User login
Paclitaxel Matches Cisplatin HIPEC in Ovarian Cancer
TOPLINE:
Patients with advanced ovarian cancer undergoing interval cytoreductive surgery who received paclitaxel-based hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) during surgery appeared to have comparable overall survival and disease-free survival rates to those who received cisplatin-based HIPEC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Although the use of HIPEC remains controversial, cisplatin-based HIPEC during cytoreductive surgery may benefit patients with advanced ovarian cancer; however, there is less evidence for paclitaxel-based HIPEC, typically used in patients who are frail or intolerant to platinum agents.
- To compare the two regimens, researchers analyzed data from the National Registry of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis, which included 846 patients (mean age, 59 years) who underwent interval cytoreductive surgery with either cisplatin-based HIPEC (n = 325) or paclitaxel-based HIPEC (n = 521). After propensity score matching, there were 199 patients per group (total = 398).
- HIPEC was administered post-surgery with cisplatin (75-100 mg/m2 for 90 minutes) or paclitaxel (120 mg/m2 for 60 minutes), both at 42-43 °C.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using cisplatin as the reference group, the median overall survival was not significantly different between the two options (hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; P = .16); however, the median overall survival was 82 months in the paclitaxel group vs 58 months in the cisplatin group.
- Disease-free survival was also not significantly different between the 2 groups, with a median of 20 months in the cisplatin group and 21 months in the paclitaxel groups (HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.72-1.25; P = .70).
- Overall survival was comparable during the first 20 months of follow-up and disease-free survival was equivalent during the first 15 months of follow-up, based on a predefined equivalence margin of 0.1.
- Paclitaxel-based HIPEC was not associated with increased morbidity (odds ratio, 1.32; P = .06).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that cisplatin and paclitaxel are two safe and effective drugs to be used for HIPEC in [interval cytoreductive surgery] for advanced ovarian cancer. As cisplatin is the preferred drug according to strong evidence, paclitaxel could be a valuable alternative for patients with any contraindication to cisplatin, with similar oncological and perioperative outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Salud González Sánchez, MD, Reina Sofía University Hospital in Córdoba, Spain, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design of this study limited causal inference. The BRCA mutation status was not captured in the national registry. Additionally, the matching procedure resulted in a moderate sample size, which could have led to residual confounding.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not declare any funding information and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with advanced ovarian cancer undergoing interval cytoreductive surgery who received paclitaxel-based hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) during surgery appeared to have comparable overall survival and disease-free survival rates to those who received cisplatin-based HIPEC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Although the use of HIPEC remains controversial, cisplatin-based HIPEC during cytoreductive surgery may benefit patients with advanced ovarian cancer; however, there is less evidence for paclitaxel-based HIPEC, typically used in patients who are frail or intolerant to platinum agents.
- To compare the two regimens, researchers analyzed data from the National Registry of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis, which included 846 patients (mean age, 59 years) who underwent interval cytoreductive surgery with either cisplatin-based HIPEC (n = 325) or paclitaxel-based HIPEC (n = 521). After propensity score matching, there were 199 patients per group (total = 398).
- HIPEC was administered post-surgery with cisplatin (75-100 mg/m2 for 90 minutes) or paclitaxel (120 mg/m2 for 60 minutes), both at 42-43 °C.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using cisplatin as the reference group, the median overall survival was not significantly different between the two options (hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; P = .16); however, the median overall survival was 82 months in the paclitaxel group vs 58 months in the cisplatin group.
- Disease-free survival was also not significantly different between the 2 groups, with a median of 20 months in the cisplatin group and 21 months in the paclitaxel groups (HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.72-1.25; P = .70).
- Overall survival was comparable during the first 20 months of follow-up and disease-free survival was equivalent during the first 15 months of follow-up, based on a predefined equivalence margin of 0.1.
- Paclitaxel-based HIPEC was not associated with increased morbidity (odds ratio, 1.32; P = .06).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that cisplatin and paclitaxel are two safe and effective drugs to be used for HIPEC in [interval cytoreductive surgery] for advanced ovarian cancer. As cisplatin is the preferred drug according to strong evidence, paclitaxel could be a valuable alternative for patients with any contraindication to cisplatin, with similar oncological and perioperative outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Salud González Sánchez, MD, Reina Sofía University Hospital in Córdoba, Spain, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design of this study limited causal inference. The BRCA mutation status was not captured in the national registry. Additionally, the matching procedure resulted in a moderate sample size, which could have led to residual confounding.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not declare any funding information and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with advanced ovarian cancer undergoing interval cytoreductive surgery who received paclitaxel-based hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) during surgery appeared to have comparable overall survival and disease-free survival rates to those who received cisplatin-based HIPEC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Although the use of HIPEC remains controversial, cisplatin-based HIPEC during cytoreductive surgery may benefit patients with advanced ovarian cancer; however, there is less evidence for paclitaxel-based HIPEC, typically used in patients who are frail or intolerant to platinum agents.
- To compare the two regimens, researchers analyzed data from the National Registry of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis, which included 846 patients (mean age, 59 years) who underwent interval cytoreductive surgery with either cisplatin-based HIPEC (n = 325) or paclitaxel-based HIPEC (n = 521). After propensity score matching, there were 199 patients per group (total = 398).
- HIPEC was administered post-surgery with cisplatin (75-100 mg/m2 for 90 minutes) or paclitaxel (120 mg/m2 for 60 minutes), both at 42-43 °C.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using cisplatin as the reference group, the median overall survival was not significantly different between the two options (hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; P = .16); however, the median overall survival was 82 months in the paclitaxel group vs 58 months in the cisplatin group.
- Disease-free survival was also not significantly different between the 2 groups, with a median of 20 months in the cisplatin group and 21 months in the paclitaxel groups (HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.72-1.25; P = .70).
- Overall survival was comparable during the first 20 months of follow-up and disease-free survival was equivalent during the first 15 months of follow-up, based on a predefined equivalence margin of 0.1.
- Paclitaxel-based HIPEC was not associated with increased morbidity (odds ratio, 1.32; P = .06).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that cisplatin and paclitaxel are two safe and effective drugs to be used for HIPEC in [interval cytoreductive surgery] for advanced ovarian cancer. As cisplatin is the preferred drug according to strong evidence, paclitaxel could be a valuable alternative for patients with any contraindication to cisplatin, with similar oncological and perioperative outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Salud González Sánchez, MD, Reina Sofía University Hospital in Córdoba, Spain, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective design of this study limited causal inference. The BRCA mutation status was not captured in the national registry. Additionally, the matching procedure resulted in a moderate sample size, which could have led to residual confounding.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not declare any funding information and reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ethnic Disparities in Cancer Reflect Disparities in HIV Care
While several cancers associated with immunosuppression are much more common in White men who have sex with men living with HIV (MSMWH) than in the male general population, they are even more frequently seen in Black and Hispanic MSMWH.
This suggests that racial and ethnic disparities in access to antiretroviral therapy and viral suppression are playing a role, said the authors of an analysis published last month in AIDS.
“Disparities in cancer risk may serve as an important proxy for disparities in HIV care,” they wrote.
The researchers at the National Cancer Institute leveraged data from the HIV/AIDS Cancer Match Study, which covers 13 US states and the District of Columbia. For this analysis, they examined cancer incidence in over 350,000 MSMWH followed for 3.2 million person years, between 2001 and 2019.
They focused on Kaposi sarcoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, anal cancer, and liver cancer — all malignancies that are associated with viral infections and immunosuppression. They restricted their analysis to MSM because behavioral factors (such as anal sex) contribute to increased exposure to viral infections in this population.
The study’s intersectional lens is valuable, Gita Suneja, MD, said in an interview. “It is looking at racial and ethnic disparities within an already minoritized group, which is men who have sex with men living with HIV,” said the professor of radiation oncology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, who was not involved in the study.
“It’s really profound to me to sit back and think about how these disparities intersect, and how somebody can be so marginalized: it’s not just race or ethnicity, it’s not just having a stigmatized medical condition, it’s the confluence of all of these factors that leads to exclusion from care and poor outcomes.”
Standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), using men of the same ethnicity and age in the general population as the comparator, were reported for MSMWH of different racial/ethnic groups. For non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIR was 3.11 for White MSMWH, rising to 4.84 for Black MSMWH and 5.46 for Hispanic MSMWH.
For Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIRs were 6.35, 7.69, and 11.5, respectively. For Kaposi sarcoma, they were many orders of magnitude higher, at 417 for White MSMWH, 772 for Black MSMWH, and 887 for Hispanic MSMWH.
In contrast, for anal cancer and liver cancer, the highest SIRs were among White MSMWH.
Given the role of immunosuppression, the researchers wanted to see whether cancer incidence differed according to prior AIDS diagnosis. However, they found that within each racial/ethnic group, there were no statistically significant differences in SIR according to AIDS status.
“There were disparities across the board for [racially minoritized] groups, regardless of immunosuppression status, which leads us to believe that it isn’t just about the diagnosis of AIDS, but about many other factors that we’re not capturing in the paper,” first author Benton Meldrum, MPH, told this news organization.
One study limitation is that AIDS diagnosis is an imprecise proxy for immunosuppression. It does not capture the duration and severity of immunosuppression, nor the extent of immune restoration. Many people with a previous AIDS diagnosis are now virally suppressed.
Database studies have inherent limitations in terms of the range of parameters recorded. In an ideal world, Meldrum said, they would have had access to information on CD4 count and viral suppression over time, as well as socioeconomic factors such as income and insurance status.
Differences in timely HIV diagnosis, viral suppression, and continued engagement in care are thought to drive the differences in cancer incidence. “HIV control today helps mitigate the risk of cancer development down the road,” Suneja said.
While not addressed by this study, there may be additional differences in cancer survival. Differences in cancer care, including prompt diagnosis and access to effective treatment, could play a role.
In terms of practical interventions to address these disparities, Suneja highlights the value of programs which help patients navigate a complex healthcare system. This may include care coordination navigation, peer navigation, and delivering services in community settings.
Such interventions don’t only benefit marginalized groups but help improve healthcare access and outcomes for everyone, she said. Even people with insurance and high health literacy often struggle to remain engaged.
“When we design healthcare systems to best serve those that have been left furthest behind, we all do better,” Suneja said.
The study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute. Suneja and Meldrum reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While several cancers associated with immunosuppression are much more common in White men who have sex with men living with HIV (MSMWH) than in the male general population, they are even more frequently seen in Black and Hispanic MSMWH.
This suggests that racial and ethnic disparities in access to antiretroviral therapy and viral suppression are playing a role, said the authors of an analysis published last month in AIDS.
“Disparities in cancer risk may serve as an important proxy for disparities in HIV care,” they wrote.
The researchers at the National Cancer Institute leveraged data from the HIV/AIDS Cancer Match Study, which covers 13 US states and the District of Columbia. For this analysis, they examined cancer incidence in over 350,000 MSMWH followed for 3.2 million person years, between 2001 and 2019.
They focused on Kaposi sarcoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, anal cancer, and liver cancer — all malignancies that are associated with viral infections and immunosuppression. They restricted their analysis to MSM because behavioral factors (such as anal sex) contribute to increased exposure to viral infections in this population.
The study’s intersectional lens is valuable, Gita Suneja, MD, said in an interview. “It is looking at racial and ethnic disparities within an already minoritized group, which is men who have sex with men living with HIV,” said the professor of radiation oncology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, who was not involved in the study.
“It’s really profound to me to sit back and think about how these disparities intersect, and how somebody can be so marginalized: it’s not just race or ethnicity, it’s not just having a stigmatized medical condition, it’s the confluence of all of these factors that leads to exclusion from care and poor outcomes.”
Standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), using men of the same ethnicity and age in the general population as the comparator, were reported for MSMWH of different racial/ethnic groups. For non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIR was 3.11 for White MSMWH, rising to 4.84 for Black MSMWH and 5.46 for Hispanic MSMWH.
For Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIRs were 6.35, 7.69, and 11.5, respectively. For Kaposi sarcoma, they were many orders of magnitude higher, at 417 for White MSMWH, 772 for Black MSMWH, and 887 for Hispanic MSMWH.
In contrast, for anal cancer and liver cancer, the highest SIRs were among White MSMWH.
Given the role of immunosuppression, the researchers wanted to see whether cancer incidence differed according to prior AIDS diagnosis. However, they found that within each racial/ethnic group, there were no statistically significant differences in SIR according to AIDS status.
“There were disparities across the board for [racially minoritized] groups, regardless of immunosuppression status, which leads us to believe that it isn’t just about the diagnosis of AIDS, but about many other factors that we’re not capturing in the paper,” first author Benton Meldrum, MPH, told this news organization.
One study limitation is that AIDS diagnosis is an imprecise proxy for immunosuppression. It does not capture the duration and severity of immunosuppression, nor the extent of immune restoration. Many people with a previous AIDS diagnosis are now virally suppressed.
Database studies have inherent limitations in terms of the range of parameters recorded. In an ideal world, Meldrum said, they would have had access to information on CD4 count and viral suppression over time, as well as socioeconomic factors such as income and insurance status.
Differences in timely HIV diagnosis, viral suppression, and continued engagement in care are thought to drive the differences in cancer incidence. “HIV control today helps mitigate the risk of cancer development down the road,” Suneja said.
While not addressed by this study, there may be additional differences in cancer survival. Differences in cancer care, including prompt diagnosis and access to effective treatment, could play a role.
In terms of practical interventions to address these disparities, Suneja highlights the value of programs which help patients navigate a complex healthcare system. This may include care coordination navigation, peer navigation, and delivering services in community settings.
Such interventions don’t only benefit marginalized groups but help improve healthcare access and outcomes for everyone, she said. Even people with insurance and high health literacy often struggle to remain engaged.
“When we design healthcare systems to best serve those that have been left furthest behind, we all do better,” Suneja said.
The study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute. Suneja and Meldrum reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While several cancers associated with immunosuppression are much more common in White men who have sex with men living with HIV (MSMWH) than in the male general population, they are even more frequently seen in Black and Hispanic MSMWH.
This suggests that racial and ethnic disparities in access to antiretroviral therapy and viral suppression are playing a role, said the authors of an analysis published last month in AIDS.
“Disparities in cancer risk may serve as an important proxy for disparities in HIV care,” they wrote.
The researchers at the National Cancer Institute leveraged data from the HIV/AIDS Cancer Match Study, which covers 13 US states and the District of Columbia. For this analysis, they examined cancer incidence in over 350,000 MSMWH followed for 3.2 million person years, between 2001 and 2019.
They focused on Kaposi sarcoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, anal cancer, and liver cancer — all malignancies that are associated with viral infections and immunosuppression. They restricted their analysis to MSM because behavioral factors (such as anal sex) contribute to increased exposure to viral infections in this population.
The study’s intersectional lens is valuable, Gita Suneja, MD, said in an interview. “It is looking at racial and ethnic disparities within an already minoritized group, which is men who have sex with men living with HIV,” said the professor of radiation oncology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, who was not involved in the study.
“It’s really profound to me to sit back and think about how these disparities intersect, and how somebody can be so marginalized: it’s not just race or ethnicity, it’s not just having a stigmatized medical condition, it’s the confluence of all of these factors that leads to exclusion from care and poor outcomes.”
Standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), using men of the same ethnicity and age in the general population as the comparator, were reported for MSMWH of different racial/ethnic groups. For non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIR was 3.11 for White MSMWH, rising to 4.84 for Black MSMWH and 5.46 for Hispanic MSMWH.
For Hodgkin lymphoma, the SIRs were 6.35, 7.69, and 11.5, respectively. For Kaposi sarcoma, they were many orders of magnitude higher, at 417 for White MSMWH, 772 for Black MSMWH, and 887 for Hispanic MSMWH.
In contrast, for anal cancer and liver cancer, the highest SIRs were among White MSMWH.
Given the role of immunosuppression, the researchers wanted to see whether cancer incidence differed according to prior AIDS diagnosis. However, they found that within each racial/ethnic group, there were no statistically significant differences in SIR according to AIDS status.
“There were disparities across the board for [racially minoritized] groups, regardless of immunosuppression status, which leads us to believe that it isn’t just about the diagnosis of AIDS, but about many other factors that we’re not capturing in the paper,” first author Benton Meldrum, MPH, told this news organization.
One study limitation is that AIDS diagnosis is an imprecise proxy for immunosuppression. It does not capture the duration and severity of immunosuppression, nor the extent of immune restoration. Many people with a previous AIDS diagnosis are now virally suppressed.
Database studies have inherent limitations in terms of the range of parameters recorded. In an ideal world, Meldrum said, they would have had access to information on CD4 count and viral suppression over time, as well as socioeconomic factors such as income and insurance status.
Differences in timely HIV diagnosis, viral suppression, and continued engagement in care are thought to drive the differences in cancer incidence. “HIV control today helps mitigate the risk of cancer development down the road,” Suneja said.
While not addressed by this study, there may be additional differences in cancer survival. Differences in cancer care, including prompt diagnosis and access to effective treatment, could play a role.
In terms of practical interventions to address these disparities, Suneja highlights the value of programs which help patients navigate a complex healthcare system. This may include care coordination navigation, peer navigation, and delivering services in community settings.
Such interventions don’t only benefit marginalized groups but help improve healthcare access and outcomes for everyone, she said. Even people with insurance and high health literacy often struggle to remain engaged.
“When we design healthcare systems to best serve those that have been left furthest behind, we all do better,” Suneja said.
The study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute. Suneja and Meldrum reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Patients Really Say No to Life-Saving Cancer Care?
Mrs G.O. is an 80-year-old retired teacher who was widowed a decade ago. With no close relatives, she lives alone, accompanied by only two cats and a dog that she has rescued. “I am alone,” she told Gustavo Kusminsky, MD, consultant in Hematology and Hematopoietic Transplant Service at Austral University Hospital and lecturer in medicine at the Hospital Universitario Austral, Buenos Aires, Argentina. She said this calmly while refusing treatment for life-threatening multiple myeloma. “Doctor, I would rather not,” she added — her words lingering in the quiet consulting room. That moment is now the focus of a recent article in the journal Medicina.
In the article, Kusminsky described how he made an effort to clarify to the patient that she needed cancer treatment. He explained that the treatment was mostly oral, required no initial hospitalization, and that consultations could be spaced out. However, Mrs G.O. maintained her position.
“The patient had no signs of depression, and her argument was logical. Mrs G.O. was already receiving several medications for high blood pressure, was on anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and managed dyslipidemia with fenofibrate. But she preferred not to receive treatment for her multiple myeloma.” Kusminsky noted.
“Doctor, I have lived my life. I am old. I am already taking too many medications. I do not have a family, and it would be very difficult to deal with the side effects and be dependent on the hospital. As long as I can take care of myself, I do not want any more treatment, at least not for now. We will talk in a few months if I am still here,” she told him before leaving.
The article mentioned that responses such as Mrs G.O. spark perplexity in modern medicine to the extent that clinicians initiate protocols to rule out depression or other psychological factors when a patient rejects treatments that could prolong their life. On the contrary, no such checks are made when patients agree to treatment, because acceptance is deemed “normal.”
Because of collective assumptions and the war metaphors often used in oncology, Mrs G.O. risked being labeled a “deserter from the battalion” of patients with cancer.
In truth, her decision invites reflection on the doctor-patient relationship, respect for autonomy, and the benefits of modern cancer care offered today, Kusminsky said.
This provides an opportunity to consider the patient’s perspective rather than a purely medical perspective.
Jennifer Hincapié Sánchez, PhD, professor in the Faculty of Medicine at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). She is the director of the UNAM University Bioethics Program and coordinates its Institutional Ethics and Bioethics Program for the Faculty of Medicine in Mexico. Although not involved in the article, she regards it as vital. “It’s crucial to remind medical staff that their role is to promote patients’ well-being and that this is related to the life plan that patients have set for themselves, even though this vision is sometimes not aligned with biomedical progress,” she said.
Patient Autonomy
Science-guided medicine aims to prolong life, improve quality, and relieve suffering. However, acceptance or refusal of treatment remains a personal choice for anyone with cancer.
Some evidence showed that patients who decline treatment do not always experience rapid decline. Many can live acceptable, even fulfilling, lives on their own for varying periods, even though they know that there is a possibility of shorter survival. Valuing fewer side effects and better quality of life. This suggested that quality of life is subjective and cannot be measured solely by biomedical standards but also by the meaning each person finds in their existence, even in the face of serious illness.
“There is a myth that quality of life is only valid when defined by objective success. Our task is to explain that it is subjective, and life can be meaningful despite limitations.” Kusminsky said.
Mrs G.O. knew her prognosis and treatment options but chose not to pursue treatment, which, while medically advisable, did not align with her values or vision of life.
Hincapié Sánchez stated that the priority is always to honor the patient’s choice. Clinicians must ensure that the patient has all necessary information that is always appropriate to their sociocultural context before making the decision.
“If the decision persists despite being informed and aware of the effects of the patient’s choice, all we can do is provide support, manage the pain, and seek the patient’s comfort,” she emphasized.
Medical Omnipotence
Physicians should not view the refusal of treatment as an abandonment of the fundamental principles of the profession. Rather, it means respecting patient priorities and recognizing medicine as a dialogue between science and humanity, not as an exercise of control.
However, many clinicians struggle with such decisions because they conflict with their impulse to act and a sense of medical omnipotence. Hincapié Sánchez attributed these difficulties to medical training.
“We are taught to preserve life at all costs. If treatment even slightly prolongs life, many doctors continue to recommend it. The question becomes: Is it valid to extend life when its quality is in doubt?” she asked.
“Medicine is more than a science; it is an art. It is the most human in the sciences and the most scientific in the humanities. Let us not lose sight of the human element that allows us to see the patient as a person, not just a disease to be treated,” Hincapié Sánchez urges.
Kusminsky describes a common therapeutic obstinacy — doctors’ reluctance to stop “doing something,” to avoid “throwing in the towel,” or to uphold “hope is the last thing to be lost.”
“But physicians are growing more aware of these situations, and change is slowly coming,” he said. However, he added: “Of course, there is the issue of the perceived omnipotence of doctors — their words descending with authority to ‘prescribe’ treatment, issue ‘medical orders,’ or dictate ‘pharmacological’ therapy.
For the specialist, such terminology reflects a view of the doctor-patient relationship not as a mutual, two-way exchange, but as a vertical, paternalistic dynamic.
He suggested looking at ancient Greece for perspective. “Hippocrates, or rather the Hippocratic school, taught that the doctor-patient encounter is inherently one of compassion. We must approach this in that way. Reflecting on that bond, improving communication, humanizing relationships, and, above all, being available to listen are key,” Kusminsky said.
Another intersection that has long fascinated Kusminsky is between literature and medicine. This interest led him to explore the field of narrative medicine, serve on the board of directors of the Argentine Society of Narrative Medicine (SAMEN), and join the roster of speakers at the upcoming second SAMEN Conference in Buenos Aires on July 10 and 11, 2025.
“Narrative medicine uses storytelling tools to absorb, process, acknowledge, and empathize with patients’ illness narratives, aiming to restore humanism to practice,” he explained.
According to Kusminsky, the circumstances under which Mrs G.O. expressed her wish not to begin treatment immediately reminded him of a text by Melville’s famous “I would prefer not to” from Bartleby, the Scrivener.
This reflection inspired him to publish an article cited at its beginning. At the same time, it reinforced his belief that what patients say can itself be a form of narrative that extends beyond the confines of clinical history.
Mrs G.O. chose not to pursue treatment for multiple myeloma. However, she returned to Kusminsky’s office approximately 2 months ago. She felt well, and her disease slowly progressed; however, she still had no clinical signs or symptoms.
Kusminsky and Hincapié Sánchez have declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mrs G.O. is an 80-year-old retired teacher who was widowed a decade ago. With no close relatives, she lives alone, accompanied by only two cats and a dog that she has rescued. “I am alone,” she told Gustavo Kusminsky, MD, consultant in Hematology and Hematopoietic Transplant Service at Austral University Hospital and lecturer in medicine at the Hospital Universitario Austral, Buenos Aires, Argentina. She said this calmly while refusing treatment for life-threatening multiple myeloma. “Doctor, I would rather not,” she added — her words lingering in the quiet consulting room. That moment is now the focus of a recent article in the journal Medicina.
In the article, Kusminsky described how he made an effort to clarify to the patient that she needed cancer treatment. He explained that the treatment was mostly oral, required no initial hospitalization, and that consultations could be spaced out. However, Mrs G.O. maintained her position.
“The patient had no signs of depression, and her argument was logical. Mrs G.O. was already receiving several medications for high blood pressure, was on anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and managed dyslipidemia with fenofibrate. But she preferred not to receive treatment for her multiple myeloma.” Kusminsky noted.
“Doctor, I have lived my life. I am old. I am already taking too many medications. I do not have a family, and it would be very difficult to deal with the side effects and be dependent on the hospital. As long as I can take care of myself, I do not want any more treatment, at least not for now. We will talk in a few months if I am still here,” she told him before leaving.
The article mentioned that responses such as Mrs G.O. spark perplexity in modern medicine to the extent that clinicians initiate protocols to rule out depression or other psychological factors when a patient rejects treatments that could prolong their life. On the contrary, no such checks are made when patients agree to treatment, because acceptance is deemed “normal.”
Because of collective assumptions and the war metaphors often used in oncology, Mrs G.O. risked being labeled a “deserter from the battalion” of patients with cancer.
In truth, her decision invites reflection on the doctor-patient relationship, respect for autonomy, and the benefits of modern cancer care offered today, Kusminsky said.
This provides an opportunity to consider the patient’s perspective rather than a purely medical perspective.
Jennifer Hincapié Sánchez, PhD, professor in the Faculty of Medicine at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). She is the director of the UNAM University Bioethics Program and coordinates its Institutional Ethics and Bioethics Program for the Faculty of Medicine in Mexico. Although not involved in the article, she regards it as vital. “It’s crucial to remind medical staff that their role is to promote patients’ well-being and that this is related to the life plan that patients have set for themselves, even though this vision is sometimes not aligned with biomedical progress,” she said.
Patient Autonomy
Science-guided medicine aims to prolong life, improve quality, and relieve suffering. However, acceptance or refusal of treatment remains a personal choice for anyone with cancer.
Some evidence showed that patients who decline treatment do not always experience rapid decline. Many can live acceptable, even fulfilling, lives on their own for varying periods, even though they know that there is a possibility of shorter survival. Valuing fewer side effects and better quality of life. This suggested that quality of life is subjective and cannot be measured solely by biomedical standards but also by the meaning each person finds in their existence, even in the face of serious illness.
“There is a myth that quality of life is only valid when defined by objective success. Our task is to explain that it is subjective, and life can be meaningful despite limitations.” Kusminsky said.
Mrs G.O. knew her prognosis and treatment options but chose not to pursue treatment, which, while medically advisable, did not align with her values or vision of life.
Hincapié Sánchez stated that the priority is always to honor the patient’s choice. Clinicians must ensure that the patient has all necessary information that is always appropriate to their sociocultural context before making the decision.
“If the decision persists despite being informed and aware of the effects of the patient’s choice, all we can do is provide support, manage the pain, and seek the patient’s comfort,” she emphasized.
Medical Omnipotence
Physicians should not view the refusal of treatment as an abandonment of the fundamental principles of the profession. Rather, it means respecting patient priorities and recognizing medicine as a dialogue between science and humanity, not as an exercise of control.
However, many clinicians struggle with such decisions because they conflict with their impulse to act and a sense of medical omnipotence. Hincapié Sánchez attributed these difficulties to medical training.
“We are taught to preserve life at all costs. If treatment even slightly prolongs life, many doctors continue to recommend it. The question becomes: Is it valid to extend life when its quality is in doubt?” she asked.
“Medicine is more than a science; it is an art. It is the most human in the sciences and the most scientific in the humanities. Let us not lose sight of the human element that allows us to see the patient as a person, not just a disease to be treated,” Hincapié Sánchez urges.
Kusminsky describes a common therapeutic obstinacy — doctors’ reluctance to stop “doing something,” to avoid “throwing in the towel,” or to uphold “hope is the last thing to be lost.”
“But physicians are growing more aware of these situations, and change is slowly coming,” he said. However, he added: “Of course, there is the issue of the perceived omnipotence of doctors — their words descending with authority to ‘prescribe’ treatment, issue ‘medical orders,’ or dictate ‘pharmacological’ therapy.
For the specialist, such terminology reflects a view of the doctor-patient relationship not as a mutual, two-way exchange, but as a vertical, paternalistic dynamic.
He suggested looking at ancient Greece for perspective. “Hippocrates, or rather the Hippocratic school, taught that the doctor-patient encounter is inherently one of compassion. We must approach this in that way. Reflecting on that bond, improving communication, humanizing relationships, and, above all, being available to listen are key,” Kusminsky said.
Another intersection that has long fascinated Kusminsky is between literature and medicine. This interest led him to explore the field of narrative medicine, serve on the board of directors of the Argentine Society of Narrative Medicine (SAMEN), and join the roster of speakers at the upcoming second SAMEN Conference in Buenos Aires on July 10 and 11, 2025.
“Narrative medicine uses storytelling tools to absorb, process, acknowledge, and empathize with patients’ illness narratives, aiming to restore humanism to practice,” he explained.
According to Kusminsky, the circumstances under which Mrs G.O. expressed her wish not to begin treatment immediately reminded him of a text by Melville’s famous “I would prefer not to” from Bartleby, the Scrivener.
This reflection inspired him to publish an article cited at its beginning. At the same time, it reinforced his belief that what patients say can itself be a form of narrative that extends beyond the confines of clinical history.
Mrs G.O. chose not to pursue treatment for multiple myeloma. However, she returned to Kusminsky’s office approximately 2 months ago. She felt well, and her disease slowly progressed; however, she still had no clinical signs or symptoms.
Kusminsky and Hincapié Sánchez have declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mrs G.O. is an 80-year-old retired teacher who was widowed a decade ago. With no close relatives, she lives alone, accompanied by only two cats and a dog that she has rescued. “I am alone,” she told Gustavo Kusminsky, MD, consultant in Hematology and Hematopoietic Transplant Service at Austral University Hospital and lecturer in medicine at the Hospital Universitario Austral, Buenos Aires, Argentina. She said this calmly while refusing treatment for life-threatening multiple myeloma. “Doctor, I would rather not,” she added — her words lingering in the quiet consulting room. That moment is now the focus of a recent article in the journal Medicina.
In the article, Kusminsky described how he made an effort to clarify to the patient that she needed cancer treatment. He explained that the treatment was mostly oral, required no initial hospitalization, and that consultations could be spaced out. However, Mrs G.O. maintained her position.
“The patient had no signs of depression, and her argument was logical. Mrs G.O. was already receiving several medications for high blood pressure, was on anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and managed dyslipidemia with fenofibrate. But she preferred not to receive treatment for her multiple myeloma.” Kusminsky noted.
“Doctor, I have lived my life. I am old. I am already taking too many medications. I do not have a family, and it would be very difficult to deal with the side effects and be dependent on the hospital. As long as I can take care of myself, I do not want any more treatment, at least not for now. We will talk in a few months if I am still here,” she told him before leaving.
The article mentioned that responses such as Mrs G.O. spark perplexity in modern medicine to the extent that clinicians initiate protocols to rule out depression or other psychological factors when a patient rejects treatments that could prolong their life. On the contrary, no such checks are made when patients agree to treatment, because acceptance is deemed “normal.”
Because of collective assumptions and the war metaphors often used in oncology, Mrs G.O. risked being labeled a “deserter from the battalion” of patients with cancer.
In truth, her decision invites reflection on the doctor-patient relationship, respect for autonomy, and the benefits of modern cancer care offered today, Kusminsky said.
This provides an opportunity to consider the patient’s perspective rather than a purely medical perspective.
Jennifer Hincapié Sánchez, PhD, professor in the Faculty of Medicine at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). She is the director of the UNAM University Bioethics Program and coordinates its Institutional Ethics and Bioethics Program for the Faculty of Medicine in Mexico. Although not involved in the article, she regards it as vital. “It’s crucial to remind medical staff that their role is to promote patients’ well-being and that this is related to the life plan that patients have set for themselves, even though this vision is sometimes not aligned with biomedical progress,” she said.
Patient Autonomy
Science-guided medicine aims to prolong life, improve quality, and relieve suffering. However, acceptance or refusal of treatment remains a personal choice for anyone with cancer.
Some evidence showed that patients who decline treatment do not always experience rapid decline. Many can live acceptable, even fulfilling, lives on their own for varying periods, even though they know that there is a possibility of shorter survival. Valuing fewer side effects and better quality of life. This suggested that quality of life is subjective and cannot be measured solely by biomedical standards but also by the meaning each person finds in their existence, even in the face of serious illness.
“There is a myth that quality of life is only valid when defined by objective success. Our task is to explain that it is subjective, and life can be meaningful despite limitations.” Kusminsky said.
Mrs G.O. knew her prognosis and treatment options but chose not to pursue treatment, which, while medically advisable, did not align with her values or vision of life.
Hincapié Sánchez stated that the priority is always to honor the patient’s choice. Clinicians must ensure that the patient has all necessary information that is always appropriate to their sociocultural context before making the decision.
“If the decision persists despite being informed and aware of the effects of the patient’s choice, all we can do is provide support, manage the pain, and seek the patient’s comfort,” she emphasized.
Medical Omnipotence
Physicians should not view the refusal of treatment as an abandonment of the fundamental principles of the profession. Rather, it means respecting patient priorities and recognizing medicine as a dialogue between science and humanity, not as an exercise of control.
However, many clinicians struggle with such decisions because they conflict with their impulse to act and a sense of medical omnipotence. Hincapié Sánchez attributed these difficulties to medical training.
“We are taught to preserve life at all costs. If treatment even slightly prolongs life, many doctors continue to recommend it. The question becomes: Is it valid to extend life when its quality is in doubt?” she asked.
“Medicine is more than a science; it is an art. It is the most human in the sciences and the most scientific in the humanities. Let us not lose sight of the human element that allows us to see the patient as a person, not just a disease to be treated,” Hincapié Sánchez urges.
Kusminsky describes a common therapeutic obstinacy — doctors’ reluctance to stop “doing something,” to avoid “throwing in the towel,” or to uphold “hope is the last thing to be lost.”
“But physicians are growing more aware of these situations, and change is slowly coming,” he said. However, he added: “Of course, there is the issue of the perceived omnipotence of doctors — their words descending with authority to ‘prescribe’ treatment, issue ‘medical orders,’ or dictate ‘pharmacological’ therapy.
For the specialist, such terminology reflects a view of the doctor-patient relationship not as a mutual, two-way exchange, but as a vertical, paternalistic dynamic.
He suggested looking at ancient Greece for perspective. “Hippocrates, or rather the Hippocratic school, taught that the doctor-patient encounter is inherently one of compassion. We must approach this in that way. Reflecting on that bond, improving communication, humanizing relationships, and, above all, being available to listen are key,” Kusminsky said.
Another intersection that has long fascinated Kusminsky is between literature and medicine. This interest led him to explore the field of narrative medicine, serve on the board of directors of the Argentine Society of Narrative Medicine (SAMEN), and join the roster of speakers at the upcoming second SAMEN Conference in Buenos Aires on July 10 and 11, 2025.
“Narrative medicine uses storytelling tools to absorb, process, acknowledge, and empathize with patients’ illness narratives, aiming to restore humanism to practice,” he explained.
According to Kusminsky, the circumstances under which Mrs G.O. expressed her wish not to begin treatment immediately reminded him of a text by Melville’s famous “I would prefer not to” from Bartleby, the Scrivener.
This reflection inspired him to publish an article cited at its beginning. At the same time, it reinforced his belief that what patients say can itself be a form of narrative that extends beyond the confines of clinical history.
Mrs G.O. chose not to pursue treatment for multiple myeloma. However, she returned to Kusminsky’s office approximately 2 months ago. She felt well, and her disease slowly progressed; however, she still had no clinical signs or symptoms.
Kusminsky and Hincapié Sánchez have declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Add-On Niraparib May Slow Hormone-Sensitive Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Adding the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone delayed disease progression and postponed the onset of symptoms in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with homologous recombination repair (HRR) genetic alterations, according to findings from the AMPLITUDE trial.
An interim analysis also demonstrated an early trend toward improved overall survival in patients who received niraparib.
These findings support adding niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone “as a new treatment option” in patients with HRR alterations, said Study Chief Gerhardt Attard, MD, PhD, chair of medical oncology, University College London Cancer Institute, London, England, speaking at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
The findings also highlight that “it’s going to be incredibly important that patients who get diagnosed with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer are tested to see if they have these mutations, so they can be offered the right therapy at the right time,” Outside Expert Bradley McGregor, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said during a press briefing.
Ultimately, “you don’t know if you don’t test,” McGregor added.
About one quarter of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer have alterations in HRR genes, about half of which are BRCA mutations. These patients typically experience faster disease progression and worse outcomes. An androgen receptor pathway inhibitor, such as abiraterone, alongside androgen deprivation therapy with or without docetaxel, is standard therapy for these patients, but “there is still a need for treatments that are tailored to patients whose tumors harbor HRR alterations,” Attard said in a press release.
Adding niraparib to this standard regimen could help improve survival in these patients.
In 2023, the FDA approved niraparib and abiraterone acetate to treat BRCA-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, after findings from the MAGNITUDE study demonstrated improved progression-free survival (PFS).
The phase 3 AMPLITUDE trial set out to evaluate whether this combination would yield similar survival benefits in metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with HRR mutations.
In the study, 696 patients (median age, 68 years) with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer and one or more HRR gene alterations were randomly allocated (1:1) to niraparib with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone or placebo with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.
Exclusion criteria included any prior PARP inhibitor therapy or androgen receptor pathway inhibitor other than abiraterone. Eligible patients could have received at most 6 months of androgen deprivation therapy, ≤ 6 cycles of docetaxel, ≤ 45 days of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone and palliative radiation.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the groups. Just over half the patients in each group had BRCA1 or BRCA2 alterations. The majority had an electrocorticogram performance status of 0, but high-risk features with a predominance for synchronous metastatic disease and metastatic high volume. About 16% had received prior docetaxel, in keeping with real world data, Attard noted.
At a median follow-up of 30.8 months, niraparib plus standard therapy led to a significant 37% reduction in the risk for radiographic progression or death. The median radiographic PFS (rPFS) was not reached in the niraparib group vs 29.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .0001).
Patients with BRCA alterations, in particular, showed the greatest benefit, with niraparib reducing the risk for radiographic progression or death by 48% compared to placebo (median rPFS not reached vs 26 months; HR, 0.52; P < .0001).
On the key secondary endpoint of time to symptomatic progression, adding niraparib led to a “statistically and clinically” significant benefit — a 50% lower in the risk for symptomatic progression in the full population (HR, 0.50), and a 56% lower risk in BRCA-mutant group (HR, 0.44).
The first interim analysis also showed an early trend toward improved overall survival favoring the niraparib combination, with a reduction in the risk for death of 21% in the HRR-mutant population (HR, 0.79; P = .10) and 25% (HR, 0.75; P = .15) in the BRCA-mutant population.
Grade 3/4 adverse events were more common with the niraparib combination group compared to the placebo group (75% vs 59%), with anemia and hypertension being the most common. However, treatment discontinuations due to adverse remained low (15% with niraparib vs 10% with placebo).
Attard noted, however, that half the target number of patients required for the final analysis died. Still, “in my view, there’s a clear trend for favoring survival in the patients randomized to niraparib,” he told attendees.
‘Exciting News’ for Patients
The AMPLITUDE results are “really exciting news for our patients,” McGregor said.
Considering the poor prognosis of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer, “it is reasonable to prioritize early access to PARP inhibitors for these men, at least for the ones with BRCA mutations,” added ASCO discussant Joaquin Mateo, MD, PhD, with Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, Spain.
However, Mateo explained, “I think that for patients with mutations in the other genes, I will be more prudent, and I’ll be on the lookout for the overall survival data to mature.”
The other key conclusion, Mateo said, is that genomic profiling “should be moved earlier into the patient course, and I am confident that embedding genomic profiling into the diagnostic evaluations of metastatic prostate cancer is also going to result in better quality of testing, more efficacious testing, and also a more equitable framework of access to testing for patients.”
This study was funded by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Attard and Mateo disclosed relationships with Janssen and other pharmaceutical companies. McGregor disclosed relationships with Arcus Biosciences, Astellas, AVEO, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone delayed disease progression and postponed the onset of symptoms in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with homologous recombination repair (HRR) genetic alterations, according to findings from the AMPLITUDE trial.
An interim analysis also demonstrated an early trend toward improved overall survival in patients who received niraparib.
These findings support adding niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone “as a new treatment option” in patients with HRR alterations, said Study Chief Gerhardt Attard, MD, PhD, chair of medical oncology, University College London Cancer Institute, London, England, speaking at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
The findings also highlight that “it’s going to be incredibly important that patients who get diagnosed with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer are tested to see if they have these mutations, so they can be offered the right therapy at the right time,” Outside Expert Bradley McGregor, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said during a press briefing.
Ultimately, “you don’t know if you don’t test,” McGregor added.
About one quarter of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer have alterations in HRR genes, about half of which are BRCA mutations. These patients typically experience faster disease progression and worse outcomes. An androgen receptor pathway inhibitor, such as abiraterone, alongside androgen deprivation therapy with or without docetaxel, is standard therapy for these patients, but “there is still a need for treatments that are tailored to patients whose tumors harbor HRR alterations,” Attard said in a press release.
Adding niraparib to this standard regimen could help improve survival in these patients.
In 2023, the FDA approved niraparib and abiraterone acetate to treat BRCA-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, after findings from the MAGNITUDE study demonstrated improved progression-free survival (PFS).
The phase 3 AMPLITUDE trial set out to evaluate whether this combination would yield similar survival benefits in metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with HRR mutations.
In the study, 696 patients (median age, 68 years) with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer and one or more HRR gene alterations were randomly allocated (1:1) to niraparib with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone or placebo with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.
Exclusion criteria included any prior PARP inhibitor therapy or androgen receptor pathway inhibitor other than abiraterone. Eligible patients could have received at most 6 months of androgen deprivation therapy, ≤ 6 cycles of docetaxel, ≤ 45 days of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone and palliative radiation.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the groups. Just over half the patients in each group had BRCA1 or BRCA2 alterations. The majority had an electrocorticogram performance status of 0, but high-risk features with a predominance for synchronous metastatic disease and metastatic high volume. About 16% had received prior docetaxel, in keeping with real world data, Attard noted.
At a median follow-up of 30.8 months, niraparib plus standard therapy led to a significant 37% reduction in the risk for radiographic progression or death. The median radiographic PFS (rPFS) was not reached in the niraparib group vs 29.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .0001).
Patients with BRCA alterations, in particular, showed the greatest benefit, with niraparib reducing the risk for radiographic progression or death by 48% compared to placebo (median rPFS not reached vs 26 months; HR, 0.52; P < .0001).
On the key secondary endpoint of time to symptomatic progression, adding niraparib led to a “statistically and clinically” significant benefit — a 50% lower in the risk for symptomatic progression in the full population (HR, 0.50), and a 56% lower risk in BRCA-mutant group (HR, 0.44).
The first interim analysis also showed an early trend toward improved overall survival favoring the niraparib combination, with a reduction in the risk for death of 21% in the HRR-mutant population (HR, 0.79; P = .10) and 25% (HR, 0.75; P = .15) in the BRCA-mutant population.
Grade 3/4 adverse events were more common with the niraparib combination group compared to the placebo group (75% vs 59%), with anemia and hypertension being the most common. However, treatment discontinuations due to adverse remained low (15% with niraparib vs 10% with placebo).
Attard noted, however, that half the target number of patients required for the final analysis died. Still, “in my view, there’s a clear trend for favoring survival in the patients randomized to niraparib,” he told attendees.
‘Exciting News’ for Patients
The AMPLITUDE results are “really exciting news for our patients,” McGregor said.
Considering the poor prognosis of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer, “it is reasonable to prioritize early access to PARP inhibitors for these men, at least for the ones with BRCA mutations,” added ASCO discussant Joaquin Mateo, MD, PhD, with Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, Spain.
However, Mateo explained, “I think that for patients with mutations in the other genes, I will be more prudent, and I’ll be on the lookout for the overall survival data to mature.”
The other key conclusion, Mateo said, is that genomic profiling “should be moved earlier into the patient course, and I am confident that embedding genomic profiling into the diagnostic evaluations of metastatic prostate cancer is also going to result in better quality of testing, more efficacious testing, and also a more equitable framework of access to testing for patients.”
This study was funded by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Attard and Mateo disclosed relationships with Janssen and other pharmaceutical companies. McGregor disclosed relationships with Arcus Biosciences, Astellas, AVEO, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone delayed disease progression and postponed the onset of symptoms in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with homologous recombination repair (HRR) genetic alterations, according to findings from the AMPLITUDE trial.
An interim analysis also demonstrated an early trend toward improved overall survival in patients who received niraparib.
These findings support adding niraparib to abiraterone acetate plus prednisone “as a new treatment option” in patients with HRR alterations, said Study Chief Gerhardt Attard, MD, PhD, chair of medical oncology, University College London Cancer Institute, London, England, speaking at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
The findings also highlight that “it’s going to be incredibly important that patients who get diagnosed with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer are tested to see if they have these mutations, so they can be offered the right therapy at the right time,” Outside Expert Bradley McGregor, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said during a press briefing.
Ultimately, “you don’t know if you don’t test,” McGregor added.
About one quarter of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer have alterations in HRR genes, about half of which are BRCA mutations. These patients typically experience faster disease progression and worse outcomes. An androgen receptor pathway inhibitor, such as abiraterone, alongside androgen deprivation therapy with or without docetaxel, is standard therapy for these patients, but “there is still a need for treatments that are tailored to patients whose tumors harbor HRR alterations,” Attard said in a press release.
Adding niraparib to this standard regimen could help improve survival in these patients.
In 2023, the FDA approved niraparib and abiraterone acetate to treat BRCA-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, after findings from the MAGNITUDE study demonstrated improved progression-free survival (PFS).
The phase 3 AMPLITUDE trial set out to evaluate whether this combination would yield similar survival benefits in metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer with HRR mutations.
In the study, 696 patients (median age, 68 years) with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer and one or more HRR gene alterations were randomly allocated (1:1) to niraparib with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone or placebo with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone.
Exclusion criteria included any prior PARP inhibitor therapy or androgen receptor pathway inhibitor other than abiraterone. Eligible patients could have received at most 6 months of androgen deprivation therapy, ≤ 6 cycles of docetaxel, ≤ 45 days of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone and palliative radiation.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the groups. Just over half the patients in each group had BRCA1 or BRCA2 alterations. The majority had an electrocorticogram performance status of 0, but high-risk features with a predominance for synchronous metastatic disease and metastatic high volume. About 16% had received prior docetaxel, in keeping with real world data, Attard noted.
At a median follow-up of 30.8 months, niraparib plus standard therapy led to a significant 37% reduction in the risk for radiographic progression or death. The median radiographic PFS (rPFS) was not reached in the niraparib group vs 29.5 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .0001).
Patients with BRCA alterations, in particular, showed the greatest benefit, with niraparib reducing the risk for radiographic progression or death by 48% compared to placebo (median rPFS not reached vs 26 months; HR, 0.52; P < .0001).
On the key secondary endpoint of time to symptomatic progression, adding niraparib led to a “statistically and clinically” significant benefit — a 50% lower in the risk for symptomatic progression in the full population (HR, 0.50), and a 56% lower risk in BRCA-mutant group (HR, 0.44).
The first interim analysis also showed an early trend toward improved overall survival favoring the niraparib combination, with a reduction in the risk for death of 21% in the HRR-mutant population (HR, 0.79; P = .10) and 25% (HR, 0.75; P = .15) in the BRCA-mutant population.
Grade 3/4 adverse events were more common with the niraparib combination group compared to the placebo group (75% vs 59%), with anemia and hypertension being the most common. However, treatment discontinuations due to adverse remained low (15% with niraparib vs 10% with placebo).
Attard noted, however, that half the target number of patients required for the final analysis died. Still, “in my view, there’s a clear trend for favoring survival in the patients randomized to niraparib,” he told attendees.
‘Exciting News’ for Patients
The AMPLITUDE results are “really exciting news for our patients,” McGregor said.
Considering the poor prognosis of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer, “it is reasonable to prioritize early access to PARP inhibitors for these men, at least for the ones with BRCA mutations,” added ASCO discussant Joaquin Mateo, MD, PhD, with Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, Spain.
However, Mateo explained, “I think that for patients with mutations in the other genes, I will be more prudent, and I’ll be on the lookout for the overall survival data to mature.”
The other key conclusion, Mateo said, is that genomic profiling “should be moved earlier into the patient course, and I am confident that embedding genomic profiling into the diagnostic evaluations of metastatic prostate cancer is also going to result in better quality of testing, more efficacious testing, and also a more equitable framework of access to testing for patients.”
This study was funded by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Attard and Mateo disclosed relationships with Janssen and other pharmaceutical companies. McGregor disclosed relationships with Arcus Biosciences, Astellas, AVEO, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2025
Can Popular Weight-Loss Drugs Protect Against Obesity-Related Cancers?
Can Popular Weight-Loss Drugs Protect Against Obesity-Related Cancers?
New data suggest that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, used to treat diabetes and obesity, may also help guard against obesity-related cancers.
In a large observational study, new GLP-1 agonist users with obesity and diabetes had a significantly lower risk for 14 obesity-related cancers than similar individuals who received dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which are weight-neutral.
This study provides a “reassuring safety signal” showing that GLP-1 drugs are linked to a modest drop in obesity-related cancer risk, and not a higher risk for these cancers, said lead investigator Lucas Mavromatis, medical student at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, during a press conference at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
However, there were some nuances to the findings. The protective effect of GLP-1 agonists was only significant for colon and rectal cancers and for women, Mavromatis reported. And although GLP-1 users had an 8% lower risk of dying from any cause, the survival benefit was also only significant for women.
Still, the overall “message to patients is GLP-1 receptor treatments remain a strong option for patients with diabetes and obesity and may have an additional, small favorable benefit in cancer,” Mavromatis explained at the press briefing.
'Intriguing Hypothesis'
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of developing more than a dozen cancer types, including esophageal, colon, rectal, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreatic, kidney, postmenopausal breast, ovarian, endometrial and thyroid, as well as multiple myeloma and meningiomas.
About 12% of Americans have been prescribed a GLP-1 medication to treat diabetes and/or obesity. However, little is known about how these drugs affect cancer risk.
To investigate, Mavromatis and colleagues used the Optum healthcare database to identify 170,030 adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes from 43 health systems in the United States.
Between 2013 and 2023, half started a GLP-1 agonist and half started a DPP-4 inhibitor, with propensity score matching used to balance characteristics of the two cohorts.
Participants were a mean age of 56.8 years, with an average body mass index of 38.5; more than 70% were White individuals and more than 14% were Black individuals.
During a mean follow-up of 3.9 years, 2501 new obesity-related cancers were identified in the GLP-1 group and 2671 in the DPP-4 group — representing a 7% overall reduced risk for any obesity-related cancer in the GLP-1 group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.93).
When analyzing each of the 14 obesity-related cancers separately, the protective link between GLP-1 use and cancer was primarily driven by colon and rectal cancers. GLP-1 users had a 16% lower risk for colon cancer (HR, 0.84) and a 28% lower risk for rectal cancer (HR, 0.72).
“No other cancers had statistically significant associations with GLP-1 use,” Mavromatis told briefing attendees. But “importantly, no cancers had statistically significant adverse associations with GLP-1 use,” he added.
Experts have expressed some concern about a possible link between GLP-1 use and pancreatic cancer given that pancreatitis is a known side effect of GLP-1 use. However, “this is not borne out by epidemiological data,” Mavromatis said.
“Additionally, we were not able to specifically assess medullary thyroid cancer, which is on the warning label for several GLP-1 medications, but we did see a reassuring lack of association between GLP-1 use and thyroid cancer as a whole,” he added.
During follow-up, there were 2783 deaths in the GLP-1 group and 2961 deaths in the DPP-4 group — translating to an 8% lower risk for death due to any cause among GLP-1 users (HR, 0.92; P = .001).
Mavromatis and colleagues observed sex differences as well. Women taking a GLP-1 had an 8% lower risk for obesity-related cancers (HR, 0.92; P = .01) and a 20% lower risk for death from any cause (HR, 0.80; P < .001) compared with women taking a DPP-4 inhibitor.
Among men, researchers found no statistically significant difference between GLP-1 and DPP-4 use for obesity-related cancer risk (HR, 0.95; P = .29) or all-cause mortality (HR, 1.04; P = .34).
Overall, Mavromatis said, it’s important to note that the absolute risk reduction seen in the study is “small and the number of patients that would need to be given one of these medications to prevent an obesity-related cancer, based on our data, would be very large.”
Mavromatis also noted that the length of follow-up was short, and the study assessed primarily older and weaker GLP-1 agonists compared with newer agents on the market. Therefore, longer-term studies with newer GLP-1s are needed to confirm the effects seen as well as safety.
In a statement, ASCO President Robin Zon, MD, said this trial raises the “intriguing hypothesis” that the increasingly popular GLP-1 medications might offer some benefit in reducing the risk of developing cancer.
Zon said she sees many patients with obesity, and given the clear link between cancer and obesity, defining the clinical role of GLP-1 medications in cancer prevention is “important.”
This study “leads us in the direction” of a potential protective effect of GLP-1s on cancer, but “there are a lot of questions that are generated by this particular study, especially as we move forward and we think about prevention of cancers,” Zon told the briefing.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Mavromatis reported no relevant disclosures. Zon reported stock or ownership interests in Oncolytics Biotech, TG Therapeutics, Select Sector SPDR Health Care, AstraZeneca, CRISPR, McKesson, and Berkshire Hathaway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data suggest that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, used to treat diabetes and obesity, may also help guard against obesity-related cancers.
In a large observational study, new GLP-1 agonist users with obesity and diabetes had a significantly lower risk for 14 obesity-related cancers than similar individuals who received dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which are weight-neutral.
This study provides a “reassuring safety signal” showing that GLP-1 drugs are linked to a modest drop in obesity-related cancer risk, and not a higher risk for these cancers, said lead investigator Lucas Mavromatis, medical student at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, during a press conference at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
However, there were some nuances to the findings. The protective effect of GLP-1 agonists was only significant for colon and rectal cancers and for women, Mavromatis reported. And although GLP-1 users had an 8% lower risk of dying from any cause, the survival benefit was also only significant for women.
Still, the overall “message to patients is GLP-1 receptor treatments remain a strong option for patients with diabetes and obesity and may have an additional, small favorable benefit in cancer,” Mavromatis explained at the press briefing.
'Intriguing Hypothesis'
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of developing more than a dozen cancer types, including esophageal, colon, rectal, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreatic, kidney, postmenopausal breast, ovarian, endometrial and thyroid, as well as multiple myeloma and meningiomas.
About 12% of Americans have been prescribed a GLP-1 medication to treat diabetes and/or obesity. However, little is known about how these drugs affect cancer risk.
To investigate, Mavromatis and colleagues used the Optum healthcare database to identify 170,030 adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes from 43 health systems in the United States.
Between 2013 and 2023, half started a GLP-1 agonist and half started a DPP-4 inhibitor, with propensity score matching used to balance characteristics of the two cohorts.
Participants were a mean age of 56.8 years, with an average body mass index of 38.5; more than 70% were White individuals and more than 14% were Black individuals.
During a mean follow-up of 3.9 years, 2501 new obesity-related cancers were identified in the GLP-1 group and 2671 in the DPP-4 group — representing a 7% overall reduced risk for any obesity-related cancer in the GLP-1 group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.93).
When analyzing each of the 14 obesity-related cancers separately, the protective link between GLP-1 use and cancer was primarily driven by colon and rectal cancers. GLP-1 users had a 16% lower risk for colon cancer (HR, 0.84) and a 28% lower risk for rectal cancer (HR, 0.72).
“No other cancers had statistically significant associations with GLP-1 use,” Mavromatis told briefing attendees. But “importantly, no cancers had statistically significant adverse associations with GLP-1 use,” he added.
Experts have expressed some concern about a possible link between GLP-1 use and pancreatic cancer given that pancreatitis is a known side effect of GLP-1 use. However, “this is not borne out by epidemiological data,” Mavromatis said.
“Additionally, we were not able to specifically assess medullary thyroid cancer, which is on the warning label for several GLP-1 medications, but we did see a reassuring lack of association between GLP-1 use and thyroid cancer as a whole,” he added.
During follow-up, there were 2783 deaths in the GLP-1 group and 2961 deaths in the DPP-4 group — translating to an 8% lower risk for death due to any cause among GLP-1 users (HR, 0.92; P = .001).
Mavromatis and colleagues observed sex differences as well. Women taking a GLP-1 had an 8% lower risk for obesity-related cancers (HR, 0.92; P = .01) and a 20% lower risk for death from any cause (HR, 0.80; P < .001) compared with women taking a DPP-4 inhibitor.
Among men, researchers found no statistically significant difference between GLP-1 and DPP-4 use for obesity-related cancer risk (HR, 0.95; P = .29) or all-cause mortality (HR, 1.04; P = .34).
Overall, Mavromatis said, it’s important to note that the absolute risk reduction seen in the study is “small and the number of patients that would need to be given one of these medications to prevent an obesity-related cancer, based on our data, would be very large.”
Mavromatis also noted that the length of follow-up was short, and the study assessed primarily older and weaker GLP-1 agonists compared with newer agents on the market. Therefore, longer-term studies with newer GLP-1s are needed to confirm the effects seen as well as safety.
In a statement, ASCO President Robin Zon, MD, said this trial raises the “intriguing hypothesis” that the increasingly popular GLP-1 medications might offer some benefit in reducing the risk of developing cancer.
Zon said she sees many patients with obesity, and given the clear link between cancer and obesity, defining the clinical role of GLP-1 medications in cancer prevention is “important.”
This study “leads us in the direction” of a potential protective effect of GLP-1s on cancer, but “there are a lot of questions that are generated by this particular study, especially as we move forward and we think about prevention of cancers,” Zon told the briefing.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Mavromatis reported no relevant disclosures. Zon reported stock or ownership interests in Oncolytics Biotech, TG Therapeutics, Select Sector SPDR Health Care, AstraZeneca, CRISPR, McKesson, and Berkshire Hathaway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data suggest that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, used to treat diabetes and obesity, may also help guard against obesity-related cancers.
In a large observational study, new GLP-1 agonist users with obesity and diabetes had a significantly lower risk for 14 obesity-related cancers than similar individuals who received dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which are weight-neutral.
This study provides a “reassuring safety signal” showing that GLP-1 drugs are linked to a modest drop in obesity-related cancer risk, and not a higher risk for these cancers, said lead investigator Lucas Mavromatis, medical student at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, during a press conference at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
However, there were some nuances to the findings. The protective effect of GLP-1 agonists was only significant for colon and rectal cancers and for women, Mavromatis reported. And although GLP-1 users had an 8% lower risk of dying from any cause, the survival benefit was also only significant for women.
Still, the overall “message to patients is GLP-1 receptor treatments remain a strong option for patients with diabetes and obesity and may have an additional, small favorable benefit in cancer,” Mavromatis explained at the press briefing.
'Intriguing Hypothesis'
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of developing more than a dozen cancer types, including esophageal, colon, rectal, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreatic, kidney, postmenopausal breast, ovarian, endometrial and thyroid, as well as multiple myeloma and meningiomas.
About 12% of Americans have been prescribed a GLP-1 medication to treat diabetes and/or obesity. However, little is known about how these drugs affect cancer risk.
To investigate, Mavromatis and colleagues used the Optum healthcare database to identify 170,030 adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes from 43 health systems in the United States.
Between 2013 and 2023, half started a GLP-1 agonist and half started a DPP-4 inhibitor, with propensity score matching used to balance characteristics of the two cohorts.
Participants were a mean age of 56.8 years, with an average body mass index of 38.5; more than 70% were White individuals and more than 14% were Black individuals.
During a mean follow-up of 3.9 years, 2501 new obesity-related cancers were identified in the GLP-1 group and 2671 in the DPP-4 group — representing a 7% overall reduced risk for any obesity-related cancer in the GLP-1 group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.93).
When analyzing each of the 14 obesity-related cancers separately, the protective link between GLP-1 use and cancer was primarily driven by colon and rectal cancers. GLP-1 users had a 16% lower risk for colon cancer (HR, 0.84) and a 28% lower risk for rectal cancer (HR, 0.72).
“No other cancers had statistically significant associations with GLP-1 use,” Mavromatis told briefing attendees. But “importantly, no cancers had statistically significant adverse associations with GLP-1 use,” he added.
Experts have expressed some concern about a possible link between GLP-1 use and pancreatic cancer given that pancreatitis is a known side effect of GLP-1 use. However, “this is not borne out by epidemiological data,” Mavromatis said.
“Additionally, we were not able to specifically assess medullary thyroid cancer, which is on the warning label for several GLP-1 medications, but we did see a reassuring lack of association between GLP-1 use and thyroid cancer as a whole,” he added.
During follow-up, there were 2783 deaths in the GLP-1 group and 2961 deaths in the DPP-4 group — translating to an 8% lower risk for death due to any cause among GLP-1 users (HR, 0.92; P = .001).
Mavromatis and colleagues observed sex differences as well. Women taking a GLP-1 had an 8% lower risk for obesity-related cancers (HR, 0.92; P = .01) and a 20% lower risk for death from any cause (HR, 0.80; P < .001) compared with women taking a DPP-4 inhibitor.
Among men, researchers found no statistically significant difference between GLP-1 and DPP-4 use for obesity-related cancer risk (HR, 0.95; P = .29) or all-cause mortality (HR, 1.04; P = .34).
Overall, Mavromatis said, it’s important to note that the absolute risk reduction seen in the study is “small and the number of patients that would need to be given one of these medications to prevent an obesity-related cancer, based on our data, would be very large.”
Mavromatis also noted that the length of follow-up was short, and the study assessed primarily older and weaker GLP-1 agonists compared with newer agents on the market. Therefore, longer-term studies with newer GLP-1s are needed to confirm the effects seen as well as safety.
In a statement, ASCO President Robin Zon, MD, said this trial raises the “intriguing hypothesis” that the increasingly popular GLP-1 medications might offer some benefit in reducing the risk of developing cancer.
Zon said she sees many patients with obesity, and given the clear link between cancer and obesity, defining the clinical role of GLP-1 medications in cancer prevention is “important.”
This study “leads us in the direction” of a potential protective effect of GLP-1s on cancer, but “there are a lot of questions that are generated by this particular study, especially as we move forward and we think about prevention of cancers,” Zon told the briefing.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Mavromatis reported no relevant disclosures. Zon reported stock or ownership interests in Oncolytics Biotech, TG Therapeutics, Select Sector SPDR Health Care, AstraZeneca, CRISPR, McKesson, and Berkshire Hathaway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Popular Weight-Loss Drugs Protect Against Obesity-Related Cancers?
Can Popular Weight-Loss Drugs Protect Against Obesity-Related Cancers?
Can Lifestyle Changes Save Lives in Colon Cancer?
Can Lifestyle Changes Save Lives in Colon Cancer?
Can exercise “therapy” and diet improve survival in patients with colon cancer? It appears so, according to two pivotal studies presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
In the CHALLENGE trial, a structured exercise program after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy cut the risk for colon cancer recurrence in patients with stage III and high-risk stage II disease by more than one quarter and the risk for death by more than one third.
“The magnitude of benefit with exercise is substantial. In fact, it is comparable, and in some cases exceeds the magnitude of benefit of many of our very good standard medical therapies in oncology,” study presenter Christopher Booth, MD, with Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, told attendees.
Results of the study were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation at the meeting.
The findings are “nothing short of a major milestone,” said study discussant Peter Campbell, PhD, with Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center, Bronx, New York.
The other study showed that eating a less inflammatory diet may reduce the risk for death in patients with colon cancer, with the greatest benefits seen in those who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly.
“Putting these two abstracts into perspective, we as physicians need to be essentially prescribing healthy diet and exercise. The combination of the two are synergistic,” Julie Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, told attendees.
Despite the benefits of these lifestyle changes, exercise and diet are meant to supplement, not replace, established colon cancer treatments.
It would be a false binary to frame this as lifestyle vs cancer treatment, explained Mark Lewis, MD, director of Gastrointestinal Oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. With exercise, for instance, “the key is giving enough chemo to protect against recurrence and eliminate micrometastases but not so much that we cause neuropathy and reduce function and ability to follow the CHALLENGE structured program,” Lewis said.
Exercise and Survival
Colon cancer remains the second-leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Even with surgery and chemotherapy, roughly 30% of patients with stage III and high-risk stage II colon cancer will experience disease recurrence.
“As oncologists, one of the most common questions we get asked by patients is — what else can I do to improve my outcome?” Booth said.
Observational studies published nearly two decades ago hinted that physically active cancer survivors fare better, but no randomized trial has definitively tested whether exercise could alter disease course. That knowledge gap prompted the Canadian Cancer Trials Group to launch the CHALLENGE trial.
Between 2009 and 2023, the phase 3 study enrolled 889 adults (median age, 61 years; 51% women) who had completed surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III (90%) or high-risk stage II (10%) colon cancer. Most patients were from Canada and Australia and were enrolled 2-6 months after completing chemotherapy.
Half of study participants were randomly allocated to a structured exercise program (n = 445) and half to receive standard health education materials promoting physical activity and healthy eating (control individuals, n = 444).
As part of the structured exercise intervention, patients met with a physical activity consultant twice a month for the first 6 months. These sessions included exercise coaching and supervised exercise. Patients could choose their preferred aerobic exercise and most picked brisk walking.
The consultants gave each patient an “exercise prescription” to hit a specific amount of exercise. The target was an additional 10 metabolic equivalent (MET)–hours of aerobic activity per week — about three to four brisk walks each lasting 45-60 minutes. After 6 months, patients met with their consultants once a month, with additional sessions available for extra support if needed.
Structured exercise led to “substantial and sustained” increases in the amount of exercise participants did, as well as physiologic measures of their fitness, with “highly relevant” improvements in VO2 max, 6-minute walk test, and patient-reported physical function, underscoring that participants were not only exercising more but also getting fitter, Booth said.
Exercise was associated with a clinically meaningful and statistically significant 28% reduction in the risk for recurrent or new cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.72; P = .017), with a 5-year disease free survival rate of 80% in the exercise group and 74% in the control group.
In other words, “for every 16 patients that went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from recurrent or new cancer” at 5 years, Booth reported.
Overall survival results were “even more impressive,” he said.
At 8 years, 90% of patients in the exercise program were alive vs 83% of those in the control group, which translated to a 37% lower risk for death (HR, 0.63; P = .022).
“For every 14 patients who went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from dying” at the 8-year mark, Booth noted.
“Notably, this difference in survival was not driven by difference in cardiovascular deaths but by a reduction in the risk of death from colon cancer,” he said.
Besides a slight uptick in musculoskeletal aches, no major safety signals emerged in the exercise group.
It’s important to note that the survival benefit associated with exercise came after patients had received surgery followed by chemotherapy — in other words, exercise did not replace established cancer treatments. It’s also unclear whether initiating an exercise intervention earlier in the treatment trajectory — before surgery or during chemotherapy, instead of after chemotherapy — could further improve cancer outcomes, the authors noted.
Still, “exercise as an intervention is a no brainer and should be implemented broadly,” said ASCO expert Pamela Kunz, MD, with Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut.
Marco Gerlinger, MD, with Barts Cancer Institute, London, England, agreed.
“Oncologists can now make a very clear evidence-based recommendation for patients who just completed their chemotherapy for bowel cancer and are fit enough for such an exercise program,” Gerlinger said in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Centre.
Booth noted that knowledge alone will not be sufficient to allow most patients to change their lifestyle and realize the health benefits.
“The policy implementation piece of this is really key, and we need health systems, hospitals, and payers to invest in these behavior support programs so that patients have access to a physical activity consultant and can realize the health benefits,” he said.
“This intervention is empowering and achievable for patients and with much, much lower cost than many of our therapies. It is also sustainable for health systems,” he concluded.
Diet and Survival
Diet can also affect outcomes in patients with colon cancer.
In the same session describing the CHALLENGE results, Sara Char, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, reported findings showing that consuming a diet high in proinflammatory foods was associated with worse overall survival in patients with stage III colon cancer. A proinflammatory diet includes red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and refined grains, while an anti-inflammatory diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil.
Chronic systemic inflammation has been implicated in both colon cancer development and in its progression, and elevated levels of inflammatory markers in the blood have previously been associated with worse survival outcomes in patients with stage III colon cancer.
Char and colleagues analyzed dietary patterns of a subset of 1625 patients (mean age, 61 years) with resected stage III colon cancer enrolled in the phase 3 CALGB/SWOG 80702 (Alliance) clinical trial, which compared 3 months of adjuvant chemotherapy with 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without the anti-inflammatory medication celecoxib.
As part of the trial, participants reported their diet and exercise habits at various timepoints. Their diets were scored using the validated empirical dietary inflammatory pattern (EDIP) tool, which is a weighted sum of 18 food groups — nine proinflammatory and nine anti-inflammatory. A high EDIP score marks a proinflammatory diet, and a low EDIP score indicates a less inflammatory diet.
During median follow-up of nearly 4 years, researchers noted a trend toward worse disease-free survival in patients with high proinflammatory diets (HR, 1.46), but this association was not significant in the multivariable adjusted model (HR, 1.36; P = .22), Char reported.
However, higher intake of proinflammatory foods was associated with significantly worse overall survival.
Patients who consumed the most proinflammatory foods (top 20%) had an 87% higher risk for death compared with those who consumed the least (bottom 20%; HR, 1.87). The median overall survival in the highest quintile was 7.7 years and was not reached in the lowest quintile.
Combine Exercise and Diet for Best Results
To examine the joint effect of physical activity and diet on overall survival, patients were divided into higher and lower levels of physical activity using a cut-off of 9 MET hours per week, which roughly correlates to 30 minutes of vigorous walking five days a week with a little bit of light yoga, Char explained.
In this analysis, patients with less proinflammatory diets and higher physical activity levels had the best overall survival outcomes, with a 63% lower risk for death compared with peers who consumed more pro-inflammatory diets and exercised less (HR, 0.37; P < .0001).
Daily celecoxib use and low-dose aspirin use (< 100 mg/d) did not affect the association between inflammatory diet and survival.
Char cautioned, that while the EDIP tool is useful to measure the inflammatory potential of a diet, “this is not a dietary recommendation, and we need further studies to be able to tailor our findings into dietary recommendations that can be provided to patients at the bedside.”
Gralow said this “early but promising observational study suggests a powerful synergy: Patients with stage III colon cancer who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly showed the best overall survival compared to those with inflammatory diets and limited exercise.”
The CHALLENGE trial was funded by the Canadian Cancer Society, the National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Research UK, and the University of Sydney Cancer Research Fund. Booth had no disclosures. The diet study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Pfizer, and the Project P Fund. Char disclosed an advisory/consultant role with Goodpath. Kunz, Gralow and Campbell had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can exercise “therapy” and diet improve survival in patients with colon cancer? It appears so, according to two pivotal studies presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
In the CHALLENGE trial, a structured exercise program after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy cut the risk for colon cancer recurrence in patients with stage III and high-risk stage II disease by more than one quarter and the risk for death by more than one third.
“The magnitude of benefit with exercise is substantial. In fact, it is comparable, and in some cases exceeds the magnitude of benefit of many of our very good standard medical therapies in oncology,” study presenter Christopher Booth, MD, with Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, told attendees.
Results of the study were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation at the meeting.
The findings are “nothing short of a major milestone,” said study discussant Peter Campbell, PhD, with Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center, Bronx, New York.
The other study showed that eating a less inflammatory diet may reduce the risk for death in patients with colon cancer, with the greatest benefits seen in those who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly.
“Putting these two abstracts into perspective, we as physicians need to be essentially prescribing healthy diet and exercise. The combination of the two are synergistic,” Julie Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, told attendees.
Despite the benefits of these lifestyle changes, exercise and diet are meant to supplement, not replace, established colon cancer treatments.
It would be a false binary to frame this as lifestyle vs cancer treatment, explained Mark Lewis, MD, director of Gastrointestinal Oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. With exercise, for instance, “the key is giving enough chemo to protect against recurrence and eliminate micrometastases but not so much that we cause neuropathy and reduce function and ability to follow the CHALLENGE structured program,” Lewis said.
Exercise and Survival
Colon cancer remains the second-leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Even with surgery and chemotherapy, roughly 30% of patients with stage III and high-risk stage II colon cancer will experience disease recurrence.
“As oncologists, one of the most common questions we get asked by patients is — what else can I do to improve my outcome?” Booth said.
Observational studies published nearly two decades ago hinted that physically active cancer survivors fare better, but no randomized trial has definitively tested whether exercise could alter disease course. That knowledge gap prompted the Canadian Cancer Trials Group to launch the CHALLENGE trial.
Between 2009 and 2023, the phase 3 study enrolled 889 adults (median age, 61 years; 51% women) who had completed surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III (90%) or high-risk stage II (10%) colon cancer. Most patients were from Canada and Australia and were enrolled 2-6 months after completing chemotherapy.
Half of study participants were randomly allocated to a structured exercise program (n = 445) and half to receive standard health education materials promoting physical activity and healthy eating (control individuals, n = 444).
As part of the structured exercise intervention, patients met with a physical activity consultant twice a month for the first 6 months. These sessions included exercise coaching and supervised exercise. Patients could choose their preferred aerobic exercise and most picked brisk walking.
The consultants gave each patient an “exercise prescription” to hit a specific amount of exercise. The target was an additional 10 metabolic equivalent (MET)–hours of aerobic activity per week — about three to four brisk walks each lasting 45-60 minutes. After 6 months, patients met with their consultants once a month, with additional sessions available for extra support if needed.
Structured exercise led to “substantial and sustained” increases in the amount of exercise participants did, as well as physiologic measures of their fitness, with “highly relevant” improvements in VO2 max, 6-minute walk test, and patient-reported physical function, underscoring that participants were not only exercising more but also getting fitter, Booth said.
Exercise was associated with a clinically meaningful and statistically significant 28% reduction in the risk for recurrent or new cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.72; P = .017), with a 5-year disease free survival rate of 80% in the exercise group and 74% in the control group.
In other words, “for every 16 patients that went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from recurrent or new cancer” at 5 years, Booth reported.
Overall survival results were “even more impressive,” he said.
At 8 years, 90% of patients in the exercise program were alive vs 83% of those in the control group, which translated to a 37% lower risk for death (HR, 0.63; P = .022).
“For every 14 patients who went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from dying” at the 8-year mark, Booth noted.
“Notably, this difference in survival was not driven by difference in cardiovascular deaths but by a reduction in the risk of death from colon cancer,” he said.
Besides a slight uptick in musculoskeletal aches, no major safety signals emerged in the exercise group.
It’s important to note that the survival benefit associated with exercise came after patients had received surgery followed by chemotherapy — in other words, exercise did not replace established cancer treatments. It’s also unclear whether initiating an exercise intervention earlier in the treatment trajectory — before surgery or during chemotherapy, instead of after chemotherapy — could further improve cancer outcomes, the authors noted.
Still, “exercise as an intervention is a no brainer and should be implemented broadly,” said ASCO expert Pamela Kunz, MD, with Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut.
Marco Gerlinger, MD, with Barts Cancer Institute, London, England, agreed.
“Oncologists can now make a very clear evidence-based recommendation for patients who just completed their chemotherapy for bowel cancer and are fit enough for such an exercise program,” Gerlinger said in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Centre.
Booth noted that knowledge alone will not be sufficient to allow most patients to change their lifestyle and realize the health benefits.
“The policy implementation piece of this is really key, and we need health systems, hospitals, and payers to invest in these behavior support programs so that patients have access to a physical activity consultant and can realize the health benefits,” he said.
“This intervention is empowering and achievable for patients and with much, much lower cost than many of our therapies. It is also sustainable for health systems,” he concluded.
Diet and Survival
Diet can also affect outcomes in patients with colon cancer.
In the same session describing the CHALLENGE results, Sara Char, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, reported findings showing that consuming a diet high in proinflammatory foods was associated with worse overall survival in patients with stage III colon cancer. A proinflammatory diet includes red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and refined grains, while an anti-inflammatory diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil.
Chronic systemic inflammation has been implicated in both colon cancer development and in its progression, and elevated levels of inflammatory markers in the blood have previously been associated with worse survival outcomes in patients with stage III colon cancer.
Char and colleagues analyzed dietary patterns of a subset of 1625 patients (mean age, 61 years) with resected stage III colon cancer enrolled in the phase 3 CALGB/SWOG 80702 (Alliance) clinical trial, which compared 3 months of adjuvant chemotherapy with 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without the anti-inflammatory medication celecoxib.
As part of the trial, participants reported their diet and exercise habits at various timepoints. Their diets were scored using the validated empirical dietary inflammatory pattern (EDIP) tool, which is a weighted sum of 18 food groups — nine proinflammatory and nine anti-inflammatory. A high EDIP score marks a proinflammatory diet, and a low EDIP score indicates a less inflammatory diet.
During median follow-up of nearly 4 years, researchers noted a trend toward worse disease-free survival in patients with high proinflammatory diets (HR, 1.46), but this association was not significant in the multivariable adjusted model (HR, 1.36; P = .22), Char reported.
However, higher intake of proinflammatory foods was associated with significantly worse overall survival.
Patients who consumed the most proinflammatory foods (top 20%) had an 87% higher risk for death compared with those who consumed the least (bottom 20%; HR, 1.87). The median overall survival in the highest quintile was 7.7 years and was not reached in the lowest quintile.
Combine Exercise and Diet for Best Results
To examine the joint effect of physical activity and diet on overall survival, patients were divided into higher and lower levels of physical activity using a cut-off of 9 MET hours per week, which roughly correlates to 30 minutes of vigorous walking five days a week with a little bit of light yoga, Char explained.
In this analysis, patients with less proinflammatory diets and higher physical activity levels had the best overall survival outcomes, with a 63% lower risk for death compared with peers who consumed more pro-inflammatory diets and exercised less (HR, 0.37; P < .0001).
Daily celecoxib use and low-dose aspirin use (< 100 mg/d) did not affect the association between inflammatory diet and survival.
Char cautioned, that while the EDIP tool is useful to measure the inflammatory potential of a diet, “this is not a dietary recommendation, and we need further studies to be able to tailor our findings into dietary recommendations that can be provided to patients at the bedside.”
Gralow said this “early but promising observational study suggests a powerful synergy: Patients with stage III colon cancer who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly showed the best overall survival compared to those with inflammatory diets and limited exercise.”
The CHALLENGE trial was funded by the Canadian Cancer Society, the National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Research UK, and the University of Sydney Cancer Research Fund. Booth had no disclosures. The diet study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Pfizer, and the Project P Fund. Char disclosed an advisory/consultant role with Goodpath. Kunz, Gralow and Campbell had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can exercise “therapy” and diet improve survival in patients with colon cancer? It appears so, according to two pivotal studies presented at American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2025 annual meeting.
In the CHALLENGE trial, a structured exercise program after surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy cut the risk for colon cancer recurrence in patients with stage III and high-risk stage II disease by more than one quarter and the risk for death by more than one third.
“The magnitude of benefit with exercise is substantial. In fact, it is comparable, and in some cases exceeds the magnitude of benefit of many of our very good standard medical therapies in oncology,” study presenter Christopher Booth, MD, with Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, told attendees.
Results of the study were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation at the meeting.
The findings are “nothing short of a major milestone,” said study discussant Peter Campbell, PhD, with Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center, Bronx, New York.
The other study showed that eating a less inflammatory diet may reduce the risk for death in patients with colon cancer, with the greatest benefits seen in those who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly.
“Putting these two abstracts into perspective, we as physicians need to be essentially prescribing healthy diet and exercise. The combination of the two are synergistic,” Julie Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, told attendees.
Despite the benefits of these lifestyle changes, exercise and diet are meant to supplement, not replace, established colon cancer treatments.
It would be a false binary to frame this as lifestyle vs cancer treatment, explained Mark Lewis, MD, director of Gastrointestinal Oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, Utah. With exercise, for instance, “the key is giving enough chemo to protect against recurrence and eliminate micrometastases but not so much that we cause neuropathy and reduce function and ability to follow the CHALLENGE structured program,” Lewis said.
Exercise and Survival
Colon cancer remains the second-leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Even with surgery and chemotherapy, roughly 30% of patients with stage III and high-risk stage II colon cancer will experience disease recurrence.
“As oncologists, one of the most common questions we get asked by patients is — what else can I do to improve my outcome?” Booth said.
Observational studies published nearly two decades ago hinted that physically active cancer survivors fare better, but no randomized trial has definitively tested whether exercise could alter disease course. That knowledge gap prompted the Canadian Cancer Trials Group to launch the CHALLENGE trial.
Between 2009 and 2023, the phase 3 study enrolled 889 adults (median age, 61 years; 51% women) who had completed surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III (90%) or high-risk stage II (10%) colon cancer. Most patients were from Canada and Australia and were enrolled 2-6 months after completing chemotherapy.
Half of study participants were randomly allocated to a structured exercise program (n = 445) and half to receive standard health education materials promoting physical activity and healthy eating (control individuals, n = 444).
As part of the structured exercise intervention, patients met with a physical activity consultant twice a month for the first 6 months. These sessions included exercise coaching and supervised exercise. Patients could choose their preferred aerobic exercise and most picked brisk walking.
The consultants gave each patient an “exercise prescription” to hit a specific amount of exercise. The target was an additional 10 metabolic equivalent (MET)–hours of aerobic activity per week — about three to four brisk walks each lasting 45-60 minutes. After 6 months, patients met with their consultants once a month, with additional sessions available for extra support if needed.
Structured exercise led to “substantial and sustained” increases in the amount of exercise participants did, as well as physiologic measures of their fitness, with “highly relevant” improvements in VO2 max, 6-minute walk test, and patient-reported physical function, underscoring that participants were not only exercising more but also getting fitter, Booth said.
Exercise was associated with a clinically meaningful and statistically significant 28% reduction in the risk for recurrent or new cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.72; P = .017), with a 5-year disease free survival rate of 80% in the exercise group and 74% in the control group.
In other words, “for every 16 patients that went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from recurrent or new cancer” at 5 years, Booth reported.
Overall survival results were “even more impressive,” he said.
At 8 years, 90% of patients in the exercise program were alive vs 83% of those in the control group, which translated to a 37% lower risk for death (HR, 0.63; P = .022).
“For every 14 patients who went on the exercise program, exercise prevented 1 person from dying” at the 8-year mark, Booth noted.
“Notably, this difference in survival was not driven by difference in cardiovascular deaths but by a reduction in the risk of death from colon cancer,” he said.
Besides a slight uptick in musculoskeletal aches, no major safety signals emerged in the exercise group.
It’s important to note that the survival benefit associated with exercise came after patients had received surgery followed by chemotherapy — in other words, exercise did not replace established cancer treatments. It’s also unclear whether initiating an exercise intervention earlier in the treatment trajectory — before surgery or during chemotherapy, instead of after chemotherapy — could further improve cancer outcomes, the authors noted.
Still, “exercise as an intervention is a no brainer and should be implemented broadly,” said ASCO expert Pamela Kunz, MD, with Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut.
Marco Gerlinger, MD, with Barts Cancer Institute, London, England, agreed.
“Oncologists can now make a very clear evidence-based recommendation for patients who just completed their chemotherapy for bowel cancer and are fit enough for such an exercise program,” Gerlinger said in a statement from the nonprofit UK Science Media Centre.
Booth noted that knowledge alone will not be sufficient to allow most patients to change their lifestyle and realize the health benefits.
“The policy implementation piece of this is really key, and we need health systems, hospitals, and payers to invest in these behavior support programs so that patients have access to a physical activity consultant and can realize the health benefits,” he said.
“This intervention is empowering and achievable for patients and with much, much lower cost than many of our therapies. It is also sustainable for health systems,” he concluded.
Diet and Survival
Diet can also affect outcomes in patients with colon cancer.
In the same session describing the CHALLENGE results, Sara Char, MD, with Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, reported findings showing that consuming a diet high in proinflammatory foods was associated with worse overall survival in patients with stage III colon cancer. A proinflammatory diet includes red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and refined grains, while an anti-inflammatory diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil.
Chronic systemic inflammation has been implicated in both colon cancer development and in its progression, and elevated levels of inflammatory markers in the blood have previously been associated with worse survival outcomes in patients with stage III colon cancer.
Char and colleagues analyzed dietary patterns of a subset of 1625 patients (mean age, 61 years) with resected stage III colon cancer enrolled in the phase 3 CALGB/SWOG 80702 (Alliance) clinical trial, which compared 3 months of adjuvant chemotherapy with 6 months of adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without the anti-inflammatory medication celecoxib.
As part of the trial, participants reported their diet and exercise habits at various timepoints. Their diets were scored using the validated empirical dietary inflammatory pattern (EDIP) tool, which is a weighted sum of 18 food groups — nine proinflammatory and nine anti-inflammatory. A high EDIP score marks a proinflammatory diet, and a low EDIP score indicates a less inflammatory diet.
During median follow-up of nearly 4 years, researchers noted a trend toward worse disease-free survival in patients with high proinflammatory diets (HR, 1.46), but this association was not significant in the multivariable adjusted model (HR, 1.36; P = .22), Char reported.
However, higher intake of proinflammatory foods was associated with significantly worse overall survival.
Patients who consumed the most proinflammatory foods (top 20%) had an 87% higher risk for death compared with those who consumed the least (bottom 20%; HR, 1.87). The median overall survival in the highest quintile was 7.7 years and was not reached in the lowest quintile.
Combine Exercise and Diet for Best Results
To examine the joint effect of physical activity and diet on overall survival, patients were divided into higher and lower levels of physical activity using a cut-off of 9 MET hours per week, which roughly correlates to 30 minutes of vigorous walking five days a week with a little bit of light yoga, Char explained.
In this analysis, patients with less proinflammatory diets and higher physical activity levels had the best overall survival outcomes, with a 63% lower risk for death compared with peers who consumed more pro-inflammatory diets and exercised less (HR, 0.37; P < .0001).
Daily celecoxib use and low-dose aspirin use (< 100 mg/d) did not affect the association between inflammatory diet and survival.
Char cautioned, that while the EDIP tool is useful to measure the inflammatory potential of a diet, “this is not a dietary recommendation, and we need further studies to be able to tailor our findings into dietary recommendations that can be provided to patients at the bedside.”
Gralow said this “early but promising observational study suggests a powerful synergy: Patients with stage III colon cancer who embraced anti-inflammatory foods and exercised regularly showed the best overall survival compared to those with inflammatory diets and limited exercise.”
The CHALLENGE trial was funded by the Canadian Cancer Society, the National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Research UK, and the University of Sydney Cancer Research Fund. Booth had no disclosures. The diet study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Pfizer, and the Project P Fund. Char disclosed an advisory/consultant role with Goodpath. Kunz, Gralow and Campbell had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Lifestyle Changes Save Lives in Colon Cancer?
Can Lifestyle Changes Save Lives in Colon Cancer?
Genomic Testing Reveals Distinct Mutation Patterns in Black and White Veterans With Metastatic Prostate Cancer
TOPLINE: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of 5015 veterans with metastatic prostate cancer reveals distinct genomic patterns between non-Hispanic Black and White patients, with Black veterans showing higher odds of immunotherapy targets but lower odds of androgen receptor axis alterations. However, the rates of survival were similar despite the differences.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing alteration frequencies between 1784 non-Hispanic Black (35.6%) and 3,231 non-Hispanic White (64.4%) veterans who underwent NGS testing from January 23, 2019, to November 2, 2023.
- Analysis included DNA sequencing data from tissue or plasma biospecimens, including prostate biopsy specimens, radical prostatectomy specimens, and prostate cancer metastases, all sequenced with FoundationOne CDx or FoundationOne Liquid CDx platforms.
- Investigators examined pathogenic alterations in individual genes, actionable targets, and canonical prostate cancer pathways, while adjusting for NGS analyte and clinicopathologic covariates.
- Researchers evaluated associations between alteration frequency and race as well as survival through Cox proportional hazards modeling, stratified by race and adjusted for clinical factors.
TAKEAWAY:
Non-Hispanic Black race and ethnicity was associated with higher odds of genomic alterations in SPOP (odds ratio [OR], 1.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.2-2.6) and immunotherapy targets (OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5), including high microsatellite instability status (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.1-9.4).
- Non-Hispanic Black veterans showed lower odds of genomic alterations in the AKT/PI3K pathway (OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.7), androgen receptor axis (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.9), and tumor suppressor genes (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.8).
- Tumor suppressor alterations were associated with shorter overall survival in both non-Hispanic Black (hazard ratio [HR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.13-2.11) and non-Hispanic White (HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.25-1.85) veterans.
- CDK12 alterations significantly increased the hazard of death in non-Hispanic Black veterans (HR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.13-3.67), while immunotherapy targets were associated with increased mortality in non-Hispanic White veterans (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02-2.02).
IN PRACTICE: " we did not identify any genomic alterations or biomarkers that should not be tested in PCa based on patient self-identified race. Ultimately, this work emphasizes that precision oncology enables the individualization of treatment decisions without having to rely on imprecise characteristics such as self-identified race.," wrote the study authors.
SOURCE: Isla P. Garraway, MD, PhD; Kosj Yamoah, MD, PhD; and Kara N. Maxwell, MD, PhD were co-senior authors. The article was published online on May 12 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, a lack of matched germline data for patients, complicated the interpretation of plasma results. In addition, survivorship bias may have inadvertently excluded the most aggressive metastatic prostate cancer phenotypes, as patients who did not live long enough to undergo NGS testing were not included. Results seen in the veteran population served by the Veterans Health Administration may not be generalizable to the broader population.
DISCLOSURES: The study received support from Challenge Award PCF22CHALO2 from the Prostate Cancer Foundation and the Veterans Affairs National Precision Oncology Program. Luca F. Valle, MD, reported receiving grant support from the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation during the conduct of the study. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of 5015 veterans with metastatic prostate cancer reveals distinct genomic patterns between non-Hispanic Black and White patients, with Black veterans showing higher odds of immunotherapy targets but lower odds of androgen receptor axis alterations. However, the rates of survival were similar despite the differences.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing alteration frequencies between 1784 non-Hispanic Black (35.6%) and 3,231 non-Hispanic White (64.4%) veterans who underwent NGS testing from January 23, 2019, to November 2, 2023.
- Analysis included DNA sequencing data from tissue or plasma biospecimens, including prostate biopsy specimens, radical prostatectomy specimens, and prostate cancer metastases, all sequenced with FoundationOne CDx or FoundationOne Liquid CDx platforms.
- Investigators examined pathogenic alterations in individual genes, actionable targets, and canonical prostate cancer pathways, while adjusting for NGS analyte and clinicopathologic covariates.
- Researchers evaluated associations between alteration frequency and race as well as survival through Cox proportional hazards modeling, stratified by race and adjusted for clinical factors.
TAKEAWAY:
Non-Hispanic Black race and ethnicity was associated with higher odds of genomic alterations in SPOP (odds ratio [OR], 1.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.2-2.6) and immunotherapy targets (OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5), including high microsatellite instability status (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.1-9.4).
- Non-Hispanic Black veterans showed lower odds of genomic alterations in the AKT/PI3K pathway (OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.7), androgen receptor axis (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.9), and tumor suppressor genes (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.8).
- Tumor suppressor alterations were associated with shorter overall survival in both non-Hispanic Black (hazard ratio [HR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.13-2.11) and non-Hispanic White (HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.25-1.85) veterans.
- CDK12 alterations significantly increased the hazard of death in non-Hispanic Black veterans (HR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.13-3.67), while immunotherapy targets were associated with increased mortality in non-Hispanic White veterans (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02-2.02).
IN PRACTICE: " we did not identify any genomic alterations or biomarkers that should not be tested in PCa based on patient self-identified race. Ultimately, this work emphasizes that precision oncology enables the individualization of treatment decisions without having to rely on imprecise characteristics such as self-identified race.," wrote the study authors.
SOURCE: Isla P. Garraway, MD, PhD; Kosj Yamoah, MD, PhD; and Kara N. Maxwell, MD, PhD were co-senior authors. The article was published online on May 12 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, a lack of matched germline data for patients, complicated the interpretation of plasma results. In addition, survivorship bias may have inadvertently excluded the most aggressive metastatic prostate cancer phenotypes, as patients who did not live long enough to undergo NGS testing were not included. Results seen in the veteran population served by the Veterans Health Administration may not be generalizable to the broader population.
DISCLOSURES: The study received support from Challenge Award PCF22CHALO2 from the Prostate Cancer Foundation and the Veterans Affairs National Precision Oncology Program. Luca F. Valle, MD, reported receiving grant support from the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation during the conduct of the study. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of 5015 veterans with metastatic prostate cancer reveals distinct genomic patterns between non-Hispanic Black and White patients, with Black veterans showing higher odds of immunotherapy targets but lower odds of androgen receptor axis alterations. However, the rates of survival were similar despite the differences.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing alteration frequencies between 1784 non-Hispanic Black (35.6%) and 3,231 non-Hispanic White (64.4%) veterans who underwent NGS testing from January 23, 2019, to November 2, 2023.
- Analysis included DNA sequencing data from tissue or plasma biospecimens, including prostate biopsy specimens, radical prostatectomy specimens, and prostate cancer metastases, all sequenced with FoundationOne CDx or FoundationOne Liquid CDx platforms.
- Investigators examined pathogenic alterations in individual genes, actionable targets, and canonical prostate cancer pathways, while adjusting for NGS analyte and clinicopathologic covariates.
- Researchers evaluated associations between alteration frequency and race as well as survival through Cox proportional hazards modeling, stratified by race and adjusted for clinical factors.
TAKEAWAY:
Non-Hispanic Black race and ethnicity was associated with higher odds of genomic alterations in SPOP (odds ratio [OR], 1.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.2-2.6) and immunotherapy targets (OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5), including high microsatellite instability status (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.1-9.4).
- Non-Hispanic Black veterans showed lower odds of genomic alterations in the AKT/PI3K pathway (OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.7), androgen receptor axis (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.9), and tumor suppressor genes (OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.8).
- Tumor suppressor alterations were associated with shorter overall survival in both non-Hispanic Black (hazard ratio [HR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.13-2.11) and non-Hispanic White (HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.25-1.85) veterans.
- CDK12 alterations significantly increased the hazard of death in non-Hispanic Black veterans (HR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.13-3.67), while immunotherapy targets were associated with increased mortality in non-Hispanic White veterans (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02-2.02).
IN PRACTICE: " we did not identify any genomic alterations or biomarkers that should not be tested in PCa based on patient self-identified race. Ultimately, this work emphasizes that precision oncology enables the individualization of treatment decisions without having to rely on imprecise characteristics such as self-identified race.," wrote the study authors.
SOURCE: Isla P. Garraway, MD, PhD; Kosj Yamoah, MD, PhD; and Kara N. Maxwell, MD, PhD were co-senior authors. The article was published online on May 12 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, a lack of matched germline data for patients, complicated the interpretation of plasma results. In addition, survivorship bias may have inadvertently excluded the most aggressive metastatic prostate cancer phenotypes, as patients who did not live long enough to undergo NGS testing were not included. Results seen in the veteran population served by the Veterans Health Administration may not be generalizable to the broader population.
DISCLOSURES: The study received support from Challenge Award PCF22CHALO2 from the Prostate Cancer Foundation and the Veterans Affairs National Precision Oncology Program. Luca F. Valle, MD, reported receiving grant support from the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation during the conduct of the study. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Hurricanes, Fires, Floods: A Rising Threat to Cancer Care
As Hurricane Helene approached western North Carolina, Martin Palmeri, MD, MBA, didn’t anticipate the storm would disrupt practice operations for more than a day or so.
But the massive rainfall and flooding damage last September proved to be far more challenging. Despite best efforts by the 13-physician practice, basic treatments for most patients were interrupted for about a week.
Flooding washed out some of the major roads leading to the main Asheville clinic and affiliated rural sites, limiting travel and slowing delivery of medications, intravenous (IV) fluids, and other supplies, Palmeri said. Some patients and employees weren’t initially reachable due to the loss of the internet and cell phone service. The storm-related fallout even forced patients to relocate elsewhere for weeks or longer.
During the storm, backup generators kept power on at the Asheville clinic, protecting chemotherapy and other refrigerated drugs, but the storm damaged the municipal water supply.
“Water was the number one thing — how do you get water to the office?” Palmeri said. “You can’t give someone an 8-hour infusion if they don’t have means of going to the toilet or having something to drink.”
Hurricanes. Wildfires. Heat waves. As climate-driven extreme weather has become more common, researchers, oncologists, and patients are increasingly being forced to consider the consequences of these disruptions.
Along with preventing patients and providers from reaching treatment sites, experts said, extreme weather can undercut patients’ health and care in other ways. Patients with more limited lung capacity following lung cancer surgery, for instance, may struggle with breathing during wildfires. Extreme heat can prove risky for patients already dehydrated or weakened by treatment-related side effects. Power outages and severe flooding can affect vital infrastructure, disrupting operations at facilities that manufacture essential drugs. Power outages can also impede radiotherapy, which requires machines powered by electricity.
“Any of these [weather] events can disrupt this critical cancer care continuum among a population of people that already are very vulnerable,” said Joan Casey, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist and associate professor at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Extreme Weather and Cancer Survival
For patients with cancer, survival often relies on highly regimented protocols, which may require surgery plus frequent visits for radiation, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy that can last months, said Eric Bernicker, MD, a Colorado oncologist and lead author of a 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology position statement about the impact of climate change on cancer care.
Interruptions to care, regardless of the cause, can lead to worse outcomes for patients, Bernicker said. “If you’re in the middle of your post-lumpectomy radiation and your radiation center shuts for 2 weeks,” he said, “that is not good.”
Research indicated that even short treatment disruptions can affect outcomes for patients with cancer and that delays caused by extreme weather — which may last for weeks — can affect survival for these patients.
One analysis, published in JAMA Oncology in 2023, found that patients exposed to wildfire within the first year after potentially curative lung cancer surgery had worse survival outcomes than those who weren’t exposed during their recovery.
In another study, patients with lung cancer who had their radiation interrupted when a hurricane struck had a 19% greater risk of dying overall compared with similar patients who were not affected. Another analysis found that patients with breast cancer who were partway through treatment when Hurricane Katrina hit the Louisiana coastline had a significantly greater risk of dying over a 10-year period compared with patients who lived elsewhere.
The potential threats to survival highlighted the impacts of extreme weather on carefully orchestrated systems of care that place patients facing already fragile situations in impossible binds, Casey said.
Douglas Flora, MD, a Kentucky oncologist and president-elect of the Association of Cancer Care Centers, Rockville, Maryland, agreed.
“We’ve seen this with an increasing frequency over the last several years,” Flora said. “It’s one thing if it’s routine follow-up or surveillance care, but many cancer patients’ survivals are directly related to not having interruptions in their care.”
Challenging Realities
Following Helene, the most pressing issue was the lack of water, Palmeri said.
The lack of reliable clean water created challenges for patients receiving radiation or chemotherapy infusions, which can cause vomiting and diarrhea that leave patients dehydrated. Toilets were also unusable.
Even when the city of Asheville said the water was likely safe enough to bathe in, local leaders still reported potential risks from bacteria and other contaminants in the water, Palmeri said. Those with a fragile immune system or breaks in the skin “could get serious and life-threatening infections,” he explained.
To make matters worse, damage to a North Carolina facility manufacturing IV fluids left the United States in shortage for months. IV fluids are key not only for providing hydration but also for easing nausea, fatigue, and other issues caused by cancer therapies.
With wildfires, as occurred in southern California early this year, patients undergoing cancer treatment might feel they have no option but to remain near home to continue getting care, Casey said. “It’s restricting their agency in the kinds of choices that they have to make during these severe weather events.”
Meanwhile, thick wildfire smoke can confine patients to their homes, said Lawrence Wagman, MD, a surgical oncologist and a regional medical director at the City of Hope network, who described its main facility in Duarte, California, coming within a dozen miles of the Eaton fire. “One of the biggest problems was so much smoke in the air,” he said. “And the air quality was so low that it was, in many ways, dangerous for patients to travel.”
“These fires were so aggressive, and they kept popping up,” Wagman said. Plus, the emotional strain of looming wildfires persisted for both patients and cancer clinicians for weeks on end, he added.
For those who evacuate, the logistics can be complex.
Not only are cancer treatment plans highly structured, but switching care to another facility is far from easy, Bernicker said. The new facility will likely need to submit a treatment plan and get insurance coverage before moving forward.
“I’m not saying that takes forever,” he said. “But what I’m saying is that it’s not like you just roll in and they hang the [infusion] bag.”
Neither is a shelter typically an option for patients during treatment, said Seth Berkowitz, a licensed clinical social worker and director of Strategic Healthcare Partnerships at The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. “They have to have a place to go that’s safe and germ-free.”
In western North Carolina, the strain on already ill patients and their caregivers could be overwhelming, Palmeri said. He recounted how the husband of one patient with advanced cancer died after the storm came through.
“He tried to go out there with a chainsaw to clear a way out so that they could get out of their house in case he needed to take her to the hospital,” Palmeri said. “And he had a heart attack there in the driveway.”
Rebuilding and Planning Ahead
Experts are only at the early stages of grasping the magnitude of extreme weather on cancer care and developing strategies to curtail care gaps and potential harm to patients, said Katie Lichter, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of California San Francisco, who studies extreme weather and cancer treatment.
“How does it impact health care delivery services at every step, from prevention to screening to treatment and survivorship?” Lichter asked. “We’re just starting to understand and to even quantify that,” she said, which included identifying patients who are most vulnerable. She worries, in particular, about patients living in rural areas who already travel longer distances and often face more difficulties accessing care.
The gap between research and reality still looms large. A recent analysis, led by Lichter, looked at 176 California radiation oncology clinics and found that all of them were located within 25 miles of a wildfire that had occurred within the prior 5 years. Yet among the 51 clinics that responded to a 2022 survey,just 47% reported that their clinic had a wildfire emergency preparedness plan.
The American Cancer Society does provide some guidance on how patients can prepare for a weather-related crisis, including having extra supplies of medications or special equipment on hand.
Still, providers are often in reaction mode when extreme weather strikes.
Without adequate clean water after Helene, leaders at Palmeri’s practice moved swiftly, purchasing 40,000-50,000 bottles of water and bringing in porta potties from elsewhere.
“I think we were able to get things up and going very quickly,” said Palmeri, who noted that full services resumed about 10 days after the storm. “For most patients, missing a week of treatment would not do a disservice to their well-being or outcome.”
Going forward, to provide a more comprehensive strategy, Lichter is working with colleagues to develop clinical tool kits to help oncology practices and patients prepare for severe weather events, such as outlining backup treatment contingency plans, ensuring early medication refills, and boosting communication with patient alert systems.
Clinicians are also implementing their own strategies. To limit communication gaps during power outages, Palmeri said that, since Helene, his practice has made sure that their clinic sites, physicians, and other key people now have cell phone service through satellite via Starlink.
“No one has phone books anymore,” he said, so cancer clinicians should keep crucial contact information on paper, such as details about businesses that distribute water and porta potties, given that online searches may not be feasible.
Clinicians should also advise patients to keep a hard copy of recent medical findings handy, including medications and lab results, in case they arrive at an emergency room far from home and physicians can’t access their electronic health record, Bernicker said.
When there is enough advance warning of an approaching weather event, clinicians can help patients keep at least a week’s worth of medication on hand for symptom-related issues, such as nausea or pain, as well as antibiotics so patients don’t have to seek out emergency care during the crisis, Bernicker said. However, Bernicker noted, some insurers may be reluctant to fill certain prescriptions in advance, like those for opioids.
Making headway on more robust preparedness strategies may be slowed. As of March, the National Institutes of Health will no longer fund research about the health effects of climate change.
Bernicker hoped that such cutbacks would be rolled back. What’s on the line, he stressed, is maintaining the highest quality of care for patients with cancer.
“We really are in a golden age of oncology therapeutics,” he said. “We have patients living longer than anyone would have predicted 20 or 25 years ago. But all those advances are contingent on people having access to their centers and not having that interrupted.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As Hurricane Helene approached western North Carolina, Martin Palmeri, MD, MBA, didn’t anticipate the storm would disrupt practice operations for more than a day or so.
But the massive rainfall and flooding damage last September proved to be far more challenging. Despite best efforts by the 13-physician practice, basic treatments for most patients were interrupted for about a week.
Flooding washed out some of the major roads leading to the main Asheville clinic and affiliated rural sites, limiting travel and slowing delivery of medications, intravenous (IV) fluids, and other supplies, Palmeri said. Some patients and employees weren’t initially reachable due to the loss of the internet and cell phone service. The storm-related fallout even forced patients to relocate elsewhere for weeks or longer.
During the storm, backup generators kept power on at the Asheville clinic, protecting chemotherapy and other refrigerated drugs, but the storm damaged the municipal water supply.
“Water was the number one thing — how do you get water to the office?” Palmeri said. “You can’t give someone an 8-hour infusion if they don’t have means of going to the toilet or having something to drink.”
Hurricanes. Wildfires. Heat waves. As climate-driven extreme weather has become more common, researchers, oncologists, and patients are increasingly being forced to consider the consequences of these disruptions.
Along with preventing patients and providers from reaching treatment sites, experts said, extreme weather can undercut patients’ health and care in other ways. Patients with more limited lung capacity following lung cancer surgery, for instance, may struggle with breathing during wildfires. Extreme heat can prove risky for patients already dehydrated or weakened by treatment-related side effects. Power outages and severe flooding can affect vital infrastructure, disrupting operations at facilities that manufacture essential drugs. Power outages can also impede radiotherapy, which requires machines powered by electricity.
“Any of these [weather] events can disrupt this critical cancer care continuum among a population of people that already are very vulnerable,” said Joan Casey, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist and associate professor at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Extreme Weather and Cancer Survival
For patients with cancer, survival often relies on highly regimented protocols, which may require surgery plus frequent visits for radiation, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy that can last months, said Eric Bernicker, MD, a Colorado oncologist and lead author of a 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology position statement about the impact of climate change on cancer care.
Interruptions to care, regardless of the cause, can lead to worse outcomes for patients, Bernicker said. “If you’re in the middle of your post-lumpectomy radiation and your radiation center shuts for 2 weeks,” he said, “that is not good.”
Research indicated that even short treatment disruptions can affect outcomes for patients with cancer and that delays caused by extreme weather — which may last for weeks — can affect survival for these patients.
One analysis, published in JAMA Oncology in 2023, found that patients exposed to wildfire within the first year after potentially curative lung cancer surgery had worse survival outcomes than those who weren’t exposed during their recovery.
In another study, patients with lung cancer who had their radiation interrupted when a hurricane struck had a 19% greater risk of dying overall compared with similar patients who were not affected. Another analysis found that patients with breast cancer who were partway through treatment when Hurricane Katrina hit the Louisiana coastline had a significantly greater risk of dying over a 10-year period compared with patients who lived elsewhere.
The potential threats to survival highlighted the impacts of extreme weather on carefully orchestrated systems of care that place patients facing already fragile situations in impossible binds, Casey said.
Douglas Flora, MD, a Kentucky oncologist and president-elect of the Association of Cancer Care Centers, Rockville, Maryland, agreed.
“We’ve seen this with an increasing frequency over the last several years,” Flora said. “It’s one thing if it’s routine follow-up or surveillance care, but many cancer patients’ survivals are directly related to not having interruptions in their care.”
Challenging Realities
Following Helene, the most pressing issue was the lack of water, Palmeri said.
The lack of reliable clean water created challenges for patients receiving radiation or chemotherapy infusions, which can cause vomiting and diarrhea that leave patients dehydrated. Toilets were also unusable.
Even when the city of Asheville said the water was likely safe enough to bathe in, local leaders still reported potential risks from bacteria and other contaminants in the water, Palmeri said. Those with a fragile immune system or breaks in the skin “could get serious and life-threatening infections,” he explained.
To make matters worse, damage to a North Carolina facility manufacturing IV fluids left the United States in shortage for months. IV fluids are key not only for providing hydration but also for easing nausea, fatigue, and other issues caused by cancer therapies.
With wildfires, as occurred in southern California early this year, patients undergoing cancer treatment might feel they have no option but to remain near home to continue getting care, Casey said. “It’s restricting their agency in the kinds of choices that they have to make during these severe weather events.”
Meanwhile, thick wildfire smoke can confine patients to their homes, said Lawrence Wagman, MD, a surgical oncologist and a regional medical director at the City of Hope network, who described its main facility in Duarte, California, coming within a dozen miles of the Eaton fire. “One of the biggest problems was so much smoke in the air,” he said. “And the air quality was so low that it was, in many ways, dangerous for patients to travel.”
“These fires were so aggressive, and they kept popping up,” Wagman said. Plus, the emotional strain of looming wildfires persisted for both patients and cancer clinicians for weeks on end, he added.
For those who evacuate, the logistics can be complex.
Not only are cancer treatment plans highly structured, but switching care to another facility is far from easy, Bernicker said. The new facility will likely need to submit a treatment plan and get insurance coverage before moving forward.
“I’m not saying that takes forever,” he said. “But what I’m saying is that it’s not like you just roll in and they hang the [infusion] bag.”
Neither is a shelter typically an option for patients during treatment, said Seth Berkowitz, a licensed clinical social worker and director of Strategic Healthcare Partnerships at The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. “They have to have a place to go that’s safe and germ-free.”
In western North Carolina, the strain on already ill patients and their caregivers could be overwhelming, Palmeri said. He recounted how the husband of one patient with advanced cancer died after the storm came through.
“He tried to go out there with a chainsaw to clear a way out so that they could get out of their house in case he needed to take her to the hospital,” Palmeri said. “And he had a heart attack there in the driveway.”
Rebuilding and Planning Ahead
Experts are only at the early stages of grasping the magnitude of extreme weather on cancer care and developing strategies to curtail care gaps and potential harm to patients, said Katie Lichter, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of California San Francisco, who studies extreme weather and cancer treatment.
“How does it impact health care delivery services at every step, from prevention to screening to treatment and survivorship?” Lichter asked. “We’re just starting to understand and to even quantify that,” she said, which included identifying patients who are most vulnerable. She worries, in particular, about patients living in rural areas who already travel longer distances and often face more difficulties accessing care.
The gap between research and reality still looms large. A recent analysis, led by Lichter, looked at 176 California radiation oncology clinics and found that all of them were located within 25 miles of a wildfire that had occurred within the prior 5 years. Yet among the 51 clinics that responded to a 2022 survey,just 47% reported that their clinic had a wildfire emergency preparedness plan.
The American Cancer Society does provide some guidance on how patients can prepare for a weather-related crisis, including having extra supplies of medications or special equipment on hand.
Still, providers are often in reaction mode when extreme weather strikes.
Without adequate clean water after Helene, leaders at Palmeri’s practice moved swiftly, purchasing 40,000-50,000 bottles of water and bringing in porta potties from elsewhere.
“I think we were able to get things up and going very quickly,” said Palmeri, who noted that full services resumed about 10 days after the storm. “For most patients, missing a week of treatment would not do a disservice to their well-being or outcome.”
Going forward, to provide a more comprehensive strategy, Lichter is working with colleagues to develop clinical tool kits to help oncology practices and patients prepare for severe weather events, such as outlining backup treatment contingency plans, ensuring early medication refills, and boosting communication with patient alert systems.
Clinicians are also implementing their own strategies. To limit communication gaps during power outages, Palmeri said that, since Helene, his practice has made sure that their clinic sites, physicians, and other key people now have cell phone service through satellite via Starlink.
“No one has phone books anymore,” he said, so cancer clinicians should keep crucial contact information on paper, such as details about businesses that distribute water and porta potties, given that online searches may not be feasible.
Clinicians should also advise patients to keep a hard copy of recent medical findings handy, including medications and lab results, in case they arrive at an emergency room far from home and physicians can’t access their electronic health record, Bernicker said.
When there is enough advance warning of an approaching weather event, clinicians can help patients keep at least a week’s worth of medication on hand for symptom-related issues, such as nausea or pain, as well as antibiotics so patients don’t have to seek out emergency care during the crisis, Bernicker said. However, Bernicker noted, some insurers may be reluctant to fill certain prescriptions in advance, like those for opioids.
Making headway on more robust preparedness strategies may be slowed. As of March, the National Institutes of Health will no longer fund research about the health effects of climate change.
Bernicker hoped that such cutbacks would be rolled back. What’s on the line, he stressed, is maintaining the highest quality of care for patients with cancer.
“We really are in a golden age of oncology therapeutics,” he said. “We have patients living longer than anyone would have predicted 20 or 25 years ago. But all those advances are contingent on people having access to their centers and not having that interrupted.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As Hurricane Helene approached western North Carolina, Martin Palmeri, MD, MBA, didn’t anticipate the storm would disrupt practice operations for more than a day or so.
But the massive rainfall and flooding damage last September proved to be far more challenging. Despite best efforts by the 13-physician practice, basic treatments for most patients were interrupted for about a week.
Flooding washed out some of the major roads leading to the main Asheville clinic and affiliated rural sites, limiting travel and slowing delivery of medications, intravenous (IV) fluids, and other supplies, Palmeri said. Some patients and employees weren’t initially reachable due to the loss of the internet and cell phone service. The storm-related fallout even forced patients to relocate elsewhere for weeks or longer.
During the storm, backup generators kept power on at the Asheville clinic, protecting chemotherapy and other refrigerated drugs, but the storm damaged the municipal water supply.
“Water was the number one thing — how do you get water to the office?” Palmeri said. “You can’t give someone an 8-hour infusion if they don’t have means of going to the toilet or having something to drink.”
Hurricanes. Wildfires. Heat waves. As climate-driven extreme weather has become more common, researchers, oncologists, and patients are increasingly being forced to consider the consequences of these disruptions.
Along with preventing patients and providers from reaching treatment sites, experts said, extreme weather can undercut patients’ health and care in other ways. Patients with more limited lung capacity following lung cancer surgery, for instance, may struggle with breathing during wildfires. Extreme heat can prove risky for patients already dehydrated or weakened by treatment-related side effects. Power outages and severe flooding can affect vital infrastructure, disrupting operations at facilities that manufacture essential drugs. Power outages can also impede radiotherapy, which requires machines powered by electricity.
“Any of these [weather] events can disrupt this critical cancer care continuum among a population of people that already are very vulnerable,” said Joan Casey, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist and associate professor at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Extreme Weather and Cancer Survival
For patients with cancer, survival often relies on highly regimented protocols, which may require surgery plus frequent visits for radiation, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy that can last months, said Eric Bernicker, MD, a Colorado oncologist and lead author of a 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology position statement about the impact of climate change on cancer care.
Interruptions to care, regardless of the cause, can lead to worse outcomes for patients, Bernicker said. “If you’re in the middle of your post-lumpectomy radiation and your radiation center shuts for 2 weeks,” he said, “that is not good.”
Research indicated that even short treatment disruptions can affect outcomes for patients with cancer and that delays caused by extreme weather — which may last for weeks — can affect survival for these patients.
One analysis, published in JAMA Oncology in 2023, found that patients exposed to wildfire within the first year after potentially curative lung cancer surgery had worse survival outcomes than those who weren’t exposed during their recovery.
In another study, patients with lung cancer who had their radiation interrupted when a hurricane struck had a 19% greater risk of dying overall compared with similar patients who were not affected. Another analysis found that patients with breast cancer who were partway through treatment when Hurricane Katrina hit the Louisiana coastline had a significantly greater risk of dying over a 10-year period compared with patients who lived elsewhere.
The potential threats to survival highlighted the impacts of extreme weather on carefully orchestrated systems of care that place patients facing already fragile situations in impossible binds, Casey said.
Douglas Flora, MD, a Kentucky oncologist and president-elect of the Association of Cancer Care Centers, Rockville, Maryland, agreed.
“We’ve seen this with an increasing frequency over the last several years,” Flora said. “It’s one thing if it’s routine follow-up or surveillance care, but many cancer patients’ survivals are directly related to not having interruptions in their care.”
Challenging Realities
Following Helene, the most pressing issue was the lack of water, Palmeri said.
The lack of reliable clean water created challenges for patients receiving radiation or chemotherapy infusions, which can cause vomiting and diarrhea that leave patients dehydrated. Toilets were also unusable.
Even when the city of Asheville said the water was likely safe enough to bathe in, local leaders still reported potential risks from bacteria and other contaminants in the water, Palmeri said. Those with a fragile immune system or breaks in the skin “could get serious and life-threatening infections,” he explained.
To make matters worse, damage to a North Carolina facility manufacturing IV fluids left the United States in shortage for months. IV fluids are key not only for providing hydration but also for easing nausea, fatigue, and other issues caused by cancer therapies.
With wildfires, as occurred in southern California early this year, patients undergoing cancer treatment might feel they have no option but to remain near home to continue getting care, Casey said. “It’s restricting their agency in the kinds of choices that they have to make during these severe weather events.”
Meanwhile, thick wildfire smoke can confine patients to their homes, said Lawrence Wagman, MD, a surgical oncologist and a regional medical director at the City of Hope network, who described its main facility in Duarte, California, coming within a dozen miles of the Eaton fire. “One of the biggest problems was so much smoke in the air,” he said. “And the air quality was so low that it was, in many ways, dangerous for patients to travel.”
“These fires were so aggressive, and they kept popping up,” Wagman said. Plus, the emotional strain of looming wildfires persisted for both patients and cancer clinicians for weeks on end, he added.
For those who evacuate, the logistics can be complex.
Not only are cancer treatment plans highly structured, but switching care to another facility is far from easy, Bernicker said. The new facility will likely need to submit a treatment plan and get insurance coverage before moving forward.
“I’m not saying that takes forever,” he said. “But what I’m saying is that it’s not like you just roll in and they hang the [infusion] bag.”
Neither is a shelter typically an option for patients during treatment, said Seth Berkowitz, a licensed clinical social worker and director of Strategic Healthcare Partnerships at The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. “They have to have a place to go that’s safe and germ-free.”
In western North Carolina, the strain on already ill patients and their caregivers could be overwhelming, Palmeri said. He recounted how the husband of one patient with advanced cancer died after the storm came through.
“He tried to go out there with a chainsaw to clear a way out so that they could get out of their house in case he needed to take her to the hospital,” Palmeri said. “And he had a heart attack there in the driveway.”
Rebuilding and Planning Ahead
Experts are only at the early stages of grasping the magnitude of extreme weather on cancer care and developing strategies to curtail care gaps and potential harm to patients, said Katie Lichter, MD, a radiation oncologist at the University of California San Francisco, who studies extreme weather and cancer treatment.
“How does it impact health care delivery services at every step, from prevention to screening to treatment and survivorship?” Lichter asked. “We’re just starting to understand and to even quantify that,” she said, which included identifying patients who are most vulnerable. She worries, in particular, about patients living in rural areas who already travel longer distances and often face more difficulties accessing care.
The gap between research and reality still looms large. A recent analysis, led by Lichter, looked at 176 California radiation oncology clinics and found that all of them were located within 25 miles of a wildfire that had occurred within the prior 5 years. Yet among the 51 clinics that responded to a 2022 survey,just 47% reported that their clinic had a wildfire emergency preparedness plan.
The American Cancer Society does provide some guidance on how patients can prepare for a weather-related crisis, including having extra supplies of medications or special equipment on hand.
Still, providers are often in reaction mode when extreme weather strikes.
Without adequate clean water after Helene, leaders at Palmeri’s practice moved swiftly, purchasing 40,000-50,000 bottles of water and bringing in porta potties from elsewhere.
“I think we were able to get things up and going very quickly,” said Palmeri, who noted that full services resumed about 10 days after the storm. “For most patients, missing a week of treatment would not do a disservice to their well-being or outcome.”
Going forward, to provide a more comprehensive strategy, Lichter is working with colleagues to develop clinical tool kits to help oncology practices and patients prepare for severe weather events, such as outlining backup treatment contingency plans, ensuring early medication refills, and boosting communication with patient alert systems.
Clinicians are also implementing their own strategies. To limit communication gaps during power outages, Palmeri said that, since Helene, his practice has made sure that their clinic sites, physicians, and other key people now have cell phone service through satellite via Starlink.
“No one has phone books anymore,” he said, so cancer clinicians should keep crucial contact information on paper, such as details about businesses that distribute water and porta potties, given that online searches may not be feasible.
Clinicians should also advise patients to keep a hard copy of recent medical findings handy, including medications and lab results, in case they arrive at an emergency room far from home and physicians can’t access their electronic health record, Bernicker said.
When there is enough advance warning of an approaching weather event, clinicians can help patients keep at least a week’s worth of medication on hand for symptom-related issues, such as nausea or pain, as well as antibiotics so patients don’t have to seek out emergency care during the crisis, Bernicker said. However, Bernicker noted, some insurers may be reluctant to fill certain prescriptions in advance, like those for opioids.
Making headway on more robust preparedness strategies may be slowed. As of March, the National Institutes of Health will no longer fund research about the health effects of climate change.
Bernicker hoped that such cutbacks would be rolled back. What’s on the line, he stressed, is maintaining the highest quality of care for patients with cancer.
“We really are in a golden age of oncology therapeutics,” he said. “We have patients living longer than anyone would have predicted 20 or 25 years ago. But all those advances are contingent on people having access to their centers and not having that interrupted.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many Early-Onset Cancers Increasing, Particularly in Women
Rates of certain cancers in the United States — including breast, colorectal, and thyroid cancers — increased between 2010 and 2019 among patients aged less than 50 years, while overall cancer incidence and mortality rates did not increase, a new study found.
Among the more than two million cases of early-onset cancer diagnosed during this period, 63.2% were in women, researchers reported recently in Cancer Discovery.
Breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma were the most common early-onset cancers in women. Among men, the most common were colorectal cancer, testicular cancer, and melanoma.
Researchers from the National Cancer Institute analyzed cancer incidence data from the United States Cancer Statistics database for 2010-2019 and national death certificate data from the National Center for Health Statistics from 2010 to 2022. The team excluded incidence data from 2020 and 2021, which was artificially low due to COVID.
The researchers divided the data according to age groups: The early-onset age groups were 15-29, 30-39, and 40-49 years, and the late-onset groups were 50-59, 60-69, and 70-79 years. The team also estimated the expected number of early-onset cases in 2019 by multiplying 2010 age-specific cancer incidence rates by population counts for 2019.
First author Meredith Shiels, of the National Cancer Institute, and colleagues found that the largest absolute increase in incidence of early-onset cancers, compared with expected incidence, were for breast (n = 4834 additional cancers), colorectal (n = 2099), kidney (n = 1793), and uterine cancers (n = 1209). These diagnoses accounted for 80% of the additional cancer diagnoses in 2019 vs 2010.
Looking at increases by age group, Shiels and colleagues reported that 1.9% of all cancers occurred in overall early-onset cohort 15- to 49-year-olds (age-standardized incidence rate of 39.8 per 100,000), and the incidence was greater in the older cohorts: 3.6% for 30- to 39-year-olds (123.5 per 100,000) and 8.8% for 40- to 49-year-olds (293.9 per 100,000).
Overall, 14 of 33 cancer types significantly increased in incidence in at least one early-onset age group. Among these 14 cancer types, five — melanoma, plasma cell neoplasms, cervical cancer, stomach cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — showed increases only in early-onset age groups, not in late-onset age groups. For example, between 2010 and 2019, cervical cancer rates increased by 1.39% per year among 30- to 39-year-olds, melanoma rates increased by 0.82% per year among 40- to 49-year-olds, and stomach cancer rates increased by 1.38% per year.
The remaining nine cancer types increased in at least one early-onset and one late-onset group. These included female breast, colorectal, kidney, testicular, uterine, pancreatic cancers as well as precursor B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome.
For four of the 14 cancer types with increasing incidence rates — testicular cancer, uterine cancer, colorectal cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — mortality also increased in at least one early-onset age group, whereas the remaining 10 cancer types increased in incidence without an increase in mortality for any age group.
Shiels and her colleagues aren’t the first to address the rising incidence of early-onset cancers. In a keynote lecture at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 Annual Meeting, Irit Ben-Aharon, MD, PhD, from the Rambam Health Care Campus in Haifa, Israel, noted that from 1990-2019, the global incidence of early-onset cancer increased by 79%.
Although the current study doesn’t identify drivers of rising cancer rates in younger patients, “descriptive data like these provide a critical starting point for understanding the drivers of rising rates of cancer in early-onset age groups and could translate to effective cancer prevention and early detection efforts,” Shiels said in a press release. For instance, “recent guidelines have lowered the age of initiation for breast and colorectal cancer screening based, at least partially, on observations that rates for these cancers are increasing at younger ages.”
This study is “a great step forward” toward understanding the increasing incidence of early-onset cancers, agreed Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who wasn’t involved in the research.
The investigators provide new details, particularly by breaking down the early- and late-onset age groups into subcategories and by comparing incidence and mortality rates, Ogino noted.
“Mortality is a great endpoint because if the increased in early incidence is just an effect of [increased] screening we won’t see a mortality increase,” Ogino said. But “we need more data and some way to tease out the screening effect.” Plus, he added, “we need more mechanistic studies and tissue-based analyses to determine if early-onset cancers that are increasing in incidence are a different beast, rather than just an earlier beast.”
This study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and the Institute of Cancer Research. Shiels declared no conflicts of interest.
version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of certain cancers in the United States — including breast, colorectal, and thyroid cancers — increased between 2010 and 2019 among patients aged less than 50 years, while overall cancer incidence and mortality rates did not increase, a new study found.
Among the more than two million cases of early-onset cancer diagnosed during this period, 63.2% were in women, researchers reported recently in Cancer Discovery.
Breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma were the most common early-onset cancers in women. Among men, the most common were colorectal cancer, testicular cancer, and melanoma.
Researchers from the National Cancer Institute analyzed cancer incidence data from the United States Cancer Statistics database for 2010-2019 and national death certificate data from the National Center for Health Statistics from 2010 to 2022. The team excluded incidence data from 2020 and 2021, which was artificially low due to COVID.
The researchers divided the data according to age groups: The early-onset age groups were 15-29, 30-39, and 40-49 years, and the late-onset groups were 50-59, 60-69, and 70-79 years. The team also estimated the expected number of early-onset cases in 2019 by multiplying 2010 age-specific cancer incidence rates by population counts for 2019.
First author Meredith Shiels, of the National Cancer Institute, and colleagues found that the largest absolute increase in incidence of early-onset cancers, compared with expected incidence, were for breast (n = 4834 additional cancers), colorectal (n = 2099), kidney (n = 1793), and uterine cancers (n = 1209). These diagnoses accounted for 80% of the additional cancer diagnoses in 2019 vs 2010.
Looking at increases by age group, Shiels and colleagues reported that 1.9% of all cancers occurred in overall early-onset cohort 15- to 49-year-olds (age-standardized incidence rate of 39.8 per 100,000), and the incidence was greater in the older cohorts: 3.6% for 30- to 39-year-olds (123.5 per 100,000) and 8.8% for 40- to 49-year-olds (293.9 per 100,000).
Overall, 14 of 33 cancer types significantly increased in incidence in at least one early-onset age group. Among these 14 cancer types, five — melanoma, plasma cell neoplasms, cervical cancer, stomach cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — showed increases only in early-onset age groups, not in late-onset age groups. For example, between 2010 and 2019, cervical cancer rates increased by 1.39% per year among 30- to 39-year-olds, melanoma rates increased by 0.82% per year among 40- to 49-year-olds, and stomach cancer rates increased by 1.38% per year.
The remaining nine cancer types increased in at least one early-onset and one late-onset group. These included female breast, colorectal, kidney, testicular, uterine, pancreatic cancers as well as precursor B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome.
For four of the 14 cancer types with increasing incidence rates — testicular cancer, uterine cancer, colorectal cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — mortality also increased in at least one early-onset age group, whereas the remaining 10 cancer types increased in incidence without an increase in mortality for any age group.
Shiels and her colleagues aren’t the first to address the rising incidence of early-onset cancers. In a keynote lecture at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 Annual Meeting, Irit Ben-Aharon, MD, PhD, from the Rambam Health Care Campus in Haifa, Israel, noted that from 1990-2019, the global incidence of early-onset cancer increased by 79%.
Although the current study doesn’t identify drivers of rising cancer rates in younger patients, “descriptive data like these provide a critical starting point for understanding the drivers of rising rates of cancer in early-onset age groups and could translate to effective cancer prevention and early detection efforts,” Shiels said in a press release. For instance, “recent guidelines have lowered the age of initiation for breast and colorectal cancer screening based, at least partially, on observations that rates for these cancers are increasing at younger ages.”
This study is “a great step forward” toward understanding the increasing incidence of early-onset cancers, agreed Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who wasn’t involved in the research.
The investigators provide new details, particularly by breaking down the early- and late-onset age groups into subcategories and by comparing incidence and mortality rates, Ogino noted.
“Mortality is a great endpoint because if the increased in early incidence is just an effect of [increased] screening we won’t see a mortality increase,” Ogino said. But “we need more data and some way to tease out the screening effect.” Plus, he added, “we need more mechanistic studies and tissue-based analyses to determine if early-onset cancers that are increasing in incidence are a different beast, rather than just an earlier beast.”
This study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and the Institute of Cancer Research. Shiels declared no conflicts of interest.
version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of certain cancers in the United States — including breast, colorectal, and thyroid cancers — increased between 2010 and 2019 among patients aged less than 50 years, while overall cancer incidence and mortality rates did not increase, a new study found.
Among the more than two million cases of early-onset cancer diagnosed during this period, 63.2% were in women, researchers reported recently in Cancer Discovery.
Breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma were the most common early-onset cancers in women. Among men, the most common were colorectal cancer, testicular cancer, and melanoma.
Researchers from the National Cancer Institute analyzed cancer incidence data from the United States Cancer Statistics database for 2010-2019 and national death certificate data from the National Center for Health Statistics from 2010 to 2022. The team excluded incidence data from 2020 and 2021, which was artificially low due to COVID.
The researchers divided the data according to age groups: The early-onset age groups were 15-29, 30-39, and 40-49 years, and the late-onset groups were 50-59, 60-69, and 70-79 years. The team also estimated the expected number of early-onset cases in 2019 by multiplying 2010 age-specific cancer incidence rates by population counts for 2019.
First author Meredith Shiels, of the National Cancer Institute, and colleagues found that the largest absolute increase in incidence of early-onset cancers, compared with expected incidence, were for breast (n = 4834 additional cancers), colorectal (n = 2099), kidney (n = 1793), and uterine cancers (n = 1209). These diagnoses accounted for 80% of the additional cancer diagnoses in 2019 vs 2010.
Looking at increases by age group, Shiels and colleagues reported that 1.9% of all cancers occurred in overall early-onset cohort 15- to 49-year-olds (age-standardized incidence rate of 39.8 per 100,000), and the incidence was greater in the older cohorts: 3.6% for 30- to 39-year-olds (123.5 per 100,000) and 8.8% for 40- to 49-year-olds (293.9 per 100,000).
Overall, 14 of 33 cancer types significantly increased in incidence in at least one early-onset age group. Among these 14 cancer types, five — melanoma, plasma cell neoplasms, cervical cancer, stomach cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — showed increases only in early-onset age groups, not in late-onset age groups. For example, between 2010 and 2019, cervical cancer rates increased by 1.39% per year among 30- to 39-year-olds, melanoma rates increased by 0.82% per year among 40- to 49-year-olds, and stomach cancer rates increased by 1.38% per year.
The remaining nine cancer types increased in at least one early-onset and one late-onset group. These included female breast, colorectal, kidney, testicular, uterine, pancreatic cancers as well as precursor B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome.
For four of the 14 cancer types with increasing incidence rates — testicular cancer, uterine cancer, colorectal cancer, and cancer of the bones and joints — mortality also increased in at least one early-onset age group, whereas the remaining 10 cancer types increased in incidence without an increase in mortality for any age group.
Shiels and her colleagues aren’t the first to address the rising incidence of early-onset cancers. In a keynote lecture at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 Annual Meeting, Irit Ben-Aharon, MD, PhD, from the Rambam Health Care Campus in Haifa, Israel, noted that from 1990-2019, the global incidence of early-onset cancer increased by 79%.
Although the current study doesn’t identify drivers of rising cancer rates in younger patients, “descriptive data like these provide a critical starting point for understanding the drivers of rising rates of cancer in early-onset age groups and could translate to effective cancer prevention and early detection efforts,” Shiels said in a press release. For instance, “recent guidelines have lowered the age of initiation for breast and colorectal cancer screening based, at least partially, on observations that rates for these cancers are increasing at younger ages.”
This study is “a great step forward” toward understanding the increasing incidence of early-onset cancers, agreed Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who wasn’t involved in the research.
The investigators provide new details, particularly by breaking down the early- and late-onset age groups into subcategories and by comparing incidence and mortality rates, Ogino noted.
“Mortality is a great endpoint because if the increased in early incidence is just an effect of [increased] screening we won’t see a mortality increase,” Ogino said. But “we need more data and some way to tease out the screening effect.” Plus, he added, “we need more mechanistic studies and tissue-based analyses to determine if early-onset cancers that are increasing in incidence are a different beast, rather than just an earlier beast.”
This study was funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and the Institute of Cancer Research. Shiels declared no conflicts of interest.
version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Community Care Radiation Oncology Cost Calculations for a VA Medical Center
Community Care Radiation Oncology Cost Calculations for a VA Medical Center
William Kissick’s description of health care’s iron triangle in 1994 still resonates. Access, quality, and cost will always come at the expense of the others.1 In 2018, Congress passed the VA MISSION Act, allowing patients to pursue community care options for extended waits (> 28 days) or longer distance drive times of > 60 minutes for specialty care services, such as radiation oncology. According to Albanese et al, the VA MISSION Act sought to address gaps in care for veterans living in rural and underserved areas.2 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continues to increase community care spending, with a 13.8% increase in fiscal year 2024 and an expected cost of > $40 billion for 2025.3 One could argue this pays for access for remote patients and quality when services are unavailable, making it a direct application of the iron triangle.
The VA MISSION Act also bolstered the expansion of existing community care department staff to expediently facilitate and coordinate care and payments.2 Cost management and monitoring have become critical in predicting future staff requirements, maintaining functionality, and ensuring patients receive optimal care. The VHA purchases care through partner networks and defines these bundled health care services as standard episodes of care (SEOCs), which are “clinically related health care services for a specific unique illness or medical condition… over a defined period of time.”4 Medicare publishes its rates quarterly, and outpatient procedure pricing is readily available online.5 Along these same lines, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) publishes a current list of available procedures and associated Current Procedure Technology (CPT) codes that are covered under its VA fee schedule for community care.
Unique challenges persist when using this system to accurately account for radiation oncology expenditures. This study was based on the current practices at the Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center (RLRVAMC), a large 1a hospital. A detailed analysis reveals the contemporaneous cost of radiation oncology cancer care from October 1, 2021, through February 1, 2024, highlights the challenges in SEOC definition and duration, communication issues between RLRVAMC and purchase partners, inconsistencies in billing, erroneous payments, and difficulty of cost categorization.
METHODS
Community care radiation oncology-related costs were examined from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024 for RLRVAMC, 6 months prior to billing data extraction. Figure 1 shows a simple radiation oncology patient pathway with consultation or visit, simulation and planning, and treatment, with codes used to check billing. It illustrates the expected relationships between the VHA (radiation oncology, primary, and specialty care) and community care (clinicians and radiation oncology treatment sites).
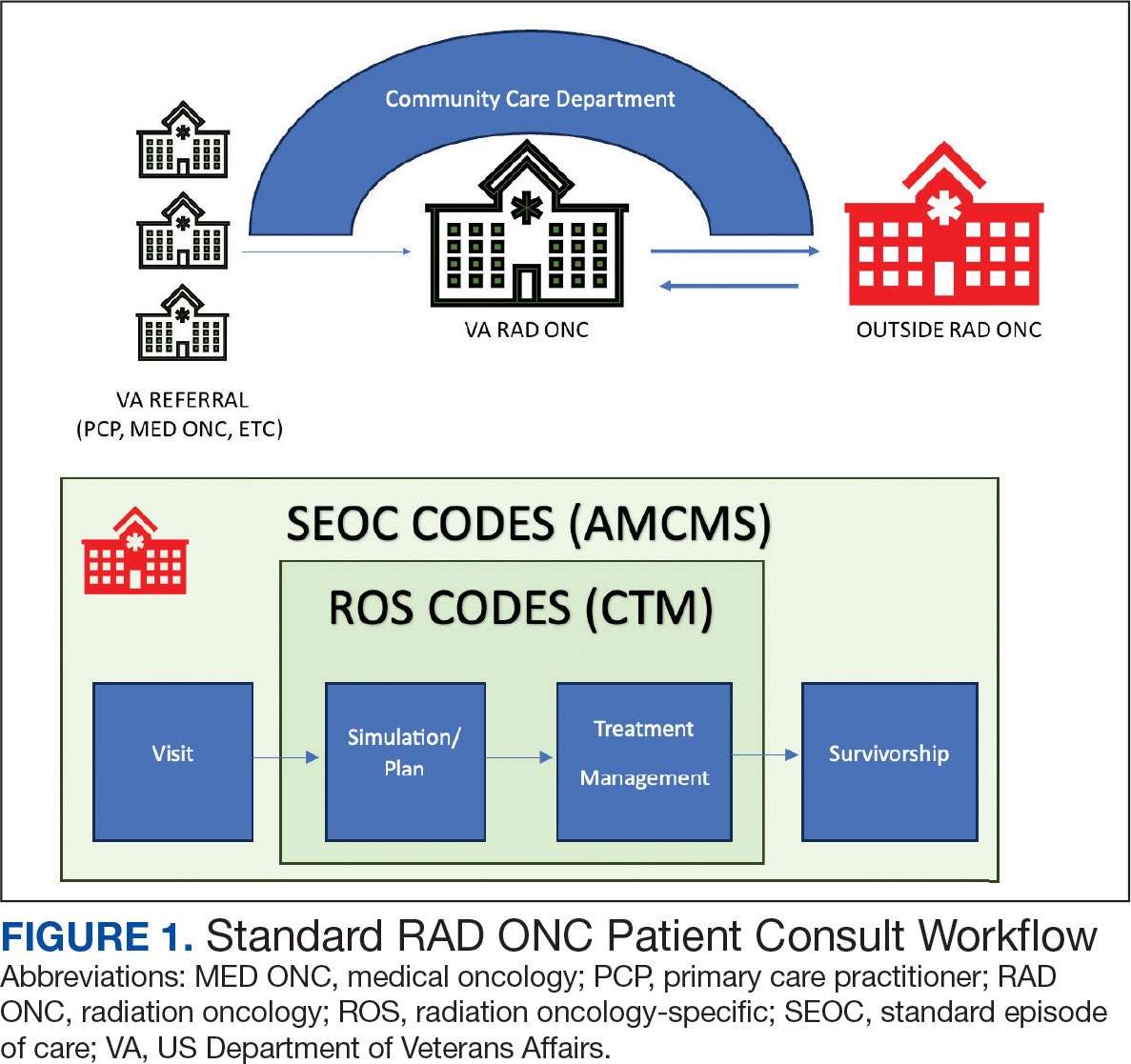
VHA standard operating procedures for a patient requesting community-based radiation oncology care require a board-certified radiation oncologist at RLRVAMC to review and approve the outside care request. Community care radiation oncology consultation data were accessed from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using Pyramid Analytics (V25.2). Nurses, physicians, and community care staff can add comments, forward consultations to other services, and mark them as complete or discontinued, when appropriate. Consultations not completed within 91 days are automatically discontinued. All community care requests from 2018 through 2024 were extracted; analysis began April 1, 2021, 6 months prior to the cost evaluation date of October 1, 2021.
An approved consultation is reviewed for eligibility by a nurse in the community care department and assigned an authorization number (a VA prefix followed by 12 digits). Billing codes are approved and organized by the community care networks, and all procedure codes should be captured and labeled under this number. The VAMC Community Care department obtains initial correspondence from the treating clinicians. Subsequent records from the treating radiation oncologist are expected to be scanned into the electronic health record and made accessible via the VA Joint Legacy Viewer (JLV) and Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS).
Radiation Oncology SEOC
The start date of the radiation oncology SEOC is determined by the community care nurse based on guidance established by the VA. It can be manually backdated or delayed, but current practice is to start at first visit or procedure code entry after approval from the VAMC Radiation Oncology department. Approved CPT codes from SEOC versions between October 1, 2021, and February 1, 2024, are in eAppendix 1 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). These generally include 10 types of encounters, about 115 different laboratory tests, 115 imaging studies, 25 simulation and planning procedures, and 115 radiation treatment codes. The radiation oncology SEOCs during the study period had an approval duration of 180 days. Advanced Medical Cost Management Solutions software (AMCMS) is the VHA data analytics platform for community care medical service costs. AMCMS includes all individual CPT codes billed by specific radiation oncology SEOC versions. Data are refreshed monthly, and all charges were extracted on September 12, 2024, > 6 months after the final evaluated service date to allow for complete billing returns.6
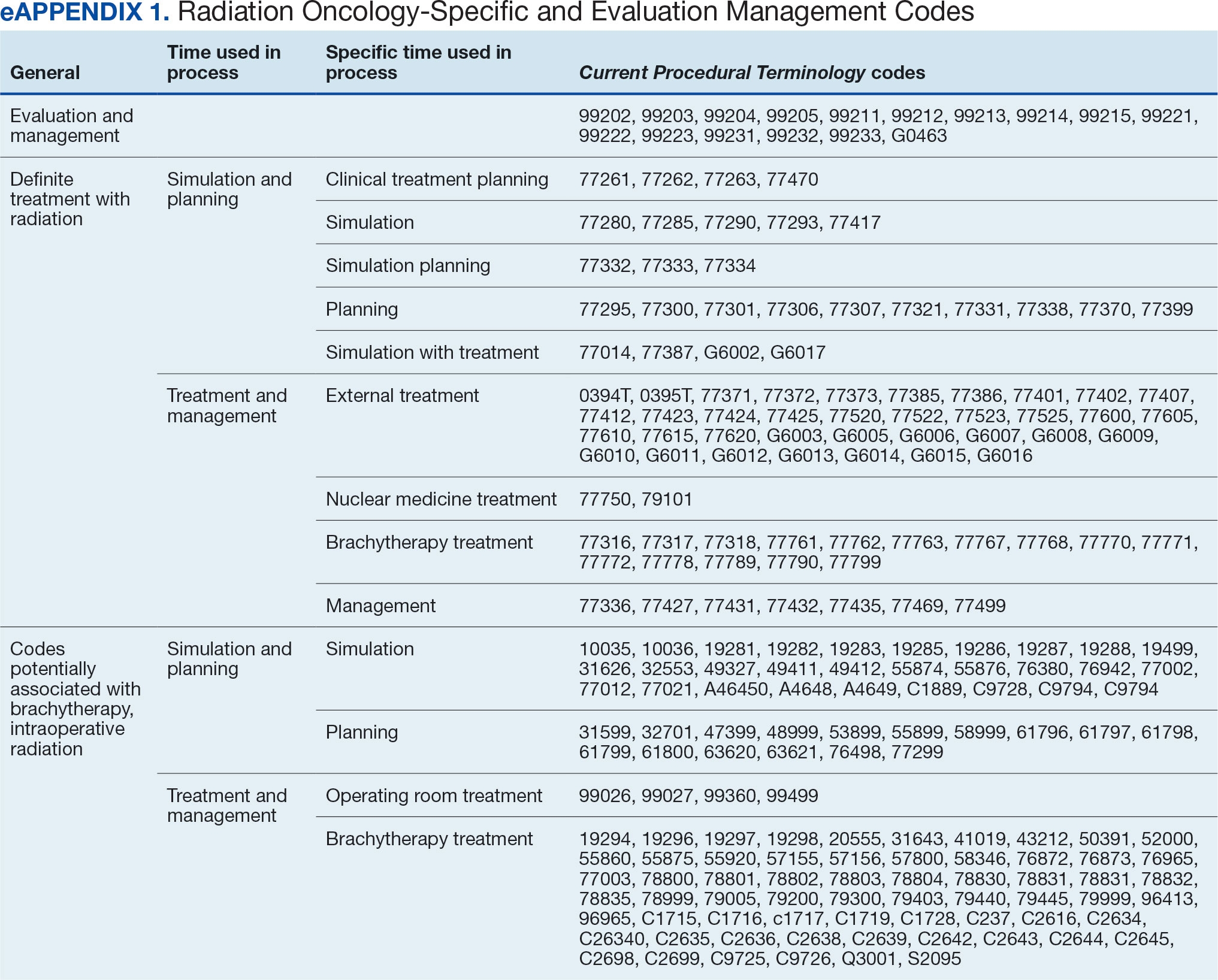
Radiation Oncology-Specific Costs
The VA Close to Me (CTM) program was used to find 84 specific radiation oncology CPT codes, nearly all within the 77.XXX or G6.XXX series, which included all radiation oncology-specific (ROS) codes (except visits accrued during consultation and return appointments). ROS costs are those that could not be performed by any other service and include procedures related to radiation oncology simulation, treatment planning, treatment delivery (with or without image guidance), and physician or physicist management. All ROS costs should be included in a patient’s radiation oncology SEOC. Other costs that may accompany operating room or brachytherapy administration did not follow a 77.XXX or G6.XXX pattern but were included in total radiation therapy operating costs.
Data obtained from AMCMS and CTM included patient name and identifier; CPT billed amount; CPT paid amount; dates of service; number of claims; International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD) diagnosis; and VA authorization numbers. Only CTM listed code modifiers. Only items categorized as paid were included in the analysis. Charges associated with discontinued consultations that had accrued costs also were included. Codes that were not directly related to ROS were separately characterized as other and further subcategorized.
Deep Dive Categorization
All scanned documents tagged to the community consultation were accessed and evaluated for completeness by a radiation oncologist (RS). The presence or absence of consultation notes and treatment summaries was evaluated based on necessity (ie, not needed for continuation of care or treatment was not given). In the absence of a specific completion summary or follow-up note detailing the treatment modality, number of fractions, and treatment sites, available documentation, including clinical notes and billing information, was used. Radical or curative therapies were identified as courses expected to eradicate disease, including stereotactic ablative radiotherapy to the brain, lung, liver, and other organs. Palliative therapies included whole-brain radiotherapy or other low-dose treatments. If the patient received the intended course, this was categorized as full. If incomplete, it was considered partial.
Billing Deviations
The complete document review allowed for close evaluation of paid therapy and identification of gaps in billing (eg, charges not found in extracted data that should have occurred) for external beam radiotherapy patients. Conversely, extra charges, such as an additional weekly treatment management charge (CPT code 77427), would be noted. Patients were expected to have the number of treatments specified in the summary, a clinical treatment planning code, and weekly treatment management notes from physicians and physicists every 5 fractions. Consultations and follow-up visits were expected to have 1 visit code; CPT codes 99205 and 99215, respectively, were used to estimate costs in their absence.
Costs were based on Medicare rates as of January 1 of the year in which they were accrued. 7-10 Duplicates were charges with the same code, date, billed quantity, and paid amounts for a given patient. These would always be considered erroneous. Medicare treatment costs for procedures such as intensity modulated radiotherapy (CPT code 77385 or 77386) are available on the Medicare website. When reviewing locality deviations for 77427, there was a maximum of 33% increase in Medicare rates. Therefore, for treatment codes, one would expect the range to be at least the Medicare rate and maximally 33% higher. These rates are negotiated with insurance companies, but this range was used for the purpose of reviewing and adjusting large data sets.
RESULTS
Since 2018, > 500 community care consults have been placed by radiation oncology for treatment in the community, with more following implementation of the VA MISSION Act. Use of radiation oncology community care services annually increased during the study period for this facility (Table 1, Figure 2). Of the 325 community care consults placed from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024, 248 radiation oncology SEOCs were recorded with charges for 181 patients (range, 1-5 SEOCs). Long drive time was the rationale for > 97% of patients directed to community care (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Based on AMCMS data, $22.2 million was billed and $2.7 million was paid (20%) for 8747 CPT codes. Each community care interval cost the VA a median (range) of $5000 ($8-$168,000 (Figure 3).
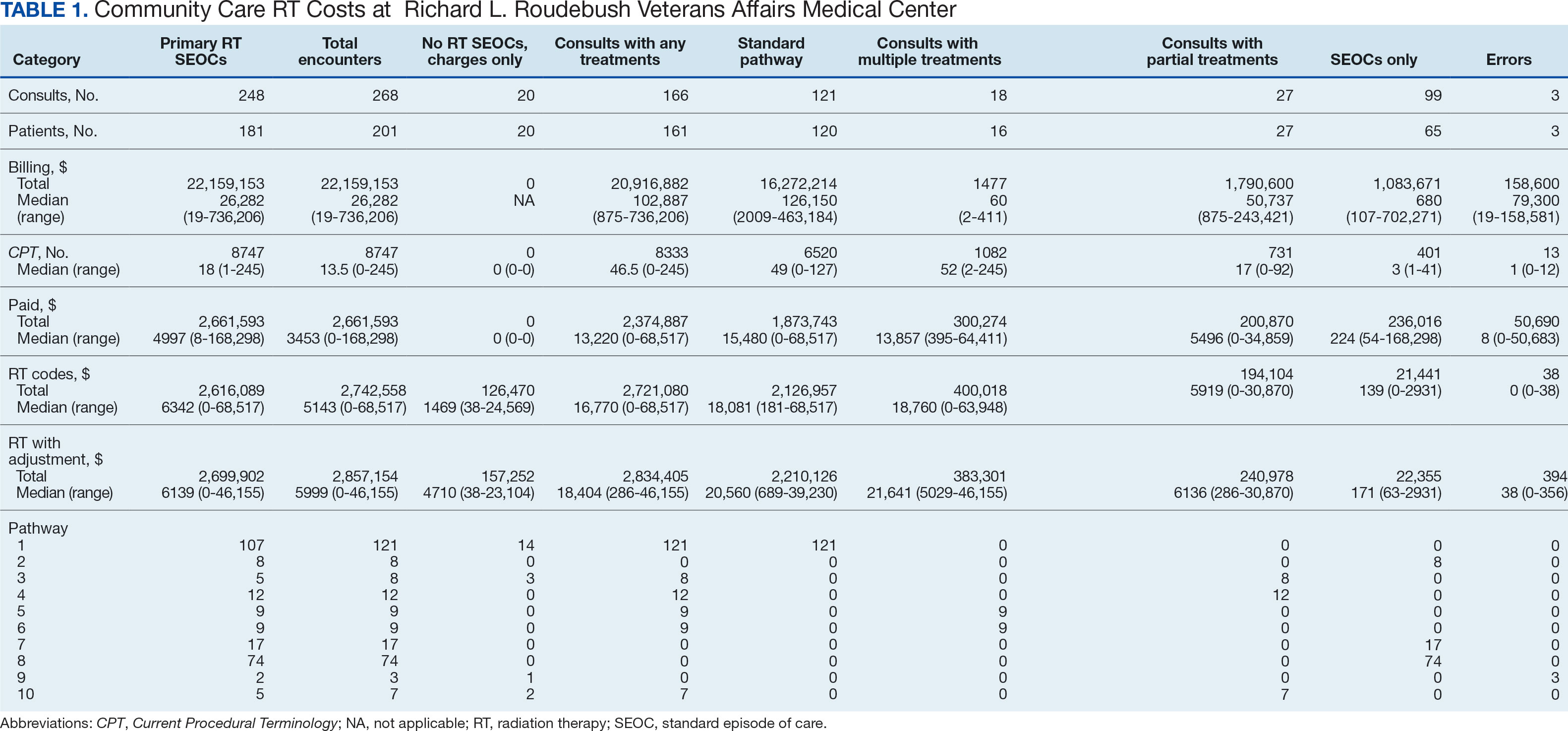
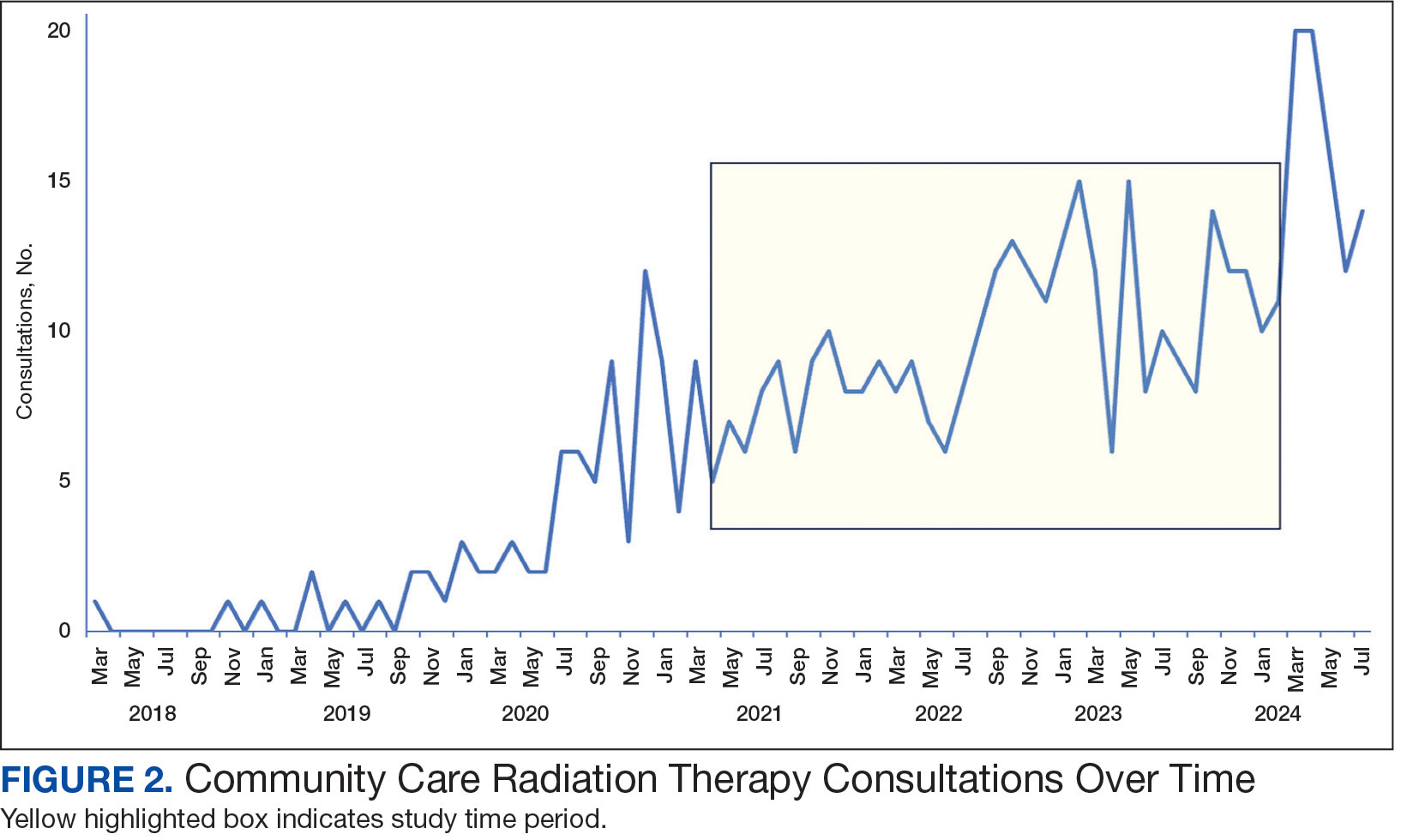
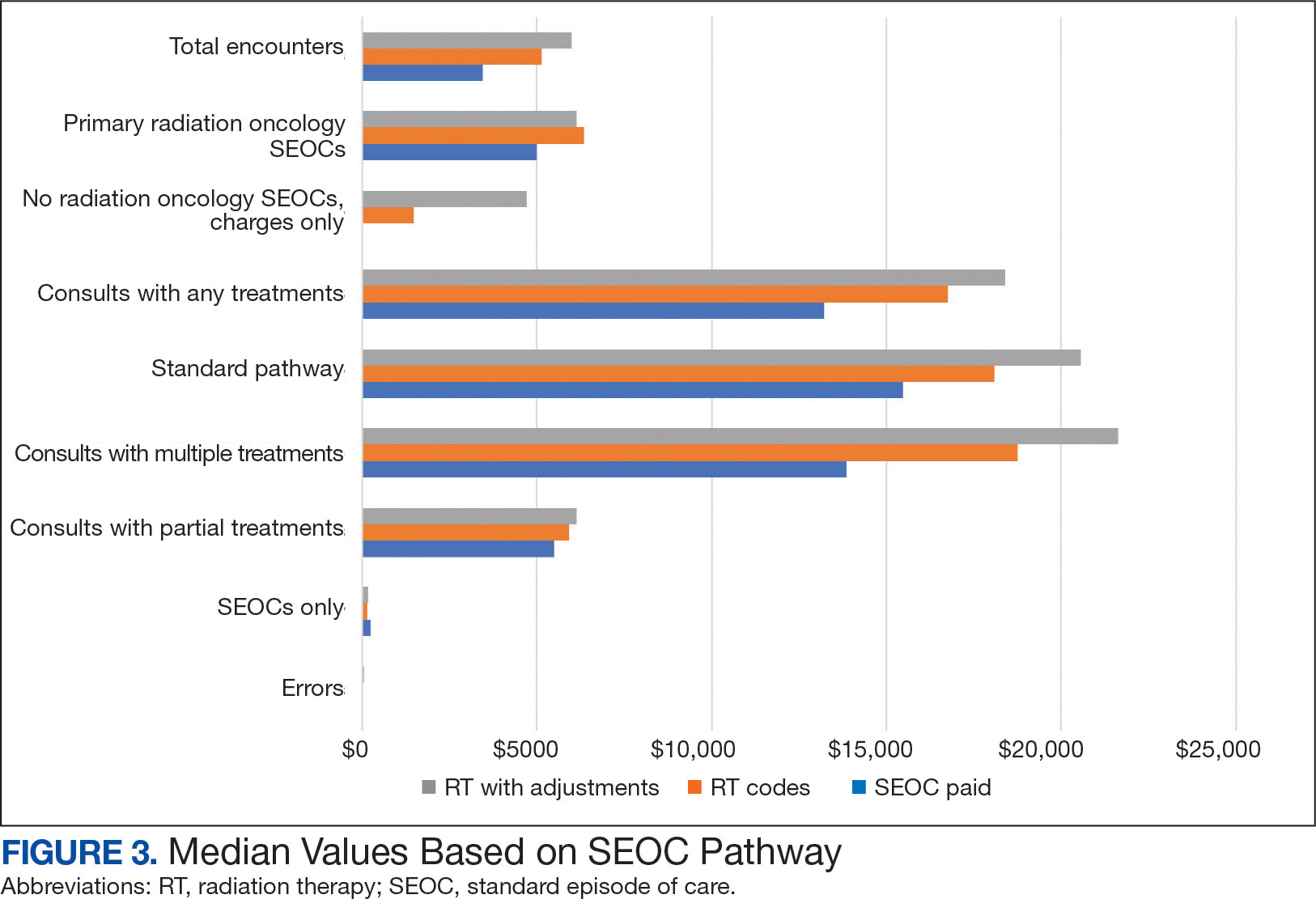
After reviewing ROS charges extracted from CTM, 20 additional patients had radiation oncology charges but did not have a radiation oncology SEOC for 268 episodes of care for 201 unique patients. In addition to the 20 patients who did not have a SEOC, 42 nonradiation oncology SEOCs contained 1148 radiation oncology codes, corresponding to almost $500,000 paid. Additional charges of about $416,000, which included biologic agents (eg, durvalumab, nivolumab), procedures (eg, mastectomies), and ambulance rides were inappropriately added to radiation oncology SEOCs.
While 77% of consultations were scanned into CPRS and JLV, only 54% of completion summaries were available with an estimated $115,000 in additional costs. The total adjusted costs was about $2.9 million. Almost 37% of SEOCs were for visits only. For the 166 SEOCs where patients received any radiation treatment or planning, the median cost was $18,000. Differences in SEOC pathways are shown in Figure 4. One hundred twenty-one SEOCs (45%) followed the standard pathway, with median SEOC costs of $15,500; when corrected for radiation-specific costs, the median cost increased to $18,000. When adjusted for billing irregularities, the median cost was $20,600. Ninety-nine SEOCs (37%) were for consultation/ follow-up visits only, with a median cost of $220. When omitting shared scans and nonradiation therapy costs and correcting for billing gaps, the median cost decreased to $170. A median of $9200 was paid per patient, with $12,900 for radiation therapy-specific costs and $13,300 adjusted for billing deviations. Narrowing to the 106 patients who received full, radical courses, the median SEOC, ROS, and adjusted radiation therapy costs increased to $19,400, $22,200, and $22,900, respectively (Table 2, Figure 5). Seventy-one SEOCs (26%) had already seen a radiation oncologist before the VA radiation oncology department was aware, and 49 SEOCs (18%) had retroactive approvals (Supplemental materials available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).
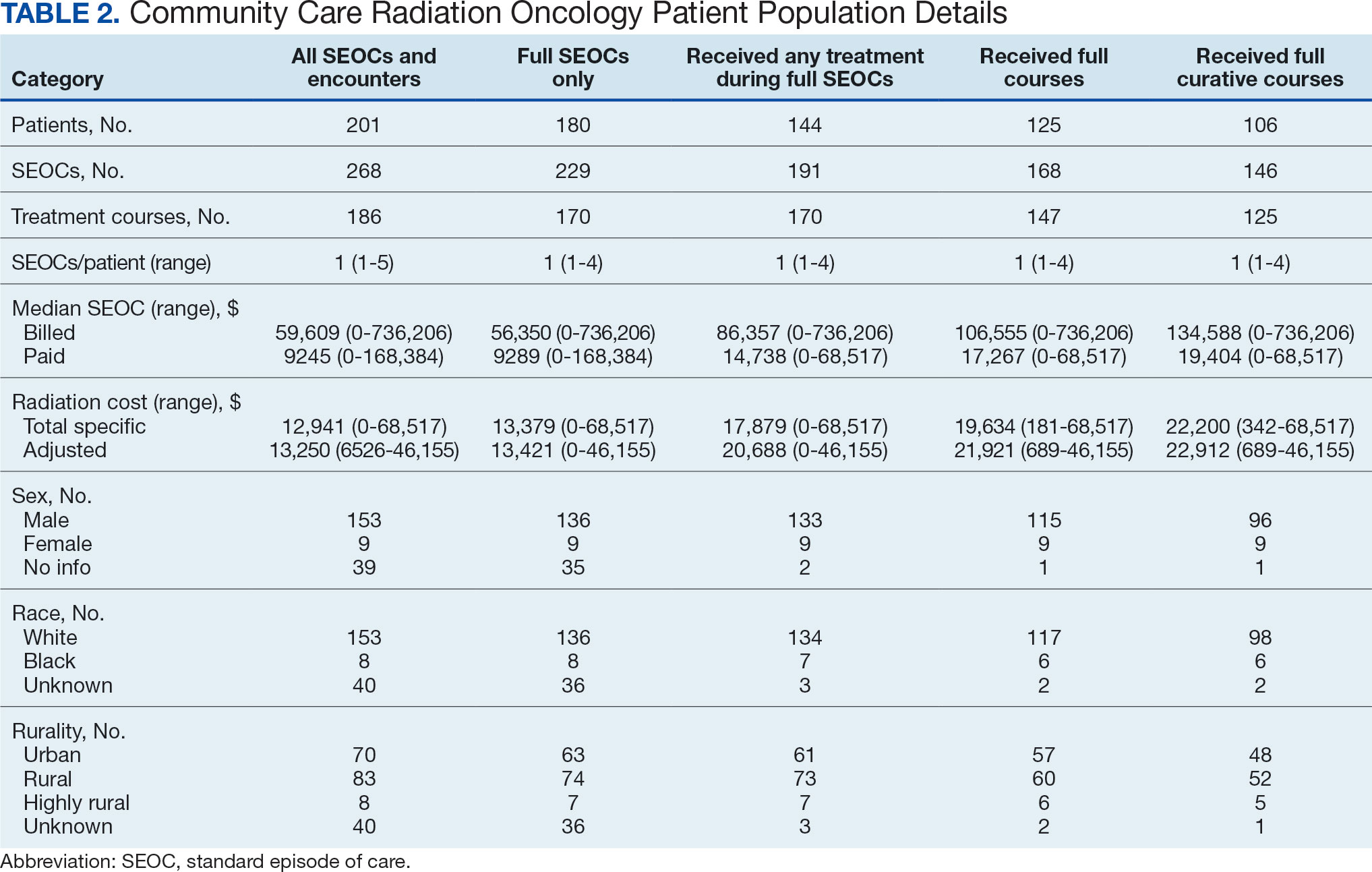
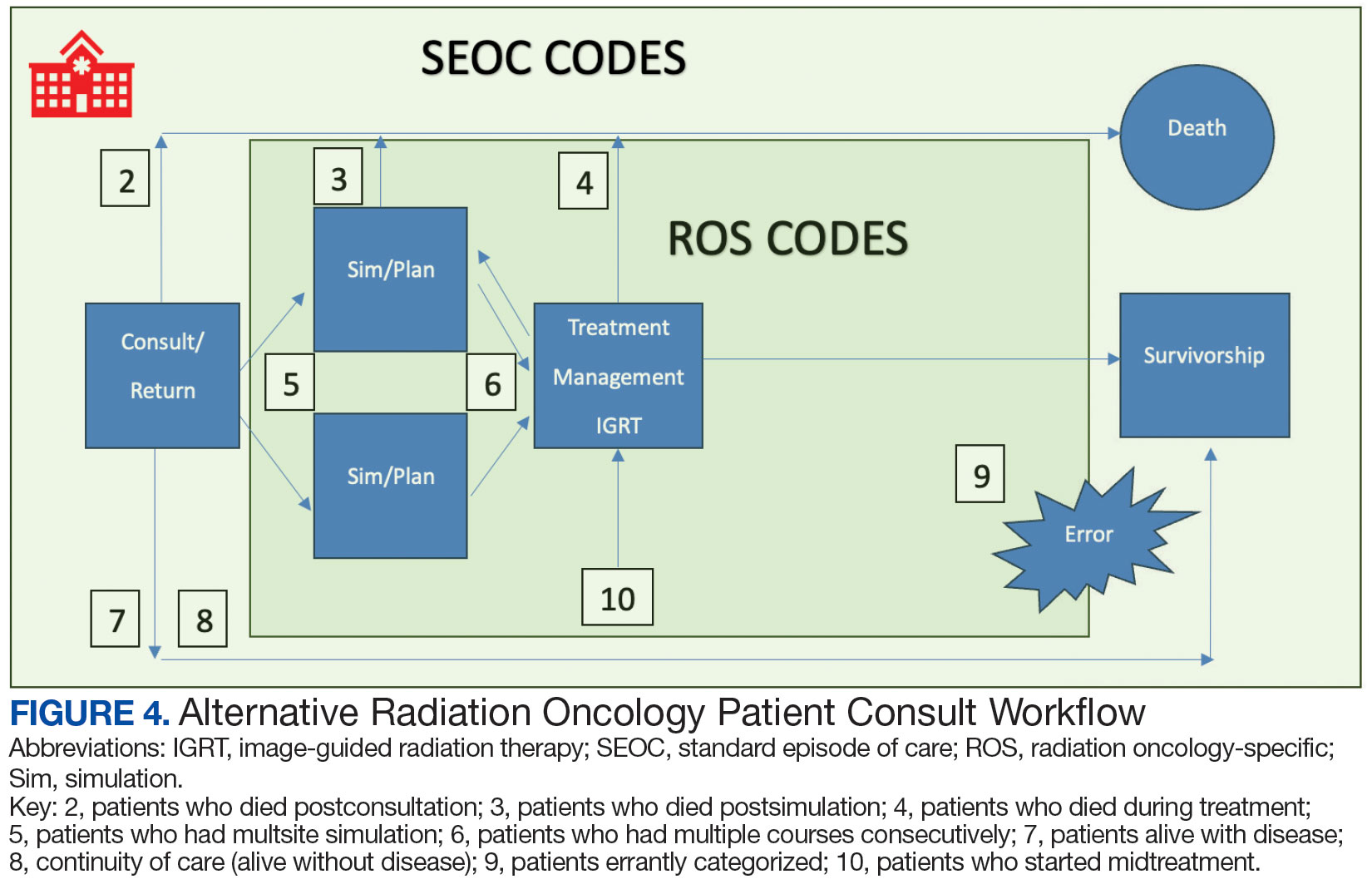
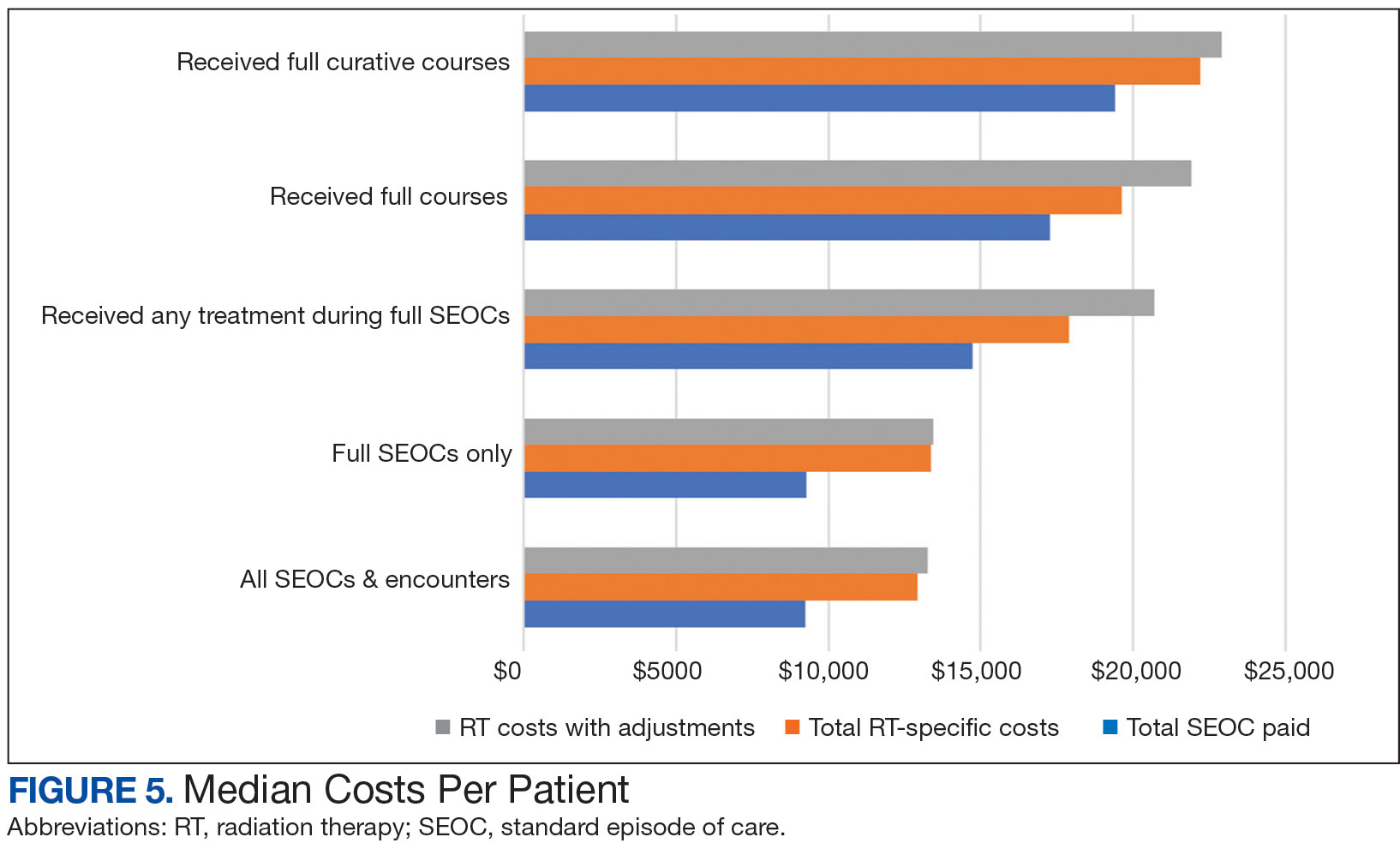
Every consultation charge was reviewed. A typical patient following the standard pathway (eAppendix 2, available at doi:10.12788/ fp.0585) exhibited a predictable pattern of consultation payment, simulation and planning, multiple radiation treatments interspersed with treatment management visits and a cone-down phase, and finishing with a follow-up visit. A less predictable case with excess CPT codes, gaps in charges, and an additional unexpected palliative course is shown in eAppendix 3 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Gaps occurred in 42% of SEOCs with missed bills costing as much as $12,000. For example, a patient with lung cancer had a treatment summary note for lung cancer after completion that showed the patient received 30 fractions of 2 Gy, a typical course. Only 10 treatment codes and 3 of 6 weekly treatment management codes were available. There was a gap of 20 volumetric modulated arc therapy treatments, 3 physics weekly status checks, 3 physician managements notes, and a computed tomography simulation charge.
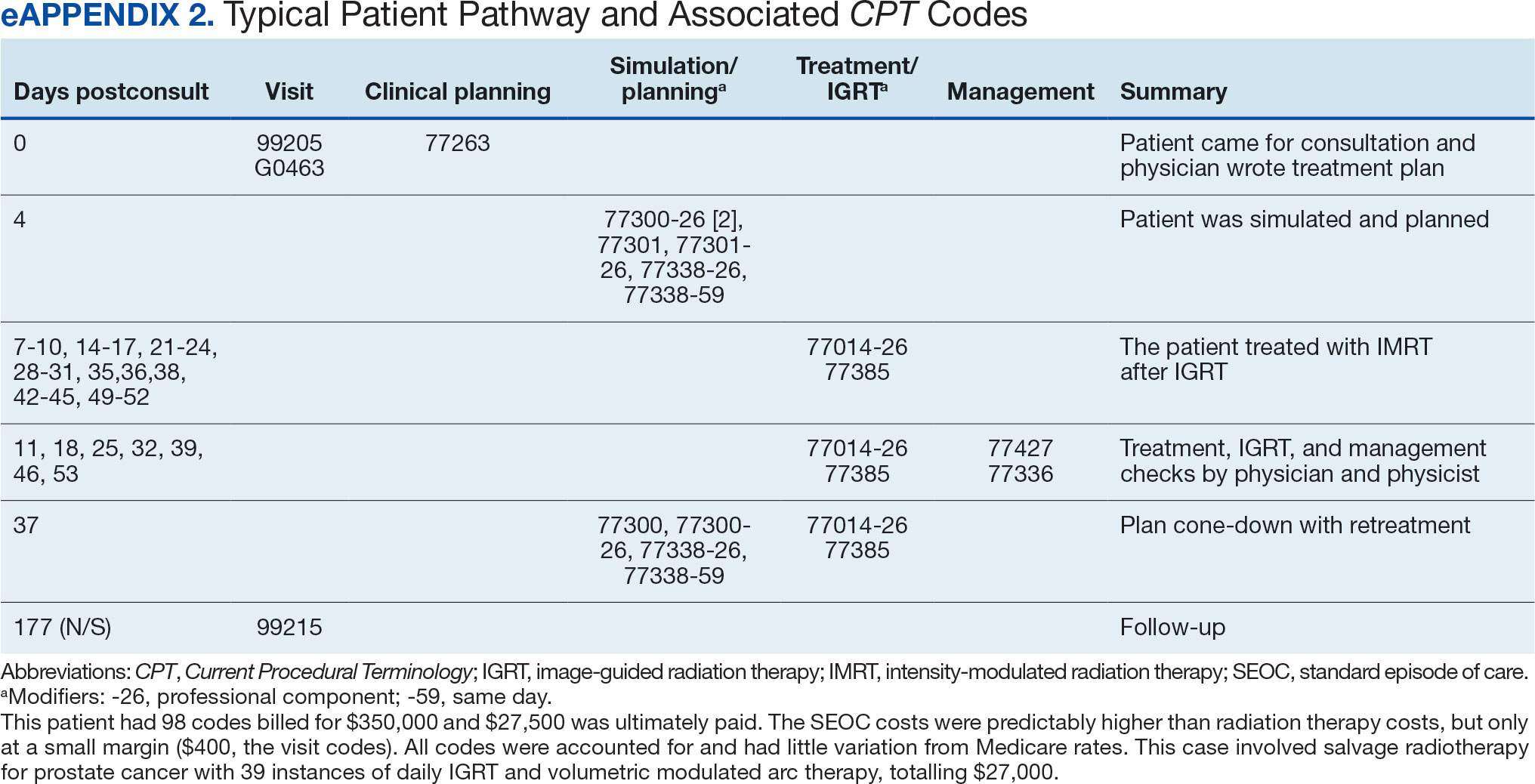

Between AMCMS and CTM, 10,005 CPT codes were evaluated; 1255 (12.5%) were unique to AMCMS (either related to the radiation oncology course, such as Evaluation and Management CPT codes or “other” unrelated codes) while 1158 (11.6%) were unique to CTM. Of the 7592 CPT codes shared between AMCMS and CTM, there was a discrepancy in 135 (1.8%); all were duplicates (CTM showed double payment while AMCMS showed $0 paid). The total CPT code costs came to $3.2 million with $560,000 unique to SEOCs and $500,000 unique to CTM. Treatment codes were the most common (33%) as shown in Table 3 and accounted for 55% of the cost ($1.8 million). About 700 CPT codes were considered “other,” typically for biologic therapeutic agents (Table 4 and eAppendix 4, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).
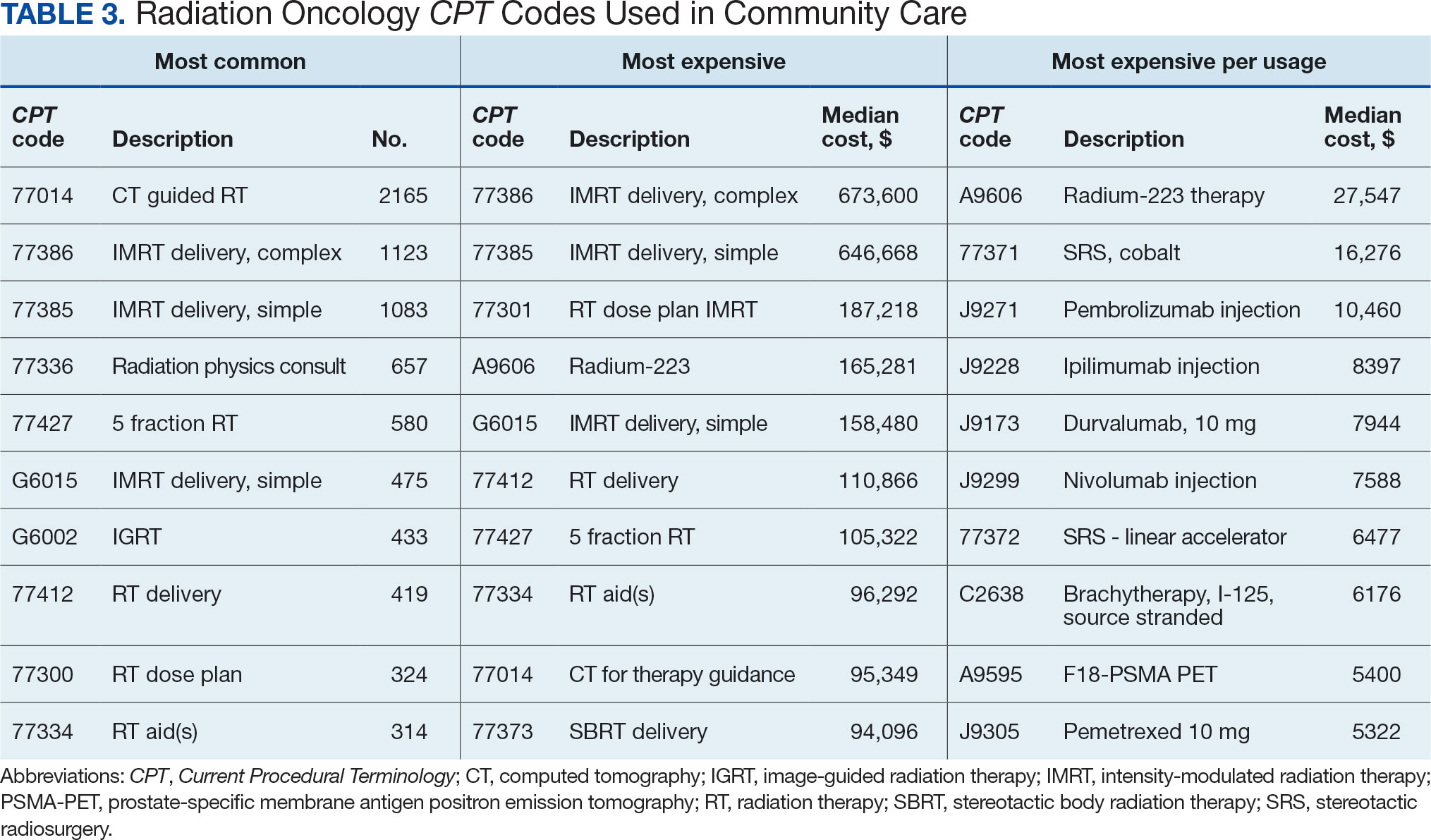
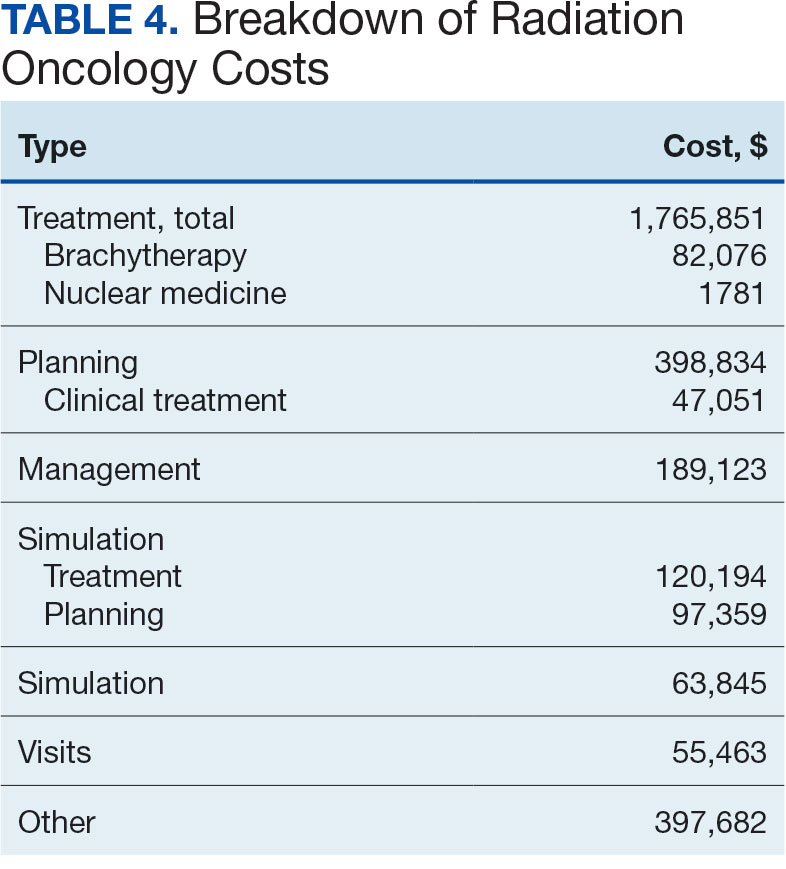

DISCUSSION
The current method of reporting radiation oncology costs used by VA is insufficient and misleading. Better data are needed to summarize purchased care costs to guide decisions about community care at the VA. Investigations into whether the extra costs for quality care (ie, expensive capital equipment, specialized staff, mandatory accreditations) are worthwhile if omitted at other facilities patients choose for their health care needs. No study has defined specialty care-specific costs by evaluating billing receipts from the CDW to answer the question. Kenamond et al highlight the need for radiation oncology for rural patients.11 Drive time was cited as the reason for community care referral for 97% of veterans, many of whom lived in rural locations. Of patients with rurality information who enrolled in community care, 57% came from rural or highly rural counties, and this ratio held for those who received full curative therapies. An executive administrator relying on AMCMS reports would see a median SEOC cost of $5000, but without ROS knowledge in coding, the administrator would miss many additional costs. For example, 2 patients who each had 5 SEOCs during the evaluated period, incurred a total cost of only $1800.
Additionally, an administrator could include miscategorized costs with significant ramifications. The 2 most expensive SEOCs were not typical radiation oncology treatments. A patient undergoing radium-223 dichloride therapy incurred charges exceeding $165,000, contributing disproportionately to the overall median cost analysis; this would normally be administered by the nuclear medicine department. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy are uniformly overseen by medical oncology services, but drug administration codes were still found in radiation oncology SEOCs. A patient (whose SEOC was discontinued but accrued charges) had an electrocardiogram interpretation for $8 as the SEOC cost; 3 other SEOCs continued to incur costs after being discontinued. There were 24 empty SEOCs for patients that had consults to the community, and 2 had notes stating treatment had been delivered yet there was no ROS costs or SEOC costs. Of the 268 encounters, 43% had some sort of billing irregularities (ie, missing treatment costs) that would be unlikely for a private practice to omit; it would be much more likely that the CDW miscategorized the payment despite confirmation of the 2 retrieval systems.
It would be inadvisable to make staffing decisions or forecast costs based on current SEOC reports without specialized curation. A simple yet effective improvement to the cost attribution process would be to restrict the analysis to encounters containing primary radiation treatment codes. This targeted approach allows more accurate identification of patients actively receiving radiation oncology treatment, while excluding those seen solely for consultations or follow-up visits. Implementing this refinement leads to a substantial increase in the median payment—from $5000 to $13,000—without requiring additional coding or data processing, thereby enhancing the accuracy of cost estimates with minimal effort.
Clarifying radiation oncology service costs requires addressing the time frame and services included, given laxity and interpretation of the SEOCs. VA community care departments have streamlined the reimbursement process at the expense of medical cost organization and accuracy; 86% of VA practitioners reported that ≥ 1 potential community health care partners had refused to work with the VA because of payment delays.12 Payments are contingent on correspondence from outside practices for community work. For radiation oncology, this includes the consultation but also critical radiation-related details of treatment, which were omitted nearly half the time. SEOC approval forms have many costly laboratory tests, imaging, and procedures that have little to do with radiation oncology cancer treatments but may be used in the workup and staging process; this creates noise when calculating radiation oncology fiscal cost.
The presumption that an episode of care equates to a completed radiation therapy course is incorrect; this occurs less than half of the time. An episode often refers to a return visit, or conversely, multiple treatment courses. As the patients’ medical homes are their VHA primary care practitioners, it would be particularly challenging to care for the patients without full treatment information, especially if adverse effects from therapy were to arise. As a tertiary specialty, radiation oncology does not seek out patients and are sent consultations from medical oncology, surgical, and medical oncologic specialties. Timesensitive processes such as workup, staging, and diagnosis often occur in parallel. This analysis revealed that patients see outside radiation oncologists prior to the VA. There are ≥ 100 patients who had radiation oncology codes without a radiation oncology SEOC or community care consultation, and in many cases, the consultation was placed after the patient was seen.
Given the lack of uniformity and standardization of patient traffic, the typical and expected pathways were insufficient to find the costs. Too many opportunities for errors and incorrect categorization of costs meant a different method would be necessary. Starting at the inception of the community care consult, only 1 diagnosis code can be entered. For patients with multiple diagnoses, one would not be able to tell what was treated without chart access. Radiation oncology consults come from primary and specialty care practitioners and nurses throughout the VA. Oftentimes, the referral would be solicited by the community radiation oncology clinic, diagnosing community specialty (ie, urology for a patient with prostate cancer), or indirectly from the patient through primary care. Many cases were retroactively approved as the veteran had already been consulted by the community care radiation oncologist. If the patient is drive-time eligible, it would be unlikely that they would leave and choose to return to the VA. There is no way for a facility VA service chief or administrator to mitigate VA community costs of care, especially as shown by the miscategorization of several codes. Database challenges exacerbate the issue: 1 patient changed her first and last name during this time frame, and 2 patients had the same name but different social security numbers. In order to strictly find costs between 2 discrete timepoints, 39 (15%) SEOCs were split and incomplete, and 6 SEOCs contained charges for 2 different patients. This was corrected, and all inadvertent charges were cancelled. Only 1 ICD code is allowed per community care consultation, so an investigation is required to find costs for patients with multiple sites of disease. Additionally, 5 of the patients marked for drive time were actually patients who received Gamma Knife and brachytherapy, services not available at the VA.
Hanks et al first attempted to calculate cost of radiation oncology services. External beam prostate cancer radiotherapy at 3 suburban California centers cost $6750 ($20,503 inflation adjusted) per patient before October 1984 and $5600 ($17,010 inflation adjusted) afterwards.13 According to the American Society for Radiation Oncology, Advocacy Radiation Oncology Case Rate Program Curative radiation courses should cost $20,000 to $30,000 and palliative courses should cost $10,000 to $15,000. These costs are consistent with totals demonstrated in this analysis and similar to the inflation-adjusted Hanks et al figures. Preliminary findings suggest that radiation treatment constituted more than half of the total expenditures, with a notable $4 million increase in adjusted cost compared to the Medicare rates, indicating significant variation. Direct comparisons with Medicaid or commercial payer rates remain unexplored.
Future Directions
During the study period, 201 patients received 186 courses of radiation therapy in the community, while 1014 patients were treated in-house for a total of 833 courses. A forthcoming analysis will directly compare the cost of in-house care with that of communitybased treatment, specifically breaking down expenditure differences by diagnosis. Future research should investigate strategies to align reimbursement with quality metrics, including the potential role of tertiary accreditation in incentivizing high-value care. Additional work is also warranted to assess patient out-ofpocket expenses across care settings and to benchmark VA reimbursement against Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance rates. In any case, with the increasing possibility of fewer fractions for treatments such as stereotactic radiotherapy or palliative care therapy, there is a clear financial incentive to treat as frequently as allowed despite equal clinical outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Veterans increasingly choose to receive care closer to home if the option is available. In the VA iron triangle, cost comes at the expense of access but quantifying this has proved elusive in the cost accounting model currently used at the VA.1 The inclusion of all charges loosely associated with SEOCs significantly impairs the ability to conduct meaningful cost analyses. The current VA methodology not only introduces substantial noise into the data but also leads to a marked underestimation of the true cost of care delivered in community settings. Such misrepresentation risks driving policy decisions that could inappropriately reduce or eliminate in-house radiation oncology services. Categorizing costs effectively in the VA could assist in making managerial and administrative decisions and would prevent damaging service lines based on misleading or incorrect data. A system which differentiates between patients who have received any treatment codes vs those who have not would increase accuracy.
- Kissick W. Medicine’s Dilemmas: Infinite Needs Versus Finite Resources. 1st ed. Yale University Press; 1994.
- Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
- Office of Management and Budget (US). Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2025. Washington, DC: US Government Publishing Office; 2024. Available from: US Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2025 Budget Submission: Budget in Brief.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran care claims. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/revenue-ops/Veteran-Care-Claims.asp
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Accessed April 3, 2025. Procedure price lookup https://www.medicare.gov/procedure-price-lookup
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. WellHive -Enterprise. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://department.va.gov/privacy/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2023/05/FY23WellHiveEnterprisePIA.pdf
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU21a physician fee schedule, January 2021 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu21a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU22a physician fee schedule, January 2022 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu22a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a physician fee schedule, January 2023 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/medicare-fee-service-payment/physicianfeesched/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu23a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a Medicare Physician Fee Schedule rates effective January 1, 2024, through March 8, 2024. Accessed on April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu24a
- Kenamond MC, Mourad WF, Randall ME, Kaushal A. No oncology patient left behind: challenges and solutions in rural radiation oncology. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100289. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100289
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Hanks GE, Dunlap K. A comparison of the cost of various treatment methods for early cancer of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12(10):1879-1881. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90334-2
- American Society of Radiation Oncology. Radiation oncology case rate program (ROCR). Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.astro.org/advocacy/key-issues-8f3e5a3b76643265ee93287d79c4fc40/rocr
William Kissick’s description of health care’s iron triangle in 1994 still resonates. Access, quality, and cost will always come at the expense of the others.1 In 2018, Congress passed the VA MISSION Act, allowing patients to pursue community care options for extended waits (> 28 days) or longer distance drive times of > 60 minutes for specialty care services, such as radiation oncology. According to Albanese et al, the VA MISSION Act sought to address gaps in care for veterans living in rural and underserved areas.2 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continues to increase community care spending, with a 13.8% increase in fiscal year 2024 and an expected cost of > $40 billion for 2025.3 One could argue this pays for access for remote patients and quality when services are unavailable, making it a direct application of the iron triangle.
The VA MISSION Act also bolstered the expansion of existing community care department staff to expediently facilitate and coordinate care and payments.2 Cost management and monitoring have become critical in predicting future staff requirements, maintaining functionality, and ensuring patients receive optimal care. The VHA purchases care through partner networks and defines these bundled health care services as standard episodes of care (SEOCs), which are “clinically related health care services for a specific unique illness or medical condition… over a defined period of time.”4 Medicare publishes its rates quarterly, and outpatient procedure pricing is readily available online.5 Along these same lines, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) publishes a current list of available procedures and associated Current Procedure Technology (CPT) codes that are covered under its VA fee schedule for community care.
Unique challenges persist when using this system to accurately account for radiation oncology expenditures. This study was based on the current practices at the Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center (RLRVAMC), a large 1a hospital. A detailed analysis reveals the contemporaneous cost of radiation oncology cancer care from October 1, 2021, through February 1, 2024, highlights the challenges in SEOC definition and duration, communication issues between RLRVAMC and purchase partners, inconsistencies in billing, erroneous payments, and difficulty of cost categorization.
METHODS
Community care radiation oncology-related costs were examined from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024 for RLRVAMC, 6 months prior to billing data extraction. Figure 1 shows a simple radiation oncology patient pathway with consultation or visit, simulation and planning, and treatment, with codes used to check billing. It illustrates the expected relationships between the VHA (radiation oncology, primary, and specialty care) and community care (clinicians and radiation oncology treatment sites).

VHA standard operating procedures for a patient requesting community-based radiation oncology care require a board-certified radiation oncologist at RLRVAMC to review and approve the outside care request. Community care radiation oncology consultation data were accessed from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using Pyramid Analytics (V25.2). Nurses, physicians, and community care staff can add comments, forward consultations to other services, and mark them as complete or discontinued, when appropriate. Consultations not completed within 91 days are automatically discontinued. All community care requests from 2018 through 2024 were extracted; analysis began April 1, 2021, 6 months prior to the cost evaluation date of October 1, 2021.
An approved consultation is reviewed for eligibility by a nurse in the community care department and assigned an authorization number (a VA prefix followed by 12 digits). Billing codes are approved and organized by the community care networks, and all procedure codes should be captured and labeled under this number. The VAMC Community Care department obtains initial correspondence from the treating clinicians. Subsequent records from the treating radiation oncologist are expected to be scanned into the electronic health record and made accessible via the VA Joint Legacy Viewer (JLV) and Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS).
Radiation Oncology SEOC
The start date of the radiation oncology SEOC is determined by the community care nurse based on guidance established by the VA. It can be manually backdated or delayed, but current practice is to start at first visit or procedure code entry after approval from the VAMC Radiation Oncology department. Approved CPT codes from SEOC versions between October 1, 2021, and February 1, 2024, are in eAppendix 1 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). These generally include 10 types of encounters, about 115 different laboratory tests, 115 imaging studies, 25 simulation and planning procedures, and 115 radiation treatment codes. The radiation oncology SEOCs during the study period had an approval duration of 180 days. Advanced Medical Cost Management Solutions software (AMCMS) is the VHA data analytics platform for community care medical service costs. AMCMS includes all individual CPT codes billed by specific radiation oncology SEOC versions. Data are refreshed monthly, and all charges were extracted on September 12, 2024, > 6 months after the final evaluated service date to allow for complete billing returns.6

Radiation Oncology-Specific Costs
The VA Close to Me (CTM) program was used to find 84 specific radiation oncology CPT codes, nearly all within the 77.XXX or G6.XXX series, which included all radiation oncology-specific (ROS) codes (except visits accrued during consultation and return appointments). ROS costs are those that could not be performed by any other service and include procedures related to radiation oncology simulation, treatment planning, treatment delivery (with or without image guidance), and physician or physicist management. All ROS costs should be included in a patient’s radiation oncology SEOC. Other costs that may accompany operating room or brachytherapy administration did not follow a 77.XXX or G6.XXX pattern but were included in total radiation therapy operating costs.
Data obtained from AMCMS and CTM included patient name and identifier; CPT billed amount; CPT paid amount; dates of service; number of claims; International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD) diagnosis; and VA authorization numbers. Only CTM listed code modifiers. Only items categorized as paid were included in the analysis. Charges associated with discontinued consultations that had accrued costs also were included. Codes that were not directly related to ROS were separately characterized as other and further subcategorized.
Deep Dive Categorization
All scanned documents tagged to the community consultation were accessed and evaluated for completeness by a radiation oncologist (RS). The presence or absence of consultation notes and treatment summaries was evaluated based on necessity (ie, not needed for continuation of care or treatment was not given). In the absence of a specific completion summary or follow-up note detailing the treatment modality, number of fractions, and treatment sites, available documentation, including clinical notes and billing information, was used. Radical or curative therapies were identified as courses expected to eradicate disease, including stereotactic ablative radiotherapy to the brain, lung, liver, and other organs. Palliative therapies included whole-brain radiotherapy or other low-dose treatments. If the patient received the intended course, this was categorized as full. If incomplete, it was considered partial.
Billing Deviations
The complete document review allowed for close evaluation of paid therapy and identification of gaps in billing (eg, charges not found in extracted data that should have occurred) for external beam radiotherapy patients. Conversely, extra charges, such as an additional weekly treatment management charge (CPT code 77427), would be noted. Patients were expected to have the number of treatments specified in the summary, a clinical treatment planning code, and weekly treatment management notes from physicians and physicists every 5 fractions. Consultations and follow-up visits were expected to have 1 visit code; CPT codes 99205 and 99215, respectively, were used to estimate costs in their absence.
Costs were based on Medicare rates as of January 1 of the year in which they were accrued. 7-10 Duplicates were charges with the same code, date, billed quantity, and paid amounts for a given patient. These would always be considered erroneous. Medicare treatment costs for procedures such as intensity modulated radiotherapy (CPT code 77385 or 77386) are available on the Medicare website. When reviewing locality deviations for 77427, there was a maximum of 33% increase in Medicare rates. Therefore, for treatment codes, one would expect the range to be at least the Medicare rate and maximally 33% higher. These rates are negotiated with insurance companies, but this range was used for the purpose of reviewing and adjusting large data sets.
RESULTS
Since 2018, > 500 community care consults have been placed by radiation oncology for treatment in the community, with more following implementation of the VA MISSION Act. Use of radiation oncology community care services annually increased during the study period for this facility (Table 1, Figure 2). Of the 325 community care consults placed from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024, 248 radiation oncology SEOCs were recorded with charges for 181 patients (range, 1-5 SEOCs). Long drive time was the rationale for > 97% of patients directed to community care (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Based on AMCMS data, $22.2 million was billed and $2.7 million was paid (20%) for 8747 CPT codes. Each community care interval cost the VA a median (range) of $5000 ($8-$168,000 (Figure 3).



After reviewing ROS charges extracted from CTM, 20 additional patients had radiation oncology charges but did not have a radiation oncology SEOC for 268 episodes of care for 201 unique patients. In addition to the 20 patients who did not have a SEOC, 42 nonradiation oncology SEOCs contained 1148 radiation oncology codes, corresponding to almost $500,000 paid. Additional charges of about $416,000, which included biologic agents (eg, durvalumab, nivolumab), procedures (eg, mastectomies), and ambulance rides were inappropriately added to radiation oncology SEOCs.
While 77% of consultations were scanned into CPRS and JLV, only 54% of completion summaries were available with an estimated $115,000 in additional costs. The total adjusted costs was about $2.9 million. Almost 37% of SEOCs were for visits only. For the 166 SEOCs where patients received any radiation treatment or planning, the median cost was $18,000. Differences in SEOC pathways are shown in Figure 4. One hundred twenty-one SEOCs (45%) followed the standard pathway, with median SEOC costs of $15,500; when corrected for radiation-specific costs, the median cost increased to $18,000. When adjusted for billing irregularities, the median cost was $20,600. Ninety-nine SEOCs (37%) were for consultation/ follow-up visits only, with a median cost of $220. When omitting shared scans and nonradiation therapy costs and correcting for billing gaps, the median cost decreased to $170. A median of $9200 was paid per patient, with $12,900 for radiation therapy-specific costs and $13,300 adjusted for billing deviations. Narrowing to the 106 patients who received full, radical courses, the median SEOC, ROS, and adjusted radiation therapy costs increased to $19,400, $22,200, and $22,900, respectively (Table 2, Figure 5). Seventy-one SEOCs (26%) had already seen a radiation oncologist before the VA radiation oncology department was aware, and 49 SEOCs (18%) had retroactive approvals (Supplemental materials available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).



Every consultation charge was reviewed. A typical patient following the standard pathway (eAppendix 2, available at doi:10.12788/ fp.0585) exhibited a predictable pattern of consultation payment, simulation and planning, multiple radiation treatments interspersed with treatment management visits and a cone-down phase, and finishing with a follow-up visit. A less predictable case with excess CPT codes, gaps in charges, and an additional unexpected palliative course is shown in eAppendix 3 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Gaps occurred in 42% of SEOCs with missed bills costing as much as $12,000. For example, a patient with lung cancer had a treatment summary note for lung cancer after completion that showed the patient received 30 fractions of 2 Gy, a typical course. Only 10 treatment codes and 3 of 6 weekly treatment management codes were available. There was a gap of 20 volumetric modulated arc therapy treatments, 3 physics weekly status checks, 3 physician managements notes, and a computed tomography simulation charge.


Between AMCMS and CTM, 10,005 CPT codes were evaluated; 1255 (12.5%) were unique to AMCMS (either related to the radiation oncology course, such as Evaluation and Management CPT codes or “other” unrelated codes) while 1158 (11.6%) were unique to CTM. Of the 7592 CPT codes shared between AMCMS and CTM, there was a discrepancy in 135 (1.8%); all were duplicates (CTM showed double payment while AMCMS showed $0 paid). The total CPT code costs came to $3.2 million with $560,000 unique to SEOCs and $500,000 unique to CTM. Treatment codes were the most common (33%) as shown in Table 3 and accounted for 55% of the cost ($1.8 million). About 700 CPT codes were considered “other,” typically for biologic therapeutic agents (Table 4 and eAppendix 4, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).



DISCUSSION
The current method of reporting radiation oncology costs used by VA is insufficient and misleading. Better data are needed to summarize purchased care costs to guide decisions about community care at the VA. Investigations into whether the extra costs for quality care (ie, expensive capital equipment, specialized staff, mandatory accreditations) are worthwhile if omitted at other facilities patients choose for their health care needs. No study has defined specialty care-specific costs by evaluating billing receipts from the CDW to answer the question. Kenamond et al highlight the need for radiation oncology for rural patients.11 Drive time was cited as the reason for community care referral for 97% of veterans, many of whom lived in rural locations. Of patients with rurality information who enrolled in community care, 57% came from rural or highly rural counties, and this ratio held for those who received full curative therapies. An executive administrator relying on AMCMS reports would see a median SEOC cost of $5000, but without ROS knowledge in coding, the administrator would miss many additional costs. For example, 2 patients who each had 5 SEOCs during the evaluated period, incurred a total cost of only $1800.
Additionally, an administrator could include miscategorized costs with significant ramifications. The 2 most expensive SEOCs were not typical radiation oncology treatments. A patient undergoing radium-223 dichloride therapy incurred charges exceeding $165,000, contributing disproportionately to the overall median cost analysis; this would normally be administered by the nuclear medicine department. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy are uniformly overseen by medical oncology services, but drug administration codes were still found in radiation oncology SEOCs. A patient (whose SEOC was discontinued but accrued charges) had an electrocardiogram interpretation for $8 as the SEOC cost; 3 other SEOCs continued to incur costs after being discontinued. There were 24 empty SEOCs for patients that had consults to the community, and 2 had notes stating treatment had been delivered yet there was no ROS costs or SEOC costs. Of the 268 encounters, 43% had some sort of billing irregularities (ie, missing treatment costs) that would be unlikely for a private practice to omit; it would be much more likely that the CDW miscategorized the payment despite confirmation of the 2 retrieval systems.
It would be inadvisable to make staffing decisions or forecast costs based on current SEOC reports without specialized curation. A simple yet effective improvement to the cost attribution process would be to restrict the analysis to encounters containing primary radiation treatment codes. This targeted approach allows more accurate identification of patients actively receiving radiation oncology treatment, while excluding those seen solely for consultations or follow-up visits. Implementing this refinement leads to a substantial increase in the median payment—from $5000 to $13,000—without requiring additional coding or data processing, thereby enhancing the accuracy of cost estimates with minimal effort.
Clarifying radiation oncology service costs requires addressing the time frame and services included, given laxity and interpretation of the SEOCs. VA community care departments have streamlined the reimbursement process at the expense of medical cost organization and accuracy; 86% of VA practitioners reported that ≥ 1 potential community health care partners had refused to work with the VA because of payment delays.12 Payments are contingent on correspondence from outside practices for community work. For radiation oncology, this includes the consultation but also critical radiation-related details of treatment, which were omitted nearly half the time. SEOC approval forms have many costly laboratory tests, imaging, and procedures that have little to do with radiation oncology cancer treatments but may be used in the workup and staging process; this creates noise when calculating radiation oncology fiscal cost.
The presumption that an episode of care equates to a completed radiation therapy course is incorrect; this occurs less than half of the time. An episode often refers to a return visit, or conversely, multiple treatment courses. As the patients’ medical homes are their VHA primary care practitioners, it would be particularly challenging to care for the patients without full treatment information, especially if adverse effects from therapy were to arise. As a tertiary specialty, radiation oncology does not seek out patients and are sent consultations from medical oncology, surgical, and medical oncologic specialties. Timesensitive processes such as workup, staging, and diagnosis often occur in parallel. This analysis revealed that patients see outside radiation oncologists prior to the VA. There are ≥ 100 patients who had radiation oncology codes without a radiation oncology SEOC or community care consultation, and in many cases, the consultation was placed after the patient was seen.
Given the lack of uniformity and standardization of patient traffic, the typical and expected pathways were insufficient to find the costs. Too many opportunities for errors and incorrect categorization of costs meant a different method would be necessary. Starting at the inception of the community care consult, only 1 diagnosis code can be entered. For patients with multiple diagnoses, one would not be able to tell what was treated without chart access. Radiation oncology consults come from primary and specialty care practitioners and nurses throughout the VA. Oftentimes, the referral would be solicited by the community radiation oncology clinic, diagnosing community specialty (ie, urology for a patient with prostate cancer), or indirectly from the patient through primary care. Many cases were retroactively approved as the veteran had already been consulted by the community care radiation oncologist. If the patient is drive-time eligible, it would be unlikely that they would leave and choose to return to the VA. There is no way for a facility VA service chief or administrator to mitigate VA community costs of care, especially as shown by the miscategorization of several codes. Database challenges exacerbate the issue: 1 patient changed her first and last name during this time frame, and 2 patients had the same name but different social security numbers. In order to strictly find costs between 2 discrete timepoints, 39 (15%) SEOCs were split and incomplete, and 6 SEOCs contained charges for 2 different patients. This was corrected, and all inadvertent charges were cancelled. Only 1 ICD code is allowed per community care consultation, so an investigation is required to find costs for patients with multiple sites of disease. Additionally, 5 of the patients marked for drive time were actually patients who received Gamma Knife and brachytherapy, services not available at the VA.
Hanks et al first attempted to calculate cost of radiation oncology services. External beam prostate cancer radiotherapy at 3 suburban California centers cost $6750 ($20,503 inflation adjusted) per patient before October 1984 and $5600 ($17,010 inflation adjusted) afterwards.13 According to the American Society for Radiation Oncology, Advocacy Radiation Oncology Case Rate Program Curative radiation courses should cost $20,000 to $30,000 and palliative courses should cost $10,000 to $15,000. These costs are consistent with totals demonstrated in this analysis and similar to the inflation-adjusted Hanks et al figures. Preliminary findings suggest that radiation treatment constituted more than half of the total expenditures, with a notable $4 million increase in adjusted cost compared to the Medicare rates, indicating significant variation. Direct comparisons with Medicaid or commercial payer rates remain unexplored.
Future Directions
During the study period, 201 patients received 186 courses of radiation therapy in the community, while 1014 patients were treated in-house for a total of 833 courses. A forthcoming analysis will directly compare the cost of in-house care with that of communitybased treatment, specifically breaking down expenditure differences by diagnosis. Future research should investigate strategies to align reimbursement with quality metrics, including the potential role of tertiary accreditation in incentivizing high-value care. Additional work is also warranted to assess patient out-ofpocket expenses across care settings and to benchmark VA reimbursement against Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance rates. In any case, with the increasing possibility of fewer fractions for treatments such as stereotactic radiotherapy or palliative care therapy, there is a clear financial incentive to treat as frequently as allowed despite equal clinical outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Veterans increasingly choose to receive care closer to home if the option is available. In the VA iron triangle, cost comes at the expense of access but quantifying this has proved elusive in the cost accounting model currently used at the VA.1 The inclusion of all charges loosely associated with SEOCs significantly impairs the ability to conduct meaningful cost analyses. The current VA methodology not only introduces substantial noise into the data but also leads to a marked underestimation of the true cost of care delivered in community settings. Such misrepresentation risks driving policy decisions that could inappropriately reduce or eliminate in-house radiation oncology services. Categorizing costs effectively in the VA could assist in making managerial and administrative decisions and would prevent damaging service lines based on misleading or incorrect data. A system which differentiates between patients who have received any treatment codes vs those who have not would increase accuracy.
William Kissick’s description of health care’s iron triangle in 1994 still resonates. Access, quality, and cost will always come at the expense of the others.1 In 2018, Congress passed the VA MISSION Act, allowing patients to pursue community care options for extended waits (> 28 days) or longer distance drive times of > 60 minutes for specialty care services, such as radiation oncology. According to Albanese et al, the VA MISSION Act sought to address gaps in care for veterans living in rural and underserved areas.2 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) continues to increase community care spending, with a 13.8% increase in fiscal year 2024 and an expected cost of > $40 billion for 2025.3 One could argue this pays for access for remote patients and quality when services are unavailable, making it a direct application of the iron triangle.
The VA MISSION Act also bolstered the expansion of existing community care department staff to expediently facilitate and coordinate care and payments.2 Cost management and monitoring have become critical in predicting future staff requirements, maintaining functionality, and ensuring patients receive optimal care. The VHA purchases care through partner networks and defines these bundled health care services as standard episodes of care (SEOCs), which are “clinically related health care services for a specific unique illness or medical condition… over a defined period of time.”4 Medicare publishes its rates quarterly, and outpatient procedure pricing is readily available online.5 Along these same lines, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) publishes a current list of available procedures and associated Current Procedure Technology (CPT) codes that are covered under its VA fee schedule for community care.
Unique challenges persist when using this system to accurately account for radiation oncology expenditures. This study was based on the current practices at the Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center (RLRVAMC), a large 1a hospital. A detailed analysis reveals the contemporaneous cost of radiation oncology cancer care from October 1, 2021, through February 1, 2024, highlights the challenges in SEOC definition and duration, communication issues between RLRVAMC and purchase partners, inconsistencies in billing, erroneous payments, and difficulty of cost categorization.
METHODS
Community care radiation oncology-related costs were examined from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024 for RLRVAMC, 6 months prior to billing data extraction. Figure 1 shows a simple radiation oncology patient pathway with consultation or visit, simulation and planning, and treatment, with codes used to check billing. It illustrates the expected relationships between the VHA (radiation oncology, primary, and specialty care) and community care (clinicians and radiation oncology treatment sites).

VHA standard operating procedures for a patient requesting community-based radiation oncology care require a board-certified radiation oncologist at RLRVAMC to review and approve the outside care request. Community care radiation oncology consultation data were accessed from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using Pyramid Analytics (V25.2). Nurses, physicians, and community care staff can add comments, forward consultations to other services, and mark them as complete or discontinued, when appropriate. Consultations not completed within 91 days are automatically discontinued. All community care requests from 2018 through 2024 were extracted; analysis began April 1, 2021, 6 months prior to the cost evaluation date of October 1, 2021.
An approved consultation is reviewed for eligibility by a nurse in the community care department and assigned an authorization number (a VA prefix followed by 12 digits). Billing codes are approved and organized by the community care networks, and all procedure codes should be captured and labeled under this number. The VAMC Community Care department obtains initial correspondence from the treating clinicians. Subsequent records from the treating radiation oncologist are expected to be scanned into the electronic health record and made accessible via the VA Joint Legacy Viewer (JLV) and Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS).
Radiation Oncology SEOC
The start date of the radiation oncology SEOC is determined by the community care nurse based on guidance established by the VA. It can be manually backdated or delayed, but current practice is to start at first visit or procedure code entry after approval from the VAMC Radiation Oncology department. Approved CPT codes from SEOC versions between October 1, 2021, and February 1, 2024, are in eAppendix 1 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). These generally include 10 types of encounters, about 115 different laboratory tests, 115 imaging studies, 25 simulation and planning procedures, and 115 radiation treatment codes. The radiation oncology SEOCs during the study period had an approval duration of 180 days. Advanced Medical Cost Management Solutions software (AMCMS) is the VHA data analytics platform for community care medical service costs. AMCMS includes all individual CPT codes billed by specific radiation oncology SEOC versions. Data are refreshed monthly, and all charges were extracted on September 12, 2024, > 6 months after the final evaluated service date to allow for complete billing returns.6

Radiation Oncology-Specific Costs
The VA Close to Me (CTM) program was used to find 84 specific radiation oncology CPT codes, nearly all within the 77.XXX or G6.XXX series, which included all radiation oncology-specific (ROS) codes (except visits accrued during consultation and return appointments). ROS costs are those that could not be performed by any other service and include procedures related to radiation oncology simulation, treatment planning, treatment delivery (with or without image guidance), and physician or physicist management. All ROS costs should be included in a patient’s radiation oncology SEOC. Other costs that may accompany operating room or brachytherapy administration did not follow a 77.XXX or G6.XXX pattern but were included in total radiation therapy operating costs.
Data obtained from AMCMS and CTM included patient name and identifier; CPT billed amount; CPT paid amount; dates of service; number of claims; International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD) diagnosis; and VA authorization numbers. Only CTM listed code modifiers. Only items categorized as paid were included in the analysis. Charges associated with discontinued consultations that had accrued costs also were included. Codes that were not directly related to ROS were separately characterized as other and further subcategorized.
Deep Dive Categorization
All scanned documents tagged to the community consultation were accessed and evaluated for completeness by a radiation oncologist (RS). The presence or absence of consultation notes and treatment summaries was evaluated based on necessity (ie, not needed for continuation of care or treatment was not given). In the absence of a specific completion summary or follow-up note detailing the treatment modality, number of fractions, and treatment sites, available documentation, including clinical notes and billing information, was used. Radical or curative therapies were identified as courses expected to eradicate disease, including stereotactic ablative radiotherapy to the brain, lung, liver, and other organs. Palliative therapies included whole-brain radiotherapy or other low-dose treatments. If the patient received the intended course, this was categorized as full. If incomplete, it was considered partial.
Billing Deviations
The complete document review allowed for close evaluation of paid therapy and identification of gaps in billing (eg, charges not found in extracted data that should have occurred) for external beam radiotherapy patients. Conversely, extra charges, such as an additional weekly treatment management charge (CPT code 77427), would be noted. Patients were expected to have the number of treatments specified in the summary, a clinical treatment planning code, and weekly treatment management notes from physicians and physicists every 5 fractions. Consultations and follow-up visits were expected to have 1 visit code; CPT codes 99205 and 99215, respectively, were used to estimate costs in their absence.
Costs were based on Medicare rates as of January 1 of the year in which they were accrued. 7-10 Duplicates were charges with the same code, date, billed quantity, and paid amounts for a given patient. These would always be considered erroneous. Medicare treatment costs for procedures such as intensity modulated radiotherapy (CPT code 77385 or 77386) are available on the Medicare website. When reviewing locality deviations for 77427, there was a maximum of 33% increase in Medicare rates. Therefore, for treatment codes, one would expect the range to be at least the Medicare rate and maximally 33% higher. These rates are negotiated with insurance companies, but this range was used for the purpose of reviewing and adjusting large data sets.
RESULTS
Since 2018, > 500 community care consults have been placed by radiation oncology for treatment in the community, with more following implementation of the VA MISSION Act. Use of radiation oncology community care services annually increased during the study period for this facility (Table 1, Figure 2). Of the 325 community care consults placed from October 1, 2021, to February 1, 2024, 248 radiation oncology SEOCs were recorded with charges for 181 patients (range, 1-5 SEOCs). Long drive time was the rationale for > 97% of patients directed to community care (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Based on AMCMS data, $22.2 million was billed and $2.7 million was paid (20%) for 8747 CPT codes. Each community care interval cost the VA a median (range) of $5000 ($8-$168,000 (Figure 3).



After reviewing ROS charges extracted from CTM, 20 additional patients had radiation oncology charges but did not have a radiation oncology SEOC for 268 episodes of care for 201 unique patients. In addition to the 20 patients who did not have a SEOC, 42 nonradiation oncology SEOCs contained 1148 radiation oncology codes, corresponding to almost $500,000 paid. Additional charges of about $416,000, which included biologic agents (eg, durvalumab, nivolumab), procedures (eg, mastectomies), and ambulance rides were inappropriately added to radiation oncology SEOCs.
While 77% of consultations were scanned into CPRS and JLV, only 54% of completion summaries were available with an estimated $115,000 in additional costs. The total adjusted costs was about $2.9 million. Almost 37% of SEOCs were for visits only. For the 166 SEOCs where patients received any radiation treatment or planning, the median cost was $18,000. Differences in SEOC pathways are shown in Figure 4. One hundred twenty-one SEOCs (45%) followed the standard pathway, with median SEOC costs of $15,500; when corrected for radiation-specific costs, the median cost increased to $18,000. When adjusted for billing irregularities, the median cost was $20,600. Ninety-nine SEOCs (37%) were for consultation/ follow-up visits only, with a median cost of $220. When omitting shared scans and nonradiation therapy costs and correcting for billing gaps, the median cost decreased to $170. A median of $9200 was paid per patient, with $12,900 for radiation therapy-specific costs and $13,300 adjusted for billing deviations. Narrowing to the 106 patients who received full, radical courses, the median SEOC, ROS, and adjusted radiation therapy costs increased to $19,400, $22,200, and $22,900, respectively (Table 2, Figure 5). Seventy-one SEOCs (26%) had already seen a radiation oncologist before the VA radiation oncology department was aware, and 49 SEOCs (18%) had retroactive approvals (Supplemental materials available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).



Every consultation charge was reviewed. A typical patient following the standard pathway (eAppendix 2, available at doi:10.12788/ fp.0585) exhibited a predictable pattern of consultation payment, simulation and planning, multiple radiation treatments interspersed with treatment management visits and a cone-down phase, and finishing with a follow-up visit. A less predictable case with excess CPT codes, gaps in charges, and an additional unexpected palliative course is shown in eAppendix 3 (available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585). Gaps occurred in 42% of SEOCs with missed bills costing as much as $12,000. For example, a patient with lung cancer had a treatment summary note for lung cancer after completion that showed the patient received 30 fractions of 2 Gy, a typical course. Only 10 treatment codes and 3 of 6 weekly treatment management codes were available. There was a gap of 20 volumetric modulated arc therapy treatments, 3 physics weekly status checks, 3 physician managements notes, and a computed tomography simulation charge.


Between AMCMS and CTM, 10,005 CPT codes were evaluated; 1255 (12.5%) were unique to AMCMS (either related to the radiation oncology course, such as Evaluation and Management CPT codes or “other” unrelated codes) while 1158 (11.6%) were unique to CTM. Of the 7592 CPT codes shared between AMCMS and CTM, there was a discrepancy in 135 (1.8%); all were duplicates (CTM showed double payment while AMCMS showed $0 paid). The total CPT code costs came to $3.2 million with $560,000 unique to SEOCs and $500,000 unique to CTM. Treatment codes were the most common (33%) as shown in Table 3 and accounted for 55% of the cost ($1.8 million). About 700 CPT codes were considered “other,” typically for biologic therapeutic agents (Table 4 and eAppendix 4, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0585).



DISCUSSION
The current method of reporting radiation oncology costs used by VA is insufficient and misleading. Better data are needed to summarize purchased care costs to guide decisions about community care at the VA. Investigations into whether the extra costs for quality care (ie, expensive capital equipment, specialized staff, mandatory accreditations) are worthwhile if omitted at other facilities patients choose for their health care needs. No study has defined specialty care-specific costs by evaluating billing receipts from the CDW to answer the question. Kenamond et al highlight the need for radiation oncology for rural patients.11 Drive time was cited as the reason for community care referral for 97% of veterans, many of whom lived in rural locations. Of patients with rurality information who enrolled in community care, 57% came from rural or highly rural counties, and this ratio held for those who received full curative therapies. An executive administrator relying on AMCMS reports would see a median SEOC cost of $5000, but without ROS knowledge in coding, the administrator would miss many additional costs. For example, 2 patients who each had 5 SEOCs during the evaluated period, incurred a total cost of only $1800.
Additionally, an administrator could include miscategorized costs with significant ramifications. The 2 most expensive SEOCs were not typical radiation oncology treatments. A patient undergoing radium-223 dichloride therapy incurred charges exceeding $165,000, contributing disproportionately to the overall median cost analysis; this would normally be administered by the nuclear medicine department. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy are uniformly overseen by medical oncology services, but drug administration codes were still found in radiation oncology SEOCs. A patient (whose SEOC was discontinued but accrued charges) had an electrocardiogram interpretation for $8 as the SEOC cost; 3 other SEOCs continued to incur costs after being discontinued. There were 24 empty SEOCs for patients that had consults to the community, and 2 had notes stating treatment had been delivered yet there was no ROS costs or SEOC costs. Of the 268 encounters, 43% had some sort of billing irregularities (ie, missing treatment costs) that would be unlikely for a private practice to omit; it would be much more likely that the CDW miscategorized the payment despite confirmation of the 2 retrieval systems.
It would be inadvisable to make staffing decisions or forecast costs based on current SEOC reports without specialized curation. A simple yet effective improvement to the cost attribution process would be to restrict the analysis to encounters containing primary radiation treatment codes. This targeted approach allows more accurate identification of patients actively receiving radiation oncology treatment, while excluding those seen solely for consultations or follow-up visits. Implementing this refinement leads to a substantial increase in the median payment—from $5000 to $13,000—without requiring additional coding or data processing, thereby enhancing the accuracy of cost estimates with minimal effort.
Clarifying radiation oncology service costs requires addressing the time frame and services included, given laxity and interpretation of the SEOCs. VA community care departments have streamlined the reimbursement process at the expense of medical cost organization and accuracy; 86% of VA practitioners reported that ≥ 1 potential community health care partners had refused to work with the VA because of payment delays.12 Payments are contingent on correspondence from outside practices for community work. For radiation oncology, this includes the consultation but also critical radiation-related details of treatment, which were omitted nearly half the time. SEOC approval forms have many costly laboratory tests, imaging, and procedures that have little to do with radiation oncology cancer treatments but may be used in the workup and staging process; this creates noise when calculating radiation oncology fiscal cost.
The presumption that an episode of care equates to a completed radiation therapy course is incorrect; this occurs less than half of the time. An episode often refers to a return visit, or conversely, multiple treatment courses. As the patients’ medical homes are their VHA primary care practitioners, it would be particularly challenging to care for the patients without full treatment information, especially if adverse effects from therapy were to arise. As a tertiary specialty, radiation oncology does not seek out patients and are sent consultations from medical oncology, surgical, and medical oncologic specialties. Timesensitive processes such as workup, staging, and diagnosis often occur in parallel. This analysis revealed that patients see outside radiation oncologists prior to the VA. There are ≥ 100 patients who had radiation oncology codes without a radiation oncology SEOC or community care consultation, and in many cases, the consultation was placed after the patient was seen.
Given the lack of uniformity and standardization of patient traffic, the typical and expected pathways were insufficient to find the costs. Too many opportunities for errors and incorrect categorization of costs meant a different method would be necessary. Starting at the inception of the community care consult, only 1 diagnosis code can be entered. For patients with multiple diagnoses, one would not be able to tell what was treated without chart access. Radiation oncology consults come from primary and specialty care practitioners and nurses throughout the VA. Oftentimes, the referral would be solicited by the community radiation oncology clinic, diagnosing community specialty (ie, urology for a patient with prostate cancer), or indirectly from the patient through primary care. Many cases were retroactively approved as the veteran had already been consulted by the community care radiation oncologist. If the patient is drive-time eligible, it would be unlikely that they would leave and choose to return to the VA. There is no way for a facility VA service chief or administrator to mitigate VA community costs of care, especially as shown by the miscategorization of several codes. Database challenges exacerbate the issue: 1 patient changed her first and last name during this time frame, and 2 patients had the same name but different social security numbers. In order to strictly find costs between 2 discrete timepoints, 39 (15%) SEOCs were split and incomplete, and 6 SEOCs contained charges for 2 different patients. This was corrected, and all inadvertent charges were cancelled. Only 1 ICD code is allowed per community care consultation, so an investigation is required to find costs for patients with multiple sites of disease. Additionally, 5 of the patients marked for drive time were actually patients who received Gamma Knife and brachytherapy, services not available at the VA.
Hanks et al first attempted to calculate cost of radiation oncology services. External beam prostate cancer radiotherapy at 3 suburban California centers cost $6750 ($20,503 inflation adjusted) per patient before October 1984 and $5600 ($17,010 inflation adjusted) afterwards.13 According to the American Society for Radiation Oncology, Advocacy Radiation Oncology Case Rate Program Curative radiation courses should cost $20,000 to $30,000 and palliative courses should cost $10,000 to $15,000. These costs are consistent with totals demonstrated in this analysis and similar to the inflation-adjusted Hanks et al figures. Preliminary findings suggest that radiation treatment constituted more than half of the total expenditures, with a notable $4 million increase in adjusted cost compared to the Medicare rates, indicating significant variation. Direct comparisons with Medicaid or commercial payer rates remain unexplored.
Future Directions
During the study period, 201 patients received 186 courses of radiation therapy in the community, while 1014 patients were treated in-house for a total of 833 courses. A forthcoming analysis will directly compare the cost of in-house care with that of communitybased treatment, specifically breaking down expenditure differences by diagnosis. Future research should investigate strategies to align reimbursement with quality metrics, including the potential role of tertiary accreditation in incentivizing high-value care. Additional work is also warranted to assess patient out-ofpocket expenses across care settings and to benchmark VA reimbursement against Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance rates. In any case, with the increasing possibility of fewer fractions for treatments such as stereotactic radiotherapy or palliative care therapy, there is a clear financial incentive to treat as frequently as allowed despite equal clinical outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
Veterans increasingly choose to receive care closer to home if the option is available. In the VA iron triangle, cost comes at the expense of access but quantifying this has proved elusive in the cost accounting model currently used at the VA.1 The inclusion of all charges loosely associated with SEOCs significantly impairs the ability to conduct meaningful cost analyses. The current VA methodology not only introduces substantial noise into the data but also leads to a marked underestimation of the true cost of care delivered in community settings. Such misrepresentation risks driving policy decisions that could inappropriately reduce or eliminate in-house radiation oncology services. Categorizing costs effectively in the VA could assist in making managerial and administrative decisions and would prevent damaging service lines based on misleading or incorrect data. A system which differentiates between patients who have received any treatment codes vs those who have not would increase accuracy.
- Kissick W. Medicine’s Dilemmas: Infinite Needs Versus Finite Resources. 1st ed. Yale University Press; 1994.
- Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
- Office of Management and Budget (US). Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2025. Washington, DC: US Government Publishing Office; 2024. Available from: US Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2025 Budget Submission: Budget in Brief.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran care claims. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/revenue-ops/Veteran-Care-Claims.asp
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Accessed April 3, 2025. Procedure price lookup https://www.medicare.gov/procedure-price-lookup
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. WellHive -Enterprise. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://department.va.gov/privacy/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2023/05/FY23WellHiveEnterprisePIA.pdf
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU21a physician fee schedule, January 2021 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu21a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU22a physician fee schedule, January 2022 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu22a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a physician fee schedule, January 2023 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/medicare-fee-service-payment/physicianfeesched/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu23a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a Medicare Physician Fee Schedule rates effective January 1, 2024, through March 8, 2024. Accessed on April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu24a
- Kenamond MC, Mourad WF, Randall ME, Kaushal A. No oncology patient left behind: challenges and solutions in rural radiation oncology. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100289. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100289
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Hanks GE, Dunlap K. A comparison of the cost of various treatment methods for early cancer of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12(10):1879-1881. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90334-2
- American Society of Radiation Oncology. Radiation oncology case rate program (ROCR). Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.astro.org/advocacy/key-issues-8f3e5a3b76643265ee93287d79c4fc40/rocr
- Kissick W. Medicine’s Dilemmas: Infinite Needs Versus Finite Resources. 1st ed. Yale University Press; 1994.
- Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
- Office of Management and Budget (US). Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2025. Washington, DC: US Government Publishing Office; 2024. Available from: US Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2025 Budget Submission: Budget in Brief.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veteran care claims. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/revenue-ops/Veteran-Care-Claims.asp
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Accessed April 3, 2025. Procedure price lookup https://www.medicare.gov/procedure-price-lookup
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. WellHive -Enterprise. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://department.va.gov/privacy/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2023/05/FY23WellHiveEnterprisePIA.pdf
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU21a physician fee schedule, January 2021 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu21a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU22a physician fee schedule, January 2022 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicaremedicare-fee-service-paymentphysicianfeeschedpfs-relative-value-files/rvu22a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a physician fee schedule, January 2023 release. Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/medicare-fee-service-payment/physicianfeesched/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu23a
- US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. RVU23a Medicare Physician Fee Schedule rates effective January 1, 2024, through March 8, 2024. Accessed on April 3, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/pfs-relative-value-files/rvu24a
- Kenamond MC, Mourad WF, Randall ME, Kaushal A. No oncology patient left behind: challenges and solutions in rural radiation oncology. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100289. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100289
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Hanks GE, Dunlap K. A comparison of the cost of various treatment methods for early cancer of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12(10):1879-1881. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(86)90334-2
- American Society of Radiation Oncology. Radiation oncology case rate program (ROCR). Accessed April 3, 2025. https://www.astro.org/advocacy/key-issues-8f3e5a3b76643265ee93287d79c4fc40/rocr
Community Care Radiation Oncology Cost Calculations for a VA Medical Center
Community Care Radiation Oncology Cost Calculations for a VA Medical Center