User login
Two congressmen targeting ‘gender transition’ physicians
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Link between pediatric hepatitis and adenovirus 41 still unclear
While two new studies reiterate a possible relationship between adenovirus 41 and acute hepatitis of unknown cause in children, whether these infections are significant or merely bystanders remains unclear.
In both studies – one conducted in Alabama and the other conducted in the United Kingdom – researchers found that 90% of children with acute hepatitis of unknown cause tested positive for adenovirus 41. The virus subtype is not an uncommon infection, but it usually causes gastroenteritis in children.
“Across the world, adenovirus continues to be a common signal” in these pediatric hepatitis cases, said Helena Gutierrez, MD, the medical director of the Pediatric Liver Transplant Program at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an interview. She led one of the studies. More data are necessary to understand what role this virus may play in these cases, she said.
In November, the Alabama Department of Public Health and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention began investigating a cluster of severe pediatric hepatitis cases at the Children’s of Alabama hospital in Birmingham. These children also tested positive for adenovirus. In April, the United Kingdom announced they were investigating similar cases, and the CDC expanded their search nationally. As of July 8, 1,010 cases in 35 countries have been reported to the World Health Organization. There are 263 confirmed cases in the United Kingdom and 332 cases under investigation by the CDC in the United States, according to the most recent counts.
The two studies, both published in the New England Journal of Medicine, provide additional clinical data on a number of these mysterious hepatitis cases. Dr. Gutierrez’s study looked at nine children admitted for hepatitis of unknown origin between October 1 and February 28. Patients had a median age of 2 years 11 months and two required liver transplants, and there were no deaths.
Eight out of nine patients (89%) tested positive for adenovirus, and all five of the samples that were of sufficient quality for gene sequencing tested positive for adenovirus 41. None of the six liver biopsies performed found signs of adenovirus infection, but the liver tissue samples of three patients tested positive for adenovirus via PCR.
The second study involved 44 children referred to a liver transplantation center in the United Kingdom between January 1 and April 11, 2022. The median age for patients was 4 years. Six children required liver transplants, and there were no deaths. Of the 30 patients who underwent molecular adenovirus testing, 27 (90%) were positive for adenovirus 41. Liver samples of nine children (3 from biopsies and 6 from explanted livers) all tested negative for adenovirus antibodies.
In both studies, however, the median adenovirus viral load of patients needing a transplant was much higher than the viral loads in children who did not require liver transplants.
Although most of the clinical features and test results of these cases suggest that adenovirus may be involved, the negative results in histology are “intriguing,” Chayarani Kelgeri, MD, a consultant pediatric hepatologist at the Birmingham Women’s and Children’s Hospital, U.K., said in an email. She is the lead author of the U.K. study. “Whether this is because the liver injury we see is an aftermath of the viral infection, the mechanism of injury is immune mediated, and if other cofactors are involved is being explored,” she added. “Further investigations being undertaken by UK Health Security Agency will add to our understanding of this illness.”
Although there is a high adenovirus positivity rate amongst these cases, there is not enough evidence yet to say adenovirus 41 is a new cause of pediatric hepatitis in previously healthy children, said Saul Karpen, MD, PhD, the division chief of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. He wrote an editorial accompanying the two NEJM studies.
The CDC has not yet found an increase in pediatric hepatitis cases, according to a recent analysis, though the United Kingdom has found an uptick in cases this year, he told this news organization. Also, the cases highlighted in both articles showed no histological evidence of adenovirus in liver biopsies. “That’s completely opposite of what we generally see in adenoviral hepatitis that can be quite severe,” he said, adding that in general, there are detectable viral particles and antigens in affected livers.
“These two important reports indicate to those inside and outside the field of pediatric hepatology that registries and clinical studies of acute hepatitis in children are sorely needed,” Dr. Karpen writes in the editorial; “It is likely that with greater attention to collecting data on cases and biospecimens from children with acute hepatitis, we will be able to determine whether this one virus, human adenovirus 41, is of relevance to this important and serious condition in children.”
Dr. Gutierrez, Dr. Kelgeri, and Dr. Karpen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While two new studies reiterate a possible relationship between adenovirus 41 and acute hepatitis of unknown cause in children, whether these infections are significant or merely bystanders remains unclear.
In both studies – one conducted in Alabama and the other conducted in the United Kingdom – researchers found that 90% of children with acute hepatitis of unknown cause tested positive for adenovirus 41. The virus subtype is not an uncommon infection, but it usually causes gastroenteritis in children.
“Across the world, adenovirus continues to be a common signal” in these pediatric hepatitis cases, said Helena Gutierrez, MD, the medical director of the Pediatric Liver Transplant Program at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an interview. She led one of the studies. More data are necessary to understand what role this virus may play in these cases, she said.
In November, the Alabama Department of Public Health and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention began investigating a cluster of severe pediatric hepatitis cases at the Children’s of Alabama hospital in Birmingham. These children also tested positive for adenovirus. In April, the United Kingdom announced they were investigating similar cases, and the CDC expanded their search nationally. As of July 8, 1,010 cases in 35 countries have been reported to the World Health Organization. There are 263 confirmed cases in the United Kingdom and 332 cases under investigation by the CDC in the United States, according to the most recent counts.
The two studies, both published in the New England Journal of Medicine, provide additional clinical data on a number of these mysterious hepatitis cases. Dr. Gutierrez’s study looked at nine children admitted for hepatitis of unknown origin between October 1 and February 28. Patients had a median age of 2 years 11 months and two required liver transplants, and there were no deaths.
Eight out of nine patients (89%) tested positive for adenovirus, and all five of the samples that were of sufficient quality for gene sequencing tested positive for adenovirus 41. None of the six liver biopsies performed found signs of adenovirus infection, but the liver tissue samples of three patients tested positive for adenovirus via PCR.
The second study involved 44 children referred to a liver transplantation center in the United Kingdom between January 1 and April 11, 2022. The median age for patients was 4 years. Six children required liver transplants, and there were no deaths. Of the 30 patients who underwent molecular adenovirus testing, 27 (90%) were positive for adenovirus 41. Liver samples of nine children (3 from biopsies and 6 from explanted livers) all tested negative for adenovirus antibodies.
In both studies, however, the median adenovirus viral load of patients needing a transplant was much higher than the viral loads in children who did not require liver transplants.
Although most of the clinical features and test results of these cases suggest that adenovirus may be involved, the negative results in histology are “intriguing,” Chayarani Kelgeri, MD, a consultant pediatric hepatologist at the Birmingham Women’s and Children’s Hospital, U.K., said in an email. She is the lead author of the U.K. study. “Whether this is because the liver injury we see is an aftermath of the viral infection, the mechanism of injury is immune mediated, and if other cofactors are involved is being explored,” she added. “Further investigations being undertaken by UK Health Security Agency will add to our understanding of this illness.”
Although there is a high adenovirus positivity rate amongst these cases, there is not enough evidence yet to say adenovirus 41 is a new cause of pediatric hepatitis in previously healthy children, said Saul Karpen, MD, PhD, the division chief of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. He wrote an editorial accompanying the two NEJM studies.
The CDC has not yet found an increase in pediatric hepatitis cases, according to a recent analysis, though the United Kingdom has found an uptick in cases this year, he told this news organization. Also, the cases highlighted in both articles showed no histological evidence of adenovirus in liver biopsies. “That’s completely opposite of what we generally see in adenoviral hepatitis that can be quite severe,” he said, adding that in general, there are detectable viral particles and antigens in affected livers.
“These two important reports indicate to those inside and outside the field of pediatric hepatology that registries and clinical studies of acute hepatitis in children are sorely needed,” Dr. Karpen writes in the editorial; “It is likely that with greater attention to collecting data on cases and biospecimens from children with acute hepatitis, we will be able to determine whether this one virus, human adenovirus 41, is of relevance to this important and serious condition in children.”
Dr. Gutierrez, Dr. Kelgeri, and Dr. Karpen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While two new studies reiterate a possible relationship between adenovirus 41 and acute hepatitis of unknown cause in children, whether these infections are significant or merely bystanders remains unclear.
In both studies – one conducted in Alabama and the other conducted in the United Kingdom – researchers found that 90% of children with acute hepatitis of unknown cause tested positive for adenovirus 41. The virus subtype is not an uncommon infection, but it usually causes gastroenteritis in children.
“Across the world, adenovirus continues to be a common signal” in these pediatric hepatitis cases, said Helena Gutierrez, MD, the medical director of the Pediatric Liver Transplant Program at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an interview. She led one of the studies. More data are necessary to understand what role this virus may play in these cases, she said.
In November, the Alabama Department of Public Health and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention began investigating a cluster of severe pediatric hepatitis cases at the Children’s of Alabama hospital in Birmingham. These children also tested positive for adenovirus. In April, the United Kingdom announced they were investigating similar cases, and the CDC expanded their search nationally. As of July 8, 1,010 cases in 35 countries have been reported to the World Health Organization. There are 263 confirmed cases in the United Kingdom and 332 cases under investigation by the CDC in the United States, according to the most recent counts.
The two studies, both published in the New England Journal of Medicine, provide additional clinical data on a number of these mysterious hepatitis cases. Dr. Gutierrez’s study looked at nine children admitted for hepatitis of unknown origin between October 1 and February 28. Patients had a median age of 2 years 11 months and two required liver transplants, and there were no deaths.
Eight out of nine patients (89%) tested positive for adenovirus, and all five of the samples that were of sufficient quality for gene sequencing tested positive for adenovirus 41. None of the six liver biopsies performed found signs of adenovirus infection, but the liver tissue samples of three patients tested positive for adenovirus via PCR.
The second study involved 44 children referred to a liver transplantation center in the United Kingdom between January 1 and April 11, 2022. The median age for patients was 4 years. Six children required liver transplants, and there were no deaths. Of the 30 patients who underwent molecular adenovirus testing, 27 (90%) were positive for adenovirus 41. Liver samples of nine children (3 from biopsies and 6 from explanted livers) all tested negative for adenovirus antibodies.
In both studies, however, the median adenovirus viral load of patients needing a transplant was much higher than the viral loads in children who did not require liver transplants.
Although most of the clinical features and test results of these cases suggest that adenovirus may be involved, the negative results in histology are “intriguing,” Chayarani Kelgeri, MD, a consultant pediatric hepatologist at the Birmingham Women’s and Children’s Hospital, U.K., said in an email. She is the lead author of the U.K. study. “Whether this is because the liver injury we see is an aftermath of the viral infection, the mechanism of injury is immune mediated, and if other cofactors are involved is being explored,” she added. “Further investigations being undertaken by UK Health Security Agency will add to our understanding of this illness.”
Although there is a high adenovirus positivity rate amongst these cases, there is not enough evidence yet to say adenovirus 41 is a new cause of pediatric hepatitis in previously healthy children, said Saul Karpen, MD, PhD, the division chief of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. He wrote an editorial accompanying the two NEJM studies.
The CDC has not yet found an increase in pediatric hepatitis cases, according to a recent analysis, though the United Kingdom has found an uptick in cases this year, he told this news organization. Also, the cases highlighted in both articles showed no histological evidence of adenovirus in liver biopsies. “That’s completely opposite of what we generally see in adenoviral hepatitis that can be quite severe,” he said, adding that in general, there are detectable viral particles and antigens in affected livers.
“These two important reports indicate to those inside and outside the field of pediatric hepatology that registries and clinical studies of acute hepatitis in children are sorely needed,” Dr. Karpen writes in the editorial; “It is likely that with greater attention to collecting data on cases and biospecimens from children with acute hepatitis, we will be able to determine whether this one virus, human adenovirus 41, is of relevance to this important and serious condition in children.”
Dr. Gutierrez, Dr. Kelgeri, and Dr. Karpen report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recommendations on breastfeeding: A case of too much information
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Study eyes characteristics of pediatric patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
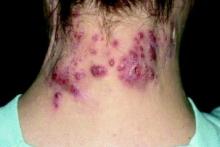
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
AT SPD 2022
In the quest for a cure for type 1 diabetes, two companies merge
The $320 million cash purchase “will accelerate our goal of transforming, if not curing, type 1 diabetes by expanding our capabilities and bringing additional tools, technologies, and assets to our current stem cell-based programs,” said Vertex Chief Executive Officer and President Reshma Kewalramani, MD, in a company statement.
Last month, Vertex reported on a phase 1/2 multicenter clinical trial for two patients with type 1 diabetes who experienced improved blood glucose control with half doses of the company’s investigational allogeneic stem cell-derived islets (VX-880).
The first person to receive the product remained completely insulin-independent at 9 months post-transplant. A third patient has received the full targeted dose, but the data for this participant have yet to be reported.
For Viacyte’s part, last week the company announced that a clinical hold placed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the trial has been lifted, allowing it to move forward with a planned total enrollment of 17 patients.
“The FDA requested additional information on the program, which we provided expeditiously. We are pleased that the hold has been lifted and look forward to continuing the Phase 1/2 trial in the U.S.,” a Vertex spokesperson told this news organization.
And a company official for ViaCyte presented results for three patients who received pancreatic precursor (PEC-01) cells derived from the company’s proprietary pluripotent stem cell line at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society held in June. The cells are housed in an open delivery device implanted into a patient’s forearm. All three participants experienced improved blood glucose levels.
That presentation followed ViaCyte’s announcement in February that the first patient with type 1 diabetes had been dosed in a Phase 1 clinical trial of its investigational allogeneic, gene-edited, stem cell-derived product, VCTX210, developed in collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics’ gene-editing technology. The aim is to generate islet cells that will produce insulin while avoiding recognition by the immune system, thus rendering immunosuppressive drugs unnecessary.
According to Vertex’s announcement, “The acquisition of ViaCyte provides Vertex with complementary assets, capabilities, and technologies, including additional human stem cell lines, intellectual property around stem cell differentiation, and Good Manufacturing Practice ... facilities for cell-based therapies that could accelerate Vertex’s ongoing type 1 diabetes programs. The acquisition also provides access to novel hypoimmune stem cell assets via the ViaCyte collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics.”
In response to the announcement, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization JDRF, which has funded the work of both companies, said in a statement that the acquisition “represents a significant stride in cures research for the type 1 diabetes community.”
“The coming together of two leaders in the cell-derived therapies field will undoubtedly accelerate the development of VX-880 by combining their resources, technologies, intellectual property, and more,” it added.
A third company developing stem cell–derived islet cell therapies, Sernova, said in a statement provided to this news organization: “We are very confident that bringing important game-changing technologies together, as we are seeing across the industry, will result in several viable technologies for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes ... We are thrilled that there are several technologies under development using different approaches that have the potential to provide a ‘functional cure’ for this disease.”
Vertex anticipates the acquisition will close later in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The $320 million cash purchase “will accelerate our goal of transforming, if not curing, type 1 diabetes by expanding our capabilities and bringing additional tools, technologies, and assets to our current stem cell-based programs,” said Vertex Chief Executive Officer and President Reshma Kewalramani, MD, in a company statement.
Last month, Vertex reported on a phase 1/2 multicenter clinical trial for two patients with type 1 diabetes who experienced improved blood glucose control with half doses of the company’s investigational allogeneic stem cell-derived islets (VX-880).
The first person to receive the product remained completely insulin-independent at 9 months post-transplant. A third patient has received the full targeted dose, but the data for this participant have yet to be reported.
For Viacyte’s part, last week the company announced that a clinical hold placed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the trial has been lifted, allowing it to move forward with a planned total enrollment of 17 patients.
“The FDA requested additional information on the program, which we provided expeditiously. We are pleased that the hold has been lifted and look forward to continuing the Phase 1/2 trial in the U.S.,” a Vertex spokesperson told this news organization.
And a company official for ViaCyte presented results for three patients who received pancreatic precursor (PEC-01) cells derived from the company’s proprietary pluripotent stem cell line at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society held in June. The cells are housed in an open delivery device implanted into a patient’s forearm. All three participants experienced improved blood glucose levels.
That presentation followed ViaCyte’s announcement in February that the first patient with type 1 diabetes had been dosed in a Phase 1 clinical trial of its investigational allogeneic, gene-edited, stem cell-derived product, VCTX210, developed in collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics’ gene-editing technology. The aim is to generate islet cells that will produce insulin while avoiding recognition by the immune system, thus rendering immunosuppressive drugs unnecessary.
According to Vertex’s announcement, “The acquisition of ViaCyte provides Vertex with complementary assets, capabilities, and technologies, including additional human stem cell lines, intellectual property around stem cell differentiation, and Good Manufacturing Practice ... facilities for cell-based therapies that could accelerate Vertex’s ongoing type 1 diabetes programs. The acquisition also provides access to novel hypoimmune stem cell assets via the ViaCyte collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics.”
In response to the announcement, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization JDRF, which has funded the work of both companies, said in a statement that the acquisition “represents a significant stride in cures research for the type 1 diabetes community.”
“The coming together of two leaders in the cell-derived therapies field will undoubtedly accelerate the development of VX-880 by combining their resources, technologies, intellectual property, and more,” it added.
A third company developing stem cell–derived islet cell therapies, Sernova, said in a statement provided to this news organization: “We are very confident that bringing important game-changing technologies together, as we are seeing across the industry, will result in several viable technologies for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes ... We are thrilled that there are several technologies under development using different approaches that have the potential to provide a ‘functional cure’ for this disease.”
Vertex anticipates the acquisition will close later in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The $320 million cash purchase “will accelerate our goal of transforming, if not curing, type 1 diabetes by expanding our capabilities and bringing additional tools, technologies, and assets to our current stem cell-based programs,” said Vertex Chief Executive Officer and President Reshma Kewalramani, MD, in a company statement.
Last month, Vertex reported on a phase 1/2 multicenter clinical trial for two patients with type 1 diabetes who experienced improved blood glucose control with half doses of the company’s investigational allogeneic stem cell-derived islets (VX-880).
The first person to receive the product remained completely insulin-independent at 9 months post-transplant. A third patient has received the full targeted dose, but the data for this participant have yet to be reported.
For Viacyte’s part, last week the company announced that a clinical hold placed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the trial has been lifted, allowing it to move forward with a planned total enrollment of 17 patients.
“The FDA requested additional information on the program, which we provided expeditiously. We are pleased that the hold has been lifted and look forward to continuing the Phase 1/2 trial in the U.S.,” a Vertex spokesperson told this news organization.
And a company official for ViaCyte presented results for three patients who received pancreatic precursor (PEC-01) cells derived from the company’s proprietary pluripotent stem cell line at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society held in June. The cells are housed in an open delivery device implanted into a patient’s forearm. All three participants experienced improved blood glucose levels.
That presentation followed ViaCyte’s announcement in February that the first patient with type 1 diabetes had been dosed in a Phase 1 clinical trial of its investigational allogeneic, gene-edited, stem cell-derived product, VCTX210, developed in collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics’ gene-editing technology. The aim is to generate islet cells that will produce insulin while avoiding recognition by the immune system, thus rendering immunosuppressive drugs unnecessary.
According to Vertex’s announcement, “The acquisition of ViaCyte provides Vertex with complementary assets, capabilities, and technologies, including additional human stem cell lines, intellectual property around stem cell differentiation, and Good Manufacturing Practice ... facilities for cell-based therapies that could accelerate Vertex’s ongoing type 1 diabetes programs. The acquisition also provides access to novel hypoimmune stem cell assets via the ViaCyte collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics.”
In response to the announcement, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization JDRF, which has funded the work of both companies, said in a statement that the acquisition “represents a significant stride in cures research for the type 1 diabetes community.”
“The coming together of two leaders in the cell-derived therapies field will undoubtedly accelerate the development of VX-880 by combining their resources, technologies, intellectual property, and more,” it added.
A third company developing stem cell–derived islet cell therapies, Sernova, said in a statement provided to this news organization: “We are very confident that bringing important game-changing technologies together, as we are seeing across the industry, will result in several viable technologies for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes ... We are thrilled that there are several technologies under development using different approaches that have the potential to provide a ‘functional cure’ for this disease.”
Vertex anticipates the acquisition will close later in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What influences a trainee’s decision to choose pediatric dermatology as a career?
INDIANAPOLIS – Three during and after fellowship.
Those are key findings from a survey of current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows, which sought to investigate what factors influence their career decisions.
According to the study’s principal investigator, Lucia Z. Diaz, MD, pediatric dermatology suffers from workforce shortages and geographic maldistribution as a subspecialty in the United States. She also noted that, from 2016 to 2021, 100% of pediatric dermatology applicants matched, yet about 15 of every 31 positions remained unfilled during each of those years. This suggests that there may be a lack of trainee mentorship secondary to a lack of available pediatric dermatologists.
“Somewhere along the way, we lose trainees to general dermatology, or they may go through a pediatric dermatology fellowship but not actually see children upon completion of their training,” Dr. Diaz, chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “We wanted to find out factors influencing this.”
For the study, Dr. Diaz, Courtney N. Haller, MD, a first-year dermatology resident at the University of Texas at Austin, and their colleagues emailed a 37-item survey to 59 current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows who trained in the United States in the past 4 years (classes of 2019-2022). Current fellows were asked to share their future plans, and past fellows were asked to share details about their current practice situation including practice type (such as academics, private practice, and a mix of adult and pediatrics), and the researchers used descriptive statistics and chi-square analyses to evaluate qualitative data.
In all, 41 survey participants gave complete responses, and 3 gave partial responses. Of these, 8 were current fellows, 36 were past fellows, and 38 were female. The researchers found that 67% of survey respondents first became interested in pediatric dermatology in medical school, while the decision to pursue a fellowship occurred then (33%) or during their third year of dermatology residency (33%). Early exposure to pediatric dermatology, from medical school through dermatology PGY-2, was significantly associated with an early decision to pursue a pediatric dermatology career (P = .004).
In addition, respondents at institutions with two or more pediatric dermatology faculty were significantly more likely to cite home institution mentorship as an influencing factor in their career decision (P = .035).
“I thought that the interest in pediatric dermatology would peak early on during dermatology residency, but it primarily happens during medical school,” said Dr. Diaz, who is also associate director of the dermatology residency program at the medical school. “Mentorship and early exposure to pediatric dermatology during medical school are really important.”
The top three factors that discouraged respondents from pursuing a pediatric dermatology fellowship included a lack of salary benefit with additional training (83%), additional time required to complete training (73%), and geographic relocation (20%). After fellowship, 51% of respondents said they plan to or currently work in academic settings, while 88% said they plan to work full time or currently were working full time.
Interestingly, fellows with additional pediatric training such as an internship or residency were not more likely to see a greater percentage of pediatric patients in practice than those without this training (P = .14). The top 3 reasons for not seeing pediatric patients 100% of the clinical time were interest in seeing adult patients (67%), financial factors (56%), and interest in performing more procedures (56%).
In other findings, the top three factors in deciding practice location were proximity to extended family (63%), practice type (59%), and income (51%).
Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the lack of salary benefit from additional training is a sticking point for many fellows. “The market trends of supply and demand do not work in pediatric dermatology,” said Dr. Hebert, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston. “You would think that, because there are fewer of us, we should be paid more, but it does not work that way.”
She characterized the overall study findings as “a real testament to what the challenges are” in recruiting trainees to pediatric dermatology. “The influence of mentors resonates in this assessment, but influences that are somewhat beyond our control also play a role, such as lack of salary benefit from additional training, interest in seeing adult patients, and financial factors.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Hebert reported having relevant financial disclosures.
INDIANAPOLIS – Three during and after fellowship.
Those are key findings from a survey of current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows, which sought to investigate what factors influence their career decisions.
According to the study’s principal investigator, Lucia Z. Diaz, MD, pediatric dermatology suffers from workforce shortages and geographic maldistribution as a subspecialty in the United States. She also noted that, from 2016 to 2021, 100% of pediatric dermatology applicants matched, yet about 15 of every 31 positions remained unfilled during each of those years. This suggests that there may be a lack of trainee mentorship secondary to a lack of available pediatric dermatologists.
“Somewhere along the way, we lose trainees to general dermatology, or they may go through a pediatric dermatology fellowship but not actually see children upon completion of their training,” Dr. Diaz, chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “We wanted to find out factors influencing this.”
For the study, Dr. Diaz, Courtney N. Haller, MD, a first-year dermatology resident at the University of Texas at Austin, and their colleagues emailed a 37-item survey to 59 current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows who trained in the United States in the past 4 years (classes of 2019-2022). Current fellows were asked to share their future plans, and past fellows were asked to share details about their current practice situation including practice type (such as academics, private practice, and a mix of adult and pediatrics), and the researchers used descriptive statistics and chi-square analyses to evaluate qualitative data.
In all, 41 survey participants gave complete responses, and 3 gave partial responses. Of these, 8 were current fellows, 36 were past fellows, and 38 were female. The researchers found that 67% of survey respondents first became interested in pediatric dermatology in medical school, while the decision to pursue a fellowship occurred then (33%) or during their third year of dermatology residency (33%). Early exposure to pediatric dermatology, from medical school through dermatology PGY-2, was significantly associated with an early decision to pursue a pediatric dermatology career (P = .004).
In addition, respondents at institutions with two or more pediatric dermatology faculty were significantly more likely to cite home institution mentorship as an influencing factor in their career decision (P = .035).
“I thought that the interest in pediatric dermatology would peak early on during dermatology residency, but it primarily happens during medical school,” said Dr. Diaz, who is also associate director of the dermatology residency program at the medical school. “Mentorship and early exposure to pediatric dermatology during medical school are really important.”
The top three factors that discouraged respondents from pursuing a pediatric dermatology fellowship included a lack of salary benefit with additional training (83%), additional time required to complete training (73%), and geographic relocation (20%). After fellowship, 51% of respondents said they plan to or currently work in academic settings, while 88% said they plan to work full time or currently were working full time.
Interestingly, fellows with additional pediatric training such as an internship or residency were not more likely to see a greater percentage of pediatric patients in practice than those without this training (P = .14). The top 3 reasons for not seeing pediatric patients 100% of the clinical time were interest in seeing adult patients (67%), financial factors (56%), and interest in performing more procedures (56%).
In other findings, the top three factors in deciding practice location were proximity to extended family (63%), practice type (59%), and income (51%).
Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the lack of salary benefit from additional training is a sticking point for many fellows. “The market trends of supply and demand do not work in pediatric dermatology,” said Dr. Hebert, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston. “You would think that, because there are fewer of us, we should be paid more, but it does not work that way.”
She characterized the overall study findings as “a real testament to what the challenges are” in recruiting trainees to pediatric dermatology. “The influence of mentors resonates in this assessment, but influences that are somewhat beyond our control also play a role, such as lack of salary benefit from additional training, interest in seeing adult patients, and financial factors.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Hebert reported having relevant financial disclosures.
INDIANAPOLIS – Three during and after fellowship.
Those are key findings from a survey of current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows, which sought to investigate what factors influence their career decisions.
According to the study’s principal investigator, Lucia Z. Diaz, MD, pediatric dermatology suffers from workforce shortages and geographic maldistribution as a subspecialty in the United States. She also noted that, from 2016 to 2021, 100% of pediatric dermatology applicants matched, yet about 15 of every 31 positions remained unfilled during each of those years. This suggests that there may be a lack of trainee mentorship secondary to a lack of available pediatric dermatologists.
“Somewhere along the way, we lose trainees to general dermatology, or they may go through a pediatric dermatology fellowship but not actually see children upon completion of their training,” Dr. Diaz, chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “We wanted to find out factors influencing this.”
For the study, Dr. Diaz, Courtney N. Haller, MD, a first-year dermatology resident at the University of Texas at Austin, and their colleagues emailed a 37-item survey to 59 current and prior pediatric dermatology fellows who trained in the United States in the past 4 years (classes of 2019-2022). Current fellows were asked to share their future plans, and past fellows were asked to share details about their current practice situation including practice type (such as academics, private practice, and a mix of adult and pediatrics), and the researchers used descriptive statistics and chi-square analyses to evaluate qualitative data.
In all, 41 survey participants gave complete responses, and 3 gave partial responses. Of these, 8 were current fellows, 36 were past fellows, and 38 were female. The researchers found that 67% of survey respondents first became interested in pediatric dermatology in medical school, while the decision to pursue a fellowship occurred then (33%) or during their third year of dermatology residency (33%). Early exposure to pediatric dermatology, from medical school through dermatology PGY-2, was significantly associated with an early decision to pursue a pediatric dermatology career (P = .004).
In addition, respondents at institutions with two or more pediatric dermatology faculty were significantly more likely to cite home institution mentorship as an influencing factor in their career decision (P = .035).
“I thought that the interest in pediatric dermatology would peak early on during dermatology residency, but it primarily happens during medical school,” said Dr. Diaz, who is also associate director of the dermatology residency program at the medical school. “Mentorship and early exposure to pediatric dermatology during medical school are really important.”
The top three factors that discouraged respondents from pursuing a pediatric dermatology fellowship included a lack of salary benefit with additional training (83%), additional time required to complete training (73%), and geographic relocation (20%). After fellowship, 51% of respondents said they plan to or currently work in academic settings, while 88% said they plan to work full time or currently were working full time.
Interestingly, fellows with additional pediatric training such as an internship or residency were not more likely to see a greater percentage of pediatric patients in practice than those without this training (P = .14). The top 3 reasons for not seeing pediatric patients 100% of the clinical time were interest in seeing adult patients (67%), financial factors (56%), and interest in performing more procedures (56%).
In other findings, the top three factors in deciding practice location were proximity to extended family (63%), practice type (59%), and income (51%).
Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the lack of salary benefit from additional training is a sticking point for many fellows. “The market trends of supply and demand do not work in pediatric dermatology,” said Dr. Hebert, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, and chief of pediatric dermatology at the University of Texas, Houston. “You would think that, because there are fewer of us, we should be paid more, but it does not work that way.”
She characterized the overall study findings as “a real testament to what the challenges are” in recruiting trainees to pediatric dermatology. “The influence of mentors resonates in this assessment, but influences that are somewhat beyond our control also play a role, such as lack of salary benefit from additional training, interest in seeing adult patients, and financial factors.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Hebert reported having relevant financial disclosures.
AT SPD 2022
Uveitis in juvenile arthritis patients persists into midlife
Active uveitis remained in 43.4% of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients up to 40 years after a diagnosis, based on data from 30 individuals.
Uveitis occurs in approximately 10%-20% of patients with JIA, but data on the long-term activity and prevalence are limited, although previous studies suggest that uveitis can persist into adulthood, wrote Dr. Angelika Skarin of Skåne University in Lund, Sweden, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatric Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed ophthalmic records from 30 JIA patients at a mean of 40.7 years after uveitis onset. They compared these records to data collected from the same patient population at a mean of 7.2 and 24.0 years after onset. In the previous follow-up studies, 49% of the patients had active uveitis at 24 years, and the prevalence of cataracts and glaucoma increased between the 7-year and 24-year assessments.
In the current study, 43.4% of the population had active uveitis at the 40-year follow-up, which corresponded to 23.6% of the original study cohort. The mean age of the participants overall was 46.9 years, the mean duration of joint disease was 42.99 years, and the mean time from onset of uveitis was 40.7 years.
In addition, 66.6% of the patients in the current study had cataracts or had undergone cataract surgery in one or both eyes, and 40.0% had glaucoma.
By the time of the current study, of the original cohort of 55 individuals, 11 were deceased; rheumatic disease was declared the main cause in four patients and a contributing factor in three others.
Potential drivers of the earliest cases of glaucoma and ocular hypertension (G/OH) include increased intraocular pressure as a result of topical corticosteroid treatment, the researchers noted in their discussion. However, G/OH occurring later than the 7-year follow-up was “more likely to be the type observed in many patients with long-standing chronic uveitis, where a gradual increase in intraocular pressure is assumed to be caused by impaired aqueous outflow,” they said.
Only 4 of the 30 patients did not have regular ophthalmology visits, which suggests a study population with ocular symptoms or concerns about their eyesight, the researchers wrote. “The fact that 13% of our original cohort were reported to have severe visual impairment or worse in both eyes at any of the three follow-ups is noteworthy,” compared to reports of visual impairment of less than 0.5% in a German study in the general population for similar ages.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, small study population, and lack of data on 25 of the original 55-member study cohort, which may reduce the reliability of the current study, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the need for JIA patients to continue regular ophthalmic checkups throughout life, they concluded.
The study was supported by Stiftelsen för Synskadade i f.d. Malmöhus län, Sweden, Skånes Universitetssjukhus Stiftelser och Donationer, Ögonfonden, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Active uveitis remained in 43.4% of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients up to 40 years after a diagnosis, based on data from 30 individuals.
Uveitis occurs in approximately 10%-20% of patients with JIA, but data on the long-term activity and prevalence are limited, although previous studies suggest that uveitis can persist into adulthood, wrote Dr. Angelika Skarin of Skåne University in Lund, Sweden, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatric Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed ophthalmic records from 30 JIA patients at a mean of 40.7 years after uveitis onset. They compared these records to data collected from the same patient population at a mean of 7.2 and 24.0 years after onset. In the previous follow-up studies, 49% of the patients had active uveitis at 24 years, and the prevalence of cataracts and glaucoma increased between the 7-year and 24-year assessments.
In the current study, 43.4% of the population had active uveitis at the 40-year follow-up, which corresponded to 23.6% of the original study cohort. The mean age of the participants overall was 46.9 years, the mean duration of joint disease was 42.99 years, and the mean time from onset of uveitis was 40.7 years.
In addition, 66.6% of the patients in the current study had cataracts or had undergone cataract surgery in one or both eyes, and 40.0% had glaucoma.
By the time of the current study, of the original cohort of 55 individuals, 11 were deceased; rheumatic disease was declared the main cause in four patients and a contributing factor in three others.
Potential drivers of the earliest cases of glaucoma and ocular hypertension (G/OH) include increased intraocular pressure as a result of topical corticosteroid treatment, the researchers noted in their discussion. However, G/OH occurring later than the 7-year follow-up was “more likely to be the type observed in many patients with long-standing chronic uveitis, where a gradual increase in intraocular pressure is assumed to be caused by impaired aqueous outflow,” they said.
Only 4 of the 30 patients did not have regular ophthalmology visits, which suggests a study population with ocular symptoms or concerns about their eyesight, the researchers wrote. “The fact that 13% of our original cohort were reported to have severe visual impairment or worse in both eyes at any of the three follow-ups is noteworthy,” compared to reports of visual impairment of less than 0.5% in a German study in the general population for similar ages.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, small study population, and lack of data on 25 of the original 55-member study cohort, which may reduce the reliability of the current study, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the need for JIA patients to continue regular ophthalmic checkups throughout life, they concluded.
The study was supported by Stiftelsen för Synskadade i f.d. Malmöhus län, Sweden, Skånes Universitetssjukhus Stiftelser och Donationer, Ögonfonden, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Active uveitis remained in 43.4% of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients up to 40 years after a diagnosis, based on data from 30 individuals.
Uveitis occurs in approximately 10%-20% of patients with JIA, but data on the long-term activity and prevalence are limited, although previous studies suggest that uveitis can persist into adulthood, wrote Dr. Angelika Skarin of Skåne University in Lund, Sweden, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatric Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed ophthalmic records from 30 JIA patients at a mean of 40.7 years after uveitis onset. They compared these records to data collected from the same patient population at a mean of 7.2 and 24.0 years after onset. In the previous follow-up studies, 49% of the patients had active uveitis at 24 years, and the prevalence of cataracts and glaucoma increased between the 7-year and 24-year assessments.
In the current study, 43.4% of the population had active uveitis at the 40-year follow-up, which corresponded to 23.6% of the original study cohort. The mean age of the participants overall was 46.9 years, the mean duration of joint disease was 42.99 years, and the mean time from onset of uveitis was 40.7 years.
In addition, 66.6% of the patients in the current study had cataracts or had undergone cataract surgery in one or both eyes, and 40.0% had glaucoma.
By the time of the current study, of the original cohort of 55 individuals, 11 were deceased; rheumatic disease was declared the main cause in four patients and a contributing factor in three others.
Potential drivers of the earliest cases of glaucoma and ocular hypertension (G/OH) include increased intraocular pressure as a result of topical corticosteroid treatment, the researchers noted in their discussion. However, G/OH occurring later than the 7-year follow-up was “more likely to be the type observed in many patients with long-standing chronic uveitis, where a gradual increase in intraocular pressure is assumed to be caused by impaired aqueous outflow,” they said.
Only 4 of the 30 patients did not have regular ophthalmology visits, which suggests a study population with ocular symptoms or concerns about their eyesight, the researchers wrote. “The fact that 13% of our original cohort were reported to have severe visual impairment or worse in both eyes at any of the three follow-ups is noteworthy,” compared to reports of visual impairment of less than 0.5% in a German study in the general population for similar ages.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, small study population, and lack of data on 25 of the original 55-member study cohort, which may reduce the reliability of the current study, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the need for JIA patients to continue regular ophthalmic checkups throughout life, they concluded.
The study was supported by Stiftelsen för Synskadade i f.d. Malmöhus län, Sweden, Skånes Universitetssjukhus Stiftelser och Donationer, Ögonfonden, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGY
Addressing posttraumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
Luke is a 12-year-old who presents for a well-child visit accompanied by his foster mother. He appears more solemn and taciturn than at previous visits. He is not interested in talking about any topics, including things he enjoys. His foster mother states that he has been more irritable, oppositional, and behaviorally dysregulated over the past 2 months. She also notes that his sleep has been poor. He reports this is because of nightmares and trouble falling asleep. Luke states that he will at times remember seeing his mother being struck by his father and – even when he does not want to – will have thoughts about hiding from his dad after being hit. You learn from the foster mother that he has been residing with her for the past 2 months and that he is now in state custody following significant parental home substance use, witnessing domestic violence, and being physically abused by his father.
The above narrative may sound all too familiar to those in pediatric primary care. You may wonder if there is a potential posttraumatic response to the witnessed trauma, but does the patient meet criteria for a trauma-related disorder? If so, what are the best next steps?
Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in the general pediatric population
According to the 2020 National Survey of Children’s Health, approximately 40% of children age 17 and under report experiencing at least one adverse childhood experience. Within the 12-17 age range, it rises to over 50%.1 Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are potentially traumatic events and include items such as experiencing violence/abuse/neglect, witnessing violence in the home or community, having a family member attempt or die by suicide, and other adverse household and environmental situations. The accumulation of these ACEs can lead to long-term adverse emotional, physical, and behavioral outcomes.2
However, adverse childhood experiences do not always translate into PTSD. According to one national survey of 13- to 18-year-olds, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD is notably lower than exposure rates to ACEs and is estimated at 5% of adolescents, with higher rates among females (8%) versus males (2.3%).3
There are various risk factors for the development of PTSD that may play a role including genetic vulnerability, length of the trauma (for example, a one-time event versus repeated trauma for years), characteristics specific to the trauma, and the aftermath of the trauma. Again, it is important to note that not all youth exposed to a traumatic event will develop PTSD. Those who do make up a small percentage of at-risk children.4
Diagnosing PTSD in a child or adolescent
For a pediatric patient to be diagnosed with PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria, they must experience a potentially traumatic event and meet criteria from four categories of symptoms. Trauma is defined as direct or indirect exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. The four symptom categories are re-experiencing, avoidance, hyperarousal, and negative alteration in cognition and mood. The number of symptoms needed from each category varies based on the child’s age, with differing cutoffs based on whether the child is younger or older than 6 years old. Moreover, symptoms must be present for at least 1 month.5
Trauma can be assessed in the office by using a focused interview that includes the full DSM diagnostic criteria. There are additional trauma rating screeners and assessment tools that can be used including the Child PTSD Symptom Scale, Child Trauma Screening Questionnaire, UCLA Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index, and the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children, to name a few. Many of these allow for multiple informants, including the child/adolescent, thereby allowing for varying perspectives regarding trauma reactions.
Treatment options
Familiarity with evidence-based treatment for trauma may be useful to ensure that referral is targeted for the patient/family. There are no Food and Drug Administrations–approved medications for children with PTSD, though medications can be used to target specific PTSD symptoms (e.g. prazosin for trauma-related nightmares) as well as commonly comorbid conditions such as depression. Becoming familiar with the available therapeutic modalities offered in your area is recommended.
Highlighting trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT)
The treatment with the most research evidence for traumatized children is trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), which is a 12- to 25-session therapeutic intervention for patients 3-18 years old (with some evidence for young adults as well) with PTSD and/or trauma-related behaviors. TF-CBT uses a components-based treatment model encompassed by the PRACTICE acronym/mnemonic.6,7
- P – Psychoeducation and parenting skills.
- R – Relaxation techniques: Focused breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and teaching the child to control their thoughts (thought stopping).
- A – Affective expression and regulation (feeling identification): To help the child and parent learn to control their emotional reaction to reminders by expanding their emotional vocabulary, enhancing their skills in identification and expression of emotions, and encouraging self-soothing activities
- C – Cognitive coping and processing: Through this component, the child learns to understand the relationships between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and think in new and healthier ways.
- T – Trauma narrative and processing: Gradual exposure exercises including verbal, written, and/or symbolic recounting of traumatic event(s) so the child learns to be able to discuss the events when they choose to in ways that do not produce overwhelming emotions. Following the completion of the narrative, clients are supported in identifying, challenging, and correcting cognitive distortions and dysfunctional beliefs.
- I – In vivo exposure: Encourage the gradual exposure to innocuous trauma reminders in the child’s environment so the child learns they can control their emotional reactions to things that remind them of the trauma, starting with nonthreatening examples of reminders.
- C – Conjoint parent/child sessions: Sessions generally deal with psycho-education, sharing the trauma narrative, anxiety management, and correction of cognitive distortions. The family works to enhance communication and create opportunities for therapeutic discussion regarding the trauma.
- E – Enhancing personal safety and future growth: Provide training and education with respect to personal safety skills and healthy sexuality and interpersonal relationships; encourage the utilization of skills learned in managing future stressors and/or trauma reminders.
Of note, some elements of this therapy that could possibly be easily incorporated into a primary care office visit include relaxation techniques and focus on coping skills/strategies.
Summary
Children and adolescents often present with trauma-related symptoms to the primary care office. Having increasing familiarity with PTSD diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities will likely lead to increased confidence and comfort recognizing symptoms and when placing a referral. This may also lead to shorter wait times for receiving targeted treatment and ultimately should lead to better outcomes for affected children and families.
Dr. Abdul-Kareem is at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
References
1. National Survey of Children’s Health (2016 - present). https://nschdata.org/browse/survey.
2. Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/index.html].
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd,
4. Martin A et al. Lewis’s Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (5th edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2017.
5. American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. In: DSM-5. 2013.
6. Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network. https://www.nctsn.org/interventions/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy.
7. Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT). California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare. https://www.cebc4cw.org/program/trauma-focused-cognitive-behavioral-therapy/.
Topical gel for epidermolysis bullosa shows ongoing benefit
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Vaccination a harder sell in the summer
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.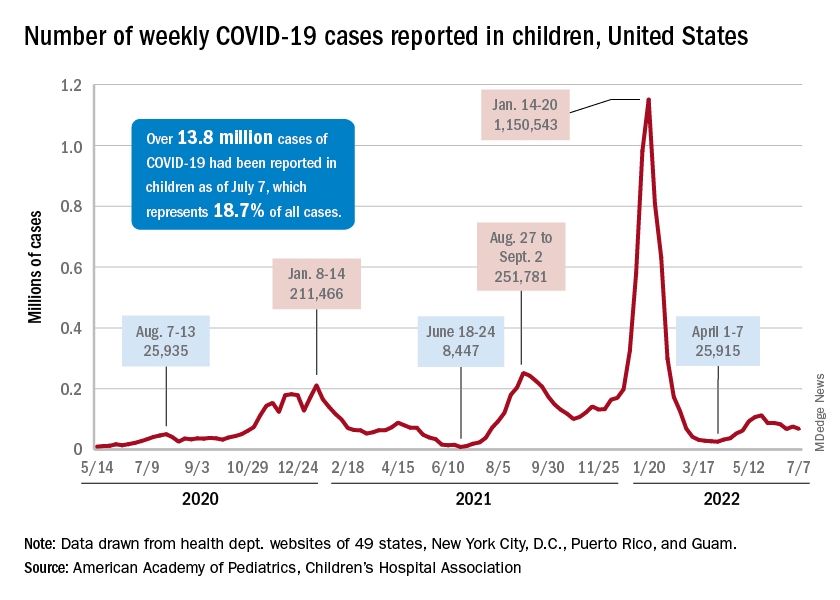
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
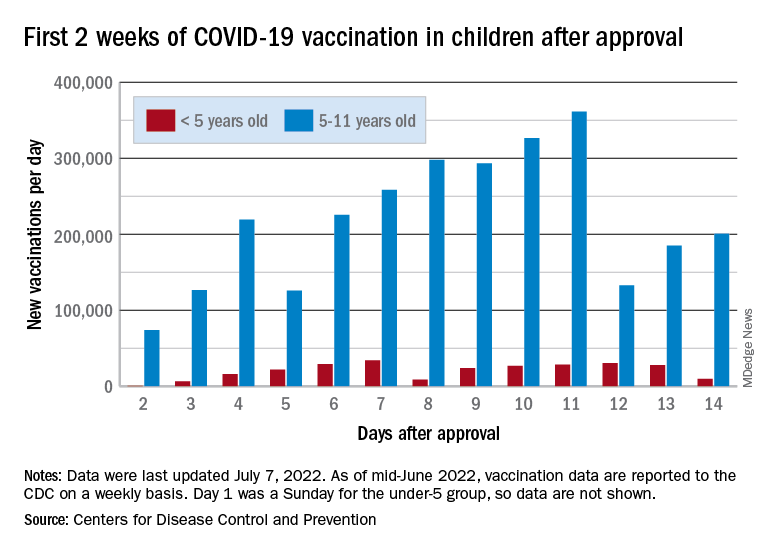
Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.