User login
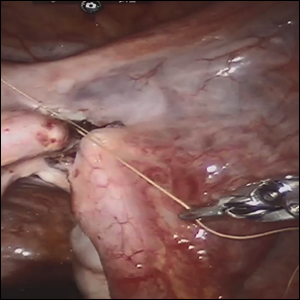
Robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis following sterilization

Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.

Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.

Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.
Drafts of new classification criteria presented for GCA, Takayasu’s arteritis
CHICAGO – Drafts of new classification criteria for giant cell arteritis and Takayasu’s arteritis developed by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) reflect the increasingly important role of advanced vascular imaging in the diagnosis and management of large-vessel vasculitis, according to Peter A. Merkel, MD.
The drafts, which are the result of a multiyear collaboration between the ACR and EULAR, were presented at the annual meeting of the ACR and will be submitted to the ACR/EULAR committee overseeing the work for comprehensive review and possible revisions. Once endorsed, the new criteria will replace the “extremely important,” but outdated, existing classification criteria, which were published in 1990.
“What we’ve done is, rather than purely revise the 1990 [criteria], we’ve started again from scratch ... with a great number of cases from a wide variety of centers throughout the world. This was a very large international effort ... really a great community effort in the field of rheumatology,” Dr. Merkel, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and one of the chief investigators for the project, said in a video interview.
The new criteria will allow for better classification of patients with giant cell arteritis versus Takayasu’s arteritis versus another form of vasculitis, he said, noting that advances in imaging that allow for “more enriched data with which to make decisions” play a large role.
However, the new criteria are not meant to be used for diagnosis, but to “sort out among the different types of vasculitis,” he said.
“It provides awareness and it provides a tool, especially for research investigation, but that seeps out into the broader community,” he added.
Dr. Merkel reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Merkel PA et al. ACR Annual Meeting, Presentation 5T116.
CHICAGO – Drafts of new classification criteria for giant cell arteritis and Takayasu’s arteritis developed by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) reflect the increasingly important role of advanced vascular imaging in the diagnosis and management of large-vessel vasculitis, according to Peter A. Merkel, MD.
The drafts, which are the result of a multiyear collaboration between the ACR and EULAR, were presented at the annual meeting of the ACR and will be submitted to the ACR/EULAR committee overseeing the work for comprehensive review and possible revisions. Once endorsed, the new criteria will replace the “extremely important,” but outdated, existing classification criteria, which were published in 1990.
“What we’ve done is, rather than purely revise the 1990 [criteria], we’ve started again from scratch ... with a great number of cases from a wide variety of centers throughout the world. This was a very large international effort ... really a great community effort in the field of rheumatology,” Dr. Merkel, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and one of the chief investigators for the project, said in a video interview.
The new criteria will allow for better classification of patients with giant cell arteritis versus Takayasu’s arteritis versus another form of vasculitis, he said, noting that advances in imaging that allow for “more enriched data with which to make decisions” play a large role.
However, the new criteria are not meant to be used for diagnosis, but to “sort out among the different types of vasculitis,” he said.
“It provides awareness and it provides a tool, especially for research investigation, but that seeps out into the broader community,” he added.
Dr. Merkel reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Merkel PA et al. ACR Annual Meeting, Presentation 5T116.
CHICAGO – Drafts of new classification criteria for giant cell arteritis and Takayasu’s arteritis developed by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) reflect the increasingly important role of advanced vascular imaging in the diagnosis and management of large-vessel vasculitis, according to Peter A. Merkel, MD.
The drafts, which are the result of a multiyear collaboration between the ACR and EULAR, were presented at the annual meeting of the ACR and will be submitted to the ACR/EULAR committee overseeing the work for comprehensive review and possible revisions. Once endorsed, the new criteria will replace the “extremely important,” but outdated, existing classification criteria, which were published in 1990.
“What we’ve done is, rather than purely revise the 1990 [criteria], we’ve started again from scratch ... with a great number of cases from a wide variety of centers throughout the world. This was a very large international effort ... really a great community effort in the field of rheumatology,” Dr. Merkel, professor and chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and one of the chief investigators for the project, said in a video interview.
The new criteria will allow for better classification of patients with giant cell arteritis versus Takayasu’s arteritis versus another form of vasculitis, he said, noting that advances in imaging that allow for “more enriched data with which to make decisions” play a large role.
However, the new criteria are not meant to be used for diagnosis, but to “sort out among the different types of vasculitis,” he said.
“It provides awareness and it provides a tool, especially for research investigation, but that seeps out into the broader community,” he added.
Dr. Merkel reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Merkel PA et al. ACR Annual Meeting, Presentation 5T116.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Innovations in Dermatology: Antibiotic Stewardship in Acne Therapy



FFR by wire may soon be obsolete
SAN DIEGO – Angiograms can be deceiving, so it’s best to measure fractional flow reserve (FFR) across coronary obstructions to gauge patients’ true need for intervention. That’s hardly news to cardiologists, but FFR is not often done. The problem is that traditional measurement requires threading wires down coronary arteries; the technique is a bit risky and takes time and training. It also has to be repeated for each lesion.
But now, several companies are developing noninvasive ways to measure FFR.
Findings from one of them, CathWorks, were presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation. Its FFRangio system uses high-quality angiograms and an algorithm to estimate resistance and flow across stenoses. After a few cases, the process takes less than 5 minutes (Circulation. 2018 Sep 24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037350).
“I think this is a big breakthrough. ... Ultimately, it should lead to better patient outcomes,” said lead investigator William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiology at Stanford University, Calif.
In an interview at TCT 2018, Dr. Fearon explained the importance of FFR, the data for FFRangio, and what’s coming down the pike from other companies. He disclosed institutional research grants from the company.
SAN DIEGO – Angiograms can be deceiving, so it’s best to measure fractional flow reserve (FFR) across coronary obstructions to gauge patients’ true need for intervention. That’s hardly news to cardiologists, but FFR is not often done. The problem is that traditional measurement requires threading wires down coronary arteries; the technique is a bit risky and takes time and training. It also has to be repeated for each lesion.
But now, several companies are developing noninvasive ways to measure FFR.
Findings from one of them, CathWorks, were presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation. Its FFRangio system uses high-quality angiograms and an algorithm to estimate resistance and flow across stenoses. After a few cases, the process takes less than 5 minutes (Circulation. 2018 Sep 24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037350).
“I think this is a big breakthrough. ... Ultimately, it should lead to better patient outcomes,” said lead investigator William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiology at Stanford University, Calif.
In an interview at TCT 2018, Dr. Fearon explained the importance of FFR, the data for FFRangio, and what’s coming down the pike from other companies. He disclosed institutional research grants from the company.
SAN DIEGO – Angiograms can be deceiving, so it’s best to measure fractional flow reserve (FFR) across coronary obstructions to gauge patients’ true need for intervention. That’s hardly news to cardiologists, but FFR is not often done. The problem is that traditional measurement requires threading wires down coronary arteries; the technique is a bit risky and takes time and training. It also has to be repeated for each lesion.
But now, several companies are developing noninvasive ways to measure FFR.
Findings from one of them, CathWorks, were presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation. Its FFRangio system uses high-quality angiograms and an algorithm to estimate resistance and flow across stenoses. After a few cases, the process takes less than 5 minutes (Circulation. 2018 Sep 24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037350).
“I think this is a big breakthrough. ... Ultimately, it should lead to better patient outcomes,” said lead investigator William Fearon, MD, professor of cardiology at Stanford University, Calif.
In an interview at TCT 2018, Dr. Fearon explained the importance of FFR, the data for FFRangio, and what’s coming down the pike from other companies. He disclosed institutional research grants from the company.
REPORTING FROM TCT 2018
Dermatology Residency Match: Data on Who Matched in 2018



PURE Healthy Diet Score validated
MUNICH – A formula for scoring diet quality that during its development phase significantly correlated with overall survival received validation when tested using three independent, large data sets that together included almost 80,000 people.

With these new findings the PURE Healthy Diet Score had now shown consistent, significant correlations with overall survival and the incidence of MI and stroke in a total of about 218,000 people from 50 countries who had been followed in any of four separate studies. This new validation is especially notable because the optimal diet identified by the scoring system diverged from current American diet recommendations in two important ways: Optimal food consumption included three daily servings of full-fat dairy and 1.5 servings daily of unprocessed red meat Andrew Mente, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. He explained this finding as possibly related to the global scope of the study, which included many people from low- or middle-income countries where average diets are usually low in important nutrients.
The PURE Healthy Diet Score should now be “considered for broad, global dietary recommendations,” Dr. Mente said in a video interview. Testing a diet profile in a large, randomized trial would be ideal, but also difficult to run. Until then, the only alternative for defining an evidence-based optimal diet is observational data, as in the current study. The PURE Healthy Diet Score “is ready for routine use,” said Dr. Mente, a clinical epidemiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada.
Dr. Mente and his associates developed the Pure Healthy Diet Score with data taken from 138,527 people enrolled in the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. They published a pair of reports in 2017 with their initial findings that also included some of their first steps toward developing the score (Lancet. 2017 Nov 4; 380[10107]:2037-49; 380[10107]:2050-62). The PURE analysis identified seven food groups for which daily intake levels significantly linked with survival: fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, dairy, red meat, and fish. Based on this, they devised a scoring formula that gives a person a rating of 1-5 for each of these seven food types, from the lowest quintile of consumption, which scores 1, to the highest quintile, which scores 5. The result is a score than can range from 7 to 35. They then divided the PURE participants into quintiles based on their intakes of all seven food types and found the highest survival rate among people in the quintile with the highest intake level for all of the food groups.
The best-outcome quintile consumed on average about eight servings of fruits and vegetables daily, 2.5 servings of legumes and nuts, three servings of full-fat daily, 1.5 servings of unprocessed red meat, and 0.3 servings of fish (or about two servings of fish weekly). Energy consumption in the best-outcome quintile received 54% of calories as carbohydrates, 28% as fat, and 18% as protein. In contrast, the worst-outcomes quintile received 69% of calories from carbohydrates, 19% from fat, and 12% from protein.
In a model that adjusted for all measured confounders the people in PURE with the best-outcome diet had a statistically significant, 25% reduced all-cause mortality, compared with people in the quintile with the worst diet.
To validate the formula the researchers used data collected from three other trials run by their group at McMaster University:
- The ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies (N Engl J Med. 2008 Apr 10;358[15]:1547-58), which together included diet and outcomes data for 31,546 patients with vascular disease. Diet analysis and scoring showed that enrolled people in the quintile with the highest score had a statistically significant 24% relative reduction in mortality, compared with the quintile with the worst score after adjusting for measured confounders.
- The INTERHEART study (Lancet. 2004 Sep 11;364[9438]:937-52), which had data for 27,098 people and showed that the primary outcome of incident MI was a statistically significant 22% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the best diet score, compared with the quintile with the worst score.
- The INTERSTROKE study (Lancet. 2016 Aug 20;388[10046]:761-75), with data for 20,834 people, showed that the rate of stroke was a statistically significant 25% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the highest diet score, compared with those with the lowest score.
Dr. Mente had no financial disclosures.
Dr. Mente and his associates have validated the PURE Healthy Diet Score. However, it remains unclear whether the score captures all of the many facets of diet, and it’s also uncertain whether the score is sensitive to changes in diet.
Another issue with the quintile analysis that the researchers used to derive the formula was that the spread between the median scores of the bottom, worst-outcome quartile and the top, best-outcome quartile was only 7 points on a scale that ranged from 7 to 35. The small magnitude of the difference in scores between the bottom and top quintiles might limit the discriminatory power of this scoring system.
Eva Prescott, MD, is a cardiologist at Bispebjerg Hospital in Copenhagen. She has been an advisor to AstraZeneca, NovoNordisk, and Sanofi. She made these comments as designated discussant for the report.
Dr. Mente and his associates have validated the PURE Healthy Diet Score. However, it remains unclear whether the score captures all of the many facets of diet, and it’s also uncertain whether the score is sensitive to changes in diet.
Another issue with the quintile analysis that the researchers used to derive the formula was that the spread between the median scores of the bottom, worst-outcome quartile and the top, best-outcome quartile was only 7 points on a scale that ranged from 7 to 35. The small magnitude of the difference in scores between the bottom and top quintiles might limit the discriminatory power of this scoring system.
Eva Prescott, MD, is a cardiologist at Bispebjerg Hospital in Copenhagen. She has been an advisor to AstraZeneca, NovoNordisk, and Sanofi. She made these comments as designated discussant for the report.
Dr. Mente and his associates have validated the PURE Healthy Diet Score. However, it remains unclear whether the score captures all of the many facets of diet, and it’s also uncertain whether the score is sensitive to changes in diet.
Another issue with the quintile analysis that the researchers used to derive the formula was that the spread between the median scores of the bottom, worst-outcome quartile and the top, best-outcome quartile was only 7 points on a scale that ranged from 7 to 35. The small magnitude of the difference in scores between the bottom and top quintiles might limit the discriminatory power of this scoring system.
Eva Prescott, MD, is a cardiologist at Bispebjerg Hospital in Copenhagen. She has been an advisor to AstraZeneca, NovoNordisk, and Sanofi. She made these comments as designated discussant for the report.
MUNICH – A formula for scoring diet quality that during its development phase significantly correlated with overall survival received validation when tested using three independent, large data sets that together included almost 80,000 people.

With these new findings the PURE Healthy Diet Score had now shown consistent, significant correlations with overall survival and the incidence of MI and stroke in a total of about 218,000 people from 50 countries who had been followed in any of four separate studies. This new validation is especially notable because the optimal diet identified by the scoring system diverged from current American diet recommendations in two important ways: Optimal food consumption included three daily servings of full-fat dairy and 1.5 servings daily of unprocessed red meat Andrew Mente, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. He explained this finding as possibly related to the global scope of the study, which included many people from low- or middle-income countries where average diets are usually low in important nutrients.
The PURE Healthy Diet Score should now be “considered for broad, global dietary recommendations,” Dr. Mente said in a video interview. Testing a diet profile in a large, randomized trial would be ideal, but also difficult to run. Until then, the only alternative for defining an evidence-based optimal diet is observational data, as in the current study. The PURE Healthy Diet Score “is ready for routine use,” said Dr. Mente, a clinical epidemiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada.
Dr. Mente and his associates developed the Pure Healthy Diet Score with data taken from 138,527 people enrolled in the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. They published a pair of reports in 2017 with their initial findings that also included some of their first steps toward developing the score (Lancet. 2017 Nov 4; 380[10107]:2037-49; 380[10107]:2050-62). The PURE analysis identified seven food groups for which daily intake levels significantly linked with survival: fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, dairy, red meat, and fish. Based on this, they devised a scoring formula that gives a person a rating of 1-5 for each of these seven food types, from the lowest quintile of consumption, which scores 1, to the highest quintile, which scores 5. The result is a score than can range from 7 to 35. They then divided the PURE participants into quintiles based on their intakes of all seven food types and found the highest survival rate among people in the quintile with the highest intake level for all of the food groups.
The best-outcome quintile consumed on average about eight servings of fruits and vegetables daily, 2.5 servings of legumes and nuts, three servings of full-fat daily, 1.5 servings of unprocessed red meat, and 0.3 servings of fish (or about two servings of fish weekly). Energy consumption in the best-outcome quintile received 54% of calories as carbohydrates, 28% as fat, and 18% as protein. In contrast, the worst-outcomes quintile received 69% of calories from carbohydrates, 19% from fat, and 12% from protein.
In a model that adjusted for all measured confounders the people in PURE with the best-outcome diet had a statistically significant, 25% reduced all-cause mortality, compared with people in the quintile with the worst diet.
To validate the formula the researchers used data collected from three other trials run by their group at McMaster University:
- The ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies (N Engl J Med. 2008 Apr 10;358[15]:1547-58), which together included diet and outcomes data for 31,546 patients with vascular disease. Diet analysis and scoring showed that enrolled people in the quintile with the highest score had a statistically significant 24% relative reduction in mortality, compared with the quintile with the worst score after adjusting for measured confounders.
- The INTERHEART study (Lancet. 2004 Sep 11;364[9438]:937-52), which had data for 27,098 people and showed that the primary outcome of incident MI was a statistically significant 22% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the best diet score, compared with the quintile with the worst score.
- The INTERSTROKE study (Lancet. 2016 Aug 20;388[10046]:761-75), with data for 20,834 people, showed that the rate of stroke was a statistically significant 25% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the highest diet score, compared with those with the lowest score.
Dr. Mente had no financial disclosures.
MUNICH – A formula for scoring diet quality that during its development phase significantly correlated with overall survival received validation when tested using three independent, large data sets that together included almost 80,000 people.

With these new findings the PURE Healthy Diet Score had now shown consistent, significant correlations with overall survival and the incidence of MI and stroke in a total of about 218,000 people from 50 countries who had been followed in any of four separate studies. This new validation is especially notable because the optimal diet identified by the scoring system diverged from current American diet recommendations in two important ways: Optimal food consumption included three daily servings of full-fat dairy and 1.5 servings daily of unprocessed red meat Andrew Mente, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology. He explained this finding as possibly related to the global scope of the study, which included many people from low- or middle-income countries where average diets are usually low in important nutrients.
The PURE Healthy Diet Score should now be “considered for broad, global dietary recommendations,” Dr. Mente said in a video interview. Testing a diet profile in a large, randomized trial would be ideal, but also difficult to run. Until then, the only alternative for defining an evidence-based optimal diet is observational data, as in the current study. The PURE Healthy Diet Score “is ready for routine use,” said Dr. Mente, a clinical epidemiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Canada.
Dr. Mente and his associates developed the Pure Healthy Diet Score with data taken from 138,527 people enrolled in the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. They published a pair of reports in 2017 with their initial findings that also included some of their first steps toward developing the score (Lancet. 2017 Nov 4; 380[10107]:2037-49; 380[10107]:2050-62). The PURE analysis identified seven food groups for which daily intake levels significantly linked with survival: fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, dairy, red meat, and fish. Based on this, they devised a scoring formula that gives a person a rating of 1-5 for each of these seven food types, from the lowest quintile of consumption, which scores 1, to the highest quintile, which scores 5. The result is a score than can range from 7 to 35. They then divided the PURE participants into quintiles based on their intakes of all seven food types and found the highest survival rate among people in the quintile with the highest intake level for all of the food groups.
The best-outcome quintile consumed on average about eight servings of fruits and vegetables daily, 2.5 servings of legumes and nuts, three servings of full-fat daily, 1.5 servings of unprocessed red meat, and 0.3 servings of fish (or about two servings of fish weekly). Energy consumption in the best-outcome quintile received 54% of calories as carbohydrates, 28% as fat, and 18% as protein. In contrast, the worst-outcomes quintile received 69% of calories from carbohydrates, 19% from fat, and 12% from protein.
In a model that adjusted for all measured confounders the people in PURE with the best-outcome diet had a statistically significant, 25% reduced all-cause mortality, compared with people in the quintile with the worst diet.
To validate the formula the researchers used data collected from three other trials run by their group at McMaster University:
- The ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies (N Engl J Med. 2008 Apr 10;358[15]:1547-58), which together included diet and outcomes data for 31,546 patients with vascular disease. Diet analysis and scoring showed that enrolled people in the quintile with the highest score had a statistically significant 24% relative reduction in mortality, compared with the quintile with the worst score after adjusting for measured confounders.
- The INTERHEART study (Lancet. 2004 Sep 11;364[9438]:937-52), which had data for 27,098 people and showed that the primary outcome of incident MI was a statistically significant 22% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the best diet score, compared with the quintile with the worst score.
- The INTERSTROKE study (Lancet. 2016 Aug 20;388[10046]:761-75), with data for 20,834 people, showed that the rate of stroke was a statistically significant 25% lower after adjustment in the quintile with the highest diet score, compared with those with the lowest score.
Dr. Mente had no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The highest-scoring quintiles had about 25% fewer deaths, MIs, and strokes, compared with the lowest-scoring quintiles.
Study details: The PURE Healthy Diet Score underwent validation using three independent data sets with a total of 79,478 people.
Disclosures: Dr. Mente had no financial disclosures.
Where docs go for info: An MDedge Short



Bias in the clinical setting can impact patient care
SAN ANTONIO – Physicians and other health care providers may harbor implicit, or unconscious, biases that contribute to health care disparities, patient communication researcher Stacey Passalacqua, PhD, said here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Implicit biases are beliefs or attitudes, for example, about certain social groups, that exist outside of a health care provider’s conscious awareness, said Dr. Passalacqua of the department of communication at the University of Texas, San Antonio. If bias is implicit, it can be difficult self-assess.
among other social, ethnic, and racial groups, Dr. Passalacqua told attendees in workshops at the meeting.
“If a health care provider has negative biases toward a particular patient – maybe they think that these patients doesn’t care that much about their health or that they really have no interest in participating – then obviously that health care provider is far less likely to engage that patient in shared decision making,” she said in a video interview.
Diagnosis and treatment are subject to influence by the bias that physicians have toward certain patient groups, according to Dr. Passalacqua. For example, she said women with heart disease are less likely to be accurately diagnosed.
The bias in the medical setting might be mitigated by the presence of more individuals from the at-risk groups in the health care workforce, she added. In one recent retrospective study, investigators found that after an MI, a woman treated by a male physician was associated with higher mortality, while women and men had similar outcomes when treated by female physicians.
“That is one of the reasons why it is so important to have a diverse workforce, to have health care providers of different ethnicities, of different genders, or different backgrounds, because they are less subject to some of these implicit biases that we know are highly problematic in health care,” she said in the interview.
Dr. Passalacqua had no disclosures related to her presentation.
SAN ANTONIO – Physicians and other health care providers may harbor implicit, or unconscious, biases that contribute to health care disparities, patient communication researcher Stacey Passalacqua, PhD, said here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Implicit biases are beliefs or attitudes, for example, about certain social groups, that exist outside of a health care provider’s conscious awareness, said Dr. Passalacqua of the department of communication at the University of Texas, San Antonio. If bias is implicit, it can be difficult self-assess.
among other social, ethnic, and racial groups, Dr. Passalacqua told attendees in workshops at the meeting.
“If a health care provider has negative biases toward a particular patient – maybe they think that these patients doesn’t care that much about their health or that they really have no interest in participating – then obviously that health care provider is far less likely to engage that patient in shared decision making,” she said in a video interview.
Diagnosis and treatment are subject to influence by the bias that physicians have toward certain patient groups, according to Dr. Passalacqua. For example, she said women with heart disease are less likely to be accurately diagnosed.
The bias in the medical setting might be mitigated by the presence of more individuals from the at-risk groups in the health care workforce, she added. In one recent retrospective study, investigators found that after an MI, a woman treated by a male physician was associated with higher mortality, while women and men had similar outcomes when treated by female physicians.
“That is one of the reasons why it is so important to have a diverse workforce, to have health care providers of different ethnicities, of different genders, or different backgrounds, because they are less subject to some of these implicit biases that we know are highly problematic in health care,” she said in the interview.
Dr. Passalacqua had no disclosures related to her presentation.
SAN ANTONIO – Physicians and other health care providers may harbor implicit, or unconscious, biases that contribute to health care disparities, patient communication researcher Stacey Passalacqua, PhD, said here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Implicit biases are beliefs or attitudes, for example, about certain social groups, that exist outside of a health care provider’s conscious awareness, said Dr. Passalacqua of the department of communication at the University of Texas, San Antonio. If bias is implicit, it can be difficult self-assess.
among other social, ethnic, and racial groups, Dr. Passalacqua told attendees in workshops at the meeting.
“If a health care provider has negative biases toward a particular patient – maybe they think that these patients doesn’t care that much about their health or that they really have no interest in participating – then obviously that health care provider is far less likely to engage that patient in shared decision making,” she said in a video interview.
Diagnosis and treatment are subject to influence by the bias that physicians have toward certain patient groups, according to Dr. Passalacqua. For example, she said women with heart disease are less likely to be accurately diagnosed.
The bias in the medical setting might be mitigated by the presence of more individuals from the at-risk groups in the health care workforce, she added. In one recent retrospective study, investigators found that after an MI, a woman treated by a male physician was associated with higher mortality, while women and men had similar outcomes when treated by female physicians.
“That is one of the reasons why it is so important to have a diverse workforce, to have health care providers of different ethnicities, of different genders, or different backgrounds, because they are less subject to some of these implicit biases that we know are highly problematic in health care,” she said in the interview.
Dr. Passalacqua had no disclosures related to her presentation.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
How can we best use diagnostic brain imaging in pregnant women with severe headache?
WHAT DOES THIS MEAN FOR PRACTICE?
- Acute, severe headache in pregnancy needs immediate attention when it includes:
- seizures
- altered sensorium, or
- loss of consciousness
- An appropriate threshold utilizing history and clinical diagnosis must be set for obtaining neurologic consultation and for the consultant to obtain imaging
- Brain scans can identify symptomatic pathologic results (27.6% in this study)
- Theoretical concerns about imaging call for the OB to be very involved in evaluation and management
- OB and neurologist should discuss risks and benefits of imaging throughout care
Adjuvanted flu vaccine reduces hospitalizations in oldest old
SAN FRANCISCO – presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“It’s one thing to say you have a more immunogenic vaccine, it’s another thing to be able to say it offers clinical benefit, especially in the oldest old and the frailest frail,” says Stefan Gravenstein, MD, professor of medicine and health services, policy and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I. Dr. Gravenstein presented a poster outlying a randomized, clinical trial of the Fluad vaccine in nursing homes.
The study randomized the nursing homes so that some facilities would offer Fluad as part of their standard of care. The design helped address the problem of consent. Any clinical trial that requires individual consent would likely exclude many of the frailest patients, leading to an unrepresentative sample. “So if you want to have a generalizable result, you’d like to have it applied to the population the way you would in the real world, so randomizing the nursing homes rather than the people makes a lot of sense,” said Dr. Gravenstein.
Dr. Gravenstein chose to test the vaccine in nursing home residents, hoping to see a signal in a population in which flu complications are more common. “If you can get a difference in a nursing home population, that’s clinically important, that gives you hope that you can see it in all the other populations, too,” he said.
SOURCE: Gravenstein S et al. IDWeek 2018, Abstract 996.
SAN FRANCISCO – presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“It’s one thing to say you have a more immunogenic vaccine, it’s another thing to be able to say it offers clinical benefit, especially in the oldest old and the frailest frail,” says Stefan Gravenstein, MD, professor of medicine and health services, policy and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I. Dr. Gravenstein presented a poster outlying a randomized, clinical trial of the Fluad vaccine in nursing homes.
The study randomized the nursing homes so that some facilities would offer Fluad as part of their standard of care. The design helped address the problem of consent. Any clinical trial that requires individual consent would likely exclude many of the frailest patients, leading to an unrepresentative sample. “So if you want to have a generalizable result, you’d like to have it applied to the population the way you would in the real world, so randomizing the nursing homes rather than the people makes a lot of sense,” said Dr. Gravenstein.
Dr. Gravenstein chose to test the vaccine in nursing home residents, hoping to see a signal in a population in which flu complications are more common. “If you can get a difference in a nursing home population, that’s clinically important, that gives you hope that you can see it in all the other populations, too,” he said.
SOURCE: Gravenstein S et al. IDWeek 2018, Abstract 996.
SAN FRANCISCO – presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
“It’s one thing to say you have a more immunogenic vaccine, it’s another thing to be able to say it offers clinical benefit, especially in the oldest old and the frailest frail,” says Stefan Gravenstein, MD, professor of medicine and health services, policy and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, R.I. Dr. Gravenstein presented a poster outlying a randomized, clinical trial of the Fluad vaccine in nursing homes.
The study randomized the nursing homes so that some facilities would offer Fluad as part of their standard of care. The design helped address the problem of consent. Any clinical trial that requires individual consent would likely exclude many of the frailest patients, leading to an unrepresentative sample. “So if you want to have a generalizable result, you’d like to have it applied to the population the way you would in the real world, so randomizing the nursing homes rather than the people makes a lot of sense,” said Dr. Gravenstein.
Dr. Gravenstein chose to test the vaccine in nursing home residents, hoping to see a signal in a population in which flu complications are more common. “If you can get a difference in a nursing home population, that’s clinically important, that gives you hope that you can see it in all the other populations, too,” he said.
SOURCE: Gravenstein S et al. IDWeek 2018, Abstract 996.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2018