User login
Prior authorizations interfere with recommended cancer care
Of 178 respondents with a prior authorization (PA) experience, 39 (22%) did not receive the care recommended by their treatment team because of a PA requirement, and 123 (69%) experienced a delay in receiving the recommended care, Fumiko Chino, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported.
Reasons for not receiving recommended care included complete denial by the insurance company (26 of 39 patients), and a change in treatment plan because of initial denial (13 of 39 patients). Delays in receiving recommended care were 2 or more weeks for 90 of 123 patients, and 1 month or more in 40 of 123 patients.
Delays in receiving recommended care were associated with increased patient anxiety, a negative perception of the PA process, and patient administrative burden, the investigators noted.
The findings, which capture patient-based perspectives in the ongoing PA debacle, were reported online in JAMA Network Open.
“Prior authorization requires clinicians and patients to navigate a complex approval pathway. Resultant delays and denial can be particularly problematic for patients with cancer, who often need urgent treatment or symptom management,” the investigators explained. “Focusing on patient experiences with PA highlights a missing perspective in policy discussions and suggests another potential factor associated with eroding trust in the health care system.”
To assess the impact of PA, they conducted an anonymous survey using a convenience sample of patients with any cancer-related PA experience from July 1 to Oct. 6, 2022. Mean self-reported PA-related anxiety scores were 74.7 on a scale of 0-100, whereas usual anxiety scores were 37.5.
PA-related anxiety scores were significantly correlated with the length of treatment delay (P = .04), time spent on PA (P < .001), and overall PA experience (P < .001).
“Dealing with PA issues adds an extra layer of stress, which is known to increase anxiety and can worsen treatment-related and disease-related symptoms and adverse effects,” the investigators noted.
PA issues also eroded trust: 89% of respondents trusted their insurance company less, and 83% trusted the health care system less after a PA experience. Patient involvement in the PA process increased the likelihood of such distrust and of having a negative experience.
Of the 178 respondents, most were women (88%), non-Hispanic White individuals (84%), college graduates (84%), and young (18-39 years, 41%; 40-54 years, 33%). Most (67%) had to personally become involved in the PA process by calling their insurance or filing an appeal.
The investigators noted that “efforts to create national health policy solutions that streamline PA and make the process more transparent have been a major lobbying effort of large oncology societies,” and that bipartisan legislation to “establish regulations on the quality and timeliness of PA in the Medicare Advantage population” has stalled.
“In the meantime, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services acted directly by issuing a final rule in April 2023 aimed at improving PA processes within the Medicare Advantage population by 2024,” they wrote, adding that “streamlining the PA process is key to optimizing the quality of care delivered and improving patients’ experience with cancer care.
“Policy interventions will be necessary to reform the PA process, as will advocacy efforts at the patient, clinician, and hospital level,” they concluded.
Chino reported funding through a National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant.
Of 178 respondents with a prior authorization (PA) experience, 39 (22%) did not receive the care recommended by their treatment team because of a PA requirement, and 123 (69%) experienced a delay in receiving the recommended care, Fumiko Chino, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported.
Reasons for not receiving recommended care included complete denial by the insurance company (26 of 39 patients), and a change in treatment plan because of initial denial (13 of 39 patients). Delays in receiving recommended care were 2 or more weeks for 90 of 123 patients, and 1 month or more in 40 of 123 patients.
Delays in receiving recommended care were associated with increased patient anxiety, a negative perception of the PA process, and patient administrative burden, the investigators noted.
The findings, which capture patient-based perspectives in the ongoing PA debacle, were reported online in JAMA Network Open.
“Prior authorization requires clinicians and patients to navigate a complex approval pathway. Resultant delays and denial can be particularly problematic for patients with cancer, who often need urgent treatment or symptom management,” the investigators explained. “Focusing on patient experiences with PA highlights a missing perspective in policy discussions and suggests another potential factor associated with eroding trust in the health care system.”
To assess the impact of PA, they conducted an anonymous survey using a convenience sample of patients with any cancer-related PA experience from July 1 to Oct. 6, 2022. Mean self-reported PA-related anxiety scores were 74.7 on a scale of 0-100, whereas usual anxiety scores were 37.5.
PA-related anxiety scores were significantly correlated with the length of treatment delay (P = .04), time spent on PA (P < .001), and overall PA experience (P < .001).
“Dealing with PA issues adds an extra layer of stress, which is known to increase anxiety and can worsen treatment-related and disease-related symptoms and adverse effects,” the investigators noted.
PA issues also eroded trust: 89% of respondents trusted their insurance company less, and 83% trusted the health care system less after a PA experience. Patient involvement in the PA process increased the likelihood of such distrust and of having a negative experience.
Of the 178 respondents, most were women (88%), non-Hispanic White individuals (84%), college graduates (84%), and young (18-39 years, 41%; 40-54 years, 33%). Most (67%) had to personally become involved in the PA process by calling their insurance or filing an appeal.
The investigators noted that “efforts to create national health policy solutions that streamline PA and make the process more transparent have been a major lobbying effort of large oncology societies,” and that bipartisan legislation to “establish regulations on the quality and timeliness of PA in the Medicare Advantage population” has stalled.
“In the meantime, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services acted directly by issuing a final rule in April 2023 aimed at improving PA processes within the Medicare Advantage population by 2024,” they wrote, adding that “streamlining the PA process is key to optimizing the quality of care delivered and improving patients’ experience with cancer care.
“Policy interventions will be necessary to reform the PA process, as will advocacy efforts at the patient, clinician, and hospital level,” they concluded.
Chino reported funding through a National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant.
Of 178 respondents with a prior authorization (PA) experience, 39 (22%) did not receive the care recommended by their treatment team because of a PA requirement, and 123 (69%) experienced a delay in receiving the recommended care, Fumiko Chino, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues reported.
Reasons for not receiving recommended care included complete denial by the insurance company (26 of 39 patients), and a change in treatment plan because of initial denial (13 of 39 patients). Delays in receiving recommended care were 2 or more weeks for 90 of 123 patients, and 1 month or more in 40 of 123 patients.
Delays in receiving recommended care were associated with increased patient anxiety, a negative perception of the PA process, and patient administrative burden, the investigators noted.
The findings, which capture patient-based perspectives in the ongoing PA debacle, were reported online in JAMA Network Open.
“Prior authorization requires clinicians and patients to navigate a complex approval pathway. Resultant delays and denial can be particularly problematic for patients with cancer, who often need urgent treatment or symptom management,” the investigators explained. “Focusing on patient experiences with PA highlights a missing perspective in policy discussions and suggests another potential factor associated with eroding trust in the health care system.”
To assess the impact of PA, they conducted an anonymous survey using a convenience sample of patients with any cancer-related PA experience from July 1 to Oct. 6, 2022. Mean self-reported PA-related anxiety scores were 74.7 on a scale of 0-100, whereas usual anxiety scores were 37.5.
PA-related anxiety scores were significantly correlated with the length of treatment delay (P = .04), time spent on PA (P < .001), and overall PA experience (P < .001).
“Dealing with PA issues adds an extra layer of stress, which is known to increase anxiety and can worsen treatment-related and disease-related symptoms and adverse effects,” the investigators noted.
PA issues also eroded trust: 89% of respondents trusted their insurance company less, and 83% trusted the health care system less after a PA experience. Patient involvement in the PA process increased the likelihood of such distrust and of having a negative experience.
Of the 178 respondents, most were women (88%), non-Hispanic White individuals (84%), college graduates (84%), and young (18-39 years, 41%; 40-54 years, 33%). Most (67%) had to personally become involved in the PA process by calling their insurance or filing an appeal.
The investigators noted that “efforts to create national health policy solutions that streamline PA and make the process more transparent have been a major lobbying effort of large oncology societies,” and that bipartisan legislation to “establish regulations on the quality and timeliness of PA in the Medicare Advantage population” has stalled.
“In the meantime, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services acted directly by issuing a final rule in April 2023 aimed at improving PA processes within the Medicare Advantage population by 2024,” they wrote, adding that “streamlining the PA process is key to optimizing the quality of care delivered and improving patients’ experience with cancer care.
“Policy interventions will be necessary to reform the PA process, as will advocacy efforts at the patient, clinician, and hospital level,” they concluded.
Chino reported funding through a National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
MOC: An ‘insult to oncologists’ engaged in patient care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I am far from the only doctor, and certainly far from the only oncologist, to recently comment on the topic of Maintenance of Certification. Of course, this is happening in a wider debate about our relationship as subspecialists to the American Board of Internal Medicine, and what they deem acceptable for the recertification of doctors in practice.
One of the things I tell my patients is that if I practiced exactly the way I was trained to practice — and I had a very good fellowship program with superb faculty – if I practiced the way they taught me, it would now be malpractice. I finished my fellowship in 2012, just over a decade ago. The rate of progress in the interim is simply staggering. It looks so different now than it did then.
For instance, 2011 was my first experience ever using a form of immunotherapy. It was an anti-CTLA4 agent, ipilimumab, and I was treating metastatic melanoma. I learned in that instance just how effective these drugs can be, but also how toxic they can be. Ever since then, I’ve been refining my use of immunotherapy. We do that iteratively. We do that as we encounter patients and as we try to meet their needs.
I do understand that the ABIM is saying they want an independent governing body to legislate that process. I think the reason this is stuck in the craw of so many oncologists is that we demonstrate our commitment to continuing medical education all the time.
I’m recording this in my office, which is separate from the space where I see patients. I see patients in a different group of exam rooms for their privacy and it’s a better setup for aspects of the physical encounter. Not a single patient has ever asked to come into my office and see my diplomas, and I sometimes wonder if I keep them here mostly as a visual cue to myself, sort of an antidote to ward off imposter syndrome and remind myself, Oh yeah – I earned these. I earned these through formal training.
Then something happens once you finish your training, whether it’s residency or fellowship, and you become an attending. I think you feel a weight of responsibility, the responsibility of independent learning. All of us are doing this. We have to do this. The field is moving along at such a rapid clip that it’s essentially built into what we do that we are going to keep up. In fact, channels such as the various aspects of social media are a way I curate my own information feed so I can stay up to speed and not feel like I’m drowning in a deluge of new data.
But what’s hard to demonstrate to the ABIM is that [this learning] is already happening. I think we can do it if we submit our records of CME credits that we formally accrue. The reason this is such an almost insult to oncologists in practice is because it is a necessary part of our day-to-day existence to keep apprised of developments so we can apply them to patient care.
One litmus test of attending a medical conference like the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology is to ask oneself, When I go back to clinic, is this meeting going to change the way that I take care of patients? The answer almost invariably these days is yes. I go to multiple meetings per year, and I think it’s the exception, not the rule, that I return home and nothing changes in my management patterns. Again, this process is happening whether the ABIM recognizes it or not.
Lastly, I sat down in the fall of 2022 and I did my recertification. I looked at the span of all the things that had happened between 2012, when I first sat for my board examination in medical oncology, and 2022. It was staggering. I think the reason that it wasn’t such an overwhelming amount of information to review is that I had actually been accreting it slowly and gradually, month by month, year by year throughout that decade.
Again, it’s necessary that the ABIM hear us, hear oncologists, and know that of all the medical subspecialties they govern, it is basically already an essential task of our day-to-day professional existence that we engage in lifelong learning. To suggest otherwise really paints us as outdated. The reason that matters so much is that if we’re not up-to-date, then we are underserving our patients.
Mark A. Lewis, MD, is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I am far from the only doctor, and certainly far from the only oncologist, to recently comment on the topic of Maintenance of Certification. Of course, this is happening in a wider debate about our relationship as subspecialists to the American Board of Internal Medicine, and what they deem acceptable for the recertification of doctors in practice.
One of the things I tell my patients is that if I practiced exactly the way I was trained to practice — and I had a very good fellowship program with superb faculty – if I practiced the way they taught me, it would now be malpractice. I finished my fellowship in 2012, just over a decade ago. The rate of progress in the interim is simply staggering. It looks so different now than it did then.
For instance, 2011 was my first experience ever using a form of immunotherapy. It was an anti-CTLA4 agent, ipilimumab, and I was treating metastatic melanoma. I learned in that instance just how effective these drugs can be, but also how toxic they can be. Ever since then, I’ve been refining my use of immunotherapy. We do that iteratively. We do that as we encounter patients and as we try to meet their needs.
I do understand that the ABIM is saying they want an independent governing body to legislate that process. I think the reason this is stuck in the craw of so many oncologists is that we demonstrate our commitment to continuing medical education all the time.
I’m recording this in my office, which is separate from the space where I see patients. I see patients in a different group of exam rooms for their privacy and it’s a better setup for aspects of the physical encounter. Not a single patient has ever asked to come into my office and see my diplomas, and I sometimes wonder if I keep them here mostly as a visual cue to myself, sort of an antidote to ward off imposter syndrome and remind myself, Oh yeah – I earned these. I earned these through formal training.
Then something happens once you finish your training, whether it’s residency or fellowship, and you become an attending. I think you feel a weight of responsibility, the responsibility of independent learning. All of us are doing this. We have to do this. The field is moving along at such a rapid clip that it’s essentially built into what we do that we are going to keep up. In fact, channels such as the various aspects of social media are a way I curate my own information feed so I can stay up to speed and not feel like I’m drowning in a deluge of new data.
But what’s hard to demonstrate to the ABIM is that [this learning] is already happening. I think we can do it if we submit our records of CME credits that we formally accrue. The reason this is such an almost insult to oncologists in practice is because it is a necessary part of our day-to-day existence to keep apprised of developments so we can apply them to patient care.
One litmus test of attending a medical conference like the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology is to ask oneself, When I go back to clinic, is this meeting going to change the way that I take care of patients? The answer almost invariably these days is yes. I go to multiple meetings per year, and I think it’s the exception, not the rule, that I return home and nothing changes in my management patterns. Again, this process is happening whether the ABIM recognizes it or not.
Lastly, I sat down in the fall of 2022 and I did my recertification. I looked at the span of all the things that had happened between 2012, when I first sat for my board examination in medical oncology, and 2022. It was staggering. I think the reason that it wasn’t such an overwhelming amount of information to review is that I had actually been accreting it slowly and gradually, month by month, year by year throughout that decade.
Again, it’s necessary that the ABIM hear us, hear oncologists, and know that of all the medical subspecialties they govern, it is basically already an essential task of our day-to-day professional existence that we engage in lifelong learning. To suggest otherwise really paints us as outdated. The reason that matters so much is that if we’re not up-to-date, then we are underserving our patients.
Mark A. Lewis, MD, is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I am far from the only doctor, and certainly far from the only oncologist, to recently comment on the topic of Maintenance of Certification. Of course, this is happening in a wider debate about our relationship as subspecialists to the American Board of Internal Medicine, and what they deem acceptable for the recertification of doctors in practice.
One of the things I tell my patients is that if I practiced exactly the way I was trained to practice — and I had a very good fellowship program with superb faculty – if I practiced the way they taught me, it would now be malpractice. I finished my fellowship in 2012, just over a decade ago. The rate of progress in the interim is simply staggering. It looks so different now than it did then.
For instance, 2011 was my first experience ever using a form of immunotherapy. It was an anti-CTLA4 agent, ipilimumab, and I was treating metastatic melanoma. I learned in that instance just how effective these drugs can be, but also how toxic they can be. Ever since then, I’ve been refining my use of immunotherapy. We do that iteratively. We do that as we encounter patients and as we try to meet their needs.
I do understand that the ABIM is saying they want an independent governing body to legislate that process. I think the reason this is stuck in the craw of so many oncologists is that we demonstrate our commitment to continuing medical education all the time.
I’m recording this in my office, which is separate from the space where I see patients. I see patients in a different group of exam rooms for their privacy and it’s a better setup for aspects of the physical encounter. Not a single patient has ever asked to come into my office and see my diplomas, and I sometimes wonder if I keep them here mostly as a visual cue to myself, sort of an antidote to ward off imposter syndrome and remind myself, Oh yeah – I earned these. I earned these through formal training.
Then something happens once you finish your training, whether it’s residency or fellowship, and you become an attending. I think you feel a weight of responsibility, the responsibility of independent learning. All of us are doing this. We have to do this. The field is moving along at such a rapid clip that it’s essentially built into what we do that we are going to keep up. In fact, channels such as the various aspects of social media are a way I curate my own information feed so I can stay up to speed and not feel like I’m drowning in a deluge of new data.
But what’s hard to demonstrate to the ABIM is that [this learning] is already happening. I think we can do it if we submit our records of CME credits that we formally accrue. The reason this is such an almost insult to oncologists in practice is because it is a necessary part of our day-to-day existence to keep apprised of developments so we can apply them to patient care.
One litmus test of attending a medical conference like the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology is to ask oneself, When I go back to clinic, is this meeting going to change the way that I take care of patients? The answer almost invariably these days is yes. I go to multiple meetings per year, and I think it’s the exception, not the rule, that I return home and nothing changes in my management patterns. Again, this process is happening whether the ABIM recognizes it or not.
Lastly, I sat down in the fall of 2022 and I did my recertification. I looked at the span of all the things that had happened between 2012, when I first sat for my board examination in medical oncology, and 2022. It was staggering. I think the reason that it wasn’t such an overwhelming amount of information to review is that I had actually been accreting it slowly and gradually, month by month, year by year throughout that decade.
Again, it’s necessary that the ABIM hear us, hear oncologists, and know that of all the medical subspecialties they govern, it is basically already an essential task of our day-to-day professional existence that we engage in lifelong learning. To suggest otherwise really paints us as outdated. The reason that matters so much is that if we’re not up-to-date, then we are underserving our patients.
Mark A. Lewis, MD, is director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Author Q&A: GI needs better parental leave policies
The authors note that this article can serve as a roadmap for institutions and practices to create a parental leave policy and return-to-work environment that attracts talent and supports a diverse and thriving workforce.
Despite a joint statement by the four main gastroenterology societies more than 25 years ago, few structural changes have been implemented to mandate a minimum of 12 weeks of parental leave for gastroenterologists.
We asked one of the article’s authors, Dr. Lauren D. Feld, a few questions about the motivation behind this article and the movement at large.
Q: What motivated you and your coauthors to write this article?
A: “It was a pleasure working with my coauthors – an incredible team of gender equity experts – Drs. Amy S. Oxentenko, Dawn Sears, Aline Charabaty, Loren G. Rabinowitz, and Julie K. Silver.
I’m grateful to Dr. May and Dr. Quezada for the invitation to write about the important topic of creating family-friendly work environments. My coauthors and I have noticed increasing support for women in gastroenterology.”
Q: Why is this issue important?
A: “Nationwide, women are leaving clinical and academic medicine at alarming rates. The incompatibility of parenthood with a traditional medical career has been identified as a major driver of retention issues across specialties. In addition to impacting retention, incompatibility with pregnancy and parenthood also impacts recruitment. Survey studies of internal medicine residents have identified concerns about family life as a major barrier to choosing gastroenterology as a specialty. Women in medicine have worked too hard to get to where they are to be excluded from or driven out of our field.
Beyond the impact on the physicians, there is a major impact on patients. Studies have identified that women patients’ preference for a woman endoscopist as well as the difficulty in finding women endoscopists has created a barrier to colon cancer screening for women. Areas of research have also gone understudied because they primarily impact women patients. We must work towards equity for the benefit of both physicians and patients.”
Q: What actions can practicing GI doctors take now to help support better parental leave and return to work policies?
A: “Start by reviewing this article and asking your human resources for your employer’s policies in this area. If your employer doesn’t have a parental leave policy, or if their policy is inadequate, discuss the importance of this with your leadership. Describing the cost impact of physicians leaving practice is a good way to justify the cost investment to support family friendly policies.”
The authors recommend policies outlined in the paper be consistent across genders with attention to equity for the LGBTQ+ community. The blueprint for parental leave and return to work department policies includes:
- Specific policies to support physicians during pregnancy, including endoscopy ergonomic accommodations.
- Components of a parental leave policy such as duration and adjusted RVUs to account for leave.
- Coverage models to consider during leave.
- How to create a family friendly return to work, including modified overnight call during postpartum and autonomy over schedule.
The authors note that this article can serve as a roadmap for institutions and practices to create a parental leave policy and return-to-work environment that attracts talent and supports a diverse and thriving workforce.
Despite a joint statement by the four main gastroenterology societies more than 25 years ago, few structural changes have been implemented to mandate a minimum of 12 weeks of parental leave for gastroenterologists.
We asked one of the article’s authors, Dr. Lauren D. Feld, a few questions about the motivation behind this article and the movement at large.
Q: What motivated you and your coauthors to write this article?
A: “It was a pleasure working with my coauthors – an incredible team of gender equity experts – Drs. Amy S. Oxentenko, Dawn Sears, Aline Charabaty, Loren G. Rabinowitz, and Julie K. Silver.
I’m grateful to Dr. May and Dr. Quezada for the invitation to write about the important topic of creating family-friendly work environments. My coauthors and I have noticed increasing support for women in gastroenterology.”
Q: Why is this issue important?
A: “Nationwide, women are leaving clinical and academic medicine at alarming rates. The incompatibility of parenthood with a traditional medical career has been identified as a major driver of retention issues across specialties. In addition to impacting retention, incompatibility with pregnancy and parenthood also impacts recruitment. Survey studies of internal medicine residents have identified concerns about family life as a major barrier to choosing gastroenterology as a specialty. Women in medicine have worked too hard to get to where they are to be excluded from or driven out of our field.
Beyond the impact on the physicians, there is a major impact on patients. Studies have identified that women patients’ preference for a woman endoscopist as well as the difficulty in finding women endoscopists has created a barrier to colon cancer screening for women. Areas of research have also gone understudied because they primarily impact women patients. We must work towards equity for the benefit of both physicians and patients.”
Q: What actions can practicing GI doctors take now to help support better parental leave and return to work policies?
A: “Start by reviewing this article and asking your human resources for your employer’s policies in this area. If your employer doesn’t have a parental leave policy, or if their policy is inadequate, discuss the importance of this with your leadership. Describing the cost impact of physicians leaving practice is a good way to justify the cost investment to support family friendly policies.”
The authors recommend policies outlined in the paper be consistent across genders with attention to equity for the LGBTQ+ community. The blueprint for parental leave and return to work department policies includes:
- Specific policies to support physicians during pregnancy, including endoscopy ergonomic accommodations.
- Components of a parental leave policy such as duration and adjusted RVUs to account for leave.
- Coverage models to consider during leave.
- How to create a family friendly return to work, including modified overnight call during postpartum and autonomy over schedule.
The authors note that this article can serve as a roadmap for institutions and practices to create a parental leave policy and return-to-work environment that attracts talent and supports a diverse and thriving workforce.
Despite a joint statement by the four main gastroenterology societies more than 25 years ago, few structural changes have been implemented to mandate a minimum of 12 weeks of parental leave for gastroenterologists.
We asked one of the article’s authors, Dr. Lauren D. Feld, a few questions about the motivation behind this article and the movement at large.
Q: What motivated you and your coauthors to write this article?
A: “It was a pleasure working with my coauthors – an incredible team of gender equity experts – Drs. Amy S. Oxentenko, Dawn Sears, Aline Charabaty, Loren G. Rabinowitz, and Julie K. Silver.
I’m grateful to Dr. May and Dr. Quezada for the invitation to write about the important topic of creating family-friendly work environments. My coauthors and I have noticed increasing support for women in gastroenterology.”
Q: Why is this issue important?
A: “Nationwide, women are leaving clinical and academic medicine at alarming rates. The incompatibility of parenthood with a traditional medical career has been identified as a major driver of retention issues across specialties. In addition to impacting retention, incompatibility with pregnancy and parenthood also impacts recruitment. Survey studies of internal medicine residents have identified concerns about family life as a major barrier to choosing gastroenterology as a specialty. Women in medicine have worked too hard to get to where they are to be excluded from or driven out of our field.
Beyond the impact on the physicians, there is a major impact on patients. Studies have identified that women patients’ preference for a woman endoscopist as well as the difficulty in finding women endoscopists has created a barrier to colon cancer screening for women. Areas of research have also gone understudied because they primarily impact women patients. We must work towards equity for the benefit of both physicians and patients.”
Q: What actions can practicing GI doctors take now to help support better parental leave and return to work policies?
A: “Start by reviewing this article and asking your human resources for your employer’s policies in this area. If your employer doesn’t have a parental leave policy, or if their policy is inadequate, discuss the importance of this with your leadership. Describing the cost impact of physicians leaving practice is a good way to justify the cost investment to support family friendly policies.”
The authors recommend policies outlined in the paper be consistent across genders with attention to equity for the LGBTQ+ community. The blueprint for parental leave and return to work department policies includes:
- Specific policies to support physicians during pregnancy, including endoscopy ergonomic accommodations.
- Components of a parental leave policy such as duration and adjusted RVUs to account for leave.
- Coverage models to consider during leave.
- How to create a family friendly return to work, including modified overnight call during postpartum and autonomy over schedule.
New evaluation and management of CPT codes for telemedicine in 2025
. The AMA says the new codes are designed to bring the coding system up to date with the changing landscape of health care and reflect the realities of modern medical practice.
The 17 new CPT codes will encompass a variety of telemedicine services. While the official language of the codes has not been released yet, codes for telemedicine visits using a real-time audio-visual platform could be organized similarly to existing office/outpatient E/M visits (99202-99205, 99212-99215). As part of these revisions, the current telephone E/M codes (99441-99443) will be deleted and replaced with new codes for audio-only E/M.
Implementation of so many codes will require health care providers and systems to adapt their documentation and coding practices. Typically, the exact language and code numbers for new and revised codes are not released to the public until fall of the preceding year, leaving only a few months for practices to educate their physicians and coding staff and prepare their internal systems for implementation starting Jan. 1, 2025. However, given the significant education and systems changes that will be necessary to prepare for so many new codes, we will advocate that the AMA release this information in early 2024.
Additionally, the reimbursement for telemedicine services may not ultimately be the same as for in-person E/M office visits. The AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) provides recommendations to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for consideration in developing Relative Value Units (RVUs) for new procedures, including the telemedicine codes. The RUC’s recommendations for the telemedicine codes are not yet publicly available. However, it is important to note that regardless of the RUC recommendations, CMS makes all final decisions about Medicare payment. CMS could decide to set the payments for the telemedicine codes at parity with in-person office E/M visits or less than, more than, or some combination at the individual code level.
If payments for telemedicine visits are set at parity with or higher than office E/M visits, practices can focus primarily on physician and staff education and system implementation of the new codes. However, if telemedicine visit payments are less than in-person E/M office visits, it would have significant implications for practices, providers, and patients. Providers might be discouraged from offering virtual care, leading to a disparity in the availability of telehealth services, with patients in some areas or with certain conditions having limited access. Additionally, not all patients have access to a smartphone or stable internet. Research has shown increased use of audio-only visits among marginalized groups including African Americans, non-English speakers, older patients, those with public insurance as opposed to private insurance and patients living in rural communities and communities with low broadband access. For these patients, audio-only is a lifeline that allows them to access needed care.
Hughes HK, Hasselfeld BW, Greene JA. Health Care Access on the Line - Audio-Only Visits and Digitally Inclusive Care. N Engl J Med. 2022 Nov 17;387(20):1823-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2118292. Epub 2022 Nov 12. PMID: 36373819.
Chen J, Li KY, Andino J, Hill CE, Ng S, Steppe E, Ellimoottil C. Predictors of Audio-Only Versus Video Telehealth Visits During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Apr;37(5):1138-1144. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-07172-y. Epub 2021 Nov 17. PMID: 34791589; PMCID: PMC8597874.
If payment for audio-only is significantly less than in-person office E/M payments, practices may not offer this option furthering health care inequities.
Beyond the extensive preparation needed and the financial implications, there could be impacts to coverage policies. Currently, telemedicine coverage is triggered by reporting the appropriate office E/M level visit with telemedicine modifier 95. If the new telemedicine codes are no longer tied to the in-person codes, laws requiring payers to provide coverage and parity may need to be adjusted accordingly or they could become less effective. If coverage parity is not maintained, that may lead to changes in practice that could also worsen access and health disparities. Some insurers have already started rolling back coverages. Recently, Aetna decided to stop covering telemedicine visits as of Dec. 1, 2023.
Other insurers may follow suit.
As practices prepare for 2024, tracking insurance coverage policies for telemedicine, staying alert for information from the AMA about the new telemedicine CPT codes, and monitoring the proposed payments for telemedicine that CMS will release in late June to early July in the 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule proposed rule will be important. Participation in advocacy efforts will be critical once the full details are released by the AMA and CMS about the new telemedicine codes and their proposed values. The AGA is monitoring this issue and will continue to fight to reduce burden to physicians and practices, which includes fighting for payment parity with in-person office E/M visits and maintaining coverage benefits for patients.
The authors have reported no conflicts of interest.
. The AMA says the new codes are designed to bring the coding system up to date with the changing landscape of health care and reflect the realities of modern medical practice.
The 17 new CPT codes will encompass a variety of telemedicine services. While the official language of the codes has not been released yet, codes for telemedicine visits using a real-time audio-visual platform could be organized similarly to existing office/outpatient E/M visits (99202-99205, 99212-99215). As part of these revisions, the current telephone E/M codes (99441-99443) will be deleted and replaced with new codes for audio-only E/M.
Implementation of so many codes will require health care providers and systems to adapt their documentation and coding practices. Typically, the exact language and code numbers for new and revised codes are not released to the public until fall of the preceding year, leaving only a few months for practices to educate their physicians and coding staff and prepare their internal systems for implementation starting Jan. 1, 2025. However, given the significant education and systems changes that will be necessary to prepare for so many new codes, we will advocate that the AMA release this information in early 2024.
Additionally, the reimbursement for telemedicine services may not ultimately be the same as for in-person E/M office visits. The AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) provides recommendations to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for consideration in developing Relative Value Units (RVUs) for new procedures, including the telemedicine codes. The RUC’s recommendations for the telemedicine codes are not yet publicly available. However, it is important to note that regardless of the RUC recommendations, CMS makes all final decisions about Medicare payment. CMS could decide to set the payments for the telemedicine codes at parity with in-person office E/M visits or less than, more than, or some combination at the individual code level.
If payments for telemedicine visits are set at parity with or higher than office E/M visits, practices can focus primarily on physician and staff education and system implementation of the new codes. However, if telemedicine visit payments are less than in-person E/M office visits, it would have significant implications for practices, providers, and patients. Providers might be discouraged from offering virtual care, leading to a disparity in the availability of telehealth services, with patients in some areas or with certain conditions having limited access. Additionally, not all patients have access to a smartphone or stable internet. Research has shown increased use of audio-only visits among marginalized groups including African Americans, non-English speakers, older patients, those with public insurance as opposed to private insurance and patients living in rural communities and communities with low broadband access. For these patients, audio-only is a lifeline that allows them to access needed care.
Hughes HK, Hasselfeld BW, Greene JA. Health Care Access on the Line - Audio-Only Visits and Digitally Inclusive Care. N Engl J Med. 2022 Nov 17;387(20):1823-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2118292. Epub 2022 Nov 12. PMID: 36373819.
Chen J, Li KY, Andino J, Hill CE, Ng S, Steppe E, Ellimoottil C. Predictors of Audio-Only Versus Video Telehealth Visits During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Apr;37(5):1138-1144. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-07172-y. Epub 2021 Nov 17. PMID: 34791589; PMCID: PMC8597874.
If payment for audio-only is significantly less than in-person office E/M payments, practices may not offer this option furthering health care inequities.
Beyond the extensive preparation needed and the financial implications, there could be impacts to coverage policies. Currently, telemedicine coverage is triggered by reporting the appropriate office E/M level visit with telemedicine modifier 95. If the new telemedicine codes are no longer tied to the in-person codes, laws requiring payers to provide coverage and parity may need to be adjusted accordingly or they could become less effective. If coverage parity is not maintained, that may lead to changes in practice that could also worsen access and health disparities. Some insurers have already started rolling back coverages. Recently, Aetna decided to stop covering telemedicine visits as of Dec. 1, 2023.
Other insurers may follow suit.
As practices prepare for 2024, tracking insurance coverage policies for telemedicine, staying alert for information from the AMA about the new telemedicine CPT codes, and monitoring the proposed payments for telemedicine that CMS will release in late June to early July in the 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule proposed rule will be important. Participation in advocacy efforts will be critical once the full details are released by the AMA and CMS about the new telemedicine codes and their proposed values. The AGA is monitoring this issue and will continue to fight to reduce burden to physicians and practices, which includes fighting for payment parity with in-person office E/M visits and maintaining coverage benefits for patients.
The authors have reported no conflicts of interest.
. The AMA says the new codes are designed to bring the coding system up to date with the changing landscape of health care and reflect the realities of modern medical practice.
The 17 new CPT codes will encompass a variety of telemedicine services. While the official language of the codes has not been released yet, codes for telemedicine visits using a real-time audio-visual platform could be organized similarly to existing office/outpatient E/M visits (99202-99205, 99212-99215). As part of these revisions, the current telephone E/M codes (99441-99443) will be deleted and replaced with new codes for audio-only E/M.
Implementation of so many codes will require health care providers and systems to adapt their documentation and coding practices. Typically, the exact language and code numbers for new and revised codes are not released to the public until fall of the preceding year, leaving only a few months for practices to educate their physicians and coding staff and prepare their internal systems for implementation starting Jan. 1, 2025. However, given the significant education and systems changes that will be necessary to prepare for so many new codes, we will advocate that the AMA release this information in early 2024.
Additionally, the reimbursement for telemedicine services may not ultimately be the same as for in-person E/M office visits. The AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) provides recommendations to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for consideration in developing Relative Value Units (RVUs) for new procedures, including the telemedicine codes. The RUC’s recommendations for the telemedicine codes are not yet publicly available. However, it is important to note that regardless of the RUC recommendations, CMS makes all final decisions about Medicare payment. CMS could decide to set the payments for the telemedicine codes at parity with in-person office E/M visits or less than, more than, or some combination at the individual code level.
If payments for telemedicine visits are set at parity with or higher than office E/M visits, practices can focus primarily on physician and staff education and system implementation of the new codes. However, if telemedicine visit payments are less than in-person E/M office visits, it would have significant implications for practices, providers, and patients. Providers might be discouraged from offering virtual care, leading to a disparity in the availability of telehealth services, with patients in some areas or with certain conditions having limited access. Additionally, not all patients have access to a smartphone or stable internet. Research has shown increased use of audio-only visits among marginalized groups including African Americans, non-English speakers, older patients, those with public insurance as opposed to private insurance and patients living in rural communities and communities with low broadband access. For these patients, audio-only is a lifeline that allows them to access needed care.
Hughes HK, Hasselfeld BW, Greene JA. Health Care Access on the Line - Audio-Only Visits and Digitally Inclusive Care. N Engl J Med. 2022 Nov 17;387(20):1823-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2118292. Epub 2022 Nov 12. PMID: 36373819.
Chen J, Li KY, Andino J, Hill CE, Ng S, Steppe E, Ellimoottil C. Predictors of Audio-Only Versus Video Telehealth Visits During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Apr;37(5):1138-1144. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-07172-y. Epub 2021 Nov 17. PMID: 34791589; PMCID: PMC8597874.
If payment for audio-only is significantly less than in-person office E/M payments, practices may not offer this option furthering health care inequities.
Beyond the extensive preparation needed and the financial implications, there could be impacts to coverage policies. Currently, telemedicine coverage is triggered by reporting the appropriate office E/M level visit with telemedicine modifier 95. If the new telemedicine codes are no longer tied to the in-person codes, laws requiring payers to provide coverage and parity may need to be adjusted accordingly or they could become less effective. If coverage parity is not maintained, that may lead to changes in practice that could also worsen access and health disparities. Some insurers have already started rolling back coverages. Recently, Aetna decided to stop covering telemedicine visits as of Dec. 1, 2023.
Other insurers may follow suit.
As practices prepare for 2024, tracking insurance coverage policies for telemedicine, staying alert for information from the AMA about the new telemedicine CPT codes, and monitoring the proposed payments for telemedicine that CMS will release in late June to early July in the 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule proposed rule will be important. Participation in advocacy efforts will be critical once the full details are released by the AMA and CMS about the new telemedicine codes and their proposed values. The AGA is monitoring this issue and will continue to fight to reduce burden to physicians and practices, which includes fighting for payment parity with in-person office E/M visits and maintaining coverage benefits for patients.
The authors have reported no conflicts of interest.
Medicare 2024 base rate cut triggers calls for pay overhaul
Physicians in 2024 can expect a 3.4% drop in the conversion factor that determines their base Medicare pay, according to federal officials, but they also will receive more money for primary care and treating complex conditions.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on Nov. 2 released its 2024 final physician fee schedule, triggering renewed concerns from doctors’ groups, who protested CMS’ cuts when they were first previewed earlier in 2023.
The 2024 conversion factor, or base rate for clinician pay, will be $32.74, a decrease of $1.15, or 3.4%, from 2023’s level. The pay cuts come as costs of providing health care are expected to rise as much as 4.6% in 2024, the American Medical Association said.
The new rule follows a 2% payment reduction in 2023, AMA president Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
“This is a recipe for financial instability,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “Patients and physicians will wonder why such thin gruel is being served.”
The AMA is among the many physician groups pressing Congress to change its approach to paying clinicians and consider inflation rates in determining future payments.
Medicare already includes automatic inflation adjusters in other payment rules, such as the ones for care provided in hospitals. But Congress in 2015 eliminated this feature for the physician fee schedule when it passed the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act.
A pending House bill, the bipartisan Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (H.R.2474), would return to permanently including a broader inflation adjuster in the Medicare physician fee schedule.
“This long-overdue change would not only help provide greater stability within the Medicare payment system, but it would also help physicians’ practices – many of whom operate as small business owners – more effectively navigate the ever-changing economic factors that impact their practices, including rising medical costs, workforce and labor challenges, administrative burdens, office rental prices and more,” Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.), Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), Raul Ruiz, MD (D-Calif.), and Mariannette Miller-Meeks, MD (R-Iowa), wrote in an opinion article in the newspaper The Hill.
Major changes to determining Medicare physician pay remain unlikely in 2023. Still, Congress has softened or blocked slated cuts in physician pay in recent years, passing temporary “doc fixes” as add-ons to spending packages.
E/M add-on payment
“We’re encouraged to see that CMS listened to our concerns and extended telehealth flexibilities as well as implemented the G2211 code, which will help Medicare beneficiaries and their physicians better manage complex and chronic rheumatic diseases,” said Douglas White, MD, PhD, president of the ACR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians in 2024 can expect a 3.4% drop in the conversion factor that determines their base Medicare pay, according to federal officials, but they also will receive more money for primary care and treating complex conditions.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on Nov. 2 released its 2024 final physician fee schedule, triggering renewed concerns from doctors’ groups, who protested CMS’ cuts when they were first previewed earlier in 2023.
The 2024 conversion factor, or base rate for clinician pay, will be $32.74, a decrease of $1.15, or 3.4%, from 2023’s level. The pay cuts come as costs of providing health care are expected to rise as much as 4.6% in 2024, the American Medical Association said.
The new rule follows a 2% payment reduction in 2023, AMA president Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
“This is a recipe for financial instability,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “Patients and physicians will wonder why such thin gruel is being served.”
The AMA is among the many physician groups pressing Congress to change its approach to paying clinicians and consider inflation rates in determining future payments.
Medicare already includes automatic inflation adjusters in other payment rules, such as the ones for care provided in hospitals. But Congress in 2015 eliminated this feature for the physician fee schedule when it passed the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act.
A pending House bill, the bipartisan Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (H.R.2474), would return to permanently including a broader inflation adjuster in the Medicare physician fee schedule.
“This long-overdue change would not only help provide greater stability within the Medicare payment system, but it would also help physicians’ practices – many of whom operate as small business owners – more effectively navigate the ever-changing economic factors that impact their practices, including rising medical costs, workforce and labor challenges, administrative burdens, office rental prices and more,” Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.), Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), Raul Ruiz, MD (D-Calif.), and Mariannette Miller-Meeks, MD (R-Iowa), wrote in an opinion article in the newspaper The Hill.
Major changes to determining Medicare physician pay remain unlikely in 2023. Still, Congress has softened or blocked slated cuts in physician pay in recent years, passing temporary “doc fixes” as add-ons to spending packages.
E/M add-on payment
“We’re encouraged to see that CMS listened to our concerns and extended telehealth flexibilities as well as implemented the G2211 code, which will help Medicare beneficiaries and their physicians better manage complex and chronic rheumatic diseases,” said Douglas White, MD, PhD, president of the ACR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians in 2024 can expect a 3.4% drop in the conversion factor that determines their base Medicare pay, according to federal officials, but they also will receive more money for primary care and treating complex conditions.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on Nov. 2 released its 2024 final physician fee schedule, triggering renewed concerns from doctors’ groups, who protested CMS’ cuts when they were first previewed earlier in 2023.
The 2024 conversion factor, or base rate for clinician pay, will be $32.74, a decrease of $1.15, or 3.4%, from 2023’s level. The pay cuts come as costs of providing health care are expected to rise as much as 4.6% in 2024, the American Medical Association said.
The new rule follows a 2% payment reduction in 2023, AMA president Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
“This is a recipe for financial instability,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “Patients and physicians will wonder why such thin gruel is being served.”
The AMA is among the many physician groups pressing Congress to change its approach to paying clinicians and consider inflation rates in determining future payments.
Medicare already includes automatic inflation adjusters in other payment rules, such as the ones for care provided in hospitals. But Congress in 2015 eliminated this feature for the physician fee schedule when it passed the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act.
A pending House bill, the bipartisan Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (H.R.2474), would return to permanently including a broader inflation adjuster in the Medicare physician fee schedule.
“This long-overdue change would not only help provide greater stability within the Medicare payment system, but it would also help physicians’ practices – many of whom operate as small business owners – more effectively navigate the ever-changing economic factors that impact their practices, including rising medical costs, workforce and labor challenges, administrative burdens, office rental prices and more,” Larry Bucshon, MD (R-Ind.), Ami Bera, MD (D-Calif.), Raul Ruiz, MD (D-Calif.), and Mariannette Miller-Meeks, MD (R-Iowa), wrote in an opinion article in the newspaper The Hill.
Major changes to determining Medicare physician pay remain unlikely in 2023. Still, Congress has softened or blocked slated cuts in physician pay in recent years, passing temporary “doc fixes” as add-ons to spending packages.
E/M add-on payment
“We’re encouraged to see that CMS listened to our concerns and extended telehealth flexibilities as well as implemented the G2211 code, which will help Medicare beneficiaries and their physicians better manage complex and chronic rheumatic diseases,” said Douglas White, MD, PhD, president of the ACR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patient contact time vs. admin: Is your contract fair?
What’s in a day’s work? For doctors, it’s typically a mix of seeing patients and completing paperwork and follow-up. Often it extends well past the standard workday.
Dennis Hursh, JD, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, describes one overwhelmed ob.gyn. who recently consulted him for this problem.
“My client had accepted a position in a group practice where his contract stated he would be working during normal office hours, Monday through Friday, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. – in other words, a 40-hour workweek,” Mr. Hursh said.
But the distressed physician discovered that actually, he was working almost twice as many hours. “He’d get to work early to do charting, then see patients during the 40 hours, perhaps grabbing a quick sandwich for a few minutes – and then stay after 5 [p.m.] for a few more hours when he’d work on charts or other administrative tasks. Then he’d get something to eat, work on more charts, then go to bed, get up in the morning, and repeat.”
Mr. Hursh summarized the client’s life: “Eating, sleeping, practicing clinical medicine, and doing nonclinical tasks.”
It turned out that the 40-hour workweek included in the contract referred to patient-facing hours, not to all of the ancillary tasks that are part of practicing medicine in this day and age. “Unfortunately, this is far from an isolated story,” said Mr. Hursh.
Be aware of what’s in the contract
“The first draft of many standard physician employment contracts often omits mention of patient contact hour requirements and rather uses vague verbiage such as ‘full-time’ employment or ‘1.0 FTE’ – or full-time equivalent – without defining that term,” said Mr. Hursh. Typically, the 40 hours exclude call coverage, but most physicians understand that and, at least at first glance, it all sounds very reasonable.
But once charting, hours on the phone, arguing with managed care companies, sending in prescriptions, administrative meetings, and other tasks are thrown in, the work hours expand dramatically. Moreover, if your employer doesn’t utilize hospitalists, you may be expected to “round” outside of the 40 hours, which can be particularly burdensome if the employer admits patients to multiple hospitals.
Amanda Hill, JD, owner of Hill Health Law based in Austin, Texas, told this news organization that this predicament isn’t unique to physicians. Exempt employees who don’t clock in and out are often expected to work overtime – that is, to “work as long as it takes to get the job done.” It can affect NPs, PAs, and many others in the health care space. But the number of tasks that fall upon a doctor’s shoulders and the fact that patients’ health and lives are at stake up the ante and make the situation far more difficult for doctors than for employees in other industries.
So it’s important to nail down precise terms in the contract and, if possible, negotiate for a more humane schedule by specifying how the working hours will be used.
“It’s true that a 1.0 FTE definition is too vague,” Ms. Hill said. “I’ve negotiated a lot of contracts where we nail down in writing that the in-office schedule equals 34 hours per week, so the physician is guaranteed an additional 6 hours for administrative time.”
Mr. Hursh usually asks for 32 hours of patient contact per week, which leaves 1 full day per week to catch up on basic administrative tasks. “It’s important for employers to recognize that seeing patients isn’t the only thing a doctor does and there’s a lot of work in addition to face-to-face time,” he said.
But he hasn’t always been successful. One physician client was seeking a workweek consisting of 36 patient contact hours, “which is 90% of the usual FTE of a 40-hour week,” said Mr. Hursh. “But the employer called it ‘part-time,’ as if the doctor were planning to be lying in the sun for the other 4 hours.”
The client decided to accept a 10% pay cut and 10% less vacation to guarantee that she had those extra hours for administrative tasks. “She’s probably working way more than 36 hours a week, but maybe closer to 50 or 60 instead of 70 or more,” he said.
Clarify call coverage
Call coverage is typically not included in the hours a physician is contracted to work on a weekly basis. “Most contracts have call, and it’s usually evenly distributed among parties in a practice, but call can expand if another doctor is out sick, for example,” said Ms. Hill.
Sometimes the language in the contract is vague regarding call coverage. “I ask, how many shifts per year is the doctor is expected to work? Then, I try to negotiate extra pay if more shifts arise,” she said. “The hospital or practice may not demand extra call because they don’t want to pay extra money to the physician.”
On the other hand, some physicians may be eager to take extra call if it means extra income.
Ms. Hill stated that one of her clients was being paid as a “part-time, 2-day-a-week provider” but was asked to be on call and take night and weekend work. When you added it all up, she was putting in almost 30 hours a week.
“This is abusive to a provider that works so hard for patients,” Ms. Hill said. “We have to protect them through the contract language, so they have something hard and fast to point to when their administrator pushes them too hard. Doctors should get value for their time.”
Ms. Hill and her client pushed for more money, and the employer gave in. “All we had to do was to point out how many hours she was actually working. She didn’t mind all the extra call, but she wanted to be compensated.” The doctor’s salary was hiked by $25,000.
Differences in specialties and settings
There are some specialties where it might be easier to have more defined hours, while other specialties are more challenging. Anu Murthy, Esq., an attorney and associate contract review specialist at Contract Diagnostics (a national firm that reviews physician contracts) told this news organization that the work of hospitalists, intensivists, and emergency department physicians, for example, is done in shifts, which tend to be fixed hours.
“They need to get their charting completed so that whoever takes over on the next shift has access to the most recent notes about the patient,” she said. By contrast, surgeons can’t always account for how long a given surgery will take. “It could be as long as 9 hours,” she said. Notes need to be written immediately for the sake of the patient’s postsurgical care.
Dermatologists tend to deal with fewer emergencies, compared with other specialists, and it’s easier for their patients to be slotted into an organized schedule. On the other hand, primary care doctors – internists, family practice physicians, and pediatricians – may be seeing 40-50 patients a day, one every 15 minutes.
Practice setting also makes a difference, said Ms. Murthy. Veterans Administration (VA) hospitals or government-run clinics tend to have more rigidly defined hours, compared with other settings, so if you’re in a VA hospital or government-run clinic, work-life balance tends to be better.
Physicians who work remotely via telehealth also tend to have a better work-life balance, compared with those who see patients in person, Ms. Murthy said. But the difference may be in not having to spend extra time commuting to work or interacting with others in the work environment, since some research has suggested that telehealth physicians may actually spend more time engaged in charting after hours, compared with their in-person counterparts.
Using scribes to maximize your time
Elliott Trotter, MD, is an emergency medicine physician, associate clinical professor of emergency medicine at Texas Christian University Medical Schools, and founder of the ScribeNest, a Texas-based company that trains health care scribes. He told this news organization that there are ways to maximize one’s time during shifts so that much of the charting can be accomplished during working hours.
“About 28 years ago, I realized that the documentation load for physicians was enormous and at that time I developed the Modern Scribe, using premed students for ‘elbow support’ to help with the workload by documenting the ED encounters in real time during the encounter so I wouldn’t have to do so later.”
Over the years, as EHRs have become more ubiquitous and onerous, the role of the scribe has “evolved from a luxury to a necessity,” said Dr. Trotter. The scribes can actually record the encounter directly into the EHR so that the physician doesn’t have to do so later and doesn’t have to look at a computer screen but can look at the patient during the encounter.
“This enhances communication and has been shown to improve patient care,” he said.
Dr. Trotter said he rarely, if ever, needs to do documentation after hours. “But one of my physician colleagues had over 500 charts in his in-basket on a regular basis, which was overwhelming and untenable.”
The use of AI in health care is rapidly growing. Tools to help hasten the process of taking notes through use of AI-generated summaries is something appealing to many doctors. Ms. Hill warned physicians to “be careful not to rely so heavily on AI that you trust it over your own words.” She noted that it can make mistakes, and the liability always remains with the clinician.
Creating time-efficient strategies
Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Teaneck, N.J., was formerly a psychiatrist in the substance abuse unit at Montefiore Hospital, New York. He told this news organization that he developed a system whereby he rarely had to take work home with him. “I was working only 20 hours a week, but I was usually able to do my charting during those hours, as well as seeing patients,” he said. “I scheduled my appointments and structured a little ‘buffer time’ between them so that I had time to document the first appointment before moving on to the next one.”
There were days when this wasn’t possible because there were too many patients who needed to be seen back-to-back. “So I developed my own template where I could take rapid, very standardized notes that fit into the format of the EHR and met those expectations.” Then, when he had finished seeing patients, he could quickly enter the content of his notes into the EHR. If necessary, he completed his charting on a different day.
Viwek Bisen, DO, assistant professor of psychiatry, Hackensack (N.J.) University Medical Center, is a psychiatrist in the emergency department. “My contract is based on a traditional 40-hour workweek, with 80% of my time allotted to seeing patients and 20% of my time allotted to administration.”
But the way his time actually plays out is that he’s seeing patients during about half of the 32 hours. “The rest of the time, I’m charting, speaking to family members of patients, writing notes, engaging in team meetings, and dealing with insurance companies.” Dr. Bisen has developed his own system of completing his notes while still in the hospital. “I’ve learned to be efficient and manage my time better, so I no longer have to take work home with me.”
“At the end of the day, doctors are people,” Ms. Hill said. “They are not machines. Maybe in residency and fellowship they may grind out impossible shifts with little sleep, but this pace isn’t tenable for an entire career.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s in a day’s work? For doctors, it’s typically a mix of seeing patients and completing paperwork and follow-up. Often it extends well past the standard workday.
Dennis Hursh, JD, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, describes one overwhelmed ob.gyn. who recently consulted him for this problem.
“My client had accepted a position in a group practice where his contract stated he would be working during normal office hours, Monday through Friday, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. – in other words, a 40-hour workweek,” Mr. Hursh said.
But the distressed physician discovered that actually, he was working almost twice as many hours. “He’d get to work early to do charting, then see patients during the 40 hours, perhaps grabbing a quick sandwich for a few minutes – and then stay after 5 [p.m.] for a few more hours when he’d work on charts or other administrative tasks. Then he’d get something to eat, work on more charts, then go to bed, get up in the morning, and repeat.”
Mr. Hursh summarized the client’s life: “Eating, sleeping, practicing clinical medicine, and doing nonclinical tasks.”
It turned out that the 40-hour workweek included in the contract referred to patient-facing hours, not to all of the ancillary tasks that are part of practicing medicine in this day and age. “Unfortunately, this is far from an isolated story,” said Mr. Hursh.
Be aware of what’s in the contract
“The first draft of many standard physician employment contracts often omits mention of patient contact hour requirements and rather uses vague verbiage such as ‘full-time’ employment or ‘1.0 FTE’ – or full-time equivalent – without defining that term,” said Mr. Hursh. Typically, the 40 hours exclude call coverage, but most physicians understand that and, at least at first glance, it all sounds very reasonable.
But once charting, hours on the phone, arguing with managed care companies, sending in prescriptions, administrative meetings, and other tasks are thrown in, the work hours expand dramatically. Moreover, if your employer doesn’t utilize hospitalists, you may be expected to “round” outside of the 40 hours, which can be particularly burdensome if the employer admits patients to multiple hospitals.
Amanda Hill, JD, owner of Hill Health Law based in Austin, Texas, told this news organization that this predicament isn’t unique to physicians. Exempt employees who don’t clock in and out are often expected to work overtime – that is, to “work as long as it takes to get the job done.” It can affect NPs, PAs, and many others in the health care space. But the number of tasks that fall upon a doctor’s shoulders and the fact that patients’ health and lives are at stake up the ante and make the situation far more difficult for doctors than for employees in other industries.
So it’s important to nail down precise terms in the contract and, if possible, negotiate for a more humane schedule by specifying how the working hours will be used.
“It’s true that a 1.0 FTE definition is too vague,” Ms. Hill said. “I’ve negotiated a lot of contracts where we nail down in writing that the in-office schedule equals 34 hours per week, so the physician is guaranteed an additional 6 hours for administrative time.”
Mr. Hursh usually asks for 32 hours of patient contact per week, which leaves 1 full day per week to catch up on basic administrative tasks. “It’s important for employers to recognize that seeing patients isn’t the only thing a doctor does and there’s a lot of work in addition to face-to-face time,” he said.
But he hasn’t always been successful. One physician client was seeking a workweek consisting of 36 patient contact hours, “which is 90% of the usual FTE of a 40-hour week,” said Mr. Hursh. “But the employer called it ‘part-time,’ as if the doctor were planning to be lying in the sun for the other 4 hours.”
The client decided to accept a 10% pay cut and 10% less vacation to guarantee that she had those extra hours for administrative tasks. “She’s probably working way more than 36 hours a week, but maybe closer to 50 or 60 instead of 70 or more,” he said.
Clarify call coverage
Call coverage is typically not included in the hours a physician is contracted to work on a weekly basis. “Most contracts have call, and it’s usually evenly distributed among parties in a practice, but call can expand if another doctor is out sick, for example,” said Ms. Hill.
Sometimes the language in the contract is vague regarding call coverage. “I ask, how many shifts per year is the doctor is expected to work? Then, I try to negotiate extra pay if more shifts arise,” she said. “The hospital or practice may not demand extra call because they don’t want to pay extra money to the physician.”
On the other hand, some physicians may be eager to take extra call if it means extra income.
Ms. Hill stated that one of her clients was being paid as a “part-time, 2-day-a-week provider” but was asked to be on call and take night and weekend work. When you added it all up, she was putting in almost 30 hours a week.
“This is abusive to a provider that works so hard for patients,” Ms. Hill said. “We have to protect them through the contract language, so they have something hard and fast to point to when their administrator pushes them too hard. Doctors should get value for their time.”
Ms. Hill and her client pushed for more money, and the employer gave in. “All we had to do was to point out how many hours she was actually working. She didn’t mind all the extra call, but she wanted to be compensated.” The doctor’s salary was hiked by $25,000.
Differences in specialties and settings
There are some specialties where it might be easier to have more defined hours, while other specialties are more challenging. Anu Murthy, Esq., an attorney and associate contract review specialist at Contract Diagnostics (a national firm that reviews physician contracts) told this news organization that the work of hospitalists, intensivists, and emergency department physicians, for example, is done in shifts, which tend to be fixed hours.
“They need to get their charting completed so that whoever takes over on the next shift has access to the most recent notes about the patient,” she said. By contrast, surgeons can’t always account for how long a given surgery will take. “It could be as long as 9 hours,” she said. Notes need to be written immediately for the sake of the patient’s postsurgical care.
Dermatologists tend to deal with fewer emergencies, compared with other specialists, and it’s easier for their patients to be slotted into an organized schedule. On the other hand, primary care doctors – internists, family practice physicians, and pediatricians – may be seeing 40-50 patients a day, one every 15 minutes.
Practice setting also makes a difference, said Ms. Murthy. Veterans Administration (VA) hospitals or government-run clinics tend to have more rigidly defined hours, compared with other settings, so if you’re in a VA hospital or government-run clinic, work-life balance tends to be better.
Physicians who work remotely via telehealth also tend to have a better work-life balance, compared with those who see patients in person, Ms. Murthy said. But the difference may be in not having to spend extra time commuting to work or interacting with others in the work environment, since some research has suggested that telehealth physicians may actually spend more time engaged in charting after hours, compared with their in-person counterparts.
Using scribes to maximize your time
Elliott Trotter, MD, is an emergency medicine physician, associate clinical professor of emergency medicine at Texas Christian University Medical Schools, and founder of the ScribeNest, a Texas-based company that trains health care scribes. He told this news organization that there are ways to maximize one’s time during shifts so that much of the charting can be accomplished during working hours.
“About 28 years ago, I realized that the documentation load for physicians was enormous and at that time I developed the Modern Scribe, using premed students for ‘elbow support’ to help with the workload by documenting the ED encounters in real time during the encounter so I wouldn’t have to do so later.”
Over the years, as EHRs have become more ubiquitous and onerous, the role of the scribe has “evolved from a luxury to a necessity,” said Dr. Trotter. The scribes can actually record the encounter directly into the EHR so that the physician doesn’t have to do so later and doesn’t have to look at a computer screen but can look at the patient during the encounter.
“This enhances communication and has been shown to improve patient care,” he said.
Dr. Trotter said he rarely, if ever, needs to do documentation after hours. “But one of my physician colleagues had over 500 charts in his in-basket on a regular basis, which was overwhelming and untenable.”
The use of AI in health care is rapidly growing. Tools to help hasten the process of taking notes through use of AI-generated summaries is something appealing to many doctors. Ms. Hill warned physicians to “be careful not to rely so heavily on AI that you trust it over your own words.” She noted that it can make mistakes, and the liability always remains with the clinician.
Creating time-efficient strategies
Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Teaneck, N.J., was formerly a psychiatrist in the substance abuse unit at Montefiore Hospital, New York. He told this news organization that he developed a system whereby he rarely had to take work home with him. “I was working only 20 hours a week, but I was usually able to do my charting during those hours, as well as seeing patients,” he said. “I scheduled my appointments and structured a little ‘buffer time’ between them so that I had time to document the first appointment before moving on to the next one.”
There were days when this wasn’t possible because there were too many patients who needed to be seen back-to-back. “So I developed my own template where I could take rapid, very standardized notes that fit into the format of the EHR and met those expectations.” Then, when he had finished seeing patients, he could quickly enter the content of his notes into the EHR. If necessary, he completed his charting on a different day.
Viwek Bisen, DO, assistant professor of psychiatry, Hackensack (N.J.) University Medical Center, is a psychiatrist in the emergency department. “My contract is based on a traditional 40-hour workweek, with 80% of my time allotted to seeing patients and 20% of my time allotted to administration.”
But the way his time actually plays out is that he’s seeing patients during about half of the 32 hours. “The rest of the time, I’m charting, speaking to family members of patients, writing notes, engaging in team meetings, and dealing with insurance companies.” Dr. Bisen has developed his own system of completing his notes while still in the hospital. “I’ve learned to be efficient and manage my time better, so I no longer have to take work home with me.”
“At the end of the day, doctors are people,” Ms. Hill said. “They are not machines. Maybe in residency and fellowship they may grind out impossible shifts with little sleep, but this pace isn’t tenable for an entire career.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s in a day’s work? For doctors, it’s typically a mix of seeing patients and completing paperwork and follow-up. Often it extends well past the standard workday.
Dennis Hursh, JD, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, describes one overwhelmed ob.gyn. who recently consulted him for this problem.
“My client had accepted a position in a group practice where his contract stated he would be working during normal office hours, Monday through Friday, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. – in other words, a 40-hour workweek,” Mr. Hursh said.
But the distressed physician discovered that actually, he was working almost twice as many hours. “He’d get to work early to do charting, then see patients during the 40 hours, perhaps grabbing a quick sandwich for a few minutes – and then stay after 5 [p.m.] for a few more hours when he’d work on charts or other administrative tasks. Then he’d get something to eat, work on more charts, then go to bed, get up in the morning, and repeat.”
Mr. Hursh summarized the client’s life: “Eating, sleeping, practicing clinical medicine, and doing nonclinical tasks.”
It turned out that the 40-hour workweek included in the contract referred to patient-facing hours, not to all of the ancillary tasks that are part of practicing medicine in this day and age. “Unfortunately, this is far from an isolated story,” said Mr. Hursh.
Be aware of what’s in the contract
“The first draft of many standard physician employment contracts often omits mention of patient contact hour requirements and rather uses vague verbiage such as ‘full-time’ employment or ‘1.0 FTE’ – or full-time equivalent – without defining that term,” said Mr. Hursh. Typically, the 40 hours exclude call coverage, but most physicians understand that and, at least at first glance, it all sounds very reasonable.
But once charting, hours on the phone, arguing with managed care companies, sending in prescriptions, administrative meetings, and other tasks are thrown in, the work hours expand dramatically. Moreover, if your employer doesn’t utilize hospitalists, you may be expected to “round” outside of the 40 hours, which can be particularly burdensome if the employer admits patients to multiple hospitals.
Amanda Hill, JD, owner of Hill Health Law based in Austin, Texas, told this news organization that this predicament isn’t unique to physicians. Exempt employees who don’t clock in and out are often expected to work overtime – that is, to “work as long as it takes to get the job done.” It can affect NPs, PAs, and many others in the health care space. But the number of tasks that fall upon a doctor’s shoulders and the fact that patients’ health and lives are at stake up the ante and make the situation far more difficult for doctors than for employees in other industries.
So it’s important to nail down precise terms in the contract and, if possible, negotiate for a more humane schedule by specifying how the working hours will be used.
“It’s true that a 1.0 FTE definition is too vague,” Ms. Hill said. “I’ve negotiated a lot of contracts where we nail down in writing that the in-office schedule equals 34 hours per week, so the physician is guaranteed an additional 6 hours for administrative time.”
Mr. Hursh usually asks for 32 hours of patient contact per week, which leaves 1 full day per week to catch up on basic administrative tasks. “It’s important for employers to recognize that seeing patients isn’t the only thing a doctor does and there’s a lot of work in addition to face-to-face time,” he said.
But he hasn’t always been successful. One physician client was seeking a workweek consisting of 36 patient contact hours, “which is 90% of the usual FTE of a 40-hour week,” said Mr. Hursh. “But the employer called it ‘part-time,’ as if the doctor were planning to be lying in the sun for the other 4 hours.”
The client decided to accept a 10% pay cut and 10% less vacation to guarantee that she had those extra hours for administrative tasks. “She’s probably working way more than 36 hours a week, but maybe closer to 50 or 60 instead of 70 or more,” he said.
Clarify call coverage
Call coverage is typically not included in the hours a physician is contracted to work on a weekly basis. “Most contracts have call, and it’s usually evenly distributed among parties in a practice, but call can expand if another doctor is out sick, for example,” said Ms. Hill.
Sometimes the language in the contract is vague regarding call coverage. “I ask, how many shifts per year is the doctor is expected to work? Then, I try to negotiate extra pay if more shifts arise,” she said. “The hospital or practice may not demand extra call because they don’t want to pay extra money to the physician.”
On the other hand, some physicians may be eager to take extra call if it means extra income.
Ms. Hill stated that one of her clients was being paid as a “part-time, 2-day-a-week provider” but was asked to be on call and take night and weekend work. When you added it all up, she was putting in almost 30 hours a week.
“This is abusive to a provider that works so hard for patients,” Ms. Hill said. “We have to protect them through the contract language, so they have something hard and fast to point to when their administrator pushes them too hard. Doctors should get value for their time.”
Ms. Hill and her client pushed for more money, and the employer gave in. “All we had to do was to point out how many hours she was actually working. She didn’t mind all the extra call, but she wanted to be compensated.” The doctor’s salary was hiked by $25,000.
Differences in specialties and settings
There are some specialties where it might be easier to have more defined hours, while other specialties are more challenging. Anu Murthy, Esq., an attorney and associate contract review specialist at Contract Diagnostics (a national firm that reviews physician contracts) told this news organization that the work of hospitalists, intensivists, and emergency department physicians, for example, is done in shifts, which tend to be fixed hours.
“They need to get their charting completed so that whoever takes over on the next shift has access to the most recent notes about the patient,” she said. By contrast, surgeons can’t always account for how long a given surgery will take. “It could be as long as 9 hours,” she said. Notes need to be written immediately for the sake of the patient’s postsurgical care.
Dermatologists tend to deal with fewer emergencies, compared with other specialists, and it’s easier for their patients to be slotted into an organized schedule. On the other hand, primary care doctors – internists, family practice physicians, and pediatricians – may be seeing 40-50 patients a day, one every 15 minutes.
Practice setting also makes a difference, said Ms. Murthy. Veterans Administration (VA) hospitals or government-run clinics tend to have more rigidly defined hours, compared with other settings, so if you’re in a VA hospital or government-run clinic, work-life balance tends to be better.
Physicians who work remotely via telehealth also tend to have a better work-life balance, compared with those who see patients in person, Ms. Murthy said. But the difference may be in not having to spend extra time commuting to work or interacting with others in the work environment, since some research has suggested that telehealth physicians may actually spend more time engaged in charting after hours, compared with their in-person counterparts.
Using scribes to maximize your time
Elliott Trotter, MD, is an emergency medicine physician, associate clinical professor of emergency medicine at Texas Christian University Medical Schools, and founder of the ScribeNest, a Texas-based company that trains health care scribes. He told this news organization that there are ways to maximize one’s time during shifts so that much of the charting can be accomplished during working hours.
“About 28 years ago, I realized that the documentation load for physicians was enormous and at that time I developed the Modern Scribe, using premed students for ‘elbow support’ to help with the workload by documenting the ED encounters in real time during the encounter so I wouldn’t have to do so later.”
Over the years, as EHRs have become more ubiquitous and onerous, the role of the scribe has “evolved from a luxury to a necessity,” said Dr. Trotter. The scribes can actually record the encounter directly into the EHR so that the physician doesn’t have to do so later and doesn’t have to look at a computer screen but can look at the patient during the encounter.
“This enhances communication and has been shown to improve patient care,” he said.
Dr. Trotter said he rarely, if ever, needs to do documentation after hours. “But one of my physician colleagues had over 500 charts in his in-basket on a regular basis, which was overwhelming and untenable.”
The use of AI in health care is rapidly growing. Tools to help hasten the process of taking notes through use of AI-generated summaries is something appealing to many doctors. Ms. Hill warned physicians to “be careful not to rely so heavily on AI that you trust it over your own words.” She noted that it can make mistakes, and the liability always remains with the clinician.
Creating time-efficient strategies
Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in Teaneck, N.J., was formerly a psychiatrist in the substance abuse unit at Montefiore Hospital, New York. He told this news organization that he developed a system whereby he rarely had to take work home with him. “I was working only 20 hours a week, but I was usually able to do my charting during those hours, as well as seeing patients,” he said. “I scheduled my appointments and structured a little ‘buffer time’ between them so that I had time to document the first appointment before moving on to the next one.”
There were days when this wasn’t possible because there were too many patients who needed to be seen back-to-back. “So I developed my own template where I could take rapid, very standardized notes that fit into the format of the EHR and met those expectations.” Then, when he had finished seeing patients, he could quickly enter the content of his notes into the EHR. If necessary, he completed his charting on a different day.
Viwek Bisen, DO, assistant professor of psychiatry, Hackensack (N.J.) University Medical Center, is a psychiatrist in the emergency department. “My contract is based on a traditional 40-hour workweek, with 80% of my time allotted to seeing patients and 20% of my time allotted to administration.”
But the way his time actually plays out is that he’s seeing patients during about half of the 32 hours. “The rest of the time, I’m charting, speaking to family members of patients, writing notes, engaging in team meetings, and dealing with insurance companies.” Dr. Bisen has developed his own system of completing his notes while still in the hospital. “I’ve learned to be efficient and manage my time better, so I no longer have to take work home with me.”
“At the end of the day, doctors are people,” Ms. Hill said. “They are not machines. Maybe in residency and fellowship they may grind out impossible shifts with little sleep, but this pace isn’t tenable for an entire career.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five personal finance questions for the young GI
While this article will get you started, these are complex topics, and each could warrant several standalone articles. I strongly encourage you to develop some basic understanding of personal finance through books, websites, and podcasts. If you can manage Barrett’s esophagus, Crohn’s, and cirrhosis, you can understand the basics of personal finance.
1. What should I do about my student loans? Go for public service loan forgiveness or pay them off?
The first step is knowing your debt burden, knowing your options, and developing a plan to pay off student loans. Public service loan forgiveness (PSLF) can be a good option in many situations. For borrowers staying in academic or other 501(c)(3) positions, PSLF is often an obvious move. Importantly, a fall 2022 statement by the U.S. Department of Education clarified that physicians working as contractors for nonprofit hospitals in California and Texas may now qualify for PSLF.1,2
For trainees debating an academic/501(c)(3) position vs. private practice, I would generally not advise making a career choice based purely on PSLF eligibility. However, borrowers with very high federal student loan burdens (e.g., debt to income ratio of > 2:1), or who are very close to the PSLF 10-year requirement may want to consider choosing a qualifying position for a few years to receive PSLF student loan forgiveness. Please see TNG’s 2020 article3 for a deeper discussion. Consultation with a company specializing in student loan advice for physicians may be well worth the upfront cost.
2. Do I need disability insurance? What should I look for?
I would strongly advise getting disability insurance as soon as possible (including while in training). While disability insurance is not cheap, it is one of the first steps you should take and one of the most important ways to protect your financial future. It is essential to look for a specialty-specific own occupation policy. Such a policy will provide disability payments if you are no longer able to work as a gastroenterologist/hepatologist (including an injury which prevents you from doing endoscopies).
There are two major types of disability policies: group policies and individual policies. See table 1 for a detailed comparison.
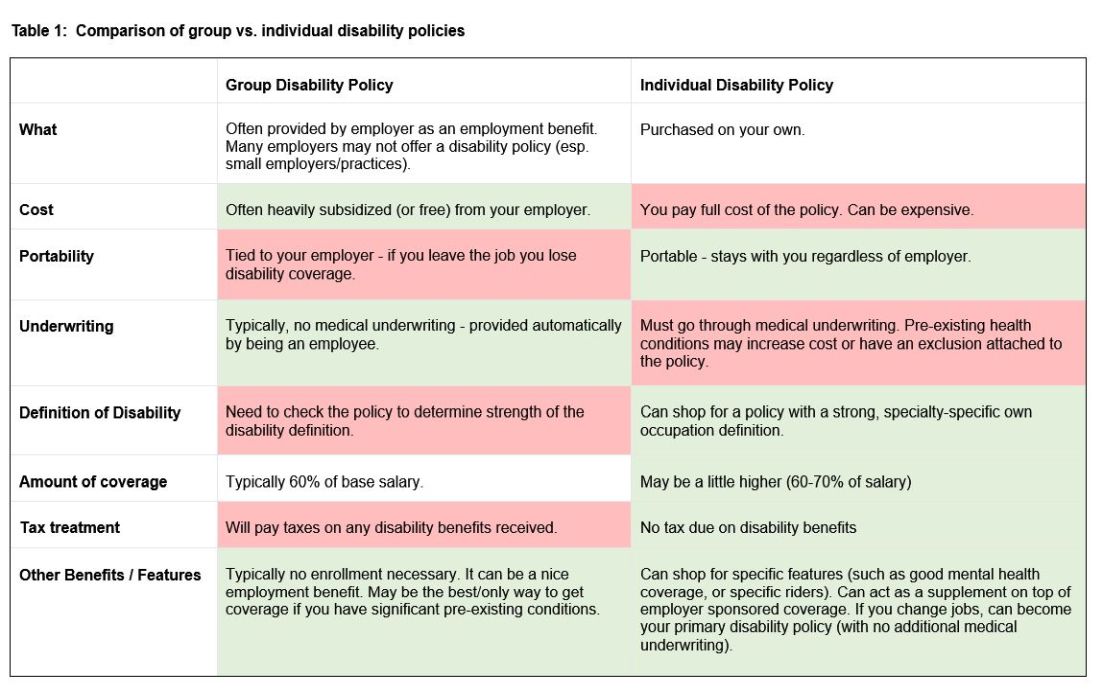
Your hospital/employer may provide a group policy at a heavily subsidized rate. Alternatively, you can purchase an individual disability policy, which is independent of your employer and will stay with you even if you change jobs. Currently, the only companies providing high quality own-occupation policies for physicians are Mass Mutual, Principal, Guardian, The Standard, and Ameritas. Because disability insurance is complicated, it is highly advisable to work with an agent experienced in physician disability policies.
Importantly, even if you have a group disability policy, you can purchase an individual policy as a supplement to provide extra coverage. If you leave employers, the individual policy can then become your primary disability policy without any additional medical underwriting.
3. Do I need life insurance? What type should I get?
If anyone is dependent on your income (partner, child, etc.), you should have life insurance. Moreover, if you expect to have dependents in the near future (e.g., children), you could consider getting life insurance now while you are younger and healthier. For a young GI with multiple financial obligations, term life insurance is generally the right product. Term life insurance is a straightforward, affordable product that can be purchased from multiple high-quality insurance carriers. There are two major considerations: The amount of coverage ($2 million, $3 million, etc.) and the length of coverage (20 years, 30 years, etc.). To estimate the appropriate amount of coverage, start with your expected annual household living expenses, and multiply by 25-30. While this is a rule of thumb, it will get you in the ballpark. For many young physicians, a $2-$5 million policy with 20- to 30-year coverage is reasonable.
Many financial advisers may suggest whole life insurance policies. These are typically not the ideal policy for young GIs who are just starting their careers. While whole life insurance may be the right choice in select cases, term life insurance will be the best product for most of TNG’s audience. As an example, a $3 million, 25-year term policy for a healthy, nonsmoking 35-year-old male would cost approximately $175 per month. A similar $3 million whole life policy could cost $2,000 per month or more.
4. What do I need to know about retirement accounts and investing?
The alphabet soup of retirement accounts can be confusing – IRA, 401k, 457. Retirement accounts provide a tax break to incentivize saving for retirement. Traditional (“non-Roth”) accounts provide a tax break today, but you will pay taxes when withdrawing the money in retirement. Roth accounts provide no tax break now but provide tax-free growth for decades, and no taxes are due when withdrawing money. See table 2 for a detailed comparison of retirement accounts.
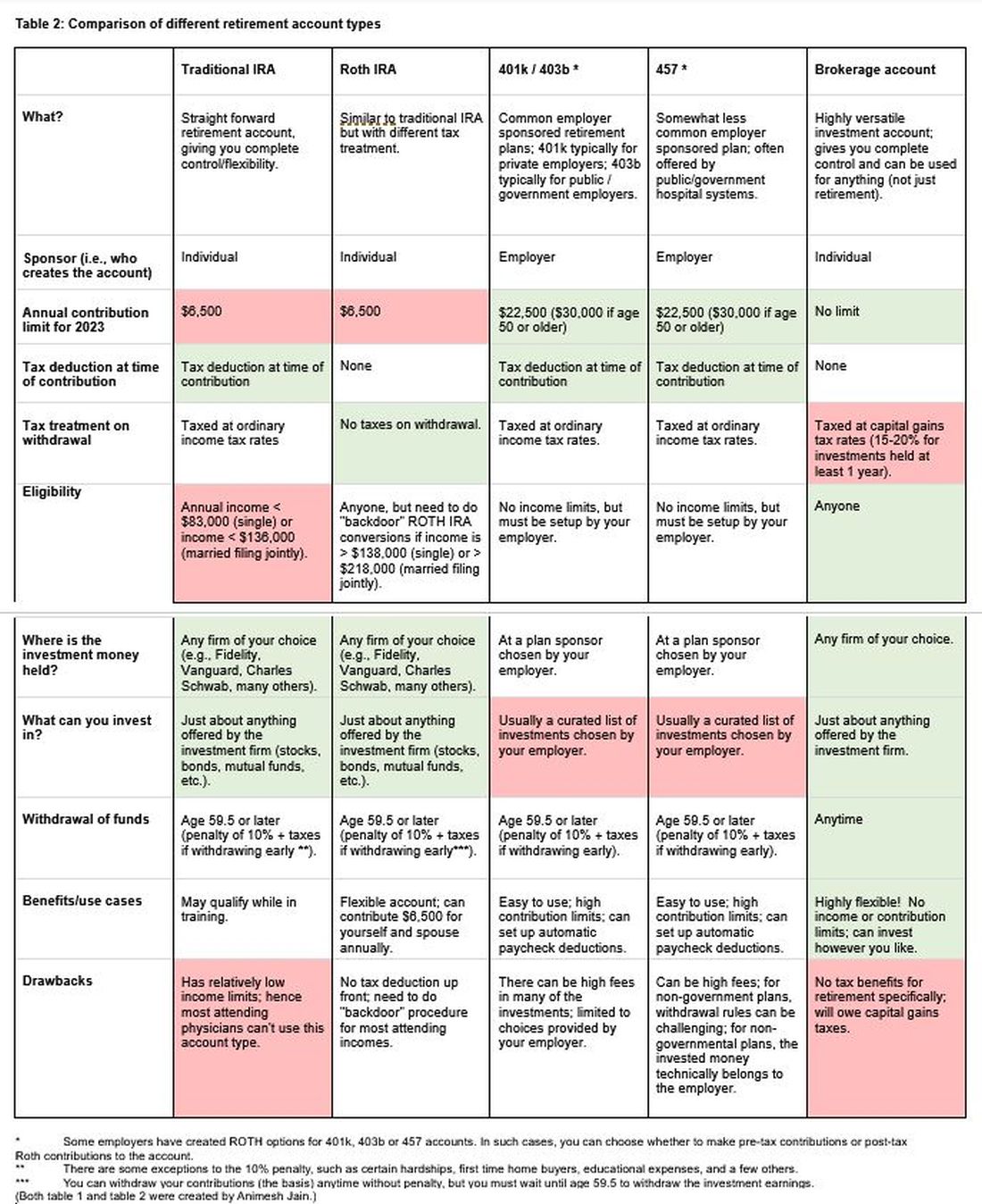
Once you place money into a retirement account, you will need to choose specific investments to grow your money. The two most common asset classes are stocks and bonds, though there are many other reasonable assets, such as real estate, commodities, and alternative currencies. It is generally recommended to have a higher proportion of stock-based investments early on (60%-90%) and then increase the ratio of bonds closer to retirement. Using low cost, passive index funds (or exchange traded funds) is a good way to get stock exposure. Target date retirement funds can be a nice tool for beginning investors since they will automatically adjust the stock/bond ratio for you.
Calculating the amount needed for retirement is beyond the scope of this article. However, saving at least 20% of your gross income specifically for retirement is a good starting point and should set you up for a reasonable retirement in about 30 years. For the average GI physician, this would mean saving $4,000 or more per month for retirement. If you aim to retire earlier, consider investing a higher percentage.
5. What do I need to know about buying a house?
The first question to ask is whether it makes sense to rent or buy a house. This is a personal and lifestyle decision, not just a financial decision. Today’s market is difficult with both high home prices and high rent costs. If there is a reasonable chance that you will be moving within 3-5 years, I would consider not buying until your long-term plans are more stable. Moreover, a high proportion of physicians change jobs.4,5,6 If you are just starting a new job, it is often wise to wait at least 6-12 months before buying a house to ensure the new job is a good fit. If you are in a stable long-term situation, it may be reasonable to buy a house. While it is commonly believed that buying a house is a “good financial move,” there are many hidden costs to home ownership, including big ticket repairs, property taxes, and real estate fees when selling a home.
First-time physician home buyers can often secure a physician mortgage with competitive interest rates and a low down payment of 0%-10% instead of the traditional 20% down payment. Moreover, a good physician mortgage should not have private mortgage insurance (PMI). Given the variation between mortgage companies, my most important piece of advice is to shop around for a good mortgage. An independent mortgage broker can be very valuable.
Dr. Jain is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. He has no conflicts of interest. The information in this article is meant for general educational purposes only. For individualized personal finance advice, please seek your own financial advisor, tax accountant, insurance broker, attorney, or other financial professional. Follow Dr. Jain @AJainMD on X.
References
1. Future of PSLF Fact Sheet
2. The Loophole That Can Get Thousands of Doctors into PSLF
3. Student loan management: An introduction for the young gastroenterologist
4. Study Shows First Job after Medical Residency Often Doesn’t Last
5. More physicians want to leave their jobs as pay rates fall, survey finds
6. Physician turnover rates are climbing as they clamor for better work-life balance
While this article will get you started, these are complex topics, and each could warrant several standalone articles. I strongly encourage you to develop some basic understanding of personal finance through books, websites, and podcasts. If you can manage Barrett’s esophagus, Crohn’s, and cirrhosis, you can understand the basics of personal finance.
1. What should I do about my student loans? Go for public service loan forgiveness or pay them off?
The first step is knowing your debt burden, knowing your options, and developing a plan to pay off student loans. Public service loan forgiveness (PSLF) can be a good option in many situations. For borrowers staying in academic or other 501(c)(3) positions, PSLF is often an obvious move. Importantly, a fall 2022 statement by the U.S. Department of Education clarified that physicians working as contractors for nonprofit hospitals in California and Texas may now qualify for PSLF.1,2
For trainees debating an academic/501(c)(3) position vs. private practice, I would generally not advise making a career choice based purely on PSLF eligibility. However, borrowers with very high federal student loan burdens (e.g., debt to income ratio of > 2:1), or who are very close to the PSLF 10-year requirement may want to consider choosing a qualifying position for a few years to receive PSLF student loan forgiveness. Please see TNG’s 2020 article3 for a deeper discussion. Consultation with a company specializing in student loan advice for physicians may be well worth the upfront cost.
2. Do I need disability insurance? What should I look for?
I would strongly advise getting disability insurance as soon as possible (including while in training). While disability insurance is not cheap, it is one of the first steps you should take and one of the most important ways to protect your financial future. It is essential to look for a specialty-specific own occupation policy. Such a policy will provide disability payments if you are no longer able to work as a gastroenterologist/hepatologist (including an injury which prevents you from doing endoscopies).
There are two major types of disability policies: group policies and individual policies. See table 1 for a detailed comparison.

Your hospital/employer may provide a group policy at a heavily subsidized rate. Alternatively, you can purchase an individual disability policy, which is independent of your employer and will stay with you even if you change jobs. Currently, the only companies providing high quality own-occupation policies for physicians are Mass Mutual, Principal, Guardian, The Standard, and Ameritas. Because disability insurance is complicated, it is highly advisable to work with an agent experienced in physician disability policies.
Importantly, even if you have a group disability policy, you can purchase an individual policy as a supplement to provide extra coverage. If you leave employers, the individual policy can then become your primary disability policy without any additional medical underwriting.
3. Do I need life insurance? What type should I get?
If anyone is dependent on your income (partner, child, etc.), you should have life insurance. Moreover, if you expect to have dependents in the near future (e.g., children), you could consider getting life insurance now while you are younger and healthier. For a young GI with multiple financial obligations, term life insurance is generally the right product. Term life insurance is a straightforward, affordable product that can be purchased from multiple high-quality insurance carriers. There are two major considerations: The amount of coverage ($2 million, $3 million, etc.) and the length of coverage (20 years, 30 years, etc.). To estimate the appropriate amount of coverage, start with your expected annual household living expenses, and multiply by 25-30. While this is a rule of thumb, it will get you in the ballpark. For many young physicians, a $2-$5 million policy with 20- to 30-year coverage is reasonable.
Many financial advisers may suggest whole life insurance policies. These are typically not the ideal policy for young GIs who are just starting their careers. While whole life insurance may be the right choice in select cases, term life insurance will be the best product for most of TNG’s audience. As an example, a $3 million, 25-year term policy for a healthy, nonsmoking 35-year-old male would cost approximately $175 per month. A similar $3 million whole life policy could cost $2,000 per month or more.
4. What do I need to know about retirement accounts and investing?
The alphabet soup of retirement accounts can be confusing – IRA, 401k, 457. Retirement accounts provide a tax break to incentivize saving for retirement. Traditional (“non-Roth”) accounts provide a tax break today, but you will pay taxes when withdrawing the money in retirement. Roth accounts provide no tax break now but provide tax-free growth for decades, and no taxes are due when withdrawing money. See table 2 for a detailed comparison of retirement accounts.

Once you place money into a retirement account, you will need to choose specific investments to grow your money. The two most common asset classes are stocks and bonds, though there are many other reasonable assets, such as real estate, commodities, and alternative currencies. It is generally recommended to have a higher proportion of stock-based investments early on (60%-90%) and then increase the ratio of bonds closer to retirement. Using low cost, passive index funds (or exchange traded funds) is a good way to get stock exposure. Target date retirement funds can be a nice tool for beginning investors since they will automatically adjust the stock/bond ratio for you.
Calculating the amount needed for retirement is beyond the scope of this article. However, saving at least 20% of your gross income specifically for retirement is a good starting point and should set you up for a reasonable retirement in about 30 years. For the average GI physician, this would mean saving $4,000 or more per month for retirement. If you aim to retire earlier, consider investing a higher percentage.
5. What do I need to know about buying a house?
The first question to ask is whether it makes sense to rent or buy a house. This is a personal and lifestyle decision, not just a financial decision. Today’s market is difficult with both high home prices and high rent costs. If there is a reasonable chance that you will be moving within 3-5 years, I would consider not buying until your long-term plans are more stable. Moreover, a high proportion of physicians change jobs.4,5,6 If you are just starting a new job, it is often wise to wait at least 6-12 months before buying a house to ensure the new job is a good fit. If you are in a stable long-term situation, it may be reasonable to buy a house. While it is commonly believed that buying a house is a “good financial move,” there are many hidden costs to home ownership, including big ticket repairs, property taxes, and real estate fees when selling a home.
First-time physician home buyers can often secure a physician mortgage with competitive interest rates and a low down payment of 0%-10% instead of the traditional 20% down payment. Moreover, a good physician mortgage should not have private mortgage insurance (PMI). Given the variation between mortgage companies, my most important piece of advice is to shop around for a good mortgage. An independent mortgage broker can be very valuable.
Dr. Jain is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. He has no conflicts of interest. The information in this article is meant for general educational purposes only. For individualized personal finance advice, please seek your own financial advisor, tax accountant, insurance broker, attorney, or other financial professional. Follow Dr. Jain @AJainMD on X.
References
1. Future of PSLF Fact Sheet
2. The Loophole That Can Get Thousands of Doctors into PSLF
3. Student loan management: An introduction for the young gastroenterologist
4. Study Shows First Job after Medical Residency Often Doesn’t Last
5. More physicians want to leave their jobs as pay rates fall, survey finds
6. Physician turnover rates are climbing as they clamor for better work-life balance
While this article will get you started, these are complex topics, and each could warrant several standalone articles. I strongly encourage you to develop some basic understanding of personal finance through books, websites, and podcasts. If you can manage Barrett’s esophagus, Crohn’s, and cirrhosis, you can understand the basics of personal finance.
1. What should I do about my student loans? Go for public service loan forgiveness or pay them off?
The first step is knowing your debt burden, knowing your options, and developing a plan to pay off student loans. Public service loan forgiveness (PSLF) can be a good option in many situations. For borrowers staying in academic or other 501(c)(3) positions, PSLF is often an obvious move. Importantly, a fall 2022 statement by the U.S. Department of Education clarified that physicians working as contractors for nonprofit hospitals in California and Texas may now qualify for PSLF.1,2
For trainees debating an academic/501(c)(3) position vs. private practice, I would generally not advise making a career choice based purely on PSLF eligibility. However, borrowers with very high federal student loan burdens (e.g., debt to income ratio of > 2:1), or who are very close to the PSLF 10-year requirement may want to consider choosing a qualifying position for a few years to receive PSLF student loan forgiveness. Please see TNG’s 2020 article3 for a deeper discussion. Consultation with a company specializing in student loan advice for physicians may be well worth the upfront cost.
2. Do I need disability insurance? What should I look for?
I would strongly advise getting disability insurance as soon as possible (including while in training). While disability insurance is not cheap, it is one of the first steps you should take and one of the most important ways to protect your financial future. It is essential to look for a specialty-specific own occupation policy. Such a policy will provide disability payments if you are no longer able to work as a gastroenterologist/hepatologist (including an injury which prevents you from doing endoscopies).
There are two major types of disability policies: group policies and individual policies. See table 1 for a detailed comparison.

Your hospital/employer may provide a group policy at a heavily subsidized rate. Alternatively, you can purchase an individual disability policy, which is independent of your employer and will stay with you even if you change jobs. Currently, the only companies providing high quality own-occupation policies for physicians are Mass Mutual, Principal, Guardian, The Standard, and Ameritas. Because disability insurance is complicated, it is highly advisable to work with an agent experienced in physician disability policies.
Importantly, even if you have a group disability policy, you can purchase an individual policy as a supplement to provide extra coverage. If you leave employers, the individual policy can then become your primary disability policy without any additional medical underwriting.
3. Do I need life insurance? What type should I get?
If anyone is dependent on your income (partner, child, etc.), you should have life insurance. Moreover, if you expect to have dependents in the near future (e.g., children), you could consider getting life insurance now while you are younger and healthier. For a young GI with multiple financial obligations, term life insurance is generally the right product. Term life insurance is a straightforward, affordable product that can be purchased from multiple high-quality insurance carriers. There are two major considerations: The amount of coverage ($2 million, $3 million, etc.) and the length of coverage (20 years, 30 years, etc.). To estimate the appropriate amount of coverage, start with your expected annual household living expenses, and multiply by 25-30. While this is a rule of thumb, it will get you in the ballpark. For many young physicians, a $2-$5 million policy with 20- to 30-year coverage is reasonable.
Many financial advisers may suggest whole life insurance policies. These are typically not the ideal policy for young GIs who are just starting their careers. While whole life insurance may be the right choice in select cases, term life insurance will be the best product for most of TNG’s audience. As an example, a $3 million, 25-year term policy for a healthy, nonsmoking 35-year-old male would cost approximately $175 per month. A similar $3 million whole life policy could cost $2,000 per month or more.
4. What do I need to know about retirement accounts and investing?
The alphabet soup of retirement accounts can be confusing – IRA, 401k, 457. Retirement accounts provide a tax break to incentivize saving for retirement. Traditional (“non-Roth”) accounts provide a tax break today, but you will pay taxes when withdrawing the money in retirement. Roth accounts provide no tax break now but provide tax-free growth for decades, and no taxes are due when withdrawing money. See table 2 for a detailed comparison of retirement accounts.

Once you place money into a retirement account, you will need to choose specific investments to grow your money. The two most common asset classes are stocks and bonds, though there are many other reasonable assets, such as real estate, commodities, and alternative currencies. It is generally recommended to have a higher proportion of stock-based investments early on (60%-90%) and then increase the ratio of bonds closer to retirement. Using low cost, passive index funds (or exchange traded funds) is a good way to get stock exposure. Target date retirement funds can be a nice tool for beginning investors since they will automatically adjust the stock/bond ratio for you.
Calculating the amount needed for retirement is beyond the scope of this article. However, saving at least 20% of your gross income specifically for retirement is a good starting point and should set you up for a reasonable retirement in about 30 years. For the average GI physician, this would mean saving $4,000 or more per month for retirement. If you aim to retire earlier, consider investing a higher percentage.
5. What do I need to know about buying a house?
The first question to ask is whether it makes sense to rent or buy a house. This is a personal and lifestyle decision, not just a financial decision. Today’s market is difficult with both high home prices and high rent costs. If there is a reasonable chance that you will be moving within 3-5 years, I would consider not buying until your long-term plans are more stable. Moreover, a high proportion of physicians change jobs.4,5,6 If you are just starting a new job, it is often wise to wait at least 6-12 months before buying a house to ensure the new job is a good fit. If you are in a stable long-term situation, it may be reasonable to buy a house. While it is commonly believed that buying a house is a “good financial move,” there are many hidden costs to home ownership, including big ticket repairs, property taxes, and real estate fees when selling a home.
First-time physician home buyers can often secure a physician mortgage with competitive interest rates and a low down payment of 0%-10% instead of the traditional 20% down payment. Moreover, a good physician mortgage should not have private mortgage insurance (PMI). Given the variation between mortgage companies, my most important piece of advice is to shop around for a good mortgage. An independent mortgage broker can be very valuable.
Dr. Jain is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill. He has no conflicts of interest. The information in this article is meant for general educational purposes only. For individualized personal finance advice, please seek your own financial advisor, tax accountant, insurance broker, attorney, or other financial professional. Follow Dr. Jain @AJainMD on X.
References
1. Future of PSLF Fact Sheet
2. The Loophole That Can Get Thousands of Doctors into PSLF
3. Student loan management: An introduction for the young gastroenterologist
4. Study Shows First Job after Medical Residency Often Doesn’t Last
5. More physicians want to leave their jobs as pay rates fall, survey finds
6. Physician turnover rates are climbing as they clamor for better work-life balance
Stripped privileges: An alarming precedent for community oncologists?
, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
The outcome, some community oncologists say, could set a new precedent in how far large health care organizations will go to take their patients or drive them out of business.
The case
On Sept. 5, Alliance sued Jefferson Health after Jefferson canceled the inpatient oncology/hematology privileges of five Alliance oncologists at three Jefferson Health-Northeast hospitals, primarily alleging that Jefferson was attempting to monopolize cancer care in the area.
Jefferson – one of the largest health care systems in the Philadelphia area that includes the NCI-designated Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center – made the move because it had entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient and outpatient oncology/hematology services at the hospitals.
In its court filings, Jefferson said it entered into the exclusive agreement because doing so was in “the best interest of patients, as it would ensure better integration and availability of care and help ensure that Jefferson consistently provides high-quality medical care in accordance with evidence-based standards.”
Tensions had been building between Alliance and Jefferson for years, ever since, according to Alliance, the community practice declined a buyout offer from Jefferson almost a decade ago.
But the revocation of privileges ultimately tipped the scales for Alliance, sparking the lawsuit.
“For us, that crossed a line,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, one of the five Alliance oncologists and a plaintiff in the suit.
Dr. Chasky and his colleagues had provided care at the hospitals for years, with about 10-15 patients admitted at any one time. The quality of their care is not in dispute. Dr. Chasky, for instance, routinely makes Philadelphia Magazine’s Top Doc List.
Under the new arrangement, the five Alliance oncologists have to hand over care of their admitted patients to Jefferson oncologists or send their patients to another hospital farther away where they do have admitting privileges.
“Without having admitting privileges,” community oncologists “can’t look a patient in the eye and say, ‘No matter what, I’ve got you,’ ” explained Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at the Community Oncology Alliance, a DC-based lobbying group for independent oncologists.
“A doctor doesn’t want to tell a patient that ‘once you go in the hospital, I have to hand you off.’ ” It undermines their practice, Mr. Ferreyros said.
The situation has caught the attention of other community oncologists who are worried that hospitals canceling admitting privileges might become a new tactic in what they characterize as an ongoing effort to elbow-out independent practitioners and corner the oncology market.
Dr. Chasky said he is getting “calls every day from independent oncologists throughout the country” who “are very concerned. People are watching this for sure.”
Alliance attorney Daniel Frier said that there is nothing unusual about hospitals entering into exclusive contracts with hospital-based practices.
But Mr. Frier said he’s never heard of a hospital entering into an exclusive contract and then terminating the privileges of community oncologists.
“There’s no direct precedent” for the move, he said.
Jefferson Health did not respond to requests for comment.
The ruling
U.S. District Court Judge Kai Scott, who ruled on Alliance’s motion to block the contract and preserve its oncologists’ admitting privileges, ultimately sided with Jefferson and allowed the contract to go forward.
Judge Scott wrote that, “while the court understands the plaintiffs’ concerns and desires to maintain the continuity of care for their own patients,” the court “is not persuaded that either of the two threshold elements for a temporary restraining order or preliminary injunction are met” – first, that Jefferson’s actions violate antitrust laws and second that the plaintiffs “will suffer immediate, irreparable harm” from having their admitting privileges rescinded.
Alliance argued that Jefferson’s contract violated federal antitrust laws and would allow Jefferson to monopolize the local oncology market.
However, Judge Scott called Alliance’s antitrust argument “lifeless” under the strict requirements for antitrust violations, explaining that, among other reasons, a monopoly is unlikely given that Jefferson competes with several high-profile oncology programs in the Philadelphia area, including the Fox Chase Cancer Center.
Judge Scott also expressed doubt that the Jefferson’s actions would cause irreparable harm to Alliance’s business. Alliance employs more than thirty oncologists affiliated with over a dozen hospitals in the greater Philadelphia area, and the inpatient services provided at Jefferson Health-Northeast did not represent a major part of its business.
Despite her ruling, Judge Scott did voice skepticism about some of Jefferson’s arguments.
“The court notes that the Jefferson defendants have briefly argued that Jefferson will be better able to ensure that its own patients receive fully integrated and coordinated care” under the exclusive provider agreement, but “it is unclear how the cooperation of ACS [Alliance Cancer Specialists] and JNE [Jefferson Health-Northeast] hospitalists really caused any problems for the coordinated care of” patients in the many years that they worked together.
It also “does not seem to necessarily serve the community to quickly sever the artery between the services that ACS provides and the services that JNE provides,” Judge Scott wrote.
She added that she would consider another motion from Alliance if the practice makes stronger arguments illustrating antitrust violations and demonstrating irreparable harm.
Currently, Dr. Chasky and Mr. Frier are considering their next steps in the case. The oncologists said they can appeal the judge’s decision or file a new complaint.
Meanwhile, Dr. Chasky and his four colleagues requested and were granted internal medicine privileges at Jefferson Health-Northeast, but given the considerable overlap between oncology and internal medicine, the line between what they can and cannot do remains unclear.
“It’s a mess,” he said.
A familiar story
Large health care entities have increasingly worked to push out or swallow up smaller, independent practices for years.
“What Dr. Chasky and his practice are going through is a little bit more of an aggressive version of what’s going on in the rest of the country,” said Michael Diaz, MD, a community oncologist at Florida Cancer Specialists, the largest independent medical oncology/hematology group in the United States. “The larger institutional hospitals try to make it a closed system so they can keep everything in-house and refer to their own physicians.”
The incentive, Dr. Diaz said, is the financial windfall that Section 340B of the 1992 Public Health Service Act generates for hospital-based oncology services at nonprofit hospitals, such as the Jefferson Health-Northeast facilities.
The 340B program allows nonprofit hospitals to buy primarily outpatient oncology drugs at steep discounts, sometimes 50% or more, and be reimbursed at full price.
When launched in 1992, the program was meant to help a handful of safety-net hospitals cover the cost of charity care, and now approximately more than half of U.S. hospitals participate in the program, particularly after requirements were loosened by the Affordable Care Act. But there’s little transparency on how the money is spent.
Critics say the incentives have created a feeding frenzy among 340B hospitals to either acquire outpatient oncology practices or take their business because of the particularly high margins on oncology drugs. There are similar incentives for hospital-based infusion centers.
In its lawsuit, Alliance alleged that such incentives are what motivated Jefferson’s recent actions.
“It’s all about the money at the end of the day,” said Christian Thomas, MD, a community oncologist with New England Cancer Specialists, Scarborough, Maine, who, like Dr. Diaz, said he’s seen the dynamic play out repeatedly in his career.
The American Hospital Association has been a vigorous defender of 340B in the courts and elsewhere, but the Association’s communications staff had little to say when this news organization reached out about the Jefferson-Alliance situation, except that they do not comment on “specific hospital circumstance.”
Reverberations around the country
Many community oncologists are keeping close tabs on the Jefferson-Alliance situation.
“Our group has been watching Jefferson closely because our [local] hospital is following the same playbook, but they have not yet gone after our privileges,” said Scott Herbert, MD, a community oncologist with the independent Nexus Health system, Sante Fe, N.M.
Dr. Herbert was referring to what has happened since he and his colleagues declined to renew an exclusive provider agreement early this year with St. Vincent Regional Medical Center, a nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe. The agreement allowed the hospital to take advantage of the 340B program because Nexus oncologists acted on its behalf.
St. Vincent’s owner, Christus Health, did not respond to inquiries from this news organization.
Nexus let the contract lapse because its oncologists wanted to provide services at a second, newer hospital in Santa Fe where some of their patients had begun seeking treatment.
The nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe is now building its own oncology practice. Similar to Dr. Chasky’s experience in Philadelphia, Dr. Herbert said his group has seen referrals from the hospital dry up and existing patients rechanneled to the hospital’s oncologists.
“We found over 109 patients in January and February that were referred to one of our docs that got rerouted to one of their docs,” he said.
Dr. Herbert has sent cease-and-desist letters, but “after we saw what Jefferson did, my group said, ‘You better back off of the hospital, or it’s going to take our privileges.’ ”
The Jefferson situation “is sending a message,” he said. “Frankly, we’ve been terrified” at the thought of losing privileges there. “It’s the busiest hospital in our area.”
The future of community oncology
Despite the challenges, Mr. Ferreyros at the Community Oncology Alliance remains optimistic about the future of independent oncology.
Under the competitive pressures, a lot of independent oncology practices have folded in recent years, but the ones that remain are strong. Payers are also increasingly noticing that community oncology practices are less expensive than hospital-based practices for comparable care, he said.
Relationships with hospitals aren’t always adversarial, either. “A lot of practices have collaborative agreements with local hospitals” that work out well, Mr. Ferreyros said, adding that sometimes hospitals even hand over oncology care to local independents after finding that starting and maintaining an oncology service is harder than they imagined.
“The last two decades have been difficult,” but the remaining community oncology practices “are going strong,” he said, and “we’ve never seen more engagement on our issues,” particularly around the issue of cost savings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
The outcome, some community oncologists say, could set a new precedent in how far large health care organizations will go to take their patients or drive them out of business.
The case
On Sept. 5, Alliance sued Jefferson Health after Jefferson canceled the inpatient oncology/hematology privileges of five Alliance oncologists at three Jefferson Health-Northeast hospitals, primarily alleging that Jefferson was attempting to monopolize cancer care in the area.
Jefferson – one of the largest health care systems in the Philadelphia area that includes the NCI-designated Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center – made the move because it had entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient and outpatient oncology/hematology services at the hospitals.
In its court filings, Jefferson said it entered into the exclusive agreement because doing so was in “the best interest of patients, as it would ensure better integration and availability of care and help ensure that Jefferson consistently provides high-quality medical care in accordance with evidence-based standards.”
Tensions had been building between Alliance and Jefferson for years, ever since, according to Alliance, the community practice declined a buyout offer from Jefferson almost a decade ago.
But the revocation of privileges ultimately tipped the scales for Alliance, sparking the lawsuit.
“For us, that crossed a line,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, one of the five Alliance oncologists and a plaintiff in the suit.
Dr. Chasky and his colleagues had provided care at the hospitals for years, with about 10-15 patients admitted at any one time. The quality of their care is not in dispute. Dr. Chasky, for instance, routinely makes Philadelphia Magazine’s Top Doc List.
Under the new arrangement, the five Alliance oncologists have to hand over care of their admitted patients to Jefferson oncologists or send their patients to another hospital farther away where they do have admitting privileges.
“Without having admitting privileges,” community oncologists “can’t look a patient in the eye and say, ‘No matter what, I’ve got you,’ ” explained Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at the Community Oncology Alliance, a DC-based lobbying group for independent oncologists.
“A doctor doesn’t want to tell a patient that ‘once you go in the hospital, I have to hand you off.’ ” It undermines their practice, Mr. Ferreyros said.
The situation has caught the attention of other community oncologists who are worried that hospitals canceling admitting privileges might become a new tactic in what they characterize as an ongoing effort to elbow-out independent practitioners and corner the oncology market.
Dr. Chasky said he is getting “calls every day from independent oncologists throughout the country” who “are very concerned. People are watching this for sure.”
Alliance attorney Daniel Frier said that there is nothing unusual about hospitals entering into exclusive contracts with hospital-based practices.
But Mr. Frier said he’s never heard of a hospital entering into an exclusive contract and then terminating the privileges of community oncologists.
“There’s no direct precedent” for the move, he said.
Jefferson Health did not respond to requests for comment.
The ruling
U.S. District Court Judge Kai Scott, who ruled on Alliance’s motion to block the contract and preserve its oncologists’ admitting privileges, ultimately sided with Jefferson and allowed the contract to go forward.
Judge Scott wrote that, “while the court understands the plaintiffs’ concerns and desires to maintain the continuity of care for their own patients,” the court “is not persuaded that either of the two threshold elements for a temporary restraining order or preliminary injunction are met” – first, that Jefferson’s actions violate antitrust laws and second that the plaintiffs “will suffer immediate, irreparable harm” from having their admitting privileges rescinded.
Alliance argued that Jefferson’s contract violated federal antitrust laws and would allow Jefferson to monopolize the local oncology market.
However, Judge Scott called Alliance’s antitrust argument “lifeless” under the strict requirements for antitrust violations, explaining that, among other reasons, a monopoly is unlikely given that Jefferson competes with several high-profile oncology programs in the Philadelphia area, including the Fox Chase Cancer Center.
Judge Scott also expressed doubt that the Jefferson’s actions would cause irreparable harm to Alliance’s business. Alliance employs more than thirty oncologists affiliated with over a dozen hospitals in the greater Philadelphia area, and the inpatient services provided at Jefferson Health-Northeast did not represent a major part of its business.
Despite her ruling, Judge Scott did voice skepticism about some of Jefferson’s arguments.
“The court notes that the Jefferson defendants have briefly argued that Jefferson will be better able to ensure that its own patients receive fully integrated and coordinated care” under the exclusive provider agreement, but “it is unclear how the cooperation of ACS [Alliance Cancer Specialists] and JNE [Jefferson Health-Northeast] hospitalists really caused any problems for the coordinated care of” patients in the many years that they worked together.
It also “does not seem to necessarily serve the community to quickly sever the artery between the services that ACS provides and the services that JNE provides,” Judge Scott wrote.
She added that she would consider another motion from Alliance if the practice makes stronger arguments illustrating antitrust violations and demonstrating irreparable harm.
Currently, Dr. Chasky and Mr. Frier are considering their next steps in the case. The oncologists said they can appeal the judge’s decision or file a new complaint.
Meanwhile, Dr. Chasky and his four colleagues requested and were granted internal medicine privileges at Jefferson Health-Northeast, but given the considerable overlap between oncology and internal medicine, the line between what they can and cannot do remains unclear.
“It’s a mess,” he said.
A familiar story
Large health care entities have increasingly worked to push out or swallow up smaller, independent practices for years.
“What Dr. Chasky and his practice are going through is a little bit more of an aggressive version of what’s going on in the rest of the country,” said Michael Diaz, MD, a community oncologist at Florida Cancer Specialists, the largest independent medical oncology/hematology group in the United States. “The larger institutional hospitals try to make it a closed system so they can keep everything in-house and refer to their own physicians.”
The incentive, Dr. Diaz said, is the financial windfall that Section 340B of the 1992 Public Health Service Act generates for hospital-based oncology services at nonprofit hospitals, such as the Jefferson Health-Northeast facilities.
The 340B program allows nonprofit hospitals to buy primarily outpatient oncology drugs at steep discounts, sometimes 50% or more, and be reimbursed at full price.
When launched in 1992, the program was meant to help a handful of safety-net hospitals cover the cost of charity care, and now approximately more than half of U.S. hospitals participate in the program, particularly after requirements were loosened by the Affordable Care Act. But there’s little transparency on how the money is spent.
Critics say the incentives have created a feeding frenzy among 340B hospitals to either acquire outpatient oncology practices or take their business because of the particularly high margins on oncology drugs. There are similar incentives for hospital-based infusion centers.
In its lawsuit, Alliance alleged that such incentives are what motivated Jefferson’s recent actions.
“It’s all about the money at the end of the day,” said Christian Thomas, MD, a community oncologist with New England Cancer Specialists, Scarborough, Maine, who, like Dr. Diaz, said he’s seen the dynamic play out repeatedly in his career.
The American Hospital Association has been a vigorous defender of 340B in the courts and elsewhere, but the Association’s communications staff had little to say when this news organization reached out about the Jefferson-Alliance situation, except that they do not comment on “specific hospital circumstance.”
Reverberations around the country
Many community oncologists are keeping close tabs on the Jefferson-Alliance situation.
“Our group has been watching Jefferson closely because our [local] hospital is following the same playbook, but they have not yet gone after our privileges,” said Scott Herbert, MD, a community oncologist with the independent Nexus Health system, Sante Fe, N.M.
Dr. Herbert was referring to what has happened since he and his colleagues declined to renew an exclusive provider agreement early this year with St. Vincent Regional Medical Center, a nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe. The agreement allowed the hospital to take advantage of the 340B program because Nexus oncologists acted on its behalf.
St. Vincent’s owner, Christus Health, did not respond to inquiries from this news organization.
Nexus let the contract lapse because its oncologists wanted to provide services at a second, newer hospital in Santa Fe where some of their patients had begun seeking treatment.
The nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe is now building its own oncology practice. Similar to Dr. Chasky’s experience in Philadelphia, Dr. Herbert said his group has seen referrals from the hospital dry up and existing patients rechanneled to the hospital’s oncologists.
“We found over 109 patients in January and February that were referred to one of our docs that got rerouted to one of their docs,” he said.
Dr. Herbert has sent cease-and-desist letters, but “after we saw what Jefferson did, my group said, ‘You better back off of the hospital, or it’s going to take our privileges.’ ”
The Jefferson situation “is sending a message,” he said. “Frankly, we’ve been terrified” at the thought of losing privileges there. “It’s the busiest hospital in our area.”
The future of community oncology
Despite the challenges, Mr. Ferreyros at the Community Oncology Alliance remains optimistic about the future of independent oncology.
Under the competitive pressures, a lot of independent oncology practices have folded in recent years, but the ones that remain are strong. Payers are also increasingly noticing that community oncology practices are less expensive than hospital-based practices for comparable care, he said.
Relationships with hospitals aren’t always adversarial, either. “A lot of practices have collaborative agreements with local hospitals” that work out well, Mr. Ferreyros said, adding that sometimes hospitals even hand over oncology care to local independents after finding that starting and maintaining an oncology service is harder than they imagined.
“The last two decades have been difficult,” but the remaining community oncology practices “are going strong,” he said, and “we’ve never seen more engagement on our issues,” particularly around the issue of cost savings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, Alliance Cancer Specialists.
The outcome, some community oncologists say, could set a new precedent in how far large health care organizations will go to take their patients or drive them out of business.
The case
On Sept. 5, Alliance sued Jefferson Health after Jefferson canceled the inpatient oncology/hematology privileges of five Alliance oncologists at three Jefferson Health-Northeast hospitals, primarily alleging that Jefferson was attempting to monopolize cancer care in the area.
Jefferson – one of the largest health care systems in the Philadelphia area that includes the NCI-designated Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center – made the move because it had entered into an exclusive agreement with its own medical group to provide inpatient and outpatient oncology/hematology services at the hospitals.
In its court filings, Jefferson said it entered into the exclusive agreement because doing so was in “the best interest of patients, as it would ensure better integration and availability of care and help ensure that Jefferson consistently provides high-quality medical care in accordance with evidence-based standards.”
Tensions had been building between Alliance and Jefferson for years, ever since, according to Alliance, the community practice declined a buyout offer from Jefferson almost a decade ago.
But the revocation of privileges ultimately tipped the scales for Alliance, sparking the lawsuit.
“For us, that crossed a line,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, one of the five Alliance oncologists and a plaintiff in the suit.
Dr. Chasky and his colleagues had provided care at the hospitals for years, with about 10-15 patients admitted at any one time. The quality of their care is not in dispute. Dr. Chasky, for instance, routinely makes Philadelphia Magazine’s Top Doc List.
Under the new arrangement, the five Alliance oncologists have to hand over care of their admitted patients to Jefferson oncologists or send their patients to another hospital farther away where they do have admitting privileges.
“Without having admitting privileges,” community oncologists “can’t look a patient in the eye and say, ‘No matter what, I’ve got you,’ ” explained Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at the Community Oncology Alliance, a DC-based lobbying group for independent oncologists.
“A doctor doesn’t want to tell a patient that ‘once you go in the hospital, I have to hand you off.’ ” It undermines their practice, Mr. Ferreyros said.
The situation has caught the attention of other community oncologists who are worried that hospitals canceling admitting privileges might become a new tactic in what they characterize as an ongoing effort to elbow-out independent practitioners and corner the oncology market.
Dr. Chasky said he is getting “calls every day from independent oncologists throughout the country” who “are very concerned. People are watching this for sure.”
Alliance attorney Daniel Frier said that there is nothing unusual about hospitals entering into exclusive contracts with hospital-based practices.
But Mr. Frier said he’s never heard of a hospital entering into an exclusive contract and then terminating the privileges of community oncologists.
“There’s no direct precedent” for the move, he said.
Jefferson Health did not respond to requests for comment.
The ruling
U.S. District Court Judge Kai Scott, who ruled on Alliance’s motion to block the contract and preserve its oncologists’ admitting privileges, ultimately sided with Jefferson and allowed the contract to go forward.
Judge Scott wrote that, “while the court understands the plaintiffs’ concerns and desires to maintain the continuity of care for their own patients,” the court “is not persuaded that either of the two threshold elements for a temporary restraining order or preliminary injunction are met” – first, that Jefferson’s actions violate antitrust laws and second that the plaintiffs “will suffer immediate, irreparable harm” from having their admitting privileges rescinded.
Alliance argued that Jefferson’s contract violated federal antitrust laws and would allow Jefferson to monopolize the local oncology market.
However, Judge Scott called Alliance’s antitrust argument “lifeless” under the strict requirements for antitrust violations, explaining that, among other reasons, a monopoly is unlikely given that Jefferson competes with several high-profile oncology programs in the Philadelphia area, including the Fox Chase Cancer Center.
Judge Scott also expressed doubt that the Jefferson’s actions would cause irreparable harm to Alliance’s business. Alliance employs more than thirty oncologists affiliated with over a dozen hospitals in the greater Philadelphia area, and the inpatient services provided at Jefferson Health-Northeast did not represent a major part of its business.
Despite her ruling, Judge Scott did voice skepticism about some of Jefferson’s arguments.
“The court notes that the Jefferson defendants have briefly argued that Jefferson will be better able to ensure that its own patients receive fully integrated and coordinated care” under the exclusive provider agreement, but “it is unclear how the cooperation of ACS [Alliance Cancer Specialists] and JNE [Jefferson Health-Northeast] hospitalists really caused any problems for the coordinated care of” patients in the many years that they worked together.
It also “does not seem to necessarily serve the community to quickly sever the artery between the services that ACS provides and the services that JNE provides,” Judge Scott wrote.
She added that she would consider another motion from Alliance if the practice makes stronger arguments illustrating antitrust violations and demonstrating irreparable harm.
Currently, Dr. Chasky and Mr. Frier are considering their next steps in the case. The oncologists said they can appeal the judge’s decision or file a new complaint.
Meanwhile, Dr. Chasky and his four colleagues requested and were granted internal medicine privileges at Jefferson Health-Northeast, but given the considerable overlap between oncology and internal medicine, the line between what they can and cannot do remains unclear.
“It’s a mess,” he said.
A familiar story
Large health care entities have increasingly worked to push out or swallow up smaller, independent practices for years.
“What Dr. Chasky and his practice are going through is a little bit more of an aggressive version of what’s going on in the rest of the country,” said Michael Diaz, MD, a community oncologist at Florida Cancer Specialists, the largest independent medical oncology/hematology group in the United States. “The larger institutional hospitals try to make it a closed system so they can keep everything in-house and refer to their own physicians.”
The incentive, Dr. Diaz said, is the financial windfall that Section 340B of the 1992 Public Health Service Act generates for hospital-based oncology services at nonprofit hospitals, such as the Jefferson Health-Northeast facilities.
The 340B program allows nonprofit hospitals to buy primarily outpatient oncology drugs at steep discounts, sometimes 50% or more, and be reimbursed at full price.
When launched in 1992, the program was meant to help a handful of safety-net hospitals cover the cost of charity care, and now approximately more than half of U.S. hospitals participate in the program, particularly after requirements were loosened by the Affordable Care Act. But there’s little transparency on how the money is spent.
Critics say the incentives have created a feeding frenzy among 340B hospitals to either acquire outpatient oncology practices or take their business because of the particularly high margins on oncology drugs. There are similar incentives for hospital-based infusion centers.
In its lawsuit, Alliance alleged that such incentives are what motivated Jefferson’s recent actions.
“It’s all about the money at the end of the day,” said Christian Thomas, MD, a community oncologist with New England Cancer Specialists, Scarborough, Maine, who, like Dr. Diaz, said he’s seen the dynamic play out repeatedly in his career.
The American Hospital Association has been a vigorous defender of 340B in the courts and elsewhere, but the Association’s communications staff had little to say when this news organization reached out about the Jefferson-Alliance situation, except that they do not comment on “specific hospital circumstance.”
Reverberations around the country
Many community oncologists are keeping close tabs on the Jefferson-Alliance situation.
“Our group has been watching Jefferson closely because our [local] hospital is following the same playbook, but they have not yet gone after our privileges,” said Scott Herbert, MD, a community oncologist with the independent Nexus Health system, Sante Fe, N.M.
Dr. Herbert was referring to what has happened since he and his colleagues declined to renew an exclusive provider agreement early this year with St. Vincent Regional Medical Center, a nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe. The agreement allowed the hospital to take advantage of the 340B program because Nexus oncologists acted on its behalf.
St. Vincent’s owner, Christus Health, did not respond to inquiries from this news organization.
Nexus let the contract lapse because its oncologists wanted to provide services at a second, newer hospital in Santa Fe where some of their patients had begun seeking treatment.
The nonprofit hospital in Sante Fe is now building its own oncology practice. Similar to Dr. Chasky’s experience in Philadelphia, Dr. Herbert said his group has seen referrals from the hospital dry up and existing patients rechanneled to the hospital’s oncologists.
“We found over 109 patients in January and February that were referred to one of our docs that got rerouted to one of their docs,” he said.
Dr. Herbert has sent cease-and-desist letters, but “after we saw what Jefferson did, my group said, ‘You better back off of the hospital, or it’s going to take our privileges.’ ”
The Jefferson situation “is sending a message,” he said. “Frankly, we’ve been terrified” at the thought of losing privileges there. “It’s the busiest hospital in our area.”
The future of community oncology
Despite the challenges, Mr. Ferreyros at the Community Oncology Alliance remains optimistic about the future of independent oncology.
Under the competitive pressures, a lot of independent oncology practices have folded in recent years, but the ones that remain are strong. Payers are also increasingly noticing that community oncology practices are less expensive than hospital-based practices for comparable care, he said.
Relationships with hospitals aren’t always adversarial, either. “A lot of practices have collaborative agreements with local hospitals” that work out well, Mr. Ferreyros said, adding that sometimes hospitals even hand over oncology care to local independents after finding that starting and maintaining an oncology service is harder than they imagined.
“The last two decades have been difficult,” but the remaining community oncology practices “are going strong,” he said, and “we’ve never seen more engagement on our issues,” particularly around the issue of cost savings.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early career considerations for gastroenterologists interested in diversity, equity, and inclusion roles

Highlighting the importance of DEI across all aspects of medicine is long overdue, and the field of gastroenterology is no exception. Diversity in the gastroenterology workforce still has significant room for improvement with only 12% of all gastroenterology fellows in 2018 identifying as Black, Latino/a/x, American Indian or Alaskan Native, or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.1 Moreover, only 4.4% of practicing gastroenterologists identify as Black, 6.7% identify as Latino/a/x, 0.1% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 0.003% as Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.2
The intensified focus on diversity in GI is welcomed, but increasing physician workforce diversity is only one of the necessary steps. If our ultimate goal is to improve health outcomes and achieve health equity for historically marginalized racial, ethnic, and socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, we must critically evaluate the path beyond just enhancing workforce diversity.
Black and Latino/a/x physicians are more likely to care for historically marginalized communities,3 which has been shown to improve all-cause mortality and reduce racial disparities.4 Additionally, diverse work teams are more innovative and productive.5 Therefore, expanding diversity must include 1) providing equitable policies and access to opportunities and promotions; 2) building inclusive environments in our institutions and practices; and 3) providing space for all people to feel like they can belong, feel respected at work, and genuinely have their opinions and ideas valued. What diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging provide for us and our patients are avenues to thrive, solve complex problems, and tackle prominent issues within our institutions, workplaces, and communities.
To this end, many academic centers, hospitals, and private practice entities have produced a flurry of new DEI initiatives coupled with titles and roles. Some of these roles have thankfully brought recognition and economic compensation to the people doing this work. Still, as an early career gastroenterologist, you may be offered or are considering taking on a DEI role during your early career. As two underrepresented minority women in medicine who took on DEI roles with their first jobs, we wanted to highlight a few aspects to think about during your early career:
Does the DEI role come with resources?
Historically, DEI efforts were treated as “extra work,” or an activity that was done using one’s own personal time. In addition, this work called upon the small number of physicians underrepresented in medicine, largely uncompensated and with an exorbitant minority tax during a critical moment in establishing their early careers. DEI should no longer be seen as an extracurricular activity but as a vital component of an institution’s success.
If you are considering a DEI role, the first question to ask is, “Does this role come with extra compensation or protected time?” We highly recommend not taking on the role if the answer is no. If your institution or employer is only offering increased minority tax, you are being set up to either fail, burn out, or both. Your employer or institution does not appear to value your time or effort in DEI, and you should interpret their lack of compensation or protected time as such.
If the answer is yes, then here are a few other things to consider: Is there institutional support for you to be successful in your new role? As DEI work challenges you to come up with solutions to combat years of historic marginalization for racial and ethnic minorities, this work can sometimes feel overwhelming and isolating. The importance of the DEI community and mentorship within and outside your institution is critical. You should consider joining DEI working groups or committees through GI national societies, the Association of American Medical Colleges, or the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. You can also connect with a fantastic network of people engaged in this work via social media and lean on friends and colleagues leading similar initiatives across the country.
Other critical logistical questions are if your role will come with administrative support, whether there is a budget for programs or events, and whether your institution/employer will support you in seeking continued professional development for your DEI role.6
Make sure to understand the “ask” from your division, department, or company.
Before confirming you are willing to take on this role, get a clear vision of what you are being asked to accomplish. There are so many opportunities to improve the DEI landscape. Therefore, knowing what you are specifically being asked to do will be critical to your success.
Are you being asked to work on diversity?
Does your institution want you to focus on and improve the recruitment and retention of trainees, physicians, or staff underrepresented in medicine? If so, you will need to have access to all the prior work and statistics. Capture the landscape before your interventions (% underrepresented in medicine [URiM] trainees, % URiM faculty at each level, % of URiM trainees retained as faculty, % of URiM faculty being promoted each year, etc.) This will allow you to determine the outcomes of your proposed improvements or programs.
Is your employer focused on equity?
Are you being asked to think about ways to operationalize improved patient health equity, or are you being asked to build equitable opportunities/programs for career advancement for URiMs at your institution? For either equity issue, you first need to understand the scope of the problem to ask for the necessary resources for a potential solution. Discuss timeline expectations, as equity work is a marathon and may take years to move the needle on any particular issue. This timeline is also critical for your employer to be aware of and support, as unrealistic timelines and expectations will also set you up for failure.
Or, are you being asked to concentrate on inclusion?
Does your institution need an assessment of how inclusive the climate is for trainees, staff, or physicians? Does this assessment align with your division or department’s impression, and how do you plan to work toward potential solutions for improvement?
Although diversity, equity, and inclusion are interconnected entities, they all have distinct objectives and solutions. It is essential to understand your vision and your employer’s vision for this role. If they are not aligned, having early and in-depth conversations about aligning your visions will set you on a path to success in your early career.
Know your why or more importantly, your who?
Early career physicians who are considering taking on DEI work do so for a reason. Being passionate about this type of work is usually born from a personal experience or your deep-rooted values. For us, experiencing and witnessing health disparities for our family members and people who look like us are what initially fueled our passion for this work. Additional experiences with trainees and patients keep us invigorated to continue highlighting the importance of DEI and encourage others to be passionate about DEI’s huge value added. As DEI work can come with challenges, remembering and re-centering on why you are passionate about this work or who you are engaging in this work for can keep you going.
There are several aspects to consider before taking on a DEI role, but overall, the work is rewarding and can be a great addition to the building blocks of your early career. In the short term, you build a DEI community network of peers, mentors, colleagues, and friends beyond your immediate institution and specialty. You also can demonstrate your leadership skills and potential early on in your career. In the long-term, engaging in these types of roles helps build a climate and culture that is conducive to enacting change for our patients and communities, including advancing healthcare equity and working toward recruitment, retention, and expansion efforts for our trainees and faculty. Overall, we think this type of work in your early career can be an integral part of your personal and professional development, while also having an impact that ripples beyond the walls of the endoscopy suite.
Dr. Fritz is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Rodriguez is a gastroenterologist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Neither Dr. Rodriguez nor Dr. Fritz disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Santhosh L,Babik JM. Trends in racial and ethnic diversity in internal medicine subspecialty fellowships from 2006 to 2018. JAMA Network Open 2020;3:e1920482-e1920482.
2. Colleges AoAM. Physician Specialty Data Report/Active physicians who identified as Black or African-American, 2021. 2022.
3. Komaromy M et al. The role of black and Hispanic physicians in providing health care for underserved populations. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334:1305-10.
4. Snyder JE et al. Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancy and mortality rates in the US. JAMA Network Open 2023;6:e236687-e236687.
5. Page S. Diversity bonuses and the business case. The Diversity Bonus: Princeton University Press, 2017:184-208.
6. Vela MB et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion officer position available: Proceed with caution. Journal of Graduate Medical Education 2021;13:771-3.
Helpful resources
Diversity and Inclusion Toolkit Resources, AAMC
Blackinggastro.org, The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists (ABGH)
Podcast: Clinical Problem Solvers: Anti-Racism in Medicine

Highlighting the importance of DEI across all aspects of medicine is long overdue, and the field of gastroenterology is no exception. Diversity in the gastroenterology workforce still has significant room for improvement with only 12% of all gastroenterology fellows in 2018 identifying as Black, Latino/a/x, American Indian or Alaskan Native, or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.1 Moreover, only 4.4% of practicing gastroenterologists identify as Black, 6.7% identify as Latino/a/x, 0.1% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 0.003% as Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.2
The intensified focus on diversity in GI is welcomed, but increasing physician workforce diversity is only one of the necessary steps. If our ultimate goal is to improve health outcomes and achieve health equity for historically marginalized racial, ethnic, and socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, we must critically evaluate the path beyond just enhancing workforce diversity.
Black and Latino/a/x physicians are more likely to care for historically marginalized communities,3 which has been shown to improve all-cause mortality and reduce racial disparities.4 Additionally, diverse work teams are more innovative and productive.5 Therefore, expanding diversity must include 1) providing equitable policies and access to opportunities and promotions; 2) building inclusive environments in our institutions and practices; and 3) providing space for all people to feel like they can belong, feel respected at work, and genuinely have their opinions and ideas valued. What diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging provide for us and our patients are avenues to thrive, solve complex problems, and tackle prominent issues within our institutions, workplaces, and communities.
To this end, many academic centers, hospitals, and private practice entities have produced a flurry of new DEI initiatives coupled with titles and roles. Some of these roles have thankfully brought recognition and economic compensation to the people doing this work. Still, as an early career gastroenterologist, you may be offered or are considering taking on a DEI role during your early career. As two underrepresented minority women in medicine who took on DEI roles with their first jobs, we wanted to highlight a few aspects to think about during your early career:
Does the DEI role come with resources?
Historically, DEI efforts were treated as “extra work,” or an activity that was done using one’s own personal time. In addition, this work called upon the small number of physicians underrepresented in medicine, largely uncompensated and with an exorbitant minority tax during a critical moment in establishing their early careers. DEI should no longer be seen as an extracurricular activity but as a vital component of an institution’s success.
If you are considering a DEI role, the first question to ask is, “Does this role come with extra compensation or protected time?” We highly recommend not taking on the role if the answer is no. If your institution or employer is only offering increased minority tax, you are being set up to either fail, burn out, or both. Your employer or institution does not appear to value your time or effort in DEI, and you should interpret their lack of compensation or protected time as such.
If the answer is yes, then here are a few other things to consider: Is there institutional support for you to be successful in your new role? As DEI work challenges you to come up with solutions to combat years of historic marginalization for racial and ethnic minorities, this work can sometimes feel overwhelming and isolating. The importance of the DEI community and mentorship within and outside your institution is critical. You should consider joining DEI working groups or committees through GI national societies, the Association of American Medical Colleges, or the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. You can also connect with a fantastic network of people engaged in this work via social media and lean on friends and colleagues leading similar initiatives across the country.
Other critical logistical questions are if your role will come with administrative support, whether there is a budget for programs or events, and whether your institution/employer will support you in seeking continued professional development for your DEI role.6
Make sure to understand the “ask” from your division, department, or company.
Before confirming you are willing to take on this role, get a clear vision of what you are being asked to accomplish. There are so many opportunities to improve the DEI landscape. Therefore, knowing what you are specifically being asked to do will be critical to your success.
Are you being asked to work on diversity?
Does your institution want you to focus on and improve the recruitment and retention of trainees, physicians, or staff underrepresented in medicine? If so, you will need to have access to all the prior work and statistics. Capture the landscape before your interventions (% underrepresented in medicine [URiM] trainees, % URiM faculty at each level, % of URiM trainees retained as faculty, % of URiM faculty being promoted each year, etc.) This will allow you to determine the outcomes of your proposed improvements or programs.
Is your employer focused on equity?
Are you being asked to think about ways to operationalize improved patient health equity, or are you being asked to build equitable opportunities/programs for career advancement for URiMs at your institution? For either equity issue, you first need to understand the scope of the problem to ask for the necessary resources for a potential solution. Discuss timeline expectations, as equity work is a marathon and may take years to move the needle on any particular issue. This timeline is also critical for your employer to be aware of and support, as unrealistic timelines and expectations will also set you up for failure.
Or, are you being asked to concentrate on inclusion?
Does your institution need an assessment of how inclusive the climate is for trainees, staff, or physicians? Does this assessment align with your division or department’s impression, and how do you plan to work toward potential solutions for improvement?
Although diversity, equity, and inclusion are interconnected entities, they all have distinct objectives and solutions. It is essential to understand your vision and your employer’s vision for this role. If they are not aligned, having early and in-depth conversations about aligning your visions will set you on a path to success in your early career.
Know your why or more importantly, your who?
Early career physicians who are considering taking on DEI work do so for a reason. Being passionate about this type of work is usually born from a personal experience or your deep-rooted values. For us, experiencing and witnessing health disparities for our family members and people who look like us are what initially fueled our passion for this work. Additional experiences with trainees and patients keep us invigorated to continue highlighting the importance of DEI and encourage others to be passionate about DEI’s huge value added. As DEI work can come with challenges, remembering and re-centering on why you are passionate about this work or who you are engaging in this work for can keep you going.
There are several aspects to consider before taking on a DEI role, but overall, the work is rewarding and can be a great addition to the building blocks of your early career. In the short term, you build a DEI community network of peers, mentors, colleagues, and friends beyond your immediate institution and specialty. You also can demonstrate your leadership skills and potential early on in your career. In the long-term, engaging in these types of roles helps build a climate and culture that is conducive to enacting change for our patients and communities, including advancing healthcare equity and working toward recruitment, retention, and expansion efforts for our trainees and faculty. Overall, we think this type of work in your early career can be an integral part of your personal and professional development, while also having an impact that ripples beyond the walls of the endoscopy suite.
Dr. Fritz is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Rodriguez is a gastroenterologist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Neither Dr. Rodriguez nor Dr. Fritz disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Santhosh L,Babik JM. Trends in racial and ethnic diversity in internal medicine subspecialty fellowships from 2006 to 2018. JAMA Network Open 2020;3:e1920482-e1920482.
2. Colleges AoAM. Physician Specialty Data Report/Active physicians who identified as Black or African-American, 2021. 2022.
3. Komaromy M et al. The role of black and Hispanic physicians in providing health care for underserved populations. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334:1305-10.
4. Snyder JE et al. Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancy and mortality rates in the US. JAMA Network Open 2023;6:e236687-e236687.
5. Page S. Diversity bonuses and the business case. The Diversity Bonus: Princeton University Press, 2017:184-208.
6. Vela MB et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion officer position available: Proceed with caution. Journal of Graduate Medical Education 2021;13:771-3.
Helpful resources
Diversity and Inclusion Toolkit Resources, AAMC
Blackinggastro.org, The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists (ABGH)
Podcast: Clinical Problem Solvers: Anti-Racism in Medicine

Highlighting the importance of DEI across all aspects of medicine is long overdue, and the field of gastroenterology is no exception. Diversity in the gastroenterology workforce still has significant room for improvement with only 12% of all gastroenterology fellows in 2018 identifying as Black, Latino/a/x, American Indian or Alaskan Native, or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.1 Moreover, only 4.4% of practicing gastroenterologists identify as Black, 6.7% identify as Latino/a/x, 0.1% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 0.003% as Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander.2
The intensified focus on diversity in GI is welcomed, but increasing physician workforce diversity is only one of the necessary steps. If our ultimate goal is to improve health outcomes and achieve health equity for historically marginalized racial, ethnic, and socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, we must critically evaluate the path beyond just enhancing workforce diversity.
Black and Latino/a/x physicians are more likely to care for historically marginalized communities,3 which has been shown to improve all-cause mortality and reduce racial disparities.4 Additionally, diverse work teams are more innovative and productive.5 Therefore, expanding diversity must include 1) providing equitable policies and access to opportunities and promotions; 2) building inclusive environments in our institutions and practices; and 3) providing space for all people to feel like they can belong, feel respected at work, and genuinely have their opinions and ideas valued. What diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging provide for us and our patients are avenues to thrive, solve complex problems, and tackle prominent issues within our institutions, workplaces, and communities.
To this end, many academic centers, hospitals, and private practice entities have produced a flurry of new DEI initiatives coupled with titles and roles. Some of these roles have thankfully brought recognition and economic compensation to the people doing this work. Still, as an early career gastroenterologist, you may be offered or are considering taking on a DEI role during your early career. As two underrepresented minority women in medicine who took on DEI roles with their first jobs, we wanted to highlight a few aspects to think about during your early career:
Does the DEI role come with resources?
Historically, DEI efforts were treated as “extra work,” or an activity that was done using one’s own personal time. In addition, this work called upon the small number of physicians underrepresented in medicine, largely uncompensated and with an exorbitant minority tax during a critical moment in establishing their early careers. DEI should no longer be seen as an extracurricular activity but as a vital component of an institution’s success.
If you are considering a DEI role, the first question to ask is, “Does this role come with extra compensation or protected time?” We highly recommend not taking on the role if the answer is no. If your institution or employer is only offering increased minority tax, you are being set up to either fail, burn out, or both. Your employer or institution does not appear to value your time or effort in DEI, and you should interpret their lack of compensation or protected time as such.
If the answer is yes, then here are a few other things to consider: Is there institutional support for you to be successful in your new role? As DEI work challenges you to come up with solutions to combat years of historic marginalization for racial and ethnic minorities, this work can sometimes feel overwhelming and isolating. The importance of the DEI community and mentorship within and outside your institution is critical. You should consider joining DEI working groups or committees through GI national societies, the Association of American Medical Colleges, or the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. You can also connect with a fantastic network of people engaged in this work via social media and lean on friends and colleagues leading similar initiatives across the country.
Other critical logistical questions are if your role will come with administrative support, whether there is a budget for programs or events, and whether your institution/employer will support you in seeking continued professional development for your DEI role.6
Make sure to understand the “ask” from your division, department, or company.
Before confirming you are willing to take on this role, get a clear vision of what you are being asked to accomplish. There are so many opportunities to improve the DEI landscape. Therefore, knowing what you are specifically being asked to do will be critical to your success.
Are you being asked to work on diversity?
Does your institution want you to focus on and improve the recruitment and retention of trainees, physicians, or staff underrepresented in medicine? If so, you will need to have access to all the prior work and statistics. Capture the landscape before your interventions (% underrepresented in medicine [URiM] trainees, % URiM faculty at each level, % of URiM trainees retained as faculty, % of URiM faculty being promoted each year, etc.) This will allow you to determine the outcomes of your proposed improvements or programs.
Is your employer focused on equity?
Are you being asked to think about ways to operationalize improved patient health equity, or are you being asked to build equitable opportunities/programs for career advancement for URiMs at your institution? For either equity issue, you first need to understand the scope of the problem to ask for the necessary resources for a potential solution. Discuss timeline expectations, as equity work is a marathon and may take years to move the needle on any particular issue. This timeline is also critical for your employer to be aware of and support, as unrealistic timelines and expectations will also set you up for failure.
Or, are you being asked to concentrate on inclusion?
Does your institution need an assessment of how inclusive the climate is for trainees, staff, or physicians? Does this assessment align with your division or department’s impression, and how do you plan to work toward potential solutions for improvement?
Although diversity, equity, and inclusion are interconnected entities, they all have distinct objectives and solutions. It is essential to understand your vision and your employer’s vision for this role. If they are not aligned, having early and in-depth conversations about aligning your visions will set you on a path to success in your early career.
Know your why or more importantly, your who?
Early career physicians who are considering taking on DEI work do so for a reason. Being passionate about this type of work is usually born from a personal experience or your deep-rooted values. For us, experiencing and witnessing health disparities for our family members and people who look like us are what initially fueled our passion for this work. Additional experiences with trainees and patients keep us invigorated to continue highlighting the importance of DEI and encourage others to be passionate about DEI’s huge value added. As DEI work can come with challenges, remembering and re-centering on why you are passionate about this work or who you are engaging in this work for can keep you going.
There are several aspects to consider before taking on a DEI role, but overall, the work is rewarding and can be a great addition to the building blocks of your early career. In the short term, you build a DEI community network of peers, mentors, colleagues, and friends beyond your immediate institution and specialty. You also can demonstrate your leadership skills and potential early on in your career. In the long-term, engaging in these types of roles helps build a climate and culture that is conducive to enacting change for our patients and communities, including advancing healthcare equity and working toward recruitment, retention, and expansion efforts for our trainees and faculty. Overall, we think this type of work in your early career can be an integral part of your personal and professional development, while also having an impact that ripples beyond the walls of the endoscopy suite.
Dr. Fritz is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Rodriguez is a gastroenterologist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Neither Dr. Rodriguez nor Dr. Fritz disclosed no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Santhosh L,Babik JM. Trends in racial and ethnic diversity in internal medicine subspecialty fellowships from 2006 to 2018. JAMA Network Open 2020;3:e1920482-e1920482.
2. Colleges AoAM. Physician Specialty Data Report/Active physicians who identified as Black or African-American, 2021. 2022.
3. Komaromy M et al. The role of black and Hispanic physicians in providing health care for underserved populations. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334:1305-10.
4. Snyder JE et al. Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancy and mortality rates in the US. JAMA Network Open 2023;6:e236687-e236687.
5. Page S. Diversity bonuses and the business case. The Diversity Bonus: Princeton University Press, 2017:184-208.
6. Vela MB et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion officer position available: Proceed with caution. Journal of Graduate Medical Education 2021;13:771-3.
Helpful resources
Diversity and Inclusion Toolkit Resources, AAMC
Blackinggastro.org, The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists (ABGH)
Podcast: Clinical Problem Solvers: Anti-Racism in Medicine
84-year-old MD contests employer’s mandatory cognitive tests for older docs
Lylas G. Mogk, MD, recently sued Henry Ford Health and Henry Ford Medical Group in federal court, alleging that the mandatory cognitive test violates the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Age Discrimination in Employment Act, and two Michigan laws.
Dr. Mogk’s lawsuit follows a widely watched 2020 case in which the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission sued Yale New Haven Hospital, the teaching hospital of Yale University, for age discrimination. According to the lawsuit, the hospital illegally required neuropsychological and eye examinations of physicians aged 70 or older who sought to gain or renew staff privileges.
According to the lawsuit, Dr. Mogk is a member of Henry Ford Medical Group, which in 2017 required all members aged 70 and older to undergo cognitive screening tests. The tests would be repeated every 5 years thereafter, the lawsuit said, and anyone who refused would have to resign or be fired.
Dr. Mogk completed the screening, although no information about the results or outcome was mentioned in the lawsuit. It’s not clear whether Henry Ford’s cognitive test mandate remains in place; a spokesperson for Henry Ford Health and attorneys for Dr. Mogk declined to comment.
The number of practicing physicians in their 70s and beyond is rising. A 2021 report found that 12% of U.S. licensed physicians in 2020 were least 70 years old, up from 9% in 2010 and an increase from 75,627 to 120,510. The percentage of doctors aged 60-69 grew to 19% from 16% in 2010.
The number of health systems requiring testing of older physicians isn’t known, although various reports suggest at least a dozen have had mandates.
The University of California, San Diego, offers a physical and mental screening program that health organizations can use to evaluate “late-career physicians,” and a 2021 report noted that “Nebraska’s Children’s Hospital requires physicians aged 70 years and older to undergo an assessment by several peers, a complete physical, and unspecified cognitive screening.” Another system, Hartford HealthCare, mandated an annual reappointment process for clinicians aged 70 or older, requiring them to undergo various exams.
There’s evidence that physician performance declines with age. However, age-based cognitive testing can run afoul of federal and state laws against age discrimination, said Sharona Hoffman, JD, professor of law and bioethics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, in an interview.
Federal law prohibits age-related restrictions on employment but allows exceptions in areas like public safety, said Ms. Hoffman, who’s written about age discrimination and testing requirements. Pilots, law enforcement officers, firefighters, and air controllers, for example, can be forced to retire at specific ages.
It’s not clear how many physicians took the cognitive tests required by Henry Ford Medical Group.
However, details are available about the policy at Yale New Haven Hospital: According to the EEOC lawsuit, from 2016 to 2019, 145 physicians aged 70 or older took the mandatory test. Of those, seven individuals failed either or both of the exams, 14 were listed as “borderline deficient,” and one was listed as “deficient.” Another five refused testing and either resigned or changed their status. The EEOC case against the hospital is still pending.
“You can make an argument that health care is like a public safety job because people put their lives in the hands of doctors,” Ms. Hoffman said.
In defending mandatory cognitive tests, she said, health care systems could say, “it’s not really discrimination; we’re not forcing them to retire, we’re not limiting their work in any way. We’re just doing testing to make sure they perform competently, and the ADA allows us to conduct testing that is job-related.”
Indeed, a Yale New Haven Hospital spokesman made an argument along these lines in a statement regarding the 2020 lawsuit: The “policy is designed to protect our patients from potential harm while including safeguards to ensure that our physicians are treated fairly. The policy is modeled on similar standards in other industries, and we are confident that no discrimination has occurred and will vigorously defend ourselves in this matter.”
However, Ms. Hoffman herself doesn’t buy these arguments. Requiring tests only for older physicians does appear to be discrimination based on age, she said. As an alternative, “employers can do close supervision of people. As soon as there are performance problems or patient complaints, you need to see a doctor or get testing done.”
Another option is to mandate tests at specific ages via licensing boards. “I don’t think that would be legally problematic,” Ms. Hoffman said.
What else can be done to protect patients from clinicians whose skills have significantly declined as they’ve aged? The 2021 report in Neurology Clinical Practice notes that there are disadvantages to several strategies.
One common approach, waiting to evaluate a clinician until an error occurs, can lead to patient harm, the report’s authors wrote. Relying on reporting by peers is problematic because “physicians have been very resistant to reporting colleagues who are impaired” and the “medical apprenticeship model discourages physicians from reporting on senior colleagues.”
Physician self-assessment is yet another option, but “loss of insight may be a component of an individual’s impairment,” the authors wrote.
So what’s the best solution? The authors recommended “a relatively brief cognitive screening followed by more extensive testing for the most impaired individuals.” This approach “appears most reliable in confidentially identifying truly impaired physicians while minimizing the chance of a falsely flagging unimpaired individuals. This strategy allows aging physicians to continue working while safeguarding both their reputations and their patients’ health.”
Ms. Hoffman has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lylas G. Mogk, MD, recently sued Henry Ford Health and Henry Ford Medical Group in federal court, alleging that the mandatory cognitive test violates the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Age Discrimination in Employment Act, and two Michigan laws.
Dr. Mogk’s lawsuit follows a widely watched 2020 case in which the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission sued Yale New Haven Hospital, the teaching hospital of Yale University, for age discrimination. According to the lawsuit, the hospital illegally required neuropsychological and eye examinations of physicians aged 70 or older who sought to gain or renew staff privileges.
According to the lawsuit, Dr. Mogk is a member of Henry Ford Medical Group, which in 2017 required all members aged 70 and older to undergo cognitive screening tests. The tests would be repeated every 5 years thereafter, the lawsuit said, and anyone who refused would have to resign or be fired.
Dr. Mogk completed the screening, although no information about the results or outcome was mentioned in the lawsuit. It’s not clear whether Henry Ford’s cognitive test mandate remains in place; a spokesperson for Henry Ford Health and attorneys for Dr. Mogk declined to comment.
The number of practicing physicians in their 70s and beyond is rising. A 2021 report found that 12% of U.S. licensed physicians in 2020 were least 70 years old, up from 9% in 2010 and an increase from 75,627 to 120,510. The percentage of doctors aged 60-69 grew to 19% from 16% in 2010.
The number of health systems requiring testing of older physicians isn’t known, although various reports suggest at least a dozen have had mandates.
The University of California, San Diego, offers a physical and mental screening program that health organizations can use to evaluate “late-career physicians,” and a 2021 report noted that “Nebraska’s Children’s Hospital requires physicians aged 70 years and older to undergo an assessment by several peers, a complete physical, and unspecified cognitive screening.” Another system, Hartford HealthCare, mandated an annual reappointment process for clinicians aged 70 or older, requiring them to undergo various exams.
There’s evidence that physician performance declines with age. However, age-based cognitive testing can run afoul of federal and state laws against age discrimination, said Sharona Hoffman, JD, professor of law and bioethics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, in an interview.
Federal law prohibits age-related restrictions on employment but allows exceptions in areas like public safety, said Ms. Hoffman, who’s written about age discrimination and testing requirements. Pilots, law enforcement officers, firefighters, and air controllers, for example, can be forced to retire at specific ages.
It’s not clear how many physicians took the cognitive tests required by Henry Ford Medical Group.
However, details are available about the policy at Yale New Haven Hospital: According to the EEOC lawsuit, from 2016 to 2019, 145 physicians aged 70 or older took the mandatory test. Of those, seven individuals failed either or both of the exams, 14 were listed as “borderline deficient,” and one was listed as “deficient.” Another five refused testing and either resigned or changed their status. The EEOC case against the hospital is still pending.
“You can make an argument that health care is like a public safety job because people put their lives in the hands of doctors,” Ms. Hoffman said.
In defending mandatory cognitive tests, she said, health care systems could say, “it’s not really discrimination; we’re not forcing them to retire, we’re not limiting their work in any way. We’re just doing testing to make sure they perform competently, and the ADA allows us to conduct testing that is job-related.”
Indeed, a Yale New Haven Hospital spokesman made an argument along these lines in a statement regarding the 2020 lawsuit: The “policy is designed to protect our patients from potential harm while including safeguards to ensure that our physicians are treated fairly. The policy is modeled on similar standards in other industries, and we are confident that no discrimination has occurred and will vigorously defend ourselves in this matter.”
However, Ms. Hoffman herself doesn’t buy these arguments. Requiring tests only for older physicians does appear to be discrimination based on age, she said. As an alternative, “employers can do close supervision of people. As soon as there are performance problems or patient complaints, you need to see a doctor or get testing done.”
Another option is to mandate tests at specific ages via licensing boards. “I don’t think that would be legally problematic,” Ms. Hoffman said.
What else can be done to protect patients from clinicians whose skills have significantly declined as they’ve aged? The 2021 report in Neurology Clinical Practice notes that there are disadvantages to several strategies.
One common approach, waiting to evaluate a clinician until an error occurs, can lead to patient harm, the report’s authors wrote. Relying on reporting by peers is problematic because “physicians have been very resistant to reporting colleagues who are impaired” and the “medical apprenticeship model discourages physicians from reporting on senior colleagues.”
Physician self-assessment is yet another option, but “loss of insight may be a component of an individual’s impairment,” the authors wrote.
So what’s the best solution? The authors recommended “a relatively brief cognitive screening followed by more extensive testing for the most impaired individuals.” This approach “appears most reliable in confidentially identifying truly impaired physicians while minimizing the chance of a falsely flagging unimpaired individuals. This strategy allows aging physicians to continue working while safeguarding both their reputations and their patients’ health.”
Ms. Hoffman has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lylas G. Mogk, MD, recently sued Henry Ford Health and Henry Ford Medical Group in federal court, alleging that the mandatory cognitive test violates the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Age Discrimination in Employment Act, and two Michigan laws.
Dr. Mogk’s lawsuit follows a widely watched 2020 case in which the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission sued Yale New Haven Hospital, the teaching hospital of Yale University, for age discrimination. According to the lawsuit, the hospital illegally required neuropsychological and eye examinations of physicians aged 70 or older who sought to gain or renew staff privileges.
According to the lawsuit, Dr. Mogk is a member of Henry Ford Medical Group, which in 2017 required all members aged 70 and older to undergo cognitive screening tests. The tests would be repeated every 5 years thereafter, the lawsuit said, and anyone who refused would have to resign or be fired.
Dr. Mogk completed the screening, although no information about the results or outcome was mentioned in the lawsuit. It’s not clear whether Henry Ford’s cognitive test mandate remains in place; a spokesperson for Henry Ford Health and attorneys for Dr. Mogk declined to comment.
The number of practicing physicians in their 70s and beyond is rising. A 2021 report found that 12% of U.S. licensed physicians in 2020 were least 70 years old, up from 9% in 2010 and an increase from 75,627 to 120,510. The percentage of doctors aged 60-69 grew to 19% from 16% in 2010.
The number of health systems requiring testing of older physicians isn’t known, although various reports suggest at least a dozen have had mandates.
The University of California, San Diego, offers a physical and mental screening program that health organizations can use to evaluate “late-career physicians,” and a 2021 report noted that “Nebraska’s Children’s Hospital requires physicians aged 70 years and older to undergo an assessment by several peers, a complete physical, and unspecified cognitive screening.” Another system, Hartford HealthCare, mandated an annual reappointment process for clinicians aged 70 or older, requiring them to undergo various exams.
There’s evidence that physician performance declines with age. However, age-based cognitive testing can run afoul of federal and state laws against age discrimination, said Sharona Hoffman, JD, professor of law and bioethics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, in an interview.
Federal law prohibits age-related restrictions on employment but allows exceptions in areas like public safety, said Ms. Hoffman, who’s written about age discrimination and testing requirements. Pilots, law enforcement officers, firefighters, and air controllers, for example, can be forced to retire at specific ages.
It’s not clear how many physicians took the cognitive tests required by Henry Ford Medical Group.
However, details are available about the policy at Yale New Haven Hospital: According to the EEOC lawsuit, from 2016 to 2019, 145 physicians aged 70 or older took the mandatory test. Of those, seven individuals failed either or both of the exams, 14 were listed as “borderline deficient,” and one was listed as “deficient.” Another five refused testing and either resigned or changed their status. The EEOC case against the hospital is still pending.
“You can make an argument that health care is like a public safety job because people put their lives in the hands of doctors,” Ms. Hoffman said.
In defending mandatory cognitive tests, she said, health care systems could say, “it’s not really discrimination; we’re not forcing them to retire, we’re not limiting their work in any way. We’re just doing testing to make sure they perform competently, and the ADA allows us to conduct testing that is job-related.”
Indeed, a Yale New Haven Hospital spokesman made an argument along these lines in a statement regarding the 2020 lawsuit: The “policy is designed to protect our patients from potential harm while including safeguards to ensure that our physicians are treated fairly. The policy is modeled on similar standards in other industries, and we are confident that no discrimination has occurred and will vigorously defend ourselves in this matter.”
However, Ms. Hoffman herself doesn’t buy these arguments. Requiring tests only for older physicians does appear to be discrimination based on age, she said. As an alternative, “employers can do close supervision of people. As soon as there are performance problems or patient complaints, you need to see a doctor or get testing done.”
Another option is to mandate tests at specific ages via licensing boards. “I don’t think that would be legally problematic,” Ms. Hoffman said.
What else can be done to protect patients from clinicians whose skills have significantly declined as they’ve aged? The 2021 report in Neurology Clinical Practice notes that there are disadvantages to several strategies.
One common approach, waiting to evaluate a clinician until an error occurs, can lead to patient harm, the report’s authors wrote. Relying on reporting by peers is problematic because “physicians have been very resistant to reporting colleagues who are impaired” and the “medical apprenticeship model discourages physicians from reporting on senior colleagues.”
Physician self-assessment is yet another option, but “loss of insight may be a component of an individual’s impairment,” the authors wrote.
So what’s the best solution? The authors recommended “a relatively brief cognitive screening followed by more extensive testing for the most impaired individuals.” This approach “appears most reliable in confidentially identifying truly impaired physicians while minimizing the chance of a falsely flagging unimpaired individuals. This strategy allows aging physicians to continue working while safeguarding both their reputations and their patients’ health.”
Ms. Hoffman has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.






