User login
December 2018
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
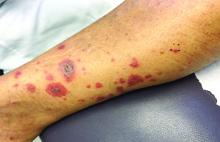
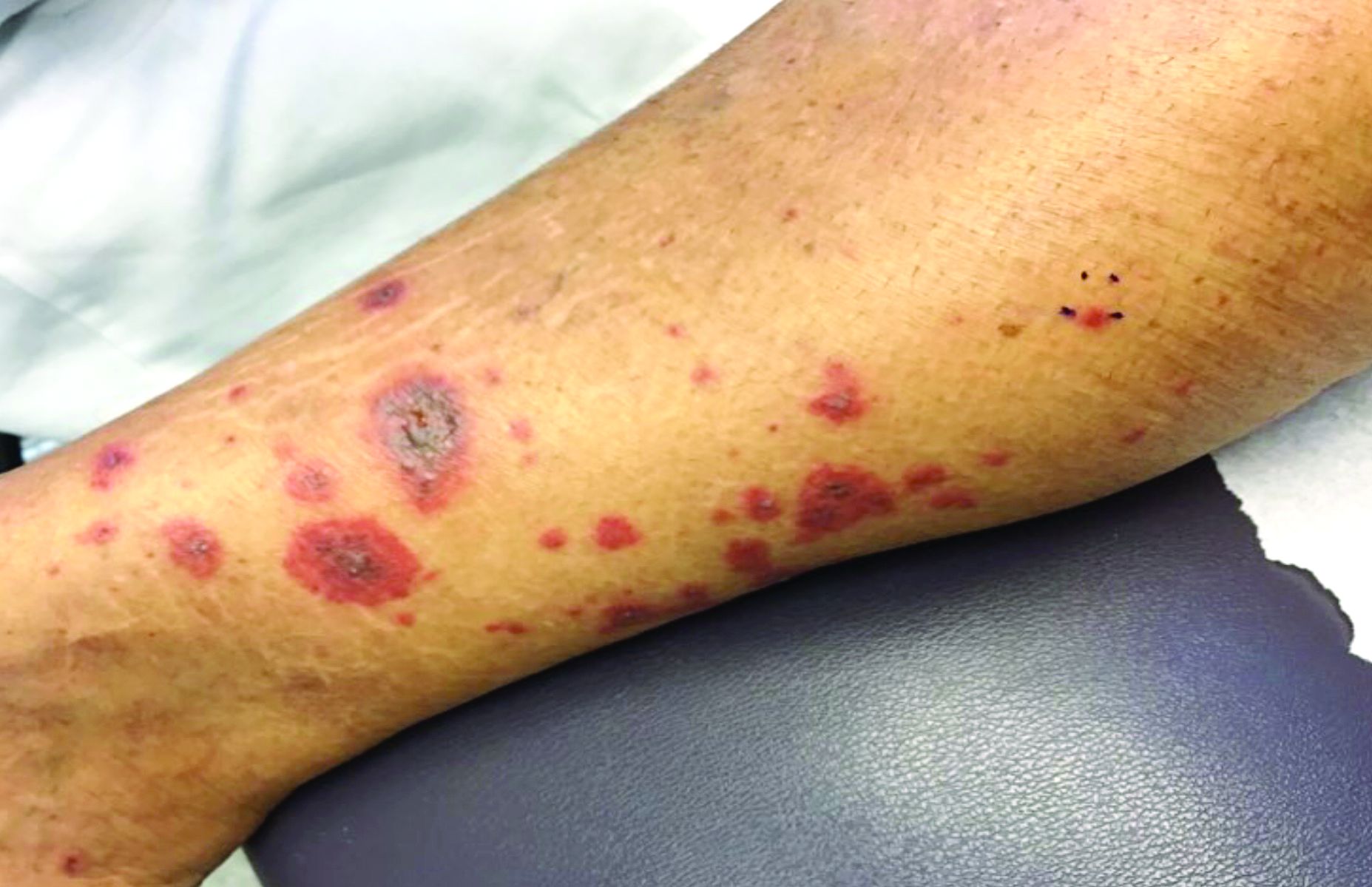
A 63-year-old white female presented with a 2-week history of hemorrhagic purpuric lesions and necrotic vesicles on the bilateral lower extremities.
Nearly 1 year prior to presentation, the patient underwent surgical resection for lung cancer. The patient also complained of joint swelling and pain in her ankles. She denied abdominal pain. She denied recent illness, including sore throat and upper respiratory infection. Skin biopsies were performed, including for direct immunofluorescence.
Novel SSc classification scheme aims to improve risk stratification
CHICAGO – A simple new classification scheme that combines autoantibody specificity and extent of skin involvement could improve risk stratification of patients with systemic sclerosis, according to researchers at University College London.
“The Le Roy et al. classification of SSc [systemic sclerosis] into limited and diffuse cutaneous subtype remains the most commonly used classification system for systemic sclerosis, but autoantibodies are much better predictors of organ involvement, and while more sophisticated approaches exist, this proposed simple classification using antibodies and skin subset is relevant to clinical practice and could help risk stratification,” Svetlana I. Nihtyanova, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Nihtyanova, a clinical research fellow at University College London, reported how she and her colleagues at UCL divided 1,025 SSc patients into 12 subgroups based on skin subset and autoantibodies and then conducted Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival and cumulative incidence of organ complications to rank these 12 subgroups by endpoint estimates. They merged subgroups with similar ranking in multiple endpoints, ending up with seven groups in the final classification.
Group 1 comprised anti–centromere antibody–positive limited cutaneous SSc (lcSSc) patients and accounted for 29% of patients.
“This was the subgroup with the highest survival (72%) and the lowest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (13%) and scleroderma renal crisis (no cases) at 20 years from onset,” she said, noting that the incidence of pulmonary hypertension in this group was similar to the average for the whole cohort.
Group 2 comprised all anti–RNA polymerase antibody–positive subjects and accounted for 11% of patients. This group had the highest incidence of scleroderma renal crisis (SRC; 32% at 20 years), but other organ complications and survival were similar to the cohort average.
Group 3 comprised Scl-70–positive lcSSc patients, and accounted for 11% of patients.
“Although incidence of pulmonary fibrosis in this group was the second highest (69% at 20 years), other complications were rare,” Dr. Nihtyanova said, adding that this group had the lowest incidence of pulmonary hypertension (6%) and the second lowest incidence of SRC (3%) at 20 years.
Group 4, conversely, included Scl-70–positive dcSSc patients and accounted for 11% of patients, who had a very poor prognosis; they had the highest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (91%) and cardiac scleroderma (14%), and the worst survival (41%) at 20 years, she said.
Group 5 included all U3 RNP–positive patients, accounting for 5% of patients.
“Although survival in this group was not bad (70% at 20 years), the group had the highest pulmonary hypertension incidence (40%) and the second highest incidence of cardiac SSc (11%) at 20 years,” she noted.
Groups 6 and 7 (comprising 22% and 11% of study subjects, respectively) included lcSSc and diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) patients with other antibody specificities. Group 6 had low overall SRC and cardiac SSc risk, while other outcomes were similar to the cohort average. Group 7, however, had poor prognosis, with the second lowest survival (42% at 20 years) and above average rates of organ disease, particularly pulmonary fibrosis and SRC, she said.
Overall, estimated survival for the entire cohort was 60% at 20 years from onset, and in that time frame 44% developed significant pulmonary fibrosis, 25% pulmonary hypertension, 7% SRC, and 6% cardiac SSc. The patients had a mean age of 47 years at disease onset, and 16% were men. Diffuse cutaneous SSc was diagnosed in 35% of the subjects, she noted.
Dr. Nihtyanova reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nihtyanova S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2935.
CHICAGO – A simple new classification scheme that combines autoantibody specificity and extent of skin involvement could improve risk stratification of patients with systemic sclerosis, according to researchers at University College London.
“The Le Roy et al. classification of SSc [systemic sclerosis] into limited and diffuse cutaneous subtype remains the most commonly used classification system for systemic sclerosis, but autoantibodies are much better predictors of organ involvement, and while more sophisticated approaches exist, this proposed simple classification using antibodies and skin subset is relevant to clinical practice and could help risk stratification,” Svetlana I. Nihtyanova, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Nihtyanova, a clinical research fellow at University College London, reported how she and her colleagues at UCL divided 1,025 SSc patients into 12 subgroups based on skin subset and autoantibodies and then conducted Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival and cumulative incidence of organ complications to rank these 12 subgroups by endpoint estimates. They merged subgroups with similar ranking in multiple endpoints, ending up with seven groups in the final classification.
Group 1 comprised anti–centromere antibody–positive limited cutaneous SSc (lcSSc) patients and accounted for 29% of patients.
“This was the subgroup with the highest survival (72%) and the lowest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (13%) and scleroderma renal crisis (no cases) at 20 years from onset,” she said, noting that the incidence of pulmonary hypertension in this group was similar to the average for the whole cohort.
Group 2 comprised all anti–RNA polymerase antibody–positive subjects and accounted for 11% of patients. This group had the highest incidence of scleroderma renal crisis (SRC; 32% at 20 years), but other organ complications and survival were similar to the cohort average.
Group 3 comprised Scl-70–positive lcSSc patients, and accounted for 11% of patients.
“Although incidence of pulmonary fibrosis in this group was the second highest (69% at 20 years), other complications were rare,” Dr. Nihtyanova said, adding that this group had the lowest incidence of pulmonary hypertension (6%) and the second lowest incidence of SRC (3%) at 20 years.
Group 4, conversely, included Scl-70–positive dcSSc patients and accounted for 11% of patients, who had a very poor prognosis; they had the highest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (91%) and cardiac scleroderma (14%), and the worst survival (41%) at 20 years, she said.
Group 5 included all U3 RNP–positive patients, accounting for 5% of patients.
“Although survival in this group was not bad (70% at 20 years), the group had the highest pulmonary hypertension incidence (40%) and the second highest incidence of cardiac SSc (11%) at 20 years,” she noted.
Groups 6 and 7 (comprising 22% and 11% of study subjects, respectively) included lcSSc and diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) patients with other antibody specificities. Group 6 had low overall SRC and cardiac SSc risk, while other outcomes were similar to the cohort average. Group 7, however, had poor prognosis, with the second lowest survival (42% at 20 years) and above average rates of organ disease, particularly pulmonary fibrosis and SRC, she said.
Overall, estimated survival for the entire cohort was 60% at 20 years from onset, and in that time frame 44% developed significant pulmonary fibrosis, 25% pulmonary hypertension, 7% SRC, and 6% cardiac SSc. The patients had a mean age of 47 years at disease onset, and 16% were men. Diffuse cutaneous SSc was diagnosed in 35% of the subjects, she noted.
Dr. Nihtyanova reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nihtyanova S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2935.
CHICAGO – A simple new classification scheme that combines autoantibody specificity and extent of skin involvement could improve risk stratification of patients with systemic sclerosis, according to researchers at University College London.
“The Le Roy et al. classification of SSc [systemic sclerosis] into limited and diffuse cutaneous subtype remains the most commonly used classification system for systemic sclerosis, but autoantibodies are much better predictors of organ involvement, and while more sophisticated approaches exist, this proposed simple classification using antibodies and skin subset is relevant to clinical practice and could help risk stratification,” Svetlana I. Nihtyanova, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Nihtyanova, a clinical research fellow at University College London, reported how she and her colleagues at UCL divided 1,025 SSc patients into 12 subgroups based on skin subset and autoantibodies and then conducted Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival and cumulative incidence of organ complications to rank these 12 subgroups by endpoint estimates. They merged subgroups with similar ranking in multiple endpoints, ending up with seven groups in the final classification.
Group 1 comprised anti–centromere antibody–positive limited cutaneous SSc (lcSSc) patients and accounted for 29% of patients.
“This was the subgroup with the highest survival (72%) and the lowest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (13%) and scleroderma renal crisis (no cases) at 20 years from onset,” she said, noting that the incidence of pulmonary hypertension in this group was similar to the average for the whole cohort.
Group 2 comprised all anti–RNA polymerase antibody–positive subjects and accounted for 11% of patients. This group had the highest incidence of scleroderma renal crisis (SRC; 32% at 20 years), but other organ complications and survival were similar to the cohort average.
Group 3 comprised Scl-70–positive lcSSc patients, and accounted for 11% of patients.
“Although incidence of pulmonary fibrosis in this group was the second highest (69% at 20 years), other complications were rare,” Dr. Nihtyanova said, adding that this group had the lowest incidence of pulmonary hypertension (6%) and the second lowest incidence of SRC (3%) at 20 years.
Group 4, conversely, included Scl-70–positive dcSSc patients and accounted for 11% of patients, who had a very poor prognosis; they had the highest incidence of pulmonary fibrosis (91%) and cardiac scleroderma (14%), and the worst survival (41%) at 20 years, she said.
Group 5 included all U3 RNP–positive patients, accounting for 5% of patients.
“Although survival in this group was not bad (70% at 20 years), the group had the highest pulmonary hypertension incidence (40%) and the second highest incidence of cardiac SSc (11%) at 20 years,” she noted.
Groups 6 and 7 (comprising 22% and 11% of study subjects, respectively) included lcSSc and diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) patients with other antibody specificities. Group 6 had low overall SRC and cardiac SSc risk, while other outcomes were similar to the cohort average. Group 7, however, had poor prognosis, with the second lowest survival (42% at 20 years) and above average rates of organ disease, particularly pulmonary fibrosis and SRC, she said.
Overall, estimated survival for the entire cohort was 60% at 20 years from onset, and in that time frame 44% developed significant pulmonary fibrosis, 25% pulmonary hypertension, 7% SRC, and 6% cardiac SSc. The patients had a mean age of 47 years at disease onset, and 16% were men. Diffuse cutaneous SSc was diagnosed in 35% of the subjects, she noted.
Dr. Nihtyanova reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nihtyanova S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2935.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The classification scheme for SSc risk stratification identified seven distinct SSc subgroups.
Study details: Development and testing of a novel risk classification scheme in 1,025 SSc patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Nihtyanova reported having no disclosures.
Source: Nihtyanova S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10):Abstract 2935.
Increased cancer risk in dermatomyositis has temporal limits
The increased risk of cancer associated with anti-TIF1-Ab-positive dermatomyositis is limited almost exclusively to 3 years on either side of the onset of dermatomyositis, new research suggests.
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy have been associated with malignancy, in particular dermatomyositis (DM) and the DM-specific antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 antibody (anti-TIF1-Ab).
Around one-fifth of the 236 patients diagnosed with DM in the current study, published online Dec. 7 in Rheumatology, were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, and these patients had a more than threefold higher risk of developing cancer comapared with patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab negative (hazard ratio = 3.4, 95% confidence interval, 2.2-5.4; P less than .01).
Overall, 38% of patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group developed cancer during the 10-year follow-up, compared with 15% of patients with anti-TIF1-Ab-negative DM.
However, all the cancers in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group occurred within the 3 years before the onset of DM or within 2.5 years after onset. No anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients developed cancers after this time, but some patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative group did.
“This finding is not likely to be due to a disparity in follow-up time between anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and -negative cases, as the median follow-up times were similar for both groups: 10 years and 12 years, respectively,” wrote Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, a clinical research fellow in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England), and his coauthors. “Further, this finding is unlikely to be due to differences in cancer detection methods, as both cohorts’ cancer diagnoses were identified through HSCIC [U.K. Health and Social Care Information Centre] data, ensuring capture of all incident cancers during the follow-up period.”
Anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients were more likely to develop cancer if they were older. None of the 15 anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged under 39 when they developed DM went on to develop cancer. But cancer developed in around half of the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged 39 years or older when their DM began.
The anti-TIF1 antibody is commonly found in juvenile DM, but previous research has not found an association with an increased risk of cancer in this younger patient population.
“Our findings add strength to the hypothesis that there exists a subset of young adult anti-TIF1-Ab-positive cases who do not have a discernible increased risk of cancer, similar to that observed in TIF1-Ab-positive juvenile DM,” the authors wrote. They suggested that given the increased risk of malignancy in older patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, this group should be subject to more detailed cancer screening.
Breast cancer was the most common malignancy among both anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (33% and 25%, respectively). However, ovarian cancer was significantly more common among the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients than among the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (19% vs. 2%; P less than .05); four of the five ovarian cancers in the entire cohort occurred in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group.
The authors noted that this confirmed the finding of a number of previous studies suggesting an increased risk of ovarian cancer with DM.
“However, this is the first large study to identify that ovarian cancer is overrepresented in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive individuals, suggesting that the true association between DM and ovarian cancer may be through possession of anti-TIF1-Abs,” they noted.
The authors wrote that they had aimed to inform cancer screening strategies among patients with DM.
“It may be that a focus on screening for cancer within the first 3 years after DM onset and particularly screening for ovarian cancer in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive female patients may be required,” they wrote. “Our findings also strengthen the hypothesis that inflammatory myopathies represent a paraneoplastic reaction initiated by attempted immune-mediated clearance of a cancer.”
The study was supported by Arthritis Research UK, Myositis UK, the European Science Foundation for EuMyoNet, Association Francaise Contre Les Myopathies, the Medical Research Council, and the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Oldroyd A et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Dec 7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key357.
The increased risk of cancer associated with anti-TIF1-Ab-positive dermatomyositis is limited almost exclusively to 3 years on either side of the onset of dermatomyositis, new research suggests.
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy have been associated with malignancy, in particular dermatomyositis (DM) and the DM-specific antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 antibody (anti-TIF1-Ab).
Around one-fifth of the 236 patients diagnosed with DM in the current study, published online Dec. 7 in Rheumatology, were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, and these patients had a more than threefold higher risk of developing cancer comapared with patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab negative (hazard ratio = 3.4, 95% confidence interval, 2.2-5.4; P less than .01).
Overall, 38% of patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group developed cancer during the 10-year follow-up, compared with 15% of patients with anti-TIF1-Ab-negative DM.
However, all the cancers in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group occurred within the 3 years before the onset of DM or within 2.5 years after onset. No anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients developed cancers after this time, but some patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative group did.
“This finding is not likely to be due to a disparity in follow-up time between anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and -negative cases, as the median follow-up times were similar for both groups: 10 years and 12 years, respectively,” wrote Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, a clinical research fellow in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England), and his coauthors. “Further, this finding is unlikely to be due to differences in cancer detection methods, as both cohorts’ cancer diagnoses were identified through HSCIC [U.K. Health and Social Care Information Centre] data, ensuring capture of all incident cancers during the follow-up period.”
Anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients were more likely to develop cancer if they were older. None of the 15 anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged under 39 when they developed DM went on to develop cancer. But cancer developed in around half of the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged 39 years or older when their DM began.
The anti-TIF1 antibody is commonly found in juvenile DM, but previous research has not found an association with an increased risk of cancer in this younger patient population.
“Our findings add strength to the hypothesis that there exists a subset of young adult anti-TIF1-Ab-positive cases who do not have a discernible increased risk of cancer, similar to that observed in TIF1-Ab-positive juvenile DM,” the authors wrote. They suggested that given the increased risk of malignancy in older patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, this group should be subject to more detailed cancer screening.
Breast cancer was the most common malignancy among both anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (33% and 25%, respectively). However, ovarian cancer was significantly more common among the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients than among the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (19% vs. 2%; P less than .05); four of the five ovarian cancers in the entire cohort occurred in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group.
The authors noted that this confirmed the finding of a number of previous studies suggesting an increased risk of ovarian cancer with DM.
“However, this is the first large study to identify that ovarian cancer is overrepresented in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive individuals, suggesting that the true association between DM and ovarian cancer may be through possession of anti-TIF1-Abs,” they noted.
The authors wrote that they had aimed to inform cancer screening strategies among patients with DM.
“It may be that a focus on screening for cancer within the first 3 years after DM onset and particularly screening for ovarian cancer in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive female patients may be required,” they wrote. “Our findings also strengthen the hypothesis that inflammatory myopathies represent a paraneoplastic reaction initiated by attempted immune-mediated clearance of a cancer.”
The study was supported by Arthritis Research UK, Myositis UK, the European Science Foundation for EuMyoNet, Association Francaise Contre Les Myopathies, the Medical Research Council, and the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Oldroyd A et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Dec 7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key357.
The increased risk of cancer associated with anti-TIF1-Ab-positive dermatomyositis is limited almost exclusively to 3 years on either side of the onset of dermatomyositis, new research suggests.
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy have been associated with malignancy, in particular dermatomyositis (DM) and the DM-specific antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1 antibody (anti-TIF1-Ab).
Around one-fifth of the 236 patients diagnosed with DM in the current study, published online Dec. 7 in Rheumatology, were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, and these patients had a more than threefold higher risk of developing cancer comapared with patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab negative (hazard ratio = 3.4, 95% confidence interval, 2.2-5.4; P less than .01).
Overall, 38% of patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group developed cancer during the 10-year follow-up, compared with 15% of patients with anti-TIF1-Ab-negative DM.
However, all the cancers in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group occurred within the 3 years before the onset of DM or within 2.5 years after onset. No anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients developed cancers after this time, but some patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative group did.
“This finding is not likely to be due to a disparity in follow-up time between anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and -negative cases, as the median follow-up times were similar for both groups: 10 years and 12 years, respectively,” wrote Alexander Oldroyd, MBChB, a clinical research fellow in the Centre for Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Manchester (England), and his coauthors. “Further, this finding is unlikely to be due to differences in cancer detection methods, as both cohorts’ cancer diagnoses were identified through HSCIC [U.K. Health and Social Care Information Centre] data, ensuring capture of all incident cancers during the follow-up period.”
Anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients were more likely to develop cancer if they were older. None of the 15 anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged under 39 when they developed DM went on to develop cancer. But cancer developed in around half of the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients who were aged 39 years or older when their DM began.
The anti-TIF1 antibody is commonly found in juvenile DM, but previous research has not found an association with an increased risk of cancer in this younger patient population.
“Our findings add strength to the hypothesis that there exists a subset of young adult anti-TIF1-Ab-positive cases who do not have a discernible increased risk of cancer, similar to that observed in TIF1-Ab-positive juvenile DM,” the authors wrote. They suggested that given the increased risk of malignancy in older patients who were anti-TIF1-Ab positive, this group should be subject to more detailed cancer screening.
Breast cancer was the most common malignancy among both anti-TIF1-Ab-positive and anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (33% and 25%, respectively). However, ovarian cancer was significantly more common among the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive patients than among the anti-TIF1-Ab-negative patients (19% vs. 2%; P less than .05); four of the five ovarian cancers in the entire cohort occurred in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group.
The authors noted that this confirmed the finding of a number of previous studies suggesting an increased risk of ovarian cancer with DM.
“However, this is the first large study to identify that ovarian cancer is overrepresented in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive individuals, suggesting that the true association between DM and ovarian cancer may be through possession of anti-TIF1-Abs,” they noted.
The authors wrote that they had aimed to inform cancer screening strategies among patients with DM.
“It may be that a focus on screening for cancer within the first 3 years after DM onset and particularly screening for ovarian cancer in anti-TIF1-Ab-positive female patients may be required,” they wrote. “Our findings also strengthen the hypothesis that inflammatory myopathies represent a paraneoplastic reaction initiated by attempted immune-mediated clearance of a cancer.”
The study was supported by Arthritis Research UK, Myositis UK, the European Science Foundation for EuMyoNet, Association Francaise Contre Les Myopathies, the Medical Research Council, and the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Oldroyd A et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Dec 7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key357.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Patients with dermatomyositis are at increased risk of cancer only in the 3-year periods before and after the onset of dermatomyositis.
Major finding: Overall, 38% of patients in the anti-TIF1-Ab-positive group developed cancer during the 10-year follow-up, compared with 15% of patients with anti-TIF1-Ab-negative DM.
Study details: Cohort study of 236 people with dermatomyositis.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Arthritis Research UK, Myositis UK, the European Science Foundation for EuMyoNet, Association Francaise Contre Les Myopathies, the Medical Research Council, and the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Oldroyd A et al. Rheumatology. 2018 Dec 7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key357.
Combination immunotherapy ups survival in ILD patients with anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis
CHICAGO – Early treatment with combined high-dose glucocorticoids, tacrolimus, and intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy significantly improves survival vs. step-up therapy in interstitial lung disease patients with anti–melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5)–positive dermatomyositis, according to findings from a prospective, multicenter study.
However, the combination therapy was associated with a high risk of cytomegalovirus reactivation and other opportunistic infections that warrants careful monitoring of treated patients, Hideaki Tsuji, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
ILD accompanied by anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis (DM) is often intractable and associated with high mortality in Japanese patients. Case reports have suggested improved outcomes with combined immunosuppressive therapy, but a standard treatment has not been established, said Dr. Tsuji of Kyoto University.
“Therefore, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy for anti-MDA5–positive DM with ILD in a prospective single-arm study,” he said, adding that early administration, a short interval of intravenous cyclophosphamide, use of plasmapheresis as an additional therapy, and control of opportunistic infections may contribute to the improved outcomes seen with the regimen in this study.
The primary endpoint of 6-month survival was reached by 24 (89%) of 27 patients treated with the combination regimen for 52 weeks, compared with 5 (33%) of 15 historical controls who received high-dose glucocorticoids followed by step-wise addition of immunosuppressants. At 12 months, the survival rates were 85% and 33%, respectively, Dr. Tsuji said.
Additionally, anti-MDA5 titer, serum ferritin level, C-reactive protein level, lactate dehydrogenase, and KL-6 level gradually decreased over the 52 months, and percent vital capacity increased with combination vs. step-up therapy, he noted.
Cytomegalovirus reactivation occurred in 90% of combination regimen patients vs. 33% of controls over the 52-week study period, he said, adding that pneumocystic pneumonia and sepsis also occurred in combination regimen group patients, and were associated with death in four patients.
When the 23 surviving patients in the combination regimen group were compared with the 4 in the group who died, it was noted that the deceased patients were significantly more likely to have cutaneous ulcers (75% vs. 13%), higher mean C-reactive protein level (2.7 vs. 0.77 mg/dL), and higher creatine kinase level (644.3 vs. 219.3 IU/L), respectively, before treatment, he said.
Study subjects were Japanese adults with new-onset anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease (ILD) who were enrolled between July 2014 and September 2017.
They were treated with 1 mg/kg/day of prednisolone for 4 weeks with reduced doses thereafter, 500-1,000 mg/m2 of IV cyclophosphamide every 2 weeks for six cycles then every 4 weeks for up to a total of 10-15 treatments, and 10-12 ng/mL of tacrolimus (12-hour trough). Plasmapheresis was allowed in patients who progressed and needed oxygenation after the regimen was initiated, and it was administered in nine patients (31%) in the combination regimen group vs. one (7%) of the historical controls.
Given the different frequencies of rapidly progressive ILD in Asian vs. Western countries (39%-71% vs. 22%-57%, respectively), it is unclear whether the results seen in this study can be extrapolated to patients from the United States and Europe. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the efficacy of the regimen in those patient populations, Dr. Tsuji said, also noting that future studies should evaluate risk-based modifications of the regimen to identify the optimal treatment for individuals based on factors such as age, respiratory dysfunction, hyperferritinemia, and treatment delay.
Dr. Tsuji reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Tsuji H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 838.
CHICAGO – Early treatment with combined high-dose glucocorticoids, tacrolimus, and intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy significantly improves survival vs. step-up therapy in interstitial lung disease patients with anti–melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5)–positive dermatomyositis, according to findings from a prospective, multicenter study.
However, the combination therapy was associated with a high risk of cytomegalovirus reactivation and other opportunistic infections that warrants careful monitoring of treated patients, Hideaki Tsuji, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
ILD accompanied by anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis (DM) is often intractable and associated with high mortality in Japanese patients. Case reports have suggested improved outcomes with combined immunosuppressive therapy, but a standard treatment has not been established, said Dr. Tsuji of Kyoto University.
“Therefore, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy for anti-MDA5–positive DM with ILD in a prospective single-arm study,” he said, adding that early administration, a short interval of intravenous cyclophosphamide, use of plasmapheresis as an additional therapy, and control of opportunistic infections may contribute to the improved outcomes seen with the regimen in this study.
The primary endpoint of 6-month survival was reached by 24 (89%) of 27 patients treated with the combination regimen for 52 weeks, compared with 5 (33%) of 15 historical controls who received high-dose glucocorticoids followed by step-wise addition of immunosuppressants. At 12 months, the survival rates were 85% and 33%, respectively, Dr. Tsuji said.
Additionally, anti-MDA5 titer, serum ferritin level, C-reactive protein level, lactate dehydrogenase, and KL-6 level gradually decreased over the 52 months, and percent vital capacity increased with combination vs. step-up therapy, he noted.
Cytomegalovirus reactivation occurred in 90% of combination regimen patients vs. 33% of controls over the 52-week study period, he said, adding that pneumocystic pneumonia and sepsis also occurred in combination regimen group patients, and were associated with death in four patients.
When the 23 surviving patients in the combination regimen group were compared with the 4 in the group who died, it was noted that the deceased patients were significantly more likely to have cutaneous ulcers (75% vs. 13%), higher mean C-reactive protein level (2.7 vs. 0.77 mg/dL), and higher creatine kinase level (644.3 vs. 219.3 IU/L), respectively, before treatment, he said.
Study subjects were Japanese adults with new-onset anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease (ILD) who were enrolled between July 2014 and September 2017.
They were treated with 1 mg/kg/day of prednisolone for 4 weeks with reduced doses thereafter, 500-1,000 mg/m2 of IV cyclophosphamide every 2 weeks for six cycles then every 4 weeks for up to a total of 10-15 treatments, and 10-12 ng/mL of tacrolimus (12-hour trough). Plasmapheresis was allowed in patients who progressed and needed oxygenation after the regimen was initiated, and it was administered in nine patients (31%) in the combination regimen group vs. one (7%) of the historical controls.
Given the different frequencies of rapidly progressive ILD in Asian vs. Western countries (39%-71% vs. 22%-57%, respectively), it is unclear whether the results seen in this study can be extrapolated to patients from the United States and Europe. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the efficacy of the regimen in those patient populations, Dr. Tsuji said, also noting that future studies should evaluate risk-based modifications of the regimen to identify the optimal treatment for individuals based on factors such as age, respiratory dysfunction, hyperferritinemia, and treatment delay.
Dr. Tsuji reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Tsuji H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 838.
CHICAGO – Early treatment with combined high-dose glucocorticoids, tacrolimus, and intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy significantly improves survival vs. step-up therapy in interstitial lung disease patients with anti–melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5)–positive dermatomyositis, according to findings from a prospective, multicenter study.
However, the combination therapy was associated with a high risk of cytomegalovirus reactivation and other opportunistic infections that warrants careful monitoring of treated patients, Hideaki Tsuji, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
ILD accompanied by anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis (DM) is often intractable and associated with high mortality in Japanese patients. Case reports have suggested improved outcomes with combined immunosuppressive therapy, but a standard treatment has not been established, said Dr. Tsuji of Kyoto University.
“Therefore, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive therapy for anti-MDA5–positive DM with ILD in a prospective single-arm study,” he said, adding that early administration, a short interval of intravenous cyclophosphamide, use of plasmapheresis as an additional therapy, and control of opportunistic infections may contribute to the improved outcomes seen with the regimen in this study.
The primary endpoint of 6-month survival was reached by 24 (89%) of 27 patients treated with the combination regimen for 52 weeks, compared with 5 (33%) of 15 historical controls who received high-dose glucocorticoids followed by step-wise addition of immunosuppressants. At 12 months, the survival rates were 85% and 33%, respectively, Dr. Tsuji said.
Additionally, anti-MDA5 titer, serum ferritin level, C-reactive protein level, lactate dehydrogenase, and KL-6 level gradually decreased over the 52 months, and percent vital capacity increased with combination vs. step-up therapy, he noted.
Cytomegalovirus reactivation occurred in 90% of combination regimen patients vs. 33% of controls over the 52-week study period, he said, adding that pneumocystic pneumonia and sepsis also occurred in combination regimen group patients, and were associated with death in four patients.
When the 23 surviving patients in the combination regimen group were compared with the 4 in the group who died, it was noted that the deceased patients were significantly more likely to have cutaneous ulcers (75% vs. 13%), higher mean C-reactive protein level (2.7 vs. 0.77 mg/dL), and higher creatine kinase level (644.3 vs. 219.3 IU/L), respectively, before treatment, he said.
Study subjects were Japanese adults with new-onset anti-MDA5–positive dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease (ILD) who were enrolled between July 2014 and September 2017.
They were treated with 1 mg/kg/day of prednisolone for 4 weeks with reduced doses thereafter, 500-1,000 mg/m2 of IV cyclophosphamide every 2 weeks for six cycles then every 4 weeks for up to a total of 10-15 treatments, and 10-12 ng/mL of tacrolimus (12-hour trough). Plasmapheresis was allowed in patients who progressed and needed oxygenation after the regimen was initiated, and it was administered in nine patients (31%) in the combination regimen group vs. one (7%) of the historical controls.
Given the different frequencies of rapidly progressive ILD in Asian vs. Western countries (39%-71% vs. 22%-57%, respectively), it is unclear whether the results seen in this study can be extrapolated to patients from the United States and Europe. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the efficacy of the regimen in those patient populations, Dr. Tsuji said, also noting that future studies should evaluate risk-based modifications of the regimen to identify the optimal treatment for individuals based on factors such as age, respiratory dysfunction, hyperferritinemia, and treatment delay.
Dr. Tsuji reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Tsuji H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 838.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: 6-month survival was 89% vs. 33% with combination immunotherapy vs. step-up therapy.
Study details: A prospective, multicenter study of 27 patients and 15 historical controls.
Disclosures: Dr. Tsuji reported having no disclosures.
Source: Tsuji H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 838.
A case of cold burn reported with whole-body cryotherapy
by Mackenzie O’Connor and her colleagues in the department of dermatology and cutaneous biology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In the report, they describe the case of a 71-year-old man who presented with a cold burn injury a day after a WBC session. These treatments typically involve sessions of 2-5 minutes, in a chamber that is cooled down to –100°C to –140°C.
The likely cause in this case was a nozzle malfunction that caused liquid nitrogen to come in direct contact with the patient’s skin for a prolonged period of time (less than 1 minute), causing stinging and pain, followed by redness and blistering of the skin. The patient had received four WBC treatments previously for arthritis and back pain, with no adverse effects. In addition to ibuprofen, he was treated with systemic steroids, topical corticosteroids, and silver sulfadiazine cream.
Despite claims that WBC can aid muscle recovery and alleviate joint pain, and can improve skin health, and is increasingly available in spas and other sites, the Food and Drug Administration has not approved the procedure for treatment of any medical conditions, the researchers noted (JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5[1]:29-30). They also referred to a 2015 Cochrane review, which found insufficient evidence that WBC treatment is beneficial for muscle recovery in active young adult men.
by Mackenzie O’Connor and her colleagues in the department of dermatology and cutaneous biology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In the report, they describe the case of a 71-year-old man who presented with a cold burn injury a day after a WBC session. These treatments typically involve sessions of 2-5 minutes, in a chamber that is cooled down to –100°C to –140°C.
The likely cause in this case was a nozzle malfunction that caused liquid nitrogen to come in direct contact with the patient’s skin for a prolonged period of time (less than 1 minute), causing stinging and pain, followed by redness and blistering of the skin. The patient had received four WBC treatments previously for arthritis and back pain, with no adverse effects. In addition to ibuprofen, he was treated with systemic steroids, topical corticosteroids, and silver sulfadiazine cream.
Despite claims that WBC can aid muscle recovery and alleviate joint pain, and can improve skin health, and is increasingly available in spas and other sites, the Food and Drug Administration has not approved the procedure for treatment of any medical conditions, the researchers noted (JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5[1]:29-30). They also referred to a 2015 Cochrane review, which found insufficient evidence that WBC treatment is beneficial for muscle recovery in active young adult men.
by Mackenzie O’Connor and her colleagues in the department of dermatology and cutaneous biology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
In the report, they describe the case of a 71-year-old man who presented with a cold burn injury a day after a WBC session. These treatments typically involve sessions of 2-5 minutes, in a chamber that is cooled down to –100°C to –140°C.
The likely cause in this case was a nozzle malfunction that caused liquid nitrogen to come in direct contact with the patient’s skin for a prolonged period of time (less than 1 minute), causing stinging and pain, followed by redness and blistering of the skin. The patient had received four WBC treatments previously for arthritis and back pain, with no adverse effects. In addition to ibuprofen, he was treated with systemic steroids, topical corticosteroids, and silver sulfadiazine cream.
Despite claims that WBC can aid muscle recovery and alleviate joint pain, and can improve skin health, and is increasingly available in spas and other sites, the Food and Drug Administration has not approved the procedure for treatment of any medical conditions, the researchers noted (JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5[1]:29-30). They also referred to a 2015 Cochrane review, which found insufficient evidence that WBC treatment is beneficial for muscle recovery in active young adult men.
FROM JAAD CASE REPORTS
Large cohort study IDs prognostic factors in thromboangiitis obliterans
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection predict poor prognosis in TAO.
Major finding: Ethnicity predicts vascular events (HR, 2.35); limb infection at diagnosis predicts vascular events and amputation (HR, 3.29 and 12.1, respectively).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 224 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
Source: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
Phase 3 study of novel pemphigus treatment is initiated
and will enroll about 120 patients with moderate to severe disease, according to Principia Biopharma, which is developing the drug.
In a press release, the company said that the randomized, double-blind PEGASYS study will compare PRN1008 with placebo, in about 120 patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing moderate to severe pemphigus.
The company also reported the results of an open label phase 2 study of patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing mild or moderate pemphigus, including pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus, which found that control of disease activity within 4 weeks of starting treatment – the primary efficacy endpoint – was achieved by more than 50% of patients taking PRN1008. Principia has extended the trial’s active treatment period from 12 to 24 weeks. The results also led the company to initiate the phase 3 trial.
PRN1008 is an inhibitor of BTK, an enzyme that “is present in the signaling pathways of most types of white blood cells except for T cells and plasma cells,” according to the company’s press release.
and will enroll about 120 patients with moderate to severe disease, according to Principia Biopharma, which is developing the drug.
In a press release, the company said that the randomized, double-blind PEGASYS study will compare PRN1008 with placebo, in about 120 patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing moderate to severe pemphigus.
The company also reported the results of an open label phase 2 study of patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing mild or moderate pemphigus, including pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus, which found that control of disease activity within 4 weeks of starting treatment – the primary efficacy endpoint – was achieved by more than 50% of patients taking PRN1008. Principia has extended the trial’s active treatment period from 12 to 24 weeks. The results also led the company to initiate the phase 3 trial.
PRN1008 is an inhibitor of BTK, an enzyme that “is present in the signaling pathways of most types of white blood cells except for T cells and plasma cells,” according to the company’s press release.
and will enroll about 120 patients with moderate to severe disease, according to Principia Biopharma, which is developing the drug.
In a press release, the company said that the randomized, double-blind PEGASYS study will compare PRN1008 with placebo, in about 120 patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing moderate to severe pemphigus.
The company also reported the results of an open label phase 2 study of patients with newly diagnosed or relapsing mild or moderate pemphigus, including pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus, which found that control of disease activity within 4 weeks of starting treatment – the primary efficacy endpoint – was achieved by more than 50% of patients taking PRN1008. Principia has extended the trial’s active treatment period from 12 to 24 weeks. The results also led the company to initiate the phase 3 trial.
PRN1008 is an inhibitor of BTK, an enzyme that “is present in the signaling pathways of most types of white blood cells except for T cells and plasma cells,” according to the company’s press release.
Lower-dose rituximab may be enough in acquired TTP
SAN DIEGO – Lower-than-usual doses of rituximab may be sufficient in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), results of a recent pilot safety and efficacy study suggest.
Patients receiving just 100 mg/week for 4 weeks had rates of relapse and exacerbation that were favorable, compared with historical controls, according to investigator Jeffrey I. Zwicker, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
However, the low-dose treatment was not without side effects, according to Dr. Zwicker, who described one case of acute respiratory failure out of the 19 patients enrolled in the ART (Adjuvant Rituximab in TTP) study.
“The likely benefit is cost savings, rather than less toxicity,” Dr. Zwicker said of the low-dose rituximab regimen.
Out of 19 patients enrolled in ART, 18 were eligible to receive the study treatment, which included low-dose rituximab plus standard plasma exchange and corticosteroids.
Following this initial therapy, all patients had a response, defined as a platelet count 150,000/mcL or greater for 2 consecutive days, with a median time to response of 5 days.
There were two exacerbations (12%) at 30 days after stopping plasma exchange and no cases of refractory TTP, which compared favorably to historical controls, Dr. Zwicker said.
The rate of relapse at 2 years was 28%, which again compared favorably with a historical control data repository in which the rate of relapse at 2 years was 51%.
One patient in the study suffered a case of acute respiratory failure requiring intubation during the third rituximab infusion and was ultimately placed on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
“The patient did survive, but this is just a reminder that there are potential side effects, even with lower doses of rituximab,” Dr. Zwicker said.
A few other serious adverse events – including central line infection and bacteremia in one patient – were more likely related to the plasma exchange, he added.
These results with low-dose rituximab are consistent with findings that rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four doses reduces the incidence of exacerbation and refractory disease and prevents or delays relapses, according to Dr. Zwicker and his coinvestigators, including J. Evan Sadler, MD, PhD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who initiated the study.
The typical TTP regimen of rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four weekly doses is borrowed from protocols for B-cell lymphomas; however, the B-cell mass in nonmalignant disease is likely to be much less than in lymphoproliferative disorders, Dr. Zwicker told attendees.
“The benefit, principally, of lower-dose rituximab is saving of thousands upon thousands of dollars,” Dr. Zwicker said.
This is not the only data set to suggest a potential role for lower-dose rituximab, he added, noting that a recently published retrospective analysis showed “fairly similar” treatment-free survival rates for standard rituximab and a reduced-dose regimen. There also are case series in other autoimmune cytopenias, namely idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and pure red cell aplasia, that provide evidence in support of low-dose rituximab, he added.
Dr. Zwicker reported research funding with Incyte and Quercegen, and consultancy with Parexel. Dr. Sadler reported consultancy with Ablynx.
SOURCE: Zwicker JI et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 374.
SAN DIEGO – Lower-than-usual doses of rituximab may be sufficient in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), results of a recent pilot safety and efficacy study suggest.
Patients receiving just 100 mg/week for 4 weeks had rates of relapse and exacerbation that were favorable, compared with historical controls, according to investigator Jeffrey I. Zwicker, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
However, the low-dose treatment was not without side effects, according to Dr. Zwicker, who described one case of acute respiratory failure out of the 19 patients enrolled in the ART (Adjuvant Rituximab in TTP) study.
“The likely benefit is cost savings, rather than less toxicity,” Dr. Zwicker said of the low-dose rituximab regimen.
Out of 19 patients enrolled in ART, 18 were eligible to receive the study treatment, which included low-dose rituximab plus standard plasma exchange and corticosteroids.
Following this initial therapy, all patients had a response, defined as a platelet count 150,000/mcL or greater for 2 consecutive days, with a median time to response of 5 days.
There were two exacerbations (12%) at 30 days after stopping plasma exchange and no cases of refractory TTP, which compared favorably to historical controls, Dr. Zwicker said.
The rate of relapse at 2 years was 28%, which again compared favorably with a historical control data repository in which the rate of relapse at 2 years was 51%.
One patient in the study suffered a case of acute respiratory failure requiring intubation during the third rituximab infusion and was ultimately placed on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
“The patient did survive, but this is just a reminder that there are potential side effects, even with lower doses of rituximab,” Dr. Zwicker said.
A few other serious adverse events – including central line infection and bacteremia in one patient – were more likely related to the plasma exchange, he added.
These results with low-dose rituximab are consistent with findings that rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four doses reduces the incidence of exacerbation and refractory disease and prevents or delays relapses, according to Dr. Zwicker and his coinvestigators, including J. Evan Sadler, MD, PhD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who initiated the study.
The typical TTP regimen of rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four weekly doses is borrowed from protocols for B-cell lymphomas; however, the B-cell mass in nonmalignant disease is likely to be much less than in lymphoproliferative disorders, Dr. Zwicker told attendees.
“The benefit, principally, of lower-dose rituximab is saving of thousands upon thousands of dollars,” Dr. Zwicker said.
This is not the only data set to suggest a potential role for lower-dose rituximab, he added, noting that a recently published retrospective analysis showed “fairly similar” treatment-free survival rates for standard rituximab and a reduced-dose regimen. There also are case series in other autoimmune cytopenias, namely idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and pure red cell aplasia, that provide evidence in support of low-dose rituximab, he added.
Dr. Zwicker reported research funding with Incyte and Quercegen, and consultancy with Parexel. Dr. Sadler reported consultancy with Ablynx.
SOURCE: Zwicker JI et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 374.
SAN DIEGO – Lower-than-usual doses of rituximab may be sufficient in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), results of a recent pilot safety and efficacy study suggest.
Patients receiving just 100 mg/week for 4 weeks had rates of relapse and exacerbation that were favorable, compared with historical controls, according to investigator Jeffrey I. Zwicker, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. He presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
However, the low-dose treatment was not without side effects, according to Dr. Zwicker, who described one case of acute respiratory failure out of the 19 patients enrolled in the ART (Adjuvant Rituximab in TTP) study.
“The likely benefit is cost savings, rather than less toxicity,” Dr. Zwicker said of the low-dose rituximab regimen.
Out of 19 patients enrolled in ART, 18 were eligible to receive the study treatment, which included low-dose rituximab plus standard plasma exchange and corticosteroids.
Following this initial therapy, all patients had a response, defined as a platelet count 150,000/mcL or greater for 2 consecutive days, with a median time to response of 5 days.
There were two exacerbations (12%) at 30 days after stopping plasma exchange and no cases of refractory TTP, which compared favorably to historical controls, Dr. Zwicker said.
The rate of relapse at 2 years was 28%, which again compared favorably with a historical control data repository in which the rate of relapse at 2 years was 51%.
One patient in the study suffered a case of acute respiratory failure requiring intubation during the third rituximab infusion and was ultimately placed on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
“The patient did survive, but this is just a reminder that there are potential side effects, even with lower doses of rituximab,” Dr. Zwicker said.
A few other serious adverse events – including central line infection and bacteremia in one patient – were more likely related to the plasma exchange, he added.
These results with low-dose rituximab are consistent with findings that rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four doses reduces the incidence of exacerbation and refractory disease and prevents or delays relapses, according to Dr. Zwicker and his coinvestigators, including J. Evan Sadler, MD, PhD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who initiated the study.
The typical TTP regimen of rituximab 375 mg/m2 for four weekly doses is borrowed from protocols for B-cell lymphomas; however, the B-cell mass in nonmalignant disease is likely to be much less than in lymphoproliferative disorders, Dr. Zwicker told attendees.
“The benefit, principally, of lower-dose rituximab is saving of thousands upon thousands of dollars,” Dr. Zwicker said.
This is not the only data set to suggest a potential role for lower-dose rituximab, he added, noting that a recently published retrospective analysis showed “fairly similar” treatment-free survival rates for standard rituximab and a reduced-dose regimen. There also are case series in other autoimmune cytopenias, namely idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and pure red cell aplasia, that provide evidence in support of low-dose rituximab, he added.
Dr. Zwicker reported research funding with Incyte and Quercegen, and consultancy with Parexel. Dr. Sadler reported consultancy with Ablynx.
SOURCE: Zwicker JI et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 374.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After low-dose rituximab plus standard plasma exchange and corticosteroids, the rate of relapse at 2 years was 28%, versus 51% in a historical control data set.
Study details: Findings of the ART (Adjuvant Rituximab in TTP) study including 19 patients with acquired TTP.
Disclosures: Dr. Zwicker reported research funding with Incyte and Quercegen, and consultancy with Parexel. Dr. Sadler reported consultancy with Ablynx.
Source: Zwicker JI et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 374.
Skin rashes often accompany drug-induced liver injury
SAN FRANCISCO – More than a quarter of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases also involve skin reactions, most often drug rash with eosinophilia and system symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. These dual cases of DILI and drug-induced skin injury (DISI) underscore the need for hepatologists to pay attention to dermatologic conditions and emphasize the need for the two specialties to work together.
The findings suggest that DISI/DILI comorbidity is not uncommon, and may hint at underlying mechanisms that could be used to tailor treatment, according to Harshad Devarbhavi, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. “My message was that people should work more and see if there’s any type of genotype or HLA [human leukocyte antigen] that produces this reaction. It’s a multisystem disease. It doesn’t belong to dermatologists, it’s a domain that also belongs to hepatologists,” said Dr. Devarbhavi, who is a hepatology fellow at St. John’s Medical College in Bangalore, India.
DISI is more common than DILI, and may or may not be caused by an immune response. The two conditions were previously known to co-occur, but it is rarely reported because dermatologists and hepatologists report findings in different journals.
The researchers defined DILI as a fivefold or greater increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT); a threefold or greater increase with symptoms, including cutaneous reactions; any elevation of AST, ALT, or alkaline phosphatase (ALP) accompanying a bilirubin increase of 2 mg/dL or more; or a twofold or higher increase in ALP combined with a cutaneous reaction.
They analyzed 921 DILI patients from a single registry in India, who were seen between 1997 and April 2018. All patients with skin reactions were seen by dermatologists and competing causes were excluded. A total of 28% of patients with DILI also had DISI, 13% of whom were also HIV positive; 56% developed jaundice. The mean age of patients with DILI/DISI was 35 years, compared with 42 years in DILI only patients (P = .001) and the mean duration of drug therapy was 42 days, compared with 89 days (P = .002). Twelve percent of DILI/DISI patients died, which was lower than the 17% mortality in those with DILI alone.
Of the DILI/DISI patients, 59% experienced DRESS, and 19% had Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Six percent of patients with DRESS died, as did 22% of those with SJS/TEN. Mortality was 16% among those with other skin manifestations. Eighteen percent of those with jaundice died, compared with 3% of those without jaundice.
Thirty patients with DILI/DISI died; 37% (11) of them had SJS/TEN, compared with 17% of survivors (P = .01). DRESS was more common in survivors (62% vs. 33%; P = .02).
Of DILI/DISI and SJS/TEN cases, 75% were associated with four drug classes: antiepileptic drugs, dapsone, antiretroviral therapies, and leflunomide.
“The liver is the biggest internal organ in the body, and skin is the largest external organ, so there is some correlation between the two, but people haven’t looked at it. People should come together and see why some drugs produce both these injuries. I think there is some mechanistic information in these drugs,” said Dr. Devarbhavi.
Source: Hepatology 2018 Oct 1;68[S1], Abstract 37.
SAN FRANCISCO – More than a quarter of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases also involve skin reactions, most often drug rash with eosinophilia and system symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. These dual cases of DILI and drug-induced skin injury (DISI) underscore the need for hepatologists to pay attention to dermatologic conditions and emphasize the need for the two specialties to work together.
The findings suggest that DISI/DILI comorbidity is not uncommon, and may hint at underlying mechanisms that could be used to tailor treatment, according to Harshad Devarbhavi, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. “My message was that people should work more and see if there’s any type of genotype or HLA [human leukocyte antigen] that produces this reaction. It’s a multisystem disease. It doesn’t belong to dermatologists, it’s a domain that also belongs to hepatologists,” said Dr. Devarbhavi, who is a hepatology fellow at St. John’s Medical College in Bangalore, India.
DISI is more common than DILI, and may or may not be caused by an immune response. The two conditions were previously known to co-occur, but it is rarely reported because dermatologists and hepatologists report findings in different journals.
The researchers defined DILI as a fivefold or greater increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT); a threefold or greater increase with symptoms, including cutaneous reactions; any elevation of AST, ALT, or alkaline phosphatase (ALP) accompanying a bilirubin increase of 2 mg/dL or more; or a twofold or higher increase in ALP combined with a cutaneous reaction.
They analyzed 921 DILI patients from a single registry in India, who were seen between 1997 and April 2018. All patients with skin reactions were seen by dermatologists and competing causes were excluded. A total of 28% of patients with DILI also had DISI, 13% of whom were also HIV positive; 56% developed jaundice. The mean age of patients with DILI/DISI was 35 years, compared with 42 years in DILI only patients (P = .001) and the mean duration of drug therapy was 42 days, compared with 89 days (P = .002). Twelve percent of DILI/DISI patients died, which was lower than the 17% mortality in those with DILI alone.
Of the DILI/DISI patients, 59% experienced DRESS, and 19% had Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Six percent of patients with DRESS died, as did 22% of those with SJS/TEN. Mortality was 16% among those with other skin manifestations. Eighteen percent of those with jaundice died, compared with 3% of those without jaundice.
Thirty patients with DILI/DISI died; 37% (11) of them had SJS/TEN, compared with 17% of survivors (P = .01). DRESS was more common in survivors (62% vs. 33%; P = .02).
Of DILI/DISI and SJS/TEN cases, 75% were associated with four drug classes: antiepileptic drugs, dapsone, antiretroviral therapies, and leflunomide.
“The liver is the biggest internal organ in the body, and skin is the largest external organ, so there is some correlation between the two, but people haven’t looked at it. People should come together and see why some drugs produce both these injuries. I think there is some mechanistic information in these drugs,” said Dr. Devarbhavi.
Source: Hepatology 2018 Oct 1;68[S1], Abstract 37.
SAN FRANCISCO – More than a quarter of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases also involve skin reactions, most often drug rash with eosinophilia and system symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. These dual cases of DILI and drug-induced skin injury (DISI) underscore the need for hepatologists to pay attention to dermatologic conditions and emphasize the need for the two specialties to work together.
The findings suggest that DISI/DILI comorbidity is not uncommon, and may hint at underlying mechanisms that could be used to tailor treatment, according to Harshad Devarbhavi, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. “My message was that people should work more and see if there’s any type of genotype or HLA [human leukocyte antigen] that produces this reaction. It’s a multisystem disease. It doesn’t belong to dermatologists, it’s a domain that also belongs to hepatologists,” said Dr. Devarbhavi, who is a hepatology fellow at St. John’s Medical College in Bangalore, India.
DISI is more common than DILI, and may or may not be caused by an immune response. The two conditions were previously known to co-occur, but it is rarely reported because dermatologists and hepatologists report findings in different journals.
The researchers defined DILI as a fivefold or greater increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT); a threefold or greater increase with symptoms, including cutaneous reactions; any elevation of AST, ALT, or alkaline phosphatase (ALP) accompanying a bilirubin increase of 2 mg/dL or more; or a twofold or higher increase in ALP combined with a cutaneous reaction.
They analyzed 921 DILI patients from a single registry in India, who were seen between 1997 and April 2018. All patients with skin reactions were seen by dermatologists and competing causes were excluded. A total of 28% of patients with DILI also had DISI, 13% of whom were also HIV positive; 56% developed jaundice. The mean age of patients with DILI/DISI was 35 years, compared with 42 years in DILI only patients (P = .001) and the mean duration of drug therapy was 42 days, compared with 89 days (P = .002). Twelve percent of DILI/DISI patients died, which was lower than the 17% mortality in those with DILI alone.
Of the DILI/DISI patients, 59% experienced DRESS, and 19% had Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Six percent of patients with DRESS died, as did 22% of those with SJS/TEN. Mortality was 16% among those with other skin manifestations. Eighteen percent of those with jaundice died, compared with 3% of those without jaundice.
Thirty patients with DILI/DISI died; 37% (11) of them had SJS/TEN, compared with 17% of survivors (P = .01). DRESS was more common in survivors (62% vs. 33%; P = .02).
Of DILI/DISI and SJS/TEN cases, 75% were associated with four drug classes: antiepileptic drugs, dapsone, antiretroviral therapies, and leflunomide.
“The liver is the biggest internal organ in the body, and skin is the largest external organ, so there is some correlation between the two, but people haven’t looked at it. People should come together and see why some drugs produce both these injuries. I think there is some mechanistic information in these drugs,” said Dr. Devarbhavi.
Source: Hepatology 2018 Oct 1;68[S1], Abstract 37.
REPORTING FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2018
Key clinical point: Researchers hope the findings will shed light on the mechanism of injury.
Major finding: 28% of patients with DILI also had a skin rash.
Study details: Retrospective analysis of 921 DILI patients.
Disclosures: No source of funding was disclosed. Dr. Devarbhavi disclosed no relevant conflicts.
Source: Hepatology 2018 Oct 1;68[S1], Abstract 37.
Three drugs disappoint in SSc trials, but show some promise
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING