User login
Benign breast disease on percutaneous biopsy increases breast cancer risk
Key clinical point: Compared with the general population, the risk for overall breast cancer (BC) was nearly double in women with benign breast disease (BBD) diagnosed by percutaneous biopsies.
Major finding: Patients with BBD vs the general population were at a significantly higher risk for overall BC (standard incidence ratio [SIR] 1.95; 95% CI 1.76-2.17), including invasive BC (SIR 1.56; 95% CI 1.37-1.78) and ductal carcinoma in situ (SIR 3.10; 95% CI 2.54-3.77). The SIR for overall BC increased progressively with increasing BBD severity (nonproliferative 1.42; 95% CI 1.19-1.71; proliferative disease without atypia 2.19; 95% CI 1.88-2.54; atypical hyperplasia 3.91; 95% CI 2.97-5.14).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 4819 female patients who underwent a BBD biopsy, of whom 338 patients had incident BC.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). Four authors declared receiving grants, research support, or personal fees from NIH and other sources.
Source: Sherman ME et al. Benign breast disease and breast cancer risk in the percutaneous biopsy era. JAMA Surg. 2023 (Dec 13). doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2023.6382
Key clinical point: Compared with the general population, the risk for overall breast cancer (BC) was nearly double in women with benign breast disease (BBD) diagnosed by percutaneous biopsies.
Major finding: Patients with BBD vs the general population were at a significantly higher risk for overall BC (standard incidence ratio [SIR] 1.95; 95% CI 1.76-2.17), including invasive BC (SIR 1.56; 95% CI 1.37-1.78) and ductal carcinoma in situ (SIR 3.10; 95% CI 2.54-3.77). The SIR for overall BC increased progressively with increasing BBD severity (nonproliferative 1.42; 95% CI 1.19-1.71; proliferative disease without atypia 2.19; 95% CI 1.88-2.54; atypical hyperplasia 3.91; 95% CI 2.97-5.14).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 4819 female patients who underwent a BBD biopsy, of whom 338 patients had incident BC.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). Four authors declared receiving grants, research support, or personal fees from NIH and other sources.
Source: Sherman ME et al. Benign breast disease and breast cancer risk in the percutaneous biopsy era. JAMA Surg. 2023 (Dec 13). doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2023.6382
Key clinical point: Compared with the general population, the risk for overall breast cancer (BC) was nearly double in women with benign breast disease (BBD) diagnosed by percutaneous biopsies.
Major finding: Patients with BBD vs the general population were at a significantly higher risk for overall BC (standard incidence ratio [SIR] 1.95; 95% CI 1.76-2.17), including invasive BC (SIR 1.56; 95% CI 1.37-1.78) and ductal carcinoma in situ (SIR 3.10; 95% CI 2.54-3.77). The SIR for overall BC increased progressively with increasing BBD severity (nonproliferative 1.42; 95% CI 1.19-1.71; proliferative disease without atypia 2.19; 95% CI 1.88-2.54; atypical hyperplasia 3.91; 95% CI 2.97-5.14).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective cohort study including 4819 female patients who underwent a BBD biopsy, of whom 338 patients had incident BC.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). Four authors declared receiving grants, research support, or personal fees from NIH and other sources.
Source: Sherman ME et al. Benign breast disease and breast cancer risk in the percutaneous biopsy era. JAMA Surg. 2023 (Dec 13). doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2023.6382
Dispelling Common Headache Myths
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.
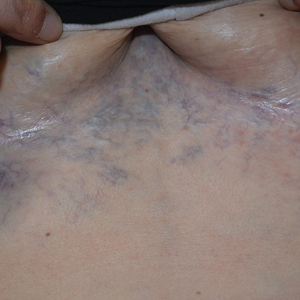
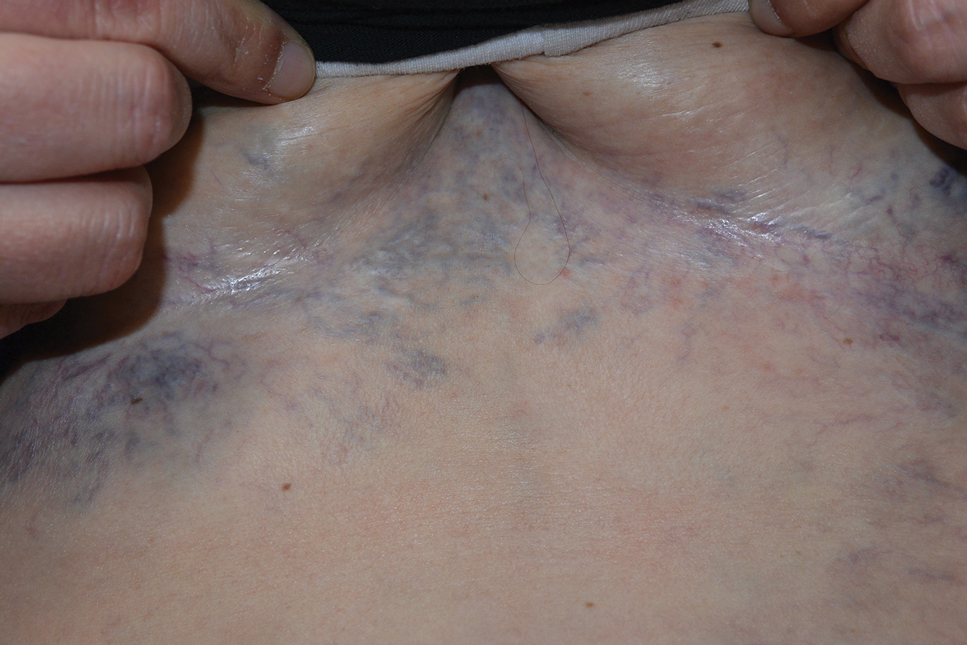
Ectatic Vessels on the Chest
The Diagnosis: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Computed tomography angiography of the chest confirmed a diagnosis of superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome due to external pressure of the indwelling catheter. Upon diagnosis, the left indwelling catheter was removed. Further testing to assess for a potential pulmonary embolism was negative. Resolution of the ectatic spider veins and patientreported intermittent facial swelling was achieved after catheter removal.
Superior vena cava syndrome occurs when the SVC is occluded due to extrinsic pressure or thrombosis. Although classically thought to be due to underlying bronchogenic carcinomas, all pathologies that cause compression of the SVC also can lead to vessel occlusion.1 Superior vena cava syndrome initially can be detected on physical examination. The most prominent skin finding includes diffusely dilated blood vessels on the central chest wall, which indicate the presence of collateral blood vessels.1 Imaging studies such as abdominal computed tomography can provide information on the etiology of the condition but are not required for diagnosis. Given the high correlation of SVC syndrome with underlying lung and mediastinal carcinomas, imaging was warranted in our patient. Imaging also can distinguish if the condition is due to external pressure or thrombosis.2 For SVC syndrome due to thrombosis, endovascular therapy is first-line management; however, mechanical thrombectomy may be preferred in patients with absolute contraindication to thrombolytic agents.3 In the setting of increased external pressure on the SVC, treatment includes the removal of the source of pressure.4
In a case series including 78 patients, ports and indwelling catheters accounted for 71% of benign SVC cases.5 Our patient’s SVC syndrome most likely was due to the indwelling catheter pressing on the SVC. The goal of treatment is to address the underlying cause—whether it be pressure or thrombosis. In the setting of increased external pressure, treatment includes removal of the source of pressure from the SVC.4
Other differential diagnoses to consider for newonset ectatic vessels on the chest wall include generalized essential telangiectasia, scleroderma, poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans, and caput medusae. Generalized essential telangiectasia is characterized by red or pink dilated capillary blood vessels in a branch or lacelike pattern predominantly on the lower limbs. The eruption primarily is asymptomatic, though tingling or numbness may be reported.6 The diagnosis can be made with a punch biopsy, with histopathology showing dilated vessels in the dermis.7
Scleroderma is a connective tissue fibrosis disorder with variable clinical presentations. The systemic sclerosis subset can be divided into localized systemic sclerosis and diffuse systemic sclerosis. Physical examination reveals cutaneous sclerosis in various areas of the body. Localized systemic sclerosis includes sclerosis of the fingers and face, while diffuse systemic sclerosis is notable for progression to the arms, legs, and trunk.8 In addition to sclerosis, diffuse telangiectases also can be observed. Systemic sclerosis is a clinical diagnosis based on physical examination and laboratory studies to identify antibodies such as antinuclear antibodies.
Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans is a variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The initial presentation is characterized by plaques of hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation with atrophy and telangiectases. The lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and classically involve the trunk and flexural areas.9 The diagnosis is made with skin biopsy and immunohistochemical studies, with findings reflective of mycosis fungoides.
Caput medusae (palm tree sign) is a cardinal feature of portal hypertension characterized by grossly dilated and engorged periumbilical veins. To shunt blood from the portal venous system, cutaneous collateral veins between the umbilical veins and abdominal wall veins are used, resulting in the appearance of engorged veins in the anterior abdominal wall.10 The diagnosis can be made with abdominal ultrasonography showing the direction of blood flow through abdominal vessels.
- Drouin L, Pistorius MA, Lafforgue A, et al. Upper-extremity venous thrombosis: a retrospective study about 160 cases [in French]. Rev Med Interne. 2019;40:9-15.
- Richie E. Clinical pearl: diagnosing superior vena cava syndrome. Emergency Medicine News. 2017;39:22. doi:10.1097/01 .EEM.0000522220.37441.d2
- Azizi A, Shafi I, Shah N, et al. Superior vena cava syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;13:2896-2910. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2020.08.038
- Dumantepe M, Tarhan A, Ozler A. Successful treatment of central venous catheter induced superior vena cava syndrome with ultrasound accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:E269-E273.
- Rice TW, Rodriguez RM, Light RW. The superior vena cava syndrome: clinical characteristics and evolving etiology. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006;85:37-42. doi:10.1097/01.md.0000198474.99876.f0
- Long D, Marshman G. Generalized essential telangiectasia. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:67-69. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.00033.x
- Braverman IM. Ultrastructure and organization of the cutaneous microvasculature in normal and pathologic states. J Invest Dermatol. 1989;93(2 suppl):2S-9S.
- Ferreli C, Gasparini G, Parodi A, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma and scleroderma-like disorders: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:306-336. doi:10.1007 /s12016-017-8625-4
- Bloom B, Marchbein S, Fischer M, et al. Poikilodermatous mycosis fungoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:4.
- Sharma B, Raina S. Caput medusae. Indian J Med Res. 2015;141:494. doi:10.4103/0971-5916.159322
The Diagnosis: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Computed tomography angiography of the chest confirmed a diagnosis of superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome due to external pressure of the indwelling catheter. Upon diagnosis, the left indwelling catheter was removed. Further testing to assess for a potential pulmonary embolism was negative. Resolution of the ectatic spider veins and patientreported intermittent facial swelling was achieved after catheter removal.
Superior vena cava syndrome occurs when the SVC is occluded due to extrinsic pressure or thrombosis. Although classically thought to be due to underlying bronchogenic carcinomas, all pathologies that cause compression of the SVC also can lead to vessel occlusion.1 Superior vena cava syndrome initially can be detected on physical examination. The most prominent skin finding includes diffusely dilated blood vessels on the central chest wall, which indicate the presence of collateral blood vessels.1 Imaging studies such as abdominal computed tomography can provide information on the etiology of the condition but are not required for diagnosis. Given the high correlation of SVC syndrome with underlying lung and mediastinal carcinomas, imaging was warranted in our patient. Imaging also can distinguish if the condition is due to external pressure or thrombosis.2 For SVC syndrome due to thrombosis, endovascular therapy is first-line management; however, mechanical thrombectomy may be preferred in patients with absolute contraindication to thrombolytic agents.3 In the setting of increased external pressure on the SVC, treatment includes the removal of the source of pressure.4
In a case series including 78 patients, ports and indwelling catheters accounted for 71% of benign SVC cases.5 Our patient’s SVC syndrome most likely was due to the indwelling catheter pressing on the SVC. The goal of treatment is to address the underlying cause—whether it be pressure or thrombosis. In the setting of increased external pressure, treatment includes removal of the source of pressure from the SVC.4
Other differential diagnoses to consider for newonset ectatic vessels on the chest wall include generalized essential telangiectasia, scleroderma, poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans, and caput medusae. Generalized essential telangiectasia is characterized by red or pink dilated capillary blood vessels in a branch or lacelike pattern predominantly on the lower limbs. The eruption primarily is asymptomatic, though tingling or numbness may be reported.6 The diagnosis can be made with a punch biopsy, with histopathology showing dilated vessels in the dermis.7
Scleroderma is a connective tissue fibrosis disorder with variable clinical presentations. The systemic sclerosis subset can be divided into localized systemic sclerosis and diffuse systemic sclerosis. Physical examination reveals cutaneous sclerosis in various areas of the body. Localized systemic sclerosis includes sclerosis of the fingers and face, while diffuse systemic sclerosis is notable for progression to the arms, legs, and trunk.8 In addition to sclerosis, diffuse telangiectases also can be observed. Systemic sclerosis is a clinical diagnosis based on physical examination and laboratory studies to identify antibodies such as antinuclear antibodies.
Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans is a variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The initial presentation is characterized by plaques of hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation with atrophy and telangiectases. The lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and classically involve the trunk and flexural areas.9 The diagnosis is made with skin biopsy and immunohistochemical studies, with findings reflective of mycosis fungoides.
Caput medusae (palm tree sign) is a cardinal feature of portal hypertension characterized by grossly dilated and engorged periumbilical veins. To shunt blood from the portal venous system, cutaneous collateral veins between the umbilical veins and abdominal wall veins are used, resulting in the appearance of engorged veins in the anterior abdominal wall.10 The diagnosis can be made with abdominal ultrasonography showing the direction of blood flow through abdominal vessels.
The Diagnosis: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Computed tomography angiography of the chest confirmed a diagnosis of superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome due to external pressure of the indwelling catheter. Upon diagnosis, the left indwelling catheter was removed. Further testing to assess for a potential pulmonary embolism was negative. Resolution of the ectatic spider veins and patientreported intermittent facial swelling was achieved after catheter removal.
Superior vena cava syndrome occurs when the SVC is occluded due to extrinsic pressure or thrombosis. Although classically thought to be due to underlying bronchogenic carcinomas, all pathologies that cause compression of the SVC also can lead to vessel occlusion.1 Superior vena cava syndrome initially can be detected on physical examination. The most prominent skin finding includes diffusely dilated blood vessels on the central chest wall, which indicate the presence of collateral blood vessels.1 Imaging studies such as abdominal computed tomography can provide information on the etiology of the condition but are not required for diagnosis. Given the high correlation of SVC syndrome with underlying lung and mediastinal carcinomas, imaging was warranted in our patient. Imaging also can distinguish if the condition is due to external pressure or thrombosis.2 For SVC syndrome due to thrombosis, endovascular therapy is first-line management; however, mechanical thrombectomy may be preferred in patients with absolute contraindication to thrombolytic agents.3 In the setting of increased external pressure on the SVC, treatment includes the removal of the source of pressure.4
In a case series including 78 patients, ports and indwelling catheters accounted for 71% of benign SVC cases.5 Our patient’s SVC syndrome most likely was due to the indwelling catheter pressing on the SVC. The goal of treatment is to address the underlying cause—whether it be pressure or thrombosis. In the setting of increased external pressure, treatment includes removal of the source of pressure from the SVC.4
Other differential diagnoses to consider for newonset ectatic vessels on the chest wall include generalized essential telangiectasia, scleroderma, poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans, and caput medusae. Generalized essential telangiectasia is characterized by red or pink dilated capillary blood vessels in a branch or lacelike pattern predominantly on the lower limbs. The eruption primarily is asymptomatic, though tingling or numbness may be reported.6 The diagnosis can be made with a punch biopsy, with histopathology showing dilated vessels in the dermis.7
Scleroderma is a connective tissue fibrosis disorder with variable clinical presentations. The systemic sclerosis subset can be divided into localized systemic sclerosis and diffuse systemic sclerosis. Physical examination reveals cutaneous sclerosis in various areas of the body. Localized systemic sclerosis includes sclerosis of the fingers and face, while diffuse systemic sclerosis is notable for progression to the arms, legs, and trunk.8 In addition to sclerosis, diffuse telangiectases also can be observed. Systemic sclerosis is a clinical diagnosis based on physical examination and laboratory studies to identify antibodies such as antinuclear antibodies.
Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans is a variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. The initial presentation is characterized by plaques of hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation with atrophy and telangiectases. The lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and classically involve the trunk and flexural areas.9 The diagnosis is made with skin biopsy and immunohistochemical studies, with findings reflective of mycosis fungoides.
Caput medusae (palm tree sign) is a cardinal feature of portal hypertension characterized by grossly dilated and engorged periumbilical veins. To shunt blood from the portal venous system, cutaneous collateral veins between the umbilical veins and abdominal wall veins are used, resulting in the appearance of engorged veins in the anterior abdominal wall.10 The diagnosis can be made with abdominal ultrasonography showing the direction of blood flow through abdominal vessels.
- Drouin L, Pistorius MA, Lafforgue A, et al. Upper-extremity venous thrombosis: a retrospective study about 160 cases [in French]. Rev Med Interne. 2019;40:9-15.
- Richie E. Clinical pearl: diagnosing superior vena cava syndrome. Emergency Medicine News. 2017;39:22. doi:10.1097/01 .EEM.0000522220.37441.d2
- Azizi A, Shafi I, Shah N, et al. Superior vena cava syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;13:2896-2910. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2020.08.038
- Dumantepe M, Tarhan A, Ozler A. Successful treatment of central venous catheter induced superior vena cava syndrome with ultrasound accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:E269-E273.
- Rice TW, Rodriguez RM, Light RW. The superior vena cava syndrome: clinical characteristics and evolving etiology. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006;85:37-42. doi:10.1097/01.md.0000198474.99876.f0
- Long D, Marshman G. Generalized essential telangiectasia. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:67-69. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.00033.x
- Braverman IM. Ultrastructure and organization of the cutaneous microvasculature in normal and pathologic states. J Invest Dermatol. 1989;93(2 suppl):2S-9S.
- Ferreli C, Gasparini G, Parodi A, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma and scleroderma-like disorders: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:306-336. doi:10.1007 /s12016-017-8625-4
- Bloom B, Marchbein S, Fischer M, et al. Poikilodermatous mycosis fungoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:4.
- Sharma B, Raina S. Caput medusae. Indian J Med Res. 2015;141:494. doi:10.4103/0971-5916.159322
- Drouin L, Pistorius MA, Lafforgue A, et al. Upper-extremity venous thrombosis: a retrospective study about 160 cases [in French]. Rev Med Interne. 2019;40:9-15.
- Richie E. Clinical pearl: diagnosing superior vena cava syndrome. Emergency Medicine News. 2017;39:22. doi:10.1097/01 .EEM.0000522220.37441.d2
- Azizi A, Shafi I, Shah N, et al. Superior vena cava syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;13:2896-2910. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2020.08.038
- Dumantepe M, Tarhan A, Ozler A. Successful treatment of central venous catheter induced superior vena cava syndrome with ultrasound accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:E269-E273.
- Rice TW, Rodriguez RM, Light RW. The superior vena cava syndrome: clinical characteristics and evolving etiology. Medicine (Baltimore) 2006;85:37-42. doi:10.1097/01.md.0000198474.99876.f0
- Long D, Marshman G. Generalized essential telangiectasia. Australas J Dermatol. 2004;45:67-69. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.00033.x
- Braverman IM. Ultrastructure and organization of the cutaneous microvasculature in normal and pathologic states. J Invest Dermatol. 1989;93(2 suppl):2S-9S.
- Ferreli C, Gasparini G, Parodi A, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma and scleroderma-like disorders: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:306-336. doi:10.1007 /s12016-017-8625-4
- Bloom B, Marchbein S, Fischer M, et al. Poikilodermatous mycosis fungoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:4.
- Sharma B, Raina S. Caput medusae. Indian J Med Res. 2015;141:494. doi:10.4103/0971-5916.159322
A 32-year-old woman presented to vascular surgery for evaluation of spider veins of 2 years’ duration that originated on the breasts but later spread to include the central chest, inframammary folds, and back. She reported associated pain and discomfort as well as intermittent facial swelling and tachycardia but denied pruritus and bleeding. The patient had a history of a kidney transplant 6 months prior, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, and Sjögren syndrome with a left indwelling catheter. Her current medications included systemic immunosuppressive agents. Physical examination revealed blue-purple ectatic vessels on the inframammary folds and central chest extending to the back. Erythema on the face, neck, and arms was not appreciated. No palpable cervical, supraclavicular, or axillary lymph nodes were noted.
Do Plant-based Psychedelics Offer a New Option for TBI Treatment?
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Lump in breast
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 34-year-old woman visits her primary care physician after detecting a lump in her right breast. The physician conducts a physical exam and finds a hard, poorly mobile mass in the outer upper quadrant. Ultrasonography reveals an irregular hypoechoic mass of 22.1 x 15.1 mm with several abnormal axillary lymph nodes. MRI of the right breast shows an irregularly shaped and lobulated mass in the outer upper quadrant with enlarged axillary lymph nodes. On further radiologic examination, there is no detectable metastatic spread to the brain, chest, or upper abdomen. The patient undergoes a core needle biopsy of the tumor, which confirms ductal carcinoma and right axillary lymph node metastasis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay of the sample is negative for hormone receptor (HR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2).
Fall Abstract Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar Compendium; Las Vegas, Nevada; November 2-4, 2023
Men with atopic dermatitis more likely to have poorer cognitive function
Key clinical point: A significant association was observed between atopic dermatitis (AD) and poorer cognitive function in men, and familial characteristics exerted a confounding effect on this association.
Major finding: After effectively controlling for familial environmental confounding factors and addressing genetic influences, AD in men was significantly associated with poorer cognitive function (regression coefficient −0.04; 95% CI −0.07 to −0.003).
Study details: This sibling-comparison study included 1,687,038 men who underwent a military conscription examination at 17-22 years of age, of which 25,995 were diagnosed with AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by grants from the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare (Forte) and the UK Economic and Social Research Council. L von Kobyletzki declared being a consultant for and receiving research funding from various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Smith KA et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive function: A sibling comparison study among males in Sweden. Br J Dermatol. 2024 (Jan 3). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae004
Key clinical point: A significant association was observed between atopic dermatitis (AD) and poorer cognitive function in men, and familial characteristics exerted a confounding effect on this association.
Major finding: After effectively controlling for familial environmental confounding factors and addressing genetic influences, AD in men was significantly associated with poorer cognitive function (regression coefficient −0.04; 95% CI −0.07 to −0.003).
Study details: This sibling-comparison study included 1,687,038 men who underwent a military conscription examination at 17-22 years of age, of which 25,995 were diagnosed with AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by grants from the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare (Forte) and the UK Economic and Social Research Council. L von Kobyletzki declared being a consultant for and receiving research funding from various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Smith KA et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive function: A sibling comparison study among males in Sweden. Br J Dermatol. 2024 (Jan 3). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae004
Key clinical point: A significant association was observed between atopic dermatitis (AD) and poorer cognitive function in men, and familial characteristics exerted a confounding effect on this association.
Major finding: After effectively controlling for familial environmental confounding factors and addressing genetic influences, AD in men was significantly associated with poorer cognitive function (regression coefficient −0.04; 95% CI −0.07 to −0.003).
Study details: This sibling-comparison study included 1,687,038 men who underwent a military conscription examination at 17-22 years of age, of which 25,995 were diagnosed with AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by grants from the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare (Forte) and the UK Economic and Social Research Council. L von Kobyletzki declared being a consultant for and receiving research funding from various organizations. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Smith KA et al. Atopic dermatitis and cognitive function: A sibling comparison study among males in Sweden. Br J Dermatol. 2024 (Jan 3). doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae004
Atopic dermatitis is associated with increased prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease
Key clinical point: Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), especially moderate-to-severe AD, had an increased prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Major finding: A significant association was observed between IBD and AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.89; P = .0169); however, when stratified by AD severity, only moderate-to-severe AD was found to be associated with IBD (aOR 4.45; P = .0102).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective observational study including 364 patients with AD and 725 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by an independent investigator grant from AbbVie. Two authors declared serving as investigators for or receiving honoraria or fees as consultants or advisory board members from various organizations, including AbbVie. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rom H et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease in adults: A cross-sectional study in a specialized atopic dermatitis clinic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Dec 21). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19769
Key clinical point: Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), especially moderate-to-severe AD, had an increased prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Major finding: A significant association was observed between IBD and AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.89; P = .0169); however, when stratified by AD severity, only moderate-to-severe AD was found to be associated with IBD (aOR 4.45; P = .0102).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective observational study including 364 patients with AD and 725 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by an independent investigator grant from AbbVie. Two authors declared serving as investigators for or receiving honoraria or fees as consultants or advisory board members from various organizations, including AbbVie. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rom H et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease in adults: A cross-sectional study in a specialized atopic dermatitis clinic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Dec 21). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19769
Key clinical point: Patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), especially moderate-to-severe AD, had an increased prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Major finding: A significant association was observed between IBD and AD (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.89; P = .0169); however, when stratified by AD severity, only moderate-to-severe AD was found to be associated with IBD (aOR 4.45; P = .0102).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective observational study including 364 patients with AD and 725 matched control individuals without AD.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by an independent investigator grant from AbbVie. Two authors declared serving as investigators for or receiving honoraria or fees as consultants or advisory board members from various organizations, including AbbVie. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Rom H et al. The association between atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease in adults: A cross-sectional study in a specialized atopic dermatitis clinic. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 (Dec 21). doi: 10.1111/jdv.19769
Real-world study confirms the multidimensional efficacy of tralokinumab in atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: The majority of tralokinumab-treated patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) attained physician- and patient-reported outcomes over 32 weeks of observation, highlighting the multidimensional efficacy of tralokinumab in real-world settings.
Major finding: The proportion of patients achieving a ≥75% improvement in the baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score increased significantly from 42% at week 4 to 76% at week 32 (P = .0075). A similar trend was observed for patient-reported outcomes. At week 16, at least one real-world therapeutic endpoint was achieved by 88% of patients treated with tralokinumab.
Study details: Findings are from a multicenter real-world retrospective cohort study including 194 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were treated with tralokinumab for ≥16 weeks.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Several authors declared serving as speakers, consultants, or scientific advisors; receiving personal fees, speaker’s honoraria, or travel support, or having other ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Chiricozzi A et al for the MEDaCoTRA Study Group. Current treatment goals are achieved by the majority of patients with atopic dermatitis treated with tralokinumab: Results from a multicentric, multinational, retrospective, cohort study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23(12):1307-1315 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2292627
Key clinical point: The majority of tralokinumab-treated patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) attained physician- and patient-reported outcomes over 32 weeks of observation, highlighting the multidimensional efficacy of tralokinumab in real-world settings.
Major finding: The proportion of patients achieving a ≥75% improvement in the baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score increased significantly from 42% at week 4 to 76% at week 32 (P = .0075). A similar trend was observed for patient-reported outcomes. At week 16, at least one real-world therapeutic endpoint was achieved by 88% of patients treated with tralokinumab.
Study details: Findings are from a multicenter real-world retrospective cohort study including 194 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were treated with tralokinumab for ≥16 weeks.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Several authors declared serving as speakers, consultants, or scientific advisors; receiving personal fees, speaker’s honoraria, or travel support, or having other ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Chiricozzi A et al for the MEDaCoTRA Study Group. Current treatment goals are achieved by the majority of patients with atopic dermatitis treated with tralokinumab: Results from a multicentric, multinational, retrospective, cohort study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23(12):1307-1315 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2292627
Key clinical point: The majority of tralokinumab-treated patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) attained physician- and patient-reported outcomes over 32 weeks of observation, highlighting the multidimensional efficacy of tralokinumab in real-world settings.
Major finding: The proportion of patients achieving a ≥75% improvement in the baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score increased significantly from 42% at week 4 to 76% at week 32 (P = .0075). A similar trend was observed for patient-reported outcomes. At week 16, at least one real-world therapeutic endpoint was achieved by 88% of patients treated with tralokinumab.
Study details: Findings are from a multicenter real-world retrospective cohort study including 194 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were treated with tralokinumab for ≥16 weeks.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Several authors declared serving as speakers, consultants, or scientific advisors; receiving personal fees, speaker’s honoraria, or travel support, or having other ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Chiricozzi A et al for the MEDaCoTRA Study Group. Current treatment goals are achieved by the majority of patients with atopic dermatitis treated with tralokinumab: Results from a multicentric, multinational, retrospective, cohort study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023;23(12):1307-1315 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2292627
Abrocitinib downregulates genes associated with atopic dermatitis pathology
Key clinical point: Abrocitinib treatment over 12 weeks significantly decreased the cutaneous expression of selected genes involved in inflammation, epidermal hyperplasia, and T-helper (Th) 2 and Th22 immune responses in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Compared with placebo, 12-week abrocitinib treatment led to a dose-dependent reduction in the cutaneous expression of genes involved in inflammation (MMP-12), epidermal hyperplasia (KRT16), Th2 (CCL17 and CCL18), and Th22 (S100A8, S100A9, and S100A12) responses (all P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2a JADE MOA trial including patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were randomly assigned to receive 100 mg (n = 16) or 200 mg (n = 14) abrocitinib monotherapy or placebo (n = 16) daily for 12 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Several authors declared being on the advisory board of; serving as consultants, advisors, or speakers for; or receiving honoraria or grants from Pfizer or others. Seven authors declared being current or former employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Guttman-Yassky E et al. Effect of abrocitinib on skin biomarkers in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1111/all.15969
Key clinical point: Abrocitinib treatment over 12 weeks significantly decreased the cutaneous expression of selected genes involved in inflammation, epidermal hyperplasia, and T-helper (Th) 2 and Th22 immune responses in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Compared with placebo, 12-week abrocitinib treatment led to a dose-dependent reduction in the cutaneous expression of genes involved in inflammation (MMP-12), epidermal hyperplasia (KRT16), Th2 (CCL17 and CCL18), and Th22 (S100A8, S100A9, and S100A12) responses (all P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2a JADE MOA trial including patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were randomly assigned to receive 100 mg (n = 16) or 200 mg (n = 14) abrocitinib monotherapy or placebo (n = 16) daily for 12 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Several authors declared being on the advisory board of; serving as consultants, advisors, or speakers for; or receiving honoraria or grants from Pfizer or others. Seven authors declared being current or former employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Guttman-Yassky E et al. Effect of abrocitinib on skin biomarkers in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1111/all.15969
Key clinical point: Abrocitinib treatment over 12 weeks significantly decreased the cutaneous expression of selected genes involved in inflammation, epidermal hyperplasia, and T-helper (Th) 2 and Th22 immune responses in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: Compared with placebo, 12-week abrocitinib treatment led to a dose-dependent reduction in the cutaneous expression of genes involved in inflammation (MMP-12), epidermal hyperplasia (KRT16), Th2 (CCL17 and CCL18), and Th22 (S100A8, S100A9, and S100A12) responses (all P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 2a JADE MOA trial including patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were randomly assigned to receive 100 mg (n = 16) or 200 mg (n = 14) abrocitinib monotherapy or placebo (n = 16) daily for 12 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Several authors declared being on the advisory board of; serving as consultants, advisors, or speakers for; or receiving honoraria or grants from Pfizer or others. Seven authors declared being current or former employees and shareholders of Pfizer.
Source: Guttman-Yassky E et al. Effect of abrocitinib on skin biomarkers in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2023 (Dec 18). doi: 10.1111/all.15969