User login
Transanal TME comparable to open, lap approaches to rectal cancer
HOUSTON – Transanal total mesorectal excision can consistently achieve good pathological results for obtaining specimens in rectal cancer, and overcome the shortcomings of the open and laparoscopic approaches to rectal cancer surgery, particularly in the distal part of the rectum where obtaining quality specimens can be technically challenging, researchers at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona have found.
Reporting at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons, Jacqueline van Laarhoven, MD, PhD, said, “Pathologically, transanal total mesorectal excision [TME] provides good results on integrity of the mesorectum, negative circumferential and distal resection margins, and lymph nodes per specimen.” This study represents the first results of a relatively large, single-institution cohort, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
The study involved 187 patients with mid- or low-rectal cancer who had transanal TME from November 2011 to June 2016. Dr. van Laarhoven explained that obtaining high-quality specimens is an important prognostic factor for determining locoregional recurrence in rectal cancer. The study analyzed results of excised specimens in the mesorectum, circumferential and distal resected margins, and lymph nodes, and compared outcomes with those in two randomized clinical trials of both open and laparoscopic TME – the COLOR II (Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:210-8) and COREAN trials (Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:767-74) – where applicable.
In the Barcelona study population, 63.1% had tumors in the midrectum and 36.9% in the low rectum. Transanal TME yielded complete mesorectal quality in 95.7% of cases, almost-complete quality in 1.6% and incomplete in 1.1%, but comparison with COLOR II and COREAN trials was difficult because of differing inclusion criteria, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
Mean distal margin was 2.1 cm in midrectal cancer with a positive distal resection margin in 3.2%. In low-rectal cancer, the mean distal margin was 1.1 cm with a positive distal resection margin in 7.8%. Dr. van Laarhoven noted the overall circumferential resection margin (CRM) was 8.6% in this study, compared with 8.3% overall for the COREAN trial. As for COLOR II, the overall rate for positive CRM in mid- and low-rectal tumors was around 9%, Dr. van Laarhoven said, but in the open group the positive CRM was 3% in the midrectal excisions and 22% in low-rectal disease.
With regard to lymph nodes, the Barcelona study reported a median of 14 per specimen, with a range of 11 to 18, Dr. van Laarhoven said. However, in nonirradiated patients, the median was 15 per specimen. “This is consistent with the fact that neoadjuvant radiotherapy leads to a decrease in the lymph-node harvest,” she said. “These results are comparable to the COREAN and the COLOR II trials.”
Sixty-two percent of patients received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, 3.2% received radiotherapy only, and 2.1% chemotherapy only.
On preoperative staging, 3.2% had T1 tumors, 20.3% T2, 67.9% T3, and 7.5% T4. The overall positive CRM (less than 1 mm) was 8.6% (including T4 tumors).
Postoperative pathological staging showed complete remission in 16% of patients, pT1 in 6.4%, pT2 in 28.9%, pT3 in 42.8%, pT4 in 2.7%, and pTis in 1.6%.
Dr. van Laarhoven commented, “As the quality of the surgical treatment is a surrogate marker for survival, transanal TME can be regarded as an oncologically safe method to treat patients with rectal cancer.”
Dr. van Laarhoven reported having no financial disclosures.
HOUSTON – Transanal total mesorectal excision can consistently achieve good pathological results for obtaining specimens in rectal cancer, and overcome the shortcomings of the open and laparoscopic approaches to rectal cancer surgery, particularly in the distal part of the rectum where obtaining quality specimens can be technically challenging, researchers at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona have found.
Reporting at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons, Jacqueline van Laarhoven, MD, PhD, said, “Pathologically, transanal total mesorectal excision [TME] provides good results on integrity of the mesorectum, negative circumferential and distal resection margins, and lymph nodes per specimen.” This study represents the first results of a relatively large, single-institution cohort, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
The study involved 187 patients with mid- or low-rectal cancer who had transanal TME from November 2011 to June 2016. Dr. van Laarhoven explained that obtaining high-quality specimens is an important prognostic factor for determining locoregional recurrence in rectal cancer. The study analyzed results of excised specimens in the mesorectum, circumferential and distal resected margins, and lymph nodes, and compared outcomes with those in two randomized clinical trials of both open and laparoscopic TME – the COLOR II (Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:210-8) and COREAN trials (Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:767-74) – where applicable.
In the Barcelona study population, 63.1% had tumors in the midrectum and 36.9% in the low rectum. Transanal TME yielded complete mesorectal quality in 95.7% of cases, almost-complete quality in 1.6% and incomplete in 1.1%, but comparison with COLOR II and COREAN trials was difficult because of differing inclusion criteria, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
Mean distal margin was 2.1 cm in midrectal cancer with a positive distal resection margin in 3.2%. In low-rectal cancer, the mean distal margin was 1.1 cm with a positive distal resection margin in 7.8%. Dr. van Laarhoven noted the overall circumferential resection margin (CRM) was 8.6% in this study, compared with 8.3% overall for the COREAN trial. As for COLOR II, the overall rate for positive CRM in mid- and low-rectal tumors was around 9%, Dr. van Laarhoven said, but in the open group the positive CRM was 3% in the midrectal excisions and 22% in low-rectal disease.
With regard to lymph nodes, the Barcelona study reported a median of 14 per specimen, with a range of 11 to 18, Dr. van Laarhoven said. However, in nonirradiated patients, the median was 15 per specimen. “This is consistent with the fact that neoadjuvant radiotherapy leads to a decrease in the lymph-node harvest,” she said. “These results are comparable to the COREAN and the COLOR II trials.”
Sixty-two percent of patients received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, 3.2% received radiotherapy only, and 2.1% chemotherapy only.
On preoperative staging, 3.2% had T1 tumors, 20.3% T2, 67.9% T3, and 7.5% T4. The overall positive CRM (less than 1 mm) was 8.6% (including T4 tumors).
Postoperative pathological staging showed complete remission in 16% of patients, pT1 in 6.4%, pT2 in 28.9%, pT3 in 42.8%, pT4 in 2.7%, and pTis in 1.6%.
Dr. van Laarhoven commented, “As the quality of the surgical treatment is a surrogate marker for survival, transanal TME can be regarded as an oncologically safe method to treat patients with rectal cancer.”
Dr. van Laarhoven reported having no financial disclosures.
HOUSTON – Transanal total mesorectal excision can consistently achieve good pathological results for obtaining specimens in rectal cancer, and overcome the shortcomings of the open and laparoscopic approaches to rectal cancer surgery, particularly in the distal part of the rectum where obtaining quality specimens can be technically challenging, researchers at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona have found.
Reporting at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons, Jacqueline van Laarhoven, MD, PhD, said, “Pathologically, transanal total mesorectal excision [TME] provides good results on integrity of the mesorectum, negative circumferential and distal resection margins, and lymph nodes per specimen.” This study represents the first results of a relatively large, single-institution cohort, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
The study involved 187 patients with mid- or low-rectal cancer who had transanal TME from November 2011 to June 2016. Dr. van Laarhoven explained that obtaining high-quality specimens is an important prognostic factor for determining locoregional recurrence in rectal cancer. The study analyzed results of excised specimens in the mesorectum, circumferential and distal resected margins, and lymph nodes, and compared outcomes with those in two randomized clinical trials of both open and laparoscopic TME – the COLOR II (Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:210-8) and COREAN trials (Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:767-74) – where applicable.
In the Barcelona study population, 63.1% had tumors in the midrectum and 36.9% in the low rectum. Transanal TME yielded complete mesorectal quality in 95.7% of cases, almost-complete quality in 1.6% and incomplete in 1.1%, but comparison with COLOR II and COREAN trials was difficult because of differing inclusion criteria, Dr. van Laarhoven said.
Mean distal margin was 2.1 cm in midrectal cancer with a positive distal resection margin in 3.2%. In low-rectal cancer, the mean distal margin was 1.1 cm with a positive distal resection margin in 7.8%. Dr. van Laarhoven noted the overall circumferential resection margin (CRM) was 8.6% in this study, compared with 8.3% overall for the COREAN trial. As for COLOR II, the overall rate for positive CRM in mid- and low-rectal tumors was around 9%, Dr. van Laarhoven said, but in the open group the positive CRM was 3% in the midrectal excisions and 22% in low-rectal disease.
With regard to lymph nodes, the Barcelona study reported a median of 14 per specimen, with a range of 11 to 18, Dr. van Laarhoven said. However, in nonirradiated patients, the median was 15 per specimen. “This is consistent with the fact that neoadjuvant radiotherapy leads to a decrease in the lymph-node harvest,” she said. “These results are comparable to the COREAN and the COLOR II trials.”
Sixty-two percent of patients received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, 3.2% received radiotherapy only, and 2.1% chemotherapy only.
On preoperative staging, 3.2% had T1 tumors, 20.3% T2, 67.9% T3, and 7.5% T4. The overall positive CRM (less than 1 mm) was 8.6% (including T4 tumors).
Postoperative pathological staging showed complete remission in 16% of patients, pT1 in 6.4%, pT2 in 28.9%, pT3 in 42.8%, pT4 in 2.7%, and pTis in 1.6%.
Dr. van Laarhoven commented, “As the quality of the surgical treatment is a surrogate marker for survival, transanal TME can be regarded as an oncologically safe method to treat patients with rectal cancer.”
Dr. van Laarhoven reported having no financial disclosures.
AT SAGES 2017
Key clinical point: Transanal total mesorectal excision (TME) is a viable alternative to open or laparoscopic TME in cancers of the low and midrectum.
Major finding: Postoperative pathological staging showed complete remission in 16%, with pT1 in 6.4%, pT2 in 28.9%, pT3 in 42.8%, pT4 in 2.7%, and pTis in 1.6%.
Data source: Analysis of 187 patients prospectively enrolled in a standardized database who had transanal TME from November 2011 to June 2016 at a single center.
Disclosures: Dr. van Laarhoven reported having no financial disclosures.
Does laparoscopy have an advantage for emergency VHR?
HOUSTON – The benefits of elective laparoscopic ventral hernia repair over the open approach have been well documented, but, when presented with emergency cases, surgeons still are about 10 times more likely to employ open surgery, possibly exposing patients to greater risk of complications, as well as longer hospital stays, according to an analysis of a national database.
“Despite the benefits of laparoscopic surgery, its utilization in ventral hernia repair (VHR) remains low,” said David Pechman, MD, MBA, of Mount Sinai Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. “This study suggests that utilization is further decreased in emergency cases. Relative to elective cases, emergency VHR is associated with markedly increased rates of morbidity, giving us more room to improve patient outcomes with the use of laparoscopy in these cases.”
The study analyzed 330 emergency VHR operations in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS NSQIP) database for 2012 and 2013. Thirty-two (9.3%) of those operations were performed laparoscopically, and the remainder were open. Because the sample size of laparoscopic operations was so small, drawing statistically significant conclusions from the findings is difficult without a larger, higher-powered study, Dr. Pechman said. “We do think that further research is warranted and believe that analysis of a larger sample would display that increased utilization of laparoscopy in emergency VHR could significantly improve outcomes.”
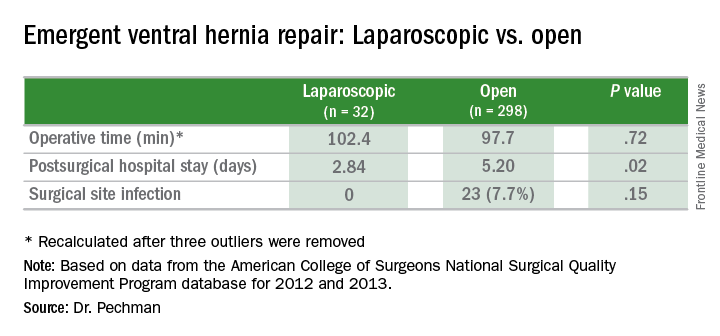
The analysis found significant differences in outcomes between the laparoscopic and the open operations for emergency VHR. Average hospital stay after laparoscopic emergency VHR was 2.8 days vs. 5.9 days for open VHR (P = .02). Surgical site infection rates were 0% vs. 7.7% (P = .15). Demographics between both laparoscopic and open groups were similar, Dr. Pechman said.
Session moderator E. Matthew Ritter, MD, of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md., noted that the study conclusion is in line with the goals of SAGES’s minimally invasive surgery initiative to increase utilization of laparoscopy. When referring to the findings Dr. Pechman reported, Dr. Ritter said, “This is a remarkably low complication rate for a procedure that could seemingly have some benefit.”
Dr. Pechman’s response acknowledged the concerns of the surgeons doing the procedures: “A lot of this has to do with surgeon comfort and the preoperative decision-making, especially in an emergency setting.”
HOUSTON – The benefits of elective laparoscopic ventral hernia repair over the open approach have been well documented, but, when presented with emergency cases, surgeons still are about 10 times more likely to employ open surgery, possibly exposing patients to greater risk of complications, as well as longer hospital stays, according to an analysis of a national database.
“Despite the benefits of laparoscopic surgery, its utilization in ventral hernia repair (VHR) remains low,” said David Pechman, MD, MBA, of Mount Sinai Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. “This study suggests that utilization is further decreased in emergency cases. Relative to elective cases, emergency VHR is associated with markedly increased rates of morbidity, giving us more room to improve patient outcomes with the use of laparoscopy in these cases.”
The study analyzed 330 emergency VHR operations in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS NSQIP) database for 2012 and 2013. Thirty-two (9.3%) of those operations were performed laparoscopically, and the remainder were open. Because the sample size of laparoscopic operations was so small, drawing statistically significant conclusions from the findings is difficult without a larger, higher-powered study, Dr. Pechman said. “We do think that further research is warranted and believe that analysis of a larger sample would display that increased utilization of laparoscopy in emergency VHR could significantly improve outcomes.”
The analysis found significant differences in outcomes between the laparoscopic and the open operations for emergency VHR. Average hospital stay after laparoscopic emergency VHR was 2.8 days vs. 5.9 days for open VHR (P = .02). Surgical site infection rates were 0% vs. 7.7% (P = .15). Demographics between both laparoscopic and open groups were similar, Dr. Pechman said.
Session moderator E. Matthew Ritter, MD, of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md., noted that the study conclusion is in line with the goals of SAGES’s minimally invasive surgery initiative to increase utilization of laparoscopy. When referring to the findings Dr. Pechman reported, Dr. Ritter said, “This is a remarkably low complication rate for a procedure that could seemingly have some benefit.”
Dr. Pechman’s response acknowledged the concerns of the surgeons doing the procedures: “A lot of this has to do with surgeon comfort and the preoperative decision-making, especially in an emergency setting.”

HOUSTON – The benefits of elective laparoscopic ventral hernia repair over the open approach have been well documented, but, when presented with emergency cases, surgeons still are about 10 times more likely to employ open surgery, possibly exposing patients to greater risk of complications, as well as longer hospital stays, according to an analysis of a national database.
“Despite the benefits of laparoscopic surgery, its utilization in ventral hernia repair (VHR) remains low,” said David Pechman, MD, MBA, of Mount Sinai Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. “This study suggests that utilization is further decreased in emergency cases. Relative to elective cases, emergency VHR is associated with markedly increased rates of morbidity, giving us more room to improve patient outcomes with the use of laparoscopy in these cases.”
The study analyzed 330 emergency VHR operations in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS NSQIP) database for 2012 and 2013. Thirty-two (9.3%) of those operations were performed laparoscopically, and the remainder were open. Because the sample size of laparoscopic operations was so small, drawing statistically significant conclusions from the findings is difficult without a larger, higher-powered study, Dr. Pechman said. “We do think that further research is warranted and believe that analysis of a larger sample would display that increased utilization of laparoscopy in emergency VHR could significantly improve outcomes.”
The analysis found significant differences in outcomes between the laparoscopic and the open operations for emergency VHR. Average hospital stay after laparoscopic emergency VHR was 2.8 days vs. 5.9 days for open VHR (P = .02). Surgical site infection rates were 0% vs. 7.7% (P = .15). Demographics between both laparoscopic and open groups were similar, Dr. Pechman said.
Session moderator E. Matthew Ritter, MD, of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md., noted that the study conclusion is in line with the goals of SAGES’s minimally invasive surgery initiative to increase utilization of laparoscopy. When referring to the findings Dr. Pechman reported, Dr. Ritter said, “This is a remarkably low complication rate for a procedure that could seemingly have some benefit.”
Dr. Pechman’s response acknowledged the concerns of the surgeons doing the procedures: “A lot of this has to do with surgeon comfort and the preoperative decision-making, especially in an emergency setting.”

Key clinical point: Outcomes of laparoscopic ventral hernia repair (VHR) may be superior to those for open surgery in the emergency setting.
Major finding: Average hospital stay after laparoscopic emergency VHR was 2.8 days vs. 5.9 days for open surgery, and surgical site infection rates were 0% vs. 7.7%.
Data source: Analysis of 329 cases of emergency VHR enrolled in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program in 2012 and 2013.
Disclosures: Dr. Pechman reported no financial disclosures.
Robot-assisted surgery: Twice the price
HOUSTON – Robot-assisted operations for inguinal hernia repair (IHR) and cholecystectomy have grown steadily in recent years, but these procedures can be done equally well by traditional operations at a fraction of the cost, according to a study from Geisinger Medical Center in Pennsylvania.
Ellen Vogels, DO, of Geisinger, reported results of a study of 1,248 cholecystectomies and 723 initial IHRs from 2007 to 2016. The cholecystectomies were done via robot-assisted surgery or laparoscopy in the hospital or via laparoscopy in an ambulatory surgery center (ASC). The IHRs were done robotically, open, or laparoscopically in the hospital, or open or laparoscopically in an ASC.
Dr. Vogels quoted statistics from the ECRI Institute that showed robotic surgery procedures have increased 178% between 2009 and 2014, and the two procedures the group studied are the most frequently performed robotic procedures.
Within the Geisinger system, the study found a 3:1 cost disparity for IHR: $6,292 total cost for hospital-based robotic surgery vs. $3,421 for ASC-based laparoscopy IHR and $1,853 for ASC-based open repair. For cholecystectomy, the disparity isn’t as wide – it’s 2:1 – but is still significant: Total costs for hospital-based robotic surgery are $6,057 vs. $3,443 for ASC-based cholecystectomy and $3,270 for hospital-based laparoscopic cholecystectomy (the study did not include any open cholecystectomies).
Total costs not only include costs for the procedure but also all related pre- and postoperative care. The cost analysis did not account for the cost of the robot, including maintenance contracts, or costs for laparoscopic instruments. Variable costs also ranged from about $3,000 for robotic IHR to $942 for ASC open repair – which means the lowest per-procedure cost for the latter was around $900.
“Translating this into the fact that cholecystectomies and inguinal hernia repairs are the most often performed general surgery procedures, ambulatory surgery centers can save over $60 billion over the next 10 years in just overhead costs as well as increased efficiency,” Dr. Vogels said.
The study also found access issues depending on where patients had their operations. “As far as service and access in our institution alone, we found that patients going to the main hospital spent as much as two times longer getting these procedures done as compared to the ambulatory surgery centers,” Dr. Vogels said.
Robotic procedures also required longer operative times, the study found – an average of 109 minutes for IHR vs. about an hour for ASC procedures and hospital-based open surgery (but averaging 78 minutes for in-hospital laparoscopy); and 73 minutes for robotic cholecystectomy, 60 minutes for hospital laparoscopy, and 45 minutes for ASC laparoscopy.
Robotic session moderator Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, asked Dr. Vogels if putting a robotic platform in an ambulatory surgery setting would make it more cost effective.
That’s not practical from a cost or efficiency perspective, she said.
“When you look at the cost of the ASCs, specifically in the hernia group, the lowest-cost hernia repair is about $800; with the robot it’s going to be significantly higher than that, up to three times higher than that,” Dr. Vogels replied. “Then you’re also changing all those simple ambulatory surgery procedures to more involved robotic procedures, so it’s hard to justify doing that in the ASC.”
Dr. Vogels and her coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
HOUSTON – Robot-assisted operations for inguinal hernia repair (IHR) and cholecystectomy have grown steadily in recent years, but these procedures can be done equally well by traditional operations at a fraction of the cost, according to a study from Geisinger Medical Center in Pennsylvania.
Ellen Vogels, DO, of Geisinger, reported results of a study of 1,248 cholecystectomies and 723 initial IHRs from 2007 to 2016. The cholecystectomies were done via robot-assisted surgery or laparoscopy in the hospital or via laparoscopy in an ambulatory surgery center (ASC). The IHRs were done robotically, open, or laparoscopically in the hospital, or open or laparoscopically in an ASC.
Dr. Vogels quoted statistics from the ECRI Institute that showed robotic surgery procedures have increased 178% between 2009 and 2014, and the two procedures the group studied are the most frequently performed robotic procedures.
Within the Geisinger system, the study found a 3:1 cost disparity for IHR: $6,292 total cost for hospital-based robotic surgery vs. $3,421 for ASC-based laparoscopy IHR and $1,853 for ASC-based open repair. For cholecystectomy, the disparity isn’t as wide – it’s 2:1 – but is still significant: Total costs for hospital-based robotic surgery are $6,057 vs. $3,443 for ASC-based cholecystectomy and $3,270 for hospital-based laparoscopic cholecystectomy (the study did not include any open cholecystectomies).
Total costs not only include costs for the procedure but also all related pre- and postoperative care. The cost analysis did not account for the cost of the robot, including maintenance contracts, or costs for laparoscopic instruments. Variable costs also ranged from about $3,000 for robotic IHR to $942 for ASC open repair – which means the lowest per-procedure cost for the latter was around $900.
“Translating this into the fact that cholecystectomies and inguinal hernia repairs are the most often performed general surgery procedures, ambulatory surgery centers can save over $60 billion over the next 10 years in just overhead costs as well as increased efficiency,” Dr. Vogels said.
The study also found access issues depending on where patients had their operations. “As far as service and access in our institution alone, we found that patients going to the main hospital spent as much as two times longer getting these procedures done as compared to the ambulatory surgery centers,” Dr. Vogels said.
Robotic procedures also required longer operative times, the study found – an average of 109 minutes for IHR vs. about an hour for ASC procedures and hospital-based open surgery (but averaging 78 minutes for in-hospital laparoscopy); and 73 minutes for robotic cholecystectomy, 60 minutes for hospital laparoscopy, and 45 minutes for ASC laparoscopy.
Robotic session moderator Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, asked Dr. Vogels if putting a robotic platform in an ambulatory surgery setting would make it more cost effective.
That’s not practical from a cost or efficiency perspective, she said.
“When you look at the cost of the ASCs, specifically in the hernia group, the lowest-cost hernia repair is about $800; with the robot it’s going to be significantly higher than that, up to three times higher than that,” Dr. Vogels replied. “Then you’re also changing all those simple ambulatory surgery procedures to more involved robotic procedures, so it’s hard to justify doing that in the ASC.”
Dr. Vogels and her coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
HOUSTON – Robot-assisted operations for inguinal hernia repair (IHR) and cholecystectomy have grown steadily in recent years, but these procedures can be done equally well by traditional operations at a fraction of the cost, according to a study from Geisinger Medical Center in Pennsylvania.
Ellen Vogels, DO, of Geisinger, reported results of a study of 1,248 cholecystectomies and 723 initial IHRs from 2007 to 2016. The cholecystectomies were done via robot-assisted surgery or laparoscopy in the hospital or via laparoscopy in an ambulatory surgery center (ASC). The IHRs were done robotically, open, or laparoscopically in the hospital, or open or laparoscopically in an ASC.
Dr. Vogels quoted statistics from the ECRI Institute that showed robotic surgery procedures have increased 178% between 2009 and 2014, and the two procedures the group studied are the most frequently performed robotic procedures.
Within the Geisinger system, the study found a 3:1 cost disparity for IHR: $6,292 total cost for hospital-based robotic surgery vs. $3,421 for ASC-based laparoscopy IHR and $1,853 for ASC-based open repair. For cholecystectomy, the disparity isn’t as wide – it’s 2:1 – but is still significant: Total costs for hospital-based robotic surgery are $6,057 vs. $3,443 for ASC-based cholecystectomy and $3,270 for hospital-based laparoscopic cholecystectomy (the study did not include any open cholecystectomies).
Total costs not only include costs for the procedure but also all related pre- and postoperative care. The cost analysis did not account for the cost of the robot, including maintenance contracts, or costs for laparoscopic instruments. Variable costs also ranged from about $3,000 for robotic IHR to $942 for ASC open repair – which means the lowest per-procedure cost for the latter was around $900.
“Translating this into the fact that cholecystectomies and inguinal hernia repairs are the most often performed general surgery procedures, ambulatory surgery centers can save over $60 billion over the next 10 years in just overhead costs as well as increased efficiency,” Dr. Vogels said.
The study also found access issues depending on where patients had their operations. “As far as service and access in our institution alone, we found that patients going to the main hospital spent as much as two times longer getting these procedures done as compared to the ambulatory surgery centers,” Dr. Vogels said.
Robotic procedures also required longer operative times, the study found – an average of 109 minutes for IHR vs. about an hour for ASC procedures and hospital-based open surgery (but averaging 78 minutes for in-hospital laparoscopy); and 73 minutes for robotic cholecystectomy, 60 minutes for hospital laparoscopy, and 45 minutes for ASC laparoscopy.
Robotic session moderator Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, asked Dr. Vogels if putting a robotic platform in an ambulatory surgery setting would make it more cost effective.
That’s not practical from a cost or efficiency perspective, she said.
“When you look at the cost of the ASCs, specifically in the hernia group, the lowest-cost hernia repair is about $800; with the robot it’s going to be significantly higher than that, up to three times higher than that,” Dr. Vogels replied. “Then you’re also changing all those simple ambulatory surgery procedures to more involved robotic procedures, so it’s hard to justify doing that in the ASC.”
Dr. Vogels and her coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT SAGES 2017
Key clinical point: Outcomes for robot-assisted inguinal hernia repair and cholecystectomy are similar to those for outpatient open and laparoscopic procedures.
Major finding: Robotic IHR costs up to three times more than open outpatient surgery, and robotic cholecystectomy costs twice as much as outpatient surgery.
Data source: Study of 1,971 in-hospital robotic, laparoscopic, and open procedures, and outpatient laparoscopic and open operations done from 2007 to 2016 at Geisinger Medical Center.
Disclosures: Dr. Vogels and coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
Robotics: General surgery goes its own way
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.
“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
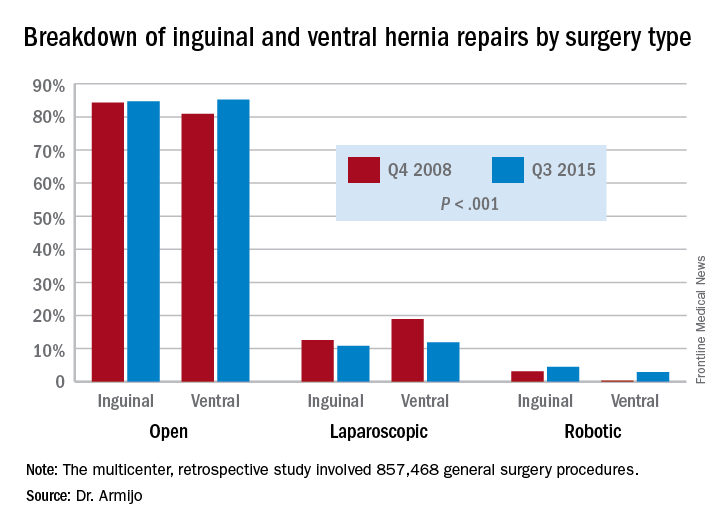
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.

“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
HOUSTON – Subspecialties such as urology and gynecology have seen a steady increase in robot-assisted surgery and an offsetting decline in open procedures, but in general surgery, robot-assisted procedures seem to be making gains at the expense of laparoscopy, according to researchers from the University of Nebraska.
In two specific operations, ventral and inguinal hernia repairs (VHR and IHR), the percentage of open procedures has increased or held steady over the 7-year study period while the share of laparoscopic operations declined and robot-assisted surgeries (RAS) increased, Priscila Rodrigues Armijo, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
This shift to RAS rather than laparoscopy could have significant implications because RAS is significantly more costly than laparoscopy, Dr. Armijo said. “In our study, the open procedures were the most expensive, followed by the robot-assisted surgeries and then laparoscopy,” she said. Median direct costs were $14,364 for open procedures, $11,376 for RAS and $7,945 for laparoscopy.
The Nebraska study retrospectively analyzed five different general surgery procedures: colectomy, cholecystectomy, and bariatric procedures in addition to VHR and IHR. The researchers analyzed 857,468 operations entered into the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager from October 2008 to September 2015.
Dr. Armijo explained that the goal was to study trends in general surgery because while several studies have examined trends in urologic and gynecologic surgery, few studies have done so in general surgery.

“There was a significant increase in minimally invasive utilizations over time, and robotic surgery increased disproportionately compared to the laparoscope counterpart,” Dr. Armijo said. “And although we cannot prove where those patients are coming from, we believe that, especially for inguinal and ventral hernia repairs, they are coming from laparoscopic surgeons who now are adopting robotic techniques and not from open surgeons switching to the robotic approach.”
In 7 years, the study showed a significant decrease in the share of open procedures in colectomy (from 71.8% to 61.9%), cholecystectomy (35.7% to 27.1%), and bariatric surgery (20.1% to 10.1%), but an increase in both laparoscopic and RAS approaches in these surgeries.
However, in IHR, open procedures held steady at around 84% through the study period, while laparoscopic procedures declined from 12.6% to 10.8% and RAS jumped 3.1% to 4.5%. For VHR, the share of open procedures actually jumped from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations jumped more than tenfold, from 0.2% to 2.9%.
“For ventral hernia repair there was a significant decrease in the laparoscopic approach with a significant increase in both open and robotic procedures, which may be due to new open techniques, including component separation, that have been shown to be more durable as a repair,” Dr. Armijo said. “In addition, those repair techniques are more easily performed with the robotic approach. Laparoscopic surgeons are finding that robotic technology is enabling them to execute surgical tasks, such as suturing mesh.”
Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, FACS, disclosed he is a stockholder in Virtual Incision Corp. Dr. Armijo and other coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
AT SAGES 2017
Key clinical point: In inguinal and ventral hernia repair, laparoscopic surgeons are more likely than are open surgery counterparts to move to surgical robot.
Major finding: Over the 7-year study period, the share of open ventral hernia repair procedures increased from 80.9% to 85.2%, while the proportion of laparoscopic procedures fell from 18.9% to 11.9% and RAS operations increased from 0.2% to 2.9%.
Data source: Multicenter, retrospective study of 857,468 general surgery procedures from 2008 to 2015 in the University HealthSystem Consortium Clinical Database Resource Manager.
Disclosures: Dr. Armijo reported having no financial disclosures. Coauthor Dmitry Oleynikov, MD, disclosed stock holding in Virtual Incision Corp.
Observation works for most smaller splanchnic artery aneurysms
CHICAGO – Guidelines for the management of splanchnic artery aneurysms have been hard to come by because of their rarity, but investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, have surveyed their 20-year experience to conclude that surveillance is appropriate for most cases of aneurysms smaller than 25 mm, and selective open or endovascular repair is indicated for larger lesions, depending on their location.
“Most of the small splanchnic artery aneurysms (SAAs) of less than 25 mm did not grow or rupture over time and can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years,” Mark F. Conrad, MD, reported at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
The predominant sites of aneurysm were the splenic artery (95, 36%) and the celiac artery (78, 30%), followed by the hepatic artery (34, 13%), pancreaticoduodenal artery (PDA; 25, 9.6%), superior mesenteric artery (SMA; 17, 6%), gastroduodenal artery (GDA; 11, 4%), jejunal artery (3, 1%) and inferior mesenteric artery (1, 0.4%).
Surveillance consisted of imaging every 3 years. Of the surveillance cohort, 138 patients had longer-term follow-up. The average aneurysm size was 16.3 mm, “so they’re small,” Dr. Conrad said. Of that whole group, only 12 (9%), of SAAs grew in size, and of those, 8 were 25 mm or smaller when they were identified; 8 of the 12 required repair. “The average time to repair was 2 years,” Dr. Conrad said. “There were no ruptures in the surveillance cohort.”
Among the early repair group, 13 (14.7%) had rupture upon presentation, 3 of which (23%) were pseudoaneurysms. The majority of aneurysms in this group were in either the splenic artery, PDA, or GDA. “Their average size was 31 mm – much larger than the patients that we watched,” he said. A total of 70% of all repairs were endovascular in nature, the remainder open, but endovascular comprised a higher percentage of rupture repairs: 10 (77%) vs. 3 (23%) that underwent open procedures.
The outcomes for endovascular and open repair were similar based on the small number of subjects, Dr. Conrad said: 30-day morbidity of 17% for endovascular repair and 22.2% for open; and 30-day mortality of 3.5% and 4.5%, respectively. However, for ruptured lesions, the outcomes were starkly significant: 54% morbidity and 8% mortality at 30 days.
The researchers performed a univariate analysis of predictors for aneurysm. They were aneurysm size with an odds ratio of 1.04 for every 1 mm of growth; PDA or GDA lesions with an OR of 11.2; and Ehlers-Danlos type IV syndrome with an OR of 32.5. The latter included all the three study patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Among patients who had splenic SAAs, 99 (93%) were asymptomatic and 5 (5.3%) had pseudoaneurysm, and almost half (47) went into surveillance. Over a mean observation period of 35 months, six (12.8%) grew in size, comprising half of the growing SAAs in the observation group. Thirty-two had endovascular repair and four open repair, with a 30-day morbidity of 22% and 30-day mortality of 2.7%.
Celiac SAAs proved most problematic in terms of symptomatology; all 78 patients with this variant were asymptomatic, and 12 (15%) had dissection. Sixty patients went into surveillance with a mean time of 43 months, and three (5) had aneurysms that grew in size. Five had intervention, four with open repair, with 30-day morbidity of 20% and no 30-day mortality.
Hepatic SAAs affected 34 study subjects, 29 (85%) of whom were asymptomatic, 4 (15%) who had dissection, and 7 (21%) with pseudoaneurysm. Eleven entered surveillance for an average of 28 months, but none showed any aneurysmal growth. The 16 who had intervention were evenly split between open and endovascular repair with 30-day morbidity of 25% and 30-day morality of 12.5%.
The PDA and GDA aneurysms “are really interesting,” Dr. Conrad said. “I think they’re different in nature than the other aneurysms,” he said, noting that 12 (33%) of these aneurysms were symptomatic and 6 (17%) were pseudoaneurysms. Because of the high rate of rupture of PDA/GDA aneurysms, Dr. Conrad advised repair at diagnosis: “97% of these patients had a celiac stenosis, and of those, two-thirds were atherosclerosis related and one-third related to the median arcuate ligament compression.” The rupture rate was comparatively high – 20%. Twenty cases underwent endovascular repair with a 90% success rate while four cases had open repair. Thirty-day morbidity for intact lesions was 11% with no deaths, and 50% with 14% mortality rate for ruptured lesions.
Of the SMA aneurysms in the study population, only 17% were mycotic with the remainder asymptomatic, Dr. Conrad said. Nine underwent surveillance, with one growing in size over a mean observation period of 28 months, four had open repair, and two endovascular repair. Morbidity was 17% at 30 days with no deaths.
The guidelines Dr. Conrad and his group developed recommend treatment for symptomatic patients and a more nuanced approach for asymptomatic patients, depending on the location and size of SAA. All lesions 25 mm or smaller, except those of the PDA/GDA, can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years, he said; intervention is indicated for all larger lesions. Endovascular repair is in order for all splenic SAAs in pregnancy, liver transplantation, and pseudoaneurysm. For hepatic SAAs, open or endovascular repair is indicated for pseudoaneurysm, but open repair only is indicated for asymptomatic celiac SAAs with pseudoaneurysm. Endovascular intervention can address most SAA aneurysms of the PDA and GDA.
Dr. Conrad disclosed he is a consultant to Medtronic and Volcano and is a member of Bard’s clinical events committee.
CHICAGO – Guidelines for the management of splanchnic artery aneurysms have been hard to come by because of their rarity, but investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, have surveyed their 20-year experience to conclude that surveillance is appropriate for most cases of aneurysms smaller than 25 mm, and selective open or endovascular repair is indicated for larger lesions, depending on their location.
“Most of the small splanchnic artery aneurysms (SAAs) of less than 25 mm did not grow or rupture over time and can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years,” Mark F. Conrad, MD, reported at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
The predominant sites of aneurysm were the splenic artery (95, 36%) and the celiac artery (78, 30%), followed by the hepatic artery (34, 13%), pancreaticoduodenal artery (PDA; 25, 9.6%), superior mesenteric artery (SMA; 17, 6%), gastroduodenal artery (GDA; 11, 4%), jejunal artery (3, 1%) and inferior mesenteric artery (1, 0.4%).
Surveillance consisted of imaging every 3 years. Of the surveillance cohort, 138 patients had longer-term follow-up. The average aneurysm size was 16.3 mm, “so they’re small,” Dr. Conrad said. Of that whole group, only 12 (9%), of SAAs grew in size, and of those, 8 were 25 mm or smaller when they were identified; 8 of the 12 required repair. “The average time to repair was 2 years,” Dr. Conrad said. “There were no ruptures in the surveillance cohort.”
Among the early repair group, 13 (14.7%) had rupture upon presentation, 3 of which (23%) were pseudoaneurysms. The majority of aneurysms in this group were in either the splenic artery, PDA, or GDA. “Their average size was 31 mm – much larger than the patients that we watched,” he said. A total of 70% of all repairs were endovascular in nature, the remainder open, but endovascular comprised a higher percentage of rupture repairs: 10 (77%) vs. 3 (23%) that underwent open procedures.
The outcomes for endovascular and open repair were similar based on the small number of subjects, Dr. Conrad said: 30-day morbidity of 17% for endovascular repair and 22.2% for open; and 30-day mortality of 3.5% and 4.5%, respectively. However, for ruptured lesions, the outcomes were starkly significant: 54% morbidity and 8% mortality at 30 days.
The researchers performed a univariate analysis of predictors for aneurysm. They were aneurysm size with an odds ratio of 1.04 for every 1 mm of growth; PDA or GDA lesions with an OR of 11.2; and Ehlers-Danlos type IV syndrome with an OR of 32.5. The latter included all the three study patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Among patients who had splenic SAAs, 99 (93%) were asymptomatic and 5 (5.3%) had pseudoaneurysm, and almost half (47) went into surveillance. Over a mean observation period of 35 months, six (12.8%) grew in size, comprising half of the growing SAAs in the observation group. Thirty-two had endovascular repair and four open repair, with a 30-day morbidity of 22% and 30-day mortality of 2.7%.
Celiac SAAs proved most problematic in terms of symptomatology; all 78 patients with this variant were asymptomatic, and 12 (15%) had dissection. Sixty patients went into surveillance with a mean time of 43 months, and three (5) had aneurysms that grew in size. Five had intervention, four with open repair, with 30-day morbidity of 20% and no 30-day mortality.
Hepatic SAAs affected 34 study subjects, 29 (85%) of whom were asymptomatic, 4 (15%) who had dissection, and 7 (21%) with pseudoaneurysm. Eleven entered surveillance for an average of 28 months, but none showed any aneurysmal growth. The 16 who had intervention were evenly split between open and endovascular repair with 30-day morbidity of 25% and 30-day morality of 12.5%.
The PDA and GDA aneurysms “are really interesting,” Dr. Conrad said. “I think they’re different in nature than the other aneurysms,” he said, noting that 12 (33%) of these aneurysms were symptomatic and 6 (17%) were pseudoaneurysms. Because of the high rate of rupture of PDA/GDA aneurysms, Dr. Conrad advised repair at diagnosis: “97% of these patients had a celiac stenosis, and of those, two-thirds were atherosclerosis related and one-third related to the median arcuate ligament compression.” The rupture rate was comparatively high – 20%. Twenty cases underwent endovascular repair with a 90% success rate while four cases had open repair. Thirty-day morbidity for intact lesions was 11% with no deaths, and 50% with 14% mortality rate for ruptured lesions.
Of the SMA aneurysms in the study population, only 17% were mycotic with the remainder asymptomatic, Dr. Conrad said. Nine underwent surveillance, with one growing in size over a mean observation period of 28 months, four had open repair, and two endovascular repair. Morbidity was 17% at 30 days with no deaths.
The guidelines Dr. Conrad and his group developed recommend treatment for symptomatic patients and a more nuanced approach for asymptomatic patients, depending on the location and size of SAA. All lesions 25 mm or smaller, except those of the PDA/GDA, can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years, he said; intervention is indicated for all larger lesions. Endovascular repair is in order for all splenic SAAs in pregnancy, liver transplantation, and pseudoaneurysm. For hepatic SAAs, open or endovascular repair is indicated for pseudoaneurysm, but open repair only is indicated for asymptomatic celiac SAAs with pseudoaneurysm. Endovascular intervention can address most SAA aneurysms of the PDA and GDA.
Dr. Conrad disclosed he is a consultant to Medtronic and Volcano and is a member of Bard’s clinical events committee.
CHICAGO – Guidelines for the management of splanchnic artery aneurysms have been hard to come by because of their rarity, but investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, have surveyed their 20-year experience to conclude that surveillance is appropriate for most cases of aneurysms smaller than 25 mm, and selective open or endovascular repair is indicated for larger lesions, depending on their location.
“Most of the small splanchnic artery aneurysms (SAAs) of less than 25 mm did not grow or rupture over time and can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years,” Mark F. Conrad, MD, reported at a symposium on vascular surgery sponsored by Northwestern University.
The predominant sites of aneurysm were the splenic artery (95, 36%) and the celiac artery (78, 30%), followed by the hepatic artery (34, 13%), pancreaticoduodenal artery (PDA; 25, 9.6%), superior mesenteric artery (SMA; 17, 6%), gastroduodenal artery (GDA; 11, 4%), jejunal artery (3, 1%) and inferior mesenteric artery (1, 0.4%).
Surveillance consisted of imaging every 3 years. Of the surveillance cohort, 138 patients had longer-term follow-up. The average aneurysm size was 16.3 mm, “so they’re small,” Dr. Conrad said. Of that whole group, only 12 (9%), of SAAs grew in size, and of those, 8 were 25 mm or smaller when they were identified; 8 of the 12 required repair. “The average time to repair was 2 years,” Dr. Conrad said. “There were no ruptures in the surveillance cohort.”
Among the early repair group, 13 (14.7%) had rupture upon presentation, 3 of which (23%) were pseudoaneurysms. The majority of aneurysms in this group were in either the splenic artery, PDA, or GDA. “Their average size was 31 mm – much larger than the patients that we watched,” he said. A total of 70% of all repairs were endovascular in nature, the remainder open, but endovascular comprised a higher percentage of rupture repairs: 10 (77%) vs. 3 (23%) that underwent open procedures.
The outcomes for endovascular and open repair were similar based on the small number of subjects, Dr. Conrad said: 30-day morbidity of 17% for endovascular repair and 22.2% for open; and 30-day mortality of 3.5% and 4.5%, respectively. However, for ruptured lesions, the outcomes were starkly significant: 54% morbidity and 8% mortality at 30 days.
The researchers performed a univariate analysis of predictors for aneurysm. They were aneurysm size with an odds ratio of 1.04 for every 1 mm of growth; PDA or GDA lesions with an OR of 11.2; and Ehlers-Danlos type IV syndrome with an OR of 32.5. The latter included all the three study patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Among patients who had splenic SAAs, 99 (93%) were asymptomatic and 5 (5.3%) had pseudoaneurysm, and almost half (47) went into surveillance. Over a mean observation period of 35 months, six (12.8%) grew in size, comprising half of the growing SAAs in the observation group. Thirty-two had endovascular repair and four open repair, with a 30-day morbidity of 22% and 30-day mortality of 2.7%.
Celiac SAAs proved most problematic in terms of symptomatology; all 78 patients with this variant were asymptomatic, and 12 (15%) had dissection. Sixty patients went into surveillance with a mean time of 43 months, and three (5) had aneurysms that grew in size. Five had intervention, four with open repair, with 30-day morbidity of 20% and no 30-day mortality.
Hepatic SAAs affected 34 study subjects, 29 (85%) of whom were asymptomatic, 4 (15%) who had dissection, and 7 (21%) with pseudoaneurysm. Eleven entered surveillance for an average of 28 months, but none showed any aneurysmal growth. The 16 who had intervention were evenly split between open and endovascular repair with 30-day morbidity of 25% and 30-day morality of 12.5%.
The PDA and GDA aneurysms “are really interesting,” Dr. Conrad said. “I think they’re different in nature than the other aneurysms,” he said, noting that 12 (33%) of these aneurysms were symptomatic and 6 (17%) were pseudoaneurysms. Because of the high rate of rupture of PDA/GDA aneurysms, Dr. Conrad advised repair at diagnosis: “97% of these patients had a celiac stenosis, and of those, two-thirds were atherosclerosis related and one-third related to the median arcuate ligament compression.” The rupture rate was comparatively high – 20%. Twenty cases underwent endovascular repair with a 90% success rate while four cases had open repair. Thirty-day morbidity for intact lesions was 11% with no deaths, and 50% with 14% mortality rate for ruptured lesions.
Of the SMA aneurysms in the study population, only 17% were mycotic with the remainder asymptomatic, Dr. Conrad said. Nine underwent surveillance, with one growing in size over a mean observation period of 28 months, four had open repair, and two endovascular repair. Morbidity was 17% at 30 days with no deaths.
The guidelines Dr. Conrad and his group developed recommend treatment for symptomatic patients and a more nuanced approach for asymptomatic patients, depending on the location and size of SAA. All lesions 25 mm or smaller, except those of the PDA/GDA, can be observed with axial imaging every 3 years, he said; intervention is indicated for all larger lesions. Endovascular repair is in order for all splenic SAAs in pregnancy, liver transplantation, and pseudoaneurysm. For hepatic SAAs, open or endovascular repair is indicated for pseudoaneurysm, but open repair only is indicated for asymptomatic celiac SAAs with pseudoaneurysm. Endovascular intervention can address most SAA aneurysms of the PDA and GDA.
Dr. Conrad disclosed he is a consultant to Medtronic and Volcano and is a member of Bard’s clinical events committee.
AT THE NORTHWESTERN VASCULAR SYMPOSIUM
Key clinical point: Surveillance imaging every three years may be adequate to manage splanchnic artery aneurysms (SAA) smaller than 25 mm, because they rarely expand significantly.
Major finding: In the surveillance group that had long-term follow-up, 9% had SAAs that grew in size.
Data source: Analysis of 250 patients with 264 SAAs during 1994-2014 in the Research Patient Data Registry at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Disclosures: Dr. Conrad disclosed he is a consultant to Medtronic and Volcano and is a member of Bard’s clinical events committee.
LVADs achieve cardiac palliation in muscular dystrophies
At one time, respiratory failure was the primary cause of death in young men and boys with muscular dystrophies, but since improvements in ventilator support have addressed this problem, cardiac complications such as cardiomyopathy have become the main cause of death in this group, with the highest risk of death in people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Researchers from Rome have reported that the novel use of ventricular assist devices in this population can prolong life.
Gianluigi Perri, MD, PhD, of University Hospital and Bambino Gesù Children Hospital in Rome, and his coauthors, shared their experience treating seven patients with dystrophinopathies and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) from February 2011 to February 2016 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153:669-74). “Our experience indicates that the use of an LVAD as destination therapy in patients with dystrophinopathies with end-stage DCM is feasible, suggesting that it may be suitable as a palliative therapy for the treatment of these patients with no other therapeutic options,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
Heart transplantation is considered the procedure of choice for children with severe advanced heart failure, but transplantation is contraindicated for children with dystrophinopathies because of the risk of respiratory failure and progression of skeletal myopathy leads to limited functional capacity. Hence, Dr. Perri and his coauthors developed their alternative treatment for end-stage heart failure in these children. They used the Jarvik 2000 LVAD (Jarvik Heart Inc., New York) as destination therapy.
Six of the seven patients they operated on had DMD and one had beta-2 sarcoglycan deficit. Their ages ranged from 14.2 to 23.4 years. Two patients had early complications: retropharyngeal bleeding and cholecystectomy; and abdominal bleeding and splenectomy. Two different patients had late complications: gastrostomy; and osteolysis and infection at the pedestal site. Three patients died after the operation: one of stroke at 15 months; one of severe bleeding about 28 months later; and one of lung infection 45 months afterward. Follow-up for the surviving patients ranged from about 2 months to 40 months. Median hospital stay was 77 days.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors noted that the DMD Care Considerations Working Group expanded acceptable therapies for DMD cardiomyopathy to include novel treatments such as mechanical circulatory support and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
“Although the best approach remains unclear, it does seem clear that treatment should be more aggressive,” the researchers said. The limited life expectancy of these patients makes transplantation a complicated choice when a shortage of donors is a concern. “Therefore, the alternative therapeutic option is the use of LVAD,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
These patients need care at centers “with a high level of experience of patients with DMD,” the researchers stated. Common comorbidities such as severe kyphoscoliosis and respiratory muscle weakness in this population increase surgical risks.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors used a surgical technique that involved avoiding the left thoracotomy approach common in adults who undergo VAD implantation, because of respiratory insufficiency in these younger patients. They also used cardiopulmonary bypass in all but one patient who had a minimally invasive off-pump procedure through a left anterior minithoracotomy.
The researchers “strongly suggest” noninvasive ventilation after surgery to assist in pulmonary function often compromised by scoliosis and muscle weakness. “Our experience shows that postoperative care can be extremely challenging and is often burdened by unexpected complications,” they noted.
Kyphoscoliosis poses challenges when placing drains, and complications of these patients should be treated only in a specialized center. “Indeed, one of our patients died in a peripheral hospital because they underwent bronchoscopic examination with an endoscope that caused severe and intractable retropharyngeal bleeding,” they said.
The researchers no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Almost all young men living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy will develop heart failure, but for many of these patients, continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices can provide “reliable support” for up to a decade, David L. S. Morales, MD, of the Heart Institute at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153:675-6)
“The current series demonstrates, as has been shown at our institute as well as others, that one can provide an effective therapy for certain patients with DMD and heart failure,” Dr. Morales said of the work of Dr. Perri and coauthors. Dr. Morales added that maximizing outcomes in this population hinges on finding the appropriate time point for intervention in the disease process.
While “there is still much to be learned,” Dr. Morales said, Dr. Perri and his coauthors have shown that LVAD therapy is an option in patients with DMD and heart failure who have failed other treatments. “These young men may, therefore, have the option to extend their lives and possibly have the opportunity to benefit from the impressive medical advances being made,” he said. “Perhaps they and their families have been provided hope.”
Dr. Morales disclosed relationships with Berlin Heart, HeartWare and Oregon Total Artificial Heart.
Almost all young men living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy will develop heart failure, but for many of these patients, continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices can provide “reliable support” for up to a decade, David L. S. Morales, MD, of the Heart Institute at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153:675-6)
“The current series demonstrates, as has been shown at our institute as well as others, that one can provide an effective therapy for certain patients with DMD and heart failure,” Dr. Morales said of the work of Dr. Perri and coauthors. Dr. Morales added that maximizing outcomes in this population hinges on finding the appropriate time point for intervention in the disease process.
While “there is still much to be learned,” Dr. Morales said, Dr. Perri and his coauthors have shown that LVAD therapy is an option in patients with DMD and heart failure who have failed other treatments. “These young men may, therefore, have the option to extend their lives and possibly have the opportunity to benefit from the impressive medical advances being made,” he said. “Perhaps they and their families have been provided hope.”
Dr. Morales disclosed relationships with Berlin Heart, HeartWare and Oregon Total Artificial Heart.
Almost all young men living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy will develop heart failure, but for many of these patients, continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices can provide “reliable support” for up to a decade, David L. S. Morales, MD, of the Heart Institute at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153:675-6)
“The current series demonstrates, as has been shown at our institute as well as others, that one can provide an effective therapy for certain patients with DMD and heart failure,” Dr. Morales said of the work of Dr. Perri and coauthors. Dr. Morales added that maximizing outcomes in this population hinges on finding the appropriate time point for intervention in the disease process.
While “there is still much to be learned,” Dr. Morales said, Dr. Perri and his coauthors have shown that LVAD therapy is an option in patients with DMD and heart failure who have failed other treatments. “These young men may, therefore, have the option to extend their lives and possibly have the opportunity to benefit from the impressive medical advances being made,” he said. “Perhaps they and their families have been provided hope.”
Dr. Morales disclosed relationships with Berlin Heart, HeartWare and Oregon Total Artificial Heart.
At one time, respiratory failure was the primary cause of death in young men and boys with muscular dystrophies, but since improvements in ventilator support have addressed this problem, cardiac complications such as cardiomyopathy have become the main cause of death in this group, with the highest risk of death in people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Researchers from Rome have reported that the novel use of ventricular assist devices in this population can prolong life.
Gianluigi Perri, MD, PhD, of University Hospital and Bambino Gesù Children Hospital in Rome, and his coauthors, shared their experience treating seven patients with dystrophinopathies and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) from February 2011 to February 2016 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153:669-74). “Our experience indicates that the use of an LVAD as destination therapy in patients with dystrophinopathies with end-stage DCM is feasible, suggesting that it may be suitable as a palliative therapy for the treatment of these patients with no other therapeutic options,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
Heart transplantation is considered the procedure of choice for children with severe advanced heart failure, but transplantation is contraindicated for children with dystrophinopathies because of the risk of respiratory failure and progression of skeletal myopathy leads to limited functional capacity. Hence, Dr. Perri and his coauthors developed their alternative treatment for end-stage heart failure in these children. They used the Jarvik 2000 LVAD (Jarvik Heart Inc., New York) as destination therapy.
Six of the seven patients they operated on had DMD and one had beta-2 sarcoglycan deficit. Their ages ranged from 14.2 to 23.4 years. Two patients had early complications: retropharyngeal bleeding and cholecystectomy; and abdominal bleeding and splenectomy. Two different patients had late complications: gastrostomy; and osteolysis and infection at the pedestal site. Three patients died after the operation: one of stroke at 15 months; one of severe bleeding about 28 months later; and one of lung infection 45 months afterward. Follow-up for the surviving patients ranged from about 2 months to 40 months. Median hospital stay was 77 days.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors noted that the DMD Care Considerations Working Group expanded acceptable therapies for DMD cardiomyopathy to include novel treatments such as mechanical circulatory support and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
“Although the best approach remains unclear, it does seem clear that treatment should be more aggressive,” the researchers said. The limited life expectancy of these patients makes transplantation a complicated choice when a shortage of donors is a concern. “Therefore, the alternative therapeutic option is the use of LVAD,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
These patients need care at centers “with a high level of experience of patients with DMD,” the researchers stated. Common comorbidities such as severe kyphoscoliosis and respiratory muscle weakness in this population increase surgical risks.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors used a surgical technique that involved avoiding the left thoracotomy approach common in adults who undergo VAD implantation, because of respiratory insufficiency in these younger patients. They also used cardiopulmonary bypass in all but one patient who had a minimally invasive off-pump procedure through a left anterior minithoracotomy.
The researchers “strongly suggest” noninvasive ventilation after surgery to assist in pulmonary function often compromised by scoliosis and muscle weakness. “Our experience shows that postoperative care can be extremely challenging and is often burdened by unexpected complications,” they noted.
Kyphoscoliosis poses challenges when placing drains, and complications of these patients should be treated only in a specialized center. “Indeed, one of our patients died in a peripheral hospital because they underwent bronchoscopic examination with an endoscope that caused severe and intractable retropharyngeal bleeding,” they said.
The researchers no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
At one time, respiratory failure was the primary cause of death in young men and boys with muscular dystrophies, but since improvements in ventilator support have addressed this problem, cardiac complications such as cardiomyopathy have become the main cause of death in this group, with the highest risk of death in people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Researchers from Rome have reported that the novel use of ventricular assist devices in this population can prolong life.
Gianluigi Perri, MD, PhD, of University Hospital and Bambino Gesù Children Hospital in Rome, and his coauthors, shared their experience treating seven patients with dystrophinopathies and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) from February 2011 to February 2016 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153:669-74). “Our experience indicates that the use of an LVAD as destination therapy in patients with dystrophinopathies with end-stage DCM is feasible, suggesting that it may be suitable as a palliative therapy for the treatment of these patients with no other therapeutic options,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
Heart transplantation is considered the procedure of choice for children with severe advanced heart failure, but transplantation is contraindicated for children with dystrophinopathies because of the risk of respiratory failure and progression of skeletal myopathy leads to limited functional capacity. Hence, Dr. Perri and his coauthors developed their alternative treatment for end-stage heart failure in these children. They used the Jarvik 2000 LVAD (Jarvik Heart Inc., New York) as destination therapy.
Six of the seven patients they operated on had DMD and one had beta-2 sarcoglycan deficit. Their ages ranged from 14.2 to 23.4 years. Two patients had early complications: retropharyngeal bleeding and cholecystectomy; and abdominal bleeding and splenectomy. Two different patients had late complications: gastrostomy; and osteolysis and infection at the pedestal site. Three patients died after the operation: one of stroke at 15 months; one of severe bleeding about 28 months later; and one of lung infection 45 months afterward. Follow-up for the surviving patients ranged from about 2 months to 40 months. Median hospital stay was 77 days.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors noted that the DMD Care Considerations Working Group expanded acceptable therapies for DMD cardiomyopathy to include novel treatments such as mechanical circulatory support and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators.
“Although the best approach remains unclear, it does seem clear that treatment should be more aggressive,” the researchers said. The limited life expectancy of these patients makes transplantation a complicated choice when a shortage of donors is a concern. “Therefore, the alternative therapeutic option is the use of LVAD,” Dr. Perri and his coauthors said.
These patients need care at centers “with a high level of experience of patients with DMD,” the researchers stated. Common comorbidities such as severe kyphoscoliosis and respiratory muscle weakness in this population increase surgical risks.
Dr. Perri and his coauthors used a surgical technique that involved avoiding the left thoracotomy approach common in adults who undergo VAD implantation, because of respiratory insufficiency in these younger patients. They also used cardiopulmonary bypass in all but one patient who had a minimally invasive off-pump procedure through a left anterior minithoracotomy.
The researchers “strongly suggest” noninvasive ventilation after surgery to assist in pulmonary function often compromised by scoliosis and muscle weakness. “Our experience shows that postoperative care can be extremely challenging and is often burdened by unexpected complications,” they noted.
Kyphoscoliosis poses challenges when placing drains, and complications of these patients should be treated only in a specialized center. “Indeed, one of our patients died in a peripheral hospital because they underwent bronchoscopic examination with an endoscope that caused severe and intractable retropharyngeal bleeding,” they said.
The researchers no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: A left ventricular assist device can be used as destination therapy in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy dystrophinopathies and end-stage dilated cardiomyopathy.
Major finding: Four of seven patients who had LVAD survived long term, and survival for the three who died ranged from 15 to 44 months.
Data source: Single-center, retrospective review of seven patients with DMD who had LVAD for DCM from February 2011 to February 2016.
Disclosure: Dr. Perri and his coauthors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Preoperative variables can predict prolonged air leak
Prolonged air leak is a well-known complication after lung cancer surgery that can worsen patient outcomes and drive up costs, and while international authors have developed tools to calculate the risk of PAL, their use has been limited in the United States for various reasons. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have reported on a predictive model that uses easy-to-obtain patient factors, such as forced expiratory volume and smoking history, to help surgeons identify patients at greatest risk for complications and implement preventative measures.
Adam Attaar and his coauthors reported that their nomogram had an accuracy rate of 76%, with a 95% confidence interval, for predicting PAL after surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153[3]:690-9). “Using readily available candidate variables, our nomogram predicts increasing risk of prolonged air leak with good discriminatory ability,” noted Mr. Attaar, a student at University of Pittsburgh, and his coauthors.
Previously published reports put the incidence of PAL complications at 6%-18%, they noted. In the University of Pittsburgh series of 2,317 patients who had pulmonary resection for lung cancer or nodules from January 2009 to June 2014, the incidence was 8.6%.
In this series, patients with PAL were more likely to be older, men, and smokers, and to have a lower body mass index, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a history of steroid use, a high Zubrod score and lower forced expiratory volume.“They were less likely to have diabetes or to be hospitalized before surgery,” the researchers said. Surgical factors that characterized patients with PAL were resection for primary lung cancer rather than benign or metastatic tumors; lobectomy/segmentectomy or bilobectomy rather than wedge resection; a right-sided resection; thoracotomy; and a surgeon with higher annual caseloads.
Not all those factors made it into the nomogram, however. The nomogram scores each of these 10 variables to calculate the risk of PAL, in order of their weighting: lower forced expiratory volume, procedure type, BMI, right-sided thoracotomy, preoperative hospitalization, annual surgeon caseload, wedge resection by thoracotomy, reoperation, smoking history, and Zubrod score. A second nomogram drops out surgeon volume to make it more generalizable to other institutions.
In explaining higher surgeon volume as a risk factor for PAL, the researchers said that high-volume surgeons may be operating on patients with variables not accounted for in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database. “These unmeasured variables … could reveal modifiable technical factors to reduce the incidence of PAL and require further study,” the researchers said.
Fast-track discharge has gained acceptance in recent years as a way to spare patients a prolonged hospital stay and cut costs, but in this series the median hospital stay for patients with PAL was 10 days vs. 4 days for non-PAL patients (P less than 0.001).
“An accurate and generalizable PAL risk stratification tool could facilitate surgical decision making and patient-specific care” and aid in the design of trials to evaluate air-leak reduction methods such as sealants, buttressed staple lines, and pneumoperitoneum the researchers wrote.
Going forward, further development of the model would involve a multicenter study and inclusion of risk factors not accounted for in the thoracic surgery database, they noted.
The researchers had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
The authors of this study “have performed a rigorous set of analyses to create this model,” Chi-Fu Jeffrey Yang, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., noted in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;53[3]:700-1). “The strengths of this study include its sound statistical analysis and study design,” Dr. Yang wrote. He gave the authors credit for using bootstrapping to internally validate the model.
However, Dr. Yang said that the database used by the researchers did not account for “numerous important variables,” including presence of pleural adhesions and emphysema status. The analysis also grouped lobectomy and segmentectomy together, and did not consider intraoperative variables such as sealant use, or postoperative management.
While Dr. Yang commended the study authors for developing a “reliable nomogram,” getting it implemented in the clinic is another hurdle. “It is commonly cited that it takes approximately 17 years for research evidence to translate into daily practice,” he said. To shorten that time line, he suggested the authors take a cue from various tech groups: Develop an app that surgeons can use.
Dr. Yang had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
The authors of this study “have performed a rigorous set of analyses to create this model,” Chi-Fu Jeffrey Yang, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., noted in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;53[3]:700-1). “The strengths of this study include its sound statistical analysis and study design,” Dr. Yang wrote. He gave the authors credit for using bootstrapping to internally validate the model.
However, Dr. Yang said that the database used by the researchers did not account for “numerous important variables,” including presence of pleural adhesions and emphysema status. The analysis also grouped lobectomy and segmentectomy together, and did not consider intraoperative variables such as sealant use, or postoperative management.
While Dr. Yang commended the study authors for developing a “reliable nomogram,” getting it implemented in the clinic is another hurdle. “It is commonly cited that it takes approximately 17 years for research evidence to translate into daily practice,” he said. To shorten that time line, he suggested the authors take a cue from various tech groups: Develop an app that surgeons can use.
Dr. Yang had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
The authors of this study “have performed a rigorous set of analyses to create this model,” Chi-Fu Jeffrey Yang, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., noted in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;53[3]:700-1). “The strengths of this study include its sound statistical analysis and study design,” Dr. Yang wrote. He gave the authors credit for using bootstrapping to internally validate the model.
However, Dr. Yang said that the database used by the researchers did not account for “numerous important variables,” including presence of pleural adhesions and emphysema status. The analysis also grouped lobectomy and segmentectomy together, and did not consider intraoperative variables such as sealant use, or postoperative management.
While Dr. Yang commended the study authors for developing a “reliable nomogram,” getting it implemented in the clinic is another hurdle. “It is commonly cited that it takes approximately 17 years for research evidence to translate into daily practice,” he said. To shorten that time line, he suggested the authors take a cue from various tech groups: Develop an app that surgeons can use.
Dr. Yang had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Prolonged air leak is a well-known complication after lung cancer surgery that can worsen patient outcomes and drive up costs, and while international authors have developed tools to calculate the risk of PAL, their use has been limited in the United States for various reasons. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have reported on a predictive model that uses easy-to-obtain patient factors, such as forced expiratory volume and smoking history, to help surgeons identify patients at greatest risk for complications and implement preventative measures.
Adam Attaar and his coauthors reported that their nomogram had an accuracy rate of 76%, with a 95% confidence interval, for predicting PAL after surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153[3]:690-9). “Using readily available candidate variables, our nomogram predicts increasing risk of prolonged air leak with good discriminatory ability,” noted Mr. Attaar, a student at University of Pittsburgh, and his coauthors.
Previously published reports put the incidence of PAL complications at 6%-18%, they noted. In the University of Pittsburgh series of 2,317 patients who had pulmonary resection for lung cancer or nodules from January 2009 to June 2014, the incidence was 8.6%.
In this series, patients with PAL were more likely to be older, men, and smokers, and to have a lower body mass index, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a history of steroid use, a high Zubrod score and lower forced expiratory volume.“They were less likely to have diabetes or to be hospitalized before surgery,” the researchers said. Surgical factors that characterized patients with PAL were resection for primary lung cancer rather than benign or metastatic tumors; lobectomy/segmentectomy or bilobectomy rather than wedge resection; a right-sided resection; thoracotomy; and a surgeon with higher annual caseloads.
Not all those factors made it into the nomogram, however. The nomogram scores each of these 10 variables to calculate the risk of PAL, in order of their weighting: lower forced expiratory volume, procedure type, BMI, right-sided thoracotomy, preoperative hospitalization, annual surgeon caseload, wedge resection by thoracotomy, reoperation, smoking history, and Zubrod score. A second nomogram drops out surgeon volume to make it more generalizable to other institutions.
In explaining higher surgeon volume as a risk factor for PAL, the researchers said that high-volume surgeons may be operating on patients with variables not accounted for in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database. “These unmeasured variables … could reveal modifiable technical factors to reduce the incidence of PAL and require further study,” the researchers said.
Fast-track discharge has gained acceptance in recent years as a way to spare patients a prolonged hospital stay and cut costs, but in this series the median hospital stay for patients with PAL was 10 days vs. 4 days for non-PAL patients (P less than 0.001).
“An accurate and generalizable PAL risk stratification tool could facilitate surgical decision making and patient-specific care” and aid in the design of trials to evaluate air-leak reduction methods such as sealants, buttressed staple lines, and pneumoperitoneum the researchers wrote.
Going forward, further development of the model would involve a multicenter study and inclusion of risk factors not accounted for in the thoracic surgery database, they noted.
The researchers had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Prolonged air leak is a well-known complication after lung cancer surgery that can worsen patient outcomes and drive up costs, and while international authors have developed tools to calculate the risk of PAL, their use has been limited in the United States for various reasons. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have reported on a predictive model that uses easy-to-obtain patient factors, such as forced expiratory volume and smoking history, to help surgeons identify patients at greatest risk for complications and implement preventative measures.
Adam Attaar and his coauthors reported that their nomogram had an accuracy rate of 76%, with a 95% confidence interval, for predicting PAL after surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 March;153[3]:690-9). “Using readily available candidate variables, our nomogram predicts increasing risk of prolonged air leak with good discriminatory ability,” noted Mr. Attaar, a student at University of Pittsburgh, and his coauthors.
Previously published reports put the incidence of PAL complications at 6%-18%, they noted. In the University of Pittsburgh series of 2,317 patients who had pulmonary resection for lung cancer or nodules from January 2009 to June 2014, the incidence was 8.6%.
In this series, patients with PAL were more likely to be older, men, and smokers, and to have a lower body mass index, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a history of steroid use, a high Zubrod score and lower forced expiratory volume.“They were less likely to have diabetes or to be hospitalized before surgery,” the researchers said. Surgical factors that characterized patients with PAL were resection for primary lung cancer rather than benign or metastatic tumors; lobectomy/segmentectomy or bilobectomy rather than wedge resection; a right-sided resection; thoracotomy; and a surgeon with higher annual caseloads.
Not all those factors made it into the nomogram, however. The nomogram scores each of these 10 variables to calculate the risk of PAL, in order of their weighting: lower forced expiratory volume, procedure type, BMI, right-sided thoracotomy, preoperative hospitalization, annual surgeon caseload, wedge resection by thoracotomy, reoperation, smoking history, and Zubrod score. A second nomogram drops out surgeon volume to make it more generalizable to other institutions.
In explaining higher surgeon volume as a risk factor for PAL, the researchers said that high-volume surgeons may be operating on patients with variables not accounted for in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Database. “These unmeasured variables … could reveal modifiable technical factors to reduce the incidence of PAL and require further study,” the researchers said.
Fast-track discharge has gained acceptance in recent years as a way to spare patients a prolonged hospital stay and cut costs, but in this series the median hospital stay for patients with PAL was 10 days vs. 4 days for non-PAL patients (P less than 0.001).
“An accurate and generalizable PAL risk stratification tool could facilitate surgical decision making and patient-specific care” and aid in the design of trials to evaluate air-leak reduction methods such as sealants, buttressed staple lines, and pneumoperitoneum the researchers wrote.
Going forward, further development of the model would involve a multicenter study and inclusion of risk factors not accounted for in the thoracic surgery database, they noted.
The researchers had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: Preoperative variables can be evaluated to determine patient risk for prolonged air leak (PAL) in lung resection for cancer.
Major finding: A nomogram demonstrated 76% discriminatory accuracy in predicting PAL after lung resection.
Data source: Analysis of 2,522 pulmonary resections performed at eight hospitals within the University of Pittsburgh health system from January 2009 to June 2014.
Disclosures: The researchers had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
STAS predictive for lung SCC recurrence
First described in 2015, tumor spread through air spaces is a recently recognized form of invasion in lung carcinoma, but it has not been well described in lung squamous cell carcinoma. However, a study out of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center reports spread through air spaces (STAS) is one of the most significant histologic findings in lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
In multivariable models for any recurrence and lung cancer–specific death, the researchers found that STAS was a significant independent predictor for both outcomes (P = .034 and .016, respectively).
“We found that STAS in lung SCC was associated with p-stage, lymphatic and vascular invasion, necrosis, larger nuclear diameter, increased mitoses and high Ki-67 labeling index,” wrote lead author Shaohua Lu, MD, and coauthors (J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Feb;12[2]:223-34). Their findings are based on an analysis of 445 patients who had resection for stage I-III SCC over a 10-year period ending in 2009.
The Sloan-Kettering Group previously reported that STAS was a predictor of recurrence in stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients who had a limited resection (J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10[5]:806-14), and others reported STAS was a clinically significant finding in the disease. In the latest study, Dr. Lu and colleagues set out to determine if STAS is associated with tumor aggressiveness in lung SCC by using a large cohort of patients who had lung SCC resection. The lung resections they studied are from the aforementioned 2015 study that used immunohistochemistry to confirm squamous differentiation in otherwise poorly differentiated tumors.
Two pathologists reviewed tumor slides and used Ki-67 staining to confirm squamous differentiation. The study population comprised 98% former smokers and the median age was 71.3; 76% (336) were older than 65.
Dr. Lu and colleagues noted how STAS in lung SCC differs from its presentation in lung adenocarcinoma. “In contrast to lung adenocarcinoma, in which STAS can manifest as micropapillary clusters, solid nests or single cells, all STAS lesions in lung SCCs consist of solid tumor cell nests,” they wrote.
They found that STAS was associated with a higher risk of recurrence in SCC patients who had lobectomy, but not sublobar resection, whereas in patients with lung adenocarcinoma STAS was associated with a high risk of recurrence if they had sublobar resection.
The study observed STAS in 132 patients (30%). With a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 61% (273) of all patients died in that time. STAS tumors were more aggressive in nature than were non-STAS tumors. Pathologic features strongly associated with STAS were lymphatic invasion (40% for STAS vs. 19% for non-STAS patients); vascular invasion (36% vs. 22%); larger tumor size (median 4 cm vs. 3 cm); higher Ki-67 labeling index (32% vs. 13%); and higher tumor stage (23% with p-stage I, 35% p-stage II, and 43% p-stage III), all significant differences. Patients with STAS also had a higher 5-year cumulative incidence of any recurrence (39% vs. 26%) and lung cancer-specific death (30% vs. 14%), both significant differences.
STAS has an “insidious pattern of tumor invasion” that can be difficult for pathologists to detect and requires the gathering of specimens that include the adjacent lung parenchyma, Dr. Lu and colleagues said. They also dispelled the myth that STAS is an ex vivo artifact. “STAS is morphologically different from tissue floaters and contaminant or extraneous tissues that can lead to diagnostic errors,” they said.
And while the study showed that STAS is an independent predictor of recurrence and cancer-specific death, it was not predictive of overall survival – perhaps because most of the study population was over age 65 and were more likely to die from other causes rather than lung cancer. “We found a strong correlation between STAS and high-grade morphologic patterns such as nuclear size, nuclear atypia, mitotic count and Ki-67 labeling index, suggesting that STAS is associated with tumor proliferation,” Dr. Lu and coauthors said.
“Because we found STAS to show greater prognostic significance than lymphatic vascular, and visceral pleural invasion, all of which are histologic features recommended to be recorded in pathology reports for lung cancer specimens, in the future, STAS may be appropriate to add to this list,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Lu and coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
STAS (spread through air spaces) has emerged as a harbinger of poor clinical behavior in adenocarcinoma of the lung. In this new manuscript, a team from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center demonstrates that this phenomenon is evident in squamous cell cancer of the lung as well.
While the study needs to be replicated in other datasets, it demonstrates the power of careful pathologic examination in predicting tumor biology. The age old concept deserves renewed emphasis in the current era of ‘Omics’ of various kinds.
Sai Yendamuri, MD, is professor and chair of the department of thoracic surgery at Roswell Park Cancer Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., and is an associate medical editor for Thoracic Surgery News. He has no relevant disclosures.
STAS (spread through air spaces) has emerged as a harbinger of poor clinical behavior in adenocarcinoma of the lung. In this new manuscript, a team from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center demonstrates that this phenomenon is evident in squamous cell cancer of the lung as well.
While the study needs to be replicated in other datasets, it demonstrates the power of careful pathologic examination in predicting tumor biology. The age old concept deserves renewed emphasis in the current era of ‘Omics’ of various kinds.
Sai Yendamuri, MD, is professor and chair of the department of thoracic surgery at Roswell Park Cancer Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., and is an associate medical editor for Thoracic Surgery News. He has no relevant disclosures.
STAS (spread through air spaces) has emerged as a harbinger of poor clinical behavior in adenocarcinoma of the lung. In this new manuscript, a team from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center demonstrates that this phenomenon is evident in squamous cell cancer of the lung as well.
While the study needs to be replicated in other datasets, it demonstrates the power of careful pathologic examination in predicting tumor biology. The age old concept deserves renewed emphasis in the current era of ‘Omics’ of various kinds.
Sai Yendamuri, MD, is professor and chair of the department of thoracic surgery at Roswell Park Cancer Institute in Buffalo, N.Y., and is an associate medical editor for Thoracic Surgery News. He has no relevant disclosures.
First described in 2015, tumor spread through air spaces is a recently recognized form of invasion in lung carcinoma, but it has not been well described in lung squamous cell carcinoma. However, a study out of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center reports spread through air spaces (STAS) is one of the most significant histologic findings in lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
In multivariable models for any recurrence and lung cancer–specific death, the researchers found that STAS was a significant independent predictor for both outcomes (P = .034 and .016, respectively).
“We found that STAS in lung SCC was associated with p-stage, lymphatic and vascular invasion, necrosis, larger nuclear diameter, increased mitoses and high Ki-67 labeling index,” wrote lead author Shaohua Lu, MD, and coauthors (J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Feb;12[2]:223-34). Their findings are based on an analysis of 445 patients who had resection for stage I-III SCC over a 10-year period ending in 2009.
The Sloan-Kettering Group previously reported that STAS was a predictor of recurrence in stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients who had a limited resection (J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10[5]:806-14), and others reported STAS was a clinically significant finding in the disease. In the latest study, Dr. Lu and colleagues set out to determine if STAS is associated with tumor aggressiveness in lung SCC by using a large cohort of patients who had lung SCC resection. The lung resections they studied are from the aforementioned 2015 study that used immunohistochemistry to confirm squamous differentiation in otherwise poorly differentiated tumors.
Two pathologists reviewed tumor slides and used Ki-67 staining to confirm squamous differentiation. The study population comprised 98% former smokers and the median age was 71.3; 76% (336) were older than 65.
Dr. Lu and colleagues noted how STAS in lung SCC differs from its presentation in lung adenocarcinoma. “In contrast to lung adenocarcinoma, in which STAS can manifest as micropapillary clusters, solid nests or single cells, all STAS lesions in lung SCCs consist of solid tumor cell nests,” they wrote.
They found that STAS was associated with a higher risk of recurrence in SCC patients who had lobectomy, but not sublobar resection, whereas in patients with lung adenocarcinoma STAS was associated with a high risk of recurrence if they had sublobar resection.
The study observed STAS in 132 patients (30%). With a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 61% (273) of all patients died in that time. STAS tumors were more aggressive in nature than were non-STAS tumors. Pathologic features strongly associated with STAS were lymphatic invasion (40% for STAS vs. 19% for non-STAS patients); vascular invasion (36% vs. 22%); larger tumor size (median 4 cm vs. 3 cm); higher Ki-67 labeling index (32% vs. 13%); and higher tumor stage (23% with p-stage I, 35% p-stage II, and 43% p-stage III), all significant differences. Patients with STAS also had a higher 5-year cumulative incidence of any recurrence (39% vs. 26%) and lung cancer-specific death (30% vs. 14%), both significant differences.
STAS has an “insidious pattern of tumor invasion” that can be difficult for pathologists to detect and requires the gathering of specimens that include the adjacent lung parenchyma, Dr. Lu and colleagues said. They also dispelled the myth that STAS is an ex vivo artifact. “STAS is morphologically different from tissue floaters and contaminant or extraneous tissues that can lead to diagnostic errors,” they said.
And while the study showed that STAS is an independent predictor of recurrence and cancer-specific death, it was not predictive of overall survival – perhaps because most of the study population was over age 65 and were more likely to die from other causes rather than lung cancer. “We found a strong correlation between STAS and high-grade morphologic patterns such as nuclear size, nuclear atypia, mitotic count and Ki-67 labeling index, suggesting that STAS is associated with tumor proliferation,” Dr. Lu and coauthors said.
“Because we found STAS to show greater prognostic significance than lymphatic vascular, and visceral pleural invasion, all of which are histologic features recommended to be recorded in pathology reports for lung cancer specimens, in the future, STAS may be appropriate to add to this list,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Lu and coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
First described in 2015, tumor spread through air spaces is a recently recognized form of invasion in lung carcinoma, but it has not been well described in lung squamous cell carcinoma. However, a study out of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center reports spread through air spaces (STAS) is one of the most significant histologic findings in lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
In multivariable models for any recurrence and lung cancer–specific death, the researchers found that STAS was a significant independent predictor for both outcomes (P = .034 and .016, respectively).
“We found that STAS in lung SCC was associated with p-stage, lymphatic and vascular invasion, necrosis, larger nuclear diameter, increased mitoses and high Ki-67 labeling index,” wrote lead author Shaohua Lu, MD, and coauthors (J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Feb;12[2]:223-34). Their findings are based on an analysis of 445 patients who had resection for stage I-III SCC over a 10-year period ending in 2009.
The Sloan-Kettering Group previously reported that STAS was a predictor of recurrence in stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients who had a limited resection (J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10[5]:806-14), and others reported STAS was a clinically significant finding in the disease. In the latest study, Dr. Lu and colleagues set out to determine if STAS is associated with tumor aggressiveness in lung SCC by using a large cohort of patients who had lung SCC resection. The lung resections they studied are from the aforementioned 2015 study that used immunohistochemistry to confirm squamous differentiation in otherwise poorly differentiated tumors.
Two pathologists reviewed tumor slides and used Ki-67 staining to confirm squamous differentiation. The study population comprised 98% former smokers and the median age was 71.3; 76% (336) were older than 65.
Dr. Lu and colleagues noted how STAS in lung SCC differs from its presentation in lung adenocarcinoma. “In contrast to lung adenocarcinoma, in which STAS can manifest as micropapillary clusters, solid nests or single cells, all STAS lesions in lung SCCs consist of solid tumor cell nests,” they wrote.
They found that STAS was associated with a higher risk of recurrence in SCC patients who had lobectomy, but not sublobar resection, whereas in patients with lung adenocarcinoma STAS was associated with a high risk of recurrence if they had sublobar resection.
The study observed STAS in 132 patients (30%). With a median follow-up of 3.4 years, 61% (273) of all patients died in that time. STAS tumors were more aggressive in nature than were non-STAS tumors. Pathologic features strongly associated with STAS were lymphatic invasion (40% for STAS vs. 19% for non-STAS patients); vascular invasion (36% vs. 22%); larger tumor size (median 4 cm vs. 3 cm); higher Ki-67 labeling index (32% vs. 13%); and higher tumor stage (23% with p-stage I, 35% p-stage II, and 43% p-stage III), all significant differences. Patients with STAS also had a higher 5-year cumulative incidence of any recurrence (39% vs. 26%) and lung cancer-specific death (30% vs. 14%), both significant differences.
STAS has an “insidious pattern of tumor invasion” that can be difficult for pathologists to detect and requires the gathering of specimens that include the adjacent lung parenchyma, Dr. Lu and colleagues said. They also dispelled the myth that STAS is an ex vivo artifact. “STAS is morphologically different from tissue floaters and contaminant or extraneous tissues that can lead to diagnostic errors,” they said.
And while the study showed that STAS is an independent predictor of recurrence and cancer-specific death, it was not predictive of overall survival – perhaps because most of the study population was over age 65 and were more likely to die from other causes rather than lung cancer. “We found a strong correlation between STAS and high-grade morphologic patterns such as nuclear size, nuclear atypia, mitotic count and Ki-67 labeling index, suggesting that STAS is associated with tumor proliferation,” Dr. Lu and coauthors said.
“Because we found STAS to show greater prognostic significance than lymphatic vascular, and visceral pleural invasion, all of which are histologic features recommended to be recorded in pathology reports for lung cancer specimens, in the future, STAS may be appropriate to add to this list,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Lu and coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Spread through air spaces (STAS) is a prognostic histologic finding in lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Major finding: STAS was observed in 30% of patients and frequency increased with age.
Data source: Retrospective analysis of 445 resections for solitary stage I-III lung squamous cell carcinoma at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center between 1999 and 2009.
Disclosure: Dr. Lu and coauthors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Can better operations improve CABG in women?
Worse outcomes after cardiovascular arterial bypass grafting (CABG) in women have been attributed to a number of clinical and nonclinical factors: older age, delayed diagnosis and treatment, more comorbidities, smaller body size, underuse of arterial grafts, and referral bias. However, a team of Cleveland Clinic researchers reported that women were less likely than men to have bilateral–internal thoracic artery (ITA) grafting and complete revascularization, both of which are linked to better long-term survival.
“Women had less favorable preoperative characteristics than men but received fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and less all-arterial grafting as part of their revascularization strategy,” Tamer Attia, MD, MSc, and his coauthors said in the study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. They also found that women were more likely to die in the hospital after CABG and had lower risk-adjusted long-term survival than men (2017 March;153:571-9).
Survival was lowest in women who were not completely revascularized and had no ITA grafting, while survival was highest in men who were completely revascularized and had bilateral grafting, Dr. Attia and coauthors said.
The researchers’ goal was to use extensive risk adjustment to evaluate how differences in revascularization strategies influenced survival of men and women after CABG. They analyzed 57,943 primary, isolated CABG procedures performed at Cleveland Clinic from 1972 to 2011, including 11,009 procedures in women.
The researchers identified differences between sexes in three key areas: revascularization strategies, in-hospital outcomes, and time-related survival.
With regard to revascularization strategies, while men were significantly more likely to have incomplete revascularization than were women, women received significantly fewer arterial grafts (8.4% vs. 9.3% for men). This included fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and radial artery grafts, less use of total arterial revascularization, and greater use of saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) to the left anterior descending artery. Women were also significantly more likely to receive only SVGs for revascularization (32% vs. 30% for men; P less than .0001). Most operations for both women and men were done with cardiopulmonary bypass, but significantly more women had off-pump procedures (5.4% vs. 2.9%).
In the hospital after operations, women were significantly more prone to postoperative deep sternal–wound infections and septicemias, as well as strokes and renal failure, including dialysis-dependent renal failure. Women also had higher rates of new-onset atrial fibrillation (15% vs. 13% in men), and higher rates of mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours (13% vs. 9.2%). Women spent more time in the ICU and hospital overall, and their in-hospital death rate was more than double that of men (2.7% vs. 1.1%).
Women also had shorter long-term survival, “and this has persisted since the beginning of CABG at Cleveland Clinic,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. What’s more, the survival gap between women in the study and women in the general population post CABG was wider than that in men. “After we adjusted for patient and revascularization strategy differences, female sex remained an independent risk factor for death overall and both early and late after CABG.”
Incomplete revascularization had greater consequences for women than for men. At 10 years, 58% of women with incomplete revascularization survived, vs. 70% of men. At 20 years, the rates were 25% for women and 35% for men. “Use of ITA grafts was associated with better survival than use of SVGs alone and was best when bilateral-ITA grafting was performed,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. However, the study determined that bilateral grafting seems less effective in women long-term. “Hence, a patient’s sex deserves special consideration in operative planning.”
Many questions about CABG in women remain: Identifying which female patients would benefit from more meticulous conduit harvesting, from better coronary artery selection, and from bilateral-ITA grafting and which are less susceptible to sternal would infections could increase appropriate use of bilateral-ITA grafting, the researchers noted. “The difference in effectiveness of bilateral-ITA grafting needs to be considered in women at elevated risk for bilateral-ITA harvesting complications.”
Coauthor Ellen Mayer Sabik, MD, is a principal investigator for Abbott Laboratories and is on the scientific advisory board of Medtronic. Dr. Attia and all other coauthors reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
As with other long-term analyses, the answer in this study “is in the shadows as opposed to the spotlight,” George L. Hicks Jr., MD, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153[3]:580-1).
Dr. Hicks of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) noted key limitations of the study: use of all-cause mortality, substandard use of bilateral– or single–internal thoracic artery grafting, little data about postdischarge cholesterol levels, diabetes incidence, or blood pressure, among others. However, “the authors raise the banner for the continued need for increased use of arterial revascularization with the eventual hope that the Arterial Revascularization Trial will reinforce the survival benefits manifested by that strategy,” he said.
Reducing risks and not changing the type of operation will even out the differences in postoperative survival between genders, he indicated. “Furthermore, the extension of similar therapies – for example, [bilateral–internal thoracic artery] or all-arterial grafting and improved long-term risk modification in both men and women – may improve the inequality but not eliminate the differences until we know that both men and women come from the same planet,” he said.
Dr. Hicks reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
As with other long-term analyses, the answer in this study “is in the shadows as opposed to the spotlight,” George L. Hicks Jr., MD, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153[3]:580-1).
Dr. Hicks of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) noted key limitations of the study: use of all-cause mortality, substandard use of bilateral– or single–internal thoracic artery grafting, little data about postdischarge cholesterol levels, diabetes incidence, or blood pressure, among others. However, “the authors raise the banner for the continued need for increased use of arterial revascularization with the eventual hope that the Arterial Revascularization Trial will reinforce the survival benefits manifested by that strategy,” he said.
Reducing risks and not changing the type of operation will even out the differences in postoperative survival between genders, he indicated. “Furthermore, the extension of similar therapies – for example, [bilateral–internal thoracic artery] or all-arterial grafting and improved long-term risk modification in both men and women – may improve the inequality but not eliminate the differences until we know that both men and women come from the same planet,” he said.
Dr. Hicks reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
As with other long-term analyses, the answer in this study “is in the shadows as opposed to the spotlight,” George L. Hicks Jr., MD, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153[3]:580-1).
Dr. Hicks of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) noted key limitations of the study: use of all-cause mortality, substandard use of bilateral– or single–internal thoracic artery grafting, little data about postdischarge cholesterol levels, diabetes incidence, or blood pressure, among others. However, “the authors raise the banner for the continued need for increased use of arterial revascularization with the eventual hope that the Arterial Revascularization Trial will reinforce the survival benefits manifested by that strategy,” he said.
Reducing risks and not changing the type of operation will even out the differences in postoperative survival between genders, he indicated. “Furthermore, the extension of similar therapies – for example, [bilateral–internal thoracic artery] or all-arterial grafting and improved long-term risk modification in both men and women – may improve the inequality but not eliminate the differences until we know that both men and women come from the same planet,” he said.
Dr. Hicks reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Worse outcomes after cardiovascular arterial bypass grafting (CABG) in women have been attributed to a number of clinical and nonclinical factors: older age, delayed diagnosis and treatment, more comorbidities, smaller body size, underuse of arterial grafts, and referral bias. However, a team of Cleveland Clinic researchers reported that women were less likely than men to have bilateral–internal thoracic artery (ITA) grafting and complete revascularization, both of which are linked to better long-term survival.
“Women had less favorable preoperative characteristics than men but received fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and less all-arterial grafting as part of their revascularization strategy,” Tamer Attia, MD, MSc, and his coauthors said in the study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. They also found that women were more likely to die in the hospital after CABG and had lower risk-adjusted long-term survival than men (2017 March;153:571-9).
Survival was lowest in women who were not completely revascularized and had no ITA grafting, while survival was highest in men who were completely revascularized and had bilateral grafting, Dr. Attia and coauthors said.
The researchers’ goal was to use extensive risk adjustment to evaluate how differences in revascularization strategies influenced survival of men and women after CABG. They analyzed 57,943 primary, isolated CABG procedures performed at Cleveland Clinic from 1972 to 2011, including 11,009 procedures in women.
The researchers identified differences between sexes in three key areas: revascularization strategies, in-hospital outcomes, and time-related survival.
With regard to revascularization strategies, while men were significantly more likely to have incomplete revascularization than were women, women received significantly fewer arterial grafts (8.4% vs. 9.3% for men). This included fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and radial artery grafts, less use of total arterial revascularization, and greater use of saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) to the left anterior descending artery. Women were also significantly more likely to receive only SVGs for revascularization (32% vs. 30% for men; P less than .0001). Most operations for both women and men were done with cardiopulmonary bypass, but significantly more women had off-pump procedures (5.4% vs. 2.9%).
In the hospital after operations, women were significantly more prone to postoperative deep sternal–wound infections and septicemias, as well as strokes and renal failure, including dialysis-dependent renal failure. Women also had higher rates of new-onset atrial fibrillation (15% vs. 13% in men), and higher rates of mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours (13% vs. 9.2%). Women spent more time in the ICU and hospital overall, and their in-hospital death rate was more than double that of men (2.7% vs. 1.1%).
Women also had shorter long-term survival, “and this has persisted since the beginning of CABG at Cleveland Clinic,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. What’s more, the survival gap between women in the study and women in the general population post CABG was wider than that in men. “After we adjusted for patient and revascularization strategy differences, female sex remained an independent risk factor for death overall and both early and late after CABG.”
Incomplete revascularization had greater consequences for women than for men. At 10 years, 58% of women with incomplete revascularization survived, vs. 70% of men. At 20 years, the rates were 25% for women and 35% for men. “Use of ITA grafts was associated with better survival than use of SVGs alone and was best when bilateral-ITA grafting was performed,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. However, the study determined that bilateral grafting seems less effective in women long-term. “Hence, a patient’s sex deserves special consideration in operative planning.”
Many questions about CABG in women remain: Identifying which female patients would benefit from more meticulous conduit harvesting, from better coronary artery selection, and from bilateral-ITA grafting and which are less susceptible to sternal would infections could increase appropriate use of bilateral-ITA grafting, the researchers noted. “The difference in effectiveness of bilateral-ITA grafting needs to be considered in women at elevated risk for bilateral-ITA harvesting complications.”
Coauthor Ellen Mayer Sabik, MD, is a principal investigator for Abbott Laboratories and is on the scientific advisory board of Medtronic. Dr. Attia and all other coauthors reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Worse outcomes after cardiovascular arterial bypass grafting (CABG) in women have been attributed to a number of clinical and nonclinical factors: older age, delayed diagnosis and treatment, more comorbidities, smaller body size, underuse of arterial grafts, and referral bias. However, a team of Cleveland Clinic researchers reported that women were less likely than men to have bilateral–internal thoracic artery (ITA) grafting and complete revascularization, both of which are linked to better long-term survival.
“Women had less favorable preoperative characteristics than men but received fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and less all-arterial grafting as part of their revascularization strategy,” Tamer Attia, MD, MSc, and his coauthors said in the study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. They also found that women were more likely to die in the hospital after CABG and had lower risk-adjusted long-term survival than men (2017 March;153:571-9).
Survival was lowest in women who were not completely revascularized and had no ITA grafting, while survival was highest in men who were completely revascularized and had bilateral grafting, Dr. Attia and coauthors said.
The researchers’ goal was to use extensive risk adjustment to evaluate how differences in revascularization strategies influenced survival of men and women after CABG. They analyzed 57,943 primary, isolated CABG procedures performed at Cleveland Clinic from 1972 to 2011, including 11,009 procedures in women.
The researchers identified differences between sexes in three key areas: revascularization strategies, in-hospital outcomes, and time-related survival.
With regard to revascularization strategies, while men were significantly more likely to have incomplete revascularization than were women, women received significantly fewer arterial grafts (8.4% vs. 9.3% for men). This included fewer bilateral-ITA grafts and radial artery grafts, less use of total arterial revascularization, and greater use of saphenous vein grafts (SVGs) to the left anterior descending artery. Women were also significantly more likely to receive only SVGs for revascularization (32% vs. 30% for men; P less than .0001). Most operations for both women and men were done with cardiopulmonary bypass, but significantly more women had off-pump procedures (5.4% vs. 2.9%).
In the hospital after operations, women were significantly more prone to postoperative deep sternal–wound infections and septicemias, as well as strokes and renal failure, including dialysis-dependent renal failure. Women also had higher rates of new-onset atrial fibrillation (15% vs. 13% in men), and higher rates of mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours (13% vs. 9.2%). Women spent more time in the ICU and hospital overall, and their in-hospital death rate was more than double that of men (2.7% vs. 1.1%).
Women also had shorter long-term survival, “and this has persisted since the beginning of CABG at Cleveland Clinic,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. What’s more, the survival gap between women in the study and women in the general population post CABG was wider than that in men. “After we adjusted for patient and revascularization strategy differences, female sex remained an independent risk factor for death overall and both early and late after CABG.”
Incomplete revascularization had greater consequences for women than for men. At 10 years, 58% of women with incomplete revascularization survived, vs. 70% of men. At 20 years, the rates were 25% for women and 35% for men. “Use of ITA grafts was associated with better survival than use of SVGs alone and was best when bilateral-ITA grafting was performed,” Dr. Attia and coauthors said. However, the study determined that bilateral grafting seems less effective in women long-term. “Hence, a patient’s sex deserves special consideration in operative planning.”
Many questions about CABG in women remain: Identifying which female patients would benefit from more meticulous conduit harvesting, from better coronary artery selection, and from bilateral-ITA grafting and which are less susceptible to sternal would infections could increase appropriate use of bilateral-ITA grafting, the researchers noted. “The difference in effectiveness of bilateral-ITA grafting needs to be considered in women at elevated risk for bilateral-ITA harvesting complications.”
Coauthor Ellen Mayer Sabik, MD, is a principal investigator for Abbott Laboratories and is on the scientific advisory board of Medtronic. Dr. Attia and all other coauthors reported having no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: Survival rates after CABG are worse for women than for men.
Major finding: In both men and women, complete revascularization and use of bilateral-ITA grafting achieve better long-term survival than incomplete revascularization and single-ITA grafting.
Data source: Analysis of 57,943 adults who had primary isolated CABG from 1972 to 2011 at Cleveland Clinic.
Disclosure: Coauthor Ellen Mayer Sabik, MD, is a principal investigator for Abbott Laboratories and is on the scientific advisory board of Medtronic. Dr. Attia and all other coauthors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Aortic repair in Loeys-Dietz syndrome requires close follow-up
The knowledge about Loeys-Dietz syndrome has evolved quickly since Hal Dietz, MD, and Bart Loeys, MD, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, first reported on it in 2005.
Now, another team of Johns Hopkins investigators have reported that an aggressive approach with aortic root replacement coupled with valve-sparing whenever possible produces favorable results, but that clinicians must follow these patients closely with cardiovascular imaging.
“Growing experience with Loeys-Dietz syndrome has confirmed early impressions of its aggressive nature and proclivity toward aortic catastrophe,” Nishant D. Patel, MD, and his coauthors said in the February issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;153:406-12). They reported on results of all 79 patients with Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) who had cardiovascular surgery at Johns Hopkins. There were two (3%) deaths during surgery and eight (10%) late deaths. Patients with LDS are at risk for dissection early when the aortic root reaches 4 cm. Despite what they termed “favorable” outcomes of surgery, Dr. Patel and his coauthors acknowledged that reintervention rates for this population are high – 19 patients (24%) had subsequent operations. That suggests cardiac surgeons must closely monitor these patients. “Meticulous follow-up with cardiovascular surveillance imaging remains important for management, particularly as clinical LDS subtypes are characterized and more tailored treatment is developed,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors reported.
They advise echocardiography every 3 to 6 months for the first year after surgery and then every 6 to 12 months afterward. Full-body imaging should occur at least every 2 years. “In particular, patients with type B dissections should be monitored aggressively for aneurysm growth,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. They recommend imaging at seven to 14 days after dissection, then repeat imaging at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, and then yearly thereafter.
They noted that four LDS subtypes have been identified. Although those with LDS1 and 2 subtypes are prone to aortic rupture at an earlier age and at smaller aortic diameters than other connective tissue disorders, the medical and surgical management for all subtypes are similar, Dr. Patel and his coauthors indicated.
“Certain congenital heart defects are more common among patients with LDS, compared with the normal population, including patent ductus arteriosus and mitral valve prolapse/insufficiency,” they said. Genotype is one factor that determines the need for surgery in LDS patients, Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. Others are growth rate, aortic valve function, family history, and severity of noncardiac phenotype.
The 79 patients in the study were divided almost evenly between gender, and the average age at first operation was 24.9 years; 38 were children younger than 18 years and 20 had a previous sternotomy. Aortic root replacement represented the predominant operation in the group, accounting for 65 operations (82.3%), of which 52 (80%) were valve-sparing procedures and the remainder were composite valve-graft procedures. The other procedures the researchers performed were nine aortic arch replacements (11.4%), three open thoracoabdominal repairs (3.8%) and two ascending aorta replacements (2.5%).
“Valve-sparing root replacement has become a safe and reliable option for appropriately selected younger patients with LDS,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors wrote. Five patients needed a second operation on the aortic valve or root; three of them had a Florida sleeve procedure. “Based on these initial outcomes with the Florida sleeve at our institution, we have abandoned this procedure in favor of conventional valve-sparing root replacement,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors stated.
Dr. Patel and his coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
A rare disease such as Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) seems more common now in vascular surgery, as we are the specialty making decisions on disorders of the descending thoracic aorta. Understanding not only the clinical presentation with the aortic root involvement but the fact that these patients require close surveillance is the key message.
Often we are consulted regarding or admit a patient with an acute type B dissection who usually has a history of poorly controlled hypertension but, also, has a history of “aneurysms” or a family member who passed away at a young age. These clues should lead us to explore the “molecular diagnosis” as well to see if patients have a connective tissue disorder such as LDS or vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (vEDS). Because many of these syndromes have overlapping symptoms, understanding the type of connective tissue disorder will allow us to appreciate the differences, especially in a syndrome such as LDS, which was first reported in 2005 and is associated with more cardiac and aortic root pathologies than vEDS.
At the University of Washington, my colleague Dr. Sherene Shalhub heads a vascular genetics clinic in which she examines patients with potential connective tissue disorders in an attempt to make the molecular diagnosis and identify surveillance protocols and study the effect of open and endovascular repairs in these patients. Pooling data on these patients from around the country and collaborating within, as well as outside of, our specialty is imperative to increasing our understanding of these disorders. I believe we are seeing a trend in which we crave studies such as Dr. Patel’s to increase our knowledge on these rare (but now more common) entities.
Niten Singh, MD, is the director of the Limb Preservation Service at the Regional Vascular Center at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle, and an Associate Editor of Vascular Specialist.
A rare disease such as Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) seems more common now in vascular surgery, as we are the specialty making decisions on disorders of the descending thoracic aorta. Understanding not only the clinical presentation with the aortic root involvement but the fact that these patients require close surveillance is the key message.
Often we are consulted regarding or admit a patient with an acute type B dissection who usually has a history of poorly controlled hypertension but, also, has a history of “aneurysms” or a family member who passed away at a young age. These clues should lead us to explore the “molecular diagnosis” as well to see if patients have a connective tissue disorder such as LDS or vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (vEDS). Because many of these syndromes have overlapping symptoms, understanding the type of connective tissue disorder will allow us to appreciate the differences, especially in a syndrome such as LDS, which was first reported in 2005 and is associated with more cardiac and aortic root pathologies than vEDS.
At the University of Washington, my colleague Dr. Sherene Shalhub heads a vascular genetics clinic in which she examines patients with potential connective tissue disorders in an attempt to make the molecular diagnosis and identify surveillance protocols and study the effect of open and endovascular repairs in these patients. Pooling data on these patients from around the country and collaborating within, as well as outside of, our specialty is imperative to increasing our understanding of these disorders. I believe we are seeing a trend in which we crave studies such as Dr. Patel’s to increase our knowledge on these rare (but now more common) entities.
Niten Singh, MD, is the director of the Limb Preservation Service at the Regional Vascular Center at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle, and an Associate Editor of Vascular Specialist.
A rare disease such as Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) seems more common now in vascular surgery, as we are the specialty making decisions on disorders of the descending thoracic aorta. Understanding not only the clinical presentation with the aortic root involvement but the fact that these patients require close surveillance is the key message.
Often we are consulted regarding or admit a patient with an acute type B dissection who usually has a history of poorly controlled hypertension but, also, has a history of “aneurysms” or a family member who passed away at a young age. These clues should lead us to explore the “molecular diagnosis” as well to see if patients have a connective tissue disorder such as LDS or vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (vEDS). Because many of these syndromes have overlapping symptoms, understanding the type of connective tissue disorder will allow us to appreciate the differences, especially in a syndrome such as LDS, which was first reported in 2005 and is associated with more cardiac and aortic root pathologies than vEDS.
At the University of Washington, my colleague Dr. Sherene Shalhub heads a vascular genetics clinic in which she examines patients with potential connective tissue disorders in an attempt to make the molecular diagnosis and identify surveillance protocols and study the effect of open and endovascular repairs in these patients. Pooling data on these patients from around the country and collaborating within, as well as outside of, our specialty is imperative to increasing our understanding of these disorders. I believe we are seeing a trend in which we crave studies such as Dr. Patel’s to increase our knowledge on these rare (but now more common) entities.
Niten Singh, MD, is the director of the Limb Preservation Service at the Regional Vascular Center at Harborview Medical Center, Seattle, and an Associate Editor of Vascular Specialist.
The knowledge about Loeys-Dietz syndrome has evolved quickly since Hal Dietz, MD, and Bart Loeys, MD, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, first reported on it in 2005.
Now, another team of Johns Hopkins investigators have reported that an aggressive approach with aortic root replacement coupled with valve-sparing whenever possible produces favorable results, but that clinicians must follow these patients closely with cardiovascular imaging.
“Growing experience with Loeys-Dietz syndrome has confirmed early impressions of its aggressive nature and proclivity toward aortic catastrophe,” Nishant D. Patel, MD, and his coauthors said in the February issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;153:406-12). They reported on results of all 79 patients with Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) who had cardiovascular surgery at Johns Hopkins. There were two (3%) deaths during surgery and eight (10%) late deaths. Patients with LDS are at risk for dissection early when the aortic root reaches 4 cm. Despite what they termed “favorable” outcomes of surgery, Dr. Patel and his coauthors acknowledged that reintervention rates for this population are high – 19 patients (24%) had subsequent operations. That suggests cardiac surgeons must closely monitor these patients. “Meticulous follow-up with cardiovascular surveillance imaging remains important for management, particularly as clinical LDS subtypes are characterized and more tailored treatment is developed,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors reported.
They advise echocardiography every 3 to 6 months for the first year after surgery and then every 6 to 12 months afterward. Full-body imaging should occur at least every 2 years. “In particular, patients with type B dissections should be monitored aggressively for aneurysm growth,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. They recommend imaging at seven to 14 days after dissection, then repeat imaging at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, and then yearly thereafter.
They noted that four LDS subtypes have been identified. Although those with LDS1 and 2 subtypes are prone to aortic rupture at an earlier age and at smaller aortic diameters than other connective tissue disorders, the medical and surgical management for all subtypes are similar, Dr. Patel and his coauthors indicated.
“Certain congenital heart defects are more common among patients with LDS, compared with the normal population, including patent ductus arteriosus and mitral valve prolapse/insufficiency,” they said. Genotype is one factor that determines the need for surgery in LDS patients, Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. Others are growth rate, aortic valve function, family history, and severity of noncardiac phenotype.
The 79 patients in the study were divided almost evenly between gender, and the average age at first operation was 24.9 years; 38 were children younger than 18 years and 20 had a previous sternotomy. Aortic root replacement represented the predominant operation in the group, accounting for 65 operations (82.3%), of which 52 (80%) were valve-sparing procedures and the remainder were composite valve-graft procedures. The other procedures the researchers performed were nine aortic arch replacements (11.4%), three open thoracoabdominal repairs (3.8%) and two ascending aorta replacements (2.5%).
“Valve-sparing root replacement has become a safe and reliable option for appropriately selected younger patients with LDS,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors wrote. Five patients needed a second operation on the aortic valve or root; three of them had a Florida sleeve procedure. “Based on these initial outcomes with the Florida sleeve at our institution, we have abandoned this procedure in favor of conventional valve-sparing root replacement,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors stated.
Dr. Patel and his coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
The knowledge about Loeys-Dietz syndrome has evolved quickly since Hal Dietz, MD, and Bart Loeys, MD, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, first reported on it in 2005.
Now, another team of Johns Hopkins investigators have reported that an aggressive approach with aortic root replacement coupled with valve-sparing whenever possible produces favorable results, but that clinicians must follow these patients closely with cardiovascular imaging.
“Growing experience with Loeys-Dietz syndrome has confirmed early impressions of its aggressive nature and proclivity toward aortic catastrophe,” Nishant D. Patel, MD, and his coauthors said in the February issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;153:406-12). They reported on results of all 79 patients with Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) who had cardiovascular surgery at Johns Hopkins. There were two (3%) deaths during surgery and eight (10%) late deaths. Patients with LDS are at risk for dissection early when the aortic root reaches 4 cm. Despite what they termed “favorable” outcomes of surgery, Dr. Patel and his coauthors acknowledged that reintervention rates for this population are high – 19 patients (24%) had subsequent operations. That suggests cardiac surgeons must closely monitor these patients. “Meticulous follow-up with cardiovascular surveillance imaging remains important for management, particularly as clinical LDS subtypes are characterized and more tailored treatment is developed,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors reported.
They advise echocardiography every 3 to 6 months for the first year after surgery and then every 6 to 12 months afterward. Full-body imaging should occur at least every 2 years. “In particular, patients with type B dissections should be monitored aggressively for aneurysm growth,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. They recommend imaging at seven to 14 days after dissection, then repeat imaging at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, and then yearly thereafter.
They noted that four LDS subtypes have been identified. Although those with LDS1 and 2 subtypes are prone to aortic rupture at an earlier age and at smaller aortic diameters than other connective tissue disorders, the medical and surgical management for all subtypes are similar, Dr. Patel and his coauthors indicated.
“Certain congenital heart defects are more common among patients with LDS, compared with the normal population, including patent ductus arteriosus and mitral valve prolapse/insufficiency,” they said. Genotype is one factor that determines the need for surgery in LDS patients, Dr. Patel and his coauthors said. Others are growth rate, aortic valve function, family history, and severity of noncardiac phenotype.
The 79 patients in the study were divided almost evenly between gender, and the average age at first operation was 24.9 years; 38 were children younger than 18 years and 20 had a previous sternotomy. Aortic root replacement represented the predominant operation in the group, accounting for 65 operations (82.3%), of which 52 (80%) were valve-sparing procedures and the remainder were composite valve-graft procedures. The other procedures the researchers performed were nine aortic arch replacements (11.4%), three open thoracoabdominal repairs (3.8%) and two ascending aorta replacements (2.5%).
“Valve-sparing root replacement has become a safe and reliable option for appropriately selected younger patients with LDS,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors wrote. Five patients needed a second operation on the aortic valve or root; three of them had a Florida sleeve procedure. “Based on these initial outcomes with the Florida sleeve at our institution, we have abandoned this procedure in favor of conventional valve-sparing root replacement,” Dr. Patel and his coauthors stated.
Dr. Patel and his coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
Key clinical point: Outcomes for aortic surgery in Loeys-Dietz syndrome are favorable, but reintervention rates are high.
Major finding: Patients require close postoperative follow-up with cardiovascular imaging.
Data source: Retrospective review of 79 patients who had cardiovascular surgery for LDS over 26 years at Johns Hopkins University.