User login
Cruel summer for medical students and Taylor Swift fans
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not an assembly line
A lot of businesses benefit from being in private equity funds.
Health care isn’t one of them, and a recent report found that
This really shouldn’t surprise anyone. Such funds may offer glittering phrases like “improved technology” and “greater efficiency” but the bottom line is that they’re run by – and for – the shareholders. The majority of them aren’t going to be medical people or realize that you can’t run a medical practice like it’s a clothing retailer or electronic car manufacturer.
I’m not saying medicine isn’t a business – it is. I depend on my little practice to support three families, so keeping it in the black is important. But it also needs to run well to do that. Measures to increase revenue, like cutting my staff down (there are only two of them) or overbooking patients would seriously impact me effectively doing my part, which is playing doctor.
You can predict pretty accurately how long it will take to put a motor and bumper assembly on a specific model of car, but you can’t do that in medicine because people aren’t standardized. Even if you control variables such as same sex, age, and diagnosis, personalities vary widely, as do treatment decisions, questions they’ll have, and the “oh, another thing” factor.
That doesn’t happen at a bottling plant.
In the business model of health care, you’re hoping revenue will pay overhead and a reasonable salary for everyone. But when you add a private equity firm in, the shareholders also expect to be paid. Which means either revenue has to go up significantly, or costs have to be cut (layoffs, short staffing, reduced benefits, etc.), or a combination of both.
Regardless of which option is chosen, it isn’t good for the medical staff or the patients. Increasing the number of people seen in a given amount of time per doctor may be good for the shareholders, but it’s not good for the doctor or the person being cared for. Think of Lucy and Ethyl at the chocolate factory.
Even in an auto factory, if you speed up the rate of cars going through the assembly line, sooner or later mistakes will be made. Humans can’t keep up, and even robots will make errors if things aren’t aligned correctly, or are a few seconds ahead or behind the program. This is why they (hopefully) have quality control, to try and catch those things before they’re on the road.
Of course, cars are more easily fixable. When the mistake is found you repair or replace the part. You can’t do that as easily in people, and when serious mistakes happen it’s the doctor who’s held at fault – not the shareholders who pressured him or her to see patients faster and with less support.
Unfortunately, this is the way the current trend is going. The more people who are involved in the practice of medicine, in person or behind the scenes, the smaller each slice of the pie gets.
That’s not good for the patient, who’s the person at the center of it all and the reason why we’re here.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A lot of businesses benefit from being in private equity funds.
Health care isn’t one of them, and a recent report found that
This really shouldn’t surprise anyone. Such funds may offer glittering phrases like “improved technology” and “greater efficiency” but the bottom line is that they’re run by – and for – the shareholders. The majority of them aren’t going to be medical people or realize that you can’t run a medical practice like it’s a clothing retailer or electronic car manufacturer.
I’m not saying medicine isn’t a business – it is. I depend on my little practice to support three families, so keeping it in the black is important. But it also needs to run well to do that. Measures to increase revenue, like cutting my staff down (there are only two of them) or overbooking patients would seriously impact me effectively doing my part, which is playing doctor.
You can predict pretty accurately how long it will take to put a motor and bumper assembly on a specific model of car, but you can’t do that in medicine because people aren’t standardized. Even if you control variables such as same sex, age, and diagnosis, personalities vary widely, as do treatment decisions, questions they’ll have, and the “oh, another thing” factor.
That doesn’t happen at a bottling plant.
In the business model of health care, you’re hoping revenue will pay overhead and a reasonable salary for everyone. But when you add a private equity firm in, the shareholders also expect to be paid. Which means either revenue has to go up significantly, or costs have to be cut (layoffs, short staffing, reduced benefits, etc.), or a combination of both.
Regardless of which option is chosen, it isn’t good for the medical staff or the patients. Increasing the number of people seen in a given amount of time per doctor may be good for the shareholders, but it’s not good for the doctor or the person being cared for. Think of Lucy and Ethyl at the chocolate factory.
Even in an auto factory, if you speed up the rate of cars going through the assembly line, sooner or later mistakes will be made. Humans can’t keep up, and even robots will make errors if things aren’t aligned correctly, or are a few seconds ahead or behind the program. This is why they (hopefully) have quality control, to try and catch those things before they’re on the road.
Of course, cars are more easily fixable. When the mistake is found you repair or replace the part. You can’t do that as easily in people, and when serious mistakes happen it’s the doctor who’s held at fault – not the shareholders who pressured him or her to see patients faster and with less support.
Unfortunately, this is the way the current trend is going. The more people who are involved in the practice of medicine, in person or behind the scenes, the smaller each slice of the pie gets.
That’s not good for the patient, who’s the person at the center of it all and the reason why we’re here.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A lot of businesses benefit from being in private equity funds.
Health care isn’t one of them, and a recent report found that
This really shouldn’t surprise anyone. Such funds may offer glittering phrases like “improved technology” and “greater efficiency” but the bottom line is that they’re run by – and for – the shareholders. The majority of them aren’t going to be medical people or realize that you can’t run a medical practice like it’s a clothing retailer or electronic car manufacturer.
I’m not saying medicine isn’t a business – it is. I depend on my little practice to support three families, so keeping it in the black is important. But it also needs to run well to do that. Measures to increase revenue, like cutting my staff down (there are only two of them) or overbooking patients would seriously impact me effectively doing my part, which is playing doctor.
You can predict pretty accurately how long it will take to put a motor and bumper assembly on a specific model of car, but you can’t do that in medicine because people aren’t standardized. Even if you control variables such as same sex, age, and diagnosis, personalities vary widely, as do treatment decisions, questions they’ll have, and the “oh, another thing” factor.
That doesn’t happen at a bottling plant.
In the business model of health care, you’re hoping revenue will pay overhead and a reasonable salary for everyone. But when you add a private equity firm in, the shareholders also expect to be paid. Which means either revenue has to go up significantly, or costs have to be cut (layoffs, short staffing, reduced benefits, etc.), or a combination of both.
Regardless of which option is chosen, it isn’t good for the medical staff or the patients. Increasing the number of people seen in a given amount of time per doctor may be good for the shareholders, but it’s not good for the doctor or the person being cared for. Think of Lucy and Ethyl at the chocolate factory.
Even in an auto factory, if you speed up the rate of cars going through the assembly line, sooner or later mistakes will be made. Humans can’t keep up, and even robots will make errors if things aren’t aligned correctly, or are a few seconds ahead or behind the program. This is why they (hopefully) have quality control, to try and catch those things before they’re on the road.
Of course, cars are more easily fixable. When the mistake is found you repair or replace the part. You can’t do that as easily in people, and when serious mistakes happen it’s the doctor who’s held at fault – not the shareholders who pressured him or her to see patients faster and with less support.
Unfortunately, this is the way the current trend is going. The more people who are involved in the practice of medicine, in person or behind the scenes, the smaller each slice of the pie gets.
That’s not good for the patient, who’s the person at the center of it all and the reason why we’re here.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
‘Patients fail’ despite benefits of sustained weight loss
Don’t look for the publication of a study detailing the probability of blood pressure reduction to normotensive among adults with hypertension who aren’t offered pharmacotherapy in a JAMA journal. It’s not because hypertension doesn’t respond to intentional behavior change. On the contrary, it absolutely does, but when it comes to hypertension, physicians don’t require patients to fail to manage their hypertension through personal responsibility before medications are discussed and involved.
Not so, of course, with obesity.
A few weeks ago a paper was published in JAMA Network Open entitled “Probability of 5% or greater weight loss or BMI reduction to healthy weight among adults with overweight or obesity,” which authors, peer reviewers, and editors deemed worthy of publication. Now, to be fair, it might be worthy of publication if the call to action and thrust of the paper was to chastise physicians for not offering patients effective treatments; the medical education system for failing to teach physicians how to effectively manage obesity; or, if medication is being offered, addressing the barriers to its use. Instead, the main thrust was that patients are failing to help themselves despite the known health benefits of sustained weight loss.
It’s not at all surprising that, despite known benefits, sustained weight loss without pharmacotherapy or surgery is elusive. Just as with virtually every other chronic noncommunicable disease with lifestyle levers, intentional behavior change as treatment – which, by definition for chronic diseases, needs to be employed in perpetuity – requires wide-ranging degrees of privilege and is not a reasonable expectation. And if outcomes from the FREEE trial are applicable broadly, this may be true even if the behavior change required is minimal, the cost is free, and the motivation is large.
The FREEE trial studied whether cost had a role to play in why so many people, even after a myocardial infarction, don’t follow through with the simplest of intentional behavior changes – taking prescribed medications – by providing free medications known to reduce the risk of having a second MI to study participants who had just suffered an MI.
Results showed that, although the group receiving free medications were taking more of them than the group that had a copay for them, at 1.5 years post-MI, only 41% of those receiving all their medications for free were taking them.
And what of those who have a copay? This study found that fewer than 30% of Medicare beneficiaries 65-74 years of age who were hospitalized for heart attacks filled their new statin prescriptions within 90 days of discharge. That the vast majority of patients who’d had actual heart attacks didn’t even take on the behavior change of simply filling their prescription for, let alone taking, a medication shown to reduce their risk of having another heart attack, speaks to the folly of believing that knowledge drives behavior change.
The message is that And yet here we have a paper that concludes with the inference of surprise that few people, without treatment, lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight “despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss.”
While this paper does suggest in passing that yes, maybe we should offer effective treatments to patients with obesity, medicine needs to stop framing obesity as some surprising personal-responsibility knowledge gap and instead focus on the real problems at hand: the barriers to physicians treating obesity as they do every other chronic noncommunicable disease; why, unlike hypertension, for example, primary care providers are generally not well trained in its effective management; and why those who aren’t, despite obesity’s prevalence and impact, don’t see it as worthwhile to go out of their way to learn.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor in the department of family medicine at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, also in Ottawa. He reported conflicts of interest with Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Don’t look for the publication of a study detailing the probability of blood pressure reduction to normotensive among adults with hypertension who aren’t offered pharmacotherapy in a JAMA journal. It’s not because hypertension doesn’t respond to intentional behavior change. On the contrary, it absolutely does, but when it comes to hypertension, physicians don’t require patients to fail to manage their hypertension through personal responsibility before medications are discussed and involved.
Not so, of course, with obesity.
A few weeks ago a paper was published in JAMA Network Open entitled “Probability of 5% or greater weight loss or BMI reduction to healthy weight among adults with overweight or obesity,” which authors, peer reviewers, and editors deemed worthy of publication. Now, to be fair, it might be worthy of publication if the call to action and thrust of the paper was to chastise physicians for not offering patients effective treatments; the medical education system for failing to teach physicians how to effectively manage obesity; or, if medication is being offered, addressing the barriers to its use. Instead, the main thrust was that patients are failing to help themselves despite the known health benefits of sustained weight loss.
It’s not at all surprising that, despite known benefits, sustained weight loss without pharmacotherapy or surgery is elusive. Just as with virtually every other chronic noncommunicable disease with lifestyle levers, intentional behavior change as treatment – which, by definition for chronic diseases, needs to be employed in perpetuity – requires wide-ranging degrees of privilege and is not a reasonable expectation. And if outcomes from the FREEE trial are applicable broadly, this may be true even if the behavior change required is minimal, the cost is free, and the motivation is large.
The FREEE trial studied whether cost had a role to play in why so many people, even after a myocardial infarction, don’t follow through with the simplest of intentional behavior changes – taking prescribed medications – by providing free medications known to reduce the risk of having a second MI to study participants who had just suffered an MI.
Results showed that, although the group receiving free medications were taking more of them than the group that had a copay for them, at 1.5 years post-MI, only 41% of those receiving all their medications for free were taking them.
And what of those who have a copay? This study found that fewer than 30% of Medicare beneficiaries 65-74 years of age who were hospitalized for heart attacks filled their new statin prescriptions within 90 days of discharge. That the vast majority of patients who’d had actual heart attacks didn’t even take on the behavior change of simply filling their prescription for, let alone taking, a medication shown to reduce their risk of having another heart attack, speaks to the folly of believing that knowledge drives behavior change.
The message is that And yet here we have a paper that concludes with the inference of surprise that few people, without treatment, lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight “despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss.”
While this paper does suggest in passing that yes, maybe we should offer effective treatments to patients with obesity, medicine needs to stop framing obesity as some surprising personal-responsibility knowledge gap and instead focus on the real problems at hand: the barriers to physicians treating obesity as they do every other chronic noncommunicable disease; why, unlike hypertension, for example, primary care providers are generally not well trained in its effective management; and why those who aren’t, despite obesity’s prevalence and impact, don’t see it as worthwhile to go out of their way to learn.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor in the department of family medicine at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, also in Ottawa. He reported conflicts of interest with Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Don’t look for the publication of a study detailing the probability of blood pressure reduction to normotensive among adults with hypertension who aren’t offered pharmacotherapy in a JAMA journal. It’s not because hypertension doesn’t respond to intentional behavior change. On the contrary, it absolutely does, but when it comes to hypertension, physicians don’t require patients to fail to manage their hypertension through personal responsibility before medications are discussed and involved.
Not so, of course, with obesity.
A few weeks ago a paper was published in JAMA Network Open entitled “Probability of 5% or greater weight loss or BMI reduction to healthy weight among adults with overweight or obesity,” which authors, peer reviewers, and editors deemed worthy of publication. Now, to be fair, it might be worthy of publication if the call to action and thrust of the paper was to chastise physicians for not offering patients effective treatments; the medical education system for failing to teach physicians how to effectively manage obesity; or, if medication is being offered, addressing the barriers to its use. Instead, the main thrust was that patients are failing to help themselves despite the known health benefits of sustained weight loss.
It’s not at all surprising that, despite known benefits, sustained weight loss without pharmacotherapy or surgery is elusive. Just as with virtually every other chronic noncommunicable disease with lifestyle levers, intentional behavior change as treatment – which, by definition for chronic diseases, needs to be employed in perpetuity – requires wide-ranging degrees of privilege and is not a reasonable expectation. And if outcomes from the FREEE trial are applicable broadly, this may be true even if the behavior change required is minimal, the cost is free, and the motivation is large.
The FREEE trial studied whether cost had a role to play in why so many people, even after a myocardial infarction, don’t follow through with the simplest of intentional behavior changes – taking prescribed medications – by providing free medications known to reduce the risk of having a second MI to study participants who had just suffered an MI.
Results showed that, although the group receiving free medications were taking more of them than the group that had a copay for them, at 1.5 years post-MI, only 41% of those receiving all their medications for free were taking them.
And what of those who have a copay? This study found that fewer than 30% of Medicare beneficiaries 65-74 years of age who were hospitalized for heart attacks filled their new statin prescriptions within 90 days of discharge. That the vast majority of patients who’d had actual heart attacks didn’t even take on the behavior change of simply filling their prescription for, let alone taking, a medication shown to reduce their risk of having another heart attack, speaks to the folly of believing that knowledge drives behavior change.
The message is that And yet here we have a paper that concludes with the inference of surprise that few people, without treatment, lost clinically meaningful amounts of weight “despite the known benefits of clinically meaningful weight loss.”
While this paper does suggest in passing that yes, maybe we should offer effective treatments to patients with obesity, medicine needs to stop framing obesity as some surprising personal-responsibility knowledge gap and instead focus on the real problems at hand: the barriers to physicians treating obesity as they do every other chronic noncommunicable disease; why, unlike hypertension, for example, primary care providers are generally not well trained in its effective management; and why those who aren’t, despite obesity’s prevalence and impact, don’t see it as worthwhile to go out of their way to learn.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor in the department of family medicine at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, also in Ottawa. He reported conflicts of interest with Constant Health, Novo Nordisk, and Weighty Matters.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A nurse’s view: Blood test for severe preeclampsia will save lives
There is amazing news for the world of obstetrics and for all pregnant women. Severe preeclampsia is a critical obstetrical condition that can have serious outcomes for a mother and baby. It can lead to eclampsia, an obstetrical emergency, which often results in death of the mother and/or baby.
Based on research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the incidence of new‐onset hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (gestational hypertension and preeclampsia/eclampsia) have nearly doubled in the United States from 2007 to 2019. And they continue to climb.
According to the Preeclampsia Foundation, 5%-8% of all pregnancies in the United States will result in preeclampsia. Black women are at a 60% higher risk than white women, and according to various sources, other risk groups include those who became pregnant via in vitro fertilization, mothers of multiples (twins and triplets), women with gestational diabetes, women over age 35, women with chronic hypertension, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, sickle cell disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, migraines, antiphospholipid syndrome, previous pregnancy with preeclampsia, family history, and scleroderma.
Screening and treatment
Preeclampsia is a multiorgan disease of pregnancy, and can be mild, but may quickly progress to severe, which can be life-threatening for mother and baby. It was previously referred to as toxemia or the high blood pressure disease of pregnancy. It primarily involves the cardiovascular, neurologic and renal systems, and the liver. Patients typically present with elevated blood pressures, but other symptoms may include headache, swelling of hands and feet, blurry/double vision or seeing spots, nausea/vomiting, and epigastric pain. It is diagnosed with elevated blood pressures, blood work, and protein in the urine.
Early screening for preeclampsia is done in the first trimester. Presently, a combination of prenatal blood work, blood pressure monitoring, and recognition of high-risk groups is used to determine a treatment plan going forward. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends women that fall into this group for potentially developing preeclampsia take daily aspirin as a preventative measure.
In its milder form, a pregnant woman can be observed as an outpatient – monitored with antepartum testing, lab work, and patient education to report significant symptoms as listed above. Teaching patients about fetal kick counts to monitor their baby’s movements is equally important. Women with mild preeclampsia usually can safely deliver at term, being induced between 37-39 weeks’ gestation.
On the other hand, if mild preeclampsia progresses to severe preeclampsia, delivery may be preterm for the safety of mother and baby. Severe preeclampsia can lead to maternal organ damage, seizures, and even death of mother and/or baby.
About 20% of women with severe preeclampsia will develop HELLP (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and Low Platelets) syndrome, a life-threatening disease that often warrants immediate delivery. According to the National Library of Medicine, the mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is up to 24% and the perinatal death rate is up as high as 37%. These serious conditions can cause ineffective maternal clotting, liver rupture, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage. It is most prevalent in the third trimester but can occur within 48 hours of delivery.
The only cure for preeclampsia in any form is delivery.
Patients with severe preeclampsia are hospitalized until delivery – sometimes a few days to a couple of weeks. Mother and baby are closely watched for further progression, including signs of organ damage in the mother and changes to the well-being of the baby. If the mother’s health is severely compromised, then the baby will be compromised as well. A preterm delivery may be necessary.
Impact of the new test
The National Institute of Health states that preterm babies born from preeclamptic mothers can suffer many health problems including cerebral palsy, deafness, blindness, epilepsy, and a host of other respiratory, cardiovascular, and endocrine issues. But the biggest issue is preterm birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks gestation. Being born preterm can require a long stay in the intensive care nursery.
This is where the first-of-its-kind prognostic blood test comes into play. The test’s ability to predict severe preeclampsia within 2 weeks can help save lives. The test can offer health care providers the ability to administer steroids for fetal lung maturity before delivery and be more prepared to care for what could be a very compromised newborn.
The blood test, which is recommended between 23-35 weeks gestation, involves analyzing a ratio between two proteins from the placenta, sFlt1 and PIGF. The higher the ratio, the higher the risk that severe preeclampsia will develop. Results can be available within 30 minutes, which is critical when contemplating treatment.
An example of the use of this ratio is illustrated with chronic hypertension in pregnancy, which is defined as elevated blood pressure before 20 weeks or even before conception. Since chronic hypertension can be a primary precursor to preeclampsia, patients with this condition are at higher risk. The FDA-approved blood test would be helpful in determining the plan of care; that is, delivery versus hospitalization versus monitor as an outpatient.
With a positive test result, a pregnant woman can be immediately hospitalized where she can get the care she and baby need as they await delivery. Since health care providers already know the high-risk groups, surveillance can begin early, utilizing this blood test to predict the progression to severe preeclampsia. Conversely, if the test is negative, a treatment plan can be made as an outpatient and the pregnancy continues.
Not all hospitals are equipped to care for premature babies. If delivery is not imminent, providers can use this blood test to identify those that should be transferred to a tertiary center for observation and monitoring. Mother and baby would then not be separated after birth.
We really don’t know who will develop severe preeclampsia and who won’t. This new blood test will be a critical tool as pregnant patients go through their second and third trimesters. It will be especially pivotal for these women, but important for all pregnant women in reducing maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity.
Ms. Barnett is a registered nurse in the department of obstetrics, Mills-Peninsula Medical Center, Burlingame, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
There is amazing news for the world of obstetrics and for all pregnant women. Severe preeclampsia is a critical obstetrical condition that can have serious outcomes for a mother and baby. It can lead to eclampsia, an obstetrical emergency, which often results in death of the mother and/or baby.
Based on research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the incidence of new‐onset hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (gestational hypertension and preeclampsia/eclampsia) have nearly doubled in the United States from 2007 to 2019. And they continue to climb.
According to the Preeclampsia Foundation, 5%-8% of all pregnancies in the United States will result in preeclampsia. Black women are at a 60% higher risk than white women, and according to various sources, other risk groups include those who became pregnant via in vitro fertilization, mothers of multiples (twins and triplets), women with gestational diabetes, women over age 35, women with chronic hypertension, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, sickle cell disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, migraines, antiphospholipid syndrome, previous pregnancy with preeclampsia, family history, and scleroderma.
Screening and treatment
Preeclampsia is a multiorgan disease of pregnancy, and can be mild, but may quickly progress to severe, which can be life-threatening for mother and baby. It was previously referred to as toxemia or the high blood pressure disease of pregnancy. It primarily involves the cardiovascular, neurologic and renal systems, and the liver. Patients typically present with elevated blood pressures, but other symptoms may include headache, swelling of hands and feet, blurry/double vision or seeing spots, nausea/vomiting, and epigastric pain. It is diagnosed with elevated blood pressures, blood work, and protein in the urine.
Early screening for preeclampsia is done in the first trimester. Presently, a combination of prenatal blood work, blood pressure monitoring, and recognition of high-risk groups is used to determine a treatment plan going forward. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends women that fall into this group for potentially developing preeclampsia take daily aspirin as a preventative measure.
In its milder form, a pregnant woman can be observed as an outpatient – monitored with antepartum testing, lab work, and patient education to report significant symptoms as listed above. Teaching patients about fetal kick counts to monitor their baby’s movements is equally important. Women with mild preeclampsia usually can safely deliver at term, being induced between 37-39 weeks’ gestation.
On the other hand, if mild preeclampsia progresses to severe preeclampsia, delivery may be preterm for the safety of mother and baby. Severe preeclampsia can lead to maternal organ damage, seizures, and even death of mother and/or baby.
About 20% of women with severe preeclampsia will develop HELLP (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and Low Platelets) syndrome, a life-threatening disease that often warrants immediate delivery. According to the National Library of Medicine, the mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is up to 24% and the perinatal death rate is up as high as 37%. These serious conditions can cause ineffective maternal clotting, liver rupture, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage. It is most prevalent in the third trimester but can occur within 48 hours of delivery.
The only cure for preeclampsia in any form is delivery.
Patients with severe preeclampsia are hospitalized until delivery – sometimes a few days to a couple of weeks. Mother and baby are closely watched for further progression, including signs of organ damage in the mother and changes to the well-being of the baby. If the mother’s health is severely compromised, then the baby will be compromised as well. A preterm delivery may be necessary.
Impact of the new test
The National Institute of Health states that preterm babies born from preeclamptic mothers can suffer many health problems including cerebral palsy, deafness, blindness, epilepsy, and a host of other respiratory, cardiovascular, and endocrine issues. But the biggest issue is preterm birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks gestation. Being born preterm can require a long stay in the intensive care nursery.
This is where the first-of-its-kind prognostic blood test comes into play. The test’s ability to predict severe preeclampsia within 2 weeks can help save lives. The test can offer health care providers the ability to administer steroids for fetal lung maturity before delivery and be more prepared to care for what could be a very compromised newborn.
The blood test, which is recommended between 23-35 weeks gestation, involves analyzing a ratio between two proteins from the placenta, sFlt1 and PIGF. The higher the ratio, the higher the risk that severe preeclampsia will develop. Results can be available within 30 minutes, which is critical when contemplating treatment.
An example of the use of this ratio is illustrated with chronic hypertension in pregnancy, which is defined as elevated blood pressure before 20 weeks or even before conception. Since chronic hypertension can be a primary precursor to preeclampsia, patients with this condition are at higher risk. The FDA-approved blood test would be helpful in determining the plan of care; that is, delivery versus hospitalization versus monitor as an outpatient.
With a positive test result, a pregnant woman can be immediately hospitalized where she can get the care she and baby need as they await delivery. Since health care providers already know the high-risk groups, surveillance can begin early, utilizing this blood test to predict the progression to severe preeclampsia. Conversely, if the test is negative, a treatment plan can be made as an outpatient and the pregnancy continues.
Not all hospitals are equipped to care for premature babies. If delivery is not imminent, providers can use this blood test to identify those that should be transferred to a tertiary center for observation and monitoring. Mother and baby would then not be separated after birth.
We really don’t know who will develop severe preeclampsia and who won’t. This new blood test will be a critical tool as pregnant patients go through their second and third trimesters. It will be especially pivotal for these women, but important for all pregnant women in reducing maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity.
Ms. Barnett is a registered nurse in the department of obstetrics, Mills-Peninsula Medical Center, Burlingame, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
There is amazing news for the world of obstetrics and for all pregnant women. Severe preeclampsia is a critical obstetrical condition that can have serious outcomes for a mother and baby. It can lead to eclampsia, an obstetrical emergency, which often results in death of the mother and/or baby.
Based on research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the incidence of new‐onset hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (gestational hypertension and preeclampsia/eclampsia) have nearly doubled in the United States from 2007 to 2019. And they continue to climb.
According to the Preeclampsia Foundation, 5%-8% of all pregnancies in the United States will result in preeclampsia. Black women are at a 60% higher risk than white women, and according to various sources, other risk groups include those who became pregnant via in vitro fertilization, mothers of multiples (twins and triplets), women with gestational diabetes, women over age 35, women with chronic hypertension, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, sickle cell disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, migraines, antiphospholipid syndrome, previous pregnancy with preeclampsia, family history, and scleroderma.
Screening and treatment
Preeclampsia is a multiorgan disease of pregnancy, and can be mild, but may quickly progress to severe, which can be life-threatening for mother and baby. It was previously referred to as toxemia or the high blood pressure disease of pregnancy. It primarily involves the cardiovascular, neurologic and renal systems, and the liver. Patients typically present with elevated blood pressures, but other symptoms may include headache, swelling of hands and feet, blurry/double vision or seeing spots, nausea/vomiting, and epigastric pain. It is diagnosed with elevated blood pressures, blood work, and protein in the urine.
Early screening for preeclampsia is done in the first trimester. Presently, a combination of prenatal blood work, blood pressure monitoring, and recognition of high-risk groups is used to determine a treatment plan going forward. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends women that fall into this group for potentially developing preeclampsia take daily aspirin as a preventative measure.
In its milder form, a pregnant woman can be observed as an outpatient – monitored with antepartum testing, lab work, and patient education to report significant symptoms as listed above. Teaching patients about fetal kick counts to monitor their baby’s movements is equally important. Women with mild preeclampsia usually can safely deliver at term, being induced between 37-39 weeks’ gestation.
On the other hand, if mild preeclampsia progresses to severe preeclampsia, delivery may be preterm for the safety of mother and baby. Severe preeclampsia can lead to maternal organ damage, seizures, and even death of mother and/or baby.
About 20% of women with severe preeclampsia will develop HELLP (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, and Low Platelets) syndrome, a life-threatening disease that often warrants immediate delivery. According to the National Library of Medicine, the mortality rate of women with HELLP syndrome is up to 24% and the perinatal death rate is up as high as 37%. These serious conditions can cause ineffective maternal clotting, liver rupture, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage. It is most prevalent in the third trimester but can occur within 48 hours of delivery.
The only cure for preeclampsia in any form is delivery.
Patients with severe preeclampsia are hospitalized until delivery – sometimes a few days to a couple of weeks. Mother and baby are closely watched for further progression, including signs of organ damage in the mother and changes to the well-being of the baby. If the mother’s health is severely compromised, then the baby will be compromised as well. A preterm delivery may be necessary.
Impact of the new test
The National Institute of Health states that preterm babies born from preeclamptic mothers can suffer many health problems including cerebral palsy, deafness, blindness, epilepsy, and a host of other respiratory, cardiovascular, and endocrine issues. But the biggest issue is preterm birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks gestation. Being born preterm can require a long stay in the intensive care nursery.
This is where the first-of-its-kind prognostic blood test comes into play. The test’s ability to predict severe preeclampsia within 2 weeks can help save lives. The test can offer health care providers the ability to administer steroids for fetal lung maturity before delivery and be more prepared to care for what could be a very compromised newborn.
The blood test, which is recommended between 23-35 weeks gestation, involves analyzing a ratio between two proteins from the placenta, sFlt1 and PIGF. The higher the ratio, the higher the risk that severe preeclampsia will develop. Results can be available within 30 minutes, which is critical when contemplating treatment.
An example of the use of this ratio is illustrated with chronic hypertension in pregnancy, which is defined as elevated blood pressure before 20 weeks or even before conception. Since chronic hypertension can be a primary precursor to preeclampsia, patients with this condition are at higher risk. The FDA-approved blood test would be helpful in determining the plan of care; that is, delivery versus hospitalization versus monitor as an outpatient.
With a positive test result, a pregnant woman can be immediately hospitalized where she can get the care she and baby need as they await delivery. Since health care providers already know the high-risk groups, surveillance can begin early, utilizing this blood test to predict the progression to severe preeclampsia. Conversely, if the test is negative, a treatment plan can be made as an outpatient and the pregnancy continues.
Not all hospitals are equipped to care for premature babies. If delivery is not imminent, providers can use this blood test to identify those that should be transferred to a tertiary center for observation and monitoring. Mother and baby would then not be separated after birth.
We really don’t know who will develop severe preeclampsia and who won’t. This new blood test will be a critical tool as pregnant patients go through their second and third trimesters. It will be especially pivotal for these women, but important for all pregnant women in reducing maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity.
Ms. Barnett is a registered nurse in the department of obstetrics, Mills-Peninsula Medical Center, Burlingame, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Answering the protein question when prescribing plant-based diets
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable. Patients know that protein is essential for their health and strength, and animal foods have developed a reputation for being the premier protein sources that humans should prioritize through diet. But widespread misconceptions about human needs for protein have inaccurately equated animal food as the best and only sources of protein, augmented by fad diets and modern food marketing. All of this leads to confusion about how much protein people should actually consume and the quality of protein found in plant foods, making many patients reluctant to fully embrace a whole food, predominately plant-based diet.
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
The recommended daily allowances for protein are easily met by consuming a variety of whole plant foods, including a variety of minimally processed vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. One cup of cooked red lentils or black beans, for example, contains between 15 g and 18 g of protein. A quarter cup of almonds contains about 7 g of protein and one cup of cooked oats has 5 g.
What about those amino acids?
An area of contention around plant food protein is “complete versus incomplete protein,” terms used to describe whether a protein contains all nine essential amino acids that our bodies require from a single source. Animal food sources usually contain all the essential amino acids, whereas plant sources of protein may contain varying amounts of these amino acids or may even be missing some.
This leads to a misconception that someone adopting a diet of predominately plant food may have to stack or combine specific plant foods in a meal to ensure their protein intake includes an appropriate proportion of amino acids. But the process of protein breakdown turnover solves this problem. The body continuously breaks down protein and recombines it with amino acids stored in tissue for use when needed. Once absorbed by the small intestine, it doesn’t matter whether the protein or amino acids came from the same meal. As long as a person is eating a variety of plant-based protein sources, they will consume adequate amounts of all essential amino acids.
This is true even for athletes, older adults and pregnant women. It is also the position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics that a whole-food, predominately plant-based eating pattern is appropriate for athletes and “all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood.”
The plant-based diet
For examples of healthy plant-based eating plans, The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a complimentary guide for a whole food, predominantly plant-based diet that demonstrates how easily the recommended dietary allowance of protein is satisfied. A breakfast of rolled oats, a lunch of bean burritos, and a dinner of mashed potatoes, with chickpeas with a couple snacks throughout the day, adds up to 71 g of protein. Other plant-based meal plans top 100 g or 90 g, with all meal plans meeting or surpassing recommended allowances.
Along with the protein, plant food delivers other beneficial nutrients and dietary components like fiber, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory properties, various vitamins and nutrients, and phytochemicals and vitamin D, without the saturated fats and sodium in meat. But U.S. adults get approximately two-thirds of their protein from animal sources, which lack fiber and have higher levels of saturated fats or sodium that can raise cholesterol and increase the risks for heart disease and stroke.
For clinicians, ACLM published a 10-part series of research white papers on the benefits of a whole food, plant-predominant dietary lifestyle and offers a catalogue of food as medicine continuing medical education and continuing education courses.
Patients hunger for knowledge about health-promoting nutrition but may have difficulty sorting myths from evidence-based facts. Each healthcare professional has an important and powerful opportunity to steer patients in a healthier direction through their diet.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development; President, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable. Patients know that protein is essential for their health and strength, and animal foods have developed a reputation for being the premier protein sources that humans should prioritize through diet. But widespread misconceptions about human needs for protein have inaccurately equated animal food as the best and only sources of protein, augmented by fad diets and modern food marketing. All of this leads to confusion about how much protein people should actually consume and the quality of protein found in plant foods, making many patients reluctant to fully embrace a whole food, predominately plant-based diet.
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
The recommended daily allowances for protein are easily met by consuming a variety of whole plant foods, including a variety of minimally processed vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. One cup of cooked red lentils or black beans, for example, contains between 15 g and 18 g of protein. A quarter cup of almonds contains about 7 g of protein and one cup of cooked oats has 5 g.
What about those amino acids?
An area of contention around plant food protein is “complete versus incomplete protein,” terms used to describe whether a protein contains all nine essential amino acids that our bodies require from a single source. Animal food sources usually contain all the essential amino acids, whereas plant sources of protein may contain varying amounts of these amino acids or may even be missing some.
This leads to a misconception that someone adopting a diet of predominately plant food may have to stack or combine specific plant foods in a meal to ensure their protein intake includes an appropriate proportion of amino acids. But the process of protein breakdown turnover solves this problem. The body continuously breaks down protein and recombines it with amino acids stored in tissue for use when needed. Once absorbed by the small intestine, it doesn’t matter whether the protein or amino acids came from the same meal. As long as a person is eating a variety of plant-based protein sources, they will consume adequate amounts of all essential amino acids.
This is true even for athletes, older adults and pregnant women. It is also the position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics that a whole-food, predominately plant-based eating pattern is appropriate for athletes and “all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood.”
The plant-based diet
For examples of healthy plant-based eating plans, The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a complimentary guide for a whole food, predominantly plant-based diet that demonstrates how easily the recommended dietary allowance of protein is satisfied. A breakfast of rolled oats, a lunch of bean burritos, and a dinner of mashed potatoes, with chickpeas with a couple snacks throughout the day, adds up to 71 g of protein. Other plant-based meal plans top 100 g or 90 g, with all meal plans meeting or surpassing recommended allowances.
Along with the protein, plant food delivers other beneficial nutrients and dietary components like fiber, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory properties, various vitamins and nutrients, and phytochemicals and vitamin D, without the saturated fats and sodium in meat. But U.S. adults get approximately two-thirds of their protein from animal sources, which lack fiber and have higher levels of saturated fats or sodium that can raise cholesterol and increase the risks for heart disease and stroke.
For clinicians, ACLM published a 10-part series of research white papers on the benefits of a whole food, plant-predominant dietary lifestyle and offers a catalogue of food as medicine continuing medical education and continuing education courses.
Patients hunger for knowledge about health-promoting nutrition but may have difficulty sorting myths from evidence-based facts. Each healthcare professional has an important and powerful opportunity to steer patients in a healthier direction through their diet.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development; President, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable. Patients know that protein is essential for their health and strength, and animal foods have developed a reputation for being the premier protein sources that humans should prioritize through diet. But widespread misconceptions about human needs for protein have inaccurately equated animal food as the best and only sources of protein, augmented by fad diets and modern food marketing. All of this leads to confusion about how much protein people should actually consume and the quality of protein found in plant foods, making many patients reluctant to fully embrace a whole food, predominately plant-based diet.
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
The recommended daily allowances for protein are easily met by consuming a variety of whole plant foods, including a variety of minimally processed vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. One cup of cooked red lentils or black beans, for example, contains between 15 g and 18 g of protein. A quarter cup of almonds contains about 7 g of protein and one cup of cooked oats has 5 g.
What about those amino acids?
An area of contention around plant food protein is “complete versus incomplete protein,” terms used to describe whether a protein contains all nine essential amino acids that our bodies require from a single source. Animal food sources usually contain all the essential amino acids, whereas plant sources of protein may contain varying amounts of these amino acids or may even be missing some.
This leads to a misconception that someone adopting a diet of predominately plant food may have to stack or combine specific plant foods in a meal to ensure their protein intake includes an appropriate proportion of amino acids. But the process of protein breakdown turnover solves this problem. The body continuously breaks down protein and recombines it with amino acids stored in tissue for use when needed. Once absorbed by the small intestine, it doesn’t matter whether the protein or amino acids came from the same meal. As long as a person is eating a variety of plant-based protein sources, they will consume adequate amounts of all essential amino acids.
This is true even for athletes, older adults and pregnant women. It is also the position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics that a whole-food, predominately plant-based eating pattern is appropriate for athletes and “all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood.”
The plant-based diet
For examples of healthy plant-based eating plans, The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a complimentary guide for a whole food, predominantly plant-based diet that demonstrates how easily the recommended dietary allowance of protein is satisfied. A breakfast of rolled oats, a lunch of bean burritos, and a dinner of mashed potatoes, with chickpeas with a couple snacks throughout the day, adds up to 71 g of protein. Other plant-based meal plans top 100 g or 90 g, with all meal plans meeting or surpassing recommended allowances.
Along with the protein, plant food delivers other beneficial nutrients and dietary components like fiber, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory properties, various vitamins and nutrients, and phytochemicals and vitamin D, without the saturated fats and sodium in meat. But U.S. adults get approximately two-thirds of their protein from animal sources, which lack fiber and have higher levels of saturated fats or sodium that can raise cholesterol and increase the risks for heart disease and stroke.
For clinicians, ACLM published a 10-part series of research white papers on the benefits of a whole food, plant-predominant dietary lifestyle and offers a catalogue of food as medicine continuing medical education and continuing education courses.
Patients hunger for knowledge about health-promoting nutrition but may have difficulty sorting myths from evidence-based facts. Each healthcare professional has an important and powerful opportunity to steer patients in a healthier direction through their diet.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development; President, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, Calif. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not ‘reckless’ to consider Ozempic
A stylish 40-something-year-old walks into my office looking mildly sheepish. She is a well-known actress who was recently panned by the paparazzi for having “too much cellulite” after they illegally photographed her playing with her child on a private beach.
Without a doubt, she will request semaglutide (Ozempic) before long, but first we will need to wade through the morass of social condemnation out there about Ozempic to assure her that she is being neither immoral nor reckless for considering it.
Ozempic is nothing new, people! Endocrinologists have been using this class of medication since Byetta hit the market in 2005. We have had 18 years to make informed risk-benefit analyses.
People are obsessed with the risk for pancreatitis. Any type of weight loss can cause gallstones, and this is what can trigger pancreatitis. Unless you’re the type of person who worries that your balanced Weight Watchers diet is going to cause pancreatitis, you should probably remove this risk from your calculations.
Glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are naturally occurring gut hormones that reduce inflammatory cascades and clotting risk. We are not giving a dangerous treatment (e.g., fen-phen) that increases cardiovascular risk – quite the contrary, in fact.
Just because influencers are promoting a product doesn’t mean the product is inherently worthless. One of my patients accused me of prescribing a medication that is the “laughingstock of America.” Try telling that to the scores of cardiologists who send patients to my colleagues and me to start Ozempic to help lower their patients’ risk for stroke and heart attack. Or tell this to my patient who survived an episode of rapid atrial fibrillation and was told by his cardiologist that he definitely would have died if he had not lost 30 pounds from Ozempic in the preceding year.
Sometimes it seems like society has become more judgmental about Ozempic than about plastic surgery for weight loss. If we have to choose between liposuction (which doesn’t reduce visceral fat – the dangerous type of fat) or Ozempic, the latter clearly wins because of its real health benefits.
How does it make any sense to say that this medication should be reserved for patients who already have obesity and type 2 diabetes? Why should we penalize patients who have not yet reached those thresholds by denying access to preventive care? Don’t we constantly hear about how our health care system would be much more efficient if we focused on preventive care and not just treatment?
Some people claim that we have to limit access to this medication because of drug shortages. Thankfully, the United States responds to supply and demand economics and will quickly adjust.
I’ve had more patients than I can possibly number with severe binge eating disorders (resistant to years of therapy and medication) who finally developed healthy relationships with food while taking these types of medications. Mounjaro, I’m talking about you…
I always hear the argument that it is immoral to give these medications to patients with a history of restrictive eating patterns. Although every patient needs to be carefully evaluated, often these medications remove food as both the enemy and primary focus of every waking thought. They allow patients to refocus on other aspects of their lives – such as family, friends, hobbies, work – and regain a sense of purpose. If anyone wants to run a trial on this little hypothesis of mine, please reach out to me.
Okay, I agree you might get a little constipated (most often described by patients as the “rabbit pellet phenomenon”), but it’s a small price to pay, no? I’ll throw in a few prunes with the prescription.
Suffice it to say, I did give my 40-something-year-old patient the medication she desired, and she has a new lease on life (as well as better blood pressure and cholesterol).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A stylish 40-something-year-old walks into my office looking mildly sheepish. She is a well-known actress who was recently panned by the paparazzi for having “too much cellulite” after they illegally photographed her playing with her child on a private beach.
Without a doubt, she will request semaglutide (Ozempic) before long, but first we will need to wade through the morass of social condemnation out there about Ozempic to assure her that she is being neither immoral nor reckless for considering it.
Ozempic is nothing new, people! Endocrinologists have been using this class of medication since Byetta hit the market in 2005. We have had 18 years to make informed risk-benefit analyses.
People are obsessed with the risk for pancreatitis. Any type of weight loss can cause gallstones, and this is what can trigger pancreatitis. Unless you’re the type of person who worries that your balanced Weight Watchers diet is going to cause pancreatitis, you should probably remove this risk from your calculations.
Glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are naturally occurring gut hormones that reduce inflammatory cascades and clotting risk. We are not giving a dangerous treatment (e.g., fen-phen) that increases cardiovascular risk – quite the contrary, in fact.
Just because influencers are promoting a product doesn’t mean the product is inherently worthless. One of my patients accused me of prescribing a medication that is the “laughingstock of America.” Try telling that to the scores of cardiologists who send patients to my colleagues and me to start Ozempic to help lower their patients’ risk for stroke and heart attack. Or tell this to my patient who survived an episode of rapid atrial fibrillation and was told by his cardiologist that he definitely would have died if he had not lost 30 pounds from Ozempic in the preceding year.
Sometimes it seems like society has become more judgmental about Ozempic than about plastic surgery for weight loss. If we have to choose between liposuction (which doesn’t reduce visceral fat – the dangerous type of fat) or Ozempic, the latter clearly wins because of its real health benefits.
How does it make any sense to say that this medication should be reserved for patients who already have obesity and type 2 diabetes? Why should we penalize patients who have not yet reached those thresholds by denying access to preventive care? Don’t we constantly hear about how our health care system would be much more efficient if we focused on preventive care and not just treatment?
Some people claim that we have to limit access to this medication because of drug shortages. Thankfully, the United States responds to supply and demand economics and will quickly adjust.
I’ve had more patients than I can possibly number with severe binge eating disorders (resistant to years of therapy and medication) who finally developed healthy relationships with food while taking these types of medications. Mounjaro, I’m talking about you…
I always hear the argument that it is immoral to give these medications to patients with a history of restrictive eating patterns. Although every patient needs to be carefully evaluated, often these medications remove food as both the enemy and primary focus of every waking thought. They allow patients to refocus on other aspects of their lives – such as family, friends, hobbies, work – and regain a sense of purpose. If anyone wants to run a trial on this little hypothesis of mine, please reach out to me.
Okay, I agree you might get a little constipated (most often described by patients as the “rabbit pellet phenomenon”), but it’s a small price to pay, no? I’ll throw in a few prunes with the prescription.
Suffice it to say, I did give my 40-something-year-old patient the medication she desired, and she has a new lease on life (as well as better blood pressure and cholesterol).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A stylish 40-something-year-old walks into my office looking mildly sheepish. She is a well-known actress who was recently panned by the paparazzi for having “too much cellulite” after they illegally photographed her playing with her child on a private beach.
Without a doubt, she will request semaglutide (Ozempic) before long, but first we will need to wade through the morass of social condemnation out there about Ozempic to assure her that she is being neither immoral nor reckless for considering it.
Ozempic is nothing new, people! Endocrinologists have been using this class of medication since Byetta hit the market in 2005. We have had 18 years to make informed risk-benefit analyses.
People are obsessed with the risk for pancreatitis. Any type of weight loss can cause gallstones, and this is what can trigger pancreatitis. Unless you’re the type of person who worries that your balanced Weight Watchers diet is going to cause pancreatitis, you should probably remove this risk from your calculations.
Glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are naturally occurring gut hormones that reduce inflammatory cascades and clotting risk. We are not giving a dangerous treatment (e.g., fen-phen) that increases cardiovascular risk – quite the contrary, in fact.
Just because influencers are promoting a product doesn’t mean the product is inherently worthless. One of my patients accused me of prescribing a medication that is the “laughingstock of America.” Try telling that to the scores of cardiologists who send patients to my colleagues and me to start Ozempic to help lower their patients’ risk for stroke and heart attack. Or tell this to my patient who survived an episode of rapid atrial fibrillation and was told by his cardiologist that he definitely would have died if he had not lost 30 pounds from Ozempic in the preceding year.
Sometimes it seems like society has become more judgmental about Ozempic than about plastic surgery for weight loss. If we have to choose between liposuction (which doesn’t reduce visceral fat – the dangerous type of fat) or Ozempic, the latter clearly wins because of its real health benefits.
How does it make any sense to say that this medication should be reserved for patients who already have obesity and type 2 diabetes? Why should we penalize patients who have not yet reached those thresholds by denying access to preventive care? Don’t we constantly hear about how our health care system would be much more efficient if we focused on preventive care and not just treatment?
Some people claim that we have to limit access to this medication because of drug shortages. Thankfully, the United States responds to supply and demand economics and will quickly adjust.
I’ve had more patients than I can possibly number with severe binge eating disorders (resistant to years of therapy and medication) who finally developed healthy relationships with food while taking these types of medications. Mounjaro, I’m talking about you…
I always hear the argument that it is immoral to give these medications to patients with a history of restrictive eating patterns. Although every patient needs to be carefully evaluated, often these medications remove food as both the enemy and primary focus of every waking thought. They allow patients to refocus on other aspects of their lives – such as family, friends, hobbies, work – and regain a sense of purpose. If anyone wants to run a trial on this little hypothesis of mine, please reach out to me.
Okay, I agree you might get a little constipated (most often described by patients as the “rabbit pellet phenomenon”), but it’s a small price to pay, no? I’ll throw in a few prunes with the prescription.
Suffice it to say, I did give my 40-something-year-old patient the medication she desired, and she has a new lease on life (as well as better blood pressure and cholesterol).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Human frailty is a cash cow
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.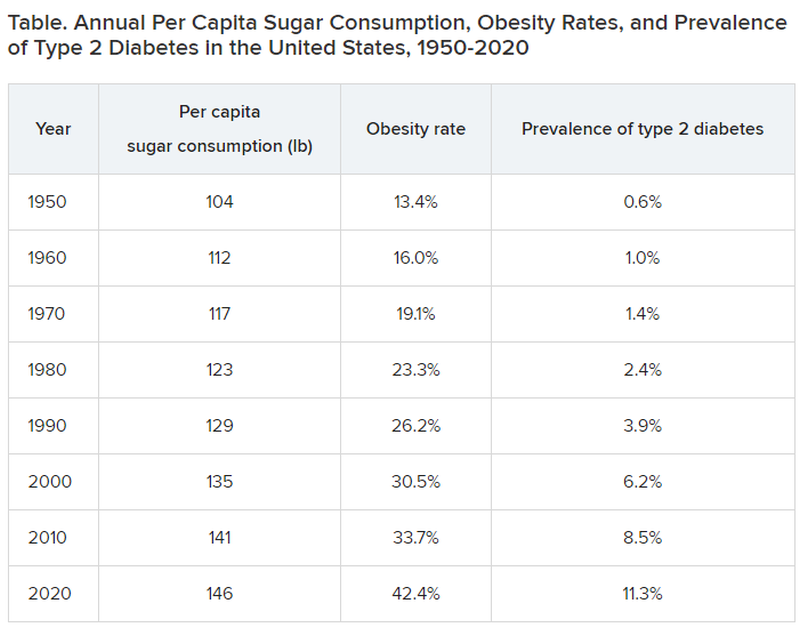
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctor, if you are caring for patients with diabetes, I sure hope you know more about it than I do. The longer I live, it seems, the less I understand.
In a free society, people can do what they want, and that’s great except when it isn’t. That’s why societies develop ethics and even public laws if ethics are not strong enough to protect us from ourselves and others.
Sugar, sugar
When I was growing up in small-town Alabama during the Depression and World War II, we called it sugar diabetes. Eat too much sugar, you got fat; your blood sugar went up, and you spilled sugar into your urine. Diabetes was fairly rare, and so was obesity. Doctors treated it by limiting the intake of sugar (and various sweet foods), along with attempting weight loss. If that didn’t do the trick, insulin injections.
From then until now, note these trends.
Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed even more infrequently before 1950:
- 1920: 0.2% of the population
- 1930: 0.3% of the population
- 1940: 0.4% of the population
In 2020, although 11.3% of the population was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the unknown undiagnosed proportion could be much higher.
Notice a correlation between sugar consumption and prevalence of diabetes? Of course, correlation is not causation, but at the same time, it sure as hell is not negation. Such concordance can be considered hypothesis generating. It may not be true causation, but it’s a good bet when 89% of people with diabetes have overweight or obesity.
What did the entire medical, public health, government, agriculture, nursing, food manufacturing, marketing, advertising, restaurant, and education constituencies do about this as it was happening? They observed, documented, gave lip service, and wrung their hands in public a bit. I do not believe that this is an organized active conspiracy; it would take too many players cooperating over too long a period of time. But it certainly may be a passive conspiracy, and primary care physicians and their patients are trapped.
The proper daily practice of medicine consists of one patient, one physician, one moment, and one decision. Let it be a shared decision, informed by the best evidence and taking cost into consideration. That encounter represents an opportunity, a responsibility, and a conundrum.
Individual health is subsumed under the collective health of the public. As such, a patient’s health is out of the control of both physician and patient; instead, patients are the beneficiaries or victims of the “marketplace.” Humans are frail and easily taken advantage of by the brilliant and highly motivated strategic planning and execution of Big Agriculture, Big Food, Big Pharma, Big Marketing, and Big Money-Driven Medicine and generally failed by Big Government, Big Public Health, Big Education, Big Psychology, and Big Religion.
Rethinking diabetes
Consider diabetes as one of many examples. What a terrific deal for capitalism. then it discovers (invents) long-term, very expensive, compelling treatments to slim us down, with no end in sight, and still without ever understanding the true nature of diabetes.
Gary Taubes’s great new book, “Rethinking Diabetes: What Science Reveals About Diet, Insulin, and Successful Treatments,” is being published by Alfred A. Knopf in early 2024.
It is 404 pages of (dense) text, with 401 numbered references and footnotes, a bibliography of 790 references, alphabetically arranged for easy cross-checking, and a 25-page index.
Remember Mr. Taubes’s earlier definitive historical treatises: “Good Calories, Bad Calories” (2007), “Why We Get Fat” (2010), “The Case Against Sugar” (2016), and “The Case for Keto” (2020)?
This new book is more like “Good Calories, Bad Calories”: long, dense, detailed, definitive, and of great historical reference value, including original research information from other countries in other languages. The author told me that the many early research reference sources were available only in German and that his use of generative artificial intelligence as an assistant researcher was of great value.
Nonphysician author Mr. Taubes uses his deep understanding of science and history to inform his long-honed talents of impartial investigative journalism as he attempts to understand and then explain why after all these years, the medical scientific community still does not have a sound consensus about the essence of diabetes, diet, insulin, and proper prevention and treatment at a level that is actually effective – amazing and so sad.
To signal these evolved and evolving conflicts, the book includes the following chapters:
- “Rise of the Carbohydrate-Rich and Very-Low-Carbohydrate Diets”
- “The Fear of Fat and High-Fat Diets”
- “Insulin and The End of Carbohydrate Restriction and Low Blood Sugar”
Yes, it is difficult. Imagine the bookend segments: “The Nature of Medical Knowledge” and “The Conflicts of Evidence-Based Medicine.” There is also a detailed discussion of good versus bad science spanning three long chapters.
If all that reads like a greatly confused mess to you then you’re beginning to understand. If you are a fan of an unbiased explication of the evolution of understanding the ins and outs of scientific history in richly documented detail, this is a book for you. It’s not a quick nor easy read. And don’t expect to discover whether the newest wonder drugs for weight loss and control of diabetes will be the long-term solution for people with obesity and diabetes worldwide.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. About 90% of patients with diabetes have either overweight or obesity. Thus, the complications of these two conditions, which largely overlap, include atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; myocardial infarction; stroke; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; lower-extremity gangrene; chronic kidney disease; retinopathy; glaucoma; cataracts; disabling osteoarthritis; breast, endometrial, colon, and other cancers; fatty liver; sleep apnea; and peripheral neuropathy. These diseases create a major lucrative business for a wide swathe of medical and surgical specialties, plus hospital, clinic, device, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
In summary, we’ve just been through 40 years of failure to recognize the sugar-elephant in the room and intervene with serious preventive efforts. Forty years of fleshing out both the populace and the American medical-industrial complex (AMIC). Talk about a sweet spot. The only successful long-term treatment of obesity (and with it, diabetes) is prevention. Don’t emphasize losing weight. Focus on preventing excessive weight gain, right now, for the population, beginning with yourselves. Otherwise, we continue openly to perpetuate a terrific deal for the AMIC, a travesty for everyone else. Time for some industrial grade penance and a course correction.
Meanwhile, here we are living out Big Pharma’s dream of a big populace, produced by the agriculture and food industries, enjoyed by capitalism after failures of education, medicine, and public health: a seemingly endless supply of people living with big complications who are ready for big (expensive, new) medications to fix the world’s big health problems.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief, Cancer Commons. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mothers in medicine: What can we learn when worlds collide?
Across all industries, studies by the U.S. Department of Labor have shown that women, on average, earn 83.7 percent of what their male peers earn. While a lot has been written about the struggles women face in medicine, there have been decidedly fewer analyses that focus on women who choose to become mothers while working in medicine.
I’ve been privileged to work with medical students and residents for the last 8 years as the director of graduate and medical student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. Often, the women I see as patients speak about their struggles with the elusive goal of “having it all.” While both men and women in medicine have difficulty maintaining a work-life balance, I’ve learned, both personally and professionally, that many women face a unique set of challenges.
No matter what their professional status, our society often views a woman as the default parent. For example, the teacher often calls the mothers first. The camp nurse calls me first, not my husband, when our child scrapes a knee. After-school play dates are arranged by the mothers, not fathers.
But mothers also bring to medicine a wealth of unique experiences, ideas, and viewpoints. They learn firsthand how to foster affect regulation and frustration tolerance in their kids and become efficient at managing the constant, conflicting tug of war of demands.
Some may argue that, over time, women end up earning significantly less than their male counterparts because they leave the workforce while on maternity leave, ultimately delaying their upward career progression. It’s likely a much more complex problem. Many of my patients believe that, in our male-dominated society (and workforce), women are punished for being aggressive or stating bold opinions, while men are rewarded for the same actions. While a man may sound forceful and in charge, a women will likely be thought of as brusque and unappreciative.
Outside of work, many women may have more on their plate. A 2020 Gallup poll of more than 3,000 heterosexual couples found that women are responsible for the majority of household chores. Women continue to handle more of the emotional labor within their families, regardless of income, age, or professional status. This is sometimes called the “Mental Load’ or “Second Shift.” As our society continues to view women as the default parent for childcare, medical issues, and overarching social and emotional tasks vital to raising happy, healthy children, the struggle a female medical professional feels is palpable.
Raising kids requires a parent to consistently dole out control, predictability, and reassurance for a child to thrive. Good limit and boundary setting leads to healthy development from a young age.
Psychiatric patients (and perhaps all patients) also require control, predictability, and reassurance from their doctor. The lessons learned in being a good mother can be directly applied in patient care, and vice versa. The cross-pollination of this relationship continues to grow more powerful as a woman’s children grow and her career matures.
Pediatrician and psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott’s idea of a “good enough” mother cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach. Women who self-select into the world of medicine often hold themselves to a higher standard than “good enough.” Acknowledging that the demands from both home and work will fluctuate is key to achieving success both personally and professionally, and lessons from home can and should be utilized to become a more effective physician. The notion of having it all, and the definition of success, must evolve over time.
Dr. Maymind is director of medical and graduate student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. She has no relevant disclosures.
Across all industries, studies by the U.S. Department of Labor have shown that women, on average, earn 83.7 percent of what their male peers earn. While a lot has been written about the struggles women face in medicine, there have been decidedly fewer analyses that focus on women who choose to become mothers while working in medicine.
I’ve been privileged to work with medical students and residents for the last 8 years as the director of graduate and medical student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. Often, the women I see as patients speak about their struggles with the elusive goal of “having it all.” While both men and women in medicine have difficulty maintaining a work-life balance, I’ve learned, both personally and professionally, that many women face a unique set of challenges.
No matter what their professional status, our society often views a woman as the default parent. For example, the teacher often calls the mothers first. The camp nurse calls me first, not my husband, when our child scrapes a knee. After-school play dates are arranged by the mothers, not fathers.
But mothers also bring to medicine a wealth of unique experiences, ideas, and viewpoints. They learn firsthand how to foster affect regulation and frustration tolerance in their kids and become efficient at managing the constant, conflicting tug of war of demands.
Some may argue that, over time, women end up earning significantly less than their male counterparts because they leave the workforce while on maternity leave, ultimately delaying their upward career progression. It’s likely a much more complex problem. Many of my patients believe that, in our male-dominated society (and workforce), women are punished for being aggressive or stating bold opinions, while men are rewarded for the same actions. While a man may sound forceful and in charge, a women will likely be thought of as brusque and unappreciative.
Outside of work, many women may have more on their plate. A 2020 Gallup poll of more than 3,000 heterosexual couples found that women are responsible for the majority of household chores. Women continue to handle more of the emotional labor within their families, regardless of income, age, or professional status. This is sometimes called the “Mental Load’ or “Second Shift.” As our society continues to view women as the default parent for childcare, medical issues, and overarching social and emotional tasks vital to raising happy, healthy children, the struggle a female medical professional feels is palpable.
Raising kids requires a parent to consistently dole out control, predictability, and reassurance for a child to thrive. Good limit and boundary setting leads to healthy development from a young age.
Psychiatric patients (and perhaps all patients) also require control, predictability, and reassurance from their doctor. The lessons learned in being a good mother can be directly applied in patient care, and vice versa. The cross-pollination of this relationship continues to grow more powerful as a woman’s children grow and her career matures.
Pediatrician and psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott’s idea of a “good enough” mother cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach. Women who self-select into the world of medicine often hold themselves to a higher standard than “good enough.” Acknowledging that the demands from both home and work will fluctuate is key to achieving success both personally and professionally, and lessons from home can and should be utilized to become a more effective physician. The notion of having it all, and the definition of success, must evolve over time.
Dr. Maymind is director of medical and graduate student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. She has no relevant disclosures.
Across all industries, studies by the U.S. Department of Labor have shown that women, on average, earn 83.7 percent of what their male peers earn. While a lot has been written about the struggles women face in medicine, there have been decidedly fewer analyses that focus on women who choose to become mothers while working in medicine.
I’ve been privileged to work with medical students and residents for the last 8 years as the director of graduate and medical student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. Often, the women I see as patients speak about their struggles with the elusive goal of “having it all.” While both men and women in medicine have difficulty maintaining a work-life balance, I’ve learned, both personally and professionally, that many women face a unique set of challenges.
No matter what their professional status, our society often views a woman as the default parent. For example, the teacher often calls the mothers first. The camp nurse calls me first, not my husband, when our child scrapes a knee. After-school play dates are arranged by the mothers, not fathers.
But mothers also bring to medicine a wealth of unique experiences, ideas, and viewpoints. They learn firsthand how to foster affect regulation and frustration tolerance in their kids and become efficient at managing the constant, conflicting tug of war of demands.
Some may argue that, over time, women end up earning significantly less than their male counterparts because they leave the workforce while on maternity leave, ultimately delaying their upward career progression. It’s likely a much more complex problem. Many of my patients believe that, in our male-dominated society (and workforce), women are punished for being aggressive or stating bold opinions, while men are rewarded for the same actions. While a man may sound forceful and in charge, a women will likely be thought of as brusque and unappreciative.
Outside of work, many women may have more on their plate. A 2020 Gallup poll of more than 3,000 heterosexual couples found that women are responsible for the majority of household chores. Women continue to handle more of the emotional labor within their families, regardless of income, age, or professional status. This is sometimes called the “Mental Load’ or “Second Shift.” As our society continues to view women as the default parent for childcare, medical issues, and overarching social and emotional tasks vital to raising happy, healthy children, the struggle a female medical professional feels is palpable.
Raising kids requires a parent to consistently dole out control, predictability, and reassurance for a child to thrive. Good limit and boundary setting leads to healthy development from a young age.
Psychiatric patients (and perhaps all patients) also require control, predictability, and reassurance from their doctor. The lessons learned in being a good mother can be directly applied in patient care, and vice versa. The cross-pollination of this relationship continues to grow more powerful as a woman’s children grow and her career matures.
Pediatrician and psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott’s idea of a “good enough” mother cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach. Women who self-select into the world of medicine often hold themselves to a higher standard than “good enough.” Acknowledging that the demands from both home and work will fluctuate is key to achieving success both personally and professionally, and lessons from home can and should be utilized to become a more effective physician. The notion of having it all, and the definition of success, must evolve over time.
Dr. Maymind is director of medical and graduate student mental health at Rowan-Virtua School of Osteopathic Medicine in Mt. Laurel, N.J. She has no relevant disclosures.
Parental bias about a doctor can’t trump a patient’s health
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to present you today with a case that raised a large amount of discussion and debate. I got involved as an ethics consultant on the case. I think you’ll find it very interesting and I also think there are going to be some differences of opinion about how to manage the case. I’ll be looking forward to getting comments and feedback on this.
The case involved a 14-year-old boy who had been brought into the hospital by his parents, suffering from severe bouts of anxiety that were just almost overwhelming to him. When he was brought in, he was assigned a health care provider who had a West African last name. Prior to meeting the patient, I have to say that the father of this kid told the intake department nurse that he requested someone else. He saw the name – he hadn’t even met the provider – and he said he wanted someone who might be Catholic.
The parents are both from the Dominican Republic. They identified as White, but they appeared to be non-White Latinx to the nurse who was doing some of the initial intake. They got reassigned to a different provider in the department who identified as African American.
The first month of treatment for the young boy went very well, and he seemed to be getting along extremely well with his provider. He was reporting relief to both parents of some of his anxiety, and the provider felt very connected to the child. A good doctor-patient alliance had been formed.
Nevertheless, at the end of the first month, the father connected back to one of the administrators at the hospital and complained, saying he still wanted a different provider. When asked why, he said, “Well, I don’t really want to answer that,” but getting pressed, he basically said he wasn’t comfortable with having an African American doctor take care of his child. He eventually went back to the argument that what he wanted was someone with a Catholic background, although I don’t know that he knew whether this particular provider was religious – Catholic or anything else.
Some people felt that, as the father in charge of the child’s care, if we could accommodate what he wanted in terms of the parents being comfortable, then that’s something we should do. I absolutely did not agree.
My view is that in a situation where a strong provider-patient relationship has been established, where trust is going both ways, where there are no issues coming up between this 14-year-old and the provider, and when a serious mental health issue is being adequately addressed, the patient’s interest must come first.
Once that therapeutic alliance had been established and both the patient and the provider felt satisfied, I don’t think the father’s wishes made any sense. He may have been acting more out of bigotry or just discomfort about difference in terms of who the provider was. I don’t think that’s something that any health system should have to accommodate unless it is getting in the way of patient care.
I hope that we treat all physicians as properly trained to deal with all kinds of patients, regardless of their religion, ethnicity, or skin color. They should have the skills to manage and do well with any patient. There may be situations where it just doesn’t work or where people don’t get along. Yes, I think we then should try, perhaps, to shift the doctor, get a different nurse, or have a different person do an exam. That’s because of the inability to get the patient’s health interests addressed.
Listening to this dad about what he preferred in terms of religion or ethnicity seemed to me to be interfering with medical success. Could I stop him from moving this patient out entirely from the care setting? Probably not, but I think the way to manage this is to try to talk to him – and, by the way, to talk to the mother.
When we did bring the mom into the situation, she was very happy with the health care provider. She didn’t agree with the dad and wanted to have a meeting with the social worker, the dad, and her to get him to get over the worries, concerns, and maybe even biases he was bringing in about the kind of provider he wanted. That’s exactly what we did.
I know that there are many instances where patients may say, “I don’t want a particular doctor or a particular type.” My view is that we shouldn’t accommodate that. We should say that our doctors are trained to help and care for all manner of people. Unless we can think of some reason that there might be a gap or a problem in the actual delivery of the quality of care, we are not going to accommodate racism, bigotry, or bias.
We certainly shouldn’t be accommodating that once a successful therapeutic relationship is established. Even when it’s a child, I would argue that the patient’s best interest has to trump parental desires, parental worries, and parental concerns about the background, ethnicity, and religion of the provider.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York. He disclosed a conflict of interest with Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to present you today with a case that raised a large amount of discussion and debate. I got involved as an ethics consultant on the case. I think you’ll find it very interesting and I also think there are going to be some differences of opinion about how to manage the case. I’ll be looking forward to getting comments and feedback on this.
The case involved a 14-year-old boy who had been brought into the hospital by his parents, suffering from severe bouts of anxiety that were just almost overwhelming to him. When he was brought in, he was assigned a health care provider who had a West African last name. Prior to meeting the patient, I have to say that the father of this kid told the intake department nurse that he requested someone else. He saw the name – he hadn’t even met the provider – and he said he wanted someone who might be Catholic.
The parents are both from the Dominican Republic. They identified as White, but they appeared to be non-White Latinx to the nurse who was doing some of the initial intake. They got reassigned to a different provider in the department who identified as African American.
The first month of treatment for the young boy went very well, and he seemed to be getting along extremely well with his provider. He was reporting relief to both parents of some of his anxiety, and the provider felt very connected to the child. A good doctor-patient alliance had been formed.
Nevertheless, at the end of the first month, the father connected back to one of the administrators at the hospital and complained, saying he still wanted a different provider. When asked why, he said, “Well, I don’t really want to answer that,” but getting pressed, he basically said he wasn’t comfortable with having an African American doctor take care of his child. He eventually went back to the argument that what he wanted was someone with a Catholic background, although I don’t know that he knew whether this particular provider was religious – Catholic or anything else.
Some people felt that, as the father in charge of the child’s care, if we could accommodate what he wanted in terms of the parents being comfortable, then that’s something we should do. I absolutely did not agree.
My view is that in a situation where a strong provider-patient relationship has been established, where trust is going both ways, where there are no issues coming up between this 14-year-old and the provider, and when a serious mental health issue is being adequately addressed, the patient’s interest must come first.
Once that therapeutic alliance had been established and both the patient and the provider felt satisfied, I don’t think the father’s wishes made any sense. He may have been acting more out of bigotry or just discomfort about difference in terms of who the provider was. I don’t think that’s something that any health system should have to accommodate unless it is getting in the way of patient care.
I hope that we treat all physicians as properly trained to deal with all kinds of patients, regardless of their religion, ethnicity, or skin color. They should have the skills to manage and do well with any patient. There may be situations where it just doesn’t work or where people don’t get along. Yes, I think we then should try, perhaps, to shift the doctor, get a different nurse, or have a different person do an exam. That’s because of the inability to get the patient’s health interests addressed.
Listening to this dad about what he preferred in terms of religion or ethnicity seemed to me to be interfering with medical success. Could I stop him from moving this patient out entirely from the care setting? Probably not, but I think the way to manage this is to try to talk to him – and, by the way, to talk to the mother.
When we did bring the mom into the situation, she was very happy with the health care provider. She didn’t agree with the dad and wanted to have a meeting with the social worker, the dad, and her to get him to get over the worries, concerns, and maybe even biases he was bringing in about the kind of provider he wanted. That’s exactly what we did.
I know that there are many instances where patients may say, “I don’t want a particular doctor or a particular type.” My view is that we shouldn’t accommodate that. We should say that our doctors are trained to help and care for all manner of people. Unless we can think of some reason that there might be a gap or a problem in the actual delivery of the quality of care, we are not going to accommodate racism, bigotry, or bias.
We certainly shouldn’t be accommodating that once a successful therapeutic relationship is established. Even when it’s a child, I would argue that the patient’s best interest has to trump parental desires, parental worries, and parental concerns about the background, ethnicity, and religion of the provider.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York. He disclosed a conflict of interest with Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to present you today with a case that raised a large amount of discussion and debate. I got involved as an ethics consultant on the case. I think you’ll find it very interesting and I also think there are going to be some differences of opinion about how to manage the case. I’ll be looking forward to getting comments and feedback on this.
The case involved a 14-year-old boy who had been brought into the hospital by his parents, suffering from severe bouts of anxiety that were just almost overwhelming to him. When he was brought in, he was assigned a health care provider who had a West African last name. Prior to meeting the patient, I have to say that the father of this kid told the intake department nurse that he requested someone else. He saw the name – he hadn’t even met the provider – and he said he wanted someone who might be Catholic.
The parents are both from the Dominican Republic. They identified as White, but they appeared to be non-White Latinx to the nurse who was doing some of the initial intake. They got reassigned to a different provider in the department who identified as African American.
The first month of treatment for the young boy went very well, and he seemed to be getting along extremely well with his provider. He was reporting relief to both parents of some of his anxiety, and the provider felt very connected to the child. A good doctor-patient alliance had been formed.
Nevertheless, at the end of the first month, the father connected back to one of the administrators at the hospital and complained, saying he still wanted a different provider. When asked why, he said, “Well, I don’t really want to answer that,” but getting pressed, he basically said he wasn’t comfortable with having an African American doctor take care of his child. He eventually went back to the argument that what he wanted was someone with a Catholic background, although I don’t know that he knew whether this particular provider was religious – Catholic or anything else.
Some people felt that, as the father in charge of the child’s care, if we could accommodate what he wanted in terms of the parents being comfortable, then that’s something we should do. I absolutely did not agree.
My view is that in a situation where a strong provider-patient relationship has been established, where trust is going both ways, where there are no issues coming up between this 14-year-old and the provider, and when a serious mental health issue is being adequately addressed, the patient’s interest must come first.
Once that therapeutic alliance had been established and both the patient and the provider felt satisfied, I don’t think the father’s wishes made any sense. He may have been acting more out of bigotry or just discomfort about difference in terms of who the provider was. I don’t think that’s something that any health system should have to accommodate unless it is getting in the way of patient care.
I hope that we treat all physicians as properly trained to deal with all kinds of patients, regardless of their religion, ethnicity, or skin color. They should have the skills to manage and do well with any patient. There may be situations where it just doesn’t work or where people don’t get along. Yes, I think we then should try, perhaps, to shift the doctor, get a different nurse, or have a different person do an exam. That’s because of the inability to get the patient’s health interests addressed.
Listening to this dad about what he preferred in terms of religion or ethnicity seemed to me to be interfering with medical success. Could I stop him from moving this patient out entirely from the care setting? Probably not, but I think the way to manage this is to try to talk to him – and, by the way, to talk to the mother.
When we did bring the mom into the situation, she was very happy with the health care provider. She didn’t agree with the dad and wanted to have a meeting with the social worker, the dad, and her to get him to get over the worries, concerns, and maybe even biases he was bringing in about the kind of provider he wanted. That’s exactly what we did.
I know that there are many instances where patients may say, “I don’t want a particular doctor or a particular type.” My view is that we shouldn’t accommodate that. We should say that our doctors are trained to help and care for all manner of people. Unless we can think of some reason that there might be a gap or a problem in the actual delivery of the quality of care, we are not going to accommodate racism, bigotry, or bias.
We certainly shouldn’t be accommodating that once a successful therapeutic relationship is established. Even when it’s a child, I would argue that the patient’s best interest has to trump parental desires, parental worries, and parental concerns about the background, ethnicity, and religion of the provider.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, New York. He disclosed a conflict of interest with Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Buyer beware
The invitation came to my house, addressed to “residential customer.” It was for my wife and me to attend a free dinner at a swanky local restaurant to learn about “revolutionary” treatments for memory loss. It was presented by a “wellness expert.”
Of course, I just had to check out the website.
The dinner was hosted by an internist pushing an unproven (except for the usual small noncontrolled studies) treatment. Although not stated, I’m sure when you call you’ll find out this is not covered by insurance; not Food and Drug Administration approved to treat, cure, diagnose, prevent any disease; your mileage may vary, etc.
The website was full of testimonials as to how well the treatments worked, primarily from people in their 20s-40s who are, realistically, unlikely to have a pathologically serious cause for memory problems. The site also mentions that you can use it to treat traumatic brain injury, ADHD, learning disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, PTSD, Parkinson’s disease, autism, dementia, and stroke, though it does clearly state that such use is not FDA approved.
Prices (I assume all cash pay) for the treatment weren’t listed. I guess you have to come to the “free” dinner for those, or submit an online form to the office.
I’m not going to say the advertised treatment doesn’t work. It might, for at least some of those things. A PubMed search tells me it’s under investigation for several of them.
But that doesn’t mean it works. It might, but a lot of things that look promising in early trials end up failing in the long run. So, at least to me, this is no different than people selling various over-the-counter supplements online with all kinds of extravagant claims and testimonials.
I also have to question a treatment targeting young people for memory loss. In neurology we see a lot of that, and know that true pathology is rare. Most of these patients have root issues with depression, or anxiety, or stress that are affecting their memory. That doesn’t make their memory issues any less real, but they shouldn’t be lumped in with neurodegenerative diseases. They need to be correctly diagnosed and treated for what they are.
Maybe it’s just me, but I often see this sort of thing as kind of sketchy – generating business for unproven treatments by selling fear – you need to do something NOW to keep from getting worse. And, of course there’s always the mysterious “they.” The treatments “they” offer don’t work. Why aren’t “they” telling you what really does?
Looking at the restaurant’s online menu, dinners are around $75 per person and the invitation says “seats are limited.” Doing some mental math gives you an idea how many diners need to come, what percentage of them need to sign up for the treatment, and how much it costs to recoup the investment.
Let the buyer beware.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The invitation came to my house, addressed to “residential customer.” It was for my wife and me to attend a free dinner at a swanky local restaurant to learn about “revolutionary” treatments for memory loss. It was presented by a “wellness expert.”
Of course, I just had to check out the website.
The dinner was hosted by an internist pushing an unproven (except for the usual small noncontrolled studies) treatment. Although not stated, I’m sure when you call you’ll find out this is not covered by insurance; not Food and Drug Administration approved to treat, cure, diagnose, prevent any disease; your mileage may vary, etc.
The website was full of testimonials as to how well the treatments worked, primarily from people in their 20s-40s who are, realistically, unlikely to have a pathologically serious cause for memory problems. The site also mentions that you can use it to treat traumatic brain injury, ADHD, learning disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, PTSD, Parkinson’s disease, autism, dementia, and stroke, though it does clearly state that such use is not FDA approved.
Prices (I assume all cash pay) for the treatment weren’t listed. I guess you have to come to the “free” dinner for those, or submit an online form to the office.
I’m not going to say the advertised treatment doesn’t work. It might, for at least some of those things. A PubMed search tells me it’s under investigation for several of them.
But that doesn’t mean it works. It might, but a lot of things that look promising in early trials end up failing in the long run. So, at least to me, this is no different than people selling various over-the-counter supplements online with all kinds of extravagant claims and testimonials.
I also have to question a treatment targeting young people for memory loss. In neurology we see a lot of that, and know that true pathology is rare. Most of these patients have root issues with depression, or anxiety, or stress that are affecting their memory. That doesn’t make their memory issues any less real, but they shouldn’t be lumped in with neurodegenerative diseases. They need to be correctly diagnosed and treated for what they are.
Maybe it’s just me, but I often see this sort of thing as kind of sketchy – generating business for unproven treatments by selling fear – you need to do something NOW to keep from getting worse. And, of course there’s always the mysterious “they.” The treatments “they” offer don’t work. Why aren’t “they” telling you what really does?
Looking at the restaurant’s online menu, dinners are around $75 per person and the invitation says “seats are limited.” Doing some mental math gives you an idea how many diners need to come, what percentage of them need to sign up for the treatment, and how much it costs to recoup the investment.
Let the buyer beware.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The invitation came to my house, addressed to “residential customer.” It was for my wife and me to attend a free dinner at a swanky local restaurant to learn about “revolutionary” treatments for memory loss. It was presented by a “wellness expert.”
Of course, I just had to check out the website.
The dinner was hosted by an internist pushing an unproven (except for the usual small noncontrolled studies) treatment. Although not stated, I’m sure when you call you’ll find out this is not covered by insurance; not Food and Drug Administration approved to treat, cure, diagnose, prevent any disease; your mileage may vary, etc.
The website was full of testimonials as to how well the treatments worked, primarily from people in their 20s-40s who are, realistically, unlikely to have a pathologically serious cause for memory problems. The site also mentions that you can use it to treat traumatic brain injury, ADHD, learning disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, PTSD, Parkinson’s disease, autism, dementia, and stroke, though it does clearly state that such use is not FDA approved.
Prices (I assume all cash pay) for the treatment weren’t listed. I guess you have to come to the “free” dinner for those, or submit an online form to the office.
I’m not going to say the advertised treatment doesn’t work. It might, for at least some of those things. A PubMed search tells me it’s under investigation for several of them.
But that doesn’t mean it works. It might, but a lot of things that look promising in early trials end up failing in the long run. So, at least to me, this is no different than people selling various over-the-counter supplements online with all kinds of extravagant claims and testimonials.
I also have to question a treatment targeting young people for memory loss. In neurology we see a lot of that, and know that true pathology is rare. Most of these patients have root issues with depression, or anxiety, or stress that are affecting their memory. That doesn’t make their memory issues any less real, but they shouldn’t be lumped in with neurodegenerative diseases. They need to be correctly diagnosed and treated for what they are.
Maybe it’s just me, but I often see this sort of thing as kind of sketchy – generating business for unproven treatments by selling fear – you need to do something NOW to keep from getting worse. And, of course there’s always the mysterious “they.” The treatments “they” offer don’t work. Why aren’t “they” telling you what really does?
Looking at the restaurant’s online menu, dinners are around $75 per person and the invitation says “seats are limited.” Doing some mental math gives you an idea how many diners need to come, what percentage of them need to sign up for the treatment, and how much it costs to recoup the investment.
Let the buyer beware.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.






