User login
The central role of informed consent in novel procedures
Mrs. Jones is a 44-year-old woman who has struggled with her weight. She has a body mass index (BMI) of 35 kg/m2 and hypertension requiring daily medication. She has tried various diets over the years and has never been able to exercise consistently. She desperately wants to lose weight to improve her confidence and to avoid developing diabetes and dialysis that her parents required. She has considered weight loss surgery but is afraid after her best friend died following uterine fibroid surgery. She saw a billboard that advertised a new weight loss procedure without surgery. She looked up the procedure, found Dr. Indo on the university medical center’s website, and booked an appointment. Dr. Indo talked about performing an incisionless procedure done with an endoscope through her mouth. It would make her stomach into a tube to reduce the amount of food she could eat as well as prevent some absorption of food in her intestines. When Mrs. Jones asked how many of these the doctor had performed, Dr. Indo remarked she personally had done “several” in the past few years including training. Dr. Indo reassured Mrs. Jones that the procedure has been performed hundreds of times around the country and has been shown to be safe. Dr. Indo also explained that studies were still ongoing, including possibly at the university medical center, but that she had never personally seen any serious complications or death, and only one patient she knew of converted to a traditional bariatric surgery.
Obesity is a large international public health problem, with the World Health Organization estimating that there are 600 million obese adults worldwide.1 Bariatric surgery has been an effective way to improve complications related to obesity and quality of life. Endoscopic approaches to bariatric surgery have appeared since at least the late 1980s and, similarly to their traditional surgical counterparts, work in two main categories: restrictive or malabsorptive.1 Restrictive endoscopic bariatric therapies (EBTs) include intragastric balloons (IGB) that are filled with saline or gas to decrease intragastric luminal size, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty that makes full-thickness plications of the gastric wall to tubularize the stomach like a sleeve gastrectomy, and AspireAssist where patients use a percutaneous gastrostomy to remove part of an ingested meal.1 Malabsorptive procedures include bypass sleeves that use a stentlike device to bypass absorption of food in the duodenum and proximal jejunum, the incisionless magnetic anastomosis system (IMAS) that creates a gastrojejunal bypass for diverting absorption, and duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) that ablates the duodenal mucosa.1,2
The benefits of EBTs over traditional bariatric surgery are that they have a lower risk profile, there is limited anatomic alternation, and they are potentially reversible.1 Although no formal guidelines exist in the United States for the use of EBTs, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) preliminary recommendations describe EBTs as applicable for patients who have failed lifestyle interventions and have BMIs between 30 and 45.1 While some of these techniques were first described in the 1980s, many individual companies and devices still do not have Food and Drug Administration approval and some have even had approval withdrawn. While traditional bariatric surgery may have complication rates up to 17%, EBTs are not without complications.1 Endoscopic barriers can migrate and occlude, cause pancreatitis, cause liver abscesses from biliary occlusion, and more severely cause GI bleeding and perforations.1 Many EBTs are also temporary treatments with IGBs and barrier bypasses placed only for 6-12 months.1 While there have been some studies looking at individual outcomes of the various EBTs, large prospective research trials looking at safety and efficacy, especially when comparing EBT to traditional bariatric surgery or in combination, are lacking.
Continued innovation in medicine and technology is critical to improving patient care. New innovations in medicine have allowed us to treat more disease, save lives, reduce complications, and better care for patients. But what exactly is innovation and when does it become research? The landmark Belmont Report in 1979 distinguishes research from innovative therapy, calling research “an activity designed to test a hypothesis, permit conclusions to be drawn, and thereby to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.”3 Patients in research thus bear the risks while others stand to benefit. The report affirms then that routine medical practice involves interventions designed specifically to benefit the individual patient. The European Association for Endoscopic Surgery defines innovations as any “significant modification of a standard technique, a new application of or new indication for an established technique, or an alternative combination of an established technique with another therapeutic modality.”4 As such, innovations should eventually be formally studied with institutional review board (IRB) approval and protocols to establish safety and efficacy. Another complicating factor is that there is no FDA approval for surgical and procedural techniques as there is for medications and certain devices. Therefore, no robust regulatory mechanisms exist to ensure patient safety and benefit. Further complicating matters is that innovative procedures often start as modifications of techniques and are often done regularly to fit specific situations – for example, an additional stitch in a different location or in a different orientation to what is done in the standard fashion. However, true innovations should be distinguished from these modifications. Perhaps then another way to think about the two is to splinter them into three types of activity: research, routine accepted practice, and innovative medicine.5
Given this potential for blurred lines about novel approaches to medical conditions, how do we communicate this to patients? This is where the role of informed consent becomes essential. Informed consent is key to respecting patients’ autonomy – a central tenet of medical ethics. For patients to make autonomous choices they need basic facts to make informed decisions.6 These facts must be unbiased and free from conflicts, and they must not only be truthful but also be comprehensive and free from omission. It is in this informed consent process that we must explain that a technique or procedure is new, outline the risks and benefits, and share our actual experiences with said procedure especially if it is limited.7 We must also be aware of how certain biases and conflicts can affect our decisions to adapt and recommend innovative therapies. We may have incentives to offer innovative therapies to be on the “cutting edge” and attract patients. We may have explicit financial gain if working directly with device manufacturers or reimbursed by our institutions per procedure. Conflicts of interest are not only financial, but they can also be the prospects of promotion or career advancement.3 Institutions as well are incentivized to advertise the “latest” to bolster their prestige and reputations. Ultimately, we should act to the highest levels of professionalism, and ethics, by ignoring benefit to ourselves as physicians and always focusing on the benefits for our patients.7
What about when patients ask for specific innovative procedures as Mrs. Jones did above? What is our responsibility then? In situations where patients specifically push for a new procedure, it remains our duty to inform patients about the novelty of the procedure and the limited study of its safety and efficacy. When speaking about the “experience” with a novel procedure, it is tempting to speak globally and broadly. For example, Dr. Indo spoke about the procedure being done hundreds of times across the country and being safe in this context. It is our duty to be transparent, disclose our own experiences, and consider our own skills when recommending a novel procedure.7 It should be noted that patients are a vulnerable population and many times at the mercy of our recommendations. We’ve often heard patients say “Whatever you say doc; You’re the doctor;” or “I’ll do what you think is best” when presented with treatment options. This is an incredible amount of power, and we must protect this trust patients place in us by clearly acknowledging the uncertainties of new procedures and placing their benefit over our own potential gain.
Dr. Williams is a general surgery resident at the University of Chicago and a fellow at the MacLean Center for clinical medical ethics. Dr. Angelos is the Linda Kohler Anderson Professor of Surgery and Surgical Ethics, vice chairman for ethics, professional development, and wellness, and chief of endocrine surgery, department of surgery, and the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics at the University of Chicago. The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Goyal H et al. Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;14. doi: 10.1177/2631774520984627.
2. Machytka E et al. Gastrointestinal Endosc. 2017;86(5):904-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.07.009.
3. Eastwood GL. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Australia). 2015;30(S1):8-11. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12755.
4. Neugebauer EAM et al. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(7):1594-1615. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0818-3.
5. Eaton, ML and Kennedy, DL. Innovation in Medical Technology: Ethical Issues and Challenges. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
6. Angelos P. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108(6):1611-2. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.08.010.
7. Angelos P. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13(1):6-9. doi: 10.1001/virtualmentor.2011.13.1.ccas1-1101.
Mrs. Jones is a 44-year-old woman who has struggled with her weight. She has a body mass index (BMI) of 35 kg/m2 and hypertension requiring daily medication. She has tried various diets over the years and has never been able to exercise consistently. She desperately wants to lose weight to improve her confidence and to avoid developing diabetes and dialysis that her parents required. She has considered weight loss surgery but is afraid after her best friend died following uterine fibroid surgery. She saw a billboard that advertised a new weight loss procedure without surgery. She looked up the procedure, found Dr. Indo on the university medical center’s website, and booked an appointment. Dr. Indo talked about performing an incisionless procedure done with an endoscope through her mouth. It would make her stomach into a tube to reduce the amount of food she could eat as well as prevent some absorption of food in her intestines. When Mrs. Jones asked how many of these the doctor had performed, Dr. Indo remarked she personally had done “several” in the past few years including training. Dr. Indo reassured Mrs. Jones that the procedure has been performed hundreds of times around the country and has been shown to be safe. Dr. Indo also explained that studies were still ongoing, including possibly at the university medical center, but that she had never personally seen any serious complications or death, and only one patient she knew of converted to a traditional bariatric surgery.
Obesity is a large international public health problem, with the World Health Organization estimating that there are 600 million obese adults worldwide.1 Bariatric surgery has been an effective way to improve complications related to obesity and quality of life. Endoscopic approaches to bariatric surgery have appeared since at least the late 1980s and, similarly to their traditional surgical counterparts, work in two main categories: restrictive or malabsorptive.1 Restrictive endoscopic bariatric therapies (EBTs) include intragastric balloons (IGB) that are filled with saline or gas to decrease intragastric luminal size, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty that makes full-thickness plications of the gastric wall to tubularize the stomach like a sleeve gastrectomy, and AspireAssist where patients use a percutaneous gastrostomy to remove part of an ingested meal.1 Malabsorptive procedures include bypass sleeves that use a stentlike device to bypass absorption of food in the duodenum and proximal jejunum, the incisionless magnetic anastomosis system (IMAS) that creates a gastrojejunal bypass for diverting absorption, and duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) that ablates the duodenal mucosa.1,2
The benefits of EBTs over traditional bariatric surgery are that they have a lower risk profile, there is limited anatomic alternation, and they are potentially reversible.1 Although no formal guidelines exist in the United States for the use of EBTs, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) preliminary recommendations describe EBTs as applicable for patients who have failed lifestyle interventions and have BMIs between 30 and 45.1 While some of these techniques were first described in the 1980s, many individual companies and devices still do not have Food and Drug Administration approval and some have even had approval withdrawn. While traditional bariatric surgery may have complication rates up to 17%, EBTs are not without complications.1 Endoscopic barriers can migrate and occlude, cause pancreatitis, cause liver abscesses from biliary occlusion, and more severely cause GI bleeding and perforations.1 Many EBTs are also temporary treatments with IGBs and barrier bypasses placed only for 6-12 months.1 While there have been some studies looking at individual outcomes of the various EBTs, large prospective research trials looking at safety and efficacy, especially when comparing EBT to traditional bariatric surgery or in combination, are lacking.
Continued innovation in medicine and technology is critical to improving patient care. New innovations in medicine have allowed us to treat more disease, save lives, reduce complications, and better care for patients. But what exactly is innovation and when does it become research? The landmark Belmont Report in 1979 distinguishes research from innovative therapy, calling research “an activity designed to test a hypothesis, permit conclusions to be drawn, and thereby to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.”3 Patients in research thus bear the risks while others stand to benefit. The report affirms then that routine medical practice involves interventions designed specifically to benefit the individual patient. The European Association for Endoscopic Surgery defines innovations as any “significant modification of a standard technique, a new application of or new indication for an established technique, or an alternative combination of an established technique with another therapeutic modality.”4 As such, innovations should eventually be formally studied with institutional review board (IRB) approval and protocols to establish safety and efficacy. Another complicating factor is that there is no FDA approval for surgical and procedural techniques as there is for medications and certain devices. Therefore, no robust regulatory mechanisms exist to ensure patient safety and benefit. Further complicating matters is that innovative procedures often start as modifications of techniques and are often done regularly to fit specific situations – for example, an additional stitch in a different location or in a different orientation to what is done in the standard fashion. However, true innovations should be distinguished from these modifications. Perhaps then another way to think about the two is to splinter them into three types of activity: research, routine accepted practice, and innovative medicine.5
Given this potential for blurred lines about novel approaches to medical conditions, how do we communicate this to patients? This is where the role of informed consent becomes essential. Informed consent is key to respecting patients’ autonomy – a central tenet of medical ethics. For patients to make autonomous choices they need basic facts to make informed decisions.6 These facts must be unbiased and free from conflicts, and they must not only be truthful but also be comprehensive and free from omission. It is in this informed consent process that we must explain that a technique or procedure is new, outline the risks and benefits, and share our actual experiences with said procedure especially if it is limited.7 We must also be aware of how certain biases and conflicts can affect our decisions to adapt and recommend innovative therapies. We may have incentives to offer innovative therapies to be on the “cutting edge” and attract patients. We may have explicit financial gain if working directly with device manufacturers or reimbursed by our institutions per procedure. Conflicts of interest are not only financial, but they can also be the prospects of promotion or career advancement.3 Institutions as well are incentivized to advertise the “latest” to bolster their prestige and reputations. Ultimately, we should act to the highest levels of professionalism, and ethics, by ignoring benefit to ourselves as physicians and always focusing on the benefits for our patients.7
What about when patients ask for specific innovative procedures as Mrs. Jones did above? What is our responsibility then? In situations where patients specifically push for a new procedure, it remains our duty to inform patients about the novelty of the procedure and the limited study of its safety and efficacy. When speaking about the “experience” with a novel procedure, it is tempting to speak globally and broadly. For example, Dr. Indo spoke about the procedure being done hundreds of times across the country and being safe in this context. It is our duty to be transparent, disclose our own experiences, and consider our own skills when recommending a novel procedure.7 It should be noted that patients are a vulnerable population and many times at the mercy of our recommendations. We’ve often heard patients say “Whatever you say doc; You’re the doctor;” or “I’ll do what you think is best” when presented with treatment options. This is an incredible amount of power, and we must protect this trust patients place in us by clearly acknowledging the uncertainties of new procedures and placing their benefit over our own potential gain.
Dr. Williams is a general surgery resident at the University of Chicago and a fellow at the MacLean Center for clinical medical ethics. Dr. Angelos is the Linda Kohler Anderson Professor of Surgery and Surgical Ethics, vice chairman for ethics, professional development, and wellness, and chief of endocrine surgery, department of surgery, and the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics at the University of Chicago. The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Goyal H et al. Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;14. doi: 10.1177/2631774520984627.
2. Machytka E et al. Gastrointestinal Endosc. 2017;86(5):904-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.07.009.
3. Eastwood GL. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Australia). 2015;30(S1):8-11. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12755.
4. Neugebauer EAM et al. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(7):1594-1615. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0818-3.
5. Eaton, ML and Kennedy, DL. Innovation in Medical Technology: Ethical Issues and Challenges. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
6. Angelos P. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108(6):1611-2. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.08.010.
7. Angelos P. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13(1):6-9. doi: 10.1001/virtualmentor.2011.13.1.ccas1-1101.
Mrs. Jones is a 44-year-old woman who has struggled with her weight. She has a body mass index (BMI) of 35 kg/m2 and hypertension requiring daily medication. She has tried various diets over the years and has never been able to exercise consistently. She desperately wants to lose weight to improve her confidence and to avoid developing diabetes and dialysis that her parents required. She has considered weight loss surgery but is afraid after her best friend died following uterine fibroid surgery. She saw a billboard that advertised a new weight loss procedure without surgery. She looked up the procedure, found Dr. Indo on the university medical center’s website, and booked an appointment. Dr. Indo talked about performing an incisionless procedure done with an endoscope through her mouth. It would make her stomach into a tube to reduce the amount of food she could eat as well as prevent some absorption of food in her intestines. When Mrs. Jones asked how many of these the doctor had performed, Dr. Indo remarked she personally had done “several” in the past few years including training. Dr. Indo reassured Mrs. Jones that the procedure has been performed hundreds of times around the country and has been shown to be safe. Dr. Indo also explained that studies were still ongoing, including possibly at the university medical center, but that she had never personally seen any serious complications or death, and only one patient she knew of converted to a traditional bariatric surgery.
Obesity is a large international public health problem, with the World Health Organization estimating that there are 600 million obese adults worldwide.1 Bariatric surgery has been an effective way to improve complications related to obesity and quality of life. Endoscopic approaches to bariatric surgery have appeared since at least the late 1980s and, similarly to their traditional surgical counterparts, work in two main categories: restrictive or malabsorptive.1 Restrictive endoscopic bariatric therapies (EBTs) include intragastric balloons (IGB) that are filled with saline or gas to decrease intragastric luminal size, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty that makes full-thickness plications of the gastric wall to tubularize the stomach like a sleeve gastrectomy, and AspireAssist where patients use a percutaneous gastrostomy to remove part of an ingested meal.1 Malabsorptive procedures include bypass sleeves that use a stentlike device to bypass absorption of food in the duodenum and proximal jejunum, the incisionless magnetic anastomosis system (IMAS) that creates a gastrojejunal bypass for diverting absorption, and duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) that ablates the duodenal mucosa.1,2
The benefits of EBTs over traditional bariatric surgery are that they have a lower risk profile, there is limited anatomic alternation, and they are potentially reversible.1 Although no formal guidelines exist in the United States for the use of EBTs, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) preliminary recommendations describe EBTs as applicable for patients who have failed lifestyle interventions and have BMIs between 30 and 45.1 While some of these techniques were first described in the 1980s, many individual companies and devices still do not have Food and Drug Administration approval and some have even had approval withdrawn. While traditional bariatric surgery may have complication rates up to 17%, EBTs are not without complications.1 Endoscopic barriers can migrate and occlude, cause pancreatitis, cause liver abscesses from biliary occlusion, and more severely cause GI bleeding and perforations.1 Many EBTs are also temporary treatments with IGBs and barrier bypasses placed only for 6-12 months.1 While there have been some studies looking at individual outcomes of the various EBTs, large prospective research trials looking at safety and efficacy, especially when comparing EBT to traditional bariatric surgery or in combination, are lacking.
Continued innovation in medicine and technology is critical to improving patient care. New innovations in medicine have allowed us to treat more disease, save lives, reduce complications, and better care for patients. But what exactly is innovation and when does it become research? The landmark Belmont Report in 1979 distinguishes research from innovative therapy, calling research “an activity designed to test a hypothesis, permit conclusions to be drawn, and thereby to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.”3 Patients in research thus bear the risks while others stand to benefit. The report affirms then that routine medical practice involves interventions designed specifically to benefit the individual patient. The European Association for Endoscopic Surgery defines innovations as any “significant modification of a standard technique, a new application of or new indication for an established technique, or an alternative combination of an established technique with another therapeutic modality.”4 As such, innovations should eventually be formally studied with institutional review board (IRB) approval and protocols to establish safety and efficacy. Another complicating factor is that there is no FDA approval for surgical and procedural techniques as there is for medications and certain devices. Therefore, no robust regulatory mechanisms exist to ensure patient safety and benefit. Further complicating matters is that innovative procedures often start as modifications of techniques and are often done regularly to fit specific situations – for example, an additional stitch in a different location or in a different orientation to what is done in the standard fashion. However, true innovations should be distinguished from these modifications. Perhaps then another way to think about the two is to splinter them into three types of activity: research, routine accepted practice, and innovative medicine.5
Given this potential for blurred lines about novel approaches to medical conditions, how do we communicate this to patients? This is where the role of informed consent becomes essential. Informed consent is key to respecting patients’ autonomy – a central tenet of medical ethics. For patients to make autonomous choices they need basic facts to make informed decisions.6 These facts must be unbiased and free from conflicts, and they must not only be truthful but also be comprehensive and free from omission. It is in this informed consent process that we must explain that a technique or procedure is new, outline the risks and benefits, and share our actual experiences with said procedure especially if it is limited.7 We must also be aware of how certain biases and conflicts can affect our decisions to adapt and recommend innovative therapies. We may have incentives to offer innovative therapies to be on the “cutting edge” and attract patients. We may have explicit financial gain if working directly with device manufacturers or reimbursed by our institutions per procedure. Conflicts of interest are not only financial, but they can also be the prospects of promotion or career advancement.3 Institutions as well are incentivized to advertise the “latest” to bolster their prestige and reputations. Ultimately, we should act to the highest levels of professionalism, and ethics, by ignoring benefit to ourselves as physicians and always focusing on the benefits for our patients.7
What about when patients ask for specific innovative procedures as Mrs. Jones did above? What is our responsibility then? In situations where patients specifically push for a new procedure, it remains our duty to inform patients about the novelty of the procedure and the limited study of its safety and efficacy. When speaking about the “experience” with a novel procedure, it is tempting to speak globally and broadly. For example, Dr. Indo spoke about the procedure being done hundreds of times across the country and being safe in this context. It is our duty to be transparent, disclose our own experiences, and consider our own skills when recommending a novel procedure.7 It should be noted that patients are a vulnerable population and many times at the mercy of our recommendations. We’ve often heard patients say “Whatever you say doc; You’re the doctor;” or “I’ll do what you think is best” when presented with treatment options. This is an incredible amount of power, and we must protect this trust patients place in us by clearly acknowledging the uncertainties of new procedures and placing their benefit over our own potential gain.
Dr. Williams is a general surgery resident at the University of Chicago and a fellow at the MacLean Center for clinical medical ethics. Dr. Angelos is the Linda Kohler Anderson Professor of Surgery and Surgical Ethics, vice chairman for ethics, professional development, and wellness, and chief of endocrine surgery, department of surgery, and the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics at the University of Chicago. The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Goyal H et al. Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;14. doi: 10.1177/2631774520984627.
2. Machytka E et al. Gastrointestinal Endosc. 2017;86(5):904-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.07.009.
3. Eastwood GL. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Australia). 2015;30(S1):8-11. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12755.
4. Neugebauer EAM et al. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(7):1594-1615. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0818-3.
5. Eaton, ML and Kennedy, DL. Innovation in Medical Technology: Ethical Issues and Challenges. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
6. Angelos P. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108(6):1611-2. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.08.010.
7. Angelos P. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13(1):6-9. doi: 10.1001/virtualmentor.2011.13.1.ccas1-1101.
Get the science right
Get the science right. I have spent years researching and reflecting on what makes the best physicians, the best medicine, the optimal organized medical system, and the best medical ethics and law to support all of it. I have traveled to almost innumerable conferences to discuss these topics with colleagues who have similar goals. Time and time again, I come back to the conclusion that, in the modern era, the second-most important thing to do is to get the science right.
The practice of medicine in my Western world can be traced back to Hippocrates and earlier. The practice of nursing has other milestones. The healing arts have different points of origin in other cultures, such as China. In a modern world of mass communication, these various historical paths are converging on scientific evidence. The science to support medicine has always had flaws, but it has fared better than the other options. Sometimes, the science was so sketchy that the key was to believe in whatever the shaman was providing. But for the past 100 years, science, rather than tradition and hierarchy, has been relied upon to guide policy and action. For the past 50 years, evidence-based medicine has ascended. Have we become better than the snake oil salesmen of the late 19th century?
Modern health care is far from perfect. The pandemic has been a major stressor to the health care system. The pandemic has revealed flaws and weaknesses, including inequity in access to care, health illiteracy, and a shaky moral compass balancing individual liberty and social good. Overall, despite multiple mistakes dealing with a novel threat, I think the institutions promoting science have performed well during the pandemic, especially when compared with the moral and governmental institutions encouraging ethical behavior and making policies to promote justice.
My highest praise would be for the professionalism of health care workers. Nurses and physicians have staffed the hospitals and clinics caring for people when the hallways were overflowing for days without end. Without the commitment, the teamwork, and the courage to provide that care, the death toll would have been much higher and the suffering unimaginable. My observation is that these people were not motivated by an abstract primum non nocere, first do no harm. It was the commitment to love one’s neighbor and care for the sick. This dedication is the first most important thing in professionalism.
Part of what fuels that commitment is a belief that what they are doing makes a difference. The belief is stronger when there is measurable, scientific evidence that a difference is being made. The scientific decisions have not been perfect, but at this point the evidence is clear that the shutdown flattened the curve. Vaccines saved lives and will continue to do so. Masks saved lives. Nursing care, particularly intensive care, reduced the case fatality rate and assuaged suffering and grief.
What lessons about training new providers can be gleaned from the past 2 years? Those who teach professionalism for physicians, nurses, and other health care workers should strengthen the common value systems that undergird the commitment people have to the patients and the professions. In the face of postmodern nihilism and relativism, virtues need to be clarified and reinforced. In the face of political polarization which seeks to make a political affiliation the locus of loyalty and commitment, emphasize the fellowship of the health care professions.
To me as a scientist, a key lesson is that we need to be better at getting the science right. Two years ago I was wiping some groceries with alcohol and quarantining cans in shopping bags in the corner of the kitchen for 24 hours before shelving them. I still push elevator buttons with my knuckles. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention needs to revamp their policy making procedures.
Institutions must work to reestablish the public trust in science. That is a challenge because while many amazing scientific advances have occurred (i.e., my MRI last week showed far more going on than my orthopedist and physical therapist detected based on clinical exam). Imaging such as MR and ultrasound have been major advances in diagnostic medicine, but there are also repeated examples demonstrating where medicine has been wrong. In the past 6 months I have read new guidelines for ear tubes, for neonatal jaundice, for newborn sepsis, and for newborn hypoglycemia. All indicate to me that my training 30 years ago was on target and the interval “improvements” in practice have been worthless Brownian motion based on false scientific discoveries. My recommendation would be that pediatrics do one-third as much research but do that research three times better and get it right.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
Get the science right. I have spent years researching and reflecting on what makes the best physicians, the best medicine, the optimal organized medical system, and the best medical ethics and law to support all of it. I have traveled to almost innumerable conferences to discuss these topics with colleagues who have similar goals. Time and time again, I come back to the conclusion that, in the modern era, the second-most important thing to do is to get the science right.
The practice of medicine in my Western world can be traced back to Hippocrates and earlier. The practice of nursing has other milestones. The healing arts have different points of origin in other cultures, such as China. In a modern world of mass communication, these various historical paths are converging on scientific evidence. The science to support medicine has always had flaws, but it has fared better than the other options. Sometimes, the science was so sketchy that the key was to believe in whatever the shaman was providing. But for the past 100 years, science, rather than tradition and hierarchy, has been relied upon to guide policy and action. For the past 50 years, evidence-based medicine has ascended. Have we become better than the snake oil salesmen of the late 19th century?
Modern health care is far from perfect. The pandemic has been a major stressor to the health care system. The pandemic has revealed flaws and weaknesses, including inequity in access to care, health illiteracy, and a shaky moral compass balancing individual liberty and social good. Overall, despite multiple mistakes dealing with a novel threat, I think the institutions promoting science have performed well during the pandemic, especially when compared with the moral and governmental institutions encouraging ethical behavior and making policies to promote justice.
My highest praise would be for the professionalism of health care workers. Nurses and physicians have staffed the hospitals and clinics caring for people when the hallways were overflowing for days without end. Without the commitment, the teamwork, and the courage to provide that care, the death toll would have been much higher and the suffering unimaginable. My observation is that these people were not motivated by an abstract primum non nocere, first do no harm. It was the commitment to love one’s neighbor and care for the sick. This dedication is the first most important thing in professionalism.
Part of what fuels that commitment is a belief that what they are doing makes a difference. The belief is stronger when there is measurable, scientific evidence that a difference is being made. The scientific decisions have not been perfect, but at this point the evidence is clear that the shutdown flattened the curve. Vaccines saved lives and will continue to do so. Masks saved lives. Nursing care, particularly intensive care, reduced the case fatality rate and assuaged suffering and grief.
What lessons about training new providers can be gleaned from the past 2 years? Those who teach professionalism for physicians, nurses, and other health care workers should strengthen the common value systems that undergird the commitment people have to the patients and the professions. In the face of postmodern nihilism and relativism, virtues need to be clarified and reinforced. In the face of political polarization which seeks to make a political affiliation the locus of loyalty and commitment, emphasize the fellowship of the health care professions.
To me as a scientist, a key lesson is that we need to be better at getting the science right. Two years ago I was wiping some groceries with alcohol and quarantining cans in shopping bags in the corner of the kitchen for 24 hours before shelving them. I still push elevator buttons with my knuckles. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention needs to revamp their policy making procedures.
Institutions must work to reestablish the public trust in science. That is a challenge because while many amazing scientific advances have occurred (i.e., my MRI last week showed far more going on than my orthopedist and physical therapist detected based on clinical exam). Imaging such as MR and ultrasound have been major advances in diagnostic medicine, but there are also repeated examples demonstrating where medicine has been wrong. In the past 6 months I have read new guidelines for ear tubes, for neonatal jaundice, for newborn sepsis, and for newborn hypoglycemia. All indicate to me that my training 30 years ago was on target and the interval “improvements” in practice have been worthless Brownian motion based on false scientific discoveries. My recommendation would be that pediatrics do one-third as much research but do that research three times better and get it right.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
Get the science right. I have spent years researching and reflecting on what makes the best physicians, the best medicine, the optimal organized medical system, and the best medical ethics and law to support all of it. I have traveled to almost innumerable conferences to discuss these topics with colleagues who have similar goals. Time and time again, I come back to the conclusion that, in the modern era, the second-most important thing to do is to get the science right.
The practice of medicine in my Western world can be traced back to Hippocrates and earlier. The practice of nursing has other milestones. The healing arts have different points of origin in other cultures, such as China. In a modern world of mass communication, these various historical paths are converging on scientific evidence. The science to support medicine has always had flaws, but it has fared better than the other options. Sometimes, the science was so sketchy that the key was to believe in whatever the shaman was providing. But for the past 100 years, science, rather than tradition and hierarchy, has been relied upon to guide policy and action. For the past 50 years, evidence-based medicine has ascended. Have we become better than the snake oil salesmen of the late 19th century?
Modern health care is far from perfect. The pandemic has been a major stressor to the health care system. The pandemic has revealed flaws and weaknesses, including inequity in access to care, health illiteracy, and a shaky moral compass balancing individual liberty and social good. Overall, despite multiple mistakes dealing with a novel threat, I think the institutions promoting science have performed well during the pandemic, especially when compared with the moral and governmental institutions encouraging ethical behavior and making policies to promote justice.
My highest praise would be for the professionalism of health care workers. Nurses and physicians have staffed the hospitals and clinics caring for people when the hallways were overflowing for days without end. Without the commitment, the teamwork, and the courage to provide that care, the death toll would have been much higher and the suffering unimaginable. My observation is that these people were not motivated by an abstract primum non nocere, first do no harm. It was the commitment to love one’s neighbor and care for the sick. This dedication is the first most important thing in professionalism.
Part of what fuels that commitment is a belief that what they are doing makes a difference. The belief is stronger when there is measurable, scientific evidence that a difference is being made. The scientific decisions have not been perfect, but at this point the evidence is clear that the shutdown flattened the curve. Vaccines saved lives and will continue to do so. Masks saved lives. Nursing care, particularly intensive care, reduced the case fatality rate and assuaged suffering and grief.
What lessons about training new providers can be gleaned from the past 2 years? Those who teach professionalism for physicians, nurses, and other health care workers should strengthen the common value systems that undergird the commitment people have to the patients and the professions. In the face of postmodern nihilism and relativism, virtues need to be clarified and reinforced. In the face of political polarization which seeks to make a political affiliation the locus of loyalty and commitment, emphasize the fellowship of the health care professions.
To me as a scientist, a key lesson is that we need to be better at getting the science right. Two years ago I was wiping some groceries with alcohol and quarantining cans in shopping bags in the corner of the kitchen for 24 hours before shelving them. I still push elevator buttons with my knuckles. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention needs to revamp their policy making procedures.
Institutions must work to reestablish the public trust in science. That is a challenge because while many amazing scientific advances have occurred (i.e., my MRI last week showed far more going on than my orthopedist and physical therapist detected based on clinical exam). Imaging such as MR and ultrasound have been major advances in diagnostic medicine, but there are also repeated examples demonstrating where medicine has been wrong. In the past 6 months I have read new guidelines for ear tubes, for neonatal jaundice, for newborn sepsis, and for newborn hypoglycemia. All indicate to me that my training 30 years ago was on target and the interval “improvements” in practice have been worthless Brownian motion based on false scientific discoveries. My recommendation would be that pediatrics do one-third as much research but do that research three times better and get it right.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
Walking 10,000 steps a day: Desirable goal or urban myth?
Some myths never die. The idea of taking 10,000 steps a day is one of them. What started as a catchy marketing slogan has become a mantra for anyone promoting physical activity.
It all began in 1965 when the Japanese company Yamasa Tokei began selling a new step-counter which they called manpo-kei (ten-thousand steps meter). They coupled the product launch with an ad campaign – “Let’s walk 10,000 steps a day!” – in a bid to encourage physical activity. The threshold was always somewhat arbitrary, but the idea of 10,000 steps cemented itself in the public consciousness from that point forward.
To be fair, there is nothing wrong with taking 10,000 steps a day, and it does roughly correlate with the generally recommended amount of physical activity. Most people will take somewhere between 5,000 and 7,500 steps a day even if they lead largely sedentary lives. If you add 30 minutes of walking to your daily routine, that will account for an extra 3,000-4,000 steps and bring you close to that 10,000-step threshold. As such, setting a 10,000-step target is a potentially useful shorthand for people aspiring to achieve ideal levels of physical activity.
But walking fewer steps still has a benefit. A study in JAMA Network Open followed a cohort of 2,110 adults from the CARDIA study and found, rather unsurprisingly, that those with more steps per day had lower rates of all-cause mortality. But interestingly, those who averaged 7,000-10,000 steps per day did just as well as those who walked more than 10,000 steps, suggesting that the lower threshold was probably the inflection point.
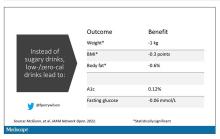
Other research has shown that improving your step count is probably more important than achieving any specific threshold. In one Canadian study, patients with diabetes were randomized to usual care or to an exercise prescription from their physicians. The intervention group improved their daily step count from around 5,000 steps per day to about 6,200 steps per day. While the increase was less than the researchers had hoped for, it still resulted in improvements in blood sugar control. In another study, a 24-week walking program reduced blood pressure by 11 points in postmenopausal women, even though their increased daily step counts fell shy of the 10,000 goal at about 9,000 steps. Similarly, a small Japanese study found that enrolling postmenopausal women in a weekly exercise program helped improve their lipid profile even though they only increased their daily step count from 6,800 to 8,500 steps per day. And an analysis of U.S. NHANES data showed a mortality benefit when individuals taking more than 8,000 steps were compared with those taking fewer than 4,000 steps per day. The benefits largely plateaued beyond 9,000-10,000 steps.
The reality is that walking 10,000 steps a day is a laudable goal and is almost certainly beneficial. But even lower levels of physical activity have benefits. The trick is not so much to aim for some theoretical ideal but to improve upon your current baseline. Encouraging patients to get into the habit of taking a daily walk (be it in the morning, during lunchtime, or in the evening) is going to pay dividends regardless of their daily step count. The point is that when it comes to physical activity, the greatest benefit seems to be when we go from doing nothing to doing something.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Queen Elizabeth Health Complex, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some myths never die. The idea of taking 10,000 steps a day is one of them. What started as a catchy marketing slogan has become a mantra for anyone promoting physical activity.
It all began in 1965 when the Japanese company Yamasa Tokei began selling a new step-counter which they called manpo-kei (ten-thousand steps meter). They coupled the product launch with an ad campaign – “Let’s walk 10,000 steps a day!” – in a bid to encourage physical activity. The threshold was always somewhat arbitrary, but the idea of 10,000 steps cemented itself in the public consciousness from that point forward.
To be fair, there is nothing wrong with taking 10,000 steps a day, and it does roughly correlate with the generally recommended amount of physical activity. Most people will take somewhere between 5,000 and 7,500 steps a day even if they lead largely sedentary lives. If you add 30 minutes of walking to your daily routine, that will account for an extra 3,000-4,000 steps and bring you close to that 10,000-step threshold. As such, setting a 10,000-step target is a potentially useful shorthand for people aspiring to achieve ideal levels of physical activity.
But walking fewer steps still has a benefit. A study in JAMA Network Open followed a cohort of 2,110 adults from the CARDIA study and found, rather unsurprisingly, that those with more steps per day had lower rates of all-cause mortality. But interestingly, those who averaged 7,000-10,000 steps per day did just as well as those who walked more than 10,000 steps, suggesting that the lower threshold was probably the inflection point.
Other research has shown that improving your step count is probably more important than achieving any specific threshold. In one Canadian study, patients with diabetes were randomized to usual care or to an exercise prescription from their physicians. The intervention group improved their daily step count from around 5,000 steps per day to about 6,200 steps per day. While the increase was less than the researchers had hoped for, it still resulted in improvements in blood sugar control. In another study, a 24-week walking program reduced blood pressure by 11 points in postmenopausal women, even though their increased daily step counts fell shy of the 10,000 goal at about 9,000 steps. Similarly, a small Japanese study found that enrolling postmenopausal women in a weekly exercise program helped improve their lipid profile even though they only increased their daily step count from 6,800 to 8,500 steps per day. And an analysis of U.S. NHANES data showed a mortality benefit when individuals taking more than 8,000 steps were compared with those taking fewer than 4,000 steps per day. The benefits largely plateaued beyond 9,000-10,000 steps.
The reality is that walking 10,000 steps a day is a laudable goal and is almost certainly beneficial. But even lower levels of physical activity have benefits. The trick is not so much to aim for some theoretical ideal but to improve upon your current baseline. Encouraging patients to get into the habit of taking a daily walk (be it in the morning, during lunchtime, or in the evening) is going to pay dividends regardless of their daily step count. The point is that when it comes to physical activity, the greatest benefit seems to be when we go from doing nothing to doing something.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Queen Elizabeth Health Complex, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some myths never die. The idea of taking 10,000 steps a day is one of them. What started as a catchy marketing slogan has become a mantra for anyone promoting physical activity.
It all began in 1965 when the Japanese company Yamasa Tokei began selling a new step-counter which they called manpo-kei (ten-thousand steps meter). They coupled the product launch with an ad campaign – “Let’s walk 10,000 steps a day!” – in a bid to encourage physical activity. The threshold was always somewhat arbitrary, but the idea of 10,000 steps cemented itself in the public consciousness from that point forward.
To be fair, there is nothing wrong with taking 10,000 steps a day, and it does roughly correlate with the generally recommended amount of physical activity. Most people will take somewhere between 5,000 and 7,500 steps a day even if they lead largely sedentary lives. If you add 30 minutes of walking to your daily routine, that will account for an extra 3,000-4,000 steps and bring you close to that 10,000-step threshold. As such, setting a 10,000-step target is a potentially useful shorthand for people aspiring to achieve ideal levels of physical activity.
But walking fewer steps still has a benefit. A study in JAMA Network Open followed a cohort of 2,110 adults from the CARDIA study and found, rather unsurprisingly, that those with more steps per day had lower rates of all-cause mortality. But interestingly, those who averaged 7,000-10,000 steps per day did just as well as those who walked more than 10,000 steps, suggesting that the lower threshold was probably the inflection point.
Other research has shown that improving your step count is probably more important than achieving any specific threshold. In one Canadian study, patients with diabetes were randomized to usual care or to an exercise prescription from their physicians. The intervention group improved their daily step count from around 5,000 steps per day to about 6,200 steps per day. While the increase was less than the researchers had hoped for, it still resulted in improvements in blood sugar control. In another study, a 24-week walking program reduced blood pressure by 11 points in postmenopausal women, even though their increased daily step counts fell shy of the 10,000 goal at about 9,000 steps. Similarly, a small Japanese study found that enrolling postmenopausal women in a weekly exercise program helped improve their lipid profile even though they only increased their daily step count from 6,800 to 8,500 steps per day. And an analysis of U.S. NHANES data showed a mortality benefit when individuals taking more than 8,000 steps were compared with those taking fewer than 4,000 steps per day. The benefits largely plateaued beyond 9,000-10,000 steps.
The reality is that walking 10,000 steps a day is a laudable goal and is almost certainly beneficial. But even lower levels of physical activity have benefits. The trick is not so much to aim for some theoretical ideal but to improve upon your current baseline. Encouraging patients to get into the habit of taking a daily walk (be it in the morning, during lunchtime, or in the evening) is going to pay dividends regardless of their daily step count. The point is that when it comes to physical activity, the greatest benefit seems to be when we go from doing nothing to doing something.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Queen Elizabeth Health Complex, Montreal. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘We don’t want to be an inspiration’
Over 2.5 million people have fled the ghastly war in Ukraine for safety. But, not everyone is trying to leave. Shockingly, hundreds of thousands are actually flocking toward the danger in Ukraine right now. Many of them are women.
I was commuting to work when I first heard this story on a podcast. In astonishing numbers, women have chosen to return to or stay in Ukraine because they’re needed to fight and to protect their families. My reaction, like yours, was to be inspired. What amazing courage! Twitter and Instagram will swell with images of their balaclava masked faces standing in the breach once more. Like the women in medicine who armed themselves with surgical masks and face shields and babies on their backs to join the fight against COVID-19. They will be poster girls, blue sleeves rolled up and red polka dotted bandanas covering their hair.
But that’s not what they want. “We don’t want to be an inspiration,” said one fearless Ukrainian fighter in the story, “we want to be alive.”
At the time of this writing as we celebrate the brilliant accomplishments of women on March 8, International Women’s Day, I wonder if we don’t have it slightly wrong.
Although acknowledgment is appreciated, the women I work alongside don’t need me to be inspired by them. They need me to stand with them, to help them. . The “she-session” it’s been called, refers to the million women who have not rejoined the workforce since COVID-19. This is especially acute for us in medicine where women are significantly more likely than are men to report not working full time, or not working at all.
The truth is that even in 2022, the burdens of family life are still not borne equally. Bias against mothers in particular can be insidious. Take academia, where there is little sympathy for not publishing on schedule. Perhaps there are unexplained gaps, but where exactly on a CV does one put “recurrent pregnancy loss?” Do you know how many clinics or ORs a woman must cancel to attempt maddeningly unpredictable egg retrievals and embryo transfers? A lot. Not to mention the financial burden of doing so.
During the pandemic, female physicians were more likely to manage child care, schooling, and household duties, compared to male physicians.
And yet (perhaps even because of that?) women in medicine make less money. How much? About $80,000 less on average in dermatology. Inspired? Indeed. No thanks. Let’s #BreakTheBias rather.
I’m not a policy expert nor a sociologist. I don’t know what advice might be helpful here. I’d say raising our collective consciousness of the unfairness, highlighting discrepancies, and advocating for equality are good starts. But, International Women’s Day isn’t new. It’s old. Like over a hundred years old (since 1909 to be exact). We don’t just need a better hashtag, we need to do something. Give equity in pay. Offer opportunities for leadership that accommodate the extra duty women might have outside work. Create flexibility in schedules and without the penalty of having to pump at work or leave early to pick up a child. Not to mention all the opportunities we men have to do more of the household work that women currently do.
The gallant women of Ukraine don’t need our approbation. They need our aid and our prayers. Like the women in my department, at my medical center, in my community, they aren’t posing to be made into posters. There’s work to be done and they are flocking toward it right now.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Over 2.5 million people have fled the ghastly war in Ukraine for safety. But, not everyone is trying to leave. Shockingly, hundreds of thousands are actually flocking toward the danger in Ukraine right now. Many of them are women.
I was commuting to work when I first heard this story on a podcast. In astonishing numbers, women have chosen to return to or stay in Ukraine because they’re needed to fight and to protect their families. My reaction, like yours, was to be inspired. What amazing courage! Twitter and Instagram will swell with images of their balaclava masked faces standing in the breach once more. Like the women in medicine who armed themselves with surgical masks and face shields and babies on their backs to join the fight against COVID-19. They will be poster girls, blue sleeves rolled up and red polka dotted bandanas covering their hair.
But that’s not what they want. “We don’t want to be an inspiration,” said one fearless Ukrainian fighter in the story, “we want to be alive.”
At the time of this writing as we celebrate the brilliant accomplishments of women on March 8, International Women’s Day, I wonder if we don’t have it slightly wrong.
Although acknowledgment is appreciated, the women I work alongside don’t need me to be inspired by them. They need me to stand with them, to help them. . The “she-session” it’s been called, refers to the million women who have not rejoined the workforce since COVID-19. This is especially acute for us in medicine where women are significantly more likely than are men to report not working full time, or not working at all.
The truth is that even in 2022, the burdens of family life are still not borne equally. Bias against mothers in particular can be insidious. Take academia, where there is little sympathy for not publishing on schedule. Perhaps there are unexplained gaps, but where exactly on a CV does one put “recurrent pregnancy loss?” Do you know how many clinics or ORs a woman must cancel to attempt maddeningly unpredictable egg retrievals and embryo transfers? A lot. Not to mention the financial burden of doing so.
During the pandemic, female physicians were more likely to manage child care, schooling, and household duties, compared to male physicians.
And yet (perhaps even because of that?) women in medicine make less money. How much? About $80,000 less on average in dermatology. Inspired? Indeed. No thanks. Let’s #BreakTheBias rather.
I’m not a policy expert nor a sociologist. I don’t know what advice might be helpful here. I’d say raising our collective consciousness of the unfairness, highlighting discrepancies, and advocating for equality are good starts. But, International Women’s Day isn’t new. It’s old. Like over a hundred years old (since 1909 to be exact). We don’t just need a better hashtag, we need to do something. Give equity in pay. Offer opportunities for leadership that accommodate the extra duty women might have outside work. Create flexibility in schedules and without the penalty of having to pump at work or leave early to pick up a child. Not to mention all the opportunities we men have to do more of the household work that women currently do.
The gallant women of Ukraine don’t need our approbation. They need our aid and our prayers. Like the women in my department, at my medical center, in my community, they aren’t posing to be made into posters. There’s work to be done and they are flocking toward it right now.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Over 2.5 million people have fled the ghastly war in Ukraine for safety. But, not everyone is trying to leave. Shockingly, hundreds of thousands are actually flocking toward the danger in Ukraine right now. Many of them are women.
I was commuting to work when I first heard this story on a podcast. In astonishing numbers, women have chosen to return to or stay in Ukraine because they’re needed to fight and to protect their families. My reaction, like yours, was to be inspired. What amazing courage! Twitter and Instagram will swell with images of their balaclava masked faces standing in the breach once more. Like the women in medicine who armed themselves with surgical masks and face shields and babies on their backs to join the fight against COVID-19. They will be poster girls, blue sleeves rolled up and red polka dotted bandanas covering their hair.
But that’s not what they want. “We don’t want to be an inspiration,” said one fearless Ukrainian fighter in the story, “we want to be alive.”
At the time of this writing as we celebrate the brilliant accomplishments of women on March 8, International Women’s Day, I wonder if we don’t have it slightly wrong.
Although acknowledgment is appreciated, the women I work alongside don’t need me to be inspired by them. They need me to stand with them, to help them. . The “she-session” it’s been called, refers to the million women who have not rejoined the workforce since COVID-19. This is especially acute for us in medicine where women are significantly more likely than are men to report not working full time, or not working at all.
The truth is that even in 2022, the burdens of family life are still not borne equally. Bias against mothers in particular can be insidious. Take academia, where there is little sympathy for not publishing on schedule. Perhaps there are unexplained gaps, but where exactly on a CV does one put “recurrent pregnancy loss?” Do you know how many clinics or ORs a woman must cancel to attempt maddeningly unpredictable egg retrievals and embryo transfers? A lot. Not to mention the financial burden of doing so.
During the pandemic, female physicians were more likely to manage child care, schooling, and household duties, compared to male physicians.
And yet (perhaps even because of that?) women in medicine make less money. How much? About $80,000 less on average in dermatology. Inspired? Indeed. No thanks. Let’s #BreakTheBias rather.
I’m not a policy expert nor a sociologist. I don’t know what advice might be helpful here. I’d say raising our collective consciousness of the unfairness, highlighting discrepancies, and advocating for equality are good starts. But, International Women’s Day isn’t new. It’s old. Like over a hundred years old (since 1909 to be exact). We don’t just need a better hashtag, we need to do something. Give equity in pay. Offer opportunities for leadership that accommodate the extra duty women might have outside work. Create flexibility in schedules and without the penalty of having to pump at work or leave early to pick up a child. Not to mention all the opportunities we men have to do more of the household work that women currently do.
The gallant women of Ukraine don’t need our approbation. They need our aid and our prayers. Like the women in my department, at my medical center, in my community, they aren’t posing to be made into posters. There’s work to be done and they are flocking toward it right now.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Waiting for the under-5 COVID-19 vaccine
In February, citing the need for more data, Pfizer and BioNTech announced that they were delaying the application for their COVID-19 vaccine for children under the age of 5. Earlier evidence suggests that two doses may not provide adequate protection in the 2- to 4-year old age group. With the larger number of infections and illness in the younger age group from the Omicron variant, Pfizer and BioNTech felt they needed more data on the effectiveness of a third dose.
This delay came as a disappointment to parents of children under 5 who have been eager to have them receive the vaccination. However, Peter Marks, MD, director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research at the Food and Drug Administration, told parents that this delay should be reassuring – that the companies were doing important due diligence before releasing a product that is both safe and effective. The American Academy of Pediatrics wisely released a similar statement of reassurance and support.
It is difficult to know how many parents will eventually immunize their young children once the vaccine is approved. Any survey done more than a few weeks ago must be viewed cautiously as “the COVID numbers” around the country continue to improve and parental attitudes are likely to change.
There will always remain subgroups of parents on either extreme of the bell-shaped curve. Some will reject the under-5 vaccine simply because it is a vaccine. Some parents are so anxious to vaccinate that they will want to be first in line even if waiting is the more prudent approach. In a recent opinion piece appearing in the New York Times, a statistician writes that he is so eager to have his young children immunized that he is encouraging the FDA to replace its traditional reliance on “statistical significance” with a less rigid and binary method such as one based on Bayesian theory (Aubrey Carlton, “I’m a parent and a statistician. There’s a smarter way to think about the under-5 vaccine.” The New York Times. 2022 Mar 1.). However, what this statistician misses in his haste to vaccinate his own children is that we are dealing with an entire population with varying levels of scientific sophistication and appetite for risk. While “statistical significance” may no longer be cutting edge to some statisticians, most of the rest of the country finds the term reassuring.
It will be interesting to see what happens if and when the vaccine is approved. Will the American Academy of Pediatrics come out with a strong recommendation? I hope they are careful and provide a sufficient number of caveats, otherwise we in the trenches will again be left to provide more nuanced advice to families who are both anxious and hesitant.
Despite the recent surge in cases among young children, apparently as a result of the Omicron variant, the disease continues to cause less and milder disease among young children than it does in adults. And the degree to which illness in the pediatric population contributes to the health of the general population appears to still be a matter of debate. This may be yet another instance of when the crafty COVID-19 has moved with a pace that will make an under–age-5 vaccine of relatively little value.
First, we must be careful to assure ourselves that any side effects the vaccine might generate are well within an even more restricted acceptable range. Second, we must be careful not to squander our persuasive currency by promoting a vaccine that in retrospect may turn out to be of relatively little value.
Although there is ample evidence that education often fails to convince the committed anti-vaxxers, pediatricians continue to be held in high regard by most parents, many of whom are understandably confused by the tsunami of health information of mixed quality generated by the pandemic. We must be cautious not to cast ourselves as a group whose knee-jerk reaction is to recommend every vaccine with equal vigor. All vaccines are not created equal. We must be patient and prepared to adjust the level of our enthusiasm. We must continue to tailor our advice based on the hard data. Otherwise, parents will stop asking for our advice because they will believe that they already know what we’re going to say.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In February, citing the need for more data, Pfizer and BioNTech announced that they were delaying the application for their COVID-19 vaccine for children under the age of 5. Earlier evidence suggests that two doses may not provide adequate protection in the 2- to 4-year old age group. With the larger number of infections and illness in the younger age group from the Omicron variant, Pfizer and BioNTech felt they needed more data on the effectiveness of a third dose.
This delay came as a disappointment to parents of children under 5 who have been eager to have them receive the vaccination. However, Peter Marks, MD, director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research at the Food and Drug Administration, told parents that this delay should be reassuring – that the companies were doing important due diligence before releasing a product that is both safe and effective. The American Academy of Pediatrics wisely released a similar statement of reassurance and support.
It is difficult to know how many parents will eventually immunize their young children once the vaccine is approved. Any survey done more than a few weeks ago must be viewed cautiously as “the COVID numbers” around the country continue to improve and parental attitudes are likely to change.
There will always remain subgroups of parents on either extreme of the bell-shaped curve. Some will reject the under-5 vaccine simply because it is a vaccine. Some parents are so anxious to vaccinate that they will want to be first in line even if waiting is the more prudent approach. In a recent opinion piece appearing in the New York Times, a statistician writes that he is so eager to have his young children immunized that he is encouraging the FDA to replace its traditional reliance on “statistical significance” with a less rigid and binary method such as one based on Bayesian theory (Aubrey Carlton, “I’m a parent and a statistician. There’s a smarter way to think about the under-5 vaccine.” The New York Times. 2022 Mar 1.). However, what this statistician misses in his haste to vaccinate his own children is that we are dealing with an entire population with varying levels of scientific sophistication and appetite for risk. While “statistical significance” may no longer be cutting edge to some statisticians, most of the rest of the country finds the term reassuring.
It will be interesting to see what happens if and when the vaccine is approved. Will the American Academy of Pediatrics come out with a strong recommendation? I hope they are careful and provide a sufficient number of caveats, otherwise we in the trenches will again be left to provide more nuanced advice to families who are both anxious and hesitant.
Despite the recent surge in cases among young children, apparently as a result of the Omicron variant, the disease continues to cause less and milder disease among young children than it does in adults. And the degree to which illness in the pediatric population contributes to the health of the general population appears to still be a matter of debate. This may be yet another instance of when the crafty COVID-19 has moved with a pace that will make an under–age-5 vaccine of relatively little value.
First, we must be careful to assure ourselves that any side effects the vaccine might generate are well within an even more restricted acceptable range. Second, we must be careful not to squander our persuasive currency by promoting a vaccine that in retrospect may turn out to be of relatively little value.
Although there is ample evidence that education often fails to convince the committed anti-vaxxers, pediatricians continue to be held in high regard by most parents, many of whom are understandably confused by the tsunami of health information of mixed quality generated by the pandemic. We must be cautious not to cast ourselves as a group whose knee-jerk reaction is to recommend every vaccine with equal vigor. All vaccines are not created equal. We must be patient and prepared to adjust the level of our enthusiasm. We must continue to tailor our advice based on the hard data. Otherwise, parents will stop asking for our advice because they will believe that they already know what we’re going to say.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
In February, citing the need for more data, Pfizer and BioNTech announced that they were delaying the application for their COVID-19 vaccine for children under the age of 5. Earlier evidence suggests that two doses may not provide adequate protection in the 2- to 4-year old age group. With the larger number of infections and illness in the younger age group from the Omicron variant, Pfizer and BioNTech felt they needed more data on the effectiveness of a third dose.
This delay came as a disappointment to parents of children under 5 who have been eager to have them receive the vaccination. However, Peter Marks, MD, director of the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research at the Food and Drug Administration, told parents that this delay should be reassuring – that the companies were doing important due diligence before releasing a product that is both safe and effective. The American Academy of Pediatrics wisely released a similar statement of reassurance and support.
It is difficult to know how many parents will eventually immunize their young children once the vaccine is approved. Any survey done more than a few weeks ago must be viewed cautiously as “the COVID numbers” around the country continue to improve and parental attitudes are likely to change.
There will always remain subgroups of parents on either extreme of the bell-shaped curve. Some will reject the under-5 vaccine simply because it is a vaccine. Some parents are so anxious to vaccinate that they will want to be first in line even if waiting is the more prudent approach. In a recent opinion piece appearing in the New York Times, a statistician writes that he is so eager to have his young children immunized that he is encouraging the FDA to replace its traditional reliance on “statistical significance” with a less rigid and binary method such as one based on Bayesian theory (Aubrey Carlton, “I’m a parent and a statistician. There’s a smarter way to think about the under-5 vaccine.” The New York Times. 2022 Mar 1.). However, what this statistician misses in his haste to vaccinate his own children is that we are dealing with an entire population with varying levels of scientific sophistication and appetite for risk. While “statistical significance” may no longer be cutting edge to some statisticians, most of the rest of the country finds the term reassuring.
It will be interesting to see what happens if and when the vaccine is approved. Will the American Academy of Pediatrics come out with a strong recommendation? I hope they are careful and provide a sufficient number of caveats, otherwise we in the trenches will again be left to provide more nuanced advice to families who are both anxious and hesitant.
Despite the recent surge in cases among young children, apparently as a result of the Omicron variant, the disease continues to cause less and milder disease among young children than it does in adults. And the degree to which illness in the pediatric population contributes to the health of the general population appears to still be a matter of debate. This may be yet another instance of when the crafty COVID-19 has moved with a pace that will make an under–age-5 vaccine of relatively little value.
First, we must be careful to assure ourselves that any side effects the vaccine might generate are well within an even more restricted acceptable range. Second, we must be careful not to squander our persuasive currency by promoting a vaccine that in retrospect may turn out to be of relatively little value.
Although there is ample evidence that education often fails to convince the committed anti-vaxxers, pediatricians continue to be held in high regard by most parents, many of whom are understandably confused by the tsunami of health information of mixed quality generated by the pandemic. We must be cautious not to cast ourselves as a group whose knee-jerk reaction is to recommend every vaccine with equal vigor. All vaccines are not created equal. We must be patient and prepared to adjust the level of our enthusiasm. We must continue to tailor our advice based on the hard data. Otherwise, parents will stop asking for our advice because they will believe that they already know what we’re going to say.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Answering parents’ questions about Cronobacter and powdered formula
A 6-month-old boy presented with 2 days of looser-than-normal stools without blood or mucous. Before the onset of diarrhea, he had been fed at least two bottles of an infant formula identified in a national recall. His mom requested testing for Cronobacter sakazakii.
In mid-February, Abbott Nutrition recalled specific lots of powdered formula produced at one Michigan manufacturing facility because of possible Cronobacter contamination. To date, a public health investigation has identified four infants in three states who developed Cronobacter infection after consuming formula that was part of the recall. Two of the infants died.
As media reports urged families to search their kitchens for containers of the implicated formula and return them for a refund, worried parents reached out to pediatric care providers for advice.
Cronobacter sakazakii and other Cronobacter species are Gram-negative environmental organisms that occasionally cause bacteremia and meningitis in young infants. Although these infections are not subject to mandatory reporting in most states, laboratory-based surveillance suggests that 18 cases occur annually in the United States (0.49 cases/100,00 infants).
While early reports in the literature described cases in hospitalized, preterm infants, infections also occur in the community and in children born at or near term. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention review of domestic and international cases identified 183 children <12 months of age between 1961 and 2018 described as diagnosed with Cronobacter bacteremia or meningitis.1 Of the 79 U.S. cases, 34 occurred in term infants and 50 were community onset. Most cases occurred in the first month of life; the oldest child was 35 days of age at the onset of symptoms. Meningitis was more likely in infants born close to term and who were not hospitalized at the time of infection. The majority of infants for whom a feeding history was available had consumed powdered formula.
Back in the exam room, the 6-month-old was examined and found to be vigorous and well-appearing with normal vital signs and no signs of dehydration. The infant’s pediatrician found no clinical indication to perform a blood culture or lumbar puncture, the tests used to diagnose invasive Cronobacter infection. She explained that stool cultures are not recommended, as Cronobacter does not usually cause diarrhea in infants and finding the bacteria in the stool may represent colonization rather than infection.
The pediatrician did take the opportunity to talk to the mom about her formula preparation practices and shared a handout. Powdered formula isn’t sterile, but it is safe for most infants when prepared according to manufacturer’s directions. Contamination of formula during or after preparation can also result in Cronobacter infection in vulnerable infants.
The mom was surprised – and unhappy – to learn that Cronobacter could be lurking in her kitchen. More than a decade ago, investigators visited 78 households in Tennessee and cultured multiple kitchen surfaces.2C. sakazakii was recovered from 21 homes. Most of the positive cultures were from sinks, counter tops, and used dishcloths. Cronobacter has also been cultured from a variety of dried food items, including powdered milk, herbal tea, and starches.
According to the CDC, liquid formula, a product that is sterile until opened, is a safer choice for formula-fed infants who are less than 3 months of age, were born prematurely, or have a compromised immune system. When these infants must be fed powdered formula, preparing it with water heated to at least 158°F or 70°C can kill Cronobacter organisms. Parents should be instructed to boil water and let it cool for about 5 minutes before using it to mix formula.
While most cases of Cronobacter in infants have been epidemiologically linked to consumption of powdered formula, sporadic case reports describe infection in infants fed expressed breast milk. In one report, identical bacterial isolates were recovered from expressed milk fed to an infected infant and the breast pump used to express the milk.3
Moms who express milk should be instructed in proper breast pump hygiene, including washing hands thoroughly before handling breast pumps; disassembling and cleaning breast pumps kits after each use, either in hot soapy water with a dedicated brush and basin or in the dishwasher; air drying on a clean surface; and sanitizing at least daily by boiling, steaming, or using a dishwasher’s sanitize cycle.
Health care providers are encouraged to report Cronobacter cases to their state or local health departments.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Strysko J et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(5):857-65.
2. Kilonzo-Nthenge A et al. J Food Protect 2012;75(8):1512-7.
3. Bowen A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:761-2.
A 6-month-old boy presented with 2 days of looser-than-normal stools without blood or mucous. Before the onset of diarrhea, he had been fed at least two bottles of an infant formula identified in a national recall. His mom requested testing for Cronobacter sakazakii.
In mid-February, Abbott Nutrition recalled specific lots of powdered formula produced at one Michigan manufacturing facility because of possible Cronobacter contamination. To date, a public health investigation has identified four infants in three states who developed Cronobacter infection after consuming formula that was part of the recall. Two of the infants died.
As media reports urged families to search their kitchens for containers of the implicated formula and return them for a refund, worried parents reached out to pediatric care providers for advice.
Cronobacter sakazakii and other Cronobacter species are Gram-negative environmental organisms that occasionally cause bacteremia and meningitis in young infants. Although these infections are not subject to mandatory reporting in most states, laboratory-based surveillance suggests that 18 cases occur annually in the United States (0.49 cases/100,00 infants).
While early reports in the literature described cases in hospitalized, preterm infants, infections also occur in the community and in children born at or near term. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention review of domestic and international cases identified 183 children <12 months of age between 1961 and 2018 described as diagnosed with Cronobacter bacteremia or meningitis.1 Of the 79 U.S. cases, 34 occurred in term infants and 50 were community onset. Most cases occurred in the first month of life; the oldest child was 35 days of age at the onset of symptoms. Meningitis was more likely in infants born close to term and who were not hospitalized at the time of infection. The majority of infants for whom a feeding history was available had consumed powdered formula.
Back in the exam room, the 6-month-old was examined and found to be vigorous and well-appearing with normal vital signs and no signs of dehydration. The infant’s pediatrician found no clinical indication to perform a blood culture or lumbar puncture, the tests used to diagnose invasive Cronobacter infection. She explained that stool cultures are not recommended, as Cronobacter does not usually cause diarrhea in infants and finding the bacteria in the stool may represent colonization rather than infection.
The pediatrician did take the opportunity to talk to the mom about her formula preparation practices and shared a handout. Powdered formula isn’t sterile, but it is safe for most infants when prepared according to manufacturer’s directions. Contamination of formula during or after preparation can also result in Cronobacter infection in vulnerable infants.
The mom was surprised – and unhappy – to learn that Cronobacter could be lurking in her kitchen. More than a decade ago, investigators visited 78 households in Tennessee and cultured multiple kitchen surfaces.2C. sakazakii was recovered from 21 homes. Most of the positive cultures were from sinks, counter tops, and used dishcloths. Cronobacter has also been cultured from a variety of dried food items, including powdered milk, herbal tea, and starches.
According to the CDC, liquid formula, a product that is sterile until opened, is a safer choice for formula-fed infants who are less than 3 months of age, were born prematurely, or have a compromised immune system. When these infants must be fed powdered formula, preparing it with water heated to at least 158°F or 70°C can kill Cronobacter organisms. Parents should be instructed to boil water and let it cool for about 5 minutes before using it to mix formula.
While most cases of Cronobacter in infants have been epidemiologically linked to consumption of powdered formula, sporadic case reports describe infection in infants fed expressed breast milk. In one report, identical bacterial isolates were recovered from expressed milk fed to an infected infant and the breast pump used to express the milk.3
Moms who express milk should be instructed in proper breast pump hygiene, including washing hands thoroughly before handling breast pumps; disassembling and cleaning breast pumps kits after each use, either in hot soapy water with a dedicated brush and basin or in the dishwasher; air drying on a clean surface; and sanitizing at least daily by boiling, steaming, or using a dishwasher’s sanitize cycle.
Health care providers are encouraged to report Cronobacter cases to their state or local health departments.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Strysko J et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(5):857-65.
2. Kilonzo-Nthenge A et al. J Food Protect 2012;75(8):1512-7.
3. Bowen A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:761-2.
A 6-month-old boy presented with 2 days of looser-than-normal stools without blood or mucous. Before the onset of diarrhea, he had been fed at least two bottles of an infant formula identified in a national recall. His mom requested testing for Cronobacter sakazakii.
In mid-February, Abbott Nutrition recalled specific lots of powdered formula produced at one Michigan manufacturing facility because of possible Cronobacter contamination. To date, a public health investigation has identified four infants in three states who developed Cronobacter infection after consuming formula that was part of the recall. Two of the infants died.
As media reports urged families to search their kitchens for containers of the implicated formula and return them for a refund, worried parents reached out to pediatric care providers for advice.
Cronobacter sakazakii and other Cronobacter species are Gram-negative environmental organisms that occasionally cause bacteremia and meningitis in young infants. Although these infections are not subject to mandatory reporting in most states, laboratory-based surveillance suggests that 18 cases occur annually in the United States (0.49 cases/100,00 infants).
While early reports in the literature described cases in hospitalized, preterm infants, infections also occur in the community and in children born at or near term. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention review of domestic and international cases identified 183 children <12 months of age between 1961 and 2018 described as diagnosed with Cronobacter bacteremia or meningitis.1 Of the 79 U.S. cases, 34 occurred in term infants and 50 were community onset. Most cases occurred in the first month of life; the oldest child was 35 days of age at the onset of symptoms. Meningitis was more likely in infants born close to term and who were not hospitalized at the time of infection. The majority of infants for whom a feeding history was available had consumed powdered formula.
Back in the exam room, the 6-month-old was examined and found to be vigorous and well-appearing with normal vital signs and no signs of dehydration. The infant’s pediatrician found no clinical indication to perform a blood culture or lumbar puncture, the tests used to diagnose invasive Cronobacter infection. She explained that stool cultures are not recommended, as Cronobacter does not usually cause diarrhea in infants and finding the bacteria in the stool may represent colonization rather than infection.
The pediatrician did take the opportunity to talk to the mom about her formula preparation practices and shared a handout. Powdered formula isn’t sterile, but it is safe for most infants when prepared according to manufacturer’s directions. Contamination of formula during or after preparation can also result in Cronobacter infection in vulnerable infants.
The mom was surprised – and unhappy – to learn that Cronobacter could be lurking in her kitchen. More than a decade ago, investigators visited 78 households in Tennessee and cultured multiple kitchen surfaces.2C. sakazakii was recovered from 21 homes. Most of the positive cultures were from sinks, counter tops, and used dishcloths. Cronobacter has also been cultured from a variety of dried food items, including powdered milk, herbal tea, and starches.
According to the CDC, liquid formula, a product that is sterile until opened, is a safer choice for formula-fed infants who are less than 3 months of age, were born prematurely, or have a compromised immune system. When these infants must be fed powdered formula, preparing it with water heated to at least 158°F or 70°C can kill Cronobacter organisms. Parents should be instructed to boil water and let it cool for about 5 minutes before using it to mix formula.
While most cases of Cronobacter in infants have been epidemiologically linked to consumption of powdered formula, sporadic case reports describe infection in infants fed expressed breast milk. In one report, identical bacterial isolates were recovered from expressed milk fed to an infected infant and the breast pump used to express the milk.3
Moms who express milk should be instructed in proper breast pump hygiene, including washing hands thoroughly before handling breast pumps; disassembling and cleaning breast pumps kits after each use, either in hot soapy water with a dedicated brush and basin or in the dishwasher; air drying on a clean surface; and sanitizing at least daily by boiling, steaming, or using a dishwasher’s sanitize cycle.
Health care providers are encouraged to report Cronobacter cases to their state or local health departments.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Strysko J et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(5):857-65.
2. Kilonzo-Nthenge A et al. J Food Protect 2012;75(8):1512-7.
3. Bowen A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:761-2.
Mercury and other risks of cosmetic skin lighteners
Skin hyperpigmentation – whether it is caused by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne or trauma to the skin, melasma, autoimmune disorders, or disorders of pigmentation – is a condition where treatment is commonly sought after in dermatology offices. Topical products used to fade hyperpigmented areas of the skin have long been used around the world, and because of safety concerns, regulations aimed at reducing potential harm or adverse effects caused by certain ingredients in these products are increasing in different countries.
For example, while extremely effective at treating most forms of hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone has been definitively linked to ochronosis, kojic acid has been linked to contact dermatitis in humans, and acid peels and retinoids are associated with irritant dermatitis, disruption of the skin barrier, and photosensitivity. In animal studies, licorice root extract has been linked to endocrine and other organ system irregularities.
Kojic acid was banned in Japan in 2003, and subsequently in South Korea and Switzerland because of concerns over animal studies indicating that its fungal metabolite might be carcinogenic (. Hydroquinone is classified as a drug and has been banned for use in cosmetic products in Japan, the European Union, Australia, and several African nations since at least 2006 because of concerns over adrenal gland dysregulation and high levels of mercury in hydroquinone products in those countries. In Africa specifically, South Africa banned all but 2% hydroquinone in 1983, the Ivory Coast banned all skin whitening creams in 2015, and in 2016, Ghana initiated a ban on certain skin products containing hydroquinone.
The United States followed suit in February 2020 with the Food and Drug Administration introducing a ban on all OTC hydroquinone-containing products because of concerns over carcinogenicity in animal studies (which has not been shown in human studies to date). The “Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security” (CARES) Act signed in March 2020 then made the changes effective by halting the sale of OTC hydroquinone products in the United States as of September 2020.
Mercury concerns
Despite these bans, hydroquinone continues to be sold in cosmetics and OTC products around the world and online. And despite being banned or limited in these products, in particular. Mercury has been used in cosmetic products as a skin lightening agent (on its own) and as a preservative.
Mercury has been shown to be carcinogenic, neurotoxic, as well as cytotoxic to the renal and endocrine systems, causes reproductive toxicity, and may be bioaccumulative in wildlife and humans. There is particular concern regarding the risks of exposure in pregnant women and babies because of potential harm to the developing brain and nervous system. Initial signs and symptoms of mercury poisoning include irritability, shyness, tremors, changes in vision or hearing, memory problems, depression, numbness and tingling in the hands, feet, or around the mouth.
Organizations such as the Zero Mercury Working Group (ZMWG) – an international coalition of public interest environmental and health nongovernmental organizations from more than 55 countries, focused on eliminating the use, release, and exposure to mercury – have been working to help ensure safety and mercury levels are below the threshold deemed allowable in hydroquinone-containing products.
On March 10, the ZMWG published the results of a new study demonstrating that skin lighteners containing mercury are still being sold online, despite bans and safety concerns. Ebay, Amazon, Shopee, Jiji, and Flipkart are among the websites still selling high mercury–containing skin lightener products. Some of them were the same offenders selling the banned products in 2019. Of the 271 online products tested from 17 countries, nearly half contained over 1 ppm of mercury, which is the legal limit that has been established by most governments and the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Based on their packaging, the majority of these products were manufactured in Asia, most often in Pakistan (43%), Thailand (8%), China (6%), and Taiwan (4%), according to the report.
In ZMWG’s prior publications, mercury concentrations reported in some of these products ranged from 93 ppm to over 16,000 ppm. Even higher concentrations have been reported by other entities. And according to a World Health Organization November 2019 report, mercury-containing skin lightening products have been manufactured in many countries and areas, including Bangladesh, China, Dominican Republic Hong Kong SAR (China), Jamaica, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Thailand, and the United States. According to the ZMWG, 137 countries have committed to the Minamata Convention to phase out and limit mercury, including in cosmetics.
Despite bans on some of these products, consumers in the United States and other countries with bans and restrictions are still at risk of exposure to mercury-containing skin lighteners because of online sales. Hopefully, the work of the ZMWG and similar entities will continue to help limit potentially harmful exposures to mercury, while maintaining access to safe and effective methods to treat hyperpigmentation.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Lily Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
Skin hyperpigmentation – whether it is caused by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne or trauma to the skin, melasma, autoimmune disorders, or disorders of pigmentation – is a condition where treatment is commonly sought after in dermatology offices. Topical products used to fade hyperpigmented areas of the skin have long been used around the world, and because of safety concerns, regulations aimed at reducing potential harm or adverse effects caused by certain ingredients in these products are increasing in different countries.
For example, while extremely effective at treating most forms of hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone has been definitively linked to ochronosis, kojic acid has been linked to contact dermatitis in humans, and acid peels and retinoids are associated with irritant dermatitis, disruption of the skin barrier, and photosensitivity. In animal studies, licorice root extract has been linked to endocrine and other organ system irregularities.
Kojic acid was banned in Japan in 2003, and subsequently in South Korea and Switzerland because of concerns over animal studies indicating that its fungal metabolite might be carcinogenic (. Hydroquinone is classified as a drug and has been banned for use in cosmetic products in Japan, the European Union, Australia, and several African nations since at least 2006 because of concerns over adrenal gland dysregulation and high levels of mercury in hydroquinone products in those countries. In Africa specifically, South Africa banned all but 2% hydroquinone in 1983, the Ivory Coast banned all skin whitening creams in 2015, and in 2016, Ghana initiated a ban on certain skin products containing hydroquinone.
The United States followed suit in February 2020 with the Food and Drug Administration introducing a ban on all OTC hydroquinone-containing products because of concerns over carcinogenicity in animal studies (which has not been shown in human studies to date). The “Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security” (CARES) Act signed in March 2020 then made the changes effective by halting the sale of OTC hydroquinone products in the United States as of September 2020.
Mercury concerns
Despite these bans, hydroquinone continues to be sold in cosmetics and OTC products around the world and online. And despite being banned or limited in these products, in particular. Mercury has been used in cosmetic products as a skin lightening agent (on its own) and as a preservative.
Mercury has been shown to be carcinogenic, neurotoxic, as well as cytotoxic to the renal and endocrine systems, causes reproductive toxicity, and may be bioaccumulative in wildlife and humans. There is particular concern regarding the risks of exposure in pregnant women and babies because of potential harm to the developing brain and nervous system. Initial signs and symptoms of mercury poisoning include irritability, shyness, tremors, changes in vision or hearing, memory problems, depression, numbness and tingling in the hands, feet, or around the mouth.
Organizations such as the Zero Mercury Working Group (ZMWG) – an international coalition of public interest environmental and health nongovernmental organizations from more than 55 countries, focused on eliminating the use, release, and exposure to mercury – have been working to help ensure safety and mercury levels are below the threshold deemed allowable in hydroquinone-containing products.
On March 10, the ZMWG published the results of a new study demonstrating that skin lighteners containing mercury are still being sold online, despite bans and safety concerns. Ebay, Amazon, Shopee, Jiji, and Flipkart are among the websites still selling high mercury–containing skin lightener products. Some of them were the same offenders selling the banned products in 2019. Of the 271 online products tested from 17 countries, nearly half contained over 1 ppm of mercury, which is the legal limit that has been established by most governments and the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Based on their packaging, the majority of these products were manufactured in Asia, most often in Pakistan (43%), Thailand (8%), China (6%), and Taiwan (4%), according to the report.
In ZMWG’s prior publications, mercury concentrations reported in some of these products ranged from 93 ppm to over 16,000 ppm. Even higher concentrations have been reported by other entities. And according to a World Health Organization November 2019 report, mercury-containing skin lightening products have been manufactured in many countries and areas, including Bangladesh, China, Dominican Republic Hong Kong SAR (China), Jamaica, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Thailand, and the United States. According to the ZMWG, 137 countries have committed to the Minamata Convention to phase out and limit mercury, including in cosmetics.
Despite bans on some of these products, consumers in the United States and other countries with bans and restrictions are still at risk of exposure to mercury-containing skin lighteners because of online sales. Hopefully, the work of the ZMWG and similar entities will continue to help limit potentially harmful exposures to mercury, while maintaining access to safe and effective methods to treat hyperpigmentation.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Lily Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
Skin hyperpigmentation – whether it is caused by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne or trauma to the skin, melasma, autoimmune disorders, or disorders of pigmentation – is a condition where treatment is commonly sought after in dermatology offices. Topical products used to fade hyperpigmented areas of the skin have long been used around the world, and because of safety concerns, regulations aimed at reducing potential harm or adverse effects caused by certain ingredients in these products are increasing in different countries.
For example, while extremely effective at treating most forms of hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone has been definitively linked to ochronosis, kojic acid has been linked to contact dermatitis in humans, and acid peels and retinoids are associated with irritant dermatitis, disruption of the skin barrier, and photosensitivity. In animal studies, licorice root extract has been linked to endocrine and other organ system irregularities.
Kojic acid was banned in Japan in 2003, and subsequently in South Korea and Switzerland because of concerns over animal studies indicating that its fungal metabolite might be carcinogenic (. Hydroquinone is classified as a drug and has been banned for use in cosmetic products in Japan, the European Union, Australia, and several African nations since at least 2006 because of concerns over adrenal gland dysregulation and high levels of mercury in hydroquinone products in those countries. In Africa specifically, South Africa banned all but 2% hydroquinone in 1983, the Ivory Coast banned all skin whitening creams in 2015, and in 2016, Ghana initiated a ban on certain skin products containing hydroquinone.
The United States followed suit in February 2020 with the Food and Drug Administration introducing a ban on all OTC hydroquinone-containing products because of concerns over carcinogenicity in animal studies (which has not been shown in human studies to date). The “Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security” (CARES) Act signed in March 2020 then made the changes effective by halting the sale of OTC hydroquinone products in the United States as of September 2020.
Mercury concerns
Despite these bans, hydroquinone continues to be sold in cosmetics and OTC products around the world and online. And despite being banned or limited in these products, in particular. Mercury has been used in cosmetic products as a skin lightening agent (on its own) and as a preservative.
Mercury has been shown to be carcinogenic, neurotoxic, as well as cytotoxic to the renal and endocrine systems, causes reproductive toxicity, and may be bioaccumulative in wildlife and humans. There is particular concern regarding the risks of exposure in pregnant women and babies because of potential harm to the developing brain and nervous system. Initial signs and symptoms of mercury poisoning include irritability, shyness, tremors, changes in vision or hearing, memory problems, depression, numbness and tingling in the hands, feet, or around the mouth.
Organizations such as the Zero Mercury Working Group (ZMWG) – an international coalition of public interest environmental and health nongovernmental organizations from more than 55 countries, focused on eliminating the use, release, and exposure to mercury – have been working to help ensure safety and mercury levels are below the threshold deemed allowable in hydroquinone-containing products.
On March 10, the ZMWG published the results of a new study demonstrating that skin lighteners containing mercury are still being sold online, despite bans and safety concerns. Ebay, Amazon, Shopee, Jiji, and Flipkart are among the websites still selling high mercury–containing skin lightener products. Some of them were the same offenders selling the banned products in 2019. Of the 271 online products tested from 17 countries, nearly half contained over 1 ppm of mercury, which is the legal limit that has been established by most governments and the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Based on their packaging, the majority of these products were manufactured in Asia, most often in Pakistan (43%), Thailand (8%), China (6%), and Taiwan (4%), according to the report.
In ZMWG’s prior publications, mercury concentrations reported in some of these products ranged from 93 ppm to over 16,000 ppm. Even higher concentrations have been reported by other entities. And according to a World Health Organization November 2019 report, mercury-containing skin lightening products have been manufactured in many countries and areas, including Bangladesh, China, Dominican Republic Hong Kong SAR (China), Jamaica, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mexico, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Thailand, and the United States. According to the ZMWG, 137 countries have committed to the Minamata Convention to phase out and limit mercury, including in cosmetics.
Despite bans on some of these products, consumers in the United States and other countries with bans and restrictions are still at risk of exposure to mercury-containing skin lighteners because of online sales. Hopefully, the work of the ZMWG and similar entities will continue to help limit potentially harmful exposures to mercury, while maintaining access to safe and effective methods to treat hyperpigmentation.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Lily Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
A 31-year-old female presented with a burning rash on upper arms, groin, and axillae
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
Betamethasone cream did not alleviate symptoms.
Don’t drink calories: Artificial sweeteners beat sugar in new analysis
This transcript of Impact Factor with F. Perry Wilson has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
When I counsel patients who are trying to lose weight, there is something I always discuss: “Don’t drink calories.” The idea is that it is so easy to consume sweetened beverages (and alcoholic ones, for that matter) and we don’t really get a sense of how many calories we’re taking in.
Some patients balk at the idea, saying they can’t stand the taste of water or just can’t bring themselves to drink it. While, as a nephrologist, this pains me deeply to hear, I often suggest going for low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks instead of the sugary stuff.
And yet ... I need to admit that recently I’ve been more nervous about that advice. A very nice study in Nature, for example, found that artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance and weight gain – in mice.
Several observational studies have suggested that the use of nonnutritive sweeteners – sucralose, aspartame, and so on – are associated with higher body weight and type 2 diabetes. Of course,
Randomized trials, as ever, are the key to deeper understanding, but most trials in this space are relatively small. That makes a good case for this study, appearing in JAMA Network Open, which combines data from 17 randomized trials to determine what effects substituting sugary drinks with low- and zero-calorie drinks truly has.
So, what’s the bottom line? Should I ditch the Splenda in my morning coffee and drop in some sugar cubes?
It turns out that the effects of drinking low- or zero-calorie drinks instead of sugary ones is modest, but overall beneficial, depending on the outcome you’re trying to achieve.
Randomized trials show that switching to low-cal drinks reduces body weight by about a kilogram, and BMI by 0.3 points. It also reduces body fat by about half a percent.
Effects on glucose homeostasis – hemoglobin A1c level and fasting glucose – were not that impressive, though.
The authors also compared sugar-sweetened beverages with plain old water. I expected this analysis to show more dramatic benefits. After all, we’re all just ugly, giant bags of mostly water. Interestingly, the effects of switching to water were not as dramatic and largely nonsignificant with respect to most outcomes evaluated.
So, what do we make of this? If someone is a habitual drinker of sugar-sweetened beverages, is it preferable to switch to a zero-calorie flavored drink, compared with plain water?
One possibility is that in the trials where people are randomized to switch to water, they aren’t as adherent. Just because we ask someone to drink water doesn’t mean they do it, and so there may be a tendency to “cheat” with sugar-sweetened beverages. However, if told that low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks are okay, maybe it’s easier to stick to the plan? This is essentially the argument you get from people who say that vaping is a good way to quit smoking. It may or may not be true.
It could also be that we just don’t have enough rigorous data to make a firm conclusion. Of the 17 trials examined, only three of them used water substitution as an intervention.
All in all, these data provide some reassurance that the zero-calorie sweeteners aren’t secretly exacerbating the obesity epidemic. I’d certainly rather my patients drink Diet Coke than regular Coke. That said, these studies are necessarily short term; the longer-term effects of sugar substitutes, while perhaps not as bad as the long-term effects of sugar, must necessarily be worse than the long-term effects of drinking water. Maybe this is the nephrologist in me talking again, but I doubt that there could possibly be a fluid better for the human body than good old H2O. Except coffee, of course.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript of Impact Factor with F. Perry Wilson has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
When I counsel patients who are trying to lose weight, there is something I always discuss: “Don’t drink calories.” The idea is that it is so easy to consume sweetened beverages (and alcoholic ones, for that matter) and we don’t really get a sense of how many calories we’re taking in.
Some patients balk at the idea, saying they can’t stand the taste of water or just can’t bring themselves to drink it. While, as a nephrologist, this pains me deeply to hear, I often suggest going for low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks instead of the sugary stuff.
And yet ... I need to admit that recently I’ve been more nervous about that advice. A very nice study in Nature, for example, found that artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance and weight gain – in mice.
Several observational studies have suggested that the use of nonnutritive sweeteners – sucralose, aspartame, and so on – are associated with higher body weight and type 2 diabetes. Of course,
Randomized trials, as ever, are the key to deeper understanding, but most trials in this space are relatively small. That makes a good case for this study, appearing in JAMA Network Open, which combines data from 17 randomized trials to determine what effects substituting sugary drinks with low- and zero-calorie drinks truly has.
So, what’s the bottom line? Should I ditch the Splenda in my morning coffee and drop in some sugar cubes?
It turns out that the effects of drinking low- or zero-calorie drinks instead of sugary ones is modest, but overall beneficial, depending on the outcome you’re trying to achieve.
Randomized trials show that switching to low-cal drinks reduces body weight by about a kilogram, and BMI by 0.3 points. It also reduces body fat by about half a percent.
Effects on glucose homeostasis – hemoglobin A1c level and fasting glucose – were not that impressive, though.
The authors also compared sugar-sweetened beverages with plain old water. I expected this analysis to show more dramatic benefits. After all, we’re all just ugly, giant bags of mostly water. Interestingly, the effects of switching to water were not as dramatic and largely nonsignificant with respect to most outcomes evaluated.
So, what do we make of this? If someone is a habitual drinker of sugar-sweetened beverages, is it preferable to switch to a zero-calorie flavored drink, compared with plain water?
One possibility is that in the trials where people are randomized to switch to water, they aren’t as adherent. Just because we ask someone to drink water doesn’t mean they do it, and so there may be a tendency to “cheat” with sugar-sweetened beverages. However, if told that low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks are okay, maybe it’s easier to stick to the plan? This is essentially the argument you get from people who say that vaping is a good way to quit smoking. It may or may not be true.
It could also be that we just don’t have enough rigorous data to make a firm conclusion. Of the 17 trials examined, only three of them used water substitution as an intervention.
All in all, these data provide some reassurance that the zero-calorie sweeteners aren’t secretly exacerbating the obesity epidemic. I’d certainly rather my patients drink Diet Coke than regular Coke. That said, these studies are necessarily short term; the longer-term effects of sugar substitutes, while perhaps not as bad as the long-term effects of sugar, must necessarily be worse than the long-term effects of drinking water. Maybe this is the nephrologist in me talking again, but I doubt that there could possibly be a fluid better for the human body than good old H2O. Except coffee, of course.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript of Impact Factor with F. Perry Wilson has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
When I counsel patients who are trying to lose weight, there is something I always discuss: “Don’t drink calories.” The idea is that it is so easy to consume sweetened beverages (and alcoholic ones, for that matter) and we don’t really get a sense of how many calories we’re taking in.
Some patients balk at the idea, saying they can’t stand the taste of water or just can’t bring themselves to drink it. While, as a nephrologist, this pains me deeply to hear, I often suggest going for low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks instead of the sugary stuff.
And yet ... I need to admit that recently I’ve been more nervous about that advice. A very nice study in Nature, for example, found that artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance and weight gain – in mice.
Several observational studies have suggested that the use of nonnutritive sweeteners – sucralose, aspartame, and so on – are associated with higher body weight and type 2 diabetes. Of course,
Randomized trials, as ever, are the key to deeper understanding, but most trials in this space are relatively small. That makes a good case for this study, appearing in JAMA Network Open, which combines data from 17 randomized trials to determine what effects substituting sugary drinks with low- and zero-calorie drinks truly has.
So, what’s the bottom line? Should I ditch the Splenda in my morning coffee and drop in some sugar cubes?
It turns out that the effects of drinking low- or zero-calorie drinks instead of sugary ones is modest, but overall beneficial, depending on the outcome you’re trying to achieve.
Randomized trials show that switching to low-cal drinks reduces body weight by about a kilogram, and BMI by 0.3 points. It also reduces body fat by about half a percent.
Effects on glucose homeostasis – hemoglobin A1c level and fasting glucose – were not that impressive, though.
The authors also compared sugar-sweetened beverages with plain old water. I expected this analysis to show more dramatic benefits. After all, we’re all just ugly, giant bags of mostly water. Interestingly, the effects of switching to water were not as dramatic and largely nonsignificant with respect to most outcomes evaluated.
So, what do we make of this? If someone is a habitual drinker of sugar-sweetened beverages, is it preferable to switch to a zero-calorie flavored drink, compared with plain water?
One possibility is that in the trials where people are randomized to switch to water, they aren’t as adherent. Just because we ask someone to drink water doesn’t mean they do it, and so there may be a tendency to “cheat” with sugar-sweetened beverages. However, if told that low- or zero-calorie flavored drinks are okay, maybe it’s easier to stick to the plan? This is essentially the argument you get from people who say that vaping is a good way to quit smoking. It may or may not be true.
It could also be that we just don’t have enough rigorous data to make a firm conclusion. Of the 17 trials examined, only three of them used water substitution as an intervention.
All in all, these data provide some reassurance that the zero-calorie sweeteners aren’t secretly exacerbating the obesity epidemic. I’d certainly rather my patients drink Diet Coke than regular Coke. That said, these studies are necessarily short term; the longer-term effects of sugar substitutes, while perhaps not as bad as the long-term effects of sugar, must necessarily be worse than the long-term effects of drinking water. Maybe this is the nephrologist in me talking again, but I doubt that there could possibly be a fluid better for the human body than good old H2O. Except coffee, of course.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Standard of care in suicide prevention in pediatrics: A review of the Blueprint for Youth Suicide Prevention
In March, an unprecedented collaboration between the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP), and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) resulted in the development of the Blueprint for Youth Suicide Prevention. The blueprint comprises a consensus summary of expert recommendations, educational resources, and specific and practical strategies for pediatricians and other health care providers to support youth at risk for suicide in pediatric primary care settings. It is ambitious and far-reaching in scope and speaks to the growing understanding that suicide care pathways offer a clear ray of hope toward a shared “zero suicide” goal.
Following the declaration of a national emergency for child and adolescent mental health, the blueprint represents a resource to help us move forward during this national emergency. It offers practically focused suggestions at the clinic site and individual level, in addition to community and school levels, to tackle the deeply concerning and alarming increasing rate of emergency department visits by 30% in the last 2 pandemic years for youth suicide attempts. A reflexive visit for an emergency mental health evaluation in an emergency department after a disclosure of suicidal ideation isn’t always the next best step in a pathway to care, nor a sustainable community solution with the dearth of mental health and crisis resources nationally.
With this new tool, let’s proceed through a case of how one would approach a patient in the office setting with a concerning disclosure.
Case
Emily is a 12-year-old girl who presents for a routine well-check in your practice. Her mother shared with you before your examination that she has wondered if Emily may need more support. Since the pandemic, Emily had increasingly spent time using social media and watching television. When you meet with Emily on her own, she says, “I know that life is getting back to normal, and I am supposed to be excited for that, but now I have some anxiety about doing what I used to do. I’ve had some thoughts that it would be better to sleep forever and not wake up ...”
Case discussion
The blueprint recommends universal screening for suicide in all youths aged 12 and over. Not all children, like Emily, will be as open about their inner thoughts. The blueprint provides a link to the ASQ, which comprises questions to ascertain suicide risk and takes 20 seconds to complete with a patient. It is recommended as a first-line screening tool by the NIMH: Suicide Risk Screening Tool. This tool can guide one’s clinical thinking beyond the question of whether or not a child feels “suicidal” after a disclosure such as Emily’s. The blueprint also provides a tip sheet on how to frame these screenings to ensure their thoroughness and interpersonal effectiveness.
Case continued
You go through the ASQ with Emily and she revealed that she has had thoughts about suicide but not currently and without further plans. According to the ASQ, this screening falls into the category of a “non-acute positive screen (potential risk identified),” and now the patient requires a brief suicide safety assessment to determine if an emergency mental health evaluation is needed.
Case discussion
An initial screen (ASQ) should be followed by a Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA). Two common ones are the ASQ-BSSA (created by the same group that created the ASQ) or the C-SSRS (Columbia suicide severity rating scale).
The blueprint suggests adding this level of depth to one’s investigation in a pediatrics office for a divulged concern with suicidal ideation and following the algorithm to ensure safety.
The complete screening process is also described, in detail, in this instructional video: Suicide Risk Screening Training: How to Manage Patients at Risk for Suicide.
Case continued
Following the ASQ-BSSA, you determine that a referral to more immediate mental health resources would be most helpful and discuss your concerns with Emily and her family. You connect her via a “warm handoff” to a therapist in the office available from the newly adopted primary care mental health integration model. Emily completes further screening for anxiety and depressive disorders and begins a course of cognitive-behavioral therapy. You feel reassured that the therapist can connect with the consulting psychiatrist in the model who can offer a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation if needed. A referral to the emergency department to complete this screening has been avoided. You also plan for a “caring contact” from the office in a day to check in on Emily and her family and, before they go, provide them with crisis services and resources.
The blueprint represents a thoughtful means to know when emergency department visits are necessary and when other forms of support such as robust safety planning, a connection to other nonemergency services, and “caring contacts” from the office within 24-48 hours are actually of more benefit. “Caring contacts,” in particular, have been lauded as having a significant impact in modifying the course of a patient with suicidal ideation. Data show that differences such as follow-up phone calls by any staff member or even postcards from the clinic over 6-12 months can affect suicide risk.
Beyond outlining suicide care pathways, the blueprint also shares clinical algorithms from the National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs (NNCPAP). These algorithms help clinicians assess common issues in pediatrics and reserve referrals to psychiatry and escalations of care to the emergency department for certain high-risk circumstances.
The blueprint seeks to provide a “one-stop-shop” for accessible and usable resources in the clinic workflow for suicide prevention. It is inspiring to see our professional organizations pursuing practical and practice-based solutions to our children’s mental health crisis in unison.
Dr. Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine. Email her at [email protected].
In March, an unprecedented collaboration between the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP), and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) resulted in the development of the Blueprint for Youth Suicide Prevention. The blueprint comprises a consensus summary of expert recommendations, educational resources, and specific and practical strategies for pediatricians and other health care providers to support youth at risk for suicide in pediatric primary care settings. It is ambitious and far-reaching in scope and speaks to the growing understanding that suicide care pathways offer a clear ray of hope toward a shared “zero suicide” goal.
Following the declaration of a national emergency for child and adolescent mental health, the blueprint represents a resource to help us move forward during this national emergency. It offers practically focused suggestions at the clinic site and individual level, in addition to community and school levels, to tackle the deeply concerning and alarming increasing rate of emergency department visits by 30% in the last 2 pandemic years for youth suicide attempts. A reflexive visit for an emergency mental health evaluation in an emergency department after a disclosure of suicidal ideation isn’t always the next best step in a pathway to care, nor a sustainable community solution with the dearth of mental health and crisis resources nationally.
With this new tool, let’s proceed through a case of how one would approach a patient in the office setting with a concerning disclosure.
Case
Emily is a 12-year-old girl who presents for a routine well-check in your practice. Her mother shared with you before your examination that she has wondered if Emily may need more support. Since the pandemic, Emily had increasingly spent time using social media and watching television. When you meet with Emily on her own, she says, “I know that life is getting back to normal, and I am supposed to be excited for that, but now I have some anxiety about doing what I used to do. I’ve had some thoughts that it would be better to sleep forever and not wake up ...”
Case discussion
The blueprint recommends universal screening for suicide in all youths aged 12 and over. Not all children, like Emily, will be as open about their inner thoughts. The blueprint provides a link to the ASQ, which comprises questions to ascertain suicide risk and takes 20 seconds to complete with a patient. It is recommended as a first-line screening tool by the NIMH: Suicide Risk Screening Tool. This tool can guide one’s clinical thinking beyond the question of whether or not a child feels “suicidal” after a disclosure such as Emily’s. The blueprint also provides a tip sheet on how to frame these screenings to ensure their thoroughness and interpersonal effectiveness.
Case continued
You go through the ASQ with Emily and she revealed that she has had thoughts about suicide but not currently and without further plans. According to the ASQ, this screening falls into the category of a “non-acute positive screen (potential risk identified),” and now the patient requires a brief suicide safety assessment to determine if an emergency mental health evaluation is needed.
Case discussion
An initial screen (ASQ) should be followed by a Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA). Two common ones are the ASQ-BSSA (created by the same group that created the ASQ) or the C-SSRS (Columbia suicide severity rating scale).
The blueprint suggests adding this level of depth to one’s investigation in a pediatrics office for a divulged concern with suicidal ideation and following the algorithm to ensure safety.
The complete screening process is also described, in detail, in this instructional video: Suicide Risk Screening Training: How to Manage Patients at Risk for Suicide.
Case continued
Following the ASQ-BSSA, you determine that a referral to more immediate mental health resources would be most helpful and discuss your concerns with Emily and her family. You connect her via a “warm handoff” to a therapist in the office available from the newly adopted primary care mental health integration model. Emily completes further screening for anxiety and depressive disorders and begins a course of cognitive-behavioral therapy. You feel reassured that the therapist can connect with the consulting psychiatrist in the model who can offer a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation if needed. A referral to the emergency department to complete this screening has been avoided. You also plan for a “caring contact” from the office in a day to check in on Emily and her family and, before they go, provide them with crisis services and resources.
The blueprint represents a thoughtful means to know when emergency department visits are necessary and when other forms of support such as robust safety planning, a connection to other nonemergency services, and “caring contacts” from the office within 24-48 hours are actually of more benefit. “Caring contacts,” in particular, have been lauded as having a significant impact in modifying the course of a patient with suicidal ideation. Data show that differences such as follow-up phone calls by any staff member or even postcards from the clinic over 6-12 months can affect suicide risk.
Beyond outlining suicide care pathways, the blueprint also shares clinical algorithms from the National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs (NNCPAP). These algorithms help clinicians assess common issues in pediatrics and reserve referrals to psychiatry and escalations of care to the emergency department for certain high-risk circumstances.
The blueprint seeks to provide a “one-stop-shop” for accessible and usable resources in the clinic workflow for suicide prevention. It is inspiring to see our professional organizations pursuing practical and practice-based solutions to our children’s mental health crisis in unison.
Dr. Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine. Email her at [email protected].
In March, an unprecedented collaboration between the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP), and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) resulted in the development of the Blueprint for Youth Suicide Prevention. The blueprint comprises a consensus summary of expert recommendations, educational resources, and specific and practical strategies for pediatricians and other health care providers to support youth at risk for suicide in pediatric primary care settings. It is ambitious and far-reaching in scope and speaks to the growing understanding that suicide care pathways offer a clear ray of hope toward a shared “zero suicide” goal.
Following the declaration of a national emergency for child and adolescent mental health, the blueprint represents a resource to help us move forward during this national emergency. It offers practically focused suggestions at the clinic site and individual level, in addition to community and school levels, to tackle the deeply concerning and alarming increasing rate of emergency department visits by 30% in the last 2 pandemic years for youth suicide attempts. A reflexive visit for an emergency mental health evaluation in an emergency department after a disclosure of suicidal ideation isn’t always the next best step in a pathway to care, nor a sustainable community solution with the dearth of mental health and crisis resources nationally.
With this new tool, let’s proceed through a case of how one would approach a patient in the office setting with a concerning disclosure.
Case
Emily is a 12-year-old girl who presents for a routine well-check in your practice. Her mother shared with you before your examination that she has wondered if Emily may need more support. Since the pandemic, Emily had increasingly spent time using social media and watching television. When you meet with Emily on her own, she says, “I know that life is getting back to normal, and I am supposed to be excited for that, but now I have some anxiety about doing what I used to do. I’ve had some thoughts that it would be better to sleep forever and not wake up ...”
Case discussion
The blueprint recommends universal screening for suicide in all youths aged 12 and over. Not all children, like Emily, will be as open about their inner thoughts. The blueprint provides a link to the ASQ, which comprises questions to ascertain suicide risk and takes 20 seconds to complete with a patient. It is recommended as a first-line screening tool by the NIMH: Suicide Risk Screening Tool. This tool can guide one’s clinical thinking beyond the question of whether or not a child feels “suicidal” after a disclosure such as Emily’s. The blueprint also provides a tip sheet on how to frame these screenings to ensure their thoroughness and interpersonal effectiveness.
Case continued
You go through the ASQ with Emily and she revealed that she has had thoughts about suicide but not currently and without further plans. According to the ASQ, this screening falls into the category of a “non-acute positive screen (potential risk identified),” and now the patient requires a brief suicide safety assessment to determine if an emergency mental health evaluation is needed.
Case discussion
An initial screen (ASQ) should be followed by a Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA). Two common ones are the ASQ-BSSA (created by the same group that created the ASQ) or the C-SSRS (Columbia suicide severity rating scale).
The blueprint suggests adding this level of depth to one’s investigation in a pediatrics office for a divulged concern with suicidal ideation and following the algorithm to ensure safety.
The complete screening process is also described, in detail, in this instructional video: Suicide Risk Screening Training: How to Manage Patients at Risk for Suicide.
Case continued
Following the ASQ-BSSA, you determine that a referral to more immediate mental health resources would be most helpful and discuss your concerns with Emily and her family. You connect her via a “warm handoff” to a therapist in the office available from the newly adopted primary care mental health integration model. Emily completes further screening for anxiety and depressive disorders and begins a course of cognitive-behavioral therapy. You feel reassured that the therapist can connect with the consulting psychiatrist in the model who can offer a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation if needed. A referral to the emergency department to complete this screening has been avoided. You also plan for a “caring contact” from the office in a day to check in on Emily and her family and, before they go, provide them with crisis services and resources.
The blueprint represents a thoughtful means to know when emergency department visits are necessary and when other forms of support such as robust safety planning, a connection to other nonemergency services, and “caring contacts” from the office within 24-48 hours are actually of more benefit. “Caring contacts,” in particular, have been lauded as having a significant impact in modifying the course of a patient with suicidal ideation. Data show that differences such as follow-up phone calls by any staff member or even postcards from the clinic over 6-12 months can affect suicide risk.
Beyond outlining suicide care pathways, the blueprint also shares clinical algorithms from the National Network of Child Psychiatry Access Programs (NNCPAP). These algorithms help clinicians assess common issues in pediatrics and reserve referrals to psychiatry and escalations of care to the emergency department for certain high-risk circumstances.
The blueprint seeks to provide a “one-stop-shop” for accessible and usable resources in the clinic workflow for suicide prevention. It is inspiring to see our professional organizations pursuing practical and practice-based solutions to our children’s mental health crisis in unison.
Dr. Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine. Email her at [email protected].