User login
A Case Report of Palliative Pembrolizumab Monotherapy for a Poorly Differentiated Malignancy
Introduction
The critical role of palliative radiotherapy (RT) in the management of advanced cancer is evolving due to the advent of novel therapeuticapproaches. We report the case of a veteran with a soft tissue metastasis who had a robust response to pembrolizumab, allowing for the deferral of palliative RT.
Case Presentation
An 86-year-old male presented with a rapidly growing, painful, malodorous, fungating right inguinal soft tissue mass measuring 10×7×3 cm that had rendered the patient non-ambulatory, with subsequent imaging also demonstrating a left pleural-based lung mass. Biopsy was consistent with a poorly differentiated carcinoma, and molecular profiling revealed a KRAS G12C mutation, high tumor mutational burden (TMB 18 mutations/megabase), and high PD-L1 expression (TPS 100%). The patient’s poor functional status precluded the use of aggressive combination chemotherapy, but the molecular features were favorable for response to immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, which is better tolerated. He was initiated on pembrolizumab with the goal of symptom palliation and potentially prolonging his life. However, as rapid responses to immunotherapy are uncommon, radiation oncology was consulted for palliative RT. Twenty days after starting pembrolizumab and 2 weeks after RT simulation, the inguinal mass had markedly regressed with an open tissue defect at the site. As the palliative goal had been achieved, RT was deferred to avoid the development of a non-healing wound.
Conclusions
Our case highlights palliative treatment modalities for soft tissue masses. Immunotherapy is now a component of first-line therapy in many cancer types, but rapid and robust responses to monotherapy are rare. There is the exciting potential to combine immunotherapy with RT, with small case series indicating synergy, although further research is needed. In cases with molecular characteristics favoring response to immunotherapy, an optimal sequencing approach may incorporate an initial run-in phase with immunotherapy to determine if symptom palliation can be achieved with unimodal therapy. The location of the mass in a non-radiation sensitive region allowed us to entertain the use of combination therapy for our patient, but ultimately was not needed. Palliative RT will remain an option at the time of cancer progression.
Introduction
The critical role of palliative radiotherapy (RT) in the management of advanced cancer is evolving due to the advent of novel therapeuticapproaches. We report the case of a veteran with a soft tissue metastasis who had a robust response to pembrolizumab, allowing for the deferral of palliative RT.
Case Presentation
An 86-year-old male presented with a rapidly growing, painful, malodorous, fungating right inguinal soft tissue mass measuring 10×7×3 cm that had rendered the patient non-ambulatory, with subsequent imaging also demonstrating a left pleural-based lung mass. Biopsy was consistent with a poorly differentiated carcinoma, and molecular profiling revealed a KRAS G12C mutation, high tumor mutational burden (TMB 18 mutations/megabase), and high PD-L1 expression (TPS 100%). The patient’s poor functional status precluded the use of aggressive combination chemotherapy, but the molecular features were favorable for response to immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, which is better tolerated. He was initiated on pembrolizumab with the goal of symptom palliation and potentially prolonging his life. However, as rapid responses to immunotherapy are uncommon, radiation oncology was consulted for palliative RT. Twenty days after starting pembrolizumab and 2 weeks after RT simulation, the inguinal mass had markedly regressed with an open tissue defect at the site. As the palliative goal had been achieved, RT was deferred to avoid the development of a non-healing wound.
Conclusions
Our case highlights palliative treatment modalities for soft tissue masses. Immunotherapy is now a component of first-line therapy in many cancer types, but rapid and robust responses to monotherapy are rare. There is the exciting potential to combine immunotherapy with RT, with small case series indicating synergy, although further research is needed. In cases with molecular characteristics favoring response to immunotherapy, an optimal sequencing approach may incorporate an initial run-in phase with immunotherapy to determine if symptom palliation can be achieved with unimodal therapy. The location of the mass in a non-radiation sensitive region allowed us to entertain the use of combination therapy for our patient, but ultimately was not needed. Palliative RT will remain an option at the time of cancer progression.
Introduction
The critical role of palliative radiotherapy (RT) in the management of advanced cancer is evolving due to the advent of novel therapeuticapproaches. We report the case of a veteran with a soft tissue metastasis who had a robust response to pembrolizumab, allowing for the deferral of palliative RT.
Case Presentation
An 86-year-old male presented with a rapidly growing, painful, malodorous, fungating right inguinal soft tissue mass measuring 10×7×3 cm that had rendered the patient non-ambulatory, with subsequent imaging also demonstrating a left pleural-based lung mass. Biopsy was consistent with a poorly differentiated carcinoma, and molecular profiling revealed a KRAS G12C mutation, high tumor mutational burden (TMB 18 mutations/megabase), and high PD-L1 expression (TPS 100%). The patient’s poor functional status precluded the use of aggressive combination chemotherapy, but the molecular features were favorable for response to immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy, which is better tolerated. He was initiated on pembrolizumab with the goal of symptom palliation and potentially prolonging his life. However, as rapid responses to immunotherapy are uncommon, radiation oncology was consulted for palliative RT. Twenty days after starting pembrolizumab and 2 weeks after RT simulation, the inguinal mass had markedly regressed with an open tissue defect at the site. As the palliative goal had been achieved, RT was deferred to avoid the development of a non-healing wound.
Conclusions
Our case highlights palliative treatment modalities for soft tissue masses. Immunotherapy is now a component of first-line therapy in many cancer types, but rapid and robust responses to monotherapy are rare. There is the exciting potential to combine immunotherapy with RT, with small case series indicating synergy, although further research is needed. In cases with molecular characteristics favoring response to immunotherapy, an optimal sequencing approach may incorporate an initial run-in phase with immunotherapy to determine if symptom palliation can be achieved with unimodal therapy. The location of the mass in a non-radiation sensitive region allowed us to entertain the use of combination therapy for our patient, but ultimately was not needed. Palliative RT will remain an option at the time of cancer progression.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy in the Veterans Affairs Network: the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System Experience
Purpose/Background
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CART) therapy has emerged as a novel treatment for hematologic malignancies, with six FDA agents approved for commercial use. The Veterans Affairs (VA) Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) is the only VA facility authorized to administer CART therapy. As these therapies are changing the paradigm of treatment, the purpose of this review will report the TVHS experience thus far.
Methods
TVHS began coordination with pharmaceutical manufacturers of CART therapies upon first approval in 2017 and became an authorized treatment center for CART therapy in September 2019 with the first CART infusion performed in December of that year. This is a retrospective electronic chart review of all CART patients referred to TVHS from the program’s inception, December 1, 2019 through June 30, 2021. The primary objective of this analysis will be to evaluate the efficacy outcomes of veterans who received CART therapy at TVHS, including overall response rates (ORR), progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Secondary objectives include assessment of toxicities, including rates and maximum grades of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).
Results
A total of 28 patients have received CART infusion at TVHS to date. Fifteen of these patients have reached one year post-CART infusion and are included in this analysis. The majority of patients were White (67%) and were treated for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (87%). All patients were male and ten (67%) were over the age of 65. ORR was 93% (73% achieved complete response [CR]). One-year PFS and OS were both 60%. Of patients who achieved CR by day 100, 89% remain in CR to date. CRS toxicity was observed in 73% of patients (no Grade 3 or higher). ICANS was observed in 26.7% of patients (20% Grade 3 or higher).
Conclusions
CART therapy within the VA has become a well-established practice at TVHS and appears to be a safe and effective therapeutic option for veterans with aggressive lymphoid malignancies.
Purpose/Background
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CART) therapy has emerged as a novel treatment for hematologic malignancies, with six FDA agents approved for commercial use. The Veterans Affairs (VA) Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) is the only VA facility authorized to administer CART therapy. As these therapies are changing the paradigm of treatment, the purpose of this review will report the TVHS experience thus far.
Methods
TVHS began coordination with pharmaceutical manufacturers of CART therapies upon first approval in 2017 and became an authorized treatment center for CART therapy in September 2019 with the first CART infusion performed in December of that year. This is a retrospective electronic chart review of all CART patients referred to TVHS from the program’s inception, December 1, 2019 through June 30, 2021. The primary objective of this analysis will be to evaluate the efficacy outcomes of veterans who received CART therapy at TVHS, including overall response rates (ORR), progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Secondary objectives include assessment of toxicities, including rates and maximum grades of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).
Results
A total of 28 patients have received CART infusion at TVHS to date. Fifteen of these patients have reached one year post-CART infusion and are included in this analysis. The majority of patients were White (67%) and were treated for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (87%). All patients were male and ten (67%) were over the age of 65. ORR was 93% (73% achieved complete response [CR]). One-year PFS and OS were both 60%. Of patients who achieved CR by day 100, 89% remain in CR to date. CRS toxicity was observed in 73% of patients (no Grade 3 or higher). ICANS was observed in 26.7% of patients (20% Grade 3 or higher).
Conclusions
CART therapy within the VA has become a well-established practice at TVHS and appears to be a safe and effective therapeutic option for veterans with aggressive lymphoid malignancies.
Purpose/Background
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CART) therapy has emerged as a novel treatment for hematologic malignancies, with six FDA agents approved for commercial use. The Veterans Affairs (VA) Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) is the only VA facility authorized to administer CART therapy. As these therapies are changing the paradigm of treatment, the purpose of this review will report the TVHS experience thus far.
Methods
TVHS began coordination with pharmaceutical manufacturers of CART therapies upon first approval in 2017 and became an authorized treatment center for CART therapy in September 2019 with the first CART infusion performed in December of that year. This is a retrospective electronic chart review of all CART patients referred to TVHS from the program’s inception, December 1, 2019 through June 30, 2021. The primary objective of this analysis will be to evaluate the efficacy outcomes of veterans who received CART therapy at TVHS, including overall response rates (ORR), progression free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Secondary objectives include assessment of toxicities, including rates and maximum grades of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).
Results
A total of 28 patients have received CART infusion at TVHS to date. Fifteen of these patients have reached one year post-CART infusion and are included in this analysis. The majority of patients were White (67%) and were treated for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (87%). All patients were male and ten (67%) were over the age of 65. ORR was 93% (73% achieved complete response [CR]). One-year PFS and OS were both 60%. Of patients who achieved CR by day 100, 89% remain in CR to date. CRS toxicity was observed in 73% of patients (no Grade 3 or higher). ICANS was observed in 26.7% of patients (20% Grade 3 or higher).
Conclusions
CART therapy within the VA has become a well-established practice at TVHS and appears to be a safe and effective therapeutic option for veterans with aggressive lymphoid malignancies.
Migraine Headache Medications
Shoulder lesion
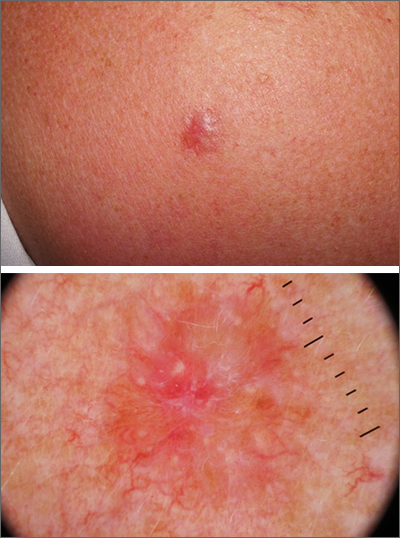
A punch biopsy of the lesion was performed and the results were consistent with a dermatofibroma, which is a benign growth.
Dermatofibromas may manifest as a pink papule on fair-skinned individuals or a darker brown papule in patients of color. Clinically, the texture can be helpful to discern an etiology—dermatofibromas may dimple when pinched laterally, while melanocytic nevi or melanomas tend to be somewhat softer on palpation. Cutaneous sarcoma, while exceedingly rare, may be firmer and chaotic, and varied with multiple colors and topographical changes.
The dermoscopic pattern of a dermatofibroma includes central scar-like areas, a peripheral pigment network, occasional shiny white lines, and confluent circular brown macules. Other less frequent dermoscopic structures may also be seen. A prospective study of the dermoscopic morphology of 412 dermatofibromas found 10 distinct dermoscopic patterns, but also noted that 25% of the dermatofibromas exhibited an atypical pattern.1 Atypical pigment, multiple scar-like areas, and dotted vessels can occur in a dermatofibroma, as well as in a Spitz nevus, and melanoma. Thus, such findings should prompt a biopsy.
Dermatofibromas are safe to observe, but they can be surgically excised if they cause pain or cosmetic concerns.
This patient was reassured to know that the lesion would not require surgical intervention and was unlikely to enlarge or change significantly over time.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, Malvehy J. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2007.8

A punch biopsy of the lesion was performed and the results were consistent with a dermatofibroma, which is a benign growth.
Dermatofibromas may manifest as a pink papule on fair-skinned individuals or a darker brown papule in patients of color. Clinically, the texture can be helpful to discern an etiology—dermatofibromas may dimple when pinched laterally, while melanocytic nevi or melanomas tend to be somewhat softer on palpation. Cutaneous sarcoma, while exceedingly rare, may be firmer and chaotic, and varied with multiple colors and topographical changes.
The dermoscopic pattern of a dermatofibroma includes central scar-like areas, a peripheral pigment network, occasional shiny white lines, and confluent circular brown macules. Other less frequent dermoscopic structures may also be seen. A prospective study of the dermoscopic morphology of 412 dermatofibromas found 10 distinct dermoscopic patterns, but also noted that 25% of the dermatofibromas exhibited an atypical pattern.1 Atypical pigment, multiple scar-like areas, and dotted vessels can occur in a dermatofibroma, as well as in a Spitz nevus, and melanoma. Thus, such findings should prompt a biopsy.
Dermatofibromas are safe to observe, but they can be surgically excised if they cause pain or cosmetic concerns.
This patient was reassured to know that the lesion would not require surgical intervention and was unlikely to enlarge or change significantly over time.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

A punch biopsy of the lesion was performed and the results were consistent with a dermatofibroma, which is a benign growth.
Dermatofibromas may manifest as a pink papule on fair-skinned individuals or a darker brown papule in patients of color. Clinically, the texture can be helpful to discern an etiology—dermatofibromas may dimple when pinched laterally, while melanocytic nevi or melanomas tend to be somewhat softer on palpation. Cutaneous sarcoma, while exceedingly rare, may be firmer and chaotic, and varied with multiple colors and topographical changes.
The dermoscopic pattern of a dermatofibroma includes central scar-like areas, a peripheral pigment network, occasional shiny white lines, and confluent circular brown macules. Other less frequent dermoscopic structures may also be seen. A prospective study of the dermoscopic morphology of 412 dermatofibromas found 10 distinct dermoscopic patterns, but also noted that 25% of the dermatofibromas exhibited an atypical pattern.1 Atypical pigment, multiple scar-like areas, and dotted vessels can occur in a dermatofibroma, as well as in a Spitz nevus, and melanoma. Thus, such findings should prompt a biopsy.
Dermatofibromas are safe to observe, but they can be surgically excised if they cause pain or cosmetic concerns.
This patient was reassured to know that the lesion would not require surgical intervention and was unlikely to enlarge or change significantly over time.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, Malvehy J. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2007.8
1. Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, Malvehy J. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: a prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:75-83. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2007.8
Commentary: Better Migraine Outcomes Measures, September 2022
The theme of this month's commentary is alternative outcomes measures for future migraine studies. The traditional outcomes measures, such as headache frequency measured in headache days, have long been considered gold standards when evaluating the efficacy of preventive interventions. When headache conditions are complicated by interictal pain or other symptoms, or when medication overuse adds a higher frequency or greater severity, those traditional measures are somewhat less exact and specific. Meaningful change for patients with higher frequency of attacks, near-continuous pain, or other migraine symptoms is quite different from that for those without these complications.
Ailani and colleagues reviewed post hoc data from the CONQUER trial, a prior study evaluating the safety and efficacy of galcanezumab vs placebo in patients who had previously not benefited from two to four categories of migraine preventive medication. This refractory population was initially noted to have 4.1 fewer headache days per month than patients taking placebo, but the authors now attempted to review these data with a focus on a different measure: total pain burden (TPB). They defined daily TPB as a single composite measure assessing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine, calculated by multiplying the number of hours of migraine by the maximum daily migraine pain severity score. The monthly TPB was calculated by adding the daily pain burden over the entire month. The Migraine Disability Assessment questionnaire (MIDAS) and Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MSQ) scores were also included to compare migraine-related disability and quality of life.
The patients who received galcanezumab were noted to have a significantly lower TPB, both in episodic and chronic migraine. Significantly greater reductions in monthly TPB relative to placebo were observed at each individual month as well. The change from baseline TPB was also noted to be significantly improved in the galcanezumab group compared with the placebo group. The reduction in TPB was noted even when migraine-day reductions were accounted for as part of a sensitivity analysis.
Preventive trials for migraine treatment focus primarily on migraine-day reduction, and for many patients with higher-frequency migraine, this measure does not adequately account for their disease-related disability. This unique way of looking at pain as part of a bigger picture is much more significant and meaningful for this patient population. Migraine frequency is still a very important outcomes measure, but it would be wise to add TBP or another measure that looks more globally at disease-related disability, especially when investigating preventive options in patients with chronic migraine.
When considering whether an intervention is helpful, most patients and clinicians follow the headache frequency, severity, or quality-of-life factors. As most patients will readily report, not all "headache-free days" are created equal. Although most people with migraine will experience days with absolutely no headache pain or other migraine-associated symptoms, on many days they will still have some symptoms of migraine. Lee and colleagues attempted to quantify the difference between headache-free days and crystal-clear days.
Most headache studies use the frequency of headache days as a primary or secondary outcome. This study collected data on both headache days and crystal-clear days, using data from a questionnaire-based large South Korean nationwide population study that evaluated headache and sleep. The study questions were validated for migraine and aura, and included: "How many days have you had a headache during the previous 30 days?" and "How many days have you had crystal-clear days without headache during the previous 30 days?" The data were then analyzed and compared with the widespread pain index (criteria for fibromyalgia) as well as sleep duration, sleep quality, depression and anxiety scales, and an allodynia checklist.
A little over 3000 respondents completed the surveys; 1938 had experienced headache over the past year, 170 were classified as having a diagnosis of migraine, and 50 of those were diagnosed with aura as well. Out of the patients with migraine, 97% had "unclear days." This was higher than the rate of those with non-migraine headaches (91%). Nearly all people surveyed had some crystal-clear days (99.4%).
The number of crystal-clear days per 30 days was significantly lower in participants with migraine than in those with non-migraine headache. Participants with migraine also had higher frequencies of cutaneous allodynia, anxiety, and depression. The weekly average sleep duration in participants with migraine did not significantly differ from that in participants with non-migraine headaches. The widespread pain index rate was much higher in those with migraine as well.
Most patients will definitely understand the difference between crystal-clear and unclear headache days. Many of the newer outcomes studies in migraine have started focusing on the most bothersome symptom, as headache pain is far from the only significant or disabling symptom associated with migraine. This study makes clear that further outcomes changes are necessary, and that a potentially more meaningful result in migraine studies may actually be crystal-clear days rather than simply headache-free days.
Although there are more acute options available for headache treatment, medication overuse headache remains a major complicating factor for most clinicians who treat headache. When educating patients, there is always a strong emphasis on guidelines for acute medication use. Many patients struggle with knowing when to use an acute treatment and when to alternate with a different treatment, and often they will withhold treatment completely due to fear of medication overuse. The new class of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonist medications has shown some potential benefit as a preventive option for both medication overuse headache and migraine.
The prospective study by Curone and colleagues enrolled 300 patients with confirmed medication overuse headache who did not undergo withdrawal of the overused acute medication. Patients who are already taking preventive medications were excluded, as were patients with diagnoses other than chronic migraine or medication overuse. Patients were given one of the three injectable CGRP antagonist medications for prevention and were followed up at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. The primary outcome was MIDAS score as well as monthly headache days and analgesic consumption.
Out of 303 patients, 242 (80%) showed both a ≥50% reduction of monthly headache days and ≥50% reduction in analgesic intake at 3-month follow-up visit. At 9 months, 198 (65%) were still responders. Monthly analgesic intake decreased ≥50% in 268 of 303 patients (88%) at 3 months and in 241 of 303 patients (79%) at the 6-month follow-up.
For years there has been a debate regarding whether withdrawal of an overused medication is necessary for effective treatment of medication overuse headache. Many preventive treatments are less effective when medication overuse is ongoing. The CGRP class of medications does appear to be effective even with ongoing acute medication overuse. This class of medications should definitely be considered when withdrawing an overused medication is complicated, or when a patient needs to continue to take analgesic medications for another condition.
The theme of this month's commentary is alternative outcomes measures for future migraine studies. The traditional outcomes measures, such as headache frequency measured in headache days, have long been considered gold standards when evaluating the efficacy of preventive interventions. When headache conditions are complicated by interictal pain or other symptoms, or when medication overuse adds a higher frequency or greater severity, those traditional measures are somewhat less exact and specific. Meaningful change for patients with higher frequency of attacks, near-continuous pain, or other migraine symptoms is quite different from that for those without these complications.
Ailani and colleagues reviewed post hoc data from the CONQUER trial, a prior study evaluating the safety and efficacy of galcanezumab vs placebo in patients who had previously not benefited from two to four categories of migraine preventive medication. This refractory population was initially noted to have 4.1 fewer headache days per month than patients taking placebo, but the authors now attempted to review these data with a focus on a different measure: total pain burden (TPB). They defined daily TPB as a single composite measure assessing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine, calculated by multiplying the number of hours of migraine by the maximum daily migraine pain severity score. The monthly TPB was calculated by adding the daily pain burden over the entire month. The Migraine Disability Assessment questionnaire (MIDAS) and Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MSQ) scores were also included to compare migraine-related disability and quality of life.
The patients who received galcanezumab were noted to have a significantly lower TPB, both in episodic and chronic migraine. Significantly greater reductions in monthly TPB relative to placebo were observed at each individual month as well. The change from baseline TPB was also noted to be significantly improved in the galcanezumab group compared with the placebo group. The reduction in TPB was noted even when migraine-day reductions were accounted for as part of a sensitivity analysis.
Preventive trials for migraine treatment focus primarily on migraine-day reduction, and for many patients with higher-frequency migraine, this measure does not adequately account for their disease-related disability. This unique way of looking at pain as part of a bigger picture is much more significant and meaningful for this patient population. Migraine frequency is still a very important outcomes measure, but it would be wise to add TBP or another measure that looks more globally at disease-related disability, especially when investigating preventive options in patients with chronic migraine.
When considering whether an intervention is helpful, most patients and clinicians follow the headache frequency, severity, or quality-of-life factors. As most patients will readily report, not all "headache-free days" are created equal. Although most people with migraine will experience days with absolutely no headache pain or other migraine-associated symptoms, on many days they will still have some symptoms of migraine. Lee and colleagues attempted to quantify the difference between headache-free days and crystal-clear days.
Most headache studies use the frequency of headache days as a primary or secondary outcome. This study collected data on both headache days and crystal-clear days, using data from a questionnaire-based large South Korean nationwide population study that evaluated headache and sleep. The study questions were validated for migraine and aura, and included: "How many days have you had a headache during the previous 30 days?" and "How many days have you had crystal-clear days without headache during the previous 30 days?" The data were then analyzed and compared with the widespread pain index (criteria for fibromyalgia) as well as sleep duration, sleep quality, depression and anxiety scales, and an allodynia checklist.
A little over 3000 respondents completed the surveys; 1938 had experienced headache over the past year, 170 were classified as having a diagnosis of migraine, and 50 of those were diagnosed with aura as well. Out of the patients with migraine, 97% had "unclear days." This was higher than the rate of those with non-migraine headaches (91%). Nearly all people surveyed had some crystal-clear days (99.4%).
The number of crystal-clear days per 30 days was significantly lower in participants with migraine than in those with non-migraine headache. Participants with migraine also had higher frequencies of cutaneous allodynia, anxiety, and depression. The weekly average sleep duration in participants with migraine did not significantly differ from that in participants with non-migraine headaches. The widespread pain index rate was much higher in those with migraine as well.
Most patients will definitely understand the difference between crystal-clear and unclear headache days. Many of the newer outcomes studies in migraine have started focusing on the most bothersome symptom, as headache pain is far from the only significant or disabling symptom associated with migraine. This study makes clear that further outcomes changes are necessary, and that a potentially more meaningful result in migraine studies may actually be crystal-clear days rather than simply headache-free days.
Although there are more acute options available for headache treatment, medication overuse headache remains a major complicating factor for most clinicians who treat headache. When educating patients, there is always a strong emphasis on guidelines for acute medication use. Many patients struggle with knowing when to use an acute treatment and when to alternate with a different treatment, and often they will withhold treatment completely due to fear of medication overuse. The new class of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonist medications has shown some potential benefit as a preventive option for both medication overuse headache and migraine.
The prospective study by Curone and colleagues enrolled 300 patients with confirmed medication overuse headache who did not undergo withdrawal of the overused acute medication. Patients who are already taking preventive medications were excluded, as were patients with diagnoses other than chronic migraine or medication overuse. Patients were given one of the three injectable CGRP antagonist medications for prevention and were followed up at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. The primary outcome was MIDAS score as well as monthly headache days and analgesic consumption.
Out of 303 patients, 242 (80%) showed both a ≥50% reduction of monthly headache days and ≥50% reduction in analgesic intake at 3-month follow-up visit. At 9 months, 198 (65%) were still responders. Monthly analgesic intake decreased ≥50% in 268 of 303 patients (88%) at 3 months and in 241 of 303 patients (79%) at the 6-month follow-up.
For years there has been a debate regarding whether withdrawal of an overused medication is necessary for effective treatment of medication overuse headache. Many preventive treatments are less effective when medication overuse is ongoing. The CGRP class of medications does appear to be effective even with ongoing acute medication overuse. This class of medications should definitely be considered when withdrawing an overused medication is complicated, or when a patient needs to continue to take analgesic medications for another condition.
The theme of this month's commentary is alternative outcomes measures for future migraine studies. The traditional outcomes measures, such as headache frequency measured in headache days, have long been considered gold standards when evaluating the efficacy of preventive interventions. When headache conditions are complicated by interictal pain or other symptoms, or when medication overuse adds a higher frequency or greater severity, those traditional measures are somewhat less exact and specific. Meaningful change for patients with higher frequency of attacks, near-continuous pain, or other migraine symptoms is quite different from that for those without these complications.
Ailani and colleagues reviewed post hoc data from the CONQUER trial, a prior study evaluating the safety and efficacy of galcanezumab vs placebo in patients who had previously not benefited from two to four categories of migraine preventive medication. This refractory population was initially noted to have 4.1 fewer headache days per month than patients taking placebo, but the authors now attempted to review these data with a focus on a different measure: total pain burden (TPB). They defined daily TPB as a single composite measure assessing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine, calculated by multiplying the number of hours of migraine by the maximum daily migraine pain severity score. The monthly TPB was calculated by adding the daily pain burden over the entire month. The Migraine Disability Assessment questionnaire (MIDAS) and Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MSQ) scores were also included to compare migraine-related disability and quality of life.
The patients who received galcanezumab were noted to have a significantly lower TPB, both in episodic and chronic migraine. Significantly greater reductions in monthly TPB relative to placebo were observed at each individual month as well. The change from baseline TPB was also noted to be significantly improved in the galcanezumab group compared with the placebo group. The reduction in TPB was noted even when migraine-day reductions were accounted for as part of a sensitivity analysis.
Preventive trials for migraine treatment focus primarily on migraine-day reduction, and for many patients with higher-frequency migraine, this measure does not adequately account for their disease-related disability. This unique way of looking at pain as part of a bigger picture is much more significant and meaningful for this patient population. Migraine frequency is still a very important outcomes measure, but it would be wise to add TBP or another measure that looks more globally at disease-related disability, especially when investigating preventive options in patients with chronic migraine.
When considering whether an intervention is helpful, most patients and clinicians follow the headache frequency, severity, or quality-of-life factors. As most patients will readily report, not all "headache-free days" are created equal. Although most people with migraine will experience days with absolutely no headache pain or other migraine-associated symptoms, on many days they will still have some symptoms of migraine. Lee and colleagues attempted to quantify the difference between headache-free days and crystal-clear days.
Most headache studies use the frequency of headache days as a primary or secondary outcome. This study collected data on both headache days and crystal-clear days, using data from a questionnaire-based large South Korean nationwide population study that evaluated headache and sleep. The study questions were validated for migraine and aura, and included: "How many days have you had a headache during the previous 30 days?" and "How many days have you had crystal-clear days without headache during the previous 30 days?" The data were then analyzed and compared with the widespread pain index (criteria for fibromyalgia) as well as sleep duration, sleep quality, depression and anxiety scales, and an allodynia checklist.
A little over 3000 respondents completed the surveys; 1938 had experienced headache over the past year, 170 were classified as having a diagnosis of migraine, and 50 of those were diagnosed with aura as well. Out of the patients with migraine, 97% had "unclear days." This was higher than the rate of those with non-migraine headaches (91%). Nearly all people surveyed had some crystal-clear days (99.4%).
The number of crystal-clear days per 30 days was significantly lower in participants with migraine than in those with non-migraine headache. Participants with migraine also had higher frequencies of cutaneous allodynia, anxiety, and depression. The weekly average sleep duration in participants with migraine did not significantly differ from that in participants with non-migraine headaches. The widespread pain index rate was much higher in those with migraine as well.
Most patients will definitely understand the difference between crystal-clear and unclear headache days. Many of the newer outcomes studies in migraine have started focusing on the most bothersome symptom, as headache pain is far from the only significant or disabling symptom associated with migraine. This study makes clear that further outcomes changes are necessary, and that a potentially more meaningful result in migraine studies may actually be crystal-clear days rather than simply headache-free days.
Although there are more acute options available for headache treatment, medication overuse headache remains a major complicating factor for most clinicians who treat headache. When educating patients, there is always a strong emphasis on guidelines for acute medication use. Many patients struggle with knowing when to use an acute treatment and when to alternate with a different treatment, and often they will withhold treatment completely due to fear of medication overuse. The new class of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonist medications has shown some potential benefit as a preventive option for both medication overuse headache and migraine.
The prospective study by Curone and colleagues enrolled 300 patients with confirmed medication overuse headache who did not undergo withdrawal of the overused acute medication. Patients who are already taking preventive medications were excluded, as were patients with diagnoses other than chronic migraine or medication overuse. Patients were given one of the three injectable CGRP antagonist medications for prevention and were followed up at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. The primary outcome was MIDAS score as well as monthly headache days and analgesic consumption.
Out of 303 patients, 242 (80%) showed both a ≥50% reduction of monthly headache days and ≥50% reduction in analgesic intake at 3-month follow-up visit. At 9 months, 198 (65%) were still responders. Monthly analgesic intake decreased ≥50% in 268 of 303 patients (88%) at 3 months and in 241 of 303 patients (79%) at the 6-month follow-up.
For years there has been a debate regarding whether withdrawal of an overused medication is necessary for effective treatment of medication overuse headache. Many preventive treatments are less effective when medication overuse is ongoing. The CGRP class of medications does appear to be effective even with ongoing acute medication overuse. This class of medications should definitely be considered when withdrawing an overused medication is complicated, or when a patient needs to continue to take analgesic medications for another condition.
Punked By the Punctum: Domestically Acquired Cutaneous Myiasis
To the Editor:
Cutaneous myiasis is a skin infestation with dipterous larvae that feed on the host’s tissue and cause a wide range of manifestations depending on the location of infestation. Cutaneous myiasis, which includes furuncular, wound, and migratory types, is the most common clinical form of this condition.1 It is endemic to tropical and subtropical areas and is not common in the United States, thus it can pose a diagnostic challenge when presenting in nonendemic areas. We present the case of a woman from Michigan who acquired furuncular myiasis without travel history to a tropical or subtropical locale.
A 72-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a chief concern of a burning, pruritic, migratory skin lesion on the left arm of approximately 1 week’s duration. She had a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, and multiple tick bites. She reported that the lesion started on the distal aspect of the left arm as an eraser-sized, perfectly round, raised bruise with a dark pepperlike bump in the center. The lesion then spread proximally over the course of 1 week, creating 3 more identical lesions. As one lesion resolved, a new lesion appeared approximately 2 to 4 cm proximal to the preceding lesion. The patient had traveled to England, Scotland, and Ireland 2 months prior but otherwise denied leaving the state of Michigan. She reported frequent exposure to gardens, meadows, and wetlands in search of milkweed and monarch butterfly larvae that she raises in northeast Michigan. She denied any recent illness or associated systemic symptoms. Initial evaluation by a primary care physician resulted in a diagnosis of a furuncle or tick bite; she completed a 10-day course of amoxicillin and a methylprednisolone dose pack without improvement.
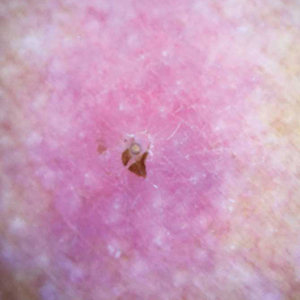
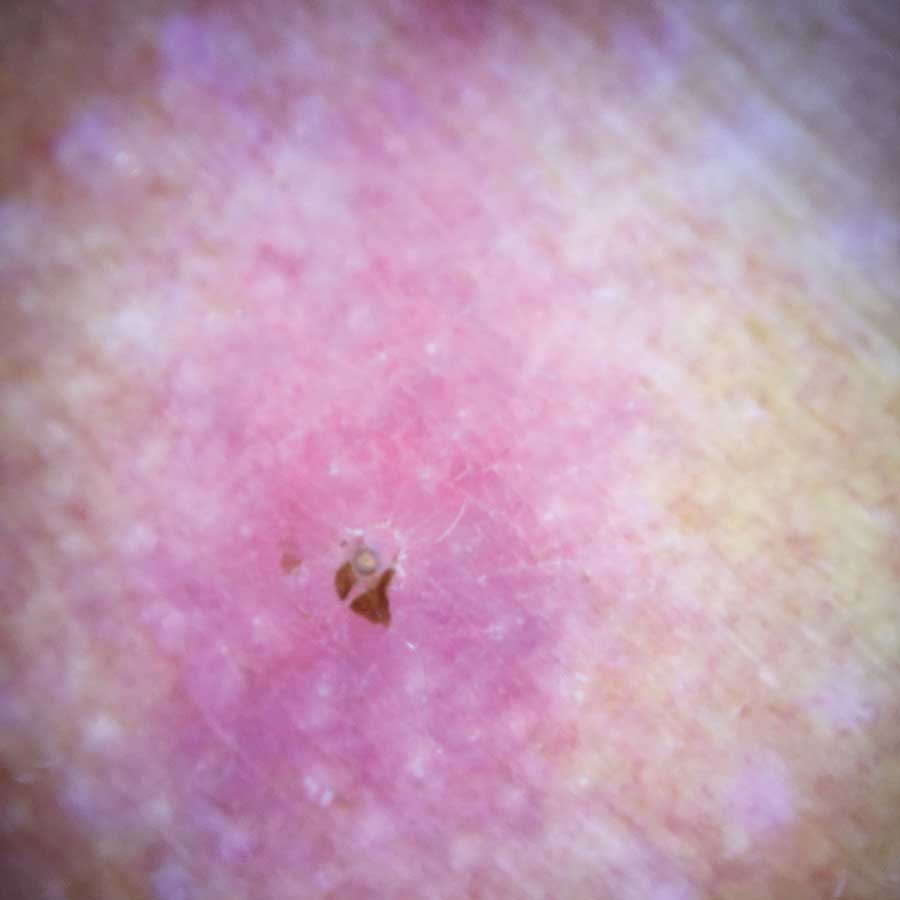
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm, firm, violaceous nodule with a small distinct central punctum and surrounding erythema on the proximal aspect of the left arm. Dermoscopy revealed a pulsating motion and expulsion of serosanguineous fluid from the central punctum (Figure 1). Further inspection of the patient’s left arm exposed several noninflammatory puncta distal to the primary lesion spaced at 2- to 4-cm intervals.
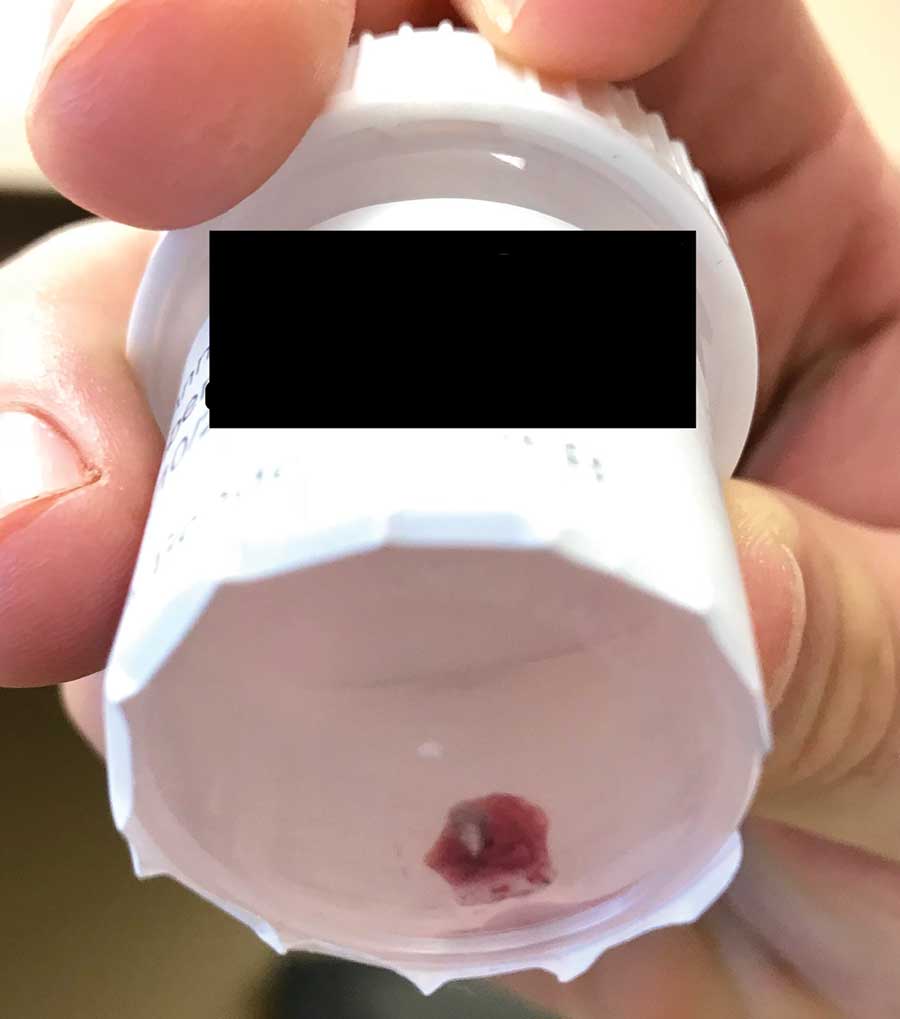
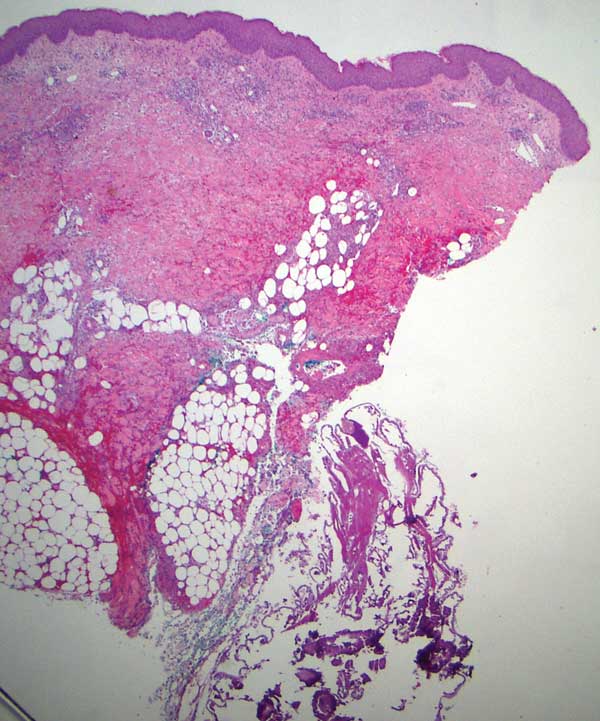
Gross examination of a 6-mm punch biopsy from the primary inflammatory nodule uncovered a small, motile, gray-white larval organism in the inferior portion of the specimen (Figure 2). Histopathology revealed superficial and deep eosinophil-rich inflammation, fibrosis, and hemorrhage. There was a complex wedge-shaped organism with extensive internal muscle bounded by a thin cuticle bearing rows of chitinous hooklets located at one side within the deep dermis (Figure 3). The findings were consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous myiasis. No further treatment was required, as the organism was completely excised with the biopsy.
The most common causative agents of furuncular myiasis obtained from travelers returning from Mexico and Central and South America are Dermatobia hominis and Cordylobia anthropophaga. Cases of furuncular myiasis acquired in the United States without recent foreign travel are rare. Most of these cases are caused by larvae of the Cuterebra species (also known as the rabbit botfly or rodent botfly).2 In a 2003 literature review by Safdar et al3 on 56 cases of furuncular myiasis in the United States, the median age of patients was 14 years, 87% of cases occurred in August and September, and most involved exposure in rural or suburban settings; 53% of cases presented in the northeastern United States.
Furuncular myiasis occurs when the organism’s ova are deposited on the skin of a human host by the parent organism or a mosquito vector. The heat of the skin causes the eggs to hatch and the dipteran larvae must penetrate the skin within 20 days.1 Signs of infection typically are seen 6 to 10 days after infestation.3 The larvae then feed on human tissue and burrow deep in the dermis, forming an erythematous furunculoid nodule containing one or multiple maggots. After 5 to 10 weeks, the adult larvae drop to the ground, where they mature into adult organisms in the soil.1
The most reported symptoms of furuncular myiasis include pruritus, pain, and movement sensation, typically occurring suddenly at night.4 The most common presentation is a furunclelike lesion that exudes serosanguineous or purulent fluid,1 but there have been reports of vesicular, bullous, pustular, erosive, ecchymotic, and ulcerative lesions.5Dermatobia hominis usually presents on an exposed site, such as the scalp, face, and extremities. It may present with paroxysmal episodes of lancinating pain. Over time, the lesion usually heals without a scar, though hyperpigmentation and scarring can occur. The most reported complication is secondary bacterial infection.4 Local lymphadenopathy or systemic symptoms should raise concern for infection. Staphylococcus aureus and group B Streptococcus have been cultured from lesions.6,7
The differential diagnosis for myiasis should include furuncle, insect bite, insect prurigo, pyoderma, inflamed cyst, and tungiasis. Myiasis also can present similarly to severe soft tissue infections or cellulitis. If located on the breasts, it can be mistaken for periductal mastitis, a benign mass with microcalcification, or inflammatory carcinoma. Lastly, due to pain, erythema, pruritus, small vesicles, and crusting, it may be confused for herpes simplex virus.1
Furuncular myiasis typically is diagnosed based on clinical presentation, especially in endemic regions. In nonendemic areas, the patient’s history may reveal recent travel or predisposition to myiasis. In cases where there is uncertainty, dermoscopy may be used to identify the maggot in the lesion, or ultrasonography can be used to confirm myiasis through the detection of larval movement.8 Dermoscopy will reveal a furuncular lesion with a central opening surrounded by dilated blood vessels and a yellowish structure with black barblike spines.9 Within the dermis is a fibrous cystic sinus tract containing the dipteran larva. Laboratory studies typically are unremarkable. In chronic cases, a complete blood cell count and other laboratory tests may show systemic inflammation, peripheral eosinophilia, and elevated IgE.10 Biopsies of furuncular myiasis are not necessary for diagnosis. Histopathology reveals an ulcerated epidermis with or without hyperkeratosis and an inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and neutrophils with eosinophils, fibroblasts, histiocytes, basophils, mast cells, plasma cells, and Langerhans cells within the dermis and subcutis.11
There are various approaches to treating furuncular myiasis, with the goal of complete removal of the larva and prevention of secondary infection. One treatment option is to apply a toxic substance to the larva, effectively killing it. Another approach is to force the larva to emerge via localized hypoxia, which can be done by occluding the punctum of the lesion for at least 24 hours. A complication of this method is suffocation of the larva without migration, leading to incomplete extraction and secondary infection.1 A third method is to surgically remove the larva, which allows for debridement of necrotic tissue surrounding the lesion if present.12 Ultrasonography also can be used therapeutically to aid in the removal of the larvae. The last method is to inject lidocaine into the base of the lesion, forcing the larva out of the punctum via fluid pressure.13 Oral treatments such as ivermectin are not recommended because they can result in the death of larvae within the lesion, leading to an inflammatory response.8
Furuncular myiasis is a form of cutaneous larvae infestation not commonly seen in individuals who do not live or travel in endemic, tropical, and subtropical regions. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation, with imaging and laboratory studies available to supplement in unclear or atypical manifestations. Treatment involves complete removal of the larva, typically through forced evacuation via hypoxia or through surgical removal. Most cases resolve without notable scarring or other sequelae; however, in those who do have complications, the most common is secondary bacterial infection. Our patient’s absence of notable travel history and frequent environmental exposure in Michigan led us to believe the organism was from a domestic source. Our case underlines the importance of a thorough history and clinical examination of furuncular lesions including the use of dermoscopy to yield an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:79-105. doi:10.1128/CMR.00010-11
- Schiff TA. Furuncular cutaneous myiasis caused by Cuterebra larva. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;28:261-263.
- Safdar N, Young DK, Andes D. Autochthonous furuncular myiasis in the United States: case report and literature review. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;26:73-80.
- Mahal JJ, Sperling JD. Furuncular myiasis from Dermatobia hominus: a case of human botfly infestation. J Emerg Med. 2012;43:618-621.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. In: Tyring SK, Lupi O, Hengge UR, eds. Tropical Dermatology. Elsevier; 2006:232-239.
- Gordon PM, Hepburn NC, Williams AE, et al. Cutaneous myiasis due to Dermatobia hominis: a report of six cases. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:811-814.
- Hubler WR Jr, Rudolph AH, Dougherty EF. Dermal myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:109-110.
- Quintanilla-Cedillo MR, León-Ureña H, Contreras-Ruiz J, et al. The value of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis in 25 cases of furunculoid myiasis. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:34-37.
- Bakos RM, Bakos L. Dermoscopic diagnosis of furuncular myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:123-124.
- Varani S, Tassinari D, Elleri D, et al. A case of furuncular myiasis associated with systemic inflammation. Parasitol Int. 2007;56:330-333.
- Grogan TM, Payne CM, Spier C, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. immunohistologic and ultrastructural morphometric features of a human botfly lesion. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:232-239.
- Krajewski A, Allen B, Hoss D, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62:383-386.
- Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al. Myiasis: Treatment of Skin Diseases. Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 2nd ed. Elsevier-Mosby; 2006.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous myiasis is a skin infestation with dipterous larvae that feed on the host’s tissue and cause a wide range of manifestations depending on the location of infestation. Cutaneous myiasis, which includes furuncular, wound, and migratory types, is the most common clinical form of this condition.1 It is endemic to tropical and subtropical areas and is not common in the United States, thus it can pose a diagnostic challenge when presenting in nonendemic areas. We present the case of a woman from Michigan who acquired furuncular myiasis without travel history to a tropical or subtropical locale.
A 72-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a chief concern of a burning, pruritic, migratory skin lesion on the left arm of approximately 1 week’s duration. She had a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, and multiple tick bites. She reported that the lesion started on the distal aspect of the left arm as an eraser-sized, perfectly round, raised bruise with a dark pepperlike bump in the center. The lesion then spread proximally over the course of 1 week, creating 3 more identical lesions. As one lesion resolved, a new lesion appeared approximately 2 to 4 cm proximal to the preceding lesion. The patient had traveled to England, Scotland, and Ireland 2 months prior but otherwise denied leaving the state of Michigan. She reported frequent exposure to gardens, meadows, and wetlands in search of milkweed and monarch butterfly larvae that she raises in northeast Michigan. She denied any recent illness or associated systemic symptoms. Initial evaluation by a primary care physician resulted in a diagnosis of a furuncle or tick bite; she completed a 10-day course of amoxicillin and a methylprednisolone dose pack without improvement.
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm, firm, violaceous nodule with a small distinct central punctum and surrounding erythema on the proximal aspect of the left arm. Dermoscopy revealed a pulsating motion and expulsion of serosanguineous fluid from the central punctum (Figure 1). Further inspection of the patient’s left arm exposed several noninflammatory puncta distal to the primary lesion spaced at 2- to 4-cm intervals.

Gross examination of a 6-mm punch biopsy from the primary inflammatory nodule uncovered a small, motile, gray-white larval organism in the inferior portion of the specimen (Figure 2). Histopathology revealed superficial and deep eosinophil-rich inflammation, fibrosis, and hemorrhage. There was a complex wedge-shaped organism with extensive internal muscle bounded by a thin cuticle bearing rows of chitinous hooklets located at one side within the deep dermis (Figure 3). The findings were consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous myiasis. No further treatment was required, as the organism was completely excised with the biopsy.

The most common causative agents of furuncular myiasis obtained from travelers returning from Mexico and Central and South America are Dermatobia hominis and Cordylobia anthropophaga. Cases of furuncular myiasis acquired in the United States without recent foreign travel are rare. Most of these cases are caused by larvae of the Cuterebra species (also known as the rabbit botfly or rodent botfly).2 In a 2003 literature review by Safdar et al3 on 56 cases of furuncular myiasis in the United States, the median age of patients was 14 years, 87% of cases occurred in August and September, and most involved exposure in rural or suburban settings; 53% of cases presented in the northeastern United States.

Furuncular myiasis occurs when the organism’s ova are deposited on the skin of a human host by the parent organism or a mosquito vector. The heat of the skin causes the eggs to hatch and the dipteran larvae must penetrate the skin within 20 days.1 Signs of infection typically are seen 6 to 10 days after infestation.3 The larvae then feed on human tissue and burrow deep in the dermis, forming an erythematous furunculoid nodule containing one or multiple maggots. After 5 to 10 weeks, the adult larvae drop to the ground, where they mature into adult organisms in the soil.1
The most reported symptoms of furuncular myiasis include pruritus, pain, and movement sensation, typically occurring suddenly at night.4 The most common presentation is a furunclelike lesion that exudes serosanguineous or purulent fluid,1 but there have been reports of vesicular, bullous, pustular, erosive, ecchymotic, and ulcerative lesions.5Dermatobia hominis usually presents on an exposed site, such as the scalp, face, and extremities. It may present with paroxysmal episodes of lancinating pain. Over time, the lesion usually heals without a scar, though hyperpigmentation and scarring can occur. The most reported complication is secondary bacterial infection.4 Local lymphadenopathy or systemic symptoms should raise concern for infection. Staphylococcus aureus and group B Streptococcus have been cultured from lesions.6,7
The differential diagnosis for myiasis should include furuncle, insect bite, insect prurigo, pyoderma, inflamed cyst, and tungiasis. Myiasis also can present similarly to severe soft tissue infections or cellulitis. If located on the breasts, it can be mistaken for periductal mastitis, a benign mass with microcalcification, or inflammatory carcinoma. Lastly, due to pain, erythema, pruritus, small vesicles, and crusting, it may be confused for herpes simplex virus.1
Furuncular myiasis typically is diagnosed based on clinical presentation, especially in endemic regions. In nonendemic areas, the patient’s history may reveal recent travel or predisposition to myiasis. In cases where there is uncertainty, dermoscopy may be used to identify the maggot in the lesion, or ultrasonography can be used to confirm myiasis through the detection of larval movement.8 Dermoscopy will reveal a furuncular lesion with a central opening surrounded by dilated blood vessels and a yellowish structure with black barblike spines.9 Within the dermis is a fibrous cystic sinus tract containing the dipteran larva. Laboratory studies typically are unremarkable. In chronic cases, a complete blood cell count and other laboratory tests may show systemic inflammation, peripheral eosinophilia, and elevated IgE.10 Biopsies of furuncular myiasis are not necessary for diagnosis. Histopathology reveals an ulcerated epidermis with or without hyperkeratosis and an inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and neutrophils with eosinophils, fibroblasts, histiocytes, basophils, mast cells, plasma cells, and Langerhans cells within the dermis and subcutis.11
There are various approaches to treating furuncular myiasis, with the goal of complete removal of the larva and prevention of secondary infection. One treatment option is to apply a toxic substance to the larva, effectively killing it. Another approach is to force the larva to emerge via localized hypoxia, which can be done by occluding the punctum of the lesion for at least 24 hours. A complication of this method is suffocation of the larva without migration, leading to incomplete extraction and secondary infection.1 A third method is to surgically remove the larva, which allows for debridement of necrotic tissue surrounding the lesion if present.12 Ultrasonography also can be used therapeutically to aid in the removal of the larvae. The last method is to inject lidocaine into the base of the lesion, forcing the larva out of the punctum via fluid pressure.13 Oral treatments such as ivermectin are not recommended because they can result in the death of larvae within the lesion, leading to an inflammatory response.8
Furuncular myiasis is a form of cutaneous larvae infestation not commonly seen in individuals who do not live or travel in endemic, tropical, and subtropical regions. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation, with imaging and laboratory studies available to supplement in unclear or atypical manifestations. Treatment involves complete removal of the larva, typically through forced evacuation via hypoxia or through surgical removal. Most cases resolve without notable scarring or other sequelae; however, in those who do have complications, the most common is secondary bacterial infection. Our patient’s absence of notable travel history and frequent environmental exposure in Michigan led us to believe the organism was from a domestic source. Our case underlines the importance of a thorough history and clinical examination of furuncular lesions including the use of dermoscopy to yield an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous myiasis is a skin infestation with dipterous larvae that feed on the host’s tissue and cause a wide range of manifestations depending on the location of infestation. Cutaneous myiasis, which includes furuncular, wound, and migratory types, is the most common clinical form of this condition.1 It is endemic to tropical and subtropical areas and is not common in the United States, thus it can pose a diagnostic challenge when presenting in nonendemic areas. We present the case of a woman from Michigan who acquired furuncular myiasis without travel history to a tropical or subtropical locale.
A 72-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a chief concern of a burning, pruritic, migratory skin lesion on the left arm of approximately 1 week’s duration. She had a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, and multiple tick bites. She reported that the lesion started on the distal aspect of the left arm as an eraser-sized, perfectly round, raised bruise with a dark pepperlike bump in the center. The lesion then spread proximally over the course of 1 week, creating 3 more identical lesions. As one lesion resolved, a new lesion appeared approximately 2 to 4 cm proximal to the preceding lesion. The patient had traveled to England, Scotland, and Ireland 2 months prior but otherwise denied leaving the state of Michigan. She reported frequent exposure to gardens, meadows, and wetlands in search of milkweed and monarch butterfly larvae that she raises in northeast Michigan. She denied any recent illness or associated systemic symptoms. Initial evaluation by a primary care physician resulted in a diagnosis of a furuncle or tick bite; she completed a 10-day course of amoxicillin and a methylprednisolone dose pack without improvement.
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm, firm, violaceous nodule with a small distinct central punctum and surrounding erythema on the proximal aspect of the left arm. Dermoscopy revealed a pulsating motion and expulsion of serosanguineous fluid from the central punctum (Figure 1). Further inspection of the patient’s left arm exposed several noninflammatory puncta distal to the primary lesion spaced at 2- to 4-cm intervals.

Gross examination of a 6-mm punch biopsy from the primary inflammatory nodule uncovered a small, motile, gray-white larval organism in the inferior portion of the specimen (Figure 2). Histopathology revealed superficial and deep eosinophil-rich inflammation, fibrosis, and hemorrhage. There was a complex wedge-shaped organism with extensive internal muscle bounded by a thin cuticle bearing rows of chitinous hooklets located at one side within the deep dermis (Figure 3). The findings were consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous myiasis. No further treatment was required, as the organism was completely excised with the biopsy.

The most common causative agents of furuncular myiasis obtained from travelers returning from Mexico and Central and South America are Dermatobia hominis and Cordylobia anthropophaga. Cases of furuncular myiasis acquired in the United States without recent foreign travel are rare. Most of these cases are caused by larvae of the Cuterebra species (also known as the rabbit botfly or rodent botfly).2 In a 2003 literature review by Safdar et al3 on 56 cases of furuncular myiasis in the United States, the median age of patients was 14 years, 87% of cases occurred in August and September, and most involved exposure in rural or suburban settings; 53% of cases presented in the northeastern United States.

Furuncular myiasis occurs when the organism’s ova are deposited on the skin of a human host by the parent organism or a mosquito vector. The heat of the skin causes the eggs to hatch and the dipteran larvae must penetrate the skin within 20 days.1 Signs of infection typically are seen 6 to 10 days after infestation.3 The larvae then feed on human tissue and burrow deep in the dermis, forming an erythematous furunculoid nodule containing one or multiple maggots. After 5 to 10 weeks, the adult larvae drop to the ground, where they mature into adult organisms in the soil.1
The most reported symptoms of furuncular myiasis include pruritus, pain, and movement sensation, typically occurring suddenly at night.4 The most common presentation is a furunclelike lesion that exudes serosanguineous or purulent fluid,1 but there have been reports of vesicular, bullous, pustular, erosive, ecchymotic, and ulcerative lesions.5Dermatobia hominis usually presents on an exposed site, such as the scalp, face, and extremities. It may present with paroxysmal episodes of lancinating pain. Over time, the lesion usually heals without a scar, though hyperpigmentation and scarring can occur. The most reported complication is secondary bacterial infection.4 Local lymphadenopathy or systemic symptoms should raise concern for infection. Staphylococcus aureus and group B Streptococcus have been cultured from lesions.6,7
The differential diagnosis for myiasis should include furuncle, insect bite, insect prurigo, pyoderma, inflamed cyst, and tungiasis. Myiasis also can present similarly to severe soft tissue infections or cellulitis. If located on the breasts, it can be mistaken for periductal mastitis, a benign mass with microcalcification, or inflammatory carcinoma. Lastly, due to pain, erythema, pruritus, small vesicles, and crusting, it may be confused for herpes simplex virus.1
Furuncular myiasis typically is diagnosed based on clinical presentation, especially in endemic regions. In nonendemic areas, the patient’s history may reveal recent travel or predisposition to myiasis. In cases where there is uncertainty, dermoscopy may be used to identify the maggot in the lesion, or ultrasonography can be used to confirm myiasis through the detection of larval movement.8 Dermoscopy will reveal a furuncular lesion with a central opening surrounded by dilated blood vessels and a yellowish structure with black barblike spines.9 Within the dermis is a fibrous cystic sinus tract containing the dipteran larva. Laboratory studies typically are unremarkable. In chronic cases, a complete blood cell count and other laboratory tests may show systemic inflammation, peripheral eosinophilia, and elevated IgE.10 Biopsies of furuncular myiasis are not necessary for diagnosis. Histopathology reveals an ulcerated epidermis with or without hyperkeratosis and an inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and neutrophils with eosinophils, fibroblasts, histiocytes, basophils, mast cells, plasma cells, and Langerhans cells within the dermis and subcutis.11
There are various approaches to treating furuncular myiasis, with the goal of complete removal of the larva and prevention of secondary infection. One treatment option is to apply a toxic substance to the larva, effectively killing it. Another approach is to force the larva to emerge via localized hypoxia, which can be done by occluding the punctum of the lesion for at least 24 hours. A complication of this method is suffocation of the larva without migration, leading to incomplete extraction and secondary infection.1 A third method is to surgically remove the larva, which allows for debridement of necrotic tissue surrounding the lesion if present.12 Ultrasonography also can be used therapeutically to aid in the removal of the larvae. The last method is to inject lidocaine into the base of the lesion, forcing the larva out of the punctum via fluid pressure.13 Oral treatments such as ivermectin are not recommended because they can result in the death of larvae within the lesion, leading to an inflammatory response.8
Furuncular myiasis is a form of cutaneous larvae infestation not commonly seen in individuals who do not live or travel in endemic, tropical, and subtropical regions. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation, with imaging and laboratory studies available to supplement in unclear or atypical manifestations. Treatment involves complete removal of the larva, typically through forced evacuation via hypoxia or through surgical removal. Most cases resolve without notable scarring or other sequelae; however, in those who do have complications, the most common is secondary bacterial infection. Our patient’s absence of notable travel history and frequent environmental exposure in Michigan led us to believe the organism was from a domestic source. Our case underlines the importance of a thorough history and clinical examination of furuncular lesions including the use of dermoscopy to yield an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:79-105. doi:10.1128/CMR.00010-11
- Schiff TA. Furuncular cutaneous myiasis caused by Cuterebra larva. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;28:261-263.
- Safdar N, Young DK, Andes D. Autochthonous furuncular myiasis in the United States: case report and literature review. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;26:73-80.
- Mahal JJ, Sperling JD. Furuncular myiasis from Dermatobia hominus: a case of human botfly infestation. J Emerg Med. 2012;43:618-621.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. In: Tyring SK, Lupi O, Hengge UR, eds. Tropical Dermatology. Elsevier; 2006:232-239.
- Gordon PM, Hepburn NC, Williams AE, et al. Cutaneous myiasis due to Dermatobia hominis: a report of six cases. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:811-814.
- Hubler WR Jr, Rudolph AH, Dougherty EF. Dermal myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:109-110.
- Quintanilla-Cedillo MR, León-Ureña H, Contreras-Ruiz J, et al. The value of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis in 25 cases of furunculoid myiasis. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:34-37.
- Bakos RM, Bakos L. Dermoscopic diagnosis of furuncular myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:123-124.
- Varani S, Tassinari D, Elleri D, et al. A case of furuncular myiasis associated with systemic inflammation. Parasitol Int. 2007;56:330-333.
- Grogan TM, Payne CM, Spier C, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. immunohistologic and ultrastructural morphometric features of a human botfly lesion. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:232-239.
- Krajewski A, Allen B, Hoss D, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62:383-386.
- Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al. Myiasis: Treatment of Skin Diseases. Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 2nd ed. Elsevier-Mosby; 2006.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:79-105. doi:10.1128/CMR.00010-11
- Schiff TA. Furuncular cutaneous myiasis caused by Cuterebra larva. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;28:261-263.
- Safdar N, Young DK, Andes D. Autochthonous furuncular myiasis in the United States: case report and literature review. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;26:73-80.
- Mahal JJ, Sperling JD. Furuncular myiasis from Dermatobia hominus: a case of human botfly infestation. J Emerg Med. 2012;43:618-621.
- Francesconi F, Lupi O. Myiasis. In: Tyring SK, Lupi O, Hengge UR, eds. Tropical Dermatology. Elsevier; 2006:232-239.
- Gordon PM, Hepburn NC, Williams AE, et al. Cutaneous myiasis due to Dermatobia hominis: a report of six cases. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:811-814.
- Hubler WR Jr, Rudolph AH, Dougherty EF. Dermal myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;110:109-110.
- Quintanilla-Cedillo MR, León-Ureña H, Contreras-Ruiz J, et al. The value of Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis in 25 cases of furunculoid myiasis. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:34-37.
- Bakos RM, Bakos L. Dermoscopic diagnosis of furuncular myiasis. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:123-124.
- Varani S, Tassinari D, Elleri D, et al. A case of furuncular myiasis associated with systemic inflammation. Parasitol Int. 2007;56:330-333.
- Grogan TM, Payne CM, Spier C, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. immunohistologic and ultrastructural morphometric features of a human botfly lesion. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:232-239.
- Krajewski A, Allen B, Hoss D, et al. Cutaneous myiasis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62:383-386.
- Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al. Myiasis: Treatment of Skin Diseases. Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 2nd ed. Elsevier-Mosby; 2006.
Practice Points
- Cutaneous myiasis is a skin infestation with dipterous larvae that feed on the host’s tissue and cause a wide range of manifestations depending on the location of infestation. It consists of 3 types: furuncular, wound, and migratory forms.
- It is uncommon in the United States and not typically seen in patients who have no history of recent travel to tropical or subtropical areas.
- The most common cause of African furuncular myiasis acquired in the United States is larvae of the Cuterebra species (also known as the rabbit botfly or rodent botfly).
Ultra-Late Cutaneous Melanoma Recurrence Following 49 Years of Quiescence
To the Editor:
Ultra-late melanoma recurrence represents a minority of cases in which the quiescent period lasts longer than 15 years, and epidemiologic studies have reported recurrence rates of 6% to 10% during the ultra-late period.1 Even more uncommon are cases that span many decades (eg, >30 years), but all are useful in understanding the cellular behavior leading to the reactivation of fully excised melanomas. Few cases have been reported in which recurrence occurs more than 35 years after the original diagnosis of melanoma. Unfortunately, mechanisms underlying this long stable quiescence and subsequent reactivation are poorly understood, which is why it is important to identify and document cases. We present a case of local recurrence of cutaneous melanoma on the patient’s lower back after a 49-year disease-free period.
A 78-year-old White woman presented to a private dermatology office for a full-body skin examination. She had a medical history of a cutaneous melanoma that had been removed on the lower back 49 years prior; Parkinson disease of 10 years’ duration; and an enlarged thyroid nodule with decreased thyrotropin and hyperthyroidism, atrial fibrillation, mitral valve prolapse, osteoarthritis in the knees, and actinic keratoses, all of which were chronic conditions lasting years to decades. She was taking several medications for these medical conditions. Her surgical history included a hysterectomy, hip replacement, hernia repair, cardioversion, and tonsillectomy in childhood. Her family medical history included breast cancer in her paternal grandmother and aunt; hypertension in her father; and sarcoma in her mother at 78 years of age, which initially was identified in the sacrum and metastasized to the lungs causing death. No family history of melanoma or other skin cancers was reported. Prior to the original diagnosis of melanoma at 29 years of age, she had no history of skin cancer or any other medical condition other than acne. The patient did report spending a great deal of time in the sun during high school.
The patient reported developing the original cutaneous melanoma during her second pregnancy at 29 years of age and recalled that it was excised with wide margins. There had been a mole on her back that was present for years but changed in size during pregnancy, prompting the original visit to the primary care physician for evaluation. Remarkably, the original pathology report was obtained from the patient and revealed a specimen consisting of a 3.7×1.7-cm skin
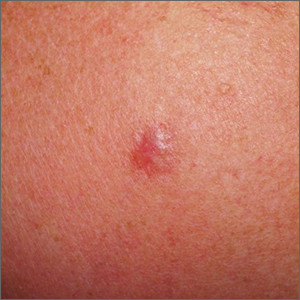
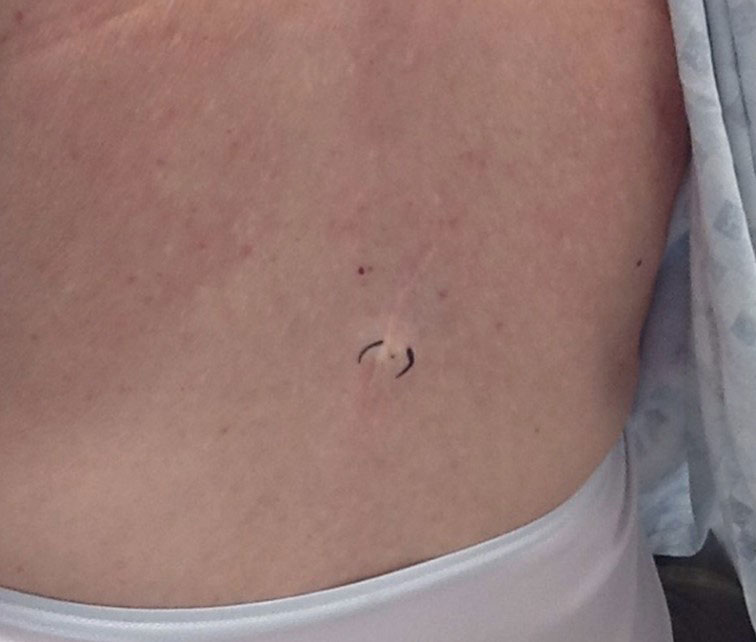
Physical examination at the current presentation 49 years later revealed an even-bordered 2-mm black macule that was located approximately 1 cm from the original melanoma excision scar line (Figure). A biopsy was performed and sent to a dermatopathologist. Microscopic evaluation revealed nests, islands, and sheets of atypical epithelioid melanocytes extending through the dermis between collagen bundles. The melanocytes varied in size and shape with moderate nuclear pleomorphism present. Scattered mitotic figures and necrotic melanocytes were present, which most likely represented cutaneous satellite metastases of melanoma. Subsequent chest radiography, full-body positron emission tomography, and standard laboratory blood tests were unremarkable except for an enlarged right thyroid gland and moderate cardiomegaly. The patient was sent to a surgical oncologist for excision with wide surgical margins, and she elected not to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy. At follow-up 3, 6, 12, and 24 months later, there were no signs of recurrence based on direct clinical examination. The patient subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Recurrence rates of melanoma vary by stage and age at diagnosis, but prior studies have reported a recurrence rate of approximately 6% after 10 or more years following the initial diagnosis.2 Ultra-late recurrences of approximately 4 decades or more are extremely rare. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and ultra-late recurrence revealed 4 reported cases with a quiescent period of 38 or more years.3-6 All cases were metastatic melanomas in women; spanned 38, 40, 41, and 45 years from the initial melanoma diagnosis to recurrence; and all of the recurrences except one were regional or distal metastatic lesions (eg, lymph node, brain). In one case, both the original and recurrent lesions occurred on the left elbow.6 The original lesions occurred on the legs, elbow, and back of the neck, and there were no notable concomitant medical conditions. The patients were aged 72, 73, 73, and 84 years at recurrence.3-6 However, generalizations from these cases are limited given the potential for selection bias (eg, men may be less likely to visit a clinic for follow-up and nevi examination) and the likelihood that many cases of ultra-late melanoma recurrence are unrecognized or unreported.
More recently, genomic analyses on melanoma lesions occurring 30 years apart confirmed that the second lesion was indeed a recurrence, although with numerous additional mutations.7 The specific mechanisms underlying the dormancy and subsequent reemergence of metastatic lesions are unclear, but
It also is worth highlighting the concomitant diagnosis of Parkinson disease in our patient. In recent years, Parkinson disease has been linked to melanoma in both epidemiologic and genetic studies. For example, one large-scale study found a 50% increased risk for developing Parkinson disease in patients with melanoma (and vice versa), and this finding has been replicated in other studies.10 Moreover, patients with Parkinson disease have a 2-fold increase in their risk for developing melanoma, demonstrating that it is a bidirectional pathway. Not surprisingly, associations between melanin and neuromelanin pathways have been identified as a potential link between these diseases, and scientists are in the process of understanding the genetic components of both.10 It is unknown if specific genetic mutations contributed to both diseases in our case, but follow-up genetic testing on the recurrent melanoma specimen currently is being pursued.
The 49-year quiescent period in our case of recurrent cutaneous malignant melanoma potentially represents the longest ultra-late recurrence of melanoma in the literature to date based on a review of indexed publications. Moreover, it is relatively unique compared to other similar cases in that the recurrence was within a centimeter of the original excisional scar. Most metastases occur in locoregional lymph nodes or the lungs3; therefore, it is unusual to find one so close to the original lesion, especially one that occurred decades later. Factors associated with ultra-late recurrences are unknown, primarily because of the rarity of these cases as well as the biases and other factors that limit existing studies. However, genetic sequencing may provide information regarding these factors and related processes. Genetic sequencing specifically points to a small cell group remaining after excision of the primary tumor, which mutates while proliferating. Low antigenicity and tolerance to immunity during the quiescent period may explain the long duration of dormancy.6 More recently, there have been efforts to identify immunohistochemical signatures that may predict late recurrences, though the data are preliminary in nature.11
Given the latency period and location of the recurrence, our case demonstrates that even fully excised melanomas may recur locally many decades later, hence patients should be aware of the importance of a lifetime of vigilance after being diagnosed with melanoma.
- Tsao H, Cosimi AB, Sober AJ. Ultra-late recurrence (15 years or longer) of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1997;79:2361-2370.
- Faries MB, Steen S, Ye X, et al. Late recurrence in melanoma: clinical implications of lost dormancy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:27-34.
- Mansour D, Kejariwal D. It is never too late: ultra-late recurrence of melanoma with distant metastases [published online March 8, 2012]. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:bcr0120125474. doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5474
- Saleh D, Peach AHS. Ultra-late recurrence of malignant melanoma after 40 years of quiescent disease. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:290-291.
- Goodenough J, Cozon CL, Liew SH. An incidental finding of a nodal recurrence of cutaneous malignant melanoma after a 45-year disease-free period [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. 2014:bcr2014204289. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204289
- Nakamura M, Obayashi M, Yoshimitsu M, et al. Comparative whole-exome sequencing of an ultra-late recurrent malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:762-763.
- Miller JJ, Lofgren KA, Hughes SR, et al. Genomic analysis of melanoma evolution following a 30-year disease-free interval. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:805-808.
- North JP, Kageshita T, Pinkel D, et al. Distribution and significance of occult intraepidermal tumor cells surrounding primary melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2024-2030.
- Massi G, LeBoit PE. Recurrent and persistent melanoma. In: Massi G, LeBoit PE, eds. Histological Diagnosis of Nevi and Melanoma. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag; 2014:689-698.
- Bose A, Petsko GA, Eliezer D. Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: co-occurrence and mechanisms. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8:385-398.
- Reschke R, Dumann K, Ziemer M. Risk stratification and clinical characteristics of patients with late recurrence of melanoma (>10 years).J Clin Med. 2022;11:2026.
To the Editor:
Ultra-late melanoma recurrence represents a minority of cases in which the quiescent period lasts longer than 15 years, and epidemiologic studies have reported recurrence rates of 6% to 10% during the ultra-late period.1 Even more uncommon are cases that span many decades (eg, >30 years), but all are useful in understanding the cellular behavior leading to the reactivation of fully excised melanomas. Few cases have been reported in which recurrence occurs more than 35 years after the original diagnosis of melanoma. Unfortunately, mechanisms underlying this long stable quiescence and subsequent reactivation are poorly understood, which is why it is important to identify and document cases. We present a case of local recurrence of cutaneous melanoma on the patient’s lower back after a 49-year disease-free period.
A 78-year-old White woman presented to a private dermatology office for a full-body skin examination. She had a medical history of a cutaneous melanoma that had been removed on the lower back 49 years prior; Parkinson disease of 10 years’ duration; and an enlarged thyroid nodule with decreased thyrotropin and hyperthyroidism, atrial fibrillation, mitral valve prolapse, osteoarthritis in the knees, and actinic keratoses, all of which were chronic conditions lasting years to decades. She was taking several medications for these medical conditions. Her surgical history included a hysterectomy, hip replacement, hernia repair, cardioversion, and tonsillectomy in childhood. Her family medical history included breast cancer in her paternal grandmother and aunt; hypertension in her father; and sarcoma in her mother at 78 years of age, which initially was identified in the sacrum and metastasized to the lungs causing death. No family history of melanoma or other skin cancers was reported. Prior to the original diagnosis of melanoma at 29 years of age, she had no history of skin cancer or any other medical condition other than acne. The patient did report spending a great deal of time in the sun during high school.
The patient reported developing the original cutaneous melanoma during her second pregnancy at 29 years of age and recalled that it was excised with wide margins. There had been a mole on her back that was present for years but changed in size during pregnancy, prompting the original visit to the primary care physician for evaluation. Remarkably, the original pathology report was obtained from the patient and revealed a specimen consisting of a 3.7×1.7-cm skin
Physical examination at the current presentation 49 years later revealed an even-bordered 2-mm black macule that was located approximately 1 cm from the original melanoma excision scar line (Figure). A biopsy was performed and sent to a dermatopathologist. Microscopic evaluation revealed nests, islands, and sheets of atypical epithelioid melanocytes extending through the dermis between collagen bundles. The melanocytes varied in size and shape with moderate nuclear pleomorphism present. Scattered mitotic figures and necrotic melanocytes were present, which most likely represented cutaneous satellite metastases of melanoma. Subsequent chest radiography, full-body positron emission tomography, and standard laboratory blood tests were unremarkable except for an enlarged right thyroid gland and moderate cardiomegaly. The patient was sent to a surgical oncologist for excision with wide surgical margins, and she elected not to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy. At follow-up 3, 6, 12, and 24 months later, there were no signs of recurrence based on direct clinical examination. The patient subsequently was lost to follow-up.

Recurrence rates of melanoma vary by stage and age at diagnosis, but prior studies have reported a recurrence rate of approximately 6% after 10 or more years following the initial diagnosis.2 Ultra-late recurrences of approximately 4 decades or more are extremely rare. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and ultra-late recurrence revealed 4 reported cases with a quiescent period of 38 or more years.3-6 All cases were metastatic melanomas in women; spanned 38, 40, 41, and 45 years from the initial melanoma diagnosis to recurrence; and all of the recurrences except one were regional or distal metastatic lesions (eg, lymph node, brain). In one case, both the original and recurrent lesions occurred on the left elbow.6 The original lesions occurred on the legs, elbow, and back of the neck, and there were no notable concomitant medical conditions. The patients were aged 72, 73, 73, and 84 years at recurrence.3-6 However, generalizations from these cases are limited given the potential for selection bias (eg, men may be less likely to visit a clinic for follow-up and nevi examination) and the likelihood that many cases of ultra-late melanoma recurrence are unrecognized or unreported.
More recently, genomic analyses on melanoma lesions occurring 30 years apart confirmed that the second lesion was indeed a recurrence, although with numerous additional mutations.7 The specific mechanisms underlying the dormancy and subsequent reemergence of metastatic lesions are unclear, but
It also is worth highlighting the concomitant diagnosis of Parkinson disease in our patient. In recent years, Parkinson disease has been linked to melanoma in both epidemiologic and genetic studies. For example, one large-scale study found a 50% increased risk for developing Parkinson disease in patients with melanoma (and vice versa), and this finding has been replicated in other studies.10 Moreover, patients with Parkinson disease have a 2-fold increase in their risk for developing melanoma, demonstrating that it is a bidirectional pathway. Not surprisingly, associations between melanin and neuromelanin pathways have been identified as a potential link between these diseases, and scientists are in the process of understanding the genetic components of both.10 It is unknown if specific genetic mutations contributed to both diseases in our case, but follow-up genetic testing on the recurrent melanoma specimen currently is being pursued.
The 49-year quiescent period in our case of recurrent cutaneous malignant melanoma potentially represents the longest ultra-late recurrence of melanoma in the literature to date based on a review of indexed publications. Moreover, it is relatively unique compared to other similar cases in that the recurrence was within a centimeter of the original excisional scar. Most metastases occur in locoregional lymph nodes or the lungs3; therefore, it is unusual to find one so close to the original lesion, especially one that occurred decades later. Factors associated with ultra-late recurrences are unknown, primarily because of the rarity of these cases as well as the biases and other factors that limit existing studies. However, genetic sequencing may provide information regarding these factors and related processes. Genetic sequencing specifically points to a small cell group remaining after excision of the primary tumor, which mutates while proliferating. Low antigenicity and tolerance to immunity during the quiescent period may explain the long duration of dormancy.6 More recently, there have been efforts to identify immunohistochemical signatures that may predict late recurrences, though the data are preliminary in nature.11
Given the latency period and location of the recurrence, our case demonstrates that even fully excised melanomas may recur locally many decades later, hence patients should be aware of the importance of a lifetime of vigilance after being diagnosed with melanoma.
To the Editor:
Ultra-late melanoma recurrence represents a minority of cases in which the quiescent period lasts longer than 15 years, and epidemiologic studies have reported recurrence rates of 6% to 10% during the ultra-late period.1 Even more uncommon are cases that span many decades (eg, >30 years), but all are useful in understanding the cellular behavior leading to the reactivation of fully excised melanomas. Few cases have been reported in which recurrence occurs more than 35 years after the original diagnosis of melanoma. Unfortunately, mechanisms underlying this long stable quiescence and subsequent reactivation are poorly understood, which is why it is important to identify and document cases. We present a case of local recurrence of cutaneous melanoma on the patient’s lower back after a 49-year disease-free period.
A 78-year-old White woman presented to a private dermatology office for a full-body skin examination. She had a medical history of a cutaneous melanoma that had been removed on the lower back 49 years prior; Parkinson disease of 10 years’ duration; and an enlarged thyroid nodule with decreased thyrotropin and hyperthyroidism, atrial fibrillation, mitral valve prolapse, osteoarthritis in the knees, and actinic keratoses, all of which were chronic conditions lasting years to decades. She was taking several medications for these medical conditions. Her surgical history included a hysterectomy, hip replacement, hernia repair, cardioversion, and tonsillectomy in childhood. Her family medical history included breast cancer in her paternal grandmother and aunt; hypertension in her father; and sarcoma in her mother at 78 years of age, which initially was identified in the sacrum and metastasized to the lungs causing death. No family history of melanoma or other skin cancers was reported. Prior to the original diagnosis of melanoma at 29 years of age, she had no history of skin cancer or any other medical condition other than acne. The patient did report spending a great deal of time in the sun during high school.
The patient reported developing the original cutaneous melanoma during her second pregnancy at 29 years of age and recalled that it was excised with wide margins. There had been a mole on her back that was present for years but changed in size during pregnancy, prompting the original visit to the primary care physician for evaluation. Remarkably, the original pathology report was obtained from the patient and revealed a specimen consisting of a 3.7×1.7-cm skin
Physical examination at the current presentation 49 years later revealed an even-bordered 2-mm black macule that was located approximately 1 cm from the original melanoma excision scar line (Figure). A biopsy was performed and sent to a dermatopathologist. Microscopic evaluation revealed nests, islands, and sheets of atypical epithelioid melanocytes extending through the dermis between collagen bundles. The melanocytes varied in size and shape with moderate nuclear pleomorphism present. Scattered mitotic figures and necrotic melanocytes were present, which most likely represented cutaneous satellite metastases of melanoma. Subsequent chest radiography, full-body positron emission tomography, and standard laboratory blood tests were unremarkable except for an enlarged right thyroid gland and moderate cardiomegaly. The patient was sent to a surgical oncologist for excision with wide surgical margins, and she elected not to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy. At follow-up 3, 6, 12, and 24 months later, there were no signs of recurrence based on direct clinical examination. The patient subsequently was lost to follow-up.

Recurrence rates of melanoma vary by stage and age at diagnosis, but prior studies have reported a recurrence rate of approximately 6% after 10 or more years following the initial diagnosis.2 Ultra-late recurrences of approximately 4 decades or more are extremely rare. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and ultra-late recurrence revealed 4 reported cases with a quiescent period of 38 or more years.3-6 All cases were metastatic melanomas in women; spanned 38, 40, 41, and 45 years from the initial melanoma diagnosis to recurrence; and all of the recurrences except one were regional or distal metastatic lesions (eg, lymph node, brain). In one case, both the original and recurrent lesions occurred on the left elbow.6 The original lesions occurred on the legs, elbow, and back of the neck, and there were no notable concomitant medical conditions. The patients were aged 72, 73, 73, and 84 years at recurrence.3-6 However, generalizations from these cases are limited given the potential for selection bias (eg, men may be less likely to visit a clinic for follow-up and nevi examination) and the likelihood that many cases of ultra-late melanoma recurrence are unrecognized or unreported.
More recently, genomic analyses on melanoma lesions occurring 30 years apart confirmed that the second lesion was indeed a recurrence, although with numerous additional mutations.7 The specific mechanisms underlying the dormancy and subsequent reemergence of metastatic lesions are unclear, but
It also is worth highlighting the concomitant diagnosis of Parkinson disease in our patient. In recent years, Parkinson disease has been linked to melanoma in both epidemiologic and genetic studies. For example, one large-scale study found a 50% increased risk for developing Parkinson disease in patients with melanoma (and vice versa), and this finding has been replicated in other studies.10 Moreover, patients with Parkinson disease have a 2-fold increase in their risk for developing melanoma, demonstrating that it is a bidirectional pathway. Not surprisingly, associations between melanin and neuromelanin pathways have been identified as a potential link between these diseases, and scientists are in the process of understanding the genetic components of both.10 It is unknown if specific genetic mutations contributed to both diseases in our case, but follow-up genetic testing on the recurrent melanoma specimen currently is being pursued.
The 49-year quiescent period in our case of recurrent cutaneous malignant melanoma potentially represents the longest ultra-late recurrence of melanoma in the literature to date based on a review of indexed publications. Moreover, it is relatively unique compared to other similar cases in that the recurrence was within a centimeter of the original excisional scar. Most metastases occur in locoregional lymph nodes or the lungs3; therefore, it is unusual to find one so close to the original lesion, especially one that occurred decades later. Factors associated with ultra-late recurrences are unknown, primarily because of the rarity of these cases as well as the biases and other factors that limit existing studies. However, genetic sequencing may provide information regarding these factors and related processes. Genetic sequencing specifically points to a small cell group remaining after excision of the primary tumor, which mutates while proliferating. Low antigenicity and tolerance to immunity during the quiescent period may explain the long duration of dormancy.6 More recently, there have been efforts to identify immunohistochemical signatures that may predict late recurrences, though the data are preliminary in nature.11
Given the latency period and location of the recurrence, our case demonstrates that even fully excised melanomas may recur locally many decades later, hence patients should be aware of the importance of a lifetime of vigilance after being diagnosed with melanoma.
- Tsao H, Cosimi AB, Sober AJ. Ultra-late recurrence (15 years or longer) of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1997;79:2361-2370.
- Faries MB, Steen S, Ye X, et al. Late recurrence in melanoma: clinical implications of lost dormancy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:27-34.
- Mansour D, Kejariwal D. It is never too late: ultra-late recurrence of melanoma with distant metastases [published online March 8, 2012]. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:bcr0120125474. doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5474
- Saleh D, Peach AHS. Ultra-late recurrence of malignant melanoma after 40 years of quiescent disease. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:290-291.
- Goodenough J, Cozon CL, Liew SH. An incidental finding of a nodal recurrence of cutaneous malignant melanoma after a 45-year disease-free period [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. 2014:bcr2014204289. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204289
- Nakamura M, Obayashi M, Yoshimitsu M, et al. Comparative whole-exome sequencing of an ultra-late recurrent malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:762-763.
- Miller JJ, Lofgren KA, Hughes SR, et al. Genomic analysis of melanoma evolution following a 30-year disease-free interval. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:805-808.
- North JP, Kageshita T, Pinkel D, et al. Distribution and significance of occult intraepidermal tumor cells surrounding primary melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2024-2030.
- Massi G, LeBoit PE. Recurrent and persistent melanoma. In: Massi G, LeBoit PE, eds. Histological Diagnosis of Nevi and Melanoma. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag; 2014:689-698.
- Bose A, Petsko GA, Eliezer D. Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: co-occurrence and mechanisms. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8:385-398.
- Reschke R, Dumann K, Ziemer M. Risk stratification and clinical characteristics of patients with late recurrence of melanoma (>10 years).J Clin Med. 2022;11:2026.
- Tsao H, Cosimi AB, Sober AJ. Ultra-late recurrence (15 years or longer) of cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1997;79:2361-2370.
- Faries MB, Steen S, Ye X, et al. Late recurrence in melanoma: clinical implications of lost dormancy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217:27-34.
- Mansour D, Kejariwal D. It is never too late: ultra-late recurrence of melanoma with distant metastases [published online March 8, 2012]. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:bcr0120125474. doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5474
- Saleh D, Peach AHS. Ultra-late recurrence of malignant melanoma after 40 years of quiescent disease. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:290-291.
- Goodenough J, Cozon CL, Liew SH. An incidental finding of a nodal recurrence of cutaneous malignant melanoma after a 45-year disease-free period [published online June 4, 2014]. BMJ Case Rep. 2014:bcr2014204289. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-204289
- Nakamura M, Obayashi M, Yoshimitsu M, et al. Comparative whole-exome sequencing of an ultra-late recurrent malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:762-763.
- Miller JJ, Lofgren KA, Hughes SR, et al. Genomic analysis of melanoma evolution following a 30-year disease-free interval. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:805-808.
- North JP, Kageshita T, Pinkel D, et al. Distribution and significance of occult intraepidermal tumor cells surrounding primary melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2024-2030.
- Massi G, LeBoit PE. Recurrent and persistent melanoma. In: Massi G, LeBoit PE, eds. Histological Diagnosis of Nevi and Melanoma. 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag; 2014:689-698.
- Bose A, Petsko GA, Eliezer D. Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: co-occurrence and mechanisms. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8:385-398.
- Reschke R, Dumann K, Ziemer M. Risk stratification and clinical characteristics of patients with late recurrence of melanoma (>10 years).J Clin Med. 2022;11:2026.
Practice Points
- In some cases of ultra-late malignant melanoma recurrence, the quiescent period can last more than 30 years.
- There does not appear to be specificity with location since ultra-late melanoma recurrences can occur locally, regionally, and distally, and original lesions appear to be randomly distributed in these cases.
- Mechanisms for ultra-late melanoma recurrence are poorly understood; histologically, unrecognizable aberrations in the skin beyond the histopathologic margins may represent an early phase of disease that lies dormant for many years before reemerging in response to external or immunologic changes.
- Patients with malignant melanoma are at a higher risk for developing Parkinson disease (and vice versa) given the link between melanin and neuromelanin pathways.
COVID-19 vaccination recap: The latest developments
In recent weeks, the COVID-19 vaccine arsenal has grown more robust. Here’s what you need to know:
Variant-specific boosters. On September 1, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) adopted a recommendation for a booster of either a new bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 12 years and older) or bivalent Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 18 years and older) at least 2 months after receipt of a primary series or prior monovalent booster dose. Both bivalent vaccines were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and offer protection against one of the more common circulating strains of SARS-COV-2 (BA.1) while boosting immunity to the original strain. Both options are approved only as booster shots, not as an original COVID vaccine series.1
Novavax vaccine. This summer, the FDA issued an EUA for the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine in adults and a later EUA for adolescents (ages 12 to 17 years).2 Novavax is the fourth vaccine available to combat COVID-19 infection. This newest addition to the COVID armamentarium consists of coronavirus protein subunits, produced using recombinant technology, and a matrix adjuvant. The primary series consists of 2 doses administered at least 3 weeks apart.3,4
A few caveats: The Novavax vaccine comes in 10-dose vials, which should be kept refrigerated until use. Once the first dose is used, the vial should be discarded after 6 hours. This may present some scheduling and logistical issues. Also, the Novavax vaccine is not currently approved for use in children younger than 12 years, or as a booster to other vaccines.3,4
The effectiveness and safety of the Novavax vaccine appears to be comparable to that of the other vaccines approved to date, although measuring vaccine effectiveness is a tricky business given the rapid mutation of the virus and changing dominant strains.3,4 The Novavax vaccine’s efficacy against currently circulating Omicron variants of the virus (eg, BA.2.12.1, BA.4, BA.5) remains to be determined.
As far as safety, preliminary studies indicate that Novavax may be associated with rare cases of myocarditis.3,4 Myocarditis can result from the COVID infection itself at an overall rate of 1 to 2 per 1000, which is 16 times the rate in adults without COVID.5
Could it provide reassurance to the hesitant? The Novavax COVID vaccine was developed using a vaccine platform and production process similar to that of other commonly administered vaccines, such as hepatitis B vaccine and human papillomavirus vaccine. This may make it an appealing option for patients who have shown hesitancy toward new vaccine technologies.
And, of course, there are the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Currently, there are 2 vaccines approved under the normal licensing process for adults, both of which are mRNA-based vaccines: Pfizer/BioNTech (Comirnaty) for those ages 12 years and older and Moderna (Spikevax) for those ages 18 and older. A third COVID vaccine option is manufactured by Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) and uses an adenovirus platform. The FDA revised its EUA in May to limit its use.6 The Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been associated with rare but serious reactions called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia. ACIP recommends all other vaccines in preference to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
For more on COVID vaccination for patients of all ages, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/downloads/COVID-19-immunization-schedule-ages-6months-older.pdf
1. Oliver S. Evidence to recommendations framework: Bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster doses. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, September 1, 2002. Accessed September 6, 2002. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-09-01/08-COVID-Oliver-508.pdf
2. FDA. Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted. Updated August 19, 2022. Accessed August 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/novavax-covid-19-vaccine-adjuvanted
3. Dubovsky F. NVX-CoV2373 (Novavax COVID-19 vaccine) in adults (≥ 18 years of age). Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/04-covid-dubovsky-508.pdf
4. Twentyman E. Evidence to recommendation framework: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted in adults ages 18 years and older. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/05-covid-twentyman-508.pdf
5. Boehmer TK, Kompaniyets L, Lavery AM, et al. Association between COVID-19 and myocarditis using hospital-based administrative data—United States, March 2020–January 2021. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1228-1232. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7035e5
6. American Hospital Association. FDA limits J&J COVID-19 vaccine use to certain adults. Published May 6, 2022. Accessed September 6, 2022. www.aha.org/news/headline/2022-05-06-fda-limits-jj-covid-19-vaccine-use-certain-adults
In recent weeks, the COVID-19 vaccine arsenal has grown more robust. Here’s what you need to know:
Variant-specific boosters. On September 1, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) adopted a recommendation for a booster of either a new bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 12 years and older) or bivalent Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 18 years and older) at least 2 months after receipt of a primary series or prior monovalent booster dose. Both bivalent vaccines were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and offer protection against one of the more common circulating strains of SARS-COV-2 (BA.1) while boosting immunity to the original strain. Both options are approved only as booster shots, not as an original COVID vaccine series.1
Novavax vaccine. This summer, the FDA issued an EUA for the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine in adults and a later EUA for adolescents (ages 12 to 17 years).2 Novavax is the fourth vaccine available to combat COVID-19 infection. This newest addition to the COVID armamentarium consists of coronavirus protein subunits, produced using recombinant technology, and a matrix adjuvant. The primary series consists of 2 doses administered at least 3 weeks apart.3,4
A few caveats: The Novavax vaccine comes in 10-dose vials, which should be kept refrigerated until use. Once the first dose is used, the vial should be discarded after 6 hours. This may present some scheduling and logistical issues. Also, the Novavax vaccine is not currently approved for use in children younger than 12 years, or as a booster to other vaccines.3,4
The effectiveness and safety of the Novavax vaccine appears to be comparable to that of the other vaccines approved to date, although measuring vaccine effectiveness is a tricky business given the rapid mutation of the virus and changing dominant strains.3,4 The Novavax vaccine’s efficacy against currently circulating Omicron variants of the virus (eg, BA.2.12.1, BA.4, BA.5) remains to be determined.
As far as safety, preliminary studies indicate that Novavax may be associated with rare cases of myocarditis.3,4 Myocarditis can result from the COVID infection itself at an overall rate of 1 to 2 per 1000, which is 16 times the rate in adults without COVID.5
Could it provide reassurance to the hesitant? The Novavax COVID vaccine was developed using a vaccine platform and production process similar to that of other commonly administered vaccines, such as hepatitis B vaccine and human papillomavirus vaccine. This may make it an appealing option for patients who have shown hesitancy toward new vaccine technologies.
And, of course, there are the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Currently, there are 2 vaccines approved under the normal licensing process for adults, both of which are mRNA-based vaccines: Pfizer/BioNTech (Comirnaty) for those ages 12 years and older and Moderna (Spikevax) for those ages 18 and older. A third COVID vaccine option is manufactured by Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) and uses an adenovirus platform. The FDA revised its EUA in May to limit its use.6 The Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been associated with rare but serious reactions called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia. ACIP recommends all other vaccines in preference to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
For more on COVID vaccination for patients of all ages, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/downloads/COVID-19-immunization-schedule-ages-6months-older.pdf
In recent weeks, the COVID-19 vaccine arsenal has grown more robust. Here’s what you need to know:
Variant-specific boosters. On September 1, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) adopted a recommendation for a booster of either a new bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 12 years and older) or bivalent Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (for individuals ages 18 years and older) at least 2 months after receipt of a primary series or prior monovalent booster dose. Both bivalent vaccines were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and offer protection against one of the more common circulating strains of SARS-COV-2 (BA.1) while boosting immunity to the original strain. Both options are approved only as booster shots, not as an original COVID vaccine series.1
Novavax vaccine. This summer, the FDA issued an EUA for the Novavax COVID-19 vaccine in adults and a later EUA for adolescents (ages 12 to 17 years).2 Novavax is the fourth vaccine available to combat COVID-19 infection. This newest addition to the COVID armamentarium consists of coronavirus protein subunits, produced using recombinant technology, and a matrix adjuvant. The primary series consists of 2 doses administered at least 3 weeks apart.3,4
A few caveats: The Novavax vaccine comes in 10-dose vials, which should be kept refrigerated until use. Once the first dose is used, the vial should be discarded after 6 hours. This may present some scheduling and logistical issues. Also, the Novavax vaccine is not currently approved for use in children younger than 12 years, or as a booster to other vaccines.3,4
The effectiveness and safety of the Novavax vaccine appears to be comparable to that of the other vaccines approved to date, although measuring vaccine effectiveness is a tricky business given the rapid mutation of the virus and changing dominant strains.3,4 The Novavax vaccine’s efficacy against currently circulating Omicron variants of the virus (eg, BA.2.12.1, BA.4, BA.5) remains to be determined.
As far as safety, preliminary studies indicate that Novavax may be associated with rare cases of myocarditis.3,4 Myocarditis can result from the COVID infection itself at an overall rate of 1 to 2 per 1000, which is 16 times the rate in adults without COVID.5
Could it provide reassurance to the hesitant? The Novavax COVID vaccine was developed using a vaccine platform and production process similar to that of other commonly administered vaccines, such as hepatitis B vaccine and human papillomavirus vaccine. This may make it an appealing option for patients who have shown hesitancy toward new vaccine technologies.
And, of course, there are the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Currently, there are 2 vaccines approved under the normal licensing process for adults, both of which are mRNA-based vaccines: Pfizer/BioNTech (Comirnaty) for those ages 12 years and older and Moderna (Spikevax) for those ages 18 and older. A third COVID vaccine option is manufactured by Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) and uses an adenovirus platform. The FDA revised its EUA in May to limit its use.6 The Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been associated with rare but serious reactions called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia. ACIP recommends all other vaccines in preference to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
For more on COVID vaccination for patients of all ages, see: www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/downloads/COVID-19-immunization-schedule-ages-6months-older.pdf
1. Oliver S. Evidence to recommendations framework: Bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster doses. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, September 1, 2002. Accessed September 6, 2002. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-09-01/08-COVID-Oliver-508.pdf
2. FDA. Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted. Updated August 19, 2022. Accessed August 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/novavax-covid-19-vaccine-adjuvanted
3. Dubovsky F. NVX-CoV2373 (Novavax COVID-19 vaccine) in adults (≥ 18 years of age). Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/04-covid-dubovsky-508.pdf
4. Twentyman E. Evidence to recommendation framework: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted in adults ages 18 years and older. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/05-covid-twentyman-508.pdf
5. Boehmer TK, Kompaniyets L, Lavery AM, et al. Association between COVID-19 and myocarditis using hospital-based administrative data—United States, March 2020–January 2021. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1228-1232. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7035e5
6. American Hospital Association. FDA limits J&J COVID-19 vaccine use to certain adults. Published May 6, 2022. Accessed September 6, 2022. www.aha.org/news/headline/2022-05-06-fda-limits-jj-covid-19-vaccine-use-certain-adults
1. Oliver S. Evidence to recommendations framework: Bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster doses. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, September 1, 2002. Accessed September 6, 2002. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-09-01/08-COVID-Oliver-508.pdf
2. FDA. Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted. Updated August 19, 2022. Accessed August 23, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/novavax-covid-19-vaccine-adjuvanted
3. Dubovsky F. NVX-CoV2373 (Novavax COVID-19 vaccine) in adults (≥ 18 years of age). Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/04-covid-dubovsky-508.pdf
4. Twentyman E. Evidence to recommendation framework: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted in adults ages 18 years and older. Presented to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, July 19, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2022-07-19/05-covid-twentyman-508.pdf
5. Boehmer TK, Kompaniyets L, Lavery AM, et al. Association between COVID-19 and myocarditis using hospital-based administrative data—United States, March 2020–January 2021. Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1228-1232. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7035e5
6. American Hospital Association. FDA limits J&J COVID-19 vaccine use to certain adults. Published May 6, 2022. Accessed September 6, 2022. www.aha.org/news/headline/2022-05-06-fda-limits-jj-covid-19-vaccine-use-certain-adults
Commentary: Clinical Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1RA, and Insulin, September 2022
Many sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are approved for use at two doses, but there are few clinical data regarding the metabolic impact of uptitrating an SGLT2 inhibitor from the lower to the higher dose in clinical practice. Matsumura and colleagues published the results of a retrospective, longitudinal study at a single institution in Japan. A total of 52 participants who were treated with 10 mg empagliflozin once daily were analyzed at 26 weeks after the dose had been increased to 25 mg once daily. The researchers reported a 0.6 kg weight reduction, a 0.15% reduction in A1c, and a 22.1 mg/dL reduction in triglycerides in the participants on the higher dose of empagliflozin. Although the benefits of the higher dose were rather small, this study does aid the clinician regarding the clinical impact of increasing the dose of empagliflozin.
Outcome studies with SGLT2 inhibitors have shown reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), heart failure hospitalization, and mortality. However, clinicians may be reluctant to initiate SGLT2 inhibitors in frail individuals as they are often excluded from randomized trials and may be more likely to have side effects from this class of medications. Wood and colleagues conducted a cohort study in Australia, comparing the effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors to that of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The study was done with individuals with type 2 diabetes who were initiated on these agents within 60 days of a hospital discharge. It was noted that SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced MACE, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors, and this benefit was present in both frail and nonfrail individuals. The study did not report on tolerability issues and is limited by the cohort design, but it does suggest a cardiovascular benefit among frail patients with type 2 diabetes who are treated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it may be reassuring when considering an SGLT2 inhibitor in a frail person.
In my July 2022 commentary, I discussed the results of AWARD-PEDS, which demonstrated a significant A1c reduction but no weight loss with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) dulaglutide in youth with type 2 diabetes. Tamborlane and colleagues have now reported the results of a randomized trial that studied the efficacy and safety of 2 mg exenatide once weekly in youth with type 2 diabetes. Similarly to the AWARD-PEDS study, A1c was significantly reduced compared with placebo, with a difference of -0.85% at 24 weeks. Also similarly to AWARD-PEDS, there was no significant difference in body weight between the GLP-1RA and placebo groups. There are now three studies showing glycemic benefits but little weight loss with GLP-1RA treatment in youth with type 2 diabetes, and while the glycemic benefits are encouraging, it remains perplexing why these studies have not demonstrated the weight loss that has consistently been demonstrated in adult studies of GLP-1RA.
Clinicians often choose a second-generation basal insulin analog (glargine U300, degludec) over a first-generation basal analog (glargine U100, detemir) because of lower rates of hypoglycemia. Randomized clinical trials and real-world evidence (RWE) studies comparing glargine U100 vs degludec have shown somewhat inconsistent results. In the newest RWE study comparing these two second-generation analogs, RESTORE-2 NAIVE, Fadini and colleagues reported that 6 months after initiating either glargine U300 or degludec in insulin-naive type 2 diabetes, there was a similar improvement in glycemia, no weight gain, and low hypoglycemia rates in each group. RESTORE-2 is another study demonstrating similar results between the two second-generation insulin analogs and helps build our understanding that these two insulins are more similar than different.
Many sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are approved for use at two doses, but there are few clinical data regarding the metabolic impact of uptitrating an SGLT2 inhibitor from the lower to the higher dose in clinical practice. Matsumura and colleagues published the results of a retrospective, longitudinal study at a single institution in Japan. A total of 52 participants who were treated with 10 mg empagliflozin once daily were analyzed at 26 weeks after the dose had been increased to 25 mg once daily. The researchers reported a 0.6 kg weight reduction, a 0.15% reduction in A1c, and a 22.1 mg/dL reduction in triglycerides in the participants on the higher dose of empagliflozin. Although the benefits of the higher dose were rather small, this study does aid the clinician regarding the clinical impact of increasing the dose of empagliflozin.
Outcome studies with SGLT2 inhibitors have shown reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), heart failure hospitalization, and mortality. However, clinicians may be reluctant to initiate SGLT2 inhibitors in frail individuals as they are often excluded from randomized trials and may be more likely to have side effects from this class of medications. Wood and colleagues conducted a cohort study in Australia, comparing the effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors to that of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The study was done with individuals with type 2 diabetes who were initiated on these agents within 60 days of a hospital discharge. It was noted that SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced MACE, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors, and this benefit was present in both frail and nonfrail individuals. The study did not report on tolerability issues and is limited by the cohort design, but it does suggest a cardiovascular benefit among frail patients with type 2 diabetes who are treated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it may be reassuring when considering an SGLT2 inhibitor in a frail person.
In my July 2022 commentary, I discussed the results of AWARD-PEDS, which demonstrated a significant A1c reduction but no weight loss with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) dulaglutide in youth with type 2 diabetes. Tamborlane and colleagues have now reported the results of a randomized trial that studied the efficacy and safety of 2 mg exenatide once weekly in youth with type 2 diabetes. Similarly to the AWARD-PEDS study, A1c was significantly reduced compared with placebo, with a difference of -0.85% at 24 weeks. Also similarly to AWARD-PEDS, there was no significant difference in body weight between the GLP-1RA and placebo groups. There are now three studies showing glycemic benefits but little weight loss with GLP-1RA treatment in youth with type 2 diabetes, and while the glycemic benefits are encouraging, it remains perplexing why these studies have not demonstrated the weight loss that has consistently been demonstrated in adult studies of GLP-1RA.
Clinicians often choose a second-generation basal insulin analog (glargine U300, degludec) over a first-generation basal analog (glargine U100, detemir) because of lower rates of hypoglycemia. Randomized clinical trials and real-world evidence (RWE) studies comparing glargine U100 vs degludec have shown somewhat inconsistent results. In the newest RWE study comparing these two second-generation analogs, RESTORE-2 NAIVE, Fadini and colleagues reported that 6 months after initiating either glargine U300 or degludec in insulin-naive type 2 diabetes, there was a similar improvement in glycemia, no weight gain, and low hypoglycemia rates in each group. RESTORE-2 is another study demonstrating similar results between the two second-generation insulin analogs and helps build our understanding that these two insulins are more similar than different.
Many sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are approved for use at two doses, but there are few clinical data regarding the metabolic impact of uptitrating an SGLT2 inhibitor from the lower to the higher dose in clinical practice. Matsumura and colleagues published the results of a retrospective, longitudinal study at a single institution in Japan. A total of 52 participants who were treated with 10 mg empagliflozin once daily were analyzed at 26 weeks after the dose had been increased to 25 mg once daily. The researchers reported a 0.6 kg weight reduction, a 0.15% reduction in A1c, and a 22.1 mg/dL reduction in triglycerides in the participants on the higher dose of empagliflozin. Although the benefits of the higher dose were rather small, this study does aid the clinician regarding the clinical impact of increasing the dose of empagliflozin.
Outcome studies with SGLT2 inhibitors have shown reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), heart failure hospitalization, and mortality. However, clinicians may be reluctant to initiate SGLT2 inhibitors in frail individuals as they are often excluded from randomized trials and may be more likely to have side effects from this class of medications. Wood and colleagues conducted a cohort study in Australia, comparing the effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors to that of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The study was done with individuals with type 2 diabetes who were initiated on these agents within 60 days of a hospital discharge. It was noted that SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced MACE, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality compared with DPP-4 inhibitors, and this benefit was present in both frail and nonfrail individuals. The study did not report on tolerability issues and is limited by the cohort design, but it does suggest a cardiovascular benefit among frail patients with type 2 diabetes who are treated with SGLT2 inhibitors, and it may be reassuring when considering an SGLT2 inhibitor in a frail person.
In my July 2022 commentary, I discussed the results of AWARD-PEDS, which demonstrated a significant A1c reduction but no weight loss with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) dulaglutide in youth with type 2 diabetes. Tamborlane and colleagues have now reported the results of a randomized trial that studied the efficacy and safety of 2 mg exenatide once weekly in youth with type 2 diabetes. Similarly to the AWARD-PEDS study, A1c was significantly reduced compared with placebo, with a difference of -0.85% at 24 weeks. Also similarly to AWARD-PEDS, there was no significant difference in body weight between the GLP-1RA and placebo groups. There are now three studies showing glycemic benefits but little weight loss with GLP-1RA treatment in youth with type 2 diabetes, and while the glycemic benefits are encouraging, it remains perplexing why these studies have not demonstrated the weight loss that has consistently been demonstrated in adult studies of GLP-1RA.
Clinicians often choose a second-generation basal insulin analog (glargine U300, degludec) over a first-generation basal analog (glargine U100, detemir) because of lower rates of hypoglycemia. Randomized clinical trials and real-world evidence (RWE) studies comparing glargine U100 vs degludec have shown somewhat inconsistent results. In the newest RWE study comparing these two second-generation analogs, RESTORE-2 NAIVE, Fadini and colleagues reported that 6 months after initiating either glargine U300 or degludec in insulin-naive type 2 diabetes, there was a similar improvement in glycemia, no weight gain, and low hypoglycemia rates in each group. RESTORE-2 is another study demonstrating similar results between the two second-generation insulin analogs and helps build our understanding that these two insulins are more similar than different.
Botanical Briefs: Tulipalin A
Cutaneous Manifestations
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
Cutaneous Manifestations
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
Cutaneous Manifestations
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
Practice Points
- Tulips are a common cause of contact dermatitis among floral workers.
- Tulipalin A is the primary sensitizer in tulips causing allergic contact dermatitis.
- The best preventative for tulip contact dermatitis is avoiding the inciting plants.