User login
Knowns and unknowns about SSRI use during pregnancy in 2022
The last 15-20 years have brought enormous attention to the relevant clinical issues regarding prescribing antidepressants during pregnancy. Concern about the effects of fetal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is appropriate given the consistent data that approximately 7% of women use antidepressants during pregnancy, and that risk for relapse of depression during pregnancy in women who have stopped antidepressants during pregnancy is very high.
We have learned so much from studies of relevant questions regarding SSRI exposure. Concerns about increased risk for organ malformation have been set aside. An extraordinary number of studies across a broad range of patients around the globe looked at the issue of risk for organ malformation following in utero SSRI exposure – even looking specifically at risk for cardiac malformations, which had been an earlier concern in the literature – with the evidence supporting absence of increased risk. Also clarified has been, first, the absence of risk of complications such as persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and, second, a delineation of the prevalence and clinical implications of transient neonatal symptoms such as jitteriness and tachypnea in offspring of women who used antidepressants during pregnancy – so-called “poor neonatal adaptation syndrome.”
However, for so many clinicians and for patients, the missing piece in the risk-benefit equation has been the issue of long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in children whose mothers used antidepressants during pregnancy. While the accumulated data have shown sparse evidence linking SSRI exposure with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the evidence has been mixed regarding neurobehavioral sequelae associated with fetal exposure using developmental outcomes such as language ability, cognition, academic performance, language, math, and other cognitive outcomes. As far back as the 1990s, colleagues in Canada failed to show a difference in neurobehavioral outcomes in 5- to 7-year-old children whose mothers used SSRIs or older tricyclic antidepressants during pregnancy compared to nonexposed women (N Engl J Med. 1997 Jan 23;336[4]:258-62). Even early on, it was noted that one of the strongest predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome was untreated maternal psychiatric illness.
Since those early studies and over the last decade, there have been numerous small studies with conflicting data regarding a whole host of neurodevelopmental outcomes with inconsistent methodologies, different assessments, and failure to control for the presence or absence of maternal psychiatric illness during pregnancy – one of the most critical predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome and one we are beginning to appreciate plays a very significant role.
Most recently, the authors of a very large population-based retrospective cohort study in Denmark linked population-based registries with obstetrical data and examined language and math performance among 575,369 public schoolchildren whose mothers used or didn’t use antidepressants during pregnancy (JAMA. 2021 Nov 2;326[17]:1725-35). These investigators found a decrease in mean test scores for language (53.4 vs. 56.6) and math (52.1 vs. 57.4) in children whose mothers received antidepressant prescriptions during pregnancy compared with children who did not have that exposure. However, when they adjusted for maternal psychiatric illness and other relevant confounders, the finding went to null for language (adjusted difference, –0.1; 95% confidence interval, –0.6 to 0.3), but did not for math (adjusted difference, −2.2; 95% CI, −2.7 to −1.6). The results ultimately showed a modest finding for exposure and a small decrement in mathematical performance. The takeaway is that antidepressant use may be a proxy for neurodevelopmental deficit but is unlikely to be the etiology or direct cause of that deficit.
With that said, patients and their doctors can be reassured with respect to how much we have learned about SSRIs during pregnancy across the last decade. Yet there are appropriate concerns about long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in this patient population. I think that what we can say in 2022 is that there is a growing appreciation for the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on long-term outcomes in children and the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on risk for postpartum depression, which we know influences long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in children. Perhaps more than in years past, there is now also an appreciation of the effect of a dysregulated stress axis on the intrauterine fetal neuronal programming, which is perhaps the newest frontier, and which may hold the answers with respect to how to weigh the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on decisions about psychotropic use during pregnancy. But for today, there is an appreciation that exposure to maternal psychopathology is not a benign exposure.
Although some of the data remain incomplete, in 2022, patients will continue to make individual decisions based on the available data, factoring in the effect of maternal adversity in a more deliberate way and with a refined lens through with which to see their options with respect to using or not using SSRIs during pregnancy.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The last 15-20 years have brought enormous attention to the relevant clinical issues regarding prescribing antidepressants during pregnancy. Concern about the effects of fetal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is appropriate given the consistent data that approximately 7% of women use antidepressants during pregnancy, and that risk for relapse of depression during pregnancy in women who have stopped antidepressants during pregnancy is very high.
We have learned so much from studies of relevant questions regarding SSRI exposure. Concerns about increased risk for organ malformation have been set aside. An extraordinary number of studies across a broad range of patients around the globe looked at the issue of risk for organ malformation following in utero SSRI exposure – even looking specifically at risk for cardiac malformations, which had been an earlier concern in the literature – with the evidence supporting absence of increased risk. Also clarified has been, first, the absence of risk of complications such as persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and, second, a delineation of the prevalence and clinical implications of transient neonatal symptoms such as jitteriness and tachypnea in offspring of women who used antidepressants during pregnancy – so-called “poor neonatal adaptation syndrome.”
However, for so many clinicians and for patients, the missing piece in the risk-benefit equation has been the issue of long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in children whose mothers used antidepressants during pregnancy. While the accumulated data have shown sparse evidence linking SSRI exposure with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the evidence has been mixed regarding neurobehavioral sequelae associated with fetal exposure using developmental outcomes such as language ability, cognition, academic performance, language, math, and other cognitive outcomes. As far back as the 1990s, colleagues in Canada failed to show a difference in neurobehavioral outcomes in 5- to 7-year-old children whose mothers used SSRIs or older tricyclic antidepressants during pregnancy compared to nonexposed women (N Engl J Med. 1997 Jan 23;336[4]:258-62). Even early on, it was noted that one of the strongest predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome was untreated maternal psychiatric illness.
Since those early studies and over the last decade, there have been numerous small studies with conflicting data regarding a whole host of neurodevelopmental outcomes with inconsistent methodologies, different assessments, and failure to control for the presence or absence of maternal psychiatric illness during pregnancy – one of the most critical predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome and one we are beginning to appreciate plays a very significant role.
Most recently, the authors of a very large population-based retrospective cohort study in Denmark linked population-based registries with obstetrical data and examined language and math performance among 575,369 public schoolchildren whose mothers used or didn’t use antidepressants during pregnancy (JAMA. 2021 Nov 2;326[17]:1725-35). These investigators found a decrease in mean test scores for language (53.4 vs. 56.6) and math (52.1 vs. 57.4) in children whose mothers received antidepressant prescriptions during pregnancy compared with children who did not have that exposure. However, when they adjusted for maternal psychiatric illness and other relevant confounders, the finding went to null for language (adjusted difference, –0.1; 95% confidence interval, –0.6 to 0.3), but did not for math (adjusted difference, −2.2; 95% CI, −2.7 to −1.6). The results ultimately showed a modest finding for exposure and a small decrement in mathematical performance. The takeaway is that antidepressant use may be a proxy for neurodevelopmental deficit but is unlikely to be the etiology or direct cause of that deficit.
With that said, patients and their doctors can be reassured with respect to how much we have learned about SSRIs during pregnancy across the last decade. Yet there are appropriate concerns about long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in this patient population. I think that what we can say in 2022 is that there is a growing appreciation for the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on long-term outcomes in children and the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on risk for postpartum depression, which we know influences long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in children. Perhaps more than in years past, there is now also an appreciation of the effect of a dysregulated stress axis on the intrauterine fetal neuronal programming, which is perhaps the newest frontier, and which may hold the answers with respect to how to weigh the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on decisions about psychotropic use during pregnancy. But for today, there is an appreciation that exposure to maternal psychopathology is not a benign exposure.
Although some of the data remain incomplete, in 2022, patients will continue to make individual decisions based on the available data, factoring in the effect of maternal adversity in a more deliberate way and with a refined lens through with which to see their options with respect to using or not using SSRIs during pregnancy.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The last 15-20 years have brought enormous attention to the relevant clinical issues regarding prescribing antidepressants during pregnancy. Concern about the effects of fetal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is appropriate given the consistent data that approximately 7% of women use antidepressants during pregnancy, and that risk for relapse of depression during pregnancy in women who have stopped antidepressants during pregnancy is very high.
We have learned so much from studies of relevant questions regarding SSRI exposure. Concerns about increased risk for organ malformation have been set aside. An extraordinary number of studies across a broad range of patients around the globe looked at the issue of risk for organ malformation following in utero SSRI exposure – even looking specifically at risk for cardiac malformations, which had been an earlier concern in the literature – with the evidence supporting absence of increased risk. Also clarified has been, first, the absence of risk of complications such as persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) and, second, a delineation of the prevalence and clinical implications of transient neonatal symptoms such as jitteriness and tachypnea in offspring of women who used antidepressants during pregnancy – so-called “poor neonatal adaptation syndrome.”
However, for so many clinicians and for patients, the missing piece in the risk-benefit equation has been the issue of long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in children whose mothers used antidepressants during pregnancy. While the accumulated data have shown sparse evidence linking SSRI exposure with autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the evidence has been mixed regarding neurobehavioral sequelae associated with fetal exposure using developmental outcomes such as language ability, cognition, academic performance, language, math, and other cognitive outcomes. As far back as the 1990s, colleagues in Canada failed to show a difference in neurobehavioral outcomes in 5- to 7-year-old children whose mothers used SSRIs or older tricyclic antidepressants during pregnancy compared to nonexposed women (N Engl J Med. 1997 Jan 23;336[4]:258-62). Even early on, it was noted that one of the strongest predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome was untreated maternal psychiatric illness.
Since those early studies and over the last decade, there have been numerous small studies with conflicting data regarding a whole host of neurodevelopmental outcomes with inconsistent methodologies, different assessments, and failure to control for the presence or absence of maternal psychiatric illness during pregnancy – one of the most critical predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome and one we are beginning to appreciate plays a very significant role.
Most recently, the authors of a very large population-based retrospective cohort study in Denmark linked population-based registries with obstetrical data and examined language and math performance among 575,369 public schoolchildren whose mothers used or didn’t use antidepressants during pregnancy (JAMA. 2021 Nov 2;326[17]:1725-35). These investigators found a decrease in mean test scores for language (53.4 vs. 56.6) and math (52.1 vs. 57.4) in children whose mothers received antidepressant prescriptions during pregnancy compared with children who did not have that exposure. However, when they adjusted for maternal psychiatric illness and other relevant confounders, the finding went to null for language (adjusted difference, –0.1; 95% confidence interval, –0.6 to 0.3), but did not for math (adjusted difference, −2.2; 95% CI, −2.7 to −1.6). The results ultimately showed a modest finding for exposure and a small decrement in mathematical performance. The takeaway is that antidepressant use may be a proxy for neurodevelopmental deficit but is unlikely to be the etiology or direct cause of that deficit.
With that said, patients and their doctors can be reassured with respect to how much we have learned about SSRIs during pregnancy across the last decade. Yet there are appropriate concerns about long-term neurodevelopmental sequelae in this patient population. I think that what we can say in 2022 is that there is a growing appreciation for the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on long-term outcomes in children and the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on risk for postpartum depression, which we know influences long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in children. Perhaps more than in years past, there is now also an appreciation of the effect of a dysregulated stress axis on the intrauterine fetal neuronal programming, which is perhaps the newest frontier, and which may hold the answers with respect to how to weigh the effect of maternal psychiatric illness on decisions about psychotropic use during pregnancy. But for today, there is an appreciation that exposure to maternal psychopathology is not a benign exposure.
Although some of the data remain incomplete, in 2022, patients will continue to make individual decisions based on the available data, factoring in the effect of maternal adversity in a more deliberate way and with a refined lens through with which to see their options with respect to using or not using SSRIs during pregnancy.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
Doctors treat osteoporosis with hormone therapy against guidelines
This type of hormone therapy (HT) can be given as estrogen or a combination of hormones including estrogen. The physicians interviewed for this piece who prescribe HT for osteoporosis suggest the benefits outweigh the downsides to its use for some of their patients. But such doctors may be a minority group, suggests Michael R. McClung, MD, founding director of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center, Portland.
According to Dr. McClung, HT is now rarely prescribed as treatment – as opposed to prevention – for osteoporosis in the absence of additional benefits such as reducing vasomotor symptoms.
Researchers’ findings on HT use in women with osteoporosis are complex. While HT is approved for menopausal prevention of osteoporosis, it is not indicated as a treatment for the disease by the Food and Drug Administration. See the prescribing information for Premarin tablets, which contain a mixture of estrogen hormones, for an example of the FDA’s indications and usage for the type of HT addressed in this article.
Women’s Health Initiative findings
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) hormone therapy trials showed that HT reduces the incidence of all osteoporosis-related fractures in postmenopausal women, even those at low risk of fracture, but osteoporosis-related fractures was not a study endpoint. These trials also revealed that HT was associated with increased risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, an increased risk of breast cancer, and other adverse health outcomes.
The release of the interim results of the WHI trials in 2002 led to a fair amount of fear and confusion about the use of HT after menopause. After the WHI findings were published, estrogen use dropped dramatically, but for everything, including for vasomotor symptoms and the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
Prior to the WHI study, it was very common for hormone therapy to be prescribed as women neared or entered menopause, said Risa Kagan MD, clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences, University of California, San Francisco.
“When a woman turned 50, that was one of the first things we did – was to put her on hormone therapy. All that changed with the WHI, but now we are coming full circle,” noted Dr. Kagan, who currently prescribes HT as first line treatment for osteoporosis to some women.
Hormone therapy’s complex history
HT’s ability to reduce bone loss in postmenopausal women is well-documented in many papers, including one published March 8, 2018, in Osteoporosis International, by Dr. Kagan and colleagues. This reduced bone loss has been shown to significantly reduce fractures in patients with low bone mass and osteoporosis.
While a growing number of therapies are now available to treat osteoporosis, HT was traditionally viewed as a standard method of preventing fractures in this population. It was also widely used to prevent other types of symptoms associated with the menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep disturbances, and multiple observational studies had demonstrated that its use appeared to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in symptomatic menopausal women who initiated HT in early menopause.
Even though the WHI studies were the largest randomized trials ever performed in postmenopausal women, they had notable limitations, according to Dr. Kagan.
“The women were older – the average age was 63 years,” she said. “And they only investigated one route and one dose of estrogen.”
Since then, many different formulations and routes of administration with more favorable safety profiles than what was used in the WHI have become available.
It’s both scientifically and clinically unsound to extrapolate the unfavorable risk-benefit profile of HT seen in the WHI trials to all women regardless of age, HT dosage or formulation, or the length of time they’re on it, she added.
Today’s use of HT in women with osteoporosis
Re-analyses and follow-up studies from the WHI trials, along with data from other studies, have suggested that the benefit-risk profiles of HT are affected by a variety of factors. These include the timing of use in relation to menopause and chronological age and the type of hormone regimen.
“Clinically, many advocate for [hormone therapy] use, especially in the newer younger postmenopausal women to prevent bone loss, but also in younger women who are diagnosed with osteoporosis and then as they get older transition to more bone specific agents,” noted Dr. Kagan.
“Some advocate preserving bone mass and preventing osteoporosis and even treating the younger newly postmenopausal women who have no contraindications with hormone therapy initially, and then gradually transitioning them to a bone specific agent as they get older and at risk for fracture.
“If a woman is already fractured and/or has very low bone density with no other obvious secondary metabolic reason, we also often advocate anabolic agents for 1-2 years then consider estrogen for maintenance – again, if [there is] no contraindication to using HT,” she added.
Thus, an individualized approach is recommended to determine a woman’s risk-benefit ratio of HT use based on the absolute risk of adverse effects, Dr. Kagan noted.
“Transdermal and low/ultra-low doses of HT, have a favorable risk profile, and are effective in preserving bone mineral density and bone quality in many women,” she said.
According to Dr. McClung, HT “is most often used for treatment in women in whom hormone therapy was begun for hot flashes and then, when osteoporosis was found later, was simply continued.
“Society guidelines are cautious about recommending hormone therapy for osteoporosis treatment since estrogen is not approved for treatment, despite the clear fracture protection benefit observed in the WHI study,” he said. “Since [women in the WHI trials] were not recruited as having osteoporosis, those results do not meet the FDA requirement for treatment approval, namely the reduction in fracture risk in patients with osteoporosis. However, knowing what we know about the salutary skeletal effects of estrogen, many of us do use them in our patients with osteoporosis – although not prescribed for that purpose.”
Additional scenarios when doctors may advise HT
“I often recommend – and I think colleagues do as well – that women with recent menopause and menopausal symptoms who also have low bone mineral density or even scores showing osteoporosis see their gynecologist to discuss HT for a few years, perhaps until age 60 if no contraindications, and if it is well tolerated,” said Ethel S. Siris, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York.
“Once they stop it we can then give one of our other bone drugs, but it delays the need to start them since on adequate estrogen the bone density should remain stable while they take it,” added Dr. Siris, an endocrinologist and internist, and director of the Toni Stabile Osteoporosis Center in New York. “They may need a bisphosphonate or another bone drug to further protect them from bone loss and future fracture [after stopping HT].”
Victor L. Roberts, MD, founder of Endocrine Associates of Florida, Lake Mary, pointed out that women now have many options for treatment of osteoporosis.
“If a woman is in early menopause and is having other symptoms, then estrogen is warranted,” he said. “If she has osteoporosis, then it’s a bonus.”
“We have better agents that are bone specific,” for a patient who presents with osteoporosis and no other symptoms, he said.
“If a woman is intolerant of alendronate or other similar drugs, or chooses not to have an injectable, then estrogen or a SERM [selective estrogen receptor modulator] would be an option.”
Dr. Roberts added that HT would be more of a niche drug.
“It has a role and documented benefit and works,” he said. “There is good scientific data for the use of estrogen.”
Dr. Kagan is a consultant for Pfizer, Therapeutics MD, Amgen, on the Medical and Scientific Advisory Board of American Bone Health. The other experts interviewed for this piece reported no conflicts.
This type of hormone therapy (HT) can be given as estrogen or a combination of hormones including estrogen. The physicians interviewed for this piece who prescribe HT for osteoporosis suggest the benefits outweigh the downsides to its use for some of their patients. But such doctors may be a minority group, suggests Michael R. McClung, MD, founding director of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center, Portland.
According to Dr. McClung, HT is now rarely prescribed as treatment – as opposed to prevention – for osteoporosis in the absence of additional benefits such as reducing vasomotor symptoms.
Researchers’ findings on HT use in women with osteoporosis are complex. While HT is approved for menopausal prevention of osteoporosis, it is not indicated as a treatment for the disease by the Food and Drug Administration. See the prescribing information for Premarin tablets, which contain a mixture of estrogen hormones, for an example of the FDA’s indications and usage for the type of HT addressed in this article.
Women’s Health Initiative findings
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) hormone therapy trials showed that HT reduces the incidence of all osteoporosis-related fractures in postmenopausal women, even those at low risk of fracture, but osteoporosis-related fractures was not a study endpoint. These trials also revealed that HT was associated with increased risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, an increased risk of breast cancer, and other adverse health outcomes.
The release of the interim results of the WHI trials in 2002 led to a fair amount of fear and confusion about the use of HT after menopause. After the WHI findings were published, estrogen use dropped dramatically, but for everything, including for vasomotor symptoms and the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
Prior to the WHI study, it was very common for hormone therapy to be prescribed as women neared or entered menopause, said Risa Kagan MD, clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences, University of California, San Francisco.
“When a woman turned 50, that was one of the first things we did – was to put her on hormone therapy. All that changed with the WHI, but now we are coming full circle,” noted Dr. Kagan, who currently prescribes HT as first line treatment for osteoporosis to some women.
Hormone therapy’s complex history
HT’s ability to reduce bone loss in postmenopausal women is well-documented in many papers, including one published March 8, 2018, in Osteoporosis International, by Dr. Kagan and colleagues. This reduced bone loss has been shown to significantly reduce fractures in patients with low bone mass and osteoporosis.
While a growing number of therapies are now available to treat osteoporosis, HT was traditionally viewed as a standard method of preventing fractures in this population. It was also widely used to prevent other types of symptoms associated with the menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep disturbances, and multiple observational studies had demonstrated that its use appeared to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in symptomatic menopausal women who initiated HT in early menopause.
Even though the WHI studies were the largest randomized trials ever performed in postmenopausal women, they had notable limitations, according to Dr. Kagan.
“The women were older – the average age was 63 years,” she said. “And they only investigated one route and one dose of estrogen.”
Since then, many different formulations and routes of administration with more favorable safety profiles than what was used in the WHI have become available.
It’s both scientifically and clinically unsound to extrapolate the unfavorable risk-benefit profile of HT seen in the WHI trials to all women regardless of age, HT dosage or formulation, or the length of time they’re on it, she added.
Today’s use of HT in women with osteoporosis
Re-analyses and follow-up studies from the WHI trials, along with data from other studies, have suggested that the benefit-risk profiles of HT are affected by a variety of factors. These include the timing of use in relation to menopause and chronological age and the type of hormone regimen.
“Clinically, many advocate for [hormone therapy] use, especially in the newer younger postmenopausal women to prevent bone loss, but also in younger women who are diagnosed with osteoporosis and then as they get older transition to more bone specific agents,” noted Dr. Kagan.
“Some advocate preserving bone mass and preventing osteoporosis and even treating the younger newly postmenopausal women who have no contraindications with hormone therapy initially, and then gradually transitioning them to a bone specific agent as they get older and at risk for fracture.
“If a woman is already fractured and/or has very low bone density with no other obvious secondary metabolic reason, we also often advocate anabolic agents for 1-2 years then consider estrogen for maintenance – again, if [there is] no contraindication to using HT,” she added.
Thus, an individualized approach is recommended to determine a woman’s risk-benefit ratio of HT use based on the absolute risk of adverse effects, Dr. Kagan noted.
“Transdermal and low/ultra-low doses of HT, have a favorable risk profile, and are effective in preserving bone mineral density and bone quality in many women,” she said.
According to Dr. McClung, HT “is most often used for treatment in women in whom hormone therapy was begun for hot flashes and then, when osteoporosis was found later, was simply continued.
“Society guidelines are cautious about recommending hormone therapy for osteoporosis treatment since estrogen is not approved for treatment, despite the clear fracture protection benefit observed in the WHI study,” he said. “Since [women in the WHI trials] were not recruited as having osteoporosis, those results do not meet the FDA requirement for treatment approval, namely the reduction in fracture risk in patients with osteoporosis. However, knowing what we know about the salutary skeletal effects of estrogen, many of us do use them in our patients with osteoporosis – although not prescribed for that purpose.”
Additional scenarios when doctors may advise HT
“I often recommend – and I think colleagues do as well – that women with recent menopause and menopausal symptoms who also have low bone mineral density or even scores showing osteoporosis see their gynecologist to discuss HT for a few years, perhaps until age 60 if no contraindications, and if it is well tolerated,” said Ethel S. Siris, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York.
“Once they stop it we can then give one of our other bone drugs, but it delays the need to start them since on adequate estrogen the bone density should remain stable while they take it,” added Dr. Siris, an endocrinologist and internist, and director of the Toni Stabile Osteoporosis Center in New York. “They may need a bisphosphonate or another bone drug to further protect them from bone loss and future fracture [after stopping HT].”
Victor L. Roberts, MD, founder of Endocrine Associates of Florida, Lake Mary, pointed out that women now have many options for treatment of osteoporosis.
“If a woman is in early menopause and is having other symptoms, then estrogen is warranted,” he said. “If she has osteoporosis, then it’s a bonus.”
“We have better agents that are bone specific,” for a patient who presents with osteoporosis and no other symptoms, he said.
“If a woman is intolerant of alendronate or other similar drugs, or chooses not to have an injectable, then estrogen or a SERM [selective estrogen receptor modulator] would be an option.”
Dr. Roberts added that HT would be more of a niche drug.
“It has a role and documented benefit and works,” he said. “There is good scientific data for the use of estrogen.”
Dr. Kagan is a consultant for Pfizer, Therapeutics MD, Amgen, on the Medical and Scientific Advisory Board of American Bone Health. The other experts interviewed for this piece reported no conflicts.
This type of hormone therapy (HT) can be given as estrogen or a combination of hormones including estrogen. The physicians interviewed for this piece who prescribe HT for osteoporosis suggest the benefits outweigh the downsides to its use for some of their patients. But such doctors may be a minority group, suggests Michael R. McClung, MD, founding director of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center, Portland.
According to Dr. McClung, HT is now rarely prescribed as treatment – as opposed to prevention – for osteoporosis in the absence of additional benefits such as reducing vasomotor symptoms.
Researchers’ findings on HT use in women with osteoporosis are complex. While HT is approved for menopausal prevention of osteoporosis, it is not indicated as a treatment for the disease by the Food and Drug Administration. See the prescribing information for Premarin tablets, which contain a mixture of estrogen hormones, for an example of the FDA’s indications and usage for the type of HT addressed in this article.
Women’s Health Initiative findings
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) hormone therapy trials showed that HT reduces the incidence of all osteoporosis-related fractures in postmenopausal women, even those at low risk of fracture, but osteoporosis-related fractures was not a study endpoint. These trials also revealed that HT was associated with increased risks of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, an increased risk of breast cancer, and other adverse health outcomes.
The release of the interim results of the WHI trials in 2002 led to a fair amount of fear and confusion about the use of HT after menopause. After the WHI findings were published, estrogen use dropped dramatically, but for everything, including for vasomotor symptoms and the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
Prior to the WHI study, it was very common for hormone therapy to be prescribed as women neared or entered menopause, said Risa Kagan MD, clinical professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences, University of California, San Francisco.
“When a woman turned 50, that was one of the first things we did – was to put her on hormone therapy. All that changed with the WHI, but now we are coming full circle,” noted Dr. Kagan, who currently prescribes HT as first line treatment for osteoporosis to some women.
Hormone therapy’s complex history
HT’s ability to reduce bone loss in postmenopausal women is well-documented in many papers, including one published March 8, 2018, in Osteoporosis International, by Dr. Kagan and colleagues. This reduced bone loss has been shown to significantly reduce fractures in patients with low bone mass and osteoporosis.
While a growing number of therapies are now available to treat osteoporosis, HT was traditionally viewed as a standard method of preventing fractures in this population. It was also widely used to prevent other types of symptoms associated with the menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and sleep disturbances, and multiple observational studies had demonstrated that its use appeared to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in symptomatic menopausal women who initiated HT in early menopause.
Even though the WHI studies were the largest randomized trials ever performed in postmenopausal women, they had notable limitations, according to Dr. Kagan.
“The women were older – the average age was 63 years,” she said. “And they only investigated one route and one dose of estrogen.”
Since then, many different formulations and routes of administration with more favorable safety profiles than what was used in the WHI have become available.
It’s both scientifically and clinically unsound to extrapolate the unfavorable risk-benefit profile of HT seen in the WHI trials to all women regardless of age, HT dosage or formulation, or the length of time they’re on it, she added.
Today’s use of HT in women with osteoporosis
Re-analyses and follow-up studies from the WHI trials, along with data from other studies, have suggested that the benefit-risk profiles of HT are affected by a variety of factors. These include the timing of use in relation to menopause and chronological age and the type of hormone regimen.
“Clinically, many advocate for [hormone therapy] use, especially in the newer younger postmenopausal women to prevent bone loss, but also in younger women who are diagnosed with osteoporosis and then as they get older transition to more bone specific agents,” noted Dr. Kagan.
“Some advocate preserving bone mass and preventing osteoporosis and even treating the younger newly postmenopausal women who have no contraindications with hormone therapy initially, and then gradually transitioning them to a bone specific agent as they get older and at risk for fracture.
“If a woman is already fractured and/or has very low bone density with no other obvious secondary metabolic reason, we also often advocate anabolic agents for 1-2 years then consider estrogen for maintenance – again, if [there is] no contraindication to using HT,” she added.
Thus, an individualized approach is recommended to determine a woman’s risk-benefit ratio of HT use based on the absolute risk of adverse effects, Dr. Kagan noted.
“Transdermal and low/ultra-low doses of HT, have a favorable risk profile, and are effective in preserving bone mineral density and bone quality in many women,” she said.
According to Dr. McClung, HT “is most often used for treatment in women in whom hormone therapy was begun for hot flashes and then, when osteoporosis was found later, was simply continued.
“Society guidelines are cautious about recommending hormone therapy for osteoporosis treatment since estrogen is not approved for treatment, despite the clear fracture protection benefit observed in the WHI study,” he said. “Since [women in the WHI trials] were not recruited as having osteoporosis, those results do not meet the FDA requirement for treatment approval, namely the reduction in fracture risk in patients with osteoporosis. However, knowing what we know about the salutary skeletal effects of estrogen, many of us do use them in our patients with osteoporosis – although not prescribed for that purpose.”
Additional scenarios when doctors may advise HT
“I often recommend – and I think colleagues do as well – that women with recent menopause and menopausal symptoms who also have low bone mineral density or even scores showing osteoporosis see their gynecologist to discuss HT for a few years, perhaps until age 60 if no contraindications, and if it is well tolerated,” said Ethel S. Siris, MD, professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York.
“Once they stop it we can then give one of our other bone drugs, but it delays the need to start them since on adequate estrogen the bone density should remain stable while they take it,” added Dr. Siris, an endocrinologist and internist, and director of the Toni Stabile Osteoporosis Center in New York. “They may need a bisphosphonate or another bone drug to further protect them from bone loss and future fracture [after stopping HT].”
Victor L. Roberts, MD, founder of Endocrine Associates of Florida, Lake Mary, pointed out that women now have many options for treatment of osteoporosis.
“If a woman is in early menopause and is having other symptoms, then estrogen is warranted,” he said. “If she has osteoporosis, then it’s a bonus.”
“We have better agents that are bone specific,” for a patient who presents with osteoporosis and no other symptoms, he said.
“If a woman is intolerant of alendronate or other similar drugs, or chooses not to have an injectable, then estrogen or a SERM [selective estrogen receptor modulator] would be an option.”
Dr. Roberts added that HT would be more of a niche drug.
“It has a role and documented benefit and works,” he said. “There is good scientific data for the use of estrogen.”
Dr. Kagan is a consultant for Pfizer, Therapeutics MD, Amgen, on the Medical and Scientific Advisory Board of American Bone Health. The other experts interviewed for this piece reported no conflicts.
Insurance mandates drive genetic testing and sex selection in IVF
The use of preimplantation genetic tests (PGT) in in vitro fertilization cycles, including tests for nonmedical sex selection, increased significantly in states without mandated insurance coverage, based on data from a study of 300,000 IVF cycles.
Previous studies have shown associations between IVF insurance coverage and various IVF practice patterns, but trends in genetic testing according to state-mandated insurance have not been explored, Bronwyn S. Bedrick, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Preimplantation genetic testing was introduced into clinical practice to prevent transmission of genetic disease and to improve uptake of single embryo transfer, but in the real world there are many potential applications,” corresponding author Emily Jungheim, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “We wanted to know how PGT is being applied given that its use is on the rise.”
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed genetic testing in deidentified autologous, nonbanking IVF cycles from 2014 to 2016 obtained through the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology Clinic Outcome Reporting System (SART CORS). The data set included 301,465 IVF cycles and 224,235 unique patients over the 3-year study period. Of these, 78,578 cycles (26%) used PGT, and overall, the proportion of IVF cycles using PGT approximately doubled, from 17% in 2014 to 34% in 2016 – a significant increase over time (risk ratio, 1.37). As of 2021, 13 states had mandates that health insurance include IVF costs.
In states with insurance mandates versus nonmandated states, the proportion of any PGT was 28.8% vs. 19.6%, and the probability was 32% lower in states with mandates (RR. 0.68; P < .001).
Aneuploidy was the most common indication for PGT, and accounted for 60% of the cycles; however, the number of cycles using PGT for elective sex selection increased from 1,314 cycles in 2014 to 2,184 in 2016 (approximately 66% increase).
In a multivariate analysis, IVF cycles for elective sex selection was 56% lower in states with mandates, compared with those without (RR, 0.44; P < .001).
In addition, cycles involving nonmedical sex selection were significantly more likely to result in male offspring, the researchers said.
“The increase in the number of cycles using elective sex selection seen in this study may reflect the growing number of clinics offering [PGT] for nonmedical sex selection as well as increasing public awareness of preimplantation genetic testing,” the researchers wrote.
However, the socioeconomic characteristics of women may play a role in the use of PGT, as those living in states with no mandate must be able pay the cost of IVF procedures, as well as the cost of PGT if desired, they noted.
“Because fertility centers may offer patients the choice to select the sex of their embryo after preimplantation genetic testing, this may in effect permit elective sex selection,” the researchers said. The shift in the male-female sex ratio in these cases “is concerning given the implications for future social demographics as IVF and preimplantation genetic testing utilization increase, and the negative effect outcomes could have on medical insurance policy and allocation of resources for medically indicated IVF and preimplantation genetic testing.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinic identifiers and lack of data characteristics including, race, ethnicity, and previous live births, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on the sex preferences of the couple, and whether the sex of the embryo was known, and whether male and female embryos were transferred. Also, no states have mandates to cover PGT, and the limited study period may not generalize to current practices.
However, the study strengths include the large size and comprehensive database, and have implications for future policies and expansion of insurance coverage for infertility treatment and for preventing transmission of genetic diseases, they said.
Be mindful of consequences of testing
In an interview, Dr. Jungheim said she was surprised by some of the findings. “I thought we would see that PGT-A utilization was lower in states without mandates given the already high cost of IVF for patients paying out of pocket. I was also surprised to see that more males were born after PGT-A; it suggests that overall, patients using PGT-A favor males.
“For clinicians, we need to be mindful of the long-term impact of our practices,” she emphasized. “Shifting the sex ratio in favor of one sex or the other is an unintended consequence of IVF with PGT-A that can have negative implications for future generations.”
In the study, the researchers proposed a revision to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine Ethics Committee opinion on sex selection to provide guidance in keeping with ASRM’s mission of “accessible, ethical, and quality reproductive care for every person.”
However, “even if the ASRM Ethics Committee Opinion was revised, it’s up to clinicians to decide what they are comfortable with,” said Dr. Jungheim. “When patients are paying out of pocket for expensive treatments that require emotional investment and time, it can be difficult to keep medical decision making strictly evidence based.” Improved insurance coverage and access to fertility care may help with some of these decisions, but more real-world evidence is needed.
Let’s talk about sex (selection)
The study findings are both “novel and sobering,” and enhance the current body of evidence of associations between state insurance mandates and IVF outcomes, Jennifer Eaton, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The association between mandate status and elective sex selection is particularly eye-opening,” said Dr. Eaton. The overall increased use of PGT for sex selection does not account for sex selection as part of testing for aneuploidy. In fact, “patients with euploid embryos of both sexes are frequently given the opportunity to select which embryo to transfer.”
The current study provides “compelling evidence that it is time to revisit the ethical dilemma of elective sex selection in the United States,” Dr. Eaton emphasized. The current ASRM guidance states that IVF clinics are not obligated to provide or refuse to provide nonmedically indicated methods of sex selection, but in light of the current study and other studies, a revision to the existing ASRM Ethics Committee opinion is needed.
The study received no outside funding. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Eaton had any financial conflicts to disclose.
The use of preimplantation genetic tests (PGT) in in vitro fertilization cycles, including tests for nonmedical sex selection, increased significantly in states without mandated insurance coverage, based on data from a study of 300,000 IVF cycles.
Previous studies have shown associations between IVF insurance coverage and various IVF practice patterns, but trends in genetic testing according to state-mandated insurance have not been explored, Bronwyn S. Bedrick, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Preimplantation genetic testing was introduced into clinical practice to prevent transmission of genetic disease and to improve uptake of single embryo transfer, but in the real world there are many potential applications,” corresponding author Emily Jungheim, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “We wanted to know how PGT is being applied given that its use is on the rise.”
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed genetic testing in deidentified autologous, nonbanking IVF cycles from 2014 to 2016 obtained through the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology Clinic Outcome Reporting System (SART CORS). The data set included 301,465 IVF cycles and 224,235 unique patients over the 3-year study period. Of these, 78,578 cycles (26%) used PGT, and overall, the proportion of IVF cycles using PGT approximately doubled, from 17% in 2014 to 34% in 2016 – a significant increase over time (risk ratio, 1.37). As of 2021, 13 states had mandates that health insurance include IVF costs.
In states with insurance mandates versus nonmandated states, the proportion of any PGT was 28.8% vs. 19.6%, and the probability was 32% lower in states with mandates (RR. 0.68; P < .001).
Aneuploidy was the most common indication for PGT, and accounted for 60% of the cycles; however, the number of cycles using PGT for elective sex selection increased from 1,314 cycles in 2014 to 2,184 in 2016 (approximately 66% increase).
In a multivariate analysis, IVF cycles for elective sex selection was 56% lower in states with mandates, compared with those without (RR, 0.44; P < .001).
In addition, cycles involving nonmedical sex selection were significantly more likely to result in male offspring, the researchers said.
“The increase in the number of cycles using elective sex selection seen in this study may reflect the growing number of clinics offering [PGT] for nonmedical sex selection as well as increasing public awareness of preimplantation genetic testing,” the researchers wrote.
However, the socioeconomic characteristics of women may play a role in the use of PGT, as those living in states with no mandate must be able pay the cost of IVF procedures, as well as the cost of PGT if desired, they noted.
“Because fertility centers may offer patients the choice to select the sex of their embryo after preimplantation genetic testing, this may in effect permit elective sex selection,” the researchers said. The shift in the male-female sex ratio in these cases “is concerning given the implications for future social demographics as IVF and preimplantation genetic testing utilization increase, and the negative effect outcomes could have on medical insurance policy and allocation of resources for medically indicated IVF and preimplantation genetic testing.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinic identifiers and lack of data characteristics including, race, ethnicity, and previous live births, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on the sex preferences of the couple, and whether the sex of the embryo was known, and whether male and female embryos were transferred. Also, no states have mandates to cover PGT, and the limited study period may not generalize to current practices.
However, the study strengths include the large size and comprehensive database, and have implications for future policies and expansion of insurance coverage for infertility treatment and for preventing transmission of genetic diseases, they said.
Be mindful of consequences of testing
In an interview, Dr. Jungheim said she was surprised by some of the findings. “I thought we would see that PGT-A utilization was lower in states without mandates given the already high cost of IVF for patients paying out of pocket. I was also surprised to see that more males were born after PGT-A; it suggests that overall, patients using PGT-A favor males.
“For clinicians, we need to be mindful of the long-term impact of our practices,” she emphasized. “Shifting the sex ratio in favor of one sex or the other is an unintended consequence of IVF with PGT-A that can have negative implications for future generations.”
In the study, the researchers proposed a revision to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine Ethics Committee opinion on sex selection to provide guidance in keeping with ASRM’s mission of “accessible, ethical, and quality reproductive care for every person.”
However, “even if the ASRM Ethics Committee Opinion was revised, it’s up to clinicians to decide what they are comfortable with,” said Dr. Jungheim. “When patients are paying out of pocket for expensive treatments that require emotional investment and time, it can be difficult to keep medical decision making strictly evidence based.” Improved insurance coverage and access to fertility care may help with some of these decisions, but more real-world evidence is needed.
Let’s talk about sex (selection)
The study findings are both “novel and sobering,” and enhance the current body of evidence of associations between state insurance mandates and IVF outcomes, Jennifer Eaton, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The association between mandate status and elective sex selection is particularly eye-opening,” said Dr. Eaton. The overall increased use of PGT for sex selection does not account for sex selection as part of testing for aneuploidy. In fact, “patients with euploid embryos of both sexes are frequently given the opportunity to select which embryo to transfer.”
The current study provides “compelling evidence that it is time to revisit the ethical dilemma of elective sex selection in the United States,” Dr. Eaton emphasized. The current ASRM guidance states that IVF clinics are not obligated to provide or refuse to provide nonmedically indicated methods of sex selection, but in light of the current study and other studies, a revision to the existing ASRM Ethics Committee opinion is needed.
The study received no outside funding. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Eaton had any financial conflicts to disclose.
The use of preimplantation genetic tests (PGT) in in vitro fertilization cycles, including tests for nonmedical sex selection, increased significantly in states without mandated insurance coverage, based on data from a study of 300,000 IVF cycles.
Previous studies have shown associations between IVF insurance coverage and various IVF practice patterns, but trends in genetic testing according to state-mandated insurance have not been explored, Bronwyn S. Bedrick, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Preimplantation genetic testing was introduced into clinical practice to prevent transmission of genetic disease and to improve uptake of single embryo transfer, but in the real world there are many potential applications,” corresponding author Emily Jungheim, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “We wanted to know how PGT is being applied given that its use is on the rise.”
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed genetic testing in deidentified autologous, nonbanking IVF cycles from 2014 to 2016 obtained through the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology Clinic Outcome Reporting System (SART CORS). The data set included 301,465 IVF cycles and 224,235 unique patients over the 3-year study period. Of these, 78,578 cycles (26%) used PGT, and overall, the proportion of IVF cycles using PGT approximately doubled, from 17% in 2014 to 34% in 2016 – a significant increase over time (risk ratio, 1.37). As of 2021, 13 states had mandates that health insurance include IVF costs.
In states with insurance mandates versus nonmandated states, the proportion of any PGT was 28.8% vs. 19.6%, and the probability was 32% lower in states with mandates (RR. 0.68; P < .001).
Aneuploidy was the most common indication for PGT, and accounted for 60% of the cycles; however, the number of cycles using PGT for elective sex selection increased from 1,314 cycles in 2014 to 2,184 in 2016 (approximately 66% increase).
In a multivariate analysis, IVF cycles for elective sex selection was 56% lower in states with mandates, compared with those without (RR, 0.44; P < .001).
In addition, cycles involving nonmedical sex selection were significantly more likely to result in male offspring, the researchers said.
“The increase in the number of cycles using elective sex selection seen in this study may reflect the growing number of clinics offering [PGT] for nonmedical sex selection as well as increasing public awareness of preimplantation genetic testing,” the researchers wrote.
However, the socioeconomic characteristics of women may play a role in the use of PGT, as those living in states with no mandate must be able pay the cost of IVF procedures, as well as the cost of PGT if desired, they noted.
“Because fertility centers may offer patients the choice to select the sex of their embryo after preimplantation genetic testing, this may in effect permit elective sex selection,” the researchers said. The shift in the male-female sex ratio in these cases “is concerning given the implications for future social demographics as IVF and preimplantation genetic testing utilization increase, and the negative effect outcomes could have on medical insurance policy and allocation of resources for medically indicated IVF and preimplantation genetic testing.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinic identifiers and lack of data characteristics including, race, ethnicity, and previous live births, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on the sex preferences of the couple, and whether the sex of the embryo was known, and whether male and female embryos were transferred. Also, no states have mandates to cover PGT, and the limited study period may not generalize to current practices.
However, the study strengths include the large size and comprehensive database, and have implications for future policies and expansion of insurance coverage for infertility treatment and for preventing transmission of genetic diseases, they said.
Be mindful of consequences of testing
In an interview, Dr. Jungheim said she was surprised by some of the findings. “I thought we would see that PGT-A utilization was lower in states without mandates given the already high cost of IVF for patients paying out of pocket. I was also surprised to see that more males were born after PGT-A; it suggests that overall, patients using PGT-A favor males.
“For clinicians, we need to be mindful of the long-term impact of our practices,” she emphasized. “Shifting the sex ratio in favor of one sex or the other is an unintended consequence of IVF with PGT-A that can have negative implications for future generations.”
In the study, the researchers proposed a revision to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine Ethics Committee opinion on sex selection to provide guidance in keeping with ASRM’s mission of “accessible, ethical, and quality reproductive care for every person.”
However, “even if the ASRM Ethics Committee Opinion was revised, it’s up to clinicians to decide what they are comfortable with,” said Dr. Jungheim. “When patients are paying out of pocket for expensive treatments that require emotional investment and time, it can be difficult to keep medical decision making strictly evidence based.” Improved insurance coverage and access to fertility care may help with some of these decisions, but more real-world evidence is needed.
Let’s talk about sex (selection)
The study findings are both “novel and sobering,” and enhance the current body of evidence of associations between state insurance mandates and IVF outcomes, Jennifer Eaton, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The association between mandate status and elective sex selection is particularly eye-opening,” said Dr. Eaton. The overall increased use of PGT for sex selection does not account for sex selection as part of testing for aneuploidy. In fact, “patients with euploid embryos of both sexes are frequently given the opportunity to select which embryo to transfer.”
The current study provides “compelling evidence that it is time to revisit the ethical dilemma of elective sex selection in the United States,” Dr. Eaton emphasized. The current ASRM guidance states that IVF clinics are not obligated to provide or refuse to provide nonmedically indicated methods of sex selection, but in light of the current study and other studies, a revision to the existing ASRM Ethics Committee opinion is needed.
The study received no outside funding. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Eaton had any financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Genomic analysis reveals possible role of AMH in PCOS infertility
A genomic study has revealed new insights into the function of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the context of reproductive biology and fertility.
Insights into the physiological, and potentially therapeutic, function were identified based on data from single-cell RNA sequencing, derived from transcriptomic analysis and immunolabeling of antral follicles.
“The specific contribution of elevated AMH to the molecular pathology of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and its defining clinical features is unclear, as no study, to date, has examined the effect of chronically elevated AMH in an experimentally controlled in vivo model,” study author Limor Man, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and colleagues wrote. The group’s findings were published in Science Advances.
The researchers used ovarian cortical xenografts with cotransplantation of engineered endothelial cells to examine the effect of chronic paracrine AMH stimulus on human folliculogenesis.
They cotransplanted human ovarian cortex with control or AMH-expressing endothelial cells in immunocompromised mice and recovered antral follicles for purification and subsequent analysis. Overall, 38 antral follicles were observed (19 control and 19 AMH) at long-term intervals, defined as intervals greater than 10 weeks.
The researchers found that long-term xenografts showed an accelerated growth rate in the setting of chronically elevated AMH and exhibited a molecular signature indicative of more advanced stages of follicle maturation, including that of luteinization.
In mice, exogenous AMH follicles showed a decreased ratio of primordial to growing follicles and antral follicles of increased diameter.
In addition, transcriptomic and immunolabeling analyses revealed that chronic high AMH had a marked influence on the growth and transcriptomic signature of antral-stage follicles, with a universal increase in factors related to the synthesis and/or metabolism of cholesterol and sex steroid hormones, as well as early expression of factors often seen at later stages of folliculogenesis.
“These data decouple elevated AMH from the metabolic and hyperandrogenic conditions that define PCOS and suggest that chronically elevated AMH induces a molecular cascade that contributes, at least in part, to the anovulatory phenotype in these patients,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest that chronic high AMH can induce expression of the luteinizing hormone receptor at earlier stages of folliculogenesis, thereby worsening the disruptive effect of elevated luteinizing hormone from the pituitary.
“[These] findings underscore the broad influence of AMH on transcriptional activity and maturation state of follicles and support an independent role for dysregulation of AMH signaling in driving anovulation in women with PCOS,” they wrote.
While these findings are intriguing, the researchers cautioned against drawing conclusions from the study since elevated AMH is almost always seen in combination with one or more symptomatic hallmarks in PCOS.
“Despite [some] limitations, [our] analysis provides a deep and high-resolution examination of AMH action on human folliculogenesis and suggests a prominent effect on antral follicle maturation,” they explained.
Expert perspective
“From age 25, AMH levels begin their decline until reaching undetectable levels at menopause,” Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. “Women with PCOS experience a chronic and frustrating pathophysiologic problem whose origins and mechanism have evaded researchers for decades.
“As AMH elevations in utero may contribute to fetal susceptibility to PCOS, this study provides another potential link by suggesting that chronically elevated AMH induces anovulation,” he added. “We await, with great anticipation, future clinical studies to potentially further illustrate the apparent and intriguing role of AMH in the development of PCOS.”
This study was supported by the Queenie Victorina Neri Scholarship and a Research Grant from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. One author reported financial relationships with Oviva Therapeutics; no other conflicts of interest were reported.
A genomic study has revealed new insights into the function of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the context of reproductive biology and fertility.
Insights into the physiological, and potentially therapeutic, function were identified based on data from single-cell RNA sequencing, derived from transcriptomic analysis and immunolabeling of antral follicles.
“The specific contribution of elevated AMH to the molecular pathology of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and its defining clinical features is unclear, as no study, to date, has examined the effect of chronically elevated AMH in an experimentally controlled in vivo model,” study author Limor Man, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and colleagues wrote. The group’s findings were published in Science Advances.
The researchers used ovarian cortical xenografts with cotransplantation of engineered endothelial cells to examine the effect of chronic paracrine AMH stimulus on human folliculogenesis.
They cotransplanted human ovarian cortex with control or AMH-expressing endothelial cells in immunocompromised mice and recovered antral follicles for purification and subsequent analysis. Overall, 38 antral follicles were observed (19 control and 19 AMH) at long-term intervals, defined as intervals greater than 10 weeks.
The researchers found that long-term xenografts showed an accelerated growth rate in the setting of chronically elevated AMH and exhibited a molecular signature indicative of more advanced stages of follicle maturation, including that of luteinization.
In mice, exogenous AMH follicles showed a decreased ratio of primordial to growing follicles and antral follicles of increased diameter.
In addition, transcriptomic and immunolabeling analyses revealed that chronic high AMH had a marked influence on the growth and transcriptomic signature of antral-stage follicles, with a universal increase in factors related to the synthesis and/or metabolism of cholesterol and sex steroid hormones, as well as early expression of factors often seen at later stages of folliculogenesis.
“These data decouple elevated AMH from the metabolic and hyperandrogenic conditions that define PCOS and suggest that chronically elevated AMH induces a molecular cascade that contributes, at least in part, to the anovulatory phenotype in these patients,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest that chronic high AMH can induce expression of the luteinizing hormone receptor at earlier stages of folliculogenesis, thereby worsening the disruptive effect of elevated luteinizing hormone from the pituitary.
“[These] findings underscore the broad influence of AMH on transcriptional activity and maturation state of follicles and support an independent role for dysregulation of AMH signaling in driving anovulation in women with PCOS,” they wrote.
While these findings are intriguing, the researchers cautioned against drawing conclusions from the study since elevated AMH is almost always seen in combination with one or more symptomatic hallmarks in PCOS.
“Despite [some] limitations, [our] analysis provides a deep and high-resolution examination of AMH action on human folliculogenesis and suggests a prominent effect on antral follicle maturation,” they explained.
Expert perspective
“From age 25, AMH levels begin their decline until reaching undetectable levels at menopause,” Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. “Women with PCOS experience a chronic and frustrating pathophysiologic problem whose origins and mechanism have evaded researchers for decades.
“As AMH elevations in utero may contribute to fetal susceptibility to PCOS, this study provides another potential link by suggesting that chronically elevated AMH induces anovulation,” he added. “We await, with great anticipation, future clinical studies to potentially further illustrate the apparent and intriguing role of AMH in the development of PCOS.”
This study was supported by the Queenie Victorina Neri Scholarship and a Research Grant from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. One author reported financial relationships with Oviva Therapeutics; no other conflicts of interest were reported.
A genomic study has revealed new insights into the function of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) in the context of reproductive biology and fertility.
Insights into the physiological, and potentially therapeutic, function were identified based on data from single-cell RNA sequencing, derived from transcriptomic analysis and immunolabeling of antral follicles.
“The specific contribution of elevated AMH to the molecular pathology of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and its defining clinical features is unclear, as no study, to date, has examined the effect of chronically elevated AMH in an experimentally controlled in vivo model,” study author Limor Man, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and colleagues wrote. The group’s findings were published in Science Advances.
The researchers used ovarian cortical xenografts with cotransplantation of engineered endothelial cells to examine the effect of chronic paracrine AMH stimulus on human folliculogenesis.
They cotransplanted human ovarian cortex with control or AMH-expressing endothelial cells in immunocompromised mice and recovered antral follicles for purification and subsequent analysis. Overall, 38 antral follicles were observed (19 control and 19 AMH) at long-term intervals, defined as intervals greater than 10 weeks.
The researchers found that long-term xenografts showed an accelerated growth rate in the setting of chronically elevated AMH and exhibited a molecular signature indicative of more advanced stages of follicle maturation, including that of luteinization.
In mice, exogenous AMH follicles showed a decreased ratio of primordial to growing follicles and antral follicles of increased diameter.
In addition, transcriptomic and immunolabeling analyses revealed that chronic high AMH had a marked influence on the growth and transcriptomic signature of antral-stage follicles, with a universal increase in factors related to the synthesis and/or metabolism of cholesterol and sex steroid hormones, as well as early expression of factors often seen at later stages of folliculogenesis.
“These data decouple elevated AMH from the metabolic and hyperandrogenic conditions that define PCOS and suggest that chronically elevated AMH induces a molecular cascade that contributes, at least in part, to the anovulatory phenotype in these patients,” the researchers wrote.
Furthermore, they found evidence to suggest that chronic high AMH can induce expression of the luteinizing hormone receptor at earlier stages of folliculogenesis, thereby worsening the disruptive effect of elevated luteinizing hormone from the pituitary.
“[These] findings underscore the broad influence of AMH on transcriptional activity and maturation state of follicles and support an independent role for dysregulation of AMH signaling in driving anovulation in women with PCOS,” they wrote.
While these findings are intriguing, the researchers cautioned against drawing conclusions from the study since elevated AMH is almost always seen in combination with one or more symptomatic hallmarks in PCOS.
“Despite [some] limitations, [our] analysis provides a deep and high-resolution examination of AMH action on human folliculogenesis and suggests a prominent effect on antral follicle maturation,” they explained.
Expert perspective
“From age 25, AMH levels begin their decline until reaching undetectable levels at menopause,” Mark P. Trolice, MD, director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. “Women with PCOS experience a chronic and frustrating pathophysiologic problem whose origins and mechanism have evaded researchers for decades.
“As AMH elevations in utero may contribute to fetal susceptibility to PCOS, this study provides another potential link by suggesting that chronically elevated AMH induces anovulation,” he added. “We await, with great anticipation, future clinical studies to potentially further illustrate the apparent and intriguing role of AMH in the development of PCOS.”
This study was supported by the Queenie Victorina Neri Scholarship and a Research Grant from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. One author reported financial relationships with Oviva Therapeutics; no other conflicts of interest were reported.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
FDA approves first PARP inhibitor for early BRCA+ breast cancer
BRCA+ breast cancer
Specifically, the new approval is for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with high-risk early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The FDA also approved BRACAnalysis CDx (Myriad Genetics), a companion diagnostic test to identify patients who may benefit from olaparib.
The latest approval was based on phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which showed a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with olaparib in comparison with placebo. Data from OlympiaA and other clinical studies also confirm BRACAnalysis CDx as “an effective test for patients deciding on their best treatment options,” Myriad Genetics noted in a press release.
The OlympiA results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2021 annual meeting and were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those findings prompted an ASCO “rapid recommendation” updating of ASCO’s 2020 guidelines for the management of hereditary breast cancer.
The latest results from OlympiA show that olaparib reduced the risk of death by 32% (hazard ratio, 0.68) in comparison with placebo, according to a company press release announcing the approval. Overall survival data are slated for presentation at a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session on March 16, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the new approval is for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with high-risk early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The FDA also approved BRACAnalysis CDx (Myriad Genetics), a companion diagnostic test to identify patients who may benefit from olaparib.
The latest approval was based on phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which showed a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with olaparib in comparison with placebo. Data from OlympiaA and other clinical studies also confirm BRACAnalysis CDx as “an effective test for patients deciding on their best treatment options,” Myriad Genetics noted in a press release.
The OlympiA results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2021 annual meeting and were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those findings prompted an ASCO “rapid recommendation” updating of ASCO’s 2020 guidelines for the management of hereditary breast cancer.
The latest results from OlympiA show that olaparib reduced the risk of death by 32% (hazard ratio, 0.68) in comparison with placebo, according to a company press release announcing the approval. Overall survival data are slated for presentation at a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session on March 16, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the new approval is for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with high-risk early-stage HER2-negative, BRCA-mutated breast cancer who have completed chemotherapy and local treatment.
The FDA also approved BRACAnalysis CDx (Myriad Genetics), a companion diagnostic test to identify patients who may benefit from olaparib.
The latest approval was based on phase 3 OlympiA trial results, which showed a 42% improvement in invasive and distant disease-free survival with olaparib in comparison with placebo. Data from OlympiaA and other clinical studies also confirm BRACAnalysis CDx as “an effective test for patients deciding on their best treatment options,” Myriad Genetics noted in a press release.
The OlympiA results, as reported by this news organization, were presented during the plenary session of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2021 annual meeting and were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those findings prompted an ASCO “rapid recommendation” updating of ASCO’s 2020 guidelines for the management of hereditary breast cancer.
The latest results from OlympiA show that olaparib reduced the risk of death by 32% (hazard ratio, 0.68) in comparison with placebo, according to a company press release announcing the approval. Overall survival data are slated for presentation at a European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Plenary session on March 16, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BRCA+ breast cancer
BRCA+ breast cancer
Big missed opportunities for BP control in premenopausal women
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shows considerable gaps in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in premenopausal women in the United States, with a key driver being regular access to health care.
In a nationally representative sample of women ages 35-54 with no prior cardiovascular disease, the prevalence of hypertension increased 8% from an estimated 15.2 million women between 2011 and 2014 to 16.4 million women between 2015 and 2018.
What’s more, the percentage of women with controlled hypertension dropped over the two time periods from 55% to 50%, which is well below the government’s Million Hearts target of 70%.
Missed opportunities for hypertension control in these premenopausal women were a lack of awareness of their hypertension in 23%, ineffective treatment in 34%, and a lack of health care access in 43%; increasing to 51% in non-Hispanic Black patients and 56% in Hispanic patients.
Notably, lack of health care access affected an estimated 3.1 million women (45%) in 2011-2014 and 3.5 million women (43%) in 2015-2018.
Equally stubborn over the two time periods was the lack of effective treatment, affecting 2.1 million (31%) versus 2.8 million (34%) women, and lack of awareness, affecting 1.6 million (24%) versus 1.9 million (23%) women.
“There’s been no improvement over the past decade, and there is evidence of race/ethnic disparities,” study author Susan Hennessy, PhD, said at the recent Epidemiology, Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health (EPI|Lifestyle) 2022 conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among non-Hispanic Whites was less than that of the U.S. population, at 44%, and most of the missed opportunities were due to uncontrolled blood pressure (BP), noted Dr. Hennessy, a researcher with the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine.
However, the uncontrolled prevalence was 54% in non-Hispanic Black women and 66% in Hispanic women. “In both of these subgroups, over half of the missed opportunities occur because these women have no regular access to health care,” she said.
In women who identified as “other,” which includes non-Hispanic Asian and mixed-race populations, the uncontrolled prevalence reached 70%, and the biggest missed opportunity was in those who were untreated.
Raising awareness, empowering women, and delivery of guideline-concordant care will help premenopausal women gain control of their blood pressure, Dr. Hennessy said. “But underpinning all of this is ensuring equitable health care access, because if we fail to get women into the system, then we have no opportunity to help them lower their blood pressure.”
She reminded the audience that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer of women in the United States and that CVD risk, mediated through hypertension, increases after menopause. Thus, managing hypertension prior to this life event is an important element of primary prevention of CVD and should be a priority.
Session moderator Sadiya S. Khan, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization that the findings should raise “alarm and concern that hypertension is not just a disease of the old but very prevalent in younger women, particularly around the time of pregnancy. And this is a clear driver of maternal morbidity and mortality as well.”
“This idea that patients should ‘Know Your Numbers’ is really important, and we talk a lot about that for hypertension, but if you don’t have a doctor, if you don’t have someone to go to, it’s very hard to know or understand what your numbers mean,” she said. “I think that’s really the main message.”
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Hennessy said there’s no simple solution to the problem, given that some women are not even in the system, whereas others are not being treated effectively, but that increasing opportunities to screen BP would be a start. That could be through community programs, similar to the Barbershop Hypertension trial, or by making BP devices available for home monitoring.
“Again, this is about empowering ourselves to take some level of control, but, as a system, we have to be able to make it equitable for everyone and make sure they have the right equipment, the right cuff size,” she said. “The disparities arise because of the social determinants of health, so if these women are struggling to put food on the table, they aren’t going to be able to afford a blood pressure cuff.”
During a discussion of the findings, audience members noted that the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data used for the analysis were somewhat dated. Dr. Hennessy also pointed out that NHANES blood pressure is measured up to three times during a single visit, which differs from clinical practice, and that responses were based on self-report and thus subject to recall bias.
The sample included 3,343 women aged 35-54 years with no prior cardiovascular disease, representing an estimated 31.6 million American women. Hypertension was defined by a systolic BP of at least 140 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of at least 90 mm Hg or current BP medication use.
The authors and Dr. Khan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antiseptic as good as antibiotics for preventing recurrent UTI
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
The antiseptic methenamine hippurate (MH) is known to sterilize urine and has been suggested to be of use in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), but firm evidence has so far been lacking. Now researchers led by clinicians and scientists from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England, have provided the ALTAR trial (Alternative to Prophylactic Antibiotics for the Treatment of Recurrent UTIs in Women).
Daily low-dose antibiotics as recommended by current guidelines for prophylactic treatment of recurrent UTI have been linked to antibiotic resistance. Using MH as an alternative could play an important role in helping to tackle the global problem of increasing antibiotic resistance, the team said.
Study details
They recruited 240 women aged 18 or over with recurrent UTIs requiring prophylactic treatment from eight secondary care urology and urogynecology centers in the United Kingdom from June 2016 to June 2018. Women were randomized to receive MH or daily low-dose antibiotics for 12 months, with follow up for a further 6 months beyond that.
Before trial entry the women had experienced an average of more than six UTI episodes per year. During the 12-month treatment period, in the modified intention-to-treat population, there were 90 symptomatic, antibiotic-treated UTI episodes reported over 101 person-years of follow-up in the antibiotic group, and 141 episodes over 102 person-years in the MH group.
This yielded a UTI rate of 0.89 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic group, compared with 1.38 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.49 episodes per person-year. In the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period, the UTI incidence rate was 1.19 episodes per person-year in the antibiotic prophylaxis group versus 1.72 in the MH group, an absolute difference of 0.53.
Before the trial, a patient and public involvement group had predefined the noninferiority margin as one episode of UTI per person-year. The small difference between the two groups was less than this, confirming noninferiority of MH to antibiotic prophylaxis in this setting. This finding was consistent across the modified intention-to-treat, strict intention-to-treat, per protocol, and modified per protocol (post hoc) analyses.
Thus the ALTAR results showed that MH was no worse than antibiotics at preventing UTIs, and MH was also associated with reduced antibiotic consumption.
The vast majority of participants were over 90% adherent with the allocated treatment. Patient satisfaction was generally high and rates of adverse events and adverse reactions generally low, and both were comparable between treatment groups. Adverse reactions were reported by 34/142 (24%) in the antibiotic group and 35/127 (28%) in the MH group, and most reactions were mild. In the antibiotic group there were two serious adverse reactions (severe abdominal pain and raised alanine transaminase), whereas six participants in the MH group reported an episode of febrile UTI and four were admitted to hospital because of UTI.
Substantial global health care problem
At least 50% and up to 80% of all women have at least one acute UTI in their lifetime, most often uncomplicated acute cystitis. About a quarter of them go on to suffer recurrent infection, defined as three or more repeat infections in the past year, or two infections in the preceding 6 months. Frequent recurrences thus represent “a substantial global health care problem,” the authors say.
Guidelines from the United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States acknowledge the need for preventive strategies and strongly recommend the use of daily, low-dose antibiotics as standard prophylactic treatment. However, the United Kingdom’s antimicrobial resistance strategy recommends a “strong focus on infection prevention,” and aims to reduce antimicrobial use in humans by 15% before 2024.
“To achieve that, exploration of nonantibiotic preventive treatments in common conditions such as UTI is essential,” the team said.
MH is one such nonantibiotic treatment. It is bactericidal and works by denaturing bacterial proteins and nucleic acids. Although previous Cochrane systematic reviews had concluded that it could be effective for preventing UTI, further large trials were needed.
“This trial adds to the evidence base for the use of MH for prophylactic treatment in adult women with recurrent UTI. Although the MH group had a 55% higher rate of UTI episodes than the antibiotics group, the absolute difference was just 0.49 UTI episodes per year, which has limited clinical consequence,” the team concluded.
Results could ‘support a change in practice’
In older patients, particularly, the risks of long-term antibiotic prophylaxis might outweigh the benefits, and the authors said that their results “could support a change in practice in terms of preventive treatments for recurrent UTI and provide patients and clinicians with a credible alternative to daily antibiotics, giving them the confidence to pursue strategies that avoid long-term antibiotic use.”
They acknowledged limitations of the study, including that treatment allocation was not masked, crossover between arms was allowed, and differences in antibiotics prescribed may have affected the results. In addition, data regarding long-term safety of MH are scarce.
However, they said that the trial accurately represented the broad range of women with recurrent UTI, and that its results “might encourage patients and clinicians to consider MH as a first line treatment for UTI prevention in women.”
In a linked editorial, scientists from the Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare at Bond University in Queensland, Australia, commented: “Although the results need cautious interpretation, they align with others, and this new research increases the confidence with which MH can be offered as an option to women needing prophylaxis against recurrent urinary tract infection.”
References
Harding C et al. Alternative to prophylactic antibiotics for the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: multicentre, open label, randomised, noninferiority trial. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:e068229.
Hoffmann TC et al. Methenamine hippurate for recurrent urinary tract infections. BMJ 2022 Mar 9;376:o533.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
‘Baby-friendly’ steps help women meet prenatal breastfeeding goals
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Does adjunctive oxytocin infusion during balloon cervical ripening improve labor induction?
Evidence summary
Time to delivery is shortened with combined therapy
Two recent high-quality meta-analyses investigated the effect of adding oxytocin to transcervical Foley balloon placement for cervical dilation. A network meta-analysis, including 30 RCTs (with 6465 pregnant patients), examined the efficacy of multiple combinations of cervical ripening methods.1 A subset of 7 trials (n = 1313) compared oxytocin infusion with transcervical Foley (inflated to 30-60 mL) to Foley alone. Patients were at > 24 weeks’ gestation with a live fetus and undergoing elective or medical induction of labor; exclusion criteria were standard contraindications to vaginal delivery.
Compared to Foley alone, Foley plus oxytocin reduced both the time to the primary outcome of vaginal delivery (mean duration [MD] = –4.2 h; 95% CI, –1.9 to –6.5) and the time to overall (vaginal and cesarean) delivery (MD = –3.1 h; 95% CI, –1.5 to –4.6). There were no differences in rates of cesarean section, chorioamnionitis, epidural use, or neonatal intensive care unit admission. This analysis did not stratify by parity.1
In a standard meta-analysis, researchers identified 6 RCTs (N = 1133) comparing transcervical Foley balloon and oxytocin to Foley balloon alone for cervical ripening in pregnant patients at > 23 weeks’ gestation (1 trial was limited to patients at > 37 weeks’ gestation).2 Foley balloons were inflated with 30 to 60 mL saline, and oxytocin infusions started at 1 to 2 mU/min and were titrated up to 10 to 40 mU/min. Balloon time was usually 12 hours, but not always stated.
The authors found no statistically significant difference in cesarean rates (the primary outcome) between Foley plus oxytocin vs Foley alone (relative risk [RR] = 0.91; 95% CI, 0.76-1.1). Overall delivery within 12 hours was more likely with combined therapy (RR of remaining pregnant = 0.46; 95% CI, 0.34-0.63), but delivery at 24 hours was not (RR = 0.94; 95% CI, 0.92-1.05). However, in a sub-analysis by parity, nulliparous women who received combined therapy had higher overall delivery rates in 24 hours than did multiparous women (RR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62-0.97).2
Adding oxytocin may allow shorter transcervical balloon times
One recent RCT (N = 177) compared labor induction with oxytocin and a single trans-cervical balloon (Cook catheter with only the intrauterine balloon inflated) removed at either 6 or 12 hours.3 Patients were pregnant women (mean age, 31 years) with a term singleton vertex pregnancy, a Bishop score ≤ 6, and no contraindications to vaginal delivery. All patients received a balloon inflated to 60 mL with an oxytocin infusion (2-30 mU/min). The intervention group had the balloon removed at 6 hours, while the control group had it removed at 12 hours.
The mean Bishop score changed by 6 points in each group. Time to overall delivery (the primary outcome) was significantly shorter with 6 hours of balloon time than with 12 hours (19.2 vs 24.3 h; P < .04). Overall delivery within 24 hours was also significantly more likely in the 6-hour group (67.4% vs 47.4%; P < .01), although vaginal delivery in 24 hours did not change (74% vs 59%; P = .07). No differences were seen in cesarean delivery rates or maternal or neonatal morbidity rates.
A look at fixed-dose vs titrated oxytocin
Another RCT (N = 116) examined the effectiveness of cervical ripening using a Foley balloon plus either fixed-dose or titrated low-dose oxytocin.4 Patients (mean age, 26 years) had singleton pregnancies at ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score < 6 and presented for induction of labor. Foley balloons were inflated to 30 mL, and patients received either a fixed oxytocin infusion of 2 mU/min or a titrated infusion starting at 1 mU/min, increasing by 2 mU/min every 30 minutes to a maximum of 20 mU/min.
Continue to: Thre was no statistically...
There was no statistically significant difference in median time from Foley placement to overall delivery (the primary outcome) between the fixed low-dose and incremental low-dose groups in either nulliparous women (24 vs 19 h; P = .18) or multiparous women (16 vs 12 h; P = .68). The authors acknowledged the study may have been underpowered to detect a true difference.
Recommendations from others
A 2009 Practice Bulletin from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommended the Foley catheter as a reasonable and effective alternative to prostaglandins for cervical ripening and the induction of labor (based on good-quality evidence).5 The guideline stated that Foley catheter placement before oxytocin induction reduced both the duration of labor and risk of cesarean delivery, but that the use of oxytocin along with a Foley catheter did not appear to shorten the time to delivery.
Editor’s takeaway
High-quality evidence shows us that the addition of oxytocin to balloon cervical ripening shortens the time to delivery. This newer evidence may prompt an update to the 2009 ACOG statement.
1. Orr L, Reisinger-Kindle K, Roy A, et al. Combination of Foley and prostaglandins versus Foley and oxytocin for cervical ripening: a network meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:743.e1-743.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.05.007
2. Gallagher LT, Gardner B, Rahman M, et al. Cervical ripening using Foley balloon with or without oxytocin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Perinatol. 2019;36:406-421. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1668577
3. Lassey SC, Haber HR, Kanbergs A, et al. Six vs twelve hours of single balloon catheter placement with oxytocin administration for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021:S0002-9378(21)00185-X. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.021
4. Fitzpatrick CB, Grotegut CA, Bishop TS, et al. Cervical ripening with Foley balloon plus fixed versus incremental low-dose oxytocin: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:1006-1010. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.607522
5. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 107: Induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114(2 pt 1):386-397. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b48ef5
Evidence summary
Time to delivery is shortened with combined therapy
Two recent high-quality meta-analyses investigated the effect of adding oxytocin to transcervical Foley balloon placement for cervical dilation. A network meta-analysis, including 30 RCTs (with 6465 pregnant patients), examined the efficacy of multiple combinations of cervical ripening methods.1 A subset of 7 trials (n = 1313) compared oxytocin infusion with transcervical Foley (inflated to 30-60 mL) to Foley alone. Patients were at > 24 weeks’ gestation with a live fetus and undergoing elective or medical induction of labor; exclusion criteria were standard contraindications to vaginal delivery.
Compared to Foley alone, Foley plus oxytocin reduced both the time to the primary outcome of vaginal delivery (mean duration [MD] = –4.2 h; 95% CI, –1.9 to –6.5) and the time to overall (vaginal and cesarean) delivery (MD = –3.1 h; 95% CI, –1.5 to –4.6). There were no differences in rates of cesarean section, chorioamnionitis, epidural use, or neonatal intensive care unit admission. This analysis did not stratify by parity.1
In a standard meta-analysis, researchers identified 6 RCTs (N = 1133) comparing transcervical Foley balloon and oxytocin to Foley balloon alone for cervical ripening in pregnant patients at > 23 weeks’ gestation (1 trial was limited to patients at > 37 weeks’ gestation).2 Foley balloons were inflated with 30 to 60 mL saline, and oxytocin infusions started at 1 to 2 mU/min and were titrated up to 10 to 40 mU/min. Balloon time was usually 12 hours, but not always stated.
The authors found no statistically significant difference in cesarean rates (the primary outcome) between Foley plus oxytocin vs Foley alone (relative risk [RR] = 0.91; 95% CI, 0.76-1.1). Overall delivery within 12 hours was more likely with combined therapy (RR of remaining pregnant = 0.46; 95% CI, 0.34-0.63), but delivery at 24 hours was not (RR = 0.94; 95% CI, 0.92-1.05). However, in a sub-analysis by parity, nulliparous women who received combined therapy had higher overall delivery rates in 24 hours than did multiparous women (RR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62-0.97).2
Adding oxytocin may allow shorter transcervical balloon times
One recent RCT (N = 177) compared labor induction with oxytocin and a single trans-cervical balloon (Cook catheter with only the intrauterine balloon inflated) removed at either 6 or 12 hours.3 Patients were pregnant women (mean age, 31 years) with a term singleton vertex pregnancy, a Bishop score ≤ 6, and no contraindications to vaginal delivery. All patients received a balloon inflated to 60 mL with an oxytocin infusion (2-30 mU/min). The intervention group had the balloon removed at 6 hours, while the control group had it removed at 12 hours.
The mean Bishop score changed by 6 points in each group. Time to overall delivery (the primary outcome) was significantly shorter with 6 hours of balloon time than with 12 hours (19.2 vs 24.3 h; P < .04). Overall delivery within 24 hours was also significantly more likely in the 6-hour group (67.4% vs 47.4%; P < .01), although vaginal delivery in 24 hours did not change (74% vs 59%; P = .07). No differences were seen in cesarean delivery rates or maternal or neonatal morbidity rates.
A look at fixed-dose vs titrated oxytocin
Another RCT (N = 116) examined the effectiveness of cervical ripening using a Foley balloon plus either fixed-dose or titrated low-dose oxytocin.4 Patients (mean age, 26 years) had singleton pregnancies at ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score < 6 and presented for induction of labor. Foley balloons were inflated to 30 mL, and patients received either a fixed oxytocin infusion of 2 mU/min or a titrated infusion starting at 1 mU/min, increasing by 2 mU/min every 30 minutes to a maximum of 20 mU/min.
Continue to: Thre was no statistically...
There was no statistically significant difference in median time from Foley placement to overall delivery (the primary outcome) between the fixed low-dose and incremental low-dose groups in either nulliparous women (24 vs 19 h; P = .18) or multiparous women (16 vs 12 h; P = .68). The authors acknowledged the study may have been underpowered to detect a true difference.
Recommendations from others
A 2009 Practice Bulletin from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommended the Foley catheter as a reasonable and effective alternative to prostaglandins for cervical ripening and the induction of labor (based on good-quality evidence).5 The guideline stated that Foley catheter placement before oxytocin induction reduced both the duration of labor and risk of cesarean delivery, but that the use of oxytocin along with a Foley catheter did not appear to shorten the time to delivery.
Editor’s takeaway
High-quality evidence shows us that the addition of oxytocin to balloon cervical ripening shortens the time to delivery. This newer evidence may prompt an update to the 2009 ACOG statement.
Evidence summary
Time to delivery is shortened with combined therapy
Two recent high-quality meta-analyses investigated the effect of adding oxytocin to transcervical Foley balloon placement for cervical dilation. A network meta-analysis, including 30 RCTs (with 6465 pregnant patients), examined the efficacy of multiple combinations of cervical ripening methods.1 A subset of 7 trials (n = 1313) compared oxytocin infusion with transcervical Foley (inflated to 30-60 mL) to Foley alone. Patients were at > 24 weeks’ gestation with a live fetus and undergoing elective or medical induction of labor; exclusion criteria were standard contraindications to vaginal delivery.
Compared to Foley alone, Foley plus oxytocin reduced both the time to the primary outcome of vaginal delivery (mean duration [MD] = –4.2 h; 95% CI, –1.9 to –6.5) and the time to overall (vaginal and cesarean) delivery (MD = –3.1 h; 95% CI, –1.5 to –4.6). There were no differences in rates of cesarean section, chorioamnionitis, epidural use, or neonatal intensive care unit admission. This analysis did not stratify by parity.1
In a standard meta-analysis, researchers identified 6 RCTs (N = 1133) comparing transcervical Foley balloon and oxytocin to Foley balloon alone for cervical ripening in pregnant patients at > 23 weeks’ gestation (1 trial was limited to patients at > 37 weeks’ gestation).2 Foley balloons were inflated with 30 to 60 mL saline, and oxytocin infusions started at 1 to 2 mU/min and were titrated up to 10 to 40 mU/min. Balloon time was usually 12 hours, but not always stated.
The authors found no statistically significant difference in cesarean rates (the primary outcome) between Foley plus oxytocin vs Foley alone (relative risk [RR] = 0.91; 95% CI, 0.76-1.1). Overall delivery within 12 hours was more likely with combined therapy (RR of remaining pregnant = 0.46; 95% CI, 0.34-0.63), but delivery at 24 hours was not (RR = 0.94; 95% CI, 0.92-1.05). However, in a sub-analysis by parity, nulliparous women who received combined therapy had higher overall delivery rates in 24 hours than did multiparous women (RR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62-0.97).2
Adding oxytocin may allow shorter transcervical balloon times
One recent RCT (N = 177) compared labor induction with oxytocin and a single trans-cervical balloon (Cook catheter with only the intrauterine balloon inflated) removed at either 6 or 12 hours.3 Patients were pregnant women (mean age, 31 years) with a term singleton vertex pregnancy, a Bishop score ≤ 6, and no contraindications to vaginal delivery. All patients received a balloon inflated to 60 mL with an oxytocin infusion (2-30 mU/min). The intervention group had the balloon removed at 6 hours, while the control group had it removed at 12 hours.
The mean Bishop score changed by 6 points in each group. Time to overall delivery (the primary outcome) was significantly shorter with 6 hours of balloon time than with 12 hours (19.2 vs 24.3 h; P < .04). Overall delivery within 24 hours was also significantly more likely in the 6-hour group (67.4% vs 47.4%; P < .01), although vaginal delivery in 24 hours did not change (74% vs 59%; P = .07). No differences were seen in cesarean delivery rates or maternal or neonatal morbidity rates.
A look at fixed-dose vs titrated oxytocin
Another RCT (N = 116) examined the effectiveness of cervical ripening using a Foley balloon plus either fixed-dose or titrated low-dose oxytocin.4 Patients (mean age, 26 years) had singleton pregnancies at ≥ 37 weeks’ gestation with a Bishop score < 6 and presented for induction of labor. Foley balloons were inflated to 30 mL, and patients received either a fixed oxytocin infusion of 2 mU/min or a titrated infusion starting at 1 mU/min, increasing by 2 mU/min every 30 minutes to a maximum of 20 mU/min.
Continue to: Thre was no statistically...
There was no statistically significant difference in median time from Foley placement to overall delivery (the primary outcome) between the fixed low-dose and incremental low-dose groups in either nulliparous women (24 vs 19 h; P = .18) or multiparous women (16 vs 12 h; P = .68). The authors acknowledged the study may have been underpowered to detect a true difference.
Recommendations from others
A 2009 Practice Bulletin from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommended the Foley catheter as a reasonable and effective alternative to prostaglandins for cervical ripening and the induction of labor (based on good-quality evidence).5 The guideline stated that Foley catheter placement before oxytocin induction reduced both the duration of labor and risk of cesarean delivery, but that the use of oxytocin along with a Foley catheter did not appear to shorten the time to delivery.
Editor’s takeaway
High-quality evidence shows us that the addition of oxytocin to balloon cervical ripening shortens the time to delivery. This newer evidence may prompt an update to the 2009 ACOG statement.
1. Orr L, Reisinger-Kindle K, Roy A, et al. Combination of Foley and prostaglandins versus Foley and oxytocin for cervical ripening: a network meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:743.e1-743.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.05.007
2. Gallagher LT, Gardner B, Rahman M, et al. Cervical ripening using Foley balloon with or without oxytocin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Perinatol. 2019;36:406-421. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1668577
3. Lassey SC, Haber HR, Kanbergs A, et al. Six vs twelve hours of single balloon catheter placement with oxytocin administration for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021:S0002-9378(21)00185-X. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.021
4. Fitzpatrick CB, Grotegut CA, Bishop TS, et al. Cervical ripening with Foley balloon plus fixed versus incremental low-dose oxytocin: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:1006-1010. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.607522
5. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 107: Induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114(2 pt 1):386-397. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b48ef5
1. Orr L, Reisinger-Kindle K, Roy A, et al. Combination of Foley and prostaglandins versus Foley and oxytocin for cervical ripening: a network meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:743.e1-743.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.05.007
2. Gallagher LT, Gardner B, Rahman M, et al. Cervical ripening using Foley balloon with or without oxytocin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Perinatol. 2019;36:406-421. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1668577
3. Lassey SC, Haber HR, Kanbergs A, et al. Six vs twelve hours of single balloon catheter placement with oxytocin administration for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021:S0002-9378(21)00185-X. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.021
4. Fitzpatrick CB, Grotegut CA, Bishop TS, et al. Cervical ripening with Foley balloon plus fixed versus incremental low-dose oxytocin: a randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:1006-1010. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.607522
5. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 107: Induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114(2 pt 1):386-397. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b48ef5
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
YES. Compared to the use of a transcervical balloon alone, combined cervical ripening with a balloon catheter and oxytocin shortens the time to overall delivery by 3 hours and the time to vaginal delivery by 4 hours, without altering the rate of cesarean section (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, network meta-analysis). The effect is more pronounced in nulliparous patients (SOR: A, meta-analysis).
When combined therapy is used, 6 hours of balloon time may result in faster delivery than 12 hours (SOR: B, single randomized controlled trial [RCT]). Fixed-dose oxytocin and titrated oxytocin appear to have similar effect when combined with a cervical ripening balloon (SOR: C, underpowered RCT).
Dyspareunia: Keys to biopsychosocial evaluation and treatment planning
Dyspareunia is persistent or recurrent pain before, during, or after sexual contact and is not limited to cisgender individuals or vaginal intercourse.1-3 With a prevalence as high as 45% in the United States,2-5 it is one of the most common complaints in gynecologic practices.5,6
Causes and contributing factors
There are many possible causes of dyspareunia.2,4,6 While some patients have a single cause, most cases are complex, with multiple overlapping causes and maintaining factors.4,6 Identifying each contributing factor can help you appropriately address all components.
Physical conditions. The range of physical contributors to dyspareunia includes inflammatory processes, structural abnormalities, musculoskeletal dysfunctions, pelvic organ disorders, injuries, iatrogenic effects, infections, allergic reactions, sensitization, hormonal changes, medication effects, adhesions, autoimmune disorders, and other pain syndromes (TABLE 12-4,6-11).

Inadequate arousal. One of the primary causes of pain during vaginal penetration is inadequate arousal and lubrication.1,2,9-11 Arousal is the phase of the sexual response cycle that leads to genital tumescence and prepares the genitals for sexual contact through penile/clitoral erection, vaginal engorgement, and lubrication, which prevents pain and enhances pleasurable sensation.9-11
While some physical conditions can lead to an inability to lubricate, the most common causes of inadequate lubrication are psychosocial-behavioral, wherein patients have the same physical ability to lubricate as patients without genital pain but do not progress through the arousal phase.9-11 Behavioral factors such as inadequate or ineffective foreplay can fail to produce engorgement and lubrication, while psychosocial factors such as low attraction to partner, relationship stressors, anxiety, or low self-esteem can have an inhibitory effect on sexual arousal.1,2,9-11 Psychosocial and behavioral factors may also be maintaining factors or consequences of dyspareunia, and need to be assessed and treated.1,2,9-11
Psychological trauma. Exposure to psychological traumas and the development of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have been linked with the development of pain disorders in general and dyspareunia specifically. Most patients seeking treatment for chronic pain disorders have a history of physical or sexual abuse.12 Changes in physiologic processes (eg, neurochemical, endocrine) that occur with PTSD interfere with the sexual response cycle, and sexual traumas specifically have been linked with pelvic floor dysfunction.13,14 Additionally, when PTSD is caused by a sexual trauma, even consensual sexual encounters can trigger flashbacks, intrusive memories, hyperarousal, and muscle tension that interfere with the sexual response cycle and contribute to genital pain.13
Vaginismus is both a physiologic and psychological contributor to dyspareunia.1,2,4 Patients experiencing pain can develop anxiety about repeated pain and involuntarily contract their pelvic muscles, thereby creating more pain, increasing anxiety, decreasing lubrication, and causing pelvic floor dysfunction.1-4,6 Consequently, all patients with dyspareunia should be assessed and continually monitored for symptoms of vaginismus.
Continue to: Anxiety
Anxiety. As with other pain disorders, anxiety develops around pain triggers.10,15 When expecting sexual activity, patients can experience extreme worry and panic attacks.10,15,16 The distress of sexual encounters can interfere with physiologic arousal and sexual desire, impacting all phases of the sexual response cycle.1,2
Relationship issues. Difficulty engaging in or avoidance of sexual activity can interfere with romantic relationships.2,10,16 Severe pain or vaginismus contractions can prevent penetration, leading to unconsummated marriages and an inability to conceive through intercourse.10 The distress surrounding sexual encounters can precipitate erectile dysfunction in male partners, or partners may continue to demand sexual encounters despite the patient’s pain, further impacting the relationship and heightening sexual distress.10 These stressors have led to relationships ending, patients reluctantly agreeing to nonmonogamy to appease their partners, and patients avoiding relationships altogether.10,16
Devalued self-image. Difficulties with sexuality and relationships impact the self-image of patients with dyspareunia. Diminished self-image may include feeling “inadequate” as a woman and as a sexual partner, or feeling like a “failure.”16 Women with dyspareunia often have more distress related to their body image, physical appearance, and genital self-image than do women without genital pain.17 Feeling resentment toward their body, or feeling “ugly,” embarrassed, shamed, “broken,” and “useless” also contribute to increased depressive symptoms found in patients with dyspareunia.16,18
Making the diagnosis
Most patients do not report symptoms unless directly asked2,7; therefore, it is recommended that all patients be screened as a part of an initial intake and before any genital exam (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20).4,7,21 If this screen is positive, a separate appointment may be needed for a thorough evaluation and before any attempt is made at a genital exam.4,7
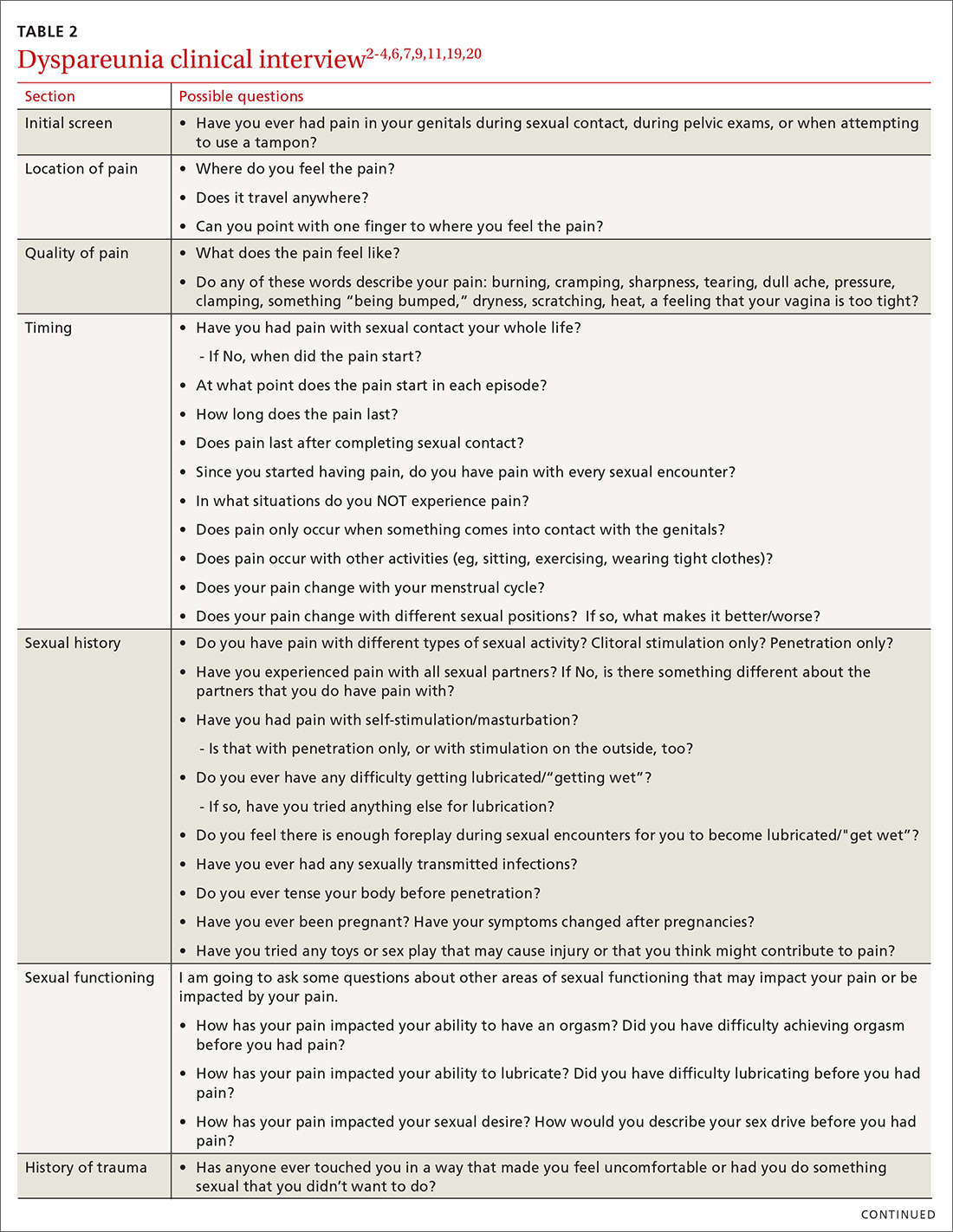
Items to include in the clinical interview
Given the range of possible causes of dyspareunia and its contributing factors and symptoms, a thorough clinical interview is essential. Begin with a review of the patient’s complete medical and surgical history to identify possible known contributors to genital pain.4 Pregnancy history is of particular importance as the prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia is 35%, with risk being greater for patients who experienced dyspareunia symptoms before pregnancy.22

Knowing the location and quality of pain is important for differentiating between possible diagnoses, as is specifying dyspareunia as lifelong or acquired, superficial or deep, and primary or secondary.1-4,6 Confirm the specific location(s) of pain—eg, at the introitus, in the vestibule, on the labia, in the perineum, or near the clitoris.2,4,6 A diagram or model may be needed to help patients to localize pain.4
To help narrow the differential, include the following elements in your assessment: pain quality, timing (eg, initial onset, episode onset, episode duration, situational triggers), alleviating factors, symptoms in surrounding structures (eg, bladder, bowel, muscles, bones), sexual history, other areas of sexual functioning, history of psychological trauma, relationship effects, and mental health (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20 and Table 323-28). Screening for a history of sexual trauma is particularly important, as a recent systematic review and meta-analysis found that women with a history of sexual assault had a 42% higher risk of gynecologic problems overall, a 74% higher risk of dyspareunia, and a 71% higher risk of vaginismus than women without a history of sexual assault.29 Using measures such as the Female Sexual Function Index or the McGill Pain Questionnaire can help patients more thoroughly describe their symptoms (TABLE 323-28).3
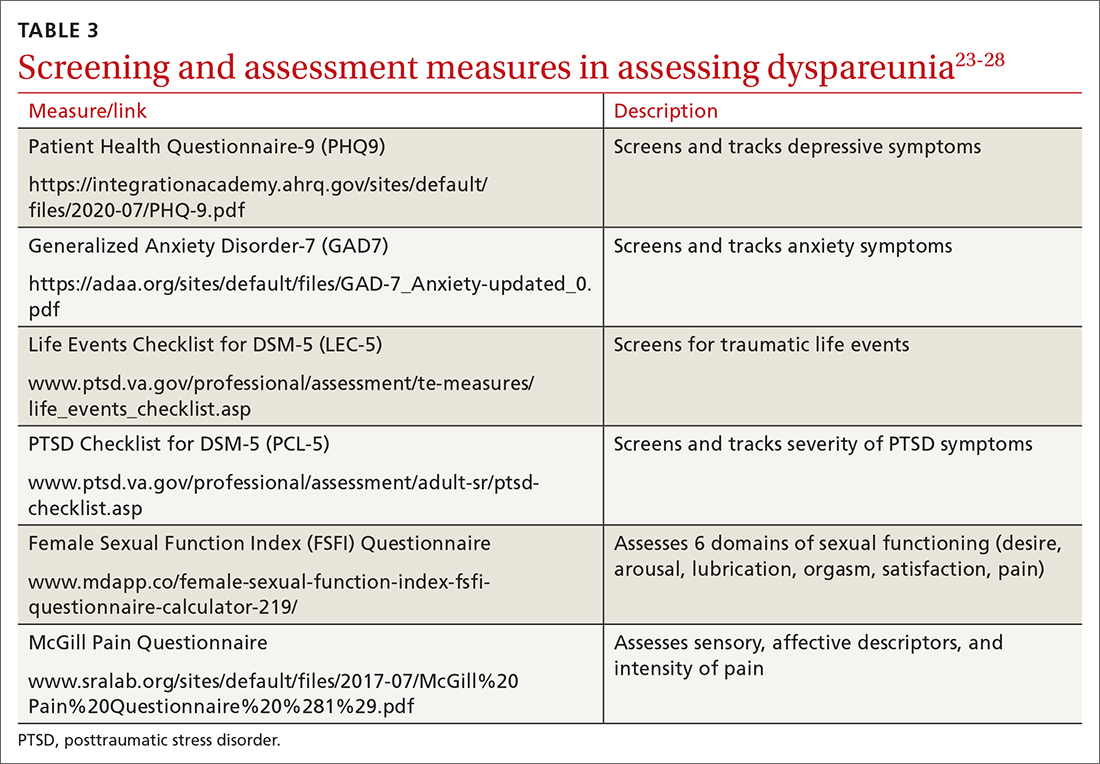
Continue to: Guidelines for the physical exam
Guidelines for the physical exam
Before the exam, ensure the patient has not used any topical genital treatment in the past 2 weeks that may interfere with sensitivity to the exam.4 To decrease patients’ anxiety about the exam, remind them that they can stop the exam at any time.7 Also consider offering the use of a mirror to better pinpoint the location of pain, and to possibly help the patient learn more about her anatomy.2,7
Begin the exam by palpating surrounding areas that may be involved in pain, including the abdomen and musculoskeletal features.3,6,19 Next visually inspect the external genitalia for lesions, abrasions, discoloration, erythema, or other abnormal findings.2,3,6 Ask the patient for permission before contacting the genitals. Because the labia may be a site of pain, apply gentle pressure in retracting it to fully examine the vestibule.6,7 Contraction of the pelvic floor muscles during approach or initial palpation could signal possible vaginismus.4
After visual inspection of external genitalia, use a cotton swab to map the vulva and vestibule in a clockwise fashion to precisely identify any painful locations.2-4,6 If the patient’s history of pain has been intermittent, it’s possible that the cotton swab will not elicit pain on the day of the initial exam, but it may on other days.4
Begin the internal exam by inserting a single finger into the first inch of the vagina and have the patient squeeze and release to assess tenderness, muscle tightness, and control.2,6 Advance the finger further into the vagina and palpate clockwise, examining the levator muscles, obturator muscles, rectum, urethra, and bladder for abnormal tightness or reproduction of pain.2,4,6 Complete a bimanual exam to evaluate the pelvic organs and adnexa.2,4 If indicated, a more thorough evaluation of pelvic floor musculature can be performed by a physical therapist or gynecologist who specializes in pelvic pain.2-4
If the patient consents to further evaluation, consider using a small speculum, advanced slowly, for further internal examination, noting any lesions, abrasions, discharge, ectropion, or tenderness.2-4,7 A rectal exam may also be needed in cases of deep dyspareunia.6 Initial work-up may include a potassium hydroxide wet prep, sexually transmitted infection testing, and pelvic ultrasound.2,4 In some cases, laparoscopy or biopsy may be needed.2,4
Treatments for common causes
Treatment often begins with education about anatomy, to help patients communicate about symptoms and engage more fully in their care.3 Additional education may be needed on genital functioning and the necessity of adequate stimulation and lubrication prior to penetration.1,2,9-11 A discussion of treatments for the wide range of possible causes of dyspareunia is outside the scope of this article. However, some basic behavioral changes may help patients address some of the more common contributing factors.
For example, if vaginal infection is suspected, advise patients to discontinue the use of harsh soaps, known vaginal irritants (eg, perfumed products, bath additives), and douches.3 Recommend using only preservative- and alcohol-free lubricants for sexual contact, and avoiding lubricants with added functions (eg, warming).3 It’s worth noting that avoidance of tight clothing and thong underwear due to possible risk for infections may not be necessary. A recent study found that women who frequently wore thong underwear (more than half of the time) were no more likely to develop urinary tract infections, yeast vaginitis, or bacterial vaginosis than those who avoid such items.30 However, noncotton underwear fabric, rather than tightness, was associated with yeast vaginitis30; therefore, patients may want to consider using only breathable underwear.3
Continue to: Medication
Medication. Medication may be used to treat the underlying contributing conditions or the symptom of pain directly. Some common options are particularly important for patients whose dyspareunia does not have an identifiable cause. These medications include anti-inflammatory agents, topical anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, and hormonal treatments.2-4 Since effectiveness varies based on subtypes of pain, select a medication according to the location, timing, and hypothesized mechanism of pain.3,31,32
Medication for deep pain. A meta-analysis and systematic review found that patients with some types of chronic pelvic pain with pain deep in the vagina or pelvis experienced greater than 50% reduction in pain using medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with placebo.33 Other treatments for deep pain depend on physical exam findings.
Medication for superficial pain. Many remedies have been tried, with at least 26 different treatments for vulvodynia pain alone.16 Only some of these treatments have supporting evidence. For patients with vulvar pain, an intent-to-treat RCT found that patients using a topical steroid experienced a 23% reduction in pain from pre-treatment to 6-month follow-up.32
Surgery is also effective for vulvar pain.34,35 For provoked vestibulodynia (in which pain is localized to the vestibule and triggered by contact with the vulva), or vulvar vestibulitis, RCTs have found that vestibulectomy has stronger effects on pain than other treatments,31,35 with a 53% reduction in pain during intercourse and a 70% reduction in vestibular pain overall.35 However, while vestibulectomy is effective for provoked vestibulodynia, it is not recommended for generalized vulvodynia, in which pain is diffuse across the vulva and occurs without vulvar contact.34
Unsupported treatments. A number of other treatments have not yet been found effective. Although lidocaine for vulvar pain is often used, RCTs have not found any significant reduction in symptoms, and a double-blind RCT found that lidocaine ointment actually performed worse than placebo.31,34 Similarly, oral tricyclics have not been found to decrease vulvar pain more than placebo in double-blind studies.31,34 Furthermore, a meta-analysis of RCTs comparing treatments with placebo for vestibular pain found no significant decrease in dyspareunia for topical conjugated estrogen, topical lidocaine, oral desipramine, oral desipramine with topical lidocaine, laser therapy, or transcranial direct current.32
Tx risks to consider. Risks and benefits of dyspareunia treatment options should be thoroughly weighed and discussed with the patient.2-4 Vestibulectomy, despite reducing pain for many patients, has led to increased pain for 9% of patients who underwent the procedure.35 Topical treatments may lead to allergic reactions, inflammation, and worsening of symptoms,4 and hormonal treatments have been found to increase the risk of weight gain and bloating and are not appropriate for patients trying to conceive.33
Coordinate care with other providers
While medications and surgery can reduce pain, they have not been shown to improve other aspects of sexual functioning such as sexual satisfaction, frequency of sexual intercourse, or overall sense of sexual functioning.35 Additionally, pain reduction does not address muscle tension, anxiety, self-esteem, and relationship problems. As a result, a multidisciplinary approach is generally needed.3,4,32,33
Continue to: Physical therapists
Physical therapists. Pelvic floor physical therapists are often members of the dyspareunia treatment team and can provide a thorough evaluation and treatment of pelvic floor disorders.2-4 An RCT with intent-to-treat analysis found that pain was reduced by 71% following pelvic floor physical therapy.36 Another RCT found that 90% of patients reported a clinically meaningful decrease in pain with pelvic floor physical therapy.37 In addition to addressing pain, pelvic floor physical therapy has also been found to improve sexual functioning, sexual satisfaction, distress, and patient perception of improvement.34,36,37
Behavioral health specialists. Psychotherapists, especially those trained in sex therapy, couples therapy, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), are also typically on the treatment team. Multiple RCTs have found evidence of CBT’s effectiveness in the direct treatment of dyspareunia pain. Bergeron et al35 found a 37.5% reduction in vulvar vestibulitis pain intensity during intercourse after patients completed group CBT. Another intent-to-treat RCT found that patients receiving CBT experienced more pain reduction (~ 30%) than patients who were treated with a topical steroid.38
In addition to having a direct impact on pain, CBT has also been found to have a clinically and statistically significant positive impact on other aspects of sexual experience, such as overall sexuality, self-efficacy, overall sexual functioning, frequency of intercourse, and catastrophizing.34,38 A recent meta-analysis of RCTs found that about 80% of vaginismus patients were able to achieve penetrative intercourse after treatment with behavioral sex therapy or CBT.39 This success rate was not exceeded by physical or surgical treatments.39
When PTSD is thought to be a contributing factor, trauma therapy will likely be needed in addition to treatments for dyspareunia. First-line treatments for PTSD include cognitive processing therapy, prolonged exposure, trauma-focused CBT, and cognitive therapy.40
Psychotherapists can also help patients reduce anxiety, reintroduce sexual contact without triggering pain or anxiety, address emotional and self-esteem effects of dyspareunia, address relationship issues, and refocus sexual encounters on pleasure rather than pain avoidance.2-4 Despite patient reports of high treatment satisfaction following therapy,38 many patients may initially lack confidence in psychotherapy as a treatment for pain35 and may need to be educated on its effectiveness and multidimensional benefits.
Gynecologists. Often a gynecologist with specialization in pelvic pain is an essential member of the team for diagnostic clarification, recommendation of treatment options, and performance of more advanced treatments.2,3 If pain has become chronic, the patient may also benefit from a pain management team and support groups.2,3
Follow-up steps
Patients who screen negative for dyspareunia should be re-screened periodically. Continue to assess patients diagnosed with dyspareunia for vaginismus symptoms (if they are not initially present) to ensure that the treatment plan is appropriately adjusted. Once treatment has begun, ask about adverse effects and confidence in the treatment plan to minimize negative impacts on treatment adherence and to anticipate a need for a change in the treatment approach.31,35 In addition to tracking treatment effects on pain, continue to assess for patient-centered outcomes such as emotional functioning, self-esteem, and sexual and relationship satisfaction.34 The Female Sexual Function Index can be a useful tool to track symptoms.27,34
Finally, patients who do not experience sufficient improvement in symptoms and functioning with initial treatment may need continued support and encouragement. Given the broad range of contributing factors and the high number of potential treatments, patients may find hope in learning that multiple other treatment options may be available.
CORRESPONDENCE
Adrienne A. Williams, PhD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, 1919 W Taylor Street, MC 663, Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
2. Seehusen DA, Baird DC, Bode DV. Dyspareunia in women. Am Fam Phys. 2014;90:465-470.
3. Sorensen J, Bautista KE, Lamvu G, et al. Evaluation and treatment of female sexual pain: a clinical review. Cureus. 2018;10:e2379.
4. MacNeill C. Dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2006;33:565-77.
5. Latthe P, Latthe M, Say L, et al. WHO systematic review of prevalence of chronic pelvic pain: a neglected reproductive health morbidity. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:177.
6. Steege JF, Zolnoun DA. Evaluation and treatment of dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1124-1136.
7. Williams AA, Williams M. A guide to performing pelvic speculum exams: a patient-centered approach to reducing iatrogenic effects. Teach Learn Med. 2013;25:383-391.
8. Ünlü Z, Yentur A, Çakil N. Pudendal nerve neuropathy: An unknown-rare cause of pelvic pain. Arch Rheumatol. 2016;31:102-103.
9. Dewitte M, Borg C, Lowenstein L. A psychosocial approach to female genital pain. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15:25-41.
10. Masters WH, Johnson VE. Human Sexual Inadequacy. 1st ed. Little, Brown; 1970.
11. Rathus SA, Nevid JS, Fichner-Rathus L. Human Sexuality in a World of Diversity. 5th ed. Allyn and Bacon; 2002.
12. Bailey BE, Freedenfeld RN, Kiser RS, et al. Lifetime physical and sexual abuse in chronic pain patients: psychosocial correlates and treatment outcomes. Disabil Rehabil. 2003;25:331-342.
13. Yehuda R, Lehrner A, Rosenbaum TY. PTSD and sexual dysfunction in men and women. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1107-1119.
14. Postma R, Bicanic I, van der Vaart H, et al. Pelvic floor muscle problems mediate sexual problems in young adult rape victims. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1978-1987.
15. Binik YM, Bergeron S, Khalifé S. Dyspareunia and vaginismus: so-called sexual pain. In: Leiblum SR, ed. 4th ed. Principles and Practice of Sex Therapy. The Guilford Press; 2007:124-156.
16. Ayling K, Ussher JM. “If sex hurts, am I still a woman?” The subjective experience of vulvodynia in hetero-sexual women. Arch Sex Behav. 2008;37:294-304.
17. Pazmany E, Bergeron S, Van Oudenhove L, et al. Body image and genital self-image in pre-menopausal women with dyspareunia. Arch Sex Behav. 2013;42:999-1010.
18. Maillé DL, Bergeron S, Lambert B. Body image in women with primary and secondary provoked vestibulodynia: a controlled study. J Sex Med. 2015;12:505-515.
19. Ryan L, Hawton K. Female dyspareunia. BMJ. 2004;328:1357.
20. Waldura JF, Arora I, Randall AM, et al. Fifty shades of stigma: exploring the health care experiences of kink-oriented patients. J Sex Med. 2016;13:1918-1929.
21. Hinchliff S, Gott M. Seeking medical help for sexual concerns in mid- and later life: a review of the literature. J Sex Res. 2011;48:106-117.
22. Banaei M, Kariman N, Ozgoli G, et al. Prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2021;153:14-24.
23. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2002;32:509-515.
24. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. PTSD: National Center for PTSD. Life events checklist for DSM-5 (LEC-5). Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/te-measures/life_events_checklist.asp
26. Weathers FW, Litz BT, Keane TM, et al. The PTSD checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5). 2013. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/adult-sr/ptsd-checklist.asp
27. Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, et al. The female sexual function index (FSFI): a multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000;26:191-208.
28. Melzack R. The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain. 1987;30:191-197.
29. Hassam T, Kelso E, Chowdary P, et al. Sexual assault as a risk factor for gynaecological morbidity: an exploratory systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020;255:222-230.
30. Hamlin AA, Sheeder J, Muffly TM. Brief versus thong hygiene in obstetrics and gynecology (B-THONG): a survey study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1190-1196.
31. Foster DC, Kotok MB, Huang LS, et al. Oral desipramine and topical lidocaine for vulvodynia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:583-593.
32. Pérez-López FR, Bueno-Notivol J, Hernandez AV, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of treatment modalities for vestibulodynia in women. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2019;24:337-346.
33. Cheong YC, Smotra G, Williams AC. Non-surgical interventions for the management of chronic pelvic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(3):CD008797.
34. Goldstein AT, Pukall CF, Brown C, et al. Vulvodynia: assessment and treatment. J Sex Med. 2016;13:572-590.
35. Bergeron S, Binik YM, Khalifé S, et al. A randomized comparison of group cognitive-behavioral therapy, surface electromyographic biofeedback, and vestibulectomy in the treatment of dyspareunia resulting from vulvar vestibulitis. Pain. 2001;91:297-306.
36. Schvartzman R, Schvartzman L, Ferreira CF, et al. Physical therapy intervention for women with dyspareunia: a randomized clinical trial. J Sex Marital Ther. 2019;45:378-394.
37. Morin M, Dumoulin C, Bergeron S, et al. Multimodal physical therapy versus topical lidocaine for provoked vestibulodynia: a multicenter, randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:189.e1-189.e12.
38. Bergeron S, Khalifé S, Dupuis M-J, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing group cognitive-behavioral therapy and a topical steroid for women with dyspareunia. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:259-268.
39. Maseroli E, Scavello I, Rastrelli G, et al. Outcome of medical and psychosexual interventions for vaginismus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1752-1764.
40. American Psychological Association. Clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. 2017. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/ptsd.pdf
Dyspareunia is persistent or recurrent pain before, during, or after sexual contact and is not limited to cisgender individuals or vaginal intercourse.1-3 With a prevalence as high as 45% in the United States,2-5 it is one of the most common complaints in gynecologic practices.5,6
Causes and contributing factors
There are many possible causes of dyspareunia.2,4,6 While some patients have a single cause, most cases are complex, with multiple overlapping causes and maintaining factors.4,6 Identifying each contributing factor can help you appropriately address all components.
Physical conditions. The range of physical contributors to dyspareunia includes inflammatory processes, structural abnormalities, musculoskeletal dysfunctions, pelvic organ disorders, injuries, iatrogenic effects, infections, allergic reactions, sensitization, hormonal changes, medication effects, adhesions, autoimmune disorders, and other pain syndromes (TABLE 12-4,6-11).

Inadequate arousal. One of the primary causes of pain during vaginal penetration is inadequate arousal and lubrication.1,2,9-11 Arousal is the phase of the sexual response cycle that leads to genital tumescence and prepares the genitals for sexual contact through penile/clitoral erection, vaginal engorgement, and lubrication, which prevents pain and enhances pleasurable sensation.9-11
While some physical conditions can lead to an inability to lubricate, the most common causes of inadequate lubrication are psychosocial-behavioral, wherein patients have the same physical ability to lubricate as patients without genital pain but do not progress through the arousal phase.9-11 Behavioral factors such as inadequate or ineffective foreplay can fail to produce engorgement and lubrication, while psychosocial factors such as low attraction to partner, relationship stressors, anxiety, or low self-esteem can have an inhibitory effect on sexual arousal.1,2,9-11 Psychosocial and behavioral factors may also be maintaining factors or consequences of dyspareunia, and need to be assessed and treated.1,2,9-11
Psychological trauma. Exposure to psychological traumas and the development of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have been linked with the development of pain disorders in general and dyspareunia specifically. Most patients seeking treatment for chronic pain disorders have a history of physical or sexual abuse.12 Changes in physiologic processes (eg, neurochemical, endocrine) that occur with PTSD interfere with the sexual response cycle, and sexual traumas specifically have been linked with pelvic floor dysfunction.13,14 Additionally, when PTSD is caused by a sexual trauma, even consensual sexual encounters can trigger flashbacks, intrusive memories, hyperarousal, and muscle tension that interfere with the sexual response cycle and contribute to genital pain.13
Vaginismus is both a physiologic and psychological contributor to dyspareunia.1,2,4 Patients experiencing pain can develop anxiety about repeated pain and involuntarily contract their pelvic muscles, thereby creating more pain, increasing anxiety, decreasing lubrication, and causing pelvic floor dysfunction.1-4,6 Consequently, all patients with dyspareunia should be assessed and continually monitored for symptoms of vaginismus.
Continue to: Anxiety
Anxiety. As with other pain disorders, anxiety develops around pain triggers.10,15 When expecting sexual activity, patients can experience extreme worry and panic attacks.10,15,16 The distress of sexual encounters can interfere with physiologic arousal and sexual desire, impacting all phases of the sexual response cycle.1,2
Relationship issues. Difficulty engaging in or avoidance of sexual activity can interfere with romantic relationships.2,10,16 Severe pain or vaginismus contractions can prevent penetration, leading to unconsummated marriages and an inability to conceive through intercourse.10 The distress surrounding sexual encounters can precipitate erectile dysfunction in male partners, or partners may continue to demand sexual encounters despite the patient’s pain, further impacting the relationship and heightening sexual distress.10 These stressors have led to relationships ending, patients reluctantly agreeing to nonmonogamy to appease their partners, and patients avoiding relationships altogether.10,16
Devalued self-image. Difficulties with sexuality and relationships impact the self-image of patients with dyspareunia. Diminished self-image may include feeling “inadequate” as a woman and as a sexual partner, or feeling like a “failure.”16 Women with dyspareunia often have more distress related to their body image, physical appearance, and genital self-image than do women without genital pain.17 Feeling resentment toward their body, or feeling “ugly,” embarrassed, shamed, “broken,” and “useless” also contribute to increased depressive symptoms found in patients with dyspareunia.16,18
Making the diagnosis
Most patients do not report symptoms unless directly asked2,7; therefore, it is recommended that all patients be screened as a part of an initial intake and before any genital exam (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20).4,7,21 If this screen is positive, a separate appointment may be needed for a thorough evaluation and before any attempt is made at a genital exam.4,7

Items to include in the clinical interview
Given the range of possible causes of dyspareunia and its contributing factors and symptoms, a thorough clinical interview is essential. Begin with a review of the patient’s complete medical and surgical history to identify possible known contributors to genital pain.4 Pregnancy history is of particular importance as the prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia is 35%, with risk being greater for patients who experienced dyspareunia symptoms before pregnancy.22

Knowing the location and quality of pain is important for differentiating between possible diagnoses, as is specifying dyspareunia as lifelong or acquired, superficial or deep, and primary or secondary.1-4,6 Confirm the specific location(s) of pain—eg, at the introitus, in the vestibule, on the labia, in the perineum, or near the clitoris.2,4,6 A diagram or model may be needed to help patients to localize pain.4
To help narrow the differential, include the following elements in your assessment: pain quality, timing (eg, initial onset, episode onset, episode duration, situational triggers), alleviating factors, symptoms in surrounding structures (eg, bladder, bowel, muscles, bones), sexual history, other areas of sexual functioning, history of psychological trauma, relationship effects, and mental health (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20 and Table 323-28). Screening for a history of sexual trauma is particularly important, as a recent systematic review and meta-analysis found that women with a history of sexual assault had a 42% higher risk of gynecologic problems overall, a 74% higher risk of dyspareunia, and a 71% higher risk of vaginismus than women without a history of sexual assault.29 Using measures such as the Female Sexual Function Index or the McGill Pain Questionnaire can help patients more thoroughly describe their symptoms (TABLE 323-28).3

Continue to: Guidelines for the physical exam
Guidelines for the physical exam
Before the exam, ensure the patient has not used any topical genital treatment in the past 2 weeks that may interfere with sensitivity to the exam.4 To decrease patients’ anxiety about the exam, remind them that they can stop the exam at any time.7 Also consider offering the use of a mirror to better pinpoint the location of pain, and to possibly help the patient learn more about her anatomy.2,7
Begin the exam by palpating surrounding areas that may be involved in pain, including the abdomen and musculoskeletal features.3,6,19 Next visually inspect the external genitalia for lesions, abrasions, discoloration, erythema, or other abnormal findings.2,3,6 Ask the patient for permission before contacting the genitals. Because the labia may be a site of pain, apply gentle pressure in retracting it to fully examine the vestibule.6,7 Contraction of the pelvic floor muscles during approach or initial palpation could signal possible vaginismus.4
After visual inspection of external genitalia, use a cotton swab to map the vulva and vestibule in a clockwise fashion to precisely identify any painful locations.2-4,6 If the patient’s history of pain has been intermittent, it’s possible that the cotton swab will not elicit pain on the day of the initial exam, but it may on other days.4
Begin the internal exam by inserting a single finger into the first inch of the vagina and have the patient squeeze and release to assess tenderness, muscle tightness, and control.2,6 Advance the finger further into the vagina and palpate clockwise, examining the levator muscles, obturator muscles, rectum, urethra, and bladder for abnormal tightness or reproduction of pain.2,4,6 Complete a bimanual exam to evaluate the pelvic organs and adnexa.2,4 If indicated, a more thorough evaluation of pelvic floor musculature can be performed by a physical therapist or gynecologist who specializes in pelvic pain.2-4
If the patient consents to further evaluation, consider using a small speculum, advanced slowly, for further internal examination, noting any lesions, abrasions, discharge, ectropion, or tenderness.2-4,7 A rectal exam may also be needed in cases of deep dyspareunia.6 Initial work-up may include a potassium hydroxide wet prep, sexually transmitted infection testing, and pelvic ultrasound.2,4 In some cases, laparoscopy or biopsy may be needed.2,4
Treatments for common causes
Treatment often begins with education about anatomy, to help patients communicate about symptoms and engage more fully in their care.3 Additional education may be needed on genital functioning and the necessity of adequate stimulation and lubrication prior to penetration.1,2,9-11 A discussion of treatments for the wide range of possible causes of dyspareunia is outside the scope of this article. However, some basic behavioral changes may help patients address some of the more common contributing factors.
For example, if vaginal infection is suspected, advise patients to discontinue the use of harsh soaps, known vaginal irritants (eg, perfumed products, bath additives), and douches.3 Recommend using only preservative- and alcohol-free lubricants for sexual contact, and avoiding lubricants with added functions (eg, warming).3 It’s worth noting that avoidance of tight clothing and thong underwear due to possible risk for infections may not be necessary. A recent study found that women who frequently wore thong underwear (more than half of the time) were no more likely to develop urinary tract infections, yeast vaginitis, or bacterial vaginosis than those who avoid such items.30 However, noncotton underwear fabric, rather than tightness, was associated with yeast vaginitis30; therefore, patients may want to consider using only breathable underwear.3
Continue to: Medication
Medication. Medication may be used to treat the underlying contributing conditions or the symptom of pain directly. Some common options are particularly important for patients whose dyspareunia does not have an identifiable cause. These medications include anti-inflammatory agents, topical anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, and hormonal treatments.2-4 Since effectiveness varies based on subtypes of pain, select a medication according to the location, timing, and hypothesized mechanism of pain.3,31,32
Medication for deep pain. A meta-analysis and systematic review found that patients with some types of chronic pelvic pain with pain deep in the vagina or pelvis experienced greater than 50% reduction in pain using medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with placebo.33 Other treatments for deep pain depend on physical exam findings.
Medication for superficial pain. Many remedies have been tried, with at least 26 different treatments for vulvodynia pain alone.16 Only some of these treatments have supporting evidence. For patients with vulvar pain, an intent-to-treat RCT found that patients using a topical steroid experienced a 23% reduction in pain from pre-treatment to 6-month follow-up.32
Surgery is also effective for vulvar pain.34,35 For provoked vestibulodynia (in which pain is localized to the vestibule and triggered by contact with the vulva), or vulvar vestibulitis, RCTs have found that vestibulectomy has stronger effects on pain than other treatments,31,35 with a 53% reduction in pain during intercourse and a 70% reduction in vestibular pain overall.35 However, while vestibulectomy is effective for provoked vestibulodynia, it is not recommended for generalized vulvodynia, in which pain is diffuse across the vulva and occurs without vulvar contact.34
Unsupported treatments. A number of other treatments have not yet been found effective. Although lidocaine for vulvar pain is often used, RCTs have not found any significant reduction in symptoms, and a double-blind RCT found that lidocaine ointment actually performed worse than placebo.31,34 Similarly, oral tricyclics have not been found to decrease vulvar pain more than placebo in double-blind studies.31,34 Furthermore, a meta-analysis of RCTs comparing treatments with placebo for vestibular pain found no significant decrease in dyspareunia for topical conjugated estrogen, topical lidocaine, oral desipramine, oral desipramine with topical lidocaine, laser therapy, or transcranial direct current.32
Tx risks to consider. Risks and benefits of dyspareunia treatment options should be thoroughly weighed and discussed with the patient.2-4 Vestibulectomy, despite reducing pain for many patients, has led to increased pain for 9% of patients who underwent the procedure.35 Topical treatments may lead to allergic reactions, inflammation, and worsening of symptoms,4 and hormonal treatments have been found to increase the risk of weight gain and bloating and are not appropriate for patients trying to conceive.33
Coordinate care with other providers
While medications and surgery can reduce pain, they have not been shown to improve other aspects of sexual functioning such as sexual satisfaction, frequency of sexual intercourse, or overall sense of sexual functioning.35 Additionally, pain reduction does not address muscle tension, anxiety, self-esteem, and relationship problems. As a result, a multidisciplinary approach is generally needed.3,4,32,33
Continue to: Physical therapists
Physical therapists. Pelvic floor physical therapists are often members of the dyspareunia treatment team and can provide a thorough evaluation and treatment of pelvic floor disorders.2-4 An RCT with intent-to-treat analysis found that pain was reduced by 71% following pelvic floor physical therapy.36 Another RCT found that 90% of patients reported a clinically meaningful decrease in pain with pelvic floor physical therapy.37 In addition to addressing pain, pelvic floor physical therapy has also been found to improve sexual functioning, sexual satisfaction, distress, and patient perception of improvement.34,36,37
Behavioral health specialists. Psychotherapists, especially those trained in sex therapy, couples therapy, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), are also typically on the treatment team. Multiple RCTs have found evidence of CBT’s effectiveness in the direct treatment of dyspareunia pain. Bergeron et al35 found a 37.5% reduction in vulvar vestibulitis pain intensity during intercourse after patients completed group CBT. Another intent-to-treat RCT found that patients receiving CBT experienced more pain reduction (~ 30%) than patients who were treated with a topical steroid.38
In addition to having a direct impact on pain, CBT has also been found to have a clinically and statistically significant positive impact on other aspects of sexual experience, such as overall sexuality, self-efficacy, overall sexual functioning, frequency of intercourse, and catastrophizing.34,38 A recent meta-analysis of RCTs found that about 80% of vaginismus patients were able to achieve penetrative intercourse after treatment with behavioral sex therapy or CBT.39 This success rate was not exceeded by physical or surgical treatments.39
When PTSD is thought to be a contributing factor, trauma therapy will likely be needed in addition to treatments for dyspareunia. First-line treatments for PTSD include cognitive processing therapy, prolonged exposure, trauma-focused CBT, and cognitive therapy.40
Psychotherapists can also help patients reduce anxiety, reintroduce sexual contact without triggering pain or anxiety, address emotional and self-esteem effects of dyspareunia, address relationship issues, and refocus sexual encounters on pleasure rather than pain avoidance.2-4 Despite patient reports of high treatment satisfaction following therapy,38 many patients may initially lack confidence in psychotherapy as a treatment for pain35 and may need to be educated on its effectiveness and multidimensional benefits.
Gynecologists. Often a gynecologist with specialization in pelvic pain is an essential member of the team for diagnostic clarification, recommendation of treatment options, and performance of more advanced treatments.2,3 If pain has become chronic, the patient may also benefit from a pain management team and support groups.2,3
Follow-up steps
Patients who screen negative for dyspareunia should be re-screened periodically. Continue to assess patients diagnosed with dyspareunia for vaginismus symptoms (if they are not initially present) to ensure that the treatment plan is appropriately adjusted. Once treatment has begun, ask about adverse effects and confidence in the treatment plan to minimize negative impacts on treatment adherence and to anticipate a need for a change in the treatment approach.31,35 In addition to tracking treatment effects on pain, continue to assess for patient-centered outcomes such as emotional functioning, self-esteem, and sexual and relationship satisfaction.34 The Female Sexual Function Index can be a useful tool to track symptoms.27,34
Finally, patients who do not experience sufficient improvement in symptoms and functioning with initial treatment may need continued support and encouragement. Given the broad range of contributing factors and the high number of potential treatments, patients may find hope in learning that multiple other treatment options may be available.
CORRESPONDENCE
Adrienne A. Williams, PhD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, 1919 W Taylor Street, MC 663, Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
Dyspareunia is persistent or recurrent pain before, during, or after sexual contact and is not limited to cisgender individuals or vaginal intercourse.1-3 With a prevalence as high as 45% in the United States,2-5 it is one of the most common complaints in gynecologic practices.5,6
Causes and contributing factors
There are many possible causes of dyspareunia.2,4,6 While some patients have a single cause, most cases are complex, with multiple overlapping causes and maintaining factors.4,6 Identifying each contributing factor can help you appropriately address all components.
Physical conditions. The range of physical contributors to dyspareunia includes inflammatory processes, structural abnormalities, musculoskeletal dysfunctions, pelvic organ disorders, injuries, iatrogenic effects, infections, allergic reactions, sensitization, hormonal changes, medication effects, adhesions, autoimmune disorders, and other pain syndromes (TABLE 12-4,6-11).

Inadequate arousal. One of the primary causes of pain during vaginal penetration is inadequate arousal and lubrication.1,2,9-11 Arousal is the phase of the sexual response cycle that leads to genital tumescence and prepares the genitals for sexual contact through penile/clitoral erection, vaginal engorgement, and lubrication, which prevents pain and enhances pleasurable sensation.9-11
While some physical conditions can lead to an inability to lubricate, the most common causes of inadequate lubrication are psychosocial-behavioral, wherein patients have the same physical ability to lubricate as patients without genital pain but do not progress through the arousal phase.9-11 Behavioral factors such as inadequate or ineffective foreplay can fail to produce engorgement and lubrication, while psychosocial factors such as low attraction to partner, relationship stressors, anxiety, or low self-esteem can have an inhibitory effect on sexual arousal.1,2,9-11 Psychosocial and behavioral factors may also be maintaining factors or consequences of dyspareunia, and need to be assessed and treated.1,2,9-11
Psychological trauma. Exposure to psychological traumas and the development of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have been linked with the development of pain disorders in general and dyspareunia specifically. Most patients seeking treatment for chronic pain disorders have a history of physical or sexual abuse.12 Changes in physiologic processes (eg, neurochemical, endocrine) that occur with PTSD interfere with the sexual response cycle, and sexual traumas specifically have been linked with pelvic floor dysfunction.13,14 Additionally, when PTSD is caused by a sexual trauma, even consensual sexual encounters can trigger flashbacks, intrusive memories, hyperarousal, and muscle tension that interfere with the sexual response cycle and contribute to genital pain.13
Vaginismus is both a physiologic and psychological contributor to dyspareunia.1,2,4 Patients experiencing pain can develop anxiety about repeated pain and involuntarily contract their pelvic muscles, thereby creating more pain, increasing anxiety, decreasing lubrication, and causing pelvic floor dysfunction.1-4,6 Consequently, all patients with dyspareunia should be assessed and continually monitored for symptoms of vaginismus.
Continue to: Anxiety
Anxiety. As with other pain disorders, anxiety develops around pain triggers.10,15 When expecting sexual activity, patients can experience extreme worry and panic attacks.10,15,16 The distress of sexual encounters can interfere with physiologic arousal and sexual desire, impacting all phases of the sexual response cycle.1,2
Relationship issues. Difficulty engaging in or avoidance of sexual activity can interfere with romantic relationships.2,10,16 Severe pain or vaginismus contractions can prevent penetration, leading to unconsummated marriages and an inability to conceive through intercourse.10 The distress surrounding sexual encounters can precipitate erectile dysfunction in male partners, or partners may continue to demand sexual encounters despite the patient’s pain, further impacting the relationship and heightening sexual distress.10 These stressors have led to relationships ending, patients reluctantly agreeing to nonmonogamy to appease their partners, and patients avoiding relationships altogether.10,16
Devalued self-image. Difficulties with sexuality and relationships impact the self-image of patients with dyspareunia. Diminished self-image may include feeling “inadequate” as a woman and as a sexual partner, or feeling like a “failure.”16 Women with dyspareunia often have more distress related to their body image, physical appearance, and genital self-image than do women without genital pain.17 Feeling resentment toward their body, or feeling “ugly,” embarrassed, shamed, “broken,” and “useless” also contribute to increased depressive symptoms found in patients with dyspareunia.16,18
Making the diagnosis
Most patients do not report symptoms unless directly asked2,7; therefore, it is recommended that all patients be screened as a part of an initial intake and before any genital exam (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20).4,7,21 If this screen is positive, a separate appointment may be needed for a thorough evaluation and before any attempt is made at a genital exam.4,7

Items to include in the clinical interview
Given the range of possible causes of dyspareunia and its contributing factors and symptoms, a thorough clinical interview is essential. Begin with a review of the patient’s complete medical and surgical history to identify possible known contributors to genital pain.4 Pregnancy history is of particular importance as the prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia is 35%, with risk being greater for patients who experienced dyspareunia symptoms before pregnancy.22

Knowing the location and quality of pain is important for differentiating between possible diagnoses, as is specifying dyspareunia as lifelong or acquired, superficial or deep, and primary or secondary.1-4,6 Confirm the specific location(s) of pain—eg, at the introitus, in the vestibule, on the labia, in the perineum, or near the clitoris.2,4,6 A diagram or model may be needed to help patients to localize pain.4
To help narrow the differential, include the following elements in your assessment: pain quality, timing (eg, initial onset, episode onset, episode duration, situational triggers), alleviating factors, symptoms in surrounding structures (eg, bladder, bowel, muscles, bones), sexual history, other areas of sexual functioning, history of psychological trauma, relationship effects, and mental health (TABLE 22-4,6,7,9,11,19,20 and Table 323-28). Screening for a history of sexual trauma is particularly important, as a recent systematic review and meta-analysis found that women with a history of sexual assault had a 42% higher risk of gynecologic problems overall, a 74% higher risk of dyspareunia, and a 71% higher risk of vaginismus than women without a history of sexual assault.29 Using measures such as the Female Sexual Function Index or the McGill Pain Questionnaire can help patients more thoroughly describe their symptoms (TABLE 323-28).3

Continue to: Guidelines for the physical exam
Guidelines for the physical exam
Before the exam, ensure the patient has not used any topical genital treatment in the past 2 weeks that may interfere with sensitivity to the exam.4 To decrease patients’ anxiety about the exam, remind them that they can stop the exam at any time.7 Also consider offering the use of a mirror to better pinpoint the location of pain, and to possibly help the patient learn more about her anatomy.2,7
Begin the exam by palpating surrounding areas that may be involved in pain, including the abdomen and musculoskeletal features.3,6,19 Next visually inspect the external genitalia for lesions, abrasions, discoloration, erythema, or other abnormal findings.2,3,6 Ask the patient for permission before contacting the genitals. Because the labia may be a site of pain, apply gentle pressure in retracting it to fully examine the vestibule.6,7 Contraction of the pelvic floor muscles during approach or initial palpation could signal possible vaginismus.4
After visual inspection of external genitalia, use a cotton swab to map the vulva and vestibule in a clockwise fashion to precisely identify any painful locations.2-4,6 If the patient’s history of pain has been intermittent, it’s possible that the cotton swab will not elicit pain on the day of the initial exam, but it may on other days.4
Begin the internal exam by inserting a single finger into the first inch of the vagina and have the patient squeeze and release to assess tenderness, muscle tightness, and control.2,6 Advance the finger further into the vagina and palpate clockwise, examining the levator muscles, obturator muscles, rectum, urethra, and bladder for abnormal tightness or reproduction of pain.2,4,6 Complete a bimanual exam to evaluate the pelvic organs and adnexa.2,4 If indicated, a more thorough evaluation of pelvic floor musculature can be performed by a physical therapist or gynecologist who specializes in pelvic pain.2-4
If the patient consents to further evaluation, consider using a small speculum, advanced slowly, for further internal examination, noting any lesions, abrasions, discharge, ectropion, or tenderness.2-4,7 A rectal exam may also be needed in cases of deep dyspareunia.6 Initial work-up may include a potassium hydroxide wet prep, sexually transmitted infection testing, and pelvic ultrasound.2,4 In some cases, laparoscopy or biopsy may be needed.2,4
Treatments for common causes
Treatment often begins with education about anatomy, to help patients communicate about symptoms and engage more fully in their care.3 Additional education may be needed on genital functioning and the necessity of adequate stimulation and lubrication prior to penetration.1,2,9-11 A discussion of treatments for the wide range of possible causes of dyspareunia is outside the scope of this article. However, some basic behavioral changes may help patients address some of the more common contributing factors.
For example, if vaginal infection is suspected, advise patients to discontinue the use of harsh soaps, known vaginal irritants (eg, perfumed products, bath additives), and douches.3 Recommend using only preservative- and alcohol-free lubricants for sexual contact, and avoiding lubricants with added functions (eg, warming).3 It’s worth noting that avoidance of tight clothing and thong underwear due to possible risk for infections may not be necessary. A recent study found that women who frequently wore thong underwear (more than half of the time) were no more likely to develop urinary tract infections, yeast vaginitis, or bacterial vaginosis than those who avoid such items.30 However, noncotton underwear fabric, rather than tightness, was associated with yeast vaginitis30; therefore, patients may want to consider using only breathable underwear.3
Continue to: Medication
Medication. Medication may be used to treat the underlying contributing conditions or the symptom of pain directly. Some common options are particularly important for patients whose dyspareunia does not have an identifiable cause. These medications include anti-inflammatory agents, topical anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, and hormonal treatments.2-4 Since effectiveness varies based on subtypes of pain, select a medication according to the location, timing, and hypothesized mechanism of pain.3,31,32
Medication for deep pain. A meta-analysis and systematic review found that patients with some types of chronic pelvic pain with pain deep in the vagina or pelvis experienced greater than 50% reduction in pain using medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with placebo.33 Other treatments for deep pain depend on physical exam findings.
Medication for superficial pain. Many remedies have been tried, with at least 26 different treatments for vulvodynia pain alone.16 Only some of these treatments have supporting evidence. For patients with vulvar pain, an intent-to-treat RCT found that patients using a topical steroid experienced a 23% reduction in pain from pre-treatment to 6-month follow-up.32
Surgery is also effective for vulvar pain.34,35 For provoked vestibulodynia (in which pain is localized to the vestibule and triggered by contact with the vulva), or vulvar vestibulitis, RCTs have found that vestibulectomy has stronger effects on pain than other treatments,31,35 with a 53% reduction in pain during intercourse and a 70% reduction in vestibular pain overall.35 However, while vestibulectomy is effective for provoked vestibulodynia, it is not recommended for generalized vulvodynia, in which pain is diffuse across the vulva and occurs without vulvar contact.34
Unsupported treatments. A number of other treatments have not yet been found effective. Although lidocaine for vulvar pain is often used, RCTs have not found any significant reduction in symptoms, and a double-blind RCT found that lidocaine ointment actually performed worse than placebo.31,34 Similarly, oral tricyclics have not been found to decrease vulvar pain more than placebo in double-blind studies.31,34 Furthermore, a meta-analysis of RCTs comparing treatments with placebo for vestibular pain found no significant decrease in dyspareunia for topical conjugated estrogen, topical lidocaine, oral desipramine, oral desipramine with topical lidocaine, laser therapy, or transcranial direct current.32
Tx risks to consider. Risks and benefits of dyspareunia treatment options should be thoroughly weighed and discussed with the patient.2-4 Vestibulectomy, despite reducing pain for many patients, has led to increased pain for 9% of patients who underwent the procedure.35 Topical treatments may lead to allergic reactions, inflammation, and worsening of symptoms,4 and hormonal treatments have been found to increase the risk of weight gain and bloating and are not appropriate for patients trying to conceive.33
Coordinate care with other providers
While medications and surgery can reduce pain, they have not been shown to improve other aspects of sexual functioning such as sexual satisfaction, frequency of sexual intercourse, or overall sense of sexual functioning.35 Additionally, pain reduction does not address muscle tension, anxiety, self-esteem, and relationship problems. As a result, a multidisciplinary approach is generally needed.3,4,32,33
Continue to: Physical therapists
Physical therapists. Pelvic floor physical therapists are often members of the dyspareunia treatment team and can provide a thorough evaluation and treatment of pelvic floor disorders.2-4 An RCT with intent-to-treat analysis found that pain was reduced by 71% following pelvic floor physical therapy.36 Another RCT found that 90% of patients reported a clinically meaningful decrease in pain with pelvic floor physical therapy.37 In addition to addressing pain, pelvic floor physical therapy has also been found to improve sexual functioning, sexual satisfaction, distress, and patient perception of improvement.34,36,37
Behavioral health specialists. Psychotherapists, especially those trained in sex therapy, couples therapy, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), are also typically on the treatment team. Multiple RCTs have found evidence of CBT’s effectiveness in the direct treatment of dyspareunia pain. Bergeron et al35 found a 37.5% reduction in vulvar vestibulitis pain intensity during intercourse after patients completed group CBT. Another intent-to-treat RCT found that patients receiving CBT experienced more pain reduction (~ 30%) than patients who were treated with a topical steroid.38
In addition to having a direct impact on pain, CBT has also been found to have a clinically and statistically significant positive impact on other aspects of sexual experience, such as overall sexuality, self-efficacy, overall sexual functioning, frequency of intercourse, and catastrophizing.34,38 A recent meta-analysis of RCTs found that about 80% of vaginismus patients were able to achieve penetrative intercourse after treatment with behavioral sex therapy or CBT.39 This success rate was not exceeded by physical or surgical treatments.39
When PTSD is thought to be a contributing factor, trauma therapy will likely be needed in addition to treatments for dyspareunia. First-line treatments for PTSD include cognitive processing therapy, prolonged exposure, trauma-focused CBT, and cognitive therapy.40
Psychotherapists can also help patients reduce anxiety, reintroduce sexual contact without triggering pain or anxiety, address emotional and self-esteem effects of dyspareunia, address relationship issues, and refocus sexual encounters on pleasure rather than pain avoidance.2-4 Despite patient reports of high treatment satisfaction following therapy,38 many patients may initially lack confidence in psychotherapy as a treatment for pain35 and may need to be educated on its effectiveness and multidimensional benefits.
Gynecologists. Often a gynecologist with specialization in pelvic pain is an essential member of the team for diagnostic clarification, recommendation of treatment options, and performance of more advanced treatments.2,3 If pain has become chronic, the patient may also benefit from a pain management team and support groups.2,3
Follow-up steps
Patients who screen negative for dyspareunia should be re-screened periodically. Continue to assess patients diagnosed with dyspareunia for vaginismus symptoms (if they are not initially present) to ensure that the treatment plan is appropriately adjusted. Once treatment has begun, ask about adverse effects and confidence in the treatment plan to minimize negative impacts on treatment adherence and to anticipate a need for a change in the treatment approach.31,35 In addition to tracking treatment effects on pain, continue to assess for patient-centered outcomes such as emotional functioning, self-esteem, and sexual and relationship satisfaction.34 The Female Sexual Function Index can be a useful tool to track symptoms.27,34
Finally, patients who do not experience sufficient improvement in symptoms and functioning with initial treatment may need continued support and encouragement. Given the broad range of contributing factors and the high number of potential treatments, patients may find hope in learning that multiple other treatment options may be available.
CORRESPONDENCE
Adrienne A. Williams, PhD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine, 1919 W Taylor Street, MC 663, Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
2. Seehusen DA, Baird DC, Bode DV. Dyspareunia in women. Am Fam Phys. 2014;90:465-470.
3. Sorensen J, Bautista KE, Lamvu G, et al. Evaluation and treatment of female sexual pain: a clinical review. Cureus. 2018;10:e2379.
4. MacNeill C. Dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2006;33:565-77.
5. Latthe P, Latthe M, Say L, et al. WHO systematic review of prevalence of chronic pelvic pain: a neglected reproductive health morbidity. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:177.
6. Steege JF, Zolnoun DA. Evaluation and treatment of dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1124-1136.
7. Williams AA, Williams M. A guide to performing pelvic speculum exams: a patient-centered approach to reducing iatrogenic effects. Teach Learn Med. 2013;25:383-391.
8. Ünlü Z, Yentur A, Çakil N. Pudendal nerve neuropathy: An unknown-rare cause of pelvic pain. Arch Rheumatol. 2016;31:102-103.
9. Dewitte M, Borg C, Lowenstein L. A psychosocial approach to female genital pain. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15:25-41.
10. Masters WH, Johnson VE. Human Sexual Inadequacy. 1st ed. Little, Brown; 1970.
11. Rathus SA, Nevid JS, Fichner-Rathus L. Human Sexuality in a World of Diversity. 5th ed. Allyn and Bacon; 2002.
12. Bailey BE, Freedenfeld RN, Kiser RS, et al. Lifetime physical and sexual abuse in chronic pain patients: psychosocial correlates and treatment outcomes. Disabil Rehabil. 2003;25:331-342.
13. Yehuda R, Lehrner A, Rosenbaum TY. PTSD and sexual dysfunction in men and women. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1107-1119.
14. Postma R, Bicanic I, van der Vaart H, et al. Pelvic floor muscle problems mediate sexual problems in young adult rape victims. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1978-1987.
15. Binik YM, Bergeron S, Khalifé S. Dyspareunia and vaginismus: so-called sexual pain. In: Leiblum SR, ed. 4th ed. Principles and Practice of Sex Therapy. The Guilford Press; 2007:124-156.
16. Ayling K, Ussher JM. “If sex hurts, am I still a woman?” The subjective experience of vulvodynia in hetero-sexual women. Arch Sex Behav. 2008;37:294-304.
17. Pazmany E, Bergeron S, Van Oudenhove L, et al. Body image and genital self-image in pre-menopausal women with dyspareunia. Arch Sex Behav. 2013;42:999-1010.
18. Maillé DL, Bergeron S, Lambert B. Body image in women with primary and secondary provoked vestibulodynia: a controlled study. J Sex Med. 2015;12:505-515.
19. Ryan L, Hawton K. Female dyspareunia. BMJ. 2004;328:1357.
20. Waldura JF, Arora I, Randall AM, et al. Fifty shades of stigma: exploring the health care experiences of kink-oriented patients. J Sex Med. 2016;13:1918-1929.
21. Hinchliff S, Gott M. Seeking medical help for sexual concerns in mid- and later life: a review of the literature. J Sex Res. 2011;48:106-117.
22. Banaei M, Kariman N, Ozgoli G, et al. Prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2021;153:14-24.
23. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2002;32:509-515.
24. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. PTSD: National Center for PTSD. Life events checklist for DSM-5 (LEC-5). Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/te-measures/life_events_checklist.asp
26. Weathers FW, Litz BT, Keane TM, et al. The PTSD checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5). 2013. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/adult-sr/ptsd-checklist.asp
27. Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, et al. The female sexual function index (FSFI): a multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000;26:191-208.
28. Melzack R. The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain. 1987;30:191-197.
29. Hassam T, Kelso E, Chowdary P, et al. Sexual assault as a risk factor for gynaecological morbidity: an exploratory systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020;255:222-230.
30. Hamlin AA, Sheeder J, Muffly TM. Brief versus thong hygiene in obstetrics and gynecology (B-THONG): a survey study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1190-1196.
31. Foster DC, Kotok MB, Huang LS, et al. Oral desipramine and topical lidocaine for vulvodynia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:583-593.
32. Pérez-López FR, Bueno-Notivol J, Hernandez AV, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of treatment modalities for vestibulodynia in women. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2019;24:337-346.
33. Cheong YC, Smotra G, Williams AC. Non-surgical interventions for the management of chronic pelvic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(3):CD008797.
34. Goldstein AT, Pukall CF, Brown C, et al. Vulvodynia: assessment and treatment. J Sex Med. 2016;13:572-590.
35. Bergeron S, Binik YM, Khalifé S, et al. A randomized comparison of group cognitive-behavioral therapy, surface electromyographic biofeedback, and vestibulectomy in the treatment of dyspareunia resulting from vulvar vestibulitis. Pain. 2001;91:297-306.
36. Schvartzman R, Schvartzman L, Ferreira CF, et al. Physical therapy intervention for women with dyspareunia: a randomized clinical trial. J Sex Marital Ther. 2019;45:378-394.
37. Morin M, Dumoulin C, Bergeron S, et al. Multimodal physical therapy versus topical lidocaine for provoked vestibulodynia: a multicenter, randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:189.e1-189.e12.
38. Bergeron S, Khalifé S, Dupuis M-J, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing group cognitive-behavioral therapy and a topical steroid for women with dyspareunia. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:259-268.
39. Maseroli E, Scavello I, Rastrelli G, et al. Outcome of medical and psychosexual interventions for vaginismus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1752-1764.
40. American Psychological Association. Clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. 2017. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/ptsd.pdf
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
2. Seehusen DA, Baird DC, Bode DV. Dyspareunia in women. Am Fam Phys. 2014;90:465-470.
3. Sorensen J, Bautista KE, Lamvu G, et al. Evaluation and treatment of female sexual pain: a clinical review. Cureus. 2018;10:e2379.
4. MacNeill C. Dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2006;33:565-77.
5. Latthe P, Latthe M, Say L, et al. WHO systematic review of prevalence of chronic pelvic pain: a neglected reproductive health morbidity. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:177.
6. Steege JF, Zolnoun DA. Evaluation and treatment of dyspareunia. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1124-1136.
7. Williams AA, Williams M. A guide to performing pelvic speculum exams: a patient-centered approach to reducing iatrogenic effects. Teach Learn Med. 2013;25:383-391.
8. Ünlü Z, Yentur A, Çakil N. Pudendal nerve neuropathy: An unknown-rare cause of pelvic pain. Arch Rheumatol. 2016;31:102-103.
9. Dewitte M, Borg C, Lowenstein L. A psychosocial approach to female genital pain. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15:25-41.
10. Masters WH, Johnson VE. Human Sexual Inadequacy. 1st ed. Little, Brown; 1970.
11. Rathus SA, Nevid JS, Fichner-Rathus L. Human Sexuality in a World of Diversity. 5th ed. Allyn and Bacon; 2002.
12. Bailey BE, Freedenfeld RN, Kiser RS, et al. Lifetime physical and sexual abuse in chronic pain patients: psychosocial correlates and treatment outcomes. Disabil Rehabil. 2003;25:331-342.
13. Yehuda R, Lehrner A, Rosenbaum TY. PTSD and sexual dysfunction in men and women. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1107-1119.
14. Postma R, Bicanic I, van der Vaart H, et al. Pelvic floor muscle problems mediate sexual problems in young adult rape victims. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1978-1987.
15. Binik YM, Bergeron S, Khalifé S. Dyspareunia and vaginismus: so-called sexual pain. In: Leiblum SR, ed. 4th ed. Principles and Practice of Sex Therapy. The Guilford Press; 2007:124-156.
16. Ayling K, Ussher JM. “If sex hurts, am I still a woman?” The subjective experience of vulvodynia in hetero-sexual women. Arch Sex Behav. 2008;37:294-304.
17. Pazmany E, Bergeron S, Van Oudenhove L, et al. Body image and genital self-image in pre-menopausal women with dyspareunia. Arch Sex Behav. 2013;42:999-1010.
18. Maillé DL, Bergeron S, Lambert B. Body image in women with primary and secondary provoked vestibulodynia: a controlled study. J Sex Med. 2015;12:505-515.
19. Ryan L, Hawton K. Female dyspareunia. BMJ. 2004;328:1357.
20. Waldura JF, Arora I, Randall AM, et al. Fifty shades of stigma: exploring the health care experiences of kink-oriented patients. J Sex Med. 2016;13:1918-1929.
21. Hinchliff S, Gott M. Seeking medical help for sexual concerns in mid- and later life: a review of the literature. J Sex Res. 2011;48:106-117.
22. Banaei M, Kariman N, Ozgoli G, et al. Prevalence of postpartum dyspareunia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2021;153:14-24.
23. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: A new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatr Ann. 2002;32:509-515.
24. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. PTSD: National Center for PTSD. Life events checklist for DSM-5 (LEC-5). Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/te-measures/life_events_checklist.asp
26. Weathers FW, Litz BT, Keane TM, et al. The PTSD checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5). 2013. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.ptsd.va.gov/professional/assessment/adult-sr/ptsd-checklist.asp
27. Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, et al. The female sexual function index (FSFI): a multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000;26:191-208.
28. Melzack R. The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain. 1987;30:191-197.
29. Hassam T, Kelso E, Chowdary P, et al. Sexual assault as a risk factor for gynaecological morbidity: an exploratory systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020;255:222-230.
30. Hamlin AA, Sheeder J, Muffly TM. Brief versus thong hygiene in obstetrics and gynecology (B-THONG): a survey study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1190-1196.
31. Foster DC, Kotok MB, Huang LS, et al. Oral desipramine and topical lidocaine for vulvodynia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:583-593.
32. Pérez-López FR, Bueno-Notivol J, Hernandez AV, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of treatment modalities for vestibulodynia in women. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2019;24:337-346.
33. Cheong YC, Smotra G, Williams AC. Non-surgical interventions for the management of chronic pelvic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(3):CD008797.
34. Goldstein AT, Pukall CF, Brown C, et al. Vulvodynia: assessment and treatment. J Sex Med. 2016;13:572-590.
35. Bergeron S, Binik YM, Khalifé S, et al. A randomized comparison of group cognitive-behavioral therapy, surface electromyographic biofeedback, and vestibulectomy in the treatment of dyspareunia resulting from vulvar vestibulitis. Pain. 2001;91:297-306.
36. Schvartzman R, Schvartzman L, Ferreira CF, et al. Physical therapy intervention for women with dyspareunia: a randomized clinical trial. J Sex Marital Ther. 2019;45:378-394.
37. Morin M, Dumoulin C, Bergeron S, et al. Multimodal physical therapy versus topical lidocaine for provoked vestibulodynia: a multicenter, randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:189.e1-189.e12.
38. Bergeron S, Khalifé S, Dupuis M-J, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing group cognitive-behavioral therapy and a topical steroid for women with dyspareunia. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:259-268.
39. Maseroli E, Scavello I, Rastrelli G, et al. Outcome of medical and psychosexual interventions for vaginismus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1752-1764.
40. American Psychological Association. Clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. 2017. Accessed February 3, 2022. www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/ptsd.pdf
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Screen all patients for sexual dysfunctions, as patients often do not report symptoms on their own. B
› Refer patients with dyspareunia for psychotherapy to address both pain and psychosocial causes and sequela of dyspareunia. A
› Refer patients with dyspareunia for pelvic floor physical therapy to address pain and sexual functioning. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series









