User login
Obesity drug shortage triggers frustrations, workarounds
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide formulated for treating obesity (Wegovy) had a roaring takeoff a little more than a year ago, with surging patient demand after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved it in June 2021. But starting doses of the Wegovy form of semaglutide went missing in action starting late 2021 and continue to date, frustrating patients and their health care providers.
The arrival of Wegovy last year was hailed by obesity medicine specialists and others as a “game changer” for treating people with obesity because of semaglutide’s proven safety and efficacy at the subcutaneous dose of 2.4 mg delivered once a week to produce at least 15% weight loss in half the people who received it, as documented last year in results from one of the drug’s pivotal clinical trials.
But during the months following semaglutide’s approval for treating obesity (it also received an FDA marketing nod in late 2017 as Ozempic for treating type 2 diabetes), a worldwide shortage of Wegovy, including in the United States, emerged.
A manufacturing glitch shut down the primary location for production of U.S.-bound Wegovy injector pens for several months starting in late 2021, according to a December report from Novo Nordisk, the company that makes and markets the agent. (The Wegovy production issue appears to have had a very modest impact, especially in U.S. pharmacies, on the supply of semaglutide formulated as Ozempic, also marketed by Novo Nordisk, although Wegovy supply and demand have dramatically limited Ozempic availability in Australia.)
‘Unprecedented demand’ for Wegovy derailed when plant went offline
The supply side for Wegovy became so hopelessly broken that just months after U.S. sales began and immediately skyrocketed, Novo Nordisk made the remarkable decision to pull starting doses of Wegovy from the market to make it much harder to initiate patients (semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists require gradual dose ramp-up to avoid gastrointestinal side effects), and the company publicly implored clinicians to not start new patients on the agent, which is where the status remains as of early August 2022.
Novo Nordisk’s financial report for the second quarter of 2022, released on Aug. 3, said the company “expects to make all Wegovy dose strengths available in the United States towards the end of 2022.”
A Dear Health Care Provider letter that Novo Nordisk posted on its U.S. Wegovy website last spring cited “unprecedented demand” that exceeded every prior product launch in the company’s history. It forced Novo Nordisk to pull the plug on all U.S. promotion of Wegovy and compelled the company to ask U.S. clinicians to halt new patient starts.
“I stopped offering Wegovy to new patients” since about the beginning of 2022, says Lauren D. Oshman, MD, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “It’s very frustrating to not have patients [with obesity] receive the optimal treatment available.” Although she adds that she tries to match obesity treatments to each patient’s clinical needs, and a GLP-1 agonist is not the first choice for every person with obesity.
“It was a disastrous rollout,” says Catherine W. Varney, DO, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “It’s frustrating to know that the treatment is there but not being able to use it,” she said in an interview.
“I had about 800 patients on Wegovy” when the supply dropped earlier this year, and “I couldn’t handle the volume of messages that I got from patients,” recalls Angela Fitch, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center, Boston. “It was painful,” she said in an interview.
“Frustrating and chaotic,” is the description from Ivania M. Rizo, MD, director of obesity medicine at Boston Medical Center.
The liraglutide/Saxenda workaround
The upshot is that people with obesity and their health care providers have been busy devising workarounds to try to meet the intense demand for this drug-assisted approach to appetite control and weight loss. Their tactics run a wide gamut based on the crazy-quilt diversity of health insurance coverage across America.
Because the bottleneck for starting Wegovy resulted from unavailable starting doses (dosing starts at 0.25 mg delivered subcutaneously once a week, eventually ramping up to a maximum of 2.4 mg weekly), one option was to start patients on a different GLP-1 agonist, such as liraglutide (Saxenda, approved for obesity).
Starting a patient on liraglutide involves the same sort of up-titration and acclimation to a GLP-1 agonist that semaglutide requires, and transition between these agents seems feasible for at least some. It also means daily injections of liraglutide rather than the weekly schedule for semaglutide, although some patients prefer maintaining a daily dosing schedule. Another limitation of liraglutide is that evidence shows it is not nearly as effective for weight loss as semaglutide.
Results from the head-to-head STEP 8 trial, published in JAMA, showed an average weight loss from baseline of about 16% with semaglutide and about 6% with liraglutide (and about 2% with placebo).
A ‘reasonable’ evidence base, but more work
Changing from Saxenda to Wegovy, or from Wegovy to Saxenda, “would be reasonably evidence-based medicine,” said Dr. Oshman in an interview. She has managed a Wegovy-to-Saxenda switch for a “handful” of patients to deal with Wegovy shortages, but she has not yet moved anyone to Wegovy after a Saxenda initiation.
“No prospective study has looked at this transition,” but dose equivalence tables exist based on expert opinion, noted Dr. Oshman, as in this 2020 report.
Dr. Varney has several patients on the Saxenda-to-Wegovy track. She up-titrates patients on Saxenda to the maximum daily dose of 3.0 mg and then switches them to the 1.7 mg weekly dose of Wegovy, one of the “destination” Wegovy doses that has remained generally available during the shortage. But Dr. Varney’s experience is that only half of her patients made the changeover smoothly, with the others having “severe gastrointestinal distress,” including vomiting, she notes.
Dr. Fitch has also successfully used this Saxenda-to-Wegovy approach for some of her patients, but it hasn’t been easy.
“It’s more work and more prior authorizations. It’s harder and adds a layer of stress,” but, Dr. Fitch adds, “people are willing to work on it because the weight loss is worth it.”
The liraglutide to semaglutide shuffle is “doable,” says Dr. Rizo, “but I’m looking forward to not having to do it and being able to just start Wegovy.”
The tirzepatide coupon program works ‘off label’ for obesity
Another workaround depends on the FDA approval in May for tirzepatide (Mounjaro) for type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide is a related GLP-1 agonist that also adds a second incretin-like agonist activity that mimics the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
Soon after approval, Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide, started a U.S. coupon program geared exclusively to people with commercial insurance. Within certain refill and dollar limits, the program lets patients buy tirzepatide at pharmacies at an out-of-pocket cost of $25 for a 4-week supply (tirzepatide is also dosed by weekly subcutaneous injections). The program will extend into 2023.
Novo Nordisk offered U.S. patients with commercial insurance a similar discount when Wegovy first hit the U.S. market in 2021, but the program closed down once the supply shortage began.
Despite tirzepatide’s current approval only for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Varney has been successfully prescribing it to patients without diabetes off-label for weight loss.
“The coupons still work even when tirzepatide is used off-label,” she notes. And while the drug’s rollout is still only a couple of months old, so far, it’s gone “beautifully” with no hints of supply issues, she says.
But a major drawback to relying on an introductory coupon program that makes these agents affordable to patients is their ability to maintain treatment once the discounts inevitably end.
“We try to only prescribe agents that patients can continue to access,” says Dr. Fitch, who has had some patients with commercial insurance start on Wegovy with coupon discounts only to later lose access.
Many commercial U.S. insurers do not cover obesity treatments, a decision often driven by the employers who sponsor the coverage, she notes.
Study results have documented that when people with obesity stop taking a GLP-1 agonist their lost weight rebounds, as in a study that tracked people who stopped taking semaglutide.
Dr. Fitch has had success prescribing tirzepatide to patients with obesity but without diabetes who have certain types of Medicare drug coverage policies, which often do not deny off-label drug coverage. That approach works until patients reach the “donut hole” in their drug coverage and are faced with a certain level of out-of-pocket costs that can balloon to several thousand dollars.
Even more workarounds
Other approaches patients have used to acquire Wegovy include purchasing it in other countries, such as Canada or Brazil, says Dr. Fitch. But prices outside the United States, while substantially lower, can still be a barrier for many patients, notes Dr. Oshman.
Semaglutide in Canada goes for about $300 for a 4-week supply, roughly a quarter the U.S. price, she says, but is “still too high for many of my patients.”
Intense patient demand sometimes bordering on desperation has prompted some to seek semaglutide from private compounding pharmacies, a step clinicians regard as downright dangerous.
“Semaglutide from compounding pharmacies is not known to be safe. We feel strongly that it’s not something that people should do,” says Dr. Fitch.
“Compounding pharmacies have no FDA regulation. People don’t know what they’re getting. It’s dangerous,” agrees Dr. Varney. Physicians who refer people for privately compounded semaglutide “are taking advantage of desperate people,” she adds.
Although it seems likely that Novo Nordisk will soon sort out the supply problems and Wegovy will once again become more widely available, some of the issues patients have had with access to the weight loss medication stem from more systemic issues in the United States health insurance landscape: an unwillingness by payers to cover the costs of weight loss medications, a shortcoming that also exists for Medicare and Medicaid.
“We need to make obesity treatment a standard benefit, and not something that can be carved out,” says Dr. Fitch. People with obesity “deserve access to effective treatments for their disease,” she declares.
Dr. Oshman, Dr. Varney, and Dr. Rizo have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fitch has reported being an advisor to Jenny Craig.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide formulated for treating obesity (Wegovy) had a roaring takeoff a little more than a year ago, with surging patient demand after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved it in June 2021. But starting doses of the Wegovy form of semaglutide went missing in action starting late 2021 and continue to date, frustrating patients and their health care providers.
The arrival of Wegovy last year was hailed by obesity medicine specialists and others as a “game changer” for treating people with obesity because of semaglutide’s proven safety and efficacy at the subcutaneous dose of 2.4 mg delivered once a week to produce at least 15% weight loss in half the people who received it, as documented last year in results from one of the drug’s pivotal clinical trials.
But during the months following semaglutide’s approval for treating obesity (it also received an FDA marketing nod in late 2017 as Ozempic for treating type 2 diabetes), a worldwide shortage of Wegovy, including in the United States, emerged.
A manufacturing glitch shut down the primary location for production of U.S.-bound Wegovy injector pens for several months starting in late 2021, according to a December report from Novo Nordisk, the company that makes and markets the agent. (The Wegovy production issue appears to have had a very modest impact, especially in U.S. pharmacies, on the supply of semaglutide formulated as Ozempic, also marketed by Novo Nordisk, although Wegovy supply and demand have dramatically limited Ozempic availability in Australia.)
‘Unprecedented demand’ for Wegovy derailed when plant went offline
The supply side for Wegovy became so hopelessly broken that just months after U.S. sales began and immediately skyrocketed, Novo Nordisk made the remarkable decision to pull starting doses of Wegovy from the market to make it much harder to initiate patients (semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists require gradual dose ramp-up to avoid gastrointestinal side effects), and the company publicly implored clinicians to not start new patients on the agent, which is where the status remains as of early August 2022.
Novo Nordisk’s financial report for the second quarter of 2022, released on Aug. 3, said the company “expects to make all Wegovy dose strengths available in the United States towards the end of 2022.”
A Dear Health Care Provider letter that Novo Nordisk posted on its U.S. Wegovy website last spring cited “unprecedented demand” that exceeded every prior product launch in the company’s history. It forced Novo Nordisk to pull the plug on all U.S. promotion of Wegovy and compelled the company to ask U.S. clinicians to halt new patient starts.
“I stopped offering Wegovy to new patients” since about the beginning of 2022, says Lauren D. Oshman, MD, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “It’s very frustrating to not have patients [with obesity] receive the optimal treatment available.” Although she adds that she tries to match obesity treatments to each patient’s clinical needs, and a GLP-1 agonist is not the first choice for every person with obesity.
“It was a disastrous rollout,” says Catherine W. Varney, DO, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “It’s frustrating to know that the treatment is there but not being able to use it,” she said in an interview.
“I had about 800 patients on Wegovy” when the supply dropped earlier this year, and “I couldn’t handle the volume of messages that I got from patients,” recalls Angela Fitch, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center, Boston. “It was painful,” she said in an interview.
“Frustrating and chaotic,” is the description from Ivania M. Rizo, MD, director of obesity medicine at Boston Medical Center.
The liraglutide/Saxenda workaround
The upshot is that people with obesity and their health care providers have been busy devising workarounds to try to meet the intense demand for this drug-assisted approach to appetite control and weight loss. Their tactics run a wide gamut based on the crazy-quilt diversity of health insurance coverage across America.
Because the bottleneck for starting Wegovy resulted from unavailable starting doses (dosing starts at 0.25 mg delivered subcutaneously once a week, eventually ramping up to a maximum of 2.4 mg weekly), one option was to start patients on a different GLP-1 agonist, such as liraglutide (Saxenda, approved for obesity).
Starting a patient on liraglutide involves the same sort of up-titration and acclimation to a GLP-1 agonist that semaglutide requires, and transition between these agents seems feasible for at least some. It also means daily injections of liraglutide rather than the weekly schedule for semaglutide, although some patients prefer maintaining a daily dosing schedule. Another limitation of liraglutide is that evidence shows it is not nearly as effective for weight loss as semaglutide.
Results from the head-to-head STEP 8 trial, published in JAMA, showed an average weight loss from baseline of about 16% with semaglutide and about 6% with liraglutide (and about 2% with placebo).
A ‘reasonable’ evidence base, but more work
Changing from Saxenda to Wegovy, or from Wegovy to Saxenda, “would be reasonably evidence-based medicine,” said Dr. Oshman in an interview. She has managed a Wegovy-to-Saxenda switch for a “handful” of patients to deal with Wegovy shortages, but she has not yet moved anyone to Wegovy after a Saxenda initiation.
“No prospective study has looked at this transition,” but dose equivalence tables exist based on expert opinion, noted Dr. Oshman, as in this 2020 report.
Dr. Varney has several patients on the Saxenda-to-Wegovy track. She up-titrates patients on Saxenda to the maximum daily dose of 3.0 mg and then switches them to the 1.7 mg weekly dose of Wegovy, one of the “destination” Wegovy doses that has remained generally available during the shortage. But Dr. Varney’s experience is that only half of her patients made the changeover smoothly, with the others having “severe gastrointestinal distress,” including vomiting, she notes.
Dr. Fitch has also successfully used this Saxenda-to-Wegovy approach for some of her patients, but it hasn’t been easy.
“It’s more work and more prior authorizations. It’s harder and adds a layer of stress,” but, Dr. Fitch adds, “people are willing to work on it because the weight loss is worth it.”
The liraglutide to semaglutide shuffle is “doable,” says Dr. Rizo, “but I’m looking forward to not having to do it and being able to just start Wegovy.”
The tirzepatide coupon program works ‘off label’ for obesity
Another workaround depends on the FDA approval in May for tirzepatide (Mounjaro) for type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide is a related GLP-1 agonist that also adds a second incretin-like agonist activity that mimics the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
Soon after approval, Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide, started a U.S. coupon program geared exclusively to people with commercial insurance. Within certain refill and dollar limits, the program lets patients buy tirzepatide at pharmacies at an out-of-pocket cost of $25 for a 4-week supply (tirzepatide is also dosed by weekly subcutaneous injections). The program will extend into 2023.
Novo Nordisk offered U.S. patients with commercial insurance a similar discount when Wegovy first hit the U.S. market in 2021, but the program closed down once the supply shortage began.
Despite tirzepatide’s current approval only for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Varney has been successfully prescribing it to patients without diabetes off-label for weight loss.
“The coupons still work even when tirzepatide is used off-label,” she notes. And while the drug’s rollout is still only a couple of months old, so far, it’s gone “beautifully” with no hints of supply issues, she says.
But a major drawback to relying on an introductory coupon program that makes these agents affordable to patients is their ability to maintain treatment once the discounts inevitably end.
“We try to only prescribe agents that patients can continue to access,” says Dr. Fitch, who has had some patients with commercial insurance start on Wegovy with coupon discounts only to later lose access.
Many commercial U.S. insurers do not cover obesity treatments, a decision often driven by the employers who sponsor the coverage, she notes.
Study results have documented that when people with obesity stop taking a GLP-1 agonist their lost weight rebounds, as in a study that tracked people who stopped taking semaglutide.
Dr. Fitch has had success prescribing tirzepatide to patients with obesity but without diabetes who have certain types of Medicare drug coverage policies, which often do not deny off-label drug coverage. That approach works until patients reach the “donut hole” in their drug coverage and are faced with a certain level of out-of-pocket costs that can balloon to several thousand dollars.
Even more workarounds
Other approaches patients have used to acquire Wegovy include purchasing it in other countries, such as Canada or Brazil, says Dr. Fitch. But prices outside the United States, while substantially lower, can still be a barrier for many patients, notes Dr. Oshman.
Semaglutide in Canada goes for about $300 for a 4-week supply, roughly a quarter the U.S. price, she says, but is “still too high for many of my patients.”
Intense patient demand sometimes bordering on desperation has prompted some to seek semaglutide from private compounding pharmacies, a step clinicians regard as downright dangerous.
“Semaglutide from compounding pharmacies is not known to be safe. We feel strongly that it’s not something that people should do,” says Dr. Fitch.
“Compounding pharmacies have no FDA regulation. People don’t know what they’re getting. It’s dangerous,” agrees Dr. Varney. Physicians who refer people for privately compounded semaglutide “are taking advantage of desperate people,” she adds.
Although it seems likely that Novo Nordisk will soon sort out the supply problems and Wegovy will once again become more widely available, some of the issues patients have had with access to the weight loss medication stem from more systemic issues in the United States health insurance landscape: an unwillingness by payers to cover the costs of weight loss medications, a shortcoming that also exists for Medicare and Medicaid.
“We need to make obesity treatment a standard benefit, and not something that can be carved out,” says Dr. Fitch. People with obesity “deserve access to effective treatments for their disease,” she declares.
Dr. Oshman, Dr. Varney, and Dr. Rizo have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fitch has reported being an advisor to Jenny Craig.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide formulated for treating obesity (Wegovy) had a roaring takeoff a little more than a year ago, with surging patient demand after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved it in June 2021. But starting doses of the Wegovy form of semaglutide went missing in action starting late 2021 and continue to date, frustrating patients and their health care providers.
The arrival of Wegovy last year was hailed by obesity medicine specialists and others as a “game changer” for treating people with obesity because of semaglutide’s proven safety and efficacy at the subcutaneous dose of 2.4 mg delivered once a week to produce at least 15% weight loss in half the people who received it, as documented last year in results from one of the drug’s pivotal clinical trials.
But during the months following semaglutide’s approval for treating obesity (it also received an FDA marketing nod in late 2017 as Ozempic for treating type 2 diabetes), a worldwide shortage of Wegovy, including in the United States, emerged.
A manufacturing glitch shut down the primary location for production of U.S.-bound Wegovy injector pens for several months starting in late 2021, according to a December report from Novo Nordisk, the company that makes and markets the agent. (The Wegovy production issue appears to have had a very modest impact, especially in U.S. pharmacies, on the supply of semaglutide formulated as Ozempic, also marketed by Novo Nordisk, although Wegovy supply and demand have dramatically limited Ozempic availability in Australia.)
‘Unprecedented demand’ for Wegovy derailed when plant went offline
The supply side for Wegovy became so hopelessly broken that just months after U.S. sales began and immediately skyrocketed, Novo Nordisk made the remarkable decision to pull starting doses of Wegovy from the market to make it much harder to initiate patients (semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists require gradual dose ramp-up to avoid gastrointestinal side effects), and the company publicly implored clinicians to not start new patients on the agent, which is where the status remains as of early August 2022.
Novo Nordisk’s financial report for the second quarter of 2022, released on Aug. 3, said the company “expects to make all Wegovy dose strengths available in the United States towards the end of 2022.”
A Dear Health Care Provider letter that Novo Nordisk posted on its U.S. Wegovy website last spring cited “unprecedented demand” that exceeded every prior product launch in the company’s history. It forced Novo Nordisk to pull the plug on all U.S. promotion of Wegovy and compelled the company to ask U.S. clinicians to halt new patient starts.
“I stopped offering Wegovy to new patients” since about the beginning of 2022, says Lauren D. Oshman, MD, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “It’s very frustrating to not have patients [with obesity] receive the optimal treatment available.” Although she adds that she tries to match obesity treatments to each patient’s clinical needs, and a GLP-1 agonist is not the first choice for every person with obesity.
“It was a disastrous rollout,” says Catherine W. Varney, DO, a family and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “It’s frustrating to know that the treatment is there but not being able to use it,” she said in an interview.
“I had about 800 patients on Wegovy” when the supply dropped earlier this year, and “I couldn’t handle the volume of messages that I got from patients,” recalls Angela Fitch, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Weight Center, Boston. “It was painful,” she said in an interview.
“Frustrating and chaotic,” is the description from Ivania M. Rizo, MD, director of obesity medicine at Boston Medical Center.
The liraglutide/Saxenda workaround
The upshot is that people with obesity and their health care providers have been busy devising workarounds to try to meet the intense demand for this drug-assisted approach to appetite control and weight loss. Their tactics run a wide gamut based on the crazy-quilt diversity of health insurance coverage across America.
Because the bottleneck for starting Wegovy resulted from unavailable starting doses (dosing starts at 0.25 mg delivered subcutaneously once a week, eventually ramping up to a maximum of 2.4 mg weekly), one option was to start patients on a different GLP-1 agonist, such as liraglutide (Saxenda, approved for obesity).
Starting a patient on liraglutide involves the same sort of up-titration and acclimation to a GLP-1 agonist that semaglutide requires, and transition between these agents seems feasible for at least some. It also means daily injections of liraglutide rather than the weekly schedule for semaglutide, although some patients prefer maintaining a daily dosing schedule. Another limitation of liraglutide is that evidence shows it is not nearly as effective for weight loss as semaglutide.
Results from the head-to-head STEP 8 trial, published in JAMA, showed an average weight loss from baseline of about 16% with semaglutide and about 6% with liraglutide (and about 2% with placebo).
A ‘reasonable’ evidence base, but more work
Changing from Saxenda to Wegovy, or from Wegovy to Saxenda, “would be reasonably evidence-based medicine,” said Dr. Oshman in an interview. She has managed a Wegovy-to-Saxenda switch for a “handful” of patients to deal with Wegovy shortages, but she has not yet moved anyone to Wegovy after a Saxenda initiation.
“No prospective study has looked at this transition,” but dose equivalence tables exist based on expert opinion, noted Dr. Oshman, as in this 2020 report.
Dr. Varney has several patients on the Saxenda-to-Wegovy track. She up-titrates patients on Saxenda to the maximum daily dose of 3.0 mg and then switches them to the 1.7 mg weekly dose of Wegovy, one of the “destination” Wegovy doses that has remained generally available during the shortage. But Dr. Varney’s experience is that only half of her patients made the changeover smoothly, with the others having “severe gastrointestinal distress,” including vomiting, she notes.
Dr. Fitch has also successfully used this Saxenda-to-Wegovy approach for some of her patients, but it hasn’t been easy.
“It’s more work and more prior authorizations. It’s harder and adds a layer of stress,” but, Dr. Fitch adds, “people are willing to work on it because the weight loss is worth it.”
The liraglutide to semaglutide shuffle is “doable,” says Dr. Rizo, “but I’m looking forward to not having to do it and being able to just start Wegovy.”
The tirzepatide coupon program works ‘off label’ for obesity
Another workaround depends on the FDA approval in May for tirzepatide (Mounjaro) for type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide is a related GLP-1 agonist that also adds a second incretin-like agonist activity that mimics the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
Soon after approval, Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide, started a U.S. coupon program geared exclusively to people with commercial insurance. Within certain refill and dollar limits, the program lets patients buy tirzepatide at pharmacies at an out-of-pocket cost of $25 for a 4-week supply (tirzepatide is also dosed by weekly subcutaneous injections). The program will extend into 2023.
Novo Nordisk offered U.S. patients with commercial insurance a similar discount when Wegovy first hit the U.S. market in 2021, but the program closed down once the supply shortage began.
Despite tirzepatide’s current approval only for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Varney has been successfully prescribing it to patients without diabetes off-label for weight loss.
“The coupons still work even when tirzepatide is used off-label,” she notes. And while the drug’s rollout is still only a couple of months old, so far, it’s gone “beautifully” with no hints of supply issues, she says.
But a major drawback to relying on an introductory coupon program that makes these agents affordable to patients is their ability to maintain treatment once the discounts inevitably end.
“We try to only prescribe agents that patients can continue to access,” says Dr. Fitch, who has had some patients with commercial insurance start on Wegovy with coupon discounts only to later lose access.
Many commercial U.S. insurers do not cover obesity treatments, a decision often driven by the employers who sponsor the coverage, she notes.
Study results have documented that when people with obesity stop taking a GLP-1 agonist their lost weight rebounds, as in a study that tracked people who stopped taking semaglutide.
Dr. Fitch has had success prescribing tirzepatide to patients with obesity but without diabetes who have certain types of Medicare drug coverage policies, which often do not deny off-label drug coverage. That approach works until patients reach the “donut hole” in their drug coverage and are faced with a certain level of out-of-pocket costs that can balloon to several thousand dollars.
Even more workarounds
Other approaches patients have used to acquire Wegovy include purchasing it in other countries, such as Canada or Brazil, says Dr. Fitch. But prices outside the United States, while substantially lower, can still be a barrier for many patients, notes Dr. Oshman.
Semaglutide in Canada goes for about $300 for a 4-week supply, roughly a quarter the U.S. price, she says, but is “still too high for many of my patients.”
Intense patient demand sometimes bordering on desperation has prompted some to seek semaglutide from private compounding pharmacies, a step clinicians regard as downright dangerous.
“Semaglutide from compounding pharmacies is not known to be safe. We feel strongly that it’s not something that people should do,” says Dr. Fitch.
“Compounding pharmacies have no FDA regulation. People don’t know what they’re getting. It’s dangerous,” agrees Dr. Varney. Physicians who refer people for privately compounded semaglutide “are taking advantage of desperate people,” she adds.
Although it seems likely that Novo Nordisk will soon sort out the supply problems and Wegovy will once again become more widely available, some of the issues patients have had with access to the weight loss medication stem from more systemic issues in the United States health insurance landscape: an unwillingness by payers to cover the costs of weight loss medications, a shortcoming that also exists for Medicare and Medicaid.
“We need to make obesity treatment a standard benefit, and not something that can be carved out,” says Dr. Fitch. People with obesity “deserve access to effective treatments for their disease,” she declares.
Dr. Oshman, Dr. Varney, and Dr. Rizo have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fitch has reported being an advisor to Jenny Craig.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Effect of Race on Outcomes in Veterans With Hepatocellular Carcinoma at a Single Center
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
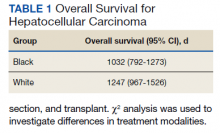
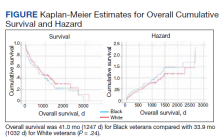
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
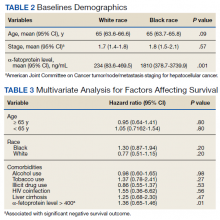
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
Short walks after meals can cut diabetes risk
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long COVID’s grip will likely tighten as infections continue
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Drug-resistant epilepsy needs earlier surgical referral
, according to expert consensus recommendations from the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) published in the journal Epilepsia.
Comprehensive epilepsy care
Such a referral is not ”a commitment to undergo brain surgery,” wrote the authors of the new recommendations study, but surgical evaluations offer patients an opportunity to learn about the range of therapies available to them and to have their diagnosis verified, as well as learning about the cause and type of epilepsy they have, even if they ultimately do not pursue surgery.
”In fact, most patients with drug-resistant epilepsy do not end up undergoing surgery after referral, but still benefit from comprehensive epilepsy care improving quality of life and lowering mortality,” wrote lead author Lara Jehi, MD, professor of neurology and epilepsy specialist at Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues. “A better characterization of the epilepsy can also help optimize medical therapy and address somatic, cognitive, behavioral, and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Is the diagnosis correct?
They noted that about one-third of patients referred to epilepsy centers with an apparent diagnosis of drug-resistant epilepsy actually have psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) – not epilepsy – and an early, accurate diagnosis of PNES can ensure they receive psychotherapy, stop taking antiseizure medications, and have better outcomes.
“These recommendations are necessary, as the delay to surgery and the overall underutilization of surgery have not improved much over the last 20 years,” said Selim R. Benbadis, MD, professor of neurology and director of the comprehensive epilepsy program at the University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital. “Comprehensive epilepsy centers offer more than surgery, including correct and precise diagnosis, drug options, three [Food and Drug Administration]–approved neurostimulation options, and more,” said Dr. Benbadis, who was not involved in the development of these recommendations.
Consensus recommendations
On behalf of the the ILAE’s Surgical Therapies Commission, the authors used the Delphi consensus process to develop expert consensus recommendations on when to refer patients with epilepsy to surgery. They conducted three Delphi rounds on 51 clinical scenarios with 61 epileptologists (38% of participants), epilepsy neurosurgeons (34%), neurologists (23%), neuropsychiatrists (2%), and neuropsychologists (3%) from 28 countries. Most of clinicians focused on adults (39%) or adults and children (41%) while 20% focused only on pediatric epilepsy.
The physicians involved had a median 22 years of practice and represented all six ILAE regions: 30% from North America, 28% from Europe, 18% from Asia/Oceania, 13% from Latin America, 7% from the Eastern Mediterranean, and 4% from Africa.
The result of these rounds were three key recommendations arising from the consensus of experts consulted. First, every patient up to 70 years old who has drug-resistant epilepsy should be offered the option of a surgical evaluation as soon as it’s apparent that they have drug resistance. The option for surgical evaluation should be provided independent of their sex or socioeconomic status and regardless of how long they have had epilepsy, their seizure type, their epilepsy type, localization, and their comorbidities, ”including severe psychiatric comorbidity like psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) or substance abuse if patients are cooperative with management,” the authors wrote.
”Resective surgery can improve quality of life and cognitive outcomes and is the only treatment demonstrated to improve survival and reverse excess mortality attributed to drug-resistant epilepsy,” the authors wrote. Evidence supports that surgical evaluation is the most cost-effective approach to treating drug-resistant epilepsy, they added. Yet, it still takes about 20 years with epilepsy before an adult patient might be referred, ”and the neurology community remains ambivalent due to ongoing barriers and misconceptions about epilepsy surgery,” they wrote.
The second recommendation is to consider a surgical referral for older patients with drug-resistant epilepsy who have no surgical contraindication. Physicians can also consider a referral for patients of any age who are seizure free while taking one to two antiseizure drugs but who have a brain lesion in the noneloquent cortex.
The third recommendation is not to offer surgery if a patient has an active substance dependency and is not cooperative with management.
“Although there is some evidence that seizure outcomes are no different in individuals with active substance use disorder who have epilepsy surgery, the literature suggests increased perioperative surgical and anesthetic risk in this cohort,” the authors wrote. ”Patients with active substance abuse are more likely to be nonadherent with their seizure medications, and to leave the hospital against medical advice.”
One area where the participants did not reach consensus was regarding whether to refer patients who did not become seizure-free after trying just one “tolerated and appropriately chosen” antiseizure medication. Half (49%) said they would be unlikely to refer or would never refer that patient while 44% said they would likely or always refer them, and 7% weren’t sure.
The ‘next level’ of epilepsy care
“Similar recommendations have been published before, by the National Association of Epilepsy Centers, more than once, and have not changed the referral patterns,” Dr. Benbadis said. “They are not implemented by the average general neurologist.” While there are many reasons for this, one with a relativity simple fix is to adjust the language doctors use to when talking with patients about getting an evaluation, Dr. Benbadis said. ”The key is to rephrase: Instead of referrals ‘for surgery,’ which can be scary to many neurologists and patients, we should use more general terms, like referrals for the ‘next level of care by epilepsy specialists,’ ” said Dr. Benbadis, who advocated for this change in terminology in a 2019 editorial. Such language is less frightening and can ease patients’ concerns about going to an epilepsy center where they can learn about more options than just surgery.
Further, surgical options have expanded in recent years, including the development of laser interstitial thermal therapy and neuromodulation. “Identifying candidacy for any of these approaches starts with a surgical referral, so a timely evaluation is key,” the authors wrote.
Referral delays persist
Despite the strong evidence for timely referrals, delays have persisted for decades, said Dr. Benbadis, echoing what the authors describe. ”Despite the results of two randomized controlled trials showing that surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy in adults, and resective surgery in children, is superior to continued antiseizure medications both in terms of seizure freedom and improved quality of life, the mean epilepsy duration to temporal lobe resection has persisted at over 20 years,” the authors wrote. ”Although drug resistance is reached with a mean latency of 9 years in epilepsy surgery candidates, these patients have experienced a decade of unabating seizures with detrimental effects including cognitive and psychiatric comorbidities, poor psychosocial outcomes, potential injuries, and risk of death.”
Surgery is not a ‘dangerous last resort’
The authors point out a variety of likely reasons for these delays, including patients experiencing temporary remissions with a new drug, lack of adequate health care access, overestimating surgery risks, and underestimating the seriousness and risk of death from ongoing seizures.
Dr. Benbadis agreed, referring to a “combination of lack of knowledge and unrealistic views about surgery outcomes and complications.” Patients and their neurologists think surgery is a “dangerous last resort, fraught with complications, and they don’t know the outcome, so it’s mainly that they are not very well-educated about epilepsy surgery,” he said. Complacency about a patient’s infrequent seizures plays a role as well, he added. “Their patient is having one seizure every 2 months, and they might say, ‘well, that’s okay, that’s not that bad,’ but it is when we can cure it.”
Similar factors are barriers to epilepsy surgery: “lack of knowledge or misconceptions about surgical risks, negative behaviors, or cultural issues and access issues.”
Another major barrier, both within neurology and throughout medicine in general, is that large academic centers that accept referrals, including epilepsy centers, have poor communication, follow-up, and scheduling, Dr. Benbadis said.
The authors provided a table with suggestions on potential solutions to those barriers, including identifying online resources to help doctors identify possible surgery candidates, such as www.toolsforepilepsy.com, and a range of educational resources. Ways to improve access and cost include mobile clinics, telehealth, coordinating with an epilepsy organization, and employing a multidisciplinary team that includes a social worker to help with support such as transportation and health insurance.
, according to expert consensus recommendations from the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) published in the journal Epilepsia.
Comprehensive epilepsy care
Such a referral is not ”a commitment to undergo brain surgery,” wrote the authors of the new recommendations study, but surgical evaluations offer patients an opportunity to learn about the range of therapies available to them and to have their diagnosis verified, as well as learning about the cause and type of epilepsy they have, even if they ultimately do not pursue surgery.
”In fact, most patients with drug-resistant epilepsy do not end up undergoing surgery after referral, but still benefit from comprehensive epilepsy care improving quality of life and lowering mortality,” wrote lead author Lara Jehi, MD, professor of neurology and epilepsy specialist at Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues. “A better characterization of the epilepsy can also help optimize medical therapy and address somatic, cognitive, behavioral, and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Is the diagnosis correct?
They noted that about one-third of patients referred to epilepsy centers with an apparent diagnosis of drug-resistant epilepsy actually have psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) – not epilepsy – and an early, accurate diagnosis of PNES can ensure they receive psychotherapy, stop taking antiseizure medications, and have better outcomes.
“These recommendations are necessary, as the delay to surgery and the overall underutilization of surgery have not improved much over the last 20 years,” said Selim R. Benbadis, MD, professor of neurology and director of the comprehensive epilepsy program at the University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital. “Comprehensive epilepsy centers offer more than surgery, including correct and precise diagnosis, drug options, three [Food and Drug Administration]–approved neurostimulation options, and more,” said Dr. Benbadis, who was not involved in the development of these recommendations.
Consensus recommendations
On behalf of the the ILAE’s Surgical Therapies Commission, the authors used the Delphi consensus process to develop expert consensus recommendations on when to refer patients with epilepsy to surgery. They conducted three Delphi rounds on 51 clinical scenarios with 61 epileptologists (38% of participants), epilepsy neurosurgeons (34%), neurologists (23%), neuropsychiatrists (2%), and neuropsychologists (3%) from 28 countries. Most of clinicians focused on adults (39%) or adults and children (41%) while 20% focused only on pediatric epilepsy.
The physicians involved had a median 22 years of practice and represented all six ILAE regions: 30% from North America, 28% from Europe, 18% from Asia/Oceania, 13% from Latin America, 7% from the Eastern Mediterranean, and 4% from Africa.
The result of these rounds were three key recommendations arising from the consensus of experts consulted. First, every patient up to 70 years old who has drug-resistant epilepsy should be offered the option of a surgical evaluation as soon as it’s apparent that they have drug resistance. The option for surgical evaluation should be provided independent of their sex or socioeconomic status and regardless of how long they have had epilepsy, their seizure type, their epilepsy type, localization, and their comorbidities, ”including severe psychiatric comorbidity like psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) or substance abuse if patients are cooperative with management,” the authors wrote.
”Resective surgery can improve quality of life and cognitive outcomes and is the only treatment demonstrated to improve survival and reverse excess mortality attributed to drug-resistant epilepsy,” the authors wrote. Evidence supports that surgical evaluation is the most cost-effective approach to treating drug-resistant epilepsy, they added. Yet, it still takes about 20 years with epilepsy before an adult patient might be referred, ”and the neurology community remains ambivalent due to ongoing barriers and misconceptions about epilepsy surgery,” they wrote.
The second recommendation is to consider a surgical referral for older patients with drug-resistant epilepsy who have no surgical contraindication. Physicians can also consider a referral for patients of any age who are seizure free while taking one to two antiseizure drugs but who have a brain lesion in the noneloquent cortex.
The third recommendation is not to offer surgery if a patient has an active substance dependency and is not cooperative with management.
“Although there is some evidence that seizure outcomes are no different in individuals with active substance use disorder who have epilepsy surgery, the literature suggests increased perioperative surgical and anesthetic risk in this cohort,” the authors wrote. ”Patients with active substance abuse are more likely to be nonadherent with their seizure medications, and to leave the hospital against medical advice.”
One area where the participants did not reach consensus was regarding whether to refer patients who did not become seizure-free after trying just one “tolerated and appropriately chosen” antiseizure medication. Half (49%) said they would be unlikely to refer or would never refer that patient while 44% said they would likely or always refer them, and 7% weren’t sure.
The ‘next level’ of epilepsy care
“Similar recommendations have been published before, by the National Association of Epilepsy Centers, more than once, and have not changed the referral patterns,” Dr. Benbadis said. “They are not implemented by the average general neurologist.” While there are many reasons for this, one with a relativity simple fix is to adjust the language doctors use to when talking with patients about getting an evaluation, Dr. Benbadis said. ”The key is to rephrase: Instead of referrals ‘for surgery,’ which can be scary to many neurologists and patients, we should use more general terms, like referrals for the ‘next level of care by epilepsy specialists,’ ” said Dr. Benbadis, who advocated for this change in terminology in a 2019 editorial. Such language is less frightening and can ease patients’ concerns about going to an epilepsy center where they can learn about more options than just surgery.
Further, surgical options have expanded in recent years, including the development of laser interstitial thermal therapy and neuromodulation. “Identifying candidacy for any of these approaches starts with a surgical referral, so a timely evaluation is key,” the authors wrote.
Referral delays persist
Despite the strong evidence for timely referrals, delays have persisted for decades, said Dr. Benbadis, echoing what the authors describe. ”Despite the results of two randomized controlled trials showing that surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy in adults, and resective surgery in children, is superior to continued antiseizure medications both in terms of seizure freedom and improved quality of life, the mean epilepsy duration to temporal lobe resection has persisted at over 20 years,” the authors wrote. ”Although drug resistance is reached with a mean latency of 9 years in epilepsy surgery candidates, these patients have experienced a decade of unabating seizures with detrimental effects including cognitive and psychiatric comorbidities, poor psychosocial outcomes, potential injuries, and risk of death.”
Surgery is not a ‘dangerous last resort’
The authors point out a variety of likely reasons for these delays, including patients experiencing temporary remissions with a new drug, lack of adequate health care access, overestimating surgery risks, and underestimating the seriousness and risk of death from ongoing seizures.
Dr. Benbadis agreed, referring to a “combination of lack of knowledge and unrealistic views about surgery outcomes and complications.” Patients and their neurologists think surgery is a “dangerous last resort, fraught with complications, and they don’t know the outcome, so it’s mainly that they are not very well-educated about epilepsy surgery,” he said. Complacency about a patient’s infrequent seizures plays a role as well, he added. “Their patient is having one seizure every 2 months, and they might say, ‘well, that’s okay, that’s not that bad,’ but it is when we can cure it.”
Similar factors are barriers to epilepsy surgery: “lack of knowledge or misconceptions about surgical risks, negative behaviors, or cultural issues and access issues.”
Another major barrier, both within neurology and throughout medicine in general, is that large academic centers that accept referrals, including epilepsy centers, have poor communication, follow-up, and scheduling, Dr. Benbadis said.
The authors provided a table with suggestions on potential solutions to those barriers, including identifying online resources to help doctors identify possible surgery candidates, such as www.toolsforepilepsy.com, and a range of educational resources. Ways to improve access and cost include mobile clinics, telehealth, coordinating with an epilepsy organization, and employing a multidisciplinary team that includes a social worker to help with support such as transportation and health insurance.
, according to expert consensus recommendations from the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) published in the journal Epilepsia.
Comprehensive epilepsy care
Such a referral is not ”a commitment to undergo brain surgery,” wrote the authors of the new recommendations study, but surgical evaluations offer patients an opportunity to learn about the range of therapies available to them and to have their diagnosis verified, as well as learning about the cause and type of epilepsy they have, even if they ultimately do not pursue surgery.
”In fact, most patients with drug-resistant epilepsy do not end up undergoing surgery after referral, but still benefit from comprehensive epilepsy care improving quality of life and lowering mortality,” wrote lead author Lara Jehi, MD, professor of neurology and epilepsy specialist at Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues. “A better characterization of the epilepsy can also help optimize medical therapy and address somatic, cognitive, behavioral, and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Is the diagnosis correct?
They noted that about one-third of patients referred to epilepsy centers with an apparent diagnosis of drug-resistant epilepsy actually have psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) – not epilepsy – and an early, accurate diagnosis of PNES can ensure they receive psychotherapy, stop taking antiseizure medications, and have better outcomes.
“These recommendations are necessary, as the delay to surgery and the overall underutilization of surgery have not improved much over the last 20 years,” said Selim R. Benbadis, MD, professor of neurology and director of the comprehensive epilepsy program at the University of South Florida and Tampa General Hospital. “Comprehensive epilepsy centers offer more than surgery, including correct and precise diagnosis, drug options, three [Food and Drug Administration]–approved neurostimulation options, and more,” said Dr. Benbadis, who was not involved in the development of these recommendations.
Consensus recommendations
On behalf of the the ILAE’s Surgical Therapies Commission, the authors used the Delphi consensus process to develop expert consensus recommendations on when to refer patients with epilepsy to surgery. They conducted three Delphi rounds on 51 clinical scenarios with 61 epileptologists (38% of participants), epilepsy neurosurgeons (34%), neurologists (23%), neuropsychiatrists (2%), and neuropsychologists (3%) from 28 countries. Most of clinicians focused on adults (39%) or adults and children (41%) while 20% focused only on pediatric epilepsy.
The physicians involved had a median 22 years of practice and represented all six ILAE regions: 30% from North America, 28% from Europe, 18% from Asia/Oceania, 13% from Latin America, 7% from the Eastern Mediterranean, and 4% from Africa.
The result of these rounds were three key recommendations arising from the consensus of experts consulted. First, every patient up to 70 years old who has drug-resistant epilepsy should be offered the option of a surgical evaluation as soon as it’s apparent that they have drug resistance. The option for surgical evaluation should be provided independent of their sex or socioeconomic status and regardless of how long they have had epilepsy, their seizure type, their epilepsy type, localization, and their comorbidities, ”including severe psychiatric comorbidity like psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) or substance abuse if patients are cooperative with management,” the authors wrote.
”Resective surgery can improve quality of life and cognitive outcomes and is the only treatment demonstrated to improve survival and reverse excess mortality attributed to drug-resistant epilepsy,” the authors wrote. Evidence supports that surgical evaluation is the most cost-effective approach to treating drug-resistant epilepsy, they added. Yet, it still takes about 20 years with epilepsy before an adult patient might be referred, ”and the neurology community remains ambivalent due to ongoing barriers and misconceptions about epilepsy surgery,” they wrote.
The second recommendation is to consider a surgical referral for older patients with drug-resistant epilepsy who have no surgical contraindication. Physicians can also consider a referral for patients of any age who are seizure free while taking one to two antiseizure drugs but who have a brain lesion in the noneloquent cortex.
The third recommendation is not to offer surgery if a patient has an active substance dependency and is not cooperative with management.
“Although there is some evidence that seizure outcomes are no different in individuals with active substance use disorder who have epilepsy surgery, the literature suggests increased perioperative surgical and anesthetic risk in this cohort,” the authors wrote. ”Patients with active substance abuse are more likely to be nonadherent with their seizure medications, and to leave the hospital against medical advice.”
One area where the participants did not reach consensus was regarding whether to refer patients who did not become seizure-free after trying just one “tolerated and appropriately chosen” antiseizure medication. Half (49%) said they would be unlikely to refer or would never refer that patient while 44% said they would likely or always refer them, and 7% weren’t sure.
The ‘next level’ of epilepsy care
“Similar recommendations have been published before, by the National Association of Epilepsy Centers, more than once, and have not changed the referral patterns,” Dr. Benbadis said. “They are not implemented by the average general neurologist.” While there are many reasons for this, one with a relativity simple fix is to adjust the language doctors use to when talking with patients about getting an evaluation, Dr. Benbadis said. ”The key is to rephrase: Instead of referrals ‘for surgery,’ which can be scary to many neurologists and patients, we should use more general terms, like referrals for the ‘next level of care by epilepsy specialists,’ ” said Dr. Benbadis, who advocated for this change in terminology in a 2019 editorial. Such language is less frightening and can ease patients’ concerns about going to an epilepsy center where they can learn about more options than just surgery.
Further, surgical options have expanded in recent years, including the development of laser interstitial thermal therapy and neuromodulation. “Identifying candidacy for any of these approaches starts with a surgical referral, so a timely evaluation is key,” the authors wrote.
Referral delays persist
Despite the strong evidence for timely referrals, delays have persisted for decades, said Dr. Benbadis, echoing what the authors describe. ”Despite the results of two randomized controlled trials showing that surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy in adults, and resective surgery in children, is superior to continued antiseizure medications both in terms of seizure freedom and improved quality of life, the mean epilepsy duration to temporal lobe resection has persisted at over 20 years,” the authors wrote. ”Although drug resistance is reached with a mean latency of 9 years in epilepsy surgery candidates, these patients have experienced a decade of unabating seizures with detrimental effects including cognitive and psychiatric comorbidities, poor psychosocial outcomes, potential injuries, and risk of death.”
Surgery is not a ‘dangerous last resort’
The authors point out a variety of likely reasons for these delays, including patients experiencing temporary remissions with a new drug, lack of adequate health care access, overestimating surgery risks, and underestimating the seriousness and risk of death from ongoing seizures.
Dr. Benbadis agreed, referring to a “combination of lack of knowledge and unrealistic views about surgery outcomes and complications.” Patients and their neurologists think surgery is a “dangerous last resort, fraught with complications, and they don’t know the outcome, so it’s mainly that they are not very well-educated about epilepsy surgery,” he said. Complacency about a patient’s infrequent seizures plays a role as well, he added. “Their patient is having one seizure every 2 months, and they might say, ‘well, that’s okay, that’s not that bad,’ but it is when we can cure it.”
Similar factors are barriers to epilepsy surgery: “lack of knowledge or misconceptions about surgical risks, negative behaviors, or cultural issues and access issues.”
Another major barrier, both within neurology and throughout medicine in general, is that large academic centers that accept referrals, including epilepsy centers, have poor communication, follow-up, and scheduling, Dr. Benbadis said.
The authors provided a table with suggestions on potential solutions to those barriers, including identifying online resources to help doctors identify possible surgery candidates, such as www.toolsforepilepsy.com, and a range of educational resources. Ways to improve access and cost include mobile clinics, telehealth, coordinating with an epilepsy organization, and employing a multidisciplinary team that includes a social worker to help with support such as transportation and health insurance.
FROM EPILEPSIA
Genetic counseling for cancer often costs patients nothing
But even among those who do, the cost is $16 or less, a cohort study shows.
“The findings highlight the relatively low financial costs of genetic counseling, a form of care with potentially substantial implications for cancer treatment,” lead author Mya Roberson, PhD, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and colleagues explained.
The study was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
Genetic counseling is an important feature of cancer care that can affect treatment decisions and surveillance. But coverage of genetic counseling services varies across insurance types.
To understand the costs to patients, the investigators used data from IBM Watson Health MarketScan to create a cohort of privately insured patients with breast, prostate, endometrial, ovarian, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer who had at least one genetic counseling session from 2013 to the end of 2019.
Dr. Roberson and colleagues then calculated out-of-pocket costs – including coinsurance, copayments, and deductibles – and total costs paid on claims for genetic counseling encounters. The cohort included 16,791 patients, the majority of whom had breast cancer.
Although the median insurance payment for genetic counseling encounters was $118 ($58-$211), most patients paid nothing out of pocket for these services. Among the 31% of patients with an out-of-pocket expense, the cost was $16 or less.
Compared with breast cancer patients, men with prostate cancer were 28% more likely to have out-of-pocket costs for genetic counseling, which may “reflect a lack of awareness about the medical necessity of genetic counseling,” the authors suggested.
Overall, the study highlights the value of genetic counseling in cancer care.
“Cancer genetic counseling not only promotes informed decision-making about genetic testing and cancer treatment in the era of precision medicine, but it also is a form of low-cost, high-value care,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Roberson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
But even among those who do, the cost is $16 or less, a cohort study shows.
“The findings highlight the relatively low financial costs of genetic counseling, a form of care with potentially substantial implications for cancer treatment,” lead author Mya Roberson, PhD, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and colleagues explained.
The study was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
Genetic counseling is an important feature of cancer care that can affect treatment decisions and surveillance. But coverage of genetic counseling services varies across insurance types.
To understand the costs to patients, the investigators used data from IBM Watson Health MarketScan to create a cohort of privately insured patients with breast, prostate, endometrial, ovarian, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer who had at least one genetic counseling session from 2013 to the end of 2019.
Dr. Roberson and colleagues then calculated out-of-pocket costs – including coinsurance, copayments, and deductibles – and total costs paid on claims for genetic counseling encounters. The cohort included 16,791 patients, the majority of whom had breast cancer.
Although the median insurance payment for genetic counseling encounters was $118 ($58-$211), most patients paid nothing out of pocket for these services. Among the 31% of patients with an out-of-pocket expense, the cost was $16 or less.
Compared with breast cancer patients, men with prostate cancer were 28% more likely to have out-of-pocket costs for genetic counseling, which may “reflect a lack of awareness about the medical necessity of genetic counseling,” the authors suggested.
Overall, the study highlights the value of genetic counseling in cancer care.
“Cancer genetic counseling not only promotes informed decision-making about genetic testing and cancer treatment in the era of precision medicine, but it also is a form of low-cost, high-value care,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Roberson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
But even among those who do, the cost is $16 or less, a cohort study shows.
“The findings highlight the relatively low financial costs of genetic counseling, a form of care with potentially substantial implications for cancer treatment,” lead author Mya Roberson, PhD, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and colleagues explained.
The study was published online in JAMA Health Forum.
Genetic counseling is an important feature of cancer care that can affect treatment decisions and surveillance. But coverage of genetic counseling services varies across insurance types.
To understand the costs to patients, the investigators used data from IBM Watson Health MarketScan to create a cohort of privately insured patients with breast, prostate, endometrial, ovarian, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer who had at least one genetic counseling session from 2013 to the end of 2019.
Dr. Roberson and colleagues then calculated out-of-pocket costs – including coinsurance, copayments, and deductibles – and total costs paid on claims for genetic counseling encounters. The cohort included 16,791 patients, the majority of whom had breast cancer.
Although the median insurance payment for genetic counseling encounters was $118 ($58-$211), most patients paid nothing out of pocket for these services. Among the 31% of patients with an out-of-pocket expense, the cost was $16 or less.
Compared with breast cancer patients, men with prostate cancer were 28% more likely to have out-of-pocket costs for genetic counseling, which may “reflect a lack of awareness about the medical necessity of genetic counseling,” the authors suggested.
Overall, the study highlights the value of genetic counseling in cancer care.
“Cancer genetic counseling not only promotes informed decision-making about genetic testing and cancer treatment in the era of precision medicine, but it also is a form of low-cost, high-value care,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by a grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Roberson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA HEALTH FORUM
Updates on treatment/prevention of VTE in cancer patients
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
Blood test for cancer available, but is it ready for prime time?
The Galleri blood test is being now offered by a number of United States health networks.
The company marketing the test, GRAIL, has established partnerships with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Mercy Health, Ochsner Health, Intermountain Healthcare, Community Health Network, Knight Cancer Institute at Oregon Health & Science University, Premier, and Cleveland Clinic, among others.
Cleveland Clinic’s Eric Klein, MD, emeritus chair of the Glickman Urological Kidney Institute, is enthusiastic about the test, describing it as a “game-changer” and emphasizing that it can detect many different cancers and at a very early stage.
“It completely changes the way we think about screening for cancer,” commented Jeff Venstrom, MD, chief medical officer at GRAIL. He joined the company because “there are not many things in life where you can be part of a disruptive paradigm and disruptive technology, and this really is disruptive,” he said in an interview.
‘The devil is in the details’
But there is some concern among clinicians that widespread clinical use of the test may be premature.
Having a blood test for multiple cancers is a “very good idea, and the scientific basis for this platform is sound,” commented Timothy R. Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and Division of Population Sciences, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
“But the devil is in the details to ensure the test can accurately detect very early cancers and there is a pathway for subsequent workup (diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, etc.),” Dr. Rebbeck told this news organization.
Galleri is offering the test to individuals who are older than 50 and have a family history of cancer or those who are high risk for cancer or immunocompromised. They suggest that interested individuals get in touch with their health care professional, who then needs to register with GRAIL and order the test.
As well as needing a prescription, interested individuals will have to pay for it out of pocket, around $950. The test is not covered by medical insurance and is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Falls into primary care setting
Dr. Rebbeck commented that Galleri is a screening test for individuals who don’t have cancer, so the test is intended to fall into the primary care setting. But he warned that “clinical pathways are not yet in place (but are being developed) so that primary care providers can effectively use them.”
The test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating tumor (or cell-free) DNA in a blood sample.
The methylation turns genes on or off, explains Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Klein in his post. “It’s like fingerprints and how fingerprints tell the difference between two people,” he wrote. “The methylation patterns are fingerprints that are characteristic of each kind of cancer. They look one way for lung cancer and different for colon cancer.”
The test returns one of two possible results: either “positive, cancer signal detected” or “negative, no cancer signal detected.”
According to the company, when a cancer signal is detected, the Galleri test predicts the cancer signal origin “with high accuracy, to help guide the next steps to diagnosis.”
However, one problem for clinical practice is all the follow-up tests an individual may undergo if their test comes back positive, said Sameek Roychowdhury, MD, PhD, an oncologist with Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
“Not everybody will have an actual cancer, but they may undergo many tests, with a lot of stress and cost and still not find anything. I can tell you every time someone undergoes a test looking for cancer, that is not an easy day,” Dr. Roychowdhury said in an interview.
In a large-scale validation study, the Galleri test had a specificity of 99.5% (false-positive rate of 0.5%), meaning in roughly 200 people tested without cancer, only one person received a false-positive result (that is, “cancer signal detected” when cancer is not present).
The overall sensitivity of the test for any stage of cancer was 51.5%, although it was higher for later-stage cancers (77% for stage III and 90.1% for stage IV) and lower for early-stage cancers (16.8% for stage I and 40.4% for stage II).
Exacerbate health disparities?
In Dr. Rebbeck’s view, the characteristics of the test are still “relatively poor for detecting very early cancers, so it will need additional tweaking before it really achieves the goal of multi-cancer EARLY detection,” he said.
Dr. Venstrom acknowledges that the test is “not perfect yet” and says the company will continue to update and improve its performance. “We have some new data coming out in September,” he said.
Clinical data are being accumulated in the United Kingdom, where the Galleri test is being investigated in a large trial run by the National Health Service (NHS). The company recently announced that the enrollment of 140,000 healthy cancer-free volunteers aged 50-77 into this trial has now been completed and claimed this the largest-ever study of a multi-cancer early detection test.
Dr. Roychowdhury said he would encourage anyone interested in the test to join a clinical trial.
Another expert approached for comment last year, when GRAIL first started marketing the test, was in agreement. This test should be viewed as one that is still under clinical investigation, commented William Grady, MD, a member of the clinical research division and public health sciences division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle.
“The Galleri test is still unproven in the clinical care setting and ... I am concerned that many of the results will be false-positives and will cause many unnecessary follow-up tests and imaging studies as well as anxiety in the people getting the test done,” Dr. Grady said.
Dr. Rebbeck said another issue that needs to be addressed is whether all populations will have access to and benefit from these types of blood tests to screen for cancer, given that they are expensive.
“There is a great danger – as we have seen with many other technological innovations – that the wealthy and connected benefit, but the majority of the population, and particularly those who are underserved, do not,” Dr. Rebbeck said.
“As a result, health disparities are created or exacerbated. This is something that needs to be addressed so that the future use of these tests will provide equitable benefits,” he added.
Dr. Rebbeck and Dr. Roychowdhury have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Venstrom is an employee of GRAIL.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Galleri blood test is being now offered by a number of United States health networks.
The company marketing the test, GRAIL, has established partnerships with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Mercy Health, Ochsner Health, Intermountain Healthcare, Community Health Network, Knight Cancer Institute at Oregon Health & Science University, Premier, and Cleveland Clinic, among others.
Cleveland Clinic’s Eric Klein, MD, emeritus chair of the Glickman Urological Kidney Institute, is enthusiastic about the test, describing it as a “game-changer” and emphasizing that it can detect many different cancers and at a very early stage.
“It completely changes the way we think about screening for cancer,” commented Jeff Venstrom, MD, chief medical officer at GRAIL. He joined the company because “there are not many things in life where you can be part of a disruptive paradigm and disruptive technology, and this really is disruptive,” he said in an interview.
‘The devil is in the details’
But there is some concern among clinicians that widespread clinical use of the test may be premature.
Having a blood test for multiple cancers is a “very good idea, and the scientific basis for this platform is sound,” commented Timothy R. Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and Division of Population Sciences, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
“But the devil is in the details to ensure the test can accurately detect very early cancers and there is a pathway for subsequent workup (diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, etc.),” Dr. Rebbeck told this news organization.
Galleri is offering the test to individuals who are older than 50 and have a family history of cancer or those who are high risk for cancer or immunocompromised. They suggest that interested individuals get in touch with their health care professional, who then needs to register with GRAIL and order the test.
As well as needing a prescription, interested individuals will have to pay for it out of pocket, around $950. The test is not covered by medical insurance and is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Falls into primary care setting
Dr. Rebbeck commented that Galleri is a screening test for individuals who don’t have cancer, so the test is intended to fall into the primary care setting. But he warned that “clinical pathways are not yet in place (but are being developed) so that primary care providers can effectively use them.”
The test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating tumor (or cell-free) DNA in a blood sample.
The methylation turns genes on or off, explains Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Klein in his post. “It’s like fingerprints and how fingerprints tell the difference between two people,” he wrote. “The methylation patterns are fingerprints that are characteristic of each kind of cancer. They look one way for lung cancer and different for colon cancer.”
The test returns one of two possible results: either “positive, cancer signal detected” or “negative, no cancer signal detected.”
According to the company, when a cancer signal is detected, the Galleri test predicts the cancer signal origin “with high accuracy, to help guide the next steps to diagnosis.”
However, one problem for clinical practice is all the follow-up tests an individual may undergo if their test comes back positive, said Sameek Roychowdhury, MD, PhD, an oncologist with Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
“Not everybody will have an actual cancer, but they may undergo many tests, with a lot of stress and cost and still not find anything. I can tell you every time someone undergoes a test looking for cancer, that is not an easy day,” Dr. Roychowdhury said in an interview.
In a large-scale validation study, the Galleri test had a specificity of 99.5% (false-positive rate of 0.5%), meaning in roughly 200 people tested without cancer, only one person received a false-positive result (that is, “cancer signal detected” when cancer is not present).
The overall sensitivity of the test for any stage of cancer was 51.5%, although it was higher for later-stage cancers (77% for stage III and 90.1% for stage IV) and lower for early-stage cancers (16.8% for stage I and 40.4% for stage II).
Exacerbate health disparities?
In Dr. Rebbeck’s view, the characteristics of the test are still “relatively poor for detecting very early cancers, so it will need additional tweaking before it really achieves the goal of multi-cancer EARLY detection,” he said.
Dr. Venstrom acknowledges that the test is “not perfect yet” and says the company will continue to update and improve its performance. “We have some new data coming out in September,” he said.
Clinical data are being accumulated in the United Kingdom, where the Galleri test is being investigated in a large trial run by the National Health Service (NHS). The company recently announced that the enrollment of 140,000 healthy cancer-free volunteers aged 50-77 into this trial has now been completed and claimed this the largest-ever study of a multi-cancer early detection test.
Dr. Roychowdhury said he would encourage anyone interested in the test to join a clinical trial.
Another expert approached for comment last year, when GRAIL first started marketing the test, was in agreement. This test should be viewed as one that is still under clinical investigation, commented William Grady, MD, a member of the clinical research division and public health sciences division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle.
“The Galleri test is still unproven in the clinical care setting and ... I am concerned that many of the results will be false-positives and will cause many unnecessary follow-up tests and imaging studies as well as anxiety in the people getting the test done,” Dr. Grady said.
Dr. Rebbeck said another issue that needs to be addressed is whether all populations will have access to and benefit from these types of blood tests to screen for cancer, given that they are expensive.
“There is a great danger – as we have seen with many other technological innovations – that the wealthy and connected benefit, but the majority of the population, and particularly those who are underserved, do not,” Dr. Rebbeck said.
“As a result, health disparities are created or exacerbated. This is something that needs to be addressed so that the future use of these tests will provide equitable benefits,” he added.
Dr. Rebbeck and Dr. Roychowdhury have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Venstrom is an employee of GRAIL.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Galleri blood test is being now offered by a number of United States health networks.
The company marketing the test, GRAIL, has established partnerships with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Mercy Health, Ochsner Health, Intermountain Healthcare, Community Health Network, Knight Cancer Institute at Oregon Health & Science University, Premier, and Cleveland Clinic, among others.
Cleveland Clinic’s Eric Klein, MD, emeritus chair of the Glickman Urological Kidney Institute, is enthusiastic about the test, describing it as a “game-changer” and emphasizing that it can detect many different cancers and at a very early stage.
“It completely changes the way we think about screening for cancer,” commented Jeff Venstrom, MD, chief medical officer at GRAIL. He joined the company because “there are not many things in life where you can be part of a disruptive paradigm and disruptive technology, and this really is disruptive,” he said in an interview.
‘The devil is in the details’
But there is some concern among clinicians that widespread clinical use of the test may be premature.
Having a blood test for multiple cancers is a “very good idea, and the scientific basis for this platform is sound,” commented Timothy R. Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and Division of Population Sciences, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
“But the devil is in the details to ensure the test can accurately detect very early cancers and there is a pathway for subsequent workup (diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, etc.),” Dr. Rebbeck told this news organization.
Galleri is offering the test to individuals who are older than 50 and have a family history of cancer or those who are high risk for cancer or immunocompromised. They suggest that interested individuals get in touch with their health care professional, who then needs to register with GRAIL and order the test.
As well as needing a prescription, interested individuals will have to pay for it out of pocket, around $950. The test is not covered by medical insurance and is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Falls into primary care setting
Dr. Rebbeck commented that Galleri is a screening test for individuals who don’t have cancer, so the test is intended to fall into the primary care setting. But he warned that “clinical pathways are not yet in place (but are being developed) so that primary care providers can effectively use them.”
The test uses next-generation sequencing to analyze the arrangement of methyl groups on circulating tumor (or cell-free) DNA in a blood sample.
The methylation turns genes on or off, explains Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Klein in his post. “It’s like fingerprints and how fingerprints tell the difference between two people,” he wrote. “The methylation patterns are fingerprints that are characteristic of each kind of cancer. They look one way for lung cancer and different for colon cancer.”
The test returns one of two possible results: either “positive, cancer signal detected” or “negative, no cancer signal detected.”
According to the company, when a cancer signal is detected, the Galleri test predicts the cancer signal origin “with high accuracy, to help guide the next steps to diagnosis.”
However, one problem for clinical practice is all the follow-up tests an individual may undergo if their test comes back positive, said Sameek Roychowdhury, MD, PhD, an oncologist with Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
“Not everybody will have an actual cancer, but they may undergo many tests, with a lot of stress and cost and still not find anything. I can tell you every time someone undergoes a test looking for cancer, that is not an easy day,” Dr. Roychowdhury said in an interview.
In a large-scale validation study, the Galleri test had a specificity of 99.5% (false-positive rate of 0.5%), meaning in roughly 200 people tested without cancer, only one person received a false-positive result (that is, “cancer signal detected” when cancer is not present).
The overall sensitivity of the test for any stage of cancer was 51.5%, although it was higher for later-stage cancers (77% for stage III and 90.1% for stage IV) and lower for early-stage cancers (16.8% for stage I and 40.4% for stage II).
Exacerbate health disparities?
In Dr. Rebbeck’s view, the characteristics of the test are still “relatively poor for detecting very early cancers, so it will need additional tweaking before it really achieves the goal of multi-cancer EARLY detection,” he said.
Dr. Venstrom acknowledges that the test is “not perfect yet” and says the company will continue to update and improve its performance. “We have some new data coming out in September,” he said.
Clinical data are being accumulated in the United Kingdom, where the Galleri test is being investigated in a large trial run by the National Health Service (NHS). The company recently announced that the enrollment of 140,000 healthy cancer-free volunteers aged 50-77 into this trial has now been completed and claimed this the largest-ever study of a multi-cancer early detection test.
Dr. Roychowdhury said he would encourage anyone interested in the test to join a clinical trial.
Another expert approached for comment last year, when GRAIL first started marketing the test, was in agreement. This test should be viewed as one that is still under clinical investigation, commented William Grady, MD, a member of the clinical research division and public health sciences division at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle.
“The Galleri test is still unproven in the clinical care setting and ... I am concerned that many of the results will be false-positives and will cause many unnecessary follow-up tests and imaging studies as well as anxiety in the people getting the test done,” Dr. Grady said.
Dr. Rebbeck said another issue that needs to be addressed is whether all populations will have access to and benefit from these types of blood tests to screen for cancer, given that they are expensive.
“There is a great danger – as we have seen with many other technological innovations – that the wealthy and connected benefit, but the majority of the population, and particularly those who are underserved, do not,” Dr. Rebbeck said.
“As a result, health disparities are created or exacerbated. This is something that needs to be addressed so that the future use of these tests will provide equitable benefits,” he added.
Dr. Rebbeck and Dr. Roychowdhury have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Venstrom is an employee of GRAIL.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CV admissions on the rise in Americans with cancer
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes
How well do vaccines protect against long COVID?
New York City veterinarian Erin Kulick used to be a weekend warrior. Only 2½ years ago, the 38-year-old new mother played ultimate Frisbee and flag football with friends. She went for regular 30-minute runs to burn off stress.
Now, Dr. Kulick is usually so exhausted, she can’t walk nonstop for 15 minutes. She recently tried to take her 4-year-old son, Cooper, to the American Museum of Natural History for his first visit, but ended up on a bench outside the museum, sobbing in the rain, because she couldn’t even get through the first hurdle of standing in line. “I just wanted to be there with my kid,” she said.
Dr. Kulick got sick with COVID-19 at the start of the pandemic in March 2020, 9 months before the first vaccine would be approved. Now she is among the estimated one in five infected Americans, or 19%, whose symptoms developed into long COVID.
Dr. Kulick also is now vaccinated and boosted. Had a vaccine been available sooner, could it have protected her from long COVID?
Evidence is starting to show it’s likely.
“The best way not to have long COVID is not to have COVID at all,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University. “To the extent that vaccination can prevent you from getting COVID at all, then it helps to reduce long COVID.”
And People with more serious initial illness appear more likely to have prolonged symptoms, but those with milder disease can certainly get it, too.
“You’re more likely to have long COVID with more severe disease, and we have ample evidence that vaccination reduces the severity of disease,” Dr. Horwitz said. “We also now have quite a lot of evidence that vaccination does reduce your risk of long COVID – probably because it reduces your risk of severe disease.”
There is little consensus about how much vaccines can lower the risk of long-term COVID symptoms, but several studies suggest that number lies anywhere from 15% to more than 80%.
That might seem like a big variation, but infectious disease experts argue that trying to interpret the gap isn’t as important as noticing what’s consistent across all these studies: “Vaccines do offer some protection, but it’s incomplete,” said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System. Dr. Al-Aly, who has led several large studies on long COVID, said focusing on the fact that vaccines do offer some protection is a much better public health message than looking at the different levels of risk.
“Vaccines do a miraculous job for what they were designed to do,” said Dr. Al-Aly. “Vaccines were designed to reduce the risk of hospitalization ... and for that, vaccines are still holding up, even with all the changes in the virus.”
Still, Elena Azzolini, MD, PhD, head of the Humanitas Research Hospital’s vaccination center in Milan, thinks some studies may have underestimated the level of long COVID protection from vaccines because of limits in the study methods, such as not including enough women, who are more affected by long COVID. Her recent study, which looked at 2,560 health care professionals working in nine Italian centers from March 2020 to April 2022, focused on the risk for healthy women and men in their 20s to their 70s.
In the paper, Dr. Azzolini and associates reported that two or three doses of vaccine reduced the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19 from 42% among those who are unvaccinated to 16%-17%. In other words, they found unvaccinated people in the study were nearly three times as likely to have serious symptoms for longer than 4 weeks.
But Dr. Azzolini and Dr. Al-Aly still say that, even for the vaccinated, as long as COVID is around, masks are necessary. That’s because current vaccines don’t do enough to reduce transmission, said Dr. Al-Aly. “The only way that can really help [stop] transmission is covering our nose and mouth with a mask.”
How vaccinations affect people who already have long COVID
Some long COVID patients have said they got better after they get boosted, while some say they’re getting worse, said Dr. Horwitz, who is also a lead investigator at the National Institutes of Health’s flagship RECOVER program, a 4-year research project to study long COVID across the United States. (The NIH is still recruiting volunteers for these studies, which are also open to people who have never had COVID.)
One study published in the British Medical Journal analyzed survey data of more than 28,000 people infected with COVID in the United Kingdom and found a 13% reduction in long-term symptoms after a first dose of the vaccine, although it was unclear from the data if the improvement was sustained.
A second dose was associated with another 8% improvement over a 2-month period. “It’s reassuring that we see an average modest improvement in symptoms, not an average worsening in symptoms,” said Daniel Ayoubkhani, principal statistician at the U.K. Office for National Statistics and lead author of the study. Of course, the experience will differ among different people.
“It doesn’t appear that vaccination is the silver bullet that’s going to eradicate long COVID,” he said, but evidence from multiple studies suggests vaccines may help people with long-term symptoms.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, an immunobiologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., told a White House summit in July that one of the best ways to prevent long COVID is to develop the next generation of vaccines that also prevent milder cases by blocking transmission in the first place.
Back in New York, Dr. Kulick is now triple vaccinated. She’s due for a fourth dose soon but admits she’s “terrified every time” that she’s going to get sicker.
In her Facebook support group for long COVID, she reads that most people with prolonged symptoms handle it well. She has also noticed some of her symptoms eased after her first two doses of vaccine.
Since being diagnosed, Dr. Kulick learned she has a genetic condition, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affects connective tissues that support skin, joints, organs, and blood vessels, and which her doctors say may have made her more prone to long COVID. She’s also being screened for autoimmune diseases, but for now, the only relief she has found has come from long COVID physical therapy, changes to her diet, and integrative medicine.
Dr. Kulick is still trying to figure out how she can get better while keeping her long hours at her veterinary job – and her health benefits. She is thankful her husband is a devoted caregiver to their son and a professional jazz musician with a schedule that allows for some flexibility.
“But it’s really hard when every week feels like I’ve run a marathon,” she said. “I can barely make it through.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New York City veterinarian Erin Kulick used to be a weekend warrior. Only 2½ years ago, the 38-year-old new mother played ultimate Frisbee and flag football with friends. She went for regular 30-minute runs to burn off stress.
Now, Dr. Kulick is usually so exhausted, she can’t walk nonstop for 15 minutes. She recently tried to take her 4-year-old son, Cooper, to the American Museum of Natural History for his first visit, but ended up on a bench outside the museum, sobbing in the rain, because she couldn’t even get through the first hurdle of standing in line. “I just wanted to be there with my kid,” she said.
Dr. Kulick got sick with COVID-19 at the start of the pandemic in March 2020, 9 months before the first vaccine would be approved. Now she is among the estimated one in five infected Americans, or 19%, whose symptoms developed into long COVID.
Dr. Kulick also is now vaccinated and boosted. Had a vaccine been available sooner, could it have protected her from long COVID?
Evidence is starting to show it’s likely.
“The best way not to have long COVID is not to have COVID at all,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University. “To the extent that vaccination can prevent you from getting COVID at all, then it helps to reduce long COVID.”
And People with more serious initial illness appear more likely to have prolonged symptoms, but those with milder disease can certainly get it, too.
“You’re more likely to have long COVID with more severe disease, and we have ample evidence that vaccination reduces the severity of disease,” Dr. Horwitz said. “We also now have quite a lot of evidence that vaccination does reduce your risk of long COVID – probably because it reduces your risk of severe disease.”
There is little consensus about how much vaccines can lower the risk of long-term COVID symptoms, but several studies suggest that number lies anywhere from 15% to more than 80%.
That might seem like a big variation, but infectious disease experts argue that trying to interpret the gap isn’t as important as noticing what’s consistent across all these studies: “Vaccines do offer some protection, but it’s incomplete,” said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System. Dr. Al-Aly, who has led several large studies on long COVID, said focusing on the fact that vaccines do offer some protection is a much better public health message than looking at the different levels of risk.
“Vaccines do a miraculous job for what they were designed to do,” said Dr. Al-Aly. “Vaccines were designed to reduce the risk of hospitalization ... and for that, vaccines are still holding up, even with all the changes in the virus.”
Still, Elena Azzolini, MD, PhD, head of the Humanitas Research Hospital’s vaccination center in Milan, thinks some studies may have underestimated the level of long COVID protection from vaccines because of limits in the study methods, such as not including enough women, who are more affected by long COVID. Her recent study, which looked at 2,560 health care professionals working in nine Italian centers from March 2020 to April 2022, focused on the risk for healthy women and men in their 20s to their 70s.
In the paper, Dr. Azzolini and associates reported that two or three doses of vaccine reduced the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19 from 42% among those who are unvaccinated to 16%-17%. In other words, they found unvaccinated people in the study were nearly three times as likely to have serious symptoms for longer than 4 weeks.
But Dr. Azzolini and Dr. Al-Aly still say that, even for the vaccinated, as long as COVID is around, masks are necessary. That’s because current vaccines don’t do enough to reduce transmission, said Dr. Al-Aly. “The only way that can really help [stop] transmission is covering our nose and mouth with a mask.”
How vaccinations affect people who already have long COVID
Some long COVID patients have said they got better after they get boosted, while some say they’re getting worse, said Dr. Horwitz, who is also a lead investigator at the National Institutes of Health’s flagship RECOVER program, a 4-year research project to study long COVID across the United States. (The NIH is still recruiting volunteers for these studies, which are also open to people who have never had COVID.)
One study published in the British Medical Journal analyzed survey data of more than 28,000 people infected with COVID in the United Kingdom and found a 13% reduction in long-term symptoms after a first dose of the vaccine, although it was unclear from the data if the improvement was sustained.
A second dose was associated with another 8% improvement over a 2-month period. “It’s reassuring that we see an average modest improvement in symptoms, not an average worsening in symptoms,” said Daniel Ayoubkhani, principal statistician at the U.K. Office for National Statistics and lead author of the study. Of course, the experience will differ among different people.
“It doesn’t appear that vaccination is the silver bullet that’s going to eradicate long COVID,” he said, but evidence from multiple studies suggests vaccines may help people with long-term symptoms.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, an immunobiologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., told a White House summit in July that one of the best ways to prevent long COVID is to develop the next generation of vaccines that also prevent milder cases by blocking transmission in the first place.
Back in New York, Dr. Kulick is now triple vaccinated. She’s due for a fourth dose soon but admits she’s “terrified every time” that she’s going to get sicker.
In her Facebook support group for long COVID, she reads that most people with prolonged symptoms handle it well. She has also noticed some of her symptoms eased after her first two doses of vaccine.
Since being diagnosed, Dr. Kulick learned she has a genetic condition, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affects connective tissues that support skin, joints, organs, and blood vessels, and which her doctors say may have made her more prone to long COVID. She’s also being screened for autoimmune diseases, but for now, the only relief she has found has come from long COVID physical therapy, changes to her diet, and integrative medicine.
Dr. Kulick is still trying to figure out how she can get better while keeping her long hours at her veterinary job – and her health benefits. She is thankful her husband is a devoted caregiver to their son and a professional jazz musician with a schedule that allows for some flexibility.
“But it’s really hard when every week feels like I’ve run a marathon,” she said. “I can barely make it through.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New York City veterinarian Erin Kulick used to be a weekend warrior. Only 2½ years ago, the 38-year-old new mother played ultimate Frisbee and flag football with friends. She went for regular 30-minute runs to burn off stress.
Now, Dr. Kulick is usually so exhausted, she can’t walk nonstop for 15 minutes. She recently tried to take her 4-year-old son, Cooper, to the American Museum of Natural History for his first visit, but ended up on a bench outside the museum, sobbing in the rain, because she couldn’t even get through the first hurdle of standing in line. “I just wanted to be there with my kid,” she said.
Dr. Kulick got sick with COVID-19 at the start of the pandemic in March 2020, 9 months before the first vaccine would be approved. Now she is among the estimated one in five infected Americans, or 19%, whose symptoms developed into long COVID.
Dr. Kulick also is now vaccinated and boosted. Had a vaccine been available sooner, could it have protected her from long COVID?
Evidence is starting to show it’s likely.
“The best way not to have long COVID is not to have COVID at all,” said Leora Horwitz, MD, a professor of population health and medicine at New York University. “To the extent that vaccination can prevent you from getting COVID at all, then it helps to reduce long COVID.”
And People with more serious initial illness appear more likely to have prolonged symptoms, but those with milder disease can certainly get it, too.
“You’re more likely to have long COVID with more severe disease, and we have ample evidence that vaccination reduces the severity of disease,” Dr. Horwitz said. “We also now have quite a lot of evidence that vaccination does reduce your risk of long COVID – probably because it reduces your risk of severe disease.”
There is little consensus about how much vaccines can lower the risk of long-term COVID symptoms, but several studies suggest that number lies anywhere from 15% to more than 80%.
That might seem like a big variation, but infectious disease experts argue that trying to interpret the gap isn’t as important as noticing what’s consistent across all these studies: “Vaccines do offer some protection, but it’s incomplete,” said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System. Dr. Al-Aly, who has led several large studies on long COVID, said focusing on the fact that vaccines do offer some protection is a much better public health message than looking at the different levels of risk.
“Vaccines do a miraculous job for what they were designed to do,” said Dr. Al-Aly. “Vaccines were designed to reduce the risk of hospitalization ... and for that, vaccines are still holding up, even with all the changes in the virus.”
Still, Elena Azzolini, MD, PhD, head of the Humanitas Research Hospital’s vaccination center in Milan, thinks some studies may have underestimated the level of long COVID protection from vaccines because of limits in the study methods, such as not including enough women, who are more affected by long COVID. Her recent study, which looked at 2,560 health care professionals working in nine Italian centers from March 2020 to April 2022, focused on the risk for healthy women and men in their 20s to their 70s.
In the paper, Dr. Azzolini and associates reported that two or three doses of vaccine reduced the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19 from 42% among those who are unvaccinated to 16%-17%. In other words, they found unvaccinated people in the study were nearly three times as likely to have serious symptoms for longer than 4 weeks.
But Dr. Azzolini and Dr. Al-Aly still say that, even for the vaccinated, as long as COVID is around, masks are necessary. That’s because current vaccines don’t do enough to reduce transmission, said Dr. Al-Aly. “The only way that can really help [stop] transmission is covering our nose and mouth with a mask.”
How vaccinations affect people who already have long COVID
Some long COVID patients have said they got better after they get boosted, while some say they’re getting worse, said Dr. Horwitz, who is also a lead investigator at the National Institutes of Health’s flagship RECOVER program, a 4-year research project to study long COVID across the United States. (The NIH is still recruiting volunteers for these studies, which are also open to people who have never had COVID.)
One study published in the British Medical Journal analyzed survey data of more than 28,000 people infected with COVID in the United Kingdom and found a 13% reduction in long-term symptoms after a first dose of the vaccine, although it was unclear from the data if the improvement was sustained.
A second dose was associated with another 8% improvement over a 2-month period. “It’s reassuring that we see an average modest improvement in symptoms, not an average worsening in symptoms,” said Daniel Ayoubkhani, principal statistician at the U.K. Office for National Statistics and lead author of the study. Of course, the experience will differ among different people.
“It doesn’t appear that vaccination is the silver bullet that’s going to eradicate long COVID,” he said, but evidence from multiple studies suggests vaccines may help people with long-term symptoms.
Akiko Iwasaki, PhD, an immunobiologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., told a White House summit in July that one of the best ways to prevent long COVID is to develop the next generation of vaccines that also prevent milder cases by blocking transmission in the first place.
Back in New York, Dr. Kulick is now triple vaccinated. She’s due for a fourth dose soon but admits she’s “terrified every time” that she’s going to get sicker.
In her Facebook support group for long COVID, she reads that most people with prolonged symptoms handle it well. She has also noticed some of her symptoms eased after her first two doses of vaccine.
Since being diagnosed, Dr. Kulick learned she has a genetic condition, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affects connective tissues that support skin, joints, organs, and blood vessels, and which her doctors say may have made her more prone to long COVID. She’s also being screened for autoimmune diseases, but for now, the only relief she has found has come from long COVID physical therapy, changes to her diet, and integrative medicine.
Dr. Kulick is still trying to figure out how she can get better while keeping her long hours at her veterinary job – and her health benefits. She is thankful her husband is a devoted caregiver to their son and a professional jazz musician with a schedule that allows for some flexibility.
“But it’s really hard when every week feels like I’ve run a marathon,” she said. “I can barely make it through.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.