User login
What will help ease the financial toll of breast cancer?
SAN ANTONIO — , new survey findings show.
Almost half of patients surveyed reported a “significant” or “catastrophic” financial burden related to their breast cancer care. But patients also found a range of resources helpful for minimizing this burden, including direct assistance programs that reduce the cost of medications, grants from nonprofits that can cover cancer-related expenses, as well as programs that offer free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments.
Financial toxicity remains a “pervasive problem in the breast cancer community and we really need to go to the next step, which is designing patient-centered, patient-facing interventions to make improvements,” Fumiko Chino, MD, with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said when presenting the survey results at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
A growing body of evidence shows that cancer care, especially for breast cancer, can take a heavy financial toll on patients. However, routine screening for financial toxicity is not necessarily a routine part of clinical care, and providers may not know the types of financial assistance patients value most, Dr. Chino explained.
Dr. Chino and colleagues surveyed 1437 women with breast cancer about their level of financial distress as well as the specific interventions or education initiatives they found most helpful.
Most patients (60%) were White, 27% were Hispanic, and 8% Black. Three quarters of patients were on active treatments, 89% had nonmetastatic disease, and 11% had metastatic disease.
Overall, 47% of patients reported a significant or catastrophic financial burden related to their breast cancer diagnosis and care. This burden was higher for those with metastatic disease (61% vs 45%).
Patients assessed 10 strategies for coping with the financial burdens of care. The top-rated interventions included patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical or medical test companies, rated highly by 32% of respondents, and grants from nonprofits, rated highly by 31% of respondents. Patients also found financial assistance departments at cancer centers or hospitals helpful (29%); coupons and savings cards to reduce the cost of prescription drugs (28%); and programs that provide free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments (28%).
In terms of education, respondents said having a checklist of questions to ask their oncology team as well as a list of breast cancer-specific financial grants to apply for would be especially helpful when navigating the financial burdens of breast cancer care.
These preferences, however, did vary by race/ethnicity and disease status. Hispanic patients, for instance, found patient assistance programs offered by companies and cancer centers as well as transportation assistance more helpful than other groups.
Patients with metastatic disease found patient assistance programs offered by medical companies particularly helpful compared with patients with nonmetastatic disease. And compared with patients with metastatic disease, those with nonmetastatic breast cancer found assistance through clinical trials and professional medical billing advocates helpful.
This study confirms the high rates of financial burden in women with breast cancer and clearly demonstrates that intervention preferences vary by sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, study discussant Claire C. Conley, PhD, from Georgetown University, Washington, DC, commented.
“This highlights that one size really doesn’t fit all when it comes to those financial burden interventions,” Dr. Conley said. “We need to think about factors at the patient level, the organizational level, and the environment level.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Chino and Dr. Conley have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — , new survey findings show.
Almost half of patients surveyed reported a “significant” or “catastrophic” financial burden related to their breast cancer care. But patients also found a range of resources helpful for minimizing this burden, including direct assistance programs that reduce the cost of medications, grants from nonprofits that can cover cancer-related expenses, as well as programs that offer free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments.
Financial toxicity remains a “pervasive problem in the breast cancer community and we really need to go to the next step, which is designing patient-centered, patient-facing interventions to make improvements,” Fumiko Chino, MD, with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said when presenting the survey results at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
A growing body of evidence shows that cancer care, especially for breast cancer, can take a heavy financial toll on patients. However, routine screening for financial toxicity is not necessarily a routine part of clinical care, and providers may not know the types of financial assistance patients value most, Dr. Chino explained.
Dr. Chino and colleagues surveyed 1437 women with breast cancer about their level of financial distress as well as the specific interventions or education initiatives they found most helpful.
Most patients (60%) were White, 27% were Hispanic, and 8% Black. Three quarters of patients were on active treatments, 89% had nonmetastatic disease, and 11% had metastatic disease.
Overall, 47% of patients reported a significant or catastrophic financial burden related to their breast cancer diagnosis and care. This burden was higher for those with metastatic disease (61% vs 45%).
Patients assessed 10 strategies for coping with the financial burdens of care. The top-rated interventions included patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical or medical test companies, rated highly by 32% of respondents, and grants from nonprofits, rated highly by 31% of respondents. Patients also found financial assistance departments at cancer centers or hospitals helpful (29%); coupons and savings cards to reduce the cost of prescription drugs (28%); and programs that provide free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments (28%).
In terms of education, respondents said having a checklist of questions to ask their oncology team as well as a list of breast cancer-specific financial grants to apply for would be especially helpful when navigating the financial burdens of breast cancer care.
These preferences, however, did vary by race/ethnicity and disease status. Hispanic patients, for instance, found patient assistance programs offered by companies and cancer centers as well as transportation assistance more helpful than other groups.
Patients with metastatic disease found patient assistance programs offered by medical companies particularly helpful compared with patients with nonmetastatic disease. And compared with patients with metastatic disease, those with nonmetastatic breast cancer found assistance through clinical trials and professional medical billing advocates helpful.
This study confirms the high rates of financial burden in women with breast cancer and clearly demonstrates that intervention preferences vary by sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, study discussant Claire C. Conley, PhD, from Georgetown University, Washington, DC, commented.
“This highlights that one size really doesn’t fit all when it comes to those financial burden interventions,” Dr. Conley said. “We need to think about factors at the patient level, the organizational level, and the environment level.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Chino and Dr. Conley have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — , new survey findings show.
Almost half of patients surveyed reported a “significant” or “catastrophic” financial burden related to their breast cancer care. But patients also found a range of resources helpful for minimizing this burden, including direct assistance programs that reduce the cost of medications, grants from nonprofits that can cover cancer-related expenses, as well as programs that offer free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments.
Financial toxicity remains a “pervasive problem in the breast cancer community and we really need to go to the next step, which is designing patient-centered, patient-facing interventions to make improvements,” Fumiko Chino, MD, with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said when presenting the survey results at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
A growing body of evidence shows that cancer care, especially for breast cancer, can take a heavy financial toll on patients. However, routine screening for financial toxicity is not necessarily a routine part of clinical care, and providers may not know the types of financial assistance patients value most, Dr. Chino explained.
Dr. Chino and colleagues surveyed 1437 women with breast cancer about their level of financial distress as well as the specific interventions or education initiatives they found most helpful.
Most patients (60%) were White, 27% were Hispanic, and 8% Black. Three quarters of patients were on active treatments, 89% had nonmetastatic disease, and 11% had metastatic disease.
Overall, 47% of patients reported a significant or catastrophic financial burden related to their breast cancer diagnosis and care. This burden was higher for those with metastatic disease (61% vs 45%).
Patients assessed 10 strategies for coping with the financial burdens of care. The top-rated interventions included patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical or medical test companies, rated highly by 32% of respondents, and grants from nonprofits, rated highly by 31% of respondents. Patients also found financial assistance departments at cancer centers or hospitals helpful (29%); coupons and savings cards to reduce the cost of prescription drugs (28%); and programs that provide free or low-cost transportation to medical appointments (28%).
In terms of education, respondents said having a checklist of questions to ask their oncology team as well as a list of breast cancer-specific financial grants to apply for would be especially helpful when navigating the financial burdens of breast cancer care.
These preferences, however, did vary by race/ethnicity and disease status. Hispanic patients, for instance, found patient assistance programs offered by companies and cancer centers as well as transportation assistance more helpful than other groups.
Patients with metastatic disease found patient assistance programs offered by medical companies particularly helpful compared with patients with nonmetastatic disease. And compared with patients with metastatic disease, those with nonmetastatic breast cancer found assistance through clinical trials and professional medical billing advocates helpful.
This study confirms the high rates of financial burden in women with breast cancer and clearly demonstrates that intervention preferences vary by sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, study discussant Claire C. Conley, PhD, from Georgetown University, Washington, DC, commented.
“This highlights that one size really doesn’t fit all when it comes to those financial burden interventions,” Dr. Conley said. “We need to think about factors at the patient level, the organizational level, and the environment level.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Chino and Dr. Conley have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SABCS 2023
Are you sure your patient is alive?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.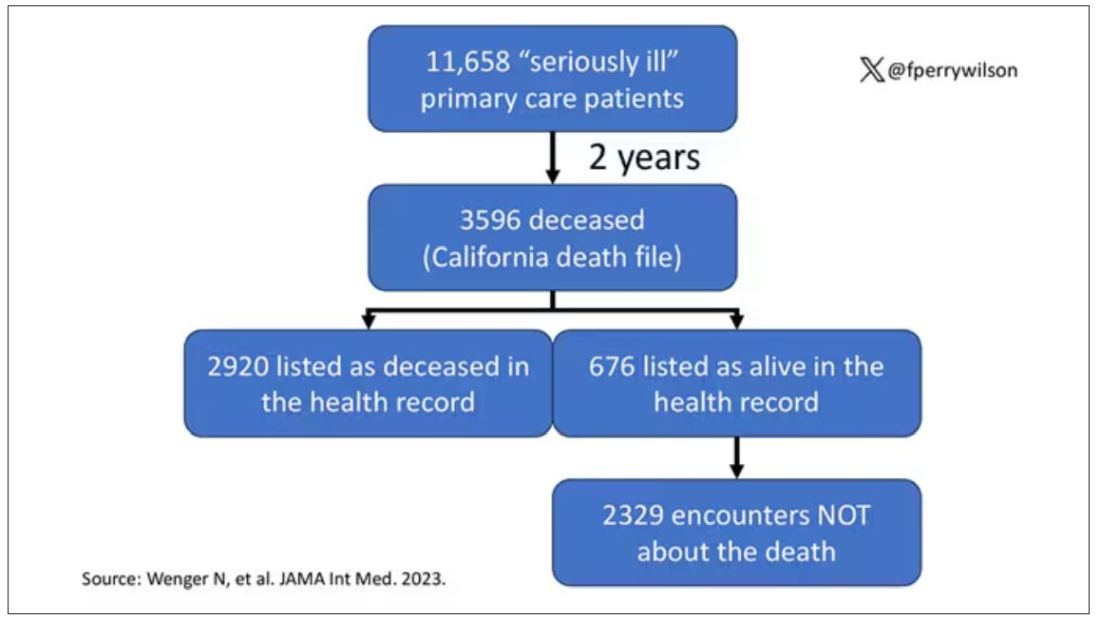
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.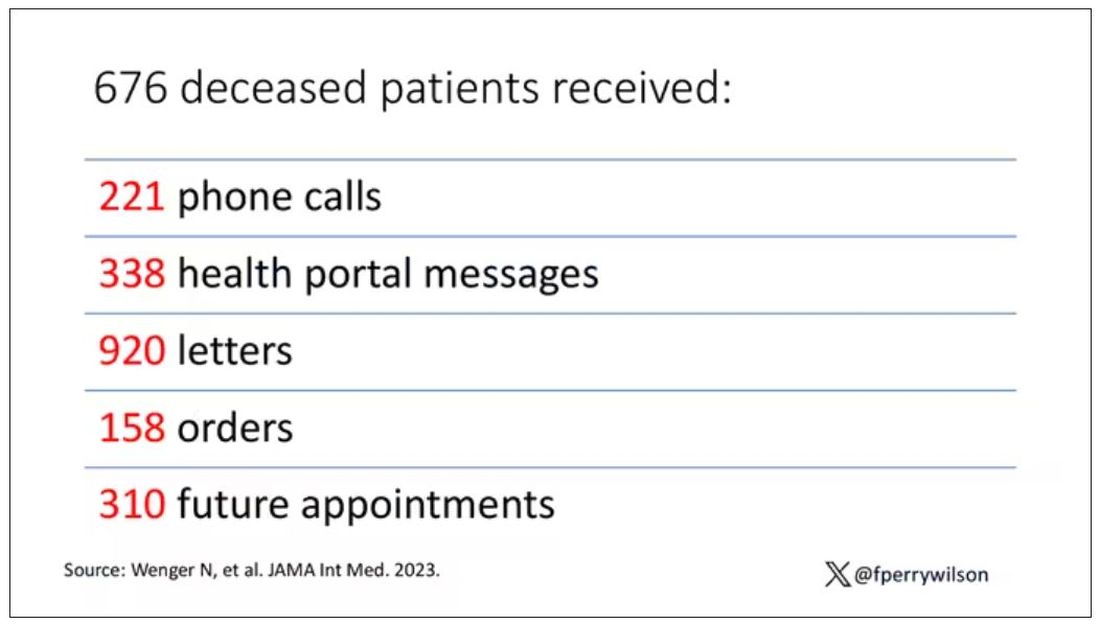
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
Even with insurance, cancer out-of-pocket costs can be punishing
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Out-of-pocket costs contribute to financial toxicity in cancer, but little is known about how they vary across various tumor types and stages over time.
- To find out, investigators reviewed claims data for 7494 US patients diagnosed with stage I-IV breast, cervical, colorectal, lung, ovarian, or prostate cancer from 2016 to 2020.
- They assessed cumulative out-of-pocket (OOP) costs — defined as copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance — in the first 3 years following diagnosis.
- Subjects had private, commercial health insurance through United Healthcare.
TAKEAWAY:
- By the end of 3 years, average cumulative OOP costs ranged from $16,673 for stage I prostate cancer to $35,253 for stage IV lung cancer.
- Across all cancer types, average OOP costs in the first year ranged from $2,754 for stage I anal cancer to $25,876 for stage IV vaginal cancer.
- However, the upper limits of OOP costs exceeded $100,000 across many tumors and stages in the first year, reaching a high of $450,374 for stage I breast cancer and far exceeding $200,000 for stage II-IV colorectal and lung cancer.
- OOP costs were generally highest during the first year of treatment and for cancers diagnosed at later stages.
IN PRACTICE:
“OOP costs may present an extreme economic stressor on patients diagnosed with cancer,” leading to emotional distress, reduced treatment adherence, and poor outcomes. “Even cancer patients with insurance coverage [are] not protected.” Future research is “needed to help clarify the type of patient most burdened by OOP costs” as well as ways to reduce them, including promoting “diagnosis at an earlier stage and increas[ing] access to health plans that minimize patient cost sharing.”
SOURCE:
The work was led by November McGarvey of BluePath Solutions, Los Angeles, and published in the Journal of Medical Economics.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not include additional OOP costs, such as transportation. It also did not assess the long-term impacts of cancer-related out-of-pocket spending. Details on health plan types and features were limited, and the results are limited to patients with commercial health insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by Grail. The investigators are employees of Grail or BluePath Solutions.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Out-of-pocket costs contribute to financial toxicity in cancer, but little is known about how they vary across various tumor types and stages over time.
- To find out, investigators reviewed claims data for 7494 US patients diagnosed with stage I-IV breast, cervical, colorectal, lung, ovarian, or prostate cancer from 2016 to 2020.
- They assessed cumulative out-of-pocket (OOP) costs — defined as copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance — in the first 3 years following diagnosis.
- Subjects had private, commercial health insurance through United Healthcare.
TAKEAWAY:
- By the end of 3 years, average cumulative OOP costs ranged from $16,673 for stage I prostate cancer to $35,253 for stage IV lung cancer.
- Across all cancer types, average OOP costs in the first year ranged from $2,754 for stage I anal cancer to $25,876 for stage IV vaginal cancer.
- However, the upper limits of OOP costs exceeded $100,000 across many tumors and stages in the first year, reaching a high of $450,374 for stage I breast cancer and far exceeding $200,000 for stage II-IV colorectal and lung cancer.
- OOP costs were generally highest during the first year of treatment and for cancers diagnosed at later stages.
IN PRACTICE:
“OOP costs may present an extreme economic stressor on patients diagnosed with cancer,” leading to emotional distress, reduced treatment adherence, and poor outcomes. “Even cancer patients with insurance coverage [are] not protected.” Future research is “needed to help clarify the type of patient most burdened by OOP costs” as well as ways to reduce them, including promoting “diagnosis at an earlier stage and increas[ing] access to health plans that minimize patient cost sharing.”
SOURCE:
The work was led by November McGarvey of BluePath Solutions, Los Angeles, and published in the Journal of Medical Economics.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not include additional OOP costs, such as transportation. It also did not assess the long-term impacts of cancer-related out-of-pocket spending. Details on health plan types and features were limited, and the results are limited to patients with commercial health insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by Grail. The investigators are employees of Grail or BluePath Solutions.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Out-of-pocket costs contribute to financial toxicity in cancer, but little is known about how they vary across various tumor types and stages over time.
- To find out, investigators reviewed claims data for 7494 US patients diagnosed with stage I-IV breast, cervical, colorectal, lung, ovarian, or prostate cancer from 2016 to 2020.
- They assessed cumulative out-of-pocket (OOP) costs — defined as copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance — in the first 3 years following diagnosis.
- Subjects had private, commercial health insurance through United Healthcare.
TAKEAWAY:
- By the end of 3 years, average cumulative OOP costs ranged from $16,673 for stage I prostate cancer to $35,253 for stage IV lung cancer.
- Across all cancer types, average OOP costs in the first year ranged from $2,754 for stage I anal cancer to $25,876 for stage IV vaginal cancer.
- However, the upper limits of OOP costs exceeded $100,000 across many tumors and stages in the first year, reaching a high of $450,374 for stage I breast cancer and far exceeding $200,000 for stage II-IV colorectal and lung cancer.
- OOP costs were generally highest during the first year of treatment and for cancers diagnosed at later stages.
IN PRACTICE:
“OOP costs may present an extreme economic stressor on patients diagnosed with cancer,” leading to emotional distress, reduced treatment adherence, and poor outcomes. “Even cancer patients with insurance coverage [are] not protected.” Future research is “needed to help clarify the type of patient most burdened by OOP costs” as well as ways to reduce them, including promoting “diagnosis at an earlier stage and increas[ing] access to health plans that minimize patient cost sharing.”
SOURCE:
The work was led by November McGarvey of BluePath Solutions, Los Angeles, and published in the Journal of Medical Economics.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not include additional OOP costs, such as transportation. It also did not assess the long-term impacts of cancer-related out-of-pocket spending. Details on health plan types and features were limited, and the results are limited to patients with commercial health insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The work was funded by Grail. The investigators are employees of Grail or BluePath Solutions.
Eight wealth tips just for doctors
The average physician makes $352,000, and some earn well into the $500,000s. So, doctors don’t have to worry about money, right?
You know the answer to that.
One thing all physicians have in common about money, says James M. Dahle, MD, FACEP, founder of The White Coat Investor, is that they don’t receive any training in business, personal finance, or investing throughout their schooling or careers unless they seek it out. This leaves many unprepared to make the best investing and money-saving decisions, while others get too frustrated about their lack of knowledge to even dip their toe into the investing pool.
Exhibit A: Four out of 10 physicians have a net worth below $1 million, according to the Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2023. Elizabeth Chiang, MD, PhD, an oculoplastic surgeon and a physician money coach at Grow Your Wealthy Mindset, notes that many of those doctors are over age 65, “which means they essentially can’t retire.”
And that’s just one pain point.
Physicians have money concerns specific to their profession and background. Luckily, some fellow doctors also serve as financial and wealth advisors just for other doctors.
Blind Spot #1
The early lean years skew doctors’ money outlook. “We have an extended training period, which commonly consists of taking on a large amount of debt, followed by 3 to 8 years of being paid a modest salary, and then finally a large boost in income,” explains Dr. Chiang. This can lay a shaky foundation for the earning years to come, and as a result, a lot of doctors just don’t think about money in healthy ways. Once their incomes increase, physicians may be surprised, for example, that making a multiple six-figure salary means paying six figures in taxes.
The Fix
Treat financial health like physical health. That means money cannot be a taboo subject. “The misguided mindset is that we didn’t become physicians to make money, we did it to help people,” explains Jordan Frey, MD, creator of the blog, The Prudent Plastic Surgeon.
Dr. Frey acknowledges that the desire to help is certainly true. But the result is a false idea that “to think about our personal finances makes us a worse doctor.”
Blind Spot #2
Because doctors know a lot about one thing (medicine), they might assume they know a lot about everything (such as investing). “Totally different fields with a different language and different way to think about it,” Dahle explains. This overconfidence could lead to some negligent or risky financial decisions.
The Fix
Educate yourself. There are several books on personal finance and investing written by physicians for physicians. Dr. Chiang recommends The Physician Philosopher’s Guide to Personal Finance, by James Turner, MD; Financial Freedom Rx, by Chirag Shah, MD, and Jayanth Sridhar, MD; and The Physician’s Guide to Finance, by Nicholas Christian and Amanda Christian, MD. There are also podcasts, blogs, and courses to help educate doctors on finance, such as the Fire Your Financial Advisor course by The White Coat Investor.
Blind Spot #3
Undersaving. Retirement saving is one thing, but 24% of doctors say they don’t even put money away in a taxable savings account, according to the Wealth & Debt Report.
Cobin Soelberg, MD, JD, a board-certified anesthesiologist and founder and principal advisor with Greeley Wealth Management, is the treasurer of his anesthesiology group. “I get to see every month how much people are saving, and even on an anesthesiologist salary, where everyone’s making about $400,000 a year, a lot of people are not saving anything, which is crazy.”
Undersaving can be both a time issue and a mindset one.
Time: Doctors often start investing in their retirement accounts later than the average professional, says Dr. Chiang. “A lot of physicians will max out their 401k or 403b,” she explains. “But if you’re putting in $20,000 a year and only starting when you’re in your early 30s, that’s not enough to get you to retirement.”
Mindset: Doctors also see people of all ages who are sick, dying, and injured. “They all know someone who worked hard and saved and then dropped dead at 55,” explains Dr. Dahle. This, he says, can lead to a bit of a “you only live once” attitude that prioritizes spending over saving.
The Fix
Shoot for 20%. If you can’t save 20% of your gross now, strive to get to that point. Think of it as telling a patient they have to change their behavior or trouble will come - not if, but when. “Develop a written investing plan and then stick with it through thick and thin,” says Dr. Dahle. “Once you have a reasonable plan, all you have to do is fund it adequately by saving 20% of your gross income, and a doctor will easily retire as a multimillionaire.”
Blind Spot #4
Bad investment strategies. Thirty-six percent of doctors experience their largest financial losses from lousy investments, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Meanwhile, 17% of PCPs and 12% of specialists say they haven’t made any investments at all. That’s a terrible mix of doing the wrong thing and doing a worse thing.
The Fix
Don’t overthink investing, but don’t underthink it either. “As high-income earners, doctors just don’t need to take this high level of risk to reach their financial goals,” Dr. Frey says. A good investment plan doesn’t require you to time the stock market or predict individual stock winners. Consider what Vanguard founder Jack Bogle once said about investing: “Be bored by the process but elated by the outcome.”
Dr. Frey suggests going super-simple: index funds. Ignore investing strategies with actively managed mutual funds or individual stocks, as well as risky alternative investments such as cryptocurrency and angel investments. Everyone assumes doctors have money to burn, and they will push sketchy investment ideas at them. Avoid.
Blind Spot #5
Not taking debt seriously enough. The average medical student debt is $250,000 and can exceed $500,000, says Dr. Soelberg. Many doctors spend the first 10 to 20 years of their careers paying this off. Today’s graduates are paying more than 7% on their loans.
And it’s not just student debt: 39% of physicians carry five or more credit cards, and 34% have mortgages larger than $300,000 (with half of those are more than than $500K), per the Wealth & Debt Report.
The Fix
Treat debt like cancer. It’s a lethal enemy you can’t get rid of right away, but a steady, aggressive, long-term attack will have the best results. Dr. Soelberg suggests allocating the most you can afford per month, whether that’s $1000 or $5000, toward debt. Raise the amount as your income grows. Do the same with your 401k or retirement plan. Whatever is left, you can spend. Five to 10 years later, you will realize, “Wow. I’m debt free.”
Blind Spot #6
Not putting in the work to improve your situation. Seventy-one percent of doctors admit they haven’t done anything to reduce major expenses, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Are you leaving major money on the table?
The Fix
Audit yourself in major areas like housing and taxes. While the average professional may need to put 10% to 20% down on a home, physicians can qualify for physician mortgage loans and can often put down 3% or less, says Dr. Chiang. If you can afford the higher mortgage payment, excess savings earmarked for a larger down payment can be put toward debt or invested.
Another trick, if you’re able, is to seek an area that is less in demand at a higher salary. “Physicians in places like New York City or San Francisco tend to make less than physicians in the Midwest or the South,” Dr. Chiang explains. A colleague of hers moved to rural Pennsylvania, where he made a high salary and had a low cost of living for 3½ years, paid off his student debt, and then relocated to an area where he wanted to live long term.
As for taxes, become familiar with tax law. Research things like, “What is considered a business expense for doctors?” says Brett Mollard, MD, a diagnostic radiologist who provides financial advice to younger physicians. “What will your estimated total tax burden be at the end of the year? Will you need to make extra payments to prevent owing a large sum of money from underpaying or to avoid tax penalties?”
Blind Spot #7
Living like a rock star on a doctor’s income. Getting caught up in trying to live the same lifestyle as your colleagues is a classic bear trap. “Sitting in the doctor’s lounge, it’s so crazy,” Dr. Soelberg says. He describes conversations like, “‘Where did you go on your trip?’ ‘What new toys are you buying?’” There’s pressure to live up to an image of what a doctor’s life is supposed to look like before you’ve sorted the basic things like paying off debt.
The Fix
Live like a resident even if you haven’t been one for years, at least until you’re in a better financial position. “You’re already used to living a life of lower means, and you’re an expert when it comes to delaying gratification,” says Dr. Mollard. “Do it a little longer.” Live frugally and spend only on things that bring you joy. “A lot of physicians are trying to be really rich in all areas of their life instead of the ones that actually matter to them,” Dr. Soelberg says. Identify what’s important to you and only splurge on that.
Blind Spot #8
Never asking for help. The right financial planner can provide expert help. Emphasis on right. “Doctors can be very trusting of other professionals, even when they should not be,” says Dr. Dahle. He notes that in financial services, many people masquerade as knowledgeable advisors who are really just salespeople. While legitimate financial advisors strive to make their clients money, they are also ultimately out to line their pockets and love to work with physician salaries. Thus, doctors can end up working with financial planners that don’t specifically understand their situations or end up taking too much from their clients.
The Fix
Find a planner who specializes in, or at least understands, physicians. Ask them how they make money, says Dr. Chiang. If someone hesitates to tell you about their fee structure or if it sounds like a lot, shop around and ask colleagues for recommendations.
“Ultimately, the path to wealth is to create and grow the margin between what you make and what you spend,” says Dr. Frey. Throw some investing into the mix and physicians can set themselves up on a path for a stress-free financial life.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The average physician makes $352,000, and some earn well into the $500,000s. So, doctors don’t have to worry about money, right?
You know the answer to that.
One thing all physicians have in common about money, says James M. Dahle, MD, FACEP, founder of The White Coat Investor, is that they don’t receive any training in business, personal finance, or investing throughout their schooling or careers unless they seek it out. This leaves many unprepared to make the best investing and money-saving decisions, while others get too frustrated about their lack of knowledge to even dip their toe into the investing pool.
Exhibit A: Four out of 10 physicians have a net worth below $1 million, according to the Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2023. Elizabeth Chiang, MD, PhD, an oculoplastic surgeon and a physician money coach at Grow Your Wealthy Mindset, notes that many of those doctors are over age 65, “which means they essentially can’t retire.”
And that’s just one pain point.
Physicians have money concerns specific to their profession and background. Luckily, some fellow doctors also serve as financial and wealth advisors just for other doctors.
Blind Spot #1
The early lean years skew doctors’ money outlook. “We have an extended training period, which commonly consists of taking on a large amount of debt, followed by 3 to 8 years of being paid a modest salary, and then finally a large boost in income,” explains Dr. Chiang. This can lay a shaky foundation for the earning years to come, and as a result, a lot of doctors just don’t think about money in healthy ways. Once their incomes increase, physicians may be surprised, for example, that making a multiple six-figure salary means paying six figures in taxes.
The Fix
Treat financial health like physical health. That means money cannot be a taboo subject. “The misguided mindset is that we didn’t become physicians to make money, we did it to help people,” explains Jordan Frey, MD, creator of the blog, The Prudent Plastic Surgeon.
Dr. Frey acknowledges that the desire to help is certainly true. But the result is a false idea that “to think about our personal finances makes us a worse doctor.”
Blind Spot #2
Because doctors know a lot about one thing (medicine), they might assume they know a lot about everything (such as investing). “Totally different fields with a different language and different way to think about it,” Dahle explains. This overconfidence could lead to some negligent or risky financial decisions.
The Fix
Educate yourself. There are several books on personal finance and investing written by physicians for physicians. Dr. Chiang recommends The Physician Philosopher’s Guide to Personal Finance, by James Turner, MD; Financial Freedom Rx, by Chirag Shah, MD, and Jayanth Sridhar, MD; and The Physician’s Guide to Finance, by Nicholas Christian and Amanda Christian, MD. There are also podcasts, blogs, and courses to help educate doctors on finance, such as the Fire Your Financial Advisor course by The White Coat Investor.
Blind Spot #3
Undersaving. Retirement saving is one thing, but 24% of doctors say they don’t even put money away in a taxable savings account, according to the Wealth & Debt Report.
Cobin Soelberg, MD, JD, a board-certified anesthesiologist and founder and principal advisor with Greeley Wealth Management, is the treasurer of his anesthesiology group. “I get to see every month how much people are saving, and even on an anesthesiologist salary, where everyone’s making about $400,000 a year, a lot of people are not saving anything, which is crazy.”
Undersaving can be both a time issue and a mindset one.
Time: Doctors often start investing in their retirement accounts later than the average professional, says Dr. Chiang. “A lot of physicians will max out their 401k or 403b,” she explains. “But if you’re putting in $20,000 a year and only starting when you’re in your early 30s, that’s not enough to get you to retirement.”
Mindset: Doctors also see people of all ages who are sick, dying, and injured. “They all know someone who worked hard and saved and then dropped dead at 55,” explains Dr. Dahle. This, he says, can lead to a bit of a “you only live once” attitude that prioritizes spending over saving.
The Fix
Shoot for 20%. If you can’t save 20% of your gross now, strive to get to that point. Think of it as telling a patient they have to change their behavior or trouble will come - not if, but when. “Develop a written investing plan and then stick with it through thick and thin,” says Dr. Dahle. “Once you have a reasonable plan, all you have to do is fund it adequately by saving 20% of your gross income, and a doctor will easily retire as a multimillionaire.”
Blind Spot #4
Bad investment strategies. Thirty-six percent of doctors experience their largest financial losses from lousy investments, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Meanwhile, 17% of PCPs and 12% of specialists say they haven’t made any investments at all. That’s a terrible mix of doing the wrong thing and doing a worse thing.
The Fix
Don’t overthink investing, but don’t underthink it either. “As high-income earners, doctors just don’t need to take this high level of risk to reach their financial goals,” Dr. Frey says. A good investment plan doesn’t require you to time the stock market or predict individual stock winners. Consider what Vanguard founder Jack Bogle once said about investing: “Be bored by the process but elated by the outcome.”
Dr. Frey suggests going super-simple: index funds. Ignore investing strategies with actively managed mutual funds or individual stocks, as well as risky alternative investments such as cryptocurrency and angel investments. Everyone assumes doctors have money to burn, and they will push sketchy investment ideas at them. Avoid.
Blind Spot #5
Not taking debt seriously enough. The average medical student debt is $250,000 and can exceed $500,000, says Dr. Soelberg. Many doctors spend the first 10 to 20 years of their careers paying this off. Today’s graduates are paying more than 7% on their loans.
And it’s not just student debt: 39% of physicians carry five or more credit cards, and 34% have mortgages larger than $300,000 (with half of those are more than than $500K), per the Wealth & Debt Report.
The Fix
Treat debt like cancer. It’s a lethal enemy you can’t get rid of right away, but a steady, aggressive, long-term attack will have the best results. Dr. Soelberg suggests allocating the most you can afford per month, whether that’s $1000 or $5000, toward debt. Raise the amount as your income grows. Do the same with your 401k or retirement plan. Whatever is left, you can spend. Five to 10 years later, you will realize, “Wow. I’m debt free.”
Blind Spot #6
Not putting in the work to improve your situation. Seventy-one percent of doctors admit they haven’t done anything to reduce major expenses, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Are you leaving major money on the table?
The Fix
Audit yourself in major areas like housing and taxes. While the average professional may need to put 10% to 20% down on a home, physicians can qualify for physician mortgage loans and can often put down 3% or less, says Dr. Chiang. If you can afford the higher mortgage payment, excess savings earmarked for a larger down payment can be put toward debt or invested.
Another trick, if you’re able, is to seek an area that is less in demand at a higher salary. “Physicians in places like New York City or San Francisco tend to make less than physicians in the Midwest or the South,” Dr. Chiang explains. A colleague of hers moved to rural Pennsylvania, where he made a high salary and had a low cost of living for 3½ years, paid off his student debt, and then relocated to an area where he wanted to live long term.
As for taxes, become familiar with tax law. Research things like, “What is considered a business expense for doctors?” says Brett Mollard, MD, a diagnostic radiologist who provides financial advice to younger physicians. “What will your estimated total tax burden be at the end of the year? Will you need to make extra payments to prevent owing a large sum of money from underpaying or to avoid tax penalties?”
Blind Spot #7
Living like a rock star on a doctor’s income. Getting caught up in trying to live the same lifestyle as your colleagues is a classic bear trap. “Sitting in the doctor’s lounge, it’s so crazy,” Dr. Soelberg says. He describes conversations like, “‘Where did you go on your trip?’ ‘What new toys are you buying?’” There’s pressure to live up to an image of what a doctor’s life is supposed to look like before you’ve sorted the basic things like paying off debt.
The Fix
Live like a resident even if you haven’t been one for years, at least until you’re in a better financial position. “You’re already used to living a life of lower means, and you’re an expert when it comes to delaying gratification,” says Dr. Mollard. “Do it a little longer.” Live frugally and spend only on things that bring you joy. “A lot of physicians are trying to be really rich in all areas of their life instead of the ones that actually matter to them,” Dr. Soelberg says. Identify what’s important to you and only splurge on that.
Blind Spot #8
Never asking for help. The right financial planner can provide expert help. Emphasis on right. “Doctors can be very trusting of other professionals, even when they should not be,” says Dr. Dahle. He notes that in financial services, many people masquerade as knowledgeable advisors who are really just salespeople. While legitimate financial advisors strive to make their clients money, they are also ultimately out to line their pockets and love to work with physician salaries. Thus, doctors can end up working with financial planners that don’t specifically understand their situations or end up taking too much from their clients.
The Fix
Find a planner who specializes in, or at least understands, physicians. Ask them how they make money, says Dr. Chiang. If someone hesitates to tell you about their fee structure or if it sounds like a lot, shop around and ask colleagues for recommendations.
“Ultimately, the path to wealth is to create and grow the margin between what you make and what you spend,” says Dr. Frey. Throw some investing into the mix and physicians can set themselves up on a path for a stress-free financial life.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The average physician makes $352,000, and some earn well into the $500,000s. So, doctors don’t have to worry about money, right?
You know the answer to that.
One thing all physicians have in common about money, says James M. Dahle, MD, FACEP, founder of The White Coat Investor, is that they don’t receive any training in business, personal finance, or investing throughout their schooling or careers unless they seek it out. This leaves many unprepared to make the best investing and money-saving decisions, while others get too frustrated about their lack of knowledge to even dip their toe into the investing pool.
Exhibit A: Four out of 10 physicians have a net worth below $1 million, according to the Medscape Physician Wealth & Debt Report 2023. Elizabeth Chiang, MD, PhD, an oculoplastic surgeon and a physician money coach at Grow Your Wealthy Mindset, notes that many of those doctors are over age 65, “which means they essentially can’t retire.”
And that’s just one pain point.
Physicians have money concerns specific to their profession and background. Luckily, some fellow doctors also serve as financial and wealth advisors just for other doctors.
Blind Spot #1
The early lean years skew doctors’ money outlook. “We have an extended training period, which commonly consists of taking on a large amount of debt, followed by 3 to 8 years of being paid a modest salary, and then finally a large boost in income,” explains Dr. Chiang. This can lay a shaky foundation for the earning years to come, and as a result, a lot of doctors just don’t think about money in healthy ways. Once their incomes increase, physicians may be surprised, for example, that making a multiple six-figure salary means paying six figures in taxes.
The Fix
Treat financial health like physical health. That means money cannot be a taboo subject. “The misguided mindset is that we didn’t become physicians to make money, we did it to help people,” explains Jordan Frey, MD, creator of the blog, The Prudent Plastic Surgeon.
Dr. Frey acknowledges that the desire to help is certainly true. But the result is a false idea that “to think about our personal finances makes us a worse doctor.”
Blind Spot #2
Because doctors know a lot about one thing (medicine), they might assume they know a lot about everything (such as investing). “Totally different fields with a different language and different way to think about it,” Dahle explains. This overconfidence could lead to some negligent or risky financial decisions.
The Fix
Educate yourself. There are several books on personal finance and investing written by physicians for physicians. Dr. Chiang recommends The Physician Philosopher’s Guide to Personal Finance, by James Turner, MD; Financial Freedom Rx, by Chirag Shah, MD, and Jayanth Sridhar, MD; and The Physician’s Guide to Finance, by Nicholas Christian and Amanda Christian, MD. There are also podcasts, blogs, and courses to help educate doctors on finance, such as the Fire Your Financial Advisor course by The White Coat Investor.
Blind Spot #3
Undersaving. Retirement saving is one thing, but 24% of doctors say they don’t even put money away in a taxable savings account, according to the Wealth & Debt Report.
Cobin Soelberg, MD, JD, a board-certified anesthesiologist and founder and principal advisor with Greeley Wealth Management, is the treasurer of his anesthesiology group. “I get to see every month how much people are saving, and even on an anesthesiologist salary, where everyone’s making about $400,000 a year, a lot of people are not saving anything, which is crazy.”
Undersaving can be both a time issue and a mindset one.
Time: Doctors often start investing in their retirement accounts later than the average professional, says Dr. Chiang. “A lot of physicians will max out their 401k or 403b,” she explains. “But if you’re putting in $20,000 a year and only starting when you’re in your early 30s, that’s not enough to get you to retirement.”
Mindset: Doctors also see people of all ages who are sick, dying, and injured. “They all know someone who worked hard and saved and then dropped dead at 55,” explains Dr. Dahle. This, he says, can lead to a bit of a “you only live once” attitude that prioritizes spending over saving.
The Fix
Shoot for 20%. If you can’t save 20% of your gross now, strive to get to that point. Think of it as telling a patient they have to change their behavior or trouble will come - not if, but when. “Develop a written investing plan and then stick with it through thick and thin,” says Dr. Dahle. “Once you have a reasonable plan, all you have to do is fund it adequately by saving 20% of your gross income, and a doctor will easily retire as a multimillionaire.”
Blind Spot #4
Bad investment strategies. Thirty-six percent of doctors experience their largest financial losses from lousy investments, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Meanwhile, 17% of PCPs and 12% of specialists say they haven’t made any investments at all. That’s a terrible mix of doing the wrong thing and doing a worse thing.
The Fix
Don’t overthink investing, but don’t underthink it either. “As high-income earners, doctors just don’t need to take this high level of risk to reach their financial goals,” Dr. Frey says. A good investment plan doesn’t require you to time the stock market or predict individual stock winners. Consider what Vanguard founder Jack Bogle once said about investing: “Be bored by the process but elated by the outcome.”
Dr. Frey suggests going super-simple: index funds. Ignore investing strategies with actively managed mutual funds or individual stocks, as well as risky alternative investments such as cryptocurrency and angel investments. Everyone assumes doctors have money to burn, and they will push sketchy investment ideas at them. Avoid.
Blind Spot #5
Not taking debt seriously enough. The average medical student debt is $250,000 and can exceed $500,000, says Dr. Soelberg. Many doctors spend the first 10 to 20 years of their careers paying this off. Today’s graduates are paying more than 7% on their loans.
And it’s not just student debt: 39% of physicians carry five or more credit cards, and 34% have mortgages larger than $300,000 (with half of those are more than than $500K), per the Wealth & Debt Report.
The Fix
Treat debt like cancer. It’s a lethal enemy you can’t get rid of right away, but a steady, aggressive, long-term attack will have the best results. Dr. Soelberg suggests allocating the most you can afford per month, whether that’s $1000 or $5000, toward debt. Raise the amount as your income grows. Do the same with your 401k or retirement plan. Whatever is left, you can spend. Five to 10 years later, you will realize, “Wow. I’m debt free.”
Blind Spot #6
Not putting in the work to improve your situation. Seventy-one percent of doctors admit they haven’t done anything to reduce major expenses, according to the Wealth & Debt Report. Are you leaving major money on the table?
The Fix
Audit yourself in major areas like housing and taxes. While the average professional may need to put 10% to 20% down on a home, physicians can qualify for physician mortgage loans and can often put down 3% or less, says Dr. Chiang. If you can afford the higher mortgage payment, excess savings earmarked for a larger down payment can be put toward debt or invested.
Another trick, if you’re able, is to seek an area that is less in demand at a higher salary. “Physicians in places like New York City or San Francisco tend to make less than physicians in the Midwest or the South,” Dr. Chiang explains. A colleague of hers moved to rural Pennsylvania, where he made a high salary and had a low cost of living for 3½ years, paid off his student debt, and then relocated to an area where he wanted to live long term.
As for taxes, become familiar with tax law. Research things like, “What is considered a business expense for doctors?” says Brett Mollard, MD, a diagnostic radiologist who provides financial advice to younger physicians. “What will your estimated total tax burden be at the end of the year? Will you need to make extra payments to prevent owing a large sum of money from underpaying or to avoid tax penalties?”
Blind Spot #7
Living like a rock star on a doctor’s income. Getting caught up in trying to live the same lifestyle as your colleagues is a classic bear trap. “Sitting in the doctor’s lounge, it’s so crazy,” Dr. Soelberg says. He describes conversations like, “‘Where did you go on your trip?’ ‘What new toys are you buying?’” There’s pressure to live up to an image of what a doctor’s life is supposed to look like before you’ve sorted the basic things like paying off debt.
The Fix
Live like a resident even if you haven’t been one for years, at least until you’re in a better financial position. “You’re already used to living a life of lower means, and you’re an expert when it comes to delaying gratification,” says Dr. Mollard. “Do it a little longer.” Live frugally and spend only on things that bring you joy. “A lot of physicians are trying to be really rich in all areas of their life instead of the ones that actually matter to them,” Dr. Soelberg says. Identify what’s important to you and only splurge on that.
Blind Spot #8
Never asking for help. The right financial planner can provide expert help. Emphasis on right. “Doctors can be very trusting of other professionals, even when they should not be,” says Dr. Dahle. He notes that in financial services, many people masquerade as knowledgeable advisors who are really just salespeople. While legitimate financial advisors strive to make their clients money, they are also ultimately out to line their pockets and love to work with physician salaries. Thus, doctors can end up working with financial planners that don’t specifically understand their situations or end up taking too much from their clients.
The Fix
Find a planner who specializes in, or at least understands, physicians. Ask them how they make money, says Dr. Chiang. If someone hesitates to tell you about their fee structure or if it sounds like a lot, shop around and ask colleagues for recommendations.
“Ultimately, the path to wealth is to create and grow the margin between what you make and what you spend,” says Dr. Frey. Throw some investing into the mix and physicians can set themselves up on a path for a stress-free financial life.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Valedictory
All that’s bright must fade,
The brightest still the fleetest;
All that’s sweet was made
But to be lost when sweetest.
Thomas Moore
I sometimes hold it half a sin
To put in words the grief I feel;
For words, like Nature, half reveal
And half conceal the Soul within.
Alfred, Lord Tennyson, In Memoriam
Dear Readers,
I have sad news to share with you. This is the last issue of
During my travels around the country over the past 2 decades, countless psychiatrists have told me that
As the saying goes: All good things eventually come to an end. I am so grateful to have had the opportunity to collaborate with a wonderful, highly competent editorial staff, as well as with outstanding colleagues who served on the editorial board all those years. A special shout-out to Jeff Bauer, the publishing staff editor, with whom I worked so closely. I very much appreciated all the authors and peer reviewers who contributed timely clinical articles month after month and made
This has been a unique journey for all of us who strived to transform
All that’s bright must fade,
The brightest still the fleetest;
All that’s sweet was made
But to be lost when sweetest.
Thomas Moore
I sometimes hold it half a sin
To put in words the grief I feel;
For words, like Nature, half reveal
And half conceal the Soul within.
Alfred, Lord Tennyson, In Memoriam
Dear Readers,
I have sad news to share with you. This is the last issue of
During my travels around the country over the past 2 decades, countless psychiatrists have told me that
As the saying goes: All good things eventually come to an end. I am so grateful to have had the opportunity to collaborate with a wonderful, highly competent editorial staff, as well as with outstanding colleagues who served on the editorial board all those years. A special shout-out to Jeff Bauer, the publishing staff editor, with whom I worked so closely. I very much appreciated all the authors and peer reviewers who contributed timely clinical articles month after month and made
This has been a unique journey for all of us who strived to transform
All that’s bright must fade,
The brightest still the fleetest;
All that’s sweet was made
But to be lost when sweetest.
Thomas Moore
I sometimes hold it half a sin
To put in words the grief I feel;
For words, like Nature, half reveal
And half conceal the Soul within.
Alfred, Lord Tennyson, In Memoriam
Dear Readers,
I have sad news to share with you. This is the last issue of
During my travels around the country over the past 2 decades, countless psychiatrists have told me that
As the saying goes: All good things eventually come to an end. I am so grateful to have had the opportunity to collaborate with a wonderful, highly competent editorial staff, as well as with outstanding colleagues who served on the editorial board all those years. A special shout-out to Jeff Bauer, the publishing staff editor, with whom I worked so closely. I very much appreciated all the authors and peer reviewers who contributed timely clinical articles month after month and made
This has been a unique journey for all of us who strived to transform
Rx for resilience: Five prescriptions for physician burnout
Physician burnout persists even as the height of the COVID-19 crisis fades farther into the rear-view mirror. The causes for the sadness, stress, and frustration among doctors vary, but the effects are universal and often debilitating: exhaustion, emotional detachment, lethargy, feeling useless, and lacking purpose.
When surveyed, physicians pointed to many systemic solutions for burnout in Medscape’s Physician Burnout & Depression Report 2023, such as a need for greater compensation, more manageable workloads and schedules, and more support staff. But for many doctors, these fixes may be years if not decades away. Equally important are strategies for relieving burnout symptoms now, especially as we head into a busy holiday season.
Because not every stress-relief practice works for everyone, it’s crucial to try various methods until you find something that makes a difference for you, said Christine Gibson, MD, a family physician and trauma therapist in Calgary, Alta., and author of The Modern Trauma Toolkit.
“Every person should have a toolkit of the things that bring them out of the psychological and physical distress that dysregulates their nervous system,” said Dr. Gibson.
Once you learn the personal ways to alleviate your specific brand of burnout, you can start working on systemic changes that might help the culture of medicine overall.
Symptoms speak louder than words
It seems obvious, but if you aren’t aware that what you’re feeling is burnout, you probably aren’t going to find effective steps to relieve it. Jessi Gold, MD, assistant professor and director of wellness, engagement, and outreach in the department of psychiatry, Washington University in St. Louis, is a psychiatrist who treats health care professionals, including frontline workers during the height of the pandemic. But even as a burnout expert, she admits that she misses the signs in herself.
“I was fighting constant fatigue, falling asleep the minute I got home from work every day, but I thought a B12 shot would solve all my problems. I didn’t realize I was having symptoms of burnout until my own therapist told me,” said Dr. Gold. “As doctors, we spend so much time focusing on other people that we don’t necessarily notice very much in ourselves – usually once it starts to impact our job.”
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can help you delve into your feelings and emotions and notice how you’re doing. But you may also need to ask spouses, partners, and friends and family – or better yet, a mental health professional – if they notice that you seem burnt out.
Practice ‘in the moment’ relief
Sometimes, walking away at the moment of stress helps like when stepping away from a heated argument. “Step out of a frustrating staff meeting to go to the bathroom and splash your face,” said Eran Magan, PhD, a psychologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and founder and CEO of the suicide prevention system EarlyAlert.me. “Tell a patient you need to check something in the next room, so you have time to take a breath.”
Dr. Magan recommended finding techniques that help lower acute stress while it’s actually happening. First, find a way to escape or excuse yourself from the event, and when possible, stop situations that are actively upsetting or triggering in their tracks.
Next, recharge by doing something that helps you feel better, like looking at a cute video of your child or grandchild or closing your eyes and taking a deep breath. You can also try to “catch” good feelings from someone else, said Dr. Magan. Ask someone about a trip, vacation, holiday, or pleasant event. “Ask a colleague about something that makes [them] happy,” he said. “Happiness can be infectious too.”
Burnout is also in the body
“Body psychotherapy” or somatic therapy is a treatment that focuses on how emotions appear within your body. Dr. Gibson said it’s a valuable tool for addressing trauma and a mainstay in many a medical career; it’s useful to help physicians learn to “befriend” their nervous system.
Somatic therapy exercises involve things like body scanning, scanning for physical sensations; conscious breathing, connecting to each inhale and exhale; grounding your weight by releasing tension through your feet, doing a total body stretch; or releasing shoulder and neck tension by consciously relaxing each of these muscle groups.
“We spend our whole day in sympathetic tone; our amygdala’s are firing, telling us that we’re in danger,” said Dr. Gibson. “We actually have to practice getting into and spending time in our parasympathetic nervous system to restore the balance in our autonomic nervous system.”
Somatic therapy includes a wide array of exercises that help reconnect you to your body through calming or activation. The movements release tension, ground you, and restore balance.
Bite-sized tools for well-being
Because of the prevalence of physician burnout, there’s been a groundswell of researchers and organizations who have turned their focus toward improving the well-being in the health care workforce.
One such effort comes from the Duke Center for the Advancement of Well-being Science, which “camouflages” well-being tools as continuing education credits to make them accessible for busy, stressed, and overworked physicians.
“They’re called bite-sized tools for well-being, and they have actual evidence behind them,” said Dr. Gold. For example, she said, one tools is a text program called Three Good Things that encourages physicians to send a text listing three positive things that happened during the day. The exercise lasts 15 days, and texters have access to others’ answers as well. After 3 months, participants’ baseline depression, gratitude, and life satisfaction had all “significantly improved.”
“It feels almost ridiculous that that could work, but it does,” said Dr. Gold. “I’ve had patients push back and say: ‘Well, isn’t that toxic positivity?’ But really what it is is dialectics. It’s not saying there’s only positive; it’s just making you realize there is more than just the negative.”
These and other short interventions focus on concepts such as joy, humor, awe, engagement, and self-kindness to build resilience and help physicians recover from burnout symptoms.
Cognitive restructuring could work
Cognitive restructuring is a therapeutic process of learning new ways of interpreting and responding to people and situations. It helps you change the “filter” through which you interact with your environment. Dr. Gibson said it’s a tool to use with care after other modes of therapy that help you understand your patterns and how they developed because of how you view and understand the world.
“The message of [cognitive-behavioral therapy] or cognitive restructuring is there’s something wrong with the way you’re thinking, and we need to change it or fix it, but in a traumatic system [like health care], you’re thinking has been an adaptive process related to the harm in the environment you’re in,” said Dr. Gibson.
“So, if you [jump straight to cognitive restructuring before other types of therapy], then we just gaslight ourselves into believing that there’s something wrong with us, that we haven’t adapted sufficiently to an environment that’s actually harmful.”
Strive for a few systemic changes
Systemic changes can be small ones within your own sphere. For example, Dr. Magan said, work toward making little tweaks to the flow of your day that will increase calm and reduce frustration.
“Make a ‘bug list,’ little, regular demands that drain your energy, and discuss them with your colleagues and supervisors to see if they can be improved,” he said. Examples include everyday frustrations like having unsolicited visitors popping into your office, scheduling complex patients too late in the day, or having a computer freeze whenever you access patient charts.
Though not always financially feasible, affecting real change and finding relief from all these insidious bugs can improve your mental health and burnout symptoms.
“Physicians tend to work extremely hard in order to keep holding together a system that is often not inherently sustainable, like the fascia of a body under tremendous strain,” said Dr. Magan. “Sometimes the brave thing to do is to refuse to continue being the lynchpin and let things break, so the system will have to start improving itself, rather than demanding more and more of the people in it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician burnout persists even as the height of the COVID-19 crisis fades farther into the rear-view mirror. The causes for the sadness, stress, and frustration among doctors vary, but the effects are universal and often debilitating: exhaustion, emotional detachment, lethargy, feeling useless, and lacking purpose.
When surveyed, physicians pointed to many systemic solutions for burnout in Medscape’s Physician Burnout & Depression Report 2023, such as a need for greater compensation, more manageable workloads and schedules, and more support staff. But for many doctors, these fixes may be years if not decades away. Equally important are strategies for relieving burnout symptoms now, especially as we head into a busy holiday season.
Because not every stress-relief practice works for everyone, it’s crucial to try various methods until you find something that makes a difference for you, said Christine Gibson, MD, a family physician and trauma therapist in Calgary, Alta., and author of The Modern Trauma Toolkit.
“Every person should have a toolkit of the things that bring them out of the psychological and physical distress that dysregulates their nervous system,” said Dr. Gibson.
Once you learn the personal ways to alleviate your specific brand of burnout, you can start working on systemic changes that might help the culture of medicine overall.
Symptoms speak louder than words
It seems obvious, but if you aren’t aware that what you’re feeling is burnout, you probably aren’t going to find effective steps to relieve it. Jessi Gold, MD, assistant professor and director of wellness, engagement, and outreach in the department of psychiatry, Washington University in St. Louis, is a psychiatrist who treats health care professionals, including frontline workers during the height of the pandemic. But even as a burnout expert, she admits that she misses the signs in herself.
“I was fighting constant fatigue, falling asleep the minute I got home from work every day, but I thought a B12 shot would solve all my problems. I didn’t realize I was having symptoms of burnout until my own therapist told me,” said Dr. Gold. “As doctors, we spend so much time focusing on other people that we don’t necessarily notice very much in ourselves – usually once it starts to impact our job.”
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can help you delve into your feelings and emotions and notice how you’re doing. But you may also need to ask spouses, partners, and friends and family – or better yet, a mental health professional – if they notice that you seem burnt out.
Practice ‘in the moment’ relief
Sometimes, walking away at the moment of stress helps like when stepping away from a heated argument. “Step out of a frustrating staff meeting to go to the bathroom and splash your face,” said Eran Magan, PhD, a psychologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and founder and CEO of the suicide prevention system EarlyAlert.me. “Tell a patient you need to check something in the next room, so you have time to take a breath.”
Dr. Magan recommended finding techniques that help lower acute stress while it’s actually happening. First, find a way to escape or excuse yourself from the event, and when possible, stop situations that are actively upsetting or triggering in their tracks.
Next, recharge by doing something that helps you feel better, like looking at a cute video of your child or grandchild or closing your eyes and taking a deep breath. You can also try to “catch” good feelings from someone else, said Dr. Magan. Ask someone about a trip, vacation, holiday, or pleasant event. “Ask a colleague about something that makes [them] happy,” he said. “Happiness can be infectious too.”
Burnout is also in the body
“Body psychotherapy” or somatic therapy is a treatment that focuses on how emotions appear within your body. Dr. Gibson said it’s a valuable tool for addressing trauma and a mainstay in many a medical career; it’s useful to help physicians learn to “befriend” their nervous system.
Somatic therapy exercises involve things like body scanning, scanning for physical sensations; conscious breathing, connecting to each inhale and exhale; grounding your weight by releasing tension through your feet, doing a total body stretch; or releasing shoulder and neck tension by consciously relaxing each of these muscle groups.
“We spend our whole day in sympathetic tone; our amygdala’s are firing, telling us that we’re in danger,” said Dr. Gibson. “We actually have to practice getting into and spending time in our parasympathetic nervous system to restore the balance in our autonomic nervous system.”
Somatic therapy includes a wide array of exercises that help reconnect you to your body through calming or activation. The movements release tension, ground you, and restore balance.
Bite-sized tools for well-being
Because of the prevalence of physician burnout, there’s been a groundswell of researchers and organizations who have turned their focus toward improving the well-being in the health care workforce.
One such effort comes from the Duke Center for the Advancement of Well-being Science, which “camouflages” well-being tools as continuing education credits to make them accessible for busy, stressed, and overworked physicians.
“They’re called bite-sized tools for well-being, and they have actual evidence behind them,” said Dr. Gold. For example, she said, one tools is a text program called Three Good Things that encourages physicians to send a text listing three positive things that happened during the day. The exercise lasts 15 days, and texters have access to others’ answers as well. After 3 months, participants’ baseline depression, gratitude, and life satisfaction had all “significantly improved.”
“It feels almost ridiculous that that could work, but it does,” said Dr. Gold. “I’ve had patients push back and say: ‘Well, isn’t that toxic positivity?’ But really what it is is dialectics. It’s not saying there’s only positive; it’s just making you realize there is more than just the negative.”
These and other short interventions focus on concepts such as joy, humor, awe, engagement, and self-kindness to build resilience and help physicians recover from burnout symptoms.
Cognitive restructuring could work
Cognitive restructuring is a therapeutic process of learning new ways of interpreting and responding to people and situations. It helps you change the “filter” through which you interact with your environment. Dr. Gibson said it’s a tool to use with care after other modes of therapy that help you understand your patterns and how they developed because of how you view and understand the world.
“The message of [cognitive-behavioral therapy] or cognitive restructuring is there’s something wrong with the way you’re thinking, and we need to change it or fix it, but in a traumatic system [like health care], you’re thinking has been an adaptive process related to the harm in the environment you’re in,” said Dr. Gibson.
“So, if you [jump straight to cognitive restructuring before other types of therapy], then we just gaslight ourselves into believing that there’s something wrong with us, that we haven’t adapted sufficiently to an environment that’s actually harmful.”
Strive for a few systemic changes
Systemic changes can be small ones within your own sphere. For example, Dr. Magan said, work toward making little tweaks to the flow of your day that will increase calm and reduce frustration.
“Make a ‘bug list,’ little, regular demands that drain your energy, and discuss them with your colleagues and supervisors to see if they can be improved,” he said. Examples include everyday frustrations like having unsolicited visitors popping into your office, scheduling complex patients too late in the day, or having a computer freeze whenever you access patient charts.
Though not always financially feasible, affecting real change and finding relief from all these insidious bugs can improve your mental health and burnout symptoms.
“Physicians tend to work extremely hard in order to keep holding together a system that is often not inherently sustainable, like the fascia of a body under tremendous strain,” said Dr. Magan. “Sometimes the brave thing to do is to refuse to continue being the lynchpin and let things break, so the system will have to start improving itself, rather than demanding more and more of the people in it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician burnout persists even as the height of the COVID-19 crisis fades farther into the rear-view mirror. The causes for the sadness, stress, and frustration among doctors vary, but the effects are universal and often debilitating: exhaustion, emotional detachment, lethargy, feeling useless, and lacking purpose.
When surveyed, physicians pointed to many systemic solutions for burnout in Medscape’s Physician Burnout & Depression Report 2023, such as a need for greater compensation, more manageable workloads and schedules, and more support staff. But for many doctors, these fixes may be years if not decades away. Equally important are strategies for relieving burnout symptoms now, especially as we head into a busy holiday season.
Because not every stress-relief practice works for everyone, it’s crucial to try various methods until you find something that makes a difference for you, said Christine Gibson, MD, a family physician and trauma therapist in Calgary, Alta., and author of The Modern Trauma Toolkit.
“Every person should have a toolkit of the things that bring them out of the psychological and physical distress that dysregulates their nervous system,” said Dr. Gibson.
Once you learn the personal ways to alleviate your specific brand of burnout, you can start working on systemic changes that might help the culture of medicine overall.
Symptoms speak louder than words
It seems obvious, but if you aren’t aware that what you’re feeling is burnout, you probably aren’t going to find effective steps to relieve it. Jessi Gold, MD, assistant professor and director of wellness, engagement, and outreach in the department of psychiatry, Washington University in St. Louis, is a psychiatrist who treats health care professionals, including frontline workers during the height of the pandemic. But even as a burnout expert, she admits that she misses the signs in herself.
“I was fighting constant fatigue, falling asleep the minute I got home from work every day, but I thought a B12 shot would solve all my problems. I didn’t realize I was having symptoms of burnout until my own therapist told me,” said Dr. Gold. “As doctors, we spend so much time focusing on other people that we don’t necessarily notice very much in ourselves – usually once it starts to impact our job.”
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can help you delve into your feelings and emotions and notice how you’re doing. But you may also need to ask spouses, partners, and friends and family – or better yet, a mental health professional – if they notice that you seem burnt out.
Practice ‘in the moment’ relief
Sometimes, walking away at the moment of stress helps like when stepping away from a heated argument. “Step out of a frustrating staff meeting to go to the bathroom and splash your face,” said Eran Magan, PhD, a psychologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and founder and CEO of the suicide prevention system EarlyAlert.me. “Tell a patient you need to check something in the next room, so you have time to take a breath.”
Dr. Magan recommended finding techniques that help lower acute stress while it’s actually happening. First, find a way to escape or excuse yourself from the event, and when possible, stop situations that are actively upsetting or triggering in their tracks.
Next, recharge by doing something that helps you feel better, like looking at a cute video of your child or grandchild or closing your eyes and taking a deep breath. You can also try to “catch” good feelings from someone else, said Dr. Magan. Ask someone about a trip, vacation, holiday, or pleasant event. “Ask a colleague about something that makes [them] happy,” he said. “Happiness can be infectious too.”
Burnout is also in the body
“Body psychotherapy” or somatic therapy is a treatment that focuses on how emotions appear within your body. Dr. Gibson said it’s a valuable tool for addressing trauma and a mainstay in many a medical career; it’s useful to help physicians learn to “befriend” their nervous system.
Somatic therapy exercises involve things like body scanning, scanning for physical sensations; conscious breathing, connecting to each inhale and exhale; grounding your weight by releasing tension through your feet, doing a total body stretch; or releasing shoulder and neck tension by consciously relaxing each of these muscle groups.
“We spend our whole day in sympathetic tone; our amygdala’s are firing, telling us that we’re in danger,” said Dr. Gibson. “We actually have to practice getting into and spending time in our parasympathetic nervous system to restore the balance in our autonomic nervous system.”
Somatic therapy includes a wide array of exercises that help reconnect you to your body through calming or activation. The movements release tension, ground you, and restore balance.
Bite-sized tools for well-being
Because of the prevalence of physician burnout, there’s been a groundswell of researchers and organizations who have turned their focus toward improving the well-being in the health care workforce.
One such effort comes from the Duke Center for the Advancement of Well-being Science, which “camouflages” well-being tools as continuing education credits to make them accessible for busy, stressed, and overworked physicians.
“They’re called bite-sized tools for well-being, and they have actual evidence behind them,” said Dr. Gold. For example, she said, one tools is a text program called Three Good Things that encourages physicians to send a text listing three positive things that happened during the day. The exercise lasts 15 days, and texters have access to others’ answers as well. After 3 months, participants’ baseline depression, gratitude, and life satisfaction had all “significantly improved.”
“It feels almost ridiculous that that could work, but it does,” said Dr. Gold. “I’ve had patients push back and say: ‘Well, isn’t that toxic positivity?’ But really what it is is dialectics. It’s not saying there’s only positive; it’s just making you realize there is more than just the negative.”
These and other short interventions focus on concepts such as joy, humor, awe, engagement, and self-kindness to build resilience and help physicians recover from burnout symptoms.
Cognitive restructuring could work
Cognitive restructuring is a therapeutic process of learning new ways of interpreting and responding to people and situations. It helps you change the “filter” through which you interact with your environment. Dr. Gibson said it’s a tool to use with care after other modes of therapy that help you understand your patterns and how they developed because of how you view and understand the world.
“The message of [cognitive-behavioral therapy] or cognitive restructuring is there’s something wrong with the way you’re thinking, and we need to change it or fix it, but in a traumatic system [like health care], you’re thinking has been an adaptive process related to the harm in the environment you’re in,” said Dr. Gibson.
“So, if you [jump straight to cognitive restructuring before other types of therapy], then we just gaslight ourselves into believing that there’s something wrong with us, that we haven’t adapted sufficiently to an environment that’s actually harmful.”
Strive for a few systemic changes
Systemic changes can be small ones within your own sphere. For example, Dr. Magan said, work toward making little tweaks to the flow of your day that will increase calm and reduce frustration.
“Make a ‘bug list,’ little, regular demands that drain your energy, and discuss them with your colleagues and supervisors to see if they can be improved,” he said. Examples include everyday frustrations like having unsolicited visitors popping into your office, scheduling complex patients too late in the day, or having a computer freeze whenever you access patient charts.
Though not always financially feasible, affecting real change and finding relief from all these insidious bugs can improve your mental health and burnout symptoms.
“Physicians tend to work extremely hard in order to keep holding together a system that is often not inherently sustainable, like the fascia of a body under tremendous strain,” said Dr. Magan. “Sometimes the brave thing to do is to refuse to continue being the lynchpin and let things break, so the system will have to start improving itself, rather than demanding more and more of the people in it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why don’t doctors feel like heroes anymore?
In April 2020, as many Americans prepared to spend the Easter holiday in lockdown, pop star Mariah Carey released a video honoring the “sacrifices and courage” of frontline workers battling COVID-19 – her 1993 hit, “Hero.”
“The sorrow that you know will melt away,” Ms. Carey sang. “When you feel like hope is gone,” the song continued, strength and answers can be found within, and “a hero lies in you.”
For health care professionals, the reality of 2020 wasn’t quite so uplifting. PPE shortages and spillover ICUs had many feeling helpless, exhausted, and overwhelmed. Few if any medical professionals felt their sorrows “melt away.”
We can’t expect depth and nuance from pop songs, but we can find in them the imagery that runs through our culture. The “hero narrative” – the idea that doctors, nurses, and others in health care have superhuman endurance and selflessness – has long been an undercurrent in the medical field.
And yet, without a workforce willing to perform without adequate sleep, food, or time off, the health care system couldn’t function, says Brian Park, MD, MPH, a family medicine physician at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. At many academic health centers, for example, residents are “the bedrock of the workforce,” he explains. If they didn’t work 80-100 hours per week, those systems wouldn’t exist.
So, how do we look at the health care system in a way that is both grateful and critical, Dr. Park wonders. “How do we honor extreme acts of heroism and also acknowledge that the system sometimes gets by on the acts of heroes to patch up some of the brokenness and fragmentation within it?”
Heroes are determined
Ala Stanford, MD, a pediatric surgeon in Philadelphia, has frequently been called a “health care hero.” Given the title by CNN in 2021, she has received numerous other awards and accolades, featured in Fortune Magazine’s “World’s 50 Greatest Leaders” in 2021 and USA Today’s “Women of the Year” in 2022.
In 2020, Dr. Stanford was sheltering in place and watching “way too much” cable news. “They would play solemn music and show photos of all the people who had died,” she recalls. “I thought, ‘All these people are Black or brown. What is going on?’”
The standard explanation was that people of color were more vulnerable because they were more likely to be essential workers or have chronic health conditions. But Dr. Stanford believed this was only part of the story. The reason she saw that local Black communities had higher positivity rates was because people couldn’t get a COVID test.
Dr. Stanford got call after call from Philadelphians who had been turned away from testing centers. When she questioned colleagues, “they gave me every reason under the sun,” Dr. Stanford says. “It was because someone took public transportation, and they were only testing people in cars, or because they weren’t over 65, or because they didn’t have other comorbid health conditions, or because they weren’t a health care worker, or because they hadn’t traveled to China ...” The list went on.
Dr. Stanford appealed to local, state, and federal health authorities. Finally, she took matters into her own hands. She found tests, packed a van with masks, gowns, and gloves, and drove across the city going door to door. Eventually, she organized testing in the parking lots of Black churches, sometimes seeing more than 400 people per day.
The services were funded entirely through her own bank account and donations until she was eventually awarded a CDC grant through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act of 2020 and began to receive contracts from the city.
Since then, Dr. Stanford’s mission has evolved. She and her team provided COVID vaccinations to thousands, and in 2021, opened the Dr. Ala Stanford Center for Health Equity. The center offers primary care for all ages in underserved communities.
Still, Dr. Stanford doesn’t think of herself as a hero, and she stresses that many other people contributed to her success. “I think the world was on fire, and we were all firefighters,” Dr. Stanford says. “Someone said to me, ‘Ala, you ran to the fire and everyone else was running away from it, and you didn’t have to.’ … I feel like I was able to galvanize people to realize the power that they actually had. Maybe independently, they couldn’t do a whole lot, but collectively, we were a force.”
Heroes are selfless
Nicole Jackson, RN, an emergency room manager and nurse at Advocate Trinity Hospital in Chicago, was recently honored as a Health Care Hero by the American Red Cross of Greater Chicago.
On June 23, 2022, Jackson’s emergency department was understaffed and struggling with an influx of patients when three gunshot victims arrived. Two needed to be transferred to a trauma center, and one – with multiple gunshot wounds – required a critical care nurse in the ambulance. But the ETA for that transport was 90 minutes, which meant the patient might not survive. Although Ms. Jackson was already working beyond her shift, she rode in the ambulance with the patient herself and probably saved his life.
While this incident stood out to a colleague who nominated her for the Red Cross award, Ms. Jackson finds herself working extra hours fairly often. “Since COVID, that’s pretty much been like any other hospital,” she says. “We’ve had staffing challenges that we work through every day. So, the nurses come, they show up, and they do the best that they can with what we have to keep our patients safe.”
A 2022 survey by McKinsey estimated that by 2025, there could be a gap of 200,000 to 450,000 nurses in the United States. A two-year impact assessment from the American Nurses Foundation found that among more than 12,500 nurses, 40% were considering leaving their positions before the pandemic. By 2022, that number had jumped to 52% with the top reasons being insufficient staffing and negative effects on health and well-being.
Can the “hero narrative” help that situation? Ms. Jackson says she doesn’t see herself as a hero, but the supportive environment and gestures of recognition by staff do make her feel appreciated. These include daily messages offering “kudos” and nominations for the DAISY Award, which she herself received in 2022.
“I have people who I have encouraged to become nurses,” Ms. Jackson says, “and when they saw [the award], they were really excited about becoming a nurse.”
Heroes are strong
Jasmine Marcelin, MD, an infectious disease physician with Nebraska Medicine in Omaha, understands the need for heroes as symbols and sources of inspiration. Dr. Marcelin is a fan of the superhero movie genre. There is value, she says, in feeling hope and excitement while watching Superman or Wonder Woman save the day. Who doesn’t want to believe (if only briefly) that the good guys will always win?
In reality, Dr. Marcelin says, “none of us are invincible.” And it’s dangerous to forget that “the people behind the symbols are also human.”
In 2021, Dr. Marcelin gave a TEDx talk entitled, “The Myth of the Health Care Hero.” In it she discussed the extreme physical and mental toll of the pandemic on health care workers and urged her audience to think less about extravagant praise and more about their personal responsibilities. “We don’t want or need to be called heroes,” Dr. Marcelin said. “Right now, our love language is action. We need your help, and we cannot save the world on our own.”
Dr. Marcelin also sees links between superhuman expectations and the high levels of burnout in the medical field.
“It’s a systemic issue,” she explains, “where it requires a revamping and revitalization of the entire psyche of health care to recognize that the people working within this profession are human. And the things that we think and feel and need are the same as anybody else.”
Heroes are self-sacrificing
Well-being, burnout, and disengagement in health care has become a focus for Oregon Health & Science’s Dr. Park, who is also director of RELATE Lab, an organization that aims to make health care more human-centered and equitable through leadership training, research, and community organizing.
For him, hearing neighbors banging pots and pans during the early pandemic was complicated. “The first phase for me was, ‘Thank you. I feel seen. I feel appreciated,’ ” he says. “Yes, I’m wearing a mask. I’m going in. I’m changing in the garage when I come home, so my kid and my partner don’t get sick.”
But after a while, the cheers started to feel like pressure. “Have I done anything heroic today?” Dr. Park asked himself. “Have I been as heroic as my friend who is in the hospital in the ICU? I don’t deserve this, so don’t bang those pots and pans for me.”
When your identity becomes about being a hero, Dr. Park says, when that becomes the standard by which you measure yourself, the result is often a sense of shame.
“I think a lot of people feel ashamed that they feel burnout,” he says, “because they’re supposed to be heroes, putting on their capes and masks. They’re waking up and saying, ‘I’m exhausted, and I can’t play that part today. But I know that’s the social expectation of me.’ “
Heroes are noble
There may not be a clear solution, but for many health care professionals, symbolic gestures alone are inadequate and, in certain cases, insulting.
On Doctor’s Day 2023, Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist, tweeted a photo of an appreciation “gift” for staff from an unnamed hospital. The small items had metaphorical meanings – a rubber band “as a reminder to stay flexible,” a quarter “as a reminder to ‘call’ for help,” etc.
“Welcome to how you give thanks to ‘health care heroes,’ ” Dr. Patel tweeted.
For Dr. Patel, the issue is not lavish gifts but a need for an attitude shift. He recalls colleagues who felt ashamed asking for mental health services or time off, “because they were bombarded by the hero narrative, by the manufactured pressure that they needed to put their jobs above their own health – because that’s what ‘heroes’ do. I’m willing to bet most physicians would rather receive a sincere email with a transparent plan to better support health care workers than any Doctor’s Day gift,” he says.
In Dr. Marcelin’s TEDx talk, she quotes Spider-Man’s classic adage, “With great power, comes great responsibility.” She argues that this motto doesn’t just apply to those who can fly or deflect bullets; that’s not what heroism is. In fact, most people have their own definition of the word.
For Dr. Stanford, a hero is “someone who is selfless, putting the needs of others before their own.” Dr. Park believes there are no individual heroes. “It’s the work of the collective that’s truly heroic.”
By those standards, clearly anyone can step up, offer help, act with courage and kindness, and be heroic. “We humans, as ordinary as we are, can be extraordinary by using our power to do what’s right,” Dr. Marcelin says, “because there’s no such thing as health care heroes, just good people doing the right thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In April 2020, as many Americans prepared to spend the Easter holiday in lockdown, pop star Mariah Carey released a video honoring the “sacrifices and courage” of frontline workers battling COVID-19 – her 1993 hit, “Hero.”
“The sorrow that you know will melt away,” Ms. Carey sang. “When you feel like hope is gone,” the song continued, strength and answers can be found within, and “a hero lies in you.”
For health care professionals, the reality of 2020 wasn’t quite so uplifting. PPE shortages and spillover ICUs had many feeling helpless, exhausted, and overwhelmed. Few if any medical professionals felt their sorrows “melt away.”
We can’t expect depth and nuance from pop songs, but we can find in them the imagery that runs through our culture. The “hero narrative” – the idea that doctors, nurses, and others in health care have superhuman endurance and selflessness – has long been an undercurrent in the medical field.
And yet, without a workforce willing to perform without adequate sleep, food, or time off, the health care system couldn’t function, says Brian Park, MD, MPH, a family medicine physician at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. At many academic health centers, for example, residents are “the bedrock of the workforce,” he explains. If they didn’t work 80-100 hours per week, those systems wouldn’t exist.
So, how do we look at the health care system in a way that is both grateful and critical, Dr. Park wonders. “How do we honor extreme acts of heroism and also acknowledge that the system sometimes gets by on the acts of heroes to patch up some of the brokenness and fragmentation within it?”
Heroes are determined
Ala Stanford, MD, a pediatric surgeon in Philadelphia, has frequently been called a “health care hero.” Given the title by CNN in 2021, she has received numerous other awards and accolades, featured in Fortune Magazine’s “World’s 50 Greatest Leaders” in 2021 and USA Today’s “Women of the Year” in 2022.
In 2020, Dr. Stanford was sheltering in place and watching “way too much” cable news. “They would play solemn music and show photos of all the people who had died,” she recalls. “I thought, ‘All these people are Black or brown. What is going on?’”
The standard explanation was that people of color were more vulnerable because they were more likely to be essential workers or have chronic health conditions. But Dr. Stanford believed this was only part of the story. The reason she saw that local Black communities had higher positivity rates was because people couldn’t get a COVID test.
Dr. Stanford got call after call from Philadelphians who had been turned away from testing centers. When she questioned colleagues, “they gave me every reason under the sun,” Dr. Stanford says. “It was because someone took public transportation, and they were only testing people in cars, or because they weren’t over 65, or because they didn’t have other comorbid health conditions, or because they weren’t a health care worker, or because they hadn’t traveled to China ...” The list went on.
Dr. Stanford appealed to local, state, and federal health authorities. Finally, she took matters into her own hands. She found tests, packed a van with masks, gowns, and gloves, and drove across the city going door to door. Eventually, she organized testing in the parking lots of Black churches, sometimes seeing more than 400 people per day.
The services were funded entirely through her own bank account and donations until she was eventually awarded a CDC grant through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act of 2020 and began to receive contracts from the city.
Since then, Dr. Stanford’s mission has evolved. She and her team provided COVID vaccinations to thousands, and in 2021, opened the Dr. Ala Stanford Center for Health Equity. The center offers primary care for all ages in underserved communities.
Still, Dr. Stanford doesn’t think of herself as a hero, and she stresses that many other people contributed to her success. “I think the world was on fire, and we were all firefighters,” Dr. Stanford says. “Someone said to me, ‘Ala, you ran to the fire and everyone else was running away from it, and you didn’t have to.’ … I feel like I was able to galvanize people to realize the power that they actually had. Maybe independently, they couldn’t do a whole lot, but collectively, we were a force.”
Heroes are selfless
Nicole Jackson, RN, an emergency room manager and nurse at Advocate Trinity Hospital in Chicago, was recently honored as a Health Care Hero by the American Red Cross of Greater Chicago.
On June 23, 2022, Jackson’s emergency department was understaffed and struggling with an influx of patients when three gunshot victims arrived. Two needed to be transferred to a trauma center, and one – with multiple gunshot wounds – required a critical care nurse in the ambulance. But the ETA for that transport was 90 minutes, which meant the patient might not survive. Although Ms. Jackson was already working beyond her shift, she rode in the ambulance with the patient herself and probably saved his life.
While this incident stood out to a colleague who nominated her for the Red Cross award, Ms. Jackson finds herself working extra hours fairly often. “Since COVID, that’s pretty much been like any other hospital,” she says. “We’ve had staffing challenges that we work through every day. So, the nurses come, they show up, and they do the best that they can with what we have to keep our patients safe.”
A 2022 survey by McKinsey estimated that by 2025, there could be a gap of 200,000 to 450,000 nurses in the United States. A two-year impact assessment from the American Nurses Foundation found that among more than 12,500 nurses, 40% were considering leaving their positions before the pandemic. By 2022, that number had jumped to 52% with the top reasons being insufficient staffing and negative effects on health and well-being.
Can the “hero narrative” help that situation? Ms. Jackson says she doesn’t see herself as a hero, but the supportive environment and gestures of recognition by staff do make her feel appreciated. These include daily messages offering “kudos” and nominations for the DAISY Award, which she herself received in 2022.
“I have people who I have encouraged to become nurses,” Ms. Jackson says, “and when they saw [the award], they were really excited about becoming a nurse.”
Heroes are strong
Jasmine Marcelin, MD, an infectious disease physician with Nebraska Medicine in Omaha, understands the need for heroes as symbols and sources of inspiration. Dr. Marcelin is a fan of the superhero movie genre. There is value, she says, in feeling hope and excitement while watching Superman or Wonder Woman save the day. Who doesn’t want to believe (if only briefly) that the good guys will always win?
In reality, Dr. Marcelin says, “none of us are invincible.” And it’s dangerous to forget that “the people behind the symbols are also human.”
In 2021, Dr. Marcelin gave a TEDx talk entitled, “The Myth of the Health Care Hero.” In it she discussed the extreme physical and mental toll of the pandemic on health care workers and urged her audience to think less about extravagant praise and more about their personal responsibilities. “We don’t want or need to be called heroes,” Dr. Marcelin said. “Right now, our love language is action. We need your help, and we cannot save the world on our own.”
Dr. Marcelin also sees links between superhuman expectations and the high levels of burnout in the medical field.
“It’s a systemic issue,” she explains, “where it requires a revamping and revitalization of the entire psyche of health care to recognize that the people working within this profession are human. And the things that we think and feel and need are the same as anybody else.”
Heroes are self-sacrificing
Well-being, burnout, and disengagement in health care has become a focus for Oregon Health & Science’s Dr. Park, who is also director of RELATE Lab, an organization that aims to make health care more human-centered and equitable through leadership training, research, and community organizing.
For him, hearing neighbors banging pots and pans during the early pandemic was complicated. “The first phase for me was, ‘Thank you. I feel seen. I feel appreciated,’ ” he says. “Yes, I’m wearing a mask. I’m going in. I’m changing in the garage when I come home, so my kid and my partner don’t get sick.”
But after a while, the cheers started to feel like pressure. “Have I done anything heroic today?” Dr. Park asked himself. “Have I been as heroic as my friend who is in the hospital in the ICU? I don’t deserve this, so don’t bang those pots and pans for me.”
When your identity becomes about being a hero, Dr. Park says, when that becomes the standard by which you measure yourself, the result is often a sense of shame.
“I think a lot of people feel ashamed that they feel burnout,” he says, “because they’re supposed to be heroes, putting on their capes and masks. They’re waking up and saying, ‘I’m exhausted, and I can’t play that part today. But I know that’s the social expectation of me.’ “
Heroes are noble
There may not be a clear solution, but for many health care professionals, symbolic gestures alone are inadequate and, in certain cases, insulting.
On Doctor’s Day 2023, Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist, tweeted a photo of an appreciation “gift” for staff from an unnamed hospital. The small items had metaphorical meanings – a rubber band “as a reminder to stay flexible,” a quarter “as a reminder to ‘call’ for help,” etc.
“Welcome to how you give thanks to ‘health care heroes,’ ” Dr. Patel tweeted.
For Dr. Patel, the issue is not lavish gifts but a need for an attitude shift. He recalls colleagues who felt ashamed asking for mental health services or time off, “because they were bombarded by the hero narrative, by the manufactured pressure that they needed to put their jobs above their own health – because that’s what ‘heroes’ do. I’m willing to bet most physicians would rather receive a sincere email with a transparent plan to better support health care workers than any Doctor’s Day gift,” he says.
In Dr. Marcelin’s TEDx talk, she quotes Spider-Man’s classic adage, “With great power, comes great responsibility.” She argues that this motto doesn’t just apply to those who can fly or deflect bullets; that’s not what heroism is. In fact, most people have their own definition of the word.
For Dr. Stanford, a hero is “someone who is selfless, putting the needs of others before their own.” Dr. Park believes there are no individual heroes. “It’s the work of the collective that’s truly heroic.”
By those standards, clearly anyone can step up, offer help, act with courage and kindness, and be heroic. “We humans, as ordinary as we are, can be extraordinary by using our power to do what’s right,” Dr. Marcelin says, “because there’s no such thing as health care heroes, just good people doing the right thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In April 2020, as many Americans prepared to spend the Easter holiday in lockdown, pop star Mariah Carey released a video honoring the “sacrifices and courage” of frontline workers battling COVID-19 – her 1993 hit, “Hero.”
“The sorrow that you know will melt away,” Ms. Carey sang. “When you feel like hope is gone,” the song continued, strength and answers can be found within, and “a hero lies in you.”
For health care professionals, the reality of 2020 wasn’t quite so uplifting. PPE shortages and spillover ICUs had many feeling helpless, exhausted, and overwhelmed. Few if any medical professionals felt their sorrows “melt away.”
We can’t expect depth and nuance from pop songs, but we can find in them the imagery that runs through our culture. The “hero narrative” – the idea that doctors, nurses, and others in health care have superhuman endurance and selflessness – has long been an undercurrent in the medical field.
And yet, without a workforce willing to perform without adequate sleep, food, or time off, the health care system couldn’t function, says Brian Park, MD, MPH, a family medicine physician at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. At many academic health centers, for example, residents are “the bedrock of the workforce,” he explains. If they didn’t work 80-100 hours per week, those systems wouldn’t exist.
So, how do we look at the health care system in a way that is both grateful and critical, Dr. Park wonders. “How do we honor extreme acts of heroism and also acknowledge that the system sometimes gets by on the acts of heroes to patch up some of the brokenness and fragmentation within it?”
Heroes are determined
Ala Stanford, MD, a pediatric surgeon in Philadelphia, has frequently been called a “health care hero.” Given the title by CNN in 2021, she has received numerous other awards and accolades, featured in Fortune Magazine’s “World’s 50 Greatest Leaders” in 2021 and USA Today’s “Women of the Year” in 2022.
In 2020, Dr. Stanford was sheltering in place and watching “way too much” cable news. “They would play solemn music and show photos of all the people who had died,” she recalls. “I thought, ‘All these people are Black or brown. What is going on?’”
The standard explanation was that people of color were more vulnerable because they were more likely to be essential workers or have chronic health conditions. But Dr. Stanford believed this was only part of the story. The reason she saw that local Black communities had higher positivity rates was because people couldn’t get a COVID test.
Dr. Stanford got call after call from Philadelphians who had been turned away from testing centers. When she questioned colleagues, “they gave me every reason under the sun,” Dr. Stanford says. “It was because someone took public transportation, and they were only testing people in cars, or because they weren’t over 65, or because they didn’t have other comorbid health conditions, or because they weren’t a health care worker, or because they hadn’t traveled to China ...” The list went on.
Dr. Stanford appealed to local, state, and federal health authorities. Finally, she took matters into her own hands. She found tests, packed a van with masks, gowns, and gloves, and drove across the city going door to door. Eventually, she organized testing in the parking lots of Black churches, sometimes seeing more than 400 people per day.
The services were funded entirely through her own bank account and donations until she was eventually awarded a CDC grant through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act of 2020 and began to receive contracts from the city.
Since then, Dr. Stanford’s mission has evolved. She and her team provided COVID vaccinations to thousands, and in 2021, opened the Dr. Ala Stanford Center for Health Equity. The center offers primary care for all ages in underserved communities.
Still, Dr. Stanford doesn’t think of herself as a hero, and she stresses that many other people contributed to her success. “I think the world was on fire, and we were all firefighters,” Dr. Stanford says. “Someone said to me, ‘Ala, you ran to the fire and everyone else was running away from it, and you didn’t have to.’ … I feel like I was able to galvanize people to realize the power that they actually had. Maybe independently, they couldn’t do a whole lot, but collectively, we were a force.”
Heroes are selfless
Nicole Jackson, RN, an emergency room manager and nurse at Advocate Trinity Hospital in Chicago, was recently honored as a Health Care Hero by the American Red Cross of Greater Chicago.
On June 23, 2022, Jackson’s emergency department was understaffed and struggling with an influx of patients when three gunshot victims arrived. Two needed to be transferred to a trauma center, and one – with multiple gunshot wounds – required a critical care nurse in the ambulance. But the ETA for that transport was 90 minutes, which meant the patient might not survive. Although Ms. Jackson was already working beyond her shift, she rode in the ambulance with the patient herself and probably saved his life.
While this incident stood out to a colleague who nominated her for the Red Cross award, Ms. Jackson finds herself working extra hours fairly often. “Since COVID, that’s pretty much been like any other hospital,” she says. “We’ve had staffing challenges that we work through every day. So, the nurses come, they show up, and they do the best that they can with what we have to keep our patients safe.”
A 2022 survey by McKinsey estimated that by 2025, there could be a gap of 200,000 to 450,000 nurses in the United States. A two-year impact assessment from the American Nurses Foundation found that among more than 12,500 nurses, 40% were considering leaving their positions before the pandemic. By 2022, that number had jumped to 52% with the top reasons being insufficient staffing and negative effects on health and well-being.
Can the “hero narrative” help that situation? Ms. Jackson says she doesn’t see herself as a hero, but the supportive environment and gestures of recognition by staff do make her feel appreciated. These include daily messages offering “kudos” and nominations for the DAISY Award, which she herself received in 2022.
“I have people who I have encouraged to become nurses,” Ms. Jackson says, “and when they saw [the award], they were really excited about becoming a nurse.”
Heroes are strong
Jasmine Marcelin, MD, an infectious disease physician with Nebraska Medicine in Omaha, understands the need for heroes as symbols and sources of inspiration. Dr. Marcelin is a fan of the superhero movie genre. There is value, she says, in feeling hope and excitement while watching Superman or Wonder Woman save the day. Who doesn’t want to believe (if only briefly) that the good guys will always win?
In reality, Dr. Marcelin says, “none of us are invincible.” And it’s dangerous to forget that “the people behind the symbols are also human.”
In 2021, Dr. Marcelin gave a TEDx talk entitled, “The Myth of the Health Care Hero.” In it she discussed the extreme physical and mental toll of the pandemic on health care workers and urged her audience to think less about extravagant praise and more about their personal responsibilities. “We don’t want or need to be called heroes,” Dr. Marcelin said. “Right now, our love language is action. We need your help, and we cannot save the world on our own.”
Dr. Marcelin also sees links between superhuman expectations and the high levels of burnout in the medical field.
“It’s a systemic issue,” she explains, “where it requires a revamping and revitalization of the entire psyche of health care to recognize that the people working within this profession are human. And the things that we think and feel and need are the same as anybody else.”
Heroes are self-sacrificing
Well-being, burnout, and disengagement in health care has become a focus for Oregon Health & Science’s Dr. Park, who is also director of RELATE Lab, an organization that aims to make health care more human-centered and equitable through leadership training, research, and community organizing.
For him, hearing neighbors banging pots and pans during the early pandemic was complicated. “The first phase for me was, ‘Thank you. I feel seen. I feel appreciated,’ ” he says. “Yes, I’m wearing a mask. I’m going in. I’m changing in the garage when I come home, so my kid and my partner don’t get sick.”
But after a while, the cheers started to feel like pressure. “Have I done anything heroic today?” Dr. Park asked himself. “Have I been as heroic as my friend who is in the hospital in the ICU? I don’t deserve this, so don’t bang those pots and pans for me.”
When your identity becomes about being a hero, Dr. Park says, when that becomes the standard by which you measure yourself, the result is often a sense of shame.
“I think a lot of people feel ashamed that they feel burnout,” he says, “because they’re supposed to be heroes, putting on their capes and masks. They’re waking up and saying, ‘I’m exhausted, and I can’t play that part today. But I know that’s the social expectation of me.’ “
Heroes are noble
There may not be a clear solution, but for many health care professionals, symbolic gestures alone are inadequate and, in certain cases, insulting.
On Doctor’s Day 2023, Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist, tweeted a photo of an appreciation “gift” for staff from an unnamed hospital. The small items had metaphorical meanings – a rubber band “as a reminder to stay flexible,” a quarter “as a reminder to ‘call’ for help,” etc.
“Welcome to how you give thanks to ‘health care heroes,’ ” Dr. Patel tweeted.
For Dr. Patel, the issue is not lavish gifts but a need for an attitude shift. He recalls colleagues who felt ashamed asking for mental health services or time off, “because they were bombarded by the hero narrative, by the manufactured pressure that they needed to put their jobs above their own health – because that’s what ‘heroes’ do. I’m willing to bet most physicians would rather receive a sincere email with a transparent plan to better support health care workers than any Doctor’s Day gift,” he says.
In Dr. Marcelin’s TEDx talk, she quotes Spider-Man’s classic adage, “With great power, comes great responsibility.” She argues that this motto doesn’t just apply to those who can fly or deflect bullets; that’s not what heroism is. In fact, most people have their own definition of the word.
For Dr. Stanford, a hero is “someone who is selfless, putting the needs of others before their own.” Dr. Park believes there are no individual heroes. “It’s the work of the collective that’s truly heroic.”
By those standards, clearly anyone can step up, offer help, act with courage and kindness, and be heroic. “We humans, as ordinary as we are, can be extraordinary by using our power to do what’s right,” Dr. Marcelin says, “because there’s no such thing as health care heroes, just good people doing the right thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Redispensing unused cancer meds cuts waste, saves money
TOPLINE:
to save money and reduce waste, a Dutch study has found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ongoing drug shortages and growing drug prices contribute to access issues in oncology.
- Researchers compared the reduction in drug waste and cost savings from redispensing oral anticancer drugs versus the standard practice of disposing of them.
- Outpatient pharmacies at four Dutch hospitals participated. A total of 1,071 patients with cancer receiving oral anticancer drugs for at-home use were given special packaging for returning unused medication to the pharmacy.
- The pharmacy ensured the quality of returned drugs based on authenticity, appearance, remaining shelf-life, and adequate storage temperature.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 13,069 oral anticancer drug packages, containing an average of 27 daily doses per package, were dispensed during the study period.
- Overall, 16% of patients (n = 171) returned 335 (2.6%) unused oral anticancer drug packages, of which 68% were redispensed after passing quality control.
- Redispensing unused oral anticancer drugs reduced waste by 68%, compared with disposing of them, and provided a mean net annual cost savings of €576 (U.S. $682) per patient per year.
- When just those patients who took targeted oral anticancer drugs for up to 24 months were looked at, the mean net annual cost savings associated with the quality check protocol increased to €934 (U.S. $1,019) per patient or of only the visual quality check was €1,348 (U.S. $1,474) per patient.
IN PRACTICE:
“New strategies targeting waste are required to improve financial and ecologic sustainability of expensive therapies, such as oral anticancer drugs, that frequently remain unused by patients,” the authors write. “These findings provide a waste-minimizing strategy to contribute to sustainable and affordable access to drugs.”
SOURCE:
The study, by Elisabeth M. Smale, PharmD, of Radboud University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
Novel drugs are substantially more expensive in the United States, and the Dutch findings might underestimate potential cost savings generated through redispensing programs in the United States. Participants were prompted to return unused oral anticancer drugs through reminders at the pharmacy, but all such drugs may not have been returned.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by ZonMw, the Dutch national organization for health research and development. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
to save money and reduce waste, a Dutch study has found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ongoing drug shortages and growing drug prices contribute to access issues in oncology.
- Researchers compared the reduction in drug waste and cost savings from redispensing oral anticancer drugs versus the standard practice of disposing of them.
- Outpatient pharmacies at four Dutch hospitals participated. A total of 1,071 patients with cancer receiving oral anticancer drugs for at-home use were given special packaging for returning unused medication to the pharmacy.
- The pharmacy ensured the quality of returned drugs based on authenticity, appearance, remaining shelf-life, and adequate storage temperature.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 13,069 oral anticancer drug packages, containing an average of 27 daily doses per package, were dispensed during the study period.
- Overall, 16% of patients (n = 171) returned 335 (2.6%) unused oral anticancer drug packages, of which 68% were redispensed after passing quality control.
- Redispensing unused oral anticancer drugs reduced waste by 68%, compared with disposing of them, and provided a mean net annual cost savings of €576 (U.S. $682) per patient per year.
- When just those patients who took targeted oral anticancer drugs for up to 24 months were looked at, the mean net annual cost savings associated with the quality check protocol increased to €934 (U.S. $1,019) per patient or of only the visual quality check was €1,348 (U.S. $1,474) per patient.
IN PRACTICE:
“New strategies targeting waste are required to improve financial and ecologic sustainability of expensive therapies, such as oral anticancer drugs, that frequently remain unused by patients,” the authors write. “These findings provide a waste-minimizing strategy to contribute to sustainable and affordable access to drugs.”
SOURCE:
The study, by Elisabeth M. Smale, PharmD, of Radboud University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
Novel drugs are substantially more expensive in the United States, and the Dutch findings might underestimate potential cost savings generated through redispensing programs in the United States. Participants were prompted to return unused oral anticancer drugs through reminders at the pharmacy, but all such drugs may not have been returned.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by ZonMw, the Dutch national organization for health research and development. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
to save money and reduce waste, a Dutch study has found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Ongoing drug shortages and growing drug prices contribute to access issues in oncology.
- Researchers compared the reduction in drug waste and cost savings from redispensing oral anticancer drugs versus the standard practice of disposing of them.
- Outpatient pharmacies at four Dutch hospitals participated. A total of 1,071 patients with cancer receiving oral anticancer drugs for at-home use were given special packaging for returning unused medication to the pharmacy.
- The pharmacy ensured the quality of returned drugs based on authenticity, appearance, remaining shelf-life, and adequate storage temperature.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 13,069 oral anticancer drug packages, containing an average of 27 daily doses per package, were dispensed during the study period.
- Overall, 16% of patients (n = 171) returned 335 (2.6%) unused oral anticancer drug packages, of which 68% were redispensed after passing quality control.
- Redispensing unused oral anticancer drugs reduced waste by 68%, compared with disposing of them, and provided a mean net annual cost savings of €576 (U.S. $682) per patient per year.
- When just those patients who took targeted oral anticancer drugs for up to 24 months were looked at, the mean net annual cost savings associated with the quality check protocol increased to €934 (U.S. $1,019) per patient or of only the visual quality check was €1,348 (U.S. $1,474) per patient.
IN PRACTICE:
“New strategies targeting waste are required to improve financial and ecologic sustainability of expensive therapies, such as oral anticancer drugs, that frequently remain unused by patients,” the authors write. “These findings provide a waste-minimizing strategy to contribute to sustainable and affordable access to drugs.”
SOURCE:
The study, by Elisabeth M. Smale, PharmD, of Radboud University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
Novel drugs are substantially more expensive in the United States, and the Dutch findings might underestimate potential cost savings generated through redispensing programs in the United States. Participants were prompted to return unused oral anticancer drugs through reminders at the pharmacy, but all such drugs may not have been returned.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by ZonMw, the Dutch national organization for health research and development. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infographic: Careers that tempt doctors to leave medicine
In a recently published Medscape report, 26% of American physicians said they were considering a career away from practicing medicine, for various reasons. Becoming a teacher was one of the nonclinical careers that most enthused them. What were the others?
For more details, check out the Medscape Physicians and Nonclinical Careers Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently published Medscape report, 26% of American physicians said they were considering a career away from practicing medicine, for various reasons. Becoming a teacher was one of the nonclinical careers that most enthused them. What were the others?
For more details, check out the Medscape Physicians and Nonclinical Careers Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently published Medscape report, 26% of American physicians said they were considering a career away from practicing medicine, for various reasons. Becoming a teacher was one of the nonclinical careers that most enthused them. What were the others?
For more details, check out the Medscape Physicians and Nonclinical Careers Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FTC considers proposals on mergers and noncompete clauses
Changes may be in store for how physicians do business based on pending proposals from the Federal Trade Commission to ban noncompete clauses and monitor potential merger monopolies.
In January 2023, the FTC announced a rule that would ban noncompete clauses, stating that such clauses reduce workers’ wages and stifle new businesses. Simply put, the rule would ban employers from entering into noncompete clauses with workers, including independent contractors.
Aspects of the rule include whether it should pertain to franchisees, whether senior executives should be exempted, and whether low-wage and high-wage workers should be treated differently.
According to the FTC, banning noncompete clauses would increase workers’ earnings by approximately $300 billion per year, save consumers as much as $148 billion in health care costs, and double the number of companies founded by former workers in the same field.
In June 2023, the FTC and the Department of Justice proposed changes to rules governing mergers, including changes to prenotification forms that would promote more efficient screening of potential mergers. According to a press release from the FTC, the proposed changes include provision of details about investments or corporate relationships, product and services, projected revenue streams, and previous acquisitions.
The proposal also includes a waiting period during which agencies would assess the risk that a merger would lessen competition or tend to create a monopoly.
What the FTC proposals mean for physicians
FTC Chair Lina M. Khan addressed attendees at the American College of Physicians at their annual meeting in October.
In March 2023, ACEP wrote to Ms. Khan in support of the banning of noncompete clauses. The ACEP also stated that the FTC should monitor the effect of a ban on the ability to recruit and maintain a stable physician workforce in rural and underserved areas “and should examine the potential impacts should nonprofit health systems be exempt from a ban.”
However, the American Medical Group Association, a nonprofit trade organization that supports multispecialty medical groups, opposes the ban. In a press release issued in March 2023, AMGA noted that, “As employers, AMGA members rely in part on noncompete agreements to build strong, sustainable care teams that work together to coordinate care for their patients. These care teams emphasize the importance of the doctor-patient relationship, which reasonable noncompete agreements help support.”
The American Medical Association supports the ban on noncompete clauses, detailed in an official AMA policy statement as, “support[ing] policies, regulations, and legislation that prohibits covenants not-to-compete for all physicians in clinical practice who hold employment contracts with for-profit or nonprofit hospital, hospital system, or staffing company employers.”
In regard to the merger guidelines, ACEP wrote a separate letter to Ms. Khan identifying some of the unique aspects of emergency medicine practice. The ACEP stressed the need for caution as the consolidation of medical practices continues, many under the umbrella of private equity investment companies.
“Unchecked mergers that substantially lessen competition in the labor market for emergency physicians, in which the employer is the buyer and the physician is the seller, can impact physicians directly by lowering wages or slowing wage growth, worsening benefits or working conditions, or contributing to other degradations in workplace quality,” according to ACEP.
The AMA also supports the FTC’s draft merger guidelines as protective of physicians and their working environments.
In September 2023, the AMA sent a letter to the FTC commending the agency on the proposed guidelines: “It is our strong contention that the agencies must have merger guidelines that protect physicians against health insurer mergers that may substantially lessen competition for the purchase of physician services and that degrade physician working conditions,” according to the AMA letter.
According the FTC, the proposed changes represent an expansion and reorganization of information along with the addition of new document requirements and represents the first comprehensive review of the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act since 1978.
After soliciting public comments, the FTC is reviewing the proposals, and no specific date for a final vote has been announced.
More specifics on the potential changes to premerger notification, reporting, and waiting period requirements are available on the FTC website.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes may be in store for how physicians do business based on pending proposals from the Federal Trade Commission to ban noncompete clauses and monitor potential merger monopolies.
In January 2023, the FTC announced a rule that would ban noncompete clauses, stating that such clauses reduce workers’ wages and stifle new businesses. Simply put, the rule would ban employers from entering into noncompete clauses with workers, including independent contractors.
Aspects of the rule include whether it should pertain to franchisees, whether senior executives should be exempted, and whether low-wage and high-wage workers should be treated differently.
According to the FTC, banning noncompete clauses would increase workers’ earnings by approximately $300 billion per year, save consumers as much as $148 billion in health care costs, and double the number of companies founded by former workers in the same field.
In June 2023, the FTC and the Department of Justice proposed changes to rules governing mergers, including changes to prenotification forms that would promote more efficient screening of potential mergers. According to a press release from the FTC, the proposed changes include provision of details about investments or corporate relationships, product and services, projected revenue streams, and previous acquisitions.
The proposal also includes a waiting period during which agencies would assess the risk that a merger would lessen competition or tend to create a monopoly.
What the FTC proposals mean for physicians
FTC Chair Lina M. Khan addressed attendees at the American College of Physicians at their annual meeting in October.
In March 2023, ACEP wrote to Ms. Khan in support of the banning of noncompete clauses. The ACEP also stated that the FTC should monitor the effect of a ban on the ability to recruit and maintain a stable physician workforce in rural and underserved areas “and should examine the potential impacts should nonprofit health systems be exempt from a ban.”
However, the American Medical Group Association, a nonprofit trade organization that supports multispecialty medical groups, opposes the ban. In a press release issued in March 2023, AMGA noted that, “As employers, AMGA members rely in part on noncompete agreements to build strong, sustainable care teams that work together to coordinate care for their patients. These care teams emphasize the importance of the doctor-patient relationship, which reasonable noncompete agreements help support.”
The American Medical Association supports the ban on noncompete clauses, detailed in an official AMA policy statement as, “support[ing] policies, regulations, and legislation that prohibits covenants not-to-compete for all physicians in clinical practice who hold employment contracts with for-profit or nonprofit hospital, hospital system, or staffing company employers.”
In regard to the merger guidelines, ACEP wrote a separate letter to Ms. Khan identifying some of the unique aspects of emergency medicine practice. The ACEP stressed the need for caution as the consolidation of medical practices continues, many under the umbrella of private equity investment companies.
“Unchecked mergers that substantially lessen competition in the labor market for emergency physicians, in which the employer is the buyer and the physician is the seller, can impact physicians directly by lowering wages or slowing wage growth, worsening benefits or working conditions, or contributing to other degradations in workplace quality,” according to ACEP.
The AMA also supports the FTC’s draft merger guidelines as protective of physicians and their working environments.
In September 2023, the AMA sent a letter to the FTC commending the agency on the proposed guidelines: “It is our strong contention that the agencies must have merger guidelines that protect physicians against health insurer mergers that may substantially lessen competition for the purchase of physician services and that degrade physician working conditions,” according to the AMA letter.
According the FTC, the proposed changes represent an expansion and reorganization of information along with the addition of new document requirements and represents the first comprehensive review of the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act since 1978.
After soliciting public comments, the FTC is reviewing the proposals, and no specific date for a final vote has been announced.
More specifics on the potential changes to premerger notification, reporting, and waiting period requirements are available on the FTC website.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Changes may be in store for how physicians do business based on pending proposals from the Federal Trade Commission to ban noncompete clauses and monitor potential merger monopolies.
In January 2023, the FTC announced a rule that would ban noncompete clauses, stating that such clauses reduce workers’ wages and stifle new businesses. Simply put, the rule would ban employers from entering into noncompete clauses with workers, including independent contractors.
Aspects of the rule include whether it should pertain to franchisees, whether senior executives should be exempted, and whether low-wage and high-wage workers should be treated differently.
According to the FTC, banning noncompete clauses would increase workers’ earnings by approximately $300 billion per year, save consumers as much as $148 billion in health care costs, and double the number of companies founded by former workers in the same field.
In June 2023, the FTC and the Department of Justice proposed changes to rules governing mergers, including changes to prenotification forms that would promote more efficient screening of potential mergers. According to a press release from the FTC, the proposed changes include provision of details about investments or corporate relationships, product and services, projected revenue streams, and previous acquisitions.
The proposal also includes a waiting period during which agencies would assess the risk that a merger would lessen competition or tend to create a monopoly.
What the FTC proposals mean for physicians
FTC Chair Lina M. Khan addressed attendees at the American College of Physicians at their annual meeting in October.
In March 2023, ACEP wrote to Ms. Khan in support of the banning of noncompete clauses. The ACEP also stated that the FTC should monitor the effect of a ban on the ability to recruit and maintain a stable physician workforce in rural and underserved areas “and should examine the potential impacts should nonprofit health systems be exempt from a ban.”
However, the American Medical Group Association, a nonprofit trade organization that supports multispecialty medical groups, opposes the ban. In a press release issued in March 2023, AMGA noted that, “As employers, AMGA members rely in part on noncompete agreements to build strong, sustainable care teams that work together to coordinate care for their patients. These care teams emphasize the importance of the doctor-patient relationship, which reasonable noncompete agreements help support.”
The American Medical Association supports the ban on noncompete clauses, detailed in an official AMA policy statement as, “support[ing] policies, regulations, and legislation that prohibits covenants not-to-compete for all physicians in clinical practice who hold employment contracts with for-profit or nonprofit hospital, hospital system, or staffing company employers.”
In regard to the merger guidelines, ACEP wrote a separate letter to Ms. Khan identifying some of the unique aspects of emergency medicine practice. The ACEP stressed the need for caution as the consolidation of medical practices continues, many under the umbrella of private equity investment companies.
“Unchecked mergers that substantially lessen competition in the labor market for emergency physicians, in which the employer is the buyer and the physician is the seller, can impact physicians directly by lowering wages or slowing wage growth, worsening benefits or working conditions, or contributing to other degradations in workplace quality,” according to ACEP.
The AMA also supports the FTC’s draft merger guidelines as protective of physicians and their working environments.
In September 2023, the AMA sent a letter to the FTC commending the agency on the proposed guidelines: “It is our strong contention that the agencies must have merger guidelines that protect physicians against health insurer mergers that may substantially lessen competition for the purchase of physician services and that degrade physician working conditions,” according to the AMA letter.
According the FTC, the proposed changes represent an expansion and reorganization of information along with the addition of new document requirements and represents the first comprehensive review of the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act since 1978.
After soliciting public comments, the FTC is reviewing the proposals, and no specific date for a final vote has been announced.
More specifics on the potential changes to premerger notification, reporting, and waiting period requirements are available on the FTC website.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
