User login
Official Newspaper of the American College of Surgeons
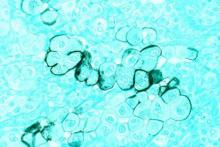
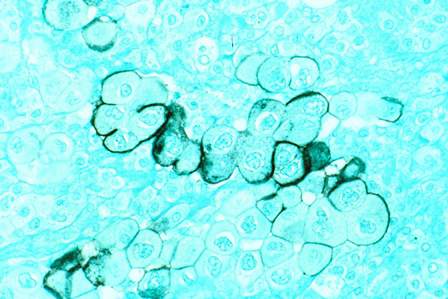
Surgery has edge over surveillance for micropapillary thyroid cancer
BALTIMORE – Hemithyroidectomy for low-risk micropapillary thyroid cancer can have advantages over active surveillance, according to findings from a study that examined outcomes by cost and quality of life data.
Endocrinologists and surgeons need to have in-depth conversations with their patients to determine their level of anxiety about cancer, surgery, and about their quality of life, to determine the best course of treatment, researchers at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) reported at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
“Our study found that hemithyroidectomy is cost effective in the majority of scenarios,” presenter Shriya Venkatesh said. “However, patient perception of micropapillary thyroid cancer as well as [the patient’s] life expectancy can play a major role in deciding which therapeutic option to choose.”
The study involved a cost-effectiveness analysis of the surgery vs. active surveillance, “which is especially relevant in our current times,” Ms. Venkatesh said in an interview. “What we wanted to do is give physicians information for when they approach their patients, not only in assessing the tumor from the medical aspect but also when looking at it from quality-of-life and cost-benefit perspectives.”
Both courses of management were modeled over a 20-year period with Medicare data and literature review to calculate costs and health utilities. The UCSF researchers used Markov statistical models for both approaches in which the reference case was a 40-year-old, otherwise healthy patient with a recent diagnosis of micropapillary thyroid cancer without high-risk factors. Either hemithyroidectomy or surveillance would be reasonable treatment options.
“We found that hemithyroidectomy was about $8,000 more costly than active surveillance, but it also afforded an increase in about 1.09 quality-adjusted life years,” Ms. Venkatesh said. Hemithyroidectomy is most cost effective for patients with a life expectancy of 3 years or more and who perceive that living with low-grade thyroid cancer would have even a modest detriment on their quality of life, she said.
“Unfortunately there is no current published quality-of-life assessment of active surveillance for thyroid cancer,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “We believe that estimating active surveillance to the equivalent of surgery underestimates the anxiety some patients may feel upon receiving their diagnosis.”
The paucity of literature on active surveillance for thyroid cancer prompted the UCSF researchers to turn to the prostate cancer literature, which has more data on active surveillance, to try to determine the disutility of active surveillance for micropapillary thyroid cancer. “Our extrapolation from the literature yields a mean disutility of 0.11,” she said.
However, the utility estimates the researchers came up with were variable, Ms. Venkatesh said. “This really pushes physicians to have that conversation with their patients, not only about the physical aspects of how they’re doing but also the mental aspects,” she said.
But quality of life is difficult to quantify, senior author Dr. Insoo Suh said in an interview. “What we found is that no matter how one measures quality of life, the qualitative degree of quality of life decrease that people associate with ‘living with cancer’ need not be that significant in order for surgery to be a potentially cost-effective treatment for them,” said Dr. Suh, an endocrine surgeon at UCSF and an ACS Fellow.
During the discussion, Dr. Peter Angelos of the University of Chicago and an ACS Fellow, said, “I’m curious how this information should impact the individual decision-making and informed consent for a specific patient, because I’m not sure that an individual patient would care if active surveillance is more cost effective or not.”
“When speaking to your patients, obviously discussing the rates of progression of the disease is important and then [so is] talking to them about different therapeutic options,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “The physician should also make an assessment about the patient’s quality of life to see if there are likely to be any changes due to the diagnosis.”
The limitations of the study include the extrapolation of data from the prostate cancer literature to define a utility scale and also the reference case used in the Markov model. Other utility measures showed variability as well.
Ms. Venkatesh, Dr. Suh and their coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
BALTIMORE – Hemithyroidectomy for low-risk micropapillary thyroid cancer can have advantages over active surveillance, according to findings from a study that examined outcomes by cost and quality of life data.
Endocrinologists and surgeons need to have in-depth conversations with their patients to determine their level of anxiety about cancer, surgery, and about their quality of life, to determine the best course of treatment, researchers at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) reported at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
“Our study found that hemithyroidectomy is cost effective in the majority of scenarios,” presenter Shriya Venkatesh said. “However, patient perception of micropapillary thyroid cancer as well as [the patient’s] life expectancy can play a major role in deciding which therapeutic option to choose.”
The study involved a cost-effectiveness analysis of the surgery vs. active surveillance, “which is especially relevant in our current times,” Ms. Venkatesh said in an interview. “What we wanted to do is give physicians information for when they approach their patients, not only in assessing the tumor from the medical aspect but also when looking at it from quality-of-life and cost-benefit perspectives.”
Both courses of management were modeled over a 20-year period with Medicare data and literature review to calculate costs and health utilities. The UCSF researchers used Markov statistical models for both approaches in which the reference case was a 40-year-old, otherwise healthy patient with a recent diagnosis of micropapillary thyroid cancer without high-risk factors. Either hemithyroidectomy or surveillance would be reasonable treatment options.
“We found that hemithyroidectomy was about $8,000 more costly than active surveillance, but it also afforded an increase in about 1.09 quality-adjusted life years,” Ms. Venkatesh said. Hemithyroidectomy is most cost effective for patients with a life expectancy of 3 years or more and who perceive that living with low-grade thyroid cancer would have even a modest detriment on their quality of life, she said.
“Unfortunately there is no current published quality-of-life assessment of active surveillance for thyroid cancer,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “We believe that estimating active surveillance to the equivalent of surgery underestimates the anxiety some patients may feel upon receiving their diagnosis.”
The paucity of literature on active surveillance for thyroid cancer prompted the UCSF researchers to turn to the prostate cancer literature, which has more data on active surveillance, to try to determine the disutility of active surveillance for micropapillary thyroid cancer. “Our extrapolation from the literature yields a mean disutility of 0.11,” she said.
However, the utility estimates the researchers came up with were variable, Ms. Venkatesh said. “This really pushes physicians to have that conversation with their patients, not only about the physical aspects of how they’re doing but also the mental aspects,” she said.
But quality of life is difficult to quantify, senior author Dr. Insoo Suh said in an interview. “What we found is that no matter how one measures quality of life, the qualitative degree of quality of life decrease that people associate with ‘living with cancer’ need not be that significant in order for surgery to be a potentially cost-effective treatment for them,” said Dr. Suh, an endocrine surgeon at UCSF and an ACS Fellow.
During the discussion, Dr. Peter Angelos of the University of Chicago and an ACS Fellow, said, “I’m curious how this information should impact the individual decision-making and informed consent for a specific patient, because I’m not sure that an individual patient would care if active surveillance is more cost effective or not.”
“When speaking to your patients, obviously discussing the rates of progression of the disease is important and then [so is] talking to them about different therapeutic options,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “The physician should also make an assessment about the patient’s quality of life to see if there are likely to be any changes due to the diagnosis.”
The limitations of the study include the extrapolation of data from the prostate cancer literature to define a utility scale and also the reference case used in the Markov model. Other utility measures showed variability as well.
Ms. Venkatesh, Dr. Suh and their coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
BALTIMORE – Hemithyroidectomy for low-risk micropapillary thyroid cancer can have advantages over active surveillance, according to findings from a study that examined outcomes by cost and quality of life data.
Endocrinologists and surgeons need to have in-depth conversations with their patients to determine their level of anxiety about cancer, surgery, and about their quality of life, to determine the best course of treatment, researchers at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) reported at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
“Our study found that hemithyroidectomy is cost effective in the majority of scenarios,” presenter Shriya Venkatesh said. “However, patient perception of micropapillary thyroid cancer as well as [the patient’s] life expectancy can play a major role in deciding which therapeutic option to choose.”
The study involved a cost-effectiveness analysis of the surgery vs. active surveillance, “which is especially relevant in our current times,” Ms. Venkatesh said in an interview. “What we wanted to do is give physicians information for when they approach their patients, not only in assessing the tumor from the medical aspect but also when looking at it from quality-of-life and cost-benefit perspectives.”
Both courses of management were modeled over a 20-year period with Medicare data and literature review to calculate costs and health utilities. The UCSF researchers used Markov statistical models for both approaches in which the reference case was a 40-year-old, otherwise healthy patient with a recent diagnosis of micropapillary thyroid cancer without high-risk factors. Either hemithyroidectomy or surveillance would be reasonable treatment options.
“We found that hemithyroidectomy was about $8,000 more costly than active surveillance, but it also afforded an increase in about 1.09 quality-adjusted life years,” Ms. Venkatesh said. Hemithyroidectomy is most cost effective for patients with a life expectancy of 3 years or more and who perceive that living with low-grade thyroid cancer would have even a modest detriment on their quality of life, she said.
“Unfortunately there is no current published quality-of-life assessment of active surveillance for thyroid cancer,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “We believe that estimating active surveillance to the equivalent of surgery underestimates the anxiety some patients may feel upon receiving their diagnosis.”
The paucity of literature on active surveillance for thyroid cancer prompted the UCSF researchers to turn to the prostate cancer literature, which has more data on active surveillance, to try to determine the disutility of active surveillance for micropapillary thyroid cancer. “Our extrapolation from the literature yields a mean disutility of 0.11,” she said.
However, the utility estimates the researchers came up with were variable, Ms. Venkatesh said. “This really pushes physicians to have that conversation with their patients, not only about the physical aspects of how they’re doing but also the mental aspects,” she said.
But quality of life is difficult to quantify, senior author Dr. Insoo Suh said in an interview. “What we found is that no matter how one measures quality of life, the qualitative degree of quality of life decrease that people associate with ‘living with cancer’ need not be that significant in order for surgery to be a potentially cost-effective treatment for them,” said Dr. Suh, an endocrine surgeon at UCSF and an ACS Fellow.
During the discussion, Dr. Peter Angelos of the University of Chicago and an ACS Fellow, said, “I’m curious how this information should impact the individual decision-making and informed consent for a specific patient, because I’m not sure that an individual patient would care if active surveillance is more cost effective or not.”
“When speaking to your patients, obviously discussing the rates of progression of the disease is important and then [so is] talking to them about different therapeutic options,” Ms. Venkatesh said. “The physician should also make an assessment about the patient’s quality of life to see if there are likely to be any changes due to the diagnosis.”
The limitations of the study include the extrapolation of data from the prostate cancer literature to define a utility scale and also the reference case used in the Markov model. Other utility measures showed variability as well.
Ms. Venkatesh, Dr. Suh and their coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
AT AAES 2016
Key clinical point: Patient psychological factors are key determinants in choosing a course of management for low-risk micropapillary thyroid cancer.
Major finding: Hemithyroidectomy typically costs about $8,000 more than active surveillance but also accounts for improved quality of life in these patients.
Data source: Markov models for both courses of management over a 20-year period with Medicare data and literature review to calculate costs and health utilities.
Disclosures: Ms. Venkatesh and her coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
Post-parathyroidectomy follow-up may need to be open-ended
BALTIMORE – Patients who have had parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism can have disease recurrence 10 years or longer after surgery, raising the possibility that postop follow-up should never end, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
Dr. Irene Lou of the University of Wisconsin–Madison reported on results of a retrospective study of 196 patients who had a presumably “curative” parathyroidectomy at the institution between November 2000 and June 2005. The mean age of the study population was 61 years.
“The long-term recurrences of primary hyperparathyroidism after curative parathyroidectomy is likely higher than previously reported, with over a third of recurrences occurring 10 years after their operation,” Dr. Lou said.
The study also identified independent predictors of recurrence, among them younger age, a drop in intraoperative parathyroid hormone less than 70%, and double adenoma, Dr. Lou said. All patients after parathyroidectomy should have at minimum an annual serum calcium test, especially younger patients with longer life expectancies, she said. This recommendation, however, may be altered for older patients or those with additional comorbidities.
The study defined recurrence as serum calcium of 10.2 mg/dL or greater 6 months or longer after the initial operation. The overall 10-year recurrence rate was 14.8% and the median time to recurrence was 6.3 years. “We found that 41.4% of patients who recurred did so by 5 years and 65.5% by 10 years,” Dr. Lou said.
The University of Wisconsin and University of Alabama at Birmingham investigators undertook the study because the recent data on recurrence was limited, with the longest study topping out at 7 years, Dr. Lou said. “We previously looked at this problem in other perspectives and we found that a lot of curves separated at around 8 years,” she said.
With regard to the type of operation the patients had, whether unilateral minimally invasive parathyroidectomy or bilateral open surgery, the study found no significant differences in recurrence rates, Dr. Lou said. “This is an excellent study,” Dr. Samuel K. Snyder of Temple, Tex., said during the discussion. “You’re telling us we need to follow patients much longer than perhaps we did previously, but we all see patients who have normal calcium and still have a residual elevated parathyroid hormone level.” He asked if the study considered parathyroid hormone levels at 6 months or more after surgery or vitamin D levels, but Dr. Lou said this information was not available, therefore could not be evaluated.
Dr. Lou and her coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
BALTIMORE – Patients who have had parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism can have disease recurrence 10 years or longer after surgery, raising the possibility that postop follow-up should never end, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
Dr. Irene Lou of the University of Wisconsin–Madison reported on results of a retrospective study of 196 patients who had a presumably “curative” parathyroidectomy at the institution between November 2000 and June 2005. The mean age of the study population was 61 years.
“The long-term recurrences of primary hyperparathyroidism after curative parathyroidectomy is likely higher than previously reported, with over a third of recurrences occurring 10 years after their operation,” Dr. Lou said.
The study also identified independent predictors of recurrence, among them younger age, a drop in intraoperative parathyroid hormone less than 70%, and double adenoma, Dr. Lou said. All patients after parathyroidectomy should have at minimum an annual serum calcium test, especially younger patients with longer life expectancies, she said. This recommendation, however, may be altered for older patients or those with additional comorbidities.
The study defined recurrence as serum calcium of 10.2 mg/dL or greater 6 months or longer after the initial operation. The overall 10-year recurrence rate was 14.8% and the median time to recurrence was 6.3 years. “We found that 41.4% of patients who recurred did so by 5 years and 65.5% by 10 years,” Dr. Lou said.
The University of Wisconsin and University of Alabama at Birmingham investigators undertook the study because the recent data on recurrence was limited, with the longest study topping out at 7 years, Dr. Lou said. “We previously looked at this problem in other perspectives and we found that a lot of curves separated at around 8 years,” she said.
With regard to the type of operation the patients had, whether unilateral minimally invasive parathyroidectomy or bilateral open surgery, the study found no significant differences in recurrence rates, Dr. Lou said. “This is an excellent study,” Dr. Samuel K. Snyder of Temple, Tex., said during the discussion. “You’re telling us we need to follow patients much longer than perhaps we did previously, but we all see patients who have normal calcium and still have a residual elevated parathyroid hormone level.” He asked if the study considered parathyroid hormone levels at 6 months or more after surgery or vitamin D levels, but Dr. Lou said this information was not available, therefore could not be evaluated.
Dr. Lou and her coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
BALTIMORE – Patients who have had parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism can have disease recurrence 10 years or longer after surgery, raising the possibility that postop follow-up should never end, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons.
Dr. Irene Lou of the University of Wisconsin–Madison reported on results of a retrospective study of 196 patients who had a presumably “curative” parathyroidectomy at the institution between November 2000 and June 2005. The mean age of the study population was 61 years.
“The long-term recurrences of primary hyperparathyroidism after curative parathyroidectomy is likely higher than previously reported, with over a third of recurrences occurring 10 years after their operation,” Dr. Lou said.
The study also identified independent predictors of recurrence, among them younger age, a drop in intraoperative parathyroid hormone less than 70%, and double adenoma, Dr. Lou said. All patients after parathyroidectomy should have at minimum an annual serum calcium test, especially younger patients with longer life expectancies, she said. This recommendation, however, may be altered for older patients or those with additional comorbidities.
The study defined recurrence as serum calcium of 10.2 mg/dL or greater 6 months or longer after the initial operation. The overall 10-year recurrence rate was 14.8% and the median time to recurrence was 6.3 years. “We found that 41.4% of patients who recurred did so by 5 years and 65.5% by 10 years,” Dr. Lou said.
The University of Wisconsin and University of Alabama at Birmingham investigators undertook the study because the recent data on recurrence was limited, with the longest study topping out at 7 years, Dr. Lou said. “We previously looked at this problem in other perspectives and we found that a lot of curves separated at around 8 years,” she said.
With regard to the type of operation the patients had, whether unilateral minimally invasive parathyroidectomy or bilateral open surgery, the study found no significant differences in recurrence rates, Dr. Lou said. “This is an excellent study,” Dr. Samuel K. Snyder of Temple, Tex., said during the discussion. “You’re telling us we need to follow patients much longer than perhaps we did previously, but we all see patients who have normal calcium and still have a residual elevated parathyroid hormone level.” He asked if the study considered parathyroid hormone levels at 6 months or more after surgery or vitamin D levels, but Dr. Lou said this information was not available, therefore could not be evaluated.
Dr. Lou and her coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose.
FROM AAES 2016
Key clinical point: Long-term recurrence rates for hyperparathyroidism (HPT) after “curative” parathyroidectomy are likely higher than previously reported.
Major finding: Approximately one-third of patients were found to have recurrences 10 or more years after the initial operation.
Data source: Single-institution cohort of 196 patients who had initial parathyroidectomy for HPT between November 2000 and June 2005.
Disclosures: Dr. Lou and her study coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
Reintubation avoided by majority of patients on noninvasive ventilation therapy, high-flow oxygen
Extubated patients who either received noninvasive ventilation (NIV) therapy or high-flow nasal cannula oxygen had a lower risk of reintubation, compared with extubated patients who received some form of standard oxygen therapy, according to the results of two multicenter, randomized clinical trials published online in JAMA.
Participants in one of the studies, which included abdominal surgery patients diagnosed with respiratory failure within 7 days following surgery, either received NIV or standard oxygen therapy for 30 days or until ICU discharge, whichever came first. While NIV has been effectively used to treat nonsurgical patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiogenic pulmonary edema, there is no evidence to support the use of NIV in surgical patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure after abdominal surgery, according to Dr. Samir Jaber of the Saint Eloi University Hospital and Montpellier School of Medicine, both in Montpellier, France, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1345-53).
The second study included adult patients who had received mechanical ventilation for more than 12 hours and who met criteria for being considered at low risk for reintubation. Patients were administered either high-flow oxygen therapy through nasal cannula immediately after extubation or continuous conventional oxygen therapy through nasal cannula or nonrebreather facemask; the patients were observed for 72 hours. High-flow therapy has been shown to improve oxygenation and survival in clinical studies of critically ill patients in the acute phase of respiratory failure. “[A study by S.M. Maggiore and his colleagues (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(3):282-8)] suggested that high-flow therapy after planned extubation decreased the reintubation rate in a general population of critical patients, but the benefits might be mainly attributable to improvements in high-risk patients,” said Dr. Gonzalo Hernandez, of the Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo, Spain, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1354-61).
In the first study, 148 patients received NIV and 145 patients received standard oxygen therapy only. NIV was administered through a facemask connected to an ICU- or a NIV-dedicated ventilator, using either a heated humidifier or heat and moisture exchanger to warm and humidify inspired gases. Patients were encouraged to use NIV for 6 hours during the first 24 hours of the study and received standard oxygen therapy at a rate of up to 15 L/minute to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate (SpO2) of at least 94% in between NIV sessions. NIV was started at an inspiratory positive airway pressure of 5 cm H2O, increasing to a maximum inspiratory pressure of 15 cm H2O, aiming to achieve an expiratory tidal volume between 6 and 8 mL/kg of predicted body weight and a respiratory rate lower than 25/min. The patients in this study’s control group only received the standard oxygen therapy.
In the other study, 263 patients received conventional therapy, with the oxygen flow having been adjusted to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate of greater than 92%. This study’s other 264 patients received high-flow oxygen therapy, with the flow having been initially set at 10 L/min and titrated upward in 5-L/min steps until patients experienced discomfort. The high-flow therapy was stopped after 24 hours and was followed by conventional oxygen therapy, when needed.
The primary outcome measure in the study involving NIV was cause for reintubation within 7 days of randomization.
Secondary outcome measures included gas exchange, healthcare-associated infection rate within 30 days, number of ventilator-free days between days 1 and 30, antibiotic use duration, ICU and in-hospital length of stay, and 30- and 90-day mortality.
Reintubation occurred in 49 patients in the NIV group and 66 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group, a significant difference (P = .03). Among the reintubated patients, those who had received NIV spent less time under invasive mechanical ventilation as did the patients given standard oxygen therapy. The interquartile ranges of days of invasive mechanical ventilation were 0-3 for patients in the NIV group and 0-5 for patients in the standard oxygen therapy group (P = .05). At 30 days, NIV was associated with significantly more ventilator-free days than standard oxygen therapy (25.4 vs. 23.2; P = .04). At 90 days, 22 patients in the NIV group and 31 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group had died (P = .15).
“Recent high-impact trials have demonstrated the benefits in nonsurgical hypoxemic respiratory failure or equivalence of high-flow nasal cannula compared with NIV in patients after cardiothoracic surgery with moderate to severe hypoxemia. Future studies comparing use of high-flow oxygen cannula vs standard oxygen therapy and NIV for patients after abdominal surgery as preventive (prophylactic) or curative applications are needed,” according to Dr. Jaber and his colleagues.
The primary outcome measure for the study of patients receiving high-flow oxygen therapy was reintubation within 72 hours after extubation; this occurred in fewer patients in the high-flow oxygen group than in the conventional therapy group (13 or 4.9% vs. 32 or 12.2%.) This statistically significant difference was mainly attributable to a lower incidence of respiratory-related reintubation in the high-flow group, compared with the conventional therapy group (1.5% vs. 8.7%), said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
Secondary outcome measures included postextubation respiratory failure, respiratory infection, sepsis, multiorgan failure, ICU and hospital length of stay and mortality, time to reintubation, and adverse effects. Postintubation respiratory failure was less common in the high-flow therapy group than in the conventional therapy group (22 patients or 8.3% vs. 38 or 14.4%). Differences between the two groups in other secondary outcomes were not statistically significant.
“The main finding of this study was that high-flow oxygen significantly reduced the reintubation rate in critically ill patients at low risk for extubation failure ... High-flow therapy improves oxygenation, and the lower rate of reintubation secondary to hypoxia in the high-flow group corroborates this finding. High-flow oxygen also seems to reduce other causes of respiratory failure such as increased work of breathing and respiratory muscle fatigue, which are frequently associated with reintubation secondary to hypoxia. Another way in which high-flow therapy improves extubation outcome is by conditioning the inspired gas,” said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
No adverse events were reported in either study.
Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jaber and his colleagues disclosed no potential conflicts of interest with their study’s sponsors, Montpellier (France) University Hospital and the APARD Foundation.
Dr. Eric Gartman, FCCP, comments: These two studies augment a growing body of literature supporting the use of adjunctive therapies immediately following extubation to prevent reintubation for respiratory failure.
It has been known for several years that the use of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) immediately after extubation in COPD patients prevents reintubation rates, and these new data demonstrate efficacy in an expanded population. Further, the use of high-flow humidified oxygen therapy in acute respiratory failure has been shown to prevent progression to initial intubation, and now these data expand potential use to prevent reintubation, as well.
While not studied, if high-flow oxygen therapy is found to be equivalent to NIV to prevent reintubation (similar to the previously-published prevention of intubation studies), that would be clinically important since there is a significant difference in tolerance to these two therapies. Across these trials, the very important point to remember is that these therapies were found to be effective if put on directly after extubation, and one cannot wait to apply them at the point where the patient shows signs of respiratory decline.
Dr. Eric Gartman, FCCP, comments: These two studies augment a growing body of literature supporting the use of adjunctive therapies immediately following extubation to prevent reintubation for respiratory failure.
It has been known for several years that the use of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) immediately after extubation in COPD patients prevents reintubation rates, and these new data demonstrate efficacy in an expanded population. Further, the use of high-flow humidified oxygen therapy in acute respiratory failure has been shown to prevent progression to initial intubation, and now these data expand potential use to prevent reintubation, as well.
While not studied, if high-flow oxygen therapy is found to be equivalent to NIV to prevent reintubation (similar to the previously-published prevention of intubation studies), that would be clinically important since there is a significant difference in tolerance to these two therapies. Across these trials, the very important point to remember is that these therapies were found to be effective if put on directly after extubation, and one cannot wait to apply them at the point where the patient shows signs of respiratory decline.
Dr. Eric Gartman, FCCP, comments: These two studies augment a growing body of literature supporting the use of adjunctive therapies immediately following extubation to prevent reintubation for respiratory failure.
It has been known for several years that the use of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) immediately after extubation in COPD patients prevents reintubation rates, and these new data demonstrate efficacy in an expanded population. Further, the use of high-flow humidified oxygen therapy in acute respiratory failure has been shown to prevent progression to initial intubation, and now these data expand potential use to prevent reintubation, as well.
While not studied, if high-flow oxygen therapy is found to be equivalent to NIV to prevent reintubation (similar to the previously-published prevention of intubation studies), that would be clinically important since there is a significant difference in tolerance to these two therapies. Across these trials, the very important point to remember is that these therapies were found to be effective if put on directly after extubation, and one cannot wait to apply them at the point where the patient shows signs of respiratory decline.
Extubated patients who either received noninvasive ventilation (NIV) therapy or high-flow nasal cannula oxygen had a lower risk of reintubation, compared with extubated patients who received some form of standard oxygen therapy, according to the results of two multicenter, randomized clinical trials published online in JAMA.
Participants in one of the studies, which included abdominal surgery patients diagnosed with respiratory failure within 7 days following surgery, either received NIV or standard oxygen therapy for 30 days or until ICU discharge, whichever came first. While NIV has been effectively used to treat nonsurgical patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiogenic pulmonary edema, there is no evidence to support the use of NIV in surgical patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure after abdominal surgery, according to Dr. Samir Jaber of the Saint Eloi University Hospital and Montpellier School of Medicine, both in Montpellier, France, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1345-53).
The second study included adult patients who had received mechanical ventilation for more than 12 hours and who met criteria for being considered at low risk for reintubation. Patients were administered either high-flow oxygen therapy through nasal cannula immediately after extubation or continuous conventional oxygen therapy through nasal cannula or nonrebreather facemask; the patients were observed for 72 hours. High-flow therapy has been shown to improve oxygenation and survival in clinical studies of critically ill patients in the acute phase of respiratory failure. “[A study by S.M. Maggiore and his colleagues (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(3):282-8)] suggested that high-flow therapy after planned extubation decreased the reintubation rate in a general population of critical patients, but the benefits might be mainly attributable to improvements in high-risk patients,” said Dr. Gonzalo Hernandez, of the Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo, Spain, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1354-61).
In the first study, 148 patients received NIV and 145 patients received standard oxygen therapy only. NIV was administered through a facemask connected to an ICU- or a NIV-dedicated ventilator, using either a heated humidifier or heat and moisture exchanger to warm and humidify inspired gases. Patients were encouraged to use NIV for 6 hours during the first 24 hours of the study and received standard oxygen therapy at a rate of up to 15 L/minute to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate (SpO2) of at least 94% in between NIV sessions. NIV was started at an inspiratory positive airway pressure of 5 cm H2O, increasing to a maximum inspiratory pressure of 15 cm H2O, aiming to achieve an expiratory tidal volume between 6 and 8 mL/kg of predicted body weight and a respiratory rate lower than 25/min. The patients in this study’s control group only received the standard oxygen therapy.
In the other study, 263 patients received conventional therapy, with the oxygen flow having been adjusted to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate of greater than 92%. This study’s other 264 patients received high-flow oxygen therapy, with the flow having been initially set at 10 L/min and titrated upward in 5-L/min steps until patients experienced discomfort. The high-flow therapy was stopped after 24 hours and was followed by conventional oxygen therapy, when needed.
The primary outcome measure in the study involving NIV was cause for reintubation within 7 days of randomization.
Secondary outcome measures included gas exchange, healthcare-associated infection rate within 30 days, number of ventilator-free days between days 1 and 30, antibiotic use duration, ICU and in-hospital length of stay, and 30- and 90-day mortality.
Reintubation occurred in 49 patients in the NIV group and 66 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group, a significant difference (P = .03). Among the reintubated patients, those who had received NIV spent less time under invasive mechanical ventilation as did the patients given standard oxygen therapy. The interquartile ranges of days of invasive mechanical ventilation were 0-3 for patients in the NIV group and 0-5 for patients in the standard oxygen therapy group (P = .05). At 30 days, NIV was associated with significantly more ventilator-free days than standard oxygen therapy (25.4 vs. 23.2; P = .04). At 90 days, 22 patients in the NIV group and 31 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group had died (P = .15).
“Recent high-impact trials have demonstrated the benefits in nonsurgical hypoxemic respiratory failure or equivalence of high-flow nasal cannula compared with NIV in patients after cardiothoracic surgery with moderate to severe hypoxemia. Future studies comparing use of high-flow oxygen cannula vs standard oxygen therapy and NIV for patients after abdominal surgery as preventive (prophylactic) or curative applications are needed,” according to Dr. Jaber and his colleagues.
The primary outcome measure for the study of patients receiving high-flow oxygen therapy was reintubation within 72 hours after extubation; this occurred in fewer patients in the high-flow oxygen group than in the conventional therapy group (13 or 4.9% vs. 32 or 12.2%.) This statistically significant difference was mainly attributable to a lower incidence of respiratory-related reintubation in the high-flow group, compared with the conventional therapy group (1.5% vs. 8.7%), said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
Secondary outcome measures included postextubation respiratory failure, respiratory infection, sepsis, multiorgan failure, ICU and hospital length of stay and mortality, time to reintubation, and adverse effects. Postintubation respiratory failure was less common in the high-flow therapy group than in the conventional therapy group (22 patients or 8.3% vs. 38 or 14.4%). Differences between the two groups in other secondary outcomes were not statistically significant.
“The main finding of this study was that high-flow oxygen significantly reduced the reintubation rate in critically ill patients at low risk for extubation failure ... High-flow therapy improves oxygenation, and the lower rate of reintubation secondary to hypoxia in the high-flow group corroborates this finding. High-flow oxygen also seems to reduce other causes of respiratory failure such as increased work of breathing and respiratory muscle fatigue, which are frequently associated with reintubation secondary to hypoxia. Another way in which high-flow therapy improves extubation outcome is by conditioning the inspired gas,” said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
No adverse events were reported in either study.
Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jaber and his colleagues disclosed no potential conflicts of interest with their study’s sponsors, Montpellier (France) University Hospital and the APARD Foundation.
Extubated patients who either received noninvasive ventilation (NIV) therapy or high-flow nasal cannula oxygen had a lower risk of reintubation, compared with extubated patients who received some form of standard oxygen therapy, according to the results of two multicenter, randomized clinical trials published online in JAMA.
Participants in one of the studies, which included abdominal surgery patients diagnosed with respiratory failure within 7 days following surgery, either received NIV or standard oxygen therapy for 30 days or until ICU discharge, whichever came first. While NIV has been effectively used to treat nonsurgical patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiogenic pulmonary edema, there is no evidence to support the use of NIV in surgical patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure after abdominal surgery, according to Dr. Samir Jaber of the Saint Eloi University Hospital and Montpellier School of Medicine, both in Montpellier, France, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1345-53).
The second study included adult patients who had received mechanical ventilation for more than 12 hours and who met criteria for being considered at low risk for reintubation. Patients were administered either high-flow oxygen therapy through nasal cannula immediately after extubation or continuous conventional oxygen therapy through nasal cannula or nonrebreather facemask; the patients were observed for 72 hours. High-flow therapy has been shown to improve oxygenation and survival in clinical studies of critically ill patients in the acute phase of respiratory failure. “[A study by S.M. Maggiore and his colleagues (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(3):282-8)] suggested that high-flow therapy after planned extubation decreased the reintubation rate in a general population of critical patients, but the benefits might be mainly attributable to improvements in high-risk patients,” said Dr. Gonzalo Hernandez, of the Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo, Spain, and his colleagues (JAMA. 2016 Apr 5;315[13]:1354-61).
In the first study, 148 patients received NIV and 145 patients received standard oxygen therapy only. NIV was administered through a facemask connected to an ICU- or a NIV-dedicated ventilator, using either a heated humidifier or heat and moisture exchanger to warm and humidify inspired gases. Patients were encouraged to use NIV for 6 hours during the first 24 hours of the study and received standard oxygen therapy at a rate of up to 15 L/minute to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate (SpO2) of at least 94% in between NIV sessions. NIV was started at an inspiratory positive airway pressure of 5 cm H2O, increasing to a maximum inspiratory pressure of 15 cm H2O, aiming to achieve an expiratory tidal volume between 6 and 8 mL/kg of predicted body weight and a respiratory rate lower than 25/min. The patients in this study’s control group only received the standard oxygen therapy.
In the other study, 263 patients received conventional therapy, with the oxygen flow having been adjusted to maintain an arterial oxygen saturation estimate of greater than 92%. This study’s other 264 patients received high-flow oxygen therapy, with the flow having been initially set at 10 L/min and titrated upward in 5-L/min steps until patients experienced discomfort. The high-flow therapy was stopped after 24 hours and was followed by conventional oxygen therapy, when needed.
The primary outcome measure in the study involving NIV was cause for reintubation within 7 days of randomization.
Secondary outcome measures included gas exchange, healthcare-associated infection rate within 30 days, number of ventilator-free days between days 1 and 30, antibiotic use duration, ICU and in-hospital length of stay, and 30- and 90-day mortality.
Reintubation occurred in 49 patients in the NIV group and 66 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group, a significant difference (P = .03). Among the reintubated patients, those who had received NIV spent less time under invasive mechanical ventilation as did the patients given standard oxygen therapy. The interquartile ranges of days of invasive mechanical ventilation were 0-3 for patients in the NIV group and 0-5 for patients in the standard oxygen therapy group (P = .05). At 30 days, NIV was associated with significantly more ventilator-free days than standard oxygen therapy (25.4 vs. 23.2; P = .04). At 90 days, 22 patients in the NIV group and 31 patients in the standard oxygen therapy group had died (P = .15).
“Recent high-impact trials have demonstrated the benefits in nonsurgical hypoxemic respiratory failure or equivalence of high-flow nasal cannula compared with NIV in patients after cardiothoracic surgery with moderate to severe hypoxemia. Future studies comparing use of high-flow oxygen cannula vs standard oxygen therapy and NIV for patients after abdominal surgery as preventive (prophylactic) or curative applications are needed,” according to Dr. Jaber and his colleagues.
The primary outcome measure for the study of patients receiving high-flow oxygen therapy was reintubation within 72 hours after extubation; this occurred in fewer patients in the high-flow oxygen group than in the conventional therapy group (13 or 4.9% vs. 32 or 12.2%.) This statistically significant difference was mainly attributable to a lower incidence of respiratory-related reintubation in the high-flow group, compared with the conventional therapy group (1.5% vs. 8.7%), said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
Secondary outcome measures included postextubation respiratory failure, respiratory infection, sepsis, multiorgan failure, ICU and hospital length of stay and mortality, time to reintubation, and adverse effects. Postintubation respiratory failure was less common in the high-flow therapy group than in the conventional therapy group (22 patients or 8.3% vs. 38 or 14.4%). Differences between the two groups in other secondary outcomes were not statistically significant.
“The main finding of this study was that high-flow oxygen significantly reduced the reintubation rate in critically ill patients at low risk for extubation failure ... High-flow therapy improves oxygenation, and the lower rate of reintubation secondary to hypoxia in the high-flow group corroborates this finding. High-flow oxygen also seems to reduce other causes of respiratory failure such as increased work of breathing and respiratory muscle fatigue, which are frequently associated with reintubation secondary to hypoxia. Another way in which high-flow therapy improves extubation outcome is by conditioning the inspired gas,” said Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues.
No adverse events were reported in either study.
Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jaber and his colleagues disclosed no potential conflicts of interest with their study’s sponsors, Montpellier (France) University Hospital and the APARD Foundation.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Extubated patients who either received noninvasive ventilation (NIV) therapy or high-flow nasal cannula oxygen reduced their risk of reintubation, compared with patients who received some form of standard oxygen therapy.
Major finding: In one study, significantly fewer of the patients who received NIV needed to be reintubated than the patients who received standard oxygen therapy.
Data source: Two multicenter, randomized clinical trials published online in JAMA.
Disclosures: Dr. Hernandez and his colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Jaber and his colleagues disclosed no potential conflicts of interest with Montpellier (France) University Hospital and the APARD Foundation, who funded their study.
Negative sestamibi scan for primary hyperparathyroidism can mean no referral or surgery
BALTIMORE – In the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism, clinical guidelines recommend using sestamibi scan for localizing adenoma, but increasingly endocrinologists are using sestamibi results to determine whether or not to refer a patient for parathyroidectomy surgery, while surgeons are using the scans as a factor in deciding whether to perform the operation.
That was the conclusion of a paper Dr. Susana Wu presented at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons annual meeting. Dr. Wu reported on behalf of her colleagues at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center and at Scripps Clinic in San Diego.
“This study suggests that negative sestamibi scan (SS) results influence management of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism,” Dr. Wu said. “Endocrinologists were less likely to refer to surgeons and surgeons were less likely to offer parathyroidectomy to a patient with a negative sestamibi scan.”
The study involved a retrospective chart review of all 539 patients with primary hyperparathyroidism in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California database from December 2011 to December 2013, 452 of whom were seen by 63 endocrinologists at 14 centers. Among these patients, 260 had SS – 120 negative and 140 positive. The study identified statistically significant variations in how both endocrinologists and surgeons managed patients depending on SS results. The researchers used Kaiser Permanente’s electronic referral system to track referrals.
“The most significant negative predictor for endocrinologists referring to surgeons was a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.36,” Dr. Wu said.
Endocrinologists referred 86% of patients with positive SS to surgeons, but only 68% of those with negative SS. Surgeons exhibited a similar practice pattern. “Surgeons were less likely to recommend parathyroidectomy for patients with a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.20,” Dr. Wu said. Surgeons operated on 87% of patients with a negative SS scan but 96% with a positive SS.
In an interview, study coauthor Dr. Philip Haigh explained that parathyroidectomy when the SS is negative is a more difficult operation for the surgeon, and that might make some physicians hesitate before going forward with surgery. “It has been previously shown by other studies that it is a more difficult operation when the sestamibi scan is negative because you have to look at four glands instead of removing just one, but if the surgeon is experienced, it should achieve a high success rate,” Dr. Haigh said. He said that parathyroidectomy in sestamibi-negative hyperparathyroidism had a cure rate as high as 98% in the study presented.
He offered two thoughts on how clinicians should use the study results. “To the endocrinologist, if you’re going to order a sestamibi scan, don’t change your referral practice depending on the result,” Dr. Haigh said. “To the surgeon, if you’re not comfortable operating on a patient with a negative sestamibi scan, then find someone who is.”
The study had a few limitations, Dr. Wu said. Along with its retrospective nature, the study also did not account for potential disparity in radiological vs. surgeon interpretation of the scans.
During the discussion, Dr. Samuel Snyder, of Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Tex., said he concurred with the results Dr. Wu reported. “It really worries me about what is happening to patients who have negative scans,” he said. “What I’ve seen in patients referred for surgery is a lot of variation in how the sestamibi scan is done.” He asked if the study accounted for the different types of sestamibi scans and how they were performed, but Dr. Wu said it did not.
Dr. Christopher McHenry of MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, also concurred. “I think this is a phenomenon that occurs more often than we think or we’re aware of,” he said. “I continue to be amazed with how clinicians equate a negative sestamibi scan with not having primary hyperparathyroidism. I think it needs to reemphasized that the sestamibi scan is not diagnostic; it’s for localization.”
He asked Dr. Wu, “How do we change behavior to deal with this problem?”
Dr. Wu said her institution is developing a safety-net program that would aim to increase the identification and chart coding of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, automate essential labs to be ordered in patients with high calcium, and automate referral to endocrinologists. The study and its findings will be disseminated to endocrinologists in the region.
The study authors had no disclosures.
BALTIMORE – In the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism, clinical guidelines recommend using sestamibi scan for localizing adenoma, but increasingly endocrinologists are using sestamibi results to determine whether or not to refer a patient for parathyroidectomy surgery, while surgeons are using the scans as a factor in deciding whether to perform the operation.
That was the conclusion of a paper Dr. Susana Wu presented at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons annual meeting. Dr. Wu reported on behalf of her colleagues at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center and at Scripps Clinic in San Diego.
“This study suggests that negative sestamibi scan (SS) results influence management of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism,” Dr. Wu said. “Endocrinologists were less likely to refer to surgeons and surgeons were less likely to offer parathyroidectomy to a patient with a negative sestamibi scan.”
The study involved a retrospective chart review of all 539 patients with primary hyperparathyroidism in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California database from December 2011 to December 2013, 452 of whom were seen by 63 endocrinologists at 14 centers. Among these patients, 260 had SS – 120 negative and 140 positive. The study identified statistically significant variations in how both endocrinologists and surgeons managed patients depending on SS results. The researchers used Kaiser Permanente’s electronic referral system to track referrals.
“The most significant negative predictor for endocrinologists referring to surgeons was a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.36,” Dr. Wu said.
Endocrinologists referred 86% of patients with positive SS to surgeons, but only 68% of those with negative SS. Surgeons exhibited a similar practice pattern. “Surgeons were less likely to recommend parathyroidectomy for patients with a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.20,” Dr. Wu said. Surgeons operated on 87% of patients with a negative SS scan but 96% with a positive SS.
In an interview, study coauthor Dr. Philip Haigh explained that parathyroidectomy when the SS is negative is a more difficult operation for the surgeon, and that might make some physicians hesitate before going forward with surgery. “It has been previously shown by other studies that it is a more difficult operation when the sestamibi scan is negative because you have to look at four glands instead of removing just one, but if the surgeon is experienced, it should achieve a high success rate,” Dr. Haigh said. He said that parathyroidectomy in sestamibi-negative hyperparathyroidism had a cure rate as high as 98% in the study presented.
He offered two thoughts on how clinicians should use the study results. “To the endocrinologist, if you’re going to order a sestamibi scan, don’t change your referral practice depending on the result,” Dr. Haigh said. “To the surgeon, if you’re not comfortable operating on a patient with a negative sestamibi scan, then find someone who is.”
The study had a few limitations, Dr. Wu said. Along with its retrospective nature, the study also did not account for potential disparity in radiological vs. surgeon interpretation of the scans.
During the discussion, Dr. Samuel Snyder, of Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Tex., said he concurred with the results Dr. Wu reported. “It really worries me about what is happening to patients who have negative scans,” he said. “What I’ve seen in patients referred for surgery is a lot of variation in how the sestamibi scan is done.” He asked if the study accounted for the different types of sestamibi scans and how they were performed, but Dr. Wu said it did not.
Dr. Christopher McHenry of MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, also concurred. “I think this is a phenomenon that occurs more often than we think or we’re aware of,” he said. “I continue to be amazed with how clinicians equate a negative sestamibi scan with not having primary hyperparathyroidism. I think it needs to reemphasized that the sestamibi scan is not diagnostic; it’s for localization.”
He asked Dr. Wu, “How do we change behavior to deal with this problem?”
Dr. Wu said her institution is developing a safety-net program that would aim to increase the identification and chart coding of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, automate essential labs to be ordered in patients with high calcium, and automate referral to endocrinologists. The study and its findings will be disseminated to endocrinologists in the region.
The study authors had no disclosures.
BALTIMORE – In the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism, clinical guidelines recommend using sestamibi scan for localizing adenoma, but increasingly endocrinologists are using sestamibi results to determine whether or not to refer a patient for parathyroidectomy surgery, while surgeons are using the scans as a factor in deciding whether to perform the operation.
That was the conclusion of a paper Dr. Susana Wu presented at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons annual meeting. Dr. Wu reported on behalf of her colleagues at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center and at Scripps Clinic in San Diego.
“This study suggests that negative sestamibi scan (SS) results influence management of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism,” Dr. Wu said. “Endocrinologists were less likely to refer to surgeons and surgeons were less likely to offer parathyroidectomy to a patient with a negative sestamibi scan.”
The study involved a retrospective chart review of all 539 patients with primary hyperparathyroidism in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California database from December 2011 to December 2013, 452 of whom were seen by 63 endocrinologists at 14 centers. Among these patients, 260 had SS – 120 negative and 140 positive. The study identified statistically significant variations in how both endocrinologists and surgeons managed patients depending on SS results. The researchers used Kaiser Permanente’s electronic referral system to track referrals.
“The most significant negative predictor for endocrinologists referring to surgeons was a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.36,” Dr. Wu said.
Endocrinologists referred 86% of patients with positive SS to surgeons, but only 68% of those with negative SS. Surgeons exhibited a similar practice pattern. “Surgeons were less likely to recommend parathyroidectomy for patients with a negative sestamibi scan, with an odds ratio of 0.20,” Dr. Wu said. Surgeons operated on 87% of patients with a negative SS scan but 96% with a positive SS.
In an interview, study coauthor Dr. Philip Haigh explained that parathyroidectomy when the SS is negative is a more difficult operation for the surgeon, and that might make some physicians hesitate before going forward with surgery. “It has been previously shown by other studies that it is a more difficult operation when the sestamibi scan is negative because you have to look at four glands instead of removing just one, but if the surgeon is experienced, it should achieve a high success rate,” Dr. Haigh said. He said that parathyroidectomy in sestamibi-negative hyperparathyroidism had a cure rate as high as 98% in the study presented.
He offered two thoughts on how clinicians should use the study results. “To the endocrinologist, if you’re going to order a sestamibi scan, don’t change your referral practice depending on the result,” Dr. Haigh said. “To the surgeon, if you’re not comfortable operating on a patient with a negative sestamibi scan, then find someone who is.”
The study had a few limitations, Dr. Wu said. Along with its retrospective nature, the study also did not account for potential disparity in radiological vs. surgeon interpretation of the scans.
During the discussion, Dr. Samuel Snyder, of Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Tex., said he concurred with the results Dr. Wu reported. “It really worries me about what is happening to patients who have negative scans,” he said. “What I’ve seen in patients referred for surgery is a lot of variation in how the sestamibi scan is done.” He asked if the study accounted for the different types of sestamibi scans and how they were performed, but Dr. Wu said it did not.
Dr. Christopher McHenry of MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, also concurred. “I think this is a phenomenon that occurs more often than we think or we’re aware of,” he said. “I continue to be amazed with how clinicians equate a negative sestamibi scan with not having primary hyperparathyroidism. I think it needs to reemphasized that the sestamibi scan is not diagnostic; it’s for localization.”
He asked Dr. Wu, “How do we change behavior to deal with this problem?”
Dr. Wu said her institution is developing a safety-net program that would aim to increase the identification and chart coding of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, automate essential labs to be ordered in patients with high calcium, and automate referral to endocrinologists. The study and its findings will be disseminated to endocrinologists in the region.
The study authors had no disclosures.
AT AAES 2016
Key clinical point: Endocrinologists and surgeons are less likely to order surgery when patients with primary hyperparathyroidism have negative sestamibi scan (SS) results.
Major finding: Endocrinologists referred 86% of patients with positive SS to surgeons, but only 68% of those with negative SS.
Data source: A retrospective chart review of all 539 patients with primary hyperparathyroidism in the Kaiser Permanente Southern California database over a 2-year period.
Disclosures: Dr. Wu and her coauthors reported having no financial disclosures.
Antithrombotics appear safe in BCVI with concomitant injuries
SAN ANTONIO – Don’t withhold antiplatelet or heparin therapy in patients with blunt cerebrovascular injury, even if they have concomitant traumatic brain or solid organ injuries, advised researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
With close monitoring, “initiation of early antithrombotic therapy for patients with BCVI [blunt cerebrovascular injury] and concomitant TBI [traumatic brain injury] or SOI [solid organ injury] does not increase the risk of worsening TBI or SOI above baseline.” It is safe, effective, and “should not be withheld,” the researchers concluded after a review of 119 BCVI patients with concomitant injuries.
Seventy four (62%) had TBIs, 26 (22%) had SOIs, and 19 (16%) had both. At some institutions, antithrombotic therapy – the mainstay for BCVI to prevent secondary ischemic stroke – would have been delayed or withheld for fear of triggering hemorrhagic complications.
But at the Health Science Center in Memphis, “we have an extremely cooperative group of neurosurgeons who take BCVI as seriously as we do, and actually allow us, more often than not, to start antithrombotic therapy pretty much immediately after the injury is identified,” investigator and surgery resident Dr. Charles Shahan said at the annual scientific assembly of the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma.
As a result, 85 patients (71%) received heparin infusions with goal-activated partial thromboplastin times of 45-60 seconds, and the rest antiplatelet therapy, typically 81-mg aspirin. The center generally uses heparin for TBI patients because of its short half-life, and aspirin for others.
Antithrombosed BCVI patients did as well as did historical controls. TBIs deteriorated – meaning worsening on clinical or CT exam, or delayed operative intervention – in 7%, vs. 10% of TBI patients without BCVI (P = .34). Three percent of SOI patients had delayed laparotomies vs. 5% of SOI patients without BCVI (P = .54). None of the BCVI patients stopped antithrombotics because of complications.
The results held regardless of the type of TBI, SOI, or antithrombotic used.
Overall, 11 patients (9%) had BCVI-related strokes. Without antithrombotic therapy, stroke rates in BCVI can approach 40%.
“Our extremely early use of antithrombotic therapy does not appear to increase our rate of worsening of our hemorrhagic injures and also gets our stroke rate within acceptable limits,” Dr. Shahan said.
The mean age in the study was 38, and just over half the subjects were men.
Dr. Shahan had no disclosures
SAN ANTONIO – Don’t withhold antiplatelet or heparin therapy in patients with blunt cerebrovascular injury, even if they have concomitant traumatic brain or solid organ injuries, advised researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
With close monitoring, “initiation of early antithrombotic therapy for patients with BCVI [blunt cerebrovascular injury] and concomitant TBI [traumatic brain injury] or SOI [solid organ injury] does not increase the risk of worsening TBI or SOI above baseline.” It is safe, effective, and “should not be withheld,” the researchers concluded after a review of 119 BCVI patients with concomitant injuries.
Seventy four (62%) had TBIs, 26 (22%) had SOIs, and 19 (16%) had both. At some institutions, antithrombotic therapy – the mainstay for BCVI to prevent secondary ischemic stroke – would have been delayed or withheld for fear of triggering hemorrhagic complications.
But at the Health Science Center in Memphis, “we have an extremely cooperative group of neurosurgeons who take BCVI as seriously as we do, and actually allow us, more often than not, to start antithrombotic therapy pretty much immediately after the injury is identified,” investigator and surgery resident Dr. Charles Shahan said at the annual scientific assembly of the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma.
As a result, 85 patients (71%) received heparin infusions with goal-activated partial thromboplastin times of 45-60 seconds, and the rest antiplatelet therapy, typically 81-mg aspirin. The center generally uses heparin for TBI patients because of its short half-life, and aspirin for others.
Antithrombosed BCVI patients did as well as did historical controls. TBIs deteriorated – meaning worsening on clinical or CT exam, or delayed operative intervention – in 7%, vs. 10% of TBI patients without BCVI (P = .34). Three percent of SOI patients had delayed laparotomies vs. 5% of SOI patients without BCVI (P = .54). None of the BCVI patients stopped antithrombotics because of complications.
The results held regardless of the type of TBI, SOI, or antithrombotic used.
Overall, 11 patients (9%) had BCVI-related strokes. Without antithrombotic therapy, stroke rates in BCVI can approach 40%.
“Our extremely early use of antithrombotic therapy does not appear to increase our rate of worsening of our hemorrhagic injures and also gets our stroke rate within acceptable limits,” Dr. Shahan said.
The mean age in the study was 38, and just over half the subjects were men.
Dr. Shahan had no disclosures
SAN ANTONIO – Don’t withhold antiplatelet or heparin therapy in patients with blunt cerebrovascular injury, even if they have concomitant traumatic brain or solid organ injuries, advised researchers from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
With close monitoring, “initiation of early antithrombotic therapy for patients with BCVI [blunt cerebrovascular injury] and concomitant TBI [traumatic brain injury] or SOI [solid organ injury] does not increase the risk of worsening TBI or SOI above baseline.” It is safe, effective, and “should not be withheld,” the researchers concluded after a review of 119 BCVI patients with concomitant injuries.
Seventy four (62%) had TBIs, 26 (22%) had SOIs, and 19 (16%) had both. At some institutions, antithrombotic therapy – the mainstay for BCVI to prevent secondary ischemic stroke – would have been delayed or withheld for fear of triggering hemorrhagic complications.
But at the Health Science Center in Memphis, “we have an extremely cooperative group of neurosurgeons who take BCVI as seriously as we do, and actually allow us, more often than not, to start antithrombotic therapy pretty much immediately after the injury is identified,” investigator and surgery resident Dr. Charles Shahan said at the annual scientific assembly of the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma.
As a result, 85 patients (71%) received heparin infusions with goal-activated partial thromboplastin times of 45-60 seconds, and the rest antiplatelet therapy, typically 81-mg aspirin. The center generally uses heparin for TBI patients because of its short half-life, and aspirin for others.
Antithrombosed BCVI patients did as well as did historical controls. TBIs deteriorated – meaning worsening on clinical or CT exam, or delayed operative intervention – in 7%, vs. 10% of TBI patients without BCVI (P = .34). Three percent of SOI patients had delayed laparotomies vs. 5% of SOI patients without BCVI (P = .54). None of the BCVI patients stopped antithrombotics because of complications.
The results held regardless of the type of TBI, SOI, or antithrombotic used.
Overall, 11 patients (9%) had BCVI-related strokes. Without antithrombotic therapy, stroke rates in BCVI can approach 40%.
“Our extremely early use of antithrombotic therapy does not appear to increase our rate of worsening of our hemorrhagic injures and also gets our stroke rate within acceptable limits,” Dr. Shahan said.
The mean age in the study was 38, and just over half the subjects were men.
Dr. Shahan had no disclosures
AT THE EAST SCIENTIFIC ASSEMBLY
Key clinical point: Antithrombotics for BCVI do not make concomitant brain and solid organ injuries worse.
Major finding: TBIs deteriorated in 7% of BCVI patients on heparin infusion, versus 10% of TBI patients without BCVI (P = .34).
Data source: Review of 119 BCVI patients.
Disclosures: The lead investigator had no disclosures.
Save the Date for ACS Clinical Congress 2016, October 16−20
Save the date for the American College of Surgeons Clinical Congress 2016, October 16−20 in Washington, DC, at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center. The Marriot Marquis Washington, DC, located next to the convention center, will serve as the headquarters hotel.
The theme of this year’s meeting, Challenges for the Second Century, recognizes the College’s second 100 years of ensuring quality surgical patient care. Clinical Congress 2016 will present hundreds of educational sessions, including Panel Sessions, Postgraduate Didactic and Skills-Oriented Courses, Meet-the-Expert Luncheons, Names Lectures, Scientific Paper Sessions, and Poster Presentations. View an ACS press release at https://www.facs.org/media/press-releases/2016/clincon0316#sthash.SnHNsOJB.dpuf for more information on Clinical Congress 2016.
Save the date for the American College of Surgeons Clinical Congress 2016, October 16−20 in Washington, DC, at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center. The Marriot Marquis Washington, DC, located next to the convention center, will serve as the headquarters hotel.
The theme of this year’s meeting, Challenges for the Second Century, recognizes the College’s second 100 years of ensuring quality surgical patient care. Clinical Congress 2016 will present hundreds of educational sessions, including Panel Sessions, Postgraduate Didactic and Skills-Oriented Courses, Meet-the-Expert Luncheons, Names Lectures, Scientific Paper Sessions, and Poster Presentations. View an ACS press release at https://www.facs.org/media/press-releases/2016/clincon0316#sthash.SnHNsOJB.dpuf for more information on Clinical Congress 2016.
Save the date for the American College of Surgeons Clinical Congress 2016, October 16−20 in Washington, DC, at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center. The Marriot Marquis Washington, DC, located next to the convention center, will serve as the headquarters hotel.
The theme of this year’s meeting, Challenges for the Second Century, recognizes the College’s second 100 years of ensuring quality surgical patient care. Clinical Congress 2016 will present hundreds of educational sessions, including Panel Sessions, Postgraduate Didactic and Skills-Oriented Courses, Meet-the-Expert Luncheons, Names Lectures, Scientific Paper Sessions, and Poster Presentations. View an ACS press release at https://www.facs.org/media/press-releases/2016/clincon0316#sthash.SnHNsOJB.dpuf for more information on Clinical Congress 2016.
JAMA Surgery publishes research agenda developed at NIH-ACS symposium on disparities
An article in the March 16 issue of JAMA Surgery summarizes the research and funding priorities for addressing health care disparities in the United States, which were identified at the inaugural National Institutes of Health (NIH)–American College of Surgeons (ACS) Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research.1 The ACS and the National Institute on Minority Health and Disparities (NIMHD) cohosted the conference, which took place in May 2015 at the NIH campus, Bethesda, MD.2
“The goal of the symposium was to create a national research agenda that could be used to prioritize funding for research. We conducted an extensive literature review of existing research, organized the results by theme, and asked attendees to identify what they saw as the top priorities for each theme,” said Adil Haider, MD, MPH, FACS. Dr. Haider is the lead author of the JAMA Surgery article; Vice-Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities; and Kessler Director, Center for Surgery and Public Health, a joint initiative of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Defining themes and priorities
The themes discussed at the symposium were as follows: patient and host factors, systemic factors and access issues, clinical care and quality, provider factors, and postoperative care and rehabilitation. The leading research and funding priorities – identified by the more than 60 researchers, surgeon-scientists, and federal leaders who attended the symposium, and articulated in the JAMA Surgery article – are as follows:
• Improve patient-provider communication by teaching providers to deliver culturally dexterous care and measuring its impact on elimination of surgical disparities.
• Foster engagement and community outreach and use technology to optimize patient education, health literacy, and shared decision making in a culturally relevant way; disseminate these techniques; and evaluate their impact on reducing surgical disparities.
• Evaluate regionalization of care versus strengthening safety-net hospitals within the context of differential access and surgical disparities.
• Gauge the long-term impact of intervention and rehabilitation support within the critical period on functional outcomes and patient-defined perceptions of quality of life.
• Improve patient engagement and identify patient expectations for postoperative and postinjury recovery, as well as their values regarding advanced health care planning and palliative care.
The authors of the JAMA Surgery article concluded that “The NIH-ACS Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research succeeded in identifying a comprehensive research agenda.” In particular, they noted that future research is needed in the areas of patients’ perspectives, workforce diversification and training, and systematic evaluation of health technologies to reduce surgical disparities. Within the context of the larger literature focused on disparity-related research, results also call for ongoing evaluation of evidence-based practice, rigorous research methodologies, incentives for standardization of care, and building on existing infrastructure to support these advances.
Just the beginning
The ACS is “confident that this is just the beginning of a much larger effort and hopeful that the National Institutes of Health and the NIMHD will continue to work with the ACS to build upon the foundation that was set during the symposium by establishing a funding stream to support this important research. Together, we can foster systemic change, effectively eliminating surgical and other health care disparities,” said L.D. Britt, MD, MPH, DSc(Hon), FACS, FCCM, FRCSEng(Hon), FRCSEd(Hon), FWACS(Hon), FRCSI(Hon), FCS(SA)(Hon), FRCSGlasg(Hon), ACS Past-President and Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities. Dr. Britt is the Brickhouse Professor of Surgery, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and played a critical role in the creation of the committee and in defining the committee’s deliverables, which included a national symposium.
1. Haider AH, Dankwa-Mullan I, Maragh-Bass, et al. Setting a national agenda for surgical disparities research: Recommendations from the National Institutes of Health and American College of Surgeons Summit. JAMA Surg. March 16, 2016. Available at http://archsurg.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=2503437. Accessed March 28, 2016.
2. Schneidman D. No quality without access: ACS and NIH collaborate to ensure access to optimal care. Bull Am Coll Surg. 2015;100(8):52-62. Available at: bulletin.facs.org/2015/08/no-quality-without-access-acs-and-nih-collaborate-to-ensure-access-to-optimal-care. Accessed March 28, 2016.
An article in the March 16 issue of JAMA Surgery summarizes the research and funding priorities for addressing health care disparities in the United States, which were identified at the inaugural National Institutes of Health (NIH)–American College of Surgeons (ACS) Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research.1 The ACS and the National Institute on Minority Health and Disparities (NIMHD) cohosted the conference, which took place in May 2015 at the NIH campus, Bethesda, MD.2
“The goal of the symposium was to create a national research agenda that could be used to prioritize funding for research. We conducted an extensive literature review of existing research, organized the results by theme, and asked attendees to identify what they saw as the top priorities for each theme,” said Adil Haider, MD, MPH, FACS. Dr. Haider is the lead author of the JAMA Surgery article; Vice-Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities; and Kessler Director, Center for Surgery and Public Health, a joint initiative of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Defining themes and priorities
The themes discussed at the symposium were as follows: patient and host factors, systemic factors and access issues, clinical care and quality, provider factors, and postoperative care and rehabilitation. The leading research and funding priorities – identified by the more than 60 researchers, surgeon-scientists, and federal leaders who attended the symposium, and articulated in the JAMA Surgery article – are as follows:
• Improve patient-provider communication by teaching providers to deliver culturally dexterous care and measuring its impact on elimination of surgical disparities.
• Foster engagement and community outreach and use technology to optimize patient education, health literacy, and shared decision making in a culturally relevant way; disseminate these techniques; and evaluate their impact on reducing surgical disparities.
• Evaluate regionalization of care versus strengthening safety-net hospitals within the context of differential access and surgical disparities.
• Gauge the long-term impact of intervention and rehabilitation support within the critical period on functional outcomes and patient-defined perceptions of quality of life.
• Improve patient engagement and identify patient expectations for postoperative and postinjury recovery, as well as their values regarding advanced health care planning and palliative care.
The authors of the JAMA Surgery article concluded that “The NIH-ACS Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research succeeded in identifying a comprehensive research agenda.” In particular, they noted that future research is needed in the areas of patients’ perspectives, workforce diversification and training, and systematic evaluation of health technologies to reduce surgical disparities. Within the context of the larger literature focused on disparity-related research, results also call for ongoing evaluation of evidence-based practice, rigorous research methodologies, incentives for standardization of care, and building on existing infrastructure to support these advances.
Just the beginning
The ACS is “confident that this is just the beginning of a much larger effort and hopeful that the National Institutes of Health and the NIMHD will continue to work with the ACS to build upon the foundation that was set during the symposium by establishing a funding stream to support this important research. Together, we can foster systemic change, effectively eliminating surgical and other health care disparities,” said L.D. Britt, MD, MPH, DSc(Hon), FACS, FCCM, FRCSEng(Hon), FRCSEd(Hon), FWACS(Hon), FRCSI(Hon), FCS(SA)(Hon), FRCSGlasg(Hon), ACS Past-President and Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities. Dr. Britt is the Brickhouse Professor of Surgery, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and played a critical role in the creation of the committee and in defining the committee’s deliverables, which included a national symposium.
1. Haider AH, Dankwa-Mullan I, Maragh-Bass, et al. Setting a national agenda for surgical disparities research: Recommendations from the National Institutes of Health and American College of Surgeons Summit. JAMA Surg. March 16, 2016. Available at http://archsurg.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=2503437. Accessed March 28, 2016.
2. Schneidman D. No quality without access: ACS and NIH collaborate to ensure access to optimal care. Bull Am Coll Surg. 2015;100(8):52-62. Available at: bulletin.facs.org/2015/08/no-quality-without-access-acs-and-nih-collaborate-to-ensure-access-to-optimal-care. Accessed March 28, 2016.
An article in the March 16 issue of JAMA Surgery summarizes the research and funding priorities for addressing health care disparities in the United States, which were identified at the inaugural National Institutes of Health (NIH)–American College of Surgeons (ACS) Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research.1 The ACS and the National Institute on Minority Health and Disparities (NIMHD) cohosted the conference, which took place in May 2015 at the NIH campus, Bethesda, MD.2
“The goal of the symposium was to create a national research agenda that could be used to prioritize funding for research. We conducted an extensive literature review of existing research, organized the results by theme, and asked attendees to identify what they saw as the top priorities for each theme,” said Adil Haider, MD, MPH, FACS. Dr. Haider is the lead author of the JAMA Surgery article; Vice-Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities; and Kessler Director, Center for Surgery and Public Health, a joint initiative of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Defining themes and priorities
The themes discussed at the symposium were as follows: patient and host factors, systemic factors and access issues, clinical care and quality, provider factors, and postoperative care and rehabilitation. The leading research and funding priorities – identified by the more than 60 researchers, surgeon-scientists, and federal leaders who attended the symposium, and articulated in the JAMA Surgery article – are as follows:
• Improve patient-provider communication by teaching providers to deliver culturally dexterous care and measuring its impact on elimination of surgical disparities.
• Foster engagement and community outreach and use technology to optimize patient education, health literacy, and shared decision making in a culturally relevant way; disseminate these techniques; and evaluate their impact on reducing surgical disparities.
• Evaluate regionalization of care versus strengthening safety-net hospitals within the context of differential access and surgical disparities.
• Gauge the long-term impact of intervention and rehabilitation support within the critical period on functional outcomes and patient-defined perceptions of quality of life.
• Improve patient engagement and identify patient expectations for postoperative and postinjury recovery, as well as their values regarding advanced health care planning and palliative care.
The authors of the JAMA Surgery article concluded that “The NIH-ACS Symposium on Surgical Disparities Research succeeded in identifying a comprehensive research agenda.” In particular, they noted that future research is needed in the areas of patients’ perspectives, workforce diversification and training, and systematic evaluation of health technologies to reduce surgical disparities. Within the context of the larger literature focused on disparity-related research, results also call for ongoing evaluation of evidence-based practice, rigorous research methodologies, incentives for standardization of care, and building on existing infrastructure to support these advances.
Just the beginning
The ACS is “confident that this is just the beginning of a much larger effort and hopeful that the National Institutes of Health and the NIMHD will continue to work with the ACS to build upon the foundation that was set during the symposium by establishing a funding stream to support this important research. Together, we can foster systemic change, effectively eliminating surgical and other health care disparities,” said L.D. Britt, MD, MPH, DSc(Hon), FACS, FCCM, FRCSEng(Hon), FRCSEd(Hon), FWACS(Hon), FRCSI(Hon), FCS(SA)(Hon), FRCSGlasg(Hon), ACS Past-President and Chair, ACS Committee on Health Care Disparities. Dr. Britt is the Brickhouse Professor of Surgery, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and played a critical role in the creation of the committee and in defining the committee’s deliverables, which included a national symposium.
1. Haider AH, Dankwa-Mullan I, Maragh-Bass, et al. Setting a national agenda for surgical disparities research: Recommendations from the National Institutes of Health and American College of Surgeons Summit. JAMA Surg. March 16, 2016. Available at http://archsurg.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=2503437. Accessed March 28, 2016.
2. Schneidman D. No quality without access: ACS and NIH collaborate to ensure access to optimal care. Bull Am Coll Surg. 2015;100(8):52-62. Available at: bulletin.facs.org/2015/08/no-quality-without-access-acs-and-nih-collaborate-to-ensure-access-to-optimal-care. Accessed March 28, 2016.
Hybrid option ‘reasonable’ for HLHS?
Although the classic Norwood palliation for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) has been well established, the procedure has had its drawbacks, namely the need for cardiopulmonary bypass with hypothermia and a because it rules out biventricular correction months later. A hybrid procedure avoids the need for bypass and accommodates short-term biventricular correction, but it has lacked strong evidence.
Researchers from Justus-Liebig University Giessen, Germany, reported on 182 patients with HLHS who had the three-stage Giessen hybrid procedure, noting 10-year survival of almost 80% with almost a third of patients requiring no artery intervention in that time (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 April;151:1112-23).
“In view of the early results and long-term outcome after Giessen hybrid palliation, the hybrid approach has become a reasonable alternative to the conventional strategy to treat neonates with HLHS and variants,” wrote Dr. Can Yerebakan and colleagues. “Further refinements are warranted to decrease patient morbidity.”
The Giessen hybrid procedure uses a technique to control pulmonary blood flow that is different from the Norwood procedure. The hybrid approach involves stenting of the arterial duct or prostaglandin therapy to maintain systemic perfusion combined with off-pump bilateral banding of the pulmonary arteries (bPAB) in the neonatal period. The Giessen hybrid operation defers the Norwood-type palliation using cardiopulmonary bypass that involves an aortic arch reconstruction, including a superior cavopulmonary connection or a biventricular correction, if indicated, until the infant is 4-8 months of age.
“In recent years, hybrid treatment has moved from a myth to an alternative modality in a growing number of institutions globally,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues said. The hybrid procedure has been used in high-risk patients. One report claimed higher morbidity in the hybrid procedure due to bPAB (Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:1382-8). Another study raised concerns about an adequate pulmonary artery rehabilitation at the time of the Fontan operation, the third stage in the hybrid strategy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:706-12).
But with the hybrid approach, patients retain the potential to receive a biventricular correction up to 8 months later without compromising survival, “postponing an immediate definitive decision in the newborn period in comparison with the classic Norwood palliation,” Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors noted.
The doctors at the Pediatric Heart Center Giessen treat all types and variants of HLHS with the modified Giessen hybrid strategy. Between 1998 and 2015, 182 patients with HLHS had the Giessen hybrid stage I operation, including 126 patients who received univentricular palliation or a heart transplant. The median age of stage I recipients was 6 days, and median weight 3.2 kg. The stage II operation was performed at 4.5 months, with a range of 2.9 to 39.5 months, and Fontan completion was established at 33.7 months, with a range of 21 to 108 months.
Median follow-up after the stage I procedure was 4.6 years, and the death rate was 2.5%. After stage II, mortality was 4.9%; no deaths were reported after Fontan completion. Body weight less than 2.5 kg and aortic atresia had no significant effect on survival. Mortality rates were 8.9% between stages I and II and 5.3% between stage II and Fontan completion. “Cumulative interstage mortality was 14.2%,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues noted. “At 10 years, the probability of survival is 77.8%.”
Also at 10 years, 32.2% of patients were free from further pulmonary artery intervention, and 16.7% needed aortic arch reconstruction. Two patients required reoperations for aortic arch reconstruction.
Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues suggested several steps to improve outcomes with the hybrid approach: “intense collaboration” with anesthesiology and pediatric cardiology during and after the procedure to risk stratify individual patients; implementation of standards for management of all stages, including out-of-hospital care, in all departments that participate in a case; and liberalized indications for use of MRI before the stage II and Fontan completion.
Among the limitations of the study the authors noted were its retrospective nature and a median follow-up of only 5 years when the center has some cases with up to 15 years of follow-up. But Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors said they could not determine if the patients benefit from the hybrid treatment in the long-term.
The researchers had no disclosures.
The study by Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues is one of the largest single-center series of patients with HLHS who routinely undergo a hybrid palliation to date, and while the study is open to criticisms, “the authors should be applauded,” Dr. Ralph S. Mosca of New York University said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:1123-25).
Among the criticisms Dr. Mosca mentioned are that the hybrid approach requires a more extensive stage II reconstruction, “often further complicated by the presence of significant branch PA stenosis and a difficult aortic arch reconstruction”; that there is “appreciable” interstage mortality at 12.2%; and that there is an absence of data on renal or respiratory insufficiency, infection rates, and neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Mosca cited the cause for applause, however: “Through their persistence and collective experience, [the authors] have achieved commendable results in this difficult patient population.”
Yet, Dr. Mosca also noted a number of “potential problems” with the hybrid approach: bilateral banding of the pulmonary artery is a “crude procedure”; arterial duct stenting can lead to retrograde aortic arch reduction; and the interstage mortality “remains significant.”
Results of the hybrid and Norwood procedures are “strikingly similar,” Dr. Mosca said. While the hybrid approach may lower neonatal mortality, it may also carry longer-term consequences “predicated upon the need to closely observe and intervene,” he said. Clinicians need more information on hybrid outcomes, but in time it will likely take its place as an option for HLHS alongside the Norwood procedure, Dr. Mosca said.
The study by Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues is one of the largest single-center series of patients with HLHS who routinely undergo a hybrid palliation to date, and while the study is open to criticisms, “the authors should be applauded,” Dr. Ralph S. Mosca of New York University said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:1123-25).
Among the criticisms Dr. Mosca mentioned are that the hybrid approach requires a more extensive stage II reconstruction, “often further complicated by the presence of significant branch PA stenosis and a difficult aortic arch reconstruction”; that there is “appreciable” interstage mortality at 12.2%; and that there is an absence of data on renal or respiratory insufficiency, infection rates, and neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Mosca cited the cause for applause, however: “Through their persistence and collective experience, [the authors] have achieved commendable results in this difficult patient population.”
Yet, Dr. Mosca also noted a number of “potential problems” with the hybrid approach: bilateral banding of the pulmonary artery is a “crude procedure”; arterial duct stenting can lead to retrograde aortic arch reduction; and the interstage mortality “remains significant.”
Results of the hybrid and Norwood procedures are “strikingly similar,” Dr. Mosca said. While the hybrid approach may lower neonatal mortality, it may also carry longer-term consequences “predicated upon the need to closely observe and intervene,” he said. Clinicians need more information on hybrid outcomes, but in time it will likely take its place as an option for HLHS alongside the Norwood procedure, Dr. Mosca said.
The study by Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues is one of the largest single-center series of patients with HLHS who routinely undergo a hybrid palliation to date, and while the study is open to criticisms, “the authors should be applauded,” Dr. Ralph S. Mosca of New York University said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:1123-25).
Among the criticisms Dr. Mosca mentioned are that the hybrid approach requires a more extensive stage II reconstruction, “often further complicated by the presence of significant branch PA stenosis and a difficult aortic arch reconstruction”; that there is “appreciable” interstage mortality at 12.2%; and that there is an absence of data on renal or respiratory insufficiency, infection rates, and neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Mosca cited the cause for applause, however: “Through their persistence and collective experience, [the authors] have achieved commendable results in this difficult patient population.”
Yet, Dr. Mosca also noted a number of “potential problems” with the hybrid approach: bilateral banding of the pulmonary artery is a “crude procedure”; arterial duct stenting can lead to retrograde aortic arch reduction; and the interstage mortality “remains significant.”
Results of the hybrid and Norwood procedures are “strikingly similar,” Dr. Mosca said. While the hybrid approach may lower neonatal mortality, it may also carry longer-term consequences “predicated upon the need to closely observe and intervene,” he said. Clinicians need more information on hybrid outcomes, but in time it will likely take its place as an option for HLHS alongside the Norwood procedure, Dr. Mosca said.
Although the classic Norwood palliation for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) has been well established, the procedure has had its drawbacks, namely the need for cardiopulmonary bypass with hypothermia and a because it rules out biventricular correction months later. A hybrid procedure avoids the need for bypass and accommodates short-term biventricular correction, but it has lacked strong evidence.
Researchers from Justus-Liebig University Giessen, Germany, reported on 182 patients with HLHS who had the three-stage Giessen hybrid procedure, noting 10-year survival of almost 80% with almost a third of patients requiring no artery intervention in that time (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 April;151:1112-23).
“In view of the early results and long-term outcome after Giessen hybrid palliation, the hybrid approach has become a reasonable alternative to the conventional strategy to treat neonates with HLHS and variants,” wrote Dr. Can Yerebakan and colleagues. “Further refinements are warranted to decrease patient morbidity.”
The Giessen hybrid procedure uses a technique to control pulmonary blood flow that is different from the Norwood procedure. The hybrid approach involves stenting of the arterial duct or prostaglandin therapy to maintain systemic perfusion combined with off-pump bilateral banding of the pulmonary arteries (bPAB) in the neonatal period. The Giessen hybrid operation defers the Norwood-type palliation using cardiopulmonary bypass that involves an aortic arch reconstruction, including a superior cavopulmonary connection or a biventricular correction, if indicated, until the infant is 4-8 months of age.
“In recent years, hybrid treatment has moved from a myth to an alternative modality in a growing number of institutions globally,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues said. The hybrid procedure has been used in high-risk patients. One report claimed higher morbidity in the hybrid procedure due to bPAB (Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:1382-8). Another study raised concerns about an adequate pulmonary artery rehabilitation at the time of the Fontan operation, the third stage in the hybrid strategy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:706-12).
But with the hybrid approach, patients retain the potential to receive a biventricular correction up to 8 months later without compromising survival, “postponing an immediate definitive decision in the newborn period in comparison with the classic Norwood palliation,” Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors noted.
The doctors at the Pediatric Heart Center Giessen treat all types and variants of HLHS with the modified Giessen hybrid strategy. Between 1998 and 2015, 182 patients with HLHS had the Giessen hybrid stage I operation, including 126 patients who received univentricular palliation or a heart transplant. The median age of stage I recipients was 6 days, and median weight 3.2 kg. The stage II operation was performed at 4.5 months, with a range of 2.9 to 39.5 months, and Fontan completion was established at 33.7 months, with a range of 21 to 108 months.
Median follow-up after the stage I procedure was 4.6 years, and the death rate was 2.5%. After stage II, mortality was 4.9%; no deaths were reported after Fontan completion. Body weight less than 2.5 kg and aortic atresia had no significant effect on survival. Mortality rates were 8.9% between stages I and II and 5.3% between stage II and Fontan completion. “Cumulative interstage mortality was 14.2%,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues noted. “At 10 years, the probability of survival is 77.8%.”
Also at 10 years, 32.2% of patients were free from further pulmonary artery intervention, and 16.7% needed aortic arch reconstruction. Two patients required reoperations for aortic arch reconstruction.
Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues suggested several steps to improve outcomes with the hybrid approach: “intense collaboration” with anesthesiology and pediatric cardiology during and after the procedure to risk stratify individual patients; implementation of standards for management of all stages, including out-of-hospital care, in all departments that participate in a case; and liberalized indications for use of MRI before the stage II and Fontan completion.
Among the limitations of the study the authors noted were its retrospective nature and a median follow-up of only 5 years when the center has some cases with up to 15 years of follow-up. But Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors said they could not determine if the patients benefit from the hybrid treatment in the long-term.
The researchers had no disclosures.
Although the classic Norwood palliation for infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) has been well established, the procedure has had its drawbacks, namely the need for cardiopulmonary bypass with hypothermia and a because it rules out biventricular correction months later. A hybrid procedure avoids the need for bypass and accommodates short-term biventricular correction, but it has lacked strong evidence.
Researchers from Justus-Liebig University Giessen, Germany, reported on 182 patients with HLHS who had the three-stage Giessen hybrid procedure, noting 10-year survival of almost 80% with almost a third of patients requiring no artery intervention in that time (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 April;151:1112-23).
“In view of the early results and long-term outcome after Giessen hybrid palliation, the hybrid approach has become a reasonable alternative to the conventional strategy to treat neonates with HLHS and variants,” wrote Dr. Can Yerebakan and colleagues. “Further refinements are warranted to decrease patient morbidity.”
The Giessen hybrid procedure uses a technique to control pulmonary blood flow that is different from the Norwood procedure. The hybrid approach involves stenting of the arterial duct or prostaglandin therapy to maintain systemic perfusion combined with off-pump bilateral banding of the pulmonary arteries (bPAB) in the neonatal period. The Giessen hybrid operation defers the Norwood-type palliation using cardiopulmonary bypass that involves an aortic arch reconstruction, including a superior cavopulmonary connection or a biventricular correction, if indicated, until the infant is 4-8 months of age.
“In recent years, hybrid treatment has moved from a myth to an alternative modality in a growing number of institutions globally,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues said. The hybrid procedure has been used in high-risk patients. One report claimed higher morbidity in the hybrid procedure due to bPAB (Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96:1382-8). Another study raised concerns about an adequate pulmonary artery rehabilitation at the time of the Fontan operation, the third stage in the hybrid strategy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:706-12).
But with the hybrid approach, patients retain the potential to receive a biventricular correction up to 8 months later without compromising survival, “postponing an immediate definitive decision in the newborn period in comparison with the classic Norwood palliation,” Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors noted.
The doctors at the Pediatric Heart Center Giessen treat all types and variants of HLHS with the modified Giessen hybrid strategy. Between 1998 and 2015, 182 patients with HLHS had the Giessen hybrid stage I operation, including 126 patients who received univentricular palliation or a heart transplant. The median age of stage I recipients was 6 days, and median weight 3.2 kg. The stage II operation was performed at 4.5 months, with a range of 2.9 to 39.5 months, and Fontan completion was established at 33.7 months, with a range of 21 to 108 months.
Median follow-up after the stage I procedure was 4.6 years, and the death rate was 2.5%. After stage II, mortality was 4.9%; no deaths were reported after Fontan completion. Body weight less than 2.5 kg and aortic atresia had no significant effect on survival. Mortality rates were 8.9% between stages I and II and 5.3% between stage II and Fontan completion. “Cumulative interstage mortality was 14.2%,” Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues noted. “At 10 years, the probability of survival is 77.8%.”
Also at 10 years, 32.2% of patients were free from further pulmonary artery intervention, and 16.7% needed aortic arch reconstruction. Two patients required reoperations for aortic arch reconstruction.
Dr. Yerebakan and colleagues suggested several steps to improve outcomes with the hybrid approach: “intense collaboration” with anesthesiology and pediatric cardiology during and after the procedure to risk stratify individual patients; implementation of standards for management of all stages, including out-of-hospital care, in all departments that participate in a case; and liberalized indications for use of MRI before the stage II and Fontan completion.
Among the limitations of the study the authors noted were its retrospective nature and a median follow-up of only 5 years when the center has some cases with up to 15 years of follow-up. But Dr. Yerebakan and coauthors said they could not determine if the patients benefit from the hybrid treatment in the long-term.
The researchers had no disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: A hybrid operation for hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) and variants in neonates is emerging as an alternative to the Norwood palliation.
Major finding: At 10 years, the probability of survival with the hybrid procedure was 77.8%. Low body weight (less than 2.5 kg) and aortic atresia had no significant impact on survival.
Data source: Retrospective study of 182 patients who had the hybrid procedure at a single center between June 1998 and February 2015.
Disclosures: The study investigators had no relationships to disclose.
Endovascular thrombectomy procedure volume for stroke may not affect outcomes
VANCOUVER – The relationship between hospitals’ procedural volume and patient outcomes that has been observed for many cardiovascular interventions and other surgeries does not hold for endovascular mechanical thrombectomy procedures for acute ischemic stroke, according to an analysis of cases during 2008-2011 in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample.
In-hospital mortality and rates for any complications were not associated with high or low endovascular mechanical thrombectomy (EMT) volume at hospitals across the United States in the analysis of 13,502 adult patients hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke and treated with EMT, neurology resident Dr. Abhishek Lunagariya of the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
A smaller prior study of 2,749 EMTs done in 296 hospitals in 2008 showed lower mortality in high-volume hospitals that performed 10 or more of the procedures per year (J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013 Nov; 22[8]:1263-9).
Of the 13,502 EMTs in the study, 25% occurred at low-volume hospitals performing less than 10 per year. Low-volume hospitals had higher in-hospital mortality than did higher-volume centers performing 10 or more of the procedures per year in an unadjusted comparison (26% vs. 21%). A comparison of a combined endpoint for any complications (in-hospital mortality, intracerebral hemorrhage, and vascular complications) was also significantly in favor of high-volume hospitals (34% vs. 30%).
However, in a multivariate hierarchical model, low-volume hospitals were not associated with higher in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.23) or rate of any complications (OR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.76-1.21). These analyses were adjusted for age, gender, ethnicity, primary payer, median household income, hospital region/teaching status/location/bed size, Charlson Comorbidity Index, calendar year, and use of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator.
Dr. Lunagariya noted that he and his associates could not adjust the comparisons for National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores because they are not recorded in the National Inpatient Sample. They also could not examine what happened to patients after discharge.
Dr. Lunagariya suggested a variety of possible reasons that might help to explain the lack of an association between hospital procedure volume and outcomes after adjustment: the availability of better thrombectomy devices since the smaller 2008 study, lesser operator variability, favorable patient selection, and an increased skill set of operators working at low-volume hospitals.
One audience member noted that some endovascular interventionalists will operate at both high-volume and low-volume hospitals and could account for some of the findings. That indeed might be happening more often and needs to happen more often, Dr. Lunagariya said in an interview, in order to combat the “common belief” that it would be better to wait for a patient to undergo the procedure at a high- rather than low-volume hospital. Patients who receive initial care for stroke at a low-volume hospital but are not stable enough or do not have enough time to be transferred could benefit from EMT if an interventionalist who performs EMT drove there instead, he said.
With even newer devices now available that are thought to be easier to use, Dr. Lunagariya suggested that the similarity in outcomes at low- and higher-volume centers may not change in updated analyses of more recent EMT procedures for ischemic stroke.
The investigators received no funding for the study, and they reported having no financial disclosures.
VANCOUVER – The relationship between hospitals’ procedural volume and patient outcomes that has been observed for many cardiovascular interventions and other surgeries does not hold for endovascular mechanical thrombectomy procedures for acute ischemic stroke, according to an analysis of cases during 2008-2011 in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample.
In-hospital mortality and rates for any complications were not associated with high or low endovascular mechanical thrombectomy (EMT) volume at hospitals across the United States in the analysis of 13,502 adult patients hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke and treated with EMT, neurology resident Dr. Abhishek Lunagariya of the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
A smaller prior study of 2,749 EMTs done in 296 hospitals in 2008 showed lower mortality in high-volume hospitals that performed 10 or more of the procedures per year (J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013 Nov; 22[8]:1263-9).
Of the 13,502 EMTs in the study, 25% occurred at low-volume hospitals performing less than 10 per year. Low-volume hospitals had higher in-hospital mortality than did higher-volume centers performing 10 or more of the procedures per year in an unadjusted comparison (26% vs. 21%). A comparison of a combined endpoint for any complications (in-hospital mortality, intracerebral hemorrhage, and vascular complications) was also significantly in favor of high-volume hospitals (34% vs. 30%).
However, in a multivariate hierarchical model, low-volume hospitals were not associated with higher in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.23) or rate of any complications (OR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.76-1.21). These analyses were adjusted for age, gender, ethnicity, primary payer, median household income, hospital region/teaching status/location/bed size, Charlson Comorbidity Index, calendar year, and use of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator.
Dr. Lunagariya noted that he and his associates could not adjust the comparisons for National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores because they are not recorded in the National Inpatient Sample. They also could not examine what happened to patients after discharge.
Dr. Lunagariya suggested a variety of possible reasons that might help to explain the lack of an association between hospital procedure volume and outcomes after adjustment: the availability of better thrombectomy devices since the smaller 2008 study, lesser operator variability, favorable patient selection, and an increased skill set of operators working at low-volume hospitals.
One audience member noted that some endovascular interventionalists will operate at both high-volume and low-volume hospitals and could account for some of the findings. That indeed might be happening more often and needs to happen more often, Dr. Lunagariya said in an interview, in order to combat the “common belief” that it would be better to wait for a patient to undergo the procedure at a high- rather than low-volume hospital. Patients who receive initial care for stroke at a low-volume hospital but are not stable enough or do not have enough time to be transferred could benefit from EMT if an interventionalist who performs EMT drove there instead, he said.
With even newer devices now available that are thought to be easier to use, Dr. Lunagariya suggested that the similarity in outcomes at low- and higher-volume centers may not change in updated analyses of more recent EMT procedures for ischemic stroke.
The investigators received no funding for the study, and they reported having no financial disclosures.
VANCOUVER – The relationship between hospitals’ procedural volume and patient outcomes that has been observed for many cardiovascular interventions and other surgeries does not hold for endovascular mechanical thrombectomy procedures for acute ischemic stroke, according to an analysis of cases during 2008-2011 in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample.
In-hospital mortality and rates for any complications were not associated with high or low endovascular mechanical thrombectomy (EMT) volume at hospitals across the United States in the analysis of 13,502 adult patients hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke and treated with EMT, neurology resident Dr. Abhishek Lunagariya of the University of Florida, Gainesville, reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
A smaller prior study of 2,749 EMTs done in 296 hospitals in 2008 showed lower mortality in high-volume hospitals that performed 10 or more of the procedures per year (J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013 Nov; 22[8]:1263-9).
Of the 13,502 EMTs in the study, 25% occurred at low-volume hospitals performing less than 10 per year. Low-volume hospitals had higher in-hospital mortality than did higher-volume centers performing 10 or more of the procedures per year in an unadjusted comparison (26% vs. 21%). A comparison of a combined endpoint for any complications (in-hospital mortality, intracerebral hemorrhage, and vascular complications) was also significantly in favor of high-volume hospitals (34% vs. 30%).
However, in a multivariate hierarchical model, low-volume hospitals were not associated with higher in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.23) or rate of any complications (OR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.76-1.21). These analyses were adjusted for age, gender, ethnicity, primary payer, median household income, hospital region/teaching status/location/bed size, Charlson Comorbidity Index, calendar year, and use of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator.
Dr. Lunagariya noted that he and his associates could not adjust the comparisons for National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores because they are not recorded in the National Inpatient Sample. They also could not examine what happened to patients after discharge.
Dr. Lunagariya suggested a variety of possible reasons that might help to explain the lack of an association between hospital procedure volume and outcomes after adjustment: the availability of better thrombectomy devices since the smaller 2008 study, lesser operator variability, favorable patient selection, and an increased skill set of operators working at low-volume hospitals.
One audience member noted that some endovascular interventionalists will operate at both high-volume and low-volume hospitals and could account for some of the findings. That indeed might be happening more often and needs to happen more often, Dr. Lunagariya said in an interview, in order to combat the “common belief” that it would be better to wait for a patient to undergo the procedure at a high- rather than low-volume hospital. Patients who receive initial care for stroke at a low-volume hospital but are not stable enough or do not have enough time to be transferred could benefit from EMT if an interventionalist who performs EMT drove there instead, he said.
With even newer devices now available that are thought to be easier to use, Dr. Lunagariya suggested that the similarity in outcomes at low- and higher-volume centers may not change in updated analyses of more recent EMT procedures for ischemic stroke.
The investigators received no funding for the study, and they reported having no financial disclosures.
AT THE AAN 2016 ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Patient outcomes after endovascular mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke do not appear to be worse at low- versus high-volume hospitals.
Major finding: In a multivariate hierarchical model, low-volume hospitals (fewer than 10 thrombectomies per year) were not associated with higher in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.23) or rate of any complications (OR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.76-1.21).
Data source: A retrospective review of 13,502 patients with acute ischemic stroke who underwent endovascular mechanical thrombectomy in 2008-2011.
Disclosures: The investigators received no funding for the study, and they reported having no financial disclosures.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy improves survival for some with pancreatic cancer
MONTREAL – For individuals with stage III pancreatic cancer, neoadjuvant therapy may improve survival, compared with surgery-first treatment. “This study supports, however does not prove, the hypothesis that early and continued control of occult metastatic disease prolongs survival in surgical patients,” said Dr. Christopher Shubert.
Dr. Shubert and his colleagues used an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis to compare overall survival (OS) for 377 patients who were to receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 216 patients who received surgery first. Median OS for the neoadjuvant group was 20.7 months, compared with 13.7 months for the surgery-first group (log-rank P less than .0001).
This study was the first to utilize national data to look at how patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III pancreatic cancer fared, when compared with those treated with a surgery-first approach, Dr. Shubert, a general surgery resident at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said at the annual meeting of the Central Surgical Association.
Stage III pancreatic cancer (T4, any N, M0) means that the cancer has invaded the celiac trunk, or there is superior mesenteric artery involvement, he noted.
Using data from the National Cancer Database from 2002 to 2011, the investigators identified patients with clinical stage III pancreatic adenocarcinoma of the head or body of the pancreas. The ITT neoadjuvant therapy cohort included all patients whose treatment recommendations included curative-intent surgery and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, regardless of what therapies the patients received. The surgery-first cohort included those who were recommended to receive adjuvant therapy.
A total of 593 patients were identified, of whom 377 (63.5%) were in the neoadjuvant group. Of these, 104 (27.6%) were lost to presurgical attrition. The surgery-first group included 216 patients (36.3%), 30 (13.9%) of whom did not receive the intended adjuvant chemotherapy. Comparing the two ITT groups yielded an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.68 (P = .001).
A secondary aim of the study was to see which aspects of therapy, and which pathologic features, were associated with longer OS. The addition of postsurgical therapy was associated with additional survival benefit (31.6 vs. 22.6 months for no postsurgical therapy; HR, 0.60; P = .002). Node-negative and R0 status were both also significantly increased among those receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and both disease characteristics were associated with increased OS, he reported.
Dr. Shubert said that study limitations included its review of a prospective database. Also, investigators could not determine the type or duration of chemotherapy; they also were unable to tell when systemic chemotherapy plus chemoradiation or just chemoradiation alone had been used. No recurrence data were available, and all cases were grouped under one procedure code, limiting information about vascular resections.
“Neoadjuvant therapy may offer survival advantages compared to a surgery-first approach,” said Dr. Shubert, and control of small occult metastases may be the mechanism behind this advantage. Still to be determined, however, are the optimal type, duration, and sequencing of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiation, he said.
Dr. Shubert reported no relevant disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
MONTREAL – For individuals with stage III pancreatic cancer, neoadjuvant therapy may improve survival, compared with surgery-first treatment. “This study supports, however does not prove, the hypothesis that early and continued control of occult metastatic disease prolongs survival in surgical patients,” said Dr. Christopher Shubert.
Dr. Shubert and his colleagues used an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis to compare overall survival (OS) for 377 patients who were to receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 216 patients who received surgery first. Median OS for the neoadjuvant group was 20.7 months, compared with 13.7 months for the surgery-first group (log-rank P less than .0001).
This study was the first to utilize national data to look at how patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III pancreatic cancer fared, when compared with those treated with a surgery-first approach, Dr. Shubert, a general surgery resident at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said at the annual meeting of the Central Surgical Association.
Stage III pancreatic cancer (T4, any N, M0) means that the cancer has invaded the celiac trunk, or there is superior mesenteric artery involvement, he noted.
Using data from the National Cancer Database from 2002 to 2011, the investigators identified patients with clinical stage III pancreatic adenocarcinoma of the head or body of the pancreas. The ITT neoadjuvant therapy cohort included all patients whose treatment recommendations included curative-intent surgery and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, regardless of what therapies the patients received. The surgery-first cohort included those who were recommended to receive adjuvant therapy.
A total of 593 patients were identified, of whom 377 (63.5%) were in the neoadjuvant group. Of these, 104 (27.6%) were lost to presurgical attrition. The surgery-first group included 216 patients (36.3%), 30 (13.9%) of whom did not receive the intended adjuvant chemotherapy. Comparing the two ITT groups yielded an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.68 (P = .001).
A secondary aim of the study was to see which aspects of therapy, and which pathologic features, were associated with longer OS. The addition of postsurgical therapy was associated with additional survival benefit (31.6 vs. 22.6 months for no postsurgical therapy; HR, 0.60; P = .002). Node-negative and R0 status were both also significantly increased among those receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and both disease characteristics were associated with increased OS, he reported.
Dr. Shubert said that study limitations included its review of a prospective database. Also, investigators could not determine the type or duration of chemotherapy; they also were unable to tell when systemic chemotherapy plus chemoradiation or just chemoradiation alone had been used. No recurrence data were available, and all cases were grouped under one procedure code, limiting information about vascular resections.
“Neoadjuvant therapy may offer survival advantages compared to a surgery-first approach,” said Dr. Shubert, and control of small occult metastases may be the mechanism behind this advantage. Still to be determined, however, are the optimal type, duration, and sequencing of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiation, he said.
Dr. Shubert reported no relevant disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
MONTREAL – For individuals with stage III pancreatic cancer, neoadjuvant therapy may improve survival, compared with surgery-first treatment. “This study supports, however does not prove, the hypothesis that early and continued control of occult metastatic disease prolongs survival in surgical patients,” said Dr. Christopher Shubert.
Dr. Shubert and his colleagues used an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis to compare overall survival (OS) for 377 patients who were to receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 216 patients who received surgery first. Median OS for the neoadjuvant group was 20.7 months, compared with 13.7 months for the surgery-first group (log-rank P less than .0001).
This study was the first to utilize national data to look at how patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III pancreatic cancer fared, when compared with those treated with a surgery-first approach, Dr. Shubert, a general surgery resident at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said at the annual meeting of the Central Surgical Association.
Stage III pancreatic cancer (T4, any N, M0) means that the cancer has invaded the celiac trunk, or there is superior mesenteric artery involvement, he noted.
Using data from the National Cancer Database from 2002 to 2011, the investigators identified patients with clinical stage III pancreatic adenocarcinoma of the head or body of the pancreas. The ITT neoadjuvant therapy cohort included all patients whose treatment recommendations included curative-intent surgery and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, regardless of what therapies the patients received. The surgery-first cohort included those who were recommended to receive adjuvant therapy.
A total of 593 patients were identified, of whom 377 (63.5%) were in the neoadjuvant group. Of these, 104 (27.6%) were lost to presurgical attrition. The surgery-first group included 216 patients (36.3%), 30 (13.9%) of whom did not receive the intended adjuvant chemotherapy. Comparing the two ITT groups yielded an adjusted hazard ratio of 0.68 (P = .001).
A secondary aim of the study was to see which aspects of therapy, and which pathologic features, were associated with longer OS. The addition of postsurgical therapy was associated with additional survival benefit (31.6 vs. 22.6 months for no postsurgical therapy; HR, 0.60; P = .002). Node-negative and R0 status were both also significantly increased among those receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and both disease characteristics were associated with increased OS, he reported.
Dr. Shubert said that study limitations included its review of a prospective database. Also, investigators could not determine the type or duration of chemotherapy; they also were unable to tell when systemic chemotherapy plus chemoradiation or just chemoradiation alone had been used. No recurrence data were available, and all cases were grouped under one procedure code, limiting information about vascular resections.
“Neoadjuvant therapy may offer survival advantages compared to a surgery-first approach,” said Dr. Shubert, and control of small occult metastases may be the mechanism behind this advantage. Still to be determined, however, are the optimal type, duration, and sequencing of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and chemoradiation, he said.
Dr. Shubert reported no relevant disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
AT THE ANNUAL MEETING OF THE CENTRAL SURGICAL ASSOCIATION
Key clinical point: Overall survival in stage III pancreatic cancer was better with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Major finding: Median survival with neoadjuvant chemotherapy was 20.7 months, compared with 13.7 months for surgery-first patients.
Data source: Review of stage III pancreatic cancer patients in the prospective National Cancer Database, comparing 377 patients recommended to receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 216 patients who were to receive surgery first.
Disclosures: Dr. Shubert reported no relevant disclosures.