User login
Teen Pregnancy Linked With Risk for Premature Death
Teen pregnancy is associated with a higher risk for premature mortality, both among those who carry the pregnancies to term and those who miscarry, according to a new study.
Among 2.2 million female teenagers in Ontario, Canada, the risk for premature death by age 31 years was 1.5 times higher among those who had one teen pregnancy and 2.1 times higher among those with two or more teen pregnancies.
“No person should die during childhood or early adulthood. Such deaths, unexpected and tragic, are often from preventable causes, including intentional injury,” lead author Joel Ray, MD, an obstetric medicine specialist and epidemiologist at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto, told this news organization.
“Women who experience teen pregnancy appear more vulnerable, often having experienced a history of adverse experiences in childhood, including abuse and economic challenges,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Pregnancy Associations
The investigators conducted a population-based cohort study of all girls who were alive at age 12 years from April 1991 to March 2021 in Ontario. They evaluated the risk for all-cause mortality from age 12 years onward in association with the number of teen pregnancies between ages 12 and 19 years and the age at first pregnancy. The investigators adjusted the hazard ratios for year of birth, comorbidities at ages 9-11 years, area-level education, income level, and rural status.
Among more than 2.2 million teens, 163,124 (7.3%) had a pregnancy at a median age of 18 years, including 121,276 (74.3%) who had one pregnancy and 41,848 (25.6%) who had two or more. These teens were more likely to live in the lowest neighborhood income quintile and in an area with a lower rate of high school completion. They also had a higher prevalence of self-harm history between ages 12 and 19 years but not a higher prevalence of physical or mental comorbidities.
Among all teens who had a pregnancy, 60,037 (36.8%) ended in a birth, including 59,485 (99.1%) live births. A further 106,135 (65.1%) ended in induced abortion, and 17,945 (11%) ended in miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Overall, there were 6030 premature deaths among those without a teen pregnancy, or 1.9 per 10,000 person-years. There were 701 deaths among those with one teen pregnancy (4.1 per 10,000 person-years) and 345 deaths among those with two or more teen pregnancies (6.1 per 10,000 person-years).
The adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for mortality were 1.51 for those with one pregnancy and 2.14 for those with two or more pregnancies. Compared with no teen pregnancy, the AHRs for premature death were 1.41 if the first teen pregnancy ended in an induced abortion and 2.10 if it ended in a miscarriage or birth.
Comparing those with a teen pregnancy and those without, the AHRs for premature death were 1.25 from noninjury, 2.06 from unintentional injury, and 2.02 from intentional injury. Among patients with teen pregnancy, noninjury-related premature mortality was more common, at 2.0 per 10,000 person-years, than unintentional and intentional injuries, at 1.0 per 10,000 person-years and 0.4 per 10,000 person-years, respectively.
A teen pregnancy before age 16 years entailed the highest associated risk for premature death, with an AHR of 2.00.
Next Research Steps
“We were not surprised by our findings, but it was new to us to see that the risk for premature death was higher for women who had an induced abortion in their teen years,” said Dr. Ray. “It was even higher in those whose pregnancy ended in a birth or miscarriage.”
The investigators plan to evaluate whether the future risk for premature death after teen pregnancy differs by the type of induced abortion, such as procedural or pharmaceutical, or by whether the pregnancy ended in a live birth, stillbirth, or miscarriage. Among those with a live birth, the researchers will also analyze the risk for premature death in relation to whether the newborn was taken into custody by child protection services in Canada.
Other factors associated with teen pregnancy and overall mortality, particularly adverse childhood experiences, may point to the reasons for premature mortality and should be studied further, the authors wrote. Structural and systems-related factors should be considered as well.
Stigmatization and Isolation
“Some teens choose to become pregnant, but most teen pregnancies are unintended, which exposes shortcomings in the systems that exist to educate, guide, and support young people,” said Elizabeth Cook, a research scientist at Child Trends in Rockville, Maryland.
Dr. Cook, who wasn’t involved with this study, wrote an accompanying editorial in JAMA Network Open. She conducts studies of sexual and reproductive health for Child Trends.
“Teens who become pregnant often experience stigmatization and isolation that can make it more difficult to thrive in adulthood, especially if they lack the necessary support to navigate such a significant decision,” she said. “Fortunately, the systems that youths encounter, such as healthcare, education, and child welfare, are taking on a larger role in prevention efforts than they have in the past.”
These systems are shifting the burden of unintended teen pregnancy from the teens themselves and their behaviors to the health and education systems, Dr. Cook noted, though more work is needed around local policies and lack of access to healthcare facilities.
“Teen pregnancy may offer an opportunity to intervene in the lives of people at higher risk for premature death, but knowing how best to offer support requires an understanding of the context of their lives,” she said. “As a starting point, we must celebrate and listen to all pregnant young people so they can tell us what they need to live long, fulfilled lives.”
The study was funded by grants from the PSI Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, as well as ICES, which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Ray and Dr. Cook reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Teen pregnancy is associated with a higher risk for premature mortality, both among those who carry the pregnancies to term and those who miscarry, according to a new study.
Among 2.2 million female teenagers in Ontario, Canada, the risk for premature death by age 31 years was 1.5 times higher among those who had one teen pregnancy and 2.1 times higher among those with two or more teen pregnancies.
“No person should die during childhood or early adulthood. Such deaths, unexpected and tragic, are often from preventable causes, including intentional injury,” lead author Joel Ray, MD, an obstetric medicine specialist and epidemiologist at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto, told this news organization.
“Women who experience teen pregnancy appear more vulnerable, often having experienced a history of adverse experiences in childhood, including abuse and economic challenges,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Pregnancy Associations
The investigators conducted a population-based cohort study of all girls who were alive at age 12 years from April 1991 to March 2021 in Ontario. They evaluated the risk for all-cause mortality from age 12 years onward in association with the number of teen pregnancies between ages 12 and 19 years and the age at first pregnancy. The investigators adjusted the hazard ratios for year of birth, comorbidities at ages 9-11 years, area-level education, income level, and rural status.
Among more than 2.2 million teens, 163,124 (7.3%) had a pregnancy at a median age of 18 years, including 121,276 (74.3%) who had one pregnancy and 41,848 (25.6%) who had two or more. These teens were more likely to live in the lowest neighborhood income quintile and in an area with a lower rate of high school completion. They also had a higher prevalence of self-harm history between ages 12 and 19 years but not a higher prevalence of physical or mental comorbidities.
Among all teens who had a pregnancy, 60,037 (36.8%) ended in a birth, including 59,485 (99.1%) live births. A further 106,135 (65.1%) ended in induced abortion, and 17,945 (11%) ended in miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Overall, there were 6030 premature deaths among those without a teen pregnancy, or 1.9 per 10,000 person-years. There were 701 deaths among those with one teen pregnancy (4.1 per 10,000 person-years) and 345 deaths among those with two or more teen pregnancies (6.1 per 10,000 person-years).
The adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for mortality were 1.51 for those with one pregnancy and 2.14 for those with two or more pregnancies. Compared with no teen pregnancy, the AHRs for premature death were 1.41 if the first teen pregnancy ended in an induced abortion and 2.10 if it ended in a miscarriage or birth.
Comparing those with a teen pregnancy and those without, the AHRs for premature death were 1.25 from noninjury, 2.06 from unintentional injury, and 2.02 from intentional injury. Among patients with teen pregnancy, noninjury-related premature mortality was more common, at 2.0 per 10,000 person-years, than unintentional and intentional injuries, at 1.0 per 10,000 person-years and 0.4 per 10,000 person-years, respectively.
A teen pregnancy before age 16 years entailed the highest associated risk for premature death, with an AHR of 2.00.
Next Research Steps
“We were not surprised by our findings, but it was new to us to see that the risk for premature death was higher for women who had an induced abortion in their teen years,” said Dr. Ray. “It was even higher in those whose pregnancy ended in a birth or miscarriage.”
The investigators plan to evaluate whether the future risk for premature death after teen pregnancy differs by the type of induced abortion, such as procedural or pharmaceutical, or by whether the pregnancy ended in a live birth, stillbirth, or miscarriage. Among those with a live birth, the researchers will also analyze the risk for premature death in relation to whether the newborn was taken into custody by child protection services in Canada.
Other factors associated with teen pregnancy and overall mortality, particularly adverse childhood experiences, may point to the reasons for premature mortality and should be studied further, the authors wrote. Structural and systems-related factors should be considered as well.
Stigmatization and Isolation
“Some teens choose to become pregnant, but most teen pregnancies are unintended, which exposes shortcomings in the systems that exist to educate, guide, and support young people,” said Elizabeth Cook, a research scientist at Child Trends in Rockville, Maryland.
Dr. Cook, who wasn’t involved with this study, wrote an accompanying editorial in JAMA Network Open. She conducts studies of sexual and reproductive health for Child Trends.
“Teens who become pregnant often experience stigmatization and isolation that can make it more difficult to thrive in adulthood, especially if they lack the necessary support to navigate such a significant decision,” she said. “Fortunately, the systems that youths encounter, such as healthcare, education, and child welfare, are taking on a larger role in prevention efforts than they have in the past.”
These systems are shifting the burden of unintended teen pregnancy from the teens themselves and their behaviors to the health and education systems, Dr. Cook noted, though more work is needed around local policies and lack of access to healthcare facilities.
“Teen pregnancy may offer an opportunity to intervene in the lives of people at higher risk for premature death, but knowing how best to offer support requires an understanding of the context of their lives,” she said. “As a starting point, we must celebrate and listen to all pregnant young people so they can tell us what they need to live long, fulfilled lives.”
The study was funded by grants from the PSI Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, as well as ICES, which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Ray and Dr. Cook reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Teen pregnancy is associated with a higher risk for premature mortality, both among those who carry the pregnancies to term and those who miscarry, according to a new study.
Among 2.2 million female teenagers in Ontario, Canada, the risk for premature death by age 31 years was 1.5 times higher among those who had one teen pregnancy and 2.1 times higher among those with two or more teen pregnancies.
“No person should die during childhood or early adulthood. Such deaths, unexpected and tragic, are often from preventable causes, including intentional injury,” lead author Joel Ray, MD, an obstetric medicine specialist and epidemiologist at St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto, told this news organization.
“Women who experience teen pregnancy appear more vulnerable, often having experienced a history of adverse experiences in childhood, including abuse and economic challenges,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Pregnancy Associations
The investigators conducted a population-based cohort study of all girls who were alive at age 12 years from April 1991 to March 2021 in Ontario. They evaluated the risk for all-cause mortality from age 12 years onward in association with the number of teen pregnancies between ages 12 and 19 years and the age at first pregnancy. The investigators adjusted the hazard ratios for year of birth, comorbidities at ages 9-11 years, area-level education, income level, and rural status.
Among more than 2.2 million teens, 163,124 (7.3%) had a pregnancy at a median age of 18 years, including 121,276 (74.3%) who had one pregnancy and 41,848 (25.6%) who had two or more. These teens were more likely to live in the lowest neighborhood income quintile and in an area with a lower rate of high school completion. They also had a higher prevalence of self-harm history between ages 12 and 19 years but not a higher prevalence of physical or mental comorbidities.
Among all teens who had a pregnancy, 60,037 (36.8%) ended in a birth, including 59,485 (99.1%) live births. A further 106,135 (65.1%) ended in induced abortion, and 17,945 (11%) ended in miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Overall, there were 6030 premature deaths among those without a teen pregnancy, or 1.9 per 10,000 person-years. There were 701 deaths among those with one teen pregnancy (4.1 per 10,000 person-years) and 345 deaths among those with two or more teen pregnancies (6.1 per 10,000 person-years).
The adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for mortality were 1.51 for those with one pregnancy and 2.14 for those with two or more pregnancies. Compared with no teen pregnancy, the AHRs for premature death were 1.41 if the first teen pregnancy ended in an induced abortion and 2.10 if it ended in a miscarriage or birth.
Comparing those with a teen pregnancy and those without, the AHRs for premature death were 1.25 from noninjury, 2.06 from unintentional injury, and 2.02 from intentional injury. Among patients with teen pregnancy, noninjury-related premature mortality was more common, at 2.0 per 10,000 person-years, than unintentional and intentional injuries, at 1.0 per 10,000 person-years and 0.4 per 10,000 person-years, respectively.
A teen pregnancy before age 16 years entailed the highest associated risk for premature death, with an AHR of 2.00.
Next Research Steps
“We were not surprised by our findings, but it was new to us to see that the risk for premature death was higher for women who had an induced abortion in their teen years,” said Dr. Ray. “It was even higher in those whose pregnancy ended in a birth or miscarriage.”
The investigators plan to evaluate whether the future risk for premature death after teen pregnancy differs by the type of induced abortion, such as procedural or pharmaceutical, or by whether the pregnancy ended in a live birth, stillbirth, or miscarriage. Among those with a live birth, the researchers will also analyze the risk for premature death in relation to whether the newborn was taken into custody by child protection services in Canada.
Other factors associated with teen pregnancy and overall mortality, particularly adverse childhood experiences, may point to the reasons for premature mortality and should be studied further, the authors wrote. Structural and systems-related factors should be considered as well.
Stigmatization and Isolation
“Some teens choose to become pregnant, but most teen pregnancies are unintended, which exposes shortcomings in the systems that exist to educate, guide, and support young people,” said Elizabeth Cook, a research scientist at Child Trends in Rockville, Maryland.
Dr. Cook, who wasn’t involved with this study, wrote an accompanying editorial in JAMA Network Open. She conducts studies of sexual and reproductive health for Child Trends.
“Teens who become pregnant often experience stigmatization and isolation that can make it more difficult to thrive in adulthood, especially if they lack the necessary support to navigate such a significant decision,” she said. “Fortunately, the systems that youths encounter, such as healthcare, education, and child welfare, are taking on a larger role in prevention efforts than they have in the past.”
These systems are shifting the burden of unintended teen pregnancy from the teens themselves and their behaviors to the health and education systems, Dr. Cook noted, though more work is needed around local policies and lack of access to healthcare facilities.
“Teen pregnancy may offer an opportunity to intervene in the lives of people at higher risk for premature death, but knowing how best to offer support requires an understanding of the context of their lives,” she said. “As a starting point, we must celebrate and listen to all pregnant young people so they can tell us what they need to live long, fulfilled lives.”
The study was funded by grants from the PSI Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, as well as ICES, which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Ray and Dr. Cook reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Active Surveillance for Cancer Doesn’t Increase Malpractice Risk
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Although practice guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network consider active surveillance an effective strategy for managing low-risk cancers, some physicians have been hesitant to incorporate it into their practice because of concerns about potential litigation.
- Researchers used Westlaw Edge and LexisNexis Advance databases to identify malpractice trends involving active surveillance related to thyroid, prostate, kidney, and or from 1990 to 2022.
- Data included unpublished cases, trial orders, jury verdicts, and administrative decisions.
- Researchers identified 201 malpractice cases across all low-risk cancers in the initial screening. Out of these, only five cases, all , involved active surveillance as the point of allegation.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of the five prostate cancer cases, two involved incarcerated patients with Gleason 6 very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma that was managed with active surveillance by their urologists.
- In these two cases, the patients claimed that active surveillance violated their 8th Amendment right to be free from cruel or unusual punishment. In both cases, there was no metastasis or spread detected and the court determined active surveillance management was performed under national standards.
- The other three cases involved litigation claiming that active surveillance was not explicitly recommended as a treatment option for patients who all had very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma and had reported negligence from an intervention ( or cryoablation). However, all cases had documented informed consent for active surveillance.
- No relevant cases were found relating to active surveillance in any other type of cancer, whether in an initial diagnosis or recurrence.
IN PRACTICE:
“This data should bolster physicians’ confidence in recommending active surveillance for their patients when it is an appropriate option,” study coauthor Timothy Daskivich, MD, assistant professor of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a statement . “Active surveillance maximizes quality of life and avoids unnecessary overtreatment, and it does not increase medicolegal liability to physicians, as detailed in the case dismissals identified in this study.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Samuel Chang, JD, with Athene Law LLP, San Francisco, was recently published in Annals of Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The Westlaw and Lexis databases may not contain all cases or decisions issued by a state regulatory agency, like a medical board. Federal and state decisions from lower courts may not be published and available. Also, settlements outside of court or suits filed and not pursued were not included in the data.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers did not provide any disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Although practice guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network consider active surveillance an effective strategy for managing low-risk cancers, some physicians have been hesitant to incorporate it into their practice because of concerns about potential litigation.
- Researchers used Westlaw Edge and LexisNexis Advance databases to identify malpractice trends involving active surveillance related to thyroid, prostate, kidney, and or from 1990 to 2022.
- Data included unpublished cases, trial orders, jury verdicts, and administrative decisions.
- Researchers identified 201 malpractice cases across all low-risk cancers in the initial screening. Out of these, only five cases, all , involved active surveillance as the point of allegation.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of the five prostate cancer cases, two involved incarcerated patients with Gleason 6 very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma that was managed with active surveillance by their urologists.
- In these two cases, the patients claimed that active surveillance violated their 8th Amendment right to be free from cruel or unusual punishment. In both cases, there was no metastasis or spread detected and the court determined active surveillance management was performed under national standards.
- The other three cases involved litigation claiming that active surveillance was not explicitly recommended as a treatment option for patients who all had very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma and had reported negligence from an intervention ( or cryoablation). However, all cases had documented informed consent for active surveillance.
- No relevant cases were found relating to active surveillance in any other type of cancer, whether in an initial diagnosis or recurrence.
IN PRACTICE:
“This data should bolster physicians’ confidence in recommending active surveillance for their patients when it is an appropriate option,” study coauthor Timothy Daskivich, MD, assistant professor of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a statement . “Active surveillance maximizes quality of life and avoids unnecessary overtreatment, and it does not increase medicolegal liability to physicians, as detailed in the case dismissals identified in this study.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Samuel Chang, JD, with Athene Law LLP, San Francisco, was recently published in Annals of Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The Westlaw and Lexis databases may not contain all cases or decisions issued by a state regulatory agency, like a medical board. Federal and state decisions from lower courts may not be published and available. Also, settlements outside of court or suits filed and not pursued were not included in the data.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers did not provide any disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Although practice guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network consider active surveillance an effective strategy for managing low-risk cancers, some physicians have been hesitant to incorporate it into their practice because of concerns about potential litigation.
- Researchers used Westlaw Edge and LexisNexis Advance databases to identify malpractice trends involving active surveillance related to thyroid, prostate, kidney, and or from 1990 to 2022.
- Data included unpublished cases, trial orders, jury verdicts, and administrative decisions.
- Researchers identified 201 malpractice cases across all low-risk cancers in the initial screening. Out of these, only five cases, all , involved active surveillance as the point of allegation.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of the five prostate cancer cases, two involved incarcerated patients with Gleason 6 very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma that was managed with active surveillance by their urologists.
- In these two cases, the patients claimed that active surveillance violated their 8th Amendment right to be free from cruel or unusual punishment. In both cases, there was no metastasis or spread detected and the court determined active surveillance management was performed under national standards.
- The other three cases involved litigation claiming that active surveillance was not explicitly recommended as a treatment option for patients who all had very-low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma and had reported negligence from an intervention ( or cryoablation). However, all cases had documented informed consent for active surveillance.
- No relevant cases were found relating to active surveillance in any other type of cancer, whether in an initial diagnosis or recurrence.
IN PRACTICE:
“This data should bolster physicians’ confidence in recommending active surveillance for their patients when it is an appropriate option,” study coauthor Timothy Daskivich, MD, assistant professor of surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a statement . “Active surveillance maximizes quality of life and avoids unnecessary overtreatment, and it does not increase medicolegal liability to physicians, as detailed in the case dismissals identified in this study.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Samuel Chang, JD, with Athene Law LLP, San Francisco, was recently published in Annals of Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The Westlaw and Lexis databases may not contain all cases or decisions issued by a state regulatory agency, like a medical board. Federal and state decisions from lower courts may not be published and available. Also, settlements outside of court or suits filed and not pursued were not included in the data.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers did not provide any disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Women’s Cancers: Clinicians Research, Advise on Sexual Dysfunction
Decreased sexual function is a side effect of many types of cancer, notably uterine, cervical, ovarian, and breast cancer, that often goes unaddressed, according to the authors of several studies presented at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Patients want to talk about sex, but not necessarily at the start of their diagnosis or treatment, suggest the findings of a study presented at the meeting. Jesse T. Brewer of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City and colleagues enrolled 63 patients who underwent surgery with documented hereditary breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or Lynch syndrome in a cross-sectional survey.
Overall, 86% said that sexuality and intimacy were very or somewhat important, and 78% said that the healthcare team addressing the issue was very or somewhat important, the researchers found. However, only 40% of the respondents said that they wanted to discuss sexuality at the time of diagnosis because the idea was too overwhelming.
Oncologists are more aware of sexual side effects and the potential for sexual issues that persist long after treatment, but many patients may not have opportunities to talk about sexual concerns, said Don S. Dizon, MD, an oncologist specializing in women’s cancers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, in an interview.
“It is important that we [oncologists] be the ones to open the door to these conversations; people with cancer will not bring it up spontaneously, for fear of making their provider uncomfortable, especially if they’ve never been asked about it before,” Dr. Dizon said in an interview.
He advised clinicians to find a network within their health systems so they can refer patients to specialized services, such as sex therapy, couples counseling, pelvic rehabilitation, or menopausal experts as needed.
In another study presented at the meeting, Naaman Mehta, MD, of NYU Langone Health, and colleagues reviewed data from 166 healthcare providers who completed a 23-item survey about evaluating and managing sexual health concerns of their patients. Most of the respondents were gynecologic oncologists (93.4%), but one radiation oncologist and 10 other healthcare providers also completed the survey.
Overall, approximately 60% of the respondents routinely asked about the sexual health concerns of their patients, and 98% of these said they believed that sexual health discussions should be held with a gynecologic oncologist. Just over half (54%) also said that the patient should be the one to initiate a discussion of sexual health concerns.
Female providers were significantly more likely to discuss sexual health with patients, compared with male providers, after controlling for the hospital setting and training level, the researchers noted (odds ratio, 1.4;P < .01).
The results suggest a need for more ways to integrate sexual health screening into gynecologic oncologic clinics, the researchers concluded.
The provider survey findings are similar to the results of a survey conducted by Dr. Dizon and colleagues in 2007. In that study, less than half of respondents took a sexual history, but 80% felt there was insufficient time to explore sexual issues.
“It is critical to understand that people with cancer do not expect their oncologists to be sexual health experts, but as with all other side effects caused by treatment and the diagnosis, we can be the ones who recognize it,” Dr. Dizon noted, in an interview.
Common Complaints and Causes
In Dr. Dizon’s experience, local symptoms including vaginal dryness, pain with penetration, and vaginal thinning, are common sexual complaints in women with cancer, as are systemic issues such as lack of interest and menopause-type symptoms.
“For those undergoing radiation, the vaginal tunnel can actually develop adhesions, and if not treated proactively this can lead to vaginal stenosis,” said Dr. Dizon, who was not involved in the studies presented at the meeting.
Comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal conditions can contribute to sexual issues in women with cancer, according to Nora Lersch, DNP, FNP-BC, AOCNP, and Nicole Dreibelbis, CRNP, the authors of other research presented at the meeting.
Culture, religion, fitness level, history of sexual violence, and gender spectrum health also play a role, as do anxiety and depression, dementia, and substance abuse disorders, the authors wrote in their presentation, “Prioritizing Sexual Health in Gynecological Oncology Care.”
Low libido is a frequent complaint across all cancer types, Ms. Dreibelbis, a nurse practitioner specializing in gynecologic oncology at the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“Breast cancer patients, especially those on [aromatase inhibitor] therapy, often experience vaginal dryness and therefore dyspareunia,” she added.
The pelvic floor muscles, with their important role in sexual response, can be weakened by cancer treatment or surgery, and the pudendal nerves, which are the primary nerves responsible for sexual response in women, can be affected as well, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote.
Taking Sex Seriously
Researchers are exploring the impact of different cancer prevention treatments for women to mitigate sexual side effects, as illustrated by another study presented at the meeting.
Dr. Barbara Norquist, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues compared the sexual function and menopausal symptoms of patients at high risk of ovarian carcinoma who underwent either interval salpingectomy/delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) or risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO).
“For patients at high risk for ovarian cancer, surgical removal of the tubes and ovaries is the mainstay of prevention, as screening is not effective at reducing death from ovarian cancer. As a result of surgery, many patients become suddenly postmenopausal from losing their ovaries,” Dr. Norquist said in an interview.
Some patients delay surgery out of concern for health and quality of life, including sexual function, she said.
In the study (known as the WISP trial) the researchers compared data from 166 patients who underwent immediate removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries and 171 who underwent fallopian tube removal and delayed oophorectomy. All patients completed questionnaires about sexual function. The primary outcome was change in sexual function based on the sexual function index (FSFI) from baseline to 6 months after surgery.
Overall, changes in sexual function were significantly greater in the immediate oophorectomy group, compared with the delayed oophorectomy group at 6 months (33% vs 17%) and also at 12 months (43% vs 20%).
A further review of patients using hormone therapy showed that those in the immediate oophorectomy group still had greater decreases in sexual function, compared with the delayed group, though the difference between groups of patients using hormone therapy was less dramatic.
“I was surprised that, even with hormone replacement therapy, patients undergoing removal of the ovaries still had significant detrimental changes to sexual function when compared to those having the tubes removed, although this was even worse in those who could not take HRT,” Dr. Norquist said, in an interview. “I was reassured that menopausal symptoms in general were well managed with HRT, as these patients did not score differently on menopause symptoms, compared with those having their tubes removed,” she said.
Patients deserve accurate information about predicted changes in menopausal symptoms and sexual function as a result of ovary removal, and HRT should be provided when there is no contraindication, Dr. Norquist told this news organization.
Dr. Norquist and colleagues are awaiting the results of clinical trials investigating the safety of salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy in terms of ovarian cancer prevention, but more research is needed to identify optimal management of the menopausal and sexual side effects associated with surgical menopause, she noted.
“Findings from the WISP study show the importance of hormones in women undergoing prophylactic surgery,” Dr. Dizon said. The findings indicate that salpingectomy has less of a negative influence on sexual function compared to removal of the ovaries, and the impact of hormone therapy and the relatively young age of the patients who took hormones reinforces current knowledge about hormones and sex, he added.
Barriers and Solutions
Barriers to asking women with cancer about sexual issues reported by providers include limited time, lack of training in sexual health, a desire to avoid offending the patient or making them uncomfortable, and uncertainty about how to answer the questions, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote in their presentation.
Barriers to asking healthcare providers about their sexual issues reported by patients include the beliefs that the clinician should initiate the discussion, that sexual function will not be taken seriously, and that they might make the provider uncomfortable.
“Fortunately, more information and research has been done on sexual health and gynecological cancer in recent years, so oncologists are becoming more aware of the issues women may have,” said Dr. Lersch who is an oncology nurse practitioner at Providence Franz Cancer Institute in Portland, Oregon, in an interview.
Telling patients early in their cancer treatment about potential sexual side effects and opportunities for help is essential, she added.
Although oncologists have become more aware of the importance of sexual health and well-being for their patients, “I think there has historically been a disconnect in including sexual health education in medical training,” Ms. Dreibelbis said in an interview.
Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis advised a multidimensional approach to managing sexual problems in cancer patients that includes consideration of biological and psychological symptoms, but also social, cultural, and interpersonal factors, in their presentation.
Their suggestions include discussing dyspareunia with their patients, asking for details such as whether the pain is internal or external, whether it occurs with activities outside of sex including masturbation, and whether bleeding is present.
Oncology therapies and surgeries can decrease or eliminate an individual’s ability to produce their own lubricant; for example, removal of the cervix eliminates cervical mucous, which helps with internal lubrication, they wrote in their presentation.
For patients with dyspareunia, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis recommend a vaginal moisturizer especially formulated for vaginal tissue that can be absorbed by the mucosal tissue of the vagina. Use of this type of product can increase the effectiveness of lubricants and help restore integrity of the vaginal tissue. Such moisturizers are available as gels, creams, or suppositories over the counter, and do not contain hormones.
Vaginal estrogen can be helpful for burning, itching, irritation, tissue fragility, and pain with sex, according to Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis. Adequate estrogen therapy can promote normalization of vaginal pH and microflora, as well increase vaginal secretion and reduce pain and dryness with intercourse, the presenters stated in their presentation. In addition, dilator therapy can be used to help prevent vaginal stenosis, and penetration bumpers can help relieve discomfort during intercourse, they wrote.
Looking ahead, more research is needed to serve a wider patient population, Ms. Dreibelbis said, in an interview.
“LGBTQIA [individuals] have not been included in sexual health research and there are more people than ever who identify within this group of people. I know there has also been some very early work on shielding the clitoris from the impacts of radiation, and I believe this is extremely important up-and-coming research,” she said.
Dr. Lersch, Ms. Dreibelbi, Dr. Dizon, Dr. Norquist, Ms. Brewer, and Dr. Mehta had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Decreased sexual function is a side effect of many types of cancer, notably uterine, cervical, ovarian, and breast cancer, that often goes unaddressed, according to the authors of several studies presented at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Patients want to talk about sex, but not necessarily at the start of their diagnosis or treatment, suggest the findings of a study presented at the meeting. Jesse T. Brewer of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City and colleagues enrolled 63 patients who underwent surgery with documented hereditary breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or Lynch syndrome in a cross-sectional survey.
Overall, 86% said that sexuality and intimacy were very or somewhat important, and 78% said that the healthcare team addressing the issue was very or somewhat important, the researchers found. However, only 40% of the respondents said that they wanted to discuss sexuality at the time of diagnosis because the idea was too overwhelming.
Oncologists are more aware of sexual side effects and the potential for sexual issues that persist long after treatment, but many patients may not have opportunities to talk about sexual concerns, said Don S. Dizon, MD, an oncologist specializing in women’s cancers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, in an interview.
“It is important that we [oncologists] be the ones to open the door to these conversations; people with cancer will not bring it up spontaneously, for fear of making their provider uncomfortable, especially if they’ve never been asked about it before,” Dr. Dizon said in an interview.
He advised clinicians to find a network within their health systems so they can refer patients to specialized services, such as sex therapy, couples counseling, pelvic rehabilitation, or menopausal experts as needed.
In another study presented at the meeting, Naaman Mehta, MD, of NYU Langone Health, and colleagues reviewed data from 166 healthcare providers who completed a 23-item survey about evaluating and managing sexual health concerns of their patients. Most of the respondents were gynecologic oncologists (93.4%), but one radiation oncologist and 10 other healthcare providers also completed the survey.
Overall, approximately 60% of the respondents routinely asked about the sexual health concerns of their patients, and 98% of these said they believed that sexual health discussions should be held with a gynecologic oncologist. Just over half (54%) also said that the patient should be the one to initiate a discussion of sexual health concerns.
Female providers were significantly more likely to discuss sexual health with patients, compared with male providers, after controlling for the hospital setting and training level, the researchers noted (odds ratio, 1.4;P < .01).
The results suggest a need for more ways to integrate sexual health screening into gynecologic oncologic clinics, the researchers concluded.
The provider survey findings are similar to the results of a survey conducted by Dr. Dizon and colleagues in 2007. In that study, less than half of respondents took a sexual history, but 80% felt there was insufficient time to explore sexual issues.
“It is critical to understand that people with cancer do not expect their oncologists to be sexual health experts, but as with all other side effects caused by treatment and the diagnosis, we can be the ones who recognize it,” Dr. Dizon noted, in an interview.
Common Complaints and Causes
In Dr. Dizon’s experience, local symptoms including vaginal dryness, pain with penetration, and vaginal thinning, are common sexual complaints in women with cancer, as are systemic issues such as lack of interest and menopause-type symptoms.
“For those undergoing radiation, the vaginal tunnel can actually develop adhesions, and if not treated proactively this can lead to vaginal stenosis,” said Dr. Dizon, who was not involved in the studies presented at the meeting.
Comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal conditions can contribute to sexual issues in women with cancer, according to Nora Lersch, DNP, FNP-BC, AOCNP, and Nicole Dreibelbis, CRNP, the authors of other research presented at the meeting.
Culture, religion, fitness level, history of sexual violence, and gender spectrum health also play a role, as do anxiety and depression, dementia, and substance abuse disorders, the authors wrote in their presentation, “Prioritizing Sexual Health in Gynecological Oncology Care.”
Low libido is a frequent complaint across all cancer types, Ms. Dreibelbis, a nurse practitioner specializing in gynecologic oncology at the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“Breast cancer patients, especially those on [aromatase inhibitor] therapy, often experience vaginal dryness and therefore dyspareunia,” she added.
The pelvic floor muscles, with their important role in sexual response, can be weakened by cancer treatment or surgery, and the pudendal nerves, which are the primary nerves responsible for sexual response in women, can be affected as well, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote.
Taking Sex Seriously
Researchers are exploring the impact of different cancer prevention treatments for women to mitigate sexual side effects, as illustrated by another study presented at the meeting.
Dr. Barbara Norquist, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues compared the sexual function and menopausal symptoms of patients at high risk of ovarian carcinoma who underwent either interval salpingectomy/delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) or risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO).
“For patients at high risk for ovarian cancer, surgical removal of the tubes and ovaries is the mainstay of prevention, as screening is not effective at reducing death from ovarian cancer. As a result of surgery, many patients become suddenly postmenopausal from losing their ovaries,” Dr. Norquist said in an interview.
Some patients delay surgery out of concern for health and quality of life, including sexual function, she said.
In the study (known as the WISP trial) the researchers compared data from 166 patients who underwent immediate removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries and 171 who underwent fallopian tube removal and delayed oophorectomy. All patients completed questionnaires about sexual function. The primary outcome was change in sexual function based on the sexual function index (FSFI) from baseline to 6 months after surgery.
Overall, changes in sexual function were significantly greater in the immediate oophorectomy group, compared with the delayed oophorectomy group at 6 months (33% vs 17%) and also at 12 months (43% vs 20%).
A further review of patients using hormone therapy showed that those in the immediate oophorectomy group still had greater decreases in sexual function, compared with the delayed group, though the difference between groups of patients using hormone therapy was less dramatic.
“I was surprised that, even with hormone replacement therapy, patients undergoing removal of the ovaries still had significant detrimental changes to sexual function when compared to those having the tubes removed, although this was even worse in those who could not take HRT,” Dr. Norquist said, in an interview. “I was reassured that menopausal symptoms in general were well managed with HRT, as these patients did not score differently on menopause symptoms, compared with those having their tubes removed,” she said.
Patients deserve accurate information about predicted changes in menopausal symptoms and sexual function as a result of ovary removal, and HRT should be provided when there is no contraindication, Dr. Norquist told this news organization.
Dr. Norquist and colleagues are awaiting the results of clinical trials investigating the safety of salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy in terms of ovarian cancer prevention, but more research is needed to identify optimal management of the menopausal and sexual side effects associated with surgical menopause, she noted.
“Findings from the WISP study show the importance of hormones in women undergoing prophylactic surgery,” Dr. Dizon said. The findings indicate that salpingectomy has less of a negative influence on sexual function compared to removal of the ovaries, and the impact of hormone therapy and the relatively young age of the patients who took hormones reinforces current knowledge about hormones and sex, he added.
Barriers and Solutions
Barriers to asking women with cancer about sexual issues reported by providers include limited time, lack of training in sexual health, a desire to avoid offending the patient or making them uncomfortable, and uncertainty about how to answer the questions, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote in their presentation.
Barriers to asking healthcare providers about their sexual issues reported by patients include the beliefs that the clinician should initiate the discussion, that sexual function will not be taken seriously, and that they might make the provider uncomfortable.
“Fortunately, more information and research has been done on sexual health and gynecological cancer in recent years, so oncologists are becoming more aware of the issues women may have,” said Dr. Lersch who is an oncology nurse practitioner at Providence Franz Cancer Institute in Portland, Oregon, in an interview.
Telling patients early in their cancer treatment about potential sexual side effects and opportunities for help is essential, she added.
Although oncologists have become more aware of the importance of sexual health and well-being for their patients, “I think there has historically been a disconnect in including sexual health education in medical training,” Ms. Dreibelbis said in an interview.
Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis advised a multidimensional approach to managing sexual problems in cancer patients that includes consideration of biological and psychological symptoms, but also social, cultural, and interpersonal factors, in their presentation.
Their suggestions include discussing dyspareunia with their patients, asking for details such as whether the pain is internal or external, whether it occurs with activities outside of sex including masturbation, and whether bleeding is present.
Oncology therapies and surgeries can decrease or eliminate an individual’s ability to produce their own lubricant; for example, removal of the cervix eliminates cervical mucous, which helps with internal lubrication, they wrote in their presentation.
For patients with dyspareunia, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis recommend a vaginal moisturizer especially formulated for vaginal tissue that can be absorbed by the mucosal tissue of the vagina. Use of this type of product can increase the effectiveness of lubricants and help restore integrity of the vaginal tissue. Such moisturizers are available as gels, creams, or suppositories over the counter, and do not contain hormones.
Vaginal estrogen can be helpful for burning, itching, irritation, tissue fragility, and pain with sex, according to Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis. Adequate estrogen therapy can promote normalization of vaginal pH and microflora, as well increase vaginal secretion and reduce pain and dryness with intercourse, the presenters stated in their presentation. In addition, dilator therapy can be used to help prevent vaginal stenosis, and penetration bumpers can help relieve discomfort during intercourse, they wrote.
Looking ahead, more research is needed to serve a wider patient population, Ms. Dreibelbis said, in an interview.
“LGBTQIA [individuals] have not been included in sexual health research and there are more people than ever who identify within this group of people. I know there has also been some very early work on shielding the clitoris from the impacts of radiation, and I believe this is extremely important up-and-coming research,” she said.
Dr. Lersch, Ms. Dreibelbi, Dr. Dizon, Dr. Norquist, Ms. Brewer, and Dr. Mehta had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Decreased sexual function is a side effect of many types of cancer, notably uterine, cervical, ovarian, and breast cancer, that often goes unaddressed, according to the authors of several studies presented at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Patients want to talk about sex, but not necessarily at the start of their diagnosis or treatment, suggest the findings of a study presented at the meeting. Jesse T. Brewer of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City and colleagues enrolled 63 patients who underwent surgery with documented hereditary breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or Lynch syndrome in a cross-sectional survey.
Overall, 86% said that sexuality and intimacy were very or somewhat important, and 78% said that the healthcare team addressing the issue was very or somewhat important, the researchers found. However, only 40% of the respondents said that they wanted to discuss sexuality at the time of diagnosis because the idea was too overwhelming.
Oncologists are more aware of sexual side effects and the potential for sexual issues that persist long after treatment, but many patients may not have opportunities to talk about sexual concerns, said Don S. Dizon, MD, an oncologist specializing in women’s cancers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, in an interview.
“It is important that we [oncologists] be the ones to open the door to these conversations; people with cancer will not bring it up spontaneously, for fear of making their provider uncomfortable, especially if they’ve never been asked about it before,” Dr. Dizon said in an interview.
He advised clinicians to find a network within their health systems so they can refer patients to specialized services, such as sex therapy, couples counseling, pelvic rehabilitation, or menopausal experts as needed.
In another study presented at the meeting, Naaman Mehta, MD, of NYU Langone Health, and colleagues reviewed data from 166 healthcare providers who completed a 23-item survey about evaluating and managing sexual health concerns of their patients. Most of the respondents were gynecologic oncologists (93.4%), but one radiation oncologist and 10 other healthcare providers also completed the survey.
Overall, approximately 60% of the respondents routinely asked about the sexual health concerns of their patients, and 98% of these said they believed that sexual health discussions should be held with a gynecologic oncologist. Just over half (54%) also said that the patient should be the one to initiate a discussion of sexual health concerns.
Female providers were significantly more likely to discuss sexual health with patients, compared with male providers, after controlling for the hospital setting and training level, the researchers noted (odds ratio, 1.4;P < .01).
The results suggest a need for more ways to integrate sexual health screening into gynecologic oncologic clinics, the researchers concluded.
The provider survey findings are similar to the results of a survey conducted by Dr. Dizon and colleagues in 2007. In that study, less than half of respondents took a sexual history, but 80% felt there was insufficient time to explore sexual issues.
“It is critical to understand that people with cancer do not expect their oncologists to be sexual health experts, but as with all other side effects caused by treatment and the diagnosis, we can be the ones who recognize it,” Dr. Dizon noted, in an interview.
Common Complaints and Causes
In Dr. Dizon’s experience, local symptoms including vaginal dryness, pain with penetration, and vaginal thinning, are common sexual complaints in women with cancer, as are systemic issues such as lack of interest and menopause-type symptoms.
“For those undergoing radiation, the vaginal tunnel can actually develop adhesions, and if not treated proactively this can lead to vaginal stenosis,” said Dr. Dizon, who was not involved in the studies presented at the meeting.
Comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal conditions can contribute to sexual issues in women with cancer, according to Nora Lersch, DNP, FNP-BC, AOCNP, and Nicole Dreibelbis, CRNP, the authors of other research presented at the meeting.
Culture, religion, fitness level, history of sexual violence, and gender spectrum health also play a role, as do anxiety and depression, dementia, and substance abuse disorders, the authors wrote in their presentation, “Prioritizing Sexual Health in Gynecological Oncology Care.”
Low libido is a frequent complaint across all cancer types, Ms. Dreibelbis, a nurse practitioner specializing in gynecologic oncology at the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, said in an interview.
“Breast cancer patients, especially those on [aromatase inhibitor] therapy, often experience vaginal dryness and therefore dyspareunia,” she added.
The pelvic floor muscles, with their important role in sexual response, can be weakened by cancer treatment or surgery, and the pudendal nerves, which are the primary nerves responsible for sexual response in women, can be affected as well, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote.
Taking Sex Seriously
Researchers are exploring the impact of different cancer prevention treatments for women to mitigate sexual side effects, as illustrated by another study presented at the meeting.
Dr. Barbara Norquist, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues compared the sexual function and menopausal symptoms of patients at high risk of ovarian carcinoma who underwent either interval salpingectomy/delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) or risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO).
“For patients at high risk for ovarian cancer, surgical removal of the tubes and ovaries is the mainstay of prevention, as screening is not effective at reducing death from ovarian cancer. As a result of surgery, many patients become suddenly postmenopausal from losing their ovaries,” Dr. Norquist said in an interview.
Some patients delay surgery out of concern for health and quality of life, including sexual function, she said.
In the study (known as the WISP trial) the researchers compared data from 166 patients who underwent immediate removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries and 171 who underwent fallopian tube removal and delayed oophorectomy. All patients completed questionnaires about sexual function. The primary outcome was change in sexual function based on the sexual function index (FSFI) from baseline to 6 months after surgery.
Overall, changes in sexual function were significantly greater in the immediate oophorectomy group, compared with the delayed oophorectomy group at 6 months (33% vs 17%) and also at 12 months (43% vs 20%).
A further review of patients using hormone therapy showed that those in the immediate oophorectomy group still had greater decreases in sexual function, compared with the delayed group, though the difference between groups of patients using hormone therapy was less dramatic.
“I was surprised that, even with hormone replacement therapy, patients undergoing removal of the ovaries still had significant detrimental changes to sexual function when compared to those having the tubes removed, although this was even worse in those who could not take HRT,” Dr. Norquist said, in an interview. “I was reassured that menopausal symptoms in general were well managed with HRT, as these patients did not score differently on menopause symptoms, compared with those having their tubes removed,” she said.
Patients deserve accurate information about predicted changes in menopausal symptoms and sexual function as a result of ovary removal, and HRT should be provided when there is no contraindication, Dr. Norquist told this news organization.
Dr. Norquist and colleagues are awaiting the results of clinical trials investigating the safety of salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy in terms of ovarian cancer prevention, but more research is needed to identify optimal management of the menopausal and sexual side effects associated with surgical menopause, she noted.
“Findings from the WISP study show the importance of hormones in women undergoing prophylactic surgery,” Dr. Dizon said. The findings indicate that salpingectomy has less of a negative influence on sexual function compared to removal of the ovaries, and the impact of hormone therapy and the relatively young age of the patients who took hormones reinforces current knowledge about hormones and sex, he added.
Barriers and Solutions
Barriers to asking women with cancer about sexual issues reported by providers include limited time, lack of training in sexual health, a desire to avoid offending the patient or making them uncomfortable, and uncertainty about how to answer the questions, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis wrote in their presentation.
Barriers to asking healthcare providers about their sexual issues reported by patients include the beliefs that the clinician should initiate the discussion, that sexual function will not be taken seriously, and that they might make the provider uncomfortable.
“Fortunately, more information and research has been done on sexual health and gynecological cancer in recent years, so oncologists are becoming more aware of the issues women may have,” said Dr. Lersch who is an oncology nurse practitioner at Providence Franz Cancer Institute in Portland, Oregon, in an interview.
Telling patients early in their cancer treatment about potential sexual side effects and opportunities for help is essential, she added.
Although oncologists have become more aware of the importance of sexual health and well-being for their patients, “I think there has historically been a disconnect in including sexual health education in medical training,” Ms. Dreibelbis said in an interview.
Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis advised a multidimensional approach to managing sexual problems in cancer patients that includes consideration of biological and psychological symptoms, but also social, cultural, and interpersonal factors, in their presentation.
Their suggestions include discussing dyspareunia with their patients, asking for details such as whether the pain is internal or external, whether it occurs with activities outside of sex including masturbation, and whether bleeding is present.
Oncology therapies and surgeries can decrease or eliminate an individual’s ability to produce their own lubricant; for example, removal of the cervix eliminates cervical mucous, which helps with internal lubrication, they wrote in their presentation.
For patients with dyspareunia, Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis recommend a vaginal moisturizer especially formulated for vaginal tissue that can be absorbed by the mucosal tissue of the vagina. Use of this type of product can increase the effectiveness of lubricants and help restore integrity of the vaginal tissue. Such moisturizers are available as gels, creams, or suppositories over the counter, and do not contain hormones.
Vaginal estrogen can be helpful for burning, itching, irritation, tissue fragility, and pain with sex, according to Dr. Lersch and Ms. Dreibelbis. Adequate estrogen therapy can promote normalization of vaginal pH and microflora, as well increase vaginal secretion and reduce pain and dryness with intercourse, the presenters stated in their presentation. In addition, dilator therapy can be used to help prevent vaginal stenosis, and penetration bumpers can help relieve discomfort during intercourse, they wrote.
Looking ahead, more research is needed to serve a wider patient population, Ms. Dreibelbis said, in an interview.
“LGBTQIA [individuals] have not been included in sexual health research and there are more people than ever who identify within this group of people. I know there has also been some very early work on shielding the clitoris from the impacts of radiation, and I believe this is extremely important up-and-coming research,” she said.
Dr. Lersch, Ms. Dreibelbi, Dr. Dizon, Dr. Norquist, Ms. Brewer, and Dr. Mehta had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SGO 2024
Ultrasound and Its Role In Diagnosing and Managing Endometriosis
Introduction: Imaging for Endometriosis — A Necessary Prerequisite
While the gold standard in the diagnosis of endometriosis remains laparoscopy, it is now recognized that thorough evaluation via ultrasound offers an acceptable, less expensive, and less invasive alternative. It is especially useful for the diagnosis of deep infiltrative disease, which penetrates more than 5 mm into the peritoneum, ovarian endometrioma, and when anatomic distortion occurs, such as to the path of the ureter.
Besides establishing the diagnosis, ultrasound imaging has become, along with MRI, the most important aid for proper preoperative planning. Not only does imaging provide the surgeon and patient with knowledge regarding the extent of the upcoming procedure, but it also allows the minimally invasive gynecologic (MIG) surgeon to involve colleagues, such as colorectal surgeons or urologists. For example, deep infiltrative endometriosis penetrating into the bowel mucosa will require a discoid or segmental bowel resection.
While many endometriosis experts rely on MRI, many MIG surgeons are dependent on ultrasound. I would not consider taking a patient with signs and symptoms suggestive of endometriosis to surgery without 2D/3D transvaginal ultrasound. If the patient possesses a uterus, a saline-infused sonogram is performed to potentially diagnose adenomyosis.
It is a pleasure and honor to welcome Professor Caterina Exacoustos MD, PhD, associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata,” to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery to discuss “Ultrasound and Its Role in the Diagnosis of and Management of Endometriosis, Including DIE.”
Prof. Exacoustos’ main areas of interest are endometriosis and benign diseases including uterine pathology and infertility. Her extensive body of work comprises over 120 scientific publications and numerous book chapters both in English and in Italian.
Prof. Exacoustos continues to be one of the most well respected lecturers speaking about ultrasound throughout the world.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest to report.
Ultrasound and Its Role In Diagnosing and Managing Endometriosis
Endometriosis affects approximately 10%-20% of premenopausal women worldwide. It is the leading cause of chronic pelvic pain, is often associated with infertility, and has a significant impact on quality of life. Although the natural history of endometriosis remains unknown, emerging evidence suggests that the pathophysiological steps of initiation and development of endometriosis must occur earlier in the lifespan. Most notably, the onset of endometriosis-associated pain symptoms is often reported during adolescence and young adulthood.1
While many patients with endometriosis are referred with dysmenorrhea at a young age, at age ≤ 25 years,2 symptoms are often highly underestimated and considered to be normal and transient.3,4 Clinical and pelvic exams are often negative in young women, and delays in endometriosis diagnosis are well known.
The presentation of primary dysmenorrhea with no anatomical cause embodies the paradigm that dysmenorrhea in adolescents is most often an insignificant disorder. This perspective is probably a root cause of delayed endometriosis diagnosis in young patients. However, another issue behind delayed diagnosis is the reluctance of the physician to perform a diagnostic laparoscopy — historically the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis — for seemingly common symptoms such as dysmenorrhea in young patients.
Today we know that there are typical aspects of ultrasound imaging that identify endometriosis in the pelvis, and notably, the 2022 European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) endometriosis guideline5 recognizes imaging (ultrasound or MRI) as the standard for endometriosis diagnosis without requiring laparoscopic or histological confirmation.
An early and noninvasive method of diagnosis aids in timely diagnosis and provides for the timely initiation of medical management to improve quality of life and prevent progression of disease (Figure 1).
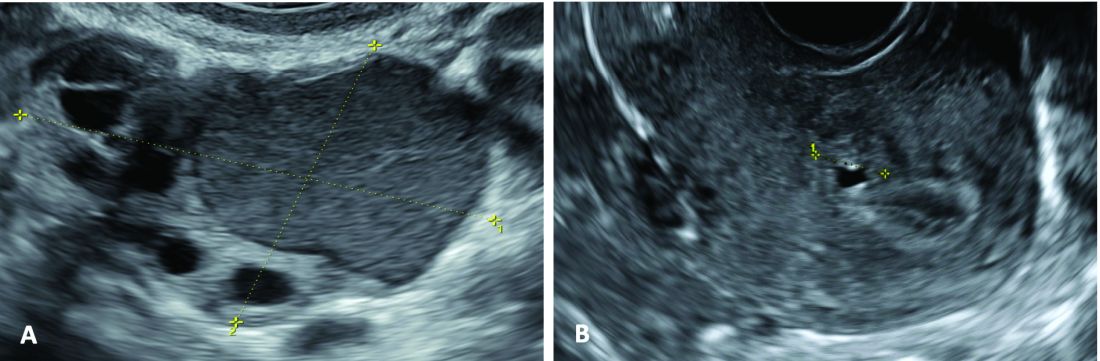
(A. Transvaginal ultrasound appearance of a small ovarian endometrioma in a 16-year-old girl. Note the unilocular cyst with ground glass echogenicity surrounded by multifollicular ovarian tissue. B. Ultrasound image of a retroverted uterus of an 18-year-old girl with focal adenomyosis of the posterior wall. Note the round cystic anechoic areas in the inner myometrium or junctional zone. The small intra-myometrial cyst is surrounded by a hyperechoic ring).
Indeed, the typical appearance of endometriotic pelvic lesions on transvaginal sonography, such as endometriomas and rectal deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) — as well as adenomyosis – can be medically treated without histologic confirmation .
When surgery is advisable, ultrasound findings also play a valuable role in presurgical staging, planning, and counseling for patients of all ages. Determining the extent and location of DIE preoperatively, for instance, facilitates the engagement of the appropriate surgical specialists so that multiple surgeries can be avoided. It also enables patients to be optimally informed before surgery of possible outcomes and complications.
Moreover, in the context of infertility, ultrasound can be a valuable tool for understanding uterine pathology and assessing for adenomyosis so that affected patients may be treated surgically or medically before turning to assisted reproductive technology.
Uniformity, Standardization in the Sonographic Assessment
In Europe, as in the United States, transvaginal sonography (TVS) is the first-line imaging tool for the diagnosis and management of endometriosis. In Europe, many ob.gyns. perform ultrasound themselves, as do treating surgeons. When diagnostic findings are negative but clinical suspicion is high, MRI is often utilized. Laparoscopy may then be considered in patients with negative imaging results.
Efforts to standardize terms, definitions, measurements, and sonographic features of different types of endometriosis have been made to make it easier for physicians to share data and communicate with each other. A lack of uniformity has contributed to variability in the reported diagnostic accuracy of TVS.
About 10 years ago, in one such effort, we assessed the accuracy of TVS for DIE by comparing TVS results with laparoscopic/histologic findings, and developed an ultrasound mapping system to accurately record the location, size and depth of lesions visualized by TVS. The accuracy of TVS ranged from 76% for the diagnosis of vaginal endometriosis to 97% for the diagnosis of bladder lesions and posterior cul-de-sac obliteration. Accuracy was 93% and 91% for detecting ureteral involvement (right and left); 87% for uterosacral ligament endometriotic lesions; and 87% for parametrial involvement.6
Shortly after, with a focus on DIE, expert sonographers and physician-sonographers from across Europe — as well as some experts from Australia, Japan, Brazil, Chile, and the United States (Y. Osuga from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School) — came together to agree on a uniform approach to the sonographic evaluation for suspected endometriosis and a standardization of terminology.
The consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group details four steps for examining women with suspected DIE: 1) Evaluation of the uterus and adnexa, 2) evaluation of transvaginal sonographic “soft markers” (ie. site-specific tenderness and ovarian mobility), 3) assessment of the status of the posterior cul-de-sac using real-time ultrasound-based “sliding sign,” and 4) assessment for DIE nodules in the anterior and posterior compartments.7
Our paper describing a mapping system and the IDEA paper describe how to detect deep endometriosis in the pelvis by utilizing an ultrasound view of normal anatomy and pelvic organ structure to provide landmarks for accurately defining the site of DIE lesions (Figure 2).
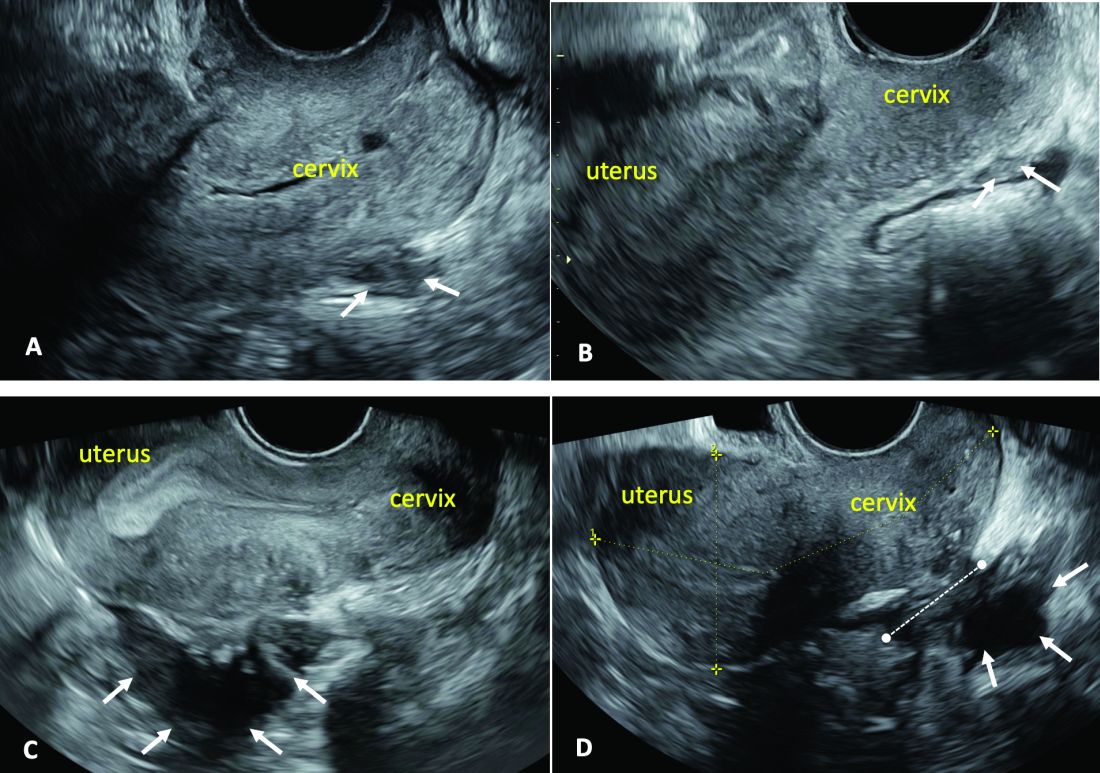
(A. Ultrasound appearance of a small DIE lesion of the retrocervical area [white arrows], which involved the torus uterinum and the right uterosacral ligament [USL]. The lesion appears as hypoechoic tissue with irregular margins caused by the fibrosis induced by the DIE. B. TVS appearance of small nodules of DIE of the left USL. Note the small retrocervical DIE lesion [white arrows], which appears hypoechoic due to the infiltration of the hyperechoic USL. C) Ultrasound appearance of a DIE nodule of the recto-sigmoid wall. Note the hypoechoic thickening of the muscular layers of the bowel wall attached to the corpus of the uterus and the adenomyosis of the posterior wall. The retrocervical area is free. D. TVS appearance of nodules of DIE of the lower rectal wall. Note the hypoechoic lesion [white arrows] of the rectum is attached to a retrocervical DIE fibrosis of the torus and USL [white dotted line]).
So-called rectovaginal endometriosis can be well assessed, for instance, since the involvement of the rectum, sigmoid colon, vaginal wall, rectovaginal septum, and posterior cul-de-sac uterosacral ligament can be seen by ultrasound as a single structure, making the location, size, and depth of any lesions discernible.
Again, this evaluation of the extent of disease is important for presurgical assessment so the surgeon can organize the right team and time of surgery and so the patient can be counseled on the advantages and possible complications of the treatment.
Notably, an accurate ultrasound description of pelvic endometriosis is helpful for accurate classification of disease. Endometriosis classification systems such as that of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL)8 and the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM),9 as well as the #Enzian surgical description system,10 have been adapted to cover findings from ultrasound as well as MRI imaging.
A Systematic Evaluation
In keeping with the IDEA consensus opinion and based on our years of experience at the University of Rome, I advise that patients with typical pain symptoms of endometriosis or infertility undergo an accurate sonographic assessment of the pelvis with particular evaluation not only of the uterus and ovaries but of all pelvic retroperitoneal spaces.
The TVS examination should start with a slightly filled bladder, which permits a better evaluation of the bladder walls and the presence of endometriotic nodules. These nodules appear as hyperechoic linear or spherical lesions bulging toward the lumen and involving the serosa, muscularis, or (sub)mucosa of the bladder.
Then, an accurate evaluation of the uterus in 2D and 3D permits the diagnosis of adenomyosis. 3D sonographic evaluation of the myometrium and of the junctional zone are important; alteration and infiltration of the junctional zone and the presence of small adenomyotic cysts in the inner or outer myometrium are direct, specific signs of adenomyosis and should be ruled out in patients with dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, infertility, and pregnancy complications.
Endometriomas of the ovaries can be easily detected as having the typical appearance of a cyst with ground glass content. Adhesions of the ovaries and the uterus also should be evaluated with a dynamic ultrasound approach that utilizes the sliding sign and mobilization by palpation of the organs during the TVS scan.
Finally, the posterior and lateral retroperitoneal compartments should be carefully evaluated, with symptoms guiding the TVS examination whenever possible. Deep endometriotic nodules of the rectum appear as hypoechoic lesions or linear or nodular retroperitoneal thickening with irregular borders, penetrating into the intestinal wall and distorting its normal structure. In young patients, it seems very important to assess for small lesions below the peritoneum between the vagina and rectum, and in the parametria and around the ureter and nerves — lesions that, notably, would not be seen by diagnostic laparoscopy.
The Evaluation of Young Patients
In adolescent and young patients, endometriosis and adenomyosis are often present with small lesions and shallow tissue invasion, making a very careful and experienced approach to ultrasound essential for detection. Endometriomas are often of small diameter, and DIE is not always easily diagnosed because retroperitoneal lesions are similarly very small.
In a series of 270 adolescents (ages 12-20) who were referred to our outpatient gynecologic ultrasound unit over a 5-year period for various indications, at least one ultrasound feature of endometriosis was observed in 13.3%. In those with dysmenorrhea, the detection of endometriosis increased to 21%. Endometrioma was the most common type of endometriosis we found in the study, but DIE and adenomyosis were found in 4%-11%.
Although endometriotic lesions typically are small in young patients, they are often associated with severe pain symptoms, including chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dysuria, and dyschezia, all of which can have a serious effect on the quality of life of these young women. These symptoms keep them away from school during menstruation, away from sports, and cause painful intercourse and infertility. In young patients, an accurate TVS can provide a lot of information, and the ability to detect retroperitoneal endometriotic lesions and adenomyosis is probably better than with purely diagnostic laparoscopy, which would evaluate only superficial lesions.
TVS or, when needed, transrectal ultrasound, can enable adequate treatment and follow-up of the disease and its symptoms. There are no guidelines recommending adequate follow-up times to evaluate the effectiveness of medical therapy in patients with ultrasound signs of endometriosis. (Likewise, there are no indications for follow-up in patients with severe dysmenorrhea without ultrasound signs of endometriosis.) Certainly, our studies suggest careful evaluation over time of young patients with severe dysmenorrhea by serial ultrasound scans. With such follow-up, disease progress can be monitored and the medical or surgical treatment approach modified if needed.
The diagnosis of endometriosis at a young age has significant benefits not only in avoiding or reducing progression of the disease, but also in improving quality of life and aiding women in their desire for pregnancy.
Dr. Exacoustos is associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata.” She has no conflicts of interest to report.
References
1. Zondervan KT et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1244-56.
2. Greene R et al. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:32-9.
3. Chapron C et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:S7-12.
4. Randhawa AE et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2021;34:643-8.
5. Becker CM et al. Hum Reprod Open. 2022(2):hoac009.
6. Exacoustos C et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:143-9. 7. Guerriero S et al. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48(3):318-32.
8. Abrao MS et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1941-50.9. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril. 1997;67:817-21. 10. Keckstein J et al. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021;100:1165-75.
11. Martire FG et al. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(5):1049-57.
Introduction: Imaging for Endometriosis — A Necessary Prerequisite
While the gold standard in the diagnosis of endometriosis remains laparoscopy, it is now recognized that thorough evaluation via ultrasound offers an acceptable, less expensive, and less invasive alternative. It is especially useful for the diagnosis of deep infiltrative disease, which penetrates more than 5 mm into the peritoneum, ovarian endometrioma, and when anatomic distortion occurs, such as to the path of the ureter.
Besides establishing the diagnosis, ultrasound imaging has become, along with MRI, the most important aid for proper preoperative planning. Not only does imaging provide the surgeon and patient with knowledge regarding the extent of the upcoming procedure, but it also allows the minimally invasive gynecologic (MIG) surgeon to involve colleagues, such as colorectal surgeons or urologists. For example, deep infiltrative endometriosis penetrating into the bowel mucosa will require a discoid or segmental bowel resection.
While many endometriosis experts rely on MRI, many MIG surgeons are dependent on ultrasound. I would not consider taking a patient with signs and symptoms suggestive of endometriosis to surgery without 2D/3D transvaginal ultrasound. If the patient possesses a uterus, a saline-infused sonogram is performed to potentially diagnose adenomyosis.
It is a pleasure and honor to welcome Professor Caterina Exacoustos MD, PhD, associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata,” to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery to discuss “Ultrasound and Its Role in the Diagnosis of and Management of Endometriosis, Including DIE.”
Prof. Exacoustos’ main areas of interest are endometriosis and benign diseases including uterine pathology and infertility. Her extensive body of work comprises over 120 scientific publications and numerous book chapters both in English and in Italian.
Prof. Exacoustos continues to be one of the most well respected lecturers speaking about ultrasound throughout the world.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest to report.
Ultrasound and Its Role In Diagnosing and Managing Endometriosis
Endometriosis affects approximately 10%-20% of premenopausal women worldwide. It is the leading cause of chronic pelvic pain, is often associated with infertility, and has a significant impact on quality of life. Although the natural history of endometriosis remains unknown, emerging evidence suggests that the pathophysiological steps of initiation and development of endometriosis must occur earlier in the lifespan. Most notably, the onset of endometriosis-associated pain symptoms is often reported during adolescence and young adulthood.1
While many patients with endometriosis are referred with dysmenorrhea at a young age, at age ≤ 25 years,2 symptoms are often highly underestimated and considered to be normal and transient.3,4 Clinical and pelvic exams are often negative in young women, and delays in endometriosis diagnosis are well known.
The presentation of primary dysmenorrhea with no anatomical cause embodies the paradigm that dysmenorrhea in adolescents is most often an insignificant disorder. This perspective is probably a root cause of delayed endometriosis diagnosis in young patients. However, another issue behind delayed diagnosis is the reluctance of the physician to perform a diagnostic laparoscopy — historically the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis — for seemingly common symptoms such as dysmenorrhea in young patients.
Today we know that there are typical aspects of ultrasound imaging that identify endometriosis in the pelvis, and notably, the 2022 European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) endometriosis guideline5 recognizes imaging (ultrasound or MRI) as the standard for endometriosis diagnosis without requiring laparoscopic or histological confirmation.
An early and noninvasive method of diagnosis aids in timely diagnosis and provides for the timely initiation of medical management to improve quality of life and prevent progression of disease (Figure 1).

(A. Transvaginal ultrasound appearance of a small ovarian endometrioma in a 16-year-old girl. Note the unilocular cyst with ground glass echogenicity surrounded by multifollicular ovarian tissue. B. Ultrasound image of a retroverted uterus of an 18-year-old girl with focal adenomyosis of the posterior wall. Note the round cystic anechoic areas in the inner myometrium or junctional zone. The small intra-myometrial cyst is surrounded by a hyperechoic ring).
Indeed, the typical appearance of endometriotic pelvic lesions on transvaginal sonography, such as endometriomas and rectal deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) — as well as adenomyosis – can be medically treated without histologic confirmation .
When surgery is advisable, ultrasound findings also play a valuable role in presurgical staging, planning, and counseling for patients of all ages. Determining the extent and location of DIE preoperatively, for instance, facilitates the engagement of the appropriate surgical specialists so that multiple surgeries can be avoided. It also enables patients to be optimally informed before surgery of possible outcomes and complications.
Moreover, in the context of infertility, ultrasound can be a valuable tool for understanding uterine pathology and assessing for adenomyosis so that affected patients may be treated surgically or medically before turning to assisted reproductive technology.
Uniformity, Standardization in the Sonographic Assessment
In Europe, as in the United States, transvaginal sonography (TVS) is the first-line imaging tool for the diagnosis and management of endometriosis. In Europe, many ob.gyns. perform ultrasound themselves, as do treating surgeons. When diagnostic findings are negative but clinical suspicion is high, MRI is often utilized. Laparoscopy may then be considered in patients with negative imaging results.
Efforts to standardize terms, definitions, measurements, and sonographic features of different types of endometriosis have been made to make it easier for physicians to share data and communicate with each other. A lack of uniformity has contributed to variability in the reported diagnostic accuracy of TVS.
About 10 years ago, in one such effort, we assessed the accuracy of TVS for DIE by comparing TVS results with laparoscopic/histologic findings, and developed an ultrasound mapping system to accurately record the location, size and depth of lesions visualized by TVS. The accuracy of TVS ranged from 76% for the diagnosis of vaginal endometriosis to 97% for the diagnosis of bladder lesions and posterior cul-de-sac obliteration. Accuracy was 93% and 91% for detecting ureteral involvement (right and left); 87% for uterosacral ligament endometriotic lesions; and 87% for parametrial involvement.6
Shortly after, with a focus on DIE, expert sonographers and physician-sonographers from across Europe — as well as some experts from Australia, Japan, Brazil, Chile, and the United States (Y. Osuga from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School) — came together to agree on a uniform approach to the sonographic evaluation for suspected endometriosis and a standardization of terminology.
The consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group details four steps for examining women with suspected DIE: 1) Evaluation of the uterus and adnexa, 2) evaluation of transvaginal sonographic “soft markers” (ie. site-specific tenderness and ovarian mobility), 3) assessment of the status of the posterior cul-de-sac using real-time ultrasound-based “sliding sign,” and 4) assessment for DIE nodules in the anterior and posterior compartments.7
Our paper describing a mapping system and the IDEA paper describe how to detect deep endometriosis in the pelvis by utilizing an ultrasound view of normal anatomy and pelvic organ structure to provide landmarks for accurately defining the site of DIE lesions (Figure 2).

(A. Ultrasound appearance of a small DIE lesion of the retrocervical area [white arrows], which involved the torus uterinum and the right uterosacral ligament [USL]. The lesion appears as hypoechoic tissue with irregular margins caused by the fibrosis induced by the DIE. B. TVS appearance of small nodules of DIE of the left USL. Note the small retrocervical DIE lesion [white arrows], which appears hypoechoic due to the infiltration of the hyperechoic USL. C) Ultrasound appearance of a DIE nodule of the recto-sigmoid wall. Note the hypoechoic thickening of the muscular layers of the bowel wall attached to the corpus of the uterus and the adenomyosis of the posterior wall. The retrocervical area is free. D. TVS appearance of nodules of DIE of the lower rectal wall. Note the hypoechoic lesion [white arrows] of the rectum is attached to a retrocervical DIE fibrosis of the torus and USL [white dotted line]).
So-called rectovaginal endometriosis can be well assessed, for instance, since the involvement of the rectum, sigmoid colon, vaginal wall, rectovaginal septum, and posterior cul-de-sac uterosacral ligament can be seen by ultrasound as a single structure, making the location, size, and depth of any lesions discernible.
Again, this evaluation of the extent of disease is important for presurgical assessment so the surgeon can organize the right team and time of surgery and so the patient can be counseled on the advantages and possible complications of the treatment.
Notably, an accurate ultrasound description of pelvic endometriosis is helpful for accurate classification of disease. Endometriosis classification systems such as that of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL)8 and the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM),9 as well as the #Enzian surgical description system,10 have been adapted to cover findings from ultrasound as well as MRI imaging.
A Systematic Evaluation
In keeping with the IDEA consensus opinion and based on our years of experience at the University of Rome, I advise that patients with typical pain symptoms of endometriosis or infertility undergo an accurate sonographic assessment of the pelvis with particular evaluation not only of the uterus and ovaries but of all pelvic retroperitoneal spaces.
The TVS examination should start with a slightly filled bladder, which permits a better evaluation of the bladder walls and the presence of endometriotic nodules. These nodules appear as hyperechoic linear or spherical lesions bulging toward the lumen and involving the serosa, muscularis, or (sub)mucosa of the bladder.
Then, an accurate evaluation of the uterus in 2D and 3D permits the diagnosis of adenomyosis. 3D sonographic evaluation of the myometrium and of the junctional zone are important; alteration and infiltration of the junctional zone and the presence of small adenomyotic cysts in the inner or outer myometrium are direct, specific signs of adenomyosis and should be ruled out in patients with dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, infertility, and pregnancy complications.
Endometriomas of the ovaries can be easily detected as having the typical appearance of a cyst with ground glass content. Adhesions of the ovaries and the uterus also should be evaluated with a dynamic ultrasound approach that utilizes the sliding sign and mobilization by palpation of the organs during the TVS scan.
Finally, the posterior and lateral retroperitoneal compartments should be carefully evaluated, with symptoms guiding the TVS examination whenever possible. Deep endometriotic nodules of the rectum appear as hypoechoic lesions or linear or nodular retroperitoneal thickening with irregular borders, penetrating into the intestinal wall and distorting its normal structure. In young patients, it seems very important to assess for small lesions below the peritoneum between the vagina and rectum, and in the parametria and around the ureter and nerves — lesions that, notably, would not be seen by diagnostic laparoscopy.
The Evaluation of Young Patients
In adolescent and young patients, endometriosis and adenomyosis are often present with small lesions and shallow tissue invasion, making a very careful and experienced approach to ultrasound essential for detection. Endometriomas are often of small diameter, and DIE is not always easily diagnosed because retroperitoneal lesions are similarly very small.
In a series of 270 adolescents (ages 12-20) who were referred to our outpatient gynecologic ultrasound unit over a 5-year period for various indications, at least one ultrasound feature of endometriosis was observed in 13.3%. In those with dysmenorrhea, the detection of endometriosis increased to 21%. Endometrioma was the most common type of endometriosis we found in the study, but DIE and adenomyosis were found in 4%-11%.
Although endometriotic lesions typically are small in young patients, they are often associated with severe pain symptoms, including chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dysuria, and dyschezia, all of which can have a serious effect on the quality of life of these young women. These symptoms keep them away from school during menstruation, away from sports, and cause painful intercourse and infertility. In young patients, an accurate TVS can provide a lot of information, and the ability to detect retroperitoneal endometriotic lesions and adenomyosis is probably better than with purely diagnostic laparoscopy, which would evaluate only superficial lesions.
TVS or, when needed, transrectal ultrasound, can enable adequate treatment and follow-up of the disease and its symptoms. There are no guidelines recommending adequate follow-up times to evaluate the effectiveness of medical therapy in patients with ultrasound signs of endometriosis. (Likewise, there are no indications for follow-up in patients with severe dysmenorrhea without ultrasound signs of endometriosis.) Certainly, our studies suggest careful evaluation over time of young patients with severe dysmenorrhea by serial ultrasound scans. With such follow-up, disease progress can be monitored and the medical or surgical treatment approach modified if needed.
The diagnosis of endometriosis at a young age has significant benefits not only in avoiding or reducing progression of the disease, but also in improving quality of life and aiding women in their desire for pregnancy.
Dr. Exacoustos is associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata.” She has no conflicts of interest to report.
References
1. Zondervan KT et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1244-56.
2. Greene R et al. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:32-9.
3. Chapron C et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:S7-12.
4. Randhawa AE et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2021;34:643-8.
5. Becker CM et al. Hum Reprod Open. 2022(2):hoac009.
6. Exacoustos C et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:143-9. 7. Guerriero S et al. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48(3):318-32.
8. Abrao MS et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1941-50.9. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril. 1997;67:817-21. 10. Keckstein J et al. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021;100:1165-75.
11. Martire FG et al. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(5):1049-57.
Introduction: Imaging for Endometriosis — A Necessary Prerequisite
While the gold standard in the diagnosis of endometriosis remains laparoscopy, it is now recognized that thorough evaluation via ultrasound offers an acceptable, less expensive, and less invasive alternative. It is especially useful for the diagnosis of deep infiltrative disease, which penetrates more than 5 mm into the peritoneum, ovarian endometrioma, and when anatomic distortion occurs, such as to the path of the ureter.
Besides establishing the diagnosis, ultrasound imaging has become, along with MRI, the most important aid for proper preoperative planning. Not only does imaging provide the surgeon and patient with knowledge regarding the extent of the upcoming procedure, but it also allows the minimally invasive gynecologic (MIG) surgeon to involve colleagues, such as colorectal surgeons or urologists. For example, deep infiltrative endometriosis penetrating into the bowel mucosa will require a discoid or segmental bowel resection.
While many endometriosis experts rely on MRI, many MIG surgeons are dependent on ultrasound. I would not consider taking a patient with signs and symptoms suggestive of endometriosis to surgery without 2D/3D transvaginal ultrasound. If the patient possesses a uterus, a saline-infused sonogram is performed to potentially diagnose adenomyosis.
It is a pleasure and honor to welcome Professor Caterina Exacoustos MD, PhD, associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata,” to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery to discuss “Ultrasound and Its Role in the Diagnosis of and Management of Endometriosis, Including DIE.”
Prof. Exacoustos’ main areas of interest are endometriosis and benign diseases including uterine pathology and infertility. Her extensive body of work comprises over 120 scientific publications and numerous book chapters both in English and in Italian.
Prof. Exacoustos continues to be one of the most well respected lecturers speaking about ultrasound throughout the world.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest to report.
Ultrasound and Its Role In Diagnosing and Managing Endometriosis
Endometriosis affects approximately 10%-20% of premenopausal women worldwide. It is the leading cause of chronic pelvic pain, is often associated with infertility, and has a significant impact on quality of life. Although the natural history of endometriosis remains unknown, emerging evidence suggests that the pathophysiological steps of initiation and development of endometriosis must occur earlier in the lifespan. Most notably, the onset of endometriosis-associated pain symptoms is often reported during adolescence and young adulthood.1
While many patients with endometriosis are referred with dysmenorrhea at a young age, at age ≤ 25 years,2 symptoms are often highly underestimated and considered to be normal and transient.3,4 Clinical and pelvic exams are often negative in young women, and delays in endometriosis diagnosis are well known.
The presentation of primary dysmenorrhea with no anatomical cause embodies the paradigm that dysmenorrhea in adolescents is most often an insignificant disorder. This perspective is probably a root cause of delayed endometriosis diagnosis in young patients. However, another issue behind delayed diagnosis is the reluctance of the physician to perform a diagnostic laparoscopy — historically the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis — for seemingly common symptoms such as dysmenorrhea in young patients.
Today we know that there are typical aspects of ultrasound imaging that identify endometriosis in the pelvis, and notably, the 2022 European Society for Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) endometriosis guideline5 recognizes imaging (ultrasound or MRI) as the standard for endometriosis diagnosis without requiring laparoscopic or histological confirmation.
An early and noninvasive method of diagnosis aids in timely diagnosis and provides for the timely initiation of medical management to improve quality of life and prevent progression of disease (Figure 1).

(A. Transvaginal ultrasound appearance of a small ovarian endometrioma in a 16-year-old girl. Note the unilocular cyst with ground glass echogenicity surrounded by multifollicular ovarian tissue. B. Ultrasound image of a retroverted uterus of an 18-year-old girl with focal adenomyosis of the posterior wall. Note the round cystic anechoic areas in the inner myometrium or junctional zone. The small intra-myometrial cyst is surrounded by a hyperechoic ring).
Indeed, the typical appearance of endometriotic pelvic lesions on transvaginal sonography, such as endometriomas and rectal deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) — as well as adenomyosis – can be medically treated without histologic confirmation .
When surgery is advisable, ultrasound findings also play a valuable role in presurgical staging, planning, and counseling for patients of all ages. Determining the extent and location of DIE preoperatively, for instance, facilitates the engagement of the appropriate surgical specialists so that multiple surgeries can be avoided. It also enables patients to be optimally informed before surgery of possible outcomes and complications.
Moreover, in the context of infertility, ultrasound can be a valuable tool for understanding uterine pathology and assessing for adenomyosis so that affected patients may be treated surgically or medically before turning to assisted reproductive technology.
Uniformity, Standardization in the Sonographic Assessment
In Europe, as in the United States, transvaginal sonography (TVS) is the first-line imaging tool for the diagnosis and management of endometriosis. In Europe, many ob.gyns. perform ultrasound themselves, as do treating surgeons. When diagnostic findings are negative but clinical suspicion is high, MRI is often utilized. Laparoscopy may then be considered in patients with negative imaging results.
Efforts to standardize terms, definitions, measurements, and sonographic features of different types of endometriosis have been made to make it easier for physicians to share data and communicate with each other. A lack of uniformity has contributed to variability in the reported diagnostic accuracy of TVS.
About 10 years ago, in one such effort, we assessed the accuracy of TVS for DIE by comparing TVS results with laparoscopic/histologic findings, and developed an ultrasound mapping system to accurately record the location, size and depth of lesions visualized by TVS. The accuracy of TVS ranged from 76% for the diagnosis of vaginal endometriosis to 97% for the diagnosis of bladder lesions and posterior cul-de-sac obliteration. Accuracy was 93% and 91% for detecting ureteral involvement (right and left); 87% for uterosacral ligament endometriotic lesions; and 87% for parametrial involvement.6
Shortly after, with a focus on DIE, expert sonographers and physician-sonographers from across Europe — as well as some experts from Australia, Japan, Brazil, Chile, and the United States (Y. Osuga from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School) — came together to agree on a uniform approach to the sonographic evaluation for suspected endometriosis and a standardization of terminology.
The consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group details four steps for examining women with suspected DIE: 1) Evaluation of the uterus and adnexa, 2) evaluation of transvaginal sonographic “soft markers” (ie. site-specific tenderness and ovarian mobility), 3) assessment of the status of the posterior cul-de-sac using real-time ultrasound-based “sliding sign,” and 4) assessment for DIE nodules in the anterior and posterior compartments.7
Our paper describing a mapping system and the IDEA paper describe how to detect deep endometriosis in the pelvis by utilizing an ultrasound view of normal anatomy and pelvic organ structure to provide landmarks for accurately defining the site of DIE lesions (Figure 2).

(A. Ultrasound appearance of a small DIE lesion of the retrocervical area [white arrows], which involved the torus uterinum and the right uterosacral ligament [USL]. The lesion appears as hypoechoic tissue with irregular margins caused by the fibrosis induced by the DIE. B. TVS appearance of small nodules of DIE of the left USL. Note the small retrocervical DIE lesion [white arrows], which appears hypoechoic due to the infiltration of the hyperechoic USL. C) Ultrasound appearance of a DIE nodule of the recto-sigmoid wall. Note the hypoechoic thickening of the muscular layers of the bowel wall attached to the corpus of the uterus and the adenomyosis of the posterior wall. The retrocervical area is free. D. TVS appearance of nodules of DIE of the lower rectal wall. Note the hypoechoic lesion [white arrows] of the rectum is attached to a retrocervical DIE fibrosis of the torus and USL [white dotted line]).
So-called rectovaginal endometriosis can be well assessed, for instance, since the involvement of the rectum, sigmoid colon, vaginal wall, rectovaginal septum, and posterior cul-de-sac uterosacral ligament can be seen by ultrasound as a single structure, making the location, size, and depth of any lesions discernible.
Again, this evaluation of the extent of disease is important for presurgical assessment so the surgeon can organize the right team and time of surgery and so the patient can be counseled on the advantages and possible complications of the treatment.
Notably, an accurate ultrasound description of pelvic endometriosis is helpful for accurate classification of disease. Endometriosis classification systems such as that of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL)8 and the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM),9 as well as the #Enzian surgical description system,10 have been adapted to cover findings from ultrasound as well as MRI imaging.
A Systematic Evaluation
In keeping with the IDEA consensus opinion and based on our years of experience at the University of Rome, I advise that patients with typical pain symptoms of endometriosis or infertility undergo an accurate sonographic assessment of the pelvis with particular evaluation not only of the uterus and ovaries but of all pelvic retroperitoneal spaces.
The TVS examination should start with a slightly filled bladder, which permits a better evaluation of the bladder walls and the presence of endometriotic nodules. These nodules appear as hyperechoic linear or spherical lesions bulging toward the lumen and involving the serosa, muscularis, or (sub)mucosa of the bladder.
Then, an accurate evaluation of the uterus in 2D and 3D permits the diagnosis of adenomyosis. 3D sonographic evaluation of the myometrium and of the junctional zone are important; alteration and infiltration of the junctional zone and the presence of small adenomyotic cysts in the inner or outer myometrium are direct, specific signs of adenomyosis and should be ruled out in patients with dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, infertility, and pregnancy complications.
Endometriomas of the ovaries can be easily detected as having the typical appearance of a cyst with ground glass content. Adhesions of the ovaries and the uterus also should be evaluated with a dynamic ultrasound approach that utilizes the sliding sign and mobilization by palpation of the organs during the TVS scan.
Finally, the posterior and lateral retroperitoneal compartments should be carefully evaluated, with symptoms guiding the TVS examination whenever possible. Deep endometriotic nodules of the rectum appear as hypoechoic lesions or linear or nodular retroperitoneal thickening with irregular borders, penetrating into the intestinal wall and distorting its normal structure. In young patients, it seems very important to assess for small lesions below the peritoneum between the vagina and rectum, and in the parametria and around the ureter and nerves — lesions that, notably, would not be seen by diagnostic laparoscopy.
The Evaluation of Young Patients
In adolescent and young patients, endometriosis and adenomyosis are often present with small lesions and shallow tissue invasion, making a very careful and experienced approach to ultrasound essential for detection. Endometriomas are often of small diameter, and DIE is not always easily diagnosed because retroperitoneal lesions are similarly very small.
In a series of 270 adolescents (ages 12-20) who were referred to our outpatient gynecologic ultrasound unit over a 5-year period for various indications, at least one ultrasound feature of endometriosis was observed in 13.3%. In those with dysmenorrhea, the detection of endometriosis increased to 21%. Endometrioma was the most common type of endometriosis we found in the study, but DIE and adenomyosis were found in 4%-11%.
Although endometriotic lesions typically are small in young patients, they are often associated with severe pain symptoms, including chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dysuria, and dyschezia, all of which can have a serious effect on the quality of life of these young women. These symptoms keep them away from school during menstruation, away from sports, and cause painful intercourse and infertility. In young patients, an accurate TVS can provide a lot of information, and the ability to detect retroperitoneal endometriotic lesions and adenomyosis is probably better than with purely diagnostic laparoscopy, which would evaluate only superficial lesions.
TVS or, when needed, transrectal ultrasound, can enable adequate treatment and follow-up of the disease and its symptoms. There are no guidelines recommending adequate follow-up times to evaluate the effectiveness of medical therapy in patients with ultrasound signs of endometriosis. (Likewise, there are no indications for follow-up in patients with severe dysmenorrhea without ultrasound signs of endometriosis.) Certainly, our studies suggest careful evaluation over time of young patients with severe dysmenorrhea by serial ultrasound scans. With such follow-up, disease progress can be monitored and the medical or surgical treatment approach modified if needed.
The diagnosis of endometriosis at a young age has significant benefits not only in avoiding or reducing progression of the disease, but also in improving quality of life and aiding women in their desire for pregnancy.
Dr. Exacoustos is associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata.” She has no conflicts of interest to report.
References
1. Zondervan KT et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1244-56.
2. Greene R et al. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:32-9.
3. Chapron C et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:S7-12.
4. Randhawa AE et al. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2021;34:643-8.
5. Becker CM et al. Hum Reprod Open. 2022(2):hoac009.
6. Exacoustos C et al. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:143-9. 7. Guerriero S et al. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48(3):318-32.
8. Abrao MS et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1941-50.9. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril. 1997;67:817-21. 10. Keckstein J et al. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021;100:1165-75.
11. Martire FG et al. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(5):1049-57.
New Data: Black Women More Likely to Die From Common Endometrial Cancer Subtype
A recent analysis identified significant disparities in survival outcomes as well as clinical and genetic features between Black and White women with a common subtype of endometrial cancer.
In addition to observing differences in clinical and molecular characteristics, the analysis of real-world registries and clinical trials revealed that Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma had about a twofold higher risk for cancer-related deaths than White patients.
“Even with propensity-score matching, Black patients had a significantly increased risk of death,” Zachary Kopelman, DO, with Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, noted in a presentation at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Importantly, Dr. Kopelman added, the analysis also confirmed “dramatic” underrepresentation of Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma in clinical trials.
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the United States, with data showing rising incidence and mortality rates. “Worryingly, endometrial cancer is estimated to overtake ovarian cancer as the deadliest gynecologic malignancy this year,” Dr. Kopelman told attendees.
Previous studies have shown that Black patients with endometrial cancer consistently are more likely to have aggressive histologic subtypes, high-grade tumors, and advanced-stage disease and are twice as likely to die from the disease as White patients, he noted.
Within endometrial cancer, the most common histologic subtype is endometrioid, comprising 65%-75% of cases. In other studies examining racial disparities, the endometrioid histology is often combined with other subtypes, such as aggressive uterine serous carcinoma, which may influence study outcomes, Dr. Kopelman explained.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues focused their analyses on Black and White women with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, with the goal of identifying disparities in cancer-related and non-cancer deaths, as well as clinical and molecular features in this patient population.
All women included in the analysis had undergone hysterectomy with or without adjuvant treatment. The researchers used a four-pronged approach incorporating data from the SEER program (2004-2016), the National Cancer Database (2004-2017), eight National Cancer Institute-sponsored randomized phase 3 clinical trials, and the Genomics Evidence Neoplasia Information Exchange project.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues then performed propensity score matching in the National Cancer Database and exact matching in the randomized controlled trials.
When comparing 47,959 White patients with 4397 Black patients in the SEER dataset, Dr. Kopelman and colleagues found that Black patients had more than two times the risk of dying from their cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 2.04) and a 22% greater risk for a non-cancer death compared with White patients (HR, 1.22).
In the overall National Cancer Database cohort comparing 155,706 White and 13,468 Black patients, Black patients had a 52% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.52). In the propensity score-matched cohort of 13,468 White and 13,468 Black patients, survival among Black patients remained significantly worse, with a 29% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.29).
When looking at clinical trial data, Black patients were more likely than White patients to have worse performance status and a higher grade or recurrent disease, Dr. Kopelman noted.
Black patients in the clinical trials also had significantly worse progression-free survival in both the original cohort (HR, 2.05) and the matched cohort (adjusted HR [aHR], 1.22), which matched patients for grade, stage, and treatment arm within each trial and balanced age and performance status. Black patients also had worse overall survival in the original cohort (HR, 2.19) and matched cohort (aHR, 1.32).
Looking at molecular features, Black patients had significantly fewer mutations in a handful of cancer-related gene pathways, including PTEN, PIK3R1, FBXW7, NF1, mTOR, CCND1, and PI3K pathways.
One caveat, said Dr. Kopelman, is that mutations in PTEN are still present in a high percentage of both Black (62%) and White (72%), which «offers a potential attractive therapeutic opportunity.»
The analysis also revealed a major gap in the number of Black vs White patients enrolled in randomized clinical trials, which is a major “problem,” said Dr. Kopelman.
The study confirms “ongoing disparities in enrollment and underrepresentation of minorities in gynecologic cancer clinical trials, as well as poor outcomes, and should really promote us to enhance research in these areas,” said study discussant Mariam AlHilli, MD, with Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio.
David M. O’Malley, MD, who gave a separate talk during the same session on practical considerations for implication of clinical trials, encouraged clinicians to “just ask.”
“Just ask the patient in front of you — no matter what their ethnicity, their race, or where they’re coming from — are they interested in participating in a clinical trial?” Or better yet, “I have a clinical trial now which I’m excited about for you,” said Dr. O’Malley, with The Ohio State University, James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, Ohio.The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Kopelman, Dr. O’Malley, and Dr. AlHilli had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A recent analysis identified significant disparities in survival outcomes as well as clinical and genetic features between Black and White women with a common subtype of endometrial cancer.
In addition to observing differences in clinical and molecular characteristics, the analysis of real-world registries and clinical trials revealed that Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma had about a twofold higher risk for cancer-related deaths than White patients.
“Even with propensity-score matching, Black patients had a significantly increased risk of death,” Zachary Kopelman, DO, with Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, noted in a presentation at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Importantly, Dr. Kopelman added, the analysis also confirmed “dramatic” underrepresentation of Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma in clinical trials.
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the United States, with data showing rising incidence and mortality rates. “Worryingly, endometrial cancer is estimated to overtake ovarian cancer as the deadliest gynecologic malignancy this year,” Dr. Kopelman told attendees.
Previous studies have shown that Black patients with endometrial cancer consistently are more likely to have aggressive histologic subtypes, high-grade tumors, and advanced-stage disease and are twice as likely to die from the disease as White patients, he noted.
Within endometrial cancer, the most common histologic subtype is endometrioid, comprising 65%-75% of cases. In other studies examining racial disparities, the endometrioid histology is often combined with other subtypes, such as aggressive uterine serous carcinoma, which may influence study outcomes, Dr. Kopelman explained.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues focused their analyses on Black and White women with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, with the goal of identifying disparities in cancer-related and non-cancer deaths, as well as clinical and molecular features in this patient population.
All women included in the analysis had undergone hysterectomy with or without adjuvant treatment. The researchers used a four-pronged approach incorporating data from the SEER program (2004-2016), the National Cancer Database (2004-2017), eight National Cancer Institute-sponsored randomized phase 3 clinical trials, and the Genomics Evidence Neoplasia Information Exchange project.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues then performed propensity score matching in the National Cancer Database and exact matching in the randomized controlled trials.
When comparing 47,959 White patients with 4397 Black patients in the SEER dataset, Dr. Kopelman and colleagues found that Black patients had more than two times the risk of dying from their cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 2.04) and a 22% greater risk for a non-cancer death compared with White patients (HR, 1.22).
In the overall National Cancer Database cohort comparing 155,706 White and 13,468 Black patients, Black patients had a 52% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.52). In the propensity score-matched cohort of 13,468 White and 13,468 Black patients, survival among Black patients remained significantly worse, with a 29% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.29).
When looking at clinical trial data, Black patients were more likely than White patients to have worse performance status and a higher grade or recurrent disease, Dr. Kopelman noted.
Black patients in the clinical trials also had significantly worse progression-free survival in both the original cohort (HR, 2.05) and the matched cohort (adjusted HR [aHR], 1.22), which matched patients for grade, stage, and treatment arm within each trial and balanced age and performance status. Black patients also had worse overall survival in the original cohort (HR, 2.19) and matched cohort (aHR, 1.32).
Looking at molecular features, Black patients had significantly fewer mutations in a handful of cancer-related gene pathways, including PTEN, PIK3R1, FBXW7, NF1, mTOR, CCND1, and PI3K pathways.
One caveat, said Dr. Kopelman, is that mutations in PTEN are still present in a high percentage of both Black (62%) and White (72%), which «offers a potential attractive therapeutic opportunity.»
The analysis also revealed a major gap in the number of Black vs White patients enrolled in randomized clinical trials, which is a major “problem,” said Dr. Kopelman.
The study confirms “ongoing disparities in enrollment and underrepresentation of minorities in gynecologic cancer clinical trials, as well as poor outcomes, and should really promote us to enhance research in these areas,” said study discussant Mariam AlHilli, MD, with Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio.
David M. O’Malley, MD, who gave a separate talk during the same session on practical considerations for implication of clinical trials, encouraged clinicians to “just ask.”
“Just ask the patient in front of you — no matter what their ethnicity, their race, or where they’re coming from — are they interested in participating in a clinical trial?” Or better yet, “I have a clinical trial now which I’m excited about for you,” said Dr. O’Malley, with The Ohio State University, James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, Ohio.The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Kopelman, Dr. O’Malley, and Dr. AlHilli had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A recent analysis identified significant disparities in survival outcomes as well as clinical and genetic features between Black and White women with a common subtype of endometrial cancer.
In addition to observing differences in clinical and molecular characteristics, the analysis of real-world registries and clinical trials revealed that Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma had about a twofold higher risk for cancer-related deaths than White patients.
“Even with propensity-score matching, Black patients had a significantly increased risk of death,” Zachary Kopelman, DO, with Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, noted in a presentation at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Importantly, Dr. Kopelman added, the analysis also confirmed “dramatic” underrepresentation of Black patients with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma in clinical trials.
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the United States, with data showing rising incidence and mortality rates. “Worryingly, endometrial cancer is estimated to overtake ovarian cancer as the deadliest gynecologic malignancy this year,” Dr. Kopelman told attendees.
Previous studies have shown that Black patients with endometrial cancer consistently are more likely to have aggressive histologic subtypes, high-grade tumors, and advanced-stage disease and are twice as likely to die from the disease as White patients, he noted.
Within endometrial cancer, the most common histologic subtype is endometrioid, comprising 65%-75% of cases. In other studies examining racial disparities, the endometrioid histology is often combined with other subtypes, such as aggressive uterine serous carcinoma, which may influence study outcomes, Dr. Kopelman explained.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues focused their analyses on Black and White women with endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, with the goal of identifying disparities in cancer-related and non-cancer deaths, as well as clinical and molecular features in this patient population.
All women included in the analysis had undergone hysterectomy with or without adjuvant treatment. The researchers used a four-pronged approach incorporating data from the SEER program (2004-2016), the National Cancer Database (2004-2017), eight National Cancer Institute-sponsored randomized phase 3 clinical trials, and the Genomics Evidence Neoplasia Information Exchange project.
Dr. Kopelman and colleagues then performed propensity score matching in the National Cancer Database and exact matching in the randomized controlled trials.
When comparing 47,959 White patients with 4397 Black patients in the SEER dataset, Dr. Kopelman and colleagues found that Black patients had more than two times the risk of dying from their cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 2.04) and a 22% greater risk for a non-cancer death compared with White patients (HR, 1.22).
In the overall National Cancer Database cohort comparing 155,706 White and 13,468 Black patients, Black patients had a 52% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.52). In the propensity score-matched cohort of 13,468 White and 13,468 Black patients, survival among Black patients remained significantly worse, with a 29% greater risk of dying from any cause (HR, 1.29).
When looking at clinical trial data, Black patients were more likely than White patients to have worse performance status and a higher grade or recurrent disease, Dr. Kopelman noted.
Black patients in the clinical trials also had significantly worse progression-free survival in both the original cohort (HR, 2.05) and the matched cohort (adjusted HR [aHR], 1.22), which matched patients for grade, stage, and treatment arm within each trial and balanced age and performance status. Black patients also had worse overall survival in the original cohort (HR, 2.19) and matched cohort (aHR, 1.32).
Looking at molecular features, Black patients had significantly fewer mutations in a handful of cancer-related gene pathways, including PTEN, PIK3R1, FBXW7, NF1, mTOR, CCND1, and PI3K pathways.
One caveat, said Dr. Kopelman, is that mutations in PTEN are still present in a high percentage of both Black (62%) and White (72%), which «offers a potential attractive therapeutic opportunity.»
The analysis also revealed a major gap in the number of Black vs White patients enrolled in randomized clinical trials, which is a major “problem,” said Dr. Kopelman.
The study confirms “ongoing disparities in enrollment and underrepresentation of minorities in gynecologic cancer clinical trials, as well as poor outcomes, and should really promote us to enhance research in these areas,” said study discussant Mariam AlHilli, MD, with Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio.
David M. O’Malley, MD, who gave a separate talk during the same session on practical considerations for implication of clinical trials, encouraged clinicians to “just ask.”
“Just ask the patient in front of you — no matter what their ethnicity, their race, or where they’re coming from — are they interested in participating in a clinical trial?” Or better yet, “I have a clinical trial now which I’m excited about for you,” said Dr. O’Malley, with The Ohio State University, James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, Ohio.The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Kopelman, Dr. O’Malley, and Dr. AlHilli had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM SGO 2024
Ovarian Cancer Red Flags: What to Know to Quicken Diagnoses
One in seven women will die within 2 months of being diagnosed with ovarian cancer, a new report from the United Kingdom states. But if diagnosed at the earliest stage, 9 in 10 women will survive. Two thirds of women are now diagnosed late, when the cancer is harder to treat.
Diagnosis is difficult for many reasons, among them that women sometimes think symptoms are a natural part of menopause and don’t acknowledge or report them. Clinicians may mistake abdominal symptoms for those of a bowel condition or bladder problem. Almost half of GPs (46%) in the UK mistakenly believe that ovarian cancer symptoms present in only the later stages of the disease.
Cervical Screening Does Not Detect Ovarian Cancer
Additionally, there are misconceptions regarding cervical cancer screening — one study found that “40% of women in the general public mistakenly believe that cervical screening detects ovarian cancer.” But there is no current screening program for ovarian cancer in the UK or United States.
During a pelvic exam, the physician feels the ovaries and uterus for size, shape, and consistency and that can be useful in finding some cancers early, but most early ovarian tumors are difficult or impossible to feel, the American Cancer Society notes.
Recognizing the Red Flags
Victoria Barber, MBBS, a general practitioner in Northamptonshire and a Primary Care Advisory Board member with the Target Ovarian Cancer program in the UK published a paper in the British Journal of Nursing (2024 Mar 7. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2024.33.5.S16) on the program’s efforts to urge clinicians to recognize ovarian cancer red flags and to “never diagnose new-onset irritable bowel syndrome or overactive bladder in women over 50 without ruling out ovarian cancer.”
She says nurses should be involved to help with earlier diagnosis of ovarian cancer as they are often involved in evaluating urine samples. Nurse practitioners, she notes, are typically included in consultations for abdominal symptoms and potential urinary tract infections.
“If the woman is recurrently presenting with urinary symptoms, sterile midstream urine samples should raise alarm,” she says. “The woman may have diabetes, an overactive bladder, or interstitial cystitis; however, urgency and frequency are some of the symptoms of ovarian cancer, and they need investigation.”
Persistent Systems Over Age 50
The paper lists ovarian cancer symptoms from the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and notes that among red flags are having any of the following persistently/frequently (particularly more than 12 times per month and especially if the woman is 50 years or older):
- Early satiety and/or loss of appetite
- Abdominal bloating
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Urinary urgency/frequency
Other symptoms could include:
- Changes in bowel habits (e.g., diarrhea or constipation)
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnosis Challenges Similar in US
Ernst Lengyel, MD, PhD, UChicago Medicine’s Chairman of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Chicago, Illinois, who was not involved with the paper, said the situation in the United States is similar to that described in the UK.
“The diagnosis is delayed because the symptoms are unspecific. The problem is that ovarian cancer is so rare, and primary care physicians or nurse practitioners have to consider over 100 differential diagnoses,” he says.
In the US, he says, it is likely easier to get in and see a physician because of the private insurance options and because there are more gynecologic oncologists in large urban areas. Getting imaging approved — such as ultrasound and computed tomography scans — is also easier in the US.
Still, “there is no effective way to diagnose ovarian cancer early,” he says. “No single test or combination of symptoms can be used as a screening test.”
The CA-125 blood test measures proteins that can be linked with ovarian cancer, but is not a screening test, he notes.
“Large UK and US studies have not been able to show a survival benefit with ultrasound, serial CA-125, or a combination thereof,” Dr. Lengyel said.
Weight Gain May Also be a Sign
A broad range of clinicians should be aware of the symptoms the author mentions, he says, especially primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, and obstetrician/gynecologists.
“Too often, symptoms that women report are ignored and treated as unspecific or psychosomatic,” Dr. Lengyel says. “It is easy to disregard recurrent complaints and move on instead of being vigilant and working them up. Ironically, women with ovarian cancer can initially gain weight, which is counterintuitive as most doctors believe that patients with cancer lose weight. However, if they develop abdominal fluid, a patient often gains weight.”
Dr. Barber and Dr. Lengyel report no relevant financial relationships.
One in seven women will die within 2 months of being diagnosed with ovarian cancer, a new report from the United Kingdom states. But if diagnosed at the earliest stage, 9 in 10 women will survive. Two thirds of women are now diagnosed late, when the cancer is harder to treat.
Diagnosis is difficult for many reasons, among them that women sometimes think symptoms are a natural part of menopause and don’t acknowledge or report them. Clinicians may mistake abdominal symptoms for those of a bowel condition or bladder problem. Almost half of GPs (46%) in the UK mistakenly believe that ovarian cancer symptoms present in only the later stages of the disease.
Cervical Screening Does Not Detect Ovarian Cancer
Additionally, there are misconceptions regarding cervical cancer screening — one study found that “40% of women in the general public mistakenly believe that cervical screening detects ovarian cancer.” But there is no current screening program for ovarian cancer in the UK or United States.
During a pelvic exam, the physician feels the ovaries and uterus for size, shape, and consistency and that can be useful in finding some cancers early, but most early ovarian tumors are difficult or impossible to feel, the American Cancer Society notes.
Recognizing the Red Flags
Victoria Barber, MBBS, a general practitioner in Northamptonshire and a Primary Care Advisory Board member with the Target Ovarian Cancer program in the UK published a paper in the British Journal of Nursing (2024 Mar 7. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2024.33.5.S16) on the program’s efforts to urge clinicians to recognize ovarian cancer red flags and to “never diagnose new-onset irritable bowel syndrome or overactive bladder in women over 50 without ruling out ovarian cancer.”
She says nurses should be involved to help with earlier diagnosis of ovarian cancer as they are often involved in evaluating urine samples. Nurse practitioners, she notes, are typically included in consultations for abdominal symptoms and potential urinary tract infections.
“If the woman is recurrently presenting with urinary symptoms, sterile midstream urine samples should raise alarm,” she says. “The woman may have diabetes, an overactive bladder, or interstitial cystitis; however, urgency and frequency are some of the symptoms of ovarian cancer, and they need investigation.”
Persistent Systems Over Age 50
The paper lists ovarian cancer symptoms from the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and notes that among red flags are having any of the following persistently/frequently (particularly more than 12 times per month and especially if the woman is 50 years or older):
- Early satiety and/or loss of appetite
- Abdominal bloating
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Urinary urgency/frequency
Other symptoms could include:
- Changes in bowel habits (e.g., diarrhea or constipation)
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnosis Challenges Similar in US
Ernst Lengyel, MD, PhD, UChicago Medicine’s Chairman of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Chicago, Illinois, who was not involved with the paper, said the situation in the United States is similar to that described in the UK.
“The diagnosis is delayed because the symptoms are unspecific. The problem is that ovarian cancer is so rare, and primary care physicians or nurse practitioners have to consider over 100 differential diagnoses,” he says.
In the US, he says, it is likely easier to get in and see a physician because of the private insurance options and because there are more gynecologic oncologists in large urban areas. Getting imaging approved — such as ultrasound and computed tomography scans — is also easier in the US.
Still, “there is no effective way to diagnose ovarian cancer early,” he says. “No single test or combination of symptoms can be used as a screening test.”
The CA-125 blood test measures proteins that can be linked with ovarian cancer, but is not a screening test, he notes.
“Large UK and US studies have not been able to show a survival benefit with ultrasound, serial CA-125, or a combination thereof,” Dr. Lengyel said.
Weight Gain May Also be a Sign
A broad range of clinicians should be aware of the symptoms the author mentions, he says, especially primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, and obstetrician/gynecologists.
“Too often, symptoms that women report are ignored and treated as unspecific or psychosomatic,” Dr. Lengyel says. “It is easy to disregard recurrent complaints and move on instead of being vigilant and working them up. Ironically, women with ovarian cancer can initially gain weight, which is counterintuitive as most doctors believe that patients with cancer lose weight. However, if they develop abdominal fluid, a patient often gains weight.”
Dr. Barber and Dr. Lengyel report no relevant financial relationships.
One in seven women will die within 2 months of being diagnosed with ovarian cancer, a new report from the United Kingdom states. But if diagnosed at the earliest stage, 9 in 10 women will survive. Two thirds of women are now diagnosed late, when the cancer is harder to treat.
Diagnosis is difficult for many reasons, among them that women sometimes think symptoms are a natural part of menopause and don’t acknowledge or report them. Clinicians may mistake abdominal symptoms for those of a bowel condition or bladder problem. Almost half of GPs (46%) in the UK mistakenly believe that ovarian cancer symptoms present in only the later stages of the disease.
Cervical Screening Does Not Detect Ovarian Cancer
Additionally, there are misconceptions regarding cervical cancer screening — one study found that “40% of women in the general public mistakenly believe that cervical screening detects ovarian cancer.” But there is no current screening program for ovarian cancer in the UK or United States.
During a pelvic exam, the physician feels the ovaries and uterus for size, shape, and consistency and that can be useful in finding some cancers early, but most early ovarian tumors are difficult or impossible to feel, the American Cancer Society notes.
Recognizing the Red Flags
Victoria Barber, MBBS, a general practitioner in Northamptonshire and a Primary Care Advisory Board member with the Target Ovarian Cancer program in the UK published a paper in the British Journal of Nursing (2024 Mar 7. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2024.33.5.S16) on the program’s efforts to urge clinicians to recognize ovarian cancer red flags and to “never diagnose new-onset irritable bowel syndrome or overactive bladder in women over 50 without ruling out ovarian cancer.”
She says nurses should be involved to help with earlier diagnosis of ovarian cancer as they are often involved in evaluating urine samples. Nurse practitioners, she notes, are typically included in consultations for abdominal symptoms and potential urinary tract infections.
“If the woman is recurrently presenting with urinary symptoms, sterile midstream urine samples should raise alarm,” she says. “The woman may have diabetes, an overactive bladder, or interstitial cystitis; however, urgency and frequency are some of the symptoms of ovarian cancer, and they need investigation.”
Persistent Systems Over Age 50
The paper lists ovarian cancer symptoms from the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and notes that among red flags are having any of the following persistently/frequently (particularly more than 12 times per month and especially if the woman is 50 years or older):
- Early satiety and/or loss of appetite
- Abdominal bloating
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Urinary urgency/frequency
Other symptoms could include:
- Changes in bowel habits (e.g., diarrhea or constipation)
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnosis Challenges Similar in US
Ernst Lengyel, MD, PhD, UChicago Medicine’s Chairman of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Chicago, Illinois, who was not involved with the paper, said the situation in the United States is similar to that described in the UK.
“The diagnosis is delayed because the symptoms are unspecific. The problem is that ovarian cancer is so rare, and primary care physicians or nurse practitioners have to consider over 100 differential diagnoses,” he says.
In the US, he says, it is likely easier to get in and see a physician because of the private insurance options and because there are more gynecologic oncologists in large urban areas. Getting imaging approved — such as ultrasound and computed tomography scans — is also easier in the US.
Still, “there is no effective way to diagnose ovarian cancer early,” he says. “No single test or combination of symptoms can be used as a screening test.”
The CA-125 blood test measures proteins that can be linked with ovarian cancer, but is not a screening test, he notes.
“Large UK and US studies have not been able to show a survival benefit with ultrasound, serial CA-125, or a combination thereof,” Dr. Lengyel said.
Weight Gain May Also be a Sign
A broad range of clinicians should be aware of the symptoms the author mentions, he says, especially primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, and obstetrician/gynecologists.
“Too often, symptoms that women report are ignored and treated as unspecific or psychosomatic,” Dr. Lengyel says. “It is easy to disregard recurrent complaints and move on instead of being vigilant and working them up. Ironically, women with ovarian cancer can initially gain weight, which is counterintuitive as most doctors believe that patients with cancer lose weight. However, if they develop abdominal fluid, a patient often gains weight.”
Dr. Barber and Dr. Lengyel report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF NURSING
Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorder Increasing Rapidly
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
New Transparent AI Predicts Breast Cancer 5 Years Out
A new way of using artificial intelligence (AI) can predict breast cancer 5 years in advance with impressive accuracy — and unlike previous AI models, we know how this one works.
The new AI system, called AsymMirai, simplifies previous models by solely comparing differences between right and left breasts to predict risk. It could potentially save lives, prevent unnecessary testing, and save the healthcare system money, its creators say.
“With traditional AI, you ask it a question and it spits out an answer, but no one really knows how it makes its decisions. It’s a black box,” said Jon Donnelly, a PhD student in the department of computer science at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and first author on a new paper in Radiology describing the model.
“With our approach, people know how the algorithm comes up with its output so they can fact-check it and trust it,” he said.
One in eight women will develop invasive breast cancer, and 1 in 39 will die from it. Mammograms miss about 20% of breast cancers. (The shortcomings of genetic screening and mammograms received extra attention recently when actress Olivia Munn disclosed that she’d been treated for an aggressive form of breast cancer despite a normal mammogram and a negative genetic test.)
The model could help doctors bring the often-abstract idea of AI to the bedside in a meaningful way, said radiologist Vivianne Freitas, MD, assistant professor of medical imaging at the University of Toronto.
“This marks a new chapter in the field of AI,” said Dr. Freitas, who authored an editorial lauding the new paper. “It makes AI more tangible and understandable, thereby improving its potential for acceptance.”
AI as a Second Set of Eyes
Mr. Donnelly described AsymMirai as a simpler, more transparent, and easier-to-use version of Mirai, a breakthrough AI model which made headlines in 2021 with its promise to determine with unprecedented accuracy whether a patient is likely to get breast cancer within the next 5 years.
Mirai identified up to twice as many future cancer diagnoses as the conventional risk calculator Tyrer-Cuzick. It also maintained accuracy across a diverse set of patients — a notable plus for two fields (AI and healthcare) notorious for delivering poorer results for minorities.
Tyrer-Cuzick and other lower-tech risk calculators use personal and family history to statistically calculate risk. Mirai, on the other hand, analyzes countless bits of raw data embedded in a mammogram to decipher patterns a radiologist’s eyes may not catch. Four images, including two angles from each breast, are fed into the model, which produces a score between 0 and 1 to indicate the person’s risk of getting breast cancer in 1, 3, or 5 years.
But even Mirai’s creators have conceded they didn’t know exactly how it arrives at that score — a fact that has fueled hesitancy among clinicians.
Study coauthor Fides Schwartz, MD, a radiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said researchers were able to crack the code on Mirai’s “black box,” finding that its scores were largely determined by assessing subtle differences between right breast tissue and left breast tissue.
Knowing this, the research team simplified the model to predict risk based solely on “local bilateral dissimilarity.” AsymMirai was born.
The team then used AsymMirai to look back at > 200,000 mammograms from nearly 82,000 patients. They found it worked nearly as well as its predecessor, assigning a higher risk to those who would go on to develop cancer 66% of the time (vs Mirai’s 71%). In patients where it noticed the same asymmetry multiple years in a row it worked even better, with an 88% chance of giving people who would develop cancer later a higher score than those who would not.
“We found that we can, with surprisingly high accuracy, predict whether a woman will develop cancer in the next 1-5 years based solely on localized differences between her left and right breast tissue,” said Mr. Donnelly.
Dr. Schwartz imagines a day when radiologists could use the model to help develop personalized screening strategies for patients. Doctors might advise those with higher scores to get screened more often than guidelines suggest, supplement mammograms with an MRI , and keep a close watch on trouble spots identified by AI.
“For people with really low risk, on the other hand, maybe we can save them an annual exam that’s not super pleasant and might not be necessary,” said Dr. Schwartz.
Cautious Optimism
Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice president of early cancer detection science at the American Cancer Society, noted that AI has been used for decades to try to reduce radiologists’ workload and improve diagnoses.
“But AI just never really lived up to its fullest potential,” Dr. Smith said, “quite often because it was being used as a crutch by inexperienced radiologists who, instead of interpreting the mammogram and then seeing what AI had to say ended up letting AI do most of the work which, frankly, just wasn’t that accurate.”
He’s hopeful that newer, more sophisticated iterations of AI medical imaging platforms (roughly 18-20 models are in development) can ultimately save women’s lives, particularly in areas where radiologists are in short supply.
But he believes it will be a long time before doctors, or their patients, are willing to risk postponing a mammogram based on an algorithm.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new way of using artificial intelligence (AI) can predict breast cancer 5 years in advance with impressive accuracy — and unlike previous AI models, we know how this one works.
The new AI system, called AsymMirai, simplifies previous models by solely comparing differences between right and left breasts to predict risk. It could potentially save lives, prevent unnecessary testing, and save the healthcare system money, its creators say.
“With traditional AI, you ask it a question and it spits out an answer, but no one really knows how it makes its decisions. It’s a black box,” said Jon Donnelly, a PhD student in the department of computer science at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and first author on a new paper in Radiology describing the model.
“With our approach, people know how the algorithm comes up with its output so they can fact-check it and trust it,” he said.
One in eight women will develop invasive breast cancer, and 1 in 39 will die from it. Mammograms miss about 20% of breast cancers. (The shortcomings of genetic screening and mammograms received extra attention recently when actress Olivia Munn disclosed that she’d been treated for an aggressive form of breast cancer despite a normal mammogram and a negative genetic test.)
The model could help doctors bring the often-abstract idea of AI to the bedside in a meaningful way, said radiologist Vivianne Freitas, MD, assistant professor of medical imaging at the University of Toronto.
“This marks a new chapter in the field of AI,” said Dr. Freitas, who authored an editorial lauding the new paper. “It makes AI more tangible and understandable, thereby improving its potential for acceptance.”
AI as a Second Set of Eyes
Mr. Donnelly described AsymMirai as a simpler, more transparent, and easier-to-use version of Mirai, a breakthrough AI model which made headlines in 2021 with its promise to determine with unprecedented accuracy whether a patient is likely to get breast cancer within the next 5 years.
Mirai identified up to twice as many future cancer diagnoses as the conventional risk calculator Tyrer-Cuzick. It also maintained accuracy across a diverse set of patients — a notable plus for two fields (AI and healthcare) notorious for delivering poorer results for minorities.
Tyrer-Cuzick and other lower-tech risk calculators use personal and family history to statistically calculate risk. Mirai, on the other hand, analyzes countless bits of raw data embedded in a mammogram to decipher patterns a radiologist’s eyes may not catch. Four images, including two angles from each breast, are fed into the model, which produces a score between 0 and 1 to indicate the person’s risk of getting breast cancer in 1, 3, or 5 years.
But even Mirai’s creators have conceded they didn’t know exactly how it arrives at that score — a fact that has fueled hesitancy among clinicians.
Study coauthor Fides Schwartz, MD, a radiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said researchers were able to crack the code on Mirai’s “black box,” finding that its scores were largely determined by assessing subtle differences between right breast tissue and left breast tissue.
Knowing this, the research team simplified the model to predict risk based solely on “local bilateral dissimilarity.” AsymMirai was born.
The team then used AsymMirai to look back at > 200,000 mammograms from nearly 82,000 patients. They found it worked nearly as well as its predecessor, assigning a higher risk to those who would go on to develop cancer 66% of the time (vs Mirai’s 71%). In patients where it noticed the same asymmetry multiple years in a row it worked even better, with an 88% chance of giving people who would develop cancer later a higher score than those who would not.
“We found that we can, with surprisingly high accuracy, predict whether a woman will develop cancer in the next 1-5 years based solely on localized differences between her left and right breast tissue,” said Mr. Donnelly.
Dr. Schwartz imagines a day when radiologists could use the model to help develop personalized screening strategies for patients. Doctors might advise those with higher scores to get screened more often than guidelines suggest, supplement mammograms with an MRI , and keep a close watch on trouble spots identified by AI.
“For people with really low risk, on the other hand, maybe we can save them an annual exam that’s not super pleasant and might not be necessary,” said Dr. Schwartz.
Cautious Optimism
Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice president of early cancer detection science at the American Cancer Society, noted that AI has been used for decades to try to reduce radiologists’ workload and improve diagnoses.
“But AI just never really lived up to its fullest potential,” Dr. Smith said, “quite often because it was being used as a crutch by inexperienced radiologists who, instead of interpreting the mammogram and then seeing what AI had to say ended up letting AI do most of the work which, frankly, just wasn’t that accurate.”
He’s hopeful that newer, more sophisticated iterations of AI medical imaging platforms (roughly 18-20 models are in development) can ultimately save women’s lives, particularly in areas where radiologists are in short supply.
But he believes it will be a long time before doctors, or their patients, are willing to risk postponing a mammogram based on an algorithm.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new way of using artificial intelligence (AI) can predict breast cancer 5 years in advance with impressive accuracy — and unlike previous AI models, we know how this one works.
The new AI system, called AsymMirai, simplifies previous models by solely comparing differences between right and left breasts to predict risk. It could potentially save lives, prevent unnecessary testing, and save the healthcare system money, its creators say.
“With traditional AI, you ask it a question and it spits out an answer, but no one really knows how it makes its decisions. It’s a black box,” said Jon Donnelly, a PhD student in the department of computer science at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, and first author on a new paper in Radiology describing the model.
“With our approach, people know how the algorithm comes up with its output so they can fact-check it and trust it,” he said.
One in eight women will develop invasive breast cancer, and 1 in 39 will die from it. Mammograms miss about 20% of breast cancers. (The shortcomings of genetic screening and mammograms received extra attention recently when actress Olivia Munn disclosed that she’d been treated for an aggressive form of breast cancer despite a normal mammogram and a negative genetic test.)
The model could help doctors bring the often-abstract idea of AI to the bedside in a meaningful way, said radiologist Vivianne Freitas, MD, assistant professor of medical imaging at the University of Toronto.
“This marks a new chapter in the field of AI,” said Dr. Freitas, who authored an editorial lauding the new paper. “It makes AI more tangible and understandable, thereby improving its potential for acceptance.”
AI as a Second Set of Eyes
Mr. Donnelly described AsymMirai as a simpler, more transparent, and easier-to-use version of Mirai, a breakthrough AI model which made headlines in 2021 with its promise to determine with unprecedented accuracy whether a patient is likely to get breast cancer within the next 5 years.
Mirai identified up to twice as many future cancer diagnoses as the conventional risk calculator Tyrer-Cuzick. It also maintained accuracy across a diverse set of patients — a notable plus for two fields (AI and healthcare) notorious for delivering poorer results for minorities.
Tyrer-Cuzick and other lower-tech risk calculators use personal and family history to statistically calculate risk. Mirai, on the other hand, analyzes countless bits of raw data embedded in a mammogram to decipher patterns a radiologist’s eyes may not catch. Four images, including two angles from each breast, are fed into the model, which produces a score between 0 and 1 to indicate the person’s risk of getting breast cancer in 1, 3, or 5 years.
But even Mirai’s creators have conceded they didn’t know exactly how it arrives at that score — a fact that has fueled hesitancy among clinicians.
Study coauthor Fides Schwartz, MD, a radiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said researchers were able to crack the code on Mirai’s “black box,” finding that its scores were largely determined by assessing subtle differences between right breast tissue and left breast tissue.
Knowing this, the research team simplified the model to predict risk based solely on “local bilateral dissimilarity.” AsymMirai was born.
The team then used AsymMirai to look back at > 200,000 mammograms from nearly 82,000 patients. They found it worked nearly as well as its predecessor, assigning a higher risk to those who would go on to develop cancer 66% of the time (vs Mirai’s 71%). In patients where it noticed the same asymmetry multiple years in a row it worked even better, with an 88% chance of giving people who would develop cancer later a higher score than those who would not.
“We found that we can, with surprisingly high accuracy, predict whether a woman will develop cancer in the next 1-5 years based solely on localized differences between her left and right breast tissue,” said Mr. Donnelly.
Dr. Schwartz imagines a day when radiologists could use the model to help develop personalized screening strategies for patients. Doctors might advise those with higher scores to get screened more often than guidelines suggest, supplement mammograms with an MRI , and keep a close watch on trouble spots identified by AI.
“For people with really low risk, on the other hand, maybe we can save them an annual exam that’s not super pleasant and might not be necessary,” said Dr. Schwartz.
Cautious Optimism
Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice president of early cancer detection science at the American Cancer Society, noted that AI has been used for decades to try to reduce radiologists’ workload and improve diagnoses.
“But AI just never really lived up to its fullest potential,” Dr. Smith said, “quite often because it was being used as a crutch by inexperienced radiologists who, instead of interpreting the mammogram and then seeing what AI had to say ended up letting AI do most of the work which, frankly, just wasn’t that accurate.”
He’s hopeful that newer, more sophisticated iterations of AI medical imaging platforms (roughly 18-20 models are in development) can ultimately save women’s lives, particularly in areas where radiologists are in short supply.
But he believes it will be a long time before doctors, or their patients, are willing to risk postponing a mammogram based on an algorithm.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Acne Risk With Progestin-Only Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives Evaluated
TOPLINE:
Despite the .
METHODOLOGY:
- Progestin-only LARC may increase the risk for acne, but this has not been well studied in adolescents and young adults.
- In the study, researchers evaluated the incidence of acne, acne as a reason for removal, and strategies used to manage acne after insertion of a progestin-only intrauterine device (IUD) or contraceptive implant in 1319 adolescents and young adults across four Adolescent Medicine LARC Collaborative study sites from January 2017 to June 2021.The mean age at insertion was 18.6 years.
- Overall, 24% of participants had acne at the time of LARC insertion.
- Worsening acne was defined as new patient reports of concern about acne, observations of acne, or addition of an acne medication after insertion; increased severity noted on an exam during follow-up or at the time of LARC removal; or acne reported as a side effect and/or reason for LARC removal.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 376 participants (28.5%) experienced worsening acne after LARC insertion, and 17% reported acne as a new concern, with no differences between those who received an IUD or an implant.
- Only 44 of the 376 participants (11.7%) who reported worsening acne were being treated with an oral agent at follow-up.
- Of the 542 individuals (41% of the total) who had the LARC device removed, 40 (7.4%) cited concerns about acne for removing the device, although just 5 (0.92%) said that acne was the only reason for removal. Of the 40 with concerns about acne when the device was removed, 18 (45%) had documented acne at the time of insertion.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors recommend that clinicians prescribing progestin-only LARC should counsel patients that acne may be a side effect, reassuring them that if they develop acne, “it typically is not problematic enough to warrant discontinuation,” and concluded that “concerns about the development or worsening of acne should not be cause to avoid these forms of contraception.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington in Seattle and Seattle Children’s Hospital, was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Individuals without documented acne were assumed to be acne-free, creating potential bias. Acne evaluation and treatment were not standardized and were not performed by dermatologists; acne severity was not recorded for many participants, possibly underestimating severity, and excluding LARC insertions without follow-up or with removal within 8 weeks may have underestimated the percentage of participants who developed new or worsening acne.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon and by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services. Many authors received grants for this work. The authors did not disclose any other competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Despite the .
METHODOLOGY:
- Progestin-only LARC may increase the risk for acne, but this has not been well studied in adolescents and young adults.
- In the study, researchers evaluated the incidence of acne, acne as a reason for removal, and strategies used to manage acne after insertion of a progestin-only intrauterine device (IUD) or contraceptive implant in 1319 adolescents and young adults across four Adolescent Medicine LARC Collaborative study sites from January 2017 to June 2021.The mean age at insertion was 18.6 years.
- Overall, 24% of participants had acne at the time of LARC insertion.
- Worsening acne was defined as new patient reports of concern about acne, observations of acne, or addition of an acne medication after insertion; increased severity noted on an exam during follow-up or at the time of LARC removal; or acne reported as a side effect and/or reason for LARC removal.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 376 participants (28.5%) experienced worsening acne after LARC insertion, and 17% reported acne as a new concern, with no differences between those who received an IUD or an implant.
- Only 44 of the 376 participants (11.7%) who reported worsening acne were being treated with an oral agent at follow-up.
- Of the 542 individuals (41% of the total) who had the LARC device removed, 40 (7.4%) cited concerns about acne for removing the device, although just 5 (0.92%) said that acne was the only reason for removal. Of the 40 with concerns about acne when the device was removed, 18 (45%) had documented acne at the time of insertion.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors recommend that clinicians prescribing progestin-only LARC should counsel patients that acne may be a side effect, reassuring them that if they develop acne, “it typically is not problematic enough to warrant discontinuation,” and concluded that “concerns about the development or worsening of acne should not be cause to avoid these forms of contraception.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington in Seattle and Seattle Children’s Hospital, was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Individuals without documented acne were assumed to be acne-free, creating potential bias. Acne evaluation and treatment were not standardized and were not performed by dermatologists; acne severity was not recorded for many participants, possibly underestimating severity, and excluding LARC insertions without follow-up or with removal within 8 weeks may have underestimated the percentage of participants who developed new or worsening acne.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon and by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services. Many authors received grants for this work. The authors did not disclose any other competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Despite the .
METHODOLOGY:
- Progestin-only LARC may increase the risk for acne, but this has not been well studied in adolescents and young adults.
- In the study, researchers evaluated the incidence of acne, acne as a reason for removal, and strategies used to manage acne after insertion of a progestin-only intrauterine device (IUD) or contraceptive implant in 1319 adolescents and young adults across four Adolescent Medicine LARC Collaborative study sites from January 2017 to June 2021.The mean age at insertion was 18.6 years.
- Overall, 24% of participants had acne at the time of LARC insertion.
- Worsening acne was defined as new patient reports of concern about acne, observations of acne, or addition of an acne medication after insertion; increased severity noted on an exam during follow-up or at the time of LARC removal; or acne reported as a side effect and/or reason for LARC removal.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 376 participants (28.5%) experienced worsening acne after LARC insertion, and 17% reported acne as a new concern, with no differences between those who received an IUD or an implant.
- Only 44 of the 376 participants (11.7%) who reported worsening acne were being treated with an oral agent at follow-up.
- Of the 542 individuals (41% of the total) who had the LARC device removed, 40 (7.4%) cited concerns about acne for removing the device, although just 5 (0.92%) said that acne was the only reason for removal. Of the 40 with concerns about acne when the device was removed, 18 (45%) had documented acne at the time of insertion.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors recommend that clinicians prescribing progestin-only LARC should counsel patients that acne may be a side effect, reassuring them that if they develop acne, “it typically is not problematic enough to warrant discontinuation,” and concluded that “concerns about the development or worsening of acne should not be cause to avoid these forms of contraception.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Markus D. Boos, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington in Seattle and Seattle Children’s Hospital, was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Individuals without documented acne were assumed to be acne-free, creating potential bias. Acne evaluation and treatment were not standardized and were not performed by dermatologists; acne severity was not recorded for many participants, possibly underestimating severity, and excluding LARC insertions without follow-up or with removal within 8 weeks may have underestimated the percentage of participants who developed new or worsening acne.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon and by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services. Many authors received grants for this work. The authors did not disclose any other competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What Do Sex Therapists Do? (Hint: It’s Not What You Think)
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: We are here at the Harvard Continuing Medical Education Course in Orlando, Florida. It’s all about testosterone therapy and sexual medicine. I have with me today the wonderful Dr. Marianne Brandon, who is an amazing sex therapist. Could you introduce yourself?
Marianne Brandon, PhD: I am a clinical psychologist and sex therapist. I’ve been in practice for more than 25 years. I’m currently located in Sarasota. I have a Psychology Today blog called The Future of Intimacy, which I have a lot of fun with.
Dr. Rubin: It’s very important, when taking care of patients, that we work in a biopsychosocial model. Yes, we can fix erectile dysfunction. We can help with menopause symptoms and that helps sexual function. But what I find makes my patients able to live their best lives is when they have a team, including a mental health professional — often a sex therapist or a couples’ therapist — where they can learn communication skills. Why is it important for primary care doctors to talk to their patients about sex? My primary care doctor has never asked me about sex.
Dr. Brandon: People have more struggles than you realize. Sexual dysfunction correlates with emotional issues such as depression and anxiety, with medical problems, and with medication use. Chances are that your patients have some kind of sexual concern, even if that’s not to the degree that it would be classified as a sexual dysfunction.
But sexual concerns wreak havoc. Believing they have a sexual problem, they stop touching, they stop relating to their partner. It becomes a really big deal in their lives. If you can open the door for a conversation about sex with your patients, it could do them a great deal of good. It’s also good for the practitioner, because if your patients think they can talk with you about anything, that’s going to establish your relationship with them. Practitioners avoid these conversations because they don’t have the time or the training to offer help.
Dr. Rubin: You don’t have to know all the answers. You just have to show empathy and compassion and say, “I hear you.” That’s the magic in the doctor-patient relationship. We refer patients to specialists when we don’t know what to do. What happens when I send a patient to a sex therapist? Do they watch them have sex? Of course not, but everyone thinks that is what sex therapists do.
Dr. Brandon: Sex therapy is just like any other type of therapy, but we discuss sexual issues. And because just about anything that’s happening in your patient’s life can trickle down into the bedroom, we end up talking about a lot of stuff that’s not directly related to sex but ultimately impacts the patient’s sex life.
Dr. Rubin: It’s true. Most medical conditions that we treat — from diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity to depression and anxiety — are strongly correlated with sexual health. We treat the underlying condition, but our patients don’t care about their A1c levels. They care about the fact that they cannot get aroused; their genitals don’t feel the same way they used to.
Dr. Brandon: I love that point because people make meaning out of their sexual concerns and dysfunction. Suddenly their body isn’t responding the way it used to. They think something’s wrong with them, or maybe they are with the wrong partner. This meaning becomes very powerful in their mind and perpetuates the sexual problem.
Dr. Rubin: First and foremost, we are educators. We can say, “You have pretty out-of-control diabetes,” or, “You’re a smoker, which can affect the health of your genitals. Have you noticed any issues going on there?” If you don’t ask, patients will not bring up their concerns with their doctors.
So how do people find a sex therapist?
Dr. Brandon: There are a few fabulous organizations that provide on their websites ways to find a therapist: the American Association of Sex Educators, Counselors and Therapists (AASECT) and Sex Therapy and Research (STAR). Giving patients this information is a huge intervention.
Other places to find a therapist include the International Society for Sexual Medicine, and the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health.
Since COVID, many therapists have gone virtual. Encourage your patients to look within their states to find options for therapists and psychologists. Recent legislation allows psychologists who have signed up for PSYPACT to practice almost throughout the entire United States. We used to think if we didn’t have a therapist in the community, we couldn’t make a referral. That›s not the case anymore.
Dr. Rubin: All doctors are really sexual medicine doctors. We can change the whole world by giving our patients a better quality of life.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, disclosed ties to Sprout, Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.






