User login
For MD-IQ use only
Hospitalists and PCPs crave greater communication
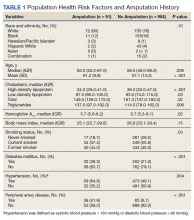
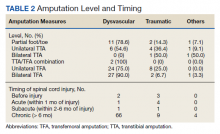
Hospitalists and PCPs want more dialogue while patients are in the hospital in order to coordinate and personalize care, according to data collected at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. The results were presented at the annual meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“I think a major takeaway is that both hospitalists and primary care doctors agree that it’s important for primary care doctors to be involved in a patient’s hospitalization. They both identified a value that PCPs can bring to the table,” coresearcher Kristen Flint, MD, a primary care resident, told this news organization.
A majority in both camps reported that communication with the other party occurred in less than 25% of cases, whereas ideally it would happen half of the time. Dr. Flint noted that communication tools differ among hospitals, limiting the applicability of the findings.
The research team surveyed 39 hospitalists and 28 PCPs employed by the medical center during the first half of 2021. They also interviewed six hospitalists as they admitted and discharged patients.
The hospitalist movement, which took hold in response to cost and efficiency demands of managed care, led to the start of inpatient specialists, thereby reducing the need for PCPs to commute between their offices and the hospital to care for patients in both settings.
Primary care involvement is important during hospitalization
In the Beth Israel Deaconess survey, four out of five hospitalists and three-quarters of PCPs agreed that primary care involvement is still important during hospitalization, most critically during discharge and admission. Hospitalists reported that PCPs provide valuable data about a patient’s medical status, social supports, mental health, and goals for care. They also said having such data helps to boost patient trust and improve the quality of inpatient care.
“Most projects around communication between inpatient and outpatient doctors have really focused on the time of discharge,” when clinicians identify what care a patient will need after they leave the hospital, Dr. Flint said. “But we found that both sides felt increased communication at time of admission would also be beneficial.”
The biggest barrier for PCPs, cited by 82% of respondents, was lack of time. Hospitalists’ top impediment was being unable to find contact information for the other party, which was cited by 79% of these survey participants.
Hospitalists operate ‘in a very stressful environment’
The Beth Israel Deaconess research “documents what has largely been suspected,” said primary care general internist Allan Goroll, MD.
Dr. Goroll, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview that hospitalists operate “in a very stressful environment.”
“They [hospitalists] appreciate accurate information about a patient’s recent medical history, test results, and responses to treatment as well as a briefing on patient values and preferences, family dynamics, and priorities for the admission. It makes for a safer, more personalized, and more efficient hospital admission,” said Dr. Goroll, who was not involved in the research.
In a 2015 article in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Goroll and Daniel Hunt, MD, director of hospital medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, proposed a collaborative model in which PCPs visit hospitalized patients and serve as consultants to inpatient staff. Dr. Goroll said Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, where he practices, initiated a study of that approach, but it was interrupted by the pandemic.
“As limited time is the most often cited barrier to communication, future interventions such as asynchronous forms of communication between the two groups should be considered,” the researchers wrote in the NEJM perspective.
To narrow the gap, Beth Israel Deaconess will study converting an admission notification letter sent to PCPs into a two-way communication tool in which PCPs can insert patient information, Dr. Flint said.
Dr. Flint and Dr. Goroll have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalists and PCPs want more dialogue while patients are in the hospital in order to coordinate and personalize care, according to data collected at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. The results were presented at the annual meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“I think a major takeaway is that both hospitalists and primary care doctors agree that it’s important for primary care doctors to be involved in a patient’s hospitalization. They both identified a value that PCPs can bring to the table,” coresearcher Kristen Flint, MD, a primary care resident, told this news organization.
A majority in both camps reported that communication with the other party occurred in less than 25% of cases, whereas ideally it would happen half of the time. Dr. Flint noted that communication tools differ among hospitals, limiting the applicability of the findings.
The research team surveyed 39 hospitalists and 28 PCPs employed by the medical center during the first half of 2021. They also interviewed six hospitalists as they admitted and discharged patients.
The hospitalist movement, which took hold in response to cost and efficiency demands of managed care, led to the start of inpatient specialists, thereby reducing the need for PCPs to commute between their offices and the hospital to care for patients in both settings.
Primary care involvement is important during hospitalization
In the Beth Israel Deaconess survey, four out of five hospitalists and three-quarters of PCPs agreed that primary care involvement is still important during hospitalization, most critically during discharge and admission. Hospitalists reported that PCPs provide valuable data about a patient’s medical status, social supports, mental health, and goals for care. They also said having such data helps to boost patient trust and improve the quality of inpatient care.
“Most projects around communication between inpatient and outpatient doctors have really focused on the time of discharge,” when clinicians identify what care a patient will need after they leave the hospital, Dr. Flint said. “But we found that both sides felt increased communication at time of admission would also be beneficial.”
The biggest barrier for PCPs, cited by 82% of respondents, was lack of time. Hospitalists’ top impediment was being unable to find contact information for the other party, which was cited by 79% of these survey participants.
Hospitalists operate ‘in a very stressful environment’
The Beth Israel Deaconess research “documents what has largely been suspected,” said primary care general internist Allan Goroll, MD.
Dr. Goroll, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview that hospitalists operate “in a very stressful environment.”
“They [hospitalists] appreciate accurate information about a patient’s recent medical history, test results, and responses to treatment as well as a briefing on patient values and preferences, family dynamics, and priorities for the admission. It makes for a safer, more personalized, and more efficient hospital admission,” said Dr. Goroll, who was not involved in the research.
In a 2015 article in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Goroll and Daniel Hunt, MD, director of hospital medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, proposed a collaborative model in which PCPs visit hospitalized patients and serve as consultants to inpatient staff. Dr. Goroll said Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, where he practices, initiated a study of that approach, but it was interrupted by the pandemic.
“As limited time is the most often cited barrier to communication, future interventions such as asynchronous forms of communication between the two groups should be considered,” the researchers wrote in the NEJM perspective.
To narrow the gap, Beth Israel Deaconess will study converting an admission notification letter sent to PCPs into a two-way communication tool in which PCPs can insert patient information, Dr. Flint said.
Dr. Flint and Dr. Goroll have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalists and PCPs want more dialogue while patients are in the hospital in order to coordinate and personalize care, according to data collected at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. The results were presented at the annual meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine.
“I think a major takeaway is that both hospitalists and primary care doctors agree that it’s important for primary care doctors to be involved in a patient’s hospitalization. They both identified a value that PCPs can bring to the table,” coresearcher Kristen Flint, MD, a primary care resident, told this news organization.
A majority in both camps reported that communication with the other party occurred in less than 25% of cases, whereas ideally it would happen half of the time. Dr. Flint noted that communication tools differ among hospitals, limiting the applicability of the findings.
The research team surveyed 39 hospitalists and 28 PCPs employed by the medical center during the first half of 2021. They also interviewed six hospitalists as they admitted and discharged patients.
The hospitalist movement, which took hold in response to cost and efficiency demands of managed care, led to the start of inpatient specialists, thereby reducing the need for PCPs to commute between their offices and the hospital to care for patients in both settings.
Primary care involvement is important during hospitalization
In the Beth Israel Deaconess survey, four out of five hospitalists and three-quarters of PCPs agreed that primary care involvement is still important during hospitalization, most critically during discharge and admission. Hospitalists reported that PCPs provide valuable data about a patient’s medical status, social supports, mental health, and goals for care. They also said having such data helps to boost patient trust and improve the quality of inpatient care.
“Most projects around communication between inpatient and outpatient doctors have really focused on the time of discharge,” when clinicians identify what care a patient will need after they leave the hospital, Dr. Flint said. “But we found that both sides felt increased communication at time of admission would also be beneficial.”
The biggest barrier for PCPs, cited by 82% of respondents, was lack of time. Hospitalists’ top impediment was being unable to find contact information for the other party, which was cited by 79% of these survey participants.
Hospitalists operate ‘in a very stressful environment’
The Beth Israel Deaconess research “documents what has largely been suspected,” said primary care general internist Allan Goroll, MD.
Dr. Goroll, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview that hospitalists operate “in a very stressful environment.”
“They [hospitalists] appreciate accurate information about a patient’s recent medical history, test results, and responses to treatment as well as a briefing on patient values and preferences, family dynamics, and priorities for the admission. It makes for a safer, more personalized, and more efficient hospital admission,” said Dr. Goroll, who was not involved in the research.
In a 2015 article in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Goroll and Daniel Hunt, MD, director of hospital medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, proposed a collaborative model in which PCPs visit hospitalized patients and serve as consultants to inpatient staff. Dr. Goroll said Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, where he practices, initiated a study of that approach, but it was interrupted by the pandemic.
“As limited time is the most often cited barrier to communication, future interventions such as asynchronous forms of communication between the two groups should be considered,” the researchers wrote in the NEJM perspective.
To narrow the gap, Beth Israel Deaconess will study converting an admission notification letter sent to PCPs into a two-way communication tool in which PCPs can insert patient information, Dr. Flint said.
Dr. Flint and Dr. Goroll have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SGIM 2022
Strawberries, spinach, kale: high on the ‘Dirty Dozen’ list
Once again, of the foods.
The yearly report comes from the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving human health and the environment, and also includes a “Clean 15” list of produce.
An industry group for growers of organic and nonorganic produce, along with some dietitians, make strong objections to the report, saying it raises unnecessary alarm and could discourage people from eating enough fruits and vegetables.
The report gives people valuable information, says the Environmental Working Group’s Alexis Temkin, PhD, a toxicologist, so they can make informed choices about the fruits and vegetables they buy.
Environmental Working Group researchers get data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s samplings of pesticide residue on produce done yearly or every 2 years, and from the Food and Drug Administration for honeydew melon, which the USDA doesn’t test for.
2022 results: Dirty Dozen
More than 70% of the conventionally grown produce had detectable pesticide residue, the Environmental Working Group found. These fruits and vegetables were found to have the most pesticide residues this year:
- 1. Strawberries
- 2. Spinach
- 3. Kale and collard and mustard greens
- 4. Nectarines
- 5. Apples
- 6. Grapes
- 7. Bell and hot peppers
- 8. Cherries
- 9. Peaches
- 10. Pears
- 11. Celery
- 12. Tomatoes
2022 results: Clean 15
Almost 70% of the Clean Fifteen fruit and vegetable samples had no detectable residues of pesticides, the Environmental Working Group found. Avocados and sweet corn were the cleanest, with less than 2% of samples showing any detectable pesticides.
- 1. Avocados
- 2. Sweet corn
- 3. Pineapple
- 4. Onions
- 5. Papaya
- 6. Sweet peas (frozen)
- 7. Asparagus
- 8. Honeydew melon
- 9. Kiwi
- 10. Cabbage
- 11. Mushrooms
- 12. Cantaloupe
- 13. Mangoes
- 14. Watermelon
- 15. Sweet potatoes
More on methods
To produce the report, the Environmental Working Group analyzed more than 44,000 samples taken by the FDA and USDA, which tests a subset of produce each year.
Before testing, USDA scientists prepare each fruit or vegetable the way people tend to do themselves, such as peeling those with inedible peels and rinsing produce with edible peels.
The Environmental Working Group takes six measures of pesticide contamination into account:
- Percent of samples tested with detectable pesticides
- Percent with two or more detectable pesticides
- Average number of pesticides in a single sample
- Average amount of pesticides, expressed in parts per million
- Maximum number of pesticides on a single sample
- Total number of pesticides found
Next, the Environmental Working Group researchers ranked the 46 fruits and vegetables analyzed, calculated a total score, and drew up the lists.
Industry criticism
The Alliance for Food and Farming, an industry group that represents organic and nonorganic farmers, growers, and shippers, takes strong issue with the annual report, noting that pesticide residues on conventional produce are low, if present at all.
“Ignore or discount the list,” says Teresa Thorne, executive director of the alliance. Like others, she fears that if an organic fruit or vegetable costs more, as they often do, consumers will bypass produce altogether, especially low-income consumers. “Pick what’s best for you and your family,” she says.
Temkin of the Environmental Working Group acknowledges that all the residues found were within legal limits set by the Environmental Protection Agency. “Although the levels are legal, that doesn’t necessarily mean they are safe,” she says.
The point of the rankings, she says, is to give people information so they can choose whether to buy organic or nonorganic produce. “Our recommendation is to buy the ones on the ‘Dirty Dozen’ list organic when available, or focus on the ‘Clean 15’ list.”
The Environmental Working Group depends on a broad base of support overall, according to information on its website, including companies that produce organic products such as Stonyfield Farms, Earthbound Farms, and Organic Valley.
But according to Iris Myers, an Environmental Working Group spokesperson, the Shopper’s Guide with the clean and dirty produce rankings “isn’t funded by any companies – only grants and individual donors. We don’t allow companies to sponsor any of our research reports.”
In the report, the Environmental Working Group also notes that the EPA has taken action to prohibit the pesticide chlorpyrifos in food, after the group and others spent years asking for the ban.
Dietitians weigh in
The report uses “fear-branded messages to steer people away from eating conventionally grown fruits and veggies,” says Christine Rosenbloom, PhD, a retired Georgia State University professor and an Atlanta nutrition consultant.
She reminds people that “both organic and conventional agriculture use pesticides to protect the crop. Organic famers use different pesticides that are described as ‘natural,’ but natural doesn’t mean safer, better, or chemical-free,” she says.
She refers people to the Pesticide Residue Calculator from toxicologists at the University of California, Riverside, posted on the consumer site the Alliance for Food and Farming.
The calculator helps reassure people that trace amounts of chemicals on conventionally grown produce are not a hazard to your health, Dr. Rosenbloom says. “Using myself as an example, I could eat 850 apples or 13,225 servings of blueberries in one day without any effect, even in the worst-case scenario of the fruit having the highest pesticide residue recorded by the USDA.”
“It’s one more example of putting good and bad food labels on foods when it isn’t deserved,” says Connie Diekman, a food and nutrition consultant in St. Louis and a former president of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. “The amounts they are measuring are so much below the tolerance level set by the EPA.”
The report shouldn’t scare people, including parents worried about serving their children conventional produce, she says.
As for how much produce to eat, “the best advice is to have half your plate be fruits and vegetables,” Ms. Diekman says. Under current Dietary Guidelines for Americans, an intake of 2½ “cups equivalent” of vegetables and 2 “cups equivalent” of fruits is recommended daily for adults.
Ms. Diekman is on the Bayer LEAD Network, Leaders Engaged in Advancing Dialogue. Dr. Rosenbloom reports an honorarium from a bean industry group for developing a webinar on healthy aging.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Once again, of the foods.
The yearly report comes from the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving human health and the environment, and also includes a “Clean 15” list of produce.
An industry group for growers of organic and nonorganic produce, along with some dietitians, make strong objections to the report, saying it raises unnecessary alarm and could discourage people from eating enough fruits and vegetables.
The report gives people valuable information, says the Environmental Working Group’s Alexis Temkin, PhD, a toxicologist, so they can make informed choices about the fruits and vegetables they buy.
Environmental Working Group researchers get data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s samplings of pesticide residue on produce done yearly or every 2 years, and from the Food and Drug Administration for honeydew melon, which the USDA doesn’t test for.
2022 results: Dirty Dozen
More than 70% of the conventionally grown produce had detectable pesticide residue, the Environmental Working Group found. These fruits and vegetables were found to have the most pesticide residues this year:
- 1. Strawberries
- 2. Spinach
- 3. Kale and collard and mustard greens
- 4. Nectarines
- 5. Apples
- 6. Grapes
- 7. Bell and hot peppers
- 8. Cherries
- 9. Peaches
- 10. Pears
- 11. Celery
- 12. Tomatoes
2022 results: Clean 15
Almost 70% of the Clean Fifteen fruit and vegetable samples had no detectable residues of pesticides, the Environmental Working Group found. Avocados and sweet corn were the cleanest, with less than 2% of samples showing any detectable pesticides.
- 1. Avocados
- 2. Sweet corn
- 3. Pineapple
- 4. Onions
- 5. Papaya
- 6. Sweet peas (frozen)
- 7. Asparagus
- 8. Honeydew melon
- 9. Kiwi
- 10. Cabbage
- 11. Mushrooms
- 12. Cantaloupe
- 13. Mangoes
- 14. Watermelon
- 15. Sweet potatoes
More on methods
To produce the report, the Environmental Working Group analyzed more than 44,000 samples taken by the FDA and USDA, which tests a subset of produce each year.
Before testing, USDA scientists prepare each fruit or vegetable the way people tend to do themselves, such as peeling those with inedible peels and rinsing produce with edible peels.
The Environmental Working Group takes six measures of pesticide contamination into account:
- Percent of samples tested with detectable pesticides
- Percent with two or more detectable pesticides
- Average number of pesticides in a single sample
- Average amount of pesticides, expressed in parts per million
- Maximum number of pesticides on a single sample
- Total number of pesticides found
Next, the Environmental Working Group researchers ranked the 46 fruits and vegetables analyzed, calculated a total score, and drew up the lists.
Industry criticism
The Alliance for Food and Farming, an industry group that represents organic and nonorganic farmers, growers, and shippers, takes strong issue with the annual report, noting that pesticide residues on conventional produce are low, if present at all.
“Ignore or discount the list,” says Teresa Thorne, executive director of the alliance. Like others, she fears that if an organic fruit or vegetable costs more, as they often do, consumers will bypass produce altogether, especially low-income consumers. “Pick what’s best for you and your family,” she says.
Temkin of the Environmental Working Group acknowledges that all the residues found were within legal limits set by the Environmental Protection Agency. “Although the levels are legal, that doesn’t necessarily mean they are safe,” she says.
The point of the rankings, she says, is to give people information so they can choose whether to buy organic or nonorganic produce. “Our recommendation is to buy the ones on the ‘Dirty Dozen’ list organic when available, or focus on the ‘Clean 15’ list.”
The Environmental Working Group depends on a broad base of support overall, according to information on its website, including companies that produce organic products such as Stonyfield Farms, Earthbound Farms, and Organic Valley.
But according to Iris Myers, an Environmental Working Group spokesperson, the Shopper’s Guide with the clean and dirty produce rankings “isn’t funded by any companies – only grants and individual donors. We don’t allow companies to sponsor any of our research reports.”
In the report, the Environmental Working Group also notes that the EPA has taken action to prohibit the pesticide chlorpyrifos in food, after the group and others spent years asking for the ban.
Dietitians weigh in
The report uses “fear-branded messages to steer people away from eating conventionally grown fruits and veggies,” says Christine Rosenbloom, PhD, a retired Georgia State University professor and an Atlanta nutrition consultant.
She reminds people that “both organic and conventional agriculture use pesticides to protect the crop. Organic famers use different pesticides that are described as ‘natural,’ but natural doesn’t mean safer, better, or chemical-free,” she says.
She refers people to the Pesticide Residue Calculator from toxicologists at the University of California, Riverside, posted on the consumer site the Alliance for Food and Farming.
The calculator helps reassure people that trace amounts of chemicals on conventionally grown produce are not a hazard to your health, Dr. Rosenbloom says. “Using myself as an example, I could eat 850 apples or 13,225 servings of blueberries in one day without any effect, even in the worst-case scenario of the fruit having the highest pesticide residue recorded by the USDA.”
“It’s one more example of putting good and bad food labels on foods when it isn’t deserved,” says Connie Diekman, a food and nutrition consultant in St. Louis and a former president of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. “The amounts they are measuring are so much below the tolerance level set by the EPA.”
The report shouldn’t scare people, including parents worried about serving their children conventional produce, she says.
As for how much produce to eat, “the best advice is to have half your plate be fruits and vegetables,” Ms. Diekman says. Under current Dietary Guidelines for Americans, an intake of 2½ “cups equivalent” of vegetables and 2 “cups equivalent” of fruits is recommended daily for adults.
Ms. Diekman is on the Bayer LEAD Network, Leaders Engaged in Advancing Dialogue. Dr. Rosenbloom reports an honorarium from a bean industry group for developing a webinar on healthy aging.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Once again, of the foods.
The yearly report comes from the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization dedicated to improving human health and the environment, and also includes a “Clean 15” list of produce.
An industry group for growers of organic and nonorganic produce, along with some dietitians, make strong objections to the report, saying it raises unnecessary alarm and could discourage people from eating enough fruits and vegetables.
The report gives people valuable information, says the Environmental Working Group’s Alexis Temkin, PhD, a toxicologist, so they can make informed choices about the fruits and vegetables they buy.
Environmental Working Group researchers get data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s samplings of pesticide residue on produce done yearly or every 2 years, and from the Food and Drug Administration for honeydew melon, which the USDA doesn’t test for.
2022 results: Dirty Dozen
More than 70% of the conventionally grown produce had detectable pesticide residue, the Environmental Working Group found. These fruits and vegetables were found to have the most pesticide residues this year:
- 1. Strawberries
- 2. Spinach
- 3. Kale and collard and mustard greens
- 4. Nectarines
- 5. Apples
- 6. Grapes
- 7. Bell and hot peppers
- 8. Cherries
- 9. Peaches
- 10. Pears
- 11. Celery
- 12. Tomatoes
2022 results: Clean 15
Almost 70% of the Clean Fifteen fruit and vegetable samples had no detectable residues of pesticides, the Environmental Working Group found. Avocados and sweet corn were the cleanest, with less than 2% of samples showing any detectable pesticides.
- 1. Avocados
- 2. Sweet corn
- 3. Pineapple
- 4. Onions
- 5. Papaya
- 6. Sweet peas (frozen)
- 7. Asparagus
- 8. Honeydew melon
- 9. Kiwi
- 10. Cabbage
- 11. Mushrooms
- 12. Cantaloupe
- 13. Mangoes
- 14. Watermelon
- 15. Sweet potatoes
More on methods
To produce the report, the Environmental Working Group analyzed more than 44,000 samples taken by the FDA and USDA, which tests a subset of produce each year.
Before testing, USDA scientists prepare each fruit or vegetable the way people tend to do themselves, such as peeling those with inedible peels and rinsing produce with edible peels.
The Environmental Working Group takes six measures of pesticide contamination into account:
- Percent of samples tested with detectable pesticides
- Percent with two or more detectable pesticides
- Average number of pesticides in a single sample
- Average amount of pesticides, expressed in parts per million
- Maximum number of pesticides on a single sample
- Total number of pesticides found
Next, the Environmental Working Group researchers ranked the 46 fruits and vegetables analyzed, calculated a total score, and drew up the lists.
Industry criticism
The Alliance for Food and Farming, an industry group that represents organic and nonorganic farmers, growers, and shippers, takes strong issue with the annual report, noting that pesticide residues on conventional produce are low, if present at all.
“Ignore or discount the list,” says Teresa Thorne, executive director of the alliance. Like others, she fears that if an organic fruit or vegetable costs more, as they often do, consumers will bypass produce altogether, especially low-income consumers. “Pick what’s best for you and your family,” she says.
Temkin of the Environmental Working Group acknowledges that all the residues found were within legal limits set by the Environmental Protection Agency. “Although the levels are legal, that doesn’t necessarily mean they are safe,” she says.
The point of the rankings, she says, is to give people information so they can choose whether to buy organic or nonorganic produce. “Our recommendation is to buy the ones on the ‘Dirty Dozen’ list organic when available, or focus on the ‘Clean 15’ list.”
The Environmental Working Group depends on a broad base of support overall, according to information on its website, including companies that produce organic products such as Stonyfield Farms, Earthbound Farms, and Organic Valley.
But according to Iris Myers, an Environmental Working Group spokesperson, the Shopper’s Guide with the clean and dirty produce rankings “isn’t funded by any companies – only grants and individual donors. We don’t allow companies to sponsor any of our research reports.”
In the report, the Environmental Working Group also notes that the EPA has taken action to prohibit the pesticide chlorpyrifos in food, after the group and others spent years asking for the ban.
Dietitians weigh in
The report uses “fear-branded messages to steer people away from eating conventionally grown fruits and veggies,” says Christine Rosenbloom, PhD, a retired Georgia State University professor and an Atlanta nutrition consultant.
She reminds people that “both organic and conventional agriculture use pesticides to protect the crop. Organic famers use different pesticides that are described as ‘natural,’ but natural doesn’t mean safer, better, or chemical-free,” she says.
She refers people to the Pesticide Residue Calculator from toxicologists at the University of California, Riverside, posted on the consumer site the Alliance for Food and Farming.
The calculator helps reassure people that trace amounts of chemicals on conventionally grown produce are not a hazard to your health, Dr. Rosenbloom says. “Using myself as an example, I could eat 850 apples or 13,225 servings of blueberries in one day without any effect, even in the worst-case scenario of the fruit having the highest pesticide residue recorded by the USDA.”
“It’s one more example of putting good and bad food labels on foods when it isn’t deserved,” says Connie Diekman, a food and nutrition consultant in St. Louis and a former president of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. “The amounts they are measuring are so much below the tolerance level set by the EPA.”
The report shouldn’t scare people, including parents worried about serving their children conventional produce, she says.
As for how much produce to eat, “the best advice is to have half your plate be fruits and vegetables,” Ms. Diekman says. Under current Dietary Guidelines for Americans, an intake of 2½ “cups equivalent” of vegetables and 2 “cups equivalent” of fruits is recommended daily for adults.
Ms. Diekman is on the Bayer LEAD Network, Leaders Engaged in Advancing Dialogue. Dr. Rosenbloom reports an honorarium from a bean industry group for developing a webinar on healthy aging.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Incorporation of Clinical Staff Pharmacists in the Emergency Department Sepsis Response at a Single Institution
Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulated host response to an infection that can progress to shock. Sepsis is a major cause of death in the United States, with > 1 million people developing sepsis and > 250,000 people dying from sepsis annually.1 The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) guidelines recommend treating sepsis as an emergency with timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, as administering antibiotics within the first hour has been found to reduce mortality and disease progression. In addition, empiric antibiotic regimens should be chosen to target the most probable pathogens and dosing should be optimized. To achieve this, the SSC guidelines recommend that hospitals develop quality improvement (QI) programs developed by a multidisciplinary group to improve sepsis recognition and response using a protocolized approach.2
There are several studies describing efforts to improve the sepsis response at facilities, some of which have evaluated the addition of a pharmacist into the sepsis response, particularly in the emergency department (ED). Some studies found improved selection and decreased time to antibiotic administration with the addition of an ED pharmacist.3-7 Despite this, ED pharmacists are not present in all hospitals, with a 2015 national survey reporting the presence of an ED pharmacist in 68.7% of respondents at 187 facilities. Even facilities with ED pharmacists often have limited hours of coverage, with at least 8 hours of coverage in 49.4% of facilities with an ED pharmacist and no weekend coverage at 34.8% of these facilities.8
While many hospitals do not routinely employ ED pharmacists, most hospitals have clinical staff pharmacists (CSPs), and many inpatient hospital pharmacies are staffed with CSPs 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. A 2017 survey conducted by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) found 43% of all hospital pharmacy departments were staffed by a CSP around the clock, with the prevalence increasing to 56.7 to 100% in hospitals with > 100 beds.9 As a result, CSPs may be a useful resource to assist with the management of patients with sepsis in hospitals without an ED pharmacist.
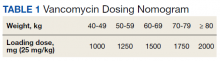
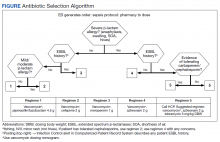
At the Lexington Veterans Affairs Health Care System (LVAHCS) in Kentucky, the inpatient pharmacy department is staffed with a CSP 24/7 but does not have an ED pharmacist. Therefore, when an interdisciplinary group developed an ED sepsis bundle as part of a QI initiative on sepsis recognition and response, the group took a unique approach of incorporating CSPs into the response team to assist with antimicrobial selection and dosing. An antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed to aid CSPs to select and dose antibiotics (Figure, Table 1). We describe the implementation of this process and evaluate CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection and vancomycin dosing.
Methods
Lexington VAHCS is a 94-bed hospital that provides services to veterans, including an ED, inpatient medical services, surgical services, acute mental health, progressive care, and intensive care units. This facility has 1 antimicrobial stewardship clinical pharmacy specialist, 2 critical care clinical pharmacy specialists, and 16 full-time CSPs with 24-hour CSP coverage. The annual ED volume at the time of this study was approximately 21,000 patients.
Consistent with the SSC guideline recommendation to develop multidisciplinary QI initiatives on sepsis recognition and response, an Interdisciplinary Sepsis Committee (ISC) was created in 2018 comprised of ED, pulmonary, critical care, and infectious diseases licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), ED nurses, and pharmacists. The ISC developed a comprehensive set of sepsis tools that included a sepsis screening tool used by ED triage nurses to provide early detection of sepsis and an updated electronic order set to decrease time to appropriate treatment. This order set included automatic orders for blood cultures and serum lactate, the initiation of IV crystalloids, as well as a Sepsis Alert order placed by ED LIPs which alerted CSPs to a patient with sepsis in the ED.
To ensure a protocol-based approach by the CSPs responding to the sepsis alert, an antibiotic algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed by the ISC based on current guideline recommendations and the local antibiogram. These were subsequently approved by ED practitioners, the pharmacy and therapeutics committee, and the critical care committee. The antibiotic algorithm prompts CSPs to perform a chart review to identify β-lactam allergies, evaluate the severity of the allergy and which agents the patient has tolerated in the past, as well as determine whether the patient has a history of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing organisms from previous cultures. A decision tree then guides CSPs toward the selection of 1 of 5 empiric antibiotic regimens to cover all likely pathogens. The medication orders are then entered by the CSPs as a telephone order from the ED LIP per protocol. Unless patients had a true vancomycin allergy, all patients received vancomycin as the empiric gram-positive backbone of the regimen. The vancomycin dosing nomogram was created to ensure an appropriate and consistent vancomycin weight-based loading dose was administered.
Prior to implementation, the antimicrobial stewardship pharmacist educated CSPs on the use of these tools, including simulated orders for mock sepsis alerts to ensure competency. A copy of the algorithm and nomogram were emailed to all CSPs and posted in a prominent location in the pharmacy.
As part of continuous performance improvement efforts of the ISC, a retrospective cohort study was conducted through chart review on patients at the Lexington VAHCS with an order for a sepsis alert in the ED from December 3, 2018 to May 31, 2020 to assess the accuracy of the CSPs’ antibiotic selection and dosing. Patients were excluded if they had a vancomycin allergy or if the ED practitioner ordered antibiotics prior to the CSPs placing orders. Patients could be included more than once in the study if they had sepsis alerts placed on different dates.
The primary outcomes were CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection with the antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram. The antibiotic selection was deemed accurate if the appropriate antibiotic regimen was selected based on allergy status and previous cultures as directed in the algorithm. The vancomycin dose was considered accurate if the dose chosen was appropriate based on the patient’s weight at the time of ED presentation. Secondary outcomes included time to administration of antibiotics from ED presentation as well as time to antibiotics administration from sepsis alert initiation. Time of administration was considered the time the antibiotics were scanned in the bar code medication administration (BCMA) system.
Descriptive statistics were used with data presented as percentages for nominal data and median as IQR for continuous data. In accordance with our facility’s project assessment process, this project was determined not to constitute human subjects research; therefore, this QI project did not require review by the institutional review board.
Results
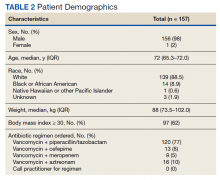
Between December 3, 2018 and May 31, 2020, 160 sepsis alerts were ordered by ED practitioners. Of the 160 patients, 157 were included in the final data analysis. Two patients were excluded due to vancomycin allergy, and 1 patient because the physician ordered antibiotics prior to pharmacist order entry. The population was largely composed of male patients (98%) with a median age of 72 years (Table 2).
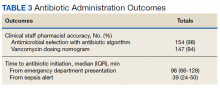
Of 157 sepsis alerts, the antibiotic selection algorithm was used appropriately in 154 (98%) instances (Table 3). Chart reviews were performed in instances of antimicrobial selection different from the algorithm. Of the 3 patients who received antibiotics not consistent with the algorithm, 1 patient without a history of ESBL-producing organisms in their culture history received meropenem instead of piperacillin/tazobactam. Another patient without a penicillin allergy received cefepime (plus metronidazole ordered separately from the ED practitioner) instead of piperacillin/tazobactam, and the third patient received piperacillin/tazobactam instead of meropenem despite a culture history of ESBL-producing organisms. Vancomycin dose was appropriate according to the weight-based nomogram in 147 cases (94%). The median time to administration of first dose antibiotics was 39 minutes after the sepsis alert order was placed and 96 minutes after initial ED presentation.
Discussion
This study found extremely high rates of accuracy among CSPs for both the antibiotic selection algorithm (98%) and the vancomycin dosing nomogram (94%). Moreover, analysis of the 3 patients who received antibiotics that were inconsistent with the algorithm revealed that 2 of these patients arguably still received adequate empiric coverage, increasing the percentage of patients receiving appropriate empiric antibiotics to 99.4%. Similarly, chart review of 10 patients who received vancomycin doses that deviated from the nomogram revealed that in at least 3 cases, patients were likely given correct vancomycin doses based on the patient’s last known weight. However, when actual current weights were recorded soon after admission, the updated weights rendered the initial vancomycin loading dose incorrect when this analysis was performed. Thus, the adherence to the vancomycin dosing nomogram is higher than it appears.
Median time to antibiotic administration from the sepsis alert was 39 minutes—well within SSC recommendations (60 minutes).2 Previous internal analyses at Lexington VAHCS demonstrated the mean time to first dose of antibiotics in the ED has been 39 minutes since about 2015. Thus, this initiative did not necessarily make this process quicker; however it did remove 1 responsibility from LIPs so that they could focus their efforts on other components of sepsis management.
Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of this initiative on other aspects of the sepsis bundle, such as volume of fluid administered and appropriateness of laboratory tests. It was noted that while the time to first-dose antibiotic administration was < 1 hour from order placement, the median time from ED presentation to antibiotic administration was 96 minutes. This suggests that another focus of the sepsis workgroup should be on speeding recognition of sepsis, triggering the sepsis alert even sooner, and evaluating the feasibility of storing first doses of antibiotics in the automatic dispensing cabinets in the ED.
Limitations
This descriptive study evaluating CSPs’ ability to accurately use the newly developed antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram had no control group for outcome comparison. This study was not designed to evaluate clinical outcomes, such as mortality, so the impact of these interventions need to be further studied. In addition, as veterans receive most of their care at our facility, with their allergies and previous cultures readily available in our electronic health record, this process may not be feasible at other facilities where patients' care is divided among multiple facilities/systems.
Moreover, as the veteran population studied was predominately male patients aged > 60 years, implementation at other hospitals may require the dosing nomograms and treatment algorithms to be adapted for a broader population, such as children and pregnant women. In particular, the ISC chose to implement an algorithm that did not differentiate between suspected source of infections and included anti-Pseudomonal coverage in all regimens based on the most encountered diseases among our veteran population and our local antibiogram; implementation at other facilities would require a thoughtful evaluation of the most appropriate site-specific regimen. Finally, many of the CSPs at our facility are board certified and/or residency trained, so more staff development may be required prior to implementation at other facilities, depending on the experience and comfort level of the CSPs.
Strengths
This study describes an example of a protocolized and multidisciplinary approach to improve sepsis recognition and standardize the response, consistent with SSC guideline recommendations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate the incorporation of CSPs into the interdisciplinary sepsis response. This allows for CSPs to practice at the top of their license and contributes to their professional development. Although it was not formally assessed, anecdotally CSPs reported that this process presented a negligible addition to their workload (< 5 minutes was the most reported time requirement), and they expressed satisfaction with their involvement in the sepsis response. Overall, this presents a possible solution to improve the sepsis response in hospitals without a dedicated ED pharmacist.
Conclusions
This study describes the successful incorporation of CSPs into the sepsis response in the ED. As CSPs are more likely than ED pharmacists to be present at a facility, they are arguably an underused resource whose clinical skills can be used to optimize the treatment of patients with sepsis.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sepsis. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/what-is-sepsis.html
2. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017 Mar;45(3):486-552. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002255
3. Denny KJ, Gartside JG, Alcorn K, et al. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Feb 1;74(2):515-520. doi:10.1093/jac/dky447
4. Laine ME, Flynn JD, Flannery AH. Impact of pharmacist intervention on selection and timing of appropriate antimicrobial therapy in septic shock. J Pharm Pract. 2018 Feb;31(1):46-51. doi:10.1177/0897190017696953
5. Weant KA, Baker SN. Emergency medicine pharmacists and sepsis management. J Pharm Pract. 2013 Aug;26(4):401-5. doi:10.1177/0897190012467211
6. Farmer BM, Hayes BD, Rao R, et al. The role of clinical pharmacists in the emergency department. J Med Toxicol. 2018 Mar;14(1):114-116. doi:10.1007/s13181-017-0634-4
7. Yarbrough N, Bloxam M, Priano J, Louzon Lynch P, Hunt LN, Elfman J. Pharmacist impact on sepsis bundle compliance through participation on an emergency department sepsis alert team. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(4):762-763. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2018.08.00
8. Thomas MC, Acquisto NM, Shirk MB, et al. A national survey of emergency pharmacy practice in the United States. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016 Mar 15;73(6):386-94. doi:10.2146/ajhp150321
9. Schneider PJ, Pedersen CA, Scheckelhoff DJ. ASHP national survey of pharmacy practice in hospital settings: dispensing and administration-2017. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(16):1203-1226. doi:10.2146/ajhp180151
Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulated host response to an infection that can progress to shock. Sepsis is a major cause of death in the United States, with > 1 million people developing sepsis and > 250,000 people dying from sepsis annually.1 The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) guidelines recommend treating sepsis as an emergency with timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, as administering antibiotics within the first hour has been found to reduce mortality and disease progression. In addition, empiric antibiotic regimens should be chosen to target the most probable pathogens and dosing should be optimized. To achieve this, the SSC guidelines recommend that hospitals develop quality improvement (QI) programs developed by a multidisciplinary group to improve sepsis recognition and response using a protocolized approach.2
There are several studies describing efforts to improve the sepsis response at facilities, some of which have evaluated the addition of a pharmacist into the sepsis response, particularly in the emergency department (ED). Some studies found improved selection and decreased time to antibiotic administration with the addition of an ED pharmacist.3-7 Despite this, ED pharmacists are not present in all hospitals, with a 2015 national survey reporting the presence of an ED pharmacist in 68.7% of respondents at 187 facilities. Even facilities with ED pharmacists often have limited hours of coverage, with at least 8 hours of coverage in 49.4% of facilities with an ED pharmacist and no weekend coverage at 34.8% of these facilities.8
While many hospitals do not routinely employ ED pharmacists, most hospitals have clinical staff pharmacists (CSPs), and many inpatient hospital pharmacies are staffed with CSPs 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. A 2017 survey conducted by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) found 43% of all hospital pharmacy departments were staffed by a CSP around the clock, with the prevalence increasing to 56.7 to 100% in hospitals with > 100 beds.9 As a result, CSPs may be a useful resource to assist with the management of patients with sepsis in hospitals without an ED pharmacist.
At the Lexington Veterans Affairs Health Care System (LVAHCS) in Kentucky, the inpatient pharmacy department is staffed with a CSP 24/7 but does not have an ED pharmacist. Therefore, when an interdisciplinary group developed an ED sepsis bundle as part of a QI initiative on sepsis recognition and response, the group took a unique approach of incorporating CSPs into the response team to assist with antimicrobial selection and dosing. An antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed to aid CSPs to select and dose antibiotics (Figure, Table 1). We describe the implementation of this process and evaluate CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection and vancomycin dosing.
Methods
Lexington VAHCS is a 94-bed hospital that provides services to veterans, including an ED, inpatient medical services, surgical services, acute mental health, progressive care, and intensive care units. This facility has 1 antimicrobial stewardship clinical pharmacy specialist, 2 critical care clinical pharmacy specialists, and 16 full-time CSPs with 24-hour CSP coverage. The annual ED volume at the time of this study was approximately 21,000 patients.
Consistent with the SSC guideline recommendation to develop multidisciplinary QI initiatives on sepsis recognition and response, an Interdisciplinary Sepsis Committee (ISC) was created in 2018 comprised of ED, pulmonary, critical care, and infectious diseases licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), ED nurses, and pharmacists. The ISC developed a comprehensive set of sepsis tools that included a sepsis screening tool used by ED triage nurses to provide early detection of sepsis and an updated electronic order set to decrease time to appropriate treatment. This order set included automatic orders for blood cultures and serum lactate, the initiation of IV crystalloids, as well as a Sepsis Alert order placed by ED LIPs which alerted CSPs to a patient with sepsis in the ED.
To ensure a protocol-based approach by the CSPs responding to the sepsis alert, an antibiotic algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed by the ISC based on current guideline recommendations and the local antibiogram. These were subsequently approved by ED practitioners, the pharmacy and therapeutics committee, and the critical care committee. The antibiotic algorithm prompts CSPs to perform a chart review to identify β-lactam allergies, evaluate the severity of the allergy and which agents the patient has tolerated in the past, as well as determine whether the patient has a history of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing organisms from previous cultures. A decision tree then guides CSPs toward the selection of 1 of 5 empiric antibiotic regimens to cover all likely pathogens. The medication orders are then entered by the CSPs as a telephone order from the ED LIP per protocol. Unless patients had a true vancomycin allergy, all patients received vancomycin as the empiric gram-positive backbone of the regimen. The vancomycin dosing nomogram was created to ensure an appropriate and consistent vancomycin weight-based loading dose was administered.
Prior to implementation, the antimicrobial stewardship pharmacist educated CSPs on the use of these tools, including simulated orders for mock sepsis alerts to ensure competency. A copy of the algorithm and nomogram were emailed to all CSPs and posted in a prominent location in the pharmacy.
As part of continuous performance improvement efforts of the ISC, a retrospective cohort study was conducted through chart review on patients at the Lexington VAHCS with an order for a sepsis alert in the ED from December 3, 2018 to May 31, 2020 to assess the accuracy of the CSPs’ antibiotic selection and dosing. Patients were excluded if they had a vancomycin allergy or if the ED practitioner ordered antibiotics prior to the CSPs placing orders. Patients could be included more than once in the study if they had sepsis alerts placed on different dates.
The primary outcomes were CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection with the antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram. The antibiotic selection was deemed accurate if the appropriate antibiotic regimen was selected based on allergy status and previous cultures as directed in the algorithm. The vancomycin dose was considered accurate if the dose chosen was appropriate based on the patient’s weight at the time of ED presentation. Secondary outcomes included time to administration of antibiotics from ED presentation as well as time to antibiotics administration from sepsis alert initiation. Time of administration was considered the time the antibiotics were scanned in the bar code medication administration (BCMA) system.
Descriptive statistics were used with data presented as percentages for nominal data and median as IQR for continuous data. In accordance with our facility’s project assessment process, this project was determined not to constitute human subjects research; therefore, this QI project did not require review by the institutional review board.
Results
Between December 3, 2018 and May 31, 2020, 160 sepsis alerts were ordered by ED practitioners. Of the 160 patients, 157 were included in the final data analysis. Two patients were excluded due to vancomycin allergy, and 1 patient because the physician ordered antibiotics prior to pharmacist order entry. The population was largely composed of male patients (98%) with a median age of 72 years (Table 2).
Of 157 sepsis alerts, the antibiotic selection algorithm was used appropriately in 154 (98%) instances (Table 3). Chart reviews were performed in instances of antimicrobial selection different from the algorithm. Of the 3 patients who received antibiotics not consistent with the algorithm, 1 patient without a history of ESBL-producing organisms in their culture history received meropenem instead of piperacillin/tazobactam. Another patient without a penicillin allergy received cefepime (plus metronidazole ordered separately from the ED practitioner) instead of piperacillin/tazobactam, and the third patient received piperacillin/tazobactam instead of meropenem despite a culture history of ESBL-producing organisms. Vancomycin dose was appropriate according to the weight-based nomogram in 147 cases (94%). The median time to administration of first dose antibiotics was 39 minutes after the sepsis alert order was placed and 96 minutes after initial ED presentation.
Discussion
This study found extremely high rates of accuracy among CSPs for both the antibiotic selection algorithm (98%) and the vancomycin dosing nomogram (94%). Moreover, analysis of the 3 patients who received antibiotics that were inconsistent with the algorithm revealed that 2 of these patients arguably still received adequate empiric coverage, increasing the percentage of patients receiving appropriate empiric antibiotics to 99.4%. Similarly, chart review of 10 patients who received vancomycin doses that deviated from the nomogram revealed that in at least 3 cases, patients were likely given correct vancomycin doses based on the patient’s last known weight. However, when actual current weights were recorded soon after admission, the updated weights rendered the initial vancomycin loading dose incorrect when this analysis was performed. Thus, the adherence to the vancomycin dosing nomogram is higher than it appears.
Median time to antibiotic administration from the sepsis alert was 39 minutes—well within SSC recommendations (60 minutes).2 Previous internal analyses at Lexington VAHCS demonstrated the mean time to first dose of antibiotics in the ED has been 39 minutes since about 2015. Thus, this initiative did not necessarily make this process quicker; however it did remove 1 responsibility from LIPs so that they could focus their efforts on other components of sepsis management.
Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of this initiative on other aspects of the sepsis bundle, such as volume of fluid administered and appropriateness of laboratory tests. It was noted that while the time to first-dose antibiotic administration was < 1 hour from order placement, the median time from ED presentation to antibiotic administration was 96 minutes. This suggests that another focus of the sepsis workgroup should be on speeding recognition of sepsis, triggering the sepsis alert even sooner, and evaluating the feasibility of storing first doses of antibiotics in the automatic dispensing cabinets in the ED.
Limitations
This descriptive study evaluating CSPs’ ability to accurately use the newly developed antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram had no control group for outcome comparison. This study was not designed to evaluate clinical outcomes, such as mortality, so the impact of these interventions need to be further studied. In addition, as veterans receive most of their care at our facility, with their allergies and previous cultures readily available in our electronic health record, this process may not be feasible at other facilities where patients' care is divided among multiple facilities/systems.
Moreover, as the veteran population studied was predominately male patients aged > 60 years, implementation at other hospitals may require the dosing nomograms and treatment algorithms to be adapted for a broader population, such as children and pregnant women. In particular, the ISC chose to implement an algorithm that did not differentiate between suspected source of infections and included anti-Pseudomonal coverage in all regimens based on the most encountered diseases among our veteran population and our local antibiogram; implementation at other facilities would require a thoughtful evaluation of the most appropriate site-specific regimen. Finally, many of the CSPs at our facility are board certified and/or residency trained, so more staff development may be required prior to implementation at other facilities, depending on the experience and comfort level of the CSPs.
Strengths
This study describes an example of a protocolized and multidisciplinary approach to improve sepsis recognition and standardize the response, consistent with SSC guideline recommendations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate the incorporation of CSPs into the interdisciplinary sepsis response. This allows for CSPs to practice at the top of their license and contributes to their professional development. Although it was not formally assessed, anecdotally CSPs reported that this process presented a negligible addition to their workload (< 5 minutes was the most reported time requirement), and they expressed satisfaction with their involvement in the sepsis response. Overall, this presents a possible solution to improve the sepsis response in hospitals without a dedicated ED pharmacist.
Conclusions
This study describes the successful incorporation of CSPs into the sepsis response in the ED. As CSPs are more likely than ED pharmacists to be present at a facility, they are arguably an underused resource whose clinical skills can be used to optimize the treatment of patients with sepsis.
Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulated host response to an infection that can progress to shock. Sepsis is a major cause of death in the United States, with > 1 million people developing sepsis and > 250,000 people dying from sepsis annually.1 The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) guidelines recommend treating sepsis as an emergency with timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, as administering antibiotics within the first hour has been found to reduce mortality and disease progression. In addition, empiric antibiotic regimens should be chosen to target the most probable pathogens and dosing should be optimized. To achieve this, the SSC guidelines recommend that hospitals develop quality improvement (QI) programs developed by a multidisciplinary group to improve sepsis recognition and response using a protocolized approach.2
There are several studies describing efforts to improve the sepsis response at facilities, some of which have evaluated the addition of a pharmacist into the sepsis response, particularly in the emergency department (ED). Some studies found improved selection and decreased time to antibiotic administration with the addition of an ED pharmacist.3-7 Despite this, ED pharmacists are not present in all hospitals, with a 2015 national survey reporting the presence of an ED pharmacist in 68.7% of respondents at 187 facilities. Even facilities with ED pharmacists often have limited hours of coverage, with at least 8 hours of coverage in 49.4% of facilities with an ED pharmacist and no weekend coverage at 34.8% of these facilities.8
While many hospitals do not routinely employ ED pharmacists, most hospitals have clinical staff pharmacists (CSPs), and many inpatient hospital pharmacies are staffed with CSPs 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. A 2017 survey conducted by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) found 43% of all hospital pharmacy departments were staffed by a CSP around the clock, with the prevalence increasing to 56.7 to 100% in hospitals with > 100 beds.9 As a result, CSPs may be a useful resource to assist with the management of patients with sepsis in hospitals without an ED pharmacist.
At the Lexington Veterans Affairs Health Care System (LVAHCS) in Kentucky, the inpatient pharmacy department is staffed with a CSP 24/7 but does not have an ED pharmacist. Therefore, when an interdisciplinary group developed an ED sepsis bundle as part of a QI initiative on sepsis recognition and response, the group took a unique approach of incorporating CSPs into the response team to assist with antimicrobial selection and dosing. An antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed to aid CSPs to select and dose antibiotics (Figure, Table 1). We describe the implementation of this process and evaluate CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection and vancomycin dosing.
Methods
Lexington VAHCS is a 94-bed hospital that provides services to veterans, including an ED, inpatient medical services, surgical services, acute mental health, progressive care, and intensive care units. This facility has 1 antimicrobial stewardship clinical pharmacy specialist, 2 critical care clinical pharmacy specialists, and 16 full-time CSPs with 24-hour CSP coverage. The annual ED volume at the time of this study was approximately 21,000 patients.
Consistent with the SSC guideline recommendation to develop multidisciplinary QI initiatives on sepsis recognition and response, an Interdisciplinary Sepsis Committee (ISC) was created in 2018 comprised of ED, pulmonary, critical care, and infectious diseases licensed independent practitioners (LIPs), ED nurses, and pharmacists. The ISC developed a comprehensive set of sepsis tools that included a sepsis screening tool used by ED triage nurses to provide early detection of sepsis and an updated electronic order set to decrease time to appropriate treatment. This order set included automatic orders for blood cultures and serum lactate, the initiation of IV crystalloids, as well as a Sepsis Alert order placed by ED LIPs which alerted CSPs to a patient with sepsis in the ED.
To ensure a protocol-based approach by the CSPs responding to the sepsis alert, an antibiotic algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram were developed by the ISC based on current guideline recommendations and the local antibiogram. These were subsequently approved by ED practitioners, the pharmacy and therapeutics committee, and the critical care committee. The antibiotic algorithm prompts CSPs to perform a chart review to identify β-lactam allergies, evaluate the severity of the allergy and which agents the patient has tolerated in the past, as well as determine whether the patient has a history of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing organisms from previous cultures. A decision tree then guides CSPs toward the selection of 1 of 5 empiric antibiotic regimens to cover all likely pathogens. The medication orders are then entered by the CSPs as a telephone order from the ED LIP per protocol. Unless patients had a true vancomycin allergy, all patients received vancomycin as the empiric gram-positive backbone of the regimen. The vancomycin dosing nomogram was created to ensure an appropriate and consistent vancomycin weight-based loading dose was administered.
Prior to implementation, the antimicrobial stewardship pharmacist educated CSPs on the use of these tools, including simulated orders for mock sepsis alerts to ensure competency. A copy of the algorithm and nomogram were emailed to all CSPs and posted in a prominent location in the pharmacy.
As part of continuous performance improvement efforts of the ISC, a retrospective cohort study was conducted through chart review on patients at the Lexington VAHCS with an order for a sepsis alert in the ED from December 3, 2018 to May 31, 2020 to assess the accuracy of the CSPs’ antibiotic selection and dosing. Patients were excluded if they had a vancomycin allergy or if the ED practitioner ordered antibiotics prior to the CSPs placing orders. Patients could be included more than once in the study if they had sepsis alerts placed on different dates.
The primary outcomes were CSPs’ accuracy in antimicrobial selection with the antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram. The antibiotic selection was deemed accurate if the appropriate antibiotic regimen was selected based on allergy status and previous cultures as directed in the algorithm. The vancomycin dose was considered accurate if the dose chosen was appropriate based on the patient’s weight at the time of ED presentation. Secondary outcomes included time to administration of antibiotics from ED presentation as well as time to antibiotics administration from sepsis alert initiation. Time of administration was considered the time the antibiotics were scanned in the bar code medication administration (BCMA) system.
Descriptive statistics were used with data presented as percentages for nominal data and median as IQR for continuous data. In accordance with our facility’s project assessment process, this project was determined not to constitute human subjects research; therefore, this QI project did not require review by the institutional review board.
Results
Between December 3, 2018 and May 31, 2020, 160 sepsis alerts were ordered by ED practitioners. Of the 160 patients, 157 were included in the final data analysis. Two patients were excluded due to vancomycin allergy, and 1 patient because the physician ordered antibiotics prior to pharmacist order entry. The population was largely composed of male patients (98%) with a median age of 72 years (Table 2).
Of 157 sepsis alerts, the antibiotic selection algorithm was used appropriately in 154 (98%) instances (Table 3). Chart reviews were performed in instances of antimicrobial selection different from the algorithm. Of the 3 patients who received antibiotics not consistent with the algorithm, 1 patient without a history of ESBL-producing organisms in their culture history received meropenem instead of piperacillin/tazobactam. Another patient without a penicillin allergy received cefepime (plus metronidazole ordered separately from the ED practitioner) instead of piperacillin/tazobactam, and the third patient received piperacillin/tazobactam instead of meropenem despite a culture history of ESBL-producing organisms. Vancomycin dose was appropriate according to the weight-based nomogram in 147 cases (94%). The median time to administration of first dose antibiotics was 39 minutes after the sepsis alert order was placed and 96 minutes after initial ED presentation.
Discussion
This study found extremely high rates of accuracy among CSPs for both the antibiotic selection algorithm (98%) and the vancomycin dosing nomogram (94%). Moreover, analysis of the 3 patients who received antibiotics that were inconsistent with the algorithm revealed that 2 of these patients arguably still received adequate empiric coverage, increasing the percentage of patients receiving appropriate empiric antibiotics to 99.4%. Similarly, chart review of 10 patients who received vancomycin doses that deviated from the nomogram revealed that in at least 3 cases, patients were likely given correct vancomycin doses based on the patient’s last known weight. However, when actual current weights were recorded soon after admission, the updated weights rendered the initial vancomycin loading dose incorrect when this analysis was performed. Thus, the adherence to the vancomycin dosing nomogram is higher than it appears.
Median time to antibiotic administration from the sepsis alert was 39 minutes—well within SSC recommendations (60 minutes).2 Previous internal analyses at Lexington VAHCS demonstrated the mean time to first dose of antibiotics in the ED has been 39 minutes since about 2015. Thus, this initiative did not necessarily make this process quicker; however it did remove 1 responsibility from LIPs so that they could focus their efforts on other components of sepsis management.
Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of this initiative on other aspects of the sepsis bundle, such as volume of fluid administered and appropriateness of laboratory tests. It was noted that while the time to first-dose antibiotic administration was < 1 hour from order placement, the median time from ED presentation to antibiotic administration was 96 minutes. This suggests that another focus of the sepsis workgroup should be on speeding recognition of sepsis, triggering the sepsis alert even sooner, and evaluating the feasibility of storing first doses of antibiotics in the automatic dispensing cabinets in the ED.
Limitations
This descriptive study evaluating CSPs’ ability to accurately use the newly developed antibiotic selection algorithm and vancomycin dosing nomogram had no control group for outcome comparison. This study was not designed to evaluate clinical outcomes, such as mortality, so the impact of these interventions need to be further studied. In addition, as veterans receive most of their care at our facility, with their allergies and previous cultures readily available in our electronic health record, this process may not be feasible at other facilities where patients' care is divided among multiple facilities/systems.
Moreover, as the veteran population studied was predominately male patients aged > 60 years, implementation at other hospitals may require the dosing nomograms and treatment algorithms to be adapted for a broader population, such as children and pregnant women. In particular, the ISC chose to implement an algorithm that did not differentiate between suspected source of infections and included anti-Pseudomonal coverage in all regimens based on the most encountered diseases among our veteran population and our local antibiogram; implementation at other facilities would require a thoughtful evaluation of the most appropriate site-specific regimen. Finally, many of the CSPs at our facility are board certified and/or residency trained, so more staff development may be required prior to implementation at other facilities, depending on the experience and comfort level of the CSPs.
Strengths
This study describes an example of a protocolized and multidisciplinary approach to improve sepsis recognition and standardize the response, consistent with SSC guideline recommendations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate the incorporation of CSPs into the interdisciplinary sepsis response. This allows for CSPs to practice at the top of their license and contributes to their professional development. Although it was not formally assessed, anecdotally CSPs reported that this process presented a negligible addition to their workload (< 5 minutes was the most reported time requirement), and they expressed satisfaction with their involvement in the sepsis response. Overall, this presents a possible solution to improve the sepsis response in hospitals without a dedicated ED pharmacist.
Conclusions
This study describes the successful incorporation of CSPs into the sepsis response in the ED. As CSPs are more likely than ED pharmacists to be present at a facility, they are arguably an underused resource whose clinical skills can be used to optimize the treatment of patients with sepsis.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sepsis. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/what-is-sepsis.html
2. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017 Mar;45(3):486-552. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002255
3. Denny KJ, Gartside JG, Alcorn K, et al. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Feb 1;74(2):515-520. doi:10.1093/jac/dky447
4. Laine ME, Flynn JD, Flannery AH. Impact of pharmacist intervention on selection and timing of appropriate antimicrobial therapy in septic shock. J Pharm Pract. 2018 Feb;31(1):46-51. doi:10.1177/0897190017696953
5. Weant KA, Baker SN. Emergency medicine pharmacists and sepsis management. J Pharm Pract. 2013 Aug;26(4):401-5. doi:10.1177/0897190012467211
6. Farmer BM, Hayes BD, Rao R, et al. The role of clinical pharmacists in the emergency department. J Med Toxicol. 2018 Mar;14(1):114-116. doi:10.1007/s13181-017-0634-4
7. Yarbrough N, Bloxam M, Priano J, Louzon Lynch P, Hunt LN, Elfman J. Pharmacist impact on sepsis bundle compliance through participation on an emergency department sepsis alert team. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(4):762-763. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2018.08.00
8. Thomas MC, Acquisto NM, Shirk MB, et al. A national survey of emergency pharmacy practice in the United States. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016 Mar 15;73(6):386-94. doi:10.2146/ajhp150321
9. Schneider PJ, Pedersen CA, Scheckelhoff DJ. ASHP national survey of pharmacy practice in hospital settings: dispensing and administration-2017. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(16):1203-1226. doi:10.2146/ajhp180151
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sepsis. Accessed March 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/what-is-sepsis.html
2. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017 Mar;45(3):486-552. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002255
3. Denny KJ, Gartside JG, Alcorn K, et al. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescribing in the emergency department. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Feb 1;74(2):515-520. doi:10.1093/jac/dky447
4. Laine ME, Flynn JD, Flannery AH. Impact of pharmacist intervention on selection and timing of appropriate antimicrobial therapy in septic shock. J Pharm Pract. 2018 Feb;31(1):46-51. doi:10.1177/0897190017696953
5. Weant KA, Baker SN. Emergency medicine pharmacists and sepsis management. J Pharm Pract. 2013 Aug;26(4):401-5. doi:10.1177/0897190012467211
6. Farmer BM, Hayes BD, Rao R, et al. The role of clinical pharmacists in the emergency department. J Med Toxicol. 2018 Mar;14(1):114-116. doi:10.1007/s13181-017-0634-4
7. Yarbrough N, Bloxam M, Priano J, Louzon Lynch P, Hunt LN, Elfman J. Pharmacist impact on sepsis bundle compliance through participation on an emergency department sepsis alert team. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(4):762-763. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2018.08.00
8. Thomas MC, Acquisto NM, Shirk MB, et al. A national survey of emergency pharmacy practice in the United States. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016 Mar 15;73(6):386-94. doi:10.2146/ajhp150321
9. Schneider PJ, Pedersen CA, Scheckelhoff DJ. ASHP national survey of pharmacy practice in hospital settings: dispensing and administration-2017. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(16):1203-1226. doi:10.2146/ajhp180151
Surgeons in China ‘are the executioners,’ procuring organs before brain death
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prevalence and Predictors of Lower Limb Amputation in the Spinal Cord Injury Population
At the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH) in Tampa, Florida, the prevalence of amputations among patients at the spinal cord injury (SCI) center seems high. Despite limited data demonstrating altered hemodynamics in the lower extremities (LEs) among the SCI population and increased frequency of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), amputations among patients with SCI have received little attention in research.1-3
In the United States, most amputations are caused by vascular disease related to peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and diabetes mellitus (DM).4 PAD primarily affects the LEs and is caused by atherosclerotic obstruction leading to insufficient blood flow. PAD can present clinically as LE pain, nonhealing ulcers, nonpalpable distal pulses, shiny or cold skin, absence of hair on the LE, or distal extremity pallor when the affected extremity is elevated. However, PAD is often asymptomatic. The diagnosis of PAD is typically made with an ankle-brachial index (ABI) ≤ 0.9.5 The prevalence of PAD is about 4.3% in Americans aged ≥ 40 years, increases with age, and is almost twice as common among Black Americans compared with that of White Americans.6 Many studies in SCI populations have documented an increased prevalence of DM, dyslipidemia, obesity, hypertension (HTN), and cigarette smoking.7-9 PAD shares these risk factors with coronary artery disease (CAD), but relative to CAD, tobacco smoking was a more substantial causative factor for PAD.10 Given the preponderance of associated risk factors in this population, PAD is likely more prevalent among patients with SCI than in the population without disabilities. Beyond these known risk factors, researchers hypothesized that SCI contributes to vascular disease by altering arterial function. However, this is still a topic of debate.11-13 Trauma also is a common cause of amputation, accounting for 45% of amputations in 2005.4 Patients with SCI may experience traumatic amputations simultaneously as their SCI, but they may also be predisposed to traumatic amputations related to osteopenia and impaired sensation.
Since amputation is an invasive surgery, knowing the severity of this issue is important in the SCI population. This study quantifies the prevalence of amputations of the LEs among the patients at our SCI center. It then characterizes these amputations’ etiology, their relationship with medical comorbidities, and certain SCI classifications.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Computerized Patient Record System. The cohort was defined as all patients who received an annual examination at our SCI center over 4 years from October 1, 2009 to September 30, 2013. Annual examination includes a physical examination, relevant surveillance laboratory tests, and imaging, such as renal ultrasound for those with indwelling urinary catheters. One characteristic of the patient population in the VA system is that diagnoses, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), that involve spinal cord lesions causing symptoms are included in the registry, besides those with other traumatic or nontraumatic SCI. October 1 to September 30 was chosen based on the VA fiscal year (FY).
During this period, 1678 patients had an annual examination. Of those, 299 patients had an SCI etiology of ALS or MS, and 41 had nonfocal SCI etiology that could not be assessed using the American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale (AIS) and were excluded. Also excluded were 283 patients who did not have an annual examination during the specified time span. Some patients do not have an annual examination every year; for those with multiple annual examinations during that time frame, the most recent was used.
One thousand fifty-five patients were included in the statistical analysis. Date of birth, sex, race, ethnicity, date of death, smoking status, DM diagnosis, HTN diagnosis, use of an antiplatelet, antihypertensive, or lipid-lowering agent, blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and lipid panel were collected. The amputation level and etiology were noted. The levels of amputation were classified as toe/partial foot,
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive data were summarized as the median and IQR for continuous variables or the number and percentage for categorical variables. The χ2 test was used to analyze the association between categorical variables and amputation status. A nonparametric Wilcoxon test was used to investigate the distribution of continuous variables across patients with amputation and patients without amputation. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to investigate amputation risk factors. We report goodness of fit using the Hosmer and Lemeshow test and the area under the curve (AUC) for the multivariate model. Statistical significance was prespecified at a 2-sided P < .05. SAS version 9.4 was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Mean age was approximately 61 years for the 91 patients at the time of the most recent amputation (Table 1). Among those with amputation, 63% were paraplegic and 37% were tetraplegic.
Of 1055 patients with SCI, 91 (8.6%) patients had an amputation. Of those, 70 (76.1%) were from nontraumatic causes (dysvascular), 17 (18.5%) were traumatic, 4 (4.3%) were from other causes (ie, cancer), and only 1 (1.1%) was of unknown cause.
Of the 91 patients with amputation, 64 (69.6%) had at least 1 TFA—33 were unilateral and 31 were bilateral. Two patients had a TFA on one side and a TTA on the other. Partial foot/toe and TTA were less common amputation levels with 14 (15.4%) and 13 (14.3%), respectively. Most amputations (86.8%) occurred over 6 months from the day of initial SCI, and were most commonly dysvascular (Table 2). Traumatic amputation occurred more evenly at various stages, pre-SCI, during acute SCI, subacute SCI, and chronic SCI.
Injury by Impairment Scale Level
Forty-nine (11.5%) of 426 patients with AIS level A SCI had undergone amputation. In order of prevalence, 23 (46.9%) were unilateral TFA, 17 (34.6%) were bilateral TFA, 10.2% were partial foot/toe, 4.1% were unilateral TTA, and 4.1% were a TTA/TFA combination. Both hip and knee disarticulations were classified in the TFA category.
Sixteen (13.0%) of 123 patients with AIS level B SCI had undergone amputation; 5 (31.3%) of those amputations were unilateral TFA, 6 (37.5%) were bilateral TFA, 3 (18.8%) were partial toe or foot, and 1 (6.3%) was for unilateral and bilateral TTA each.
Twelve (8.4%) of 143 patients with AIS level C SCI had undergone amputation: 6 (50.0%) were bilateral TFA; 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TFA; and 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TTA.
Fourteen (3.9%) of 356 patients with AIS level D SCI had undergone amputation. Of those 6 (42.9%) underwent a partial foot/toe amputation; 5 (35.7%) had undergone a unilateral TTA, and 1 (7.1%) underwent amputation in each of the following categories: bilateral TTA, unilateral TFA, and bilateral TFA each.
None of the 7 individuals with AIS E level SCI had undergone amputation.
Health Risk Factors
Of the 91 patients with amputation, the majority (81.3%) were either former or current smokers. Thirty-six percent of those who had undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM, while only 21% of those who had not undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM.
At the time of their annual examination 532 patients had a diagnosis of HTN while 523 patients did not. Among patients with amputations, 59 (64.8%) had HTN, while 32 (35.2%) did not. Of the 964 patients without amputation, the prevalence of HTN was 50.9%
.Of 1055 patients with SCI, only 103 (9.8%) had a PAD diagnosis, including 38 (41.9%) patients with amputation. Just 65 (6.7%) patients with SCI without amputation had PAD (P < .001). PAD is highly correlated with dysvascular causes of amputation. Among those with amputations due to dysvascular etiology, 50.0% (35/70) had PAD, but for the 21 amputations due to nondysvascular etiology, only 3 (14.3%) had PAD (P = .004).
Amputation Predictive Model
A multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to build a predictive model for amputation among patients with SCI while controlling for covariates. In our multivariate analysis, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), tetraplegia, and PAD were predictive factors for amputation. Patients with SCI who had PAD were 8.6 times more likely to undergo amputation compared to those without PAD (odds ratio [OR], 9.8; P < .001; 95% CI, 5.9-16.3). Every unit of HDL-C decreased the odds of amputation by 5% (OR, 0.95; P < .001; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).
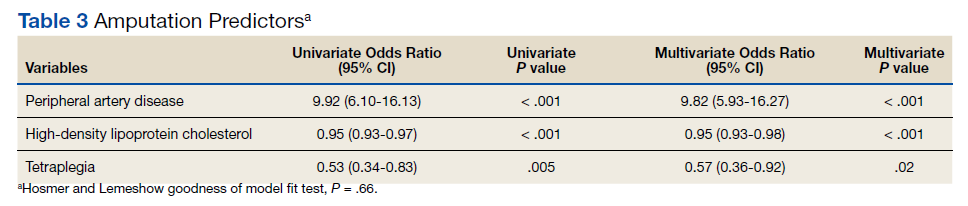
Having tetraplegia decreased the odds of amputation by 43%, compared with those with paraplegia (OR, 0.57; P = .02; 95% CI, 0.36 - 0.92). AUC was 0.76, and the Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of model fit test P value was .66, indicating the good predictive power of the model (Table 3).
Discussion
In the US, 54 to 82% of amputations occur secondary to chronic vascular disease. Our study showed similar results: 76.1% of amputations were dysvascular.4,16 Even in a 2019 systematic review, the most recent prevalence of amputation data was in 2005.17 The study concluded that among the general population in the US, prevalence of amputation was estimated to be 1 in 190 people, or about 0.5% of the population.4 We found that the prevalence of amputation among the SCI population in this study was 8.7%. This result is consistent with our initial hypothesis that the prevalence of amputation would be higher among the people with SCI. Using a different case acquisition method, Svircev and colleagues reported that about a 4% prevalence of LE amputation among veterans with chronic SCI (over 1 year from the initial SCI), with an emphasis that it was not a study of amputation incidence.18 In comparison, we calculated a 7.5% prevalence of amputation during the chronic SCI stage, which showed institutional variation and a consistent observation that LE amputations occurred more frequently in the SCI population.
Our results showed a positive correlation between the completeness of injury and the prevalence of amputation. Those individuals with a motor complete injury, AIS A (40.3%) or AIS B (11.7%) account for approximately half of all amputations in our population with SCI. Another finding was that proximal amputations were more frequent with more neurologically complete SCIs. Of those with an injury classified as AIS A and an amputation, 42 of 49 subjects underwent at least 1 TFA (23 were unilateral TFA, 17 were bilateral TFA, 2 were a TFA/TTA combination). Of those with an AIS B injury and an amputation, 11 of 16 subjects (68.8%) had at least 1 TFA (5 unilateral TFA and 6 bilateral TFA). Among patients with AIS C injury and amputation, 75% had a TFA. At the same time, only 13.3% of all amputations were at the transfemoral level in those with an AIS D injury. None of the participants with an injury classified as AIS E had undergone an amputation.
Given a paucity of literature available regarding amputation levels in patients with SCI, a discussion with a JAHVH vascular surgeon helped explain the rationale behind different levels of amputation among the SCI population—TFA was performed in 64 of 91 cases (70%). Institutionally, TFAs were performed more often because this level had the greatest chance of healing, avoiding infection, and eliminating knee contracture issues, which may affect quality of life. This was believed to be the best option in those individuals who were already nonambulatory. Although this study did not collect data on ambulatory status, this helps explain why those with an SCI classification of AIS D were more likely to have had a more distal amputation to preserve current or a future chance of ambulation, provided that whether the limb is salvageable is the priority of surgical decision.
The prevalence of PAD among veterans is generally higher than it is in the nonveteran population. Studies show that the prevalence of PAD risk factors in the veteran population exceeds national estimates. Nearly two-thirds of veterans have HTN, 1 in 4 has DM, and 1 in 4 is a current smoker, placing veterans at a significantly increased risk of PADand, therefore, amputation.19,20 These rates were about the same or greater in our SCI population: 50.4% had HTN, 22.3% had a diagnosis of DM, and 71.8% smoked previously or currently smoked. In 3 large studies, HTN was second only to current smoking as the most attributable risk factor for PAD.21
Ongoing research by JAHVH vascular surgeons suggests that patients with SCI were younger and less likely to have HTN, PAD, and/or CAD compared with patients undergoing TFA without SCI. Additionally, patients with SCI had better postoperative outcomes in terms of 30-day mortality, 3-year mortality, and had no increased rate of surgical revisions, strokes, or wound-healing complications. This supports the previous thought that the AIS classification plays a large role in determining amputation levels.
One result in this study is that paraplegia is one of the predictors of future amputation compared with tetraplegia. To our knowledge, there is no literature that supports or explains this finding. A hypothetical factor that could explain this observation is the difference in duration of survival—those with paraplegia who live longer are more likely to experience end-stage consequence of vascular diseases. Another proposed factor is that those with paraplegia are generally more active and have a higher likelihood of sustaining a traumatic cause of amputation, even though this etiology of amputation is minor.An unexpected finding in our study was that of 1055 patients with SCI, only 9.8% had a PAD diagnosis. In contrast, 41.3% of those with amputation had a PAD diagnosis. JAHVH does not screen for PAD, so this likely represents only the symptomatic cases.
Diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI is challenging as they may lack classic clinical symptoms, such as pain with ambulation and impotence, secondary to their neurologic injury. Instead, the health care practitioner must rely on physical signs, such as necrosis.22 Of note given the undetermined utility of diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI, early endovascular interventions are not typically performed. We could not find literature regarding when intervention for PAD in patients with SCI should be performed or how frequently those with SCI should be assessed for PAD. One study showed impaired ambulation prior to limb salvage procedures was associated with poor functional outcomes in terms of survival, independent living, and ambulatory status.23 This could help explain why endovascular procedures are done relatively infrequently in this population. With the lack of studies regarding PAD in the SCI population, outcomes analysis of these patients, including the rate of initial interventions, re-intervention for re-amputation (possibly at a higher level), or vascular inflow procedures, are needed.
It would be beneficial for future studies to examine whether inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), were more elevated in patients with SCI who underwent amputation compared with those who did not. Chronic underlying inflammation has been shown to be a risk factor for PAD. One study showed that, independently of other risk factors, elevated CRP levels roughly tripled the risk of developing PAD.24 This study suggested that there is an increased risk of dysvascular amputation among the SCI population at this center. This information is significant because it can help influence JAHVH clinical practice for veterans with SCI and vascular diseases.
Limitations
As a single-center study carried out at an SCI specialized center of a VA hospital, this study's finding may not be generalizable. Incomplete documentation in the health record may have led to underreporting of amputations and other information. The practice of the vascular surgeons at JAHVH may not represent the approach of vascular surgeons nationwide. Another limitation of this study is that the duration of SCI was not considered when looking at health risk factors associated with amputation in the SCI population (ie, total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, etc). Finally, the medication regimens were not reviewed to determine whether they meet the standard of care in relation to eventual diagnosis of PAD.
A prospective study comparing the prevalence of amputation between veterans with SCI vs veterans without SCI could better investigate the difference in amputation risks. This study only compared our veterans with SCI in reference to the general population. Veterans are more likely to be smokers than the general population, contributing to PAD.17 In addition, data regarding patients’ functional status in regard to transferring and ambulation before and after amputation were not collected, which would have contributed to an understanding of how amputation affects functional status in this population.
Conclusions
There is an increased prevalence of amputation among veterans with SCI compared with that of the nationwide population and a plurality were TFAs. This data suggest that those with a motor complete SCI are more likely to undergo a more proximal amputation. This is likely secondary to a lower likelihood of ambulation with more neurologically complete injuries along with a greater chance of healing with a more proximal amputation. It is challenging to correlate any variables specific to SCI (ie, immobility, time since injury, level of injury, etc) with an increased risk of amputation as the known comorbidities associated with PAD are highly prevalent in this population. Having PAD, low HDL-C (< 40 mg/dL), and paraplegia instead of tetraplegia were independent predictors of amputation.
Health care professionals need to be aware of the high prevalence of amputation in the SCI population. Comorbidities should be aggressively treated as PAD, in addition to being associated with amputation, has been linked with increased mortality.25 Studies using a larger population and multiple centers are needed to confirm such a concerning finding.
Acknowledgments
This material is based on work supported (or supported in part) with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH). Authors gratefully acknowledge the inputs and support of Dr. James Brooks, MD, RPVI, assistant professor of surgery, University of South Florida (USF), and attending surgeon, vascular surgery service, medical director of the peripheral vascular laboratory, JAHVH; and Dr. Kevin White, MD, assistant professor, USF, and Chief of Spinal Cord Injury Center, JAHVH.
1. Hopman MT, Nommensen E, van Asten WN, Oeseburg B, Binkhorst RA. Properties of the venous vascular system in the lower extremities of individuals with paraplegia. Paraplegia. 1994;32(12):810-816. doi:10.1038/sc.1994.128
2. Theisen D, Vanlandewijck Y, Sturbois X, Francaux M. Central and peripheral haemodynamics in individuals with paraplegia during light and heavy exercise. J Rehabil Med. 2001;33(1):16-20. doi:10.1080/165019701300006489
3. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Evidence for greater burden of peripheral arterial disease in lower extremity arteries of spinal cord-injured individuals. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(3):H766-H772. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00507.2011
4. Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
5. Hennion DR, Siano KA. Diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Am Fam Physician. 2013;88(5):306-310.
6. Selvin E, Erlinger TP. Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2000. Circulation. 2004;110(6):738-743. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000137913.26087.F0
7. Bauman WA, Spungen AM. Disorders of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in veterans with paraplegia or quadriplegia: a model of premature aging. Metabolism. 1994;43(6):749-756. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(94)90126-0
8. Jörgensen S, Hill M, Lexell J. Cardiovascular risk factors among older adults with long-term spinal cord injury. PM R. 2019;11(1):8-16. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2018.06.008
9. Wu JC, Chen YC, Liu L, et al. Increased risk of stroke after spinal cord injury: a nationwide 4-year follow-up cohort study. Neurology. 2012;78(14):1051-1057. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824e8eaa
10. Price JF, Mowbray PI, Lee AJ, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Fowkes FG. Relationship between smoking and cardiovascular risk factors in the development of peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease: Edinburgh Artery Study. Eur Heart J. 1999;20(5):344-353. doi:10.1053/euhj.1998.1194
11. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Altered resting hemodynamics in lower-extremity arteries of individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(2):104-111. doi:10.1179/2045772312Y.0000000052
12. Miyatani M, Masani K, Oh PI, Miyachi M, Popovic MR, Craven BC. Pulse wave velocity for assessment of arterial stiffness among people with spinal cord injury: a pilot study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2009;32(1):72-78. doi:10.1080/10790268.2009.11760755
13. Oliver JJ, Webb DJ. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(4):554-566. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000060460.52916.D6
14. Ephraim PL, Dillifngham TR, Sector M, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Epidemiology of limb loss and congenital limb deficiency: a review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84(5): 747-761. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(02)04932-8.15. Levin ME. Preventing amputation in the patient with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(10)1383-1394. doi:10.2337/diacare.18.10.1383
16. Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the United States. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611- 200208000-00018
17. Lo J, Chan L, Flynn S. A systematic review of the incidence, prevalence, costs, and activity and work limitations of amputation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury in the United States: a 2019 update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102:115-131. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2020.04.001
18. Svircev, J, Tan D, Garrison A, Pennelly, B, Burns SP. Limb loss in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. doi:10.1080/10790268.2020.1800964
19. Brown DW. Smoking prevalence among US veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(2):147-149. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1160-0
20. Selim AJ, Berlowitz DR, Fincke G, et al. The health status of elderly veteran enrollees in the Veterans Health Administration. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(8):1271-1276. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52355.x
21. Criqui MH, Aboyans V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(9):1509-1526. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303849
22. Yokoo KM, Kronon M, Lewis VL Jr, McCarthy WJ, McMillan WD, Meyer PR Jr. Peripheral vascular disease in spinal cord injury patients: a difficult diagnosis. Ann Plast Surg. 1996;37(5):495-499. doi:10.1097/00000637-199611000-00007
23. Taylor SM, Kalbaugh CA, Blackhurst DW, Cass, et al. Determinants of functional outcome after revascularization for critical limb ischemia: an analysis of 1000 consecutive vascular interventions. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44(4):747–756. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2006.06.015
24. Abdellaoui A, Al-Khaffaf H. C-reactive protein (CRP) as a marker in peripheral vascular disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007;34(1):18-22. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.10.040
25. Caro J, Migliaccio-Walle K, Ishak KJ, Proskorovsky I. The morbidity and mortality following a diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease: long-term follow-up of a large database. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2005;5:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-5-14
At the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH) in Tampa, Florida, the prevalence of amputations among patients at the spinal cord injury (SCI) center seems high. Despite limited data demonstrating altered hemodynamics in the lower extremities (LEs) among the SCI population and increased frequency of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), amputations among patients with SCI have received little attention in research.1-3
In the United States, most amputations are caused by vascular disease related to peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and diabetes mellitus (DM).4 PAD primarily affects the LEs and is caused by atherosclerotic obstruction leading to insufficient blood flow. PAD can present clinically as LE pain, nonhealing ulcers, nonpalpable distal pulses, shiny or cold skin, absence of hair on the LE, or distal extremity pallor when the affected extremity is elevated. However, PAD is often asymptomatic. The diagnosis of PAD is typically made with an ankle-brachial index (ABI) ≤ 0.9.5 The prevalence of PAD is about 4.3% in Americans aged ≥ 40 years, increases with age, and is almost twice as common among Black Americans compared with that of White Americans.6 Many studies in SCI populations have documented an increased prevalence of DM, dyslipidemia, obesity, hypertension (HTN), and cigarette smoking.7-9 PAD shares these risk factors with coronary artery disease (CAD), but relative to CAD, tobacco smoking was a more substantial causative factor for PAD.10 Given the preponderance of associated risk factors in this population, PAD is likely more prevalent among patients with SCI than in the population without disabilities. Beyond these known risk factors, researchers hypothesized that SCI contributes to vascular disease by altering arterial function. However, this is still a topic of debate.11-13 Trauma also is a common cause of amputation, accounting for 45% of amputations in 2005.4 Patients with SCI may experience traumatic amputations simultaneously as their SCI, but they may also be predisposed to traumatic amputations related to osteopenia and impaired sensation.
Since amputation is an invasive surgery, knowing the severity of this issue is important in the SCI population. This study quantifies the prevalence of amputations of the LEs among the patients at our SCI center. It then characterizes these amputations’ etiology, their relationship with medical comorbidities, and certain SCI classifications.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Computerized Patient Record System. The cohort was defined as all patients who received an annual examination at our SCI center over 4 years from October 1, 2009 to September 30, 2013. Annual examination includes a physical examination, relevant surveillance laboratory tests, and imaging, such as renal ultrasound for those with indwelling urinary catheters. One characteristic of the patient population in the VA system is that diagnoses, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), that involve spinal cord lesions causing symptoms are included in the registry, besides those with other traumatic or nontraumatic SCI. October 1 to September 30 was chosen based on the VA fiscal year (FY).
During this period, 1678 patients had an annual examination. Of those, 299 patients had an SCI etiology of ALS or MS, and 41 had nonfocal SCI etiology that could not be assessed using the American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale (AIS) and were excluded. Also excluded were 283 patients who did not have an annual examination during the specified time span. Some patients do not have an annual examination every year; for those with multiple annual examinations during that time frame, the most recent was used.
One thousand fifty-five patients were included in the statistical analysis. Date of birth, sex, race, ethnicity, date of death, smoking status, DM diagnosis, HTN diagnosis, use of an antiplatelet, antihypertensive, or lipid-lowering agent, blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and lipid panel were collected. The amputation level and etiology were noted. The levels of amputation were classified as toe/partial foot,
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive data were summarized as the median and IQR for continuous variables or the number and percentage for categorical variables. The χ2 test was used to analyze the association between categorical variables and amputation status. A nonparametric Wilcoxon test was used to investigate the distribution of continuous variables across patients with amputation and patients without amputation. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to investigate amputation risk factors. We report goodness of fit using the Hosmer and Lemeshow test and the area under the curve (AUC) for the multivariate model. Statistical significance was prespecified at a 2-sided P < .05. SAS version 9.4 was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Mean age was approximately 61 years for the 91 patients at the time of the most recent amputation (Table 1). Among those with amputation, 63% were paraplegic and 37% were tetraplegic.
Of 1055 patients with SCI, 91 (8.6%) patients had an amputation. Of those, 70 (76.1%) were from nontraumatic causes (dysvascular), 17 (18.5%) were traumatic, 4 (4.3%) were from other causes (ie, cancer), and only 1 (1.1%) was of unknown cause.
Of the 91 patients with amputation, 64 (69.6%) had at least 1 TFA—33 were unilateral and 31 were bilateral. Two patients had a TFA on one side and a TTA on the other. Partial foot/toe and TTA were less common amputation levels with 14 (15.4%) and 13 (14.3%), respectively. Most amputations (86.8%) occurred over 6 months from the day of initial SCI, and were most commonly dysvascular (Table 2). Traumatic amputation occurred more evenly at various stages, pre-SCI, during acute SCI, subacute SCI, and chronic SCI.
Injury by Impairment Scale Level
Forty-nine (11.5%) of 426 patients with AIS level A SCI had undergone amputation. In order of prevalence, 23 (46.9%) were unilateral TFA, 17 (34.6%) were bilateral TFA, 10.2% were partial foot/toe, 4.1% were unilateral TTA, and 4.1% were a TTA/TFA combination. Both hip and knee disarticulations were classified in the TFA category.
Sixteen (13.0%) of 123 patients with AIS level B SCI had undergone amputation; 5 (31.3%) of those amputations were unilateral TFA, 6 (37.5%) were bilateral TFA, 3 (18.8%) were partial toe or foot, and 1 (6.3%) was for unilateral and bilateral TTA each.
Twelve (8.4%) of 143 patients with AIS level C SCI had undergone amputation: 6 (50.0%) were bilateral TFA; 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TFA; and 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TTA.
Fourteen (3.9%) of 356 patients with AIS level D SCI had undergone amputation. Of those 6 (42.9%) underwent a partial foot/toe amputation; 5 (35.7%) had undergone a unilateral TTA, and 1 (7.1%) underwent amputation in each of the following categories: bilateral TTA, unilateral TFA, and bilateral TFA each.
None of the 7 individuals with AIS E level SCI had undergone amputation.
Health Risk Factors
Of the 91 patients with amputation, the majority (81.3%) were either former or current smokers. Thirty-six percent of those who had undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM, while only 21% of those who had not undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM.
At the time of their annual examination 532 patients had a diagnosis of HTN while 523 patients did not. Among patients with amputations, 59 (64.8%) had HTN, while 32 (35.2%) did not. Of the 964 patients without amputation, the prevalence of HTN was 50.9%
.Of 1055 patients with SCI, only 103 (9.8%) had a PAD diagnosis, including 38 (41.9%) patients with amputation. Just 65 (6.7%) patients with SCI without amputation had PAD (P < .001). PAD is highly correlated with dysvascular causes of amputation. Among those with amputations due to dysvascular etiology, 50.0% (35/70) had PAD, but for the 21 amputations due to nondysvascular etiology, only 3 (14.3%) had PAD (P = .004).
Amputation Predictive Model
A multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to build a predictive model for amputation among patients with SCI while controlling for covariates. In our multivariate analysis, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), tetraplegia, and PAD were predictive factors for amputation. Patients with SCI who had PAD were 8.6 times more likely to undergo amputation compared to those without PAD (odds ratio [OR], 9.8; P < .001; 95% CI, 5.9-16.3). Every unit of HDL-C decreased the odds of amputation by 5% (OR, 0.95; P < .001; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).

Having tetraplegia decreased the odds of amputation by 43%, compared with those with paraplegia (OR, 0.57; P = .02; 95% CI, 0.36 - 0.92). AUC was 0.76, and the Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of model fit test P value was .66, indicating the good predictive power of the model (Table 3).
Discussion
In the US, 54 to 82% of amputations occur secondary to chronic vascular disease. Our study showed similar results: 76.1% of amputations were dysvascular.4,16 Even in a 2019 systematic review, the most recent prevalence of amputation data was in 2005.17 The study concluded that among the general population in the US, prevalence of amputation was estimated to be 1 in 190 people, or about 0.5% of the population.4 We found that the prevalence of amputation among the SCI population in this study was 8.7%. This result is consistent with our initial hypothesis that the prevalence of amputation would be higher among the people with SCI. Using a different case acquisition method, Svircev and colleagues reported that about a 4% prevalence of LE amputation among veterans with chronic SCI (over 1 year from the initial SCI), with an emphasis that it was not a study of amputation incidence.18 In comparison, we calculated a 7.5% prevalence of amputation during the chronic SCI stage, which showed institutional variation and a consistent observation that LE amputations occurred more frequently in the SCI population.
Our results showed a positive correlation between the completeness of injury and the prevalence of amputation. Those individuals with a motor complete injury, AIS A (40.3%) or AIS B (11.7%) account for approximately half of all amputations in our population with SCI. Another finding was that proximal amputations were more frequent with more neurologically complete SCIs. Of those with an injury classified as AIS A and an amputation, 42 of 49 subjects underwent at least 1 TFA (23 were unilateral TFA, 17 were bilateral TFA, 2 were a TFA/TTA combination). Of those with an AIS B injury and an amputation, 11 of 16 subjects (68.8%) had at least 1 TFA (5 unilateral TFA and 6 bilateral TFA). Among patients with AIS C injury and amputation, 75% had a TFA. At the same time, only 13.3% of all amputations were at the transfemoral level in those with an AIS D injury. None of the participants with an injury classified as AIS E had undergone an amputation.
Given a paucity of literature available regarding amputation levels in patients with SCI, a discussion with a JAHVH vascular surgeon helped explain the rationale behind different levels of amputation among the SCI population—TFA was performed in 64 of 91 cases (70%). Institutionally, TFAs were performed more often because this level had the greatest chance of healing, avoiding infection, and eliminating knee contracture issues, which may affect quality of life. This was believed to be the best option in those individuals who were already nonambulatory. Although this study did not collect data on ambulatory status, this helps explain why those with an SCI classification of AIS D were more likely to have had a more distal amputation to preserve current or a future chance of ambulation, provided that whether the limb is salvageable is the priority of surgical decision.
The prevalence of PAD among veterans is generally higher than it is in the nonveteran population. Studies show that the prevalence of PAD risk factors in the veteran population exceeds national estimates. Nearly two-thirds of veterans have HTN, 1 in 4 has DM, and 1 in 4 is a current smoker, placing veterans at a significantly increased risk of PADand, therefore, amputation.19,20 These rates were about the same or greater in our SCI population: 50.4% had HTN, 22.3% had a diagnosis of DM, and 71.8% smoked previously or currently smoked. In 3 large studies, HTN was second only to current smoking as the most attributable risk factor for PAD.21
Ongoing research by JAHVH vascular surgeons suggests that patients with SCI were younger and less likely to have HTN, PAD, and/or CAD compared with patients undergoing TFA without SCI. Additionally, patients with SCI had better postoperative outcomes in terms of 30-day mortality, 3-year mortality, and had no increased rate of surgical revisions, strokes, or wound-healing complications. This supports the previous thought that the AIS classification plays a large role in determining amputation levels.
One result in this study is that paraplegia is one of the predictors of future amputation compared with tetraplegia. To our knowledge, there is no literature that supports or explains this finding. A hypothetical factor that could explain this observation is the difference in duration of survival—those with paraplegia who live longer are more likely to experience end-stage consequence of vascular diseases. Another proposed factor is that those with paraplegia are generally more active and have a higher likelihood of sustaining a traumatic cause of amputation, even though this etiology of amputation is minor.An unexpected finding in our study was that of 1055 patients with SCI, only 9.8% had a PAD diagnosis. In contrast, 41.3% of those with amputation had a PAD diagnosis. JAHVH does not screen for PAD, so this likely represents only the symptomatic cases.
Diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI is challenging as they may lack classic clinical symptoms, such as pain with ambulation and impotence, secondary to their neurologic injury. Instead, the health care practitioner must rely on physical signs, such as necrosis.22 Of note given the undetermined utility of diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI, early endovascular interventions are not typically performed. We could not find literature regarding when intervention for PAD in patients with SCI should be performed or how frequently those with SCI should be assessed for PAD. One study showed impaired ambulation prior to limb salvage procedures was associated with poor functional outcomes in terms of survival, independent living, and ambulatory status.23 This could help explain why endovascular procedures are done relatively infrequently in this population. With the lack of studies regarding PAD in the SCI population, outcomes analysis of these patients, including the rate of initial interventions, re-intervention for re-amputation (possibly at a higher level), or vascular inflow procedures, are needed.
It would be beneficial for future studies to examine whether inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), were more elevated in patients with SCI who underwent amputation compared with those who did not. Chronic underlying inflammation has been shown to be a risk factor for PAD. One study showed that, independently of other risk factors, elevated CRP levels roughly tripled the risk of developing PAD.24 This study suggested that there is an increased risk of dysvascular amputation among the SCI population at this center. This information is significant because it can help influence JAHVH clinical practice for veterans with SCI and vascular diseases.
Limitations
As a single-center study carried out at an SCI specialized center of a VA hospital, this study's finding may not be generalizable. Incomplete documentation in the health record may have led to underreporting of amputations and other information. The practice of the vascular surgeons at JAHVH may not represent the approach of vascular surgeons nationwide. Another limitation of this study is that the duration of SCI was not considered when looking at health risk factors associated with amputation in the SCI population (ie, total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, etc). Finally, the medication regimens were not reviewed to determine whether they meet the standard of care in relation to eventual diagnosis of PAD.
A prospective study comparing the prevalence of amputation between veterans with SCI vs veterans without SCI could better investigate the difference in amputation risks. This study only compared our veterans with SCI in reference to the general population. Veterans are more likely to be smokers than the general population, contributing to PAD.17 In addition, data regarding patients’ functional status in regard to transferring and ambulation before and after amputation were not collected, which would have contributed to an understanding of how amputation affects functional status in this population.
Conclusions
There is an increased prevalence of amputation among veterans with SCI compared with that of the nationwide population and a plurality were TFAs. This data suggest that those with a motor complete SCI are more likely to undergo a more proximal amputation. This is likely secondary to a lower likelihood of ambulation with more neurologically complete injuries along with a greater chance of healing with a more proximal amputation. It is challenging to correlate any variables specific to SCI (ie, immobility, time since injury, level of injury, etc) with an increased risk of amputation as the known comorbidities associated with PAD are highly prevalent in this population. Having PAD, low HDL-C (< 40 mg/dL), and paraplegia instead of tetraplegia were independent predictors of amputation.
Health care professionals need to be aware of the high prevalence of amputation in the SCI population. Comorbidities should be aggressively treated as PAD, in addition to being associated with amputation, has been linked with increased mortality.25 Studies using a larger population and multiple centers are needed to confirm such a concerning finding.
Acknowledgments
This material is based on work supported (or supported in part) with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH). Authors gratefully acknowledge the inputs and support of Dr. James Brooks, MD, RPVI, assistant professor of surgery, University of South Florida (USF), and attending surgeon, vascular surgery service, medical director of the peripheral vascular laboratory, JAHVH; and Dr. Kevin White, MD, assistant professor, USF, and Chief of Spinal Cord Injury Center, JAHVH.
At the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH) in Tampa, Florida, the prevalence of amputations among patients at the spinal cord injury (SCI) center seems high. Despite limited data demonstrating altered hemodynamics in the lower extremities (LEs) among the SCI population and increased frequency of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), amputations among patients with SCI have received little attention in research.1-3
In the United States, most amputations are caused by vascular disease related to peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and diabetes mellitus (DM).4 PAD primarily affects the LEs and is caused by atherosclerotic obstruction leading to insufficient blood flow. PAD can present clinically as LE pain, nonhealing ulcers, nonpalpable distal pulses, shiny or cold skin, absence of hair on the LE, or distal extremity pallor when the affected extremity is elevated. However, PAD is often asymptomatic. The diagnosis of PAD is typically made with an ankle-brachial index (ABI) ≤ 0.9.5 The prevalence of PAD is about 4.3% in Americans aged ≥ 40 years, increases with age, and is almost twice as common among Black Americans compared with that of White Americans.6 Many studies in SCI populations have documented an increased prevalence of DM, dyslipidemia, obesity, hypertension (HTN), and cigarette smoking.7-9 PAD shares these risk factors with coronary artery disease (CAD), but relative to CAD, tobacco smoking was a more substantial causative factor for PAD.10 Given the preponderance of associated risk factors in this population, PAD is likely more prevalent among patients with SCI than in the population without disabilities. Beyond these known risk factors, researchers hypothesized that SCI contributes to vascular disease by altering arterial function. However, this is still a topic of debate.11-13 Trauma also is a common cause of amputation, accounting for 45% of amputations in 2005.4 Patients with SCI may experience traumatic amputations simultaneously as their SCI, but they may also be predisposed to traumatic amputations related to osteopenia and impaired sensation.
Since amputation is an invasive surgery, knowing the severity of this issue is important in the SCI population. This study quantifies the prevalence of amputations of the LEs among the patients at our SCI center. It then characterizes these amputations’ etiology, their relationship with medical comorbidities, and certain SCI classifications.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Computerized Patient Record System. The cohort was defined as all patients who received an annual examination at our SCI center over 4 years from October 1, 2009 to September 30, 2013. Annual examination includes a physical examination, relevant surveillance laboratory tests, and imaging, such as renal ultrasound for those with indwelling urinary catheters. One characteristic of the patient population in the VA system is that diagnoses, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), that involve spinal cord lesions causing symptoms are included in the registry, besides those with other traumatic or nontraumatic SCI. October 1 to September 30 was chosen based on the VA fiscal year (FY).
During this period, 1678 patients had an annual examination. Of those, 299 patients had an SCI etiology of ALS or MS, and 41 had nonfocal SCI etiology that could not be assessed using the American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale (AIS) and were excluded. Also excluded were 283 patients who did not have an annual examination during the specified time span. Some patients do not have an annual examination every year; for those with multiple annual examinations during that time frame, the most recent was used.
One thousand fifty-five patients were included in the statistical analysis. Date of birth, sex, race, ethnicity, date of death, smoking status, DM diagnosis, HTN diagnosis, use of an antiplatelet, antihypertensive, or lipid-lowering agent, blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and lipid panel were collected. The amputation level and etiology were noted. The levels of amputation were classified as toe/partial foot,
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive data were summarized as the median and IQR for continuous variables or the number and percentage for categorical variables. The χ2 test was used to analyze the association between categorical variables and amputation status. A nonparametric Wilcoxon test was used to investigate the distribution of continuous variables across patients with amputation and patients without amputation. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to investigate amputation risk factors. We report goodness of fit using the Hosmer and Lemeshow test and the area under the curve (AUC) for the multivariate model. Statistical significance was prespecified at a 2-sided P < .05. SAS version 9.4 was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Mean age was approximately 61 years for the 91 patients at the time of the most recent amputation (Table 1). Among those with amputation, 63% were paraplegic and 37% were tetraplegic.
Of 1055 patients with SCI, 91 (8.6%) patients had an amputation. Of those, 70 (76.1%) were from nontraumatic causes (dysvascular), 17 (18.5%) were traumatic, 4 (4.3%) were from other causes (ie, cancer), and only 1 (1.1%) was of unknown cause.
Of the 91 patients with amputation, 64 (69.6%) had at least 1 TFA—33 were unilateral and 31 were bilateral. Two patients had a TFA on one side and a TTA on the other. Partial foot/toe and TTA were less common amputation levels with 14 (15.4%) and 13 (14.3%), respectively. Most amputations (86.8%) occurred over 6 months from the day of initial SCI, and were most commonly dysvascular (Table 2). Traumatic amputation occurred more evenly at various stages, pre-SCI, during acute SCI, subacute SCI, and chronic SCI.
Injury by Impairment Scale Level
Forty-nine (11.5%) of 426 patients with AIS level A SCI had undergone amputation. In order of prevalence, 23 (46.9%) were unilateral TFA, 17 (34.6%) were bilateral TFA, 10.2% were partial foot/toe, 4.1% were unilateral TTA, and 4.1% were a TTA/TFA combination. Both hip and knee disarticulations were classified in the TFA category.
Sixteen (13.0%) of 123 patients with AIS level B SCI had undergone amputation; 5 (31.3%) of those amputations were unilateral TFA, 6 (37.5%) were bilateral TFA, 3 (18.8%) were partial toe or foot, and 1 (6.3%) was for unilateral and bilateral TTA each.
Twelve (8.4%) of 143 patients with AIS level C SCI had undergone amputation: 6 (50.0%) were bilateral TFA; 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TFA; and 3 (25.0%) were unilateral TTA.
Fourteen (3.9%) of 356 patients with AIS level D SCI had undergone amputation. Of those 6 (42.9%) underwent a partial foot/toe amputation; 5 (35.7%) had undergone a unilateral TTA, and 1 (7.1%) underwent amputation in each of the following categories: bilateral TTA, unilateral TFA, and bilateral TFA each.
None of the 7 individuals with AIS E level SCI had undergone amputation.
Health Risk Factors
Of the 91 patients with amputation, the majority (81.3%) were either former or current smokers. Thirty-six percent of those who had undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM, while only 21% of those who had not undergone amputation had a diagnosis of DM.
At the time of their annual examination 532 patients had a diagnosis of HTN while 523 patients did not. Among patients with amputations, 59 (64.8%) had HTN, while 32 (35.2%) did not. Of the 964 patients without amputation, the prevalence of HTN was 50.9%
.Of 1055 patients with SCI, only 103 (9.8%) had a PAD diagnosis, including 38 (41.9%) patients with amputation. Just 65 (6.7%) patients with SCI without amputation had PAD (P < .001). PAD is highly correlated with dysvascular causes of amputation. Among those with amputations due to dysvascular etiology, 50.0% (35/70) had PAD, but for the 21 amputations due to nondysvascular etiology, only 3 (14.3%) had PAD (P = .004).
Amputation Predictive Model
A multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to build a predictive model for amputation among patients with SCI while controlling for covariates. In our multivariate analysis, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), tetraplegia, and PAD were predictive factors for amputation. Patients with SCI who had PAD were 8.6 times more likely to undergo amputation compared to those without PAD (odds ratio [OR], 9.8; P < .001; 95% CI, 5.9-16.3). Every unit of HDL-C decreased the odds of amputation by 5% (OR, 0.95; P < .001; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).

Having tetraplegia decreased the odds of amputation by 43%, compared with those with paraplegia (OR, 0.57; P = .02; 95% CI, 0.36 - 0.92). AUC was 0.76, and the Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of model fit test P value was .66, indicating the good predictive power of the model (Table 3).
Discussion
In the US, 54 to 82% of amputations occur secondary to chronic vascular disease. Our study showed similar results: 76.1% of amputations were dysvascular.4,16 Even in a 2019 systematic review, the most recent prevalence of amputation data was in 2005.17 The study concluded that among the general population in the US, prevalence of amputation was estimated to be 1 in 190 people, or about 0.5% of the population.4 We found that the prevalence of amputation among the SCI population in this study was 8.7%. This result is consistent with our initial hypothesis that the prevalence of amputation would be higher among the people with SCI. Using a different case acquisition method, Svircev and colleagues reported that about a 4% prevalence of LE amputation among veterans with chronic SCI (over 1 year from the initial SCI), with an emphasis that it was not a study of amputation incidence.18 In comparison, we calculated a 7.5% prevalence of amputation during the chronic SCI stage, which showed institutional variation and a consistent observation that LE amputations occurred more frequently in the SCI population.
Our results showed a positive correlation between the completeness of injury and the prevalence of amputation. Those individuals with a motor complete injury, AIS A (40.3%) or AIS B (11.7%) account for approximately half of all amputations in our population with SCI. Another finding was that proximal amputations were more frequent with more neurologically complete SCIs. Of those with an injury classified as AIS A and an amputation, 42 of 49 subjects underwent at least 1 TFA (23 were unilateral TFA, 17 were bilateral TFA, 2 were a TFA/TTA combination). Of those with an AIS B injury and an amputation, 11 of 16 subjects (68.8%) had at least 1 TFA (5 unilateral TFA and 6 bilateral TFA). Among patients with AIS C injury and amputation, 75% had a TFA. At the same time, only 13.3% of all amputations were at the transfemoral level in those with an AIS D injury. None of the participants with an injury classified as AIS E had undergone an amputation.
Given a paucity of literature available regarding amputation levels in patients with SCI, a discussion with a JAHVH vascular surgeon helped explain the rationale behind different levels of amputation among the SCI population—TFA was performed in 64 of 91 cases (70%). Institutionally, TFAs were performed more often because this level had the greatest chance of healing, avoiding infection, and eliminating knee contracture issues, which may affect quality of life. This was believed to be the best option in those individuals who were already nonambulatory. Although this study did not collect data on ambulatory status, this helps explain why those with an SCI classification of AIS D were more likely to have had a more distal amputation to preserve current or a future chance of ambulation, provided that whether the limb is salvageable is the priority of surgical decision.
The prevalence of PAD among veterans is generally higher than it is in the nonveteran population. Studies show that the prevalence of PAD risk factors in the veteran population exceeds national estimates. Nearly two-thirds of veterans have HTN, 1 in 4 has DM, and 1 in 4 is a current smoker, placing veterans at a significantly increased risk of PADand, therefore, amputation.19,20 These rates were about the same or greater in our SCI population: 50.4% had HTN, 22.3% had a diagnosis of DM, and 71.8% smoked previously or currently smoked. In 3 large studies, HTN was second only to current smoking as the most attributable risk factor for PAD.21
Ongoing research by JAHVH vascular surgeons suggests that patients with SCI were younger and less likely to have HTN, PAD, and/or CAD compared with patients undergoing TFA without SCI. Additionally, patients with SCI had better postoperative outcomes in terms of 30-day mortality, 3-year mortality, and had no increased rate of surgical revisions, strokes, or wound-healing complications. This supports the previous thought that the AIS classification plays a large role in determining amputation levels.
One result in this study is that paraplegia is one of the predictors of future amputation compared with tetraplegia. To our knowledge, there is no literature that supports or explains this finding. A hypothetical factor that could explain this observation is the difference in duration of survival—those with paraplegia who live longer are more likely to experience end-stage consequence of vascular diseases. Another proposed factor is that those with paraplegia are generally more active and have a higher likelihood of sustaining a traumatic cause of amputation, even though this etiology of amputation is minor.An unexpected finding in our study was that of 1055 patients with SCI, only 9.8% had a PAD diagnosis. In contrast, 41.3% of those with amputation had a PAD diagnosis. JAHVH does not screen for PAD, so this likely represents only the symptomatic cases.
Diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI is challenging as they may lack classic clinical symptoms, such as pain with ambulation and impotence, secondary to their neurologic injury. Instead, the health care practitioner must rely on physical signs, such as necrosis.22 Of note given the undetermined utility of diagnosing PAD in patients with SCI, early endovascular interventions are not typically performed. We could not find literature regarding when intervention for PAD in patients with SCI should be performed or how frequently those with SCI should be assessed for PAD. One study showed impaired ambulation prior to limb salvage procedures was associated with poor functional outcomes in terms of survival, independent living, and ambulatory status.23 This could help explain why endovascular procedures are done relatively infrequently in this population. With the lack of studies regarding PAD in the SCI population, outcomes analysis of these patients, including the rate of initial interventions, re-intervention for re-amputation (possibly at a higher level), or vascular inflow procedures, are needed.
It would be beneficial for future studies to examine whether inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), were more elevated in patients with SCI who underwent amputation compared with those who did not. Chronic underlying inflammation has been shown to be a risk factor for PAD. One study showed that, independently of other risk factors, elevated CRP levels roughly tripled the risk of developing PAD.24 This study suggested that there is an increased risk of dysvascular amputation among the SCI population at this center. This information is significant because it can help influence JAHVH clinical practice for veterans with SCI and vascular diseases.
Limitations
As a single-center study carried out at an SCI specialized center of a VA hospital, this study's finding may not be generalizable. Incomplete documentation in the health record may have led to underreporting of amputations and other information. The practice of the vascular surgeons at JAHVH may not represent the approach of vascular surgeons nationwide. Another limitation of this study is that the duration of SCI was not considered when looking at health risk factors associated with amputation in the SCI population (ie, total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, etc). Finally, the medication regimens were not reviewed to determine whether they meet the standard of care in relation to eventual diagnosis of PAD.
A prospective study comparing the prevalence of amputation between veterans with SCI vs veterans without SCI could better investigate the difference in amputation risks. This study only compared our veterans with SCI in reference to the general population. Veterans are more likely to be smokers than the general population, contributing to PAD.17 In addition, data regarding patients’ functional status in regard to transferring and ambulation before and after amputation were not collected, which would have contributed to an understanding of how amputation affects functional status in this population.
Conclusions
There is an increased prevalence of amputation among veterans with SCI compared with that of the nationwide population and a plurality were TFAs. This data suggest that those with a motor complete SCI are more likely to undergo a more proximal amputation. This is likely secondary to a lower likelihood of ambulation with more neurologically complete injuries along with a greater chance of healing with a more proximal amputation. It is challenging to correlate any variables specific to SCI (ie, immobility, time since injury, level of injury, etc) with an increased risk of amputation as the known comorbidities associated with PAD are highly prevalent in this population. Having PAD, low HDL-C (< 40 mg/dL), and paraplegia instead of tetraplegia were independent predictors of amputation.
Health care professionals need to be aware of the high prevalence of amputation in the SCI population. Comorbidities should be aggressively treated as PAD, in addition to being associated with amputation, has been linked with increased mortality.25 Studies using a larger population and multiple centers are needed to confirm such a concerning finding.
Acknowledgments
This material is based on work supported (or supported in part) with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (JAHVH). Authors gratefully acknowledge the inputs and support of Dr. James Brooks, MD, RPVI, assistant professor of surgery, University of South Florida (USF), and attending surgeon, vascular surgery service, medical director of the peripheral vascular laboratory, JAHVH; and Dr. Kevin White, MD, assistant professor, USF, and Chief of Spinal Cord Injury Center, JAHVH.
1. Hopman MT, Nommensen E, van Asten WN, Oeseburg B, Binkhorst RA. Properties of the venous vascular system in the lower extremities of individuals with paraplegia. Paraplegia. 1994;32(12):810-816. doi:10.1038/sc.1994.128
2. Theisen D, Vanlandewijck Y, Sturbois X, Francaux M. Central and peripheral haemodynamics in individuals with paraplegia during light and heavy exercise. J Rehabil Med. 2001;33(1):16-20. doi:10.1080/165019701300006489
3. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Evidence for greater burden of peripheral arterial disease in lower extremity arteries of spinal cord-injured individuals. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(3):H766-H772. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00507.2011
4. Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
5. Hennion DR, Siano KA. Diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Am Fam Physician. 2013;88(5):306-310.
6. Selvin E, Erlinger TP. Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2000. Circulation. 2004;110(6):738-743. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000137913.26087.F0
7. Bauman WA, Spungen AM. Disorders of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in veterans with paraplegia or quadriplegia: a model of premature aging. Metabolism. 1994;43(6):749-756. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(94)90126-0
8. Jörgensen S, Hill M, Lexell J. Cardiovascular risk factors among older adults with long-term spinal cord injury. PM R. 2019;11(1):8-16. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2018.06.008
9. Wu JC, Chen YC, Liu L, et al. Increased risk of stroke after spinal cord injury: a nationwide 4-year follow-up cohort study. Neurology. 2012;78(14):1051-1057. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824e8eaa
10. Price JF, Mowbray PI, Lee AJ, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Fowkes FG. Relationship between smoking and cardiovascular risk factors in the development of peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease: Edinburgh Artery Study. Eur Heart J. 1999;20(5):344-353. doi:10.1053/euhj.1998.1194
11. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Altered resting hemodynamics in lower-extremity arteries of individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(2):104-111. doi:10.1179/2045772312Y.0000000052
12. Miyatani M, Masani K, Oh PI, Miyachi M, Popovic MR, Craven BC. Pulse wave velocity for assessment of arterial stiffness among people with spinal cord injury: a pilot study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2009;32(1):72-78. doi:10.1080/10790268.2009.11760755
13. Oliver JJ, Webb DJ. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(4):554-566. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000060460.52916.D6
14. Ephraim PL, Dillifngham TR, Sector M, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Epidemiology of limb loss and congenital limb deficiency: a review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84(5): 747-761. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(02)04932-8.15. Levin ME. Preventing amputation in the patient with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(10)1383-1394. doi:10.2337/diacare.18.10.1383
16. Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the United States. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611- 200208000-00018
17. Lo J, Chan L, Flynn S. A systematic review of the incidence, prevalence, costs, and activity and work limitations of amputation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury in the United States: a 2019 update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102:115-131. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2020.04.001
18. Svircev, J, Tan D, Garrison A, Pennelly, B, Burns SP. Limb loss in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. doi:10.1080/10790268.2020.1800964
19. Brown DW. Smoking prevalence among US veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(2):147-149. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1160-0
20. Selim AJ, Berlowitz DR, Fincke G, et al. The health status of elderly veteran enrollees in the Veterans Health Administration. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(8):1271-1276. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52355.x
21. Criqui MH, Aboyans V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(9):1509-1526. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303849
22. Yokoo KM, Kronon M, Lewis VL Jr, McCarthy WJ, McMillan WD, Meyer PR Jr. Peripheral vascular disease in spinal cord injury patients: a difficult diagnosis. Ann Plast Surg. 1996;37(5):495-499. doi:10.1097/00000637-199611000-00007
23. Taylor SM, Kalbaugh CA, Blackhurst DW, Cass, et al. Determinants of functional outcome after revascularization for critical limb ischemia: an analysis of 1000 consecutive vascular interventions. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44(4):747–756. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2006.06.015
24. Abdellaoui A, Al-Khaffaf H. C-reactive protein (CRP) as a marker in peripheral vascular disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007;34(1):18-22. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.10.040
25. Caro J, Migliaccio-Walle K, Ishak KJ, Proskorovsky I. The morbidity and mortality following a diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease: long-term follow-up of a large database. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2005;5:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-5-14
1. Hopman MT, Nommensen E, van Asten WN, Oeseburg B, Binkhorst RA. Properties of the venous vascular system in the lower extremities of individuals with paraplegia. Paraplegia. 1994;32(12):810-816. doi:10.1038/sc.1994.128
2. Theisen D, Vanlandewijck Y, Sturbois X, Francaux M. Central and peripheral haemodynamics in individuals with paraplegia during light and heavy exercise. J Rehabil Med. 2001;33(1):16-20. doi:10.1080/165019701300006489
3. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Evidence for greater burden of peripheral arterial disease in lower extremity arteries of spinal cord-injured individuals. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(3):H766-H772. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00507.2011
4. Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
5. Hennion DR, Siano KA. Diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Am Fam Physician. 2013;88(5):306-310.
6. Selvin E, Erlinger TP. Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2000. Circulation. 2004;110(6):738-743. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000137913.26087.F0
7. Bauman WA, Spungen AM. Disorders of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in veterans with paraplegia or quadriplegia: a model of premature aging. Metabolism. 1994;43(6):749-756. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(94)90126-0
8. Jörgensen S, Hill M, Lexell J. Cardiovascular risk factors among older adults with long-term spinal cord injury. PM R. 2019;11(1):8-16. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2018.06.008
9. Wu JC, Chen YC, Liu L, et al. Increased risk of stroke after spinal cord injury: a nationwide 4-year follow-up cohort study. Neurology. 2012;78(14):1051-1057. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824e8eaa
10. Price JF, Mowbray PI, Lee AJ, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Fowkes FG. Relationship between smoking and cardiovascular risk factors in the development of peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease: Edinburgh Artery Study. Eur Heart J. 1999;20(5):344-353. doi:10.1053/euhj.1998.1194
11. Bell JW, Chen D, Bahls M, Newcomer SC. Altered resting hemodynamics in lower-extremity arteries of individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(2):104-111. doi:10.1179/2045772312Y.0000000052
12. Miyatani M, Masani K, Oh PI, Miyachi M, Popovic MR, Craven BC. Pulse wave velocity for assessment of arterial stiffness among people with spinal cord injury: a pilot study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2009;32(1):72-78. doi:10.1080/10790268.2009.11760755
13. Oliver JJ, Webb DJ. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(4):554-566. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000060460.52916.D6
14. Ephraim PL, Dillifngham TR, Sector M, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Epidemiology of limb loss and congenital limb deficiency: a review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84(5): 747-761. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(02)04932-8.15. Levin ME. Preventing amputation in the patient with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(10)1383-1394. doi:10.2337/diacare.18.10.1383
16. Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the United States. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611- 200208000-00018
17. Lo J, Chan L, Flynn S. A systematic review of the incidence, prevalence, costs, and activity and work limitations of amputation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, back pain, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury in the United States: a 2019 update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102:115-131. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2020.04.001
18. Svircev, J, Tan D, Garrison A, Pennelly, B, Burns SP. Limb loss in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. doi:10.1080/10790268.2020.1800964
19. Brown DW. Smoking prevalence among US veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(2):147-149. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1160-0
20. Selim AJ, Berlowitz DR, Fincke G, et al. The health status of elderly veteran enrollees in the Veterans Health Administration. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(8):1271-1276. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52355.x
21. Criqui MH, Aboyans V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(9):1509-1526. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303849
22. Yokoo KM, Kronon M, Lewis VL Jr, McCarthy WJ, McMillan WD, Meyer PR Jr. Peripheral vascular disease in spinal cord injury patients: a difficult diagnosis. Ann Plast Surg. 1996;37(5):495-499. doi:10.1097/00000637-199611000-00007
23. Taylor SM, Kalbaugh CA, Blackhurst DW, Cass, et al. Determinants of functional outcome after revascularization for critical limb ischemia: an analysis of 1000 consecutive vascular interventions. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44(4):747–756. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2006.06.015
24. Abdellaoui A, Al-Khaffaf H. C-reactive protein (CRP) as a marker in peripheral vascular disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007;34(1):18-22. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.10.040
25. Caro J, Migliaccio-Walle K, Ishak KJ, Proskorovsky I. The morbidity and mortality following a diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease: long-term follow-up of a large database. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2005;5:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-5-14
The VA Goes Its Own Way on Aducanumab
In the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), the current prevalence of veterans with dementia is estimated to be about 10%.1 A 2013 report from the VHA Office of Policy and Planning projected a 22% increase in patients with dementia between 2020 and 2033. That increase amounts to between 276,000 and 335,000 additional veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care.2 Of course, these alarming statistics can in no way begin to convey the devastating biopsychosocial impact of Alzheimer disease and other dementias on veterans and their families. In many cases, veterans’ service to their country resulted in injuries and illnesses that increased the risk that they would develop dementia, such as traumatic brain injuries and posttraumatic stress disorder.3
Confronted with these concerning statistics, why didn’t VA Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) follow the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of aduncanumab-avwa for patients with dementia? Instead, PBM issued a monograph in July 2021 that recommended against providing aduncanumab-avwa to patients with Alzheimer dementia (mild or otherwise) or mild cognitive impairment, “given the lack of evidence of a robust and meaningful clinical benefit and the known safety signal.”4
In this editorial, I examine the reasons for the PBM recommendation, explain how the VA denial of approval for this new drug for dementia contravened that of the FDA and the ethical implications of this decision for veterans with dementia and the health care professionals (HCPs) who treat them.
The VA PBM national drug monographs are scientific reviews of clinical data supporting the potential inclusion of new medications in the VHA formulary.Aducanumab-avwa is a human monoclonal antibody. Its mechanism of action is to stimulate clearance of β-amyloid plaques from the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. β-amyloid is a protein byproduct of amyloid precursor protein. Abnormal levels of β-amyloid build up in the brain of a patient with Alzheimer disease, forming clumps that disrupt neuronal connections that enable information transmission and other functions contributing to the death of brain cells.5
The FDA approved aducanumab on June 7, 2021, through the accelerated approval pathway.6 Drugs approved through the regular pathway must show a clinical benefit. Because detecting and demonstrating clinical benefit through research can be a lengthy process, in 1992 the FDA initiated the accelerated approval pathway. This alternative regulatory option permits the agency to approve a drug that “filled an unmet medical need” for a serious or life-threatening condition based on a surrogate endpoint.7 Examples of such endpoints are laboratory values, imaging evidence, physical signs, or other objective findings that are believed to predict a clinical benefit. In 2012, the FDA Safety Innovations Act expanded the basis for approval to an intermediate clinical endpoint: a measure of a therapeutic effect that demonstrates a “reasonable likelihood” of predicting clinical benefit.7
The FDA, unlike the PBM, found that aducanumab “provided a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments.” The FDA underscored that unlike other medications currently available to treat Alzheimer dementias that target symptoms, aducanumab acts on the underlying neurophysiology and neuropathology of the disease based on the decrease in β-amyloid plaques in participants in 2 large clinical trials. The FDA approved the drug for the treatment of patients with either mild cognitive impairment or in the mild state of Alzheimer dementia.
From the time of its announcement, the FDA decision to approve the drug was controversial and criticized in both professional articles and the news media. A particular poignant charge by Largent and Lynch was that the FDA had exploited the desperation of vulnerable patients with dementia and their families willing to try medications with unclear value and uncertain risk precisely because they believed they had no other viable options.8 Critics charged that the FDA took the unusual step of overruling the recommendations of a council of its senior advisors, claiming that there was insufficient evidence for approval; that there was a potential conflict of interest between the agency and the pharmaceutical industry; and that the FDA inappropriately used the accelerated approval pathway.9 In August 2021, in response to these critiques, the Office of the Inspector General announced that it would review the process the agency used in approving the drug.10 Nor was the VA alone in its refusal: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) has proposed to cover the drug for its beneficiaries enrolled in CMS-endorsed clinical trials with the caveat that the drug’s manufacturer, Biogen, must continue to conduct studies on the safety and effectiveness of the drug.11
Why did VHA come to a different scientific conclusion than that of the FDA? In reviewing the data from the 2 major studies, PBM did not find that this surrogate endpoint of reduction in β-amyloid plaques was a valid measure of a meaningful clinical benefit. Further, this lack of valid therapeutic change could not outweigh the risks of the amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in research participants. ARIA include cerebral vasogenic edema, effusions in sulci, microhemorrhages in the brain, and/or localized superficial siderosis. These findings are thought to be the result of the antibody binding to β-amyloid deposits that in turn increase cerebrovascular permeability.5
Thus, in not approving aducanumab, PBM and VHA leadership acted on the core bioethical principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence to prevent harms that proportionally outweighed benefits. Another ethical consideration for the VHA was that of distributive justice given the expense of the medication and the VHA obligation to be responsible stewards of public resources. At the time of the VHA decision, a year’s worth of aducanumab cost about $56,000: In December 2021, the manufacturer announced a dramatic decrease in the drug’s price.12 Although it may seem that fairness requires the VHA to provide any possible treatment for veterans whose cognitive impairment is in part an adverse effect of their time in uniform, a stronger counter argument is that the same high safety and scientific standard should be used for the approval of medications for patients with dementia as for any other disorder.
Among VHA HCPs and their patients with new and early diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia, what is lacking in PBM’s clinical ethics analysis is the important principle of autonomy. PBM did carve out a space for the use of the drug in “highly selected patients by experts and centers that have the necessary diagnostic and management expertise.”5 The series of safety standards that must be met along with monitoring for the drug to be prescribed is PBM’s effort to obtain an equilibrium between preventing harm while respecting professional judgment and patient choice. PBM and VHA will reconsider its criteria if research shows improved effectiveness and safety. As with most debated decisions, for some patients and HCPs that balancing act may not have gone far enough, yet many believe that VHA for now is on the right side of the controversy.
1. Williamson V, Stevelink SAM, Greenberg K, Greenberg N. Prevalence of mental health disorders in elderly U.S. military veterans: a metaanalysis and systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26:534-545. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2017.11.001
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of the Assistant Deputy Under Secretary for Health for Policy and Planning. Projections of the prevalence and incidence of dementias. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. www.va.gov/geriatrics/GEC_Data_Reports.asp
3. Zhu CW, Sano M. Demographic, health, and exposure risks associated with cognitive loss, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in US military veterans. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:610334. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.610334
4. VHA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, and VISN Pharmacist Executives. Aducanumab-avwa (ADUHELM) National Drug Monograph. Published July 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/drugmonographs/Aducanumab_ADUHELM_monograph_508.pdf
5. National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging. What happens to the brain in Alzheimer’s disease? Updated May 16, 2017. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-happens-brain-alzheimers-disease
6. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval for Alzheimer’s drug. News release. Published June 7, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-alzheimers-drug
7. US Food and Drug Administration. Accelerated approval. Updated January 4, 2018. Accessed March 21,2022.https://www.fda.gov/patients/fast-track-breakthrough-therapy-accelerated-approval-priority-review/accelerated-approval
8. Largent EL, Peterson E, Lynch HF. FDA approval and the ethics of desperation. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181(12):1555-1556. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6045
9. Belluck P, Kaplan S, Robbins R. How an unproven Alzheimer’s drug got approved. New York Times, Updated October 21, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/19/health/alzheimers-drug-aduhelm-fda.html
10. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Inspector General. Review of the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000608.asp
11. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease decision summary. Published January 11, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=Y&NCAId=305
12. Gleckman H. What’s behind Biogen’s move to cut prices on its controversial Alzheimer’s drug alduhelm. Forbes. Published December 23, 2021. Accessed March 21,2022. https://www.forbes.com/sites/howardgleckman/2021/12/23/whats-behind-biogens-move-to-cut-prices-on-its-controversial-alzheimers-drug-aduhelm/?sh=498c6a235154
In the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), the current prevalence of veterans with dementia is estimated to be about 10%.1 A 2013 report from the VHA Office of Policy and Planning projected a 22% increase in patients with dementia between 2020 and 2033. That increase amounts to between 276,000 and 335,000 additional veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care.2 Of course, these alarming statistics can in no way begin to convey the devastating biopsychosocial impact of Alzheimer disease and other dementias on veterans and their families. In many cases, veterans’ service to their country resulted in injuries and illnesses that increased the risk that they would develop dementia, such as traumatic brain injuries and posttraumatic stress disorder.3
Confronted with these concerning statistics, why didn’t VA Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) follow the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of aduncanumab-avwa for patients with dementia? Instead, PBM issued a monograph in July 2021 that recommended against providing aduncanumab-avwa to patients with Alzheimer dementia (mild or otherwise) or mild cognitive impairment, “given the lack of evidence of a robust and meaningful clinical benefit and the known safety signal.”4
In this editorial, I examine the reasons for the PBM recommendation, explain how the VA denial of approval for this new drug for dementia contravened that of the FDA and the ethical implications of this decision for veterans with dementia and the health care professionals (HCPs) who treat them.
The VA PBM national drug monographs are scientific reviews of clinical data supporting the potential inclusion of new medications in the VHA formulary.Aducanumab-avwa is a human monoclonal antibody. Its mechanism of action is to stimulate clearance of β-amyloid plaques from the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. β-amyloid is a protein byproduct of amyloid precursor protein. Abnormal levels of β-amyloid build up in the brain of a patient with Alzheimer disease, forming clumps that disrupt neuronal connections that enable information transmission and other functions contributing to the death of brain cells.5
The FDA approved aducanumab on June 7, 2021, through the accelerated approval pathway.6 Drugs approved through the regular pathway must show a clinical benefit. Because detecting and demonstrating clinical benefit through research can be a lengthy process, in 1992 the FDA initiated the accelerated approval pathway. This alternative regulatory option permits the agency to approve a drug that “filled an unmet medical need” for a serious or life-threatening condition based on a surrogate endpoint.7 Examples of such endpoints are laboratory values, imaging evidence, physical signs, or other objective findings that are believed to predict a clinical benefit. In 2012, the FDA Safety Innovations Act expanded the basis for approval to an intermediate clinical endpoint: a measure of a therapeutic effect that demonstrates a “reasonable likelihood” of predicting clinical benefit.7
The FDA, unlike the PBM, found that aducanumab “provided a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments.” The FDA underscored that unlike other medications currently available to treat Alzheimer dementias that target symptoms, aducanumab acts on the underlying neurophysiology and neuropathology of the disease based on the decrease in β-amyloid plaques in participants in 2 large clinical trials. The FDA approved the drug for the treatment of patients with either mild cognitive impairment or in the mild state of Alzheimer dementia.
From the time of its announcement, the FDA decision to approve the drug was controversial and criticized in both professional articles and the news media. A particular poignant charge by Largent and Lynch was that the FDA had exploited the desperation of vulnerable patients with dementia and their families willing to try medications with unclear value and uncertain risk precisely because they believed they had no other viable options.8 Critics charged that the FDA took the unusual step of overruling the recommendations of a council of its senior advisors, claiming that there was insufficient evidence for approval; that there was a potential conflict of interest between the agency and the pharmaceutical industry; and that the FDA inappropriately used the accelerated approval pathway.9 In August 2021, in response to these critiques, the Office of the Inspector General announced that it would review the process the agency used in approving the drug.10 Nor was the VA alone in its refusal: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) has proposed to cover the drug for its beneficiaries enrolled in CMS-endorsed clinical trials with the caveat that the drug’s manufacturer, Biogen, must continue to conduct studies on the safety and effectiveness of the drug.11
Why did VHA come to a different scientific conclusion than that of the FDA? In reviewing the data from the 2 major studies, PBM did not find that this surrogate endpoint of reduction in β-amyloid plaques was a valid measure of a meaningful clinical benefit. Further, this lack of valid therapeutic change could not outweigh the risks of the amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in research participants. ARIA include cerebral vasogenic edema, effusions in sulci, microhemorrhages in the brain, and/or localized superficial siderosis. These findings are thought to be the result of the antibody binding to β-amyloid deposits that in turn increase cerebrovascular permeability.5
Thus, in not approving aducanumab, PBM and VHA leadership acted on the core bioethical principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence to prevent harms that proportionally outweighed benefits. Another ethical consideration for the VHA was that of distributive justice given the expense of the medication and the VHA obligation to be responsible stewards of public resources. At the time of the VHA decision, a year’s worth of aducanumab cost about $56,000: In December 2021, the manufacturer announced a dramatic decrease in the drug’s price.12 Although it may seem that fairness requires the VHA to provide any possible treatment for veterans whose cognitive impairment is in part an adverse effect of their time in uniform, a stronger counter argument is that the same high safety and scientific standard should be used for the approval of medications for patients with dementia as for any other disorder.
Among VHA HCPs and their patients with new and early diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia, what is lacking in PBM’s clinical ethics analysis is the important principle of autonomy. PBM did carve out a space for the use of the drug in “highly selected patients by experts and centers that have the necessary diagnostic and management expertise.”5 The series of safety standards that must be met along with monitoring for the drug to be prescribed is PBM’s effort to obtain an equilibrium between preventing harm while respecting professional judgment and patient choice. PBM and VHA will reconsider its criteria if research shows improved effectiveness and safety. As with most debated decisions, for some patients and HCPs that balancing act may not have gone far enough, yet many believe that VHA for now is on the right side of the controversy.
In the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), the current prevalence of veterans with dementia is estimated to be about 10%.1 A 2013 report from the VHA Office of Policy and Planning projected a 22% increase in patients with dementia between 2020 and 2033. That increase amounts to between 276,000 and 335,000 additional veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care.2 Of course, these alarming statistics can in no way begin to convey the devastating biopsychosocial impact of Alzheimer disease and other dementias on veterans and their families. In many cases, veterans’ service to their country resulted in injuries and illnesses that increased the risk that they would develop dementia, such as traumatic brain injuries and posttraumatic stress disorder.3
Confronted with these concerning statistics, why didn’t VA Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) follow the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of aduncanumab-avwa for patients with dementia? Instead, PBM issued a monograph in July 2021 that recommended against providing aduncanumab-avwa to patients with Alzheimer dementia (mild or otherwise) or mild cognitive impairment, “given the lack of evidence of a robust and meaningful clinical benefit and the known safety signal.”4
In this editorial, I examine the reasons for the PBM recommendation, explain how the VA denial of approval for this new drug for dementia contravened that of the FDA and the ethical implications of this decision for veterans with dementia and the health care professionals (HCPs) who treat them.
The VA PBM national drug monographs are scientific reviews of clinical data supporting the potential inclusion of new medications in the VHA formulary.Aducanumab-avwa is a human monoclonal antibody. Its mechanism of action is to stimulate clearance of β-amyloid plaques from the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. β-amyloid is a protein byproduct of amyloid precursor protein. Abnormal levels of β-amyloid build up in the brain of a patient with Alzheimer disease, forming clumps that disrupt neuronal connections that enable information transmission and other functions contributing to the death of brain cells.5
The FDA approved aducanumab on June 7, 2021, through the accelerated approval pathway.6 Drugs approved through the regular pathway must show a clinical benefit. Because detecting and demonstrating clinical benefit through research can be a lengthy process, in 1992 the FDA initiated the accelerated approval pathway. This alternative regulatory option permits the agency to approve a drug that “filled an unmet medical need” for a serious or life-threatening condition based on a surrogate endpoint.7 Examples of such endpoints are laboratory values, imaging evidence, physical signs, or other objective findings that are believed to predict a clinical benefit. In 2012, the FDA Safety Innovations Act expanded the basis for approval to an intermediate clinical endpoint: a measure of a therapeutic effect that demonstrates a “reasonable likelihood” of predicting clinical benefit.7
The FDA, unlike the PBM, found that aducanumab “provided a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments.” The FDA underscored that unlike other medications currently available to treat Alzheimer dementias that target symptoms, aducanumab acts on the underlying neurophysiology and neuropathology of the disease based on the decrease in β-amyloid plaques in participants in 2 large clinical trials. The FDA approved the drug for the treatment of patients with either mild cognitive impairment or in the mild state of Alzheimer dementia.
From the time of its announcement, the FDA decision to approve the drug was controversial and criticized in both professional articles and the news media. A particular poignant charge by Largent and Lynch was that the FDA had exploited the desperation of vulnerable patients with dementia and their families willing to try medications with unclear value and uncertain risk precisely because they believed they had no other viable options.8 Critics charged that the FDA took the unusual step of overruling the recommendations of a council of its senior advisors, claiming that there was insufficient evidence for approval; that there was a potential conflict of interest between the agency and the pharmaceutical industry; and that the FDA inappropriately used the accelerated approval pathway.9 In August 2021, in response to these critiques, the Office of the Inspector General announced that it would review the process the agency used in approving the drug.10 Nor was the VA alone in its refusal: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) has proposed to cover the drug for its beneficiaries enrolled in CMS-endorsed clinical trials with the caveat that the drug’s manufacturer, Biogen, must continue to conduct studies on the safety and effectiveness of the drug.11
Why did VHA come to a different scientific conclusion than that of the FDA? In reviewing the data from the 2 major studies, PBM did not find that this surrogate endpoint of reduction in β-amyloid plaques was a valid measure of a meaningful clinical benefit. Further, this lack of valid therapeutic change could not outweigh the risks of the amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in research participants. ARIA include cerebral vasogenic edema, effusions in sulci, microhemorrhages in the brain, and/or localized superficial siderosis. These findings are thought to be the result of the antibody binding to β-amyloid deposits that in turn increase cerebrovascular permeability.5
Thus, in not approving aducanumab, PBM and VHA leadership acted on the core bioethical principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence to prevent harms that proportionally outweighed benefits. Another ethical consideration for the VHA was that of distributive justice given the expense of the medication and the VHA obligation to be responsible stewards of public resources. At the time of the VHA decision, a year’s worth of aducanumab cost about $56,000: In December 2021, the manufacturer announced a dramatic decrease in the drug’s price.12 Although it may seem that fairness requires the VHA to provide any possible treatment for veterans whose cognitive impairment is in part an adverse effect of their time in uniform, a stronger counter argument is that the same high safety and scientific standard should be used for the approval of medications for patients with dementia as for any other disorder.
Among VHA HCPs and their patients with new and early diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia, what is lacking in PBM’s clinical ethics analysis is the important principle of autonomy. PBM did carve out a space for the use of the drug in “highly selected patients by experts and centers that have the necessary diagnostic and management expertise.”5 The series of safety standards that must be met along with monitoring for the drug to be prescribed is PBM’s effort to obtain an equilibrium between preventing harm while respecting professional judgment and patient choice. PBM and VHA will reconsider its criteria if research shows improved effectiveness and safety. As with most debated decisions, for some patients and HCPs that balancing act may not have gone far enough, yet many believe that VHA for now is on the right side of the controversy.
1. Williamson V, Stevelink SAM, Greenberg K, Greenberg N. Prevalence of mental health disorders in elderly U.S. military veterans: a metaanalysis and systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26:534-545. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2017.11.001
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of the Assistant Deputy Under Secretary for Health for Policy and Planning. Projections of the prevalence and incidence of dementias. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. www.va.gov/geriatrics/GEC_Data_Reports.asp
3. Zhu CW, Sano M. Demographic, health, and exposure risks associated with cognitive loss, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in US military veterans. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:610334. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.610334
4. VHA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, and VISN Pharmacist Executives. Aducanumab-avwa (ADUHELM) National Drug Monograph. Published July 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/drugmonographs/Aducanumab_ADUHELM_monograph_508.pdf
5. National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging. What happens to the brain in Alzheimer’s disease? Updated May 16, 2017. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-happens-brain-alzheimers-disease
6. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval for Alzheimer’s drug. News release. Published June 7, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-alzheimers-drug
7. US Food and Drug Administration. Accelerated approval. Updated January 4, 2018. Accessed March 21,2022.https://www.fda.gov/patients/fast-track-breakthrough-therapy-accelerated-approval-priority-review/accelerated-approval
8. Largent EL, Peterson E, Lynch HF. FDA approval and the ethics of desperation. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181(12):1555-1556. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6045
9. Belluck P, Kaplan S, Robbins R. How an unproven Alzheimer’s drug got approved. New York Times, Updated October 21, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/19/health/alzheimers-drug-aduhelm-fda.html
10. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Inspector General. Review of the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000608.asp
11. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease decision summary. Published January 11, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=Y&NCAId=305
12. Gleckman H. What’s behind Biogen’s move to cut prices on its controversial Alzheimer’s drug alduhelm. Forbes. Published December 23, 2021. Accessed March 21,2022. https://www.forbes.com/sites/howardgleckman/2021/12/23/whats-behind-biogens-move-to-cut-prices-on-its-controversial-alzheimers-drug-aduhelm/?sh=498c6a235154
1. Williamson V, Stevelink SAM, Greenberg K, Greenberg N. Prevalence of mental health disorders in elderly U.S. military veterans: a metaanalysis and systematic review. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;26:534-545. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2017.11.001
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of the Assistant Deputy Under Secretary for Health for Policy and Planning. Projections of the prevalence and incidence of dementias. Updated November 5, 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. www.va.gov/geriatrics/GEC_Data_Reports.asp
3. Zhu CW, Sano M. Demographic, health, and exposure risks associated with cognitive loss, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in US military veterans. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:610334. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.610334
4. VHA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, and VISN Pharmacist Executives. Aducanumab-avwa (ADUHELM) National Drug Monograph. Published July 2021. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/drugmonographs/Aducanumab_ADUHELM_monograph_508.pdf
5. National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging. What happens to the brain in Alzheimer’s disease? Updated May 16, 2017. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-happens-brain-alzheimers-disease
6. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval for Alzheimer’s drug. News release. Published June 7, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-alzheimers-drug
7. US Food and Drug Administration. Accelerated approval. Updated January 4, 2018. Accessed March 21,2022.https://www.fda.gov/patients/fast-track-breakthrough-therapy-accelerated-approval-priority-review/accelerated-approval
8. Largent EL, Peterson E, Lynch HF. FDA approval and the ethics of desperation. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181(12):1555-1556. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6045
9. Belluck P, Kaplan S, Robbins R. How an unproven Alzheimer’s drug got approved. New York Times, Updated October 21, 2021. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/19/health/alzheimers-drug-aduhelm-fda.html
10. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Inspector General. Review of the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/summary/wp-summary-0000608.asp
11. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Monoclonal antibodies directed against amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease decision summary. Published January 11, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2022. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=Y&NCAId=305
12. Gleckman H. What’s behind Biogen’s move to cut prices on its controversial Alzheimer’s drug alduhelm. Forbes. Published December 23, 2021. Accessed March 21,2022. https://www.forbes.com/sites/howardgleckman/2021/12/23/whats-behind-biogens-move-to-cut-prices-on-its-controversial-alzheimers-drug-aduhelm/?sh=498c6a235154
Apremilast has neutral effect on vascular inflammation in psoriasis study
BOSTON – Treatment with , and glucose metabolism, in a study presented at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In the phase 4, open-label, single arm trial, participants also lost subcutaneous and visceral fat after 16 weeks on the oral medication, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and maintained that loss at 52 weeks.
People with psoriasis have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Patients with more significant psoriasis “tend to die about 5 years younger than they should, based on their risk factors for mortality,” Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
He led the research and presented the findings at the AAD meeting March 26. “As a result, there has been a keen interest in understanding how psoriasis therapies impact cardiovascular risk, the idea being that by controlling inflammation, you may lower the risk of these patients developing cardiovascular disease over time,” he said.
Previous trials looking at the effect of psoriasis therapies on vascular inflammation “have been, for the most part, inconclusive,” Michael Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at NYU Langone Health, told this news organization. Dr. Garshick was not involved with the research. A 2021 systematic review of psoriasis clinicals trials reported that the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker adalimumab (Humira) and phototherapy had the greatest effect on cardiometabolic markers, while ustekinumab (Stelara), an interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, was the only treatment that improved vascular inflammation. These variable findings make this area “ripe for study,” noted Dr. Garshick.
To observe how apremilast, which is approved by the FDA for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, affected vascular inflammation, adiposity, and blood-based cardiometabolic markers, Dr. Gelfand organized an open-label study in adults with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. All participants were 18 years or older, had psoriasis for at least 6 months, and were candidates for systemic therapy. All patients underwent FDG PET/CT scans to assess aortic vascular inflammation and had blood work at baseline. Of the 70 patients originally enrolled in the study, 60 remained in the study at week 16, including 57 who underwent imaging for the second time. Thirty-nine participants remained in the study until week 52, and all except one had another scan.
The average age of participants was 47 years, and their mean BMI was 30. More than 80% of participants were White (83%) and 77% were male. The study population had lived with psoriasis for an average of 16 years and 8 patients also had psoriatic arthritis. At baseline, on average, participants had a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 18.62, a dermatology life quality index (DLQI) score of 11.60, and 22% of participants’ BSA (body surface area) were affected. The mean TBRmax, the marker for vascular inflammation, was 1.61.
Treatment responses were as expected for apremilast, with 35% of patients achieving PASI 75 and 65% of participants reporting DLQI scores of 5 or less by 16 weeks. At 52 weeks, 31% of the cohort had achieved PASI 75, and 67% reported DLQI score of 5 or higher. All psoriasis endpoints had improved since baseline (P = .001).
Throughout the study period, there was no significant change in TBRmax. However, in a sensitivity analysis, the 16 patients with a baseline TBRmax of 1.6 or higher had an absolute reduction of 0.21 in TBR by week 52. “That suggests that maybe a subset of people who have higher levels of aortic inflammation at baseline may experience some reduction that portend, potentially, some health benefits over time,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Ultimately, I wouldn’t hang my hat on the finding,” he said, noting that additional research comparing the treatment to placebo is necessary.
Both visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue (VAT and SAT) decreased by week 16, and this reduction was maintained through week 52. In the first 16 weeks of the study, VAT decreased by 5.32% (P = .0009), and SAT decreased by 5.53% (P = .0005). From baseline to 52 weeks, VAT decreased by 5.52% (P = .0148), and SAT decreased by 5.50% (P = .0096). There were no significant differences between week 16 and week 52 in VAT or SAT.
Of the 68 blood biomarkers analyzed, there were significant decreases in the inflammatory markers ferritin (P = .015) and IL-beta (P = .006), the lipid metabolism biomarker HDL-cholesterol efflux (P = .008), and ketone bodies (P = .006). There were also increases in the inflammatory marker IL-8 (P = .003), the lipid metabolism marker ApoA (P = .05), and insulin (P = .05). Ferritin was the only biomarker that was reduced on both week 16 and week 52.
“If you want to be a purist, this was a negative trial,” said Dr. Garshick, because apremilast was not found to decrease vascular inflammation; however, he noted that the biomarker changes “were hopeful secondary endpoints.” It could be, he said, that another outcome measure may be better able to show changes in vascular inflammation compared with FDG. “It’s always hard to figure out what a good surrogate endpoint is in cardiovascular trials,” he noted, “so it may be that FDG/PET is too noisy or not reliable enough to see the outcome that we want to see.”
Dr. Gelfand reports consulting fees/grants from Amgen, AbbVie, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biologics, Novartis Corp, Pfizer, and UCB (DSMB). He serves as the Deputy Editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and the Chief Medical Editor at Healio Psoriatic Disease and receives honoraria for both roles. Dr. Garshick has received consulting fees from AbbVie.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – Treatment with , and glucose metabolism, in a study presented at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In the phase 4, open-label, single arm trial, participants also lost subcutaneous and visceral fat after 16 weeks on the oral medication, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and maintained that loss at 52 weeks.
People with psoriasis have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Patients with more significant psoriasis “tend to die about 5 years younger than they should, based on their risk factors for mortality,” Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
He led the research and presented the findings at the AAD meeting March 26. “As a result, there has been a keen interest in understanding how psoriasis therapies impact cardiovascular risk, the idea being that by controlling inflammation, you may lower the risk of these patients developing cardiovascular disease over time,” he said.
Previous trials looking at the effect of psoriasis therapies on vascular inflammation “have been, for the most part, inconclusive,” Michael Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at NYU Langone Health, told this news organization. Dr. Garshick was not involved with the research. A 2021 systematic review of psoriasis clinicals trials reported that the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker adalimumab (Humira) and phototherapy had the greatest effect on cardiometabolic markers, while ustekinumab (Stelara), an interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, was the only treatment that improved vascular inflammation. These variable findings make this area “ripe for study,” noted Dr. Garshick.
To observe how apremilast, which is approved by the FDA for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, affected vascular inflammation, adiposity, and blood-based cardiometabolic markers, Dr. Gelfand organized an open-label study in adults with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. All participants were 18 years or older, had psoriasis for at least 6 months, and were candidates for systemic therapy. All patients underwent FDG PET/CT scans to assess aortic vascular inflammation and had blood work at baseline. Of the 70 patients originally enrolled in the study, 60 remained in the study at week 16, including 57 who underwent imaging for the second time. Thirty-nine participants remained in the study until week 52, and all except one had another scan.
The average age of participants was 47 years, and their mean BMI was 30. More than 80% of participants were White (83%) and 77% were male. The study population had lived with psoriasis for an average of 16 years and 8 patients also had psoriatic arthritis. At baseline, on average, participants had a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 18.62, a dermatology life quality index (DLQI) score of 11.60, and 22% of participants’ BSA (body surface area) were affected. The mean TBRmax, the marker for vascular inflammation, was 1.61.
Treatment responses were as expected for apremilast, with 35% of patients achieving PASI 75 and 65% of participants reporting DLQI scores of 5 or less by 16 weeks. At 52 weeks, 31% of the cohort had achieved PASI 75, and 67% reported DLQI score of 5 or higher. All psoriasis endpoints had improved since baseline (P = .001).
Throughout the study period, there was no significant change in TBRmax. However, in a sensitivity analysis, the 16 patients with a baseline TBRmax of 1.6 or higher had an absolute reduction of 0.21 in TBR by week 52. “That suggests that maybe a subset of people who have higher levels of aortic inflammation at baseline may experience some reduction that portend, potentially, some health benefits over time,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Ultimately, I wouldn’t hang my hat on the finding,” he said, noting that additional research comparing the treatment to placebo is necessary.
Both visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue (VAT and SAT) decreased by week 16, and this reduction was maintained through week 52. In the first 16 weeks of the study, VAT decreased by 5.32% (P = .0009), and SAT decreased by 5.53% (P = .0005). From baseline to 52 weeks, VAT decreased by 5.52% (P = .0148), and SAT decreased by 5.50% (P = .0096). There were no significant differences between week 16 and week 52 in VAT or SAT.
Of the 68 blood biomarkers analyzed, there were significant decreases in the inflammatory markers ferritin (P = .015) and IL-beta (P = .006), the lipid metabolism biomarker HDL-cholesterol efflux (P = .008), and ketone bodies (P = .006). There were also increases in the inflammatory marker IL-8 (P = .003), the lipid metabolism marker ApoA (P = .05), and insulin (P = .05). Ferritin was the only biomarker that was reduced on both week 16 and week 52.
“If you want to be a purist, this was a negative trial,” said Dr. Garshick, because apremilast was not found to decrease vascular inflammation; however, he noted that the biomarker changes “were hopeful secondary endpoints.” It could be, he said, that another outcome measure may be better able to show changes in vascular inflammation compared with FDG. “It’s always hard to figure out what a good surrogate endpoint is in cardiovascular trials,” he noted, “so it may be that FDG/PET is too noisy or not reliable enough to see the outcome that we want to see.”
Dr. Gelfand reports consulting fees/grants from Amgen, AbbVie, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biologics, Novartis Corp, Pfizer, and UCB (DSMB). He serves as the Deputy Editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and the Chief Medical Editor at Healio Psoriatic Disease and receives honoraria for both roles. Dr. Garshick has received consulting fees from AbbVie.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – Treatment with , and glucose metabolism, in a study presented at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
In the phase 4, open-label, single arm trial, participants also lost subcutaneous and visceral fat after 16 weeks on the oral medication, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and maintained that loss at 52 weeks.
People with psoriasis have an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Patients with more significant psoriasis “tend to die about 5 years younger than they should, based on their risk factors for mortality,” Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology and vice chair of clinical research in dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
He led the research and presented the findings at the AAD meeting March 26. “As a result, there has been a keen interest in understanding how psoriasis therapies impact cardiovascular risk, the idea being that by controlling inflammation, you may lower the risk of these patients developing cardiovascular disease over time,” he said.
Previous trials looking at the effect of psoriasis therapies on vascular inflammation “have been, for the most part, inconclusive,” Michael Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at NYU Langone Health, told this news organization. Dr. Garshick was not involved with the research. A 2021 systematic review of psoriasis clinicals trials reported that the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker adalimumab (Humira) and phototherapy had the greatest effect on cardiometabolic markers, while ustekinumab (Stelara), an interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 antagonist, was the only treatment that improved vascular inflammation. These variable findings make this area “ripe for study,” noted Dr. Garshick.
To observe how apremilast, which is approved by the FDA for treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, affected vascular inflammation, adiposity, and blood-based cardiometabolic markers, Dr. Gelfand organized an open-label study in adults with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. All participants were 18 years or older, had psoriasis for at least 6 months, and were candidates for systemic therapy. All patients underwent FDG PET/CT scans to assess aortic vascular inflammation and had blood work at baseline. Of the 70 patients originally enrolled in the study, 60 remained in the study at week 16, including 57 who underwent imaging for the second time. Thirty-nine participants remained in the study until week 52, and all except one had another scan.
The average age of participants was 47 years, and their mean BMI was 30. More than 80% of participants were White (83%) and 77% were male. The study population had lived with psoriasis for an average of 16 years and 8 patients also had psoriatic arthritis. At baseline, on average, participants had a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 18.62, a dermatology life quality index (DLQI) score of 11.60, and 22% of participants’ BSA (body surface area) were affected. The mean TBRmax, the marker for vascular inflammation, was 1.61.
Treatment responses were as expected for apremilast, with 35% of patients achieving PASI 75 and 65% of participants reporting DLQI scores of 5 or less by 16 weeks. At 52 weeks, 31% of the cohort had achieved PASI 75, and 67% reported DLQI score of 5 or higher. All psoriasis endpoints had improved since baseline (P = .001).
Throughout the study period, there was no significant change in TBRmax. However, in a sensitivity analysis, the 16 patients with a baseline TBRmax of 1.6 or higher had an absolute reduction of 0.21 in TBR by week 52. “That suggests that maybe a subset of people who have higher levels of aortic inflammation at baseline may experience some reduction that portend, potentially, some health benefits over time,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Ultimately, I wouldn’t hang my hat on the finding,” he said, noting that additional research comparing the treatment to placebo is necessary.
Both visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue (VAT and SAT) decreased by week 16, and this reduction was maintained through week 52. In the first 16 weeks of the study, VAT decreased by 5.32% (P = .0009), and SAT decreased by 5.53% (P = .0005). From baseline to 52 weeks, VAT decreased by 5.52% (P = .0148), and SAT decreased by 5.50% (P = .0096). There were no significant differences between week 16 and week 52 in VAT or SAT.
Of the 68 blood biomarkers analyzed, there were significant decreases in the inflammatory markers ferritin (P = .015) and IL-beta (P = .006), the lipid metabolism biomarker HDL-cholesterol efflux (P = .008), and ketone bodies (P = .006). There were also increases in the inflammatory marker IL-8 (P = .003), the lipid metabolism marker ApoA (P = .05), and insulin (P = .05). Ferritin was the only biomarker that was reduced on both week 16 and week 52.
“If you want to be a purist, this was a negative trial,” said Dr. Garshick, because apremilast was not found to decrease vascular inflammation; however, he noted that the biomarker changes “were hopeful secondary endpoints.” It could be, he said, that another outcome measure may be better able to show changes in vascular inflammation compared with FDG. “It’s always hard to figure out what a good surrogate endpoint is in cardiovascular trials,” he noted, “so it may be that FDG/PET is too noisy or not reliable enough to see the outcome that we want to see.”
Dr. Gelfand reports consulting fees/grants from Amgen, AbbVie, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biologics, Novartis Corp, Pfizer, and UCB (DSMB). He serves as the Deputy Editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and the Chief Medical Editor at Healio Psoriatic Disease and receives honoraria for both roles. Dr. Garshick has received consulting fees from AbbVie.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2022
COMMENT & CONTROVERSY
UTIs IN PREGNANCY: MANAGING URETHRITIS, ASYMPTOMATIC BACTERIURIA, CYSTITIS, AND PYELONEPHRITIS
PATRICK DUFF, MD (JANUARY 2022)
Clarification on UTI issues
Regarding the article on urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy, I have 3 points of clarification. First, in 27 years of practice in which I universally performed screening urine cultures on prenatal patients plus all of those with symptoms, I have seen a total of 2 cultures with Staphylococcus saprophyticus. I see this organism listed in references as a major UTI causative, but is that the case? Second, the clinical case and symptoms discussed are accurate, but costovertebral angle tenderness or fever of 101 °F or higher indicate pyelonephritis and should be treated aggressively. Many of these patients will have nausea and vomiting and will be dehydrated. This decreases urine flow, allowing progressive bacterial growth in renal parenchyma. An initial bolus of intravenous fluids, at least 2 L wide open through a large-bore catheter, rapidly decreases fever, flushes the urinary tract, and improves nausea, headaches, and malaise. Finally, nitrofurantoin is excreted in the urine so rapidly that it does not achieve adequate tissue levels, and it should never be used to treat pyelonephritis or, for that matter, any infection other than uncomplicated cystitis/urethritis.
David Janowitz, MD
Houston, Texas
Dr. Duff responds
I appreciate Dr. Janowitz’s interest and thoughtful comments. The patient presented in the case study has acute cystitis, characterized by a low-grade fever, suprapubic pain, dysuria, frequency, and hesitancy. Patients with pyelonephritis typically have a higher fever and significant costovertebral angle pain and tenderness. I agree completely with Dr. Janowitz’s observations about the seriousness of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. Pyelonephritis is an important cause of preterm labor, bacteremia, and even septic shock. As I point out in the article, women with moderate to severe kidney infections should be hospitalized and treated with intravenous fluids, antipyretics, antiemetics, and intravenous antibiotics. My usual recommendation is ceftriaxone. Intravenous antibiotics should be continued until the patient has been afebrile and asymptomatic for 24 to 48 hours. Once patients improve, they can be transitioned to oral antibiotics to complete a 10-day course of therapy. Again, I agree with Dr. Janowitz’s statement that nitrofurantoin is not an appropriate drug for treatment of pyelonephritis because it does not reach acceptable concentrations in either the blood or the renal parenchyma. Rather, amoxicillin-clavulanate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are much better choices for oral therapy. However, once the infection is cleared, nitrofurantoin is an excellent agent for suppression of recurrent infection.
Finally, there is no doubt that the principal pathogens that cause UTIs in pregnant women are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus species. However, 3 aerobic Gram-positive cocci do, in fact, cause a small percentage of infections: group B streptococci, enterococci, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. When the latter bacterium is identified as a single organism in high colony count, particularly in a catheterized urine specimen, it should be considered a true pathogen and not simply a contaminant.
CAN WE RETURN TO THE ABCs OF CRAFTING A MEDICAL RECORD NOTE?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (OCTOBER 2021)
Another suggestion for reducing note bloat in the EMR
Thank you for picking up a topic that is important for all physicians and one that has been annoying me since the introduction of electronic medical records (EMRs). I like the APSO approach, that works well. My idea for reducing “note bloat” is to eliminate all normal and routine findings and to hide them behind a hyperlink or behind a QR code. This would give you a truly short note and, should you need or want more details, you could always scan the QR code for access to the complete (and bloated) note. I would also recommend hiding all details that do not contribute to the immediate pressing issue at hand (for example, routine depression screening) behind a hyperlink or QR code. The same principle should apply to sending faxes to other physicians’ offices. I “love” receiving a chart an inch thick, only to discover that the whole pile of paper could be reduced to a single page of true information. Too few people speak up about this major time and productivity thief. Thank you!
Matthias Muenzer, MD
Rochester, New Hampshire
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Muenzer for his innovative suggestions for improving medical record notes. We spend many hours per week crafting notes in the medical record. Yet, very little attention is given to the development of best practices for improving the value and effectiveness of our notes for our patients and colleagues.
UTIs IN PREGNANCY: MANAGING URETHRITIS, ASYMPTOMATIC BACTERIURIA, CYSTITIS, AND PYELONEPHRITIS
PATRICK DUFF, MD (JANUARY 2022)
Clarification on UTI issues
Regarding the article on urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy, I have 3 points of clarification. First, in 27 years of practice in which I universally performed screening urine cultures on prenatal patients plus all of those with symptoms, I have seen a total of 2 cultures with Staphylococcus saprophyticus. I see this organism listed in references as a major UTI causative, but is that the case? Second, the clinical case and symptoms discussed are accurate, but costovertebral angle tenderness or fever of 101 °F or higher indicate pyelonephritis and should be treated aggressively. Many of these patients will have nausea and vomiting and will be dehydrated. This decreases urine flow, allowing progressive bacterial growth in renal parenchyma. An initial bolus of intravenous fluids, at least 2 L wide open through a large-bore catheter, rapidly decreases fever, flushes the urinary tract, and improves nausea, headaches, and malaise. Finally, nitrofurantoin is excreted in the urine so rapidly that it does not achieve adequate tissue levels, and it should never be used to treat pyelonephritis or, for that matter, any infection other than uncomplicated cystitis/urethritis.
David Janowitz, MD
Houston, Texas
Dr. Duff responds
I appreciate Dr. Janowitz’s interest and thoughtful comments. The patient presented in the case study has acute cystitis, characterized by a low-grade fever, suprapubic pain, dysuria, frequency, and hesitancy. Patients with pyelonephritis typically have a higher fever and significant costovertebral angle pain and tenderness. I agree completely with Dr. Janowitz’s observations about the seriousness of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. Pyelonephritis is an important cause of preterm labor, bacteremia, and even septic shock. As I point out in the article, women with moderate to severe kidney infections should be hospitalized and treated with intravenous fluids, antipyretics, antiemetics, and intravenous antibiotics. My usual recommendation is ceftriaxone. Intravenous antibiotics should be continued until the patient has been afebrile and asymptomatic for 24 to 48 hours. Once patients improve, they can be transitioned to oral antibiotics to complete a 10-day course of therapy. Again, I agree with Dr. Janowitz’s statement that nitrofurantoin is not an appropriate drug for treatment of pyelonephritis because it does not reach acceptable concentrations in either the blood or the renal parenchyma. Rather, amoxicillin-clavulanate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are much better choices for oral therapy. However, once the infection is cleared, nitrofurantoin is an excellent agent for suppression of recurrent infection.
Finally, there is no doubt that the principal pathogens that cause UTIs in pregnant women are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus species. However, 3 aerobic Gram-positive cocci do, in fact, cause a small percentage of infections: group B streptococci, enterococci, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. When the latter bacterium is identified as a single organism in high colony count, particularly in a catheterized urine specimen, it should be considered a true pathogen and not simply a contaminant.
CAN WE RETURN TO THE ABCs OF CRAFTING A MEDICAL RECORD NOTE?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (OCTOBER 2021)
Another suggestion for reducing note bloat in the EMR
Thank you for picking up a topic that is important for all physicians and one that has been annoying me since the introduction of electronic medical records (EMRs). I like the APSO approach, that works well. My idea for reducing “note bloat” is to eliminate all normal and routine findings and to hide them behind a hyperlink or behind a QR code. This would give you a truly short note and, should you need or want more details, you could always scan the QR code for access to the complete (and bloated) note. I would also recommend hiding all details that do not contribute to the immediate pressing issue at hand (for example, routine depression screening) behind a hyperlink or QR code. The same principle should apply to sending faxes to other physicians’ offices. I “love” receiving a chart an inch thick, only to discover that the whole pile of paper could be reduced to a single page of true information. Too few people speak up about this major time and productivity thief. Thank you!
Matthias Muenzer, MD
Rochester, New Hampshire
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Muenzer for his innovative suggestions for improving medical record notes. We spend many hours per week crafting notes in the medical record. Yet, very little attention is given to the development of best practices for improving the value and effectiveness of our notes for our patients and colleagues.
UTIs IN PREGNANCY: MANAGING URETHRITIS, ASYMPTOMATIC BACTERIURIA, CYSTITIS, AND PYELONEPHRITIS
PATRICK DUFF, MD (JANUARY 2022)
Clarification on UTI issues
Regarding the article on urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy, I have 3 points of clarification. First, in 27 years of practice in which I universally performed screening urine cultures on prenatal patients plus all of those with symptoms, I have seen a total of 2 cultures with Staphylococcus saprophyticus. I see this organism listed in references as a major UTI causative, but is that the case? Second, the clinical case and symptoms discussed are accurate, but costovertebral angle tenderness or fever of 101 °F or higher indicate pyelonephritis and should be treated aggressively. Many of these patients will have nausea and vomiting and will be dehydrated. This decreases urine flow, allowing progressive bacterial growth in renal parenchyma. An initial bolus of intravenous fluids, at least 2 L wide open through a large-bore catheter, rapidly decreases fever, flushes the urinary tract, and improves nausea, headaches, and malaise. Finally, nitrofurantoin is excreted in the urine so rapidly that it does not achieve adequate tissue levels, and it should never be used to treat pyelonephritis or, for that matter, any infection other than uncomplicated cystitis/urethritis.
David Janowitz, MD
Houston, Texas
Dr. Duff responds
I appreciate Dr. Janowitz’s interest and thoughtful comments. The patient presented in the case study has acute cystitis, characterized by a low-grade fever, suprapubic pain, dysuria, frequency, and hesitancy. Patients with pyelonephritis typically have a higher fever and significant costovertebral angle pain and tenderness. I agree completely with Dr. Janowitz’s observations about the seriousness of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. Pyelonephritis is an important cause of preterm labor, bacteremia, and even septic shock. As I point out in the article, women with moderate to severe kidney infections should be hospitalized and treated with intravenous fluids, antipyretics, antiemetics, and intravenous antibiotics. My usual recommendation is ceftriaxone. Intravenous antibiotics should be continued until the patient has been afebrile and asymptomatic for 24 to 48 hours. Once patients improve, they can be transitioned to oral antibiotics to complete a 10-day course of therapy. Again, I agree with Dr. Janowitz’s statement that nitrofurantoin is not an appropriate drug for treatment of pyelonephritis because it does not reach acceptable concentrations in either the blood or the renal parenchyma. Rather, amoxicillin-clavulanate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are much better choices for oral therapy. However, once the infection is cleared, nitrofurantoin is an excellent agent for suppression of recurrent infection.
Finally, there is no doubt that the principal pathogens that cause UTIs in pregnant women are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus species. However, 3 aerobic Gram-positive cocci do, in fact, cause a small percentage of infections: group B streptococci, enterococci, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. When the latter bacterium is identified as a single organism in high colony count, particularly in a catheterized urine specimen, it should be considered a true pathogen and not simply a contaminant.
CAN WE RETURN TO THE ABCs OF CRAFTING A MEDICAL RECORD NOTE?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (OCTOBER 2021)
Another suggestion for reducing note bloat in the EMR
Thank you for picking up a topic that is important for all physicians and one that has been annoying me since the introduction of electronic medical records (EMRs). I like the APSO approach, that works well. My idea for reducing “note bloat” is to eliminate all normal and routine findings and to hide them behind a hyperlink or behind a QR code. This would give you a truly short note and, should you need or want more details, you could always scan the QR code for access to the complete (and bloated) note. I would also recommend hiding all details that do not contribute to the immediate pressing issue at hand (for example, routine depression screening) behind a hyperlink or QR code. The same principle should apply to sending faxes to other physicians’ offices. I “love” receiving a chart an inch thick, only to discover that the whole pile of paper could be reduced to a single page of true information. Too few people speak up about this major time and productivity thief. Thank you!
Matthias Muenzer, MD
Rochester, New Hampshire
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Muenzer for his innovative suggestions for improving medical record notes. We spend many hours per week crafting notes in the medical record. Yet, very little attention is given to the development of best practices for improving the value and effectiveness of our notes for our patients and colleagues.
May 2022 - ICYMI
Gastroenterology
February 2022
How to Succeed in Digestive Research
Sonnenberg A, Inadomi JM. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):385-389. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.229.
Incidence and Mortality in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer After Negative Endoscopy for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Holmberg H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):431-438.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.003.
March 2022
Global Prevalence and Impact of Rumination Syndrome
Josefsson A et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):731-742.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.008.
A Clinical Approach to Chronic Diarrhea
Dutra B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):707-709. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.038.
Timeline of Development of Pancreatic Cancer and Implications for Successful Early Detection in High-Risk Individuals
Overbeek KA et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):772-785.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.014.
April 2022
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning for Upper Gastrointestinal Neoplasia
Sharma P, Hassan C. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1056-1066. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.040.
Associations of Body Mass Index at Different Ages With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Li H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1088-1097.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.239.
Inadequate Rectal Pressure and Insufficient Relaxation and Abdominopelvic Coordination in Defecatory Disorders
Deb B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1111-1122.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.257.
AGA Clinical Practice Update on De-Prescribing of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review
Targownik LE et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1334-1342. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
February 2022
Restarting Warfarin vs Direct Oral Anticoagulants After Major Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Associated Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation: A Cohort Study
Tapaskar N et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):381-389.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.11.029.
Cancer Risk in 47,241 Individuals With Celiac Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Lebwohl B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):e111-e131. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.034.
Main Duct Thresholds for Malignancy Are Different in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreatic Head and Body-Tail
Crippa S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):390-399.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.12.028.
Frequency of Bowel Movements and Risk of Diverticulitis
Jovani M et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):325-333.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.003.
March 2022
AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Expert Review
Lacy BE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.10.038.
Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Ulcerative Colitis Based on Prior Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Failure Status
Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):591-601.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.043.
April 2022
What Faculty and Fellows Should Know About Milestones 2.0
Donnangelo JL, Brijen SJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):720-722. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.017.
Patient Experience in the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Unit
Day LW, Savides TJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):723-726. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.001.
Tailoring Surveillance Colonoscopy in Patients With Advanced Adenomas
Kahi CJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):847-854.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.027.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Primary CT Angiography Vs Colonoscopy in Acute Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
Lipcsey MS et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Jan 01;24(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2021.11.004.
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology
The Role of Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Cancer Treatment: Chance or Curse?
Smet A et al. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(3):857-874. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.08.013.
Gastroenterology
February 2022
How to Succeed in Digestive Research
Sonnenberg A, Inadomi JM. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):385-389. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.229.
Incidence and Mortality in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer After Negative Endoscopy for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Holmberg H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):431-438.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.003.
March 2022
Global Prevalence and Impact of Rumination Syndrome
Josefsson A et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):731-742.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.008.
A Clinical Approach to Chronic Diarrhea
Dutra B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):707-709. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.038.
Timeline of Development of Pancreatic Cancer and Implications for Successful Early Detection in High-Risk Individuals
Overbeek KA et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):772-785.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.014.
April 2022
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning for Upper Gastrointestinal Neoplasia
Sharma P, Hassan C. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1056-1066. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.040.
Associations of Body Mass Index at Different Ages With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Li H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1088-1097.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.239.
Inadequate Rectal Pressure and Insufficient Relaxation and Abdominopelvic Coordination in Defecatory Disorders
Deb B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1111-1122.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.257.
AGA Clinical Practice Update on De-Prescribing of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review
Targownik LE et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1334-1342. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
February 2022
Restarting Warfarin vs Direct Oral Anticoagulants After Major Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Associated Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation: A Cohort Study
Tapaskar N et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):381-389.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.11.029.
Cancer Risk in 47,241 Individuals With Celiac Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Lebwohl B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):e111-e131. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.034.
Main Duct Thresholds for Malignancy Are Different in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreatic Head and Body-Tail
Crippa S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):390-399.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.12.028.
Frequency of Bowel Movements and Risk of Diverticulitis
Jovani M et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):325-333.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.003.
March 2022
AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Expert Review
Lacy BE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.10.038.
Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Ulcerative Colitis Based on Prior Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Failure Status
Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):591-601.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.043.
April 2022
What Faculty and Fellows Should Know About Milestones 2.0
Donnangelo JL, Brijen SJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):720-722. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.017.
Patient Experience in the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Unit
Day LW, Savides TJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):723-726. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.001.
Tailoring Surveillance Colonoscopy in Patients With Advanced Adenomas
Kahi CJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):847-854.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.027.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Primary CT Angiography Vs Colonoscopy in Acute Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
Lipcsey MS et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Jan 01;24(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2021.11.004.
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology
The Role of Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Cancer Treatment: Chance or Curse?
Smet A et al. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(3):857-874. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.08.013.
Gastroenterology
February 2022
How to Succeed in Digestive Research
Sonnenberg A, Inadomi JM. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):385-389. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.229.
Incidence and Mortality in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer After Negative Endoscopy for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Holmberg H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):431-438.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.003.
March 2022
Global Prevalence and Impact of Rumination Syndrome
Josefsson A et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):731-742.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.008.
A Clinical Approach to Chronic Diarrhea
Dutra B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):707-709. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.038.
Timeline of Development of Pancreatic Cancer and Implications for Successful Early Detection in High-Risk Individuals
Overbeek KA et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):772-785.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.014.
April 2022
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning for Upper Gastrointestinal Neoplasia
Sharma P, Hassan C. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1056-1066. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.040.
Associations of Body Mass Index at Different Ages With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Li H et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1088-1097.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.239.
Inadequate Rectal Pressure and Insufficient Relaxation and Abdominopelvic Coordination in Defecatory Disorders
Deb B et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1111-1122.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.257.
AGA Clinical Practice Update on De-Prescribing of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review
Targownik LE et al. Gastroenterology. 2022 Apr;162(4):1334-1342. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
February 2022
Restarting Warfarin vs Direct Oral Anticoagulants After Major Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Associated Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation: A Cohort Study
Tapaskar N et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):381-389.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.11.029.
Cancer Risk in 47,241 Individuals With Celiac Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Lebwohl B et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):e111-e131. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.034.
Main Duct Thresholds for Malignancy Are Different in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreatic Head and Body-Tail
Crippa S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):390-399.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.12.028.
Frequency of Bowel Movements and Risk of Diverticulitis
Jovani M et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Feb;20(2):325-333.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.003.
March 2022
AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Expert Review
Lacy BE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.10.038.
Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Ulcerative Colitis Based on Prior Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Failure Status
Sandborn WJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar;20(3):591-601.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.02.043.
April 2022
What Faculty and Fellows Should Know About Milestones 2.0
Donnangelo JL, Brijen SJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):720-722. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.017.
Patient Experience in the Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Unit
Day LW, Savides TJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):723-726. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.001.
Tailoring Surveillance Colonoscopy in Patients With Advanced Adenomas
Kahi CJ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Apr;20(4):847-854.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.027.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Primary CT Angiography Vs Colonoscopy in Acute Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
Lipcsey MS et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Jan 01;24(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2021.11.004.
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology
The Role of Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Cancer Treatment: Chance or Curse?
Smet A et al. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(3):857-874. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.08.013.
Residency Roundup: Introducing a New Partnership Between Cutis and the APD-RPDS
We are excited to announce a new partnership between Cutis and the Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section (APD-RPDS). The new APD-RPDS column Residency Roundup will contain quarterly communications and submissions that we hope will facilitate greater dissemination of information that is useful to the dermatology teaching community.
The APD is a group of academic dermatologists whose membership comprises chairs, chiefs, residency and fellowship program directors, and teaching faculty. Each fall, the group convenes in Chicago, Illinois, for a 2-day meeting centered around departmental and program leadership with a focus on education. The APD-RPDS was formed in 2020 and is led by a steering committee of 9 members, including our current Chair, Ilana S. Rosman, MD (Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri), and Vice Chair, Jo-Ann M. Latkowski, MD (New York University, New York). Committee members are elected from and by the APD membership and must serve in program leadership at their home programs. The APD-RPDS helps plan and coordinate breakout sessions and lectures at the annual APD meeting, which typically relate to program director duties, changing policies within the American Board of Dermatology or Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, ideas for future growth, and changes in our specialty and in resident education. Members of the APD-RPDS have access to the APD listserv, a valuable resource for discussing issues affecting residency training. We also have work groups led by our members, which include diversity, equity, and inclusion; resource development; communications; and the annual survey. To join the APD, the RPDS, and/or any of our workgroups, please reach out to us or visit the APD website (https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org).
We look forward to welcoming and expediently reviewing members’ submissions to the new Residency Roundup column falling into 2 principal categories within the scope of dermatologic recruitment, didactic education, and clinical training. The first category will feature novel tools, programs, and platforms to improve dermatology training through collaboration. This could entail a description of a new platform designed for sharing resources among programs and specialties to enhance learning for trainees and faculty alike. For example, if a database is created that contains prerecorded lectures pertaining to alopecia, a potential article submission might introduce the database and provide information on what topics are covered and how to access these lectures for readers worldwide. Likewise, if a new technology emerges that allows for easier collaboration among programs, a possible submission would introduce the technology and discuss its potential benefits to trainees, faculty, and practicing dermatologists.
Secondly and more commonly, we anticipate the Residency Roundup column will feature articles that delve into the critical issues and challenges currently impacting recruitment, training, and administration in dermatology residency programs. Specific topics may include but are not limited to recruitment of underrepresented in medicine applicants to dermatology, technological advances to improve teaching methods within training programs, surveys delving into the dermatology match process, and educational gaps or future directions in the specialty. The column occasionally may be used to disseminate information from our section of the APD, including consensus statements or editorials related to changes implemented in the dermatology residency application process. A prospective editorial on this subject could explore varying viewpoints of implemented and proposed changes as well as the reasons behind the changes.
Our group is collaborative, and our aim is to improve education, equity, management of program director responsibilities, and the dermatology application process for programs and applicants alike. With your input, experience, and varied perspectives, we look forward to moving the field of dermatology to a better future by working together.
We are excited to announce a new partnership between Cutis and the Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section (APD-RPDS). The new APD-RPDS column Residency Roundup will contain quarterly communications and submissions that we hope will facilitate greater dissemination of information that is useful to the dermatology teaching community.
The APD is a group of academic dermatologists whose membership comprises chairs, chiefs, residency and fellowship program directors, and teaching faculty. Each fall, the group convenes in Chicago, Illinois, for a 2-day meeting centered around departmental and program leadership with a focus on education. The APD-RPDS was formed in 2020 and is led by a steering committee of 9 members, including our current Chair, Ilana S. Rosman, MD (Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri), and Vice Chair, Jo-Ann M. Latkowski, MD (New York University, New York). Committee members are elected from and by the APD membership and must serve in program leadership at their home programs. The APD-RPDS helps plan and coordinate breakout sessions and lectures at the annual APD meeting, which typically relate to program director duties, changing policies within the American Board of Dermatology or Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, ideas for future growth, and changes in our specialty and in resident education. Members of the APD-RPDS have access to the APD listserv, a valuable resource for discussing issues affecting residency training. We also have work groups led by our members, which include diversity, equity, and inclusion; resource development; communications; and the annual survey. To join the APD, the RPDS, and/or any of our workgroups, please reach out to us or visit the APD website (https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org).
We look forward to welcoming and expediently reviewing members’ submissions to the new Residency Roundup column falling into 2 principal categories within the scope of dermatologic recruitment, didactic education, and clinical training. The first category will feature novel tools, programs, and platforms to improve dermatology training through collaboration. This could entail a description of a new platform designed for sharing resources among programs and specialties to enhance learning for trainees and faculty alike. For example, if a database is created that contains prerecorded lectures pertaining to alopecia, a potential article submission might introduce the database and provide information on what topics are covered and how to access these lectures for readers worldwide. Likewise, if a new technology emerges that allows for easier collaboration among programs, a possible submission would introduce the technology and discuss its potential benefits to trainees, faculty, and practicing dermatologists.
Secondly and more commonly, we anticipate the Residency Roundup column will feature articles that delve into the critical issues and challenges currently impacting recruitment, training, and administration in dermatology residency programs. Specific topics may include but are not limited to recruitment of underrepresented in medicine applicants to dermatology, technological advances to improve teaching methods within training programs, surveys delving into the dermatology match process, and educational gaps or future directions in the specialty. The column occasionally may be used to disseminate information from our section of the APD, including consensus statements or editorials related to changes implemented in the dermatology residency application process. A prospective editorial on this subject could explore varying viewpoints of implemented and proposed changes as well as the reasons behind the changes.
Our group is collaborative, and our aim is to improve education, equity, management of program director responsibilities, and the dermatology application process for programs and applicants alike. With your input, experience, and varied perspectives, we look forward to moving the field of dermatology to a better future by working together.
We are excited to announce a new partnership between Cutis and the Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section (APD-RPDS). The new APD-RPDS column Residency Roundup will contain quarterly communications and submissions that we hope will facilitate greater dissemination of information that is useful to the dermatology teaching community.
The APD is a group of academic dermatologists whose membership comprises chairs, chiefs, residency and fellowship program directors, and teaching faculty. Each fall, the group convenes in Chicago, Illinois, for a 2-day meeting centered around departmental and program leadership with a focus on education. The APD-RPDS was formed in 2020 and is led by a steering committee of 9 members, including our current Chair, Ilana S. Rosman, MD (Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri), and Vice Chair, Jo-Ann M. Latkowski, MD (New York University, New York). Committee members are elected from and by the APD membership and must serve in program leadership at their home programs. The APD-RPDS helps plan and coordinate breakout sessions and lectures at the annual APD meeting, which typically relate to program director duties, changing policies within the American Board of Dermatology or Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, ideas for future growth, and changes in our specialty and in resident education. Members of the APD-RPDS have access to the APD listserv, a valuable resource for discussing issues affecting residency training. We also have work groups led by our members, which include diversity, equity, and inclusion; resource development; communications; and the annual survey. To join the APD, the RPDS, and/or any of our workgroups, please reach out to us or visit the APD website (https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org).
We look forward to welcoming and expediently reviewing members’ submissions to the new Residency Roundup column falling into 2 principal categories within the scope of dermatologic recruitment, didactic education, and clinical training. The first category will feature novel tools, programs, and platforms to improve dermatology training through collaboration. This could entail a description of a new platform designed for sharing resources among programs and specialties to enhance learning for trainees and faculty alike. For example, if a database is created that contains prerecorded lectures pertaining to alopecia, a potential article submission might introduce the database and provide information on what topics are covered and how to access these lectures for readers worldwide. Likewise, if a new technology emerges that allows for easier collaboration among programs, a possible submission would introduce the technology and discuss its potential benefits to trainees, faculty, and practicing dermatologists.
Secondly and more commonly, we anticipate the Residency Roundup column will feature articles that delve into the critical issues and challenges currently impacting recruitment, training, and administration in dermatology residency programs. Specific topics may include but are not limited to recruitment of underrepresented in medicine applicants to dermatology, technological advances to improve teaching methods within training programs, surveys delving into the dermatology match process, and educational gaps or future directions in the specialty. The column occasionally may be used to disseminate information from our section of the APD, including consensus statements or editorials related to changes implemented in the dermatology residency application process. A prospective editorial on this subject could explore varying viewpoints of implemented and proposed changes as well as the reasons behind the changes.
Our group is collaborative, and our aim is to improve education, equity, management of program director responsibilities, and the dermatology application process for programs and applicants alike. With your input, experience, and varied perspectives, we look forward to moving the field of dermatology to a better future by working together.