User login
Increased body temperature triggers flares in rare autoinflammatory disorder
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
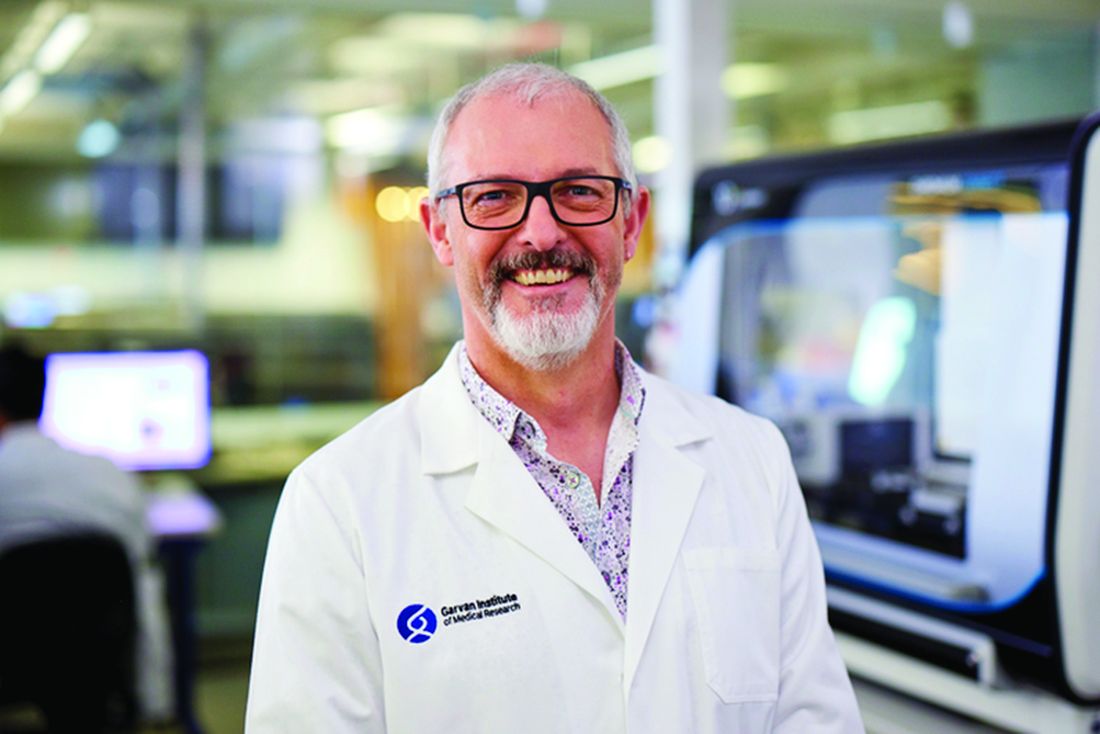
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
Early FMT shows promise for preventing recurrent C. difficile
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Help your patients understand their C. difficile diagnosis by sharing patient education from the AGA GI Patient Center (www.gastro.org/Cdiff).
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Help your patients understand their C. difficile diagnosis by sharing patient education from the AGA GI Patient Center (www.gastro.org/Cdiff).
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Help your patients understand their C. difficile diagnosis by sharing patient education from the AGA GI Patient Center (www.gastro.org/Cdiff).
FROM THE LANCET GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY
Early FMT shows promise for preventing recurrent C. difficile
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is safe and highly effective as first-line therapy for patients with first or second Clostridioides difficile infection, according to the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of its kind.
Study enrollment was halted after an interim analysis revealed significantly better outcomes among patients who received vancomycin plus FMT versus vancomycin alone, reported lead author Simon Mark Dahl Baunwall, MD, of Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The investigators noted that the participants represented a real-world patient population, so the data support FMT “as a necessary, effective first-line option” in routine management of C. difficile infection.
“Previous studies have demonstrated clinical cure rates [with FMT] of up to 92%,” Dr. Baunwall and colleagues wrote. “Early use of FMT for first or second C. difficile infection has therapeutic potential, but no formal randomized trials to support use of the approach as a first-line therapy have been done.”
The present trial, conducted at a university hospital in Denmark, involved 42 adult patients with first or second C. difficile infection. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either vancomycin alone or vancomycin plus FMT. All patients received 125 mg oral vancomycin four times daily for a minimum of 10 days after diagnosis. On day 1 after completion of vancomycin therapy and again between day 3 and 7, patients received either oral FMT or matching placebo, depending on their group. After completing the protocol, patients were followed for 8 weeks or C. difficile recurrence to evaluate resolution of C. difficile–associated diarrhea.
“In this trial, patients were treated with two sequential FMT procedures on separate days,” the investigators noted. “This practice might have overtreated some patients and differs from previous trials. It remains unknown whether optimal effect is achieved by one or two treatments.”
The trial design called for 84 patients, but enrollment was halted after an interim analysis of the above cohort of 42 patients because of significantly lower rate resolution in the placebo group. At the 2-month mark, 90% (95% confidence interval, 70%-99%) of patients in the FMT group had resolution, compared with only 33% (95% CI, 15%-57%) of patients in the placebo group (P = .0003), constituting a 57% (95% CI, 33%-81%) absolute risk reduction.
Most patients experienced adverse events, including 20 in the FMT group and all 21 in the placebo group, although most were transient and nonserious. The most common adverse events were diarrhea, which occurred more frequently in the FMT group (23 vs. 14 events), followed by abdominal pain(14 vs. 11 events) and nausea (12 vs. 5 events).
One limitation of the study was its single-center design with regional uptake; the authors noted that, despite having high statistical power for the clinical effect, the study’s premature termination and low patient number prevent inferences regarding mortality, time to effect, and cost.
“The results of this trial highlight how the use of fecal microbiota transplantation as a first-line treatment can effectively prevent C. difficile recurrence and suggests that microbiota restoration might be necessary to obtain sustained resolution,” the investigators wrote. “At present, only 10% of patients with multiple, recurrent C. difficile infection and indication for FMT receive it. International initiatives address the unmet need, but logistic and regulatory obstacles remain unsolved.”
Encouraging findings, lingering concerns
Nicholas Turner, MD, assistant professor in the division of infectious diseases at Duke University, Durham, N.C., praised the study for “pushing the boundaries for FMT,” and noted that the methodology appeared sound. Results in the placebo group, however, cast doubt on the generalizability of the findings, he said.
“If you look at the group that received vancomycin plus placebo, their failure rate was really astoundingly high,” Dr. Turner said in an interview, referring to the 67% failure rate in the control group; he noted previous studies had reported failure rates closer to 10%. “I think that just calls into question just a little bit what happened with that control group.”
Dr. Turner said his confidence would go “way, way up” if the findings were reproduced in a larger study. Ideally, these future trials would use fidaxomicin, he added, which is becoming the preferred option over vancomycin for treating C. difficile.
John Y. Kao, MD, professor of medicine and codirector of the FMT program at University of Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, offered a different perspective, suggesting that the control group findings shouldn’t overshadow the efficacy of FMT.
“I agree that historical data would tell us that the placebo population should see a much higher response,” Dr. Kao said in an interview. “In my mind though, the success rate of FMT over placebo is what I would expect. The message of the study should be upheld: that FMT is an effective therapy whether it’s given early or, as the way we give it now, as a sort of rescue therapy.”
Despite this confidence in FMT as an efficacious first-line option, Dr. Kao said it is unlikely to be routinely used in this way anytime soon, even if a larger trial echoes the present results.
“We don’t know the long-term risks of FMT therapy, although we’ve been doing this now probably close to 20 years,” Dr. Kao said.
Specifically, Dr. Kao was most concerned about the long-term risk of colon cancer, as mouse models suggest that microbiome characteristics may affect risk level, and risk may vary based on host-microbiome relationships. In other words, an organism may pose no risk in the gut of the donor, but the same may not be true for the recipient.
While increased rates of colon cancer or other serious illnesses have not been detected in humans who have undergone FMT over the past 2 decades, Dr. Kao said that these findings cannot be extrapolated over a patient’s entire lifetime, especially for younger individuals.
“In a patient that’s 80, you would say, yeah, let’s go ahead and treat you [with FMT] as first-line therapy, whereas someone who’s 20, and has maybe another 50 or 60 years longevity, you may not want to give FMT as first-line therapy,” Dr. Kao said.
This study was supported by Innovation Fund Denmark. The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Turner previously performed statistical analyses for a Merck study comparing vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole for C. difficile infection. Dr. Kao disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM THE LANCET GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY
New liver stiffness thresholds refine NASH risk stratification
New liver stiffness (LS) thresholds offer accurate prediction of disease progression and clinical outcomes in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis, according to investigators.
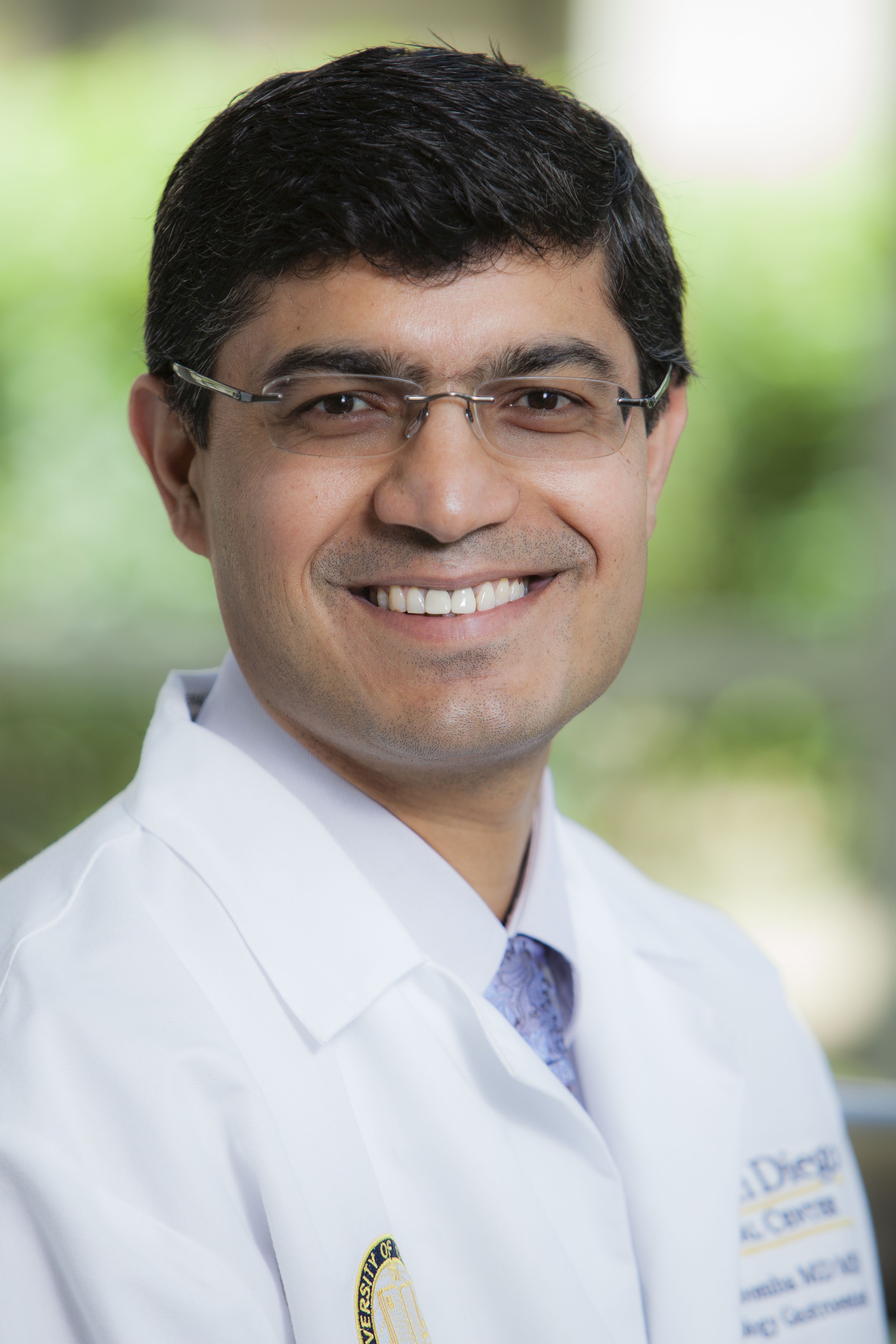
These new LS thresholds are more reliable because they are based on high-quality prospective data drawn from four randomized controlled trials, reported lead author Rohit Loomba, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
“Retrospective studies report that increasing baseline LS by VCTE [vibration-controlled transient elastography] is associated with the risk of disease progression in patients with NAFLD [non-alcoholic fatty liver disease], but prospective data in well-characterized NASH cohorts with biopsy-confirmed advanced fibrosis are limited,” the investigators wrote in Gut. “The optimal LS thresholds for prognostication of fibrosis progression and decompensation are unknown.”
Seeking clarity, Dr. Loomba and colleagues leveraged data from two phase 3 placebo-controlled trials for selonsertib and two phase 2b placebo-controlled trials for simtuzumab.
“While the studies were discontinued prematurely due to lack of efficacy, the prospectively collected data in these well-characterized participants with serial liver biopsies provides a unique opportunity to study the association between baseline LS by VCTE and disease progression,” the investigators wrote.
Across all four studies, bridging fibrosis (F3) was present in 664 participants, while 734 individuals had cirrhosis (F4). In the selonsertib studies, fibrosis was staged at baseline and week 48. The simtuzumab studies measured liver fibrosis at baseline and week 96. Out of the 664 participants with bridging fibrosis, 103 (16%) progressed to cirrhosis. Among the 734 patients with cirrhosis, 27 (4%) experienced liver-related events. Comparing these outcomes with LS data at baseline and throughout the study revealed optimal LS thresholds.
The best threshold for predicting progression from bridging fibrosis to cirrhosis was 16.6 kPa. According to the authors, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of this threshold for progression to cirrhosis were 58%, 76%, 31%, and 91%, respectively. Among patients at or above 16.6 kPa, 31% progressed to cirrhosis, compared with 9.1% of those under that threshold. Furthermore, individuals with a baseline LS at or above 16.6 kPa had nearly four times greater risk of developing cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.66-5.98; P < .0001).
For patients with cirrhosis at baseline, the optimal threshold for predicting liver-related events, such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and portal hypertension–related GI bleeding, liver transplantation, or mortality, was 30.7 kPa. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of this threshold for liver-related events were 62%, 87%, 10%, and 99%, respectively, according to the authors. Patients with an LS above this mark were 10 times as likely to experience liver-related events (aHR, 10.13; 95% CI, 4.38-23.41; P < .0001).
Scott L. Friedman, MD, chief of the division of liver diseases and dean for Therapeutic Discovery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the study “an important effort” that offers valuable insights for both researchers and practitioners.
“For clinical trials, [these thresholds] really allow for greater refinement or enrichment of patients who are suitable for enrollment in the trial because they’re at a higher risk of clinical problems that might be mitigated if the drug is effective,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “For clinical practice, it might indicate that the patient should either be fast tracked for a clinical trial or, more importantly, maybe needs to be referred for evaluation for a liver transplant. It may also indicate – although they didn’t look at it in this study – that there’s a need to begin or accelerate screening for liver cancer, which becomes an encroaching risk as the fibrosis advances to later stages.”
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Eli Lilly, CohBar, and others. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
New liver stiffness (LS) thresholds offer accurate prediction of disease progression and clinical outcomes in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis, according to investigators.
These new LS thresholds are more reliable because they are based on high-quality prospective data drawn from four randomized controlled trials, reported lead author Rohit Loomba, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
“Retrospective studies report that increasing baseline LS by VCTE [vibration-controlled transient elastography] is associated with the risk of disease progression in patients with NAFLD [non-alcoholic fatty liver disease], but prospective data in well-characterized NASH cohorts with biopsy-confirmed advanced fibrosis are limited,” the investigators wrote in Gut. “The optimal LS thresholds for prognostication of fibrosis progression and decompensation are unknown.”
Seeking clarity, Dr. Loomba and colleagues leveraged data from two phase 3 placebo-controlled trials for selonsertib and two phase 2b placebo-controlled trials for simtuzumab.
“While the studies were discontinued prematurely due to lack of efficacy, the prospectively collected data in these well-characterized participants with serial liver biopsies provides a unique opportunity to study the association between baseline LS by VCTE and disease progression,” the investigators wrote.
Across all four studies, bridging fibrosis (F3) was present in 664 participants, while 734 individuals had cirrhosis (F4). In the selonsertib studies, fibrosis was staged at baseline and week 48. The simtuzumab studies measured liver fibrosis at baseline and week 96. Out of the 664 participants with bridging fibrosis, 103 (16%) progressed to cirrhosis. Among the 734 patients with cirrhosis, 27 (4%) experienced liver-related events. Comparing these outcomes with LS data at baseline and throughout the study revealed optimal LS thresholds.
The best threshold for predicting progression from bridging fibrosis to cirrhosis was 16.6 kPa. According to the authors, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of this threshold for progression to cirrhosis were 58%, 76%, 31%, and 91%, respectively. Among patients at or above 16.6 kPa, 31% progressed to cirrhosis, compared with 9.1% of those under that threshold. Furthermore, individuals with a baseline LS at or above 16.6 kPa had nearly four times greater risk of developing cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.66-5.98; P < .0001).
For patients with cirrhosis at baseline, the optimal threshold for predicting liver-related events, such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and portal hypertension–related GI bleeding, liver transplantation, or mortality, was 30.7 kPa. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of this threshold for liver-related events were 62%, 87%, 10%, and 99%, respectively, according to the authors. Patients with an LS above this mark were 10 times as likely to experience liver-related events (aHR, 10.13; 95% CI, 4.38-23.41; P < .0001).
Scott L. Friedman, MD, chief of the division of liver diseases and dean for Therapeutic Discovery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the study “an important effort” that offers valuable insights for both researchers and practitioners.
“For clinical trials, [these thresholds] really allow for greater refinement or enrichment of patients who are suitable for enrollment in the trial because they’re at a higher risk of clinical problems that might be mitigated if the drug is effective,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “For clinical practice, it might indicate that the patient should either be fast tracked for a clinical trial or, more importantly, maybe needs to be referred for evaluation for a liver transplant. It may also indicate – although they didn’t look at it in this study – that there’s a need to begin or accelerate screening for liver cancer, which becomes an encroaching risk as the fibrosis advances to later stages.”
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Eli Lilly, CohBar, and others. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
New liver stiffness (LS) thresholds offer accurate prediction of disease progression and clinical outcomes in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis, according to investigators.
These new LS thresholds are more reliable because they are based on high-quality prospective data drawn from four randomized controlled trials, reported lead author Rohit Loomba, MD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
“Retrospective studies report that increasing baseline LS by VCTE [vibration-controlled transient elastography] is associated with the risk of disease progression in patients with NAFLD [non-alcoholic fatty liver disease], but prospective data in well-characterized NASH cohorts with biopsy-confirmed advanced fibrosis are limited,” the investigators wrote in Gut. “The optimal LS thresholds for prognostication of fibrosis progression and decompensation are unknown.”
Seeking clarity, Dr. Loomba and colleagues leveraged data from two phase 3 placebo-controlled trials for selonsertib and two phase 2b placebo-controlled trials for simtuzumab.
“While the studies were discontinued prematurely due to lack of efficacy, the prospectively collected data in these well-characterized participants with serial liver biopsies provides a unique opportunity to study the association between baseline LS by VCTE and disease progression,” the investigators wrote.
Across all four studies, bridging fibrosis (F3) was present in 664 participants, while 734 individuals had cirrhosis (F4). In the selonsertib studies, fibrosis was staged at baseline and week 48. The simtuzumab studies measured liver fibrosis at baseline and week 96. Out of the 664 participants with bridging fibrosis, 103 (16%) progressed to cirrhosis. Among the 734 patients with cirrhosis, 27 (4%) experienced liver-related events. Comparing these outcomes with LS data at baseline and throughout the study revealed optimal LS thresholds.
The best threshold for predicting progression from bridging fibrosis to cirrhosis was 16.6 kPa. According to the authors, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of this threshold for progression to cirrhosis were 58%, 76%, 31%, and 91%, respectively. Among patients at or above 16.6 kPa, 31% progressed to cirrhosis, compared with 9.1% of those under that threshold. Furthermore, individuals with a baseline LS at or above 16.6 kPa had nearly four times greater risk of developing cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.66-5.98; P < .0001).
For patients with cirrhosis at baseline, the optimal threshold for predicting liver-related events, such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and portal hypertension–related GI bleeding, liver transplantation, or mortality, was 30.7 kPa. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of this threshold for liver-related events were 62%, 87%, 10%, and 99%, respectively, according to the authors. Patients with an LS above this mark were 10 times as likely to experience liver-related events (aHR, 10.13; 95% CI, 4.38-23.41; P < .0001).
Scott L. Friedman, MD, chief of the division of liver diseases and dean for Therapeutic Discovery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, called the study “an important effort” that offers valuable insights for both researchers and practitioners.
“For clinical trials, [these thresholds] really allow for greater refinement or enrichment of patients who are suitable for enrollment in the trial because they’re at a higher risk of clinical problems that might be mitigated if the drug is effective,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “For clinical practice, it might indicate that the patient should either be fast tracked for a clinical trial or, more importantly, maybe needs to be referred for evaluation for a liver transplant. It may also indicate – although they didn’t look at it in this study – that there’s a need to begin or accelerate screening for liver cancer, which becomes an encroaching risk as the fibrosis advances to later stages.”
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Amgen, Eli Lilly, CohBar, and others. Dr. Friedman reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM GUT
Night owls may have greater risks of T2D and CVD
In the study involving 51 people, night owls metabolized fat less efficiently, showed less insulin sensitivity, and demonstrated lower physical fitness than early birds, lead author Steven K. Malin, PhD, of Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and colleagues reported.
Prior publications have suggested that night owls, formally known as “late chronotypes,” have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Malin said in an interview. But no previous research involved the gold-standard measurement tools used in this study, including euglycemic clamp and indirect calorimetry to quantify fat metabolism.
Dr. Malin also noted that this is the first study of its kind to characterize metabolism during both rest and exercise.
The study, published in Experimental Physiology, involved 24 early birds and 27 night owls classified by the Morning-Eveningness Questionnaire. All participants were sedentary, reporting less than one hour of structured exercise per week, and had metabolic syndrome according to Adult Treatment Panel III report criteria. Groups were otherwise demographically similar, with average ages in each group of approximately 54-55 years.
Compared with night owls, early birds were more physically active during the morning into midday. During exercise, they metabolized more fat and demonstrated greater physical fitness based on VO2max readings. At rest, early birds also came out ahead – they had higher fat oxidation and non–oxidative glucose disposal, suggesting more sensitivity to insulin.
“Collectively, this work highlights and supports chronotype as a potential risk factor related to type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk,” the investigators concluded.
Night owls have less metabolic control
Jed Friedman, PhD, director of OU Health Harold Hamm Diabetes Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, praised the study for the size of the groups the researchers compared with each other and how well matched those groups were, as well as the “state-of-the-art” measurement tools employed.
The findings show that night owls have “less metabolic control,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview.
“That’s a term that’s frequently invoked in [regard to] prediabetes,” he said. “Blood sugar goes up, because when you’re eating a high carbohydrate diet, your cells aren’t metabolizing sugar properly. That tends to raise your risk for a lot of diseases.”
Dr. Friedman added that the findings align with those of previous studies that have linked less sleep with changes in brain biology, and therefore behavior, especially in dietary choices.
“When you’re tired, the mechanisms for appetite control go haywire,” Dr. Friedman explained. “The evidence suggests that sugar is the primary driver for what people eat when they’re tired. That obviously has implications for diabetes and metabolic syndrome. So sleeping more really can help you control cravings.”
Dr. Friedman also noted that people who are tired tend to engage in less physical activity, further increasing their risk of metabolic issues. To control this risk, he advised people to return to their circadian rhythms, which could mean forgetting the midnight snack.
“Having a daily pattern that’s in sync with chronicity, or these daily rhythms, is associated with greater health,” Dr. Friedman said. “We’re not really made to eat at night. I think this [study] kind of reinforces that.”
Can a night owl become an early bird?
When asked if a person’s natural circadian rhythm can be later, Dr. Malin responded that chronotypes may be dictated by genetics and age, as well as external drivers like work schedule. For these reasons, it’s “tricky” to answer whether night owls can turn into early birds and reap the potential health benefits of making that shift.
“Given that so many life factors can influence what our routine entails, it’s hard to know if we [can] truly change our chronotype or if rather we [can] learn to manage,” Dr. Malin said. “In either case, there is some work that suggests people can adopt earlier bedtimes and waketimes through practical recommendations.”
Specifically, he suggested increasing physical activity during the day, and adjusting bedtimes gradually by 15-minute increments.
“Go to bed 15 minutes earlier then wake up 15 minutes earlier,” Dr. Malin said. “In time, and depending on how things are going, this can expand to another 15-minute window. Then, during the earlier time waking up, a person can engage in light physical activity to help with promoting general fitness. If they can get outside with sunlight, that would be great too, as the natural sunlight would provide cues to the circadian system to adjust.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Friedman disclosed no conflicts of interest.
In the study involving 51 people, night owls metabolized fat less efficiently, showed less insulin sensitivity, and demonstrated lower physical fitness than early birds, lead author Steven K. Malin, PhD, of Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and colleagues reported.
Prior publications have suggested that night owls, formally known as “late chronotypes,” have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Malin said in an interview. But no previous research involved the gold-standard measurement tools used in this study, including euglycemic clamp and indirect calorimetry to quantify fat metabolism.
Dr. Malin also noted that this is the first study of its kind to characterize metabolism during both rest and exercise.
The study, published in Experimental Physiology, involved 24 early birds and 27 night owls classified by the Morning-Eveningness Questionnaire. All participants were sedentary, reporting less than one hour of structured exercise per week, and had metabolic syndrome according to Adult Treatment Panel III report criteria. Groups were otherwise demographically similar, with average ages in each group of approximately 54-55 years.
Compared with night owls, early birds were more physically active during the morning into midday. During exercise, they metabolized more fat and demonstrated greater physical fitness based on VO2max readings. At rest, early birds also came out ahead – they had higher fat oxidation and non–oxidative glucose disposal, suggesting more sensitivity to insulin.
“Collectively, this work highlights and supports chronotype as a potential risk factor related to type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk,” the investigators concluded.
Night owls have less metabolic control
Jed Friedman, PhD, director of OU Health Harold Hamm Diabetes Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, praised the study for the size of the groups the researchers compared with each other and how well matched those groups were, as well as the “state-of-the-art” measurement tools employed.
The findings show that night owls have “less metabolic control,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview.
“That’s a term that’s frequently invoked in [regard to] prediabetes,” he said. “Blood sugar goes up, because when you’re eating a high carbohydrate diet, your cells aren’t metabolizing sugar properly. That tends to raise your risk for a lot of diseases.”
Dr. Friedman added that the findings align with those of previous studies that have linked less sleep with changes in brain biology, and therefore behavior, especially in dietary choices.
“When you’re tired, the mechanisms for appetite control go haywire,” Dr. Friedman explained. “The evidence suggests that sugar is the primary driver for what people eat when they’re tired. That obviously has implications for diabetes and metabolic syndrome. So sleeping more really can help you control cravings.”
Dr. Friedman also noted that people who are tired tend to engage in less physical activity, further increasing their risk of metabolic issues. To control this risk, he advised people to return to their circadian rhythms, which could mean forgetting the midnight snack.
“Having a daily pattern that’s in sync with chronicity, or these daily rhythms, is associated with greater health,” Dr. Friedman said. “We’re not really made to eat at night. I think this [study] kind of reinforces that.”
Can a night owl become an early bird?
When asked if a person’s natural circadian rhythm can be later, Dr. Malin responded that chronotypes may be dictated by genetics and age, as well as external drivers like work schedule. For these reasons, it’s “tricky” to answer whether night owls can turn into early birds and reap the potential health benefits of making that shift.
“Given that so many life factors can influence what our routine entails, it’s hard to know if we [can] truly change our chronotype or if rather we [can] learn to manage,” Dr. Malin said. “In either case, there is some work that suggests people can adopt earlier bedtimes and waketimes through practical recommendations.”
Specifically, he suggested increasing physical activity during the day, and adjusting bedtimes gradually by 15-minute increments.
“Go to bed 15 minutes earlier then wake up 15 minutes earlier,” Dr. Malin said. “In time, and depending on how things are going, this can expand to another 15-minute window. Then, during the earlier time waking up, a person can engage in light physical activity to help with promoting general fitness. If they can get outside with sunlight, that would be great too, as the natural sunlight would provide cues to the circadian system to adjust.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Friedman disclosed no conflicts of interest.
In the study involving 51 people, night owls metabolized fat less efficiently, showed less insulin sensitivity, and demonstrated lower physical fitness than early birds, lead author Steven K. Malin, PhD, of Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and colleagues reported.
Prior publications have suggested that night owls, formally known as “late chronotypes,” have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, Dr. Malin said in an interview. But no previous research involved the gold-standard measurement tools used in this study, including euglycemic clamp and indirect calorimetry to quantify fat metabolism.
Dr. Malin also noted that this is the first study of its kind to characterize metabolism during both rest and exercise.
The study, published in Experimental Physiology, involved 24 early birds and 27 night owls classified by the Morning-Eveningness Questionnaire. All participants were sedentary, reporting less than one hour of structured exercise per week, and had metabolic syndrome according to Adult Treatment Panel III report criteria. Groups were otherwise demographically similar, with average ages in each group of approximately 54-55 years.
Compared with night owls, early birds were more physically active during the morning into midday. During exercise, they metabolized more fat and demonstrated greater physical fitness based on VO2max readings. At rest, early birds also came out ahead – they had higher fat oxidation and non–oxidative glucose disposal, suggesting more sensitivity to insulin.
“Collectively, this work highlights and supports chronotype as a potential risk factor related to type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk,” the investigators concluded.
Night owls have less metabolic control
Jed Friedman, PhD, director of OU Health Harold Hamm Diabetes Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, praised the study for the size of the groups the researchers compared with each other and how well matched those groups were, as well as the “state-of-the-art” measurement tools employed.
The findings show that night owls have “less metabolic control,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview.
“That’s a term that’s frequently invoked in [regard to] prediabetes,” he said. “Blood sugar goes up, because when you’re eating a high carbohydrate diet, your cells aren’t metabolizing sugar properly. That tends to raise your risk for a lot of diseases.”
Dr. Friedman added that the findings align with those of previous studies that have linked less sleep with changes in brain biology, and therefore behavior, especially in dietary choices.
“When you’re tired, the mechanisms for appetite control go haywire,” Dr. Friedman explained. “The evidence suggests that sugar is the primary driver for what people eat when they’re tired. That obviously has implications for diabetes and metabolic syndrome. So sleeping more really can help you control cravings.”
Dr. Friedman also noted that people who are tired tend to engage in less physical activity, further increasing their risk of metabolic issues. To control this risk, he advised people to return to their circadian rhythms, which could mean forgetting the midnight snack.
“Having a daily pattern that’s in sync with chronicity, or these daily rhythms, is associated with greater health,” Dr. Friedman said. “We’re not really made to eat at night. I think this [study] kind of reinforces that.”
Can a night owl become an early bird?
When asked if a person’s natural circadian rhythm can be later, Dr. Malin responded that chronotypes may be dictated by genetics and age, as well as external drivers like work schedule. For these reasons, it’s “tricky” to answer whether night owls can turn into early birds and reap the potential health benefits of making that shift.
“Given that so many life factors can influence what our routine entails, it’s hard to know if we [can] truly change our chronotype or if rather we [can] learn to manage,” Dr. Malin said. “In either case, there is some work that suggests people can adopt earlier bedtimes and waketimes through practical recommendations.”
Specifically, he suggested increasing physical activity during the day, and adjusting bedtimes gradually by 15-minute increments.
“Go to bed 15 minutes earlier then wake up 15 minutes earlier,” Dr. Malin said. “In time, and depending on how things are going, this can expand to another 15-minute window. Then, during the earlier time waking up, a person can engage in light physical activity to help with promoting general fitness. If they can get outside with sunlight, that would be great too, as the natural sunlight would provide cues to the circadian system to adjust.”
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Friedman disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY
Online yoga program improves physical function in OA
Although pain did not significantly improve in the yoga group, participants only completed about two-thirds of the recommended sessions, suggesting that more benefit may be possible with greater adherence, wrote lead author Kim L. Bennell, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“To date, an online yoga program specifically for people with knee osteoarthritis has not been investigated,” the investigators said. “The need for such evidence-based packaged online exercise programs is highlighted in the 2020 U.S. National Public Health Agenda for Osteoarthritis.”
Methods and results
The trial involved 212 adults aged 45 years or older with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. All patients had access to online educational materials about managing osteoarthritis.
Half of the participants were randomized into the 12-week online yoga program. This self-directed, unsupervised course consisted of 12 prerecorded 30-minute instructional yoga sessions, each with a unique sequence of poses to be completed three times in one week before moving on to the next class the following week. After 12 weeks, these participants could choose to continue doing yoga via the online program for 12 additional weeks, if desired.
The primary outcomes were knee pain and physical function, gauged by a 10-point numerical rating scale and the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), respectively. Adherence was defined as completion of at least 2 yoga sessions within the preceding week.
At the 12-week mark, the yoga group did not show any significant improvement in knee pain (–0.6; 95% confidence interval, –1.2 to 0.1), but they did achieve a mean 4-point reduction in WOMAC, suggesting significant improvement in knee function (–4.0; 95% CI, –6.8 to –1.3). Of note, however, this improvement was not enough to meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference. At 24 weeks, the yoga group no longer showed significant improvement in knee function versus baseline.
“I don’t think a longer program would necessarily reduce knee pain, as benefits from a whole range of different types of exercise for knee osteoarthritis generally can show benefits within 8 weeks,” Dr. Bennell said in an interview.
Still, she noted that the average outcome in the trial may not represent what is possible if a patient commits to a regular yoga routine.
“I think it relates more to adherence [than duration], and I think benefits for knee pain would have been seen if a greater number of people had fully adhered to the program three times a week,” she said.
At 12 weeks, 68.8% of those in the yoga group were adherent, while just 28.4% were still adherent at week 24 after the optional extension period.
“As this was a self-directed program, adherence might be expected to be less than that of a supervised program,” Dr. Bennell noted.
Referring to unpublished data, Dr. Bennell said a sensitivity analysis showed that participants in the yoga group who completed yoga at least twice a week did show greater improvements in function and pain than those who did yoga less than twice per week.
“So it does suggest that adherence is important, as we might expect,” she said.
Another tool in the OA toolbox
Nick Trasolini, MD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., described the benefits in the trial as “modest” and noted that the improvement in function did not meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference.
“Nevertheless,” he said in a written comment, “the [yoga] program was safe and associated with high participant satisfaction [mean satisfaction, 8 out of 10]. While this may not be the ‘silver bullet,’ it is another tool that we can offer to sufficiently motivated patients seeking non-operative solutions for knee osteoarthritis.”
Unfortunately, these tools remain “fraught with challenges,” Dr. Trasolini added.
“While multiple injection options are available (including corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation, and biologic injections), the benefits of these injections can be short-lived,” he said. “This is frustrating to patients and physicians alike. Physical therapy is beneficial for knee osteoarthritis when deconditioning has led to decreased knee, hip, and core stability. However, physical therapy can be time consuming, painful, and cost prohibitive.”
In the present study, participants in the yoga group were somewhat willing (mean willingness, 5 out of 10) to pay for their 12-week yoga program. They reported that they would pay approximately $80 U.S. dollars for chance to do it all again.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council Program and the Centres of Research Excellence. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Pfizer, Lilly, TLCBio, and others. Dr. Trasolini disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Although pain did not significantly improve in the yoga group, participants only completed about two-thirds of the recommended sessions, suggesting that more benefit may be possible with greater adherence, wrote lead author Kim L. Bennell, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“To date, an online yoga program specifically for people with knee osteoarthritis has not been investigated,” the investigators said. “The need for such evidence-based packaged online exercise programs is highlighted in the 2020 U.S. National Public Health Agenda for Osteoarthritis.”
Methods and results
The trial involved 212 adults aged 45 years or older with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. All patients had access to online educational materials about managing osteoarthritis.
Half of the participants were randomized into the 12-week online yoga program. This self-directed, unsupervised course consisted of 12 prerecorded 30-minute instructional yoga sessions, each with a unique sequence of poses to be completed three times in one week before moving on to the next class the following week. After 12 weeks, these participants could choose to continue doing yoga via the online program for 12 additional weeks, if desired.
The primary outcomes were knee pain and physical function, gauged by a 10-point numerical rating scale and the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), respectively. Adherence was defined as completion of at least 2 yoga sessions within the preceding week.
At the 12-week mark, the yoga group did not show any significant improvement in knee pain (–0.6; 95% confidence interval, –1.2 to 0.1), but they did achieve a mean 4-point reduction in WOMAC, suggesting significant improvement in knee function (–4.0; 95% CI, –6.8 to –1.3). Of note, however, this improvement was not enough to meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference. At 24 weeks, the yoga group no longer showed significant improvement in knee function versus baseline.
“I don’t think a longer program would necessarily reduce knee pain, as benefits from a whole range of different types of exercise for knee osteoarthritis generally can show benefits within 8 weeks,” Dr. Bennell said in an interview.
Still, she noted that the average outcome in the trial may not represent what is possible if a patient commits to a regular yoga routine.
“I think it relates more to adherence [than duration], and I think benefits for knee pain would have been seen if a greater number of people had fully adhered to the program three times a week,” she said.
At 12 weeks, 68.8% of those in the yoga group were adherent, while just 28.4% were still adherent at week 24 after the optional extension period.
“As this was a self-directed program, adherence might be expected to be less than that of a supervised program,” Dr. Bennell noted.
Referring to unpublished data, Dr. Bennell said a sensitivity analysis showed that participants in the yoga group who completed yoga at least twice a week did show greater improvements in function and pain than those who did yoga less than twice per week.
“So it does suggest that adherence is important, as we might expect,” she said.
Another tool in the OA toolbox
Nick Trasolini, MD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., described the benefits in the trial as “modest” and noted that the improvement in function did not meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference.
“Nevertheless,” he said in a written comment, “the [yoga] program was safe and associated with high participant satisfaction [mean satisfaction, 8 out of 10]. While this may not be the ‘silver bullet,’ it is another tool that we can offer to sufficiently motivated patients seeking non-operative solutions for knee osteoarthritis.”
Unfortunately, these tools remain “fraught with challenges,” Dr. Trasolini added.
“While multiple injection options are available (including corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation, and biologic injections), the benefits of these injections can be short-lived,” he said. “This is frustrating to patients and physicians alike. Physical therapy is beneficial for knee osteoarthritis when deconditioning has led to decreased knee, hip, and core stability. However, physical therapy can be time consuming, painful, and cost prohibitive.”
In the present study, participants in the yoga group were somewhat willing (mean willingness, 5 out of 10) to pay for their 12-week yoga program. They reported that they would pay approximately $80 U.S. dollars for chance to do it all again.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council Program and the Centres of Research Excellence. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Pfizer, Lilly, TLCBio, and others. Dr. Trasolini disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Although pain did not significantly improve in the yoga group, participants only completed about two-thirds of the recommended sessions, suggesting that more benefit may be possible with greater adherence, wrote lead author Kim L. Bennell, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and colleagues in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“To date, an online yoga program specifically for people with knee osteoarthritis has not been investigated,” the investigators said. “The need for such evidence-based packaged online exercise programs is highlighted in the 2020 U.S. National Public Health Agenda for Osteoarthritis.”
Methods and results
The trial involved 212 adults aged 45 years or older with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. All patients had access to online educational materials about managing osteoarthritis.
Half of the participants were randomized into the 12-week online yoga program. This self-directed, unsupervised course consisted of 12 prerecorded 30-minute instructional yoga sessions, each with a unique sequence of poses to be completed three times in one week before moving on to the next class the following week. After 12 weeks, these participants could choose to continue doing yoga via the online program for 12 additional weeks, if desired.
The primary outcomes were knee pain and physical function, gauged by a 10-point numerical rating scale and the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), respectively. Adherence was defined as completion of at least 2 yoga sessions within the preceding week.
At the 12-week mark, the yoga group did not show any significant improvement in knee pain (–0.6; 95% confidence interval, –1.2 to 0.1), but they did achieve a mean 4-point reduction in WOMAC, suggesting significant improvement in knee function (–4.0; 95% CI, –6.8 to –1.3). Of note, however, this improvement was not enough to meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference. At 24 weeks, the yoga group no longer showed significant improvement in knee function versus baseline.
“I don’t think a longer program would necessarily reduce knee pain, as benefits from a whole range of different types of exercise for knee osteoarthritis generally can show benefits within 8 weeks,” Dr. Bennell said in an interview.
Still, she noted that the average outcome in the trial may not represent what is possible if a patient commits to a regular yoga routine.
“I think it relates more to adherence [than duration], and I think benefits for knee pain would have been seen if a greater number of people had fully adhered to the program three times a week,” she said.
At 12 weeks, 68.8% of those in the yoga group were adherent, while just 28.4% were still adherent at week 24 after the optional extension period.
“As this was a self-directed program, adherence might be expected to be less than that of a supervised program,” Dr. Bennell noted.
Referring to unpublished data, Dr. Bennell said a sensitivity analysis showed that participants in the yoga group who completed yoga at least twice a week did show greater improvements in function and pain than those who did yoga less than twice per week.
“So it does suggest that adherence is important, as we might expect,” she said.
Another tool in the OA toolbox
Nick Trasolini, MD, of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., described the benefits in the trial as “modest” and noted that the improvement in function did not meet the threshold for minimal clinically important difference.
“Nevertheless,” he said in a written comment, “the [yoga] program was safe and associated with high participant satisfaction [mean satisfaction, 8 out of 10]. While this may not be the ‘silver bullet,’ it is another tool that we can offer to sufficiently motivated patients seeking non-operative solutions for knee osteoarthritis.”
Unfortunately, these tools remain “fraught with challenges,” Dr. Trasolini added.
“While multiple injection options are available (including corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation, and biologic injections), the benefits of these injections can be short-lived,” he said. “This is frustrating to patients and physicians alike. Physical therapy is beneficial for knee osteoarthritis when deconditioning has led to decreased knee, hip, and core stability. However, physical therapy can be time consuming, painful, and cost prohibitive.”
In the present study, participants in the yoga group were somewhat willing (mean willingness, 5 out of 10) to pay for their 12-week yoga program. They reported that they would pay approximately $80 U.S. dollars for chance to do it all again.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council Program and the Centres of Research Excellence. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Pfizer, Lilly, TLCBio, and others. Dr. Trasolini disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
One in three MS patients reports chronic itch
, according to investigators.
Itch is historically underrecognized as a symptom of MS, but physicians should know that it is common and may negatively impact quality of life, reported lead author Giuseppe Ingrasci, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, and colleagues.
While previous publications suggest that pruritus occurs in just 2%-6% of patients with MS, principal author Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor, Stiefel Chair of Medical Dermatology, and director of the Miami Itch Center in the Dr. Phillip Frost department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, encountered itch in enough patients with MS that he presented his observations to a group of neurologists.
Most of them dismissed him, he recalled in an interview: “The neurologists said, ‘Very interesting, but we don’t really see it.’ ”
One of those neurologists, however, decided to take a closer look.
Andrew Brown, MD, assistant professor of clinical neurology and chief of the general neurology division at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, began asking his patients with MS if they were experiencing itch and soon found that it was “a very common problem,” according to Dr. Yosipovitch.
Dr. Yosipovitch, who was the first to report pruritus in patients with psoriasis, launched the present investigation with Dr. Brown to determine if itch is also a blind spot in the world of MS. Their results, and their uphill battle to publication, suggest that it very well could be.
After being rejected from six neurology journals, with one editor suggesting that itch is “not relevant at all to neurology,” their findings were published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology.
A common problem that may indicate more severe disease
At the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Excellence in Miami, 27 out of 79 outpatients with MS (35%) reported pruritus, with an average severity of 5.42 out of 10. Among those with itch, the extremities were affected in about half of the patients, while the face, scalp, and trunk were affected in about one-third of the patients. Many described paroxysmal itch that was aggravated by heat, and about half experienced itch on a weekly basis.
Further investigation showed that itch was associated with more severe MS. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, those with itch were significantly more likely to report fatigue (77% vs. 44%), anxiety or depression (48% vs. 16%), and cognitive impairment (62% vs. 26%).
MRI findings backed up these clinical results. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, patients with itch had significantly more T2 hyperintensities in the posterior cervical cord (74.1% vs. 46.0%) and anterior pons/ventromedial medulla (62% vs. 26%). These hyperintensities in the medulla were also associated with an 11-fold increased rate of itch on the face or scalp (odds ratio, 11.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-78.6, P = 0.025).
“Health care providers should be aware of episodes of localized, neuropathic itch in MS patients, as they appear to be more prevalent than previously thought and may impair these patients’ quality of life,” the investigators concluded.
Challenges with symptom characterization, management
“This is an important study for both patients and clinicians,” said Justin Abbatemarco, MD, of Cleveland Clinic’s Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis, in a written comment. “As the authors mention, many of our patients experience transient symptoms, including many different types of sensory disturbance (that is, pins & needles, burning, electrical shocks, and itching). These symptoms can be really distressing for patients and their caregivers.”
While Dr. Abbatemarco has encountered severe itching in “several patients” with MS, he maintained that it is “relatively uncommon” and noted that MS symptomatology is an inherently cloudy subject.
“I think it is difficult to be definite in any opinion on this topic,” Dr. Abbatemarco said. “How patients experience these symptoms is very subjective and can be difficult to describe/characterize.”
Dr. Abbatemarco emphasized that transient symptoms “do not usually represent MS relapse/flare or new inflammatory disease activity. Instead, we believe these symptoms are related to old areas of injury or demyelination.”
Symptom management can be challenging, he added. He recommended setting realistic expectations, and in the case of pruritus, asking dermatologists to rule out other causes of itch, and to offer “unique treatment approaches.”
Cool the itch?
Noting how heat appears to aggravate itch in patients with MS, Dr. Yosipovitch suggested that one of those unique – and simple – treatment approaches may be cooling itchy areas. Alternatively, clinicians may consider oral agents, like gabapentin to dampen neural transmission, or compounded formulations applied to the skin to reduce neural sensitivity, such as topical ketamine. Finally, Dr. Yosipovitch speculated that newer antibody agents for MS could potentially reduce itch.
All these treatment suggestions are purely hypothetical, he said, and require further investigation before they can be recommended with confidence.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Galderma, Pfizer, Novartis, and others. Dr. Abbatemarco disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Correction, 9/19/22: An earlier version of this article misidentified the photo of Dr. Justin Abbatemarco.
, according to investigators.
Itch is historically underrecognized as a symptom of MS, but physicians should know that it is common and may negatively impact quality of life, reported lead author Giuseppe Ingrasci, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, and colleagues.
While previous publications suggest that pruritus occurs in just 2%-6% of patients with MS, principal author Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor, Stiefel Chair of Medical Dermatology, and director of the Miami Itch Center in the Dr. Phillip Frost department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, encountered itch in enough patients with MS that he presented his observations to a group of neurologists.
Most of them dismissed him, he recalled in an interview: “The neurologists said, ‘Very interesting, but we don’t really see it.’ ”
One of those neurologists, however, decided to take a closer look.
Andrew Brown, MD, assistant professor of clinical neurology and chief of the general neurology division at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, began asking his patients with MS if they were experiencing itch and soon found that it was “a very common problem,” according to Dr. Yosipovitch.
Dr. Yosipovitch, who was the first to report pruritus in patients with psoriasis, launched the present investigation with Dr. Brown to determine if itch is also a blind spot in the world of MS. Their results, and their uphill battle to publication, suggest that it very well could be.
After being rejected from six neurology journals, with one editor suggesting that itch is “not relevant at all to neurology,” their findings were published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology.
A common problem that may indicate more severe disease
At the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Excellence in Miami, 27 out of 79 outpatients with MS (35%) reported pruritus, with an average severity of 5.42 out of 10. Among those with itch, the extremities were affected in about half of the patients, while the face, scalp, and trunk were affected in about one-third of the patients. Many described paroxysmal itch that was aggravated by heat, and about half experienced itch on a weekly basis.
Further investigation showed that itch was associated with more severe MS. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, those with itch were significantly more likely to report fatigue (77% vs. 44%), anxiety or depression (48% vs. 16%), and cognitive impairment (62% vs. 26%).
MRI findings backed up these clinical results. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, patients with itch had significantly more T2 hyperintensities in the posterior cervical cord (74.1% vs. 46.0%) and anterior pons/ventromedial medulla (62% vs. 26%). These hyperintensities in the medulla were also associated with an 11-fold increased rate of itch on the face or scalp (odds ratio, 11.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-78.6, P = 0.025).
“Health care providers should be aware of episodes of localized, neuropathic itch in MS patients, as they appear to be more prevalent than previously thought and may impair these patients’ quality of life,” the investigators concluded.
Challenges with symptom characterization, management
“This is an important study for both patients and clinicians,” said Justin Abbatemarco, MD, of Cleveland Clinic’s Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis, in a written comment. “As the authors mention, many of our patients experience transient symptoms, including many different types of sensory disturbance (that is, pins & needles, burning, electrical shocks, and itching). These symptoms can be really distressing for patients and their caregivers.”
While Dr. Abbatemarco has encountered severe itching in “several patients” with MS, he maintained that it is “relatively uncommon” and noted that MS symptomatology is an inherently cloudy subject.
“I think it is difficult to be definite in any opinion on this topic,” Dr. Abbatemarco said. “How patients experience these symptoms is very subjective and can be difficult to describe/characterize.”
Dr. Abbatemarco emphasized that transient symptoms “do not usually represent MS relapse/flare or new inflammatory disease activity. Instead, we believe these symptoms are related to old areas of injury or demyelination.”
Symptom management can be challenging, he added. He recommended setting realistic expectations, and in the case of pruritus, asking dermatologists to rule out other causes of itch, and to offer “unique treatment approaches.”
Cool the itch?
Noting how heat appears to aggravate itch in patients with MS, Dr. Yosipovitch suggested that one of those unique – and simple – treatment approaches may be cooling itchy areas. Alternatively, clinicians may consider oral agents, like gabapentin to dampen neural transmission, or compounded formulations applied to the skin to reduce neural sensitivity, such as topical ketamine. Finally, Dr. Yosipovitch speculated that newer antibody agents for MS could potentially reduce itch.
All these treatment suggestions are purely hypothetical, he said, and require further investigation before they can be recommended with confidence.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Galderma, Pfizer, Novartis, and others. Dr. Abbatemarco disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Correction, 9/19/22: An earlier version of this article misidentified the photo of Dr. Justin Abbatemarco.
, according to investigators.
Itch is historically underrecognized as a symptom of MS, but physicians should know that it is common and may negatively impact quality of life, reported lead author Giuseppe Ingrasci, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, and colleagues.
While previous publications suggest that pruritus occurs in just 2%-6% of patients with MS, principal author Gil Yosipovitch, MD, professor, Stiefel Chair of Medical Dermatology, and director of the Miami Itch Center in the Dr. Phillip Frost department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, encountered itch in enough patients with MS that he presented his observations to a group of neurologists.
Most of them dismissed him, he recalled in an interview: “The neurologists said, ‘Very interesting, but we don’t really see it.’ ”
One of those neurologists, however, decided to take a closer look.
Andrew Brown, MD, assistant professor of clinical neurology and chief of the general neurology division at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, began asking his patients with MS if they were experiencing itch and soon found that it was “a very common problem,” according to Dr. Yosipovitch.
Dr. Yosipovitch, who was the first to report pruritus in patients with psoriasis, launched the present investigation with Dr. Brown to determine if itch is also a blind spot in the world of MS. Their results, and their uphill battle to publication, suggest that it very well could be.
After being rejected from six neurology journals, with one editor suggesting that itch is “not relevant at all to neurology,” their findings were published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology.
A common problem that may indicate more severe disease
At the Multiple Sclerosis Center of Excellence in Miami, 27 out of 79 outpatients with MS (35%) reported pruritus, with an average severity of 5.42 out of 10. Among those with itch, the extremities were affected in about half of the patients, while the face, scalp, and trunk were affected in about one-third of the patients. Many described paroxysmal itch that was aggravated by heat, and about half experienced itch on a weekly basis.
Further investigation showed that itch was associated with more severe MS. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, those with itch were significantly more likely to report fatigue (77% vs. 44%), anxiety or depression (48% vs. 16%), and cognitive impairment (62% vs. 26%).
MRI findings backed up these clinical results. Compared with patients not experiencing itch, patients with itch had significantly more T2 hyperintensities in the posterior cervical cord (74.1% vs. 46.0%) and anterior pons/ventromedial medulla (62% vs. 26%). These hyperintensities in the medulla were also associated with an 11-fold increased rate of itch on the face or scalp (odds ratio, 11.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-78.6, P = 0.025).
“Health care providers should be aware of episodes of localized, neuropathic itch in MS patients, as they appear to be more prevalent than previously thought and may impair these patients’ quality of life,” the investigators concluded.
Challenges with symptom characterization, management
“This is an important study for both patients and clinicians,” said Justin Abbatemarco, MD, of Cleveland Clinic’s Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis, in a written comment. “As the authors mention, many of our patients experience transient symptoms, including many different types of sensory disturbance (that is, pins & needles, burning, electrical shocks, and itching). These symptoms can be really distressing for patients and their caregivers.”
While Dr. Abbatemarco has encountered severe itching in “several patients” with MS, he maintained that it is “relatively uncommon” and noted that MS symptomatology is an inherently cloudy subject.
“I think it is difficult to be definite in any opinion on this topic,” Dr. Abbatemarco said. “How patients experience these symptoms is very subjective and can be difficult to describe/characterize.”
Dr. Abbatemarco emphasized that transient symptoms “do not usually represent MS relapse/flare or new inflammatory disease activity. Instead, we believe these symptoms are related to old areas of injury or demyelination.”
Symptom management can be challenging, he added. He recommended setting realistic expectations, and in the case of pruritus, asking dermatologists to rule out other causes of itch, and to offer “unique treatment approaches.”
Cool the itch?
Noting how heat appears to aggravate itch in patients with MS, Dr. Yosipovitch suggested that one of those unique – and simple – treatment approaches may be cooling itchy areas. Alternatively, clinicians may consider oral agents, like gabapentin to dampen neural transmission, or compounded formulations applied to the skin to reduce neural sensitivity, such as topical ketamine. Finally, Dr. Yosipovitch speculated that newer antibody agents for MS could potentially reduce itch.
All these treatment suggestions are purely hypothetical, he said, and require further investigation before they can be recommended with confidence.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Galderma, Pfizer, Novartis, and others. Dr. Abbatemarco disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Correction, 9/19/22: An earlier version of this article misidentified the photo of Dr. Justin Abbatemarco.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY & VENEREOLOGY
Ultrasound offers noninvasive alternative for monitoring ulcerative colitis
Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) findings correlate strongly with endoscopy results in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), with treatment responses detected as soon as 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib, a longitudinal prospective study has found.
IUS accurately detected improvements and remission across a variety of scoring methodologies, suggesting that it may be a cost-effective, noninvasive alternative to endoscopic monitoring, reported lead author Floris de Voogd, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and colleagues.
“Endoscopy is generally considered as the gold standard for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with UC,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “However, endoscopy is an invasive and costly modality and therefore less attractive to perform frequently during the disease course.”
Whereas noninvasive fecal biomarkers are a more economical method of monitoring inflammation and treatment responses, they fail to characterize disease extent and fall short in detecting early endoscopic responses, the investigators added.
The present study aimed to determine if IUS could offer more clinical insight by measuring bowel wall thickness. Thirty patients were enrolled with moderate to severe UC, all with an endoscopic Mayo score of at least 2. Twenty-seven of these patients were evaluable through follow-up, having undergone both IUS and endoscopy at baseline and 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib.
At both time points, IUS findings correlated significantly with endoscopic Mayo score (EMS), UC endoscopic index for severity, and Robarts Histopathology Index, with correlation coefficients of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.49, respectively. Remission according to EMS was defined as a score of 0, and improvement was defined as a score of 1 or less.
Patients with EMS improvement showed lower median bowel wall thickness in the sigmoid colon after 8 weeks of treatment than did patients without improvement (1.8 mm vs. 4.5 mm; P < .0001); patients who were in EMS remission after 8 weeks also had lower median bowel wall thickness of the sigmoid colon (1.4 mm vs. 4.0 mm; P = .016).
The investigators also sought to define cutoff values for bowel wall thickness. The most accurate cutoff values for identifying endoscopic remission and improvement were 2.8 mm (area under the receiver operating curve, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.00; P = .006) and 3.9 mm (AUROC, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.82-1.00; P < .0001), respectively. Treatment response was best identified by a 32% threshold reduction in thickness (AUROC, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00; P = .002).
“Intestinal ultrasound, with bowel wall thickness as the single most important parameter is accurate to determine treatment response to tofacitinib in patients with moderate-severe UC when compared against endoscopy,” the investigators concluded.
Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA, assistant professor of pediatrics and the associate pediatric gastroenterology fellowship program director at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the study is noteworthy because it is the first of its kind to show that IUS can accurately monitor treatment responses in UC.
“This study is what we’re looking for now, and in the future,” Dr. Dolinger said in an interview. “We’re looking for noninvasive biomarkers to predict early responses so that we know as clinicians ... if our medicines are working or if we need to pivot and switch effectively.”
For patients, this can mean feeling better quicker while reducing burden of care, he added.
“We can use this study to predict patient responses without having to potentially rescope them in 8 weeks using a 5-minute point-of-care test in the clinic,” Dr. Dolinger said. “It’s huge to be able to say that for patients with colitis, and to provide reassurance that not only are they potentially feeling better, but the medicine is working to change and heal their bowel wall really quickly as well.”
Dr. Dolinger speaks from clinical experience. Over the past 2 years, he and his colleagues at Mount Sinai have been implementing IUS for patients with both UC and Crohn’s disease.
“It’s become part of our standard of care,” Dr. Dolinger said. “This is now emerging in the United States and will soon take hold. There is a lot of interest.”
Dr. Dolinger is one of just a few American physicians credentialed by the International Bowel Ultrasound Group, an organization based out of Europe, Israel, and Canada. Formalized training and certification are necessary, Dr. Dolinger noted, to ensure that this new clinical approach maintains consistency as it is rolled out across the United States.
“We have the unique opportunity to do something from the ground up quickly, but also correctly, meaning that we can train everyone to speak the same language and do the same standardized exams so that all the findings and research are relatable,” Dr. Dolinger said.
He advised interested physicians to contact their local inflammatory bowel disease center to find out if training is available, and if it is, devoting “a lot of time” to the learning process.
“If you’re going to use this potentially as a clinical decision-making tool without using other invasive procedures, you really want to make sure what you’re doing is accurate and correct,” Dr. Dolinger said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, and others. Dr. Dolinger disclosed a relationship with NeuroLogica, a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics.
Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) findings correlate strongly with endoscopy results in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), with treatment responses detected as soon as 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib, a longitudinal prospective study has found.
IUS accurately detected improvements and remission across a variety of scoring methodologies, suggesting that it may be a cost-effective, noninvasive alternative to endoscopic monitoring, reported lead author Floris de Voogd, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and colleagues.
“Endoscopy is generally considered as the gold standard for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with UC,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “However, endoscopy is an invasive and costly modality and therefore less attractive to perform frequently during the disease course.”
Whereas noninvasive fecal biomarkers are a more economical method of monitoring inflammation and treatment responses, they fail to characterize disease extent and fall short in detecting early endoscopic responses, the investigators added.
The present study aimed to determine if IUS could offer more clinical insight by measuring bowel wall thickness. Thirty patients were enrolled with moderate to severe UC, all with an endoscopic Mayo score of at least 2. Twenty-seven of these patients were evaluable through follow-up, having undergone both IUS and endoscopy at baseline and 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib.
At both time points, IUS findings correlated significantly with endoscopic Mayo score (EMS), UC endoscopic index for severity, and Robarts Histopathology Index, with correlation coefficients of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.49, respectively. Remission according to EMS was defined as a score of 0, and improvement was defined as a score of 1 or less.
Patients with EMS improvement showed lower median bowel wall thickness in the sigmoid colon after 8 weeks of treatment than did patients without improvement (1.8 mm vs. 4.5 mm; P < .0001); patients who were in EMS remission after 8 weeks also had lower median bowel wall thickness of the sigmoid colon (1.4 mm vs. 4.0 mm; P = .016).
The investigators also sought to define cutoff values for bowel wall thickness. The most accurate cutoff values for identifying endoscopic remission and improvement were 2.8 mm (area under the receiver operating curve, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.00; P = .006) and 3.9 mm (AUROC, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.82-1.00; P < .0001), respectively. Treatment response was best identified by a 32% threshold reduction in thickness (AUROC, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00; P = .002).
“Intestinal ultrasound, with bowel wall thickness as the single most important parameter is accurate to determine treatment response to tofacitinib in patients with moderate-severe UC when compared against endoscopy,” the investigators concluded.
Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA, assistant professor of pediatrics and the associate pediatric gastroenterology fellowship program director at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the study is noteworthy because it is the first of its kind to show that IUS can accurately monitor treatment responses in UC.
“This study is what we’re looking for now, and in the future,” Dr. Dolinger said in an interview. “We’re looking for noninvasive biomarkers to predict early responses so that we know as clinicians ... if our medicines are working or if we need to pivot and switch effectively.”
For patients, this can mean feeling better quicker while reducing burden of care, he added.
“We can use this study to predict patient responses without having to potentially rescope them in 8 weeks using a 5-minute point-of-care test in the clinic,” Dr. Dolinger said. “It’s huge to be able to say that for patients with colitis, and to provide reassurance that not only are they potentially feeling better, but the medicine is working to change and heal their bowel wall really quickly as well.”
Dr. Dolinger speaks from clinical experience. Over the past 2 years, he and his colleagues at Mount Sinai have been implementing IUS for patients with both UC and Crohn’s disease.
“It’s become part of our standard of care,” Dr. Dolinger said. “This is now emerging in the United States and will soon take hold. There is a lot of interest.”
Dr. Dolinger is one of just a few American physicians credentialed by the International Bowel Ultrasound Group, an organization based out of Europe, Israel, and Canada. Formalized training and certification are necessary, Dr. Dolinger noted, to ensure that this new clinical approach maintains consistency as it is rolled out across the United States.
“We have the unique opportunity to do something from the ground up quickly, but also correctly, meaning that we can train everyone to speak the same language and do the same standardized exams so that all the findings and research are relatable,” Dr. Dolinger said.
He advised interested physicians to contact their local inflammatory bowel disease center to find out if training is available, and if it is, devoting “a lot of time” to the learning process.
“If you’re going to use this potentially as a clinical decision-making tool without using other invasive procedures, you really want to make sure what you’re doing is accurate and correct,” Dr. Dolinger said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, and others. Dr. Dolinger disclosed a relationship with NeuroLogica, a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics.
Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) findings correlate strongly with endoscopy results in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), with treatment responses detected as soon as 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib, a longitudinal prospective study has found.
IUS accurately detected improvements and remission across a variety of scoring methodologies, suggesting that it may be a cost-effective, noninvasive alternative to endoscopic monitoring, reported lead author Floris de Voogd, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and colleagues.
“Endoscopy is generally considered as the gold standard for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with UC,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “However, endoscopy is an invasive and costly modality and therefore less attractive to perform frequently during the disease course.”
Whereas noninvasive fecal biomarkers are a more economical method of monitoring inflammation and treatment responses, they fail to characterize disease extent and fall short in detecting early endoscopic responses, the investigators added.
The present study aimed to determine if IUS could offer more clinical insight by measuring bowel wall thickness. Thirty patients were enrolled with moderate to severe UC, all with an endoscopic Mayo score of at least 2. Twenty-seven of these patients were evaluable through follow-up, having undergone both IUS and endoscopy at baseline and 8 weeks after starting tofacitinib.
At both time points, IUS findings correlated significantly with endoscopic Mayo score (EMS), UC endoscopic index for severity, and Robarts Histopathology Index, with correlation coefficients of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.49, respectively. Remission according to EMS was defined as a score of 0, and improvement was defined as a score of 1 or less.
Patients with EMS improvement showed lower median bowel wall thickness in the sigmoid colon after 8 weeks of treatment than did patients without improvement (1.8 mm vs. 4.5 mm; P < .0001); patients who were in EMS remission after 8 weeks also had lower median bowel wall thickness of the sigmoid colon (1.4 mm vs. 4.0 mm; P = .016).
The investigators also sought to define cutoff values for bowel wall thickness. The most accurate cutoff values for identifying endoscopic remission and improvement were 2.8 mm (area under the receiver operating curve, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.00; P = .006) and 3.9 mm (AUROC, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.82-1.00; P < .0001), respectively. Treatment response was best identified by a 32% threshold reduction in thickness (AUROC, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.74-1.00; P = .002).
“Intestinal ultrasound, with bowel wall thickness as the single most important parameter is accurate to determine treatment response to tofacitinib in patients with moderate-severe UC when compared against endoscopy,” the investigators concluded.
Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA, assistant professor of pediatrics and the associate pediatric gastroenterology fellowship program director at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said the study is noteworthy because it is the first of its kind to show that IUS can accurately monitor treatment responses in UC.
“This study is what we’re looking for now, and in the future,” Dr. Dolinger said in an interview. “We’re looking for noninvasive biomarkers to predict early responses so that we know as clinicians ... if our medicines are working or if we need to pivot and switch effectively.”
For patients, this can mean feeling better quicker while reducing burden of care, he added.
“We can use this study to predict patient responses without having to potentially rescope them in 8 weeks using a 5-minute point-of-care test in the clinic,” Dr. Dolinger said. “It’s huge to be able to say that for patients with colitis, and to provide reassurance that not only are they potentially feeling better, but the medicine is working to change and heal their bowel wall really quickly as well.”
Dr. Dolinger speaks from clinical experience. Over the past 2 years, he and his colleagues at Mount Sinai have been implementing IUS for patients with both UC and Crohn’s disease.
“It’s become part of our standard of care,” Dr. Dolinger said. “This is now emerging in the United States and will soon take hold. There is a lot of interest.”
Dr. Dolinger is one of just a few American physicians credentialed by the International Bowel Ultrasound Group, an organization based out of Europe, Israel, and Canada. Formalized training and certification are necessary, Dr. Dolinger noted, to ensure that this new clinical approach maintains consistency as it is rolled out across the United States.
“We have the unique opportunity to do something from the ground up quickly, but also correctly, meaning that we can train everyone to speak the same language and do the same standardized exams so that all the findings and research are relatable,” Dr. Dolinger said.
He advised interested physicians to contact their local inflammatory bowel disease center to find out if training is available, and if it is, devoting “a lot of time” to the learning process.
“If you’re going to use this potentially as a clinical decision-making tool without using other invasive procedures, you really want to make sure what you’re doing is accurate and correct,” Dr. Dolinger said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Merck, Takeda, and others. Dr. Dolinger disclosed a relationship with NeuroLogica, a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Unvaccinated 10 times more likely to be hospitalized for Omicron
The data, which included almost 200,000 COVID-19–associated hospitalizations across 13 states, also showed that vaccinated, hospitalized patients were more often older and already dealing with other health conditions, compared with unvaccinated, hospitalized patients, reported lead author Fiona P. Havers, MD, of the CDC, Atlanta.
“Unlike previously published reports and web pages … this study reports hospitalization rates by vaccination status and clinical and demographic characteristics of hospitalized patients, beginning with the period when vaccines first became available, and includes comparisons of unvaccinated persons, persons vaccinated with a primary series without a booster dose, and those vaccinated with a primary series and at least 1 booster dose,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In total, the investigators reviewed 192,509 hospitalizations involving patients 18 years and older. The study period spanned from Jan. 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022. Data were reported month by month, showing that the relative monthly hospitalization rate peaked in May 2021, when it was 17.7 times higher for unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals (with or without a booster).
To account for differences in clinical course between Delta and Omicron, the investigators also analyzed data sorted into two time periods: July-December 2021 (Delta predominant) and January-April 2022 (Omicron BA.1 predominant). These analyses revealed the greater hospitalization risk presented by Delta. Specifically, unvaccinated people were 12.2 times more likely to be hospitalized for Delta than vaccinated people, with or without a booster, versus 6.8 times for Omicron BA.1.
Study shows power of the booster
A closer look at the Omicron BA.1 data showed the power of a booster dose. From January to April 2022, individuals who were fully vaccinated with a booster dose were 10.5 times less likely than unvaccinated individuals to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1. Plus, boosted people were 2.5 times less likely to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1 than people who got vaccinated but skipped the booster.
“The high hospitalization rates in unvaccinated compared with vaccinated persons with and without a booster dose underscores the importance of COVID-19 vaccinations in preventing hospitalizations and suggests that increasing vaccination coverage, including booster dose coverage, can prevent hospitalizations, serious illness, and death,” the investigators wrote.
The study also revealed that vaccinated hospitalized patients were significantly older, on average, than unvaccinated hospitalized patients (median, 70 vs. 58 years; P < .001). They were also significantly more likely to have three or more underlying medical conditions (77.8% vs. 51.6%; P < .001)
“A greater proportion of hospitalized cases among vaccinated persons occurred in individuals with medical fragility who were older, more likely to reside in long-term care facilities, and have three or more underlying medical conditions, including immunosuppressive conditions,” the investigators wrote.
New variants outpacing data, vaccines remain essential
While data from April 2022 alone showed a 3.5-fold higher rate of hospitalization among unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals with or without a booster, newer data suggest that emerging strains of Omicron are putting more people in the hospital.
A recent report by the CDC showed weekly hospitalization rates climbing from March 20 to May 31, 2022, which coincided with predominance of the newer Omicron BA.2 variant. While unvaccinated people were still around 3.5 times more likely to be hospitalized than vaccinated people, overall hospitalization rates jumped 3-fold for people 65 years and older, and 1.7-fold for adults younger than 65. Adding further complexity to this constantly evolving situation is that Omicron BA.2 has since been joined by the BA.4 and BA.5 lineages, for which vaccines are now available.
In the paper published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the CDC report, and in a comment for this article, the CDC offered the same take-home message: Get vaccinated.
“These findings reinforce previous research illustrating how vaccination provides protection from hospitalization due to COVID-19,” a CDC spokesperson said. “COVID-19 vaccines are proven to help prevent serious COVID-19 illness, and everyone ages 6 months and older should stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines.”
The study published in JAMA Internal Medicine was supported by the CDC. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Sanofi, GSK, MedImmune, and others.
The data, which included almost 200,000 COVID-19–associated hospitalizations across 13 states, also showed that vaccinated, hospitalized patients were more often older and already dealing with other health conditions, compared with unvaccinated, hospitalized patients, reported lead author Fiona P. Havers, MD, of the CDC, Atlanta.
“Unlike previously published reports and web pages … this study reports hospitalization rates by vaccination status and clinical and demographic characteristics of hospitalized patients, beginning with the period when vaccines first became available, and includes comparisons of unvaccinated persons, persons vaccinated with a primary series without a booster dose, and those vaccinated with a primary series and at least 1 booster dose,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In total, the investigators reviewed 192,509 hospitalizations involving patients 18 years and older. The study period spanned from Jan. 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022. Data were reported month by month, showing that the relative monthly hospitalization rate peaked in May 2021, when it was 17.7 times higher for unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals (with or without a booster).
To account for differences in clinical course between Delta and Omicron, the investigators also analyzed data sorted into two time periods: July-December 2021 (Delta predominant) and January-April 2022 (Omicron BA.1 predominant). These analyses revealed the greater hospitalization risk presented by Delta. Specifically, unvaccinated people were 12.2 times more likely to be hospitalized for Delta than vaccinated people, with or without a booster, versus 6.8 times for Omicron BA.1.
Study shows power of the booster
A closer look at the Omicron BA.1 data showed the power of a booster dose. From January to April 2022, individuals who were fully vaccinated with a booster dose were 10.5 times less likely than unvaccinated individuals to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1. Plus, boosted people were 2.5 times less likely to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1 than people who got vaccinated but skipped the booster.
“The high hospitalization rates in unvaccinated compared with vaccinated persons with and without a booster dose underscores the importance of COVID-19 vaccinations in preventing hospitalizations and suggests that increasing vaccination coverage, including booster dose coverage, can prevent hospitalizations, serious illness, and death,” the investigators wrote.
The study also revealed that vaccinated hospitalized patients were significantly older, on average, than unvaccinated hospitalized patients (median, 70 vs. 58 years; P < .001). They were also significantly more likely to have three or more underlying medical conditions (77.8% vs. 51.6%; P < .001)
“A greater proportion of hospitalized cases among vaccinated persons occurred in individuals with medical fragility who were older, more likely to reside in long-term care facilities, and have three or more underlying medical conditions, including immunosuppressive conditions,” the investigators wrote.
New variants outpacing data, vaccines remain essential
While data from April 2022 alone showed a 3.5-fold higher rate of hospitalization among unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals with or without a booster, newer data suggest that emerging strains of Omicron are putting more people in the hospital.
A recent report by the CDC showed weekly hospitalization rates climbing from March 20 to May 31, 2022, which coincided with predominance of the newer Omicron BA.2 variant. While unvaccinated people were still around 3.5 times more likely to be hospitalized than vaccinated people, overall hospitalization rates jumped 3-fold for people 65 years and older, and 1.7-fold for adults younger than 65. Adding further complexity to this constantly evolving situation is that Omicron BA.2 has since been joined by the BA.4 and BA.5 lineages, for which vaccines are now available.
In the paper published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the CDC report, and in a comment for this article, the CDC offered the same take-home message: Get vaccinated.
“These findings reinforce previous research illustrating how vaccination provides protection from hospitalization due to COVID-19,” a CDC spokesperson said. “COVID-19 vaccines are proven to help prevent serious COVID-19 illness, and everyone ages 6 months and older should stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines.”
The study published in JAMA Internal Medicine was supported by the CDC. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Sanofi, GSK, MedImmune, and others.
The data, which included almost 200,000 COVID-19–associated hospitalizations across 13 states, also showed that vaccinated, hospitalized patients were more often older and already dealing with other health conditions, compared with unvaccinated, hospitalized patients, reported lead author Fiona P. Havers, MD, of the CDC, Atlanta.
“Unlike previously published reports and web pages … this study reports hospitalization rates by vaccination status and clinical and demographic characteristics of hospitalized patients, beginning with the period when vaccines first became available, and includes comparisons of unvaccinated persons, persons vaccinated with a primary series without a booster dose, and those vaccinated with a primary series and at least 1 booster dose,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine.
In total, the investigators reviewed 192,509 hospitalizations involving patients 18 years and older. The study period spanned from Jan. 1, 2021, to April 30, 2022. Data were reported month by month, showing that the relative monthly hospitalization rate peaked in May 2021, when it was 17.7 times higher for unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals (with or without a booster).
To account for differences in clinical course between Delta and Omicron, the investigators also analyzed data sorted into two time periods: July-December 2021 (Delta predominant) and January-April 2022 (Omicron BA.1 predominant). These analyses revealed the greater hospitalization risk presented by Delta. Specifically, unvaccinated people were 12.2 times more likely to be hospitalized for Delta than vaccinated people, with or without a booster, versus 6.8 times for Omicron BA.1.
Study shows power of the booster
A closer look at the Omicron BA.1 data showed the power of a booster dose. From January to April 2022, individuals who were fully vaccinated with a booster dose were 10.5 times less likely than unvaccinated individuals to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1. Plus, boosted people were 2.5 times less likely to be hospitalized for Omicron BA.1 than people who got vaccinated but skipped the booster.
“The high hospitalization rates in unvaccinated compared with vaccinated persons with and without a booster dose underscores the importance of COVID-19 vaccinations in preventing hospitalizations and suggests that increasing vaccination coverage, including booster dose coverage, can prevent hospitalizations, serious illness, and death,” the investigators wrote.
The study also revealed that vaccinated hospitalized patients were significantly older, on average, than unvaccinated hospitalized patients (median, 70 vs. 58 years; P < .001). They were also significantly more likely to have three or more underlying medical conditions (77.8% vs. 51.6%; P < .001)
“A greater proportion of hospitalized cases among vaccinated persons occurred in individuals with medical fragility who were older, more likely to reside in long-term care facilities, and have three or more underlying medical conditions, including immunosuppressive conditions,” the investigators wrote.
New variants outpacing data, vaccines remain essential
While data from April 2022 alone showed a 3.5-fold higher rate of hospitalization among unvaccinated versus vaccinated individuals with or without a booster, newer data suggest that emerging strains of Omicron are putting more people in the hospital.
A recent report by the CDC showed weekly hospitalization rates climbing from March 20 to May 31, 2022, which coincided with predominance of the newer Omicron BA.2 variant. While unvaccinated people were still around 3.5 times more likely to be hospitalized than vaccinated people, overall hospitalization rates jumped 3-fold for people 65 years and older, and 1.7-fold for adults younger than 65. Adding further complexity to this constantly evolving situation is that Omicron BA.2 has since been joined by the BA.4 and BA.5 lineages, for which vaccines are now available.
In the paper published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the CDC report, and in a comment for this article, the CDC offered the same take-home message: Get vaccinated.
“These findings reinforce previous research illustrating how vaccination provides protection from hospitalization due to COVID-19,” a CDC spokesperson said. “COVID-19 vaccines are proven to help prevent serious COVID-19 illness, and everyone ages 6 months and older should stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines.”
The study published in JAMA Internal Medicine was supported by the CDC. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Sanofi, GSK, MedImmune, and others.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
WIC review finds broad benefits, knowledge gaps
How exactly the national program achieves these outcomes, however, remains unclear, and study quality shows room for improvement, reported co–lead authors Maya Venkataramani, MD, MPH and S. Michelle Ogunwole, MD, PhD of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The WIC program, which has been serving low-income women and young children since 1974, “provides supplemental foods, nutrition education and breastfeeding support, screening and referrals to medical and social services, and support for high-risk pregnancies,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. The U.S. Food and Nutrition Service administers the program.
The authors conducted a systematic review of 20 observational studies aimed at determining the impacts of WIC participation on maternal, neonatal-birth, and infant-child health outcomes.
All studies included in the review began in or after 2009, when the WIC food package was revised to better address diet-related chronic diseases. For inclusion in the review, studies were required to have a WIC-eligible comparison group. Included research also evaluated the relationship between WIC participation and the prespecified health outcomes.
“We found only 20 studies that fulfilled our rigorous study inclusion criteria for these specific outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “In some areas, the evidence was absent, and in others, the strength of evidence (SOE) was moderate or low.”
Six outcome categories were assessed: maternal morbidity, maternal pregnancy outcomes, maternal health behaviors, maternal health care utilization, child morbidity, and childhood health care utilization. Of these, maternal health care utilization had the most robust body of evidence, while data from studies evaluating maternal morbidity and child morbidity were deemed insufficient.
Based on eligible studies, WIC participation was associated with reduced risks of insufficient weight gain in pregnancy, preterm birth, low infant birthweight, and infant mortality. Participation was also associated with an increased likelihood of infant and child health care utilization, such as routine immunizations.
Growing evidence should drive enrollment
“Growing evidence points to WIC as a way to reduce risk of preterm birth and other adverse outcomes,” said Laura Jelliffe-Pawlowski, PhD, MS, professor at the University of California, San Francisco and a director for the UCSF California Preterm Birth Initiative.
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski, who conducted a California-based study included in the paper, said the review is noteworthy because it shows that WIC-associated benefits are observed across locations.
“It’s not just in California; it’s across the country,” she said. “It’s a national call to action – where there’s partnership between national-, state- and community-level WIC programs – to make WIC as accessible as possible, and reflect community wants and needs, so that more people enroll, and more people stay enrolled.”
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski’s coauthor on the California study, Rita Hamad, MD, PhD, associate professor of family & community medicine at UCSF and associate director of the UCSF Center for Health Equity, encouraged health care providers to drive WIC enrollment, noting that, presently, only one in four eligible 4-year-olds participates.
“Physicians and other health care stakeholders can help patients benefit from this program by encouraging them to sign up, and even by providing sign-up support in the form of a social worker or other staff member,” Dr. Hamad said. “There is also literature on the types of interventions that improve take-up of safety net programs that providers can look to.”
Goals of future research
Optimizing WIC operations, however, is only half the battle, considering the evidence gaps revealed by the review.
“We still need stronger studies that use more rigorous study designs ... to provide more convincing evidence to policymakers, as well as more evidence on long-term impacts,” Dr. Hamad said. “We also need to better understand why take-up is low in these programs despite these potential health benefits. Then we can make sure that economically disadvantaged families receive the benefits for which they are eligible through interventions to improve participation rates.”
Ideally, WIC programs would receive additional funding for independent parties to evaluate health outcomes, according to Ashwini Lakshmanan, MD, MS, MPH, associate professor in the department of health systems science at Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, Calif.
Dr. Lakshmanan, who previously evaluated the benefits of WIC participation for high-risk infants, noted that randomized clinical trials would be unethical in this setting, yet data collection can still be “very conscientious and intentional,” with a focus on policy-shaping outcome metrics like immunizations and pediatric health care visits.
“The main point is thinking about it at the forefront, and not retrospectively,” Dr. Lakshmanan said.
Dr. Ogunwole, who led the present review, suggested in a written comment that future studies “could employ robust statistical methods (propensity matching, fixed effects models, etc.) to help reduce bias.”
She also recommended evaluating innovations in WIC programs; for example, adding a health coach, or conducting a cooking skills intervention.
Studies are also needed to better understand the various obstacles to WIC success, such as misconceptions about the program, discrimination, and barriers to enrollment, Dr. Ogunwole added.
“WIC enrollment has been decreasing for a number of years, and this was occurring prepandemic as well,” she said. “More work needs to be done to understand this issue.”
The study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators and interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
How exactly the national program achieves these outcomes, however, remains unclear, and study quality shows room for improvement, reported co–lead authors Maya Venkataramani, MD, MPH and S. Michelle Ogunwole, MD, PhD of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The WIC program, which has been serving low-income women and young children since 1974, “provides supplemental foods, nutrition education and breastfeeding support, screening and referrals to medical and social services, and support for high-risk pregnancies,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. The U.S. Food and Nutrition Service administers the program.
The authors conducted a systematic review of 20 observational studies aimed at determining the impacts of WIC participation on maternal, neonatal-birth, and infant-child health outcomes.
All studies included in the review began in or after 2009, when the WIC food package was revised to better address diet-related chronic diseases. For inclusion in the review, studies were required to have a WIC-eligible comparison group. Included research also evaluated the relationship between WIC participation and the prespecified health outcomes.
“We found only 20 studies that fulfilled our rigorous study inclusion criteria for these specific outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “In some areas, the evidence was absent, and in others, the strength of evidence (SOE) was moderate or low.”
Six outcome categories were assessed: maternal morbidity, maternal pregnancy outcomes, maternal health behaviors, maternal health care utilization, child morbidity, and childhood health care utilization. Of these, maternal health care utilization had the most robust body of evidence, while data from studies evaluating maternal morbidity and child morbidity were deemed insufficient.
Based on eligible studies, WIC participation was associated with reduced risks of insufficient weight gain in pregnancy, preterm birth, low infant birthweight, and infant mortality. Participation was also associated with an increased likelihood of infant and child health care utilization, such as routine immunizations.
Growing evidence should drive enrollment
“Growing evidence points to WIC as a way to reduce risk of preterm birth and other adverse outcomes,” said Laura Jelliffe-Pawlowski, PhD, MS, professor at the University of California, San Francisco and a director for the UCSF California Preterm Birth Initiative.
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski, who conducted a California-based study included in the paper, said the review is noteworthy because it shows that WIC-associated benefits are observed across locations.
“It’s not just in California; it’s across the country,” she said. “It’s a national call to action – where there’s partnership between national-, state- and community-level WIC programs – to make WIC as accessible as possible, and reflect community wants and needs, so that more people enroll, and more people stay enrolled.”
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski’s coauthor on the California study, Rita Hamad, MD, PhD, associate professor of family & community medicine at UCSF and associate director of the UCSF Center for Health Equity, encouraged health care providers to drive WIC enrollment, noting that, presently, only one in four eligible 4-year-olds participates.
“Physicians and other health care stakeholders can help patients benefit from this program by encouraging them to sign up, and even by providing sign-up support in the form of a social worker or other staff member,” Dr. Hamad said. “There is also literature on the types of interventions that improve take-up of safety net programs that providers can look to.”
Goals of future research
Optimizing WIC operations, however, is only half the battle, considering the evidence gaps revealed by the review.
“We still need stronger studies that use more rigorous study designs ... to provide more convincing evidence to policymakers, as well as more evidence on long-term impacts,” Dr. Hamad said. “We also need to better understand why take-up is low in these programs despite these potential health benefits. Then we can make sure that economically disadvantaged families receive the benefits for which they are eligible through interventions to improve participation rates.”
Ideally, WIC programs would receive additional funding for independent parties to evaluate health outcomes, according to Ashwini Lakshmanan, MD, MS, MPH, associate professor in the department of health systems science at Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, Calif.
Dr. Lakshmanan, who previously evaluated the benefits of WIC participation for high-risk infants, noted that randomized clinical trials would be unethical in this setting, yet data collection can still be “very conscientious and intentional,” with a focus on policy-shaping outcome metrics like immunizations and pediatric health care visits.
“The main point is thinking about it at the forefront, and not retrospectively,” Dr. Lakshmanan said.
Dr. Ogunwole, who led the present review, suggested in a written comment that future studies “could employ robust statistical methods (propensity matching, fixed effects models, etc.) to help reduce bias.”
She also recommended evaluating innovations in WIC programs; for example, adding a health coach, or conducting a cooking skills intervention.
Studies are also needed to better understand the various obstacles to WIC success, such as misconceptions about the program, discrimination, and barriers to enrollment, Dr. Ogunwole added.
“WIC enrollment has been decreasing for a number of years, and this was occurring prepandemic as well,” she said. “More work needs to be done to understand this issue.”
The study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators and interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
How exactly the national program achieves these outcomes, however, remains unclear, and study quality shows room for improvement, reported co–lead authors Maya Venkataramani, MD, MPH and S. Michelle Ogunwole, MD, PhD of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The WIC program, which has been serving low-income women and young children since 1974, “provides supplemental foods, nutrition education and breastfeeding support, screening and referrals to medical and social services, and support for high-risk pregnancies,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. The U.S. Food and Nutrition Service administers the program.
The authors conducted a systematic review of 20 observational studies aimed at determining the impacts of WIC participation on maternal, neonatal-birth, and infant-child health outcomes.
All studies included in the review began in or after 2009, when the WIC food package was revised to better address diet-related chronic diseases. For inclusion in the review, studies were required to have a WIC-eligible comparison group. Included research also evaluated the relationship between WIC participation and the prespecified health outcomes.
“We found only 20 studies that fulfilled our rigorous study inclusion criteria for these specific outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “In some areas, the evidence was absent, and in others, the strength of evidence (SOE) was moderate or low.”
Six outcome categories were assessed: maternal morbidity, maternal pregnancy outcomes, maternal health behaviors, maternal health care utilization, child morbidity, and childhood health care utilization. Of these, maternal health care utilization had the most robust body of evidence, while data from studies evaluating maternal morbidity and child morbidity were deemed insufficient.
Based on eligible studies, WIC participation was associated with reduced risks of insufficient weight gain in pregnancy, preterm birth, low infant birthweight, and infant mortality. Participation was also associated with an increased likelihood of infant and child health care utilization, such as routine immunizations.
Growing evidence should drive enrollment
“Growing evidence points to WIC as a way to reduce risk of preterm birth and other adverse outcomes,” said Laura Jelliffe-Pawlowski, PhD, MS, professor at the University of California, San Francisco and a director for the UCSF California Preterm Birth Initiative.
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski, who conducted a California-based study included in the paper, said the review is noteworthy because it shows that WIC-associated benefits are observed across locations.
“It’s not just in California; it’s across the country,” she said. “It’s a national call to action – where there’s partnership between national-, state- and community-level WIC programs – to make WIC as accessible as possible, and reflect community wants and needs, so that more people enroll, and more people stay enrolled.”
Dr. Jelliffe-Pawlowski’s coauthor on the California study, Rita Hamad, MD, PhD, associate professor of family & community medicine at UCSF and associate director of the UCSF Center for Health Equity, encouraged health care providers to drive WIC enrollment, noting that, presently, only one in four eligible 4-year-olds participates.
“Physicians and other health care stakeholders can help patients benefit from this program by encouraging them to sign up, and even by providing sign-up support in the form of a social worker or other staff member,” Dr. Hamad said. “There is also literature on the types of interventions that improve take-up of safety net programs that providers can look to.”
Goals of future research
Optimizing WIC operations, however, is only half the battle, considering the evidence gaps revealed by the review.
“We still need stronger studies that use more rigorous study designs ... to provide more convincing evidence to policymakers, as well as more evidence on long-term impacts,” Dr. Hamad said. “We also need to better understand why take-up is low in these programs despite these potential health benefits. Then we can make sure that economically disadvantaged families receive the benefits for which they are eligible through interventions to improve participation rates.”
Ideally, WIC programs would receive additional funding for independent parties to evaluate health outcomes, according to Ashwini Lakshmanan, MD, MS, MPH, associate professor in the department of health systems science at Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, Calif.
Dr. Lakshmanan, who previously evaluated the benefits of WIC participation for high-risk infants, noted that randomized clinical trials would be unethical in this setting, yet data collection can still be “very conscientious and intentional,” with a focus on policy-shaping outcome metrics like immunizations and pediatric health care visits.
“The main point is thinking about it at the forefront, and not retrospectively,” Dr. Lakshmanan said.
Dr. Ogunwole, who led the present review, suggested in a written comment that future studies “could employ robust statistical methods (propensity matching, fixed effects models, etc.) to help reduce bias.”
She also recommended evaluating innovations in WIC programs; for example, adding a health coach, or conducting a cooking skills intervention.
Studies are also needed to better understand the various obstacles to WIC success, such as misconceptions about the program, discrimination, and barriers to enrollment, Dr. Ogunwole added.
“WIC enrollment has been decreasing for a number of years, and this was occurring prepandemic as well,” she said. “More work needs to be done to understand this issue.”
The study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators and interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE