User login
Methemoglobinemia Induced by Application of an Anesthetic Cream
To the Editor:
Methemoglobinemia (MetHb) is a condition caused by elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood, which leads to an overall reduced ability of red blood cells to release oxygen to tissues, causing tissue hypoxia. Methemoglobinemia may be congenital or acquired. Various antibiotics and local anesthetics have been reported to induce acquired MetHb.1 We describe an adult who presented with MetHb resulting from excessive topical application of local anesthetics for painful scrotal ulcers.
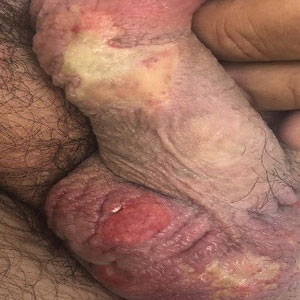
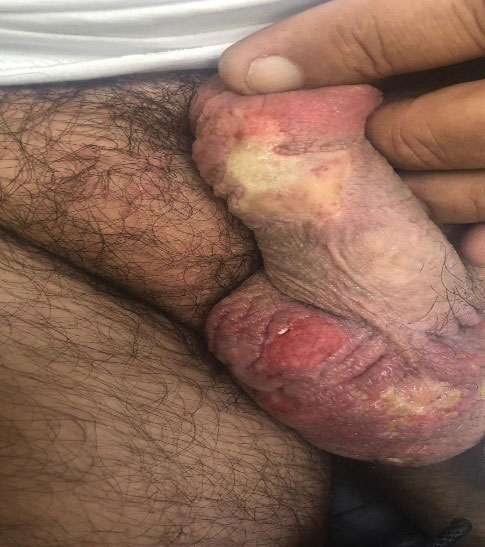
A 54-year-old man presented with multiple scrotal and penile shaft ulcers of a few weeks’ duration with no systemic concerns. His medical history included chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) and lumbar disc disease. Physical examination revealed multiple erosions and ulcers on an erythematous base involving the scrotal skin and distal penile shaft (Figure). Histopathology revealed acute leukocytoclastic vasculitis, and a laboratory workup was positive for mixed cryoglobulinemia that was thought to be HCV related. The patient was started on a systemic corticosteroid treatment in addition to sofosbuvir-velpatasvir for the treatment of HCV-related mixed cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Concomitantly, the patient self-treated for pain with a local anesthetic cream containing lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5%, applying it excessively every few hours daily for 2 weeks. He also intermittently used occlusive dressings.
After 2 weeks of application, the patient developed lightheadedness and shortness of breath. He returned and was admitted for further evaluation. He had dyspnea and tachypnea of 22 breaths per minute. He also had mild tachycardia (109 beats per minute). He did not have a fever, and his blood pressure was normal. The oxygen saturation measured in ambient room air by pulse oximetry was 82%. A neurologic examination was normal except for mild drowsiness. The lungs were clear, and heart sounds were normal. A 12-lead electrocardiogram also was normal. A complete blood cell count showed severe macrocytic anemia with a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL, which was a severe decline from the patient’s baseline level of 14 g/dL (reference range, 13–17 g/dL). A MetHb blood level of 11% was reported on co-oximetry. An arterial blood gas analysis revealed a pH of 7.46; partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 41 mm Hg; and partial pressure of oxygen of 63 mm Hg. The haptoglobin level was low at 2.6 mg/dL (reference range, 30–200 mg/dL). An absolute reticulocyte count was markedly elevated at 0.4×106/mL (reference range, 0.03–0.08×106/mL), lactate dehydrogenase was elevated at 430 U/L (reference range, 125–220 U/L), and indirect billirubin was high at 0.9 mg/dL (reference range, 0–0.5 mg/dL), consistent with hemolytic anemia. Electrolyte serum levels and renal function tests were within reference range. A diagnosis of MetHb induced by the lidocaine-prilocaine cream was rendered, and intravenous methylene blue 72 mg (1 mg/kg) was administered over 10 minutes. Within the next 60 minutes, the patient’s drowsiness and arterial desaturation resolved. A subsequent MetHb measurement taken several hours later was reduced to 4%. The patient remained asymptomatic and was eventually discharged.
Methemoglobinemia is an altered state of hemoglobin where the ferrous (Fe2+) ions of heme are oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state. These ferric ions are unable to bind oxygen, resulting in impaired oxygen delivery to tissues.1 Local anesthetics, which are strong oxidizers, have been reported to induce MetHb.2 In our patient, the extensive use of lidocaine 2.5%–prilocaine 2.5% cream resulted in severe life-threatening MetHb. The oxidizing properties of local anesthetics can be attributed to their chemical structure. Benzocaine is metabolized to potent oxidizers such as aniline, phenylhydroxylamine, and nitrobenzene.3 Prilocaine and another potent oxidizer, ortho-toluidine, which is a metabolite of prilocaine, can oxidize the iron in hemoglobin from ferrous (Fe2+) to ferric (Fe3+), leading to MetHb.2,3
Cases of anesthetic-induced MetHb primarily are associated with overuse of the product by applying it to large surface areas or using it for prolonged periods of time. In one case report, the occlusive dressing of the lidocaine-prilocaine cream applied to skin of the legs that was already abraded by laser epilation therapy resulted in MetHb.4 In our patient, applying the topical anesthetic to the eroded high-absorptive mucosal surface of the scrotal skin and the use of occlusive dressings increased the risk for toxicity. Absorption from scrotal skin is 40-times higher than the forearm.5 The face, axillae, and scalp also exhibit increased absorption compared to the forearm—10-, 4-, and 3-times higher, respectively.
In recent years, the use of topical anesthetics has greatly expanded due to the popularity of aesthetic and cosmetic procedures. These procedures often are performed in an outpatient setting.6 Dermatologists should be well aware of MetHb as a serious adverse effect and guide patients accordingly, as patients do not tend to consider a local anesthetic to be a drug. Drug interactions also may affect free lidocaine concentrations by liver cytochrome P450 metabolism; although this was not the case with our patient, special attention should be given to potential interactions that may exacerbate this serious adverse effect. Consideration should be given to patients applying the anesthetic to areas with high absorption capacity.
- Wright RO, Lewander WJ, Woolf AD. Methemoglobinemia: etiology, pharmacology, and clinical management. Ann Emerg Med. 1999;34:646-656.
- Guay J. Methemoglobinemia related to local anesthetics: a summary of 242 episodes. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:837-845.
- Jakobson B, Nilsson A. Methemoglobinemia associated with a prilocaine-lidocaine cream and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. a case report. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985;29:453-455.
- Hahn I, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. EMLA®-induced methemoglobinemia and systemic topical anesthetic toxicity. J Emerg Med. 2004;26:85-88.
- Feldmann RJ, Maibach HI. Regional variation in percutaneous penetration of 14C cortisol in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1967;48:181-183.
- Alster T. Review of lidocaine/tetracaine cream as a topical anesthetic for dermatologic laser procedures. Pain Ther. 2013;2:11-19.
To the Editor:
Methemoglobinemia (MetHb) is a condition caused by elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood, which leads to an overall reduced ability of red blood cells to release oxygen to tissues, causing tissue hypoxia. Methemoglobinemia may be congenital or acquired. Various antibiotics and local anesthetics have been reported to induce acquired MetHb.1 We describe an adult who presented with MetHb resulting from excessive topical application of local anesthetics for painful scrotal ulcers.
A 54-year-old man presented with multiple scrotal and penile shaft ulcers of a few weeks’ duration with no systemic concerns. His medical history included chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) and lumbar disc disease. Physical examination revealed multiple erosions and ulcers on an erythematous base involving the scrotal skin and distal penile shaft (Figure). Histopathology revealed acute leukocytoclastic vasculitis, and a laboratory workup was positive for mixed cryoglobulinemia that was thought to be HCV related. The patient was started on a systemic corticosteroid treatment in addition to sofosbuvir-velpatasvir for the treatment of HCV-related mixed cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Concomitantly, the patient self-treated for pain with a local anesthetic cream containing lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5%, applying it excessively every few hours daily for 2 weeks. He also intermittently used occlusive dressings.

After 2 weeks of application, the patient developed lightheadedness and shortness of breath. He returned and was admitted for further evaluation. He had dyspnea and tachypnea of 22 breaths per minute. He also had mild tachycardia (109 beats per minute). He did not have a fever, and his blood pressure was normal. The oxygen saturation measured in ambient room air by pulse oximetry was 82%. A neurologic examination was normal except for mild drowsiness. The lungs were clear, and heart sounds were normal. A 12-lead electrocardiogram also was normal. A complete blood cell count showed severe macrocytic anemia with a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL, which was a severe decline from the patient’s baseline level of 14 g/dL (reference range, 13–17 g/dL). A MetHb blood level of 11% was reported on co-oximetry. An arterial blood gas analysis revealed a pH of 7.46; partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 41 mm Hg; and partial pressure of oxygen of 63 mm Hg. The haptoglobin level was low at 2.6 mg/dL (reference range, 30–200 mg/dL). An absolute reticulocyte count was markedly elevated at 0.4×106/mL (reference range, 0.03–0.08×106/mL), lactate dehydrogenase was elevated at 430 U/L (reference range, 125–220 U/L), and indirect billirubin was high at 0.9 mg/dL (reference range, 0–0.5 mg/dL), consistent with hemolytic anemia. Electrolyte serum levels and renal function tests were within reference range. A diagnosis of MetHb induced by the lidocaine-prilocaine cream was rendered, and intravenous methylene blue 72 mg (1 mg/kg) was administered over 10 minutes. Within the next 60 minutes, the patient’s drowsiness and arterial desaturation resolved. A subsequent MetHb measurement taken several hours later was reduced to 4%. The patient remained asymptomatic and was eventually discharged.
Methemoglobinemia is an altered state of hemoglobin where the ferrous (Fe2+) ions of heme are oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state. These ferric ions are unable to bind oxygen, resulting in impaired oxygen delivery to tissues.1 Local anesthetics, which are strong oxidizers, have been reported to induce MetHb.2 In our patient, the extensive use of lidocaine 2.5%–prilocaine 2.5% cream resulted in severe life-threatening MetHb. The oxidizing properties of local anesthetics can be attributed to their chemical structure. Benzocaine is metabolized to potent oxidizers such as aniline, phenylhydroxylamine, and nitrobenzene.3 Prilocaine and another potent oxidizer, ortho-toluidine, which is a metabolite of prilocaine, can oxidize the iron in hemoglobin from ferrous (Fe2+) to ferric (Fe3+), leading to MetHb.2,3
Cases of anesthetic-induced MetHb primarily are associated with overuse of the product by applying it to large surface areas or using it for prolonged periods of time. In one case report, the occlusive dressing of the lidocaine-prilocaine cream applied to skin of the legs that was already abraded by laser epilation therapy resulted in MetHb.4 In our patient, applying the topical anesthetic to the eroded high-absorptive mucosal surface of the scrotal skin and the use of occlusive dressings increased the risk for toxicity. Absorption from scrotal skin is 40-times higher than the forearm.5 The face, axillae, and scalp also exhibit increased absorption compared to the forearm—10-, 4-, and 3-times higher, respectively.
In recent years, the use of topical anesthetics has greatly expanded due to the popularity of aesthetic and cosmetic procedures. These procedures often are performed in an outpatient setting.6 Dermatologists should be well aware of MetHb as a serious adverse effect and guide patients accordingly, as patients do not tend to consider a local anesthetic to be a drug. Drug interactions also may affect free lidocaine concentrations by liver cytochrome P450 metabolism; although this was not the case with our patient, special attention should be given to potential interactions that may exacerbate this serious adverse effect. Consideration should be given to patients applying the anesthetic to areas with high absorption capacity.
To the Editor:
Methemoglobinemia (MetHb) is a condition caused by elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood, which leads to an overall reduced ability of red blood cells to release oxygen to tissues, causing tissue hypoxia. Methemoglobinemia may be congenital or acquired. Various antibiotics and local anesthetics have been reported to induce acquired MetHb.1 We describe an adult who presented with MetHb resulting from excessive topical application of local anesthetics for painful scrotal ulcers.
A 54-year-old man presented with multiple scrotal and penile shaft ulcers of a few weeks’ duration with no systemic concerns. His medical history included chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) and lumbar disc disease. Physical examination revealed multiple erosions and ulcers on an erythematous base involving the scrotal skin and distal penile shaft (Figure). Histopathology revealed acute leukocytoclastic vasculitis, and a laboratory workup was positive for mixed cryoglobulinemia that was thought to be HCV related. The patient was started on a systemic corticosteroid treatment in addition to sofosbuvir-velpatasvir for the treatment of HCV-related mixed cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Concomitantly, the patient self-treated for pain with a local anesthetic cream containing lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5%, applying it excessively every few hours daily for 2 weeks. He also intermittently used occlusive dressings.

After 2 weeks of application, the patient developed lightheadedness and shortness of breath. He returned and was admitted for further evaluation. He had dyspnea and tachypnea of 22 breaths per minute. He also had mild tachycardia (109 beats per minute). He did not have a fever, and his blood pressure was normal. The oxygen saturation measured in ambient room air by pulse oximetry was 82%. A neurologic examination was normal except for mild drowsiness. The lungs were clear, and heart sounds were normal. A 12-lead electrocardiogram also was normal. A complete blood cell count showed severe macrocytic anemia with a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL, which was a severe decline from the patient’s baseline level of 14 g/dL (reference range, 13–17 g/dL). A MetHb blood level of 11% was reported on co-oximetry. An arterial blood gas analysis revealed a pH of 7.46; partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 41 mm Hg; and partial pressure of oxygen of 63 mm Hg. The haptoglobin level was low at 2.6 mg/dL (reference range, 30–200 mg/dL). An absolute reticulocyte count was markedly elevated at 0.4×106/mL (reference range, 0.03–0.08×106/mL), lactate dehydrogenase was elevated at 430 U/L (reference range, 125–220 U/L), and indirect billirubin was high at 0.9 mg/dL (reference range, 0–0.5 mg/dL), consistent with hemolytic anemia. Electrolyte serum levels and renal function tests were within reference range. A diagnosis of MetHb induced by the lidocaine-prilocaine cream was rendered, and intravenous methylene blue 72 mg (1 mg/kg) was administered over 10 minutes. Within the next 60 minutes, the patient’s drowsiness and arterial desaturation resolved. A subsequent MetHb measurement taken several hours later was reduced to 4%. The patient remained asymptomatic and was eventually discharged.
Methemoglobinemia is an altered state of hemoglobin where the ferrous (Fe2+) ions of heme are oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state. These ferric ions are unable to bind oxygen, resulting in impaired oxygen delivery to tissues.1 Local anesthetics, which are strong oxidizers, have been reported to induce MetHb.2 In our patient, the extensive use of lidocaine 2.5%–prilocaine 2.5% cream resulted in severe life-threatening MetHb. The oxidizing properties of local anesthetics can be attributed to their chemical structure. Benzocaine is metabolized to potent oxidizers such as aniline, phenylhydroxylamine, and nitrobenzene.3 Prilocaine and another potent oxidizer, ortho-toluidine, which is a metabolite of prilocaine, can oxidize the iron in hemoglobin from ferrous (Fe2+) to ferric (Fe3+), leading to MetHb.2,3
Cases of anesthetic-induced MetHb primarily are associated with overuse of the product by applying it to large surface areas or using it for prolonged periods of time. In one case report, the occlusive dressing of the lidocaine-prilocaine cream applied to skin of the legs that was already abraded by laser epilation therapy resulted in MetHb.4 In our patient, applying the topical anesthetic to the eroded high-absorptive mucosal surface of the scrotal skin and the use of occlusive dressings increased the risk for toxicity. Absorption from scrotal skin is 40-times higher than the forearm.5 The face, axillae, and scalp also exhibit increased absorption compared to the forearm—10-, 4-, and 3-times higher, respectively.
In recent years, the use of topical anesthetics has greatly expanded due to the popularity of aesthetic and cosmetic procedures. These procedures often are performed in an outpatient setting.6 Dermatologists should be well aware of MetHb as a serious adverse effect and guide patients accordingly, as patients do not tend to consider a local anesthetic to be a drug. Drug interactions also may affect free lidocaine concentrations by liver cytochrome P450 metabolism; although this was not the case with our patient, special attention should be given to potential interactions that may exacerbate this serious adverse effect. Consideration should be given to patients applying the anesthetic to areas with high absorption capacity.
- Wright RO, Lewander WJ, Woolf AD. Methemoglobinemia: etiology, pharmacology, and clinical management. Ann Emerg Med. 1999;34:646-656.
- Guay J. Methemoglobinemia related to local anesthetics: a summary of 242 episodes. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:837-845.
- Jakobson B, Nilsson A. Methemoglobinemia associated with a prilocaine-lidocaine cream and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. a case report. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985;29:453-455.
- Hahn I, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. EMLA®-induced methemoglobinemia and systemic topical anesthetic toxicity. J Emerg Med. 2004;26:85-88.
- Feldmann RJ, Maibach HI. Regional variation in percutaneous penetration of 14C cortisol in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1967;48:181-183.
- Alster T. Review of lidocaine/tetracaine cream as a topical anesthetic for dermatologic laser procedures. Pain Ther. 2013;2:11-19.
- Wright RO, Lewander WJ, Woolf AD. Methemoglobinemia: etiology, pharmacology, and clinical management. Ann Emerg Med. 1999;34:646-656.
- Guay J. Methemoglobinemia related to local anesthetics: a summary of 242 episodes. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:837-845.
- Jakobson B, Nilsson A. Methemoglobinemia associated with a prilocaine-lidocaine cream and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. a case report. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985;29:453-455.
- Hahn I, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. EMLA®-induced methemoglobinemia and systemic topical anesthetic toxicity. J Emerg Med. 2004;26:85-88.
- Feldmann RJ, Maibach HI. Regional variation in percutaneous penetration of 14C cortisol in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1967;48:181-183.
- Alster T. Review of lidocaine/tetracaine cream as a topical anesthetic for dermatologic laser procedures. Pain Ther. 2013;2:11-19.
Practice Points
- Consideration should be given to patients applying anesthetic creams to areas with high absorption capacity.
- Dermatologists should be aware of methemoglobinemia as a serious adverse effect of local anesthetics and guide patients accordingly, as patients do not tend to consider these products to be drugs.
Commentary: Meningioma, Radiotherapy Interruptions, Therapy Persistence, and Lymphocytes in BC, August 2023
Data are limited regarding the effect of interrupting radiation therapy for patients with BC. A retrospective study by Chow and colleagues looked at 35,845 patients with nonmetastatic triple-negative BC from the National Cancer Database who had received external beam radiation therapy as part of the management of their BC. The analysis showed inferior overall survival in patients with a longer duration of radiation treatment (hazard ratio 1.023; 95% CI 1.015-1.031) The more days of interruption, the higher the likelihood of mortality seen. In reference to 0-1 days of interruption, patients with 2-5 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.069; 95% CI 1.002-1.140), 6-10 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.239; 95% CI 1.140-1.348), and 11-15 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.265; 95% CI 1.126-1.431) did worse. These findings should encourage further studies to explore ways to minimize treatment interruptions among patients with BC.
A lack of adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy has been associated with increased mortality among women with BC. The retrospective study by Zheng and Thomas included 25,796 older women (> 65 years old) diagnosed with stage I-III hormone receptor–positive BC and looked at associations between adherence to and persistence with adjuvant endocrine therapy and mortality in this cohort. Their findings showed that the risk for all-cause mortality was reduced by 25% in patients with vs without cumulative adherence to endocrine therapy (hazard ratio 0.75; P < .001), although no association was seen with BC-specific mortality. Persistence with endocrine therapy, which was defined as having taken the treatment for ≥ 180 continuous days, was associated with 11% reduction in all-cause mortality and 37% reduction in BC-specific mortality. This study supports prior studies in highlighting the importance of endocrine therapy adherence among women with hormone-positive BC.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are considered significant prognostic markers in patients with BC, although the prognostic effect of TIL in human epidermal growth factor reception 2 (HER2)–low BC has not been identified. A large-cohort, single-institution retrospective analysis by Sun and colleagues investigated the prognostic role of TIL in HER2-low early-stage BC. The analysis included 1763 patients with early-stage BC who underwent surgery, of whom 429 patients were HER2+, 739 were HER2-low, and 595 were HER2-0. No differences in disease-free survival (DFS) were seen between the three cohorts. However, in patients with HER2-low BC, high (>10%) vs low (≤10%) TIL levels were associated with a 53% improvement in DFS overall (hazard ratio 0.47; P = .035), and a 58% improvement in DFS was seen for the hormone receptor–positive/HER2-low cohort (hazard ratio 0.42; P = .032).
Data are limited regarding the effect of interrupting radiation therapy for patients with BC. A retrospective study by Chow and colleagues looked at 35,845 patients with nonmetastatic triple-negative BC from the National Cancer Database who had received external beam radiation therapy as part of the management of their BC. The analysis showed inferior overall survival in patients with a longer duration of radiation treatment (hazard ratio 1.023; 95% CI 1.015-1.031) The more days of interruption, the higher the likelihood of mortality seen. In reference to 0-1 days of interruption, patients with 2-5 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.069; 95% CI 1.002-1.140), 6-10 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.239; 95% CI 1.140-1.348), and 11-15 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.265; 95% CI 1.126-1.431) did worse. These findings should encourage further studies to explore ways to minimize treatment interruptions among patients with BC.
A lack of adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy has been associated with increased mortality among women with BC. The retrospective study by Zheng and Thomas included 25,796 older women (> 65 years old) diagnosed with stage I-III hormone receptor–positive BC and looked at associations between adherence to and persistence with adjuvant endocrine therapy and mortality in this cohort. Their findings showed that the risk for all-cause mortality was reduced by 25% in patients with vs without cumulative adherence to endocrine therapy (hazard ratio 0.75; P < .001), although no association was seen with BC-specific mortality. Persistence with endocrine therapy, which was defined as having taken the treatment for ≥ 180 continuous days, was associated with 11% reduction in all-cause mortality and 37% reduction in BC-specific mortality. This study supports prior studies in highlighting the importance of endocrine therapy adherence among women with hormone-positive BC.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are considered significant prognostic markers in patients with BC, although the prognostic effect of TIL in human epidermal growth factor reception 2 (HER2)–low BC has not been identified. A large-cohort, single-institution retrospective analysis by Sun and colleagues investigated the prognostic role of TIL in HER2-low early-stage BC. The analysis included 1763 patients with early-stage BC who underwent surgery, of whom 429 patients were HER2+, 739 were HER2-low, and 595 were HER2-0. No differences in disease-free survival (DFS) were seen between the three cohorts. However, in patients with HER2-low BC, high (>10%) vs low (≤10%) TIL levels were associated with a 53% improvement in DFS overall (hazard ratio 0.47; P = .035), and a 58% improvement in DFS was seen for the hormone receptor–positive/HER2-low cohort (hazard ratio 0.42; P = .032).
Data are limited regarding the effect of interrupting radiation therapy for patients with BC. A retrospective study by Chow and colleagues looked at 35,845 patients with nonmetastatic triple-negative BC from the National Cancer Database who had received external beam radiation therapy as part of the management of their BC. The analysis showed inferior overall survival in patients with a longer duration of radiation treatment (hazard ratio 1.023; 95% CI 1.015-1.031) The more days of interruption, the higher the likelihood of mortality seen. In reference to 0-1 days of interruption, patients with 2-5 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.069; 95% CI 1.002-1.140), 6-10 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.239; 95% CI 1.140-1.348), and 11-15 interrupted days (hazard ratio 1.265; 95% CI 1.126-1.431) did worse. These findings should encourage further studies to explore ways to minimize treatment interruptions among patients with BC.
A lack of adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy has been associated with increased mortality among women with BC. The retrospective study by Zheng and Thomas included 25,796 older women (> 65 years old) diagnosed with stage I-III hormone receptor–positive BC and looked at associations between adherence to and persistence with adjuvant endocrine therapy and mortality in this cohort. Their findings showed that the risk for all-cause mortality was reduced by 25% in patients with vs without cumulative adherence to endocrine therapy (hazard ratio 0.75; P < .001), although no association was seen with BC-specific mortality. Persistence with endocrine therapy, which was defined as having taken the treatment for ≥ 180 continuous days, was associated with 11% reduction in all-cause mortality and 37% reduction in BC-specific mortality. This study supports prior studies in highlighting the importance of endocrine therapy adherence among women with hormone-positive BC.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are considered significant prognostic markers in patients with BC, although the prognostic effect of TIL in human epidermal growth factor reception 2 (HER2)–low BC has not been identified. A large-cohort, single-institution retrospective analysis by Sun and colleagues investigated the prognostic role of TIL in HER2-low early-stage BC. The analysis included 1763 patients with early-stage BC who underwent surgery, of whom 429 patients were HER2+, 739 were HER2-low, and 595 were HER2-0. No differences in disease-free survival (DFS) were seen between the three cohorts. However, in patients with HER2-low BC, high (>10%) vs low (≤10%) TIL levels were associated with a 53% improvement in DFS overall (hazard ratio 0.47; P = .035), and a 58% improvement in DFS was seen for the hormone receptor–positive/HER2-low cohort (hazard ratio 0.42; P = .032).
Commentary: Node irradiation, HER2+ treatment, and diet in BC, August 2023
The addition of pertuzumab to trastuzumab plus chemotherapy has demonstrated improvement in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared with trastuzumab plus chemotherapy in early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.3 The framework of oncology is built on clinical trials through their rigorous design, enrollment, and synthesis of data; however, real-world studies are an integral component of cancer research because they provide a more representative sample of the general population treated in routine clinical practice. Neopearl was a retrospective, observational, real-world study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy with or without pertuzumab among 271 patients with stage II-III HER2-positive breast cancer (Fabbri et al). The addition of pertuzumab led to an increase in pCR rate (49% vs 62%; odds ratio 1.74; P = .032) and improvement in 5-year event-free survival (81% vs 93%; hazard ratio 2.22; P = .041), and the benefit on univariate analysis was restricted to patients with positive axillary nodes. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in adverse events, including cardiac, between the two groups. These results serve to strengthen the available data regarding the clinical efficacy and favorable safety profile of dual HER2-targeted therapy combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Lifestyle factors, including physical activity and diet, are becoming increasingly recognized as important determinants of various cancer-specific outcomes and overall health. Furthermore, because these are modifiable, there is often motivation on behalf of an individual to change behaviors that can affect their outcome. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet (MD) has been associated with reduced risk for breast cancer development and lower mortality among women with breast cancer.4,5 Data from a prospective multicenter European cohort including 13,270 breast cancer survivors demonstrated that low compared with medium adherence to a MD before a breast cancer diagnosis was associated with a 13% higher risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio 1.13; 95% CI 1.01-1.26). A three-unit increase in the adapted relative MD score was associated with an 8% reduced risk for overall mortality (hazard ratio3-unit 0.92; 95% CI 0.87-0.97); this result was sustained in the postmenopausal population and strengthened in metastatic disease (Castro-Espin et al). The connection between diet and cancer outcomes is complex, and future research evaluating specific dietary interventions and the underlying biologic pathways by which nutrition exerts its effects will be important to inform our counseling for patients with breast cancer in the survivorship setting.
Additional References
- Whelan TJ, Olivotto IA, Parulekar WR, et al, for the MA.20 Study Investigators. Regional nodal irradiation in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:307-16. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415340
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Regional radiotherapy in biomarker low-risk node positive and T3N0 breast cancer (TAILOR RT). National Library of Medicine. Last updated November 23, 2022. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03488693
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, et al. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): A randomised multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:25-32. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70336-9
- Buckland G, Travier N, Cottet V, et al. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:2918-27. doi:10.1002/ijc.27958
- Haslam DE, John EM, Knight JA, et al. Diet quality and all-cause mortality in women with breast cancer from the Breast Cancer Family Registry. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023;32:678-686. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-1198
The addition of pertuzumab to trastuzumab plus chemotherapy has demonstrated improvement in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared with trastuzumab plus chemotherapy in early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.3 The framework of oncology is built on clinical trials through their rigorous design, enrollment, and synthesis of data; however, real-world studies are an integral component of cancer research because they provide a more representative sample of the general population treated in routine clinical practice. Neopearl was a retrospective, observational, real-world study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy with or without pertuzumab among 271 patients with stage II-III HER2-positive breast cancer (Fabbri et al). The addition of pertuzumab led to an increase in pCR rate (49% vs 62%; odds ratio 1.74; P = .032) and improvement in 5-year event-free survival (81% vs 93%; hazard ratio 2.22; P = .041), and the benefit on univariate analysis was restricted to patients with positive axillary nodes. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in adverse events, including cardiac, between the two groups. These results serve to strengthen the available data regarding the clinical efficacy and favorable safety profile of dual HER2-targeted therapy combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Lifestyle factors, including physical activity and diet, are becoming increasingly recognized as important determinants of various cancer-specific outcomes and overall health. Furthermore, because these are modifiable, there is often motivation on behalf of an individual to change behaviors that can affect their outcome. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet (MD) has been associated with reduced risk for breast cancer development and lower mortality among women with breast cancer.4,5 Data from a prospective multicenter European cohort including 13,270 breast cancer survivors demonstrated that low compared with medium adherence to a MD before a breast cancer diagnosis was associated with a 13% higher risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio 1.13; 95% CI 1.01-1.26). A three-unit increase in the adapted relative MD score was associated with an 8% reduced risk for overall mortality (hazard ratio3-unit 0.92; 95% CI 0.87-0.97); this result was sustained in the postmenopausal population and strengthened in metastatic disease (Castro-Espin et al). The connection between diet and cancer outcomes is complex, and future research evaluating specific dietary interventions and the underlying biologic pathways by which nutrition exerts its effects will be important to inform our counseling for patients with breast cancer in the survivorship setting.
Additional References
- Whelan TJ, Olivotto IA, Parulekar WR, et al, for the MA.20 Study Investigators. Regional nodal irradiation in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:307-16. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415340
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Regional radiotherapy in biomarker low-risk node positive and T3N0 breast cancer (TAILOR RT). National Library of Medicine. Last updated November 23, 2022. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03488693
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, et al. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): A randomised multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:25-32. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70336-9
- Buckland G, Travier N, Cottet V, et al. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:2918-27. doi:10.1002/ijc.27958
- Haslam DE, John EM, Knight JA, et al. Diet quality and all-cause mortality in women with breast cancer from the Breast Cancer Family Registry. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023;32:678-686. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-1198
The addition of pertuzumab to trastuzumab plus chemotherapy has demonstrated improvement in pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared with trastuzumab plus chemotherapy in early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.3 The framework of oncology is built on clinical trials through their rigorous design, enrollment, and synthesis of data; however, real-world studies are an integral component of cancer research because they provide a more representative sample of the general population treated in routine clinical practice. Neopearl was a retrospective, observational, real-world study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy with or without pertuzumab among 271 patients with stage II-III HER2-positive breast cancer (Fabbri et al). The addition of pertuzumab led to an increase in pCR rate (49% vs 62%; odds ratio 1.74; P = .032) and improvement in 5-year event-free survival (81% vs 93%; hazard ratio 2.22; P = .041), and the benefit on univariate analysis was restricted to patients with positive axillary nodes. Furthermore, there were no significant differences in adverse events, including cardiac, between the two groups. These results serve to strengthen the available data regarding the clinical efficacy and favorable safety profile of dual HER2-targeted therapy combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Lifestyle factors, including physical activity and diet, are becoming increasingly recognized as important determinants of various cancer-specific outcomes and overall health. Furthermore, because these are modifiable, there is often motivation on behalf of an individual to change behaviors that can affect their outcome. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet (MD) has been associated with reduced risk for breast cancer development and lower mortality among women with breast cancer.4,5 Data from a prospective multicenter European cohort including 13,270 breast cancer survivors demonstrated that low compared with medium adherence to a MD before a breast cancer diagnosis was associated with a 13% higher risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio 1.13; 95% CI 1.01-1.26). A three-unit increase in the adapted relative MD score was associated with an 8% reduced risk for overall mortality (hazard ratio3-unit 0.92; 95% CI 0.87-0.97); this result was sustained in the postmenopausal population and strengthened in metastatic disease (Castro-Espin et al). The connection between diet and cancer outcomes is complex, and future research evaluating specific dietary interventions and the underlying biologic pathways by which nutrition exerts its effects will be important to inform our counseling for patients with breast cancer in the survivorship setting.
Additional References
- Whelan TJ, Olivotto IA, Parulekar WR, et al, for the MA.20 Study Investigators. Regional nodal irradiation in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:307-16. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415340
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Regional radiotherapy in biomarker low-risk node positive and T3N0 breast cancer (TAILOR RT). National Library of Medicine. Last updated November 23, 2022. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03488693
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, et al. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): A randomised multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:25-32. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70336-9
- Buckland G, Travier N, Cottet V, et al. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:2918-27. doi:10.1002/ijc.27958
- Haslam DE, John EM, Knight JA, et al. Diet quality and all-cause mortality in women with breast cancer from the Breast Cancer Family Registry. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2023;32:678-686. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-1198
Squamous cell carcinoma
THE COMPARISON
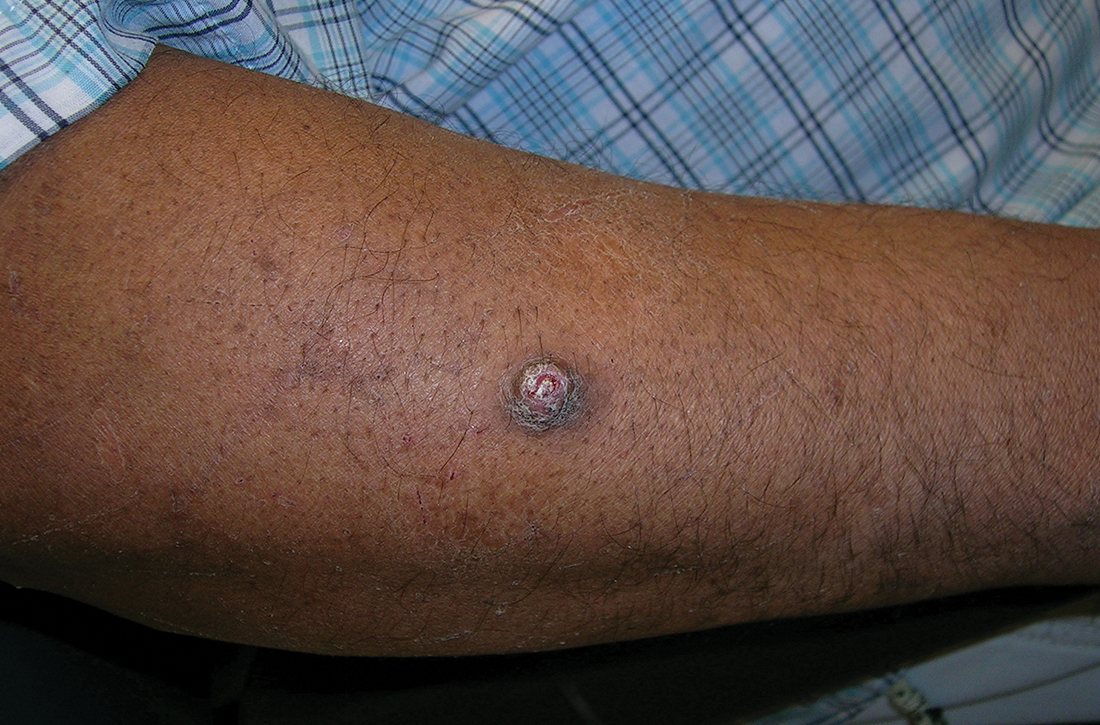
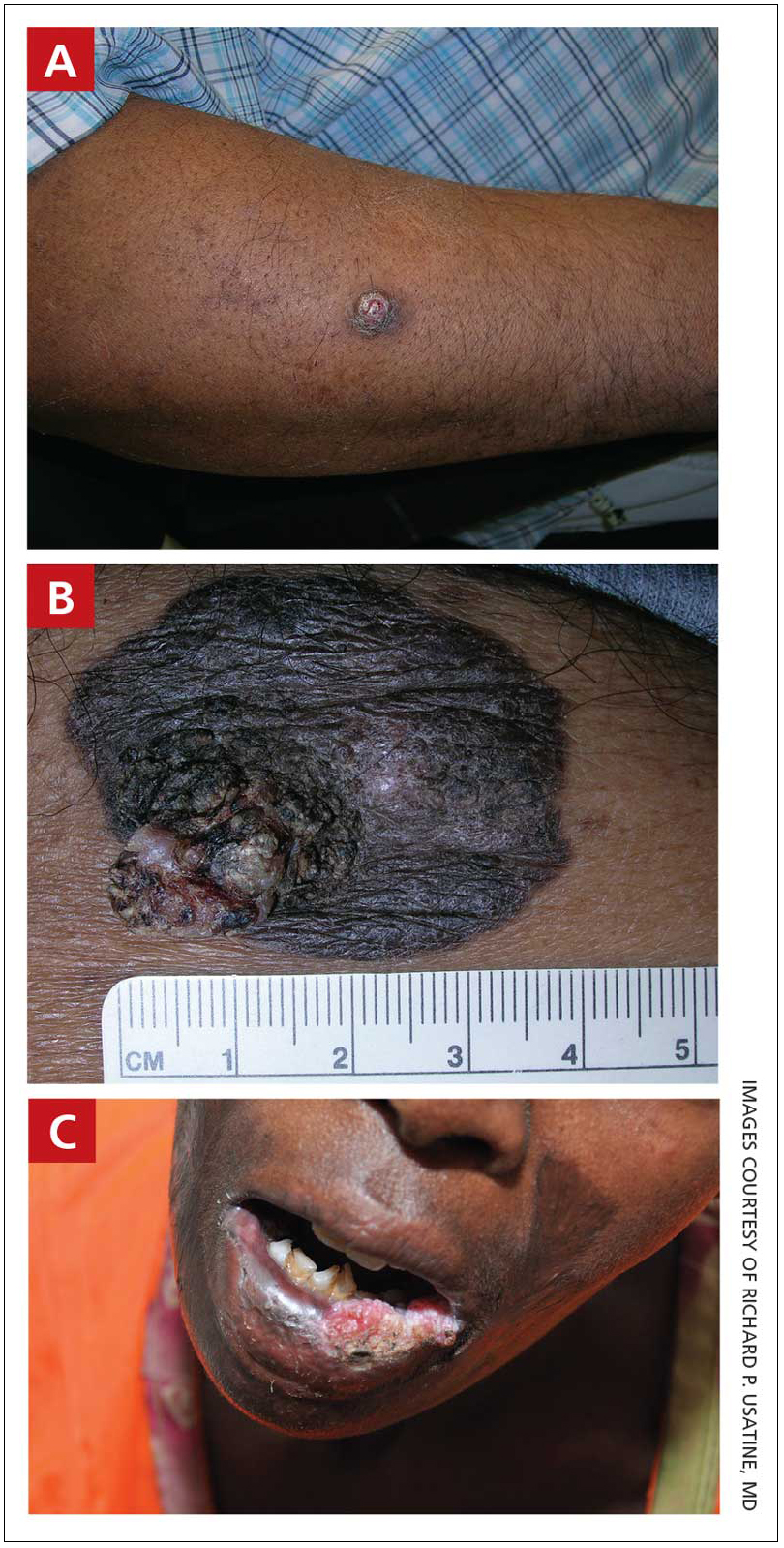
A A 51-year-old Hispanic man with a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the keratoacanthoma type on the arm.
B A 75-year-old Black man with an SCC of the keratoacanthoma type on the abdomen.
C An African woman with an SCC on the lower lip decades after a large facial burn, which is known as a Marjolin ulcer.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) develops from a malignant tumor of the keratinocytes, eccrine glands, or pilosebaceous units that invades the dermis. Risk factors include lighter skin tone, higher cumulative sun exposure, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), lichen sclerosus, family history of skin cancer,1 and immunosuppression.2 It typically affects sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, scalp, neck, and extensor surfaces of the arms (FIGURE A).3,4 However, in those with darker skin tones, the most common anatomic sites are those that are not exposed to the sun (FIGURE B). SCC is diagnosed via skin biopsy. Treatment options include surgical excision, destructive methods such as electrodesiccation and curettage, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Cutaneous SCC has a cure rate of more than 95% and a mortality rate of 1.5% to 2% in the United States.3
Epidemiology
SCC is the most common skin cancer occurring in Black individuals, manifesting primarily in the fifth decade of life.5-7 It is the second most common skin cancer in White, Hispanic, and Asian individuals and is more common in males.8 In a study of organ transplant recipients (N = 413), Pritchett et al9 reported that HPV infection was a major risk factor in Hispanic patients because 66.7% of those with SCC had a history of HPV. However, HPV is a risk factor for SCC in all ethnic groups.10
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Anatomic location
- The lower legs and anogenital areas are the most common sites for SCC in patients with skin of color.4,11
- In Black women, SCC occurs more often on sun-exposed areas such as the arms and legs compared to Black men.7,12-14
- The genitalia, perianal area, ocular mucosa, and oral mucosa are the least likely areas to be routinely examined, even in skin cancer clinics that see highrisk patients, despite the SCC risk in the anogenital area.15,16
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the lips and scalp is more likely to occur in Black women vs Black men.4,7,17
Clinical appearance
- In those with darker skin tones, SCCs may appear hyperpigmented4 or hyperkeratotic with a lack of erythema and an inconsistent appearance.6,7,18
- A nonhealing ulceration of the skin should prompt a biopsy to rule out SCC.3,19
Worth noting
In patients with darker skin tones, the risk for SCC increases in areas with chronic inflammation and scarring of the skin.4,6,7,11,18,20-22 In Black patients, 20% to 40% of cases of SCC occur in the setting of chronic inflammation and scarring.6,7,18 Chronic inflammatory conditions include ulcers, lupus vulgaris, discoid lupus erythematosus, and HPV. In patients with discoid lupus erythematosus, there is an additive effect of sun exposure on the scars, which may play a role in the pathogenesis and metastasis risk for skin cancer in Black patients.4 Other scarring conditions include thermal or chemical burn scars, areas of physical trauma, and prior sites of radiation treatment.14,23 SCC arising in a burn scar is called a Marjolin ulcer or malignant degeneration of a scar (FIGURE C). It is reported more often in lower-income, underresourced countries, which may suggest the need for early detection in populations with skin of color.24
SCC is more aggressive in sites that are not exposed to sun compared to sun-exposed areas.17,25
Continue to: The risk for SCC...
The risk for SCC is increased in immunocompromised patients,2 especially those with HPV.10
The prevalence of SCC in those with HS is approximately 4.6%. The chronic inflammation and irritation from HS in association with other risk factors such as tobacco use may contribute to the malignant transformation to SCC.26
Health disparity highlight
- The risk for metastasis from SCC is 20% to 40% in Black patients vs 1% to 4% in White patients.4,6,27
- Penile SCC was associated with a lower overall survival rate in patients of African descent.20,21
- The increased morbidity and mortality from SCC in patients with skin of color may be attributed to delays in diagnosis and treatment as well as an incomplete understanding of tumor genetics.4,6,18
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Elyse Gadra (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
1. Asgari MM, Warton EM, Whittemore AS. Family history of skin cancer is associated with increased risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:481-486. doi: 10.1097/ DSS.0000000000000292
2. Harwood CA, Surentheran T, McGregor JM, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and non-melanoma skin cancer in immunosuppressed and immunocompetent individuals. J Med Virol. 2000;61:289-297. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(200007)61:3<289::aidjmv2> 3.0.co;2-z
3. Kallini JR, Nouran H, Khachemoune A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: epidemiology, classification, management, and novel trends. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:130-140. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12553.
4. Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.038
5. Bradford PT. Skin cancer in skin of color. Dermatol Nurse. 2009;21:170-177.
6. Gloster HM, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
7. Davis DS, Robinson C, Callender VD. Skin cancer in women of color: epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:127-134. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijwd.2021.01.017
8. Baum B, Duarte AM. Skin cancer epidemic in American Hispanic and Latino patients. In: Silverberg N, Duran-McKinster C, Tay Y-K, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:453-460.
9. Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152: 1348-1353. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3328
10. Karagas MR, Nelson HH, Sehr P, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and incidence of squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas of the skin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:389-395. doi: 10.1093/jnci/ djj092
11. Gohara M. Skin cancer: an African perspective. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:17-21. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13380
12. Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi: 10.1016/ s1011-1344(01)00198-1
13. Halder RM, Bang KM. Skin cancer in African Americans in the United States. Dermatol Clin. 1988;6:397-407.
14. Mora RG, Perniciaro C. Cancer of the skin in blacks. I. a review of 163 black patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;5:535-543. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622 (81)70113-0
15. Bajaj S, Wolner ZJ, Dusza SW, et al. Total body skin examination practices: a survey study amongst dermatologists at high-risk skin cancer clinics. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2019;9:132-138. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0902a09
16. Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
17. Halder RM, Ara CJ. Skin cancer and photoaging in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:725-732, x. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8635 (03)00085-8
18. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Chow M, et al. Review of nonmelanoma skin cancer in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:903-910.
19. Sng J, Koh D, Siong WC, et al. Skin cancer trends among Asians living in Singapore from 1968 to 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61:426-432.
20. Shao K, Feng H. Racial and ethnic healthcare disparities in skin cancer in the United States: a review of existing inequities, contributing factors, and potential solutions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:16-22.
21. Shao K, Hooper J, Feng H. Racial and ethnic health disparities in dermatology in the United States. Part 2: disease-specific epidemiology, characteristics, management, and outcomes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:733-744. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021. 12.062
22. Zakhem GA, Pulavarty AN, Lester JC, et al. Skin cancer in people of color: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:137- 151. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00662-z
23. Copcu E, Aktas A, Sis¸man N, et al. Thirty-one cases of Marjolin’s ulcer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:138-141. doi: 10.1046/j.1365- 2230.2003.01210.x
24. Abdi MA, Yan M, Hanna TP. Systematic review of modern case series of squamous cell cancer arising in a chronic ulcer (Marjolin’s ulcer) of the skin. JCO Glob Oncol. 2020;6:809-818. doi: 10.1200/ GO.20.00094
25. Hogue L, Harvey VM. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and cutaneous melanoma in skin of color patients. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:519-526. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2019.05.009
26. Chapman S, Delgadillo D, Barber C, et al. Cutanteous squamous cell complicating hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of this dreaded complication. Acta Dermatovenerol Al Pannocica Adriat. 2018;27:25-28.
27. Kailas A, Botwin AL, Pritchett EN, et al. Assessing the effectiveness of knowledge-based interventions in increasing skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behaviors in skin of color populations. Cutis. 2017;100:235-240.
THE COMPARISON
A A 51-year-old Hispanic man with a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the keratoacanthoma type on the arm.
B A 75-year-old Black man with an SCC of the keratoacanthoma type on the abdomen.
C An African woman with an SCC on the lower lip decades after a large facial burn, which is known as a Marjolin ulcer.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) develops from a malignant tumor of the keratinocytes, eccrine glands, or pilosebaceous units that invades the dermis. Risk factors include lighter skin tone, higher cumulative sun exposure, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), lichen sclerosus, family history of skin cancer,1 and immunosuppression.2 It typically affects sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, scalp, neck, and extensor surfaces of the arms (FIGURE A).3,4 However, in those with darker skin tones, the most common anatomic sites are those that are not exposed to the sun (FIGURE B). SCC is diagnosed via skin biopsy. Treatment options include surgical excision, destructive methods such as electrodesiccation and curettage, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Cutaneous SCC has a cure rate of more than 95% and a mortality rate of 1.5% to 2% in the United States.3

Epidemiology
SCC is the most common skin cancer occurring in Black individuals, manifesting primarily in the fifth decade of life.5-7 It is the second most common skin cancer in White, Hispanic, and Asian individuals and is more common in males.8 In a study of organ transplant recipients (N = 413), Pritchett et al9 reported that HPV infection was a major risk factor in Hispanic patients because 66.7% of those with SCC had a history of HPV. However, HPV is a risk factor for SCC in all ethnic groups.10
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Anatomic location
- The lower legs and anogenital areas are the most common sites for SCC in patients with skin of color.4,11
- In Black women, SCC occurs more often on sun-exposed areas such as the arms and legs compared to Black men.7,12-14
- The genitalia, perianal area, ocular mucosa, and oral mucosa are the least likely areas to be routinely examined, even in skin cancer clinics that see highrisk patients, despite the SCC risk in the anogenital area.15,16
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the lips and scalp is more likely to occur in Black women vs Black men.4,7,17
Clinical appearance
- In those with darker skin tones, SCCs may appear hyperpigmented4 or hyperkeratotic with a lack of erythema and an inconsistent appearance.6,7,18
- A nonhealing ulceration of the skin should prompt a biopsy to rule out SCC.3,19
Worth noting
In patients with darker skin tones, the risk for SCC increases in areas with chronic inflammation and scarring of the skin.4,6,7,11,18,20-22 In Black patients, 20% to 40% of cases of SCC occur in the setting of chronic inflammation and scarring.6,7,18 Chronic inflammatory conditions include ulcers, lupus vulgaris, discoid lupus erythematosus, and HPV. In patients with discoid lupus erythematosus, there is an additive effect of sun exposure on the scars, which may play a role in the pathogenesis and metastasis risk for skin cancer in Black patients.4 Other scarring conditions include thermal or chemical burn scars, areas of physical trauma, and prior sites of radiation treatment.14,23 SCC arising in a burn scar is called a Marjolin ulcer or malignant degeneration of a scar (FIGURE C). It is reported more often in lower-income, underresourced countries, which may suggest the need for early detection in populations with skin of color.24
SCC is more aggressive in sites that are not exposed to sun compared to sun-exposed areas.17,25
Continue to: The risk for SCC...
The risk for SCC is increased in immunocompromised patients,2 especially those with HPV.10
The prevalence of SCC in those with HS is approximately 4.6%. The chronic inflammation and irritation from HS in association with other risk factors such as tobacco use may contribute to the malignant transformation to SCC.26
Health disparity highlight
- The risk for metastasis from SCC is 20% to 40% in Black patients vs 1% to 4% in White patients.4,6,27
- Penile SCC was associated with a lower overall survival rate in patients of African descent.20,21
- The increased morbidity and mortality from SCC in patients with skin of color may be attributed to delays in diagnosis and treatment as well as an incomplete understanding of tumor genetics.4,6,18
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Elyse Gadra (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
THE COMPARISON
A A 51-year-old Hispanic man with a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the keratoacanthoma type on the arm.
B A 75-year-old Black man with an SCC of the keratoacanthoma type on the abdomen.
C An African woman with an SCC on the lower lip decades after a large facial burn, which is known as a Marjolin ulcer.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) develops from a malignant tumor of the keratinocytes, eccrine glands, or pilosebaceous units that invades the dermis. Risk factors include lighter skin tone, higher cumulative sun exposure, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), lichen sclerosus, family history of skin cancer,1 and immunosuppression.2 It typically affects sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, scalp, neck, and extensor surfaces of the arms (FIGURE A).3,4 However, in those with darker skin tones, the most common anatomic sites are those that are not exposed to the sun (FIGURE B). SCC is diagnosed via skin biopsy. Treatment options include surgical excision, destructive methods such as electrodesiccation and curettage, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Cutaneous SCC has a cure rate of more than 95% and a mortality rate of 1.5% to 2% in the United States.3

Epidemiology
SCC is the most common skin cancer occurring in Black individuals, manifesting primarily in the fifth decade of life.5-7 It is the second most common skin cancer in White, Hispanic, and Asian individuals and is more common in males.8 In a study of organ transplant recipients (N = 413), Pritchett et al9 reported that HPV infection was a major risk factor in Hispanic patients because 66.7% of those with SCC had a history of HPV. However, HPV is a risk factor for SCC in all ethnic groups.10
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
Anatomic location
- The lower legs and anogenital areas are the most common sites for SCC in patients with skin of color.4,11
- In Black women, SCC occurs more often on sun-exposed areas such as the arms and legs compared to Black men.7,12-14
- The genitalia, perianal area, ocular mucosa, and oral mucosa are the least likely areas to be routinely examined, even in skin cancer clinics that see highrisk patients, despite the SCC risk in the anogenital area.15,16
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the lips and scalp is more likely to occur in Black women vs Black men.4,7,17
Clinical appearance
- In those with darker skin tones, SCCs may appear hyperpigmented4 or hyperkeratotic with a lack of erythema and an inconsistent appearance.6,7,18
- A nonhealing ulceration of the skin should prompt a biopsy to rule out SCC.3,19
Worth noting
In patients with darker skin tones, the risk for SCC increases in areas with chronic inflammation and scarring of the skin.4,6,7,11,18,20-22 In Black patients, 20% to 40% of cases of SCC occur in the setting of chronic inflammation and scarring.6,7,18 Chronic inflammatory conditions include ulcers, lupus vulgaris, discoid lupus erythematosus, and HPV. In patients with discoid lupus erythematosus, there is an additive effect of sun exposure on the scars, which may play a role in the pathogenesis and metastasis risk for skin cancer in Black patients.4 Other scarring conditions include thermal or chemical burn scars, areas of physical trauma, and prior sites of radiation treatment.14,23 SCC arising in a burn scar is called a Marjolin ulcer or malignant degeneration of a scar (FIGURE C). It is reported more often in lower-income, underresourced countries, which may suggest the need for early detection in populations with skin of color.24
SCC is more aggressive in sites that are not exposed to sun compared to sun-exposed areas.17,25
Continue to: The risk for SCC...
The risk for SCC is increased in immunocompromised patients,2 especially those with HPV.10
The prevalence of SCC in those with HS is approximately 4.6%. The chronic inflammation and irritation from HS in association with other risk factors such as tobacco use may contribute to the malignant transformation to SCC.26
Health disparity highlight
- The risk for metastasis from SCC is 20% to 40% in Black patients vs 1% to 4% in White patients.4,6,27
- Penile SCC was associated with a lower overall survival rate in patients of African descent.20,21
- The increased morbidity and mortality from SCC in patients with skin of color may be attributed to delays in diagnosis and treatment as well as an incomplete understanding of tumor genetics.4,6,18
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Elyse Gadra (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
1. Asgari MM, Warton EM, Whittemore AS. Family history of skin cancer is associated with increased risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:481-486. doi: 10.1097/ DSS.0000000000000292
2. Harwood CA, Surentheran T, McGregor JM, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and non-melanoma skin cancer in immunosuppressed and immunocompetent individuals. J Med Virol. 2000;61:289-297. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(200007)61:3<289::aidjmv2> 3.0.co;2-z
3. Kallini JR, Nouran H, Khachemoune A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: epidemiology, classification, management, and novel trends. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:130-140. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12553.
4. Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.038
5. Bradford PT. Skin cancer in skin of color. Dermatol Nurse. 2009;21:170-177.
6. Gloster HM, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
7. Davis DS, Robinson C, Callender VD. Skin cancer in women of color: epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:127-134. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijwd.2021.01.017
8. Baum B, Duarte AM. Skin cancer epidemic in American Hispanic and Latino patients. In: Silverberg N, Duran-McKinster C, Tay Y-K, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:453-460.
9. Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152: 1348-1353. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3328
10. Karagas MR, Nelson HH, Sehr P, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and incidence of squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas of the skin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:389-395. doi: 10.1093/jnci/ djj092
11. Gohara M. Skin cancer: an African perspective. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:17-21. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13380
12. Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi: 10.1016/ s1011-1344(01)00198-1
13. Halder RM, Bang KM. Skin cancer in African Americans in the United States. Dermatol Clin. 1988;6:397-407.
14. Mora RG, Perniciaro C. Cancer of the skin in blacks. I. a review of 163 black patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;5:535-543. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622 (81)70113-0
15. Bajaj S, Wolner ZJ, Dusza SW, et al. Total body skin examination practices: a survey study amongst dermatologists at high-risk skin cancer clinics. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2019;9:132-138. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0902a09
16. Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
17. Halder RM, Ara CJ. Skin cancer and photoaging in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:725-732, x. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8635 (03)00085-8
18. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Chow M, et al. Review of nonmelanoma skin cancer in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:903-910.
19. Sng J, Koh D, Siong WC, et al. Skin cancer trends among Asians living in Singapore from 1968 to 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61:426-432.
20. Shao K, Feng H. Racial and ethnic healthcare disparities in skin cancer in the United States: a review of existing inequities, contributing factors, and potential solutions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:16-22.
21. Shao K, Hooper J, Feng H. Racial and ethnic health disparities in dermatology in the United States. Part 2: disease-specific epidemiology, characteristics, management, and outcomes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:733-744. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021. 12.062
22. Zakhem GA, Pulavarty AN, Lester JC, et al. Skin cancer in people of color: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:137- 151. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00662-z
23. Copcu E, Aktas A, Sis¸man N, et al. Thirty-one cases of Marjolin’s ulcer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:138-141. doi: 10.1046/j.1365- 2230.2003.01210.x
24. Abdi MA, Yan M, Hanna TP. Systematic review of modern case series of squamous cell cancer arising in a chronic ulcer (Marjolin’s ulcer) of the skin. JCO Glob Oncol. 2020;6:809-818. doi: 10.1200/ GO.20.00094
25. Hogue L, Harvey VM. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and cutaneous melanoma in skin of color patients. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:519-526. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2019.05.009
26. Chapman S, Delgadillo D, Barber C, et al. Cutanteous squamous cell complicating hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of this dreaded complication. Acta Dermatovenerol Al Pannocica Adriat. 2018;27:25-28.
27. Kailas A, Botwin AL, Pritchett EN, et al. Assessing the effectiveness of knowledge-based interventions in increasing skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behaviors in skin of color populations. Cutis. 2017;100:235-240.
1. Asgari MM, Warton EM, Whittemore AS. Family history of skin cancer is associated with increased risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41:481-486. doi: 10.1097/ DSS.0000000000000292
2. Harwood CA, Surentheran T, McGregor JM, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and non-melanoma skin cancer in immunosuppressed and immunocompetent individuals. J Med Virol. 2000;61:289-297. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(200007)61:3<289::aidjmv2> 3.0.co;2-z
3. Kallini JR, Nouran H, Khachemoune A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: epidemiology, classification, management, and novel trends. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:130-140. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12553.
4. Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.038
5. Bradford PT. Skin cancer in skin of color. Dermatol Nurse. 2009;21:170-177.
6. Gloster HM, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
7. Davis DS, Robinson C, Callender VD. Skin cancer in women of color: epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:127-134. doi: 10.1016/ j.ijwd.2021.01.017
8. Baum B, Duarte AM. Skin cancer epidemic in American Hispanic and Latino patients. In: Silverberg N, Duran-McKinster C, Tay Y-K, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:453-460.
9. Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152: 1348-1353. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3328
10. Karagas MR, Nelson HH, Sehr P, et al. Human papillomavirus infection and incidence of squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas of the skin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:389-395. doi: 10.1093/jnci/ djj092
11. Gohara M. Skin cancer: an African perspective. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:17-21. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13380
12. Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi: 10.1016/ s1011-1344(01)00198-1
13. Halder RM, Bang KM. Skin cancer in African Americans in the United States. Dermatol Clin. 1988;6:397-407.
14. Mora RG, Perniciaro C. Cancer of the skin in blacks. I. a review of 163 black patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;5:535-543. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622 (81)70113-0
15. Bajaj S, Wolner ZJ, Dusza SW, et al. Total body skin examination practices: a survey study amongst dermatologists at high-risk skin cancer clinics. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2019;9:132-138. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0902a09
16. Rieder EA, Mu EW, Wang J, et al. Dermatologist practices during total body skin examinations: a survey study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:516-520.
17. Halder RM, Ara CJ. Skin cancer and photoaging in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:725-732, x. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8635 (03)00085-8
18. Higgins S, Nazemi A, Chow M, et al. Review of nonmelanoma skin cancer in African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:903-910.
19. Sng J, Koh D, Siong WC, et al. Skin cancer trends among Asians living in Singapore from 1968 to 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61:426-432.
20. Shao K, Feng H. Racial and ethnic healthcare disparities in skin cancer in the United States: a review of existing inequities, contributing factors, and potential solutions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:16-22.
21. Shao K, Hooper J, Feng H. Racial and ethnic health disparities in dermatology in the United States. Part 2: disease-specific epidemiology, characteristics, management, and outcomes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:733-744. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021. 12.062
22. Zakhem GA, Pulavarty AN, Lester JC, et al. Skin cancer in people of color: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:137- 151. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00662-z
23. Copcu E, Aktas A, Sis¸man N, et al. Thirty-one cases of Marjolin’s ulcer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:138-141. doi: 10.1046/j.1365- 2230.2003.01210.x
24. Abdi MA, Yan M, Hanna TP. Systematic review of modern case series of squamous cell cancer arising in a chronic ulcer (Marjolin’s ulcer) of the skin. JCO Glob Oncol. 2020;6:809-818. doi: 10.1200/ GO.20.00094
25. Hogue L, Harvey VM. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and cutaneous melanoma in skin of color patients. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:519-526. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2019.05.009
26. Chapman S, Delgadillo D, Barber C, et al. Cutanteous squamous cell complicating hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of the prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of this dreaded complication. Acta Dermatovenerol Al Pannocica Adriat. 2018;27:25-28.
27. Kailas A, Botwin AL, Pritchett EN, et al. Assessing the effectiveness of knowledge-based interventions in increasing skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behaviors in skin of color populations. Cutis. 2017;100:235-240.
Reducing Risk for Clostridioides difficile Recurrence
Incidence of C difficile infection has been increasing over the past two decades, accounting for nearly 460,000 cases of illness and 20,000 deaths annually in the United States.
Antibiotic treatment is the standard of care for C difficile infection, but the treatment can disrupt a patient's gastrointestinal microbiome, thereby contributing to the risk for disease recurrence.
Recurrence rates are proven to increase with each episode of C difficile, making prevention essential.
In this ReCAP, Dr David Johnson, of Eastern Virginia Medical School, discusses treatment options to avoid recurrence. He considers multiple means of prevention, including disinfection, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and the latest advances in fecal microbiota-based biotherapies. Dr Johnson provides data regarding the success rates of pharmaceutical-grade options for prevention of relapse of C difficile.
--
David A. Johnson, MD, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School; Chief of Gastroenterology, Digestive and Liver Disease Specialists, Division of Capital Digestive Care, Norfolk, Virginia
David A. Johnson, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) on a board for: ACG Institute for Clinical Research and Education; Adjudication Board Parexel
Serve(d) as a consultant for: Johnson & Johnson; Isothrive
Received research grant from: ISOThrive
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: American College of Gastroenterology
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Parexel; Johnson & Johnson
Incidence of C difficile infection has been increasing over the past two decades, accounting for nearly 460,000 cases of illness and 20,000 deaths annually in the United States.
Antibiotic treatment is the standard of care for C difficile infection, but the treatment can disrupt a patient's gastrointestinal microbiome, thereby contributing to the risk for disease recurrence.
Recurrence rates are proven to increase with each episode of C difficile, making prevention essential.
In this ReCAP, Dr David Johnson, of Eastern Virginia Medical School, discusses treatment options to avoid recurrence. He considers multiple means of prevention, including disinfection, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and the latest advances in fecal microbiota-based biotherapies. Dr Johnson provides data regarding the success rates of pharmaceutical-grade options for prevention of relapse of C difficile.
--
David A. Johnson, MD, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School; Chief of Gastroenterology, Digestive and Liver Disease Specialists, Division of Capital Digestive Care, Norfolk, Virginia
David A. Johnson, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) on a board for: ACG Institute for Clinical Research and Education; Adjudication Board Parexel
Serve(d) as a consultant for: Johnson & Johnson; Isothrive
Received research grant from: ISOThrive
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: American College of Gastroenterology
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Parexel; Johnson & Johnson
Incidence of C difficile infection has been increasing over the past two decades, accounting for nearly 460,000 cases of illness and 20,000 deaths annually in the United States.
Antibiotic treatment is the standard of care for C difficile infection, but the treatment can disrupt a patient's gastrointestinal microbiome, thereby contributing to the risk for disease recurrence.
Recurrence rates are proven to increase with each episode of C difficile, making prevention essential.
In this ReCAP, Dr David Johnson, of Eastern Virginia Medical School, discusses treatment options to avoid recurrence. He considers multiple means of prevention, including disinfection, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and the latest advances in fecal microbiota-based biotherapies. Dr Johnson provides data regarding the success rates of pharmaceutical-grade options for prevention of relapse of C difficile.
--
David A. Johnson, MD, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School; Chief of Gastroenterology, Digestive and Liver Disease Specialists, Division of Capital Digestive Care, Norfolk, Virginia
David A. Johnson, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) on a board for: ACG Institute for Clinical Research and Education; Adjudication Board Parexel
Serve(d) as a consultant for: Johnson & Johnson; Isothrive
Received research grant from: ISOThrive
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: American College of Gastroenterology
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Parexel; Johnson & Johnson

Cancer Patients: Who’s at Risk for Venous Thromboembolism?
Patients with cancer are at a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE)—in fact, it’s one of the leading causes of death in patients who receive systemic therapy for cancer. But as cancer treatment has evolved, have the incidence and risk of VTE changed too?
Researchers from Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts conducted a study with 434,203 veterans to evaluate the pattern of VTE incidence over 16 years, focusing on the types of cancer, treatment, race and ethnicity, and other factors related to cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT).
In contrast with other large population studies, this study found the overall incidence of CAT remained largely stable over time. At 12 months, the incidence was 4.5%, with yearly trends ranging between 4.2% and 4.7%. “As expected,” the researchers say, the subset of patients receiving systemic therapy had a higher incidence of VTE at 12 months (7.7%) than did the overall cohort. The pattern was “particularly pronounced” in gynecologic, testicular, and kidney cancers, where the incidence of VTE was 2 to 3 times higher in the treated cohort compared with the overall cohort.
Cancer type and diagnosis were the most statistically and clinically significant associations with CAT, with up to a 6-fold difference between cancer subtypes. The patients at the highest risk of VTE were those with pancreatic cancer and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Most studies have focused only on patients with solid tumors, but these researchers observed novel patterns among patients with hematologic neoplasms. Specifically, a higher incidence of VTE among patients with aggressive vs indolent leukemias and lymphomas. This trend, the researchers say, may be associated in part with catheter-related events.
Furthermore, the type of system treatment was associated with the risk of VTE, the researchers say, although to a lesser extent. Chemotherapy- and immunotherapy-based regimens had the highest risk of VTE, relative to no treatment. Targeted and endocrine therapy also carried a higher risk compared with no treatment but to a lesser degree.
The researchers found significant heterogeneity by race and ethnicity across cancer types. Non-Hispanic Black patients had about 20% higher risk of VTE compared with non-Hispanic White patients. Asian and Pacific Islander patients had about 20% lower risk compared with non-Hispanic White patients.
Male sex was also associated with VTE. However, “interestingly,” the researchers note, neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors and patients’ comorbidities were not associated with CAT but were associated with mortality.
Their results suggest that patient- and treatment-specific factors play a critical role in assessing the risk of CAT, and “ongoing efforts to identify these patterns are of utmost importance for risk stratification and prognostic assessment.”
Patients with cancer are at a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE)—in fact, it’s one of the leading causes of death in patients who receive systemic therapy for cancer. But as cancer treatment has evolved, have the incidence and risk of VTE changed too?
Researchers from Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts conducted a study with 434,203 veterans to evaluate the pattern of VTE incidence over 16 years, focusing on the types of cancer, treatment, race and ethnicity, and other factors related to cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT).
In contrast with other large population studies, this study found the overall incidence of CAT remained largely stable over time. At 12 months, the incidence was 4.5%, with yearly trends ranging between 4.2% and 4.7%. “As expected,” the researchers say, the subset of patients receiving systemic therapy had a higher incidence of VTE at 12 months (7.7%) than did the overall cohort. The pattern was “particularly pronounced” in gynecologic, testicular, and kidney cancers, where the incidence of VTE was 2 to 3 times higher in the treated cohort compared with the overall cohort.
Cancer type and diagnosis were the most statistically and clinically significant associations with CAT, with up to a 6-fold difference between cancer subtypes. The patients at the highest risk of VTE were those with pancreatic cancer and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Most studies have focused only on patients with solid tumors, but these researchers observed novel patterns among patients with hematologic neoplasms. Specifically, a higher incidence of VTE among patients with aggressive vs indolent leukemias and lymphomas. This trend, the researchers say, may be associated in part with catheter-related events.
Furthermore, the type of system treatment was associated with the risk of VTE, the researchers say, although to a lesser extent. Chemotherapy- and immunotherapy-based regimens had the highest risk of VTE, relative to no treatment. Targeted and endocrine therapy also carried a higher risk compared with no treatment but to a lesser degree.
The researchers found significant heterogeneity by race and ethnicity across cancer types. Non-Hispanic Black patients had about 20% higher risk of VTE compared with non-Hispanic White patients. Asian and Pacific Islander patients had about 20% lower risk compared with non-Hispanic White patients.
Male sex was also associated with VTE. However, “interestingly,” the researchers note, neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors and patients’ comorbidities were not associated with CAT but were associated with mortality.
Their results suggest that patient- and treatment-specific factors play a critical role in assessing the risk of CAT, and “ongoing efforts to identify these patterns are of utmost importance for risk stratification and prognostic assessment.”
Patients with cancer are at a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE)—in fact, it’s one of the leading causes of death in patients who receive systemic therapy for cancer. But as cancer treatment has evolved, have the incidence and risk of VTE changed too?
Researchers from Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System in Massachusetts conducted a study with 434,203 veterans to evaluate the pattern of VTE incidence over 16 years, focusing on the types of cancer, treatment, race and ethnicity, and other factors related to cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT).
In contrast with other large population studies, this study found the overall incidence of CAT remained largely stable over time. At 12 months, the incidence was 4.5%, with yearly trends ranging between 4.2% and 4.7%. “As expected,” the researchers say, the subset of patients receiving systemic therapy had a higher incidence of VTE at 12 months (7.7%) than did the overall cohort. The pattern was “particularly pronounced” in gynecologic, testicular, and kidney cancers, where the incidence of VTE was 2 to 3 times higher in the treated cohort compared with the overall cohort.
Cancer type and diagnosis were the most statistically and clinically significant associations with CAT, with up to a 6-fold difference between cancer subtypes. The patients at the highest risk of VTE were those with pancreatic cancer and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Most studies have focused only on patients with solid tumors, but these researchers observed novel patterns among patients with hematologic neoplasms. Specifically, a higher incidence of VTE among patients with aggressive vs indolent leukemias and lymphomas. This trend, the researchers say, may be associated in part with catheter-related events.
Furthermore, the type of system treatment was associated with the risk of VTE, the researchers say, although to a lesser extent. Chemotherapy- and immunotherapy-based regimens had the highest risk of VTE, relative to no treatment. Targeted and endocrine therapy also carried a higher risk compared with no treatment but to a lesser degree.
The researchers found significant heterogeneity by race and ethnicity across cancer types. Non-Hispanic Black patients had about 20% higher risk of VTE compared with non-Hispanic White patients. Asian and Pacific Islander patients had about 20% lower risk compared with non-Hispanic White patients.
Male sex was also associated with VTE. However, “interestingly,” the researchers note, neighborhood-level socioeconomic factors and patients’ comorbidities were not associated with CAT but were associated with mortality.
Their results suggest that patient- and treatment-specific factors play a critical role in assessing the risk of CAT, and “ongoing efforts to identify these patterns are of utmost importance for risk stratification and prognostic assessment.”
Regional Meeting Focuses on Women’s Cancer Survivorship
As the number of female veterans continues to grow, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is adjusting by focusing more on breast/gynecological cancer and referring fewer cases to outside clinicians.
The VA’s effort reflects the reality that female veterans from the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq are approaching the ages—50s, 60s, and 70s—when cancer diagnoses become more common, said Sarah Colonna, MD, national medical director of breast oncology for VA's Breast and Gynecologic Oncology System of Excellence and an oncologist at the Huntsman Cancer Institute and Wahlen VA Medical Center in Salt Lake City, Utah. “This is preparation for the change that we know is coming.”
In response, the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is devoting a regional meeting in Tampa, Florida (July 29, 2023) to improving survivorship for patients with women’s cancers. “This meeting is designed to educate both cancer experts and primary care providers on the care of women who have already gone through breast and gynecological cancer treatment,” Colonna explained.
Adherence Challenges
Colonna will speak in a session about the importance of adherence to endocrine therapy. “When we prescribe endocrine therapy for breast cancer, we usually ask women to stay on it for 5 to 10 years, and sometimes that’s hard for them,” she said. “I’ll talk about tips and tricks to help women stay on endocrine therapy for the long haul because we know that is linked to better survival.”
Between two-thirds and three-quarters of women with breast cancer are advised to stay on endocrine drugs, she said, but the medications can be difficult to tolerate due to adverse effects such as hot flashes and sleep disturbances.
In addition, patients are often anxious about the medications. “Women are very leery of anything that changes or makes their hormones different,” Colonna noted. “They feel like it’s messing with something that is natural for them.”
Colonna urges colleagues to focus on their “soft skills,” the ability to absorb and validate the worries of patients. Instead of dismissing them, she said, focus on messages that acknowledge concerns but are also firm: “That’s real, that sucks. But we’ve got to do it.”
It’s also helpful to guide patients away from thinking that taking a pill every day means they’re sick. “I try to flip that paradigm: ‘You’re taking this pill every day because you have power over this thing that happened to you.’”
Education is also key, she said, so that patients “understand very clearly why this medication is important for them: It increases the chance of surviving breast cancer or it increases the chances that the cancer will never come back in your arm or in your breast. Then, whether they make a decision to take it or not, at least they’re making the choice with knowledge.”
As for adverse effects, Colonna said medications such as antidepressants and painkillers can relieve hot flashes, which can disturb sleep.
Identifying the best strategy to address adverse effects “requires keeping in frequent contact with the patient during the first 6 months of endocrine therapy, which are really critical,” she said. “Once they’ve been on it for a year, they can see the light at the end of the tunnel and hang in there even if they have adverse effects.”
Some guidelines suggest that no doctor visits are needed until the 6-month mark, but Colonna prefers to check in at the 4- to 6-week mark, even if it’s just via a phone call. Otherwise, “often they’ll stop taking the pill, and then you won’t know about it until you see them at 6 six months.” At that point, she said, a critical period for treatment has passed.
The Role of Nurse Navigators
In another session at the Tampa regional meeting, AVAHO president-elect Cindy Bowman, MSN, RN, OCN, will moderate a session about the role of nurse navigators in VA cancer care. She is the coordinator of the Cancer Care Navigation Program at the C. W. Bill Young VA Medical Center in Bay Pines, Florida.
“Veterans become survivors the day they’re diagnosed with cancer,” she said. Within the VA, cancer-care navigator teams developed over the past decade aim to help patients find their way forward through survivorship, she said, and nurses are crucial to the effort.
As Sharp and Scheid reported in a 2018 Journal Oncology Navigation Survivorship article, “research demonstrates that navigation can improve access to the cancer care system by addressing barriers, as well as facilitating quality care. The benefits of patient navigation for improving cancer patient outcomes is considerable.” McKenney and colleagues found that “patient navigation has been demonstrated to increase access to screening, shorten time to diagnostic resolution, and improve cancer outcomes, particularly in health disparity populations, such as women of color, rural populations, and poor women.”
According to Bowman, “it has become standard practice to have nurse navigators be there each step of the way from a high suspicion of cancer to diagnosis and through the clinical workup into active treatment and survivorship.” Within the VA, she said, “the focus right now is to look at standardizing care that all VAs will be able to offer holistic, comprehensive cancer-care navigation teams.”
At the regional meeting, Bowman’s session will include updates from nurse navigators about helping patients through breast/gynecological cancer, abnormal mammograms, and survivorship.
Nurse navigators are typically the second medical professionals who talk to cancer patients after their physicians, Bowman said. The unique knowledge of oncology nurse navigators gives them invaluable insight into treatment plans and cancer drug regimens, she said.
“They’re able to sit down and discuss the actual cancer drug regimen with patients—what each of those drugs do, how they’re administered, the short-term and long-term side effects,” she said. “They have the knowledge about all aspects of cancer care that can really only come from somebody who’s specialty trained.”
Other sessions at the AVAHO regional meeting will highlight breast cancer and lymphedema, breast cancer and bone health; diet, exercise and cancer; sexual health for breast/gynecological cancer survivors; and imaging surveillance after diagnosis.
As the number of female veterans continues to grow, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is adjusting by focusing more on breast/gynecological cancer and referring fewer cases to outside clinicians.
The VA’s effort reflects the reality that female veterans from the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq are approaching the ages—50s, 60s, and 70s—when cancer diagnoses become more common, said Sarah Colonna, MD, national medical director of breast oncology for VA's Breast and Gynecologic Oncology System of Excellence and an oncologist at the Huntsman Cancer Institute and Wahlen VA Medical Center in Salt Lake City, Utah. “This is preparation for the change that we know is coming.”
In response, the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is devoting a regional meeting in Tampa, Florida (July 29, 2023) to improving survivorship for patients with women’s cancers. “This meeting is designed to educate both cancer experts and primary care providers on the care of women who have already gone through breast and gynecological cancer treatment,” Colonna explained.
Adherence Challenges
Colonna will speak in a session about the importance of adherence to endocrine therapy. “When we prescribe endocrine therapy for breast cancer, we usually ask women to stay on it for 5 to 10 years, and sometimes that’s hard for them,” she said. “I’ll talk about tips and tricks to help women stay on endocrine therapy for the long haul because we know that is linked to better survival.”
Between two-thirds and three-quarters of women with breast cancer are advised to stay on endocrine drugs, she said, but the medications can be difficult to tolerate due to adverse effects such as hot flashes and sleep disturbances.
In addition, patients are often anxious about the medications. “Women are very leery of anything that changes or makes their hormones different,” Colonna noted. “They feel like it’s messing with something that is natural for them.”
Colonna urges colleagues to focus on their “soft skills,” the ability to absorb and validate the worries of patients. Instead of dismissing them, she said, focus on messages that acknowledge concerns but are also firm: “That’s real, that sucks. But we’ve got to do it.”
It’s also helpful to guide patients away from thinking that taking a pill every day means they’re sick. “I try to flip that paradigm: ‘You’re taking this pill every day because you have power over this thing that happened to you.’”
Education is also key, she said, so that patients “understand very clearly why this medication is important for them: It increases the chance of surviving breast cancer or it increases the chances that the cancer will never come back in your arm or in your breast. Then, whether they make a decision to take it or not, at least they’re making the choice with knowledge.”
As for adverse effects, Colonna said medications such as antidepressants and painkillers can relieve hot flashes, which can disturb sleep.
Identifying the best strategy to address adverse effects “requires keeping in frequent contact with the patient during the first 6 months of endocrine therapy, which are really critical,” she said. “Once they’ve been on it for a year, they can see the light at the end of the tunnel and hang in there even if they have adverse effects.”
Some guidelines suggest that no doctor visits are needed until the 6-month mark, but Colonna prefers to check in at the 4- to 6-week mark, even if it’s just via a phone call. Otherwise, “often they’ll stop taking the pill, and then you won’t know about it until you see them at 6 six months.” At that point, she said, a critical period for treatment has passed.
The Role of Nurse Navigators
In another session at the Tampa regional meeting, AVAHO president-elect Cindy Bowman, MSN, RN, OCN, will moderate a session about the role of nurse navigators in VA cancer care. She is the coordinator of the Cancer Care Navigation Program at the C. W. Bill Young VA Medical Center in Bay Pines, Florida.
“Veterans become survivors the day they’re diagnosed with cancer,” she said. Within the VA, cancer-care navigator teams developed over the past decade aim to help patients find their way forward through survivorship, she said, and nurses are crucial to the effort.
As Sharp and Scheid reported in a 2018 Journal Oncology Navigation Survivorship article, “research demonstrates that navigation can improve access to the cancer care system by addressing barriers, as well as facilitating quality care. The benefits of patient navigation for improving cancer patient outcomes is considerable.” McKenney and colleagues found that “patient navigation has been demonstrated to increase access to screening, shorten time to diagnostic resolution, and improve cancer outcomes, particularly in health disparity populations, such as women of color, rural populations, and poor women.”
According to Bowman, “it has become standard practice to have nurse navigators be there each step of the way from a high suspicion of cancer to diagnosis and through the clinical workup into active treatment and survivorship.” Within the VA, she said, “the focus right now is to look at standardizing care that all VAs will be able to offer holistic, comprehensive cancer-care navigation teams.”
At the regional meeting, Bowman’s session will include updates from nurse navigators about helping patients through breast/gynecological cancer, abnormal mammograms, and survivorship.
Nurse navigators are typically the second medical professionals who talk to cancer patients after their physicians, Bowman said. The unique knowledge of oncology nurse navigators gives them invaluable insight into treatment plans and cancer drug regimens, she said.
“They’re able to sit down and discuss the actual cancer drug regimen with patients—what each of those drugs do, how they’re administered, the short-term and long-term side effects,” she said. “They have the knowledge about all aspects of cancer care that can really only come from somebody who’s specialty trained.”
Other sessions at the AVAHO regional meeting will highlight breast cancer and lymphedema, breast cancer and bone health; diet, exercise and cancer; sexual health for breast/gynecological cancer survivors; and imaging surveillance after diagnosis.
As the number of female veterans continues to grow, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is adjusting by focusing more on breast/gynecological cancer and referring fewer cases to outside clinicians.
The VA’s effort reflects the reality that female veterans from the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq are approaching the ages—50s, 60s, and 70s—when cancer diagnoses become more common, said Sarah Colonna, MD, national medical director of breast oncology for VA's Breast and Gynecologic Oncology System of Excellence and an oncologist at the Huntsman Cancer Institute and Wahlen VA Medical Center in Salt Lake City, Utah. “This is preparation for the change that we know is coming.”
In response, the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) is devoting a regional meeting in Tampa, Florida (July 29, 2023) to improving survivorship for patients with women’s cancers. “This meeting is designed to educate both cancer experts and primary care providers on the care of women who have already gone through breast and gynecological cancer treatment,” Colonna explained.
Adherence Challenges
Colonna will speak in a session about the importance of adherence to endocrine therapy. “When we prescribe endocrine therapy for breast cancer, we usually ask women to stay on it for 5 to 10 years, and sometimes that’s hard for them,” she said. “I’ll talk about tips and tricks to help women stay on endocrine therapy for the long haul because we know that is linked to better survival.”
Between two-thirds and three-quarters of women with breast cancer are advised to stay on endocrine drugs, she said, but the medications can be difficult to tolerate due to adverse effects such as hot flashes and sleep disturbances.
In addition, patients are often anxious about the medications. “Women are very leery of anything that changes or makes their hormones different,” Colonna noted. “They feel like it’s messing with something that is natural for them.”
Colonna urges colleagues to focus on their “soft skills,” the ability to absorb and validate the worries of patients. Instead of dismissing them, she said, focus on messages that acknowledge concerns but are also firm: “That’s real, that sucks. But we’ve got to do it.”
It’s also helpful to guide patients away from thinking that taking a pill every day means they’re sick. “I try to flip that paradigm: ‘You’re taking this pill every day because you have power over this thing that happened to you.’”
Education is also key, she said, so that patients “understand very clearly why this medication is important for them: It increases the chance of surviving breast cancer or it increases the chances that the cancer will never come back in your arm or in your breast. Then, whether they make a decision to take it or not, at least they’re making the choice with knowledge.”
As for adverse effects, Colonna said medications such as antidepressants and painkillers can relieve hot flashes, which can disturb sleep.
Identifying the best strategy to address adverse effects “requires keeping in frequent contact with the patient during the first 6 months of endocrine therapy, which are really critical,” she said. “Once they’ve been on it for a year, they can see the light at the end of the tunnel and hang in there even if they have adverse effects.”
Some guidelines suggest that no doctor visits are needed until the 6-month mark, but Colonna prefers to check in at the 4- to 6-week mark, even if it’s just via a phone call. Otherwise, “often they’ll stop taking the pill, and then you won’t know about it until you see them at 6 six months.” At that point, she said, a critical period for treatment has passed.
The Role of Nurse Navigators
In another session at the Tampa regional meeting, AVAHO president-elect Cindy Bowman, MSN, RN, OCN, will moderate a session about the role of nurse navigators in VA cancer care. She is the coordinator of the Cancer Care Navigation Program at the C. W. Bill Young VA Medical Center in Bay Pines, Florida.
“Veterans become survivors the day they’re diagnosed with cancer,” she said. Within the VA, cancer-care navigator teams developed over the past decade aim to help patients find their way forward through survivorship, she said, and nurses are crucial to the effort.
As Sharp and Scheid reported in a 2018 Journal Oncology Navigation Survivorship article, “research demonstrates that navigation can improve access to the cancer care system by addressing barriers, as well as facilitating quality care. The benefits of patient navigation for improving cancer patient outcomes is considerable.” McKenney and colleagues found that “patient navigation has been demonstrated to increase access to screening, shorten time to diagnostic resolution, and improve cancer outcomes, particularly in health disparity populations, such as women of color, rural populations, and poor women.”
According to Bowman, “it has become standard practice to have nurse navigators be there each step of the way from a high suspicion of cancer to diagnosis and through the clinical workup into active treatment and survivorship.” Within the VA, she said, “the focus right now is to look at standardizing care that all VAs will be able to offer holistic, comprehensive cancer-care navigation teams.”
At the regional meeting, Bowman’s session will include updates from nurse navigators about helping patients through breast/gynecological cancer, abnormal mammograms, and survivorship.
Nurse navigators are typically the second medical professionals who talk to cancer patients after their physicians, Bowman said. The unique knowledge of oncology nurse navigators gives them invaluable insight into treatment plans and cancer drug regimens, she said.
“They’re able to sit down and discuss the actual cancer drug regimen with patients—what each of those drugs do, how they’re administered, the short-term and long-term side effects,” she said. “They have the knowledge about all aspects of cancer care that can really only come from somebody who’s specialty trained.”
Other sessions at the AVAHO regional meeting will highlight breast cancer and lymphedema, breast cancer and bone health; diet, exercise and cancer; sexual health for breast/gynecological cancer survivors; and imaging surveillance after diagnosis.