User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Flu vaccination associated with reduced stroke risk
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM LANCET PUBLIC HEALTH
Give bacterial diversity a chance: The antibiotic dichotomy
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
What’s the opposite of an antibiotic?
Everyone knows that LOTME loves a good dichotomy: yin/yang, good/evil, heads/tails, particle/wave, peanut butter/jelly. They’re all great. We’re also big fans of microbiomes, particularly the gut microbiome. But what if we could combine the two? A healthy and nutritious story about the gut microbiome, with a dash of added dichotomy for flavor. Is such a thing even possible? Let’s find out.
First, we need an antibiotic, a drug designed to fight bacterial infections. If you’ve got strep throat, otitis media, or bubonic plague, there’s a good chance you will receive an antibiotic. That antibiotic will kill the bad bacteria that are making you sick, but it will also kill a lot of the good bacteria that inhabit your gut microbiome, which results in side effects like bloating and diarrhea.
It comes down to diversity, explained Elisa Marroquin, PhD, of Texas Christian University (Go Horned Frogs!): “In a human community, we need people that have different professions because we don’t all know how to do every single job. And so the same happens with bacteria. We need lots of different gut bacteria that know how to do different things.”
She and her colleagues reviewed 29 studies published over the last 7 years and found a way to preserve the diversity of a human gut microbiome that’s dealing with an antibiotic. Their solution? Prescribe a probiotic.
The way to fight the effects of stopping a bacterial infection is to provide food for what are, basically, other bacterial infections. Antibiotic/probiotic is a prescription for dichotomy, and it means we managed to combine gut microbiomes with a dichotomy. And you didn’t think we could do it.
The earphone of hearing aids
It’s estimated that up to 75% of people who need hearing aids don’t wear them. Why? Well, there’s the social stigma about not wanting to appear too old, and then there’s the cost factor.
Is there a cheaper, less stigmatizing option to amplify hearing? The answer, according to otolaryngologist Yen-fu Cheng, MD, of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and associates, is wireless earphones. AirPods, if you want to be brand specific.
Airpods can be on the more expensive side – running about $129 for AirPods 2 and $249 for AirPods Pro – but when compared with premium hearing aids ($10,000), or even basic aids (about $1,500), the Apple products come off inexpensive after all.
The team tested the premium and basic hearing aids against the AirPods 2 and the AirPod Pro using Apple’s Live Listen feature, which helps amplify sound through the company’s wireless earphones and iPhones and was initially designed to assist people with normal hearing in situations such as birdwatching.
The AirPods Pro worked just as well as the basic hearing aid but not quite as well as the premium hearing aid in a quiet setting, while the AirPods 2 performed the worst. When tested in a noisy setting, the AirPods Pro was pretty comparable to the premium hearing aid, as long as the noise came from a lateral direction. Neither of the AirPod models did as well as the hearing aids with head-on noises.
Wireless earbuds may not be the perfect solution from a clinical standpoint, but they’re a good start for people who don’t have access to hearing aids, Dr. Cheng noted.
So who says headphones damage your hearing? They might actually help.
Now I lay me down to sleep, I pray the computer my soul to keep
Radiation is the boring hazard of space travel. No one dies in a space horror movie because they’ve been slowly exposed to too much cosmic radiation. It’s always “thrown out the airlock” this and “eaten by a xenomorph” that.
Radiation, however, is not something that can be ignored, but it turns out that a potential solution is another science fiction staple: artificial hibernation. Generally in sci-fi, hibernation is a plot convenience to get people from point A to point B in a ship that doesn’t break the laws of physics. Here on Earth, though, it is well known that animals naturally entering a state of torpor during hibernation gain significant resistance to radiation.
The problem, of course, is that humans don’t hibernate, and no matter how hard people who work 100-hour weeks for Elon Musk try, sleeping for months on end is simply something we can’t do. However, a new study shows that it’s possible to induce this torpor state in animals that don’t naturally hibernate. By injecting rats with adenosine 5’-monophosphate monohydrate and keeping them in a room held at 16° C, an international team of scientists successfully induced a synthetic torpor state.
That’s not all they did: The scientists also exposed the hibernating rats to a large dose of radiation approximating that found in deep space. Which isn’t something we’d like to explain to our significant other when we got home from work. “So how was your day?” “Oh, I irradiated a bunch of sleeping rats. … Don’t worry they’re fine!” Which they were. Thanks to the hypoxic and hypothermic state, the tissue was spared damage from the high-energy ion radiation.
Obviously, there’s a big difference between a rat and a human and a lot of work to be done, but the study does show that artificial hibernation is possible. Perhaps one day we’ll be able to fall asleep and wake up light-years away under an alien sky, and we won’t be horrifically mutated or riddled with cancer. If, however, you find yourself in hibernation on your way to Jupiter (or Saturn) to investigate a mysterious black monolith, we suggest sleeping with one eye open and gripping your pillow tight.
‘A huge deal’: Millions have long COVID, and more are expected
with symptoms that have lasted 3 months or longer, according to the latest U.S. government survey done in October. More than a quarter say their condition is severe enough to significantly limit their day-to-day activities – yet the problem is only barely starting to get the attention of employers, the health care system, and policymakers.
With no cure or treatment in sight, long COVID is already burdening not only the health care system, but also the economy – and that burden is set to grow. Many experts worry about the possible long-term ripple effects, from increased spending on medical care costs to lost wages due to not being able to work, as well as the policy implications that come with addressing these issues.
“At this point, anyone who’s looking at this seriously would say this is a huge deal,” says senior Brookings Institution fellow Katie Bach, the author of a study that analyzed long COVID’s impact on the labor market.
“We need a real concerted focus on treating these people, which means both research and the clinical side, and figuring out how to build a labor market that is more inclusive of people with disabilities,” she said.
It’s not only that many people are affected. It’s that they are often affected for months and possibly even years.
The U.S. government figures suggest more than 18 million people could have symptoms of long COVID right now. The latest Household Pulse Survey by the Census Bureau and the National Center for Health Statistics takes data from 41,415 people.
A preprint of a study by researchers from City University of New York, posted on medRxiv in September and based on a similar population survey done between June 30 and July 2, drew comparable results. The study has not been peer reviewed.
More than 7% of all those who answered said they had long COVID at the time of the survey, which the researchers said corresponded to approximately 18.5 million U.S. adults. The same study found that a quarter of those, or an estimated 4.7 million adults, said their daily activities were impacted “a lot.”
This can translate into pain not only for the patients, but for governments and employers, too.
In high-income countries around the world, government surveys and other studies are shedding light on the extent to which post-COVID-19 symptoms – commonly known as long COVID – are affecting populations. While results vary, they generally fall within similar ranges.
The World Health Organization estimates that between 10% and 20% of those with COVID-19 go on to have an array of medium- to long-term post-COVID-19 symptoms that range from mild to debilitating. The U.S. Government Accountability Office puts that estimate at 10% to 30%; one of the latest studies published at the end of October in The Journal of the American Medical Association found that 15% of U.S. adults who had tested positive for COVID-19 reported current long COVID symptoms. Elsewhere, a study from the Netherlands published in The Lancet in August found that one in eight COVID-19 cases, or 12.7%, were likely to become long COVID.
“It’s very clear that the condition is devastating people’s lives and livelihoods,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus wrote in an article for The Guardian newspaper in October.
“The world has already lost a significant number of the workforce to illness, death, fatigue, unplanned retirement due to an increase in long-term disability, which not only impacts the health system, but is a hit to the overarching economy … the impact of long COVID for all countries is very serious and needs immediate and sustained action equivalent to its scale.”
Global snapshot: Lasting symptoms, impact on activities
Patients describe a spectrum of persistent issues, with extreme fatigue, brain fog or cognitive problems, and shortness of breath among the most common complaints. Many also have manageable symptoms that worsen significantly after even mild physical or mental exertion.
Women appear almost twice as likely as men to get long COVID. Many patients have other medical conditions and disabilities that make them more vulnerable to the condition. Those who face greater obstacles accessing health care due to discrimination or socioeconomic inequity are at higher risk as well.
While many are older, a large number are also in their prime working age. The Census Bureau data show that people ages 40-49 are more likely than any other group to get long COVID, which has broader implications for labor markets and the global economy. Already, experts have estimated that long COVID is likely to cost the U.S. trillions of dollars and affect multiple industries.
“Whether they’re in the financial world, the medical system, lawyers, they’re telling me they’re sitting at the computer screen and they’re unable to process the data,” said Zachary Schwartz, MD, medical director for Vancouver General Hospital’s Post-COVID-19 Recovery Clinic.
“That is what’s most distressing for people, in that they’re not working, they’re not making money, and they don’t know when, or if, they’re going to get better.”
Nearly a third of respondents in the Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey who said they have had COVID-19 reported symptoms that lasted 3 months or longer. People between the ages of 30 and 59 were the most affected, with about 32% reporting symptoms. Across the entire adult U.S. population, the survey found that 1 in 7 adults have had long COVID at some point during the pandemic, with about 1 in 18 saying it limited their activity to some degree, and 1 in 50 saying they have faced “a lot” of limits on their activities. Any way these numbers are dissected, long COVID has impacted a large swath of the population.
Yet research into the causes and possible treatments of long COVID is just getting underway.
“The amount of energy and time devoted to it is way, way less than it should, given how many people are likely affected,” said David Cutler, PhD, professor of economics at Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., who has written about the economic cost of long COVID. “We’re way, way underdoing it here. And I think that’s really a terrible thing.”
Population surveys and studies from around the world show that long COVID lives up to its name, with people reporting serious symptoms for months on end.
In October, Statistics Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada published early results from a questionnaire done between spring and summer 2022 that found just under 15% of adults who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID-19 went on to have new or continuing symptoms 3 or more months later. Nearly half, or 47.3%, dealt with symptoms that lasted a year or more. More than one in five said their symptoms “often or always” limited their day-to-day activities, which included routine tasks such as preparing meals, doing errands and chores, and basic functions such as personal care and moving around in their homes.
Nearly three-quarters of workers or students said they missed an average of 20 days of work or school.
“We haven’t yet been able to determine exactly when symptoms resolve,” said Rainu Kaushal, MD, the senior associate dean for clinical research at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York. She is co-leading a national study on long COVID in adults and children, funded by the National Institutes of Health RECOVER Initiative.
“But there does seem to be, for many of the milder symptoms, resolution at about 4-6 weeks. There seems to be a second point of resolution around 6 months for certain symptoms, and then some symptoms do seem to be permanent, and those tend to be patients who have underlying conditions,” she said.
Reducing the risk
Given all the data so far, experts recommend urgent policy changes to help people with long COVID.
“The population needs to be prepared, that understanding long COVID is going to be a very long and difficult process,” said Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor and the lead principal investigator of the RECOVER adult cohort at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York. He said the government can do a great deal to help, including setting up a network of connected clinics treating long COVID, standardizing best practices, and sharing information.
“That would go a long way towards making sure that every person feels like they’re not too far away from a clinic where they can get treated for this particular condition,” he said.
But the only known way to prevent long COVID is to prevent COVID-19 infections in the first place, experts say. That means equitable access to tests, therapeutics, and vaccines.
“I will say that avoiding COVID remains the best treatment in the arsenal right now,” said Dr. Kaushal. This means masking, avoiding crowded places with poor ventilation and high exposure risk, and being up to date on vaccinations, she said.
A number of papers – including a large U.K. study published in May 2022, another one from July, and the JAMA study from October – all suggest that vaccinations can help reduce the risk of long COVID.
“I am absolutely of the belief that vaccination has reduced the incidence and overall amount of long COVID … [and is] still by far the best thing the public can do,” said Dr. Schwartz.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
with symptoms that have lasted 3 months or longer, according to the latest U.S. government survey done in October. More than a quarter say their condition is severe enough to significantly limit their day-to-day activities – yet the problem is only barely starting to get the attention of employers, the health care system, and policymakers.
With no cure or treatment in sight, long COVID is already burdening not only the health care system, but also the economy – and that burden is set to grow. Many experts worry about the possible long-term ripple effects, from increased spending on medical care costs to lost wages due to not being able to work, as well as the policy implications that come with addressing these issues.
“At this point, anyone who’s looking at this seriously would say this is a huge deal,” says senior Brookings Institution fellow Katie Bach, the author of a study that analyzed long COVID’s impact on the labor market.
“We need a real concerted focus on treating these people, which means both research and the clinical side, and figuring out how to build a labor market that is more inclusive of people with disabilities,” she said.
It’s not only that many people are affected. It’s that they are often affected for months and possibly even years.
The U.S. government figures suggest more than 18 million people could have symptoms of long COVID right now. The latest Household Pulse Survey by the Census Bureau and the National Center for Health Statistics takes data from 41,415 people.
A preprint of a study by researchers from City University of New York, posted on medRxiv in September and based on a similar population survey done between June 30 and July 2, drew comparable results. The study has not been peer reviewed.
More than 7% of all those who answered said they had long COVID at the time of the survey, which the researchers said corresponded to approximately 18.5 million U.S. adults. The same study found that a quarter of those, or an estimated 4.7 million adults, said their daily activities were impacted “a lot.”
This can translate into pain not only for the patients, but for governments and employers, too.
In high-income countries around the world, government surveys and other studies are shedding light on the extent to which post-COVID-19 symptoms – commonly known as long COVID – are affecting populations. While results vary, they generally fall within similar ranges.
The World Health Organization estimates that between 10% and 20% of those with COVID-19 go on to have an array of medium- to long-term post-COVID-19 symptoms that range from mild to debilitating. The U.S. Government Accountability Office puts that estimate at 10% to 30%; one of the latest studies published at the end of October in The Journal of the American Medical Association found that 15% of U.S. adults who had tested positive for COVID-19 reported current long COVID symptoms. Elsewhere, a study from the Netherlands published in The Lancet in August found that one in eight COVID-19 cases, or 12.7%, were likely to become long COVID.
“It’s very clear that the condition is devastating people’s lives and livelihoods,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus wrote in an article for The Guardian newspaper in October.
“The world has already lost a significant number of the workforce to illness, death, fatigue, unplanned retirement due to an increase in long-term disability, which not only impacts the health system, but is a hit to the overarching economy … the impact of long COVID for all countries is very serious and needs immediate and sustained action equivalent to its scale.”
Global snapshot: Lasting symptoms, impact on activities
Patients describe a spectrum of persistent issues, with extreme fatigue, brain fog or cognitive problems, and shortness of breath among the most common complaints. Many also have manageable symptoms that worsen significantly after even mild physical or mental exertion.
Women appear almost twice as likely as men to get long COVID. Many patients have other medical conditions and disabilities that make them more vulnerable to the condition. Those who face greater obstacles accessing health care due to discrimination or socioeconomic inequity are at higher risk as well.
While many are older, a large number are also in their prime working age. The Census Bureau data show that people ages 40-49 are more likely than any other group to get long COVID, which has broader implications for labor markets and the global economy. Already, experts have estimated that long COVID is likely to cost the U.S. trillions of dollars and affect multiple industries.
“Whether they’re in the financial world, the medical system, lawyers, they’re telling me they’re sitting at the computer screen and they’re unable to process the data,” said Zachary Schwartz, MD, medical director for Vancouver General Hospital’s Post-COVID-19 Recovery Clinic.
“That is what’s most distressing for people, in that they’re not working, they’re not making money, and they don’t know when, or if, they’re going to get better.”
Nearly a third of respondents in the Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey who said they have had COVID-19 reported symptoms that lasted 3 months or longer. People between the ages of 30 and 59 were the most affected, with about 32% reporting symptoms. Across the entire adult U.S. population, the survey found that 1 in 7 adults have had long COVID at some point during the pandemic, with about 1 in 18 saying it limited their activity to some degree, and 1 in 50 saying they have faced “a lot” of limits on their activities. Any way these numbers are dissected, long COVID has impacted a large swath of the population.
Yet research into the causes and possible treatments of long COVID is just getting underway.
“The amount of energy and time devoted to it is way, way less than it should, given how many people are likely affected,” said David Cutler, PhD, professor of economics at Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., who has written about the economic cost of long COVID. “We’re way, way underdoing it here. And I think that’s really a terrible thing.”
Population surveys and studies from around the world show that long COVID lives up to its name, with people reporting serious symptoms for months on end.
In October, Statistics Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada published early results from a questionnaire done between spring and summer 2022 that found just under 15% of adults who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID-19 went on to have new or continuing symptoms 3 or more months later. Nearly half, or 47.3%, dealt with symptoms that lasted a year or more. More than one in five said their symptoms “often or always” limited their day-to-day activities, which included routine tasks such as preparing meals, doing errands and chores, and basic functions such as personal care and moving around in their homes.
Nearly three-quarters of workers or students said they missed an average of 20 days of work or school.
“We haven’t yet been able to determine exactly when symptoms resolve,” said Rainu Kaushal, MD, the senior associate dean for clinical research at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York. She is co-leading a national study on long COVID in adults and children, funded by the National Institutes of Health RECOVER Initiative.
“But there does seem to be, for many of the milder symptoms, resolution at about 4-6 weeks. There seems to be a second point of resolution around 6 months for certain symptoms, and then some symptoms do seem to be permanent, and those tend to be patients who have underlying conditions,” she said.
Reducing the risk
Given all the data so far, experts recommend urgent policy changes to help people with long COVID.
“The population needs to be prepared, that understanding long COVID is going to be a very long and difficult process,” said Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor and the lead principal investigator of the RECOVER adult cohort at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York. He said the government can do a great deal to help, including setting up a network of connected clinics treating long COVID, standardizing best practices, and sharing information.
“That would go a long way towards making sure that every person feels like they’re not too far away from a clinic where they can get treated for this particular condition,” he said.
But the only known way to prevent long COVID is to prevent COVID-19 infections in the first place, experts say. That means equitable access to tests, therapeutics, and vaccines.
“I will say that avoiding COVID remains the best treatment in the arsenal right now,” said Dr. Kaushal. This means masking, avoiding crowded places with poor ventilation and high exposure risk, and being up to date on vaccinations, she said.
A number of papers – including a large U.K. study published in May 2022, another one from July, and the JAMA study from October – all suggest that vaccinations can help reduce the risk of long COVID.
“I am absolutely of the belief that vaccination has reduced the incidence and overall amount of long COVID … [and is] still by far the best thing the public can do,” said Dr. Schwartz.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
with symptoms that have lasted 3 months or longer, according to the latest U.S. government survey done in October. More than a quarter say their condition is severe enough to significantly limit their day-to-day activities – yet the problem is only barely starting to get the attention of employers, the health care system, and policymakers.
With no cure or treatment in sight, long COVID is already burdening not only the health care system, but also the economy – and that burden is set to grow. Many experts worry about the possible long-term ripple effects, from increased spending on medical care costs to lost wages due to not being able to work, as well as the policy implications that come with addressing these issues.
“At this point, anyone who’s looking at this seriously would say this is a huge deal,” says senior Brookings Institution fellow Katie Bach, the author of a study that analyzed long COVID’s impact on the labor market.
“We need a real concerted focus on treating these people, which means both research and the clinical side, and figuring out how to build a labor market that is more inclusive of people with disabilities,” she said.
It’s not only that many people are affected. It’s that they are often affected for months and possibly even years.
The U.S. government figures suggest more than 18 million people could have symptoms of long COVID right now. The latest Household Pulse Survey by the Census Bureau and the National Center for Health Statistics takes data from 41,415 people.
A preprint of a study by researchers from City University of New York, posted on medRxiv in September and based on a similar population survey done between June 30 and July 2, drew comparable results. The study has not been peer reviewed.
More than 7% of all those who answered said they had long COVID at the time of the survey, which the researchers said corresponded to approximately 18.5 million U.S. adults. The same study found that a quarter of those, or an estimated 4.7 million adults, said their daily activities were impacted “a lot.”
This can translate into pain not only for the patients, but for governments and employers, too.
In high-income countries around the world, government surveys and other studies are shedding light on the extent to which post-COVID-19 symptoms – commonly known as long COVID – are affecting populations. While results vary, they generally fall within similar ranges.
The World Health Organization estimates that between 10% and 20% of those with COVID-19 go on to have an array of medium- to long-term post-COVID-19 symptoms that range from mild to debilitating. The U.S. Government Accountability Office puts that estimate at 10% to 30%; one of the latest studies published at the end of October in The Journal of the American Medical Association found that 15% of U.S. adults who had tested positive for COVID-19 reported current long COVID symptoms. Elsewhere, a study from the Netherlands published in The Lancet in August found that one in eight COVID-19 cases, or 12.7%, were likely to become long COVID.
“It’s very clear that the condition is devastating people’s lives and livelihoods,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus wrote in an article for The Guardian newspaper in October.
“The world has already lost a significant number of the workforce to illness, death, fatigue, unplanned retirement due to an increase in long-term disability, which not only impacts the health system, but is a hit to the overarching economy … the impact of long COVID for all countries is very serious and needs immediate and sustained action equivalent to its scale.”
Global snapshot: Lasting symptoms, impact on activities
Patients describe a spectrum of persistent issues, with extreme fatigue, brain fog or cognitive problems, and shortness of breath among the most common complaints. Many also have manageable symptoms that worsen significantly after even mild physical or mental exertion.
Women appear almost twice as likely as men to get long COVID. Many patients have other medical conditions and disabilities that make them more vulnerable to the condition. Those who face greater obstacles accessing health care due to discrimination or socioeconomic inequity are at higher risk as well.
While many are older, a large number are also in their prime working age. The Census Bureau data show that people ages 40-49 are more likely than any other group to get long COVID, which has broader implications for labor markets and the global economy. Already, experts have estimated that long COVID is likely to cost the U.S. trillions of dollars and affect multiple industries.
“Whether they’re in the financial world, the medical system, lawyers, they’re telling me they’re sitting at the computer screen and they’re unable to process the data,” said Zachary Schwartz, MD, medical director for Vancouver General Hospital’s Post-COVID-19 Recovery Clinic.
“That is what’s most distressing for people, in that they’re not working, they’re not making money, and they don’t know when, or if, they’re going to get better.”
Nearly a third of respondents in the Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey who said they have had COVID-19 reported symptoms that lasted 3 months or longer. People between the ages of 30 and 59 were the most affected, with about 32% reporting symptoms. Across the entire adult U.S. population, the survey found that 1 in 7 adults have had long COVID at some point during the pandemic, with about 1 in 18 saying it limited their activity to some degree, and 1 in 50 saying they have faced “a lot” of limits on their activities. Any way these numbers are dissected, long COVID has impacted a large swath of the population.
Yet research into the causes and possible treatments of long COVID is just getting underway.
“The amount of energy and time devoted to it is way, way less than it should, given how many people are likely affected,” said David Cutler, PhD, professor of economics at Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass., who has written about the economic cost of long COVID. “We’re way, way underdoing it here. And I think that’s really a terrible thing.”
Population surveys and studies from around the world show that long COVID lives up to its name, with people reporting serious symptoms for months on end.
In October, Statistics Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada published early results from a questionnaire done between spring and summer 2022 that found just under 15% of adults who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID-19 went on to have new or continuing symptoms 3 or more months later. Nearly half, or 47.3%, dealt with symptoms that lasted a year or more. More than one in five said their symptoms “often or always” limited their day-to-day activities, which included routine tasks such as preparing meals, doing errands and chores, and basic functions such as personal care and moving around in their homes.
Nearly three-quarters of workers or students said they missed an average of 20 days of work or school.
“We haven’t yet been able to determine exactly when symptoms resolve,” said Rainu Kaushal, MD, the senior associate dean for clinical research at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York. She is co-leading a national study on long COVID in adults and children, funded by the National Institutes of Health RECOVER Initiative.
“But there does seem to be, for many of the milder symptoms, resolution at about 4-6 weeks. There seems to be a second point of resolution around 6 months for certain symptoms, and then some symptoms do seem to be permanent, and those tend to be patients who have underlying conditions,” she said.
Reducing the risk
Given all the data so far, experts recommend urgent policy changes to help people with long COVID.
“The population needs to be prepared, that understanding long COVID is going to be a very long and difficult process,” said Alexander Charney, MD, PhD, associate professor and the lead principal investigator of the RECOVER adult cohort at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York. He said the government can do a great deal to help, including setting up a network of connected clinics treating long COVID, standardizing best practices, and sharing information.
“That would go a long way towards making sure that every person feels like they’re not too far away from a clinic where they can get treated for this particular condition,” he said.
But the only known way to prevent long COVID is to prevent COVID-19 infections in the first place, experts say. That means equitable access to tests, therapeutics, and vaccines.
“I will say that avoiding COVID remains the best treatment in the arsenal right now,” said Dr. Kaushal. This means masking, avoiding crowded places with poor ventilation and high exposure risk, and being up to date on vaccinations, she said.
A number of papers – including a large U.K. study published in May 2022, another one from July, and the JAMA study from October – all suggest that vaccinations can help reduce the risk of long COVID.
“I am absolutely of the belief that vaccination has reduced the incidence and overall amount of long COVID … [and is] still by far the best thing the public can do,” said Dr. Schwartz.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Buzz kill: Lung damage looks worse in pot smokers
Scans of the lungs of pot users have turned up an alarming surprise:
“There’s a public perception that marijuana is safe,” said Giselle Revah, MD, a radiologist at the University of Ottawa. “This study is raising concern that this might not be true.”
Dr. Revah said she can often tell immediately if a CT scan is from a heavy or long-time cigarette smoker. But with the legalization and increased use of marijuana in Canada and many U.S. states, she began to wonder what cannabis use does to the lungs and whether she would be able to differentiate its effects from those of cigarette smoking.
She and her colleagues retrospectively examined chest CT scans from 56 marijuana smokers and compared them to scans of 57 nonsmokers and 33 users of tobacco alone.
Emphysema was significantly more common among marijuana smokers (75%) than among nonsmokers (5%). When matched for age and sex, 93% of marijuana smokers had emphysema, vs. 67% of those who smoked tobacco only (P = .009).
Without age matching, rates of emphysema remained slightly higher among the marijuana users (75% vs. 67%), although the difference was no longer statistically significant. Yet more than 40% of the marijuana group was younger than 50 years, and all of the tobacco-only users were 50 or older – meaning that marijuana smokers may develop lung damage earlier or with less exposure, Dr. Revah said.
Dr. Revah added that her colleagues in family medicine have said the findings match their clinical experience. “In their practices, they have younger patients with emphysema,” she said.
Marijuana smokers also showed higher rates of airway inflammation, including bronchial thickening, bronchiectasis, and mucoid impaction, with and without sex- and age-matching, the researchers found.
The findings are “not even a little bit surprising,” according to Alan Kaplan, MD, a family physician in Ontario who has expertise in respiratory health. He is the author of a 2021 review on cannabis and lung health.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article by Dr. Revah and colleagues , pulmonary experts noted that the new data give context to a recent uptick in referrals for nontraumatic pneumothorax. The authors said they had received 22 of these referrals during the past 2 years but that they had received only 6 between 2012 and 2020. “Many, but not all, of these patients have a documented history of marijuana use,” they wrote.
One reason for the additional damage may be the way marijuana is inhaled, Dr. Kaplan said. Marijuana smokers “take a big breath in, and they really push it into lungs and hold pressure on it, which may actually cause alveoli to distend over time.”
Because most marijuana smokers in the study also smoked cigarettes, whether the observed damage was caused by marijuana alone or occurred through a synergy with tobacco is impossible to discern, Dr. Revah said.
Still, the results are striking, she said, because the marijuana group was compared to tobacco users who had an extensive smoking history – 25 to 100 pack-years – and who were from a high-risk lung cancer screening program.
Dr. Revah and her colleagues are now conducting a larger, prospective study to see whether they can confirm their findings.
“The message to physicians is to ask about cannabis smoking,” Dr. Kaplan said. In the past, people have been reluctant to admit to using cannabis. Even with legalization, they may be slow to tell their physicians. But clinicians should still try to identify frequent users, especially those who are predisposed for lung conditions. If they intend to use the drug, the advice should be, “There are safer ways to use cannabis,” he said.
Dr. Revah and Dr. Kaplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scans of the lungs of pot users have turned up an alarming surprise:
“There’s a public perception that marijuana is safe,” said Giselle Revah, MD, a radiologist at the University of Ottawa. “This study is raising concern that this might not be true.”
Dr. Revah said she can often tell immediately if a CT scan is from a heavy or long-time cigarette smoker. But with the legalization and increased use of marijuana in Canada and many U.S. states, she began to wonder what cannabis use does to the lungs and whether she would be able to differentiate its effects from those of cigarette smoking.
She and her colleagues retrospectively examined chest CT scans from 56 marijuana smokers and compared them to scans of 57 nonsmokers and 33 users of tobacco alone.
Emphysema was significantly more common among marijuana smokers (75%) than among nonsmokers (5%). When matched for age and sex, 93% of marijuana smokers had emphysema, vs. 67% of those who smoked tobacco only (P = .009).
Without age matching, rates of emphysema remained slightly higher among the marijuana users (75% vs. 67%), although the difference was no longer statistically significant. Yet more than 40% of the marijuana group was younger than 50 years, and all of the tobacco-only users were 50 or older – meaning that marijuana smokers may develop lung damage earlier or with less exposure, Dr. Revah said.
Dr. Revah added that her colleagues in family medicine have said the findings match their clinical experience. “In their practices, they have younger patients with emphysema,” she said.
Marijuana smokers also showed higher rates of airway inflammation, including bronchial thickening, bronchiectasis, and mucoid impaction, with and without sex- and age-matching, the researchers found.
The findings are “not even a little bit surprising,” according to Alan Kaplan, MD, a family physician in Ontario who has expertise in respiratory health. He is the author of a 2021 review on cannabis and lung health.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article by Dr. Revah and colleagues , pulmonary experts noted that the new data give context to a recent uptick in referrals for nontraumatic pneumothorax. The authors said they had received 22 of these referrals during the past 2 years but that they had received only 6 between 2012 and 2020. “Many, but not all, of these patients have a documented history of marijuana use,” they wrote.
One reason for the additional damage may be the way marijuana is inhaled, Dr. Kaplan said. Marijuana smokers “take a big breath in, and they really push it into lungs and hold pressure on it, which may actually cause alveoli to distend over time.”
Because most marijuana smokers in the study also smoked cigarettes, whether the observed damage was caused by marijuana alone or occurred through a synergy with tobacco is impossible to discern, Dr. Revah said.
Still, the results are striking, she said, because the marijuana group was compared to tobacco users who had an extensive smoking history – 25 to 100 pack-years – and who were from a high-risk lung cancer screening program.
Dr. Revah and her colleagues are now conducting a larger, prospective study to see whether they can confirm their findings.
“The message to physicians is to ask about cannabis smoking,” Dr. Kaplan said. In the past, people have been reluctant to admit to using cannabis. Even with legalization, they may be slow to tell their physicians. But clinicians should still try to identify frequent users, especially those who are predisposed for lung conditions. If they intend to use the drug, the advice should be, “There are safer ways to use cannabis,” he said.
Dr. Revah and Dr. Kaplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scans of the lungs of pot users have turned up an alarming surprise:
“There’s a public perception that marijuana is safe,” said Giselle Revah, MD, a radiologist at the University of Ottawa. “This study is raising concern that this might not be true.”
Dr. Revah said she can often tell immediately if a CT scan is from a heavy or long-time cigarette smoker. But with the legalization and increased use of marijuana in Canada and many U.S. states, she began to wonder what cannabis use does to the lungs and whether she would be able to differentiate its effects from those of cigarette smoking.
She and her colleagues retrospectively examined chest CT scans from 56 marijuana smokers and compared them to scans of 57 nonsmokers and 33 users of tobacco alone.
Emphysema was significantly more common among marijuana smokers (75%) than among nonsmokers (5%). When matched for age and sex, 93% of marijuana smokers had emphysema, vs. 67% of those who smoked tobacco only (P = .009).
Without age matching, rates of emphysema remained slightly higher among the marijuana users (75% vs. 67%), although the difference was no longer statistically significant. Yet more than 40% of the marijuana group was younger than 50 years, and all of the tobacco-only users were 50 or older – meaning that marijuana smokers may develop lung damage earlier or with less exposure, Dr. Revah said.
Dr. Revah added that her colleagues in family medicine have said the findings match their clinical experience. “In their practices, they have younger patients with emphysema,” she said.
Marijuana smokers also showed higher rates of airway inflammation, including bronchial thickening, bronchiectasis, and mucoid impaction, with and without sex- and age-matching, the researchers found.
The findings are “not even a little bit surprising,” according to Alan Kaplan, MD, a family physician in Ontario who has expertise in respiratory health. He is the author of a 2021 review on cannabis and lung health.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article by Dr. Revah and colleagues , pulmonary experts noted that the new data give context to a recent uptick in referrals for nontraumatic pneumothorax. The authors said they had received 22 of these referrals during the past 2 years but that they had received only 6 between 2012 and 2020. “Many, but not all, of these patients have a documented history of marijuana use,” they wrote.
One reason for the additional damage may be the way marijuana is inhaled, Dr. Kaplan said. Marijuana smokers “take a big breath in, and they really push it into lungs and hold pressure on it, which may actually cause alveoli to distend over time.”
Because most marijuana smokers in the study also smoked cigarettes, whether the observed damage was caused by marijuana alone or occurred through a synergy with tobacco is impossible to discern, Dr. Revah said.
Still, the results are striking, she said, because the marijuana group was compared to tobacco users who had an extensive smoking history – 25 to 100 pack-years – and who were from a high-risk lung cancer screening program.
Dr. Revah and her colleagues are now conducting a larger, prospective study to see whether they can confirm their findings.
“The message to physicians is to ask about cannabis smoking,” Dr. Kaplan said. In the past, people have been reluctant to admit to using cannabis. Even with legalization, they may be slow to tell their physicians. But clinicians should still try to identify frequent users, especially those who are predisposed for lung conditions. If they intend to use the drug, the advice should be, “There are safer ways to use cannabis,” he said.
Dr. Revah and Dr. Kaplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM RADIOLOGY
Is there a doctor on the plane? Tips for providing in-flight assistance
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.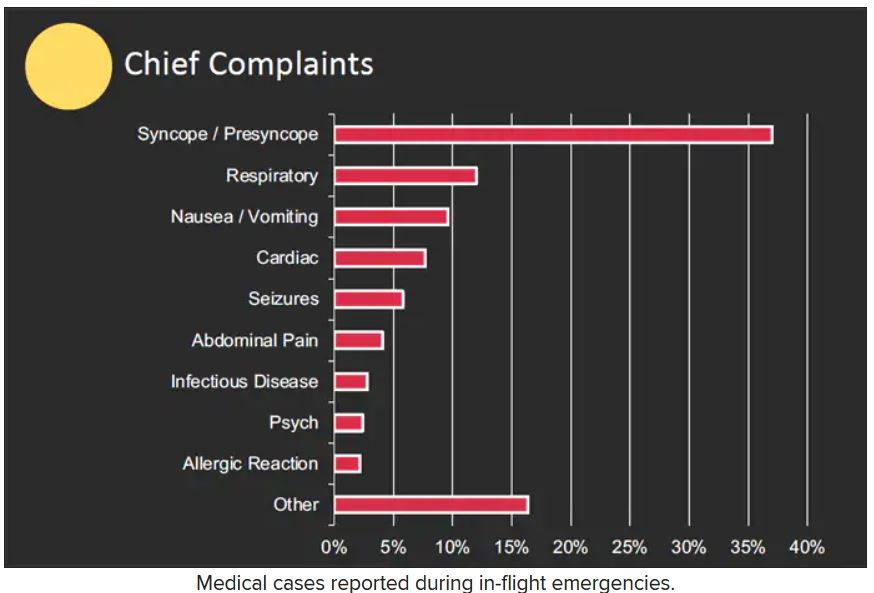
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
OSA raises risk of atrial fibrillation and stroke
compared with controls, based on data from 303 individuals.
OSA has become a common chronic disease, and cardiovascular diseases including AFib also are known independent risk factors associated with OSA, Anna Hojager, MD, of Zealand University Hospital, Roskilde, Denmark, and colleagues wrote. Previous studies have shown a significant increase in AFib risk in OSA patients with severe disease, but the prevalence of undiagnosed AFib in OSA patients has not been explored.
In a study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers enrolled 238 adults with severe OSA (based on apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or higher) and 65 with mild or no OSA (based on an AHI of less than 15). The mean AHI across all participants was 34.2, and ranged from 0.2 to 115.8.
Participants underwent heart rhythm monitoring using a home system or standard ECG for 7 days; they were instructed to carry the device at all times except when showering or sweating heavily. The primary outcome was the detection of AFib, defined as at least one period of 30 seconds or longer with an irregular heart rhythm but without detectable evidence of another diagnosis. Sleep was assessed for one night using a portable sleep monitoring device. All participants were examined at baseline and measured for blood pressure, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and ECG.
Overall, AFib occurred in 21 patients with moderate to severe OSA and 1 patient with mild/no OSA (8.8% vs. 1.5%, P = .045). The majority of patients across both groups had hypertension (66%) and dyslipidemia (77.6%), but the severe OSA group was more likely to be dysregulated and to have unknown prediabetes. Participants who were deemed candidates for anticoagulation therapy were referred for additional treatment. None of the 22 total patients with AFib had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and 68.2% had normal ejection fraction and ventricle function.
The researchers noted that no guidelines currently exist for systematic opportunistic screening for comorbidities in OSA patients, although the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends patient education as part of a multidisciplinary chronic disease management strategy. The high prevalence of AFib in OSA patients, as seen in the current study, “might warrant a recommendation of screening for paroxysmal [AFib] and could be valuable in the management of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in patients with OSA,” they wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and absence of polysomnography to assess OSA, the researchers noted. However, the study has the highest known prevalence of silent AFib in patients with moderate to severe OSA, and supports the value of screening and management for known comorbidities of OSA.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
compared with controls, based on data from 303 individuals.
OSA has become a common chronic disease, and cardiovascular diseases including AFib also are known independent risk factors associated with OSA, Anna Hojager, MD, of Zealand University Hospital, Roskilde, Denmark, and colleagues wrote. Previous studies have shown a significant increase in AFib risk in OSA patients with severe disease, but the prevalence of undiagnosed AFib in OSA patients has not been explored.
In a study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers enrolled 238 adults with severe OSA (based on apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or higher) and 65 with mild or no OSA (based on an AHI of less than 15). The mean AHI across all participants was 34.2, and ranged from 0.2 to 115.8.
Participants underwent heart rhythm monitoring using a home system or standard ECG for 7 days; they were instructed to carry the device at all times except when showering or sweating heavily. The primary outcome was the detection of AFib, defined as at least one period of 30 seconds or longer with an irregular heart rhythm but without detectable evidence of another diagnosis. Sleep was assessed for one night using a portable sleep monitoring device. All participants were examined at baseline and measured for blood pressure, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and ECG.
Overall, AFib occurred in 21 patients with moderate to severe OSA and 1 patient with mild/no OSA (8.8% vs. 1.5%, P = .045). The majority of patients across both groups had hypertension (66%) and dyslipidemia (77.6%), but the severe OSA group was more likely to be dysregulated and to have unknown prediabetes. Participants who were deemed candidates for anticoagulation therapy were referred for additional treatment. None of the 22 total patients with AFib had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and 68.2% had normal ejection fraction and ventricle function.
The researchers noted that no guidelines currently exist for systematic opportunistic screening for comorbidities in OSA patients, although the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends patient education as part of a multidisciplinary chronic disease management strategy. The high prevalence of AFib in OSA patients, as seen in the current study, “might warrant a recommendation of screening for paroxysmal [AFib] and could be valuable in the management of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in patients with OSA,” they wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and absence of polysomnography to assess OSA, the researchers noted. However, the study has the highest known prevalence of silent AFib in patients with moderate to severe OSA, and supports the value of screening and management for known comorbidities of OSA.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
compared with controls, based on data from 303 individuals.
OSA has become a common chronic disease, and cardiovascular diseases including AFib also are known independent risk factors associated with OSA, Anna Hojager, MD, of Zealand University Hospital, Roskilde, Denmark, and colleagues wrote. Previous studies have shown a significant increase in AFib risk in OSA patients with severe disease, but the prevalence of undiagnosed AFib in OSA patients has not been explored.
In a study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers enrolled 238 adults with severe OSA (based on apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or higher) and 65 with mild or no OSA (based on an AHI of less than 15). The mean AHI across all participants was 34.2, and ranged from 0.2 to 115.8.
Participants underwent heart rhythm monitoring using a home system or standard ECG for 7 days; they were instructed to carry the device at all times except when showering or sweating heavily. The primary outcome was the detection of AFib, defined as at least one period of 30 seconds or longer with an irregular heart rhythm but without detectable evidence of another diagnosis. Sleep was assessed for one night using a portable sleep monitoring device. All participants were examined at baseline and measured for blood pressure, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and ECG.
Overall, AFib occurred in 21 patients with moderate to severe OSA and 1 patient with mild/no OSA (8.8% vs. 1.5%, P = .045). The majority of patients across both groups had hypertension (66%) and dyslipidemia (77.6%), but the severe OSA group was more likely to be dysregulated and to have unknown prediabetes. Participants who were deemed candidates for anticoagulation therapy were referred for additional treatment. None of the 22 total patients with AFib had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and 68.2% had normal ejection fraction and ventricle function.
The researchers noted that no guidelines currently exist for systematic opportunistic screening for comorbidities in OSA patients, although the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends patient education as part of a multidisciplinary chronic disease management strategy. The high prevalence of AFib in OSA patients, as seen in the current study, “might warrant a recommendation of screening for paroxysmal [AFib] and could be valuable in the management of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in patients with OSA,” they wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and absence of polysomnography to assess OSA, the researchers noted. However, the study has the highest known prevalence of silent AFib in patients with moderate to severe OSA, and supports the value of screening and management for known comorbidities of OSA.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SLEEP MEDICINE
Children and COVID: Weekly cases continue to hold fairly steady
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.
The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.

The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
The incidence of new COVID-19 cases in children seems to have stabilized as the national count remained under 30,000 for the fifth consecutive week, but hospitalization data may indicate some possible turbulence.
Just over 28,000 pediatric cases were reported during the week of Nov. 4-10, a drop of 5.4% from the previous week, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report involving data from state and territorial health departments, several of which are no longer updating their websites.

The stability in weekly cases, however, comes in contrast to a very recent and considerable increase in new hospital admissions of children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID-19. That rate, which was 0.18 hospitalizations per 100,000 population on Nov. 7 and 0.19 per 100,000 on Nov. 8 and 9, jumped all the way to 0.34 on Nov. 10 and 0.48 on Nov. 11, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That is the highest rate since the closing days of the Omicron surge in February.
The rate for Nov. 12, the most recent one available, was down slightly to 0.47 admissions per 100,000. There doesn’t seem to be any evidence in the CDC’s data of a similar sudden increase in new hospitalizations among any other age group, and no age group, including children, shows any sign of a recent increase in emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID. (The CDC has not yet responded to our inquiry about this development.)
The two most recent 7-day averages for new admissions in children aged 0-17 show a small increase, but they cover the periods of Oct. 15 to Oct. 31, when there were 126 admissions per day, and Nov. 1 to Nov. 7, when the average went up to 133 per day, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The CDC does not publish a weekly count of new COVID cases, but its latest data on the rate of incident cases seem to agree with the AAP/CHA figures: A gradual decline in all age groups, including children, since the beginning of September.
Vaccinations, on the other hand, bucked their recent trend and increased in the last week. About 43,000 children under age 5 years received their initial dose of COVID vaccine during Nov. 3-9, compared with 30,000 and 33,000 the 2 previous weeks, while 5- to 11-year-olds hit their highest weekly mark (31,000) since late August and 12- to 17-year-olds had their biggest week (27,000) since mid-August, the AAP reported based on CDC data.
Combination therapy shows mixed results for scleroderma-related lung disease
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
PHILADELPHIA – Combining the immunomodulatory agent mycophenolate with the antifibrotic pirfenidone led to more rapid improvement and showed a trend to be more effective than mycophenolate mofetil alone for treating the signs and symptoms of scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease, but the combination therapy came with an increase in side effects, according to results from the Scleroderma Lung Study III.
Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, presented the results at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He noted some problems with the study – namely its small size, enrolling only 51 patients, about one-third of its original goal. But he also said it showed a potential signal for efficacy and that the study itself could serve as a “template” for future studies of combination mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus pirfenidone therapy for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
“The pirfenidone patients had quite a bit more GI side effects and photosensitivity, and those are known side effects,” Dr. Khanna said in an interview. “So the combination therapy had more side effects but trends to higher efficacy.”
The design of SLS-III, a phase 2 clinical trial, was a challenge, Dr. Khanna explained. The goal was to enroll 150 SSc-ILD patients who hadn’t had any previous treatment for their disease. Finding those patients proved difficult. “In fact, if you look at the recent history, 70% of the patients with early diffuse scleroderma are on MMF,” he said in his presentation. Compounding low study enrollment was the intervening COVID-19 pandemic, he added.
Testing a faster-acting combination
Nonetheless, the trial managed to enroll 27 patients in the combination therapy group and 24 in the MMF-plus-placebo group and compared their outcomes over 18 months. Study dosing was 1,500 mg MMF twice daily and pirfenidone 801 mg three times daily, titrated to the tolerable dose.
Despite the study’s being underpowered, Dr. Khanna said, it still reported some notable outcomes that merit further investigation. “I think what was intriguing in the study was the long-term benefit in the patient-reported outcomes and the structural changes,” he said in the interview.
Among those notable outcomes was a clinically significant change in forced vital capacity (FVC) percentage for the combination vs. the placebo groups: 2.24% vs. 2.09%. He also noted that the combination group saw a somewhat more robust improvement in FVC at six months: 2.59% (± 0.98%) vs. 0.92% (± 1.1%) in the placebo group.
The combination group showed greater improvements in high-resolution computed tomography-evaluated lung involvement and lung fibrosis and patient-reported outcomes, including a statistically significant 3.67-point greater improvement in PROMIS-29 physical function score (4.42 vs. 0.75).
The patients on combination therapy had higher rates of serious adverse events (SAEs), and seven discontinued one or both study drugs early, all in the combined arm. Four combination therapy patients had six SAEs, compared to two placebo patients with three SAEs. In the combination group, SAEs included chest pain, herpes zoster ophthalmicus, nodular basal cell cancer, marginal zone B cell lymphoma, renal crisis, and dyspnea. SAEs in the placebo group were colitis, COVID-19 and hypoxic respiratory failure.
Study design challenges
Nonetheless, Dr. Khanna said the SLS-III data are consistent with the SLS-II findings, with mean improvements in FVC of 2.24% and 2.1%, respectively.
“The next study may be able to replicate what we tried to do, keeping in mind that there are really no MMF-naive patients who are walking around,” Dr. Khanna said. “So the challenge is about the feasibility of recruiting within a trial vs. trying to show a statistical difference between the drug and placebo.”
This study could serve as a foundation for future studies of MMF in patients with SSc-ILD, Robert Spiera, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “There are lessons to be learned both from the study but also from prior studies looking at MMF use in the background in patients treated with other drugs in clinical trials,” he said.
Dr. Spiera noted that the study had other challenges besides the difficulty in recruiting patients who hadn’t been on MMF therapy. “A great challenge is that the benefit with regard to the impact on the lungs from MMF seems most prominent in the first 6 months to a year to even 2 years that somebody is on the drug,” he said.
The other challenge with this study is that a large proportion of patients had limited systemic disease and relatively lower levels of skin disease compared with other studies of patients on MMF, Dr. Spiera said.
“The optimal treatment of scleroderma-associated lung disease remains a very important and not-adequately met need,” he said. “Particularly, we’re looking for drugs that are tolerable in a patient population that are very prone to GI side effects in general. This study and others have taught us a lot about trial design, and I think more globally this will allow us to move this field forward.”
Dr. Khanna disclosed relationships with Actelion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Horizon Therapeutics USA, Janssen Global Services, Prometheus Biosciences, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Genentech/Roche, Theraly, and Pfizer. Genentech provided funding for the study and pirfenidone and placebo drugs at no cost.
Dr. Spiera disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche and Vera.
AT ACR 2022
The body of evidence for Paxlovid therapy
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Repeat COVID infection doubles mortality risk
Getting COVID-19 a second time doubles a person’s chance of dying and triples the likelihood of being hospitalized in the next 6 months, a new study found.
Vaccination and booster status did not improve survival or hospitalization rates among people who were infected more than once.
“Reinfection with COVID-19 increases the risk of both acute outcomes and long COVID,” study author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, told Reuters. “This was evident in unvaccinated, vaccinated and boosted people.”
The study was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
Researchers analyzed U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs data, including 443,588 people with a first infection of SARS-CoV-2, 40,947 people who were infected two or more times, and 5.3 million people who had not been infected with coronavirus, whose data served as the control group.
“During the past few months, there’s been an air of invincibility among people who have had COVID-19 or their vaccinations and boosters, and especially among people who have had an infection and also received vaccines; some people started to [refer] to these individuals as having a sort of superimmunity to the virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said in a press release from Washington University in St. Louis. “Without ambiguity, our research showed that getting an infection a second, third or fourth time contributes to additional health risks in the acute phase, meaning the first 30 days after infection, and in the months beyond, meaning the long COVID phase.”
Being infected with COVID-19 more than once also dramatically increased the risk of developing lung problems, heart conditions, or brain conditions. The heightened risks persisted for 6 months.
Researchers said a limitation of their study was that data primarily came from White males.
An expert not involved in the study told Reuters that the Veterans Affairs population does not reflect the general population. Patients at VA health facilities are generally older with more than normal health complications, said John Moore, PhD, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Al-Aly encouraged people to be vigilant as they plan for the holiday season, Reuters reported.
“We had started seeing a lot of patients coming to the clinic with an air of invincibility,” he told Reuters. “They wondered, ‘Does getting a reinfection really matter?’ The answer is yes, it absolutely does.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Getting COVID-19 a second time doubles a person’s chance of dying and triples the likelihood of being hospitalized in the next 6 months, a new study found.
Vaccination and booster status did not improve survival or hospitalization rates among people who were infected more than once.
“Reinfection with COVID-19 increases the risk of both acute outcomes and long COVID,” study author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, told Reuters. “This was evident in unvaccinated, vaccinated and boosted people.”
The study was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
Researchers analyzed U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs data, including 443,588 people with a first infection of SARS-CoV-2, 40,947 people who were infected two or more times, and 5.3 million people who had not been infected with coronavirus, whose data served as the control group.
“During the past few months, there’s been an air of invincibility among people who have had COVID-19 or their vaccinations and boosters, and especially among people who have had an infection and also received vaccines; some people started to [refer] to these individuals as having a sort of superimmunity to the virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said in a press release from Washington University in St. Louis. “Without ambiguity, our research showed that getting an infection a second, third or fourth time contributes to additional health risks in the acute phase, meaning the first 30 days after infection, and in the months beyond, meaning the long COVID phase.”
Being infected with COVID-19 more than once also dramatically increased the risk of developing lung problems, heart conditions, or brain conditions. The heightened risks persisted for 6 months.
Researchers said a limitation of their study was that data primarily came from White males.
An expert not involved in the study told Reuters that the Veterans Affairs population does not reflect the general population. Patients at VA health facilities are generally older with more than normal health complications, said John Moore, PhD, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Al-Aly encouraged people to be vigilant as they plan for the holiday season, Reuters reported.
“We had started seeing a lot of patients coming to the clinic with an air of invincibility,” he told Reuters. “They wondered, ‘Does getting a reinfection really matter?’ The answer is yes, it absolutely does.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Getting COVID-19 a second time doubles a person’s chance of dying and triples the likelihood of being hospitalized in the next 6 months, a new study found.
Vaccination and booster status did not improve survival or hospitalization rates among people who were infected more than once.
“Reinfection with COVID-19 increases the risk of both acute outcomes and long COVID,” study author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, told Reuters. “This was evident in unvaccinated, vaccinated and boosted people.”
The study was published in the journal Nature Medicine.
Researchers analyzed U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs data, including 443,588 people with a first infection of SARS-CoV-2, 40,947 people who were infected two or more times, and 5.3 million people who had not been infected with coronavirus, whose data served as the control group.
“During the past few months, there’s been an air of invincibility among people who have had COVID-19 or their vaccinations and boosters, and especially among people who have had an infection and also received vaccines; some people started to [refer] to these individuals as having a sort of superimmunity to the virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said in a press release from Washington University in St. Louis. “Without ambiguity, our research showed that getting an infection a second, third or fourth time contributes to additional health risks in the acute phase, meaning the first 30 days after infection, and in the months beyond, meaning the long COVID phase.”
Being infected with COVID-19 more than once also dramatically increased the risk of developing lung problems, heart conditions, or brain conditions. The heightened risks persisted for 6 months.
Researchers said a limitation of their study was that data primarily came from White males.
An expert not involved in the study told Reuters that the Veterans Affairs population does not reflect the general population. Patients at VA health facilities are generally older with more than normal health complications, said John Moore, PhD, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Al-Aly encouraged people to be vigilant as they plan for the holiday season, Reuters reported.
“We had started seeing a lot of patients coming to the clinic with an air of invincibility,” he told Reuters. “They wondered, ‘Does getting a reinfection really matter?’ The answer is yes, it absolutely does.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE