User login
An Unusual Metastasis of Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Background
Anal squamous cell carcinoma is a rare cancer which usually has locoregional spread. We report a case of distant metastasis of primary anal squamous cell carcinoma to the posterior mediastinal lymph node without lung involvement.
Case Presentation
A 63-year-old female presented with a painful anal mass, bleeding, and fluid leakage for around six months. The patient was found to have a near-circumferential fungating anal mass with bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy. MR imaging revealed an 8.7 x 5.9 cm anal mass extending beyond the mesorectal fascia, with lymphadenopathy involving inguinal, pelvic sidewall, and iliac regions. A biopsy of the mass confirmed anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC). Initial treatment included diverting colostomy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy with Mitomycin and 5-Fluorouracil. Colonoscopy post-treatment revealed tubular adenomas and a hyperplastic polyp, with no malignancy detected. The patient demonstrated a strong therapeutic response, with resolution of the anal mass and improved symptoms. However, one year later, new FDG-avid mediastinal lymph node were detected on the CT/PET scan with no pulmonary involvement. Metastatic ASCC of the Mediastinal lymph node was confirmed by biopsy. Salvage chemotherapy with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel every three weeks for six cycles achieved complete resolution of metastases.
Conclusions
This case underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing advanced ASCC and highlights the efficacy of salvage chemotherapy in addressing metastases. Close monitoring of disease progression following surgery and chemotherapy is crucial due to the risk of recurrence.
Background
Anal squamous cell carcinoma is a rare cancer which usually has locoregional spread. We report a case of distant metastasis of primary anal squamous cell carcinoma to the posterior mediastinal lymph node without lung involvement.
Case Presentation
A 63-year-old female presented with a painful anal mass, bleeding, and fluid leakage for around six months. The patient was found to have a near-circumferential fungating anal mass with bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy. MR imaging revealed an 8.7 x 5.9 cm anal mass extending beyond the mesorectal fascia, with lymphadenopathy involving inguinal, pelvic sidewall, and iliac regions. A biopsy of the mass confirmed anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC). Initial treatment included diverting colostomy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy with Mitomycin and 5-Fluorouracil. Colonoscopy post-treatment revealed tubular adenomas and a hyperplastic polyp, with no malignancy detected. The patient demonstrated a strong therapeutic response, with resolution of the anal mass and improved symptoms. However, one year later, new FDG-avid mediastinal lymph node were detected on the CT/PET scan with no pulmonary involvement. Metastatic ASCC of the Mediastinal lymph node was confirmed by biopsy. Salvage chemotherapy with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel every three weeks for six cycles achieved complete resolution of metastases.
Conclusions
This case underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing advanced ASCC and highlights the efficacy of salvage chemotherapy in addressing metastases. Close monitoring of disease progression following surgery and chemotherapy is crucial due to the risk of recurrence.
Background
Anal squamous cell carcinoma is a rare cancer which usually has locoregional spread. We report a case of distant metastasis of primary anal squamous cell carcinoma to the posterior mediastinal lymph node without lung involvement.
Case Presentation
A 63-year-old female presented with a painful anal mass, bleeding, and fluid leakage for around six months. The patient was found to have a near-circumferential fungating anal mass with bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy. MR imaging revealed an 8.7 x 5.9 cm anal mass extending beyond the mesorectal fascia, with lymphadenopathy involving inguinal, pelvic sidewall, and iliac regions. A biopsy of the mass confirmed anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC). Initial treatment included diverting colostomy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy with Mitomycin and 5-Fluorouracil. Colonoscopy post-treatment revealed tubular adenomas and a hyperplastic polyp, with no malignancy detected. The patient demonstrated a strong therapeutic response, with resolution of the anal mass and improved symptoms. However, one year later, new FDG-avid mediastinal lymph node were detected on the CT/PET scan with no pulmonary involvement. Metastatic ASCC of the Mediastinal lymph node was confirmed by biopsy. Salvage chemotherapy with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel every three weeks for six cycles achieved complete resolution of metastases.
Conclusions
This case underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing advanced ASCC and highlights the efficacy of salvage chemotherapy in addressing metastases. Close monitoring of disease progression following surgery and chemotherapy is crucial due to the risk of recurrence.
Walking the Line: Balancing Autonomy and Safety at End-of-Life
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Successful Targeted Therapy with Alectinib in ALK-Positive Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Lung Cancer Exposome in U.S. Military Veterans: Study of Environment and Epigenetic Factors on Risk and Survival
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Access to Germline Genetic Testing through Clinical Pathways in Veterans With Prostate Cancer
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
VA Ann Arbor Immunotherapy Stewardship Program
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
From Screening to Support: Enhancing Cancer Care Through eScreener Technology
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Case Presentation: First Ever VA "Bloodless" Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Was a Success
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
Generalized Erythematous Plaques and Pustules in a Pregnant Patient
Generalized Erythematous Plaques and Pustules in a Pregnant Patient
THE DIAGNOSIS: Impetigo Herpetiformis
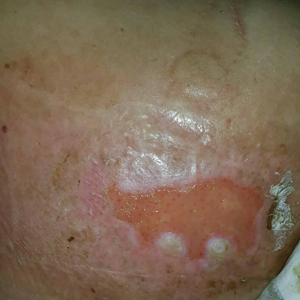
Histopathology revealed epidermal acanthosis and spongiosis with overlying parakeratosis associated with subcorneal and intracorneal neutrophils, papillary dermal edema, and dermal mixed inflammation with neutrophils and eosinophils. Both direct immunofluorescence and periodic acid–Schiff studies were negative. Blood and pustule cultures were sterile and the skin flora were normal. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of impetigo herpetiformis (IH) was made. The condition improved with systemic and topical steroids, supportive care, and an intravenous infusion of infliximab 5 mg/kg. At 3 weeks’ follow-up, the patient demonstrated near-complete resolution and later delivered successfully at 40 weeks’ gestation without complications.
Impetigo herpetiformis, also known as pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is an exceedingly rare gestational dermatosis that typically manifests in the third trimester and can be life-threatening for both the mother and fetus. The term was first used in 1872 to describe 5 pregnant women with extensive acute pustular eruptions, all in unstable condition; 4 (80%)of the cases resulted in maternal death, and all resulted in fetal death.1 Impetigo herpetiformis is characterized by pruritic and painful erythematous patches studded at the periphery with subcorneal pustules. Eruptions usually occur in the flexural areas and spread centrifugally, with extension of the lesions peripherally as the center erodes and crusts. Sparing of the face, palms, and soles is expected, and mucosal involvement is rare. Generalized involvement and exfoliation may occur in extreme cases.2 While IH typically manifests during the third trimester, it may occur any time throughout pregnancy or immediately postpartum.3 A few cases have been reported in the puerperium.2 Common symptoms include fever, chills, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and arthralgias. Less common complications include hypoalbuminemia and severe hypocalcemia leading to tetany, seizures, and delirium.2,3 While maternal mortality is uncommon, fetal mortality often is a more pressing risk and is attributed to placental insufficiency.3,4 For this reason, early delivery commonly is considered in severe cases.
Whether IH is a separate entity or a variant of pustular psoriasis remains heavily debated. Although the histopathology of IH is identical to pustular psoriasis, the lack of a personal and family history of psoriasis, symptom resolution with delivery, and possible recurrence during successive pregnancies help differentiate IH from generalized pustular psoriasis.2,5 Earlier onset, diffuse involvement, faster progression, and recurrence in subsequent pregnancies all have been linked to a worse prognosis.4
The differential diagnosis for IH includes acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, pemphigoid gestationis, dermatitis herpetiformis, and subcorneal pustular dermatosis. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is an uncommon severe cutaneous drug reaction characterized by the sudden onset of numerous sterile pustules on erythematous skin within 48 hours of exposure. The most common offending medications include pristinamycin and beta-lactam antibiotics. A high fever, neutrophilic leukocytosis, and hypocalcemia often accompany acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.6 Prompt diagnosis and withdrawal of the offending drug as well as supportive care and symptomatic treatment are crucial for disease management, as systemic symptoms and even organ involvement may occur.6
Pemphigoid gestationis, also known as gestational pemphigoid or herpes gestationis, is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that primarily affects pregnant women. It typically manifests in the second or third trimester or shortly after delivery. Clinically, it manifests as an intensely pruritic polymorphic eruption of urticarial papules and plaques accompanied by vesicles and bullae and often is distributed on the abdomen and extends to other body regions. Although the exact etiology is unknown, pemphigoid gestationis is caused by autoantibodies targeting the BP180 and BP230 hemidesmosomal proteins.7 Treatment usually involves systemic corticosteroids and may require additional immunosuppressive therapy. In most cases, patients see resolution within 6 months of delivery.7
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin disorder characterized by intensely pruritic, grouped vesicles and papules, often distributed symmetrically on extensor surfaces such as the elbows, knees, buttocks, and back. It is closely associated with celiac disease and is triggered by gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed individuals with human leukocyte antigen DQ2 and DQ8 haplotypes. Dermatitis herpetiformis is caused by deposition of IgA antibodies that target tissue transglutaminase 3 at the dermal papillae, leading to inflammation and blister formation. 8 Treatment typically involves a gluten-free diet and medications such as dapsone to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Subcorneal pustular dermatosis, also known as Sneddon-Wilkinson disease, is a rare chronic relapsing pustular dermatosis characterized by sterile superficial pustules arranged in annular or circinate patterns on erythematous plaques. It predominantly affects middleaged women and often is associated with underlying conditions such as IgA gammopathy or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but immune dysregulation is thought to play a role. Some authors still question whether subcorneal pustular dermatosis is a distinct entity from pustular psoriasis.4,5,12 Dapsone is the preferred first-line treatment, with adjunct therapies including topical or systemic corticosteroids, other immunosuppressive agents, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, and UV light therapy.9
Definitive management of IH is achieved through early delivery; however, systemic corticosteroids often are used in varying doses to control the disease and to extend the pregnancy period closer to term or until delivery is considered viable. Additional therapies that can be considered include infliximab, cyclosporine, and topical corticosteroids, in conjunction with fluid and electrolyte maintenance.2,4,10 If symptoms persist despite supportive care and pharmacologic intervention, induction of labor or termination of pregnancy may be indicated. In nonbreastfeeding postpartum mothers with persistent disease, therapies commonly used in generalized pustular psoriasis may be given.11
- Hebra F. Ueber einzelne wahrend Schwangerschaft, des wacherbette unde bei uterinal. Krankheiten der Frauen zu beobachtende Hautkrankheiten. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1872;48:1197-1202.
- Fouda UM, Fouda RM, Ammar HM, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis during the puerperium triggered by secondary hypoparathyroidism: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:9338. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-2-9338
- Kroumpouzos G, Cohen LM. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:1-22. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114595
- Liu J, Ali K, Lou H, et al. First-trimester impetigo herpetiformis leads to stillbirth: a case report. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1271-1279. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00735-9
- Lotem M, Katzenelson V, Rotem A, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis: a variant of pustular psoriasis or a separate entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:338-41. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70042-6
- Stadler PC, Oschmann A, Kerl-French K, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: clinical characteristics, pathogenesis, and management. Dermatology. 2023;239:328-333. doi:10.1159/000529218
- Abdelhafez MMA, Ahmed KAM, Daud MNBM, et al. Pemphigoid gestationis and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a literature review. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022;51:102370. doi:10.1016 /j.jogoh.2022.102370
- Reunala T, Hervonen K, Salmi T. Dermatitis herpetiformis: an update on diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:329-338. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00584-2
- Watts PJ, Khachemoune A. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a review of 30 years of progress. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:653-671. doi:10.1007 /s40257-016-0202-8
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.032
- Bukhari IA. Impetigo herpetiformis in a primigravida: successful treatment with etanercept. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:449-451.
- Chang SE, Kim HH, Choi JH, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis followed by generalized pustular psoriasis: more evidence of same disease entity. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42(9):754-755.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Impetigo Herpetiformis
Histopathology revealed epidermal acanthosis and spongiosis with overlying parakeratosis associated with subcorneal and intracorneal neutrophils, papillary dermal edema, and dermal mixed inflammation with neutrophils and eosinophils. Both direct immunofluorescence and periodic acid–Schiff studies were negative. Blood and pustule cultures were sterile and the skin flora were normal. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of impetigo herpetiformis (IH) was made. The condition improved with systemic and topical steroids, supportive care, and an intravenous infusion of infliximab 5 mg/kg. At 3 weeks’ follow-up, the patient demonstrated near-complete resolution and later delivered successfully at 40 weeks’ gestation without complications.
Impetigo herpetiformis, also known as pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is an exceedingly rare gestational dermatosis that typically manifests in the third trimester and can be life-threatening for both the mother and fetus. The term was first used in 1872 to describe 5 pregnant women with extensive acute pustular eruptions, all in unstable condition; 4 (80%)of the cases resulted in maternal death, and all resulted in fetal death.1 Impetigo herpetiformis is characterized by pruritic and painful erythematous patches studded at the periphery with subcorneal pustules. Eruptions usually occur in the flexural areas and spread centrifugally, with extension of the lesions peripherally as the center erodes and crusts. Sparing of the face, palms, and soles is expected, and mucosal involvement is rare. Generalized involvement and exfoliation may occur in extreme cases.2 While IH typically manifests during the third trimester, it may occur any time throughout pregnancy or immediately postpartum.3 A few cases have been reported in the puerperium.2 Common symptoms include fever, chills, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and arthralgias. Less common complications include hypoalbuminemia and severe hypocalcemia leading to tetany, seizures, and delirium.2,3 While maternal mortality is uncommon, fetal mortality often is a more pressing risk and is attributed to placental insufficiency.3,4 For this reason, early delivery commonly is considered in severe cases.
Whether IH is a separate entity or a variant of pustular psoriasis remains heavily debated. Although the histopathology of IH is identical to pustular psoriasis, the lack of a personal and family history of psoriasis, symptom resolution with delivery, and possible recurrence during successive pregnancies help differentiate IH from generalized pustular psoriasis.2,5 Earlier onset, diffuse involvement, faster progression, and recurrence in subsequent pregnancies all have been linked to a worse prognosis.4
The differential diagnosis for IH includes acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, pemphigoid gestationis, dermatitis herpetiformis, and subcorneal pustular dermatosis. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is an uncommon severe cutaneous drug reaction characterized by the sudden onset of numerous sterile pustules on erythematous skin within 48 hours of exposure. The most common offending medications include pristinamycin and beta-lactam antibiotics. A high fever, neutrophilic leukocytosis, and hypocalcemia often accompany acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.6 Prompt diagnosis and withdrawal of the offending drug as well as supportive care and symptomatic treatment are crucial for disease management, as systemic symptoms and even organ involvement may occur.6
Pemphigoid gestationis, also known as gestational pemphigoid or herpes gestationis, is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that primarily affects pregnant women. It typically manifests in the second or third trimester or shortly after delivery. Clinically, it manifests as an intensely pruritic polymorphic eruption of urticarial papules and plaques accompanied by vesicles and bullae and often is distributed on the abdomen and extends to other body regions. Although the exact etiology is unknown, pemphigoid gestationis is caused by autoantibodies targeting the BP180 and BP230 hemidesmosomal proteins.7 Treatment usually involves systemic corticosteroids and may require additional immunosuppressive therapy. In most cases, patients see resolution within 6 months of delivery.7
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin disorder characterized by intensely pruritic, grouped vesicles and papules, often distributed symmetrically on extensor surfaces such as the elbows, knees, buttocks, and back. It is closely associated with celiac disease and is triggered by gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed individuals with human leukocyte antigen DQ2 and DQ8 haplotypes. Dermatitis herpetiformis is caused by deposition of IgA antibodies that target tissue transglutaminase 3 at the dermal papillae, leading to inflammation and blister formation. 8 Treatment typically involves a gluten-free diet and medications such as dapsone to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Subcorneal pustular dermatosis, also known as Sneddon-Wilkinson disease, is a rare chronic relapsing pustular dermatosis characterized by sterile superficial pustules arranged in annular or circinate patterns on erythematous plaques. It predominantly affects middleaged women and often is associated with underlying conditions such as IgA gammopathy or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but immune dysregulation is thought to play a role. Some authors still question whether subcorneal pustular dermatosis is a distinct entity from pustular psoriasis.4,5,12 Dapsone is the preferred first-line treatment, with adjunct therapies including topical or systemic corticosteroids, other immunosuppressive agents, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, and UV light therapy.9
Definitive management of IH is achieved through early delivery; however, systemic corticosteroids often are used in varying doses to control the disease and to extend the pregnancy period closer to term or until delivery is considered viable. Additional therapies that can be considered include infliximab, cyclosporine, and topical corticosteroids, in conjunction with fluid and electrolyte maintenance.2,4,10 If symptoms persist despite supportive care and pharmacologic intervention, induction of labor or termination of pregnancy may be indicated. In nonbreastfeeding postpartum mothers with persistent disease, therapies commonly used in generalized pustular psoriasis may be given.11
THE DIAGNOSIS: Impetigo Herpetiformis
Histopathology revealed epidermal acanthosis and spongiosis with overlying parakeratosis associated with subcorneal and intracorneal neutrophils, papillary dermal edema, and dermal mixed inflammation with neutrophils and eosinophils. Both direct immunofluorescence and periodic acid–Schiff studies were negative. Blood and pustule cultures were sterile and the skin flora were normal. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of impetigo herpetiformis (IH) was made. The condition improved with systemic and topical steroids, supportive care, and an intravenous infusion of infliximab 5 mg/kg. At 3 weeks’ follow-up, the patient demonstrated near-complete resolution and later delivered successfully at 40 weeks’ gestation without complications.
Impetigo herpetiformis, also known as pustular psoriasis of pregnancy, is an exceedingly rare gestational dermatosis that typically manifests in the third trimester and can be life-threatening for both the mother and fetus. The term was first used in 1872 to describe 5 pregnant women with extensive acute pustular eruptions, all in unstable condition; 4 (80%)of the cases resulted in maternal death, and all resulted in fetal death.1 Impetigo herpetiformis is characterized by pruritic and painful erythematous patches studded at the periphery with subcorneal pustules. Eruptions usually occur in the flexural areas and spread centrifugally, with extension of the lesions peripherally as the center erodes and crusts. Sparing of the face, palms, and soles is expected, and mucosal involvement is rare. Generalized involvement and exfoliation may occur in extreme cases.2 While IH typically manifests during the third trimester, it may occur any time throughout pregnancy or immediately postpartum.3 A few cases have been reported in the puerperium.2 Common symptoms include fever, chills, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and arthralgias. Less common complications include hypoalbuminemia and severe hypocalcemia leading to tetany, seizures, and delirium.2,3 While maternal mortality is uncommon, fetal mortality often is a more pressing risk and is attributed to placental insufficiency.3,4 For this reason, early delivery commonly is considered in severe cases.
Whether IH is a separate entity or a variant of pustular psoriasis remains heavily debated. Although the histopathology of IH is identical to pustular psoriasis, the lack of a personal and family history of psoriasis, symptom resolution with delivery, and possible recurrence during successive pregnancies help differentiate IH from generalized pustular psoriasis.2,5 Earlier onset, diffuse involvement, faster progression, and recurrence in subsequent pregnancies all have been linked to a worse prognosis.4
The differential diagnosis for IH includes acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, pemphigoid gestationis, dermatitis herpetiformis, and subcorneal pustular dermatosis. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is an uncommon severe cutaneous drug reaction characterized by the sudden onset of numerous sterile pustules on erythematous skin within 48 hours of exposure. The most common offending medications include pristinamycin and beta-lactam antibiotics. A high fever, neutrophilic leukocytosis, and hypocalcemia often accompany acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.6 Prompt diagnosis and withdrawal of the offending drug as well as supportive care and symptomatic treatment are crucial for disease management, as systemic symptoms and even organ involvement may occur.6
Pemphigoid gestationis, also known as gestational pemphigoid or herpes gestationis, is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that primarily affects pregnant women. It typically manifests in the second or third trimester or shortly after delivery. Clinically, it manifests as an intensely pruritic polymorphic eruption of urticarial papules and plaques accompanied by vesicles and bullae and often is distributed on the abdomen and extends to other body regions. Although the exact etiology is unknown, pemphigoid gestationis is caused by autoantibodies targeting the BP180 and BP230 hemidesmosomal proteins.7 Treatment usually involves systemic corticosteroids and may require additional immunosuppressive therapy. In most cases, patients see resolution within 6 months of delivery.7
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin disorder characterized by intensely pruritic, grouped vesicles and papules, often distributed symmetrically on extensor surfaces such as the elbows, knees, buttocks, and back. It is closely associated with celiac disease and is triggered by gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed individuals with human leukocyte antigen DQ2 and DQ8 haplotypes. Dermatitis herpetiformis is caused by deposition of IgA antibodies that target tissue transglutaminase 3 at the dermal papillae, leading to inflammation and blister formation. 8 Treatment typically involves a gluten-free diet and medications such as dapsone to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Subcorneal pustular dermatosis, also known as Sneddon-Wilkinson disease, is a rare chronic relapsing pustular dermatosis characterized by sterile superficial pustules arranged in annular or circinate patterns on erythematous plaques. It predominantly affects middleaged women and often is associated with underlying conditions such as IgA gammopathy or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but immune dysregulation is thought to play a role. Some authors still question whether subcorneal pustular dermatosis is a distinct entity from pustular psoriasis.4,5,12 Dapsone is the preferred first-line treatment, with adjunct therapies including topical or systemic corticosteroids, other immunosuppressive agents, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, and UV light therapy.9
Definitive management of IH is achieved through early delivery; however, systemic corticosteroids often are used in varying doses to control the disease and to extend the pregnancy period closer to term or until delivery is considered viable. Additional therapies that can be considered include infliximab, cyclosporine, and topical corticosteroids, in conjunction with fluid and electrolyte maintenance.2,4,10 If symptoms persist despite supportive care and pharmacologic intervention, induction of labor or termination of pregnancy may be indicated. In nonbreastfeeding postpartum mothers with persistent disease, therapies commonly used in generalized pustular psoriasis may be given.11
- Hebra F. Ueber einzelne wahrend Schwangerschaft, des wacherbette unde bei uterinal. Krankheiten der Frauen zu beobachtende Hautkrankheiten. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1872;48:1197-1202.
- Fouda UM, Fouda RM, Ammar HM, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis during the puerperium triggered by secondary hypoparathyroidism: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:9338. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-2-9338
- Kroumpouzos G, Cohen LM. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:1-22. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114595
- Liu J, Ali K, Lou H, et al. First-trimester impetigo herpetiformis leads to stillbirth: a case report. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1271-1279. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00735-9
- Lotem M, Katzenelson V, Rotem A, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis: a variant of pustular psoriasis or a separate entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:338-41. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70042-6
- Stadler PC, Oschmann A, Kerl-French K, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: clinical characteristics, pathogenesis, and management. Dermatology. 2023;239:328-333. doi:10.1159/000529218
- Abdelhafez MMA, Ahmed KAM, Daud MNBM, et al. Pemphigoid gestationis and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a literature review. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022;51:102370. doi:10.1016 /j.jogoh.2022.102370
- Reunala T, Hervonen K, Salmi T. Dermatitis herpetiformis: an update on diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:329-338. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00584-2
- Watts PJ, Khachemoune A. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a review of 30 years of progress. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:653-671. doi:10.1007 /s40257-016-0202-8
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.032
- Bukhari IA. Impetigo herpetiformis in a primigravida: successful treatment with etanercept. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:449-451.
- Chang SE, Kim HH, Choi JH, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis followed by generalized pustular psoriasis: more evidence of same disease entity. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42(9):754-755.
- Hebra F. Ueber einzelne wahrend Schwangerschaft, des wacherbette unde bei uterinal. Krankheiten der Frauen zu beobachtende Hautkrankheiten. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1872;48:1197-1202.
- Fouda UM, Fouda RM, Ammar HM, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis during the puerperium triggered by secondary hypoparathyroidism: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:9338. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-2-9338
- Kroumpouzos G, Cohen LM. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:1-22. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114595
- Liu J, Ali K, Lou H, et al. First-trimester impetigo herpetiformis leads to stillbirth: a case report. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1271-1279. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00735-9
- Lotem M, Katzenelson V, Rotem A, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis: a variant of pustular psoriasis or a separate entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:338-41. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70042-6
- Stadler PC, Oschmann A, Kerl-French K, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: clinical characteristics, pathogenesis, and management. Dermatology. 2023;239:328-333. doi:10.1159/000529218
- Abdelhafez MMA, Ahmed KAM, Daud MNBM, et al. Pemphigoid gestationis and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a literature review. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022;51:102370. doi:10.1016 /j.jogoh.2022.102370
- Reunala T, Hervonen K, Salmi T. Dermatitis herpetiformis: an update on diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:329-338. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00584-2
- Watts PJ, Khachemoune A. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a review of 30 years of progress. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:653-671. doi:10.1007 /s40257-016-0202-8
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.032
- Bukhari IA. Impetigo herpetiformis in a primigravida: successful treatment with etanercept. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:449-451.
- Chang SE, Kim HH, Choi JH, et al. Impetigo herpetiformis followed by generalized pustular psoriasis: more evidence of same disease entity. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42(9):754-755.
Generalized Erythematous Plaques and Pustules in a Pregnant Patient
Generalized Erythematous Plaques and Pustules in a Pregnant Patient
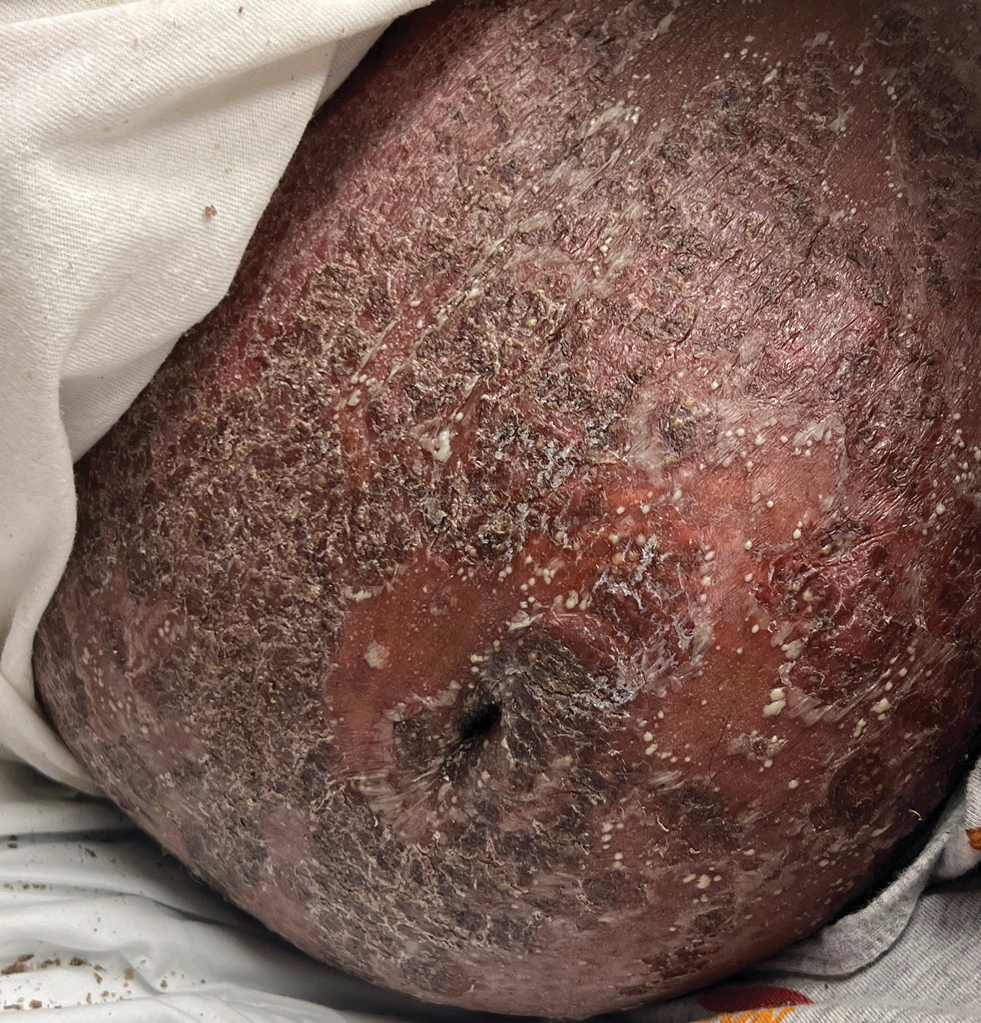
A 17-year-old girl was admitted to the hospital at 19 weeks' gestation for a widespread eruption of erythematous plaques with pustules covering more than 60% of the body and signs of sepsis. The rash initially appeared as a few small spots on the upper chest and under the breasts 5 weeks prior to hospital admission with subsequent spread to the abdomen and groin. At admission, the patient had a mild fever and tachycardia. She reported a history of eczema, herpes simplex virus, and intertrigo. Physical examination performed by dermatology revealed generalized erythematous plaques with pustule-studded margins and overlying scale involving the neck, torso, arms, and legs favoring the flexural areas. There was no involvement of the face, eyes, oral mucosa, palms, soles, or nails. Laboratory testing revealed hypoalbuminemia (2.4 g/dL [reference range, 3.5-5.5 g/dL]) and elevated inflammatory markers, including leukocytosis (15.83×103μL [reference range, 4.50- 11.00×103/μL]), absolute neutrophil count (12.87×103/μL [reference range, 1.50-8.00×103/μL]), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (124 mm/h [reference range, 0-20 mm/h]). A culture from an abdominal pustule grew 1 colony of taphylococcus epidermidis, a suspected contaminant. A biopsy from a lesion on the right chest was performed.
Fluoroscopy-Induced Chronic Radiation Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review and Reappraisal
Fluoroscopy-Induced Chronic Radiation Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review and Reappraisal
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique that allows for real-time visualization of internal structures in the body using continuous radiography beams. More than 1 million fluoroscopy-guided procedures are performed annually in the United States.1 Utilization of these procedures continues to increase, and so does the probability of related complications, as prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation can cause skin injuries.2 Fortunately, the incidence of radiation-induced skin injuries compared with the total number of fluoroscopic procedures performed remains small,2 although one study suggested the incidence may be as high as 8.9% in at-risk populations.3
Radiation dermatitis is well recognized in dermatology as a complication of oncologic management; however, radiation dermatitis as a complication of fluoroscopic procedures is underrecognized.4 Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis can be categorized as acute, subacute, or chronic.5 Common fluoroscopic procedures that have been associated with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis include interventional cardiac procedures, neurovascular procedures, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures, and endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs.6,7
Patients with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis, particularly fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD), can present to dermatology up to several years after the initial fluoroscopy procedure with no awareness of the association between the procedure and their skin findings. This presents a diagnostic challenge, and FICRD often is overlooked.5,8-10
We conducted a literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms fluoroscopy and dermatitis. In this reappraisal, we will provide a comprehensive overview of fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis with an emphasis on FICRD, covering its clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, risk factors, differential diagnosis, histology, and management. The aim of this review is to highlight the salient features and mimickers of FICRD and inform readers how to approach suspected cases, leading to accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Pathophysiology
Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis is the result of dose-dependent radiation-induced tissue damage. As the peak skin dosage (PSD) of radiation increases over the course of a procedure or multiple procedures, the severity of skin injury predictably increases. During fluoroscopic procedures, the standard irradiation dosage ranges from 0.02 Gy/min to 0.05 Gy/min.11 Transient skin changes may start to be seen around 2 Gy of cumulative exposure. Fluoroscopic procedures typically range in duration from 60 to 120 minutes; however, complex cases may exceed that. Additionally, multiple procedures performed within shorter intervals can result in greater PSD accumulation. Shorter intervals between procedures do not allow enough time for damage repair from the previous procedure and can result in further severe damage when the skin is re-exposed to radiation.2 The American College of Radiology recommends medical follow-up after 10 Gy of cumulative exposure, while cumulative exposure above 15 Gy within a 6- to 12-month period is defined as a sentinel event, according to The Joint Commission.12-14
Depending on the patient’s total radiation dosage during one or more procedures, the result of the tissue damage manifests differently at varying times: early skin changes are categorized as fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis, and late skin changes are categorized as FICRD (Table 1).
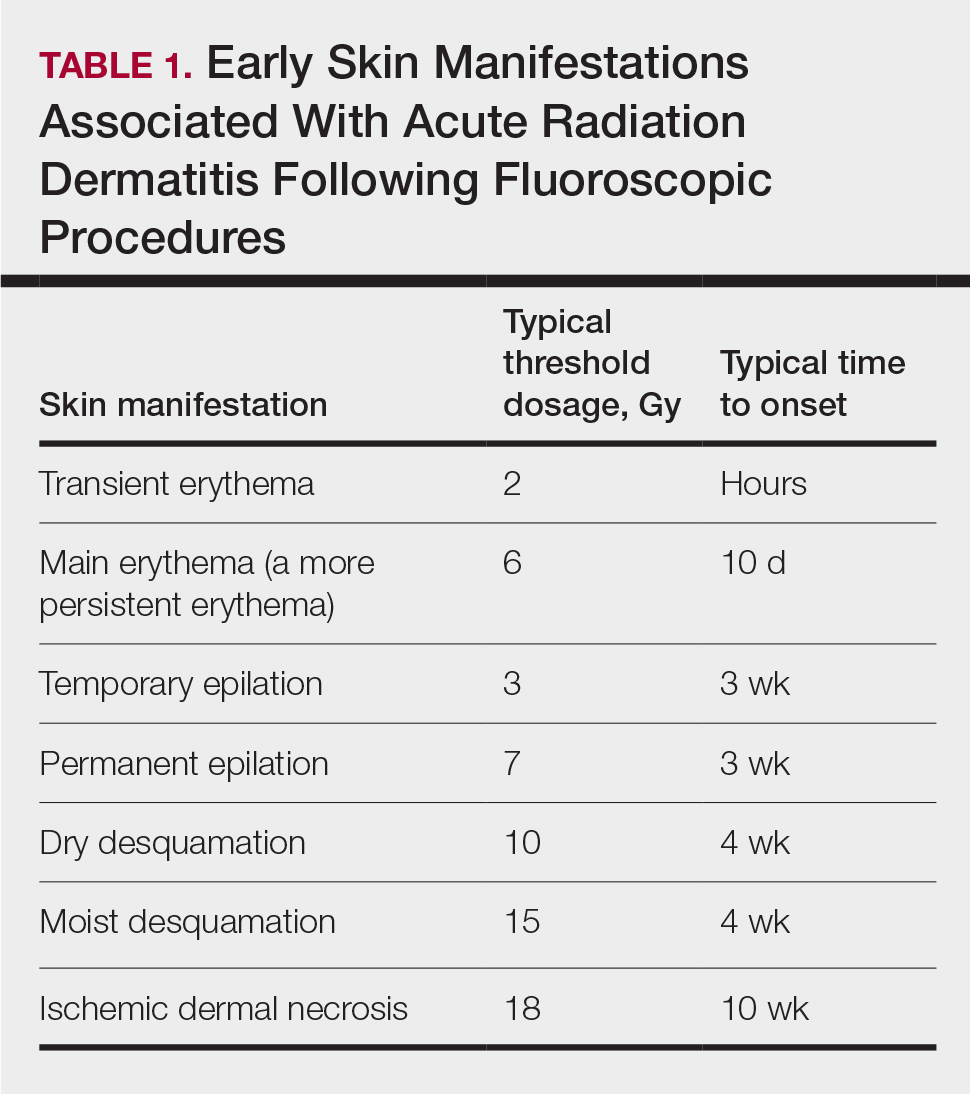
Clinical Manifestations
Acute radiation dermatitis from fluoroscopic procedures manifests within hours to days up to 90 days following radiation exposure and can be characterized by erythema with blistering, desquamation, epilation, pigmentation changes, and even necrosis if the accumulated dosage exceeds 15 Gy.15 Chronic radiation dermatitis (which as related to fluoroscopic procedures is termed FICRD) has a longer onset of weeks to years and is clinically characterized by telangiectasias, permanent erythema, dermal atrophy, or ulcerations. Clinically, subacute radiation dermatitis shares features of both acute and chronic radiation dermatitis; therefore, it is differentiated based on its histologic features.5,16
Although fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis (Table 1) may precede FICRD, acute manifestations of fluoroscopy-related dermatitis can be subtle and often manifest in areas not easily visualized. Because referrals to dermatologists for full-skin examinations after fluoroscopy procedures are not standard, patients may not be aware of the association between these procedures and the development of skin lesions. Nonetheless, some patients may report a history of skin changes such as redness days or weeks after a fluoroscopic procedure with accompanying pain and pruritus limited to the fluoroscopy-exposed region, which tend to self-resolve.17 The risk for FICRD is thought to increase if a history of fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis is present.18
The location of the skin findings correlates to the area exposed to prolonged radiation during the procedure(s). The most common areas include the scapular and subscapular regions, the right lateral trunk inferior to the axilla, the mid back, and the right anterolateral chest.16,19,20 These regions are associated with more complex (eg, cardiac) procedures that have been reported to lead to prolonged radiation exposure. The skin findings in FICRD are described as geometric, corresponding to the squarish or rectangular radiography beam that is directed at the patient. Additionally, radiography beams spread outward as they travel in space; therefore, skin injuries are common at the region more distal to the path of origination of the beam.21-23 Subsequently, a geometric, dyspigmented, indurated or atrophic plaque with telangiectasias and erosions or ulcerations with progressive worsening is a common manifestation of FICRD.5,16,23 Patients also commonly present with pruritus or severe pain associated with the lesion.24,25
Dermatologic Manifestations of FICRD
Skin responses seen weeks to years after a fluoroscopic procedure and typically after cumulative radiation exposure of 10 Gy or greater are categorized as FICRD (Table 2). These changes also can be clinically graded based on the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group classification of radiation dermatitis (Tables 3 and 4).26 Chronic changes in the skin largely result from remodeling of the vasculature and the subcutaneous tissue over time. Unlike acute changes, chronic changes typically persist and continue to worsen.27

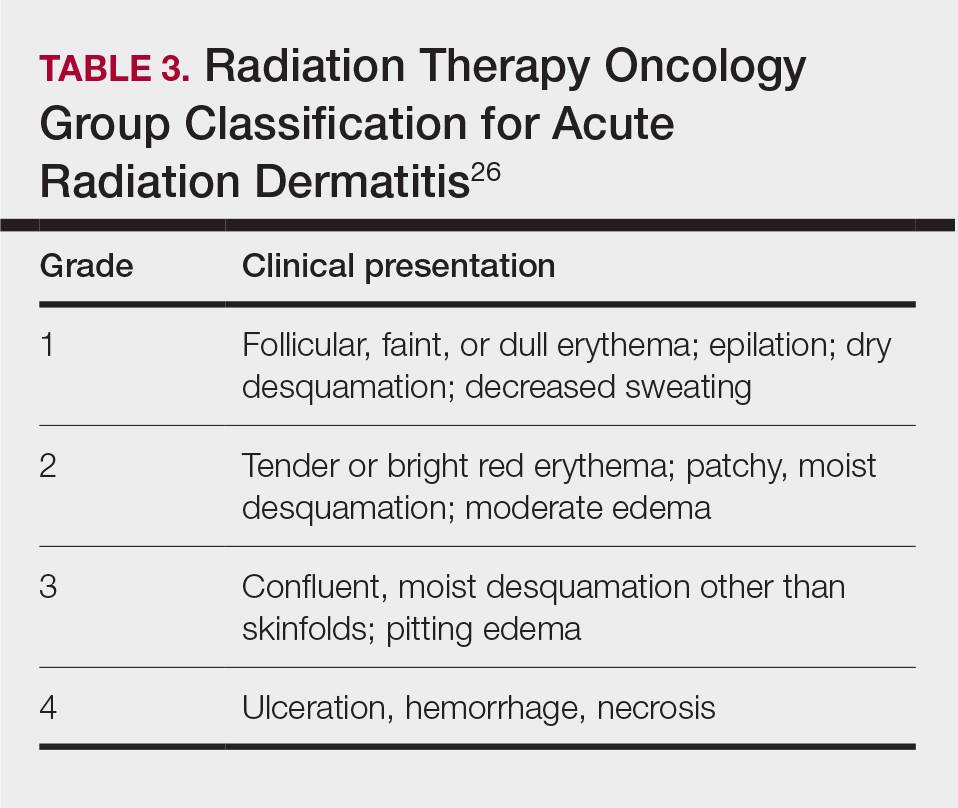
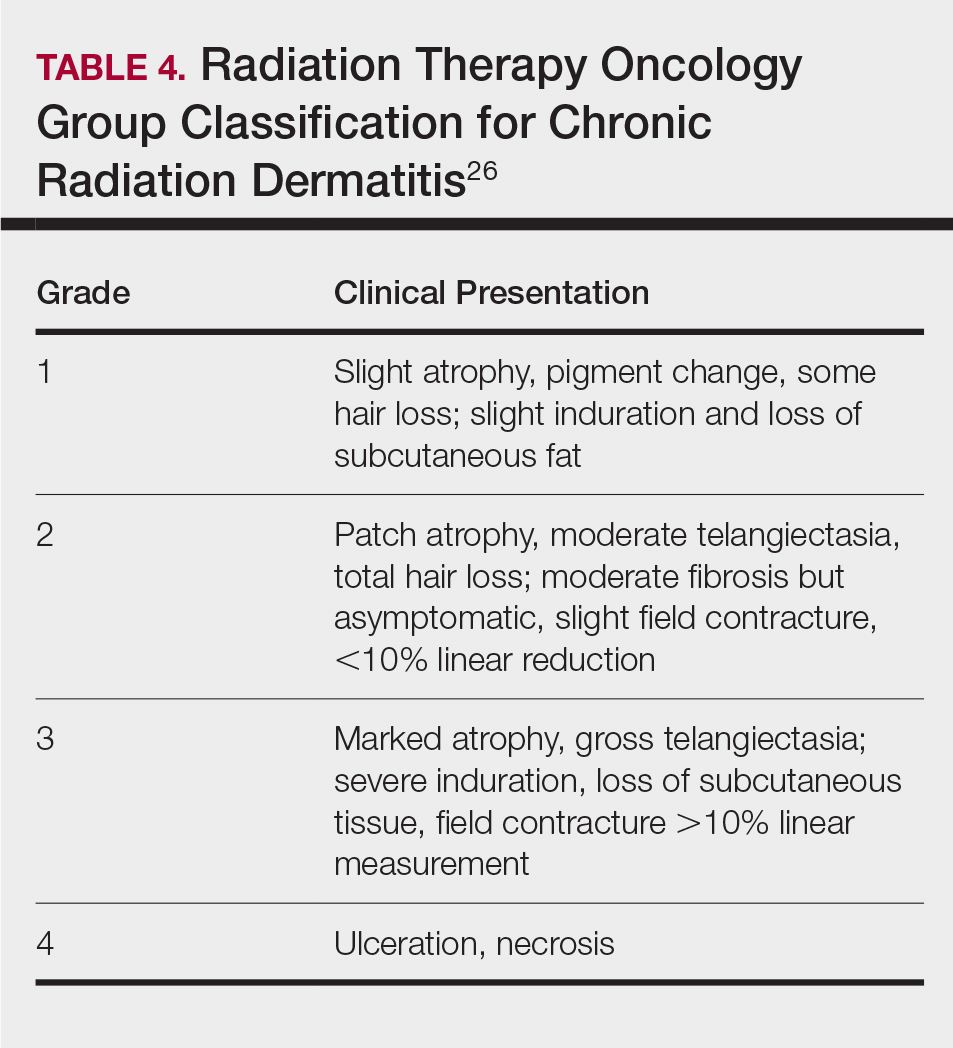
Telangiectasias—Anywhere from months to 1 year after exposure to 10 Gy of radiation, proliferation of atypical superficial vessels in the dermis can be seen, typically manifesting as telangiectasias on physical examination. Telangiectasias can increase with time and can even exhibit a dose-dependent relationship to the radiation exposure.28
Atrophy—Atrophic-appearing skin after radiation exposure is the result of direct injury to both the epidermis and fibroblasts in the dermis. The destruction of keratinocytes leads to a thin epidermis, and destruction of dermal fibroblasts causes insufficient collagen production.29 Clinically, this process manifests as an atrophic plaque that can be seen 12 weeks to 1 year after the procedure.
Fibrosis—Approximately 1 year after the exposure, the initial damage can lead to disruption of molecular pathways, causing fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 is the main factor involved.29 Damage to the endothelial cells results in increased TGF-β1 levels, which causes increased stimulation of remaining atypical fibroblasts and thus increased irregular collagen deposition.30 Further adding to this knowledge, Wei et al31 recently proposed that damage to the epidermal keratinocytes leads to disruption of yes-associated protein 1, which is a protective factor released from keratinocytes that regulates the dermal fibroblasts. However, extensive damage to the keratinocytes can lead to lower yes-associated protein 1 levels and its downstream activity, leading to increased levels of TGF-β1 and fibroblast activity.31 Clinically, this fibrotic stage is seen as indurated plaques in patients.
Necrosis—There are 2 forms of necrosis that can be seen. Ischemic dermal necrosis typically occurs in the acute phase after 10 weeks and approximately 18 Gy of cumulative exposure. It results from substantial skin damage, including microvascular damage and reduction in dermal capillaries, leading to ischemia of the tissue.2 Late dermal necrosis is the process seen in the chronic stage of FICRD and radiation dermatitis not related to fluoroscopy. It results from the inability of the fibrotic dermis to vascularly support the epidermis above it.2 It can be seen anywhere from 1 to 4 years after the procedure. This stage clinically manifests as worsening ulcerations with major pain and increased risk for secondary infections.16
Dyspigmentation—Dyspigmentation at the site of the radiation exposure can be seen acutely and chronically. Dosage above 15 to 18 Gy can lead to destruction of melanocytes, which can cause hypopigmentation in exposed areas. However, melanocytes are relatively resistant to radiation; therefore, dosages below the threshold of destruction of 15 to 18 Gy can cause melanocytic hyperactivity leading to hyperpigmentation.32 Hence, pigmentary changes can vary greatly. Classically, a central area of hypopigmentation with surrounding hyperpigmentation is seen.
Histology
Histologic appearance of radiation dermatitis varies depending on its stage. Acute radiation dermatitis primarily demonstrates superficial dermal edema, damage to the basal cell layer, small vessel dilation with thrombi, and hemorrhage along with a sparse inflammatory cell infiltrate.33 Histology typically is the only way to characterize subacute radiation dermatitis.5 Lichenoid tissue reaction is its characteristic feature. Mononuclear cells are found adjected to necrotic keratinocytes along with prominent vacuolization of the basal cell layer.33
The key histologic features of chronic radiation dermatitis include epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, telangiectasias, loss of adnexal structures, and dermal fibrosis along with sparse atypical stellate fibroblasts.34 However, clinical context of fluoroscopic exposure is required for the dermatopathologist to differentiate chronic radiation dermatitis from its histologic differential of morphea and lichen sclerosus. In a cross-sectional study, only 1 of 6 cases (16.7%) was correctly diagnosed as chronic radiation dermatitis in the absence of correlating clinical history.35
Risk Factors for FICRD
Since the diagnosis of FICRD can be a clinical challenge, understanding the risk factors can be helpful. The general likelihood of developing FICRD is related to the duration, frequency, interval, intensity, and area of radiation exposure. Procedures exceeding the normal duration of 60 to 120 minutes have been well documented as a substantial risk factor for radiation dermatitis and FICRD.36-38 The risk tends to be higher in longer procedures because they result in more radiation exposure and higher accumulated PSD. Obesity (ie, body mass index >26) is the major risk factor that has been associated with longer procedure times, as higher radiation dosages are necessary to penetrate the body of a larger patient and a larger skin surface area is exposed.37-39
Other risk factors associated with FICRD relate to how prone a patient is to radiation-induced DNA damage. Older patients are at higher risk due to lower intrinsic ability of the tissue to repair itself.11 Patients with a history of connective tissue diseases—particularly lupus, scleroderma, and mixed connective tissue disease—are at an increased risk.40 Furthermore, patients with genetic disorders that impair DNA repair are more susceptible to radiation-induced DNA damage; therefore, patients with ataxia-telangiectasia, xeroderma pigmentosum, Fanconi anemia, and hereditary nevoid basal cell carcinoma are at higher risk for FICRD.39 Similarly, medications that can affect DNA repair also have been shown to be risk factors. These medications include chemotherapeutic agents such as actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil.2,39 Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and tobacco use also have been shown to increase a patient’s risk for FICRD.39 It also is reasonable to believe that patients with defects in fibroblasts or with elastin or collagen disorders (eg, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) would be at higher risk, but there are no known studies highlighting the association in the literature.
Differential Diagnosis of FICRD
Acute allergic or irritant contact dermatitis manifests with a localized area of erythematous skin accompanied by pruritus.41 Patients with FICRD can present with a localized area of erythema and hyperpigmentation with minimal atrophy. The lesion may accompany substantial pruritus, which can favor the more common diagnosis of contact dermatitis.35,42,43
Fixed-drug eruption manifests as a well-defined, hyperpigmented plaque in a fixed location that occurs upon ingestion of a drug.44 Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis lesions are well demarcated and geometrically shaped and therefore can mimic lesions seen in fixed-drug eruptions.45 Additionally, the patient population undergoing fluoroscopic procedures tends to have major comorbidities requiring multiple medications.4
Decubitus ulcers are a result of vascular compromise to an area of skin due to constant pressure and are most commonly seen in the sacral region of patients with obesity.46 Ulcerated FICRD lesions can manifest on the lower midback. These lesions can be seen after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm or prostatic artery embolization.20,21 The location of these lesions can mimic decubitus ulcers if fluoroscopic history is unknown. As mentioned, obesity also increases the risk for FICRD.
Morphea can manifest as a localized area of induration and hyperpigmentation of the skin.47 When FICRD has progressed to dermal fibrosis, patients can present with indurated plaques without ulcerations, which can be hard to differentiate from morphea.16,48 However, the presence of ulcerations or hyperkeratosis can differentiate morphea from FICRD.16
Ultimately, it is the location of FICRD lesions that remains the biggest diagnostic clue. Any suspicious lesion present on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and/or mid back should prompt an investigation into recent or remote history of fluoroscopic procedures.
Management of FICRD
Diagnosis of FICRD should be made clinically based on the history and physical examination whenever possible, since a biopsy is not recommended.35 Wound healing in FICRD is delayed, and biopsies can lead to ulcerations or secondary infections.17 Therefore, it is important to remain suspicious for FICRD. Management of FICRD should correspond to the clinical findings outlined by a recent Delphi consensus survey.49 Regardless, the core of FICRD management framework should always include good hygiene, maintenance of skin hydration to improve epithelialization, and sufficient photoprotection.49,50
Among the first signs of FICRD are telangiectasias. Although asymptomatic, their appearance can be distressing for patients. Pulsed dye laser therapy is a first-line option that has been studied and has shown clinical efficacy for treatment of telangiectasias and vascular changes in patients with FICRD.49,51
If patients develop fibrotic changes, treatment options are limited. Fibrosis is hard to reverse, and the management approach is limited to symptomatic relief. Mechanical and deep-friction massages have been shown to be effective at reducing skin induration in patients.52 Fractional ablative lasers also may be utilized for skin contractures, especially if range of motion is affected.53,54 Although it comes with its own challenges, autologous fat grafting has shown promise in reducing postradiation fibrosis and inducing angiogenesis in tissue.55 Oral pentoxifylline also has shown mild efficacy, as it may be able to suppress TGF-β1 levels.53 However, prevention of fibrotic changes may be the most important. Wei et al31 suggested that low-dose oral prednisolone at 5 mg twice daily for 3 weeks might be an option to prevent the progression of skin changes and even reverse fibrosis to an extent; however, further evidence regarding its efficacy still is necessary. Additionally, no evidence was identified to support the use of topical corticosteroids for fibrotic changes seen in FICRD.56
Patients with FICRD or even acute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy tend to develop superficial ulcerations from minor traumas. Good wound hygiene, antiseptic care, and absorbent dressings, such as hydrogel and hydrocolloid, may be sufficient for treating these wounds, as seen in the Figure.42,48 However, once patients develop refractory ulcerations or necrosis, treatment options are then limited to surgical removal with a flap or graft.5,33,42,45
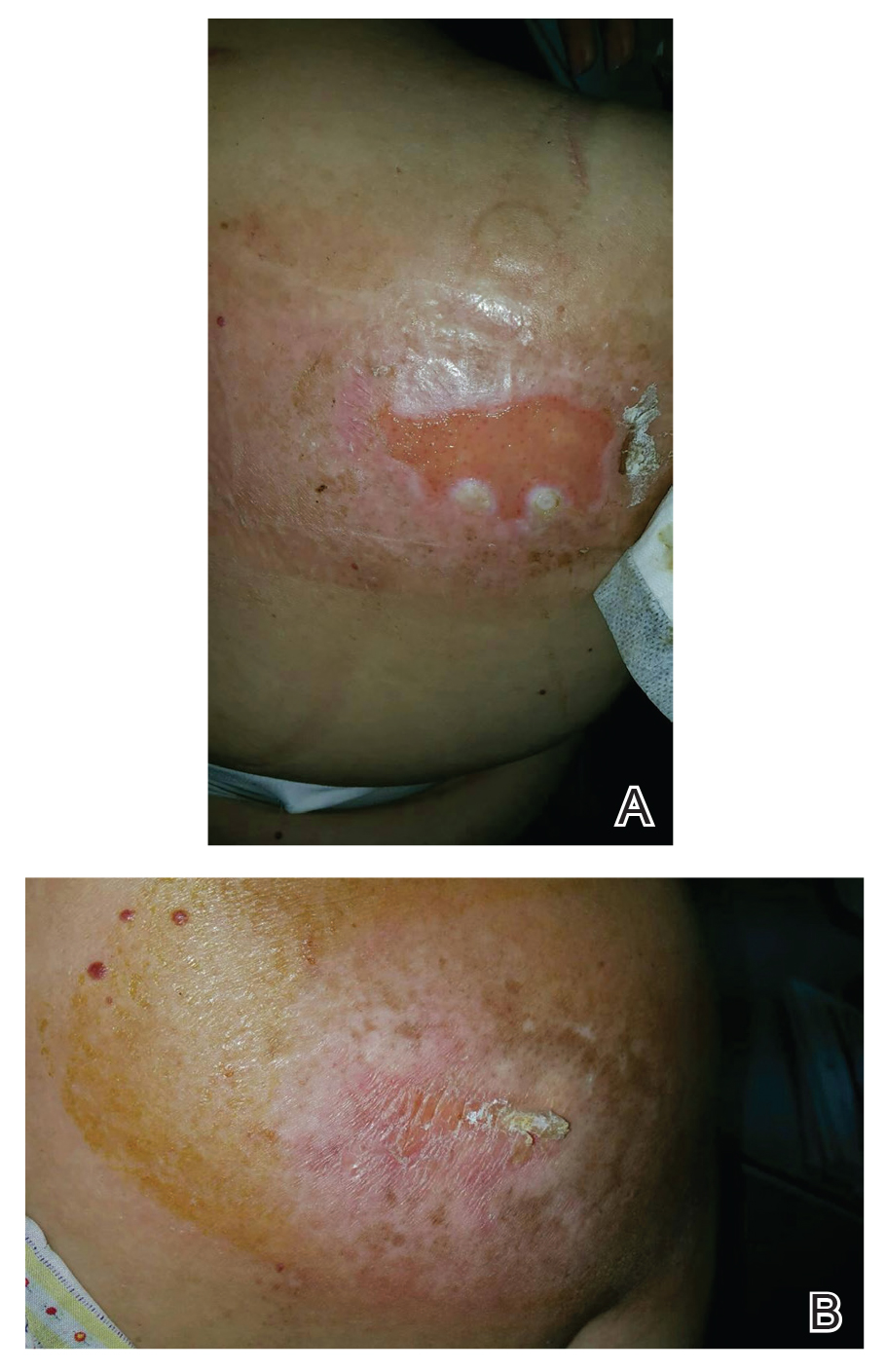
Risk for basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas is higher in patients with radiation exposure; however, the exact risk from fluoroscopic procedures is unknown. One study demonstrated an increased risk of 6.9% in development of skin cancer after a median radiation exposure of 15.5 Gy and a mean latency period of 38.3 years,57 and in another retrospective study, the risk was higher in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II.58 Unlike the development of radiodermatitis itself, which shows a dose-dependent response, development of skin cancers follows a stochastic pattern (not dose dependent).59 Therefore, it is important to identify these high-risk patients and establish follow-up.
Conclusion
Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis can be a diagnostic challenge, as skin changes may not be readily associated with the procedure by patients. Therefore, any lesion with a geometric shape and accompanying chronic radiation dermatitis features located on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and midback should prompt an investigation into history of fluoroscopic procedures. Treatment of chronic skin changes in FICRD depends on the clinical manifestations. Good hygiene, skin hydration, and sufficient photoprotection are crucial. Finally, long-term monitoring with skin examinations is important to assess for the development of skin cancers in the treated area.
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:E56-E528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. Published correction appears in Circulation. 2020;141:E33.
- Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, et al. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:3-11. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770003
- Guesnier-Dopagne M, Boyer L, Pereira B, et al. Incidence of chronic radiodermatitis after fluoroscopically guided interventions: a retrospective study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:692-698.e13. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2019.01.010
- Cunha N, Cardoso P, Cabete J. Subacute radiation dermatitis following an interventional cardiology procedure. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017;36:297-299. doi:10.1080/15569527.2016.1254649
- Frazier TH, Richardson JB, Fabré VC, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation skin injury: a disease perhaps often overlooked. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:637-640. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.5.637
- Koenig TR, Mettler FA, Wagner LK. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 2, review of 73 cases and recommendations for minimizing dose delivered to patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:13-20. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770013
- Shope TB. Radiation-induced skin injuries from fluoroscopy. Radiographics. 1996;16:1195-1199. doi:10.1148/radiographics.16.5.8888398
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Isseroff RR, Silverstein MA. Fluoroscopy induced chronic radiation dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis of notalgia paresthetica. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0kh726m9.
- Berlin L. Radiation-induced skin injuries and fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:21-25. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770021
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Kamangar F, Ho B, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced radionecrosis. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt68w910t2.
- Wagner LK, Eifel PJ, Geise RA. Potential biological effects following high X-ray dose interventional procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1994;5:71-84. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(94)71456-1
- Balter S, Hopewell JW, Miller DL, et al. Fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures: a review of radiation effects on patients’ skin and hair. Radiology. 2010;254:326-341. doi:10.1148/radiol.2542082312
- Vance AZ, Weinberg BD, Arbique GM, et al. Fluoroscopic sentinel events in neuroendovascular procedures: how to screen, prevent, and address occurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:1513-1515. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3185
- Aerts A, Decraene T, van den Oord JJ, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following percutaneous coronary interventions: a report of two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:340-343. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2003.00687.x
- Rosenthal A, Israilevich R, Moy R. Management of acute radiation dermatitis: a review of the literature and proposal for treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:558-567. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.047
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Spiker A, Zinn Z, Carter WH, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:1861-1863. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.023
- Batrani M, Kubba A, Sundharam J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis masquerading as morphea: a diagnostic pitfall. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018;61:393-396. doi:10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_566_17
- Jeskowiak A, Hubmer M, Prenner G, et al. Radiation induced cutaneous ulcer on the back in a patient with congenital anomaly of the upper cava system. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011;12:290-292.
- Laborda A, De Assis AM, Ioakeim I, et al. Radiodermitis after prostatic artery embolization: case report and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:755-759. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1083-6
- Lyons AB, Harvey VM, Gusev J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD) after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm endoleak repair. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:403-405. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.09.022
- Mossman KL. Analysis of risk in computerized tomography and other diagnostic radiology procedures. Comput Radiol. 1982;6:251-256. doi:10.1016/0730-4862(82)90109-3
- Henry MF, Maender JL, Shen Y, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of three cases. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:3.
- Balter S, Miller DL. Patient skin reactions from interventional fluoroscopy procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202:W335-W342. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.12029
- Nishimoto S, Fukuda K, Kawai K, et al. Supplementation of bone marrow aspirate-derived platelet-rich plasma for treating radiation-induced ulcer after cardiac fluoroscopic procedures: a preliminary report. Indian J Plast Surg. 2012;45:109-114. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.96599
- Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:1341-1346. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(95)00060-C
- Wong RK, Bensadoun RJ, Boers-Doets CB, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of acute and late radiation reactions from the MASCC Skin Toxicity Study Group. Support Care Cancer. 2013;21:2933-2948. doi:10.1007/s00520-013-1896-2
- Turesson I, Notter G. The predictive value of skin telangiectasia for late radiation effects in different normal tissues. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12:603-609. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90069-6
- Hegedus F, Mathew LM, Schwartz RA. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:909-914. doi:10.1111/ijd.13371
- Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M. The radiotherapeutic injury—a complex ‘wound.’ Radiother Oncol. 2002;63:129-145. doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00060-9
- Wei KC, Lai SF, Huang WL, et al. An innovative targeted therapy for fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100:135-146. doi:10.1007/s00109-021-02146-3
- Sitton E. Early and late radiation-induced skin alterations. part I: mechanisms of skin changes. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1992;19:801-807.
- Pruitt LG, Rogers W, Byarlay JA, et al. Subacute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1091-1095. doi:10.1111/cup.12815
- Anderson EB, Draft KS, Lee RA, et al. Update in dermatopathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125(Suppl):S50-S70. doi:10.1309/GMUFNP6LFMPNR86R
- Wei KC, Yang KC, Mar GY, et al. STROBE—radiation ulcer: an overlooked complication of fluoroscopic intervention: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e2178. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002178
- Otterburn D, Losken A. Iatrogenic fluoroscopy injury to the skin. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65:462-465. doi:10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181d6e2d3
- Cha MJ, Jo SJ, Cho Y, et al. Patient characteristics and the incidence of radiation-induced dermatitis following radiofrequency catheter ablation. Korean Circ J. 2016;46:646-653. doi:10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.646
- Dehen L, Vilmer C, Humilière C, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following cardiac catheterisation: a report of two cases and a brief review of the literature. Heart. 1999;81:308-312. doi:10.1136/hrt.81.3.308
- Brown KR, Rzucidlo E. Acute and chronic radiation injury. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53(Suppl 1):15S-21S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.175. Published correction appears in J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:627.
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Scheinman PL, Vocanson M, Thyssen JP, et al. Contact dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00271-4
- Cheng TT, Yang HJ. Chronic radiation dermatitis induced by cardiac catheterization: a case report and literature review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2022;31:147-149.
- Minni JP, Nowak M, Usmani A, et al. A unique case of subacute radiodermatitis. Cutis. 2013;91:230-232.
- Flowers H, Brodell R, Brents M, et al. Fixed drug eruptions: presentation, diagnosis, and management. South Med J. 2014;107:724-727. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000195
- Hashimoto I, Sedo H, Inatsugi K, et al. Severe radiation-induced injury after cardiac catheter ablation: a case requiring free anterolateral thigh flap and vastus lateralis muscle flap reconstruction on the upper arm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:704-708. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2007.01.003
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure ulcers: pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:881-890. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.069
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Herz-Ruelas ME, Gómez-Flores M, Moxica-Del Angel J, et al. Ulcerated radiodermatitis induced after fluoroscopically guided stent implantation angioplasty. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:768624. doi:10.1155/2014/768624
- Wilson BN, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Consensus on the clinical management of chronic radiation dermatitis and radiation fibrosis: a Delphi survey. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:1054-1056. doi:10.1111/bjd.21852
- Khanna NR, Kumar DP, Laskar SG, et al. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Indian J Burns. 2013;21:24-31. doi:10.4103/0971-653x.121877
- Spalek M. Chronic radiation-induced dermatitis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:473-482. doi:10.2147/CCID.S94320
- Bourgeois JF, Gourgou S, Kramar A, et al. A randomized, prospective study using the LPG technique in treating radiation-induced skin fibrosis: clinical and profilometric analysis. Skin Res Technol. 2008;14:71-76. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0846.2007.00263.x
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skinfibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4S Suppl 1):S59-S64. doi:10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Wilson B, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Laser therapy as a treatment for chronic radiation fibrosis. Lasers Surg Med. 2023;55:82-88. doi:10.1002/lsm.23617
- Rigotti G, Marchi A, Galiè M, et al. Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:1409-1422. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000256047.47909.71
- Leventhal J, Young MR. Radiation dermatitis: recognition, prevention, and management. Oncology (Williston Park). 2017;31:885-899.
- van Vloten WA, Hermans J, van Daal WA. Radiation-induced skin cancer and radiodermatitis of the head and neck. Cancer. 1987;59:411-414. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3<411::aid-cncr2820590310>3.0.co;2-z
- Davis MM, Hanke CW, Zollinger TW, et al. Skin cancer in patients with chronic radiation dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:608-616. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70072-4
- Miller DL, Balter S, Schueler BA, et al. Clinical radiation management for fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiology. 2010;257:321-332. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091269
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique that allows for real-time visualization of internal structures in the body using continuous radiography beams. More than 1 million fluoroscopy-guided procedures are performed annually in the United States.1 Utilization of these procedures continues to increase, and so does the probability of related complications, as prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation can cause skin injuries.2 Fortunately, the incidence of radiation-induced skin injuries compared with the total number of fluoroscopic procedures performed remains small,2 although one study suggested the incidence may be as high as 8.9% in at-risk populations.3
Radiation dermatitis is well recognized in dermatology as a complication of oncologic management; however, radiation dermatitis as a complication of fluoroscopic procedures is underrecognized.4 Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis can be categorized as acute, subacute, or chronic.5 Common fluoroscopic procedures that have been associated with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis include interventional cardiac procedures, neurovascular procedures, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures, and endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs.6,7
Patients with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis, particularly fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD), can present to dermatology up to several years after the initial fluoroscopy procedure with no awareness of the association between the procedure and their skin findings. This presents a diagnostic challenge, and FICRD often is overlooked.5,8-10
We conducted a literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms fluoroscopy and dermatitis. In this reappraisal, we will provide a comprehensive overview of fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis with an emphasis on FICRD, covering its clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, risk factors, differential diagnosis, histology, and management. The aim of this review is to highlight the salient features and mimickers of FICRD and inform readers how to approach suspected cases, leading to accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Pathophysiology
Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis is the result of dose-dependent radiation-induced tissue damage. As the peak skin dosage (PSD) of radiation increases over the course of a procedure or multiple procedures, the severity of skin injury predictably increases. During fluoroscopic procedures, the standard irradiation dosage ranges from 0.02 Gy/min to 0.05 Gy/min.11 Transient skin changes may start to be seen around 2 Gy of cumulative exposure. Fluoroscopic procedures typically range in duration from 60 to 120 minutes; however, complex cases may exceed that. Additionally, multiple procedures performed within shorter intervals can result in greater PSD accumulation. Shorter intervals between procedures do not allow enough time for damage repair from the previous procedure and can result in further severe damage when the skin is re-exposed to radiation.2 The American College of Radiology recommends medical follow-up after 10 Gy of cumulative exposure, while cumulative exposure above 15 Gy within a 6- to 12-month period is defined as a sentinel event, according to The Joint Commission.12-14
Depending on the patient’s total radiation dosage during one or more procedures, the result of the tissue damage manifests differently at varying times: early skin changes are categorized as fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis, and late skin changes are categorized as FICRD (Table 1).

Clinical Manifestations
Acute radiation dermatitis from fluoroscopic procedures manifests within hours to days up to 90 days following radiation exposure and can be characterized by erythema with blistering, desquamation, epilation, pigmentation changes, and even necrosis if the accumulated dosage exceeds 15 Gy.15 Chronic radiation dermatitis (which as related to fluoroscopic procedures is termed FICRD) has a longer onset of weeks to years and is clinically characterized by telangiectasias, permanent erythema, dermal atrophy, or ulcerations. Clinically, subacute radiation dermatitis shares features of both acute and chronic radiation dermatitis; therefore, it is differentiated based on its histologic features.5,16
Although fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis (Table 1) may precede FICRD, acute manifestations of fluoroscopy-related dermatitis can be subtle and often manifest in areas not easily visualized. Because referrals to dermatologists for full-skin examinations after fluoroscopy procedures are not standard, patients may not be aware of the association between these procedures and the development of skin lesions. Nonetheless, some patients may report a history of skin changes such as redness days or weeks after a fluoroscopic procedure with accompanying pain and pruritus limited to the fluoroscopy-exposed region, which tend to self-resolve.17 The risk for FICRD is thought to increase if a history of fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis is present.18
The location of the skin findings correlates to the area exposed to prolonged radiation during the procedure(s). The most common areas include the scapular and subscapular regions, the right lateral trunk inferior to the axilla, the mid back, and the right anterolateral chest.16,19,20 These regions are associated with more complex (eg, cardiac) procedures that have been reported to lead to prolonged radiation exposure. The skin findings in FICRD are described as geometric, corresponding to the squarish or rectangular radiography beam that is directed at the patient. Additionally, radiography beams spread outward as they travel in space; therefore, skin injuries are common at the region more distal to the path of origination of the beam.21-23 Subsequently, a geometric, dyspigmented, indurated or atrophic plaque with telangiectasias and erosions or ulcerations with progressive worsening is a common manifestation of FICRD.5,16,23 Patients also commonly present with pruritus or severe pain associated with the lesion.24,25
Dermatologic Manifestations of FICRD
Skin responses seen weeks to years after a fluoroscopic procedure and typically after cumulative radiation exposure of 10 Gy or greater are categorized as FICRD (Table 2). These changes also can be clinically graded based on the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group classification of radiation dermatitis (Tables 3 and 4).26 Chronic changes in the skin largely result from remodeling of the vasculature and the subcutaneous tissue over time. Unlike acute changes, chronic changes typically persist and continue to worsen.27



Telangiectasias—Anywhere from months to 1 year after exposure to 10 Gy of radiation, proliferation of atypical superficial vessels in the dermis can be seen, typically manifesting as telangiectasias on physical examination. Telangiectasias can increase with time and can even exhibit a dose-dependent relationship to the radiation exposure.28
Atrophy—Atrophic-appearing skin after radiation exposure is the result of direct injury to both the epidermis and fibroblasts in the dermis. The destruction of keratinocytes leads to a thin epidermis, and destruction of dermal fibroblasts causes insufficient collagen production.29 Clinically, this process manifests as an atrophic plaque that can be seen 12 weeks to 1 year after the procedure.
Fibrosis—Approximately 1 year after the exposure, the initial damage can lead to disruption of molecular pathways, causing fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 is the main factor involved.29 Damage to the endothelial cells results in increased TGF-β1 levels, which causes increased stimulation of remaining atypical fibroblasts and thus increased irregular collagen deposition.30 Further adding to this knowledge, Wei et al31 recently proposed that damage to the epidermal keratinocytes leads to disruption of yes-associated protein 1, which is a protective factor released from keratinocytes that regulates the dermal fibroblasts. However, extensive damage to the keratinocytes can lead to lower yes-associated protein 1 levels and its downstream activity, leading to increased levels of TGF-β1 and fibroblast activity.31 Clinically, this fibrotic stage is seen as indurated plaques in patients.
Necrosis—There are 2 forms of necrosis that can be seen. Ischemic dermal necrosis typically occurs in the acute phase after 10 weeks and approximately 18 Gy of cumulative exposure. It results from substantial skin damage, including microvascular damage and reduction in dermal capillaries, leading to ischemia of the tissue.2 Late dermal necrosis is the process seen in the chronic stage of FICRD and radiation dermatitis not related to fluoroscopy. It results from the inability of the fibrotic dermis to vascularly support the epidermis above it.2 It can be seen anywhere from 1 to 4 years after the procedure. This stage clinically manifests as worsening ulcerations with major pain and increased risk for secondary infections.16
Dyspigmentation—Dyspigmentation at the site of the radiation exposure can be seen acutely and chronically. Dosage above 15 to 18 Gy can lead to destruction of melanocytes, which can cause hypopigmentation in exposed areas. However, melanocytes are relatively resistant to radiation; therefore, dosages below the threshold of destruction of 15 to 18 Gy can cause melanocytic hyperactivity leading to hyperpigmentation.32 Hence, pigmentary changes can vary greatly. Classically, a central area of hypopigmentation with surrounding hyperpigmentation is seen.
Histology
Histologic appearance of radiation dermatitis varies depending on its stage. Acute radiation dermatitis primarily demonstrates superficial dermal edema, damage to the basal cell layer, small vessel dilation with thrombi, and hemorrhage along with a sparse inflammatory cell infiltrate.33 Histology typically is the only way to characterize subacute radiation dermatitis.5 Lichenoid tissue reaction is its characteristic feature. Mononuclear cells are found adjected to necrotic keratinocytes along with prominent vacuolization of the basal cell layer.33
The key histologic features of chronic radiation dermatitis include epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, telangiectasias, loss of adnexal structures, and dermal fibrosis along with sparse atypical stellate fibroblasts.34 However, clinical context of fluoroscopic exposure is required for the dermatopathologist to differentiate chronic radiation dermatitis from its histologic differential of morphea and lichen sclerosus. In a cross-sectional study, only 1 of 6 cases (16.7%) was correctly diagnosed as chronic radiation dermatitis in the absence of correlating clinical history.35
Risk Factors for FICRD
Since the diagnosis of FICRD can be a clinical challenge, understanding the risk factors can be helpful. The general likelihood of developing FICRD is related to the duration, frequency, interval, intensity, and area of radiation exposure. Procedures exceeding the normal duration of 60 to 120 minutes have been well documented as a substantial risk factor for radiation dermatitis and FICRD.36-38 The risk tends to be higher in longer procedures because they result in more radiation exposure and higher accumulated PSD. Obesity (ie, body mass index >26) is the major risk factor that has been associated with longer procedure times, as higher radiation dosages are necessary to penetrate the body of a larger patient and a larger skin surface area is exposed.37-39
Other risk factors associated with FICRD relate to how prone a patient is to radiation-induced DNA damage. Older patients are at higher risk due to lower intrinsic ability of the tissue to repair itself.11 Patients with a history of connective tissue diseases—particularly lupus, scleroderma, and mixed connective tissue disease—are at an increased risk.40 Furthermore, patients with genetic disorders that impair DNA repair are more susceptible to radiation-induced DNA damage; therefore, patients with ataxia-telangiectasia, xeroderma pigmentosum, Fanconi anemia, and hereditary nevoid basal cell carcinoma are at higher risk for FICRD.39 Similarly, medications that can affect DNA repair also have been shown to be risk factors. These medications include chemotherapeutic agents such as actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil.2,39 Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and tobacco use also have been shown to increase a patient’s risk for FICRD.39 It also is reasonable to believe that patients with defects in fibroblasts or with elastin or collagen disorders (eg, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) would be at higher risk, but there are no known studies highlighting the association in the literature.
Differential Diagnosis of FICRD
Acute allergic or irritant contact dermatitis manifests with a localized area of erythematous skin accompanied by pruritus.41 Patients with FICRD can present with a localized area of erythema and hyperpigmentation with minimal atrophy. The lesion may accompany substantial pruritus, which can favor the more common diagnosis of contact dermatitis.35,42,43
Fixed-drug eruption manifests as a well-defined, hyperpigmented plaque in a fixed location that occurs upon ingestion of a drug.44 Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis lesions are well demarcated and geometrically shaped and therefore can mimic lesions seen in fixed-drug eruptions.45 Additionally, the patient population undergoing fluoroscopic procedures tends to have major comorbidities requiring multiple medications.4
Decubitus ulcers are a result of vascular compromise to an area of skin due to constant pressure and are most commonly seen in the sacral region of patients with obesity.46 Ulcerated FICRD lesions can manifest on the lower midback. These lesions can be seen after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm or prostatic artery embolization.20,21 The location of these lesions can mimic decubitus ulcers if fluoroscopic history is unknown. As mentioned, obesity also increases the risk for FICRD.
Morphea can manifest as a localized area of induration and hyperpigmentation of the skin.47 When FICRD has progressed to dermal fibrosis, patients can present with indurated plaques without ulcerations, which can be hard to differentiate from morphea.16,48 However, the presence of ulcerations or hyperkeratosis can differentiate morphea from FICRD.16
Ultimately, it is the location of FICRD lesions that remains the biggest diagnostic clue. Any suspicious lesion present on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and/or mid back should prompt an investigation into recent or remote history of fluoroscopic procedures.
Management of FICRD
Diagnosis of FICRD should be made clinically based on the history and physical examination whenever possible, since a biopsy is not recommended.35 Wound healing in FICRD is delayed, and biopsies can lead to ulcerations or secondary infections.17 Therefore, it is important to remain suspicious for FICRD. Management of FICRD should correspond to the clinical findings outlined by a recent Delphi consensus survey.49 Regardless, the core of FICRD management framework should always include good hygiene, maintenance of skin hydration to improve epithelialization, and sufficient photoprotection.49,50
Among the first signs of FICRD are telangiectasias. Although asymptomatic, their appearance can be distressing for patients. Pulsed dye laser therapy is a first-line option that has been studied and has shown clinical efficacy for treatment of telangiectasias and vascular changes in patients with FICRD.49,51
If patients develop fibrotic changes, treatment options are limited. Fibrosis is hard to reverse, and the management approach is limited to symptomatic relief. Mechanical and deep-friction massages have been shown to be effective at reducing skin induration in patients.52 Fractional ablative lasers also may be utilized for skin contractures, especially if range of motion is affected.53,54 Although it comes with its own challenges, autologous fat grafting has shown promise in reducing postradiation fibrosis and inducing angiogenesis in tissue.55 Oral pentoxifylline also has shown mild efficacy, as it may be able to suppress TGF-β1 levels.53 However, prevention of fibrotic changes may be the most important. Wei et al31 suggested that low-dose oral prednisolone at 5 mg twice daily for 3 weeks might be an option to prevent the progression of skin changes and even reverse fibrosis to an extent; however, further evidence regarding its efficacy still is necessary. Additionally, no evidence was identified to support the use of topical corticosteroids for fibrotic changes seen in FICRD.56
Patients with FICRD or even acute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy tend to develop superficial ulcerations from minor traumas. Good wound hygiene, antiseptic care, and absorbent dressings, such as hydrogel and hydrocolloid, may be sufficient for treating these wounds, as seen in the Figure.42,48 However, once patients develop refractory ulcerations or necrosis, treatment options are then limited to surgical removal with a flap or graft.5,33,42,45

Risk for basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas is higher in patients with radiation exposure; however, the exact risk from fluoroscopic procedures is unknown. One study demonstrated an increased risk of 6.9% in development of skin cancer after a median radiation exposure of 15.5 Gy and a mean latency period of 38.3 years,57 and in another retrospective study, the risk was higher in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II.58 Unlike the development of radiodermatitis itself, which shows a dose-dependent response, development of skin cancers follows a stochastic pattern (not dose dependent).59 Therefore, it is important to identify these high-risk patients and establish follow-up.
Conclusion
Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis can be a diagnostic challenge, as skin changes may not be readily associated with the procedure by patients. Therefore, any lesion with a geometric shape and accompanying chronic radiation dermatitis features located on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and midback should prompt an investigation into history of fluoroscopic procedures. Treatment of chronic skin changes in FICRD depends on the clinical manifestations. Good hygiene, skin hydration, and sufficient photoprotection are crucial. Finally, long-term monitoring with skin examinations is important to assess for the development of skin cancers in the treated area.
Fluoroscopy is an imaging technique that allows for real-time visualization of internal structures in the body using continuous radiography beams. More than 1 million fluoroscopy-guided procedures are performed annually in the United States.1 Utilization of these procedures continues to increase, and so does the probability of related complications, as prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation can cause skin injuries.2 Fortunately, the incidence of radiation-induced skin injuries compared with the total number of fluoroscopic procedures performed remains small,2 although one study suggested the incidence may be as high as 8.9% in at-risk populations.3
Radiation dermatitis is well recognized in dermatology as a complication of oncologic management; however, radiation dermatitis as a complication of fluoroscopic procedures is underrecognized.4 Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis can be categorized as acute, subacute, or chronic.5 Common fluoroscopic procedures that have been associated with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis include interventional cardiac procedures, neurovascular procedures, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures, and endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repairs.6,7
Patients with fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis, particularly fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD), can present to dermatology up to several years after the initial fluoroscopy procedure with no awareness of the association between the procedure and their skin findings. This presents a diagnostic challenge, and FICRD often is overlooked.5,8-10
We conducted a literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms fluoroscopy and dermatitis. In this reappraisal, we will provide a comprehensive overview of fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis with an emphasis on FICRD, covering its clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, risk factors, differential diagnosis, histology, and management. The aim of this review is to highlight the salient features and mimickers of FICRD and inform readers how to approach suspected cases, leading to accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Pathophysiology
Fluoroscopy-induced radiation dermatitis is the result of dose-dependent radiation-induced tissue damage. As the peak skin dosage (PSD) of radiation increases over the course of a procedure or multiple procedures, the severity of skin injury predictably increases. During fluoroscopic procedures, the standard irradiation dosage ranges from 0.02 Gy/min to 0.05 Gy/min.11 Transient skin changes may start to be seen around 2 Gy of cumulative exposure. Fluoroscopic procedures typically range in duration from 60 to 120 minutes; however, complex cases may exceed that. Additionally, multiple procedures performed within shorter intervals can result in greater PSD accumulation. Shorter intervals between procedures do not allow enough time for damage repair from the previous procedure and can result in further severe damage when the skin is re-exposed to radiation.2 The American College of Radiology recommends medical follow-up after 10 Gy of cumulative exposure, while cumulative exposure above 15 Gy within a 6- to 12-month period is defined as a sentinel event, according to The Joint Commission.12-14
Depending on the patient’s total radiation dosage during one or more procedures, the result of the tissue damage manifests differently at varying times: early skin changes are categorized as fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis, and late skin changes are categorized as FICRD (Table 1).

Clinical Manifestations
Acute radiation dermatitis from fluoroscopic procedures manifests within hours to days up to 90 days following radiation exposure and can be characterized by erythema with blistering, desquamation, epilation, pigmentation changes, and even necrosis if the accumulated dosage exceeds 15 Gy.15 Chronic radiation dermatitis (which as related to fluoroscopic procedures is termed FICRD) has a longer onset of weeks to years and is clinically characterized by telangiectasias, permanent erythema, dermal atrophy, or ulcerations. Clinically, subacute radiation dermatitis shares features of both acute and chronic radiation dermatitis; therefore, it is differentiated based on its histologic features.5,16
Although fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis (Table 1) may precede FICRD, acute manifestations of fluoroscopy-related dermatitis can be subtle and often manifest in areas not easily visualized. Because referrals to dermatologists for full-skin examinations after fluoroscopy procedures are not standard, patients may not be aware of the association between these procedures and the development of skin lesions. Nonetheless, some patients may report a history of skin changes such as redness days or weeks after a fluoroscopic procedure with accompanying pain and pruritus limited to the fluoroscopy-exposed region, which tend to self-resolve.17 The risk for FICRD is thought to increase if a history of fluoroscopy-induced acute radiation dermatitis is present.18
The location of the skin findings correlates to the area exposed to prolonged radiation during the procedure(s). The most common areas include the scapular and subscapular regions, the right lateral trunk inferior to the axilla, the mid back, and the right anterolateral chest.16,19,20 These regions are associated with more complex (eg, cardiac) procedures that have been reported to lead to prolonged radiation exposure. The skin findings in FICRD are described as geometric, corresponding to the squarish or rectangular radiography beam that is directed at the patient. Additionally, radiography beams spread outward as they travel in space; therefore, skin injuries are common at the region more distal to the path of origination of the beam.21-23 Subsequently, a geometric, dyspigmented, indurated or atrophic plaque with telangiectasias and erosions or ulcerations with progressive worsening is a common manifestation of FICRD.5,16,23 Patients also commonly present with pruritus or severe pain associated with the lesion.24,25
Dermatologic Manifestations of FICRD
Skin responses seen weeks to years after a fluoroscopic procedure and typically after cumulative radiation exposure of 10 Gy or greater are categorized as FICRD (Table 2). These changes also can be clinically graded based on the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group classification of radiation dermatitis (Tables 3 and 4).26 Chronic changes in the skin largely result from remodeling of the vasculature and the subcutaneous tissue over time. Unlike acute changes, chronic changes typically persist and continue to worsen.27



Telangiectasias—Anywhere from months to 1 year after exposure to 10 Gy of radiation, proliferation of atypical superficial vessels in the dermis can be seen, typically manifesting as telangiectasias on physical examination. Telangiectasias can increase with time and can even exhibit a dose-dependent relationship to the radiation exposure.28
Atrophy—Atrophic-appearing skin after radiation exposure is the result of direct injury to both the epidermis and fibroblasts in the dermis. The destruction of keratinocytes leads to a thin epidermis, and destruction of dermal fibroblasts causes insufficient collagen production.29 Clinically, this process manifests as an atrophic plaque that can be seen 12 weeks to 1 year after the procedure.
Fibrosis—Approximately 1 year after the exposure, the initial damage can lead to disruption of molecular pathways, causing fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 is the main factor involved.29 Damage to the endothelial cells results in increased TGF-β1 levels, which causes increased stimulation of remaining atypical fibroblasts and thus increased irregular collagen deposition.30 Further adding to this knowledge, Wei et al31 recently proposed that damage to the epidermal keratinocytes leads to disruption of yes-associated protein 1, which is a protective factor released from keratinocytes that regulates the dermal fibroblasts. However, extensive damage to the keratinocytes can lead to lower yes-associated protein 1 levels and its downstream activity, leading to increased levels of TGF-β1 and fibroblast activity.31 Clinically, this fibrotic stage is seen as indurated plaques in patients.
Necrosis—There are 2 forms of necrosis that can be seen. Ischemic dermal necrosis typically occurs in the acute phase after 10 weeks and approximately 18 Gy of cumulative exposure. It results from substantial skin damage, including microvascular damage and reduction in dermal capillaries, leading to ischemia of the tissue.2 Late dermal necrosis is the process seen in the chronic stage of FICRD and radiation dermatitis not related to fluoroscopy. It results from the inability of the fibrotic dermis to vascularly support the epidermis above it.2 It can be seen anywhere from 1 to 4 years after the procedure. This stage clinically manifests as worsening ulcerations with major pain and increased risk for secondary infections.16
Dyspigmentation—Dyspigmentation at the site of the radiation exposure can be seen acutely and chronically. Dosage above 15 to 18 Gy can lead to destruction of melanocytes, which can cause hypopigmentation in exposed areas. However, melanocytes are relatively resistant to radiation; therefore, dosages below the threshold of destruction of 15 to 18 Gy can cause melanocytic hyperactivity leading to hyperpigmentation.32 Hence, pigmentary changes can vary greatly. Classically, a central area of hypopigmentation with surrounding hyperpigmentation is seen.
Histology
Histologic appearance of radiation dermatitis varies depending on its stage. Acute radiation dermatitis primarily demonstrates superficial dermal edema, damage to the basal cell layer, small vessel dilation with thrombi, and hemorrhage along with a sparse inflammatory cell infiltrate.33 Histology typically is the only way to characterize subacute radiation dermatitis.5 Lichenoid tissue reaction is its characteristic feature. Mononuclear cells are found adjected to necrotic keratinocytes along with prominent vacuolization of the basal cell layer.33
The key histologic features of chronic radiation dermatitis include epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, telangiectasias, loss of adnexal structures, and dermal fibrosis along with sparse atypical stellate fibroblasts.34 However, clinical context of fluoroscopic exposure is required for the dermatopathologist to differentiate chronic radiation dermatitis from its histologic differential of morphea and lichen sclerosus. In a cross-sectional study, only 1 of 6 cases (16.7%) was correctly diagnosed as chronic radiation dermatitis in the absence of correlating clinical history.35
Risk Factors for FICRD
Since the diagnosis of FICRD can be a clinical challenge, understanding the risk factors can be helpful. The general likelihood of developing FICRD is related to the duration, frequency, interval, intensity, and area of radiation exposure. Procedures exceeding the normal duration of 60 to 120 minutes have been well documented as a substantial risk factor for radiation dermatitis and FICRD.36-38 The risk tends to be higher in longer procedures because they result in more radiation exposure and higher accumulated PSD. Obesity (ie, body mass index >26) is the major risk factor that has been associated with longer procedure times, as higher radiation dosages are necessary to penetrate the body of a larger patient and a larger skin surface area is exposed.37-39
Other risk factors associated with FICRD relate to how prone a patient is to radiation-induced DNA damage. Older patients are at higher risk due to lower intrinsic ability of the tissue to repair itself.11 Patients with a history of connective tissue diseases—particularly lupus, scleroderma, and mixed connective tissue disease—are at an increased risk.40 Furthermore, patients with genetic disorders that impair DNA repair are more susceptible to radiation-induced DNA damage; therefore, patients with ataxia-telangiectasia, xeroderma pigmentosum, Fanconi anemia, and hereditary nevoid basal cell carcinoma are at higher risk for FICRD.39 Similarly, medications that can affect DNA repair also have been shown to be risk factors. These medications include chemotherapeutic agents such as actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil.2,39 Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and tobacco use also have been shown to increase a patient’s risk for FICRD.39 It also is reasonable to believe that patients with defects in fibroblasts or with elastin or collagen disorders (eg, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) would be at higher risk, but there are no known studies highlighting the association in the literature.
Differential Diagnosis of FICRD
Acute allergic or irritant contact dermatitis manifests with a localized area of erythematous skin accompanied by pruritus.41 Patients with FICRD can present with a localized area of erythema and hyperpigmentation with minimal atrophy. The lesion may accompany substantial pruritus, which can favor the more common diagnosis of contact dermatitis.35,42,43
Fixed-drug eruption manifests as a well-defined, hyperpigmented plaque in a fixed location that occurs upon ingestion of a drug.44 Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis lesions are well demarcated and geometrically shaped and therefore can mimic lesions seen in fixed-drug eruptions.45 Additionally, the patient population undergoing fluoroscopic procedures tends to have major comorbidities requiring multiple medications.4
Decubitus ulcers are a result of vascular compromise to an area of skin due to constant pressure and are most commonly seen in the sacral region of patients with obesity.46 Ulcerated FICRD lesions can manifest on the lower midback. These lesions can be seen after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm or prostatic artery embolization.20,21 The location of these lesions can mimic decubitus ulcers if fluoroscopic history is unknown. As mentioned, obesity also increases the risk for FICRD.
Morphea can manifest as a localized area of induration and hyperpigmentation of the skin.47 When FICRD has progressed to dermal fibrosis, patients can present with indurated plaques without ulcerations, which can be hard to differentiate from morphea.16,48 However, the presence of ulcerations or hyperkeratosis can differentiate morphea from FICRD.16
Ultimately, it is the location of FICRD lesions that remains the biggest diagnostic clue. Any suspicious lesion present on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and/or mid back should prompt an investigation into recent or remote history of fluoroscopic procedures.
Management of FICRD
Diagnosis of FICRD should be made clinically based on the history and physical examination whenever possible, since a biopsy is not recommended.35 Wound healing in FICRD is delayed, and biopsies can lead to ulcerations or secondary infections.17 Therefore, it is important to remain suspicious for FICRD. Management of FICRD should correspond to the clinical findings outlined by a recent Delphi consensus survey.49 Regardless, the core of FICRD management framework should always include good hygiene, maintenance of skin hydration to improve epithelialization, and sufficient photoprotection.49,50
Among the first signs of FICRD are telangiectasias. Although asymptomatic, their appearance can be distressing for patients. Pulsed dye laser therapy is a first-line option that has been studied and has shown clinical efficacy for treatment of telangiectasias and vascular changes in patients with FICRD.49,51
If patients develop fibrotic changes, treatment options are limited. Fibrosis is hard to reverse, and the management approach is limited to symptomatic relief. Mechanical and deep-friction massages have been shown to be effective at reducing skin induration in patients.52 Fractional ablative lasers also may be utilized for skin contractures, especially if range of motion is affected.53,54 Although it comes with its own challenges, autologous fat grafting has shown promise in reducing postradiation fibrosis and inducing angiogenesis in tissue.55 Oral pentoxifylline also has shown mild efficacy, as it may be able to suppress TGF-β1 levels.53 However, prevention of fibrotic changes may be the most important. Wei et al31 suggested that low-dose oral prednisolone at 5 mg twice daily for 3 weeks might be an option to prevent the progression of skin changes and even reverse fibrosis to an extent; however, further evidence regarding its efficacy still is necessary. Additionally, no evidence was identified to support the use of topical corticosteroids for fibrotic changes seen in FICRD.56
Patients with FICRD or even acute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy tend to develop superficial ulcerations from minor traumas. Good wound hygiene, antiseptic care, and absorbent dressings, such as hydrogel and hydrocolloid, may be sufficient for treating these wounds, as seen in the Figure.42,48 However, once patients develop refractory ulcerations or necrosis, treatment options are then limited to surgical removal with a flap or graft.5,33,42,45

Risk for basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas is higher in patients with radiation exposure; however, the exact risk from fluoroscopic procedures is unknown. One study demonstrated an increased risk of 6.9% in development of skin cancer after a median radiation exposure of 15.5 Gy and a mean latency period of 38.3 years,57 and in another retrospective study, the risk was higher in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II.58 Unlike the development of radiodermatitis itself, which shows a dose-dependent response, development of skin cancers follows a stochastic pattern (not dose dependent).59 Therefore, it is important to identify these high-risk patients and establish follow-up.
Conclusion
Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis can be a diagnostic challenge, as skin changes may not be readily associated with the procedure by patients. Therefore, any lesion with a geometric shape and accompanying chronic radiation dermatitis features located on the scapular or subscapular areas, anterolateral chest, and midback should prompt an investigation into history of fluoroscopic procedures. Treatment of chronic skin changes in FICRD depends on the clinical manifestations. Good hygiene, skin hydration, and sufficient photoprotection are crucial. Finally, long-term monitoring with skin examinations is important to assess for the development of skin cancers in the treated area.
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:E56-E528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. Published correction appears in Circulation. 2020;141:E33.
- Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, et al. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:3-11. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770003
- Guesnier-Dopagne M, Boyer L, Pereira B, et al. Incidence of chronic radiodermatitis after fluoroscopically guided interventions: a retrospective study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:692-698.e13. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2019.01.010
- Cunha N, Cardoso P, Cabete J. Subacute radiation dermatitis following an interventional cardiology procedure. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017;36:297-299. doi:10.1080/15569527.2016.1254649
- Frazier TH, Richardson JB, Fabré VC, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation skin injury: a disease perhaps often overlooked. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:637-640. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.5.637
- Koenig TR, Mettler FA, Wagner LK. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 2, review of 73 cases and recommendations for minimizing dose delivered to patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:13-20. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770013
- Shope TB. Radiation-induced skin injuries from fluoroscopy. Radiographics. 1996;16:1195-1199. doi:10.1148/radiographics.16.5.8888398
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Isseroff RR, Silverstein MA. Fluoroscopy induced chronic radiation dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis of notalgia paresthetica. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0kh726m9.
- Berlin L. Radiation-induced skin injuries and fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:21-25. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770021
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Kamangar F, Ho B, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced radionecrosis. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt68w910t2.
- Wagner LK, Eifel PJ, Geise RA. Potential biological effects following high X-ray dose interventional procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1994;5:71-84. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(94)71456-1
- Balter S, Hopewell JW, Miller DL, et al. Fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures: a review of radiation effects on patients’ skin and hair. Radiology. 2010;254:326-341. doi:10.1148/radiol.2542082312
- Vance AZ, Weinberg BD, Arbique GM, et al. Fluoroscopic sentinel events in neuroendovascular procedures: how to screen, prevent, and address occurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:1513-1515. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3185
- Aerts A, Decraene T, van den Oord JJ, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following percutaneous coronary interventions: a report of two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:340-343. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2003.00687.x
- Rosenthal A, Israilevich R, Moy R. Management of acute radiation dermatitis: a review of the literature and proposal for treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:558-567. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.047
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Spiker A, Zinn Z, Carter WH, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:1861-1863. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.023
- Batrani M, Kubba A, Sundharam J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis masquerading as morphea: a diagnostic pitfall. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018;61:393-396. doi:10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_566_17
- Jeskowiak A, Hubmer M, Prenner G, et al. Radiation induced cutaneous ulcer on the back in a patient with congenital anomaly of the upper cava system. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011;12:290-292.
- Laborda A, De Assis AM, Ioakeim I, et al. Radiodermitis after prostatic artery embolization: case report and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:755-759. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1083-6
- Lyons AB, Harvey VM, Gusev J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD) after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm endoleak repair. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:403-405. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.09.022
- Mossman KL. Analysis of risk in computerized tomography and other diagnostic radiology procedures. Comput Radiol. 1982;6:251-256. doi:10.1016/0730-4862(82)90109-3
- Henry MF, Maender JL, Shen Y, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of three cases. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:3.
- Balter S, Miller DL. Patient skin reactions from interventional fluoroscopy procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202:W335-W342. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.12029
- Nishimoto S, Fukuda K, Kawai K, et al. Supplementation of bone marrow aspirate-derived platelet-rich plasma for treating radiation-induced ulcer after cardiac fluoroscopic procedures: a preliminary report. Indian J Plast Surg. 2012;45:109-114. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.96599
- Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:1341-1346. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(95)00060-C
- Wong RK, Bensadoun RJ, Boers-Doets CB, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of acute and late radiation reactions from the MASCC Skin Toxicity Study Group. Support Care Cancer. 2013;21:2933-2948. doi:10.1007/s00520-013-1896-2
- Turesson I, Notter G. The predictive value of skin telangiectasia for late radiation effects in different normal tissues. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12:603-609. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90069-6
- Hegedus F, Mathew LM, Schwartz RA. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:909-914. doi:10.1111/ijd.13371
- Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M. The radiotherapeutic injury—a complex ‘wound.’ Radiother Oncol. 2002;63:129-145. doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00060-9
- Wei KC, Lai SF, Huang WL, et al. An innovative targeted therapy for fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100:135-146. doi:10.1007/s00109-021-02146-3
- Sitton E. Early and late radiation-induced skin alterations. part I: mechanisms of skin changes. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1992;19:801-807.
- Pruitt LG, Rogers W, Byarlay JA, et al. Subacute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1091-1095. doi:10.1111/cup.12815
- Anderson EB, Draft KS, Lee RA, et al. Update in dermatopathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125(Suppl):S50-S70. doi:10.1309/GMUFNP6LFMPNR86R
- Wei KC, Yang KC, Mar GY, et al. STROBE—radiation ulcer: an overlooked complication of fluoroscopic intervention: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e2178. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002178
- Otterburn D, Losken A. Iatrogenic fluoroscopy injury to the skin. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65:462-465. doi:10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181d6e2d3
- Cha MJ, Jo SJ, Cho Y, et al. Patient characteristics and the incidence of radiation-induced dermatitis following radiofrequency catheter ablation. Korean Circ J. 2016;46:646-653. doi:10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.646
- Dehen L, Vilmer C, Humilière C, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following cardiac catheterisation: a report of two cases and a brief review of the literature. Heart. 1999;81:308-312. doi:10.1136/hrt.81.3.308
- Brown KR, Rzucidlo E. Acute and chronic radiation injury. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53(Suppl 1):15S-21S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.175. Published correction appears in J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:627.
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Scheinman PL, Vocanson M, Thyssen JP, et al. Contact dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00271-4
- Cheng TT, Yang HJ. Chronic radiation dermatitis induced by cardiac catheterization: a case report and literature review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2022;31:147-149.
- Minni JP, Nowak M, Usmani A, et al. A unique case of subacute radiodermatitis. Cutis. 2013;91:230-232.
- Flowers H, Brodell R, Brents M, et al. Fixed drug eruptions: presentation, diagnosis, and management. South Med J. 2014;107:724-727. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000195
- Hashimoto I, Sedo H, Inatsugi K, et al. Severe radiation-induced injury after cardiac catheter ablation: a case requiring free anterolateral thigh flap and vastus lateralis muscle flap reconstruction on the upper arm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:704-708. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2007.01.003
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure ulcers: pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:881-890. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.069
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Herz-Ruelas ME, Gómez-Flores M, Moxica-Del Angel J, et al. Ulcerated radiodermatitis induced after fluoroscopically guided stent implantation angioplasty. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:768624. doi:10.1155/2014/768624
- Wilson BN, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Consensus on the clinical management of chronic radiation dermatitis and radiation fibrosis: a Delphi survey. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:1054-1056. doi:10.1111/bjd.21852
- Khanna NR, Kumar DP, Laskar SG, et al. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Indian J Burns. 2013;21:24-31. doi:10.4103/0971-653x.121877
- Spalek M. Chronic radiation-induced dermatitis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:473-482. doi:10.2147/CCID.S94320
- Bourgeois JF, Gourgou S, Kramar A, et al. A randomized, prospective study using the LPG technique in treating radiation-induced skin fibrosis: clinical and profilometric analysis. Skin Res Technol. 2008;14:71-76. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0846.2007.00263.x
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skinfibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4S Suppl 1):S59-S64. doi:10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Wilson B, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Laser therapy as a treatment for chronic radiation fibrosis. Lasers Surg Med. 2023;55:82-88. doi:10.1002/lsm.23617
- Rigotti G, Marchi A, Galiè M, et al. Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:1409-1422. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000256047.47909.71
- Leventhal J, Young MR. Radiation dermatitis: recognition, prevention, and management. Oncology (Williston Park). 2017;31:885-899.
- van Vloten WA, Hermans J, van Daal WA. Radiation-induced skin cancer and radiodermatitis of the head and neck. Cancer. 1987;59:411-414. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3<411::aid-cncr2820590310>3.0.co;2-z
- Davis MM, Hanke CW, Zollinger TW, et al. Skin cancer in patients with chronic radiation dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:608-616. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70072-4
- Miller DL, Balter S, Schueler BA, et al. Clinical radiation management for fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiology. 2010;257:321-332. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091269
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:E56-E528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. Published correction appears in Circulation. 2020;141:E33.
- Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, et al. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:3-11. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770003
- Guesnier-Dopagne M, Boyer L, Pereira B, et al. Incidence of chronic radiodermatitis after fluoroscopically guided interventions: a retrospective study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:692-698.e13. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2019.01.010
- Cunha N, Cardoso P, Cabete J. Subacute radiation dermatitis following an interventional cardiology procedure. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017;36:297-299. doi:10.1080/15569527.2016.1254649
- Frazier TH, Richardson JB, Fabré VC, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation skin injury: a disease perhaps often overlooked. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:637-640. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.5.637
- Koenig TR, Mettler FA, Wagner LK. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 2, review of 73 cases and recommendations for minimizing dose delivered to patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:13-20. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770013
- Shope TB. Radiation-induced skin injuries from fluoroscopy. Radiographics. 1996;16:1195-1199. doi:10.1148/radiographics.16.5.8888398
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Isseroff RR, Silverstein MA. Fluoroscopy induced chronic radiation dermatitis should be included in the differential diagnosis of notalgia paresthetica. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0kh726m9.
- Berlin L. Radiation-induced skin injuries and fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:21-25. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.1.1770021
- Tchanque-Fossuo CN, Kamangar F, Ho B, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced radionecrosis. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt68w910t2.
- Wagner LK, Eifel PJ, Geise RA. Potential biological effects following high X-ray dose interventional procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1994;5:71-84. doi:10.1016/s1051-0443(94)71456-1
- Balter S, Hopewell JW, Miller DL, et al. Fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures: a review of radiation effects on patients’ skin and hair. Radiology. 2010;254:326-341. doi:10.1148/radiol.2542082312
- Vance AZ, Weinberg BD, Arbique GM, et al. Fluoroscopic sentinel events in neuroendovascular procedures: how to screen, prevent, and address occurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:1513-1515. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3185
- Aerts A, Decraene T, van den Oord JJ, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following percutaneous coronary interventions: a report of two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:340-343. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2003.00687.x
- Rosenthal A, Israilevich R, Moy R. Management of acute radiation dermatitis: a review of the literature and proposal for treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:558-567. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.047
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Spiker A, Zinn Z, Carter WH, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:1861-1863. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.023
- Batrani M, Kubba A, Sundharam J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis masquerading as morphea: a diagnostic pitfall. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018;61:393-396. doi:10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_566_17
- Jeskowiak A, Hubmer M, Prenner G, et al. Radiation induced cutaneous ulcer on the back in a patient with congenital anomaly of the upper cava system. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011;12:290-292.
- Laborda A, De Assis AM, Ioakeim I, et al. Radiodermitis after prostatic artery embolization: case report and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:755-759. doi:10.1007/s00270-015-1083-6
- Lyons AB, Harvey VM, Gusev J. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis (FICRD) after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm endoleak repair. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:403-405. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.09.022
- Mossman KL. Analysis of risk in computerized tomography and other diagnostic radiology procedures. Comput Radiol. 1982;6:251-256. doi:10.1016/0730-4862(82)90109-3
- Henry MF, Maender JL, Shen Y, et al. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of three cases. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:3.
- Balter S, Miller DL. Patient skin reactions from interventional fluoroscopy procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202:W335-W342. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.12029
- Nishimoto S, Fukuda K, Kawai K, et al. Supplementation of bone marrow aspirate-derived platelet-rich plasma for treating radiation-induced ulcer after cardiac fluoroscopic procedures: a preliminary report. Indian J Plast Surg. 2012;45:109-114. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.96599
- Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:1341-1346. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(95)00060-C
- Wong RK, Bensadoun RJ, Boers-Doets CB, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of acute and late radiation reactions from the MASCC Skin Toxicity Study Group. Support Care Cancer. 2013;21:2933-2948. doi:10.1007/s00520-013-1896-2
- Turesson I, Notter G. The predictive value of skin telangiectasia for late radiation effects in different normal tissues. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12:603-609. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90069-6
- Hegedus F, Mathew LM, Schwartz RA. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:909-914. doi:10.1111/ijd.13371
- Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M. The radiotherapeutic injury—a complex ‘wound.’ Radiother Oncol. 2002;63:129-145. doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00060-9
- Wei KC, Lai SF, Huang WL, et al. An innovative targeted therapy for fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100:135-146. doi:10.1007/s00109-021-02146-3
- Sitton E. Early and late radiation-induced skin alterations. part I: mechanisms of skin changes. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1992;19:801-807.
- Pruitt LG, Rogers W, Byarlay JA, et al. Subacute radiation dermatitis after fluoroscopy. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1091-1095. doi:10.1111/cup.12815
- Anderson EB, Draft KS, Lee RA, et al. Update in dermatopathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125(Suppl):S50-S70. doi:10.1309/GMUFNP6LFMPNR86R
- Wei KC, Yang KC, Mar GY, et al. STROBE—radiation ulcer: an overlooked complication of fluoroscopic intervention: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e2178. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002178
- Otterburn D, Losken A. Iatrogenic fluoroscopy injury to the skin. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65:462-465. doi:10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181d6e2d3
- Cha MJ, Jo SJ, Cho Y, et al. Patient characteristics and the incidence of radiation-induced dermatitis following radiofrequency catheter ablation. Korean Circ J. 2016;46:646-653. doi:10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.646
- Dehen L, Vilmer C, Humilière C, et al. Chronic radiodermatitis following cardiac catheterisation: a report of two cases and a brief review of the literature. Heart. 1999;81:308-312. doi:10.1136/hrt.81.3.308
- Brown KR, Rzucidlo E. Acute and chronic radiation injury. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53(Suppl 1):15S-21S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.175. Published correction appears in J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:627.
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Scheinman PL, Vocanson M, Thyssen JP, et al. Contact dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-021-00271-4
- Cheng TT, Yang HJ. Chronic radiation dermatitis induced by cardiac catheterization: a case report and literature review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2022;31:147-149.
- Minni JP, Nowak M, Usmani A, et al. A unique case of subacute radiodermatitis. Cutis. 2013;91:230-232.
- Flowers H, Brodell R, Brents M, et al. Fixed drug eruptions: presentation, diagnosis, and management. South Med J. 2014;107:724-727. doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000195
- Hashimoto I, Sedo H, Inatsugi K, et al. Severe radiation-induced injury after cardiac catheter ablation: a case requiring free anterolateral thigh flap and vastus lateralis muscle flap reconstruction on the upper arm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:704-708. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2007.01.003
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure ulcers: pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:881-890. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.069
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Herz-Ruelas ME, Gómez-Flores M, Moxica-Del Angel J, et al. Ulcerated radiodermatitis induced after fluoroscopically guided stent implantation angioplasty. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2014;2014:768624. doi:10.1155/2014/768624
- Wilson BN, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Consensus on the clinical management of chronic radiation dermatitis and radiation fibrosis: a Delphi survey. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:1054-1056. doi:10.1111/bjd.21852
- Khanna NR, Kumar DP, Laskar SG, et al. Radiation dermatitis: an overview. Indian J Burns. 2013;21:24-31. doi:10.4103/0971-653x.121877
- Spalek M. Chronic radiation-induced dermatitis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:473-482. doi:10.2147/CCID.S94320
- Bourgeois JF, Gourgou S, Kramar A, et al. A randomized, prospective study using the LPG technique in treating radiation-induced skin fibrosis: clinical and profilometric analysis. Skin Res Technol. 2008;14:71-76. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0846.2007.00263.x
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skinfibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4S Suppl 1):S59-S64. doi:10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Wilson B, Shah R, Menzer C, et al. Laser therapy as a treatment for chronic radiation fibrosis. Lasers Surg Med. 2023;55:82-88. doi:10.1002/lsm.23617
- Rigotti G, Marchi A, Galiè M, et al. Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119:1409-1422. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000256047.47909.71
- Leventhal J, Young MR. Radiation dermatitis: recognition, prevention, and management. Oncology (Williston Park). 2017;31:885-899.
- van Vloten WA, Hermans J, van Daal WA. Radiation-induced skin cancer and radiodermatitis of the head and neck. Cancer. 1987;59:411-414. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3<411::aid-cncr2820590310>3.0.co;2-z
- Davis MM, Hanke CW, Zollinger TW, et al. Skin cancer in patients with chronic radiation dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:608-616. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70072-4
- Miller DL, Balter S, Schueler BA, et al. Clinical radiation management for fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiology. 2010;257:321-332. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091269
Fluoroscopy-Induced Chronic Radiation Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review and Reappraisal
Fluoroscopy-Induced Chronic Radiation Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review and Reappraisal
PRACTICE POINTS
- Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis poses diagnostic challenges, as patients often are unable to associate a history of fluoroscopic procedures with the development of skin lesions.
- Scapular and subscapular lesions as well as those on the anterolateral chest and mid back should prompt clinicians to inquire about the patient’s history of fluoroscopic procedures.
- Because lesions can remain refractory to treatment, longterm monitoring is necessary if they are not excised.