User login
Richard Franki is the associate editor who writes and creates graphs. He started with the company in 1987, when it was known as the International Medical News Group. In his years as a journalist, Richard has worked for Cap Cities/ABC, Disney, Harcourt, Elsevier, Quadrant, Frontline, and Internet Brands. In the 1990s, he was a contributor to the ill-fated Indications column, predecessor of Livin' on the MDedge.
Almost 90% of COVID-19 admissions involve comorbidities
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
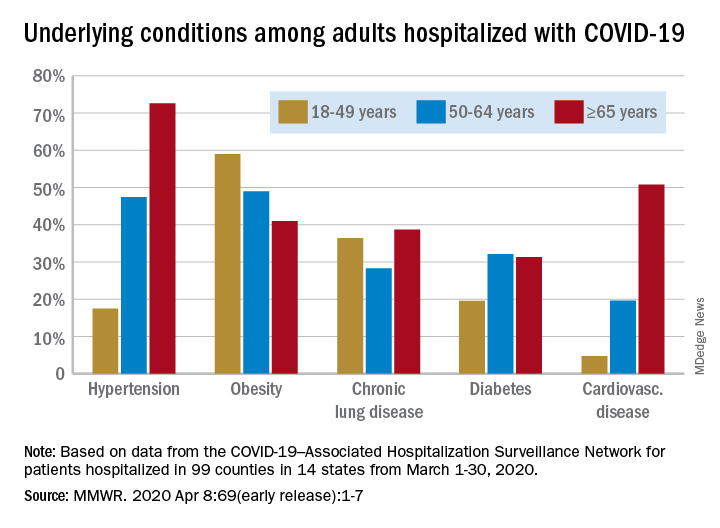
Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
FROM THE MMWR
Autism prevalence: ‘Diminishing disparity’ between black and white children
For the first time since detailed measurement began in 2000, there was no significant difference in autism prevalence between black and white 8-year-olds in 2016, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
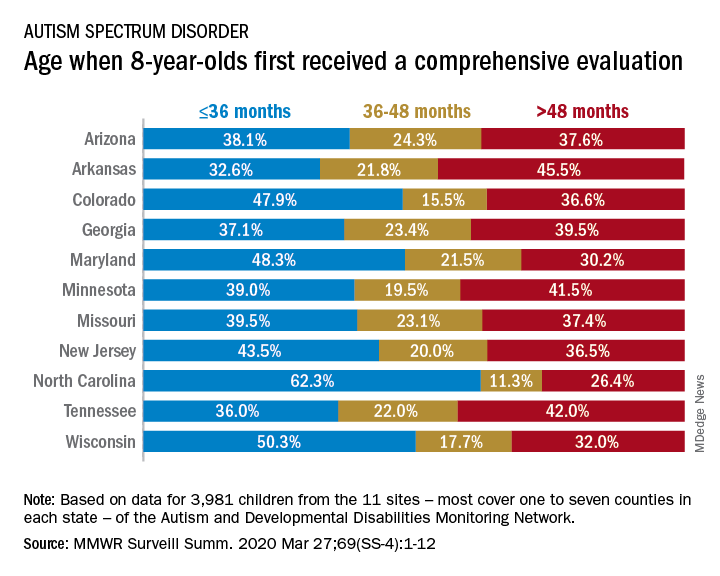
The latest analysis from the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network puts the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) at 18.3 per 1,000 children aged 8 years among black children and 18.5 per 1,000 in white children, Matthew J. Maenner, PhD, and associates said in MMWR Surveillance Summaries. Overall prevalence was 18.5 per 1,000 children, or 1 in 54 children, aged 8 years.
“This diminishing disparity in ASD prevalence might signify progress toward earlier and more equitable identification of ASD,” they wrote, while also noting that “black children with ASD were more likely than white children to have an intellectual disability” and were less likely to undergo evaluation by age 36 months.
and 42.9% of Hispanic children, said Dr. Maenner of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities.
The overall rate of early evaluation was 44% for the cohort of 3,981 children who were born in 2008 and included in the 2016 analysis of the 11 ADDM Network sites, they reported.
There was, however, considerable variation in the timing of that initial evaluation for ASD among the sites, which largely consisted of one to seven counties in most states, except for Arkansas (all 75 counties), Tennessee (11 counties), and Wisconsin (10 counties), Dr. Maenner and associates noted.
The two ADDM Network sites at the extremes of that variation were North Carolina and Arkansas. In North Carolina, almost twice as many children (62.3%) had an evaluation by 36 months than in Arkansas (32.6%), although Arkansas closed the gap a bit by evaluating 21.8% of children aged 37-48 months, compared with 11.3% in North Carolina, the investigators said.
“ASD continues to be a public health concern; the latest data from the ADDM Network underscore the ongoing need for timely and accessible developmental assessments, educational supports, and services for persons with ASD and their families,” they concluded.
SOURCE: Maenner MJ et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020 Mar 27;69(SS-4):1-12.
For the first time since detailed measurement began in 2000, there was no significant difference in autism prevalence between black and white 8-year-olds in 2016, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest analysis from the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network puts the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) at 18.3 per 1,000 children aged 8 years among black children and 18.5 per 1,000 in white children, Matthew J. Maenner, PhD, and associates said in MMWR Surveillance Summaries. Overall prevalence was 18.5 per 1,000 children, or 1 in 54 children, aged 8 years.
“This diminishing disparity in ASD prevalence might signify progress toward earlier and more equitable identification of ASD,” they wrote, while also noting that “black children with ASD were more likely than white children to have an intellectual disability” and were less likely to undergo evaluation by age 36 months.
and 42.9% of Hispanic children, said Dr. Maenner of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities.
The overall rate of early evaluation was 44% for the cohort of 3,981 children who were born in 2008 and included in the 2016 analysis of the 11 ADDM Network sites, they reported.
There was, however, considerable variation in the timing of that initial evaluation for ASD among the sites, which largely consisted of one to seven counties in most states, except for Arkansas (all 75 counties), Tennessee (11 counties), and Wisconsin (10 counties), Dr. Maenner and associates noted.
The two ADDM Network sites at the extremes of that variation were North Carolina and Arkansas. In North Carolina, almost twice as many children (62.3%) had an evaluation by 36 months than in Arkansas (32.6%), although Arkansas closed the gap a bit by evaluating 21.8% of children aged 37-48 months, compared with 11.3% in North Carolina, the investigators said.
“ASD continues to be a public health concern; the latest data from the ADDM Network underscore the ongoing need for timely and accessible developmental assessments, educational supports, and services for persons with ASD and their families,” they concluded.
SOURCE: Maenner MJ et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020 Mar 27;69(SS-4):1-12.
For the first time since detailed measurement began in 2000, there was no significant difference in autism prevalence between black and white 8-year-olds in 2016, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest analysis from the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network puts the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) at 18.3 per 1,000 children aged 8 years among black children and 18.5 per 1,000 in white children, Matthew J. Maenner, PhD, and associates said in MMWR Surveillance Summaries. Overall prevalence was 18.5 per 1,000 children, or 1 in 54 children, aged 8 years.
“This diminishing disparity in ASD prevalence might signify progress toward earlier and more equitable identification of ASD,” they wrote, while also noting that “black children with ASD were more likely than white children to have an intellectual disability” and were less likely to undergo evaluation by age 36 months.
and 42.9% of Hispanic children, said Dr. Maenner of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities.
The overall rate of early evaluation was 44% for the cohort of 3,981 children who were born in 2008 and included in the 2016 analysis of the 11 ADDM Network sites, they reported.
There was, however, considerable variation in the timing of that initial evaluation for ASD among the sites, which largely consisted of one to seven counties in most states, except for Arkansas (all 75 counties), Tennessee (11 counties), and Wisconsin (10 counties), Dr. Maenner and associates noted.
The two ADDM Network sites at the extremes of that variation were North Carolina and Arkansas. In North Carolina, almost twice as many children (62.3%) had an evaluation by 36 months than in Arkansas (32.6%), although Arkansas closed the gap a bit by evaluating 21.8% of children aged 37-48 months, compared with 11.3% in North Carolina, the investigators said.
“ASD continues to be a public health concern; the latest data from the ADDM Network underscore the ongoing need for timely and accessible developmental assessments, educational supports, and services for persons with ASD and their families,” they concluded.
SOURCE: Maenner MJ et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020 Mar 27;69(SS-4):1-12.
FROM MMWR SURVEILLANCE SUMMARIES
Comorbidities the rule in New York’s COVID-19 deaths
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.
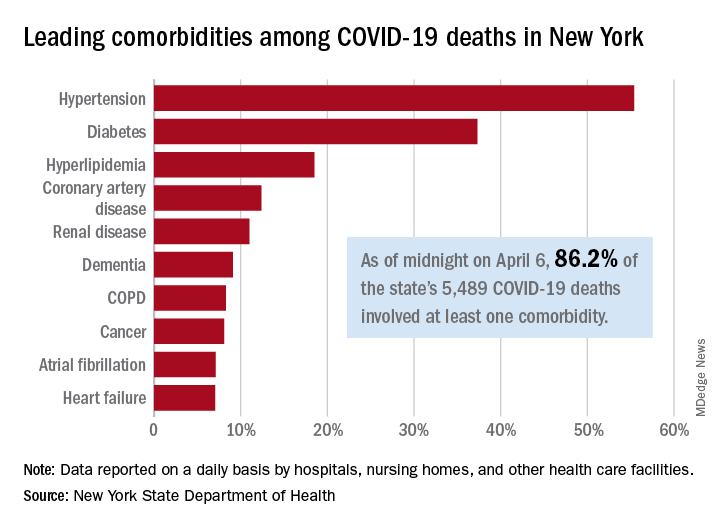
As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
Many children with COVID-19 don’t have cough or fever
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.
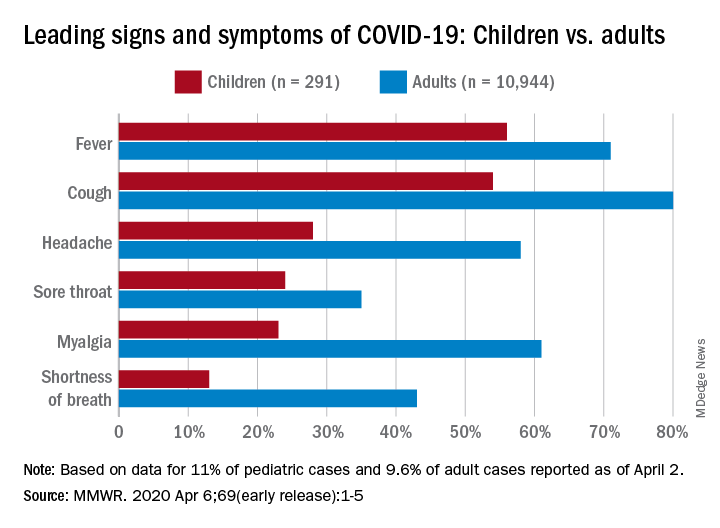
Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
FROM MMWR
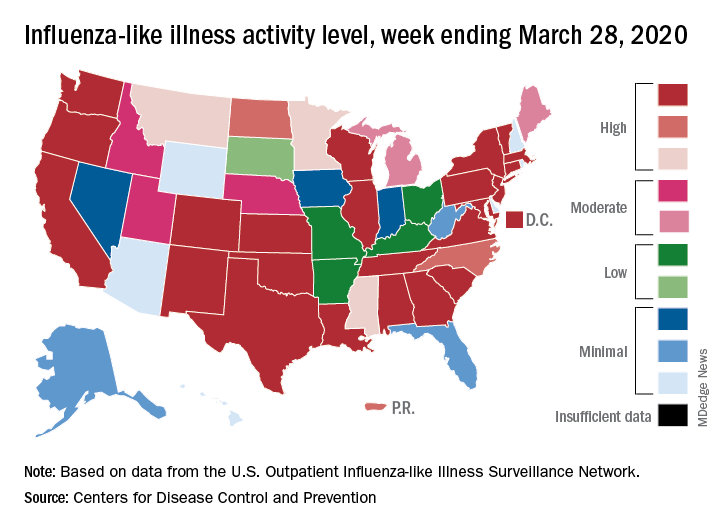
Flu activity down from its third peak of the season, COVID-19 still a factor
Influenza activity measures dropped during the week ending March 28, but the percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) has risen into epidemic territory, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This influenza news, however, needs to be viewed through a COVID-19 lens.
The P&I mortality data are reported together and are always a week behind the other measures, in this case covering the week ending March 21, but they show influenza deaths dropping to 0.8% as the overall P&I rate rose from 7.4% to 8.2%, a pneumonia-fueled increase that was “likely associated with COVID-19 rather than influenza,” the CDC’s influenza division noted.
The two main activity measures, at least, are on the same page for the first time since the end of February.
The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) had been dropping up to that point but then rose for an unprecedented third time this season, a change probably brought about by COVID-related health care–seeking behavior, the influenza division reported in its weekly FluView report.
This corresponding third drop in ILI activity brought the rate down to 5.4% this week from 6.2% the previous week, the CDC reported. The two previous high points occurred during the weeks ending Dec. 28 (7.0%) and Feb. 8 (6.7%)
The COVID-related changes, such as increased use of telemedicine and social distancing, “impact data from [the Outpatient Influenza-Like Illness Surveillance Network] in ways that are difficult to differentiate from changes in illness levels and should be interpreted with caution,” the CDC investigators noted.
The other activity measure, positive tests of respiratory specimens for influenza at clinical laboratories, continued the decline that started in mid-February by falling from 7.3% to 2.1%, its lowest rate since October, CDC data show.
Overall flu-related deaths may be down, but mortality in children continued at a near-record level. Seven such deaths were reported this past week, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 162. “This number is higher than recorded at the same time in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Influenza activity measures dropped during the week ending March 28, but the percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) has risen into epidemic territory, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This influenza news, however, needs to be viewed through a COVID-19 lens.
The P&I mortality data are reported together and are always a week behind the other measures, in this case covering the week ending March 21, but they show influenza deaths dropping to 0.8% as the overall P&I rate rose from 7.4% to 8.2%, a pneumonia-fueled increase that was “likely associated with COVID-19 rather than influenza,” the CDC’s influenza division noted.
The two main activity measures, at least, are on the same page for the first time since the end of February.
The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) had been dropping up to that point but then rose for an unprecedented third time this season, a change probably brought about by COVID-related health care–seeking behavior, the influenza division reported in its weekly FluView report.
This corresponding third drop in ILI activity brought the rate down to 5.4% this week from 6.2% the previous week, the CDC reported. The two previous high points occurred during the weeks ending Dec. 28 (7.0%) and Feb. 8 (6.7%)
The COVID-related changes, such as increased use of telemedicine and social distancing, “impact data from [the Outpatient Influenza-Like Illness Surveillance Network] in ways that are difficult to differentiate from changes in illness levels and should be interpreted with caution,” the CDC investigators noted.
The other activity measure, positive tests of respiratory specimens for influenza at clinical laboratories, continued the decline that started in mid-February by falling from 7.3% to 2.1%, its lowest rate since October, CDC data show.
Overall flu-related deaths may be down, but mortality in children continued at a near-record level. Seven such deaths were reported this past week, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 162. “This number is higher than recorded at the same time in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Influenza activity measures dropped during the week ending March 28, but the percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) has risen into epidemic territory, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This influenza news, however, needs to be viewed through a COVID-19 lens.
The P&I mortality data are reported together and are always a week behind the other measures, in this case covering the week ending March 21, but they show influenza deaths dropping to 0.8% as the overall P&I rate rose from 7.4% to 8.2%, a pneumonia-fueled increase that was “likely associated with COVID-19 rather than influenza,” the CDC’s influenza division noted.
The two main activity measures, at least, are on the same page for the first time since the end of February.
The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) had been dropping up to that point but then rose for an unprecedented third time this season, a change probably brought about by COVID-related health care–seeking behavior, the influenza division reported in its weekly FluView report.
This corresponding third drop in ILI activity brought the rate down to 5.4% this week from 6.2% the previous week, the CDC reported. The two previous high points occurred during the weeks ending Dec. 28 (7.0%) and Feb. 8 (6.7%)
The COVID-related changes, such as increased use of telemedicine and social distancing, “impact data from [the Outpatient Influenza-Like Illness Surveillance Network] in ways that are difficult to differentiate from changes in illness levels and should be interpreted with caution,” the CDC investigators noted.
The other activity measure, positive tests of respiratory specimens for influenza at clinical laboratories, continued the decline that started in mid-February by falling from 7.3% to 2.1%, its lowest rate since October, CDC data show.
Overall flu-related deaths may be down, but mortality in children continued at a near-record level. Seven such deaths were reported this past week, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 162. “This number is higher than recorded at the same time in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Survey: COVID-19 is getting in our heads
As the COVID-19 pandemic sweeps across the United States, it is increasingly affecting those who are not infected. Social bonds are being broken, businesses are closing, jobs are being lost, and the stress is mounting.

In a poll conducted March 25-30, 45% of Americans said that stress resulting from the pandemic is having a negative impact on their mental health, compared with 32% expressing that view just 2 weeks earlier, the Kaiser Family Foundation reported April 2.
In the later survey, the effect looked like this: 19% of all respondents said that the pandemic has had a major negative impact and 26% said it has been minor so far. Women were more likely than men (24% vs. 15%) to report a major impact, as were blacks and Hispanic adults (both at 24%) compared with whites (17%), the KFF investigators said.
More Hispanic (44%) and black (42%) respondents also said that they had already lost their job, lost income, or had their hours reduced without pay as a result of the pandemic, compared with whites (36%). Among all respondents, 26% had lost income from a job or business and 28% had lost their job, been laid off, or had their hours reduced without pay, according to KFF.
A majority of respondents (57%) reported “being worried they will put themselves at risk of exposure to coronavirus because they can’t afford to stay home and miss work,” the researchers said. That figure is up from 35% in the earlier survey.
Anxiety about work-related exposure was even higher among hourly workers or those who get paid by the job (61%) and among employed adults who earn less than $40,000 annually (72%), they reported.
Overall, 72% of respondents said that their lives have been disrupted “a lot” or “some” by the coronavirus outbreak, and that is a jump of 32 percentage points over the previous poll, the investigators noted.
The disruption is expected to continue, it seems, as 74% believe that the worst is yet to come “in spite of the health, social and economic upheaval that Americans are already experiencing,” they wrote.
As the COVID-19 pandemic sweeps across the United States, it is increasingly affecting those who are not infected. Social bonds are being broken, businesses are closing, jobs are being lost, and the stress is mounting.

In a poll conducted March 25-30, 45% of Americans said that stress resulting from the pandemic is having a negative impact on their mental health, compared with 32% expressing that view just 2 weeks earlier, the Kaiser Family Foundation reported April 2.
In the later survey, the effect looked like this: 19% of all respondents said that the pandemic has had a major negative impact and 26% said it has been minor so far. Women were more likely than men (24% vs. 15%) to report a major impact, as were blacks and Hispanic adults (both at 24%) compared with whites (17%), the KFF investigators said.
More Hispanic (44%) and black (42%) respondents also said that they had already lost their job, lost income, or had their hours reduced without pay as a result of the pandemic, compared with whites (36%). Among all respondents, 26% had lost income from a job or business and 28% had lost their job, been laid off, or had their hours reduced without pay, according to KFF.
A majority of respondents (57%) reported “being worried they will put themselves at risk of exposure to coronavirus because they can’t afford to stay home and miss work,” the researchers said. That figure is up from 35% in the earlier survey.
Anxiety about work-related exposure was even higher among hourly workers or those who get paid by the job (61%) and among employed adults who earn less than $40,000 annually (72%), they reported.
Overall, 72% of respondents said that their lives have been disrupted “a lot” or “some” by the coronavirus outbreak, and that is a jump of 32 percentage points over the previous poll, the investigators noted.
The disruption is expected to continue, it seems, as 74% believe that the worst is yet to come “in spite of the health, social and economic upheaval that Americans are already experiencing,” they wrote.
As the COVID-19 pandemic sweeps across the United States, it is increasingly affecting those who are not infected. Social bonds are being broken, businesses are closing, jobs are being lost, and the stress is mounting.

In a poll conducted March 25-30, 45% of Americans said that stress resulting from the pandemic is having a negative impact on their mental health, compared with 32% expressing that view just 2 weeks earlier, the Kaiser Family Foundation reported April 2.
In the later survey, the effect looked like this: 19% of all respondents said that the pandemic has had a major negative impact and 26% said it has been minor so far. Women were more likely than men (24% vs. 15%) to report a major impact, as were blacks and Hispanic adults (both at 24%) compared with whites (17%), the KFF investigators said.
More Hispanic (44%) and black (42%) respondents also said that they had already lost their job, lost income, or had their hours reduced without pay as a result of the pandemic, compared with whites (36%). Among all respondents, 26% had lost income from a job or business and 28% had lost their job, been laid off, or had their hours reduced without pay, according to KFF.
A majority of respondents (57%) reported “being worried they will put themselves at risk of exposure to coronavirus because they can’t afford to stay home and miss work,” the researchers said. That figure is up from 35% in the earlier survey.
Anxiety about work-related exposure was even higher among hourly workers or those who get paid by the job (61%) and among employed adults who earn less than $40,000 annually (72%), they reported.
Overall, 72% of respondents said that their lives have been disrupted “a lot” or “some” by the coronavirus outbreak, and that is a jump of 32 percentage points over the previous poll, the investigators noted.
The disruption is expected to continue, it seems, as 74% believe that the worst is yet to come “in spite of the health, social and economic upheaval that Americans are already experiencing,” they wrote.
COVID-19 transmission can occur before symptom onset
based on clinical and epidemiologic data for all cases reported in the country by March 16.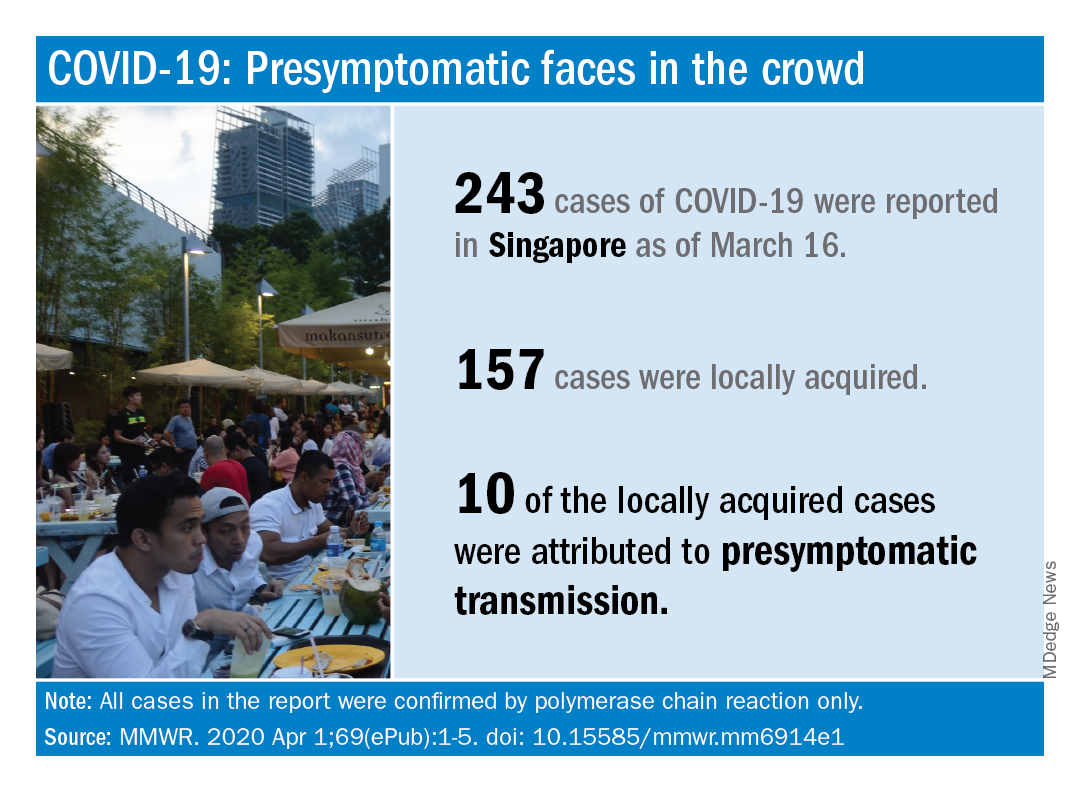
As of that date, there had been 243 cases of COVID-19, of which 157 were locally acquired. Among those 157 were 10 cases (6.4%) that involved probable presymptomatic transmission, Wycliffe E. Wei, MPH, and associates said April 1 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
They defined presymptomatic transmission “as the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected person (source patient) to a secondary patient before the source patient developed symptoms, as ascertained by exposure and symptom onset dates, with no evidence that the secondary patient had been exposed to anyone else with COVID-19.”
Investigation of all 243 cases in Singapore identified seven clusters, each involving two to five patients, as sources of presymptomatic transmission. In four of the clusters, the “exposure occurred 1-3 days before the source patient developed symptoms,” said Mr. Wei of the Singapore Ministry of Health and associates.
These findings, along with evidence from Chinese studies – one of which reported presymptomatic transmission in 12.6% of cases – support “the likelihood that viral shedding can occur in the absence of symptoms and before symptom onset,” they said.
SOURCE: Wei WE et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 1;69(ePub):1-5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6914e1.
based on clinical and epidemiologic data for all cases reported in the country by March 16.
As of that date, there had been 243 cases of COVID-19, of which 157 were locally acquired. Among those 157 were 10 cases (6.4%) that involved probable presymptomatic transmission, Wycliffe E. Wei, MPH, and associates said April 1 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
They defined presymptomatic transmission “as the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected person (source patient) to a secondary patient before the source patient developed symptoms, as ascertained by exposure and symptom onset dates, with no evidence that the secondary patient had been exposed to anyone else with COVID-19.”
Investigation of all 243 cases in Singapore identified seven clusters, each involving two to five patients, as sources of presymptomatic transmission. In four of the clusters, the “exposure occurred 1-3 days before the source patient developed symptoms,” said Mr. Wei of the Singapore Ministry of Health and associates.
These findings, along with evidence from Chinese studies – one of which reported presymptomatic transmission in 12.6% of cases – support “the likelihood that viral shedding can occur in the absence of symptoms and before symptom onset,” they said.
SOURCE: Wei WE et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 1;69(ePub):1-5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6914e1.
based on clinical and epidemiologic data for all cases reported in the country by March 16.
As of that date, there had been 243 cases of COVID-19, of which 157 were locally acquired. Among those 157 were 10 cases (6.4%) that involved probable presymptomatic transmission, Wycliffe E. Wei, MPH, and associates said April 1 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
They defined presymptomatic transmission “as the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected person (source patient) to a secondary patient before the source patient developed symptoms, as ascertained by exposure and symptom onset dates, with no evidence that the secondary patient had been exposed to anyone else with COVID-19.”
Investigation of all 243 cases in Singapore identified seven clusters, each involving two to five patients, as sources of presymptomatic transmission. In four of the clusters, the “exposure occurred 1-3 days before the source patient developed symptoms,” said Mr. Wei of the Singapore Ministry of Health and associates.
These findings, along with evidence from Chinese studies – one of which reported presymptomatic transmission in 12.6% of cases – support “the likelihood that viral shedding can occur in the absence of symptoms and before symptom onset,” they said.
SOURCE: Wei WE et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 1;69(ePub):1-5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6914e1.
FROM MMWR
Comorbidities more common in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
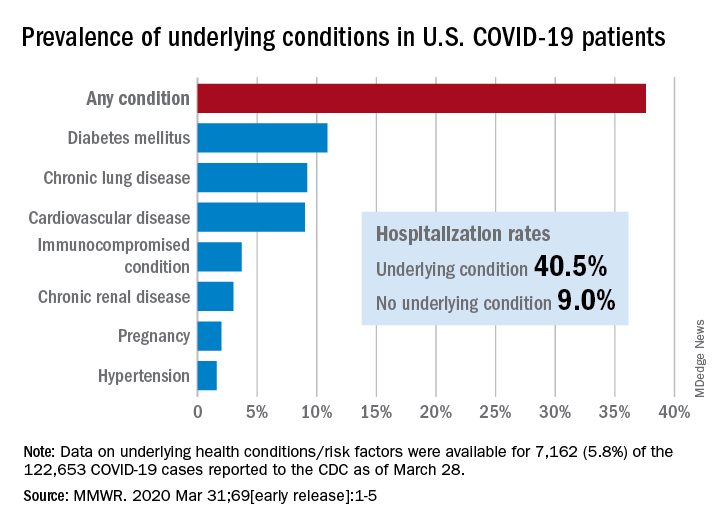
Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
FROM MMWR
Rise in autism prevalence indicates earlier diagnosis
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
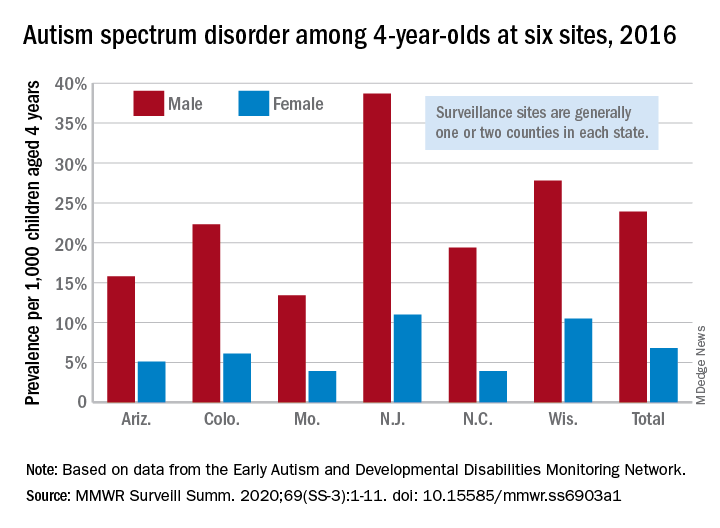
Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
FROM MMWR SURVEILLANCE SUMMARIES
Flu activity measures continue COVID-19–related divergence
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.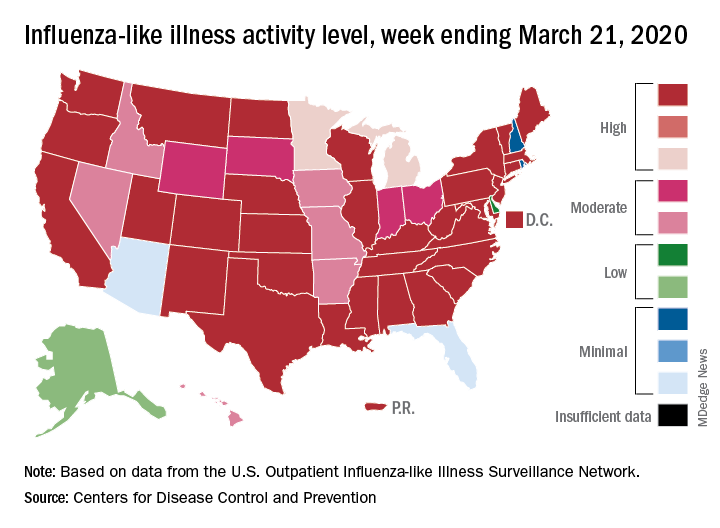
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.
The 2019-2020 flu paradox continues in the United States: Fewer respiratory samples are testing positive for influenza, but more people are seeking care for respiratory symptoms because of COVID-19, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
compared with 14.9% the week before, but outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) rose from 5.6% of all visits to 6.2% for third week of March, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
The CDC defines ILI as “fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and a cough and/or a sore throat without a known cause other than influenza.” The outpatient ILI visit rate needs to get below the national baseline of 2.4% for the CDC to call the end of the 2019-2020 flu season.
This week’s map shows that fewer states are at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale: 33 states plus Puerto Rico for the week ending March 21, compared with 35 and Puerto Rico the previous week. The number of states at level 10 had risen the two previous weeks, CDC data show.
“Influenza severity indicators remain moderate to low overall, but hospitalization rates differ by age group, with high rates among children and young adults,” the influenza division said.
Overall mortality also has not been high, but 155 children have died from the flu so far in 2019-2020, which is more than any season since the 2009 pandemic, the CDC noted.