User login
Allopurinol found safe in patients with concomitant gout, CKD
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
HIV+ patients get good outcomes after kidney or liver transplant
in new research that represents some of the longest follow-up on these patients to date.
The findings further support the inclusion of people with HIV in transplant resource allocation, say the researchers.
“Overall, the excellent outcomes following liver and kidney transplant recipients in HIV-infected recipients justify the utilization of a scarce resource,” senior author Peter G. Stock, MD, PhD, surgical director of the Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program and surgical director of the Pediatric Renal Transplant Program at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
“Many centers still view HIV as a strict contraindication [for transplantation]. This data shows it is not,” he emphasized.
The study, published in JAMA Surgery, involved HIV-positive patients who received kidney or liver transplants between 2000 and 2019 at UCSF, which has unique access to some of the longest-term data on those outcomes.
“UCSF was the first U.S. center to do transplants routinely in people with HIV, and based on the large volume of transplants that are performed, we were able to use propensity matching to address the comparison of HIV-positive and negative liver and kidney transplant recipients at a single center,” Dr. Stock explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, there are no long-term reports [greater than 10 years] on [transplant] outcomes in the HIV-positive population.”
Commenting on the study, David Klassen, MD, chief medical officer of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS), noted that the findings “confirm previous research done at UCSF and reported in the New England Journal of Medicine” in 2010. “It extends the previous findings.”
“The take-home message is that these HIV-positive patients can be successfully transplanted with expected good outcomes and will derive substantial benefit from transplantation,” Dr. Klassen said.
Kidney transplant patient survival lower, graft survival similar
For the kidney transplant analysis, 119 HIV-positive recipients were propensity matched with 655 recipients who were HIV-negative, with the patients’ mean age about 52 and approximately 70% male.
At 15-years post-transplant, patient survival was 53.6% among the HIV-positive patients versus 79.6% for HIV-negative (P = .03).
Graft survival among the kidney transplant patients was proportionally higher among HIV-positive patients after 15 years (75% vs. 57%); however, the difference was not statistically significant (P = .77).
First author Arya Zarinsefat, MD, of the Department of Surgery at UCSF, speculated that the lower long-term patient survival among HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients may reflect known cardiovascular risks among those patients.
“We postulated that part of this may be due to the fact that HIV-positive patients certainly have additional comorbidities, specifically cardiovascular” ones, he told this news organization.
“When looking at the survival curve, survival was nearly identical at 5 years and only started to diverge at 10 years post-transplant,” he noted.
A further evaluation of patients with HIV who were co-infected with hepatitis C (HCV) showed that those with HIV-HCV co-infection prior to the center’s introduction of anti-HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications in 2014 had the lowest survival rate of all subgroups, at 57.1% at 5 years post-transplant (P = .045 vs. those treated after 2014).
Liver transplant patient survival similar
In terms of liver transplant outcomes, among 83 HIV-positive recipients who were propensity-matched with 468 HIV-negative recipients, the mean age was about 53 and about 66% were male.
The patient survival rates at 15 years were not significantly different between the groups, at 70% for HIV-positive and 75.7% for HIV-negative, (P = .12).
Similar to the kidney transplant recipients, the worst survival among all liver transplant subgroups was among HIV-HCV co-infected patients prior to access to HCV direct-acting antivirals in 2014, with a 5-year survival of 59.5% (P = .04).
“Since the advent of HCV direct-acting antivirals, liver transplant outcomes in HCV mono-infected patients are comparable to HCV/HIV co-infected recipients,” Dr. Stock said.
Acute rejection rates higher with HIV-positivity versus national averages
The rates of acute rejection at 1 year in the kidney and liver transplant, HIV-positive groups – at about 20% and 30%, respectively – were, however, higher than national average incidence rates of about 10% at 1 year.
Long-term data on those patients showed the acute rejection affected graft survival outcomes with kidney transplant recipients: HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients who had at least one episode of acute rejection had a graft survival of just 52.8% at 15 years post-transplant, compared with 91.8% among recipients without acute rejection.
Such differences were not observed among HIV-positive liver transplant recipients.
The authors note that the increased risk of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant patients is consistent with previous studies, with causes that may be multifactorial.
Top theories include drug interactions with protease inhibitors, resulting in some centers transitioning HIV-infected patients from those regimens to integrase-based regimens prior to transplant.
“The management and prevention of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant [patients] will therefore continue to be a key component in the care of these patients,” the authors note in their study.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and Dr. Klassen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new research that represents some of the longest follow-up on these patients to date.
The findings further support the inclusion of people with HIV in transplant resource allocation, say the researchers.
“Overall, the excellent outcomes following liver and kidney transplant recipients in HIV-infected recipients justify the utilization of a scarce resource,” senior author Peter G. Stock, MD, PhD, surgical director of the Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program and surgical director of the Pediatric Renal Transplant Program at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
“Many centers still view HIV as a strict contraindication [for transplantation]. This data shows it is not,” he emphasized.
The study, published in JAMA Surgery, involved HIV-positive patients who received kidney or liver transplants between 2000 and 2019 at UCSF, which has unique access to some of the longest-term data on those outcomes.
“UCSF was the first U.S. center to do transplants routinely in people with HIV, and based on the large volume of transplants that are performed, we were able to use propensity matching to address the comparison of HIV-positive and negative liver and kidney transplant recipients at a single center,” Dr. Stock explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, there are no long-term reports [greater than 10 years] on [transplant] outcomes in the HIV-positive population.”
Commenting on the study, David Klassen, MD, chief medical officer of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS), noted that the findings “confirm previous research done at UCSF and reported in the New England Journal of Medicine” in 2010. “It extends the previous findings.”
“The take-home message is that these HIV-positive patients can be successfully transplanted with expected good outcomes and will derive substantial benefit from transplantation,” Dr. Klassen said.
Kidney transplant patient survival lower, graft survival similar
For the kidney transplant analysis, 119 HIV-positive recipients were propensity matched with 655 recipients who were HIV-negative, with the patients’ mean age about 52 and approximately 70% male.
At 15-years post-transplant, patient survival was 53.6% among the HIV-positive patients versus 79.6% for HIV-negative (P = .03).
Graft survival among the kidney transplant patients was proportionally higher among HIV-positive patients after 15 years (75% vs. 57%); however, the difference was not statistically significant (P = .77).
First author Arya Zarinsefat, MD, of the Department of Surgery at UCSF, speculated that the lower long-term patient survival among HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients may reflect known cardiovascular risks among those patients.
“We postulated that part of this may be due to the fact that HIV-positive patients certainly have additional comorbidities, specifically cardiovascular” ones, he told this news organization.
“When looking at the survival curve, survival was nearly identical at 5 years and only started to diverge at 10 years post-transplant,” he noted.
A further evaluation of patients with HIV who were co-infected with hepatitis C (HCV) showed that those with HIV-HCV co-infection prior to the center’s introduction of anti-HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications in 2014 had the lowest survival rate of all subgroups, at 57.1% at 5 years post-transplant (P = .045 vs. those treated after 2014).
Liver transplant patient survival similar
In terms of liver transplant outcomes, among 83 HIV-positive recipients who were propensity-matched with 468 HIV-negative recipients, the mean age was about 53 and about 66% were male.
The patient survival rates at 15 years were not significantly different between the groups, at 70% for HIV-positive and 75.7% for HIV-negative, (P = .12).
Similar to the kidney transplant recipients, the worst survival among all liver transplant subgroups was among HIV-HCV co-infected patients prior to access to HCV direct-acting antivirals in 2014, with a 5-year survival of 59.5% (P = .04).
“Since the advent of HCV direct-acting antivirals, liver transplant outcomes in HCV mono-infected patients are comparable to HCV/HIV co-infected recipients,” Dr. Stock said.
Acute rejection rates higher with HIV-positivity versus national averages
The rates of acute rejection at 1 year in the kidney and liver transplant, HIV-positive groups – at about 20% and 30%, respectively – were, however, higher than national average incidence rates of about 10% at 1 year.
Long-term data on those patients showed the acute rejection affected graft survival outcomes with kidney transplant recipients: HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients who had at least one episode of acute rejection had a graft survival of just 52.8% at 15 years post-transplant, compared with 91.8% among recipients without acute rejection.
Such differences were not observed among HIV-positive liver transplant recipients.
The authors note that the increased risk of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant patients is consistent with previous studies, with causes that may be multifactorial.
Top theories include drug interactions with protease inhibitors, resulting in some centers transitioning HIV-infected patients from those regimens to integrase-based regimens prior to transplant.
“The management and prevention of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant [patients] will therefore continue to be a key component in the care of these patients,” the authors note in their study.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and Dr. Klassen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new research that represents some of the longest follow-up on these patients to date.
The findings further support the inclusion of people with HIV in transplant resource allocation, say the researchers.
“Overall, the excellent outcomes following liver and kidney transplant recipients in HIV-infected recipients justify the utilization of a scarce resource,” senior author Peter G. Stock, MD, PhD, surgical director of the Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program and surgical director of the Pediatric Renal Transplant Program at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
“Many centers still view HIV as a strict contraindication [for transplantation]. This data shows it is not,” he emphasized.
The study, published in JAMA Surgery, involved HIV-positive patients who received kidney or liver transplants between 2000 and 2019 at UCSF, which has unique access to some of the longest-term data on those outcomes.
“UCSF was the first U.S. center to do transplants routinely in people with HIV, and based on the large volume of transplants that are performed, we were able to use propensity matching to address the comparison of HIV-positive and negative liver and kidney transplant recipients at a single center,” Dr. Stock explained.
“To the best of our knowledge, there are no long-term reports [greater than 10 years] on [transplant] outcomes in the HIV-positive population.”
Commenting on the study, David Klassen, MD, chief medical officer of the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS), noted that the findings “confirm previous research done at UCSF and reported in the New England Journal of Medicine” in 2010. “It extends the previous findings.”
“The take-home message is that these HIV-positive patients can be successfully transplanted with expected good outcomes and will derive substantial benefit from transplantation,” Dr. Klassen said.
Kidney transplant patient survival lower, graft survival similar
For the kidney transplant analysis, 119 HIV-positive recipients were propensity matched with 655 recipients who were HIV-negative, with the patients’ mean age about 52 and approximately 70% male.
At 15-years post-transplant, patient survival was 53.6% among the HIV-positive patients versus 79.6% for HIV-negative (P = .03).
Graft survival among the kidney transplant patients was proportionally higher among HIV-positive patients after 15 years (75% vs. 57%); however, the difference was not statistically significant (P = .77).
First author Arya Zarinsefat, MD, of the Department of Surgery at UCSF, speculated that the lower long-term patient survival among HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients may reflect known cardiovascular risks among those patients.
“We postulated that part of this may be due to the fact that HIV-positive patients certainly have additional comorbidities, specifically cardiovascular” ones, he told this news organization.
“When looking at the survival curve, survival was nearly identical at 5 years and only started to diverge at 10 years post-transplant,” he noted.
A further evaluation of patients with HIV who were co-infected with hepatitis C (HCV) showed that those with HIV-HCV co-infection prior to the center’s introduction of anti-HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications in 2014 had the lowest survival rate of all subgroups, at 57.1% at 5 years post-transplant (P = .045 vs. those treated after 2014).
Liver transplant patient survival similar
In terms of liver transplant outcomes, among 83 HIV-positive recipients who were propensity-matched with 468 HIV-negative recipients, the mean age was about 53 and about 66% were male.
The patient survival rates at 15 years were not significantly different between the groups, at 70% for HIV-positive and 75.7% for HIV-negative, (P = .12).
Similar to the kidney transplant recipients, the worst survival among all liver transplant subgroups was among HIV-HCV co-infected patients prior to access to HCV direct-acting antivirals in 2014, with a 5-year survival of 59.5% (P = .04).
“Since the advent of HCV direct-acting antivirals, liver transplant outcomes in HCV mono-infected patients are comparable to HCV/HIV co-infected recipients,” Dr. Stock said.
Acute rejection rates higher with HIV-positivity versus national averages
The rates of acute rejection at 1 year in the kidney and liver transplant, HIV-positive groups – at about 20% and 30%, respectively – were, however, higher than national average incidence rates of about 10% at 1 year.
Long-term data on those patients showed the acute rejection affected graft survival outcomes with kidney transplant recipients: HIV-positive kidney transplant recipients who had at least one episode of acute rejection had a graft survival of just 52.8% at 15 years post-transplant, compared with 91.8% among recipients without acute rejection.
Such differences were not observed among HIV-positive liver transplant recipients.
The authors note that the increased risk of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant patients is consistent with previous studies, with causes that may be multifactorial.
Top theories include drug interactions with protease inhibitors, resulting in some centers transitioning HIV-infected patients from those regimens to integrase-based regimens prior to transplant.
“The management and prevention of acute rejection in HIV-positive kidney transplant [patients] will therefore continue to be a key component in the care of these patients,” the authors note in their study.
The study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and Dr. Klassen have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pheochromocytoma: An Incidental Finding in an Asymptomatic Older Adult With Renal Oncocytoma
A high index of suspicion for pheochromocytoma is necessary during the workup of secondary hypertension as untreated pheochromocytoma may lead to significant morbidity and mortality, especially in patients who require any surgical treatment.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare catecholamine-secreting tumor of chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla or sympathetic ganglia, occurring in about 0.2 to 0.5% of patients with hypertension.1-3 However, in a review of 54 autopsy-proven cases of pheochromocytoma, about 50% of the patients with hypertension were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma.4
Pheochromocytoma is usually diagnosed based on symptoms of hyperadrenergic spells, resistant hypertension, especially in the young, with a pressor response to the anesthesia stress test and adrenal incidentaloma.
The classic triad of symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma includes episodic headache (90%), sweating (60-70%), and palpitations (70%).2,5 Sustained or paroxysmal hypertension is the most common symptom reported in about 95% of patients with pheochromocytoma. Other symptoms include pallor, tremors, dyspnea, generalized weakness, orthostatic hypotension, cardiomyopathy, or hyperglycemia.6 However, about 10% of patients with pheochromocytoma are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Secondary causes of hypertension are usually suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension.8
Approximately 10% of catecholamine-secreting tumors are malignant.9-11 Benign and malignant pheochromocytoma have a similar biochemical and histologic presentation and are differentiated based on local invasion into the surrounding tissues and organs (eg, kidney, liver) or distant metastasis.
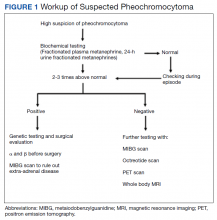
A typical workup of a suspected patient with pheochromocytoma includes biochemical tests, including measurements of urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamine. Patients with positive biochemical tests should undergo localization of the tumor with an imaging study either with an adrenal/abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan. If a patient has paraganglioma or an adrenal mass > 10 cm or negative abdominal imaging with a positive biochemical test, further imaging with an iobenguane I-123 scan is needed (Figure 1).
In this article, we present an unusual case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma in a patient with right-sided renal oncocytoma who underwent an uneventful nephrectomy and adrenalectomy.
Case Presentation
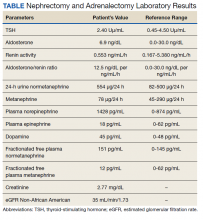
A 72-year-old male with a medical history of diabetes, hypertension, sensory neuropathy, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) status posttransurethral resection of the prostate, and chronic renal failure presented to establish care with the Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center. His medications included losartan 50 mg by mouth daily, diltiazem 180 mg extended-release by mouth daily, carvedilol 6.25 mg by mouth twice a day, and tamsulosin 0.4 mg by mouth daily. His presenting vitals were blood pressure (BP), 112/74 left arm sitting, pulse, 63/beats per min, and body mass index, 34. On physical examination, the patient was alert and oriented, and the chest was clear to auscultation without wheeze or rhonchi. On cardiac examination, heart rate and rhythm were regular; S1 and S2 were normal with no added murmurs, rubs or gallops, and no jugular venous distension. The abdomen was soft, nontender, with no palpable mass. His laboratory results showed sodium, 142 mmol/L; potassium, 5.3 mmol/L; chloride, 101 mmol/L; carbon dioxide, 24 mmol/L; albumin, 4.3 g/dL; creatinine, 1.89 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen, 29 mg/dL; estimated glomerular filtration rate non-African American, 35 mL/min/1.73; 24-h urine creatinine clearance, 105 mL/min; protein, 1306 mg/24 h (Table).
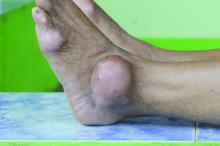
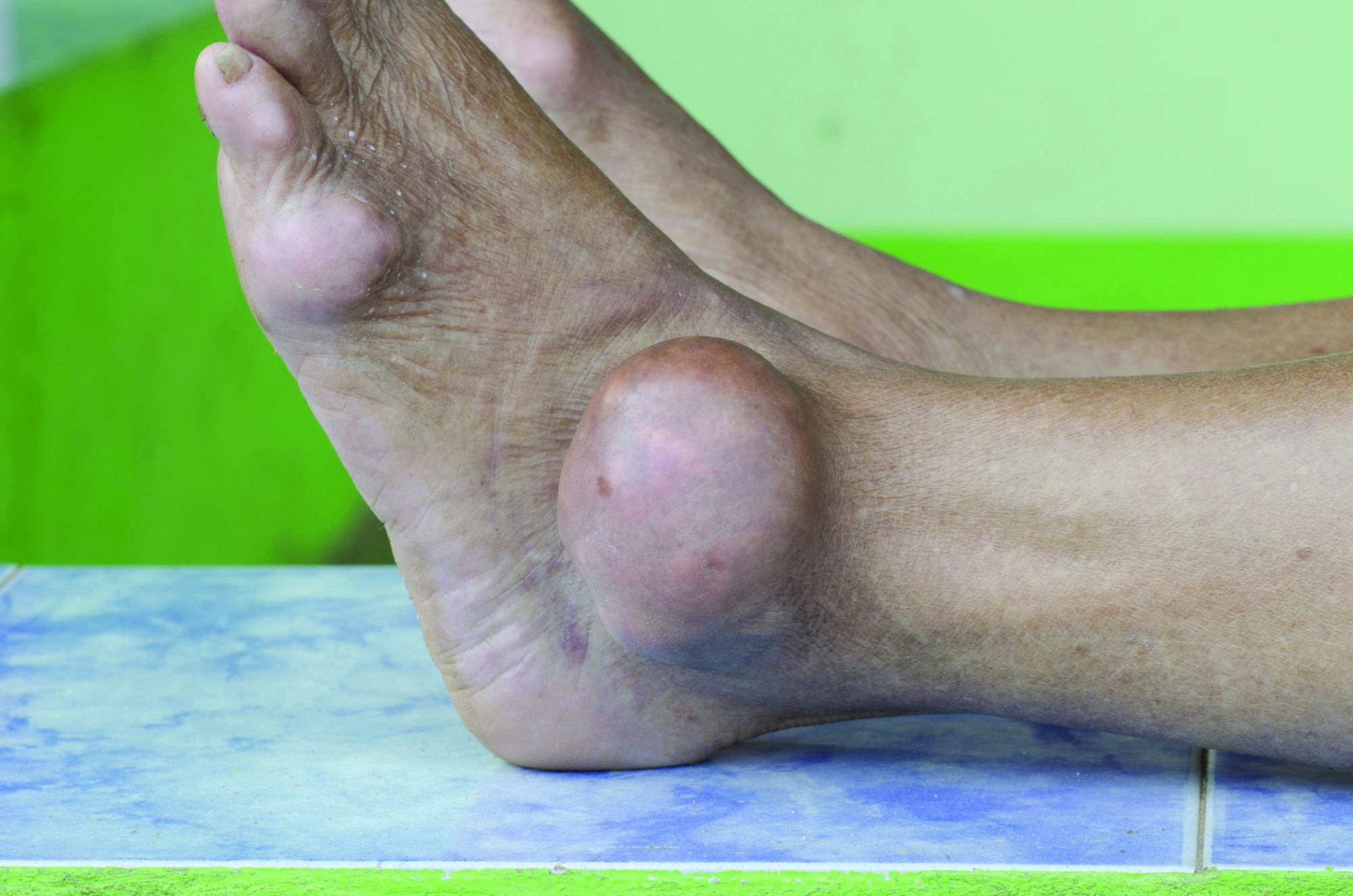
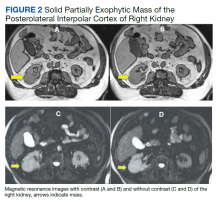
His renal ultrasound showed an exophytic isoechoic mass or complex cyst at the lateral aspect of the lower pole of the right kidney, measuring 45 mm in diameter. An MRI of the abdomen with and without contrast showed a solid partially exophytic mass of the posterolateral interpolar cortex of the right kidney, measuring 5.9 cm in the greatest dimension (Figure 2). No definite involvement of Gerota fascia was noted, a 1-cm metastasis to the right adrenal gland was present, renal veins were patent, and there was no upper retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy.
Treatment and Follow-up
The patient underwent right-hand-assisted lap-aroscopic radical nephrectomy and right adre-nalectomy without any complications. However, the surgical pathology report showed oncocytoma of the kidney (5.7 cm), pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland (1.4 cm), and papillary adenoma of the kidney (0.7 cm). Right kidney nephrectomy showed non-neoplastic renal parenchyma, diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Renal Pathology Society 2010 diabetic nephropathy class IIb), severe mesangial expansion, moderate interstitial fibrosis, moderate arteriosclerosis, and mild arteriolosclerosis.
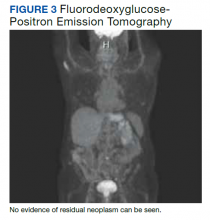
A fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan was significant for right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy and showed no significant evidence of residual neoplasm or local or distant metastases. A nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor and single positron emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan showed normal activity throughout the body and no evidence of abnormal activity (Figure 3).
Discussion
Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension. However, the real numbers are thought to be > 0.2 to 0.5%.1,2,4 Patients with pheochromocytoma should undergo surgical adrenal resection after appropriate medical preparation. Patients with pheochromocytoma who are not diagnosed preoperatively have increased surgical mortality rates due to fatal hypertensive crises, malignant arrhythmia, and multiorgan failure as a result of hypertensive crisis.15 Anesthetic drugs during surgery also can exacerbate the cardiotoxic effects of catecholamines. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are used in patients with pheochromocytoma.16
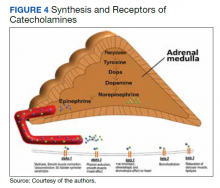
This case of pheochromocytoma illustrated no classic symptoms of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia, and the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. BP was well controlled with losartan, diltiazem, and a β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol). As the patient was not known to have pheochromocytoma, he did not undergo preoperative medical therapy. Figure 4 illustrates the receptors stimulate catecholamines, and the drugs blocking these receptors prevent hypertensive crisis during surgery. However, the surgery was without potential complications (ie, hypertensive crisis, malignant arrhythmia, or multiorgan failure). The patient was diagnosed incidentally on histopathology after right radical nephrectomy and adrenalectomy due to solid partially exophytic right renal mass (5.9 cm) with right adrenal metastasis. About 10% of patients are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Sometimes, the symptoms may be ignored because of the episodic nature. Other possible reasons can be small, nonfunctional tumors or the use of antihypertensive medications suppressing the symptoms.7
The adrenal mass that was initially thought to be a metastasis of right kidney mass was later confirmed as pheochromocytoma. One possible explanation for uneventful surgery could be the use of β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol), α-1 adrenergic blocker (tamsulosin) along with nondihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (diltiazem) as part of the patient’s antihypertensive and BPH medication regimen. Another possible explanation could be silent or episodically secreting pheochromocytoma with a small functional portion.
Subsequent workup after adrenalectomy, including urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamines, were not consistent with catecholamine hypersecretion. A 24-hour urine fractionated metanephrines test has about 98% sensitivity and 98% specificity. Elevated plasma norepinephrine was thought to be due to renal failure because it was < 3-fold the upper limit of normal, which is considered to be a possible indication of pheochromocytoma.17,18 The nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor, SPECT, and FDG-PET CT studies were negative for residual pheochromocytoma. Other imaging studies to consider in patients with suspected catecholamine-secreting tumor with positive biochemical test and negative abdominal imaging are a whole-body MRI scan, 68-Ga DOTATATE (gallium 68 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10 tetraacetic acid-octreotate) or FDG-PET scan.19
In a review of 54 autopsy-proven pheochromocytoma cases by Sutton and colleagues in 1981, 74% of the patients were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma in their life.4 Similarly, in a retrospective study of hospital autopsies by McNeil and colleagues, one incidental pheochromocytoma was detected in every 2031 autopsies (0.05%).20 In another case series of 41 patients with pheochromocytoma-related adrenalectomy, almost 50% of the pheochromocytomas were detected incidentally on imaging studies.21 Although the number of incidental findings are decreasing due to advances in screening techniques, a significant number of patients remain undiagnosed. Multiple cases of diagnosis of pheochromocytoma on autopsy of patients who died of hemodynamic instability (ie, hypertensive crisis, hypotension crisis precipitated by surgery for adrenal or nonadrenal conditions) are reported.3 To the best of our knowledge, there are no case reports published on the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma after adrenalectomy in an asymptomatic patient without intraoperative complications.
The goal of preoperative medical therapy includes BP control, prevention of tachycardia, and volume expansion. The preoperative medications regimens are combined α- and β-adrenergic blockade, calcium channel blockers, and metyrosine. According to clinical practice guidelines of the Endocrine Society in 2014, the α-adrenergic blockers should be started first at least 7 days before surgery to control BP and to cause vasodilation. Early use of α-blockers is required to prevent cardiotoxicity. The β-adrenergic blockers should be started after the adequate α-adrenergic blockade, typically 2 to 3 days before surgery, as early use can cause vasoconstriction in patients with pheochromocytoma. The α-adrenergic blockers include phenoxybenzamine (nonselective long-acting nonspecific α-adrenergic blocking agent), and selective α-1 adrenergic blockers (doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin). The β-adrenergic blocker (ie, propranolol, metoprolol) should be started cautiously with a low dose and slowly titrated to control heart rate. A high sodium diet and increased fluid intake also are recommended 7 to 14 days before surgery. A sudden drop in catecholamines can cause hypotension during an operation. Continuous fluid infusions are given to prevent hypotension.22 Similarly, anesthetic agents also should be modified to prevent cardiotoxic effects. Rocuronium and vecuronium are less cardiotoxic compared with other sympathomimetic muscle relaxants. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are preferred. α-blockers are continued throughout the operation. Biochemical testing with fractionated metanephrines is performed about 1 to 2 weeks postoperatively to look for recurrence of the disease.23
Secondary causes of hypertension are suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension before aged 40 years. Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension, and older adult patients are rarely diagnosed with pheochromocytoma.24 In this report, pheochromocytoma was detected in a 72-year-old hypertensive patient. Therefore, a pheochromocytoma diagnosis should not be ignored in the older adult patient with adrenal mass and hypertension treated with more than one drug. The authors recommend any patient undergoing surgery with adrenal lesion should be considered for the screening of possible pheochromocytoma and prepared preoperatively, especially any patient with renal cell carcinoma with adrenal metastasis.
Conclusions
Asymptomatic pheochromocytoma is an unusual but serious condition, especially for patients undergoing a surgical procedure. An adrenal mass may be ignored in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic older adult patients and is mostly considered as adrenal metastasis when present with other malignancies. Fortunately, the nephrectomy and adrenalectomy in our case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma was uneventful, but pheochromocytoma should be ruled out before a surgical procedure, as an absence of medical pretreatment can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, we suggest a more careful screening of pheochromocytoma in patients with an adrenal mass (primary or metastatic) and hypertension treated with multiple antihypertensive drugs, even in older adult patients.
1. Omura M, Saito J, Yamaguchi K, Kakuta Y, Nishikawa T. Prospective study on the prevalence of secondary hypertension among hypertensive patients visiting a general outpatient clinic in Japan. Hypertens Res. 2004;27(3):193-202. doi:10.1291/hypres.27.193
2. Stein PP, Black HR. A simplified diagnostic approach to pheochromocytoma: a review of the literature and report of one institution’s experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991;70(1):46-66. doi:10.1097/00005792-199101000-00004
3. Beard CM, Sheps SG, Kurland LT, Carney JA, Lie JT. Occurrence of pheochromocytoma in Rochester, Minnesota, 1950 through 1979. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983;58(12):802-804.
4. Sutton MG, Sheps SG, Lie JT. Prevalence of clinically unsuspected pheochromocytoma: review of a 50-year autopsy series. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56(6):354-360.
5. Manger WM, Gifford RW Jr. Pheochromocytoma. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4(1):62-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.01452.x
6. Kassim TA, Clarke DD, Mai VQ, Clyde PW, Mohamed Shakir KM. Catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy. Endocr Pract. 2008;14(9):1137-1149. doi:10.4158/EP.14.9.1137
7. Kudva YC, Young WF, Thompson GB, Grant CS, Van Heerden JA. Adrenal incidentaloma: an important component of the clinical presentation spectrum of benign sporadic adrenal pheochromocytoma. The Endocrinologist. 1999;9(2):77-80. doi:10.1097/00019616-199903000-00002
8. Puar TH, Mok Y, Debajyoti R, Khoo J, How CH, Ng AK. Secondary hypertension in adults. Singapore Med J. 2016;57(5):228-232. doi:10.11622/smedj.2016087
9. Bravo EL. Pheochromocytoma: new concepts and future trends. Kidney Int. 1991;40(3):544-556. doi:10.1038/ki.1991.244
10. Plouin PF, Chatellier G, Fofol I, Corvol P. Tumor recurrence and hypertension persistence after successful pheochromocytoma operation. Hypertension. 1997;29(5):1133-1139. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.29.5.1133
11. Hamidi O, Young WF Jr, Iñiguez-Ariza NM, et al. Malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: 272 patients over 55 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(9):3296-3305. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00992
12. Kenny L, Rizzo V, Trevis J, Assimakopoulou E, Timon D. The unexpected diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma in the anaesthetic room. Ann Card Anaesth. 2018;21(3):307-310. doi:10.4103/aca.ACA_206_17
13. Johnston PC, Silversides JA, Wallace H, et al. Phaeochromocytoma crisis: two cases of undiagnosed phaeochromocytoma presenting after elective nonrelated surgical procedures. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2013;2013:514714. doi:10.1155/2013/514714
14. Shen SJ, Cheng HM, Chiu AW, Chou CW, Chen JY. Perioperative hypertensive crisis in clinically silent pheochromocytomas: report of four cases. Chang Gung Med J. 2005;28(1):44-50.
15. Lo CY, Lam KY, Wat MS, Lam KS. Adrenal pheochromocytoma remains a frequently overlooked diagnosis. Am J Surg. 2000;179(3):212-215. doi:10.1016/s0002-9610(00)00296-8
16. Myklejord DJ. Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma: the anesthesiologist nightmare. Clin Med Res. 2004;2(1):59-62. doi:10.3121/cmr.2.1.59
17. Stumvoll M, Radjaipour M, Seif F. Diagnostic considerations in pheochromocytoma and chronic hemodialysis: case report and review of the literature. Am J Nephrol. 1995;15(2):147-151. doi:10.1159/000168820
18. Morioka M, Yuihama S, Nakajima T, et al. Incidentally discovered pheochromocytoma in long-term hemodialysis patients. Int J Urol. 2002;9(12):700-703. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2002.00553.x
19. ˇCtvrtlík F, Koranda P, Schovánek J, Škarda J, Hartmann I, Tüdös Z. Current diagnostic imaging of pheochromocytomas and implications for therapeutic strategy. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3151-3160. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.5871
20. McNeil AR, Blok BH, Koelmeyer TD, Burke MP, Hilton JM. Phaeochromocytomas discovered during coronial autopsies in Sydney, Melbourne and Auckland. Aust N Z J Med. 2000;30(6):648-652. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2000.tb04358.x
21. Baguet JP, Hammer L, Mazzuco TL, et al. Circumstances of discovery of phaeochromocytoma: a retrospective study of 41 consecutive patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150(5):681-686. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1500681
22. Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(6):1915-1942. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-1498
23. Dortzbach K, Gainsburg DM, Frost EA. Variants of pheochromocytoma and their anesthetic implications--a case report and literature review. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2010;20(6):897-905.
24. Januszewicz W, Chodakowska J, Styczy´nski G. Secondary hypertension in the elderly. J Hum Hypertens. 1998;12(9):603-606. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1000673
A high index of suspicion for pheochromocytoma is necessary during the workup of secondary hypertension as untreated pheochromocytoma may lead to significant morbidity and mortality, especially in patients who require any surgical treatment.
A high index of suspicion for pheochromocytoma is necessary during the workup of secondary hypertension as untreated pheochromocytoma may lead to significant morbidity and mortality, especially in patients who require any surgical treatment.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare catecholamine-secreting tumor of chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla or sympathetic ganglia, occurring in about 0.2 to 0.5% of patients with hypertension.1-3 However, in a review of 54 autopsy-proven cases of pheochromocytoma, about 50% of the patients with hypertension were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma.4
Pheochromocytoma is usually diagnosed based on symptoms of hyperadrenergic spells, resistant hypertension, especially in the young, with a pressor response to the anesthesia stress test and adrenal incidentaloma.
The classic triad of symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma includes episodic headache (90%), sweating (60-70%), and palpitations (70%).2,5 Sustained or paroxysmal hypertension is the most common symptom reported in about 95% of patients with pheochromocytoma. Other symptoms include pallor, tremors, dyspnea, generalized weakness, orthostatic hypotension, cardiomyopathy, or hyperglycemia.6 However, about 10% of patients with pheochromocytoma are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Secondary causes of hypertension are usually suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension.8
Approximately 10% of catecholamine-secreting tumors are malignant.9-11 Benign and malignant pheochromocytoma have a similar biochemical and histologic presentation and are differentiated based on local invasion into the surrounding tissues and organs (eg, kidney, liver) or distant metastasis.
A typical workup of a suspected patient with pheochromocytoma includes biochemical tests, including measurements of urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamine. Patients with positive biochemical tests should undergo localization of the tumor with an imaging study either with an adrenal/abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan. If a patient has paraganglioma or an adrenal mass > 10 cm or negative abdominal imaging with a positive biochemical test, further imaging with an iobenguane I-123 scan is needed (Figure 1).
In this article, we present an unusual case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma in a patient with right-sided renal oncocytoma who underwent an uneventful nephrectomy and adrenalectomy.
Case Presentation
A 72-year-old male with a medical history of diabetes, hypertension, sensory neuropathy, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) status posttransurethral resection of the prostate, and chronic renal failure presented to establish care with the Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center. His medications included losartan 50 mg by mouth daily, diltiazem 180 mg extended-release by mouth daily, carvedilol 6.25 mg by mouth twice a day, and tamsulosin 0.4 mg by mouth daily. His presenting vitals were blood pressure (BP), 112/74 left arm sitting, pulse, 63/beats per min, and body mass index, 34. On physical examination, the patient was alert and oriented, and the chest was clear to auscultation without wheeze or rhonchi. On cardiac examination, heart rate and rhythm were regular; S1 and S2 were normal with no added murmurs, rubs or gallops, and no jugular venous distension. The abdomen was soft, nontender, with no palpable mass. His laboratory results showed sodium, 142 mmol/L; potassium, 5.3 mmol/L; chloride, 101 mmol/L; carbon dioxide, 24 mmol/L; albumin, 4.3 g/dL; creatinine, 1.89 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen, 29 mg/dL; estimated glomerular filtration rate non-African American, 35 mL/min/1.73; 24-h urine creatinine clearance, 105 mL/min; protein, 1306 mg/24 h (Table).
His renal ultrasound showed an exophytic isoechoic mass or complex cyst at the lateral aspect of the lower pole of the right kidney, measuring 45 mm in diameter. An MRI of the abdomen with and without contrast showed a solid partially exophytic mass of the posterolateral interpolar cortex of the right kidney, measuring 5.9 cm in the greatest dimension (Figure 2). No definite involvement of Gerota fascia was noted, a 1-cm metastasis to the right adrenal gland was present, renal veins were patent, and there was no upper retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy.
Treatment and Follow-up
The patient underwent right-hand-assisted lap-aroscopic radical nephrectomy and right adre-nalectomy without any complications. However, the surgical pathology report showed oncocytoma of the kidney (5.7 cm), pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland (1.4 cm), and papillary adenoma of the kidney (0.7 cm). Right kidney nephrectomy showed non-neoplastic renal parenchyma, diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Renal Pathology Society 2010 diabetic nephropathy class IIb), severe mesangial expansion, moderate interstitial fibrosis, moderate arteriosclerosis, and mild arteriolosclerosis.
A fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan was significant for right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy and showed no significant evidence of residual neoplasm or local or distant metastases. A nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor and single positron emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan showed normal activity throughout the body and no evidence of abnormal activity (Figure 3).
Discussion
Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension. However, the real numbers are thought to be > 0.2 to 0.5%.1,2,4 Patients with pheochromocytoma should undergo surgical adrenal resection after appropriate medical preparation. Patients with pheochromocytoma who are not diagnosed preoperatively have increased surgical mortality rates due to fatal hypertensive crises, malignant arrhythmia, and multiorgan failure as a result of hypertensive crisis.15 Anesthetic drugs during surgery also can exacerbate the cardiotoxic effects of catecholamines. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are used in patients with pheochromocytoma.16
This case of pheochromocytoma illustrated no classic symptoms of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia, and the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. BP was well controlled with losartan, diltiazem, and a β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol). As the patient was not known to have pheochromocytoma, he did not undergo preoperative medical therapy. Figure 4 illustrates the receptors stimulate catecholamines, and the drugs blocking these receptors prevent hypertensive crisis during surgery. However, the surgery was without potential complications (ie, hypertensive crisis, malignant arrhythmia, or multiorgan failure). The patient was diagnosed incidentally on histopathology after right radical nephrectomy and adrenalectomy due to solid partially exophytic right renal mass (5.9 cm) with right adrenal metastasis. About 10% of patients are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Sometimes, the symptoms may be ignored because of the episodic nature. Other possible reasons can be small, nonfunctional tumors or the use of antihypertensive medications suppressing the symptoms.7
The adrenal mass that was initially thought to be a metastasis of right kidney mass was later confirmed as pheochromocytoma. One possible explanation for uneventful surgery could be the use of β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol), α-1 adrenergic blocker (tamsulosin) along with nondihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (diltiazem) as part of the patient’s antihypertensive and BPH medication regimen. Another possible explanation could be silent or episodically secreting pheochromocytoma with a small functional portion.
Subsequent workup after adrenalectomy, including urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamines, were not consistent with catecholamine hypersecretion. A 24-hour urine fractionated metanephrines test has about 98% sensitivity and 98% specificity. Elevated plasma norepinephrine was thought to be due to renal failure because it was < 3-fold the upper limit of normal, which is considered to be a possible indication of pheochromocytoma.17,18 The nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor, SPECT, and FDG-PET CT studies were negative for residual pheochromocytoma. Other imaging studies to consider in patients with suspected catecholamine-secreting tumor with positive biochemical test and negative abdominal imaging are a whole-body MRI scan, 68-Ga DOTATATE (gallium 68 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10 tetraacetic acid-octreotate) or FDG-PET scan.19
In a review of 54 autopsy-proven pheochromocytoma cases by Sutton and colleagues in 1981, 74% of the patients were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma in their life.4 Similarly, in a retrospective study of hospital autopsies by McNeil and colleagues, one incidental pheochromocytoma was detected in every 2031 autopsies (0.05%).20 In another case series of 41 patients with pheochromocytoma-related adrenalectomy, almost 50% of the pheochromocytomas were detected incidentally on imaging studies.21 Although the number of incidental findings are decreasing due to advances in screening techniques, a significant number of patients remain undiagnosed. Multiple cases of diagnosis of pheochromocytoma on autopsy of patients who died of hemodynamic instability (ie, hypertensive crisis, hypotension crisis precipitated by surgery for adrenal or nonadrenal conditions) are reported.3 To the best of our knowledge, there are no case reports published on the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma after adrenalectomy in an asymptomatic patient without intraoperative complications.
The goal of preoperative medical therapy includes BP control, prevention of tachycardia, and volume expansion. The preoperative medications regimens are combined α- and β-adrenergic blockade, calcium channel blockers, and metyrosine. According to clinical practice guidelines of the Endocrine Society in 2014, the α-adrenergic blockers should be started first at least 7 days before surgery to control BP and to cause vasodilation. Early use of α-blockers is required to prevent cardiotoxicity. The β-adrenergic blockers should be started after the adequate α-adrenergic blockade, typically 2 to 3 days before surgery, as early use can cause vasoconstriction in patients with pheochromocytoma. The α-adrenergic blockers include phenoxybenzamine (nonselective long-acting nonspecific α-adrenergic blocking agent), and selective α-1 adrenergic blockers (doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin). The β-adrenergic blocker (ie, propranolol, metoprolol) should be started cautiously with a low dose and slowly titrated to control heart rate. A high sodium diet and increased fluid intake also are recommended 7 to 14 days before surgery. A sudden drop in catecholamines can cause hypotension during an operation. Continuous fluid infusions are given to prevent hypotension.22 Similarly, anesthetic agents also should be modified to prevent cardiotoxic effects. Rocuronium and vecuronium are less cardiotoxic compared with other sympathomimetic muscle relaxants. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are preferred. α-blockers are continued throughout the operation. Biochemical testing with fractionated metanephrines is performed about 1 to 2 weeks postoperatively to look for recurrence of the disease.23
Secondary causes of hypertension are suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension before aged 40 years. Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension, and older adult patients are rarely diagnosed with pheochromocytoma.24 In this report, pheochromocytoma was detected in a 72-year-old hypertensive patient. Therefore, a pheochromocytoma diagnosis should not be ignored in the older adult patient with adrenal mass and hypertension treated with more than one drug. The authors recommend any patient undergoing surgery with adrenal lesion should be considered for the screening of possible pheochromocytoma and prepared preoperatively, especially any patient with renal cell carcinoma with adrenal metastasis.
Conclusions
Asymptomatic pheochromocytoma is an unusual but serious condition, especially for patients undergoing a surgical procedure. An adrenal mass may be ignored in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic older adult patients and is mostly considered as adrenal metastasis when present with other malignancies. Fortunately, the nephrectomy and adrenalectomy in our case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma was uneventful, but pheochromocytoma should be ruled out before a surgical procedure, as an absence of medical pretreatment can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, we suggest a more careful screening of pheochromocytoma in patients with an adrenal mass (primary or metastatic) and hypertension treated with multiple antihypertensive drugs, even in older adult patients.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare catecholamine-secreting tumor of chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla or sympathetic ganglia, occurring in about 0.2 to 0.5% of patients with hypertension.1-3 However, in a review of 54 autopsy-proven cases of pheochromocytoma, about 50% of the patients with hypertension were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma.4
Pheochromocytoma is usually diagnosed based on symptoms of hyperadrenergic spells, resistant hypertension, especially in the young, with a pressor response to the anesthesia stress test and adrenal incidentaloma.
The classic triad of symptoms associated with pheochromocytoma includes episodic headache (90%), sweating (60-70%), and palpitations (70%).2,5 Sustained or paroxysmal hypertension is the most common symptom reported in about 95% of patients with pheochromocytoma. Other symptoms include pallor, tremors, dyspnea, generalized weakness, orthostatic hypotension, cardiomyopathy, or hyperglycemia.6 However, about 10% of patients with pheochromocytoma are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Secondary causes of hypertension are usually suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension.8
Approximately 10% of catecholamine-secreting tumors are malignant.9-11 Benign and malignant pheochromocytoma have a similar biochemical and histologic presentation and are differentiated based on local invasion into the surrounding tissues and organs (eg, kidney, liver) or distant metastasis.
A typical workup of a suspected patient with pheochromocytoma includes biochemical tests, including measurements of urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamine. Patients with positive biochemical tests should undergo localization of the tumor with an imaging study either with an adrenal/abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan. If a patient has paraganglioma or an adrenal mass > 10 cm or negative abdominal imaging with a positive biochemical test, further imaging with an iobenguane I-123 scan is needed (Figure 1).
In this article, we present an unusual case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma in a patient with right-sided renal oncocytoma who underwent an uneventful nephrectomy and adrenalectomy.
Case Presentation
A 72-year-old male with a medical history of diabetes, hypertension, sensory neuropathy, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) status posttransurethral resection of the prostate, and chronic renal failure presented to establish care with the Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center. His medications included losartan 50 mg by mouth daily, diltiazem 180 mg extended-release by mouth daily, carvedilol 6.25 mg by mouth twice a day, and tamsulosin 0.4 mg by mouth daily. His presenting vitals were blood pressure (BP), 112/74 left arm sitting, pulse, 63/beats per min, and body mass index, 34. On physical examination, the patient was alert and oriented, and the chest was clear to auscultation without wheeze or rhonchi. On cardiac examination, heart rate and rhythm were regular; S1 and S2 were normal with no added murmurs, rubs or gallops, and no jugular venous distension. The abdomen was soft, nontender, with no palpable mass. His laboratory results showed sodium, 142 mmol/L; potassium, 5.3 mmol/L; chloride, 101 mmol/L; carbon dioxide, 24 mmol/L; albumin, 4.3 g/dL; creatinine, 1.89 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen, 29 mg/dL; estimated glomerular filtration rate non-African American, 35 mL/min/1.73; 24-h urine creatinine clearance, 105 mL/min; protein, 1306 mg/24 h (Table).
His renal ultrasound showed an exophytic isoechoic mass or complex cyst at the lateral aspect of the lower pole of the right kidney, measuring 45 mm in diameter. An MRI of the abdomen with and without contrast showed a solid partially exophytic mass of the posterolateral interpolar cortex of the right kidney, measuring 5.9 cm in the greatest dimension (Figure 2). No definite involvement of Gerota fascia was noted, a 1-cm metastasis to the right adrenal gland was present, renal veins were patent, and there was no upper retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy.
Treatment and Follow-up
The patient underwent right-hand-assisted lap-aroscopic radical nephrectomy and right adre-nalectomy without any complications. However, the surgical pathology report showed oncocytoma of the kidney (5.7 cm), pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland (1.4 cm), and papillary adenoma of the kidney (0.7 cm). Right kidney nephrectomy showed non-neoplastic renal parenchyma, diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Renal Pathology Society 2010 diabetic nephropathy class IIb), severe mesangial expansion, moderate interstitial fibrosis, moderate arteriosclerosis, and mild arteriolosclerosis.
A fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan was significant for right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy and showed no significant evidence of residual neoplasm or local or distant metastases. A nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor and single positron emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan showed normal activity throughout the body and no evidence of abnormal activity (Figure 3).
Discussion
Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension. However, the real numbers are thought to be > 0.2 to 0.5%.1,2,4 Patients with pheochromocytoma should undergo surgical adrenal resection after appropriate medical preparation. Patients with pheochromocytoma who are not diagnosed preoperatively have increased surgical mortality rates due to fatal hypertensive crises, malignant arrhythmia, and multiorgan failure as a result of hypertensive crisis.15 Anesthetic drugs during surgery also can exacerbate the cardiotoxic effects of catecholamines. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are used in patients with pheochromocytoma.16
This case of pheochromocytoma illustrated no classic symptoms of episodic headache, sweating, and tachycardia, and the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. BP was well controlled with losartan, diltiazem, and a β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol). As the patient was not known to have pheochromocytoma, he did not undergo preoperative medical therapy. Figure 4 illustrates the receptors stimulate catecholamines, and the drugs blocking these receptors prevent hypertensive crisis during surgery. However, the surgery was without potential complications (ie, hypertensive crisis, malignant arrhythmia, or multiorgan failure). The patient was diagnosed incidentally on histopathology after right radical nephrectomy and adrenalectomy due to solid partially exophytic right renal mass (5.9 cm) with right adrenal metastasis. About 10% of patients are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.7 Sometimes, the symptoms may be ignored because of the episodic nature. Other possible reasons can be small, nonfunctional tumors or the use of antihypertensive medications suppressing the symptoms.7
The adrenal mass that was initially thought to be a metastasis of right kidney mass was later confirmed as pheochromocytoma. One possible explanation for uneventful surgery could be the use of β-blocker with α-blocking activity (carvedilol), α-1 adrenergic blocker (tamsulosin) along with nondihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (diltiazem) as part of the patient’s antihypertensive and BPH medication regimen. Another possible explanation could be silent or episodically secreting pheochromocytoma with a small functional portion.
Subsequent workup after adrenalectomy, including urinary and fractionated plasma metanephrines and catecholamines, were not consistent with catecholamine hypersecretion. A 24-hour urine fractionated metanephrines test has about 98% sensitivity and 98% specificity. Elevated plasma norepinephrine was thought to be due to renal failure because it was < 3-fold the upper limit of normal, which is considered to be a possible indication of pheochromocytoma.17,18 The nuclear medicine (iobenguane I-123) tumor, SPECT, and FDG-PET CT studies were negative for residual pheochromocytoma. Other imaging studies to consider in patients with suspected catecholamine-secreting tumor with positive biochemical test and negative abdominal imaging are a whole-body MRI scan, 68-Ga DOTATATE (gallium 68 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10 tetraacetic acid-octreotate) or FDG-PET scan.19
In a review of 54 autopsy-proven pheochromocytoma cases by Sutton and colleagues in 1981, 74% of the patients were not clinically suspected for pheochromocytoma in their life.4 Similarly, in a retrospective study of hospital autopsies by McNeil and colleagues, one incidental pheochromocytoma was detected in every 2031 autopsies (0.05%).20 In another case series of 41 patients with pheochromocytoma-related adrenalectomy, almost 50% of the pheochromocytomas were detected incidentally on imaging studies.21 Although the number of incidental findings are decreasing due to advances in screening techniques, a significant number of patients remain undiagnosed. Multiple cases of diagnosis of pheochromocytoma on autopsy of patients who died of hemodynamic instability (ie, hypertensive crisis, hypotension crisis precipitated by surgery for adrenal or nonadrenal conditions) are reported.3 To the best of our knowledge, there are no case reports published on the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma after adrenalectomy in an asymptomatic patient without intraoperative complications.
The goal of preoperative medical therapy includes BP control, prevention of tachycardia, and volume expansion. The preoperative medications regimens are combined α- and β-adrenergic blockade, calcium channel blockers, and metyrosine. According to clinical practice guidelines of the Endocrine Society in 2014, the α-adrenergic blockers should be started first at least 7 days before surgery to control BP and to cause vasodilation. Early use of α-blockers is required to prevent cardiotoxicity. The β-adrenergic blockers should be started after the adequate α-adrenergic blockade, typically 2 to 3 days before surgery, as early use can cause vasoconstriction in patients with pheochromocytoma. The α-adrenergic blockers include phenoxybenzamine (nonselective long-acting nonspecific α-adrenergic blocking agent), and selective α-1 adrenergic blockers (doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin). The β-adrenergic blocker (ie, propranolol, metoprolol) should be started cautiously with a low dose and slowly titrated to control heart rate. A high sodium diet and increased fluid intake also are recommended 7 to 14 days before surgery. A sudden drop in catecholamines can cause hypotension during an operation. Continuous fluid infusions are given to prevent hypotension.22 Similarly, anesthetic agents also should be modified to prevent cardiotoxic effects. Rocuronium and vecuronium are less cardiotoxic compared with other sympathomimetic muscle relaxants. Short-acting anesthetic agents, such as fentanyl, are preferred. α-blockers are continued throughout the operation. Biochemical testing with fractionated metanephrines is performed about 1 to 2 weeks postoperatively to look for recurrence of the disease.23
Secondary causes of hypertension are suspected in multidrug resistant or sudden early onset of hypertension before aged 40 years. Pheochromocytoma is a rare cause of secondary hypertension, and older adult patients are rarely diagnosed with pheochromocytoma.24 In this report, pheochromocytoma was detected in a 72-year-old hypertensive patient. Therefore, a pheochromocytoma diagnosis should not be ignored in the older adult patient with adrenal mass and hypertension treated with more than one drug. The authors recommend any patient undergoing surgery with adrenal lesion should be considered for the screening of possible pheochromocytoma and prepared preoperatively, especially any patient with renal cell carcinoma with adrenal metastasis.
Conclusions
Asymptomatic pheochromocytoma is an unusual but serious condition, especially for patients undergoing a surgical procedure. An adrenal mass may be ignored in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic older adult patients and is mostly considered as adrenal metastasis when present with other malignancies. Fortunately, the nephrectomy and adrenalectomy in our case of asymptomatic pheochromocytoma was uneventful, but pheochromocytoma should be ruled out before a surgical procedure, as an absence of medical pretreatment can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, we suggest a more careful screening of pheochromocytoma in patients with an adrenal mass (primary or metastatic) and hypertension treated with multiple antihypertensive drugs, even in older adult patients.
1. Omura M, Saito J, Yamaguchi K, Kakuta Y, Nishikawa T. Prospective study on the prevalence of secondary hypertension among hypertensive patients visiting a general outpatient clinic in Japan. Hypertens Res. 2004;27(3):193-202. doi:10.1291/hypres.27.193
2. Stein PP, Black HR. A simplified diagnostic approach to pheochromocytoma: a review of the literature and report of one institution’s experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991;70(1):46-66. doi:10.1097/00005792-199101000-00004
3. Beard CM, Sheps SG, Kurland LT, Carney JA, Lie JT. Occurrence of pheochromocytoma in Rochester, Minnesota, 1950 through 1979. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983;58(12):802-804.
4. Sutton MG, Sheps SG, Lie JT. Prevalence of clinically unsuspected pheochromocytoma: review of a 50-year autopsy series. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56(6):354-360.
5. Manger WM, Gifford RW Jr. Pheochromocytoma. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4(1):62-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.01452.x
6. Kassim TA, Clarke DD, Mai VQ, Clyde PW, Mohamed Shakir KM. Catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy. Endocr Pract. 2008;14(9):1137-1149. doi:10.4158/EP.14.9.1137
7. Kudva YC, Young WF, Thompson GB, Grant CS, Van Heerden JA. Adrenal incidentaloma: an important component of the clinical presentation spectrum of benign sporadic adrenal pheochromocytoma. The Endocrinologist. 1999;9(2):77-80. doi:10.1097/00019616-199903000-00002
8. Puar TH, Mok Y, Debajyoti R, Khoo J, How CH, Ng AK. Secondary hypertension in adults. Singapore Med J. 2016;57(5):228-232. doi:10.11622/smedj.2016087
9. Bravo EL. Pheochromocytoma: new concepts and future trends. Kidney Int. 1991;40(3):544-556. doi:10.1038/ki.1991.244
10. Plouin PF, Chatellier G, Fofol I, Corvol P. Tumor recurrence and hypertension persistence after successful pheochromocytoma operation. Hypertension. 1997;29(5):1133-1139. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.29.5.1133
11. Hamidi O, Young WF Jr, Iñiguez-Ariza NM, et al. Malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: 272 patients over 55 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(9):3296-3305. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00992
12. Kenny L, Rizzo V, Trevis J, Assimakopoulou E, Timon D. The unexpected diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma in the anaesthetic room. Ann Card Anaesth. 2018;21(3):307-310. doi:10.4103/aca.ACA_206_17
13. Johnston PC, Silversides JA, Wallace H, et al. Phaeochromocytoma crisis: two cases of undiagnosed phaeochromocytoma presenting after elective nonrelated surgical procedures. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2013;2013:514714. doi:10.1155/2013/514714
14. Shen SJ, Cheng HM, Chiu AW, Chou CW, Chen JY. Perioperative hypertensive crisis in clinically silent pheochromocytomas: report of four cases. Chang Gung Med J. 2005;28(1):44-50.
15. Lo CY, Lam KY, Wat MS, Lam KS. Adrenal pheochromocytoma remains a frequently overlooked diagnosis. Am J Surg. 2000;179(3):212-215. doi:10.1016/s0002-9610(00)00296-8
16. Myklejord DJ. Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma: the anesthesiologist nightmare. Clin Med Res. 2004;2(1):59-62. doi:10.3121/cmr.2.1.59
17. Stumvoll M, Radjaipour M, Seif F. Diagnostic considerations in pheochromocytoma and chronic hemodialysis: case report and review of the literature. Am J Nephrol. 1995;15(2):147-151. doi:10.1159/000168820
18. Morioka M, Yuihama S, Nakajima T, et al. Incidentally discovered pheochromocytoma in long-term hemodialysis patients. Int J Urol. 2002;9(12):700-703. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2002.00553.x
19. ˇCtvrtlík F, Koranda P, Schovánek J, Škarda J, Hartmann I, Tüdös Z. Current diagnostic imaging of pheochromocytomas and implications for therapeutic strategy. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3151-3160. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.5871
20. McNeil AR, Blok BH, Koelmeyer TD, Burke MP, Hilton JM. Phaeochromocytomas discovered during coronial autopsies in Sydney, Melbourne and Auckland. Aust N Z J Med. 2000;30(6):648-652. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2000.tb04358.x
21. Baguet JP, Hammer L, Mazzuco TL, et al. Circumstances of discovery of phaeochromocytoma: a retrospective study of 41 consecutive patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150(5):681-686. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1500681
22. Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(6):1915-1942. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-1498
23. Dortzbach K, Gainsburg DM, Frost EA. Variants of pheochromocytoma and their anesthetic implications--a case report and literature review. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2010;20(6):897-905.
24. Januszewicz W, Chodakowska J, Styczy´nski G. Secondary hypertension in the elderly. J Hum Hypertens. 1998;12(9):603-606. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1000673
1. Omura M, Saito J, Yamaguchi K, Kakuta Y, Nishikawa T. Prospective study on the prevalence of secondary hypertension among hypertensive patients visiting a general outpatient clinic in Japan. Hypertens Res. 2004;27(3):193-202. doi:10.1291/hypres.27.193
2. Stein PP, Black HR. A simplified diagnostic approach to pheochromocytoma: a review of the literature and report of one institution’s experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991;70(1):46-66. doi:10.1097/00005792-199101000-00004
3. Beard CM, Sheps SG, Kurland LT, Carney JA, Lie JT. Occurrence of pheochromocytoma in Rochester, Minnesota, 1950 through 1979. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983;58(12):802-804.
4. Sutton MG, Sheps SG, Lie JT. Prevalence of clinically unsuspected pheochromocytoma: review of a 50-year autopsy series. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56(6):354-360.
5. Manger WM, Gifford RW Jr. Pheochromocytoma. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4(1):62-72. doi:10.1111/j.1524-6175.2002.01452.x
6. Kassim TA, Clarke DD, Mai VQ, Clyde PW, Mohamed Shakir KM. Catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy. Endocr Pract. 2008;14(9):1137-1149. doi:10.4158/EP.14.9.1137
7. Kudva YC, Young WF, Thompson GB, Grant CS, Van Heerden JA. Adrenal incidentaloma: an important component of the clinical presentation spectrum of benign sporadic adrenal pheochromocytoma. The Endocrinologist. 1999;9(2):77-80. doi:10.1097/00019616-199903000-00002
8. Puar TH, Mok Y, Debajyoti R, Khoo J, How CH, Ng AK. Secondary hypertension in adults. Singapore Med J. 2016;57(5):228-232. doi:10.11622/smedj.2016087
9. Bravo EL. Pheochromocytoma: new concepts and future trends. Kidney Int. 1991;40(3):544-556. doi:10.1038/ki.1991.244
10. Plouin PF, Chatellier G, Fofol I, Corvol P. Tumor recurrence and hypertension persistence after successful pheochromocytoma operation. Hypertension. 1997;29(5):1133-1139. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.29.5.1133
11. Hamidi O, Young WF Jr, Iñiguez-Ariza NM, et al. Malignant pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: 272 patients over 55 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(9):3296-3305. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00992
12. Kenny L, Rizzo V, Trevis J, Assimakopoulou E, Timon D. The unexpected diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma in the anaesthetic room. Ann Card Anaesth. 2018;21(3):307-310. doi:10.4103/aca.ACA_206_17
13. Johnston PC, Silversides JA, Wallace H, et al. Phaeochromocytoma crisis: two cases of undiagnosed phaeochromocytoma presenting after elective nonrelated surgical procedures. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2013;2013:514714. doi:10.1155/2013/514714
14. Shen SJ, Cheng HM, Chiu AW, Chou CW, Chen JY. Perioperative hypertensive crisis in clinically silent pheochromocytomas: report of four cases. Chang Gung Med J. 2005;28(1):44-50.
15. Lo CY, Lam KY, Wat MS, Lam KS. Adrenal pheochromocytoma remains a frequently overlooked diagnosis. Am J Surg. 2000;179(3):212-215. doi:10.1016/s0002-9610(00)00296-8
16. Myklejord DJ. Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma: the anesthesiologist nightmare. Clin Med Res. 2004;2(1):59-62. doi:10.3121/cmr.2.1.59
17. Stumvoll M, Radjaipour M, Seif F. Diagnostic considerations in pheochromocytoma and chronic hemodialysis: case report and review of the literature. Am J Nephrol. 1995;15(2):147-151. doi:10.1159/000168820
18. Morioka M, Yuihama S, Nakajima T, et al. Incidentally discovered pheochromocytoma in long-term hemodialysis patients. Int J Urol. 2002;9(12):700-703. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2042.2002.00553.x
19. ˇCtvrtlík F, Koranda P, Schovánek J, Škarda J, Hartmann I, Tüdös Z. Current diagnostic imaging of pheochromocytomas and implications for therapeutic strategy. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3151-3160. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.5871
20. McNeil AR, Blok BH, Koelmeyer TD, Burke MP, Hilton JM. Phaeochromocytomas discovered during coronial autopsies in Sydney, Melbourne and Auckland. Aust N Z J Med. 2000;30(6):648-652. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2000.tb04358.x
21. Baguet JP, Hammer L, Mazzuco TL, et al. Circumstances of discovery of phaeochromocytoma: a retrospective study of 41 consecutive patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150(5):681-686. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1500681
22. Lenders JW, Duh QY, Eisenhofer G, et al. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(6):1915-1942. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-1498
23. Dortzbach K, Gainsburg DM, Frost EA. Variants of pheochromocytoma and their anesthetic implications--a case report and literature review. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2010;20(6):897-905.
24. Januszewicz W, Chodakowska J, Styczy´nski G. Secondary hypertension in the elderly. J Hum Hypertens. 1998;12(9):603-606. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1000673
Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Salt Wasting Syndrome
A treatment strategy that incorporates both water restrictions and sodium supplementation may be appropriate when differentiating between diagnoses of renal salt wasting syndrome and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Cisplatin is a potent antineoplastic agent derived from platinum and commonly used in the treatment of head and neck, bladder, ovarian, and testicular malignancies.1,2 Approximately 20% of all cancer patients are prescribed platinum-based chemotherapeutics.3 Although considered highly effective, cisplatin is also a dose-dependent nephrotoxin, inducing apoptosis in the proximal tubules of the nephron and reducing glomerular filtration rate. This nephron injury leads to inflammation and reduced medullary blood flow, causing further ischemic damage to the tubular cells.4 Given that the proximal tubule reabsorbs 67% of all sodium, cisplatin-induced nephron injuries can also lead to hyponatremia.5
The primary mechanisms of hyponatremia following cisplatin chemotherapy are syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) and renal salt wasting syndrome (RSWS). Though these diagnoses have similar presentations, the treatment recommendations are different due to pathophysiologic differences. Fluid restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment, while increased sodium intake remains the hallmark of RSWS treatment.6 This patient presented with a combination of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and hyponatremia secondary to RSWS. While RSWS and AKI are known complications of cisplatin chemotherapy, the combination is underreported in the literature. Therefore, this case report highlights the combination of these cisplatin-induced complications, emphasizes the clinical challenges in differentiating SIADH from RSWS, especially in the presence of a concomitant AKI, and suggests a treatment approach during diagnostic uncertainty.
Case Presentation
A 71-year-old man with a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the left neck on cycle 1, day 8 of cisplatin-based chemotherapy and ongoing radiation therapy (720 cGy of 6300 cGy), lung adenocarcinoma status postresection, and hyperlipidemia presented to the emergency department (ED) at the request of his oncologist for abnormal laboratory values. In the ED, his metabolic panel showed a 131-mmol/L serum sodium, 3.3 mmol/L potassium, 83 mmol/L chloride, 29 mmol/L bicarbonate, 61 mg/dL blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and 8.8 mg/dL creatinine (baseline, 0.9 mg/dL). The patient reported throbbing headaches, persistent nausea, and multiple episodes of nonbloody emesis for several days that he attributed to his chemotherapy. He noted decreased urination without discomfort or changes in color or odor and no fatigue, fevers, chills, hematuria, flank, abdominal pain, thirst, or polydipsia. He reported no toxic ingestions or IV drug use. The patient had no relevant family history or additional social history. His outpatient medications included 10 mg cetirizine, 8 mg ondansetron, and 81 mg aspirin. On initial examination, his 137/66 mm Hg blood pressure was mildly elevated. The physical examination findings were notable for a 5-cm mass in the left neck that was firm and irregularly-shaped. His physical examination was otherwise unremarkable. He was admitted to the inpatient medicine service for an AKI complicated by symptomatic hyponatremia.
Investigations
We evaluated the patient’s AKI based on treatment responsiveness, imaging, and laboratory testing. Renal and bladder ultrasound showed no evidence of hydronephrosis or obstruction. He had a benign urinalysis with microscopy absent for protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and cellular casts. His urine pH was 5.5 (reference range, 5.0-9.0) and specific gravity was 1.011 (reference range, 1.005-1.030). His urine electrolytes revealed 45-mmol/L urine sodium (reference range, 40-220), 33-mmol/L urine chloride (reference range, 110-250), 10-mmol/L urine potassium (reference range, 25-120), 106.7-mg/dL urine creatinine (reference range, 10-400) and a calculated 2.7% fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) and 22.0-mEq/L elevated urine anion gap. As a fluid challenge, he was treated with IV 0.9% sodium chloride at 100-125 mL/h, receiving 3 liters over the first 48 hours of his hospitalization. His creatinine peaked at 9.2 mg/dL and stabilized before improving later in his hospitalization (Figure 1). The patient initially had oliguria (< 0.5 mL/kg/h), which slowly improved over his hospital course. Unfortunately, due to multiple system and clinical factors, accurate inputs and outputs were not adequately maintained during his hospitalization.
We evaluated hyponatremia with a combination of serum and urine laboratory tests. In addition to urine electrolytes, the initial evaluation focused on trending his clinical trajectory. We repeated a basic metabolic panel every 4 to 6 hours. He had 278-mOsm/kg serum osmolality (reference range, 285-295) with an effective 217-mOsm/kg serum tonicity. His urine osmolality was 270.5 mOsm/kg.
Despite administering 462 mEq sodium via crystalloid, his sodium worsened over the first 48 hours, reaching a nadir at 125 mmol/L on hospital day 3 (Figure 2). While he continued to appear euvolemic on physical examination, his blood pressure became difficult to control with 160- to 180-mm Hg systolic blood pressure readings. His thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was normal and aldosterone was low (4 ng/dL). Additional urine studies, including a 24-hour urine sample, were collected for further evaluation. His urine uric acid was 140 mg/d (reference range, 120-820); his serum uric acid level was 8.2 mg/dL (reference range, 3.0-9.0). His 24-hour urine creatinine was 0.57 g/d (reference range, 0.50-2.15) and uric acid to creatinine ratio was 246 mg/g (reference range, 60-580). His serum creatinine collected from the same day as his 24-hour urine sample was 7.3 mg/dL. His fractional excretion of uric acid (FEurate) was 21.9%.
Differential Diagnosis
The patient’s recent administration of cisplatin raised clinical suspicion of cisplatin-induced AKI. To avoid premature diagnostic closure, we used a systematic approach for thinking about our patient’s AKI, considering prerenal, intrarenal, and postrenal etiologies. The unremarkable renal and bladder ultrasound made a postrenal etiology unlikely. The patient’s 2.7% FENa in the absence of a diuretic, limited responsiveness to crystalloid fluid resuscitation, 7.5 serum BUN/creatinine ratio, and 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality suggested an intrarenal etiology, which can be further divided into problems with glomeruli, tubules, small vessels, or interstitial space. The patient’s normal urinary microscopy with no evidence of protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or cellular casts made a glomerular etiology less likely. The acute onset and lack of additional systemic features, other than hypertension, made a vascular etiology less likely. A tubular etiology, such as acute tubular necrosis (ATN), was highest on the differential and was followed by an interstitial etiology, such as acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).
Patients with drug-induced AIN commonly present with signs and symptoms of an allergic-type reaction, including fever, rash, hematuria, pyuria, and costovertebral angle tenderness. The patient lacked these symptoms. However, cisplatin is known to cause ATN in up to 20-30% of patients.7 Therefore, despite the lack of the classic muddy-brown, granular casts on urine microscopy, cisplatin-induced ATN remained the most likely etiology of his AKI. Moreover, ATN can cause hyponatremia. ATN is characterized by 3 phases: initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases.8 Hyponatremia occurs during the recovery phase, typically starting weeks after renal insult and associated with high urine output and diuresis. This patient presented 1 week after injury and had persistent oliguria, making ATN an unlikely culprit of his hyponatremia.
Our patient presented with hypotonic hyponatremia with a 131 mmol/L initial sodium level and an < 280 mOsm/kg effective serum osmolality, or serum tonicity. The serum tonicity is equivalent to the difference between the measured serum osmolality and the BUN. In the setting of profound AKI, this adjustment is essential for correctly categorizing a patient’s hyponatremia as hyper-, iso-, or hypotonic. The differential diagnosis for this patient’s hypotonic hyponatremia included dilutional effects of hypervolemia, SIADH, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and RSWS. The patient’s volume examination, lack of predisposing comorbidities or suggestive biomarkers, and > 20 mmol/L urinary sodium made hypervolemia unlikely. His urinary osmolality and specific gravity made primary polydipsia unlikely. We worked up his hyponatremia according to a diagnostic algorithm (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0198).
The patient had a 217 mOsm/kg serum tonicity and a 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality, consistent with impaired water excretion. His presentation, TSH, and concordant decrease in sodium and potassium made an endocrine etiology of his hyponatremia less likely. In hindsight, a serum cortisol would have been beneficial to more completely exclude adrenal insufficiency. His urine sodium was elevated at 45 mmol/L, raising concern for RSWS or SIADH. The FEurate helped to distinguish between SIADH and RSWS. While FEurate is often elevated in both SIADH and RSWS initially, the FEurate normalizes in SIADH with normalization of the serum sodium. The ideal cutoff for posthyponatremia correction FEurate is debated; however, a FEurate value after sodium correction < 11% suggests SIADH while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.9 Our patient’s FEurate following the sodium correction (serum sodium 134 mmol/L) was 21.9%, most suggestive of RSWS.
Treatment
Upon admission, initial treatment focused on resolving the patient’s AKI. The oncology team discontinued the cisplatin-based chemotherapy. His medication dosages were adjusted for his renal function and additional nephrotoxins avoided. In consultation, the nephrology service recommended 100 mL/h fluid resuscitation. After the patient received 3 L of 0.9% sodium chloride, his creatinine showed limited improvement and his sodium worsened, trending from 131 mmol/L to a nadir of 125 mmol/L. We initiated oral free-water restriction while continuing IV infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride at 125 mL/h.
We further augmented his sodium intake with 1-g sodium chloride tablets with each meal. By hospital day 6, the patient’s serum sodium, BUN, and creatinine improved to 130 mEq/L, 50 mg/dL, and 7.7 mg/dL, respectively. We then discontinued the oral sodium chloride tablets, fluid restriction, and IV fluids in a stepwise fashion prior to discharge. At discharge, the patient’s serum sodium was 136 mEq/L and creatinine, 4.8 mg/dL. The patient’s clinical course was complicated by symptomatic hypertension with systolic blood pressures about 180 mm Hg, requiring intermittent IV hydralazine, which was transitioned to daily nifedipine. Concerned that fluid resuscitation contributed to his hypertension, the patient also received several doses of furosemide. At time of discharge, the patient remained hypertensive and was discharged with nifedipine 90 mg daily.
Outcome and Follow-up
The patient has remained stable clinically since discharge. One week after discharge, his serum sodium and creatinine were 138 mmol/L and 3.8 mg/dL, respectively. More than 1 month after discharge, his sodium remains in the reference range and his creatinine was stable at about 3.5 mg/dL. He continues to follow-up with nephrology, oncology, and radiation oncology. He has restarted chemotherapy with a carboplatin-based regimen without recurrence of hyponatremia or AKI. His blood pressure has gradually improved to the point where he no longer requires nifedipine.
Discussion
The US Food and Drug Administration first approved the use of cisplatin, an alkylating agent that inhibits DNA replication, in 1978 for the treatment of testicular cancer.10 Since its approval, cisplatin has increased in popularity and is now considered one of the most effective antineoplastic agents for the treatment of solid tumors.1 Unfortunately, cisplatin has a well-documented adverse effect profile that includes neurotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, nephrotoxicity, and ototoxicity.4 Despite frequent nephrotoxicity, cisplatin only occasionally causes hyponatremia and rarely causes RSWS, a known but potentially fatal complication. Moreover, the combination of AKI and RSWS is unique. Our patient presented with the unique combination of AKI and hyponatremia, most consistent with RSWS, likely precipitated from cisplatin chemotherapy. Through this case, we review cisplatin-associated electrolyte abnormalities, highlight the challenge of differentiating SIADH and RSWS, and suggest a treatment approach for hyponatremia during the period of diagnostic uncertainty.
Blachley and colleagues first discussed renal and electrolyte disturbances, specifically magnesium wasting, secondary to cisplatin use in 1981. In 1984, Kurtzberg and colleagues noted salt wasting in 2 patients receiving cisplatin therapy. The authors suggested that cisplatin inhibits solute transport in the thick ascending limb, causing clinically significant electrolyte abnormalities, coining the term cisplatin-induced salt wasting.11
The prevalence of cisplatin-induced salt wasting is unclear and likely underreported. In 1988, Hutchinson and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study and noted 10% of patients (n = 70) developed RSWS at some point over 18 months of cisplatin therapy—a higher rate than previously estimated.12 In 1992, another prospective cohort study evaluated the adverse effects of 47 patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin and reported hyponatremia in 43% of its 93 courses of chemotherapy. The authors did not report the etiology of these hyponatremia cases.13 Given the diagnostic challenge, RSWS may be underrepresented as a confirmed etiology of hyponatremia in cisplatin treatment.
Hyponatremia from cisplatin may present as either SIADH or RSWS, complicating treatment decisions. Both conditions lead to hypotonic hyponatremia with urine osmolality > 100 mOSm/kg and urine sodium levels > 40 mmol/L. However, pathophysiology behind SIADH and RSWS is different. In RSWS, proximal tubule damage causes hyponatremia, decreasing sodium reabsorption, and leading to impaired concentration gradient in every segment of the nephron. As a result, RSWS can lead to profound hyponatremia. Treatment typically consists of increasing sodium intake to correct serum sodium with salt tablets and hypertonic sodium chloride while treating the underlying etiology, in our case removing the offending agent, and waiting for proximal tubule function to recover.6 On the other hand, in SIADH, elevated antidiuretic hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the collecting duct, which has no impact on concentration gradients of the other nephron segments.14 Free-water restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment. Severe SIADH may require sodium repletion and/or the initiation of vaptans, ADH antagonists that competitively inhibit V2 receptors in the collecting duct to prevent water reabsorption.15
Our patient had an uncertain etiology of his hyponatremia throughout most of his treatment course, complicating our treatment decision-making. Initially, his measured serum osmolality was 278 mOsm/kg; however, his effective tonicity was lower. His AKI elevated his BUN, which in turnrequired us to calculate his serum tonicity (217 mOsm/kg) that was consistent with hypotonic hyponatremia. His elevated urine osmolality and urine sodium levels made SIADH and RSWS the most likely etiologies of his hyponatremia. To confirm the etiology, we waited for correction of his serum sodium. Therefore, we treated him with a combination of sodium repletion with 0.9% sodium chloride (154 mEq/L), hypertonic relative to his serum sodium, sodium chloride tablets, and free-water restriction. In this approach, we attempted to harmonize the treatment strategies for both SIADH and RSWS and effectively corrected his serum sodium. We evaluated his response to our treatment with a basic metabolic panel every 6 to 8 hours. Had his serum sodium decreased < 120 mmol/L, we planned to transfer the patient to the intensive care unit for 3% sodium chloride and/or intensification of his fluid restriction. A significant worsening of his hyponatremia would have strongly suggested hyponatremia secondary to SIADH since isotonic saline can worsen hyponatremia due to increased free-water reabsorption in the collecting duct.16
To differentiate between SIADH and RSWS, we relied on the FEurate after sodium correction. Multiple case reports from Japan have characterized the distinction between the processes through FEurate and serum uric acid. While the optimal cut-off values for FEurate require additional investigation, values < 11% after serum sodium correction suggests SIADH, while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.17 Prior cases have also emphasized serum hypouricemia as a distinguishing characteristic in RSWS. However, our case illustrates that serum hypouricemia is less reliable in the setting of AKI. Due to his severe AKI, our patient could not efficiently clear uric acid, likely contributing to his hyperuricemia.
Ultimately, our patient had an FEurate > 20%, which was suggestive of RSWS. Nevertheless, we recognize limitations and confounders in our diagnosis and have reflected on our diagnostic and management choices. First, the sensitivity and specificity of postsodium correction FEurate is unknown. Tracking the change in FEurate with our interventions would have increased our diagnostic utility, as suggested by Maesaka and colleagues.14 Second, our patient’s serum sodium was still at the lower end of the reference range after treatment, which may decrease the specificity of FEurate. Third, a plasma ADH collected during the initial phase of symptomatic hyponatremia would have helped differentiate between SIADH and RSWS.
Other diagnostic tests that could have excluded alternative diagnoses with even greater certainty include plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone, B-type natriuretic peptide, renin, cortisol, and thyroid function tests. From a practical standpoint, these laboratory results (excluding thyroid function test and brain natriuretic peptide) would have taken several weeks to result at our institution, limiting their clinical utility. Similarly, FEurate also has limited clinical utility, requiring effective treatment as part of the diagnostic test. Therefore, we recommend focusing on optimal treatment for hyponatremia of uncertain etiology, especially where SIADH and RSWS are the leading diagnoses.
Conclusions
We described a rare case of concomitant cisplatin-induced severe AKI and RSWS. We have emphasized the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing between SIADH and RSWS, especially with concomitant AKI, and have acknowledged that optimal treatment relies on accurate differentiation. However, differentiation may not be clinically feasible. Therefore, we suggest a treatment strategy that incorporates both free-water restriction and sodium supplementation via IV and/or oral administration.
1. Dasari S, Tchounwou PB. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740:364-378. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
2. Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen KN, Edelstein CL. Recent advances in models, mechanisms, biomarkers, and interventions in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3011. Published 2019 Jun 20. doi:10.3390/ijms20123011
3. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. The “accidental” cure—platinum-based treatment for cancer: the discovery of cisplatin. Published May 30, 2014. Accessed November 10, 2021. https://www.cancer.gov/research/progress/discovery/cisplatin
4. Ozkok A, Edelstein CL. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:967826. doi:10.1155/2014/967826
5. Palmer LG, Schnermann J. Integrated control of Na transport along the nephron. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(4):676-687. doi:10.2215/CJN.12391213
6. Bitew S, Imbriano L, Miyawaki N, Fishbane S, Maesaka JK. More on renal salt wasting without cerebral disease: response to saline infusion. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(2):309-315. doi:10.2215/CJN.02740608
7. Shirali AC, Perazella MA. Tubulointerstitial injury associated with chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014;21(1):56-63. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2013.06.010
8. Agrawal M, Swartz R. Acute renal failure [published correction appears in Am Fam Physician 2001 Feb 1;63(3):445]. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(7):2077-2088.
9. Milionis HJ, Liamis GL, Elisaf MS. The hyponatremic patient: a systematic approach to laboratory diagnosis. CMAJ. 2002;166(8):1056-1062.
10. Monneret C. Platinum anticancer drugs. From serendipity to rational design. Ann Pharm Fr. 2011;69(6):286-295. doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2011.10.001
11. Kurtzberg J, Dennis VW, Kinney TR. Cisplatinum-induced renal salt wasting. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1984;12(2):150-154. doi:10.1002/mpo.2950120219
12. Hutchison FN, Perez EA, Gandara DR, Lawrence HJ, Kaysen GA. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1988;108(1):21-25. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-108-1-21
13. Lee YK, Shin DM. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with high-dose cisplatin, etoposide, and mitomycin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 1992;7(2):118-121. doi:10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.118
14. Maesaka JK, Imbriano L, Mattana J, Gallagher D, Bade N, Sharif S. Differentiating SIADH from cerebral/renal salt wasting: failure of the volume approach and need for a new approach to hyponatremia. J Clin Med. 2014;3(4):1373-1385. Published 2014 Dec 8. doi:10.3390/jcm3041373
15. Palmer BF. The role of v2 receptor antagonists in the treatment of hyponatremia. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013;11(1):1-8. doi:10.5049/EBP.2013.11.1.1
16. Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Schrier RW, Sterns RH. Hyponatremia treatment guidelines 2007: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2007;120(11 Suppl 1):S1-S21. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.09.001
17. Maesaka JK, Imbriano LJ, Miyawaki N. High prevalence of renal salt wasting without cerebral disease as cause of hyponatremia in general medical wards. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(1):15-22. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.03.02
A treatment strategy that incorporates both water restrictions and sodium supplementation may be appropriate when differentiating between diagnoses of renal salt wasting syndrome and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
A treatment strategy that incorporates both water restrictions and sodium supplementation may be appropriate when differentiating between diagnoses of renal salt wasting syndrome and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Cisplatin is a potent antineoplastic agent derived from platinum and commonly used in the treatment of head and neck, bladder, ovarian, and testicular malignancies.1,2 Approximately 20% of all cancer patients are prescribed platinum-based chemotherapeutics.3 Although considered highly effective, cisplatin is also a dose-dependent nephrotoxin, inducing apoptosis in the proximal tubules of the nephron and reducing glomerular filtration rate. This nephron injury leads to inflammation and reduced medullary blood flow, causing further ischemic damage to the tubular cells.4 Given that the proximal tubule reabsorbs 67% of all sodium, cisplatin-induced nephron injuries can also lead to hyponatremia.5
The primary mechanisms of hyponatremia following cisplatin chemotherapy are syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) and renal salt wasting syndrome (RSWS). Though these diagnoses have similar presentations, the treatment recommendations are different due to pathophysiologic differences. Fluid restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment, while increased sodium intake remains the hallmark of RSWS treatment.6 This patient presented with a combination of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and hyponatremia secondary to RSWS. While RSWS and AKI are known complications of cisplatin chemotherapy, the combination is underreported in the literature. Therefore, this case report highlights the combination of these cisplatin-induced complications, emphasizes the clinical challenges in differentiating SIADH from RSWS, especially in the presence of a concomitant AKI, and suggests a treatment approach during diagnostic uncertainty.
Case Presentation
A 71-year-old man with a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the left neck on cycle 1, day 8 of cisplatin-based chemotherapy and ongoing radiation therapy (720 cGy of 6300 cGy), lung adenocarcinoma status postresection, and hyperlipidemia presented to the emergency department (ED) at the request of his oncologist for abnormal laboratory values. In the ED, his metabolic panel showed a 131-mmol/L serum sodium, 3.3 mmol/L potassium, 83 mmol/L chloride, 29 mmol/L bicarbonate, 61 mg/dL blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and 8.8 mg/dL creatinine (baseline, 0.9 mg/dL). The patient reported throbbing headaches, persistent nausea, and multiple episodes of nonbloody emesis for several days that he attributed to his chemotherapy. He noted decreased urination without discomfort or changes in color or odor and no fatigue, fevers, chills, hematuria, flank, abdominal pain, thirst, or polydipsia. He reported no toxic ingestions or IV drug use. The patient had no relevant family history or additional social history. His outpatient medications included 10 mg cetirizine, 8 mg ondansetron, and 81 mg aspirin. On initial examination, his 137/66 mm Hg blood pressure was mildly elevated. The physical examination findings were notable for a 5-cm mass in the left neck that was firm and irregularly-shaped. His physical examination was otherwise unremarkable. He was admitted to the inpatient medicine service for an AKI complicated by symptomatic hyponatremia.
Investigations
We evaluated the patient’s AKI based on treatment responsiveness, imaging, and laboratory testing. Renal and bladder ultrasound showed no evidence of hydronephrosis or obstruction. He had a benign urinalysis with microscopy absent for protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and cellular casts. His urine pH was 5.5 (reference range, 5.0-9.0) and specific gravity was 1.011 (reference range, 1.005-1.030). His urine electrolytes revealed 45-mmol/L urine sodium (reference range, 40-220), 33-mmol/L urine chloride (reference range, 110-250), 10-mmol/L urine potassium (reference range, 25-120), 106.7-mg/dL urine creatinine (reference range, 10-400) and a calculated 2.7% fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) and 22.0-mEq/L elevated urine anion gap. As a fluid challenge, he was treated with IV 0.9% sodium chloride at 100-125 mL/h, receiving 3 liters over the first 48 hours of his hospitalization. His creatinine peaked at 9.2 mg/dL and stabilized before improving later in his hospitalization (Figure 1). The patient initially had oliguria (< 0.5 mL/kg/h), which slowly improved over his hospital course. Unfortunately, due to multiple system and clinical factors, accurate inputs and outputs were not adequately maintained during his hospitalization.
We evaluated hyponatremia with a combination of serum and urine laboratory tests. In addition to urine electrolytes, the initial evaluation focused on trending his clinical trajectory. We repeated a basic metabolic panel every 4 to 6 hours. He had 278-mOsm/kg serum osmolality (reference range, 285-295) with an effective 217-mOsm/kg serum tonicity. His urine osmolality was 270.5 mOsm/kg.
Despite administering 462 mEq sodium via crystalloid, his sodium worsened over the first 48 hours, reaching a nadir at 125 mmol/L on hospital day 3 (Figure 2). While he continued to appear euvolemic on physical examination, his blood pressure became difficult to control with 160- to 180-mm Hg systolic blood pressure readings. His thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was normal and aldosterone was low (4 ng/dL). Additional urine studies, including a 24-hour urine sample, were collected for further evaluation. His urine uric acid was 140 mg/d (reference range, 120-820); his serum uric acid level was 8.2 mg/dL (reference range, 3.0-9.0). His 24-hour urine creatinine was 0.57 g/d (reference range, 0.50-2.15) and uric acid to creatinine ratio was 246 mg/g (reference range, 60-580). His serum creatinine collected from the same day as his 24-hour urine sample was 7.3 mg/dL. His fractional excretion of uric acid (FEurate) was 21.9%.
Differential Diagnosis
The patient’s recent administration of cisplatin raised clinical suspicion of cisplatin-induced AKI. To avoid premature diagnostic closure, we used a systematic approach for thinking about our patient’s AKI, considering prerenal, intrarenal, and postrenal etiologies. The unremarkable renal and bladder ultrasound made a postrenal etiology unlikely. The patient’s 2.7% FENa in the absence of a diuretic, limited responsiveness to crystalloid fluid resuscitation, 7.5 serum BUN/creatinine ratio, and 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality suggested an intrarenal etiology, which can be further divided into problems with glomeruli, tubules, small vessels, or interstitial space. The patient’s normal urinary microscopy with no evidence of protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or cellular casts made a glomerular etiology less likely. The acute onset and lack of additional systemic features, other than hypertension, made a vascular etiology less likely. A tubular etiology, such as acute tubular necrosis (ATN), was highest on the differential and was followed by an interstitial etiology, such as acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).
Patients with drug-induced AIN commonly present with signs and symptoms of an allergic-type reaction, including fever, rash, hematuria, pyuria, and costovertebral angle tenderness. The patient lacked these symptoms. However, cisplatin is known to cause ATN in up to 20-30% of patients.7 Therefore, despite the lack of the classic muddy-brown, granular casts on urine microscopy, cisplatin-induced ATN remained the most likely etiology of his AKI. Moreover, ATN can cause hyponatremia. ATN is characterized by 3 phases: initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases.8 Hyponatremia occurs during the recovery phase, typically starting weeks after renal insult and associated with high urine output and diuresis. This patient presented 1 week after injury and had persistent oliguria, making ATN an unlikely culprit of his hyponatremia.
Our patient presented with hypotonic hyponatremia with a 131 mmol/L initial sodium level and an < 280 mOsm/kg effective serum osmolality, or serum tonicity. The serum tonicity is equivalent to the difference between the measured serum osmolality and the BUN. In the setting of profound AKI, this adjustment is essential for correctly categorizing a patient’s hyponatremia as hyper-, iso-, or hypotonic. The differential diagnosis for this patient’s hypotonic hyponatremia included dilutional effects of hypervolemia, SIADH, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and RSWS. The patient’s volume examination, lack of predisposing comorbidities or suggestive biomarkers, and > 20 mmol/L urinary sodium made hypervolemia unlikely. His urinary osmolality and specific gravity made primary polydipsia unlikely. We worked up his hyponatremia according to a diagnostic algorithm (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0198).
The patient had a 217 mOsm/kg serum tonicity and a 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality, consistent with impaired water excretion. His presentation, TSH, and concordant decrease in sodium and potassium made an endocrine etiology of his hyponatremia less likely. In hindsight, a serum cortisol would have been beneficial to more completely exclude adrenal insufficiency. His urine sodium was elevated at 45 mmol/L, raising concern for RSWS or SIADH. The FEurate helped to distinguish between SIADH and RSWS. While FEurate is often elevated in both SIADH and RSWS initially, the FEurate normalizes in SIADH with normalization of the serum sodium. The ideal cutoff for posthyponatremia correction FEurate is debated; however, a FEurate value after sodium correction < 11% suggests SIADH while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.9 Our patient’s FEurate following the sodium correction (serum sodium 134 mmol/L) was 21.9%, most suggestive of RSWS.
Treatment
Upon admission, initial treatment focused on resolving the patient’s AKI. The oncology team discontinued the cisplatin-based chemotherapy. His medication dosages were adjusted for his renal function and additional nephrotoxins avoided. In consultation, the nephrology service recommended 100 mL/h fluid resuscitation. After the patient received 3 L of 0.9% sodium chloride, his creatinine showed limited improvement and his sodium worsened, trending from 131 mmol/L to a nadir of 125 mmol/L. We initiated oral free-water restriction while continuing IV infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride at 125 mL/h.
We further augmented his sodium intake with 1-g sodium chloride tablets with each meal. By hospital day 6, the patient’s serum sodium, BUN, and creatinine improved to 130 mEq/L, 50 mg/dL, and 7.7 mg/dL, respectively. We then discontinued the oral sodium chloride tablets, fluid restriction, and IV fluids in a stepwise fashion prior to discharge. At discharge, the patient’s serum sodium was 136 mEq/L and creatinine, 4.8 mg/dL. The patient’s clinical course was complicated by symptomatic hypertension with systolic blood pressures about 180 mm Hg, requiring intermittent IV hydralazine, which was transitioned to daily nifedipine. Concerned that fluid resuscitation contributed to his hypertension, the patient also received several doses of furosemide. At time of discharge, the patient remained hypertensive and was discharged with nifedipine 90 mg daily.
Outcome and Follow-up
The patient has remained stable clinically since discharge. One week after discharge, his serum sodium and creatinine were 138 mmol/L and 3.8 mg/dL, respectively. More than 1 month after discharge, his sodium remains in the reference range and his creatinine was stable at about 3.5 mg/dL. He continues to follow-up with nephrology, oncology, and radiation oncology. He has restarted chemotherapy with a carboplatin-based regimen without recurrence of hyponatremia or AKI. His blood pressure has gradually improved to the point where he no longer requires nifedipine.
Discussion
The US Food and Drug Administration first approved the use of cisplatin, an alkylating agent that inhibits DNA replication, in 1978 for the treatment of testicular cancer.10 Since its approval, cisplatin has increased in popularity and is now considered one of the most effective antineoplastic agents for the treatment of solid tumors.1 Unfortunately, cisplatin has a well-documented adverse effect profile that includes neurotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, nephrotoxicity, and ototoxicity.4 Despite frequent nephrotoxicity, cisplatin only occasionally causes hyponatremia and rarely causes RSWS, a known but potentially fatal complication. Moreover, the combination of AKI and RSWS is unique. Our patient presented with the unique combination of AKI and hyponatremia, most consistent with RSWS, likely precipitated from cisplatin chemotherapy. Through this case, we review cisplatin-associated electrolyte abnormalities, highlight the challenge of differentiating SIADH and RSWS, and suggest a treatment approach for hyponatremia during the period of diagnostic uncertainty.
Blachley and colleagues first discussed renal and electrolyte disturbances, specifically magnesium wasting, secondary to cisplatin use in 1981. In 1984, Kurtzberg and colleagues noted salt wasting in 2 patients receiving cisplatin therapy. The authors suggested that cisplatin inhibits solute transport in the thick ascending limb, causing clinically significant electrolyte abnormalities, coining the term cisplatin-induced salt wasting.11
The prevalence of cisplatin-induced salt wasting is unclear and likely underreported. In 1988, Hutchinson and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study and noted 10% of patients (n = 70) developed RSWS at some point over 18 months of cisplatin therapy—a higher rate than previously estimated.12 In 1992, another prospective cohort study evaluated the adverse effects of 47 patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin and reported hyponatremia in 43% of its 93 courses of chemotherapy. The authors did not report the etiology of these hyponatremia cases.13 Given the diagnostic challenge, RSWS may be underrepresented as a confirmed etiology of hyponatremia in cisplatin treatment.
Hyponatremia from cisplatin may present as either SIADH or RSWS, complicating treatment decisions. Both conditions lead to hypotonic hyponatremia with urine osmolality > 100 mOSm/kg and urine sodium levels > 40 mmol/L. However, pathophysiology behind SIADH and RSWS is different. In RSWS, proximal tubule damage causes hyponatremia, decreasing sodium reabsorption, and leading to impaired concentration gradient in every segment of the nephron. As a result, RSWS can lead to profound hyponatremia. Treatment typically consists of increasing sodium intake to correct serum sodium with salt tablets and hypertonic sodium chloride while treating the underlying etiology, in our case removing the offending agent, and waiting for proximal tubule function to recover.6 On the other hand, in SIADH, elevated antidiuretic hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the collecting duct, which has no impact on concentration gradients of the other nephron segments.14 Free-water restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment. Severe SIADH may require sodium repletion and/or the initiation of vaptans, ADH antagonists that competitively inhibit V2 receptors in the collecting duct to prevent water reabsorption.15
Our patient had an uncertain etiology of his hyponatremia throughout most of his treatment course, complicating our treatment decision-making. Initially, his measured serum osmolality was 278 mOsm/kg; however, his effective tonicity was lower. His AKI elevated his BUN, which in turnrequired us to calculate his serum tonicity (217 mOsm/kg) that was consistent with hypotonic hyponatremia. His elevated urine osmolality and urine sodium levels made SIADH and RSWS the most likely etiologies of his hyponatremia. To confirm the etiology, we waited for correction of his serum sodium. Therefore, we treated him with a combination of sodium repletion with 0.9% sodium chloride (154 mEq/L), hypertonic relative to his serum sodium, sodium chloride tablets, and free-water restriction. In this approach, we attempted to harmonize the treatment strategies for both SIADH and RSWS and effectively corrected his serum sodium. We evaluated his response to our treatment with a basic metabolic panel every 6 to 8 hours. Had his serum sodium decreased < 120 mmol/L, we planned to transfer the patient to the intensive care unit for 3% sodium chloride and/or intensification of his fluid restriction. A significant worsening of his hyponatremia would have strongly suggested hyponatremia secondary to SIADH since isotonic saline can worsen hyponatremia due to increased free-water reabsorption in the collecting duct.16
To differentiate between SIADH and RSWS, we relied on the FEurate after sodium correction. Multiple case reports from Japan have characterized the distinction between the processes through FEurate and serum uric acid. While the optimal cut-off values for FEurate require additional investigation, values < 11% after serum sodium correction suggests SIADH, while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.17 Prior cases have also emphasized serum hypouricemia as a distinguishing characteristic in RSWS. However, our case illustrates that serum hypouricemia is less reliable in the setting of AKI. Due to his severe AKI, our patient could not efficiently clear uric acid, likely contributing to his hyperuricemia.
Ultimately, our patient had an FEurate > 20%, which was suggestive of RSWS. Nevertheless, we recognize limitations and confounders in our diagnosis and have reflected on our diagnostic and management choices. First, the sensitivity and specificity of postsodium correction FEurate is unknown. Tracking the change in FEurate with our interventions would have increased our diagnostic utility, as suggested by Maesaka and colleagues.14 Second, our patient’s serum sodium was still at the lower end of the reference range after treatment, which may decrease the specificity of FEurate. Third, a plasma ADH collected during the initial phase of symptomatic hyponatremia would have helped differentiate between SIADH and RSWS.
Other diagnostic tests that could have excluded alternative diagnoses with even greater certainty include plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone, B-type natriuretic peptide, renin, cortisol, and thyroid function tests. From a practical standpoint, these laboratory results (excluding thyroid function test and brain natriuretic peptide) would have taken several weeks to result at our institution, limiting their clinical utility. Similarly, FEurate also has limited clinical utility, requiring effective treatment as part of the diagnostic test. Therefore, we recommend focusing on optimal treatment for hyponatremia of uncertain etiology, especially where SIADH and RSWS are the leading diagnoses.
Conclusions
We described a rare case of concomitant cisplatin-induced severe AKI and RSWS. We have emphasized the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing between SIADH and RSWS, especially with concomitant AKI, and have acknowledged that optimal treatment relies on accurate differentiation. However, differentiation may not be clinically feasible. Therefore, we suggest a treatment strategy that incorporates both free-water restriction and sodium supplementation via IV and/or oral administration.
Cisplatin is a potent antineoplastic agent derived from platinum and commonly used in the treatment of head and neck, bladder, ovarian, and testicular malignancies.1,2 Approximately 20% of all cancer patients are prescribed platinum-based chemotherapeutics.3 Although considered highly effective, cisplatin is also a dose-dependent nephrotoxin, inducing apoptosis in the proximal tubules of the nephron and reducing glomerular filtration rate. This nephron injury leads to inflammation and reduced medullary blood flow, causing further ischemic damage to the tubular cells.4 Given that the proximal tubule reabsorbs 67% of all sodium, cisplatin-induced nephron injuries can also lead to hyponatremia.5
The primary mechanisms of hyponatremia following cisplatin chemotherapy are syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) and renal salt wasting syndrome (RSWS). Though these diagnoses have similar presentations, the treatment recommendations are different due to pathophysiologic differences. Fluid restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment, while increased sodium intake remains the hallmark of RSWS treatment.6 This patient presented with a combination of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and hyponatremia secondary to RSWS. While RSWS and AKI are known complications of cisplatin chemotherapy, the combination is underreported in the literature. Therefore, this case report highlights the combination of these cisplatin-induced complications, emphasizes the clinical challenges in differentiating SIADH from RSWS, especially in the presence of a concomitant AKI, and suggests a treatment approach during diagnostic uncertainty.
Case Presentation
A 71-year-old man with a medical history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the left neck on cycle 1, day 8 of cisplatin-based chemotherapy and ongoing radiation therapy (720 cGy of 6300 cGy), lung adenocarcinoma status postresection, and hyperlipidemia presented to the emergency department (ED) at the request of his oncologist for abnormal laboratory values. In the ED, his metabolic panel showed a 131-mmol/L serum sodium, 3.3 mmol/L potassium, 83 mmol/L chloride, 29 mmol/L bicarbonate, 61 mg/dL blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and 8.8 mg/dL creatinine (baseline, 0.9 mg/dL). The patient reported throbbing headaches, persistent nausea, and multiple episodes of nonbloody emesis for several days that he attributed to his chemotherapy. He noted decreased urination without discomfort or changes in color or odor and no fatigue, fevers, chills, hematuria, flank, abdominal pain, thirst, or polydipsia. He reported no toxic ingestions or IV drug use. The patient had no relevant family history or additional social history. His outpatient medications included 10 mg cetirizine, 8 mg ondansetron, and 81 mg aspirin. On initial examination, his 137/66 mm Hg blood pressure was mildly elevated. The physical examination findings were notable for a 5-cm mass in the left neck that was firm and irregularly-shaped. His physical examination was otherwise unremarkable. He was admitted to the inpatient medicine service for an AKI complicated by symptomatic hyponatremia.
Investigations
We evaluated the patient’s AKI based on treatment responsiveness, imaging, and laboratory testing. Renal and bladder ultrasound showed no evidence of hydronephrosis or obstruction. He had a benign urinalysis with microscopy absent for protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and cellular casts. His urine pH was 5.5 (reference range, 5.0-9.0) and specific gravity was 1.011 (reference range, 1.005-1.030). His urine electrolytes revealed 45-mmol/L urine sodium (reference range, 40-220), 33-mmol/L urine chloride (reference range, 110-250), 10-mmol/L urine potassium (reference range, 25-120), 106.7-mg/dL urine creatinine (reference range, 10-400) and a calculated 2.7% fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) and 22.0-mEq/L elevated urine anion gap. As a fluid challenge, he was treated with IV 0.9% sodium chloride at 100-125 mL/h, receiving 3 liters over the first 48 hours of his hospitalization. His creatinine peaked at 9.2 mg/dL and stabilized before improving later in his hospitalization (Figure 1). The patient initially had oliguria (< 0.5 mL/kg/h), which slowly improved over his hospital course. Unfortunately, due to multiple system and clinical factors, accurate inputs and outputs were not adequately maintained during his hospitalization.
We evaluated hyponatremia with a combination of serum and urine laboratory tests. In addition to urine electrolytes, the initial evaluation focused on trending his clinical trajectory. We repeated a basic metabolic panel every 4 to 6 hours. He had 278-mOsm/kg serum osmolality (reference range, 285-295) with an effective 217-mOsm/kg serum tonicity. His urine osmolality was 270.5 mOsm/kg.
Despite administering 462 mEq sodium via crystalloid, his sodium worsened over the first 48 hours, reaching a nadir at 125 mmol/L on hospital day 3 (Figure 2). While he continued to appear euvolemic on physical examination, his blood pressure became difficult to control with 160- to 180-mm Hg systolic blood pressure readings. His thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was normal and aldosterone was low (4 ng/dL). Additional urine studies, including a 24-hour urine sample, were collected for further evaluation. His urine uric acid was 140 mg/d (reference range, 120-820); his serum uric acid level was 8.2 mg/dL (reference range, 3.0-9.0). His 24-hour urine creatinine was 0.57 g/d (reference range, 0.50-2.15) and uric acid to creatinine ratio was 246 mg/g (reference range, 60-580). His serum creatinine collected from the same day as his 24-hour urine sample was 7.3 mg/dL. His fractional excretion of uric acid (FEurate) was 21.9%.
Differential Diagnosis
The patient’s recent administration of cisplatin raised clinical suspicion of cisplatin-induced AKI. To avoid premature diagnostic closure, we used a systematic approach for thinking about our patient’s AKI, considering prerenal, intrarenal, and postrenal etiologies. The unremarkable renal and bladder ultrasound made a postrenal etiology unlikely. The patient’s 2.7% FENa in the absence of a diuretic, limited responsiveness to crystalloid fluid resuscitation, 7.5 serum BUN/creatinine ratio, and 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality suggested an intrarenal etiology, which can be further divided into problems with glomeruli, tubules, small vessels, or interstitial space. The patient’s normal urinary microscopy with no evidence of protein, blood, ketones, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or cellular casts made a glomerular etiology less likely. The acute onset and lack of additional systemic features, other than hypertension, made a vascular etiology less likely. A tubular etiology, such as acute tubular necrosis (ATN), was highest on the differential and was followed by an interstitial etiology, such as acute interstitial nephritis (AIN).
Patients with drug-induced AIN commonly present with signs and symptoms of an allergic-type reaction, including fever, rash, hematuria, pyuria, and costovertebral angle tenderness. The patient lacked these symptoms. However, cisplatin is known to cause ATN in up to 20-30% of patients.7 Therefore, despite the lack of the classic muddy-brown, granular casts on urine microscopy, cisplatin-induced ATN remained the most likely etiology of his AKI. Moreover, ATN can cause hyponatremia. ATN is characterized by 3 phases: initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases.8 Hyponatremia occurs during the recovery phase, typically starting weeks after renal insult and associated with high urine output and diuresis. This patient presented 1 week after injury and had persistent oliguria, making ATN an unlikely culprit of his hyponatremia.
Our patient presented with hypotonic hyponatremia with a 131 mmol/L initial sodium level and an < 280 mOsm/kg effective serum osmolality, or serum tonicity. The serum tonicity is equivalent to the difference between the measured serum osmolality and the BUN. In the setting of profound AKI, this adjustment is essential for correctly categorizing a patient’s hyponatremia as hyper-, iso-, or hypotonic. The differential diagnosis for this patient’s hypotonic hyponatremia included dilutional effects of hypervolemia, SIADH, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and RSWS. The patient’s volume examination, lack of predisposing comorbidities or suggestive biomarkers, and > 20 mmol/L urinary sodium made hypervolemia unlikely. His urinary osmolality and specific gravity made primary polydipsia unlikely. We worked up his hyponatremia according to a diagnostic algorithm (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0198).
The patient had a 217 mOsm/kg serum tonicity and a 270.5 mOsm/kg urine osmolality, consistent with impaired water excretion. His presentation, TSH, and concordant decrease in sodium and potassium made an endocrine etiology of his hyponatremia less likely. In hindsight, a serum cortisol would have been beneficial to more completely exclude adrenal insufficiency. His urine sodium was elevated at 45 mmol/L, raising concern for RSWS or SIADH. The FEurate helped to distinguish between SIADH and RSWS. While FEurate is often elevated in both SIADH and RSWS initially, the FEurate normalizes in SIADH with normalization of the serum sodium. The ideal cutoff for posthyponatremia correction FEurate is debated; however, a FEurate value after sodium correction < 11% suggests SIADH while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.9 Our patient’s FEurate following the sodium correction (serum sodium 134 mmol/L) was 21.9%, most suggestive of RSWS.
Treatment
Upon admission, initial treatment focused on resolving the patient’s AKI. The oncology team discontinued the cisplatin-based chemotherapy. His medication dosages were adjusted for his renal function and additional nephrotoxins avoided. In consultation, the nephrology service recommended 100 mL/h fluid resuscitation. After the patient received 3 L of 0.9% sodium chloride, his creatinine showed limited improvement and his sodium worsened, trending from 131 mmol/L to a nadir of 125 mmol/L. We initiated oral free-water restriction while continuing IV infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride at 125 mL/h.
We further augmented his sodium intake with 1-g sodium chloride tablets with each meal. By hospital day 6, the patient’s serum sodium, BUN, and creatinine improved to 130 mEq/L, 50 mg/dL, and 7.7 mg/dL, respectively. We then discontinued the oral sodium chloride tablets, fluid restriction, and IV fluids in a stepwise fashion prior to discharge. At discharge, the patient’s serum sodium was 136 mEq/L and creatinine, 4.8 mg/dL. The patient’s clinical course was complicated by symptomatic hypertension with systolic blood pressures about 180 mm Hg, requiring intermittent IV hydralazine, which was transitioned to daily nifedipine. Concerned that fluid resuscitation contributed to his hypertension, the patient also received several doses of furosemide. At time of discharge, the patient remained hypertensive and was discharged with nifedipine 90 mg daily.
Outcome and Follow-up
The patient has remained stable clinically since discharge. One week after discharge, his serum sodium and creatinine were 138 mmol/L and 3.8 mg/dL, respectively. More than 1 month after discharge, his sodium remains in the reference range and his creatinine was stable at about 3.5 mg/dL. He continues to follow-up with nephrology, oncology, and radiation oncology. He has restarted chemotherapy with a carboplatin-based regimen without recurrence of hyponatremia or AKI. His blood pressure has gradually improved to the point where he no longer requires nifedipine.
Discussion
The US Food and Drug Administration first approved the use of cisplatin, an alkylating agent that inhibits DNA replication, in 1978 for the treatment of testicular cancer.10 Since its approval, cisplatin has increased in popularity and is now considered one of the most effective antineoplastic agents for the treatment of solid tumors.1 Unfortunately, cisplatin has a well-documented adverse effect profile that includes neurotoxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, nephrotoxicity, and ototoxicity.4 Despite frequent nephrotoxicity, cisplatin only occasionally causes hyponatremia and rarely causes RSWS, a known but potentially fatal complication. Moreover, the combination of AKI and RSWS is unique. Our patient presented with the unique combination of AKI and hyponatremia, most consistent with RSWS, likely precipitated from cisplatin chemotherapy. Through this case, we review cisplatin-associated electrolyte abnormalities, highlight the challenge of differentiating SIADH and RSWS, and suggest a treatment approach for hyponatremia during the period of diagnostic uncertainty.
Blachley and colleagues first discussed renal and electrolyte disturbances, specifically magnesium wasting, secondary to cisplatin use in 1981. In 1984, Kurtzberg and colleagues noted salt wasting in 2 patients receiving cisplatin therapy. The authors suggested that cisplatin inhibits solute transport in the thick ascending limb, causing clinically significant electrolyte abnormalities, coining the term cisplatin-induced salt wasting.11
The prevalence of cisplatin-induced salt wasting is unclear and likely underreported. In 1988, Hutchinson and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study and noted 10% of patients (n = 70) developed RSWS at some point over 18 months of cisplatin therapy—a higher rate than previously estimated.12 In 1992, another prospective cohort study evaluated the adverse effects of 47 patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin and reported hyponatremia in 43% of its 93 courses of chemotherapy. The authors did not report the etiology of these hyponatremia cases.13 Given the diagnostic challenge, RSWS may be underrepresented as a confirmed etiology of hyponatremia in cisplatin treatment.
Hyponatremia from cisplatin may present as either SIADH or RSWS, complicating treatment decisions. Both conditions lead to hypotonic hyponatremia with urine osmolality > 100 mOSm/kg and urine sodium levels > 40 mmol/L. However, pathophysiology behind SIADH and RSWS is different. In RSWS, proximal tubule damage causes hyponatremia, decreasing sodium reabsorption, and leading to impaired concentration gradient in every segment of the nephron. As a result, RSWS can lead to profound hyponatremia. Treatment typically consists of increasing sodium intake to correct serum sodium with salt tablets and hypertonic sodium chloride while treating the underlying etiology, in our case removing the offending agent, and waiting for proximal tubule function to recover.6 On the other hand, in SIADH, elevated antidiuretic hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the collecting duct, which has no impact on concentration gradients of the other nephron segments.14 Free-water restriction is the hallmark of SIADH treatment. Severe SIADH may require sodium repletion and/or the initiation of vaptans, ADH antagonists that competitively inhibit V2 receptors in the collecting duct to prevent water reabsorption.15
Our patient had an uncertain etiology of his hyponatremia throughout most of his treatment course, complicating our treatment decision-making. Initially, his measured serum osmolality was 278 mOsm/kg; however, his effective tonicity was lower. His AKI elevated his BUN, which in turnrequired us to calculate his serum tonicity (217 mOsm/kg) that was consistent with hypotonic hyponatremia. His elevated urine osmolality and urine sodium levels made SIADH and RSWS the most likely etiologies of his hyponatremia. To confirm the etiology, we waited for correction of his serum sodium. Therefore, we treated him with a combination of sodium repletion with 0.9% sodium chloride (154 mEq/L), hypertonic relative to his serum sodium, sodium chloride tablets, and free-water restriction. In this approach, we attempted to harmonize the treatment strategies for both SIADH and RSWS and effectively corrected his serum sodium. We evaluated his response to our treatment with a basic metabolic panel every 6 to 8 hours. Had his serum sodium decreased < 120 mmol/L, we planned to transfer the patient to the intensive care unit for 3% sodium chloride and/or intensification of his fluid restriction. A significant worsening of his hyponatremia would have strongly suggested hyponatremia secondary to SIADH since isotonic saline can worsen hyponatremia due to increased free-water reabsorption in the collecting duct.16
To differentiate between SIADH and RSWS, we relied on the FEurate after sodium correction. Multiple case reports from Japan have characterized the distinction between the processes through FEurate and serum uric acid. While the optimal cut-off values for FEurate require additional investigation, values < 11% after serum sodium correction suggests SIADH, while a value > 11% suggests RSWS.17 Prior cases have also emphasized serum hypouricemia as a distinguishing characteristic in RSWS. However, our case illustrates that serum hypouricemia is less reliable in the setting of AKI. Due to his severe AKI, our patient could not efficiently clear uric acid, likely contributing to his hyperuricemia.
Ultimately, our patient had an FEurate > 20%, which was suggestive of RSWS. Nevertheless, we recognize limitations and confounders in our diagnosis and have reflected on our diagnostic and management choices. First, the sensitivity and specificity of postsodium correction FEurate is unknown. Tracking the change in FEurate with our interventions would have increased our diagnostic utility, as suggested by Maesaka and colleagues.14 Second, our patient’s serum sodium was still at the lower end of the reference range after treatment, which may decrease the specificity of FEurate. Third, a plasma ADH collected during the initial phase of symptomatic hyponatremia would have helped differentiate between SIADH and RSWS.
Other diagnostic tests that could have excluded alternative diagnoses with even greater certainty include plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone, B-type natriuretic peptide, renin, cortisol, and thyroid function tests. From a practical standpoint, these laboratory results (excluding thyroid function test and brain natriuretic peptide) would have taken several weeks to result at our institution, limiting their clinical utility. Similarly, FEurate also has limited clinical utility, requiring effective treatment as part of the diagnostic test. Therefore, we recommend focusing on optimal treatment for hyponatremia of uncertain etiology, especially where SIADH and RSWS are the leading diagnoses.
Conclusions
We described a rare case of concomitant cisplatin-induced severe AKI and RSWS. We have emphasized the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing between SIADH and RSWS, especially with concomitant AKI, and have acknowledged that optimal treatment relies on accurate differentiation. However, differentiation may not be clinically feasible. Therefore, we suggest a treatment strategy that incorporates both free-water restriction and sodium supplementation via IV and/or oral administration.
1. Dasari S, Tchounwou PB. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740:364-378. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
2. Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen KN, Edelstein CL. Recent advances in models, mechanisms, biomarkers, and interventions in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3011. Published 2019 Jun 20. doi:10.3390/ijms20123011
3. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. The “accidental” cure—platinum-based treatment for cancer: the discovery of cisplatin. Published May 30, 2014. Accessed November 10, 2021. https://www.cancer.gov/research/progress/discovery/cisplatin
4. Ozkok A, Edelstein CL. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:967826. doi:10.1155/2014/967826
5. Palmer LG, Schnermann J. Integrated control of Na transport along the nephron. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(4):676-687. doi:10.2215/CJN.12391213
6. Bitew S, Imbriano L, Miyawaki N, Fishbane S, Maesaka JK. More on renal salt wasting without cerebral disease: response to saline infusion. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(2):309-315. doi:10.2215/CJN.02740608
7. Shirali AC, Perazella MA. Tubulointerstitial injury associated with chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014;21(1):56-63. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2013.06.010
8. Agrawal M, Swartz R. Acute renal failure [published correction appears in Am Fam Physician 2001 Feb 1;63(3):445]. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(7):2077-2088.
9. Milionis HJ, Liamis GL, Elisaf MS. The hyponatremic patient: a systematic approach to laboratory diagnosis. CMAJ. 2002;166(8):1056-1062.
10. Monneret C. Platinum anticancer drugs. From serendipity to rational design. Ann Pharm Fr. 2011;69(6):286-295. doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2011.10.001
11. Kurtzberg J, Dennis VW, Kinney TR. Cisplatinum-induced renal salt wasting. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1984;12(2):150-154. doi:10.1002/mpo.2950120219
12. Hutchison FN, Perez EA, Gandara DR, Lawrence HJ, Kaysen GA. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1988;108(1):21-25. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-108-1-21
13. Lee YK, Shin DM. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with high-dose cisplatin, etoposide, and mitomycin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 1992;7(2):118-121. doi:10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.118
14. Maesaka JK, Imbriano L, Mattana J, Gallagher D, Bade N, Sharif S. Differentiating SIADH from cerebral/renal salt wasting: failure of the volume approach and need for a new approach to hyponatremia. J Clin Med. 2014;3(4):1373-1385. Published 2014 Dec 8. doi:10.3390/jcm3041373
15. Palmer BF. The role of v2 receptor antagonists in the treatment of hyponatremia. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013;11(1):1-8. doi:10.5049/EBP.2013.11.1.1
16. Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Schrier RW, Sterns RH. Hyponatremia treatment guidelines 2007: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2007;120(11 Suppl 1):S1-S21. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.09.001
17. Maesaka JK, Imbriano LJ, Miyawaki N. High prevalence of renal salt wasting without cerebral disease as cause of hyponatremia in general medical wards. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(1):15-22. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.03.02
1. Dasari S, Tchounwou PB. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740:364-378. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
2. Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen KN, Edelstein CL. Recent advances in models, mechanisms, biomarkers, and interventions in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3011. Published 2019 Jun 20. doi:10.3390/ijms20123011
3. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. The “accidental” cure—platinum-based treatment for cancer: the discovery of cisplatin. Published May 30, 2014. Accessed November 10, 2021. https://www.cancer.gov/research/progress/discovery/cisplatin
4. Ozkok A, Edelstein CL. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:967826. doi:10.1155/2014/967826
5. Palmer LG, Schnermann J. Integrated control of Na transport along the nephron. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(4):676-687. doi:10.2215/CJN.12391213
6. Bitew S, Imbriano L, Miyawaki N, Fishbane S, Maesaka JK. More on renal salt wasting without cerebral disease: response to saline infusion. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(2):309-315. doi:10.2215/CJN.02740608
7. Shirali AC, Perazella MA. Tubulointerstitial injury associated with chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014;21(1):56-63. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2013.06.010
8. Agrawal M, Swartz R. Acute renal failure [published correction appears in Am Fam Physician 2001 Feb 1;63(3):445]. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(7):2077-2088.
9. Milionis HJ, Liamis GL, Elisaf MS. The hyponatremic patient: a systematic approach to laboratory diagnosis. CMAJ. 2002;166(8):1056-1062.
10. Monneret C. Platinum anticancer drugs. From serendipity to rational design. Ann Pharm Fr. 2011;69(6):286-295. doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2011.10.001
11. Kurtzberg J, Dennis VW, Kinney TR. Cisplatinum-induced renal salt wasting. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1984;12(2):150-154. doi:10.1002/mpo.2950120219
12. Hutchison FN, Perez EA, Gandara DR, Lawrence HJ, Kaysen GA. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with cisplatin. Ann Intern Med. 1988;108(1):21-25. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-108-1-21
13. Lee YK, Shin DM. Renal salt wasting in patients treated with high-dose cisplatin, etoposide, and mitomycin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med. 1992;7(2):118-121. doi:10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.118
14. Maesaka JK, Imbriano L, Mattana J, Gallagher D, Bade N, Sharif S. Differentiating SIADH from cerebral/renal salt wasting: failure of the volume approach and need for a new approach to hyponatremia. J Clin Med. 2014;3(4):1373-1385. Published 2014 Dec 8. doi:10.3390/jcm3041373
15. Palmer BF. The role of v2 receptor antagonists in the treatment of hyponatremia. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013;11(1):1-8. doi:10.5049/EBP.2013.11.1.1
16. Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Schrier RW, Sterns RH. Hyponatremia treatment guidelines 2007: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2007;120(11 Suppl 1):S1-S21. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.09.001
17. Maesaka JK, Imbriano LJ, Miyawaki N. High prevalence of renal salt wasting without cerebral disease as cause of hyponatremia in general medical wards. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(1):15-22. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.03.02
Apixaban a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication that occurs in seriously ill patients admitted to the ICU, and many of these patients eventually require RRT. When complicated by major metabolic disorders, it is usually clear when therapy should be initiated. However, when these complications are absent, the most appropriate time to initiate RRT is unclear. There are potential advantages to performing early RRT in patients with severe AKI, such as restoring acid-base balance, preventing fluid accumulation, and preventing major electrolyte disturbances.
Study design: Multinational, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Eligible patients were adults admitted to an ICU with severe AKI. Patients were randomly assigned to an accelerated strategy of RRT (initiated within 12 hours, 1,465 patients) or a standard strategy of RRT (held until conventional indications developed or AKI lasted more than 72 hours, 1,462 patients). RRT was performed in 1,418 (96.8%) in the accelerated group and 903 (61.8%) in the standard group. At 90 days, 643 deaths (43.9%) occurred in the accelerated group and 639 deaths (43.7%) occurred in the standard group (RR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.93-1.09; P = .92). Among survivors at 90 days, 85 out of 814 accelerated patients (10.4%) and 49 of 815 standard patients (6.0%) continued to require RRT (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.24-2.43), suggesting the possibility of increased dependence on long-term RRT if introduced early. Limitations include use of clinical equipoise to confirm full eligibility, introducing possible patient heterogeneity into the trial. In addition, broad discretion was given to clinicians on when to start RRT in the standard group resulting in variable initiation times.
Bottom line: In critically ill patients with severe AKI, earlier RRT did not result in lower mortality at 90 days compared with standard therapy and increased the risk of requiring RRT at 90 days.
Citation: Bagshaw SM et al. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Kim is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication that occurs in seriously ill patients admitted to the ICU, and many of these patients eventually require RRT. When complicated by major metabolic disorders, it is usually clear when therapy should be initiated. However, when these complications are absent, the most appropriate time to initiate RRT is unclear. There are potential advantages to performing early RRT in patients with severe AKI, such as restoring acid-base balance, preventing fluid accumulation, and preventing major electrolyte disturbances.
Study design: Multinational, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Eligible patients were adults admitted to an ICU with severe AKI. Patients were randomly assigned to an accelerated strategy of RRT (initiated within 12 hours, 1,465 patients) or a standard strategy of RRT (held until conventional indications developed or AKI lasted more than 72 hours, 1,462 patients). RRT was performed in 1,418 (96.8%) in the accelerated group and 903 (61.8%) in the standard group. At 90 days, 643 deaths (43.9%) occurred in the accelerated group and 639 deaths (43.7%) occurred in the standard group (RR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.93-1.09; P = .92). Among survivors at 90 days, 85 out of 814 accelerated patients (10.4%) and 49 of 815 standard patients (6.0%) continued to require RRT (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.24-2.43), suggesting the possibility of increased dependence on long-term RRT if introduced early. Limitations include use of clinical equipoise to confirm full eligibility, introducing possible patient heterogeneity into the trial. In addition, broad discretion was given to clinicians on when to start RRT in the standard group resulting in variable initiation times.
Bottom line: In critically ill patients with severe AKI, earlier RRT did not result in lower mortality at 90 days compared with standard therapy and increased the risk of requiring RRT at 90 days.
Citation: Bagshaw SM et al. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Kim is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication that occurs in seriously ill patients admitted to the ICU, and many of these patients eventually require RRT. When complicated by major metabolic disorders, it is usually clear when therapy should be initiated. However, when these complications are absent, the most appropriate time to initiate RRT is unclear. There are potential advantages to performing early RRT in patients with severe AKI, such as restoring acid-base balance, preventing fluid accumulation, and preventing major electrolyte disturbances.
Study design: Multinational, randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Eligible patients were adults admitted to an ICU with severe AKI. Patients were randomly assigned to an accelerated strategy of RRT (initiated within 12 hours, 1,465 patients) or a standard strategy of RRT (held until conventional indications developed or AKI lasted more than 72 hours, 1,462 patients). RRT was performed in 1,418 (96.8%) in the accelerated group and 903 (61.8%) in the standard group. At 90 days, 643 deaths (43.9%) occurred in the accelerated group and 639 deaths (43.7%) occurred in the standard group (RR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.93-1.09; P = .92). Among survivors at 90 days, 85 out of 814 accelerated patients (10.4%) and 49 of 815 standard patients (6.0%) continued to require RRT (RR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.24-2.43), suggesting the possibility of increased dependence on long-term RRT if introduced early. Limitations include use of clinical equipoise to confirm full eligibility, introducing possible patient heterogeneity into the trial. In addition, broad discretion was given to clinicians on when to start RRT in the standard group resulting in variable initiation times.
Bottom line: In critically ill patients with severe AKI, earlier RRT did not result in lower mortality at 90 days compared with standard therapy and increased the risk of requiring RRT at 90 days.
Citation: Bagshaw SM et al. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Kim is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Comparing the efficacy and safety of common SIADH treatments
Background: Hyponatremia caused by SIADH is common in hospitalized patients, and most evidence for treatment comes from noncontrolled studies. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of fluid restriction compared with furosemide, with or without NaCl supplementation, for treating SIADH.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: Single center in Thailand.
Synopsis: There were 92 participants randomized to fluid restriction alone, fluid restriction and furosemide, or fluid restriction, furosemide, and NaCl supplementation. The authors assessed the primary outcome, change in sodium, at 4, 7, 14, and 28 days (baseline mean Na 125 mmol/L). By day 4, all groups had a significant increase in sodium (mean delta 5 mmol/L). The time to achieve a safe sodium level (Na less than 130 mmol/L) was not different among groups. Acute kidney injury was most common in patients who received furosemide and NaCl supplementation, compared with the fluid restriction and fluid restriction plus furosemide groups (32%, 10%, 17%, respectively; P = .07). Hypokalemia was also most common in the furosemide and NaCl group (42%, 13%, 23%, respectively; P = .01). Limitations include open-label study design, poor fluid restriction adherence (63% overall), and inflexible treatment regimens that excluded treatment with oral potassium.
Bottom line: In treatment of hyponatremia caused by SIADH, there was no benefit to adding furosemide with or without NaCl supplementation to fluid restriction. However, there was potential associated risk of acute kidney injury and hypokalemia.Citation: Krisanapan P et al. Efficacy of furosemide, oral sodium chloride, and fluid restriction for treatment of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIADH): An open-label randomized controlled study (the EFFUSE-FLUID trial). Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):203-12. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.11.012.
Dr. Welter is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
Background: Hyponatremia caused by SIADH is common in hospitalized patients, and most evidence for treatment comes from noncontrolled studies. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of fluid restriction compared with furosemide, with or without NaCl supplementation, for treating SIADH.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: Single center in Thailand.
Synopsis: There were 92 participants randomized to fluid restriction alone, fluid restriction and furosemide, or fluid restriction, furosemide, and NaCl supplementation. The authors assessed the primary outcome, change in sodium, at 4, 7, 14, and 28 days (baseline mean Na 125 mmol/L). By day 4, all groups had a significant increase in sodium (mean delta 5 mmol/L). The time to achieve a safe sodium level (Na less than 130 mmol/L) was not different among groups. Acute kidney injury was most common in patients who received furosemide and NaCl supplementation, compared with the fluid restriction and fluid restriction plus furosemide groups (32%, 10%, 17%, respectively; P = .07). Hypokalemia was also most common in the furosemide and NaCl group (42%, 13%, 23%, respectively; P = .01). Limitations include open-label study design, poor fluid restriction adherence (63% overall), and inflexible treatment regimens that excluded treatment with oral potassium.
Bottom line: In treatment of hyponatremia caused by SIADH, there was no benefit to adding furosemide with or without NaCl supplementation to fluid restriction. However, there was potential associated risk of acute kidney injury and hypokalemia.Citation: Krisanapan P et al. Efficacy of furosemide, oral sodium chloride, and fluid restriction for treatment of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIADH): An open-label randomized controlled study (the EFFUSE-FLUID trial). Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):203-12. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.11.012.
Dr. Welter is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
Background: Hyponatremia caused by SIADH is common in hospitalized patients, and most evidence for treatment comes from noncontrolled studies. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of fluid restriction compared with furosemide, with or without NaCl supplementation, for treating SIADH.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: Single center in Thailand.
Synopsis: There were 92 participants randomized to fluid restriction alone, fluid restriction and furosemide, or fluid restriction, furosemide, and NaCl supplementation. The authors assessed the primary outcome, change in sodium, at 4, 7, 14, and 28 days (baseline mean Na 125 mmol/L). By day 4, all groups had a significant increase in sodium (mean delta 5 mmol/L). The time to achieve a safe sodium level (Na less than 130 mmol/L) was not different among groups. Acute kidney injury was most common in patients who received furosemide and NaCl supplementation, compared with the fluid restriction and fluid restriction plus furosemide groups (32%, 10%, 17%, respectively; P = .07). Hypokalemia was also most common in the furosemide and NaCl group (42%, 13%, 23%, respectively; P = .01). Limitations include open-label study design, poor fluid restriction adherence (63% overall), and inflexible treatment regimens that excluded treatment with oral potassium.
Bottom line: In treatment of hyponatremia caused by SIADH, there was no benefit to adding furosemide with or without NaCl supplementation to fluid restriction. However, there was potential associated risk of acute kidney injury and hypokalemia.Citation: Krisanapan P et al. Efficacy of furosemide, oral sodium chloride, and fluid restriction for treatment of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIADH): An open-label randomized controlled study (the EFFUSE-FLUID trial). Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):203-12. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.11.012.
Dr. Welter is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and instructor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, both in Chicago.
What makes a urinary tract infection complicated?
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.
This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.
The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Consider anatomical and severity risk factors
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.

This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.

The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Case
A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with acute dysuria, fever, and flank pain. She had a urinary tract infection (UTI) 3 months prior treated with nitrofurantoin. Temperature is 102° F, heart rate 112 beats per minute, and the remainder of vital signs are normal. She has left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine microscopy shows 70 WBCs per high power field and bacteria. Is this urinary tract infection complicated?
Background
The urinary tract is divided into the upper tract, which includes the kidneys and ureters, and the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder, urethra, and prostate. Infection of the lower urinary tract is referred to as cystitis while infection of the upper urinary tract is pyelonephritis. A UTI is the colonization of pathogen(s) within the urinary system that causes an inflammatory response resulting in symptoms and requiring treatment. UTIs occur when there is reduced urine flow, an increase in colonization risk, and when there are factors that facilitate ascent such as catheterization or incontinence.
There are an estimated 150 million cases of UTIs worldwide per year, accounting for $6 billion in health care expenditures.1 In the inpatient setting, about 40% of nosocomial infections are associated with urinary catheters. This equates to about 1 million catheter-associated UTIs per year in the United States, and up to 40% of hospital gram-negative bacteremia per year are caused by UTIs.1
UTIs are often classified as either uncomplicated or complicated infections, which can influence the depth of management. UTIs have a wide spectrum of symptoms and can manifest anywhere from mild dysuria treated successfully with outpatient antibiotics to florid sepsis. Uncomplicated simple cystitis is often treated as an outpatient with oral nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.2 Complicated UTIs are treated with broader antimicrobial coverage, and depending on severity, could require intravenous antibiotics. Many factors affect how a UTI manifests and determining whether an infection is “uncomplicated” or “complicated” is an important first step in guiding management. Unfortunately, there are differing classifications of “complicated” UTIs, making it a complicated issue itself. We outline two common approaches.
Anatomic approach
A commonly recognized definition is from the American Urological Association, which states that complicated UTIs are symptomatic cases associated with the presence of “underlying, predisposing conditions and not necessarily clinical severity, invasiveness, or complications.”3 These factors include structural or functional urinary tract abnormalities or urinary instrumentation (see Table 1). These predisposing conditions can increase microbial colonization and decrease therapy efficacy, thus increasing the frequency of infection and relapse.

This population of patients is at high risk of infections with more resistant bacteria such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli since they often lack the natural genitourinary barriers to infection. In addition, these patients more often undergo multiple antibiotic courses for their frequent infections, which also contributes to their risk of ESBL infections. Genitourinary abnormalities interfere with normal voiding, resulting in impaired flushing of bacteria. For instance, obstruction inhibits complete urinary drainage and increases the persistence of bacteria in biofilms, especially if there are stones or indwelling devices present. Biofilms usually contain a high concentration of organisms including Proteus mirabilis, Morgenella morganii, and Providencia spp.4 Keep in mind that, if there is an obstruction, the urinalysis might be without pyuria or bacteriuria.
Instrumentation increases infection risks through the direct introduction of bacteria into the genitourinary tract. Despite the efforts in maintaining sterility in urinary catheter placement, catheters provide a nidus for infection. Catheter-associated UTI (CAUTI) is defined by the Infectious Disease Society of America as UTIs that occur in patients with an indwelling catheter or who had a catheter removed for less than 48 hours who develop urinary symptoms and cultures positive for uropathogenic bacteria.4 Studies show that in general, patients with indwelling catheters will develop bacteriuria over time, with 10%-25% eventually developing symptoms.
Severity approach
There are other schools of thought that categorize uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs based on the severity of presentation (see Table 2). An uncomplicated UTI would be classified as symptoms and signs of simple cystitis limited to dysuria, frequency, urgency, and suprapubic pain. Using a symptom severity approach, systemic findings such as fever, chills, emesis, flank pain, costovertebral angle tenderness, or other findings of sepsis would be classified as a complicated UTI. These systemic findings would suggest an extension of infection beyond the bladder.

The argument for a symptomatic-based approach of classification is that the severity of symptoms should dictate the degree of management. Not all UTIs in the anatomic approach are severe. In fact, populations that are considered at risk for complicated UTIs by the AUA guidelines in Table 1 often have mild symptomatic cystitis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is the colonization of organisms in the urinary tract without active infection. For instance, bacteriuria is present in almost 100% of people with chronic indwelling catheters, 30%-40% of neurogenic bladder requiring intermittent catheterization, and 50% of elderly nursing home residents.4 Not all bacteriuria triggers enough of an inflammatory response to cause symptoms that require treatment.
Ultimate clinical judgment
Although there are multiple different society recommendations in distinguishing uncomplicated versus complicated UTIs, considering both anatomical and severity risk factors can better aid in clinical decision-making rather than abiding by one classification method alone.
Uncomplicated UTIs from the AUA guidelines can cause severe infections that might require longer courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics. On the other hand, people with anatomic abnormalities can present with mild symptoms that can be treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for a standard time course. Recognizing the severity of the infection and using clinical judgment aids in antibiotic stewardship.
Although the existence of algorithmic approaches can help guide clinical judgment, accounting for the spectrum of host and bacterial factors should ultimately determine the complexity of the disease and management.3 Using clinical suspicion to determine when a UTI should be treated as a complicated infection can ensure effective treatment and decrease the likelihood of sepsis, renal scarring, or end-stage disease.5
Back to the case
The case presents an elderly woman with diabetes presenting with sepsis from a UTI. Because of a normal urinary tract and no prior instrumentation, by the AUA definition, she would be classified as an uncomplicated UTI; however, we would classify her as a complicated UTI based on the severity of her presentation. She has a fever, tachycardia, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness that are evidence of infection extending beyond the bladder. She has sepsis warranting inpatient management. Prior urine culture results could aid in determining empiric treatment while waiting for new cultures. In her case, an intravenous antibiotic with broad gram-negative coverage such as ceftriaxone would be appropriate.
Bottom line
There are multiple interpretations of complicated UTIs including both an anatomical and severity approach. Clinical judgment regarding infection severity should determine the depth of management.
Dr. Vu is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Dr. Gray is a hospitalist at the University of Kentucky and the Lexington Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
References
1. Folk CS. AUA Core Curriculum: Urinary Tract Infection (Adult). 2021 Mar 1. https://university.auanet.org/core_topic.cfm?coreid=92.
2. Gupta K et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 1;52(5):e103-20. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257.
3. Johnson JR. Definition of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2017 February 15;64(4):529. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw751.
4. Nicolle LE, AMMI Canada Guidelines Committee. Complicated urinary tract infection in adults. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005;16(6):349-60. doi: 10.1155/2005/385768.
5. Melekos MD and Naber KG. Complicated urinary tract infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;15(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(00)00168-0.
Key points
- The anatomical approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the presence of underlying, predisposing conditions such as structurally or functionally abnormal genitourinary tract or urinary instrumentation or foreign bodies.
- The severity approach to defining complicated UTIs considers the severity of presentation including the presence of systemic manifestations.
- Both approaches should consider populations that are at risk for recurrent or multidrug-resistant infections and infections that can lead to high morbidity.
- Either approach can be used as a guide, but neither should replace clinical suspicion and judgment in determining the depth of treatment.
Additional reading
Choe HS et al. Summary of the UAA‐AAUS guidelines for urinary tract infections. Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):175-85. doi:10.1111/iju.13493.
Nicolle LE et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;40(5):643-54. doi: 10.1086/427507.
Wagenlehner FME et al. Epidemiology, definition and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17:586-600. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0362-4.
Wallace DW et al. Urinalysis: A simple test with complicated interpretation. J Urgent Care Med. 2020 July-Aug;14(10):11-4.
Quiz
A 68-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with acute fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has associated nausea, malaise, and fatigue. She takes metformin and denies recent antibiotic use. Her temperature is 102.8° F, heart rate 118 beats per minute, blood pressure 118/71 mm Hg, and her respiratory rate is 24 breaths per minute. She is ill-appearing and has mild suprapubic tenderness. White blood cell count is 18 k/mcL. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and bacteria. Urine microscopy has 120 white blood cells per high power field. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Azithromycin
B. Ceftriaxone
C. Cefepime and vancomycin
D. Nitrofurantoin
The answer is B. The patient presents with sepsis secondary to a urinary tract infection. Using the anatomic approach this would be classified as uncomplicated. Using the severity approach, this would be classified as a complicated urinary tract infection. With fever, chills, and signs of sepsis, it’s likely her infection extends beyond the bladder. Given the severity of her presentation, we’d favor treating her as a complicated urinary tract infection with intravenous ceftriaxone. There is no suggestion of resistance or additional MRSA risk factors requiring intravenous vancomycin or cefepime. Nitrofurantoin, although a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis, would not be appropriate if there is suspicion infection extends beyond the bladder. Azithromycin is a first-line option for chlamydia trachomatis, but not a urinary tract infection.
Timing of renal-replacement therapy for AKI in the ICU
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) in the ICU is associated with high mortality. It is hypothesized that earlier initiation of RRT may benefit patients by controlling fluid overload and reducing metabolic stress caused by electrolyte and acid-base imbalances. However, prior studies have been conflicting, with the IDEAL-ICU study (2018) demonstrating no improvement in 90-day mortality with early RRT in septic shock.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Of ICU patients with severe AKI, 3,019 were randomized to either early or standard initiation of RRT. Early RRT was defined as occurring within 12 hours of eligibility; in the standard-therapy group, RRT was delayed until specifically indicated or if there was no improvement after 72 hours. Those needing immediate renal replacement or deemed likely to recover without need for RRT were excluded in order to study only those in whom ideal timing of dialysis was uncertain. There was no difference in 90-day mortality between the groups (43.9% vs. 43.7%; P = .92). Early initiation did not improve length of ICU stay, ventilator-free days, days out of the hospital, or quality of life. The early-initiation patients experienced more adverse events related to RRT and were more likely to have continued dependence on RRT at 90 days (10.4% vs. 6.0% in standard initiation). Of note, approximately 40% of those randomized to standard initiation never required RRT.
Bottom line: This large, multicenter, well-conducted trial demonstrates no benefit for early initiation of RRT in critically ill patients.
Citation: STARRT-AKI investigators. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Lee is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, all in Chicago.
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) in the ICU is associated with high mortality. It is hypothesized that earlier initiation of RRT may benefit patients by controlling fluid overload and reducing metabolic stress caused by electrolyte and acid-base imbalances. However, prior studies have been conflicting, with the IDEAL-ICU study (2018) demonstrating no improvement in 90-day mortality with early RRT in septic shock.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Of ICU patients with severe AKI, 3,019 were randomized to either early or standard initiation of RRT. Early RRT was defined as occurring within 12 hours of eligibility; in the standard-therapy group, RRT was delayed until specifically indicated or if there was no improvement after 72 hours. Those needing immediate renal replacement or deemed likely to recover without need for RRT were excluded in order to study only those in whom ideal timing of dialysis was uncertain. There was no difference in 90-day mortality between the groups (43.9% vs. 43.7%; P = .92). Early initiation did not improve length of ICU stay, ventilator-free days, days out of the hospital, or quality of life. The early-initiation patients experienced more adverse events related to RRT and were more likely to have continued dependence on RRT at 90 days (10.4% vs. 6.0% in standard initiation). Of note, approximately 40% of those randomized to standard initiation never required RRT.
Bottom line: This large, multicenter, well-conducted trial demonstrates no benefit for early initiation of RRT in critically ill patients.
Citation: STARRT-AKI investigators. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Lee is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, all in Chicago.
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) in the ICU is associated with high mortality. It is hypothesized that earlier initiation of RRT may benefit patients by controlling fluid overload and reducing metabolic stress caused by electrolyte and acid-base imbalances. However, prior studies have been conflicting, with the IDEAL-ICU study (2018) demonstrating no improvement in 90-day mortality with early RRT in septic shock.
Study design: Open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting: 168 hospitals in 15 countries.
Synopsis: Of ICU patients with severe AKI, 3,019 were randomized to either early or standard initiation of RRT. Early RRT was defined as occurring within 12 hours of eligibility; in the standard-therapy group, RRT was delayed until specifically indicated or if there was no improvement after 72 hours. Those needing immediate renal replacement or deemed likely to recover without need for RRT were excluded in order to study only those in whom ideal timing of dialysis was uncertain. There was no difference in 90-day mortality between the groups (43.9% vs. 43.7%; P = .92). Early initiation did not improve length of ICU stay, ventilator-free days, days out of the hospital, or quality of life. The early-initiation patients experienced more adverse events related to RRT and were more likely to have continued dependence on RRT at 90 days (10.4% vs. 6.0% in standard initiation). Of note, approximately 40% of those randomized to standard initiation never required RRT.
Bottom line: This large, multicenter, well-conducted trial demonstrates no benefit for early initiation of RRT in critically ill patients.
Citation: STARRT-AKI investigators. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:240-51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000741.
Dr. Lee is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, all in Chicago.
Advanced CKD doesn’t derail empagliflozin in EMPEROR-preserved
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of the nearly 6,000 patients with heart failure and HFpEF enrolled in EMPEROR-Preserved had CKD (although renal function was not an enrollment criterion), including 10% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) that fell in the range of 20-29 mL/min/1.73 m2, which categorized them as having stage 4 CKD.
The results showed, in a prespecified analysis, that treatment with empagliflozin led to a consistent, significant relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure “across the full spectrum of kidney function, down to an eGFR of 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” said Faiez Zannad, MD, PhD, who presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Among the 46.5% of enrolled patients without CKD, empagliflozin produced a significant 20% drop in the primary outcome relative to those who received placebo. Among the 53.5% of patients with CKD at time of randomization (defined as an eGFR <60 mL/min/1/73 m2 or a urinary albumin to creatinine ratio >300 mg/g), treatment with empagliflozin was associated with a significant 25% cut in the primary endpoint compared with placebo.
Empagliflozin was also “well tolerated” by patients with HFpEF, whether or not they also had CKD, “including patients with severely impaired kidney function,” said Dr. Zannad, a professor of cardiology therapeutics at the University of Lorraine in Nancy, France, at the virtual meeting.
An end to ‘renalism’
“This is a nail in the coffin for the concept of ‘renalism,’” the erroneous notion held by many clinicians and researchers that various treatments are not as effective and potentially more likely to cause adverse effects in patients with CKD compared with those with better renal function, commented Janani Rangaswami, MD, a nephrologist who is a professor and director of the cardiorenal program at George Washington University, Washington, D.C.
In addition to EMPEROR-Preserved, other large trials of agents from the SGLT2 inhibitor class bucked the premise of renalism and took the “groundbreaking step” of enrolling patients with moderate-severe CKD, noted Dr. Rangaswami in an interview. In particular, two trials took this approach when enrolling patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), EMPEROR-Reduced (which also tested empagliflozin and matched the design of EMPEROR-Preserved) and DAPA-HF (which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin [Farxiga, AstraZeneca]).
“It was a huge, bold step, especially in EMPEROR-Preserved and in EMPEROR-Reduced, which both enrolled patients with eGFRs as low as 20 mL/min/1.73m2,” Dr. Rangaswami said. DAPA-HF included patients with eGFRs as low as 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
EMPEROR-Reduced and DAPA-HF – published earlier this year – both had similar findings as EMPEROR-Preserved as reported by Dr. Zannad: consistent benefit from empagliflozin or dapagliflozin regardless of eGFR level and no signal of increased adverse events from treatment.
In fact, all three analyses show that patients with worse renal function had the highest risk for cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure; hence, the beneficial impact from SGLT2 inhibitors is greatest in these patients.
These observations “make it easier to focus on the group with moderate-to-severe CKD,” both in the routine care setting as well as in future trials, said Dr. Rangaswami.
“This is a welcome trend that paves the way to test more treatments in patients with stage 4 and even stage 5 CKD, patients ... excluded from trials in the past,” she said.
In addition, the consistent benefit from SGLT2 inhibitors in these three heart failure trials regardless of CKD “means there is simply no room for renalism. There is no room for clinicians to say that because a patient’s eGFR is 30 mL/min/1.73m2 they are worried about starting an SGLT2 inhibitor,” she stressed.
More CKD-independent effects of empagliflozin
Results of other new analyses from EMPEROR-Preserved, also reported by Dr. Zannad, included the finding that empagliflozin was associated with a similar slowing of loss of renal function over time compared with placebo, regardless of CKD status.
In patients with CKD, empagliflozin slowed eGFR loss by 1.4 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, and in those without CKD, by 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m2/year, relative to placebo.
“Even in patients without CKD, there was a relevant eGFR decline in the placebo group that was attenuated by empagliflozin,” Dr. Zannad said.
At the end of the study, when empagliflozin was stopped, patients with or without CKD had their eGFR bounce back by an identical 2.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 relative to placebo.
Empagliflozin slowed progression to macroalbuminuria and significantly reduced the incidence of acute kidney injury by a similar amount regardless of CKD status compared with placebo.
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled patients with function-limiting HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction >40%, and a minimum level of a reliable serum marker of heart failure, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Compared with placebo, empagliflozin reduced the trial’s primary outcome by an absolute 3.3 percentage points and by a significant relative risk reduction of 21% after a median 26 months of follow-up, according to a report published in October 2021.
EMPEROR-Preserved is the first prospective, randomized trial to unequivocally show the efficacy and safety of a drug for improving outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Lilly, which market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Zannad has reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as other companies. Dr. Rangaswami has reported being a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM KIDNEY WEEK 2021