User login
Emerging data point to underlying autoimmunity in ME/CFS
Emerging evidence suggests that autoimmunity plays a role in postinfectious myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and that targeting autoantibodies could be a promising treatment approach.
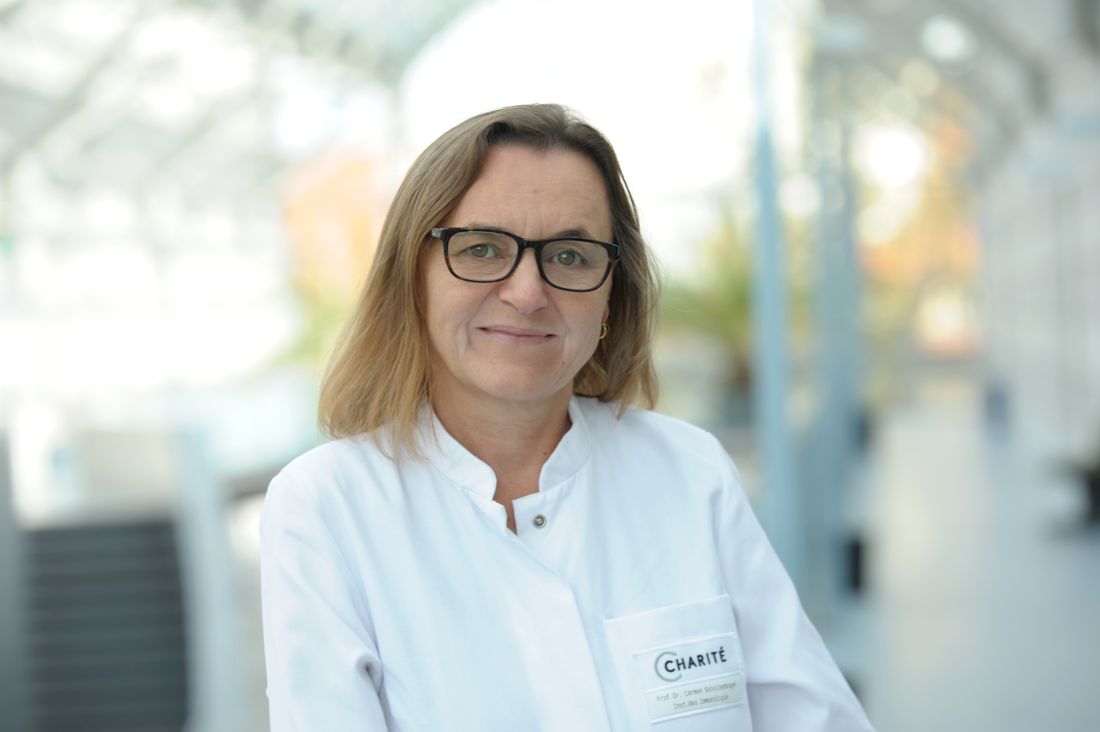
The same may also apply to many cases of “long COVID,” in which many of the symptoms overlap with those of ME/CFS, Carmen Scheibenbogen, MD, professor of clinical immunology and director of the Institute for Medical Immunology, Charité University Medicine, Berlin, said during the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis.
Several groups, including Dr. Scheibenbogen’s, have reported finding autoantibodies against neurotransmitter receptor antigens in people with ME/CFS. And, in a paper published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine the day that Dr. Scheibenbogen spoke at the meeting, her team reported significant correlations between autoantibodies to vasoregulative G-protein–coupled receptors and symptom severity, autonomic dysfunction, and disability among 116 patients with infection-triggered ME/CFS who were diagnosed using the symptom-based 2003 Canadian consensus criteria.
People with ME/CFS are also more likely to have genetic risk factors associated with autoimmunity and personal and/or family histories of autoimmune conditions. And, clinical trials have demonstrated early success with various immunomodulatory treatments in subsets of people with ME/CFS, including endoxan, rituximab, and immunoadsorption.
“We have evidence that ME/CFS is an autoantibody-mediated disease, and we have evidence that autoantibody targeting is effective in this disease. So far ... we have few and underfinanced clinical studies, but the good news is we have promising emerging treatment options,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Asked to comment, ME/CFS expert Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said: “There is already strong evidence that there are autoantibodies in ME/CFS. Dr. Scheibenbogen’s work is the latest and employs the latest technology. ... I would bet that autoantibodies to neural targets are likely to cause some of the symptoms of ME/CFS and some of the symptoms of long COVID.”
However, he cautioned, “that has not been proven, and even if it were proven you would have to demonstrate that treatments based on that theory worked.”
Dr. Komaroff said he views autoimmunity as a likely component of the ME/CFS spectrum, but not the only one. “My current view of this illness is that there’s a final common pathway in the brain that leads to the symptoms of the illness. But that final common pathway can be triggered by a variety of different things, one of which could be autoantibodies while another could be infection or inflammation in the brain.”
Emerging evidence points to autoimmunity
Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized the work published in this area over the past few years by her group and others.
In a comparison of ME/CFS patients with 201 healthy controls, significant associations were seen with two specific autoimmunity-related risk alleles only in the ME/CFS patients who reported acute onset of disease with an infection but not in those with ME/CFS without infection-triggered onset or the controls. Both genes play roles in regulating B- and T-cell activation.
Another recent study found associations with ME/CFS and major histocompatibility complex class II molecules, a typical feature of autoimmune diseases, in a comparison between 426 adult Norwegian ME/CFS patients who were diagnosed with the Canadian consensus criteria and 4,511 healthy, ethnically matched controls.
In a 2020 paper, Dr. Scheibenbogen and pharmacologist Klaus Wirth presented a “unifying hypothesis” of ME/CFS pathophysiology based on the finding of elevations in autoantibodies against beta2-adrenergic receptors and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in some individuals with the condition. Since both of those receptors are important vasodilators, their functional disturbance would be expected to cause vasoconstriction and hypoxemia, which would explain many of the symptoms of ME/CFS. This mechanism would align with other findings of muscular and cerebral hypoperfusion that correlate with fatigue, particularly post exertion, as well as metabolic changes that are in line with the concepts of hypoxemia and ischemia.
Further evidence for vascular dysfunction in ME/CFS came from her group’s study finding evidence of peripheral endothelial dysfunction that was associated with symptom severity in 35 adult patients. “Vasoconstriction, hypovolemia, and release of vasoactive and algesic mediators is probably a key pathomechanism of the disease,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Treatments: Will targeting autoantibodies work?
In the second part of her talk, Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized clinical trials of the following treatment approaches that involve targeting autoantibodies as a way to alleviate ME/CFS symptoms:
Rituximab: Work on infusions of the B-cell depleting agent has been conducted by Norwegian researchers beginning in 2011 with a small randomized trial and an open-label, phase 2 study in 2015, both showing clinical responses in ME/CFS. However, a subsequent phase 3, randomized clinical trial of 151 patients, again diagnosed using the Canadian criteria, was negative.
There are several possible explanations for this, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted. For one, the maintenance dose had to be reduced because of a lack of financial support. “This was probably critical. The lower dose was insufficient to adequately deplete B cells.” Also, there may have been a strong placebo response in the control group since they were being given better care than they normally would receive during the trial. “I think probably nobody will again do a rituximab trial. This was very disappointing for all of us. But, we still have other opportunities to follow this path,” she said.
Dr. Komaroff agreed. “I don’t think the failure of one drug that hits malignant B cells is proof against the autoimmune hypothesis per se. I think the evidence is that rituximab doesn’t work, but that doesn’t invalidate the autoimmunity hypothesis.”
Cyclophosphamide: The same Norwegian group also showed positive findings in an open-label, phase 2 trial of the immune-modifying drug cyclophosphamide in 22 of 40 patients. Interestingly, HLA risk alleles were much more common in responders than nonresponders, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted.
Immunoadsorption: This technique, similar to dialysis, involves separating out the blood plasma by centrifugation and removing IgG autoantibodies by a binding column, then returning the plasma back to the patient. It is used, primarily in Europe, to treat severe autoimmune diseases including dilative cardiomyopathy and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s group has conducted two studies of immunoadsorption in ME/CFS. In one, a 5-day procedure led to rapid symptom improvement in 7 of 10 patients, with sustained improvement in 3 patients after 2 years. Autoantibodies decreased rapidly in 9 of the 10 patients. In a follow-up study of five of the responders 2 years later, retreatment with a modified immunoadsorption protocol led to rapid and sustained improvement in four. Further study has been on hold because of the pandemic.
Next-gen IgG-targeting therapies: Another approach that could offer promise for ME/CFS involves therapies that block the Fc receptors of IgG. Several are in phase 1-3 trials for autoimmune conditions. One candidate drug, the Fc fragment efgartigimod, is currently in phase 3 trials for several conditions, including generalized myasthenia gravis, primary immune thrombocytopenia, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Phase 3 trials are planned for the monoclonal antibody rozanolixizumab in those same conditions.
Newer-generation monoclonal antibodies targeting CD19 or CD20 that show benefit in various autoimmune conditions are another possibility for ME/CFS. These include ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), approved in the United States for treating relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis and in trials for SLE; obinutuzumab (Gazyva), approved for treating lymphoma and also in development for SLE; and ublituximab, in phase 3 trials for multiple sclerosis.
“Most of them are more effective than rituximab,” Dr. Scheibenbogen noted, adding that “currently the data look quite promising. They are effective in different autoimmune diseases and they are quite well tolerated. There’s great hope now with COVID-19 that we can convince some companies to do such trials in ME/CFS as well.”
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s institution, the Charité Fatigue Center, has a patent for beta2-adrenergic receptor antibodies for diagnosing ME/CFS under her name together with Celltrend. Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune.
Emerging evidence suggests that autoimmunity plays a role in postinfectious myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and that targeting autoantibodies could be a promising treatment approach.
The same may also apply to many cases of “long COVID,” in which many of the symptoms overlap with those of ME/CFS, Carmen Scheibenbogen, MD, professor of clinical immunology and director of the Institute for Medical Immunology, Charité University Medicine, Berlin, said during the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis.
Several groups, including Dr. Scheibenbogen’s, have reported finding autoantibodies against neurotransmitter receptor antigens in people with ME/CFS. And, in a paper published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine the day that Dr. Scheibenbogen spoke at the meeting, her team reported significant correlations between autoantibodies to vasoregulative G-protein–coupled receptors and symptom severity, autonomic dysfunction, and disability among 116 patients with infection-triggered ME/CFS who were diagnosed using the symptom-based 2003 Canadian consensus criteria.
People with ME/CFS are also more likely to have genetic risk factors associated with autoimmunity and personal and/or family histories of autoimmune conditions. And, clinical trials have demonstrated early success with various immunomodulatory treatments in subsets of people with ME/CFS, including endoxan, rituximab, and immunoadsorption.
“We have evidence that ME/CFS is an autoantibody-mediated disease, and we have evidence that autoantibody targeting is effective in this disease. So far ... we have few and underfinanced clinical studies, but the good news is we have promising emerging treatment options,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Asked to comment, ME/CFS expert Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said: “There is already strong evidence that there are autoantibodies in ME/CFS. Dr. Scheibenbogen’s work is the latest and employs the latest technology. ... I would bet that autoantibodies to neural targets are likely to cause some of the symptoms of ME/CFS and some of the symptoms of long COVID.”
However, he cautioned, “that has not been proven, and even if it were proven you would have to demonstrate that treatments based on that theory worked.”
Dr. Komaroff said he views autoimmunity as a likely component of the ME/CFS spectrum, but not the only one. “My current view of this illness is that there’s a final common pathway in the brain that leads to the symptoms of the illness. But that final common pathway can be triggered by a variety of different things, one of which could be autoantibodies while another could be infection or inflammation in the brain.”
Emerging evidence points to autoimmunity
Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized the work published in this area over the past few years by her group and others.
In a comparison of ME/CFS patients with 201 healthy controls, significant associations were seen with two specific autoimmunity-related risk alleles only in the ME/CFS patients who reported acute onset of disease with an infection but not in those with ME/CFS without infection-triggered onset or the controls. Both genes play roles in regulating B- and T-cell activation.
Another recent study found associations with ME/CFS and major histocompatibility complex class II molecules, a typical feature of autoimmune diseases, in a comparison between 426 adult Norwegian ME/CFS patients who were diagnosed with the Canadian consensus criteria and 4,511 healthy, ethnically matched controls.
In a 2020 paper, Dr. Scheibenbogen and pharmacologist Klaus Wirth presented a “unifying hypothesis” of ME/CFS pathophysiology based on the finding of elevations in autoantibodies against beta2-adrenergic receptors and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in some individuals with the condition. Since both of those receptors are important vasodilators, their functional disturbance would be expected to cause vasoconstriction and hypoxemia, which would explain many of the symptoms of ME/CFS. This mechanism would align with other findings of muscular and cerebral hypoperfusion that correlate with fatigue, particularly post exertion, as well as metabolic changes that are in line with the concepts of hypoxemia and ischemia.
Further evidence for vascular dysfunction in ME/CFS came from her group’s study finding evidence of peripheral endothelial dysfunction that was associated with symptom severity in 35 adult patients. “Vasoconstriction, hypovolemia, and release of vasoactive and algesic mediators is probably a key pathomechanism of the disease,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Treatments: Will targeting autoantibodies work?
In the second part of her talk, Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized clinical trials of the following treatment approaches that involve targeting autoantibodies as a way to alleviate ME/CFS symptoms:
Rituximab: Work on infusions of the B-cell depleting agent has been conducted by Norwegian researchers beginning in 2011 with a small randomized trial and an open-label, phase 2 study in 2015, both showing clinical responses in ME/CFS. However, a subsequent phase 3, randomized clinical trial of 151 patients, again diagnosed using the Canadian criteria, was negative.
There are several possible explanations for this, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted. For one, the maintenance dose had to be reduced because of a lack of financial support. “This was probably critical. The lower dose was insufficient to adequately deplete B cells.” Also, there may have been a strong placebo response in the control group since they were being given better care than they normally would receive during the trial. “I think probably nobody will again do a rituximab trial. This was very disappointing for all of us. But, we still have other opportunities to follow this path,” she said.
Dr. Komaroff agreed. “I don’t think the failure of one drug that hits malignant B cells is proof against the autoimmune hypothesis per se. I think the evidence is that rituximab doesn’t work, but that doesn’t invalidate the autoimmunity hypothesis.”
Cyclophosphamide: The same Norwegian group also showed positive findings in an open-label, phase 2 trial of the immune-modifying drug cyclophosphamide in 22 of 40 patients. Interestingly, HLA risk alleles were much more common in responders than nonresponders, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted.
Immunoadsorption: This technique, similar to dialysis, involves separating out the blood plasma by centrifugation and removing IgG autoantibodies by a binding column, then returning the plasma back to the patient. It is used, primarily in Europe, to treat severe autoimmune diseases including dilative cardiomyopathy and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s group has conducted two studies of immunoadsorption in ME/CFS. In one, a 5-day procedure led to rapid symptom improvement in 7 of 10 patients, with sustained improvement in 3 patients after 2 years. Autoantibodies decreased rapidly in 9 of the 10 patients. In a follow-up study of five of the responders 2 years later, retreatment with a modified immunoadsorption protocol led to rapid and sustained improvement in four. Further study has been on hold because of the pandemic.
Next-gen IgG-targeting therapies: Another approach that could offer promise for ME/CFS involves therapies that block the Fc receptors of IgG. Several are in phase 1-3 trials for autoimmune conditions. One candidate drug, the Fc fragment efgartigimod, is currently in phase 3 trials for several conditions, including generalized myasthenia gravis, primary immune thrombocytopenia, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Phase 3 trials are planned for the monoclonal antibody rozanolixizumab in those same conditions.
Newer-generation monoclonal antibodies targeting CD19 or CD20 that show benefit in various autoimmune conditions are another possibility for ME/CFS. These include ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), approved in the United States for treating relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis and in trials for SLE; obinutuzumab (Gazyva), approved for treating lymphoma and also in development for SLE; and ublituximab, in phase 3 trials for multiple sclerosis.
“Most of them are more effective than rituximab,” Dr. Scheibenbogen noted, adding that “currently the data look quite promising. They are effective in different autoimmune diseases and they are quite well tolerated. There’s great hope now with COVID-19 that we can convince some companies to do such trials in ME/CFS as well.”
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s institution, the Charité Fatigue Center, has a patent for beta2-adrenergic receptor antibodies for diagnosing ME/CFS under her name together with Celltrend. Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune.
Emerging evidence suggests that autoimmunity plays a role in postinfectious myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and that targeting autoantibodies could be a promising treatment approach.
The same may also apply to many cases of “long COVID,” in which many of the symptoms overlap with those of ME/CFS, Carmen Scheibenbogen, MD, professor of clinical immunology and director of the Institute for Medical Immunology, Charité University Medicine, Berlin, said during the annual meeting of the International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis.
Several groups, including Dr. Scheibenbogen’s, have reported finding autoantibodies against neurotransmitter receptor antigens in people with ME/CFS. And, in a paper published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine the day that Dr. Scheibenbogen spoke at the meeting, her team reported significant correlations between autoantibodies to vasoregulative G-protein–coupled receptors and symptom severity, autonomic dysfunction, and disability among 116 patients with infection-triggered ME/CFS who were diagnosed using the symptom-based 2003 Canadian consensus criteria.
People with ME/CFS are also more likely to have genetic risk factors associated with autoimmunity and personal and/or family histories of autoimmune conditions. And, clinical trials have demonstrated early success with various immunomodulatory treatments in subsets of people with ME/CFS, including endoxan, rituximab, and immunoadsorption.
“We have evidence that ME/CFS is an autoantibody-mediated disease, and we have evidence that autoantibody targeting is effective in this disease. So far ... we have few and underfinanced clinical studies, but the good news is we have promising emerging treatment options,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Asked to comment, ME/CFS expert Anthony L. Komaroff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said: “There is already strong evidence that there are autoantibodies in ME/CFS. Dr. Scheibenbogen’s work is the latest and employs the latest technology. ... I would bet that autoantibodies to neural targets are likely to cause some of the symptoms of ME/CFS and some of the symptoms of long COVID.”
However, he cautioned, “that has not been proven, and even if it were proven you would have to demonstrate that treatments based on that theory worked.”
Dr. Komaroff said he views autoimmunity as a likely component of the ME/CFS spectrum, but not the only one. “My current view of this illness is that there’s a final common pathway in the brain that leads to the symptoms of the illness. But that final common pathway can be triggered by a variety of different things, one of which could be autoantibodies while another could be infection or inflammation in the brain.”
Emerging evidence points to autoimmunity
Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized the work published in this area over the past few years by her group and others.
In a comparison of ME/CFS patients with 201 healthy controls, significant associations were seen with two specific autoimmunity-related risk alleles only in the ME/CFS patients who reported acute onset of disease with an infection but not in those with ME/CFS without infection-triggered onset or the controls. Both genes play roles in regulating B- and T-cell activation.
Another recent study found associations with ME/CFS and major histocompatibility complex class II molecules, a typical feature of autoimmune diseases, in a comparison between 426 adult Norwegian ME/CFS patients who were diagnosed with the Canadian consensus criteria and 4,511 healthy, ethnically matched controls.
In a 2020 paper, Dr. Scheibenbogen and pharmacologist Klaus Wirth presented a “unifying hypothesis” of ME/CFS pathophysiology based on the finding of elevations in autoantibodies against beta2-adrenergic receptors and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in some individuals with the condition. Since both of those receptors are important vasodilators, their functional disturbance would be expected to cause vasoconstriction and hypoxemia, which would explain many of the symptoms of ME/CFS. This mechanism would align with other findings of muscular and cerebral hypoperfusion that correlate with fatigue, particularly post exertion, as well as metabolic changes that are in line with the concepts of hypoxemia and ischemia.
Further evidence for vascular dysfunction in ME/CFS came from her group’s study finding evidence of peripheral endothelial dysfunction that was associated with symptom severity in 35 adult patients. “Vasoconstriction, hypovolemia, and release of vasoactive and algesic mediators is probably a key pathomechanism of the disease,” Dr. Scheibenbogen said.
Treatments: Will targeting autoantibodies work?
In the second part of her talk, Dr. Scheibenbogen summarized clinical trials of the following treatment approaches that involve targeting autoantibodies as a way to alleviate ME/CFS symptoms:
Rituximab: Work on infusions of the B-cell depleting agent has been conducted by Norwegian researchers beginning in 2011 with a small randomized trial and an open-label, phase 2 study in 2015, both showing clinical responses in ME/CFS. However, a subsequent phase 3, randomized clinical trial of 151 patients, again diagnosed using the Canadian criteria, was negative.
There are several possible explanations for this, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted. For one, the maintenance dose had to be reduced because of a lack of financial support. “This was probably critical. The lower dose was insufficient to adequately deplete B cells.” Also, there may have been a strong placebo response in the control group since they were being given better care than they normally would receive during the trial. “I think probably nobody will again do a rituximab trial. This was very disappointing for all of us. But, we still have other opportunities to follow this path,” she said.
Dr. Komaroff agreed. “I don’t think the failure of one drug that hits malignant B cells is proof against the autoimmune hypothesis per se. I think the evidence is that rituximab doesn’t work, but that doesn’t invalidate the autoimmunity hypothesis.”
Cyclophosphamide: The same Norwegian group also showed positive findings in an open-label, phase 2 trial of the immune-modifying drug cyclophosphamide in 22 of 40 patients. Interestingly, HLA risk alleles were much more common in responders than nonresponders, Dr. Scheibenbogen noted.
Immunoadsorption: This technique, similar to dialysis, involves separating out the blood plasma by centrifugation and removing IgG autoantibodies by a binding column, then returning the plasma back to the patient. It is used, primarily in Europe, to treat severe autoimmune diseases including dilative cardiomyopathy and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s group has conducted two studies of immunoadsorption in ME/CFS. In one, a 5-day procedure led to rapid symptom improvement in 7 of 10 patients, with sustained improvement in 3 patients after 2 years. Autoantibodies decreased rapidly in 9 of the 10 patients. In a follow-up study of five of the responders 2 years later, retreatment with a modified immunoadsorption protocol led to rapid and sustained improvement in four. Further study has been on hold because of the pandemic.
Next-gen IgG-targeting therapies: Another approach that could offer promise for ME/CFS involves therapies that block the Fc receptors of IgG. Several are in phase 1-3 trials for autoimmune conditions. One candidate drug, the Fc fragment efgartigimod, is currently in phase 3 trials for several conditions, including generalized myasthenia gravis, primary immune thrombocytopenia, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Phase 3 trials are planned for the monoclonal antibody rozanolixizumab in those same conditions.
Newer-generation monoclonal antibodies targeting CD19 or CD20 that show benefit in various autoimmune conditions are another possibility for ME/CFS. These include ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), approved in the United States for treating relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis and in trials for SLE; obinutuzumab (Gazyva), approved for treating lymphoma and also in development for SLE; and ublituximab, in phase 3 trials for multiple sclerosis.
“Most of them are more effective than rituximab,” Dr. Scheibenbogen noted, adding that “currently the data look quite promising. They are effective in different autoimmune diseases and they are quite well tolerated. There’s great hope now with COVID-19 that we can convince some companies to do such trials in ME/CFS as well.”
Dr. Scheibenbogen’s institution, the Charité Fatigue Center, has a patent for beta2-adrenergic receptor antibodies for diagnosing ME/CFS under her name together with Celltrend. Dr. Komaroff has received personal fees from Serimmune.
FROM IACFS/ME 2021
NIH to study COVID vaccine booster in people with autoimmune disease
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.
Experts debate merits of dual therapy for lupus nephritis
With the approval by the Food and Drug Administration of the calcineurin inhibitor voclosporin (Lupkynis) in January and belimumab (Benlysta) a month before that, clinicians now have new options for treating lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive agent, such as mycophenolate mofetil.
But which combination should clinicians choose?
Brad Rovin, MD, a nephrologist with the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, who worked on the phase 3 voclosprin trial, pointed to that drug’s fast reduction in proteinuria in a session of the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting. That effect on proteinuria is likely due to its effect on podocytes, special epithelial cells that cover the outside of capillaries in the kidney, he said.
These crucial cells have an elaborate cytoskeleton that is stabilized by the protein synaptopodin, which can be subject to harm from calcineurin. But because voclosporin blocks calcineurin, synaptopodin is protected, which consequently protects podocytes and the kidney, Dr. Rovin said.
“There’s a lot of data in the nephrology literature that suggests as you lose podocytes, you actually can develop glomerular sclerosis and loss of renal function,” he said. “In fact, if you lose a critical number of podocytes, then no matter what you do, the kidney is likely to progress to end-stage kidney disease.
“The way I think about it now is, what else do these drugs add? And this idea of preserving the histology of the kidney is really important, and this can be done with voclosporin,” Dr. Rovin said.
Belimumab is also hailed as an effective tool, particularly for the prevention of flares. In the trial leading to its approval), just under 16% of patients experienced a renal-related event or death over 2 years, compared with 28% of the group that received placebo. Those receiving belimumab had a 50% greater chance of reaching the primary efficacy renal response, which was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of 0.7 or less, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the pre-flare value or at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and no use of rescue therapy for treatment failure.
The endpoints in the belimumab lupus nephritis trial were “quite rigorous,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said in the same session at the meeting. Patients with class V lupus nephritis were included in the trial, although disease of this severity is known to be particularly difficult to treat, he noted.
“There’s little question that our patients with lupus nephritis will benefit from such a therapeutic approach” with belimumab and mycophenolate, said Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, in Hempstead, N.Y. “But regardless of which combination clinicians use, we are making advances, and that means better outcomes for our patients with lupus and lupus nephritis.”
Graciela Alarcon, MD, MPH, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, who moderated the discussion, said there is no sure answer regarding the best choice for clinicians.
“As long as there’s no head-to-head comparison between the two new compounds, I don’t think that the question can be answered,” she said.
Indeed, the answer for many clinicians might be that for certain patients, dual therapy isn’t necessary, Dr. Furie said.
“The fundamental question, before we choose the second drug, is whether a second drug should be chosen,” he said. “There’s a lot of people in the community who are just sticking to the old-fashioned algorithm and that is just choosing one drug, like mycophenolate. ... Others might pick a second drug, but not until they see that mycophenolate is not doing an effective job.”
All agreed that the response rates are still not optimal for patients with lupus nephritis, even with these new combinations – they are still only in the 30%-40% range.
“We haven’t really boosted the response rate to where we want it to be, at least as measured by our current measurements and composite renal response,” Dr. Rovin said.
With voclosporin’s protective effects and belimumab’s flare prevention, the two could potentially be used together at some point, he suggested.
“I think these two drugs show us the possibility that we might use them together and get rid of the older drugs, and really minimize the older drugs and then use them on a longer-term basis to preserve kidney function, as well as keep the lupus in check,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the approval by the Food and Drug Administration of the calcineurin inhibitor voclosporin (Lupkynis) in January and belimumab (Benlysta) a month before that, clinicians now have new options for treating lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive agent, such as mycophenolate mofetil.
But which combination should clinicians choose?
Brad Rovin, MD, a nephrologist with the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, who worked on the phase 3 voclosprin trial, pointed to that drug’s fast reduction in proteinuria in a session of the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting. That effect on proteinuria is likely due to its effect on podocytes, special epithelial cells that cover the outside of capillaries in the kidney, he said.
These crucial cells have an elaborate cytoskeleton that is stabilized by the protein synaptopodin, which can be subject to harm from calcineurin. But because voclosporin blocks calcineurin, synaptopodin is protected, which consequently protects podocytes and the kidney, Dr. Rovin said.
“There’s a lot of data in the nephrology literature that suggests as you lose podocytes, you actually can develop glomerular sclerosis and loss of renal function,” he said. “In fact, if you lose a critical number of podocytes, then no matter what you do, the kidney is likely to progress to end-stage kidney disease.
“The way I think about it now is, what else do these drugs add? And this idea of preserving the histology of the kidney is really important, and this can be done with voclosporin,” Dr. Rovin said.
Belimumab is also hailed as an effective tool, particularly for the prevention of flares. In the trial leading to its approval), just under 16% of patients experienced a renal-related event or death over 2 years, compared with 28% of the group that received placebo. Those receiving belimumab had a 50% greater chance of reaching the primary efficacy renal response, which was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of 0.7 or less, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the pre-flare value or at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and no use of rescue therapy for treatment failure.
The endpoints in the belimumab lupus nephritis trial were “quite rigorous,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said in the same session at the meeting. Patients with class V lupus nephritis were included in the trial, although disease of this severity is known to be particularly difficult to treat, he noted.
“There’s little question that our patients with lupus nephritis will benefit from such a therapeutic approach” with belimumab and mycophenolate, said Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, in Hempstead, N.Y. “But regardless of which combination clinicians use, we are making advances, and that means better outcomes for our patients with lupus and lupus nephritis.”
Graciela Alarcon, MD, MPH, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, who moderated the discussion, said there is no sure answer regarding the best choice for clinicians.
“As long as there’s no head-to-head comparison between the two new compounds, I don’t think that the question can be answered,” she said.
Indeed, the answer for many clinicians might be that for certain patients, dual therapy isn’t necessary, Dr. Furie said.
“The fundamental question, before we choose the second drug, is whether a second drug should be chosen,” he said. “There’s a lot of people in the community who are just sticking to the old-fashioned algorithm and that is just choosing one drug, like mycophenolate. ... Others might pick a second drug, but not until they see that mycophenolate is not doing an effective job.”
All agreed that the response rates are still not optimal for patients with lupus nephritis, even with these new combinations – they are still only in the 30%-40% range.
“We haven’t really boosted the response rate to where we want it to be, at least as measured by our current measurements and composite renal response,” Dr. Rovin said.
With voclosporin’s protective effects and belimumab’s flare prevention, the two could potentially be used together at some point, he suggested.
“I think these two drugs show us the possibility that we might use them together and get rid of the older drugs, and really minimize the older drugs and then use them on a longer-term basis to preserve kidney function, as well as keep the lupus in check,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the approval by the Food and Drug Administration of the calcineurin inhibitor voclosporin (Lupkynis) in January and belimumab (Benlysta) a month before that, clinicians now have new options for treating lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive agent, such as mycophenolate mofetil.
But which combination should clinicians choose?
Brad Rovin, MD, a nephrologist with the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, who worked on the phase 3 voclosprin trial, pointed to that drug’s fast reduction in proteinuria in a session of the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting. That effect on proteinuria is likely due to its effect on podocytes, special epithelial cells that cover the outside of capillaries in the kidney, he said.
These crucial cells have an elaborate cytoskeleton that is stabilized by the protein synaptopodin, which can be subject to harm from calcineurin. But because voclosporin blocks calcineurin, synaptopodin is protected, which consequently protects podocytes and the kidney, Dr. Rovin said.
“There’s a lot of data in the nephrology literature that suggests as you lose podocytes, you actually can develop glomerular sclerosis and loss of renal function,” he said. “In fact, if you lose a critical number of podocytes, then no matter what you do, the kidney is likely to progress to end-stage kidney disease.
“The way I think about it now is, what else do these drugs add? And this idea of preserving the histology of the kidney is really important, and this can be done with voclosporin,” Dr. Rovin said.
Belimumab is also hailed as an effective tool, particularly for the prevention of flares. In the trial leading to its approval), just under 16% of patients experienced a renal-related event or death over 2 years, compared with 28% of the group that received placebo. Those receiving belimumab had a 50% greater chance of reaching the primary efficacy renal response, which was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of 0.7 or less, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the pre-flare value or at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and no use of rescue therapy for treatment failure.
The endpoints in the belimumab lupus nephritis trial were “quite rigorous,” Richard A. Furie, MD, said in the same session at the meeting. Patients with class V lupus nephritis were included in the trial, although disease of this severity is known to be particularly difficult to treat, he noted.
“There’s little question that our patients with lupus nephritis will benefit from such a therapeutic approach” with belimumab and mycophenolate, said Dr. Furie, professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, in Hempstead, N.Y. “But regardless of which combination clinicians use, we are making advances, and that means better outcomes for our patients with lupus and lupus nephritis.”
Graciela Alarcon, MD, MPH, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, who moderated the discussion, said there is no sure answer regarding the best choice for clinicians.
“As long as there’s no head-to-head comparison between the two new compounds, I don’t think that the question can be answered,” she said.
Indeed, the answer for many clinicians might be that for certain patients, dual therapy isn’t necessary, Dr. Furie said.
“The fundamental question, before we choose the second drug, is whether a second drug should be chosen,” he said. “There’s a lot of people in the community who are just sticking to the old-fashioned algorithm and that is just choosing one drug, like mycophenolate. ... Others might pick a second drug, but not until they see that mycophenolate is not doing an effective job.”
All agreed that the response rates are still not optimal for patients with lupus nephritis, even with these new combinations – they are still only in the 30%-40% range.
“We haven’t really boosted the response rate to where we want it to be, at least as measured by our current measurements and composite renal response,” Dr. Rovin said.
With voclosporin’s protective effects and belimumab’s flare prevention, the two could potentially be used together at some point, he suggested.
“I think these two drugs show us the possibility that we might use them together and get rid of the older drugs, and really minimize the older drugs and then use them on a longer-term basis to preserve kidney function, as well as keep the lupus in check,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New options explored for sarcopenia in rheumatic diseases
New efforts – including the development of drugs that target mitochondrial pathways and others that target androgen receptors selectively – are underway for treating sarcopenia in rheumatic diseases, but so far the results have been mixed, an expert said at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
Addressing the problem of reduced muscle mass – experienced by many patients with rheumatic diseases, owing in part to the processes of inflammation and to pain interfering with exercise – is bound to help with outcomes, inasmuch as lean mass and fat mass are linked with disability and early mortality, said Joshua Baker, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Elamipretide, which works by stabilizing mitochondrial pathways that are disrupted in people with sarcopenia, in particular those with mitochondrial disorders, might be the most promising of the therapies being developed. In a study published last year, patients with mitochondrial myopathy experienced significant improvement in gait speed, fatigue, and physical function after 4 weeks, Dr. Baker said.
It’s “an interesting and exciting approach that we need to see more studies about in the future,” he said.
Studies of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), which are similar to anabolic steroids but only target certain androgen receptors so as to prevent side effects, have been a letdown, Dr. Baker said. The idea with SARMs is to enhance growth of certain tissue, such as muscle, without causing side effects in other tissues. Previous trials found that although this approach increased muscle mass, it didn’t produce improvements in measures of physical function.
A myostatin/activin type II receptor blocker, bimagrumab, was recently found to boost lean mass but without improvement in physical function or gait speed.
Still, the focus on improving sarcopenia is an encouraging development, Dr. Baker said.
“New therapies are in the pipeline, and let’s be optimistic and hope that in the future we’ll have lots of options for these patients,” he said.
For now, resistance training remains the best way to tackle the problem. However, the need to have access to trainers, equipment, and gyms, as well as the presence of comorbidities, can make exercise difficult, he said. In addition, routine nutritional supplements, such as with vitamin D, have not been found to improve outcomes, he noted.
The sheer number of people with sarcopenia should make the search for better inventions a priority, suggested Maria Lorena Brance, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the National University of Rosario, Argentina.
“Prevalence of sarcopenia is very high in autoimmune disease, with representation between 20% and 30%, depending on the pathology,” she said. “So it’s very important to study the presence of sarcopenia.”
Identifying the problem – by first noticing symptoms and then confirming with tests of muscle strength, such as grip tests – would be a big step, the panelists said. Dr. Baker said that among patients with obesity, sarcopenia is more likely to be overlooked, because such patients might not be weak in an absolute sense but might be weak relative to their size.
Dr. Brance said that it’s important to differentiate the value of vitamin D for someone with normal levels in comparison with someone who has a deficiency. Although evidence does not support the use of vitamin D supplements across the board, supplements have been shown to be helpful for patients with low vitamin D levels, she said.
Xavier Ricardo, MD, PhD, professor at Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil, suggested that sarcopenia may differ from what meets the eye. At his hospital, researchers are studying sarcopenia in patients with systemic sclerosis and have found that in about 20% to 25% of patients, it is present in levels similar to those that occur in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Researchers are now examining tissue from biopsies to see whether there are differences between the two conditions in the processes of muscle wasting.
“So far, we’re a little bit surprised,” he said. “We expected to have more sarcopenia in these patients, because they do look more frail, more cachexic sometimes.”
Dr. Baker has received consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Burns-White, and Gilead. Dr. Ricardo has received consulting fees, speaker fees, or both from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Brance has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New efforts – including the development of drugs that target mitochondrial pathways and others that target androgen receptors selectively – are underway for treating sarcopenia in rheumatic diseases, but so far the results have been mixed, an expert said at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
Addressing the problem of reduced muscle mass – experienced by many patients with rheumatic diseases, owing in part to the processes of inflammation and to pain interfering with exercise – is bound to help with outcomes, inasmuch as lean mass and fat mass are linked with disability and early mortality, said Joshua Baker, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Elamipretide, which works by stabilizing mitochondrial pathways that are disrupted in people with sarcopenia, in particular those with mitochondrial disorders, might be the most promising of the therapies being developed. In a study published last year, patients with mitochondrial myopathy experienced significant improvement in gait speed, fatigue, and physical function after 4 weeks, Dr. Baker said.
It’s “an interesting and exciting approach that we need to see more studies about in the future,” he said.
Studies of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), which are similar to anabolic steroids but only target certain androgen receptors so as to prevent side effects, have been a letdown, Dr. Baker said. The idea with SARMs is to enhance growth of certain tissue, such as muscle, without causing side effects in other tissues. Previous trials found that although this approach increased muscle mass, it didn’t produce improvements in measures of physical function.
A myostatin/activin type II receptor blocker, bimagrumab, was recently found to boost lean mass but without improvement in physical function or gait speed.
Still, the focus on improving sarcopenia is an encouraging development, Dr. Baker said.
“New therapies are in the pipeline, and let’s be optimistic and hope that in the future we’ll have lots of options for these patients,” he said.
For now, resistance training remains the best way to tackle the problem. However, the need to have access to trainers, equipment, and gyms, as well as the presence of comorbidities, can make exercise difficult, he said. In addition, routine nutritional supplements, such as with vitamin D, have not been found to improve outcomes, he noted.
The sheer number of people with sarcopenia should make the search for better inventions a priority, suggested Maria Lorena Brance, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the National University of Rosario, Argentina.
“Prevalence of sarcopenia is very high in autoimmune disease, with representation between 20% and 30%, depending on the pathology,” she said. “So it’s very important to study the presence of sarcopenia.”
Identifying the problem – by first noticing symptoms and then confirming with tests of muscle strength, such as grip tests – would be a big step, the panelists said. Dr. Baker said that among patients with obesity, sarcopenia is more likely to be overlooked, because such patients might not be weak in an absolute sense but might be weak relative to their size.
Dr. Brance said that it’s important to differentiate the value of vitamin D for someone with normal levels in comparison with someone who has a deficiency. Although evidence does not support the use of vitamin D supplements across the board, supplements have been shown to be helpful for patients with low vitamin D levels, she said.
Xavier Ricardo, MD, PhD, professor at Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil, suggested that sarcopenia may differ from what meets the eye. At his hospital, researchers are studying sarcopenia in patients with systemic sclerosis and have found that in about 20% to 25% of patients, it is present in levels similar to those that occur in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Researchers are now examining tissue from biopsies to see whether there are differences between the two conditions in the processes of muscle wasting.
“So far, we’re a little bit surprised,” he said. “We expected to have more sarcopenia in these patients, because they do look more frail, more cachexic sometimes.”
Dr. Baker has received consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Burns-White, and Gilead. Dr. Ricardo has received consulting fees, speaker fees, or both from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Brance has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New efforts – including the development of drugs that target mitochondrial pathways and others that target androgen receptors selectively – are underway for treating sarcopenia in rheumatic diseases, but so far the results have been mixed, an expert said at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) 2021 Annual Meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
Addressing the problem of reduced muscle mass – experienced by many patients with rheumatic diseases, owing in part to the processes of inflammation and to pain interfering with exercise – is bound to help with outcomes, inasmuch as lean mass and fat mass are linked with disability and early mortality, said Joshua Baker, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Elamipretide, which works by stabilizing mitochondrial pathways that are disrupted in people with sarcopenia, in particular those with mitochondrial disorders, might be the most promising of the therapies being developed. In a study published last year, patients with mitochondrial myopathy experienced significant improvement in gait speed, fatigue, and physical function after 4 weeks, Dr. Baker said.
It’s “an interesting and exciting approach that we need to see more studies about in the future,” he said.
Studies of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), which are similar to anabolic steroids but only target certain androgen receptors so as to prevent side effects, have been a letdown, Dr. Baker said. The idea with SARMs is to enhance growth of certain tissue, such as muscle, without causing side effects in other tissues. Previous trials found that although this approach increased muscle mass, it didn’t produce improvements in measures of physical function.
A myostatin/activin type II receptor blocker, bimagrumab, was recently found to boost lean mass but without improvement in physical function or gait speed.
Still, the focus on improving sarcopenia is an encouraging development, Dr. Baker said.
“New therapies are in the pipeline, and let’s be optimistic and hope that in the future we’ll have lots of options for these patients,” he said.
For now, resistance training remains the best way to tackle the problem. However, the need to have access to trainers, equipment, and gyms, as well as the presence of comorbidities, can make exercise difficult, he said. In addition, routine nutritional supplements, such as with vitamin D, have not been found to improve outcomes, he noted.
The sheer number of people with sarcopenia should make the search for better inventions a priority, suggested Maria Lorena Brance, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the National University of Rosario, Argentina.
“Prevalence of sarcopenia is very high in autoimmune disease, with representation between 20% and 30%, depending on the pathology,” she said. “So it’s very important to study the presence of sarcopenia.”
Identifying the problem – by first noticing symptoms and then confirming with tests of muscle strength, such as grip tests – would be a big step, the panelists said. Dr. Baker said that among patients with obesity, sarcopenia is more likely to be overlooked, because such patients might not be weak in an absolute sense but might be weak relative to their size.
Dr. Brance said that it’s important to differentiate the value of vitamin D for someone with normal levels in comparison with someone who has a deficiency. Although evidence does not support the use of vitamin D supplements across the board, supplements have been shown to be helpful for patients with low vitamin D levels, she said.
Xavier Ricardo, MD, PhD, professor at Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil, suggested that sarcopenia may differ from what meets the eye. At his hospital, researchers are studying sarcopenia in patients with systemic sclerosis and have found that in about 20% to 25% of patients, it is present in levels similar to those that occur in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Researchers are now examining tissue from biopsies to see whether there are differences between the two conditions in the processes of muscle wasting.
“So far, we’re a little bit surprised,” he said. “We expected to have more sarcopenia in these patients, because they do look more frail, more cachexic sometimes.”
Dr. Baker has received consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Burns-White, and Gilead. Dr. Ricardo has received consulting fees, speaker fees, or both from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Dr. Brance has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tocilizumab shortage continues as pandemic wears on
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CAR T-cell therapy drives refractory SLE into remission
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy, a life-extending treatment for patients with advanced B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma, has now been shown to be effective for treating refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in at least one patient.
A 20-year-old woman with severe, refractory SLE, active lupus nephritis, pericarditis, and other serious symptoms had both serologic and clinical remission follow the infusion of a CAR T cell product directed against the B-cell surface antigen CD19, reported Georg Schett, MD, and colleagues from the German Center for Immunotherapy at Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg in Erlangen, Germany.
“Given the role of B cells in a variety of severe autoimmune diseases, CAR T-cell therapy that targets B-cell antigens may have wider application,” they wrote in a letter to the editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Schett said in an email response to an interview request that the patient has remained healthy and asymptomatic without further treatment after 6 months of follow-up.
“The key question will be whether B cells return and whether these B cells will carry on to make antibodies against double-stranded DNA,” he said. “We think that the loss of B cells could be sustained given that CAR T cells are still present in the patient. The main question will be how long CAR T cells will be there and how long they deplete the B cells.”
Not just for cancer anymore
CAR T therapy involves harvesting autologous T cells and transducing them with a lentiviral vector to recognize CD19 or other B-cell surface antigens. The transduced cells are then expanded and reinfused into the patient following a lymphodepletion regimen.
There are currently five CAR T constructs approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and other B-lineage lymphomas, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and other hematologic malignancies.
For this patient, however, Dr. Schett and colleagues created their own CAR T construct rather than adapting an off-the-shelf product.
The use of this groundbreaking therapy to treat an autoimmune condition is novel, the investigators noted: “This technological breakthrough, together with recent convincing data on the role of B cells in disease pathogenesis derived from preclinical lupus models, provides a rationale for the use of CAR T-cell therapies in patients with SLE,” they wrote.
One such preclinical study was reported in Science Translational Medicine in 2019 by Marko Z. Radic, PhD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, and colleagues.
Those investigators generated CD19-targeted CAR T constructs and demonstrated that in mouse models of lupus, CD8-positive T cells from two different lupus strains could be successfully transfected, and that transfer of the CD19-targeting CAR T cells ablated both autoantibodies and CD19-positive cells.
“In both models, survival was remarkably extended, and target organs were spared. These exciting results could pave the way for using CD19-targeted T cells to treat patients with lupus,” they wrote.
Now, that prediction has come to fruition.
“It’s brilliant that the first case report has now been accomplished. I am fully convinced that this method will rid therapy refractory patients of their symptoms,” Dr. Radic said in an interview.
Anti-CD20 failures
B-cell depletion with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab has been shown to be an effective therapeutic strategy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, but was ineffective in two separate clinical trials for SLE.
“Incomplete B-cell depletion of tissue-resident B cells, or the transient nature of the treatment, may have contributed to the failure of the initial rituximab trials to attain satisfactory outcomes,” Dr. Radic and coauthors wrote.
In patients with severe lupus, autoreactive B cells may lurk in lymphatic organs and/or inflamed tissues. Alternatively, CD20-negative plasma cells, which are unaffected by rituximab, could also be a source of SLE autoantibodies, Dr. Schett and coinvestigators said.
Case details
As noted before, the 20-year-old patient described by Dr. Schett and colleagues presented with World Health Organization class IIIA active lupus nephritis, indicating focal proliferative disease. In addition, she also had nephritic syndrome, pericarditis, pleurisy, rash, and arthritis, and had a history of Libman-Sacks endocarditis.
Her disease was refractory to treatment with all the usual suspects, including hydroxychloroquine, high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, rituximab, and belimumab, another B-cell targeted agent.
The T cell collection, transduction, expansion, and infusion were all successfully performed. By day 9 following infusion, CAR T cells comprised nearly one-third of her total circulating T cells, and then began to decrease, but remained detectable in circulation for the ensuing 7 weeks.
Levels of anti–double-stranded DNA decreased from above 5,000 U/mL to 4 U/mL within 5 weeks, and her complement levels (C3 and C4) normalized.
“These signs of serologic remission were paralleled by clinical remission with proteinuria decreasing from above 2,000 mg of protein per gram of creatinine to less than 250 mg of protein per gram of creatinine,” the investigators wrote.
The patient’s SLE Disease Activity Index score with SELENA (Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment) modification dropped from 16 at baseline to 0 at follow-up.
The patient did not experience any of the adverse events that are commonly seen in patients treated with CAR T therapy, such as the cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxic adverse events, or prolonged cytopenias.
Unanswered questions
Dr. Radic said that it was unclear from the brief case report whether Dr. Schett and colleagues considered including a “kill switch” in their CAR T construct, which could be activated in the case of serious toxicities.
In addition, their use of both CD4-positive T cells in addition to CD8-positive cells in their construct raises some concern, because in patients with SLE there is evidence that CD4-positive helper T cells can be autoreactive, he noted.
The work by Dr. Schett and colleagues was supported by grants from the German government, European Union, and the Innovative Medicines Initiative. Dr. Schett reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Radic is listed as inventor on a patent for anti-CD19 CAR T cells in lupus.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy, a life-extending treatment for patients with advanced B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma, has now been shown to be effective for treating refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in at least one patient.
A 20-year-old woman with severe, refractory SLE, active lupus nephritis, pericarditis, and other serious symptoms had both serologic and clinical remission follow the infusion of a CAR T cell product directed against the B-cell surface antigen CD19, reported Georg Schett, MD, and colleagues from the German Center for Immunotherapy at Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg in Erlangen, Germany.
“Given the role of B cells in a variety of severe autoimmune diseases, CAR T-cell therapy that targets B-cell antigens may have wider application,” they wrote in a letter to the editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Schett said in an email response to an interview request that the patient has remained healthy and asymptomatic without further treatment after 6 months of follow-up.
“The key question will be whether B cells return and whether these B cells will carry on to make antibodies against double-stranded DNA,” he said. “We think that the loss of B cells could be sustained given that CAR T cells are still present in the patient. The main question will be how long CAR T cells will be there and how long they deplete the B cells.”
Not just for cancer anymore
CAR T therapy involves harvesting autologous T cells and transducing them with a lentiviral vector to recognize CD19 or other B-cell surface antigens. The transduced cells are then expanded and reinfused into the patient following a lymphodepletion regimen.
There are currently five CAR T constructs approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and other B-lineage lymphomas, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and other hematologic malignancies.
For this patient, however, Dr. Schett and colleagues created their own CAR T construct rather than adapting an off-the-shelf product.
The use of this groundbreaking therapy to treat an autoimmune condition is novel, the investigators noted: “This technological breakthrough, together with recent convincing data on the role of B cells in disease pathogenesis derived from preclinical lupus models, provides a rationale for the use of CAR T-cell therapies in patients with SLE,” they wrote.
One such preclinical study was reported in Science Translational Medicine in 2019 by Marko Z. Radic, PhD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, and colleagues.
Those investigators generated CD19-targeted CAR T constructs and demonstrated that in mouse models of lupus, CD8-positive T cells from two different lupus strains could be successfully transfected, and that transfer of the CD19-targeting CAR T cells ablated both autoantibodies and CD19-positive cells.
“In both models, survival was remarkably extended, and target organs were spared. These exciting results could pave the way for using CD19-targeted T cells to treat patients with lupus,” they wrote.
Now, that prediction has come to fruition.
“It’s brilliant that the first case report has now been accomplished. I am fully convinced that this method will rid therapy refractory patients of their symptoms,” Dr. Radic said in an interview.
Anti-CD20 failures
B-cell depletion with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab has been shown to be an effective therapeutic strategy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, but was ineffective in two separate clinical trials for SLE.
“Incomplete B-cell depletion of tissue-resident B cells, or the transient nature of the treatment, may have contributed to the failure of the initial rituximab trials to attain satisfactory outcomes,” Dr. Radic and coauthors wrote.
In patients with severe lupus, autoreactive B cells may lurk in lymphatic organs and/or inflamed tissues. Alternatively, CD20-negative plasma cells, which are unaffected by rituximab, could also be a source of SLE autoantibodies, Dr. Schett and coinvestigators said.
Case details
As noted before, the 20-year-old patient described by Dr. Schett and colleagues presented with World Health Organization class IIIA active lupus nephritis, indicating focal proliferative disease. In addition, she also had nephritic syndrome, pericarditis, pleurisy, rash, and arthritis, and had a history of Libman-Sacks endocarditis.
Her disease was refractory to treatment with all the usual suspects, including hydroxychloroquine, high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, rituximab, and belimumab, another B-cell targeted agent.
The T cell collection, transduction, expansion, and infusion were all successfully performed. By day 9 following infusion, CAR T cells comprised nearly one-third of her total circulating T cells, and then began to decrease, but remained detectable in circulation for the ensuing 7 weeks.
Levels of anti–double-stranded DNA decreased from above 5,000 U/mL to 4 U/mL within 5 weeks, and her complement levels (C3 and C4) normalized.
“These signs of serologic remission were paralleled by clinical remission with proteinuria decreasing from above 2,000 mg of protein per gram of creatinine to less than 250 mg of protein per gram of creatinine,” the investigators wrote.
The patient’s SLE Disease Activity Index score with SELENA (Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment) modification dropped from 16 at baseline to 0 at follow-up.
The patient did not experience any of the adverse events that are commonly seen in patients treated with CAR T therapy, such as the cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxic adverse events, or prolonged cytopenias.
Unanswered questions
Dr. Radic said that it was unclear from the brief case report whether Dr. Schett and colleagues considered including a “kill switch” in their CAR T construct, which could be activated in the case of serious toxicities.
In addition, their use of both CD4-positive T cells in addition to CD8-positive cells in their construct raises some concern, because in patients with SLE there is evidence that CD4-positive helper T cells can be autoreactive, he noted.
The work by Dr. Schett and colleagues was supported by grants from the German government, European Union, and the Innovative Medicines Initiative. Dr. Schett reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Radic is listed as inventor on a patent for anti-CD19 CAR T cells in lupus.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy, a life-extending treatment for patients with advanced B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma, has now been shown to be effective for treating refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in at least one patient.
A 20-year-old woman with severe, refractory SLE, active lupus nephritis, pericarditis, and other serious symptoms had both serologic and clinical remission follow the infusion of a CAR T cell product directed against the B-cell surface antigen CD19, reported Georg Schett, MD, and colleagues from the German Center for Immunotherapy at Friedrich Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg in Erlangen, Germany.
“Given the role of B cells in a variety of severe autoimmune diseases, CAR T-cell therapy that targets B-cell antigens may have wider application,” they wrote in a letter to the editor of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Schett said in an email response to an interview request that the patient has remained healthy and asymptomatic without further treatment after 6 months of follow-up.
“The key question will be whether B cells return and whether these B cells will carry on to make antibodies against double-stranded DNA,” he said. “We think that the loss of B cells could be sustained given that CAR T cells are still present in the patient. The main question will be how long CAR T cells will be there and how long they deplete the B cells.”
Not just for cancer anymore
CAR T therapy involves harvesting autologous T cells and transducing them with a lentiviral vector to recognize CD19 or other B-cell surface antigens. The transduced cells are then expanded and reinfused into the patient following a lymphodepletion regimen.
There are currently five CAR T constructs approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and other B-lineage lymphomas, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and other hematologic malignancies.
For this patient, however, Dr. Schett and colleagues created their own CAR T construct rather than adapting an off-the-shelf product.
The use of this groundbreaking therapy to treat an autoimmune condition is novel, the investigators noted: “This technological breakthrough, together with recent convincing data on the role of B cells in disease pathogenesis derived from preclinical lupus models, provides a rationale for the use of CAR T-cell therapies in patients with SLE,” they wrote.
One such preclinical study was reported in Science Translational Medicine in 2019 by Marko Z. Radic, PhD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, and colleagues.
Those investigators generated CD19-targeted CAR T constructs and demonstrated that in mouse models of lupus, CD8-positive T cells from two different lupus strains could be successfully transfected, and that transfer of the CD19-targeting CAR T cells ablated both autoantibodies and CD19-positive cells.
“In both models, survival was remarkably extended, and target organs were spared. These exciting results could pave the way for using CD19-targeted T cells to treat patients with lupus,” they wrote.
Now, that prediction has come to fruition.
“It’s brilliant that the first case report has now been accomplished. I am fully convinced that this method will rid therapy refractory patients of their symptoms,” Dr. Radic said in an interview.
Anti-CD20 failures
B-cell depletion with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab has been shown to be an effective therapeutic strategy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, but was ineffective in two separate clinical trials for SLE.
“Incomplete B-cell depletion of tissue-resident B cells, or the transient nature of the treatment, may have contributed to the failure of the initial rituximab trials to attain satisfactory outcomes,” Dr. Radic and coauthors wrote.
In patients with severe lupus, autoreactive B cells may lurk in lymphatic organs and/or inflamed tissues. Alternatively, CD20-negative plasma cells, which are unaffected by rituximab, could also be a source of SLE autoantibodies, Dr. Schett and coinvestigators said.
Case details
As noted before, the 20-year-old patient described by Dr. Schett and colleagues presented with World Health Organization class IIIA active lupus nephritis, indicating focal proliferative disease. In addition, she also had nephritic syndrome, pericarditis, pleurisy, rash, and arthritis, and had a history of Libman-Sacks endocarditis.
Her disease was refractory to treatment with all the usual suspects, including hydroxychloroquine, high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, rituximab, and belimumab, another B-cell targeted agent.
The T cell collection, transduction, expansion, and infusion were all successfully performed. By day 9 following infusion, CAR T cells comprised nearly one-third of her total circulating T cells, and then began to decrease, but remained detectable in circulation for the ensuing 7 weeks.
Levels of anti–double-stranded DNA decreased from above 5,000 U/mL to 4 U/mL within 5 weeks, and her complement levels (C3 and C4) normalized.
“These signs of serologic remission were paralleled by clinical remission with proteinuria decreasing from above 2,000 mg of protein per gram of creatinine to less than 250 mg of protein per gram of creatinine,” the investigators wrote.
The patient’s SLE Disease Activity Index score with SELENA (Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment) modification dropped from 16 at baseline to 0 at follow-up.
The patient did not experience any of the adverse events that are commonly seen in patients treated with CAR T therapy, such as the cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxic adverse events, or prolonged cytopenias.
Unanswered questions
Dr. Radic said that it was unclear from the brief case report whether Dr. Schett and colleagues considered including a “kill switch” in their CAR T construct, which could be activated in the case of serious toxicities.
In addition, their use of both CD4-positive T cells in addition to CD8-positive cells in their construct raises some concern, because in patients with SLE there is evidence that CD4-positive helper T cells can be autoreactive, he noted.
The work by Dr. Schett and colleagues was supported by grants from the German government, European Union, and the Innovative Medicines Initiative. Dr. Schett reported having no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Radic is listed as inventor on a patent for anti-CD19 CAR T cells in lupus.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
HBV screening often incomplete or forgone when starting tocilizumab, tofacitinib
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
People beginning treatment with the immunosuppressive drugs tocilizumab (Actemra) or tofacitinib (Xeljanz) are infrequently screened for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, according to a new study of patients with rheumatic diseases who are starting one of the two treatments.
“Perhaps not unexpectedly, these screening patterns conform more with recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology, which do not explicitly stipulate universal HBV screening,” wrote lead author Amir M. Mohareb, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The study was published in The Journal of Rheumatology.
To determine the frequency of HBV screening among this specific population, the researchers conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional study of patients 18 years or older within the Mass General Brigham health system in the Boston area who initiated either of the two drugs before Dec. 31, 2018. Tocilizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 11, 2010, and tofacitinib was approved on Nov. 6, 2012.
The final study population included 678 patients on tocilizumab and 391 patients on tofacitinib. The mean age of the patients in each group was 61 years for tocilizumab and 60 years for tofacitinib. A large majority were female (78% of the tocilizumab group, 88% of the tofacitinib group) and 84% of patients in both groups were white. Their primary diagnosis was rheumatoid arthritis (53% of the tocilizumab group, 77% of the tofacitinib group), and most of them – 57% of patients on tocilizumab and 72% of patients on tofacitinib – had a history of being on both conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
HBV screening patterns were classified into three categories: complete (all three of the HBV surface antigen [HBsAg], total core antibody [anti-HBcAb], and surface antibody [HBsAb] tests); partial (any one to two tests); and none. Of the 678 patients on tocilizumab, 194 (29%) underwent complete screening, 307 (45%) underwent partial screening, and 177 (26%) had no screening. Of the 391 patients on tofacitinib, 94 (24%) underwent complete screening, 195 (50%) underwent partial screening, and 102 (26%) had none.
Inappropriate testing – defined as either HBV e-antigen (HBeAg), anti-HBcAb IgM, or HBV DNA without a positive HBsAg or total anti-HBcAb – occurred in 22% of patients on tocilizumab and 23% of patients on tofacitinib. After multivariable analysis, the authors found that Whites were less likely to undergo complete screening (odds ratio, 0.74; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.95) compared to non-Whites. Previous use of immunosuppressive agents such as conventional synthetic DMARDs (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.72-1.55) and biologic DMARDs with or without prior csDMARDs (OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48-1.12) was not associated with a likelihood of complete appropriate screening.
“These data add to the evidence indicating that clinicians are not completing pretreatment screening for latent infections prior to patients starting high-risk immunosuppressant drugs,” Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “It can be dangerous, since a fraction of these patients may reactivate latent infections with HBV that can result in liver failure or death.
“On the bright side,” she added, “we have antivirals that can be given as prophylaxis against reactivation of latent HBV if patients do test positive.”
Dr. Schmajuk was previously the senior author of a similar study from the 2019 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting that found only a small percentage of patients who were new users of biologics or new synthetic DMARDs were screened for HBV or hepatitis C virus.
When asked if anything in the study stood out, she acknowledged being “somewhat surprised that patients with prior immunosuppression did not have higher rates of screening. One might expect that since those patients had more opportunities for screening – since they started new medications more times – they would have higher rates, but this did not appear to be the case.”
As a message to rheumatologists who may be starting their patients on any biologic or new synthetic DMARD, she reinforced that “we need universal HBV screening for patients starting these medications. Many clinicians are used to ordering a hepatitis B surface antigen test, but one key message is that we also need to be ordering hepatitis B core antibody tests. Patients with a positive core antibody are still at risk for reactivation.”
The authors noted their study’s limitations, including the data being retrospectively collected and some of the subjects potentially being screened in laboratories outside of the Mass General Brigham health system. In addition, they stated that their findings “may not be generalizable to nonrheumatologic settings or other immunomodulators,” although they added that studies of other patient populations have also uncovered “similarly low HBV screening frequencies.”
Several of the authors reported being supported by institutes within the National Institutes of Health. Beyond that, they declared no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF RHEUMATOLOGY
FDA approves anifrolumab (Saphnelo) as first new lupus treatment in more than 10 years
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
COVID-19 vaccination does not increase risk of flare in patients with lupus
COVID-19 vaccinations appear to be well tolerated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and come with a low risk of flare, according to the results of a global, web-based survey.
“Disseminating these reassuring data might prove crucial to increasing vaccine coverage in patients with SLE,” wrote lead author Renaud Felten, MD, of Strasbourg (France) University Hospital. Their results were published as a comment in Lancet Rheumatology.
To assess vaccine tolerability among lupus patients, the cross-sectional Tolerance and Consequences of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Lupus Patients (VACOLUP) study analyzed a 43-question survey of 696 participants with a self-reported, medically confirmed diagnosis of SLE from 30 countries between March 22, 2021, and May 17, 2021. The cohort was 96% women, and their median age was 42 (interquartile range, 34-51). Nearly 36% of respondents were from Italy, 27% were from Chile, 13% were from France, and just under 9% were Americans. All participants received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and 49% received a second dose. The most common vaccines were Pfizer-BioNTech (57%), Sinovac (22%), AstraZeneca (10%), and Moderna (8%).
Only 21 participants (3%) reported a medically confirmed SLE flare after a median of 3 days (IQR, 0-29) post COVID vaccination, with most experiencing musculoskeletal symptoms (90%) and fatigue (86%). Of the 21 cases, 15 reported a subsequent change in SLE treatment and 4 were admitted to the hospital. A previous flare that occurred within a year before vaccination was associated with an increased risk of flare post vaccination (relative risk, 5.52; 95% confidence interval, 2.17-14.03; P < .0001).
Side effects – including swelling, soreness, fever, chills, fatigue, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and headache – were reported in 45% of participants (n = 316) after their first dose and in 53% of the 343 participants who received a second dose. There was no notable difference in the likelihood of side effects across gender and age or in patients who received mRNA vaccines, compared with vaccines with other modes of action. Patients who reported side effects after the first dose were more likely to also report them after the second, compared with those who reported none (109 [81%] of 135 vs. 72 [35%] of 205; RR, 2.30; 95% CI, 1.88-2.82; P < .0001).
In the majority of cases (2,232 of 2,683), the side effects were of minor or moderate intensity and did not affect the participants’ ability to perform daily tasks. The study found no significant association between side effects and a SLE flare and SLE medications or previous SLE disease manifestations.
When asked to comment on the study, Amit Saxena, MD, of the Lupus Center at New York University Langone Health, said: “What we are seeing is pretty mild to moderate in terms of follow-up side effects or lupus-related activity. Several studies have shown this amongst our autoimmune rheumatology cohort, as well as what I’ve seen clinically in my own patients. More than anything else, numbers are the most important, and this is a large study.”
He acknowledged the benefits of going directly to patients to gauge their responses and reactions, giving them the opportunity to share concerns that physicians may not think about.
“As rheumatologists, we tend to focus on certain things that might not necessarily be what the patients themselves focus on,” he said. “I think the fact that this questionnaire dealt with a lot of what people complain about – fatigue, sore arm, things that we know are part of getting the vaccine – they aren’t necessarily things we capture with tools that screen for lupus flares, for example.”
More than anything, Dr. Saxena commended the study’s timeliness. “Patients are constantly asking us about the vaccine, and there’s so much misinformation,” he said. “People say, ‘Because I have lupus, I was told not to get vaccinated.’ I don’t know where they get that information from; we are telling everyone to get it, especially our lupus patients.”
The authors recognized their study’s main limitation as the self-reported and subjective nature of the survey, which they attempted to mitigate by asking for medically confirmed flares only. They noted, however, that the short median time between vaccination and flare onset could be caused by patients confusing expected side effects for something more serious, meaning the 3% figure “could be an overestimation of the actual flare rate.”
“Vaccination is recommended for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases according to the American College of Rheumatology,” they added, “irrespective of disease activity and severity.”
Several authors reported potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consultancy fees and grants from Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, and Janssen, all unrelated to the study.
COVID-19 vaccinations appear to be well tolerated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and come with a low risk of flare, according to the results of a global, web-based survey.
“Disseminating these reassuring data might prove crucial to increasing vaccine coverage in patients with SLE,” wrote lead author Renaud Felten, MD, of Strasbourg (France) University Hospital. Their results were published as a comment in Lancet Rheumatology.
To assess vaccine tolerability among lupus patients, the cross-sectional Tolerance and Consequences of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Lupus Patients (VACOLUP) study analyzed a 43-question survey of 696 participants with a self-reported, medically confirmed diagnosis of SLE from 30 countries between March 22, 2021, and May 17, 2021. The cohort was 96% women, and their median age was 42 (interquartile range, 34-51). Nearly 36% of respondents were from Italy, 27% were from Chile, 13% were from France, and just under 9% were Americans. All participants received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and 49% received a second dose. The most common vaccines were Pfizer-BioNTech (57%), Sinovac (22%), AstraZeneca (10%), and Moderna (8%).
Only 21 participants (3%) reported a medically confirmed SLE flare after a median of 3 days (IQR, 0-29) post COVID vaccination, with most experiencing musculoskeletal symptoms (90%) and fatigue (86%). Of the 21 cases, 15 reported a subsequent change in SLE treatment and 4 were admitted to the hospital. A previous flare that occurred within a year before vaccination was associated with an increased risk of flare post vaccination (relative risk, 5.52; 95% confidence interval, 2.17-14.03; P < .0001).
Side effects – including swelling, soreness, fever, chills, fatigue, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and headache – were reported in 45% of participants (n = 316) after their first dose and in 53% of the 343 participants who received a second dose. There was no notable difference in the likelihood of side effects across gender and age or in patients who received mRNA vaccines, compared with vaccines with other modes of action. Patients who reported side effects after the first dose were more likely to also report them after the second, compared with those who reported none (109 [81%] of 135 vs. 72 [35%] of 205; RR, 2.30; 95% CI, 1.88-2.82; P < .0001).
In the majority of cases (2,232 of 2,683), the side effects were of minor or moderate intensity and did not affect the participants’ ability to perform daily tasks. The study found no significant association between side effects and a SLE flare and SLE medications or previous SLE disease manifestations.
When asked to comment on the study, Amit Saxena, MD, of the Lupus Center at New York University Langone Health, said: “What we are seeing is pretty mild to moderate in terms of follow-up side effects or lupus-related activity. Several studies have shown this amongst our autoimmune rheumatology cohort, as well as what I’ve seen clinically in my own patients. More than anything else, numbers are the most important, and this is a large study.”
He acknowledged the benefits of going directly to patients to gauge their responses and reactions, giving them the opportunity to share concerns that physicians may not think about.
“As rheumatologists, we tend to focus on certain things that might not necessarily be what the patients themselves focus on,” he said. “I think the fact that this questionnaire dealt with a lot of what people complain about – fatigue, sore arm, things that we know are part of getting the vaccine – they aren’t necessarily things we capture with tools that screen for lupus flares, for example.”
More than anything, Dr. Saxena commended the study’s timeliness. “Patients are constantly asking us about the vaccine, and there’s so much misinformation,” he said. “People say, ‘Because I have lupus, I was told not to get vaccinated.’ I don’t know where they get that information from; we are telling everyone to get it, especially our lupus patients.”
The authors recognized their study’s main limitation as the self-reported and subjective nature of the survey, which they attempted to mitigate by asking for medically confirmed flares only. They noted, however, that the short median time between vaccination and flare onset could be caused by patients confusing expected side effects for something more serious, meaning the 3% figure “could be an overestimation of the actual flare rate.”
“Vaccination is recommended for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases according to the American College of Rheumatology,” they added, “irrespective of disease activity and severity.”
Several authors reported potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consultancy fees and grants from Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, and Janssen, all unrelated to the study.
COVID-19 vaccinations appear to be well tolerated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and come with a low risk of flare, according to the results of a global, web-based survey.
“Disseminating these reassuring data might prove crucial to increasing vaccine coverage in patients with SLE,” wrote lead author Renaud Felten, MD, of Strasbourg (France) University Hospital. Their results were published as a comment in Lancet Rheumatology.
To assess vaccine tolerability among lupus patients, the cross-sectional Tolerance and Consequences of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Lupus Patients (VACOLUP) study analyzed a 43-question survey of 696 participants with a self-reported, medically confirmed diagnosis of SLE from 30 countries between March 22, 2021, and May 17, 2021. The cohort was 96% women, and their median age was 42 (interquartile range, 34-51). Nearly 36% of respondents were from Italy, 27% were from Chile, 13% were from France, and just under 9% were Americans. All participants received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and 49% received a second dose. The most common vaccines were Pfizer-BioNTech (57%), Sinovac (22%), AstraZeneca (10%), and Moderna (8%).
Only 21 participants (3%) reported a medically confirmed SLE flare after a median of 3 days (IQR, 0-29) post COVID vaccination, with most experiencing musculoskeletal symptoms (90%) and fatigue (86%). Of the 21 cases, 15 reported a subsequent change in SLE treatment and 4 were admitted to the hospital. A previous flare that occurred within a year before vaccination was associated with an increased risk of flare post vaccination (relative risk, 5.52; 95% confidence interval, 2.17-14.03; P < .0001).
Side effects – including swelling, soreness, fever, chills, fatigue, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and headache – were reported in 45% of participants (n = 316) after their first dose and in 53% of the 343 participants who received a second dose. There was no notable difference in the likelihood of side effects across gender and age or in patients who received mRNA vaccines, compared with vaccines with other modes of action. Patients who reported side effects after the first dose were more likely to also report them after the second, compared with those who reported none (109 [81%] of 135 vs. 72 [35%] of 205; RR, 2.30; 95% CI, 1.88-2.82; P < .0001).
In the majority of cases (2,232 of 2,683), the side effects were of minor or moderate intensity and did not affect the participants’ ability to perform daily tasks. The study found no significant association between side effects and a SLE flare and SLE medications or previous SLE disease manifestations.
When asked to comment on the study, Amit Saxena, MD, of the Lupus Center at New York University Langone Health, said: “What we are seeing is pretty mild to moderate in terms of follow-up side effects or lupus-related activity. Several studies have shown this amongst our autoimmune rheumatology cohort, as well as what I’ve seen clinically in my own patients. More than anything else, numbers are the most important, and this is a large study.”
He acknowledged the benefits of going directly to patients to gauge their responses and reactions, giving them the opportunity to share concerns that physicians may not think about.
“As rheumatologists, we tend to focus on certain things that might not necessarily be what the patients themselves focus on,” he said. “I think the fact that this questionnaire dealt with a lot of what people complain about – fatigue, sore arm, things that we know are part of getting the vaccine – they aren’t necessarily things we capture with tools that screen for lupus flares, for example.”
More than anything, Dr. Saxena commended the study’s timeliness. “Patients are constantly asking us about the vaccine, and there’s so much misinformation,” he said. “People say, ‘Because I have lupus, I was told not to get vaccinated.’ I don’t know where they get that information from; we are telling everyone to get it, especially our lupus patients.”
The authors recognized their study’s main limitation as the self-reported and subjective nature of the survey, which they attempted to mitigate by asking for medically confirmed flares only. They noted, however, that the short median time between vaccination and flare onset could be caused by patients confusing expected side effects for something more serious, meaning the 3% figure “could be an overestimation of the actual flare rate.”
“Vaccination is recommended for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases according to the American College of Rheumatology,” they added, “irrespective of disease activity and severity.”
Several authors reported potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consultancy fees and grants from Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, and Janssen, all unrelated to the study.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy still weighs heavy for some rheumatic disease patients
With 49% of the U.S. population fully vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, a new study highlights the degree of vaccine hesitancy among patients with rheumatic disease to get the vaccine.
The international study, published in May 2021 in Rheumatology, suggests that, of 1,258 patients surveyed worldwide, approximately 40% of patients said they would decline the vaccine.
“Sometimes it’s helpful to talk through their concerns,” said Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, a University of Alabama at Birmingham rheumatologist who leads the American College of Rheumatology COVID-19 vaccine task force. Dr. Curtis recently reviewed the current literature on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
COVID-19 vaccinations for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIIRD) is not straightforward. The immune response can be blunted by existing treatments and disease flares can occur.
The latest version of COVID-19 vaccination guidance for patients with RMDs from the ACR addresses vaccine use and implementation strategies. The guidance was issued as conditional or provisional because of the lack of evidence. Its principals are largely based on accepted practice for other vaccines. The guidance is routinely updated as new evidence becomes available. In his presentation at GRAPPA, Dr. Curtis reviewed the latest version of the guidance, which he emphasized is a guidance only and not meant to replace clinical judgment or shared decision-making with patients.
“This is a platform for you to start from as you are thinking about and discussing with your patient what might be best for him or her,” he said.
Concerns about impact of disease activity, treatments on effectiveness
Dr. Curtis highlighted some controversial aspects of COVID-19 vaccines, including heterogeneity of rheumatic diseases and treatment. Patients with AIIRD, including psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, RA, and lupus, are at higher risk for hospitalized COVID-19 and worse outcomes, and as such, they are prioritized for vaccination by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
However, for AIIRD patients, the immune response to COVID-19 vaccination can be “blunted,” according to one study. This may be because of glucocorticoid use or high disease activity. Immunomodulatory therapies, such as methotrexate, rituximab, and abatacept, are known to diminish vaccine response in general. The evidence is less clear for tumor necrosis factor and Janus kinase inhibitors, but they are thought to have the same impact on vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Curtis said. But in these cases, if the effect of a COVID-19 vaccine drops from 90% to 70%, the benefits of vaccination still far outweighs the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“Although we don’t have strong data with clinical outcomes for autoimmune disease or inflammatory disease patients, I’ll run a hypothetical and say: ‘Look, if this vaccine starts 90%-95% effective, even if it’s only 70% effective in somebody with lupus or vasculitis or someone who is taking a higher dose of steroids, I’ll take 70% over nothing if you chose to be vaccinated,’ ” he said.
The benefit of vaccination also outweighs the potential risk of disease flare, he said. The risk is real, but to date, no studies have pointed to a significant risk of disease flare or worsening. However, there have been reported cases of myocardial infarction.
Autoimmune manifestations after vaccination vs. after infection
Researchers writing in the June 29, 2021, issue of JAMA Cardiology described case reports of acute myocarditis in 23 people who received the BNT162b2-mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) messenger RNA (mRNA) COVID-19 vaccines. Plus, there been subsequent reports of myocarditis in other patients, wrote David K. Shay, MD, MPH, in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Shay is a member of the CDC COVID-19 Response Team.
“What do we know about this possible association between myocarditis and immunization with mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and what remains unclear? Acute onset of chest pain 3-5 days after vaccine administration, usually after a second dose, is a typical feature of reported cases and suggests an immune-mediated mechanism,” he said.
The cases of myocarditis are concerning, Dr. Curtis said, but the risk is very low with relatively few cases reported among 161 million fully vaccinated people in the United States.
“Certainly, we’re not seeking to minimize that, but the risk of getting COVID and some of the downstream sequelae (autoimmune manifestations) almost certainly outweigh the risks for some of the autoimmune manifestations or worsening [condition],” he said.
A nationwide cohort study from Denmark of 58,052 patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease published in December 2020 in Rheumatology, found that patients with COVID-19 who had an inflammatory rheumatic disease were more likely to be admitted to the hospital, compared with COVID-19 patients without rheumatic disease. Patients with rheumatic disease had a higher risk of a severe COVID-19 outcome, but it was not a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Curtis, adding that the individual factors such as age and treatment currently received largely determines the risk. The strongest associations between hospitalization for COVID-19 and rheumatic disease were found among patients with RA, vasculitis, and connective tissue disease. Dr. Curtis noted that his own new study results show that risk of death from a COVID-19 infection is higher for patients who have RA or psoriatic arthritis.
There have been published case reports of patients who have developed new-onset lupus, vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune cytopenias, and other manifestations after a COVID-19 infection. “These authors suggest that perhaps there is a transient influence on the immune system that leads to a loss of self-tolerance to antigens,” Dr. Curtis said. “Some patients may have an underlying predisposition to autoimmunity in which infections just unmask as we sometimes see with other infections – chronic hepatitis for example.”
Antibody tests not recommended
In its COVID-19 guidance, the ACR, like the Food and Drug Administration, recommends health care providers not to routinely order antibody tests for IgM or IgG to assess immunity after a person has been vaccinated or to assess the need for vaccination in an unvaccinated person. More research is needed to determine if antibodies provide protection, and if so, for how long and how much. Plus, the antibody testing process is not clear cut, so ordering the wrong test is possible, Dr. Curtis said. The tests should clearly differentiate between spike proteins or nucleocapsid proteins.
“The bottom line is that you might be ordering the wrong lab test. Even if you’re ordering the right lab test, I would assert that you probably don’t know what to do with the result. I would then ask you, ‘Does it mean they are protected? Does it mean they are not protected? What are you going to do with the results?’ ” he asked.
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, a specialist in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that, at this point, it’s too early to know what antibody tests mean. “I think it is tempting to test some people, especially patients on B-cell depletion therapy and those on mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Outside of those two types of [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] users, I wouldn’t be tempted to test. We don’t know how well protected they are, but we assume they are protected to some extent,” he said. “They’re probably partially protected and as such, they should take the same precautions they were taking a year ago: masking and avoidance. I think that’s just how it’s going to be for those folks for another year until we get this thing sorted out.”
Modifications to existing rheumatic disease therapies
In its COVID-19 vaccine guidance, the ACR issued recommendations for some common rheumatic disease therapeutics before and/or after the COVID-19 vaccine is administered. The modifications are limited to MMF, methotrexate, JAK inhibitors, subcutaneous abatacept, acetaminophen, and NSAIDs. The recommendations include: hold mycophenolate for 1 week after vaccination if disease is stable; for patients with well-controlled disease, hold methotrexate for 1 week after each of the two mRNA vaccine doses; for patients with well-controlled disease receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, hold methotrexate for 2 weeks after receiving the vaccine; hold JAK inhibitors for 1 week after each dose; for abatacept subcutaneous, hold treatment for 1 week before and after the first dose; and in patients with stable disease, hold acetaminophen and NSAIDs for 24 hours before vaccination, because taking either before vaccination could blunt the vaccine response, Dr. Curtis said.
Holding medication, such as methotrexate, could risk having a flare-up of disease. One study showed the rate of disease flare-up because of withholding standard treatment may be up to 11%, compared with 5.1% in patients who did not hold treatment, he said.
“The point is, if you hold some of these therapies, whether methotrexate or tofacitinib, arthritis will get a little bit worse,” Dr. Curtis said.
A study published on the preprint server medRxiv found that immunosuppressive therapies blunted the response of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, most significantly with glucocorticoids and B-cell therapies.
“That’s what’s led to a lot of the guidance statements about holding treatments for a week or 2 for rituximab. If you’re giving it at 6-month intervals, you want to schedule the vaccine dose or series at about month 5, or a month before the next cycle,” he said.
Talking with patients about COVID-19 vaccination
In talking with patients about vaccine safety, Dr. Curtis recommends addressing a few common misperceptions. First, COVID-19 viruses were not created with a live-attenuated virus (which would be contraindicated for immunosuppressed patients). “You can put patients’ mind at ease that none of the vaccine candidates or platforms – even those that say viral vector – put patients at risk for contracting the infection. These are nonreplicating. So, it’s like you extracted the engine that would allow this virus to replicate,” he said.
Of three COVID-19 vaccinations available in the United States, is one better than the other? The ACR COVID-19 vaccine task force did not reach a consensus on safety profiles of the vaccines because, without head-to-head comparisons, it’s impossible to know, he said.
In talking with patients, review the protocol for continuing with prescribed treatment modalities before the patient receives a COVID-19 vaccine. Safety concerns and concerns about the possibility of having a disease flare-up should be addressed, he said.
With 49% of the U.S. population fully vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, a new study highlights the degree of vaccine hesitancy among patients with rheumatic disease to get the vaccine.
The international study, published in May 2021 in Rheumatology, suggests that, of 1,258 patients surveyed worldwide, approximately 40% of patients said they would decline the vaccine.
“Sometimes it’s helpful to talk through their concerns,” said Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, a University of Alabama at Birmingham rheumatologist who leads the American College of Rheumatology COVID-19 vaccine task force. Dr. Curtis recently reviewed the current literature on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
COVID-19 vaccinations for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIIRD) is not straightforward. The immune response can be blunted by existing treatments and disease flares can occur.
The latest version of COVID-19 vaccination guidance for patients with RMDs from the ACR addresses vaccine use and implementation strategies. The guidance was issued as conditional or provisional because of the lack of evidence. Its principals are largely based on accepted practice for other vaccines. The guidance is routinely updated as new evidence becomes available. In his presentation at GRAPPA, Dr. Curtis reviewed the latest version of the guidance, which he emphasized is a guidance only and not meant to replace clinical judgment or shared decision-making with patients.
“This is a platform for you to start from as you are thinking about and discussing with your patient what might be best for him or her,” he said.
Concerns about impact of disease activity, treatments on effectiveness
Dr. Curtis highlighted some controversial aspects of COVID-19 vaccines, including heterogeneity of rheumatic diseases and treatment. Patients with AIIRD, including psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, RA, and lupus, are at higher risk for hospitalized COVID-19 and worse outcomes, and as such, they are prioritized for vaccination by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
However, for AIIRD patients, the immune response to COVID-19 vaccination can be “blunted,” according to one study. This may be because of glucocorticoid use or high disease activity. Immunomodulatory therapies, such as methotrexate, rituximab, and abatacept, are known to diminish vaccine response in general. The evidence is less clear for tumor necrosis factor and Janus kinase inhibitors, but they are thought to have the same impact on vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Curtis said. But in these cases, if the effect of a COVID-19 vaccine drops from 90% to 70%, the benefits of vaccination still far outweighs the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“Although we don’t have strong data with clinical outcomes for autoimmune disease or inflammatory disease patients, I’ll run a hypothetical and say: ‘Look, if this vaccine starts 90%-95% effective, even if it’s only 70% effective in somebody with lupus or vasculitis or someone who is taking a higher dose of steroids, I’ll take 70% over nothing if you chose to be vaccinated,’ ” he said.
The benefit of vaccination also outweighs the potential risk of disease flare, he said. The risk is real, but to date, no studies have pointed to a significant risk of disease flare or worsening. However, there have been reported cases of myocardial infarction.
Autoimmune manifestations after vaccination vs. after infection
Researchers writing in the June 29, 2021, issue of JAMA Cardiology described case reports of acute myocarditis in 23 people who received the BNT162b2-mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) messenger RNA (mRNA) COVID-19 vaccines. Plus, there been subsequent reports of myocarditis in other patients, wrote David K. Shay, MD, MPH, in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Shay is a member of the CDC COVID-19 Response Team.
“What do we know about this possible association between myocarditis and immunization with mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and what remains unclear? Acute onset of chest pain 3-5 days after vaccine administration, usually after a second dose, is a typical feature of reported cases and suggests an immune-mediated mechanism,” he said.
The cases of myocarditis are concerning, Dr. Curtis said, but the risk is very low with relatively few cases reported among 161 million fully vaccinated people in the United States.
“Certainly, we’re not seeking to minimize that, but the risk of getting COVID and some of the downstream sequelae (autoimmune manifestations) almost certainly outweigh the risks for some of the autoimmune manifestations or worsening [condition],” he said.
A nationwide cohort study from Denmark of 58,052 patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease published in December 2020 in Rheumatology, found that patients with COVID-19 who had an inflammatory rheumatic disease were more likely to be admitted to the hospital, compared with COVID-19 patients without rheumatic disease. Patients with rheumatic disease had a higher risk of a severe COVID-19 outcome, but it was not a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Curtis, adding that the individual factors such as age and treatment currently received largely determines the risk. The strongest associations between hospitalization for COVID-19 and rheumatic disease were found among patients with RA, vasculitis, and connective tissue disease. Dr. Curtis noted that his own new study results show that risk of death from a COVID-19 infection is higher for patients who have RA or psoriatic arthritis.
There have been published case reports of patients who have developed new-onset lupus, vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune cytopenias, and other manifestations after a COVID-19 infection. “These authors suggest that perhaps there is a transient influence on the immune system that leads to a loss of self-tolerance to antigens,” Dr. Curtis said. “Some patients may have an underlying predisposition to autoimmunity in which infections just unmask as we sometimes see with other infections – chronic hepatitis for example.”
Antibody tests not recommended
In its COVID-19 guidance, the ACR, like the Food and Drug Administration, recommends health care providers not to routinely order antibody tests for IgM or IgG to assess immunity after a person has been vaccinated or to assess the need for vaccination in an unvaccinated person. More research is needed to determine if antibodies provide protection, and if so, for how long and how much. Plus, the antibody testing process is not clear cut, so ordering the wrong test is possible, Dr. Curtis said. The tests should clearly differentiate between spike proteins or nucleocapsid proteins.
“The bottom line is that you might be ordering the wrong lab test. Even if you’re ordering the right lab test, I would assert that you probably don’t know what to do with the result. I would then ask you, ‘Does it mean they are protected? Does it mean they are not protected? What are you going to do with the results?’ ” he asked.
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, a specialist in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that, at this point, it’s too early to know what antibody tests mean. “I think it is tempting to test some people, especially patients on B-cell depletion therapy and those on mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Outside of those two types of [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] users, I wouldn’t be tempted to test. We don’t know how well protected they are, but we assume they are protected to some extent,” he said. “They’re probably partially protected and as such, they should take the same precautions they were taking a year ago: masking and avoidance. I think that’s just how it’s going to be for those folks for another year until we get this thing sorted out.”
Modifications to existing rheumatic disease therapies
In its COVID-19 vaccine guidance, the ACR issued recommendations for some common rheumatic disease therapeutics before and/or after the COVID-19 vaccine is administered. The modifications are limited to MMF, methotrexate, JAK inhibitors, subcutaneous abatacept, acetaminophen, and NSAIDs. The recommendations include: hold mycophenolate for 1 week after vaccination if disease is stable; for patients with well-controlled disease, hold methotrexate for 1 week after each of the two mRNA vaccine doses; for patients with well-controlled disease receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, hold methotrexate for 2 weeks after receiving the vaccine; hold JAK inhibitors for 1 week after each dose; for abatacept subcutaneous, hold treatment for 1 week before and after the first dose; and in patients with stable disease, hold acetaminophen and NSAIDs for 24 hours before vaccination, because taking either before vaccination could blunt the vaccine response, Dr. Curtis said.
Holding medication, such as methotrexate, could risk having a flare-up of disease. One study showed the rate of disease flare-up because of withholding standard treatment may be up to 11%, compared with 5.1% in patients who did not hold treatment, he said.
“The point is, if you hold some of these therapies, whether methotrexate or tofacitinib, arthritis will get a little bit worse,” Dr. Curtis said.
A study published on the preprint server medRxiv found that immunosuppressive therapies blunted the response of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, most significantly with glucocorticoids and B-cell therapies.
“That’s what’s led to a lot of the guidance statements about holding treatments for a week or 2 for rituximab. If you’re giving it at 6-month intervals, you want to schedule the vaccine dose or series at about month 5, or a month before the next cycle,” he said.
Talking with patients about COVID-19 vaccination
In talking with patients about vaccine safety, Dr. Curtis recommends addressing a few common misperceptions. First, COVID-19 viruses were not created with a live-attenuated virus (which would be contraindicated for immunosuppressed patients). “You can put patients’ mind at ease that none of the vaccine candidates or platforms – even those that say viral vector – put patients at risk for contracting the infection. These are nonreplicating. So, it’s like you extracted the engine that would allow this virus to replicate,” he said.
Of three COVID-19 vaccinations available in the United States, is one better than the other? The ACR COVID-19 vaccine task force did not reach a consensus on safety profiles of the vaccines because, without head-to-head comparisons, it’s impossible to know, he said.
In talking with patients, review the protocol for continuing with prescribed treatment modalities before the patient receives a COVID-19 vaccine. Safety concerns and concerns about the possibility of having a disease flare-up should be addressed, he said.
With 49% of the U.S. population fully vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, a new study highlights the degree of vaccine hesitancy among patients with rheumatic disease to get the vaccine.
The international study, published in May 2021 in Rheumatology, suggests that, of 1,258 patients surveyed worldwide, approximately 40% of patients said they would decline the vaccine.
“Sometimes it’s helpful to talk through their concerns,” said Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, a University of Alabama at Birmingham rheumatologist who leads the American College of Rheumatology COVID-19 vaccine task force. Dr. Curtis recently reviewed the current literature on COVID-19 vaccination in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
COVID-19 vaccinations for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIIRD) is not straightforward. The immune response can be blunted by existing treatments and disease flares can occur.
The latest version of COVID-19 vaccination guidance for patients with RMDs from the ACR addresses vaccine use and implementation strategies. The guidance was issued as conditional or provisional because of the lack of evidence. Its principals are largely based on accepted practice for other vaccines. The guidance is routinely updated as new evidence becomes available. In his presentation at GRAPPA, Dr. Curtis reviewed the latest version of the guidance, which he emphasized is a guidance only and not meant to replace clinical judgment or shared decision-making with patients.
“This is a platform for you to start from as you are thinking about and discussing with your patient what might be best for him or her,” he said.
Concerns about impact of disease activity, treatments on effectiveness
Dr. Curtis highlighted some controversial aspects of COVID-19 vaccines, including heterogeneity of rheumatic diseases and treatment. Patients with AIIRD, including psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, RA, and lupus, are at higher risk for hospitalized COVID-19 and worse outcomes, and as such, they are prioritized for vaccination by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
However, for AIIRD patients, the immune response to COVID-19 vaccination can be “blunted,” according to one study. This may be because of glucocorticoid use or high disease activity. Immunomodulatory therapies, such as methotrexate, rituximab, and abatacept, are known to diminish vaccine response in general. The evidence is less clear for tumor necrosis factor and Janus kinase inhibitors, but they are thought to have the same impact on vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Curtis said. But in these cases, if the effect of a COVID-19 vaccine drops from 90% to 70%, the benefits of vaccination still far outweighs the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“Although we don’t have strong data with clinical outcomes for autoimmune disease or inflammatory disease patients, I’ll run a hypothetical and say: ‘Look, if this vaccine starts 90%-95% effective, even if it’s only 70% effective in somebody with lupus or vasculitis or someone who is taking a higher dose of steroids, I’ll take 70% over nothing if you chose to be vaccinated,’ ” he said.
The benefit of vaccination also outweighs the potential risk of disease flare, he said. The risk is real, but to date, no studies have pointed to a significant risk of disease flare or worsening. However, there have been reported cases of myocardial infarction.
Autoimmune manifestations after vaccination vs. after infection
Researchers writing in the June 29, 2021, issue of JAMA Cardiology described case reports of acute myocarditis in 23 people who received the BNT162b2-mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) messenger RNA (mRNA) COVID-19 vaccines. Plus, there been subsequent reports of myocarditis in other patients, wrote David K. Shay, MD, MPH, in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Shay is a member of the CDC COVID-19 Response Team.
“What do we know about this possible association between myocarditis and immunization with mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and what remains unclear? Acute onset of chest pain 3-5 days after vaccine administration, usually after a second dose, is a typical feature of reported cases and suggests an immune-mediated mechanism,” he said.
The cases of myocarditis are concerning, Dr. Curtis said, but the risk is very low with relatively few cases reported among 161 million fully vaccinated people in the United States.
“Certainly, we’re not seeking to minimize that, but the risk of getting COVID and some of the downstream sequelae (autoimmune manifestations) almost certainly outweigh the risks for some of the autoimmune manifestations or worsening [condition],” he said.
A nationwide cohort study from Denmark of 58,052 patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease published in December 2020 in Rheumatology, found that patients with COVID-19 who had an inflammatory rheumatic disease were more likely to be admitted to the hospital, compared with COVID-19 patients without rheumatic disease. Patients with rheumatic disease had a higher risk of a severe COVID-19 outcome, but it was not a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Curtis, adding that the individual factors such as age and treatment currently received largely determines the risk. The strongest associations between hospitalization for COVID-19 and rheumatic disease were found among patients with RA, vasculitis, and connective tissue disease. Dr. Curtis noted that his own new study results show that risk of death from a COVID-19 infection is higher for patients who have RA or psoriatic arthritis.
There have been published case reports of patients who have developed new-onset lupus, vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune cytopenias, and other manifestations after a COVID-19 infection. “These authors suggest that perhaps there is a transient influence on the immune system that leads to a loss of self-tolerance to antigens,” Dr. Curtis said. “Some patients may have an underlying predisposition to autoimmunity in which infections just unmask as we sometimes see with other infections – chronic hepatitis for example.”
Antibody tests not recommended
In its COVID-19 guidance, the ACR, like the Food and Drug Administration, recommends health care providers not to routinely order antibody tests for IgM or IgG to assess immunity after a person has been vaccinated or to assess the need for vaccination in an unvaccinated person. More research is needed to determine if antibodies provide protection, and if so, for how long and how much. Plus, the antibody testing process is not clear cut, so ordering the wrong test is possible, Dr. Curtis said. The tests should clearly differentiate between spike proteins or nucleocapsid proteins.
“The bottom line is that you might be ordering the wrong lab test. Even if you’re ordering the right lab test, I would assert that you probably don’t know what to do with the result. I would then ask you, ‘Does it mean they are protected? Does it mean they are not protected? What are you going to do with the results?’ ” he asked.
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, a specialist in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that, at this point, it’s too early to know what antibody tests mean. “I think it is tempting to test some people, especially patients on B-cell depletion therapy and those on mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). Outside of those two types of [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] users, I wouldn’t be tempted to test. We don’t know how well protected they are, but we assume they are protected to some extent,” he said. “They’re probably partially protected and as such, they should take the same precautions they were taking a year ago: masking and avoidance. I think that’s just how it’s going to be for those folks for another year until we get this thing sorted out.”
Modifications to existing rheumatic disease therapies
In its COVID-19 vaccine guidance, the ACR issued recommendations for some common rheumatic disease therapeutics before and/or after the COVID-19 vaccine is administered. The modifications are limited to MMF, methotrexate, JAK inhibitors, subcutaneous abatacept, acetaminophen, and NSAIDs. The recommendations include: hold mycophenolate for 1 week after vaccination if disease is stable; for patients with well-controlled disease, hold methotrexate for 1 week after each of the two mRNA vaccine doses; for patients with well-controlled disease receiving the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, hold methotrexate for 2 weeks after receiving the vaccine; hold JAK inhibitors for 1 week after each dose; for abatacept subcutaneous, hold treatment for 1 week before and after the first dose; and in patients with stable disease, hold acetaminophen and NSAIDs for 24 hours before vaccination, because taking either before vaccination could blunt the vaccine response, Dr. Curtis said.
Holding medication, such as methotrexate, could risk having a flare-up of disease. One study showed the rate of disease flare-up because of withholding standard treatment may be up to 11%, compared with 5.1% in patients who did not hold treatment, he said.
“The point is, if you hold some of these therapies, whether methotrexate or tofacitinib, arthritis will get a little bit worse,” Dr. Curtis said.
A study published on the preprint server medRxiv found that immunosuppressive therapies blunted the response of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, most significantly with glucocorticoids and B-cell therapies.
“That’s what’s led to a lot of the guidance statements about holding treatments for a week or 2 for rituximab. If you’re giving it at 6-month intervals, you want to schedule the vaccine dose or series at about month 5, or a month before the next cycle,” he said.
Talking with patients about COVID-19 vaccination
In talking with patients about vaccine safety, Dr. Curtis recommends addressing a few common misperceptions. First, COVID-19 viruses were not created with a live-attenuated virus (which would be contraindicated for immunosuppressed patients). “You can put patients’ mind at ease that none of the vaccine candidates or platforms – even those that say viral vector – put patients at risk for contracting the infection. These are nonreplicating. So, it’s like you extracted the engine that would allow this virus to replicate,” he said.
Of three COVID-19 vaccinations available in the United States, is one better than the other? The ACR COVID-19 vaccine task force did not reach a consensus on safety profiles of the vaccines because, without head-to-head comparisons, it’s impossible to know, he said.
In talking with patients, review the protocol for continuing with prescribed treatment modalities before the patient receives a COVID-19 vaccine. Safety concerns and concerns about the possibility of having a disease flare-up should be addressed, he said.
FROM THE GRAPPA 2021 ANNUAL MEETING