmed or suspected COVID-19, a different infection, or unknown trigger(s).
Dr. Bateman advised that clinicians assess patients for each of the symptoms individually. “Besides exercise intolerance and PEM, the most commonly missed is orthostatic intolerance. It really doesn’t matter what the cause is, it’s amenable to supportive treatment. It’s one aspect of the illness that contributes to severely impaired function. My plea to all physicians would be for sure to assess for [orthostatic intolerance], and gain an understanding about activity management and avoiding PEM symptoms.”
Dr. Nath noted that an often-challenging situation is when tests for the infectious agent and other blood work come back negative, yet the patient still reports multiple debilitating symptoms. This has been a particular issue with long COVID-19, since many patients became ill early in the pandemic before the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for SARS-CoV-2 were widely available.
“The physician can only order tests that are available at their labs. I think what the physician should do is handle symptoms symptomatically but also refer patients to specialists who are taking care of these patients or to research studies,” he said.
Dr. Bateman added, “Whether they had a documented COVID infection – we just have to let go of that in 2020. Way too many people didn’t have access to a test or the timing wasn’t amenable. If people meet criteria for ME/CFS, it’s irrelevant … It’s mainly a clinical diagnosis. It’s not reliant on identifying the infectious trigger.”
Dr. Komaroff, who began caring for then-termed “chronic fatigue syndrome” patients and researching the condition more than 30 years ago, said that “every cloud has its silver lining. The increased focus on postinfectious fatigue syndrome is a silver lining in my mind around the terrible dark cloud that is the pandemic of COVID.”
Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune Inc., Ono Pharma, and Deallus, and grants from the NIH. Dr. Bateman is employed by the Bateman Horne Center, which receives grants from the NIH, and fees from Exagen Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical. Dr. Nath is an NIH employee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People experiencing long-term symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection are increasingly meeting criteria for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), a phenomenon that highlights the need for unified research and clinical approaches, speakers said at a press briefing March 25 held by the advocacy group MEAction.
“Post-COVID lingering illness was predictable. Similar lingering fatigue syndromes have been reported in the scientific literature for nearly 100 years, following a variety of well-documented infections with viruses, bacteria, fungi, and even protozoa,” said Anthony Komaroff, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Core criteria for ME/CFS established by the Institute of Medicine in 2015 include substantial decrement in functioning for at least 6 months, postexertional malaise (PEM), or a worsening of symptoms following even minor exertion (often described as “crashes”), unrefreshing sleep, and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
Patients with ME/CFS also commonly experience painful headaches, muscle or joint aches, and allergies/other sensitivities. Although many patients can trace their symptoms to an initiating infection, “the cause is often unclear because the diagnosis is often delayed for months or years after symptom onset,” said Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, who leads a clinician coalition that aims to improve ME/CFS management.
In an international survey of 3762 COVID-19 “long-haulers” published in a preprint in December of 2020, the most frequent symptoms reported at least 6 months after illness onset were fatigue in 78%, PEM in 72%, and cognitive dysfunction (“brain fog”) in 55%. At the time of the survey, 45% reported requiring reduced work schedules because of their illness, and 22% reported being unable to work at all.
Dr. Bateman said those findings align with her experience so far with 12 COVID-19 “long haulers” who self-referred to her ME/CFS and fibromyalgia specialty clinic. Nine of the 12 met criteria for postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) based on the 10-minute NASA Lean Test, she said, and half also met the 2016 American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia.
“Some were severely impaired. We suspect a small fiber polyneuropathy in about half, and mast cell activation syndrome in more than half. We look forward to doing more testing,” Dr. Bateman said.
To be sure, Dr. Komaroff noted, there are some differences. “Long COVID” patients will often experience breathlessness and ongoing anosmia (loss of taste and smell), which aren’t typical of ME/CFS.
But, he said, “many of the symptoms are quite similar ... My guess is that ME/CFS is an illness with a final common pathway that can be triggered by different things,” said Dr. Komaroff, a senior physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and editor-in-chief of the Harvard Health Letter.
Based on previous data about CFS suggesting a 10% rate of symptoms persisting at least a year following a variety of infectious agents and the predicted 200 million COVID-19 cases globally by the end of 2021, Dr. Komaroff estimated that about 20 million cases of “long COVID” would be expected in the next year.
‘A huge investment’
On the research side, the National Institutes of Health recently appropriated $1.15 billion dollars over the next 4 years to investigate “the heterogeneity in the recovery process after COVID and to develop treatments for those suffering from [postacute COVID-19 syndrome]” according to a Feb. 5, 2021, blog from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
That same day, another NINDS blog announced “new resources for large-scale ME/CFS research” and emphasized the tie-in with long–COVID-19 syndrome.
“That’s a huge investment. In my opinion, there will be several lingering illnesses following COVID,” Dr. Komaroff said, adding, “It’s my bet that long COVID will prove to be caused by certain kinds of abnormalities in the brain, some of the same abnormalities already identified in ME/CFS. Research will determine whether that’s right or wrong.”
In 2017, NINDS had announced a large increase in funding for ME/CFS research, including the creation of four dedicated research centers. In April 2019, NINDS held a 2-day conference highlighting that ongoing work, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
During the briefing, NINDS clinical director Avindra Nath, MD, described a comprehensive ongoing ME/CFS intramural study he’s been leading since 2016.
He’s now also overseeing two long–COVID-19 studies, one of which has a protocol similar to that of the ME/CFS study and will include individuals who are still experiencing long-term symptoms following confirmed cases of COVID-19. The aim is to screen about 1,300 patients. Several task forces are now examining all of these data together.
“Each aspect is now being analyzed … What we learn from one applies to the other,” Dr. Nath said.
Advice for clinicians
In interviews, Dr. Bateman and Dr. Nath offered clinical advice for managing patients who meet ME/CFS criteria, whether they had confirmed or suspected COVID-19, a different infection, or unknown trigger(s).
Dr. Bateman advised that clinicians assess patients for each of the symptoms individually. “Besides exercise intolerance and PEM, the most commonly missed is orthostatic intolerance. It really doesn’t matter what the cause is, it’s amenable to supportive treatment. It’s one aspect of the illness that contributes to severely impaired function. My plea to all physicians would be for sure to assess for [orthostatic intolerance], and gain an understanding about activity management and avoiding PEM symptoms.”
Dr. Nath noted that an often-challenging situation is when tests for the infectious agent and other blood work come back negative, yet the patient still reports multiple debilitating symptoms. This has been a particular issue with long COVID-19, since many patients became ill early in the pandemic before the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for SARS-CoV-2 were widely available.
“The physician can only order tests that are available at their labs. I think what the physician should do is handle symptoms symptomatically but also refer patients to specialists who are taking care of these patients or to research studies,” he said.
Dr. Bateman added, “Whether they had a documented COVID infection – we just have to let go of that in 2020. Way too many people didn’t have access to a test or the timing wasn’t amenable. If people meet criteria for ME/CFS, it’s irrelevant … It’s mainly a clinical diagnosis. It’s not reliant on identifying the infectious trigger.”
Dr. Komaroff, who began caring for then-termed “chronic fatigue syndrome” patients and researching the condition more than 30 years ago, said that “every cloud has its silver lining. The increased focus on postinfectious fatigue syndrome is a silver lining in my mind around the terrible dark cloud that is the pandemic of COVID.”
Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune Inc., Ono Pharma, and Deallus, and grants from the NIH. Dr. Bateman is employed by the Bateman Horne Center, which receives grants from the NIH, and fees from Exagen Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical. Dr. Nath is an NIH employee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People experiencing long-term symptoms following acute COVID-19 infection are increasingly meeting criteria for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), a phenomenon that highlights the need for unified research and clinical approaches, speakers said at a press briefing March 25 held by the advocacy group MEAction.
“Post-COVID lingering illness was predictable. Similar lingering fatigue syndromes have been reported in the scientific literature for nearly 100 years, following a variety of well-documented infections with viruses, bacteria, fungi, and even protozoa,” said Anthony Komaroff, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Core criteria for ME/CFS established by the Institute of Medicine in 2015 include substantial decrement in functioning for at least 6 months, postexertional malaise (PEM), or a worsening of symptoms following even minor exertion (often described as “crashes”), unrefreshing sleep, and cognitive impairment and/or orthostatic intolerance.
Patients with ME/CFS also commonly experience painful headaches, muscle or joint aches, and allergies/other sensitivities. Although many patients can trace their symptoms to an initiating infection, “the cause is often unclear because the diagnosis is often delayed for months or years after symptom onset,” said Lucinda Bateman, MD, founder of the Bateman Horne Center, Salt Lake City, who leads a clinician coalition that aims to improve ME/CFS management.
In an international survey of 3762 COVID-19 “long-haulers” published in a preprint in December of 2020, the most frequent symptoms reported at least 6 months after illness onset were fatigue in 78%, PEM in 72%, and cognitive dysfunction (“brain fog”) in 55%. At the time of the survey, 45% reported requiring reduced work schedules because of their illness, and 22% reported being unable to work at all.
Dr. Bateman said those findings align with her experience so far with 12 COVID-19 “long haulers” who self-referred to her ME/CFS and fibromyalgia specialty clinic. Nine of the 12 met criteria for postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) based on the 10-minute NASA Lean Test, she said, and half also met the 2016 American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia.
“Some were severely impaired. We suspect a small fiber polyneuropathy in about half, and mast cell activation syndrome in more than half. We look forward to doing more testing,” Dr. Bateman said.
To be sure, Dr. Komaroff noted, there are some differences. “Long COVID” patients will often experience breathlessness and ongoing anosmia (loss of taste and smell), which aren’t typical of ME/CFS.
But, he said, “many of the symptoms are quite similar ... My guess is that ME/CFS is an illness with a final common pathway that can be triggered by different things,” said Dr. Komaroff, a senior physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and editor-in-chief of the Harvard Health Letter.
Based on previous data about CFS suggesting a 10% rate of symptoms persisting at least a year following a variety of infectious agents and the predicted 200 million COVID-19 cases globally by the end of 2021, Dr. Komaroff estimated that about 20 million cases of “long COVID” would be expected in the next year.
‘A huge investment’
On the research side, the National Institutes of Health recently appropriated $1.15 billion dollars over the next 4 years to investigate “the heterogeneity in the recovery process after COVID and to develop treatments for those suffering from [postacute COVID-19 syndrome]” according to a Feb. 5, 2021, blog from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
That same day, another NINDS blog announced “new resources for large-scale ME/CFS research” and emphasized the tie-in with long–COVID-19 syndrome.
“That’s a huge investment. In my opinion, there will be several lingering illnesses following COVID,” Dr. Komaroff said, adding, “It’s my bet that long COVID will prove to be caused by certain kinds of abnormalities in the brain, some of the same abnormalities already identified in ME/CFS. Research will determine whether that’s right or wrong.”
In 2017, NINDS had announced a large increase in funding for ME/CFS research, including the creation of four dedicated research centers. In April 2019, NINDS held a 2-day conference highlighting that ongoing work, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
During the briefing, NINDS clinical director Avindra Nath, MD, described a comprehensive ongoing ME/CFS intramural study he’s been leading since 2016.
He’s now also overseeing two long–COVID-19 studies, one of which has a protocol similar to that of the ME/CFS study and will include individuals who are still experiencing long-term symptoms following confirmed cases of COVID-19. The aim is to screen about 1,300 patients. Several task forces are now examining all of these data together.
“Each aspect is now being analyzed … What we learn from one applies to the other,” Dr. Nath said.
Advice for clinicians
In interviews, Dr. Bateman and Dr. Nath offered clinical advice for managing patients who meet ME/CFS criteria, whether they had confirmed or suspected COVID-19, a different infection, or unknown trigger(s).
Dr. Bateman advised that clinicians assess patients for each of the symptoms individually. “Besides exercise intolerance and PEM, the most commonly missed is orthostatic intolerance. It really doesn’t matter what the cause is, it’s amenable to supportive treatment. It’s one aspect of the illness that contributes to severely impaired function. My plea to all physicians would be for sure to assess for [orthostatic intolerance], and gain an understanding about activity management and avoiding PEM symptoms.”
Dr. Nath noted that an often-challenging situation is when tests for the infectious agent and other blood work come back negative, yet the patient still reports multiple debilitating symptoms. This has been a particular issue with long COVID-19, since many patients became ill early in the pandemic before the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for SARS-CoV-2 were widely available.
“The physician can only order tests that are available at their labs. I think what the physician should do is handle symptoms symptomatically but also refer patients to specialists who are taking care of these patients or to research studies,” he said.
Dr. Bateman added, “Whether they had a documented COVID infection – we just have to let go of that in 2020. Way too many people didn’t have access to a test or the timing wasn’t amenable. If people meet criteria for ME/CFS, it’s irrelevant … It’s mainly a clinical diagnosis. It’s not reliant on identifying the infectious trigger.”
Dr. Komaroff, who began caring for then-termed “chronic fatigue syndrome” patients and researching the condition more than 30 years ago, said that “every cloud has its silver lining. The increased focus on postinfectious fatigue syndrome is a silver lining in my mind around the terrible dark cloud that is the pandemic of COVID.”
Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune Inc., Ono Pharma, and Deallus, and grants from the NIH. Dr. Bateman is employed by the Bateman Horne Center, which receives grants from the NIH, and fees from Exagen Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical. Dr. Nath is an NIH employee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Step therapy: Inside the fight against insurance companies and fail-first medicine
Every day Melissa Fulton, RN, MSN, FNP, APRN-C, shows up to work, she’s ready for another fight. An advanced practice nurse who specializes in multiple sclerosis care, Ms. Fulton said she typically spends more than a third of her time battling it out with insurance companies over drugs she knows her patients need but that insurers don’t want to cover. Instead, they want the patient to first receive less expensive and often less efficacious drugs, even if that goes against recommendations and, in some cases, against the patient’s medical history.
The maddening protocol – familiar to health care providers everywhere – is known as “step therapy.” It forces patients to try alternative medications – medications that often fail – before receiving the one initially prescribed. The process can take weeks or months, which is time that some patients don’t have. Step therapy was sold as a way to lower costs. However, beyond the ethically problematic notion of forcing sick patients to receiver cheaper alternatives that are ineffective, research has also shown it may actually be more costly in the long run.
Ms. Fulton, who works at Saunders Medical Center in Wahoo, Neb., is a veteran in the war against step therapy. She is used to pushing her appeals up the insurance company chain of command, past nonmedical reviewers, until her patient’s case finally lands on the desk of someone with a neurology background. She said that can take three or four appeals – a judge might even get involved – and the patient could still lose. “This happens constantly,” she said, “but we fight like hell.”
Fortunately, life may soon get a little easier for Ms. Fulton. In late March, a bill to restrict step therapy made it through the Nebraska state legislature and is on its way to the governor’s desk. The Step Therapy Reform Act doesn’t outright ban the practice; however, it will put guardrails in place. It requires that insurers respond to appeals within certain time frames, and it creates key exemptions.
When the governor signs off, Nebraska will join more than two dozen other states that already have step therapy restrictions on the books, according to Hannah Lynch, MPS, associate director of federal government relations and health policy at the National Psoriasis Foundation, a leading advocate to reform and protect against the insurance practice. “There’s a lot of frustration out there,” Ms. Lynch said. “It really hinders providers’ ability to make decisions they think will have the best outcomes.”
Driven by coalitions of doctors, nurses, and patients, laws reining in step therapy have been adopted at a relatively quick clip, mostly within the past 5 years. Recent additions include South Dakota and North Carolina, which adopted step therapy laws in 2020, and Arkansas, which passed a law earlier this year.
Ms. Lynch attributed growing support to rising out-of-pocket drug costs and the introduction of biologic drugs, which are often more effective but also more expensive. Like Nebraska’s law, most step therapy reform legislation carves out exemptions and requires timely appeals processes; however, many of the laws still have significant gaps, such as not including certain types of insurance plans.
Ideally, Ms. Lynch said, the protections would apply to all types of health plans that are regulated at the state level, such as Medicaid, state employee health plans, and coverage sold through state insurance exchanges. Closing loopholes in the laws is a top priority for advocates, she added, pointing to work currently underway in Arkansas to extend its new protections to Medicaid expansion patients.
“With so many outside stakeholders, you have to compromise – it’s a give and take,” Ms. Lynch said. Still, when it comes to fighting step therapy, she says, “Any protection on the books is always our first goal when we go into a state.”
Putting patients first
Lisa Arkin, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said she finds herself “swimming upstream every day in the fight with insurance.” Her patients are typically on their second or third stop and have more complex disorders. Dr. Arkin said that the problem with step therapy is that it tries to squeeze all patients into the same box, even if the circumstances don’t fit.
Her state passed restrictions on step therapy in 2019, but the measures only went into effect last year. Under the Wisconsin law, patients can be granted an exemption if an alternative treatment is contraindicated, likely to cause harm, or expected to be ineffective. Patients can also be exempt if their current treatment is working.
Dr. Arkin, an outspoken advocate for curbing step therapy, says the Wisconsin law is “very strong.” However, because it only applies to certain health plans – state employee health plans and those purchased in the state’s health insurance exchange – fewer than half the state’s patients benefit from its protections. She notes that some of the most severe presentations she treats occur in patients who rely on Medicaid coverage and already face barriers to care.
“I’m a doctor who puts up a fuss [with insurers], but that’s not fair – we shouldn’t have to do that,” Dr. Arkin said. “To me, it’s really critical to make this an even playing field so this law affords protection to everyone I see in the clinic.”
Major medical associations caution against step therapy as well. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the American Medical Association have called out the risks to patient safety and health. In fact, in 2019, after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services gave new authority to Medicare Advantage plans to start using step therapy, dozens of national medical groups called out the agency for allowing a practice that could potentially hurt patients and undercut the physician-patient decision-making process.
Last year, in a new position paper from the American College of Physicians, authors laid out recommendations for combating step therapy’s side effects. These recommendations included making related data transparent to the public and minimizing the policy’s disruptions to care. Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, a member of the committee that issued the position paper and who is a primary care physician in Georgia, said such insurance practices need to be designed with “strong input from frontline physicians, not clipboard physicians.
“What we want from insurers is understanding, transparency, and the least burdensome protocol to provide patients the care they need at a cost-effective price they can afford,” said Dr. Fincher, who is also the current president of the ACP. “The focus needs to be on what’s in the patient’s best interest.”
Every year a new fight
“We all dread January,” said Dr. Fincher. That is the worst month, she added, because new health benefits go into effect, which means patients who are responding well to certain treatments may suddenly face new restrictions.
Another aggravating aspect of step therapy? It is often difficult – if not impossible – to access information on specific step therapy protocols in a patient’s health plan in real time in the exam room, where treatment conversations actually take place. In a more patient-centered world, Dr. Fincher said, she would be able to use the electronic health record system to quickly identify whether a patient’s plan covers a particular treatment and, if not, what the alternatives are.
Georgia’s new step therapy law went into effect last year. Like laws in other states, it spells out step therapy exemptions and sets time frames in which insurers must respond to exceptions and appeals. Dr. Fincher, who spoke in favor of the new law, said she’s “happy for any step forward.” Still, the growing burden of prior authorization rules are an utter “time sink” for her and her staff.
“I have to justify my decisions to nondoctors before I even get to a doctor, and that’s really frustrating,” she said. “We’re talking about people here, not widgets.”
Advocates in Nevada are hoping this is the year a step therapy bill will make it into law in their state. As of March, one had yet to be introduced in the state legislature. Tom McCoy, director of state government affairs at the Nevada Chronic Care Collaborative, said existing Nevada law already prohibits nonmedical drug switching during a policy year; however, insurers can still make changes the following year.
A bill to rein in step therapy was proposed previously, Mr. McCoy said, but it never got off the ground. The collaborative, as well as about two dozen organizations representing Nevada providers and patients, are now calling on state lawmakers to make the issue a priority in the current session.
“The health plans have a lot of power – a lot,” Mr. McCoy said. “We’re hoping to get a [legislative] sponsor in 2021 ... but it’s also been a really hard year to connect legislators with patients and doctors, and being able to hear their stories really does make a difference.”
In Nebraska, Marcus Snow, MD, a rheumatologist at Nebraska Medicine, in Omaha, said that the state’s new step therapy law will be a “great first step in helping to provide some guardrails” around the practice. He noted that turnaround requirements for insurer responses are “sorely needed.” However, he said that, because the bill doesn’t apply to all health plans, many Nebraskans still won’t benefit.
Dealing with step therapy is a daily “headache” for Dr. Snow, who says navigating the bureaucracy of prior authorization seems to be getting worse every year. Like his peers around the country, he spends an inordinate amount of time pushing appeals up the insurance company ranks to get access to treatments he believes will be most effective. But Snow says that, more than just being a mountain of tiresome red tape, these practices also intrude on the patient-provider relationship, casting an unsettling sense of uncertainty that the ultimate decision about the best course of action isn’t up to the doctor and patient at all.
“In the end, the insurance company is the judge and jury of my prescription,” Dr. Snow said. “They’d argue I can still prescribe it, but if it costs $70,000 a year – I don’t know who can afford that.”
Ms. Lynch, at the National Psoriasis Foundation, said their step therapy advocacy will continue to take a two-pronged approach. They will push for new and expanded protections at both state and federal levels. Protections are needed at both levels to make sure that all health plans regulated by all entities are covered. In the U.S. Senate and the House, step therapy bills were reintroduced this year. They would apply to health plans subject to the federal Employee Retirement Income Security Act, which governs employer-sponsored health coverage, and could close a big gap in existing protections. Oregon, New Jersey, and Arizona are at the top of the foundation’s advocacy list this year, according to Ms. Lynch.
“Folks are really starting to pay more attention to this issue,” she said. “And hearing those real-world stories and frustrations is definitely one of the most effective tools we have.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Every day Melissa Fulton, RN, MSN, FNP, APRN-C, shows up to work, she’s ready for another fight. An advanced practice nurse who specializes in multiple sclerosis care, Ms. Fulton said she typically spends more than a third of her time battling it out with insurance companies over drugs she knows her patients need but that insurers don’t want to cover. Instead, they want the patient to first receive less expensive and often less efficacious drugs, even if that goes against recommendations and, in some cases, against the patient’s medical history.
The maddening protocol – familiar to health care providers everywhere – is known as “step therapy.” It forces patients to try alternative medications – medications that often fail – before receiving the one initially prescribed. The process can take weeks or months, which is time that some patients don’t have. Step therapy was sold as a way to lower costs. However, beyond the ethically problematic notion of forcing sick patients to receiver cheaper alternatives that are ineffective, research has also shown it may actually be more costly in the long run.
Ms. Fulton, who works at Saunders Medical Center in Wahoo, Neb., is a veteran in the war against step therapy. She is used to pushing her appeals up the insurance company chain of command, past nonmedical reviewers, until her patient’s case finally lands on the desk of someone with a neurology background. She said that can take three or four appeals – a judge might even get involved – and the patient could still lose. “This happens constantly,” she said, “but we fight like hell.”
Fortunately, life may soon get a little easier for Ms. Fulton. In late March, a bill to restrict step therapy made it through the Nebraska state legislature and is on its way to the governor’s desk. The Step Therapy Reform Act doesn’t outright ban the practice; however, it will put guardrails in place. It requires that insurers respond to appeals within certain time frames, and it creates key exemptions.
When the governor signs off, Nebraska will join more than two dozen other states that already have step therapy restrictions on the books, according to Hannah Lynch, MPS, associate director of federal government relations and health policy at the National Psoriasis Foundation, a leading advocate to reform and protect against the insurance practice. “There’s a lot of frustration out there,” Ms. Lynch said. “It really hinders providers’ ability to make decisions they think will have the best outcomes.”
Driven by coalitions of doctors, nurses, and patients, laws reining in step therapy have been adopted at a relatively quick clip, mostly within the past 5 years. Recent additions include South Dakota and North Carolina, which adopted step therapy laws in 2020, and Arkansas, which passed a law earlier this year.
Ms. Lynch attributed growing support to rising out-of-pocket drug costs and the introduction of biologic drugs, which are often more effective but also more expensive. Like Nebraska’s law, most step therapy reform legislation carves out exemptions and requires timely appeals processes; however, many of the laws still have significant gaps, such as not including certain types of insurance plans.
Ideally, Ms. Lynch said, the protections would apply to all types of health plans that are regulated at the state level, such as Medicaid, state employee health plans, and coverage sold through state insurance exchanges. Closing loopholes in the laws is a top priority for advocates, she added, pointing to work currently underway in Arkansas to extend its new protections to Medicaid expansion patients.
“With so many outside stakeholders, you have to compromise – it’s a give and take,” Ms. Lynch said. Still, when it comes to fighting step therapy, she says, “Any protection on the books is always our first goal when we go into a state.”
Putting patients first
Lisa Arkin, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said she finds herself “swimming upstream every day in the fight with insurance.” Her patients are typically on their second or third stop and have more complex disorders. Dr. Arkin said that the problem with step therapy is that it tries to squeeze all patients into the same box, even if the circumstances don’t fit.
Her state passed restrictions on step therapy in 2019, but the measures only went into effect last year. Under the Wisconsin law, patients can be granted an exemption if an alternative treatment is contraindicated, likely to cause harm, or expected to be ineffective. Patients can also be exempt if their current treatment is working.
Dr. Arkin, an outspoken advocate for curbing step therapy, says the Wisconsin law is “very strong.” However, because it only applies to certain health plans – state employee health plans and those purchased in the state’s health insurance exchange – fewer than half the state’s patients benefit from its protections. She notes that some of the most severe presentations she treats occur in patients who rely on Medicaid coverage and already face barriers to care.
“I’m a doctor who puts up a fuss [with insurers], but that’s not fair – we shouldn’t have to do that,” Dr. Arkin said. “To me, it’s really critical to make this an even playing field so this law affords protection to everyone I see in the clinic.”
Major medical associations caution against step therapy as well. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the American Medical Association have called out the risks to patient safety and health. In fact, in 2019, after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services gave new authority to Medicare Advantage plans to start using step therapy, dozens of national medical groups called out the agency for allowing a practice that could potentially hurt patients and undercut the physician-patient decision-making process.
Last year, in a new position paper from the American College of Physicians, authors laid out recommendations for combating step therapy’s side effects. These recommendations included making related data transparent to the public and minimizing the policy’s disruptions to care. Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, a member of the committee that issued the position paper and who is a primary care physician in Georgia, said such insurance practices need to be designed with “strong input from frontline physicians, not clipboard physicians.
“What we want from insurers is understanding, transparency, and the least burdensome protocol to provide patients the care they need at a cost-effective price they can afford,” said Dr. Fincher, who is also the current president of the ACP. “The focus needs to be on what’s in the patient’s best interest.”
Every year a new fight
“We all dread January,” said Dr. Fincher. That is the worst month, she added, because new health benefits go into effect, which means patients who are responding well to certain treatments may suddenly face new restrictions.
Another aggravating aspect of step therapy? It is often difficult – if not impossible – to access information on specific step therapy protocols in a patient’s health plan in real time in the exam room, where treatment conversations actually take place. In a more patient-centered world, Dr. Fincher said, she would be able to use the electronic health record system to quickly identify whether a patient’s plan covers a particular treatment and, if not, what the alternatives are.
Georgia’s new step therapy law went into effect last year. Like laws in other states, it spells out step therapy exemptions and sets time frames in which insurers must respond to exceptions and appeals. Dr. Fincher, who spoke in favor of the new law, said she’s “happy for any step forward.” Still, the growing burden of prior authorization rules are an utter “time sink” for her and her staff.
“I have to justify my decisions to nondoctors before I even get to a doctor, and that’s really frustrating,” she said. “We’re talking about people here, not widgets.”
Advocates in Nevada are hoping this is the year a step therapy bill will make it into law in their state. As of March, one had yet to be introduced in the state legislature. Tom McCoy, director of state government affairs at the Nevada Chronic Care Collaborative, said existing Nevada law already prohibits nonmedical drug switching during a policy year; however, insurers can still make changes the following year.
A bill to rein in step therapy was proposed previously, Mr. McCoy said, but it never got off the ground. The collaborative, as well as about two dozen organizations representing Nevada providers and patients, are now calling on state lawmakers to make the issue a priority in the current session.
“The health plans have a lot of power – a lot,” Mr. McCoy said. “We’re hoping to get a [legislative] sponsor in 2021 ... but it’s also been a really hard year to connect legislators with patients and doctors, and being able to hear their stories really does make a difference.”
In Nebraska, Marcus Snow, MD, a rheumatologist at Nebraska Medicine, in Omaha, said that the state’s new step therapy law will be a “great first step in helping to provide some guardrails” around the practice. He noted that turnaround requirements for insurer responses are “sorely needed.” However, he said that, because the bill doesn’t apply to all health plans, many Nebraskans still won’t benefit.
Dealing with step therapy is a daily “headache” for Dr. Snow, who says navigating the bureaucracy of prior authorization seems to be getting worse every year. Like his peers around the country, he spends an inordinate amount of time pushing appeals up the insurance company ranks to get access to treatments he believes will be most effective. But Snow says that, more than just being a mountain of tiresome red tape, these practices also intrude on the patient-provider relationship, casting an unsettling sense of uncertainty that the ultimate decision about the best course of action isn’t up to the doctor and patient at all.
“In the end, the insurance company is the judge and jury of my prescription,” Dr. Snow said. “They’d argue I can still prescribe it, but if it costs $70,000 a year – I don’t know who can afford that.”
Ms. Lynch, at the National Psoriasis Foundation, said their step therapy advocacy will continue to take a two-pronged approach. They will push for new and expanded protections at both state and federal levels. Protections are needed at both levels to make sure that all health plans regulated by all entities are covered. In the U.S. Senate and the House, step therapy bills were reintroduced this year. They would apply to health plans subject to the federal Employee Retirement Income Security Act, which governs employer-sponsored health coverage, and could close a big gap in existing protections. Oregon, New Jersey, and Arizona are at the top of the foundation’s advocacy list this year, according to Ms. Lynch.
“Folks are really starting to pay more attention to this issue,” she said. “And hearing those real-world stories and frustrations is definitely one of the most effective tools we have.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Every day Melissa Fulton, RN, MSN, FNP, APRN-C, shows up to work, she’s ready for another fight. An advanced practice nurse who specializes in multiple sclerosis care, Ms. Fulton said she typically spends more than a third of her time battling it out with insurance companies over drugs she knows her patients need but that insurers don’t want to cover. Instead, they want the patient to first receive less expensive and often less efficacious drugs, even if that goes against recommendations and, in some cases, against the patient’s medical history.
The maddening protocol – familiar to health care providers everywhere – is known as “step therapy.” It forces patients to try alternative medications – medications that often fail – before receiving the one initially prescribed. The process can take weeks or months, which is time that some patients don’t have. Step therapy was sold as a way to lower costs. However, beyond the ethically problematic notion of forcing sick patients to receiver cheaper alternatives that are ineffective, research has also shown it may actually be more costly in the long run.
Ms. Fulton, who works at Saunders Medical Center in Wahoo, Neb., is a veteran in the war against step therapy. She is used to pushing her appeals up the insurance company chain of command, past nonmedical reviewers, until her patient’s case finally lands on the desk of someone with a neurology background. She said that can take three or four appeals – a judge might even get involved – and the patient could still lose. “This happens constantly,” she said, “but we fight like hell.”
Fortunately, life may soon get a little easier for Ms. Fulton. In late March, a bill to restrict step therapy made it through the Nebraska state legislature and is on its way to the governor’s desk. The Step Therapy Reform Act doesn’t outright ban the practice; however, it will put guardrails in place. It requires that insurers respond to appeals within certain time frames, and it creates key exemptions.
When the governor signs off, Nebraska will join more than two dozen other states that already have step therapy restrictions on the books, according to Hannah Lynch, MPS, associate director of federal government relations and health policy at the National Psoriasis Foundation, a leading advocate to reform and protect against the insurance practice. “There’s a lot of frustration out there,” Ms. Lynch said. “It really hinders providers’ ability to make decisions they think will have the best outcomes.”
Driven by coalitions of doctors, nurses, and patients, laws reining in step therapy have been adopted at a relatively quick clip, mostly within the past 5 years. Recent additions include South Dakota and North Carolina, which adopted step therapy laws in 2020, and Arkansas, which passed a law earlier this year.
Ms. Lynch attributed growing support to rising out-of-pocket drug costs and the introduction of biologic drugs, which are often more effective but also more expensive. Like Nebraska’s law, most step therapy reform legislation carves out exemptions and requires timely appeals processes; however, many of the laws still have significant gaps, such as not including certain types of insurance plans.
Ideally, Ms. Lynch said, the protections would apply to all types of health plans that are regulated at the state level, such as Medicaid, state employee health plans, and coverage sold through state insurance exchanges. Closing loopholes in the laws is a top priority for advocates, she added, pointing to work currently underway in Arkansas to extend its new protections to Medicaid expansion patients.
“With so many outside stakeholders, you have to compromise – it’s a give and take,” Ms. Lynch said. Still, when it comes to fighting step therapy, she says, “Any protection on the books is always our first goal when we go into a state.”
Putting patients first
Lisa Arkin, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said she finds herself “swimming upstream every day in the fight with insurance.” Her patients are typically on their second or third stop and have more complex disorders. Dr. Arkin said that the problem with step therapy is that it tries to squeeze all patients into the same box, even if the circumstances don’t fit.
Her state passed restrictions on step therapy in 2019, but the measures only went into effect last year. Under the Wisconsin law, patients can be granted an exemption if an alternative treatment is contraindicated, likely to cause harm, or expected to be ineffective. Patients can also be exempt if their current treatment is working.
Dr. Arkin, an outspoken advocate for curbing step therapy, says the Wisconsin law is “very strong.” However, because it only applies to certain health plans – state employee health plans and those purchased in the state’s health insurance exchange – fewer than half the state’s patients benefit from its protections. She notes that some of the most severe presentations she treats occur in patients who rely on Medicaid coverage and already face barriers to care.
“I’m a doctor who puts up a fuss [with insurers], but that’s not fair – we shouldn’t have to do that,” Dr. Arkin said. “To me, it’s really critical to make this an even playing field so this law affords protection to everyone I see in the clinic.”
Major medical associations caution against step therapy as well. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the American Medical Association have called out the risks to patient safety and health. In fact, in 2019, after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services gave new authority to Medicare Advantage plans to start using step therapy, dozens of national medical groups called out the agency for allowing a practice that could potentially hurt patients and undercut the physician-patient decision-making process.
Last year, in a new position paper from the American College of Physicians, authors laid out recommendations for combating step therapy’s side effects. These recommendations included making related data transparent to the public and minimizing the policy’s disruptions to care. Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, a member of the committee that issued the position paper and who is a primary care physician in Georgia, said such insurance practices need to be designed with “strong input from frontline physicians, not clipboard physicians.
“What we want from insurers is understanding, transparency, and the least burdensome protocol to provide patients the care they need at a cost-effective price they can afford,” said Dr. Fincher, who is also the current president of the ACP. “The focus needs to be on what’s in the patient’s best interest.”
Every year a new fight
“We all dread January,” said Dr. Fincher. That is the worst month, she added, because new health benefits go into effect, which means patients who are responding well to certain treatments may suddenly face new restrictions.
Another aggravating aspect of step therapy? It is often difficult – if not impossible – to access information on specific step therapy protocols in a patient’s health plan in real time in the exam room, where treatment conversations actually take place. In a more patient-centered world, Dr. Fincher said, she would be able to use the electronic health record system to quickly identify whether a patient’s plan covers a particular treatment and, if not, what the alternatives are.
Georgia’s new step therapy law went into effect last year. Like laws in other states, it spells out step therapy exemptions and sets time frames in which insurers must respond to exceptions and appeals. Dr. Fincher, who spoke in favor of the new law, said she’s “happy for any step forward.” Still, the growing burden of prior authorization rules are an utter “time sink” for her and her staff.
“I have to justify my decisions to nondoctors before I even get to a doctor, and that’s really frustrating,” she said. “We’re talking about people here, not widgets.”
Advocates in Nevada are hoping this is the year a step therapy bill will make it into law in their state. As of March, one had yet to be introduced in the state legislature. Tom McCoy, director of state government affairs at the Nevada Chronic Care Collaborative, said existing Nevada law already prohibits nonmedical drug switching during a policy year; however, insurers can still make changes the following year.
A bill to rein in step therapy was proposed previously, Mr. McCoy said, but it never got off the ground. The collaborative, as well as about two dozen organizations representing Nevada providers and patients, are now calling on state lawmakers to make the issue a priority in the current session.
“The health plans have a lot of power – a lot,” Mr. McCoy said. “We’re hoping to get a [legislative] sponsor in 2021 ... but it’s also been a really hard year to connect legislators with patients and doctors, and being able to hear their stories really does make a difference.”
In Nebraska, Marcus Snow, MD, a rheumatologist at Nebraska Medicine, in Omaha, said that the state’s new step therapy law will be a “great first step in helping to provide some guardrails” around the practice. He noted that turnaround requirements for insurer responses are “sorely needed.” However, he said that, because the bill doesn’t apply to all health plans, many Nebraskans still won’t benefit.
Dealing with step therapy is a daily “headache” for Dr. Snow, who says navigating the bureaucracy of prior authorization seems to be getting worse every year. Like his peers around the country, he spends an inordinate amount of time pushing appeals up the insurance company ranks to get access to treatments he believes will be most effective. But Snow says that, more than just being a mountain of tiresome red tape, these practices also intrude on the patient-provider relationship, casting an unsettling sense of uncertainty that the ultimate decision about the best course of action isn’t up to the doctor and patient at all.
“In the end, the insurance company is the judge and jury of my prescription,” Dr. Snow said. “They’d argue I can still prescribe it, but if it costs $70,000 a year – I don’t know who can afford that.”
Ms. Lynch, at the National Psoriasis Foundation, said their step therapy advocacy will continue to take a two-pronged approach. They will push for new and expanded protections at both state and federal levels. Protections are needed at both levels to make sure that all health plans regulated by all entities are covered. In the U.S. Senate and the House, step therapy bills were reintroduced this year. They would apply to health plans subject to the federal Employee Retirement Income Security Act, which governs employer-sponsored health coverage, and could close a big gap in existing protections. Oregon, New Jersey, and Arizona are at the top of the foundation’s advocacy list this year, according to Ms. Lynch.
“Folks are really starting to pay more attention to this issue,” she said. “And hearing those real-world stories and frustrations is definitely one of the most effective tools we have.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.