User login
Surgeons in China ‘are the executioners,’ procuring organs before brain death
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a deep dive into obscure Chinese language transplant journals, a pair of researchers from Australia and Israel have added a new layer of horror to what’s already known about forced organ harvesting in China.
Searching for documentation that vital organs are being harvested from nonconsenting executed prisoners, a practice that the China Tribunal confirmed “beyond any reasonable doubt” in 2020, Jacob Lavee, MD, an Israeli heart transplant surgeon, and Matthew Roberston, a PhD student at Australian National University, uncovered something even more shocking: that vital organs are being explanted from patients who are still alive.
“We have shown for the first time that the transplant surgeons are the executioners – that the mode of execution is organ procurement. These are self-admissions of executing the patient,” Dr. Lavee told this news organization. “Up until now, there has been what we call circumstantial evidence of this, but our paper is what you’d call the smoking gun, because it’s in the words of the physicians themselves that they are doing it. In the words of these surgeons, intubation was done only after the beginning of surgery, which means the patients were breathing spontaneously up until the moment the operation started ... meaning they were not brain dead.”
The research, published in the American Journal of Transplantation, involved intricate analysis of thousands of Chinese language transplant articles and identified 71 articles in which transplant surgeons describe starting organ procurement surgery before declaring their patients brain dead.
“What we found were improper, illegitimate, nonexistent, or false declarations of brain death,” Mr. Robertson said in an interview. He explained that this violates what’s known as the dead donor rule, which is fundamental in transplant ethics. “The surgeons wrote that the donor was brain dead, but according to everything we know about medical science, they could not possibly have been brain dead because there was no apnea test performed. Brain death is not just something you say, there’s this whole battery of tests, and the key is the apnea test, [in which] the patient is already intubated and ventilated, they turn the machine off, and they’re looking for carbon dioxide in the blood above a certain level.”
Mr. Robertson and Dr. Lavee have painstakingly documented “incriminating sentences” in each of the 71 articles proving that brain death had not occurred before the organ explantation procedure began. “There were two criteria by which we claimed a problematic brain death declaration,” said Mr. Robertson, who translated the Chinese. “One was where the patient was not ventilated and was only intubated after they were declared brain dead; the other was that the intubation took place immediately prior to the surgery beginning.”
“It was mind-boggling,” said Dr. Lavee, from Tel Aviv University. “When I first started reading, my initial reaction is, ‘This can’t be.’ I read it once, and again, and I insisted that Matt get another independent translation of the Chinese just to be sure. I told him, ‘There’s no way a physician, a surgeon could write this – it doesn’t make sense.’ But the more of these papers we read, we saw it was a pattern – and they didn’t come out of a single medical center, they are spread all over China.”
For the analysis, Mr. Robertson wrote code and customized an algorithm to examine 124,770 medical articles from official Chinese databases between 1980 and 2020. The 71 articles revealing cases involving problematic brain death came from 56 hospitals (of which 12 were military) in 33 cities across 15 provinces, they report. In total, 348 surgeons, nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical workers or researchers were listed as authors of these publications.
Why would these medical personnel write such self-incriminating evidence? The researchers say it’s unclear. “They don’t think anyone’s reading this stuff,” Mr. Robertson suggests. “Sometimes it’s revealed in just five or six characters in a paper of eight pages.” Dr. Lavee wonders if it’s also ignorance. “If this has been a practice for 20 or 30 years in China, I guess nobody at that time was aware they were doing something wrong, although how to declare brain death is something that is known in China. They’ve published a lot about it.”
The article is “evidence that this barbarity continues and is a very valuable contribution that continues to bring attention to an enormous human rights violation,” said Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine. “What they’ve reported has been going on for many, many years, the data are very clear that China’s doing many more transplants than they have cadaver organ donors,” he said, adding that the country’s well-documented and lucrative involvement in transplant tourism “means you have to have a donor ready when the would-be recipient appears; you have to have a matched organ available, and that’s hard to do waiting on a cadaver donor.”
Although the researchers found no incriminating publications after 2015, they speculate that this is likely due to growing awareness among Chinese surgeons that publishing the information would attract international condemnation. “We think these practices are continuing to go on,” said Dr. Lavee. He acknowledged that a voluntary organ donation program is slowly developing in parallel to this. He said, given China’s place as the world’s second largest transplant country behind the U.S., as well as its low rate of voluntary donation, it’s reasonable to conclude that the main source of organs remains prisoners on death row.
Dr. Caplan and the researchers have called for academic institutions and medical journals to resume their previous boycotts of Chinese transplant publications and speakers, but as long as China denies the practices, economic and political leaders will turn a blind eye. “In the past, I don’t think the question of China’s medical professional involvement in the execution of donors has been taken as seriously as it should have,” said Mr. Robertson. “I certainly hope that with the publication of this paper in the leading journal in the field, this will change.”
The study was supported by the Google Cloud Research Credits program, the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Mr. Robertson, Dr. Lavee, and Dr. Caplan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Extraction of infected implanted cardiac devices rare, despite guidelines
The rates of infection involving cardiac implanted electronic devices (CIEDs), like pacemakers and cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), are substantial, but only a minority of patients in the United States receive the guideline-directed recommendation of device removal, according to data from a Medicare population.
The study was conducted on the hypothesis that adherence to guidelines were low, “but we were surprised by how low the extraction rates turned out to be,” Sean D. Pokorney, MD, an electrophysiologist at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The major U.S. and European guidelines are uniform in recommending complete extraction for a CIED infection. The American Heart Association and the Heart Rhythm Society and two out of the three other guidelines cited by Dr. Pokorney not only recommend extraction but specify prompt extraction.
Neither complete extraction nor prompt extraction are typical.
Of the 11,619 CIED infection cases identified in the Medicare database, 18.2% underwent extraction within 30 days of diagnosis. Only 13% were extracted within 6 days.
Lack of extraction may cause avoidable mortality
The result is likely to be avoidable mortality. Among those with extraction within 30 days, 80% were still alive 1 year later. Survival at 1 year fell to 67.6% in those without an extraction within this time frame.
This translated to a 22% lower rate of death at 1 year (hazard ratio, 0.78; P = .008) in those who underwent extraction within 30 days.
For those in whom the device was extracted within 7 days, the associated HR for death at 1 year was more than 40% lower (HR, 0.59; P < .001), reported Dr. Pokorney, who characterized these reductions as occurring in “a dose-response fashion.”
The very high risk of relapse despite antibiotics is the reason that “there is a class 1 indication for complete hardware removal,” Dr. Pokorney. He cited five studies that addressed this question. With partial device removal or medical therapy alone, relapse was consistently 50% or greater. In one study, it was 67%. In another it was 100%.
With complete removal, the rate of infection relapse was 1% or lower in four. In the fifth, the rate was 4.2%.
Infections can occur early or late after implantation, but cases accumulate over time. In the Medicare data sample, infection rates climbed from 0.3% at 1 year to 0.6% at 2 years and then to 1.1% at 3 years, Dr. Pokorney reported.
Other studies have also shown a steady increase in the proportion of implanted devices associated with infection over time. In a cohort study conducted in Olmstead County, Minnesota, the cumulative probability of a CIED infection reached 6.2% after 15 years and 11.7% after 25 years. While about half of these were infections localized to the device pocket, the others were potentially life-threatening systemic infections, according to Dr. Pokorney, who cited this study.
In his analysis of the Medicare data, all fee-for-service patients receiving a first CIED implant over a period of 14 years were included. The 14-year period ended just before the COVID-19 epidemic.
The more than 11,000 CIED infections were identified in 1,065,549 total CIED patients. Most (72%) had received a pacemaker. Of the others , more than half received an ICD and the others received a cardiac resynchronization device. The median age was 78 years.
Female and Black patients even less likely to undergo extraction
About half (49.1%) of the overall study population was female, but females represented only about 40% of those who developed an infection. Blacks represented just under 8% of the population but nearly 16% of the CIED infections. Both females and Blacks were significantly less likely than the overall study population to undergo extraction for their infection (P < .001 for both).
Perhaps predictably, patients with comorbidities were more likely to develop CIED infections. For example, 87% of those with infection, versus only 64.9% of the overall population, were in heart failure at the time of implantation. Diabetes (68.3% vs. 49.3%), ischemic heart disease (91.9% vs. 79.4%), renal disease (70.5% vs. 37.9%), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (70.6% vs. 55.0%) were also more common at baseline in those who went on to a CIED infection than in the overall population.
Based on the evidence that there is a large unmet need to improve adherence to the guidelines, Dr. Pokorney called for care pathways and other quality initiatives to address the problem.
The reasons that so many patients are not undergoing prompt device extraction at the time of infection is unclear, but Dr. Pokorney offered some hypotheses.
“There appears to be a false belief in the efficacy of antibiotics for treating CIED infections,” Dr. Pokorney said.
Comorbidities shouldn’t delay extraction
It is also possible that clinicians are concerned about performing extractions in patients with multiple comorbidities. If clinicians are delaying extractions for this reason, Dr. Pokorney suggested this behavior is misdirected given the fact that delays appear to increase mortality risk.
Several experts, including Rachel Lambert, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., agreed that these data deserve a response.
“I was not surprised by the mortality data, but I was surprised at this low extraction rate,” said Dr. Lambert, who concurs with the guidelines. She indicated this study provides teeth to prompt action.
“It is great to have these data about the increased mortality risk to back up the guidelines,” she said.
More information is needed to understand exactly why CIED infection is not now leading to guideline-directed care. Dr. Pokorney said: “Where do we go from here is a key question.”
While several different types of initiatives might be needed, Dr. Pokorney called for regionalization of care to address the fact that not every center that places CIEDs has the capability to perform extractions.
“Extraction is not available at every center, and it probably should not be available at every center, so mechanisms are need to get patients with infection to the specialized centers that provide care,” he said.
Dr. Pokorney has financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Philips. Dr. Lambert reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic.
The rates of infection involving cardiac implanted electronic devices (CIEDs), like pacemakers and cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), are substantial, but only a minority of patients in the United States receive the guideline-directed recommendation of device removal, according to data from a Medicare population.
The study was conducted on the hypothesis that adherence to guidelines were low, “but we were surprised by how low the extraction rates turned out to be,” Sean D. Pokorney, MD, an electrophysiologist at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The major U.S. and European guidelines are uniform in recommending complete extraction for a CIED infection. The American Heart Association and the Heart Rhythm Society and two out of the three other guidelines cited by Dr. Pokorney not only recommend extraction but specify prompt extraction.
Neither complete extraction nor prompt extraction are typical.
Of the 11,619 CIED infection cases identified in the Medicare database, 18.2% underwent extraction within 30 days of diagnosis. Only 13% were extracted within 6 days.
Lack of extraction may cause avoidable mortality
The result is likely to be avoidable mortality. Among those with extraction within 30 days, 80% were still alive 1 year later. Survival at 1 year fell to 67.6% in those without an extraction within this time frame.
This translated to a 22% lower rate of death at 1 year (hazard ratio, 0.78; P = .008) in those who underwent extraction within 30 days.
For those in whom the device was extracted within 7 days, the associated HR for death at 1 year was more than 40% lower (HR, 0.59; P < .001), reported Dr. Pokorney, who characterized these reductions as occurring in “a dose-response fashion.”
The very high risk of relapse despite antibiotics is the reason that “there is a class 1 indication for complete hardware removal,” Dr. Pokorney. He cited five studies that addressed this question. With partial device removal or medical therapy alone, relapse was consistently 50% or greater. In one study, it was 67%. In another it was 100%.
With complete removal, the rate of infection relapse was 1% or lower in four. In the fifth, the rate was 4.2%.
Infections can occur early or late after implantation, but cases accumulate over time. In the Medicare data sample, infection rates climbed from 0.3% at 1 year to 0.6% at 2 years and then to 1.1% at 3 years, Dr. Pokorney reported.
Other studies have also shown a steady increase in the proportion of implanted devices associated with infection over time. In a cohort study conducted in Olmstead County, Minnesota, the cumulative probability of a CIED infection reached 6.2% after 15 years and 11.7% after 25 years. While about half of these were infections localized to the device pocket, the others were potentially life-threatening systemic infections, according to Dr. Pokorney, who cited this study.
In his analysis of the Medicare data, all fee-for-service patients receiving a first CIED implant over a period of 14 years were included. The 14-year period ended just before the COVID-19 epidemic.
The more than 11,000 CIED infections were identified in 1,065,549 total CIED patients. Most (72%) had received a pacemaker. Of the others , more than half received an ICD and the others received a cardiac resynchronization device. The median age was 78 years.
Female and Black patients even less likely to undergo extraction
About half (49.1%) of the overall study population was female, but females represented only about 40% of those who developed an infection. Blacks represented just under 8% of the population but nearly 16% of the CIED infections. Both females and Blacks were significantly less likely than the overall study population to undergo extraction for their infection (P < .001 for both).
Perhaps predictably, patients with comorbidities were more likely to develop CIED infections. For example, 87% of those with infection, versus only 64.9% of the overall population, were in heart failure at the time of implantation. Diabetes (68.3% vs. 49.3%), ischemic heart disease (91.9% vs. 79.4%), renal disease (70.5% vs. 37.9%), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (70.6% vs. 55.0%) were also more common at baseline in those who went on to a CIED infection than in the overall population.
Based on the evidence that there is a large unmet need to improve adherence to the guidelines, Dr. Pokorney called for care pathways and other quality initiatives to address the problem.
The reasons that so many patients are not undergoing prompt device extraction at the time of infection is unclear, but Dr. Pokorney offered some hypotheses.
“There appears to be a false belief in the efficacy of antibiotics for treating CIED infections,” Dr. Pokorney said.
Comorbidities shouldn’t delay extraction
It is also possible that clinicians are concerned about performing extractions in patients with multiple comorbidities. If clinicians are delaying extractions for this reason, Dr. Pokorney suggested this behavior is misdirected given the fact that delays appear to increase mortality risk.
Several experts, including Rachel Lambert, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., agreed that these data deserve a response.
“I was not surprised by the mortality data, but I was surprised at this low extraction rate,” said Dr. Lambert, who concurs with the guidelines. She indicated this study provides teeth to prompt action.
“It is great to have these data about the increased mortality risk to back up the guidelines,” she said.
More information is needed to understand exactly why CIED infection is not now leading to guideline-directed care. Dr. Pokorney said: “Where do we go from here is a key question.”
While several different types of initiatives might be needed, Dr. Pokorney called for regionalization of care to address the fact that not every center that places CIEDs has the capability to perform extractions.
“Extraction is not available at every center, and it probably should not be available at every center, so mechanisms are need to get patients with infection to the specialized centers that provide care,” he said.
Dr. Pokorney has financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Philips. Dr. Lambert reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic.
The rates of infection involving cardiac implanted electronic devices (CIEDs), like pacemakers and cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), are substantial, but only a minority of patients in the United States receive the guideline-directed recommendation of device removal, according to data from a Medicare population.
The study was conducted on the hypothesis that adherence to guidelines were low, “but we were surprised by how low the extraction rates turned out to be,” Sean D. Pokorney, MD, an electrophysiologist at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The major U.S. and European guidelines are uniform in recommending complete extraction for a CIED infection. The American Heart Association and the Heart Rhythm Society and two out of the three other guidelines cited by Dr. Pokorney not only recommend extraction but specify prompt extraction.
Neither complete extraction nor prompt extraction are typical.
Of the 11,619 CIED infection cases identified in the Medicare database, 18.2% underwent extraction within 30 days of diagnosis. Only 13% were extracted within 6 days.
Lack of extraction may cause avoidable mortality
The result is likely to be avoidable mortality. Among those with extraction within 30 days, 80% were still alive 1 year later. Survival at 1 year fell to 67.6% in those without an extraction within this time frame.
This translated to a 22% lower rate of death at 1 year (hazard ratio, 0.78; P = .008) in those who underwent extraction within 30 days.
For those in whom the device was extracted within 7 days, the associated HR for death at 1 year was more than 40% lower (HR, 0.59; P < .001), reported Dr. Pokorney, who characterized these reductions as occurring in “a dose-response fashion.”
The very high risk of relapse despite antibiotics is the reason that “there is a class 1 indication for complete hardware removal,” Dr. Pokorney. He cited five studies that addressed this question. With partial device removal or medical therapy alone, relapse was consistently 50% or greater. In one study, it was 67%. In another it was 100%.
With complete removal, the rate of infection relapse was 1% or lower in four. In the fifth, the rate was 4.2%.
Infections can occur early or late after implantation, but cases accumulate over time. In the Medicare data sample, infection rates climbed from 0.3% at 1 year to 0.6% at 2 years and then to 1.1% at 3 years, Dr. Pokorney reported.
Other studies have also shown a steady increase in the proportion of implanted devices associated with infection over time. In a cohort study conducted in Olmstead County, Minnesota, the cumulative probability of a CIED infection reached 6.2% after 15 years and 11.7% after 25 years. While about half of these were infections localized to the device pocket, the others were potentially life-threatening systemic infections, according to Dr. Pokorney, who cited this study.
In his analysis of the Medicare data, all fee-for-service patients receiving a first CIED implant over a period of 14 years were included. The 14-year period ended just before the COVID-19 epidemic.
The more than 11,000 CIED infections were identified in 1,065,549 total CIED patients. Most (72%) had received a pacemaker. Of the others , more than half received an ICD and the others received a cardiac resynchronization device. The median age was 78 years.
Female and Black patients even less likely to undergo extraction
About half (49.1%) of the overall study population was female, but females represented only about 40% of those who developed an infection. Blacks represented just under 8% of the population but nearly 16% of the CIED infections. Both females and Blacks were significantly less likely than the overall study population to undergo extraction for their infection (P < .001 for both).
Perhaps predictably, patients with comorbidities were more likely to develop CIED infections. For example, 87% of those with infection, versus only 64.9% of the overall population, were in heart failure at the time of implantation. Diabetes (68.3% vs. 49.3%), ischemic heart disease (91.9% vs. 79.4%), renal disease (70.5% vs. 37.9%), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (70.6% vs. 55.0%) were also more common at baseline in those who went on to a CIED infection than in the overall population.
Based on the evidence that there is a large unmet need to improve adherence to the guidelines, Dr. Pokorney called for care pathways and other quality initiatives to address the problem.
The reasons that so many patients are not undergoing prompt device extraction at the time of infection is unclear, but Dr. Pokorney offered some hypotheses.
“There appears to be a false belief in the efficacy of antibiotics for treating CIED infections,” Dr. Pokorney said.
Comorbidities shouldn’t delay extraction
It is also possible that clinicians are concerned about performing extractions in patients with multiple comorbidities. If clinicians are delaying extractions for this reason, Dr. Pokorney suggested this behavior is misdirected given the fact that delays appear to increase mortality risk.
Several experts, including Rachel Lambert, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., agreed that these data deserve a response.
“I was not surprised by the mortality data, but I was surprised at this low extraction rate,” said Dr. Lambert, who concurs with the guidelines. She indicated this study provides teeth to prompt action.
“It is great to have these data about the increased mortality risk to back up the guidelines,” she said.
More information is needed to understand exactly why CIED infection is not now leading to guideline-directed care. Dr. Pokorney said: “Where do we go from here is a key question.”
While several different types of initiatives might be needed, Dr. Pokorney called for regionalization of care to address the fact that not every center that places CIEDs has the capability to perform extractions.
“Extraction is not available at every center, and it probably should not be available at every center, so mechanisms are need to get patients with infection to the specialized centers that provide care,” he said.
Dr. Pokorney has financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Philips. Dr. Lambert reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic.
FROM ACC 2022
Performance anxiety highly common among surgeons
a new study of surgeons in the United Kingdom shows.
“Performance anxiety or stage fright is a widely recognized problem in music and sports, and there are many similarities between these arenas and the operating theater,” first author Robert Miller, MRCS, of the Surgical Psychology and Performance Group and the department of plastic and reconstructive surgery at St. George’s Hospital NHS Trust, London, said in an interview. “We were aware of it anecdotally in a surgical context, but for one reason or another, perhaps professional pride and fear of negative perception, this is rarely openly discussed amongst surgeons.”
In the cross-sectional study, published in Annals of Surgery, Dr. Miller and colleagues surveyed surgeons in all specialties working in the United Kingdom who had at least 1 year of postgraduate surgical training.
Of a total of 631 responses received, 523 (83%) were included in the analysis. The median age of those who responded was 41.2 years, and the mean duration of surgical experience was 15.3 years (range, 1-52 years). Among them, 62% were men, and 52% were of consultant/attending grade.
All of the respondents – 100% – said they believed that performance anxiety affected surgeons, 87% reported having experienced it themselves, and 65% said they felt that performance anxiety had an effect on their surgical performance.
Both male and female surgeons who reported experiencing performance anxiety had significantly worse mental well-being, as assessed using the Short Warwick Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale, compared with those who did not have performance anxiety (P < .0001 for men and P < .001 for women).
Overall, however, male surgeons had significantly better mental well-being, compared with female surgeons (P = .003), yet both genders had significantly lower mental well-being scores compared with U.K. population norms (P = .0019 for men and P = .0001 for women).
The gender differences are “clearly an important topic, which is likely multifactorial,” Dr. Miller told this news organization. “The gender well-being gap requires more in-depth research, and qualitative work involving female surgeons is critical.”
Surgical perfectionism was significantly more common among respondents who did have performance anxiety in comparison with those who did not (P < .0001).
“Although perfectionism may be a beneficial trait in surgery, our findings from hierarchical multiple regression analysis also indicate that perfectionism, [as well as] sex and experience, may drive surgical performance anxiety and help predict those experiencing [the anxiety],” the authors noted.
Performing in presence of colleagues a key trigger
By far, the leading trigger that was identified as prompting surgeon performance anxiety was the presence – and scrutiny – of colleagues within the parent specialty. This was reported by 151 respondents. Other triggers were having to perform on highly complex or high-risk cases (66 responses) and a lack of experience (30 responses).
Next to planning and preparation, opening up and talking about the anxiety and shedding light on the issue was seen as a leading strategy to help with the problem, but very few respondents reported openly sharing their struggles. Only 9% reported that they had shared it openly; 27% said they had confided in someone, and 47% did not respond to the question.
“I wish we talked about it more and shared our insecurities,” one respondent lamented. “Most of my colleagues pretend they are living gods.”
Only about 45% of respondents reported a specific technique for overcoming their anxiety. In addition to being open about the problem, other techniques included self-care, such as exercise; and distraction outside of work to get perspective; relaxation techniques such as deep or controlled breathing; music; mindfulness; and positive self-statements.
About 9% said they had received psychological counseling for performance anxiety, and only 3% reported using medication for the problem.
Anxiety a positive factor?
Surprisingly, 70% of respondents reported feeling that surgical performance anxiety could have a positive impact on surgical performance, which the authors noted is consistent with some theories.
“This may be explained by the traditional bell-curve relationship between arousal and performance, which describes a dose-dependent relationship between performance and arousal until a ‘tipping point,’ after which performance declines,” the authors explained. “A heightened awareness secondary to anxiety may be beneficial, but at high doses, anxiety can negatively affect attentional control and cause somatic symptoms.”
They noted that “the challenge would be to reap the benefits of low-level stimulation without incurring possible adverse effects.”
Dr. Miller said that, in determining whether selection bias had a role in the results, a detailed analysis showed that “our respondents were not skewed to those with only high levels of trait anxiety.
“We also had a good spread of consultants versus trainees [about half and half], and different specialties, so we feel this is likely to be a representative sample,” he told this news organization.
That being said, the results underscore the need for increased awareness – and open discussion – of the issue of surgical performance anxiety.
“Within other professions, particularly the performing arts and sports, performance psychology is becoming an integral part of training and development,” Dr. Miller said. “We feel surgeons should be supported in a similar manner.
“Surgical performance anxiety is normal for surgeons at all levels and not something to be ashamed about,” Dr. Miller added. “Talk about it, acknowledge it, and be supportive to your colleagues.”
Many keep it to themselves in ‘prevailing culture of stoicism’
Commenting on the study, Carter C. Lebares, MD, an associate professor of surgery and director of the Center for Mindfulness in Surgery, department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, said she was not surprised to see the high rates of performance anxiety among surgeons.
“As surgeons, no matter how hard we train or how thoroughly we prepare our intellectual understanding or the patient, the disease process, and the operation, there may be surprises, unforeseen challenges, or off days,” Dr. Lebares said.
“And whatever we encounter, we are managing these things directly under the scrutiny of others – people who can affect our reputation, operating privileges, and mental health. So, I am not surprised this is a prevalent and widely recognized issue.”
Dr. Lebares noted that the reluctance to share the anxiety is part of a “challenging and recognized conundrum in both medicine and surgery and is a matter of the prevailing culture of stoicism.
“We often are called to shoulder tremendous weight intraoperatively (having perseverance, self-confidence, or sustained focus), and in owning the weight of complications (which eventually we all will have),” she said.
“So, we do need to be strong and not complain, [but] we also need to be able to set that aside [when appropriate] and ask for help or allow others to shoulder the weight for a while, and this is not [yet] a common part of surgical culture.”
Dr. Lebares added that randomized, controlled trials have shown benefits of mindfulness interventions on burnout and anxiety.
“We have observed positive effects on mental noise, self-perception, conflict resolution, and resilience in surgical residents trained in mindfulness-based cognitive skills,” she said. “[Residents] report applying these skills in the OR, in their home lives, and in how they approach their training/education.”
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lebares has developed mindfulness-based cognitive skills training for surgeons but receives no financial compensation for the activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study of surgeons in the United Kingdom shows.
“Performance anxiety or stage fright is a widely recognized problem in music and sports, and there are many similarities between these arenas and the operating theater,” first author Robert Miller, MRCS, of the Surgical Psychology and Performance Group and the department of plastic and reconstructive surgery at St. George’s Hospital NHS Trust, London, said in an interview. “We were aware of it anecdotally in a surgical context, but for one reason or another, perhaps professional pride and fear of negative perception, this is rarely openly discussed amongst surgeons.”
In the cross-sectional study, published in Annals of Surgery, Dr. Miller and colleagues surveyed surgeons in all specialties working in the United Kingdom who had at least 1 year of postgraduate surgical training.
Of a total of 631 responses received, 523 (83%) were included in the analysis. The median age of those who responded was 41.2 years, and the mean duration of surgical experience was 15.3 years (range, 1-52 years). Among them, 62% were men, and 52% were of consultant/attending grade.
All of the respondents – 100% – said they believed that performance anxiety affected surgeons, 87% reported having experienced it themselves, and 65% said they felt that performance anxiety had an effect on their surgical performance.
Both male and female surgeons who reported experiencing performance anxiety had significantly worse mental well-being, as assessed using the Short Warwick Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale, compared with those who did not have performance anxiety (P < .0001 for men and P < .001 for women).
Overall, however, male surgeons had significantly better mental well-being, compared with female surgeons (P = .003), yet both genders had significantly lower mental well-being scores compared with U.K. population norms (P = .0019 for men and P = .0001 for women).
The gender differences are “clearly an important topic, which is likely multifactorial,” Dr. Miller told this news organization. “The gender well-being gap requires more in-depth research, and qualitative work involving female surgeons is critical.”
Surgical perfectionism was significantly more common among respondents who did have performance anxiety in comparison with those who did not (P < .0001).
“Although perfectionism may be a beneficial trait in surgery, our findings from hierarchical multiple regression analysis also indicate that perfectionism, [as well as] sex and experience, may drive surgical performance anxiety and help predict those experiencing [the anxiety],” the authors noted.
Performing in presence of colleagues a key trigger
By far, the leading trigger that was identified as prompting surgeon performance anxiety was the presence – and scrutiny – of colleagues within the parent specialty. This was reported by 151 respondents. Other triggers were having to perform on highly complex or high-risk cases (66 responses) and a lack of experience (30 responses).
Next to planning and preparation, opening up and talking about the anxiety and shedding light on the issue was seen as a leading strategy to help with the problem, but very few respondents reported openly sharing their struggles. Only 9% reported that they had shared it openly; 27% said they had confided in someone, and 47% did not respond to the question.
“I wish we talked about it more and shared our insecurities,” one respondent lamented. “Most of my colleagues pretend they are living gods.”
Only about 45% of respondents reported a specific technique for overcoming their anxiety. In addition to being open about the problem, other techniques included self-care, such as exercise; and distraction outside of work to get perspective; relaxation techniques such as deep or controlled breathing; music; mindfulness; and positive self-statements.
About 9% said they had received psychological counseling for performance anxiety, and only 3% reported using medication for the problem.
Anxiety a positive factor?
Surprisingly, 70% of respondents reported feeling that surgical performance anxiety could have a positive impact on surgical performance, which the authors noted is consistent with some theories.
“This may be explained by the traditional bell-curve relationship between arousal and performance, which describes a dose-dependent relationship between performance and arousal until a ‘tipping point,’ after which performance declines,” the authors explained. “A heightened awareness secondary to anxiety may be beneficial, but at high doses, anxiety can negatively affect attentional control and cause somatic symptoms.”
They noted that “the challenge would be to reap the benefits of low-level stimulation without incurring possible adverse effects.”
Dr. Miller said that, in determining whether selection bias had a role in the results, a detailed analysis showed that “our respondents were not skewed to those with only high levels of trait anxiety.
“We also had a good spread of consultants versus trainees [about half and half], and different specialties, so we feel this is likely to be a representative sample,” he told this news organization.
That being said, the results underscore the need for increased awareness – and open discussion – of the issue of surgical performance anxiety.
“Within other professions, particularly the performing arts and sports, performance psychology is becoming an integral part of training and development,” Dr. Miller said. “We feel surgeons should be supported in a similar manner.
“Surgical performance anxiety is normal for surgeons at all levels and not something to be ashamed about,” Dr. Miller added. “Talk about it, acknowledge it, and be supportive to your colleagues.”
Many keep it to themselves in ‘prevailing culture of stoicism’
Commenting on the study, Carter C. Lebares, MD, an associate professor of surgery and director of the Center for Mindfulness in Surgery, department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, said she was not surprised to see the high rates of performance anxiety among surgeons.
“As surgeons, no matter how hard we train or how thoroughly we prepare our intellectual understanding or the patient, the disease process, and the operation, there may be surprises, unforeseen challenges, or off days,” Dr. Lebares said.
“And whatever we encounter, we are managing these things directly under the scrutiny of others – people who can affect our reputation, operating privileges, and mental health. So, I am not surprised this is a prevalent and widely recognized issue.”
Dr. Lebares noted that the reluctance to share the anxiety is part of a “challenging and recognized conundrum in both medicine and surgery and is a matter of the prevailing culture of stoicism.
“We often are called to shoulder tremendous weight intraoperatively (having perseverance, self-confidence, or sustained focus), and in owning the weight of complications (which eventually we all will have),” she said.
“So, we do need to be strong and not complain, [but] we also need to be able to set that aside [when appropriate] and ask for help or allow others to shoulder the weight for a while, and this is not [yet] a common part of surgical culture.”
Dr. Lebares added that randomized, controlled trials have shown benefits of mindfulness interventions on burnout and anxiety.
“We have observed positive effects on mental noise, self-perception, conflict resolution, and resilience in surgical residents trained in mindfulness-based cognitive skills,” she said. “[Residents] report applying these skills in the OR, in their home lives, and in how they approach their training/education.”
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lebares has developed mindfulness-based cognitive skills training for surgeons but receives no financial compensation for the activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new study of surgeons in the United Kingdom shows.
“Performance anxiety or stage fright is a widely recognized problem in music and sports, and there are many similarities between these arenas and the operating theater,” first author Robert Miller, MRCS, of the Surgical Psychology and Performance Group and the department of plastic and reconstructive surgery at St. George’s Hospital NHS Trust, London, said in an interview. “We were aware of it anecdotally in a surgical context, but for one reason or another, perhaps professional pride and fear of negative perception, this is rarely openly discussed amongst surgeons.”
In the cross-sectional study, published in Annals of Surgery, Dr. Miller and colleagues surveyed surgeons in all specialties working in the United Kingdom who had at least 1 year of postgraduate surgical training.
Of a total of 631 responses received, 523 (83%) were included in the analysis. The median age of those who responded was 41.2 years, and the mean duration of surgical experience was 15.3 years (range, 1-52 years). Among them, 62% were men, and 52% were of consultant/attending grade.
All of the respondents – 100% – said they believed that performance anxiety affected surgeons, 87% reported having experienced it themselves, and 65% said they felt that performance anxiety had an effect on their surgical performance.
Both male and female surgeons who reported experiencing performance anxiety had significantly worse mental well-being, as assessed using the Short Warwick Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale, compared with those who did not have performance anxiety (P < .0001 for men and P < .001 for women).
Overall, however, male surgeons had significantly better mental well-being, compared with female surgeons (P = .003), yet both genders had significantly lower mental well-being scores compared with U.K. population norms (P = .0019 for men and P = .0001 for women).
The gender differences are “clearly an important topic, which is likely multifactorial,” Dr. Miller told this news organization. “The gender well-being gap requires more in-depth research, and qualitative work involving female surgeons is critical.”
Surgical perfectionism was significantly more common among respondents who did have performance anxiety in comparison with those who did not (P < .0001).
“Although perfectionism may be a beneficial trait in surgery, our findings from hierarchical multiple regression analysis also indicate that perfectionism, [as well as] sex and experience, may drive surgical performance anxiety and help predict those experiencing [the anxiety],” the authors noted.
Performing in presence of colleagues a key trigger
By far, the leading trigger that was identified as prompting surgeon performance anxiety was the presence – and scrutiny – of colleagues within the parent specialty. This was reported by 151 respondents. Other triggers were having to perform on highly complex or high-risk cases (66 responses) and a lack of experience (30 responses).
Next to planning and preparation, opening up and talking about the anxiety and shedding light on the issue was seen as a leading strategy to help with the problem, but very few respondents reported openly sharing their struggles. Only 9% reported that they had shared it openly; 27% said they had confided in someone, and 47% did not respond to the question.
“I wish we talked about it more and shared our insecurities,” one respondent lamented. “Most of my colleagues pretend they are living gods.”
Only about 45% of respondents reported a specific technique for overcoming their anxiety. In addition to being open about the problem, other techniques included self-care, such as exercise; and distraction outside of work to get perspective; relaxation techniques such as deep or controlled breathing; music; mindfulness; and positive self-statements.
About 9% said they had received psychological counseling for performance anxiety, and only 3% reported using medication for the problem.
Anxiety a positive factor?
Surprisingly, 70% of respondents reported feeling that surgical performance anxiety could have a positive impact on surgical performance, which the authors noted is consistent with some theories.
“This may be explained by the traditional bell-curve relationship between arousal and performance, which describes a dose-dependent relationship between performance and arousal until a ‘tipping point,’ after which performance declines,” the authors explained. “A heightened awareness secondary to anxiety may be beneficial, but at high doses, anxiety can negatively affect attentional control and cause somatic symptoms.”
They noted that “the challenge would be to reap the benefits of low-level stimulation without incurring possible adverse effects.”
Dr. Miller said that, in determining whether selection bias had a role in the results, a detailed analysis showed that “our respondents were not skewed to those with only high levels of trait anxiety.
“We also had a good spread of consultants versus trainees [about half and half], and different specialties, so we feel this is likely to be a representative sample,” he told this news organization.
That being said, the results underscore the need for increased awareness – and open discussion – of the issue of surgical performance anxiety.
“Within other professions, particularly the performing arts and sports, performance psychology is becoming an integral part of training and development,” Dr. Miller said. “We feel surgeons should be supported in a similar manner.
“Surgical performance anxiety is normal for surgeons at all levels and not something to be ashamed about,” Dr. Miller added. “Talk about it, acknowledge it, and be supportive to your colleagues.”
Many keep it to themselves in ‘prevailing culture of stoicism’
Commenting on the study, Carter C. Lebares, MD, an associate professor of surgery and director of the Center for Mindfulness in Surgery, department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, said she was not surprised to see the high rates of performance anxiety among surgeons.
“As surgeons, no matter how hard we train or how thoroughly we prepare our intellectual understanding or the patient, the disease process, and the operation, there may be surprises, unforeseen challenges, or off days,” Dr. Lebares said.
“And whatever we encounter, we are managing these things directly under the scrutiny of others – people who can affect our reputation, operating privileges, and mental health. So, I am not surprised this is a prevalent and widely recognized issue.”
Dr. Lebares noted that the reluctance to share the anxiety is part of a “challenging and recognized conundrum in both medicine and surgery and is a matter of the prevailing culture of stoicism.
“We often are called to shoulder tremendous weight intraoperatively (having perseverance, self-confidence, or sustained focus), and in owning the weight of complications (which eventually we all will have),” she said.
“So, we do need to be strong and not complain, [but] we also need to be able to set that aside [when appropriate] and ask for help or allow others to shoulder the weight for a while, and this is not [yet] a common part of surgical culture.”
Dr. Lebares added that randomized, controlled trials have shown benefits of mindfulness interventions on burnout and anxiety.
“We have observed positive effects on mental noise, self-perception, conflict resolution, and resilience in surgical residents trained in mindfulness-based cognitive skills,” she said. “[Residents] report applying these skills in the OR, in their home lives, and in how they approach their training/education.”
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lebares has developed mindfulness-based cognitive skills training for surgeons but receives no financial compensation for the activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF SURGERY
Anticoagulation not routinely needed after TAVR: ADAPT-TAVR
In patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), the incidence of leaflet thrombosis was numerically lower in those treated with the anticoagulant edoxaban for 6 months after the procedure than in those who received dual antiplatelet therapy, although the difference was not statistically significant, in the ADAPT-TAVR study.
There was no difference in new cerebral thromboembolism or neurologic/neurocognitive function between the two groups in the study.
Also, there was no significant relation between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and increased risk for cerebral thromboembolism and neurologic dysfunction.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was presented April 4 at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2022 Scientific Session by Duk-Woo Park, MD, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. It was simultaneously published online in Circulation.
“The key messages from this study are that subclinical leaflet thrombosis has not been proven to affect clinical outcomes for patients undergoing valve replacement and that in patients in whom leaflet thrombosis causes no symptoms or complications, its presence should not dictate the type of antithrombotic therapy that patients receive following the implantation of an artificial heart valve,” Dr. Park said.
“These findings do not support the routine use of computed tomography scans to detect subclinical leaflet thrombosis,” he added.
Commenting on the study at an ACC press conference, Megan Coylewright, MD, director of the Structural Heart Program at Erlanger Health System, Chattanooga, Tennessee, said: “Oftentimes when studies are negative, we’re disappointed. In this case, I think we are pleased that the study is negative because it suggests we do not have to expose our TAVR patients to anticoagulation for benefit.”
Dr. Coylewright explained that the ADAPT-TAVR study was asking whether clots form on the valve, as defined by CT.
“We are worried about that for two reasons: could that clot cause a stroke, and could that clot cause the valve to break down over time. This study looked at the first issue. And it found that there was some clot build up on the valve, but that it wasn’t significantly different between the anticoagulant and dual antiplatelet groups. And there was no correlation with embolic events, she noted.
“It shows how fast our field moves. In the U.S. now, we are using aspirin alone at 81 mg for patients who do not have an indication for oral anticoagulation after TAVR. We are moving away from dual antiplatelet therapy because the bleeding risk is so bad,” Dr. Coylewright said.
In his presentation, Dr. Park explained that it is believed that oral anticoagulants are more effective than antiplatelet therapy at reducing subclinical leaflet thrombosis, but it is not known whether there is a causal association between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and cerebral embolism, or whether oral anticoagulation can reduce cerebral embolism related to subclinical leaflet thrombosis.
The ADAPT-TAVR was conducted to look at these issues. The open-label randomized trial was conducted in five centers in Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan.
For the study, 229 patients who had undergone successful TAVR and did not have an indication for anticoagulation were randomized to edoxaban 60 mg once daily, edoxaban 30 mg once daily for patients needing a reduced dose, or dual antiplatelet therapy for 6 months.
The primary endpoint was an incidence of leaflet thrombosis on four-dimensional CT at 6 months.
Results showed a strong trend toward a lower incidence of leaflet thrombosis in the edoxaban groups than in the dual antiplatelet group (9.8% vs. 18.4%; P = .076).
There was a nonsignificant difference in the percentage of patients with new cerebral lesions identified on brain MRI between the edoxaban and dual antiplatelet groups (25.0% vs. 20.2%).
The percentage of patients with worsening of neurologic and neurocognitive function was not different among the groups.
The incidence of any or major bleeding events was not different between two therapies.
There was also no significant association of the presence or extent of leaflet thrombosis with new cerebral lesions or change of neurologic or neurocognitive function.
Dr. Park noted that the trial had several limitations, including an open-label design, use of surrogate imaging outcomes for the primary outcome, and the relatively short follow-up period, so the study was underpowered to detect any meaningful differences in clinical efficacy and safety outcomes. The results should thus be considered hypothesis-generating, highlighting the need for further research, he added.
The long-term effect of leaflet thrombosis or different antithrombotic strategies on bioprosthetic valve durability is still unknown, Dr. Park said.
He also pointed out that the findings cannot be directly extrapolated to patients with an established indication for oral anticoagulant therapy.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was an investigator-initiated trial and was funded by the CardioVascular Research Foundation (Seoul, Korea) and Daiichi Sankyo Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), the incidence of leaflet thrombosis was numerically lower in those treated with the anticoagulant edoxaban for 6 months after the procedure than in those who received dual antiplatelet therapy, although the difference was not statistically significant, in the ADAPT-TAVR study.
There was no difference in new cerebral thromboembolism or neurologic/neurocognitive function between the two groups in the study.
Also, there was no significant relation between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and increased risk for cerebral thromboembolism and neurologic dysfunction.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was presented April 4 at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2022 Scientific Session by Duk-Woo Park, MD, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. It was simultaneously published online in Circulation.
“The key messages from this study are that subclinical leaflet thrombosis has not been proven to affect clinical outcomes for patients undergoing valve replacement and that in patients in whom leaflet thrombosis causes no symptoms or complications, its presence should not dictate the type of antithrombotic therapy that patients receive following the implantation of an artificial heart valve,” Dr. Park said.
“These findings do not support the routine use of computed tomography scans to detect subclinical leaflet thrombosis,” he added.
Commenting on the study at an ACC press conference, Megan Coylewright, MD, director of the Structural Heart Program at Erlanger Health System, Chattanooga, Tennessee, said: “Oftentimes when studies are negative, we’re disappointed. In this case, I think we are pleased that the study is negative because it suggests we do not have to expose our TAVR patients to anticoagulation for benefit.”
Dr. Coylewright explained that the ADAPT-TAVR study was asking whether clots form on the valve, as defined by CT.
“We are worried about that for two reasons: could that clot cause a stroke, and could that clot cause the valve to break down over time. This study looked at the first issue. And it found that there was some clot build up on the valve, but that it wasn’t significantly different between the anticoagulant and dual antiplatelet groups. And there was no correlation with embolic events, she noted.
“It shows how fast our field moves. In the U.S. now, we are using aspirin alone at 81 mg for patients who do not have an indication for oral anticoagulation after TAVR. We are moving away from dual antiplatelet therapy because the bleeding risk is so bad,” Dr. Coylewright said.
In his presentation, Dr. Park explained that it is believed that oral anticoagulants are more effective than antiplatelet therapy at reducing subclinical leaflet thrombosis, but it is not known whether there is a causal association between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and cerebral embolism, or whether oral anticoagulation can reduce cerebral embolism related to subclinical leaflet thrombosis.
The ADAPT-TAVR was conducted to look at these issues. The open-label randomized trial was conducted in five centers in Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan.
For the study, 229 patients who had undergone successful TAVR and did not have an indication for anticoagulation were randomized to edoxaban 60 mg once daily, edoxaban 30 mg once daily for patients needing a reduced dose, or dual antiplatelet therapy for 6 months.
The primary endpoint was an incidence of leaflet thrombosis on four-dimensional CT at 6 months.
Results showed a strong trend toward a lower incidence of leaflet thrombosis in the edoxaban groups than in the dual antiplatelet group (9.8% vs. 18.4%; P = .076).
There was a nonsignificant difference in the percentage of patients with new cerebral lesions identified on brain MRI between the edoxaban and dual antiplatelet groups (25.0% vs. 20.2%).
The percentage of patients with worsening of neurologic and neurocognitive function was not different among the groups.
The incidence of any or major bleeding events was not different between two therapies.
There was also no significant association of the presence or extent of leaflet thrombosis with new cerebral lesions or change of neurologic or neurocognitive function.
Dr. Park noted that the trial had several limitations, including an open-label design, use of surrogate imaging outcomes for the primary outcome, and the relatively short follow-up period, so the study was underpowered to detect any meaningful differences in clinical efficacy and safety outcomes. The results should thus be considered hypothesis-generating, highlighting the need for further research, he added.
The long-term effect of leaflet thrombosis or different antithrombotic strategies on bioprosthetic valve durability is still unknown, Dr. Park said.
He also pointed out that the findings cannot be directly extrapolated to patients with an established indication for oral anticoagulant therapy.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was an investigator-initiated trial and was funded by the CardioVascular Research Foundation (Seoul, Korea) and Daiichi Sankyo Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), the incidence of leaflet thrombosis was numerically lower in those treated with the anticoagulant edoxaban for 6 months after the procedure than in those who received dual antiplatelet therapy, although the difference was not statistically significant, in the ADAPT-TAVR study.
There was no difference in new cerebral thromboembolism or neurologic/neurocognitive function between the two groups in the study.
Also, there was no significant relation between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and increased risk for cerebral thromboembolism and neurologic dysfunction.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was presented April 4 at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2022 Scientific Session by Duk-Woo Park, MD, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. It was simultaneously published online in Circulation.
“The key messages from this study are that subclinical leaflet thrombosis has not been proven to affect clinical outcomes for patients undergoing valve replacement and that in patients in whom leaflet thrombosis causes no symptoms or complications, its presence should not dictate the type of antithrombotic therapy that patients receive following the implantation of an artificial heart valve,” Dr. Park said.
“These findings do not support the routine use of computed tomography scans to detect subclinical leaflet thrombosis,” he added.
Commenting on the study at an ACC press conference, Megan Coylewright, MD, director of the Structural Heart Program at Erlanger Health System, Chattanooga, Tennessee, said: “Oftentimes when studies are negative, we’re disappointed. In this case, I think we are pleased that the study is negative because it suggests we do not have to expose our TAVR patients to anticoagulation for benefit.”
Dr. Coylewright explained that the ADAPT-TAVR study was asking whether clots form on the valve, as defined by CT.
“We are worried about that for two reasons: could that clot cause a stroke, and could that clot cause the valve to break down over time. This study looked at the first issue. And it found that there was some clot build up on the valve, but that it wasn’t significantly different between the anticoagulant and dual antiplatelet groups. And there was no correlation with embolic events, she noted.
“It shows how fast our field moves. In the U.S. now, we are using aspirin alone at 81 mg for patients who do not have an indication for oral anticoagulation after TAVR. We are moving away from dual antiplatelet therapy because the bleeding risk is so bad,” Dr. Coylewright said.
In his presentation, Dr. Park explained that it is believed that oral anticoagulants are more effective than antiplatelet therapy at reducing subclinical leaflet thrombosis, but it is not known whether there is a causal association between subclinical leaflet thrombosis and cerebral embolism, or whether oral anticoagulation can reduce cerebral embolism related to subclinical leaflet thrombosis.
The ADAPT-TAVR was conducted to look at these issues. The open-label randomized trial was conducted in five centers in Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan.
For the study, 229 patients who had undergone successful TAVR and did not have an indication for anticoagulation were randomized to edoxaban 60 mg once daily, edoxaban 30 mg once daily for patients needing a reduced dose, or dual antiplatelet therapy for 6 months.
The primary endpoint was an incidence of leaflet thrombosis on four-dimensional CT at 6 months.
Results showed a strong trend toward a lower incidence of leaflet thrombosis in the edoxaban groups than in the dual antiplatelet group (9.8% vs. 18.4%; P = .076).
There was a nonsignificant difference in the percentage of patients with new cerebral lesions identified on brain MRI between the edoxaban and dual antiplatelet groups (25.0% vs. 20.2%).
The percentage of patients with worsening of neurologic and neurocognitive function was not different among the groups.
The incidence of any or major bleeding events was not different between two therapies.
There was also no significant association of the presence or extent of leaflet thrombosis with new cerebral lesions or change of neurologic or neurocognitive function.
Dr. Park noted that the trial had several limitations, including an open-label design, use of surrogate imaging outcomes for the primary outcome, and the relatively short follow-up period, so the study was underpowered to detect any meaningful differences in clinical efficacy and safety outcomes. The results should thus be considered hypothesis-generating, highlighting the need for further research, he added.
The long-term effect of leaflet thrombosis or different antithrombotic strategies on bioprosthetic valve durability is still unknown, Dr. Park said.
He also pointed out that the findings cannot be directly extrapolated to patients with an established indication for oral anticoagulant therapy.
The ADAPT-TAVR trial was an investigator-initiated trial and was funded by the CardioVascular Research Foundation (Seoul, Korea) and Daiichi Sankyo Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early PCSK9 inhibition in AMI yields plaque regression
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
FROM ACC 2022
FDA approves leadless, single-chamber pacemaker system
The Food and Drug Administration has granted approval to Abbott’s Aveir leadless, single-chamber pacemaker system for patients with bradycardia.
In a press release, Abbott said the device has a unique mapping capability that allows interventionists implanting the device to measure electrical signals within the heart to determine the correct placement before final implantation. Aveir is implanted directly into the right ventricle via a catheter.
The company also said Aveir has a battery life that’s up to twice as long as other commercially available leadless pacemakers when following International Association for Standardization (ISO) standard settings. And the device can be retrieved if necessary, the press release said.
“Leadless pacemakers address known complications associated with traditional pacemakers,” Rahul Doshi, MD, director of electrophysiology at Honor Health in Scottsdale, Ariz., said in the press release. “In addition, the Aveir leadless pacemaker brings unique innovations we’ve been seeking, such as the ability to ensure electrical performance before we commit to placement.”
Investigators of the LEADLESS II phase 2 study reported last year on what they called “key design improvements” of the Aveir device compared to the first leadless pacemaker, the discontinued Nanostim. They included a 12% longer battery life, a shorter and wider form factor, a modified docking button that allows for retrievability, a modified delivery system, and an application-specific integrated circuit chip that can support a dual-chamber pacing system in the future.
The study reported that 96% of the 200 enrolled patients met the primary safety endpoint of no serious device-related adverse events at 6 weeks after implantation. A similar percentage achieved therapeutic pacing and sensing amplitude.
The study also reported that interventionists accurately positioned Aveir the first time or with a single repositioning in 96% of cases.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted approval to Abbott’s Aveir leadless, single-chamber pacemaker system for patients with bradycardia.
In a press release, Abbott said the device has a unique mapping capability that allows interventionists implanting the device to measure electrical signals within the heart to determine the correct placement before final implantation. Aveir is implanted directly into the right ventricle via a catheter.
The company also said Aveir has a battery life that’s up to twice as long as other commercially available leadless pacemakers when following International Association for Standardization (ISO) standard settings. And the device can be retrieved if necessary, the press release said.
“Leadless pacemakers address known complications associated with traditional pacemakers,” Rahul Doshi, MD, director of electrophysiology at Honor Health in Scottsdale, Ariz., said in the press release. “In addition, the Aveir leadless pacemaker brings unique innovations we’ve been seeking, such as the ability to ensure electrical performance before we commit to placement.”
Investigators of the LEADLESS II phase 2 study reported last year on what they called “key design improvements” of the Aveir device compared to the first leadless pacemaker, the discontinued Nanostim. They included a 12% longer battery life, a shorter and wider form factor, a modified docking button that allows for retrievability, a modified delivery system, and an application-specific integrated circuit chip that can support a dual-chamber pacing system in the future.
The study reported that 96% of the 200 enrolled patients met the primary safety endpoint of no serious device-related adverse events at 6 weeks after implantation. A similar percentage achieved therapeutic pacing and sensing amplitude.
The study also reported that interventionists accurately positioned Aveir the first time or with a single repositioning in 96% of cases.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted approval to Abbott’s Aveir leadless, single-chamber pacemaker system for patients with bradycardia.
In a press release, Abbott said the device has a unique mapping capability that allows interventionists implanting the device to measure electrical signals within the heart to determine the correct placement before final implantation. Aveir is implanted directly into the right ventricle via a catheter.
The company also said Aveir has a battery life that’s up to twice as long as other commercially available leadless pacemakers when following International Association for Standardization (ISO) standard settings. And the device can be retrieved if necessary, the press release said.
“Leadless pacemakers address known complications associated with traditional pacemakers,” Rahul Doshi, MD, director of electrophysiology at Honor Health in Scottsdale, Ariz., said in the press release. “In addition, the Aveir leadless pacemaker brings unique innovations we’ve been seeking, such as the ability to ensure electrical performance before we commit to placement.”
Investigators of the LEADLESS II phase 2 study reported last year on what they called “key design improvements” of the Aveir device compared to the first leadless pacemaker, the discontinued Nanostim. They included a 12% longer battery life, a shorter and wider form factor, a modified docking button that allows for retrievability, a modified delivery system, and an application-specific integrated circuit chip that can support a dual-chamber pacing system in the future.
The study reported that 96% of the 200 enrolled patients met the primary safety endpoint of no serious device-related adverse events at 6 weeks after implantation. A similar percentage achieved therapeutic pacing and sensing amplitude.
The study also reported that interventionists accurately positioned Aveir the first time or with a single repositioning in 96% of cases.
New HF guidelines feature ‘quad’ therapy, tweaked terminology
The new heart failure (HF) guidelines released by three North American societies had a lot of catching up to do given the significant, even paradigm-shifting, additions to available treatment options in the last few years.
The landscape now includes both new and repurposed drug therapies that benefit almost without regard to ejection fraction (EF), and evidence-based urgency to engage patients early on with at least four core medication classes, so-called quadruple therapy.
The guideline document offers a roadmap for navigating those key issues and many others and uses some creative tactics. They include the introduction of generalist-friendly labels for the traditional but obscurely named four stages of HF severity that, it is hoped, will have wider reach and expand the use of effective therapies.
It introduces additional disease-staging terminology that characterizes the syndrome as a continuum:
- “At risk for HF” for stage A, applied to asymptomatic patients with risk factors such as diabetes or hypertension but no known cardiac changes.
- “Pre-HF” for stage B, which adds cardiac structural changes or elevated natriuretic peptides, still in the absence of symptoms.
- “Symptomatic HF” for stage C, that is, structural disease with current or previous symptoms.
- “Advanced HF” for stage D, characterized by severe debilitating symptoms or repeated hospitalizations even with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT).
The new terms should be “easier for primary care physicians as well as nonspecialists” to remember and use effectively “and easier to translate to the patients,” compared with the solely alphabetical staging labels appearing in the guidelines for more than 15 years, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
An emphasis on “at risk for HF” and “pre-HF” in the new document may help efforts to expand primary prevention of HF and management of preclinical HF. The guideline, Dr. Bozkurt said, includes specific treatment recommendations for those early stages.
The document also updates and sometimes introduces “recommendations for advanced heart failure, acute heart failure, and comorbidities – specifically for atrial fibrillation, iron deficiency, sleep apnea, coronary artery disease, and valvular heart disease,” Dr. Bozkurt observed, as well as for cardiomyopathy and HF related to pregnancy and cancer chemotherapy. “So, it’s a very comprehensive guideline.”
Dr. Bozkurt is vice chair of the guideline writing committee and helped introduce the guideline at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The document, developed by the ACC, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America, was published April 1, 2022, in the societies’ flagship journals, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Circulation, and the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively. It replaces the 2013 guideline from the ACC and AHA and the ACC/AHA/HFSA–focused update from 2017.
“We really need to treat early, and then we need to treat appropriately,” Douglas L. Mann, MD, Washington University in St. Louis, said in an interview. Dr. Mann, who was not involved in development of the new guideline, said he is “enthusiastic” about the new staging terminology.
“I think it makes it easier to convey the message that these people do need medicines, will benefit from medicines, and in some cases heart failure can be preventable,” he said. “I’m in favor of anything that simplifies it and makes it more readily interpretable by busy doctors who aren’t specialists.”
With the new staging terminology and in other ways, the guideline seems to appreciate cardiomyopathy as a journey from preclinical to advanced symptomatic stages – the preclinical “at-risk” stage tightening focus on primary prevention – and updated thinking on classification of HF by EF.
For example, there is new consideration of “HF with improved ejection fraction” (HFimpEF), which suggests the patient may be evolving from HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) to HF with EF that is preserved or mildly reduced, or vice versa.
With HFimpEF, which identifies patients previously with an EF of 40% or lower that improves to beyond 40% at follow-up testing, patients should continue on the medications they had been previously taking for HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt said.
Patients at risk for HF, in stage A by the older terminology, are characterized by one or more significant HF risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary disease, as they have been in prior guidelines. But the new document, Dr. Bozkurt observed, adds genetic cardiomyopathies and exposure to cardiotoxic agents to the list.
Perhaps surprisingly, the guideline also includes elevated natriuretic peptides as an indicator of “at risk for HF,” with implications for screening. The evidence suggests that, “for patients who are at risk for heart failure, natriuretic peptide-based screening, followed by team-based care, can prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction in heart failure,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
Persons at risk for HF realistically encompass a huge swath of the population given the world prevalence of high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes. Management of stage A, therefore, focuses on established tenets of primary cardiovascular prevention, such as weight and BP control, exercise, and healthy dietary choices.
They may well be eligible for treatment with sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been “game changers,” Dr. Mann said. “Now you can give them to diabetics and it’s going to prevent heart failure and [cardiovascular] events. We didn’t have a drug like that before, so I think that places a lot of emphasis on aggressive treatment of diabetes.”
For patients with symptomatic HF, the document touts multidisciplinary care and early initiation of drugs from each of four drug classes. Such quadruple therapy includes an SGLT2 inhibitor along with a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor: the “core foundational therapies” for patients with HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt observed.
Of note, she said, the angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis) is the preferred RAS inhibitor. But “if the ARNI cannot be used, then use ACE inhibitors.” If the patient is intolerant of ACE inhibitors because of cough or angioedema, then the choice should be an angiotensin-receptor blocker.
“We have very effective therapies offering survival and morbidity benefits as well as improvements in quality of life and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Bozkurt observed. “The most important message is that optimization of therapies, including all of these medication classes, saves lives.”
The guideline also includes, for the first time, a series of “value statements” on cost-effectiveness of different therapies that assign a “high-value” rating to MRAs, hydralazine, and isosorbide dinitrate in otherwise optimally treated self-identified African Americans, and device therapy in appropriately selected patients. The statements hold SGLT2 inhibitors in chronic symptomatic HF and cardiac transplantation in advanced GDMT-resistant HF to be of “intermediate” value.
The value statements, Dr. Bozkurt noted, “are included throughout the document when there is evidence; when there is a high-quality cost-effectiveness study published.”
Dr. Bozkurt disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter International, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi-Aventis, scPharmaceuticals, and Vifor Pharma; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA; and holding other relationships with Abbott Laboratories and Relypsa. Dr. Mann disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from MyoKardia, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new heart failure (HF) guidelines released by three North American societies had a lot of catching up to do given the significant, even paradigm-shifting, additions to available treatment options in the last few years.
The landscape now includes both new and repurposed drug therapies that benefit almost without regard to ejection fraction (EF), and evidence-based urgency to engage patients early on with at least four core medication classes, so-called quadruple therapy.
The guideline document offers a roadmap for navigating those key issues and many others and uses some creative tactics. They include the introduction of generalist-friendly labels for the traditional but obscurely named four stages of HF severity that, it is hoped, will have wider reach and expand the use of effective therapies.
It introduces additional disease-staging terminology that characterizes the syndrome as a continuum:
- “At risk for HF” for stage A, applied to asymptomatic patients with risk factors such as diabetes or hypertension but no known cardiac changes.
- “Pre-HF” for stage B, which adds cardiac structural changes or elevated natriuretic peptides, still in the absence of symptoms.
- “Symptomatic HF” for stage C, that is, structural disease with current or previous symptoms.
- “Advanced HF” for stage D, characterized by severe debilitating symptoms or repeated hospitalizations even with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT).
The new terms should be “easier for primary care physicians as well as nonspecialists” to remember and use effectively “and easier to translate to the patients,” compared with the solely alphabetical staging labels appearing in the guidelines for more than 15 years, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
An emphasis on “at risk for HF” and “pre-HF” in the new document may help efforts to expand primary prevention of HF and management of preclinical HF. The guideline, Dr. Bozkurt said, includes specific treatment recommendations for those early stages.
The document also updates and sometimes introduces “recommendations for advanced heart failure, acute heart failure, and comorbidities – specifically for atrial fibrillation, iron deficiency, sleep apnea, coronary artery disease, and valvular heart disease,” Dr. Bozkurt observed, as well as for cardiomyopathy and HF related to pregnancy and cancer chemotherapy. “So, it’s a very comprehensive guideline.”
Dr. Bozkurt is vice chair of the guideline writing committee and helped introduce the guideline at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The document, developed by the ACC, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America, was published April 1, 2022, in the societies’ flagship journals, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Circulation, and the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively. It replaces the 2013 guideline from the ACC and AHA and the ACC/AHA/HFSA–focused update from 2017.
“We really need to treat early, and then we need to treat appropriately,” Douglas L. Mann, MD, Washington University in St. Louis, said in an interview. Dr. Mann, who was not involved in development of the new guideline, said he is “enthusiastic” about the new staging terminology.
“I think it makes it easier to convey the message that these people do need medicines, will benefit from medicines, and in some cases heart failure can be preventable,” he said. “I’m in favor of anything that simplifies it and makes it more readily interpretable by busy doctors who aren’t specialists.”
With the new staging terminology and in other ways, the guideline seems to appreciate cardiomyopathy as a journey from preclinical to advanced symptomatic stages – the preclinical “at-risk” stage tightening focus on primary prevention – and updated thinking on classification of HF by EF.
For example, there is new consideration of “HF with improved ejection fraction” (HFimpEF), which suggests the patient may be evolving from HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) to HF with EF that is preserved or mildly reduced, or vice versa.
With HFimpEF, which identifies patients previously with an EF of 40% or lower that improves to beyond 40% at follow-up testing, patients should continue on the medications they had been previously taking for HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt said.
Patients at risk for HF, in stage A by the older terminology, are characterized by one or more significant HF risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary disease, as they have been in prior guidelines. But the new document, Dr. Bozkurt observed, adds genetic cardiomyopathies and exposure to cardiotoxic agents to the list.
Perhaps surprisingly, the guideline also includes elevated natriuretic peptides as an indicator of “at risk for HF,” with implications for screening. The evidence suggests that, “for patients who are at risk for heart failure, natriuretic peptide-based screening, followed by team-based care, can prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction in heart failure,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
Persons at risk for HF realistically encompass a huge swath of the population given the world prevalence of high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes. Management of stage A, therefore, focuses on established tenets of primary cardiovascular prevention, such as weight and BP control, exercise, and healthy dietary choices.
They may well be eligible for treatment with sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been “game changers,” Dr. Mann said. “Now you can give them to diabetics and it’s going to prevent heart failure and [cardiovascular] events. We didn’t have a drug like that before, so I think that places a lot of emphasis on aggressive treatment of diabetes.”
For patients with symptomatic HF, the document touts multidisciplinary care and early initiation of drugs from each of four drug classes. Such quadruple therapy includes an SGLT2 inhibitor along with a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor: the “core foundational therapies” for patients with HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt observed.
Of note, she said, the angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis) is the preferred RAS inhibitor. But “if the ARNI cannot be used, then use ACE inhibitors.” If the patient is intolerant of ACE inhibitors because of cough or angioedema, then the choice should be an angiotensin-receptor blocker.
“We have very effective therapies offering survival and morbidity benefits as well as improvements in quality of life and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Bozkurt observed. “The most important message is that optimization of therapies, including all of these medication classes, saves lives.”
The guideline also includes, for the first time, a series of “value statements” on cost-effectiveness of different therapies that assign a “high-value” rating to MRAs, hydralazine, and isosorbide dinitrate in otherwise optimally treated self-identified African Americans, and device therapy in appropriately selected patients. The statements hold SGLT2 inhibitors in chronic symptomatic HF and cardiac transplantation in advanced GDMT-resistant HF to be of “intermediate” value.
The value statements, Dr. Bozkurt noted, “are included throughout the document when there is evidence; when there is a high-quality cost-effectiveness study published.”
Dr. Bozkurt disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter International, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi-Aventis, scPharmaceuticals, and Vifor Pharma; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA; and holding other relationships with Abbott Laboratories and Relypsa. Dr. Mann disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from MyoKardia, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new heart failure (HF) guidelines released by three North American societies had a lot of catching up to do given the significant, even paradigm-shifting, additions to available treatment options in the last few years.
The landscape now includes both new and repurposed drug therapies that benefit almost without regard to ejection fraction (EF), and evidence-based urgency to engage patients early on with at least four core medication classes, so-called quadruple therapy.
The guideline document offers a roadmap for navigating those key issues and many others and uses some creative tactics. They include the introduction of generalist-friendly labels for the traditional but obscurely named four stages of HF severity that, it is hoped, will have wider reach and expand the use of effective therapies.
It introduces additional disease-staging terminology that characterizes the syndrome as a continuum:
- “At risk for HF” for stage A, applied to asymptomatic patients with risk factors such as diabetes or hypertension but no known cardiac changes.
- “Pre-HF” for stage B, which adds cardiac structural changes or elevated natriuretic peptides, still in the absence of symptoms.
- “Symptomatic HF” for stage C, that is, structural disease with current or previous symptoms.
- “Advanced HF” for stage D, characterized by severe debilitating symptoms or repeated hospitalizations even with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT).
The new terms should be “easier for primary care physicians as well as nonspecialists” to remember and use effectively “and easier to translate to the patients,” compared with the solely alphabetical staging labels appearing in the guidelines for more than 15 years, Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview.
An emphasis on “at risk for HF” and “pre-HF” in the new document may help efforts to expand primary prevention of HF and management of preclinical HF. The guideline, Dr. Bozkurt said, includes specific treatment recommendations for those early stages.
The document also updates and sometimes introduces “recommendations for advanced heart failure, acute heart failure, and comorbidities – specifically for atrial fibrillation, iron deficiency, sleep apnea, coronary artery disease, and valvular heart disease,” Dr. Bozkurt observed, as well as for cardiomyopathy and HF related to pregnancy and cancer chemotherapy. “So, it’s a very comprehensive guideline.”
Dr. Bozkurt is vice chair of the guideline writing committee and helped introduce the guideline at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The document, developed by the ACC, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America, was published April 1, 2022, in the societies’ flagship journals, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Circulation, and the Journal of Cardiac Failure, respectively. It replaces the 2013 guideline from the ACC and AHA and the ACC/AHA/HFSA–focused update from 2017.
“We really need to treat early, and then we need to treat appropriately,” Douglas L. Mann, MD, Washington University in St. Louis, said in an interview. Dr. Mann, who was not involved in development of the new guideline, said he is “enthusiastic” about the new staging terminology.
“I think it makes it easier to convey the message that these people do need medicines, will benefit from medicines, and in some cases heart failure can be preventable,” he said. “I’m in favor of anything that simplifies it and makes it more readily interpretable by busy doctors who aren’t specialists.”
With the new staging terminology and in other ways, the guideline seems to appreciate cardiomyopathy as a journey from preclinical to advanced symptomatic stages – the preclinical “at-risk” stage tightening focus on primary prevention – and updated thinking on classification of HF by EF.
For example, there is new consideration of “HF with improved ejection fraction” (HFimpEF), which suggests the patient may be evolving from HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) to HF with EF that is preserved or mildly reduced, or vice versa.
With HFimpEF, which identifies patients previously with an EF of 40% or lower that improves to beyond 40% at follow-up testing, patients should continue on the medications they had been previously taking for HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt said.
Patients at risk for HF, in stage A by the older terminology, are characterized by one or more significant HF risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary disease, as they have been in prior guidelines. But the new document, Dr. Bozkurt observed, adds genetic cardiomyopathies and exposure to cardiotoxic agents to the list.
Perhaps surprisingly, the guideline also includes elevated natriuretic peptides as an indicator of “at risk for HF,” with implications for screening. The evidence suggests that, “for patients who are at risk for heart failure, natriuretic peptide-based screening, followed by team-based care, can prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction in heart failure,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
Persons at risk for HF realistically encompass a huge swath of the population given the world prevalence of high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes. Management of stage A, therefore, focuses on established tenets of primary cardiovascular prevention, such as weight and BP control, exercise, and healthy dietary choices.
They may well be eligible for treatment with sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been “game changers,” Dr. Mann said. “Now you can give them to diabetics and it’s going to prevent heart failure and [cardiovascular] events. We didn’t have a drug like that before, so I think that places a lot of emphasis on aggressive treatment of diabetes.”
For patients with symptomatic HF, the document touts multidisciplinary care and early initiation of drugs from each of four drug classes. Such quadruple therapy includes an SGLT2 inhibitor along with a beta-blocker, a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA), and a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor: the “core foundational therapies” for patients with HFrEF, Dr. Bozkurt observed.
Of note, she said, the angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis) is the preferred RAS inhibitor. But “if the ARNI cannot be used, then use ACE inhibitors.” If the patient is intolerant of ACE inhibitors because of cough or angioedema, then the choice should be an angiotensin-receptor blocker.
“We have very effective therapies offering survival and morbidity benefits as well as improvements in quality of life and reverse remodeling,” Dr. Bozkurt observed. “The most important message is that optimization of therapies, including all of these medication classes, saves lives.”
The guideline also includes, for the first time, a series of “value statements” on cost-effectiveness of different therapies that assign a “high-value” rating to MRAs, hydralazine, and isosorbide dinitrate in otherwise optimally treated self-identified African Americans, and device therapy in appropriately selected patients. The statements hold SGLT2 inhibitors in chronic symptomatic HF and cardiac transplantation in advanced GDMT-resistant HF to be of “intermediate” value.
The value statements, Dr. Bozkurt noted, “are included throughout the document when there is evidence; when there is a high-quality cost-effectiveness study published.”
Dr. Bozkurt disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter International, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi-Aventis, scPharmaceuticals, and Vifor Pharma; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA; and holding other relationships with Abbott Laboratories and Relypsa. Dr. Mann disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from MyoKardia, Novartis, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022
VALOR-HCM: Novel drug may delay, avert invasive therapy in OHCM
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.
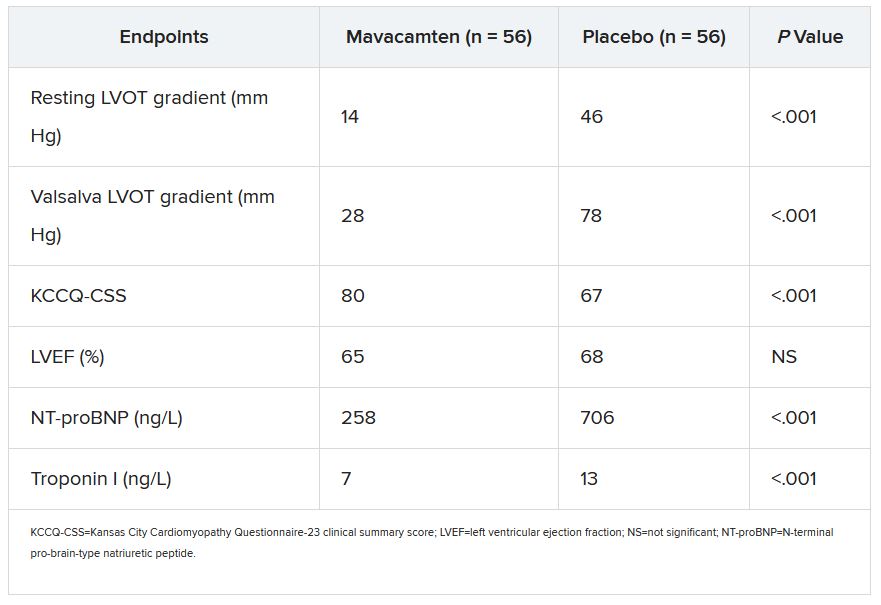
The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.

The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a novel myosin-inhibiting agent may improve symptoms and hemodynamics enough in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (OHCM) so that they can avoid or at least delay septal reduction therapy (SRT), suggests a randomized trial of modest size and duration.
Of 112 patients with OHCM who were sick enough while receiving standard medications to qualify for SRT, those assigned to take mavacamten (MyoKardia) instead of placebo were far less likely to still be eligible for SRT 16 weeks later.
In other words, their OHCM had improved enough during therapy with mavacamten such that SRT, either surgical septal myectomy or transcatheter alcohol septal ablation, could no longer be recommended per guidelines.
Mavacamten, which lessens myocardial contractility by selective inhibition of cardiac myosin, is the first agent tested in prospective trials to appear as a viable medical option in patients with severe, symptomatic OHCM, observed principal investigator Milind Y. Desai, MD, MBA, of the Cleveland Clinic.
“There’s clearly an unmet need for noninvasive therapies, medical therapies, that work in OHCM,” he said in an interview. Mavacamten “adds to the armamentarium” of OHCM management options and may give patients with symptoms despite conventional medications an alternative to SRT, which is considered definitive but has drawbacks.
The goal of SRT is to alleviate obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), but surgical SRT requires a sternotomy, with all the risks and recovery time that entails. Catheter-based alcohol septal ablation is a less common alternative for some patients with suitable anatomy, Dr. Desai noted.
But those procedures “are not uniformly available, and even when available, the outcomes are fairly heterogeneous,” he said. “The guidelines recommend that you should go to a center with a mortality rate of less than 1% with these procedures. Centers like that are very few across the world,” and procedural mortality can be much higher at centers with less SRT experience.
Dr. Desai presented the results of VALOR-HCM at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. Of the 56 patients assigned to mavacamten, 10 (17.9%) decided to undergo SRT by the end of the trial, or otherwise still met guideline-recommended criteria for receiving SRT, the primary endpoint. In comparison, 43 of the 56 patients (76.8%) in the control group (P < .0001) met that endpoint.
More patients receiving mavacamten improved by at least one New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class during the trial’s 16 weeks: 63% versus 21% for those assigned to placebo. And 27% and 2%, respectively, improved by at least two NYHA classes, Dr. Desai said.
Guidelines recommend that SRT be reserved for patients in NYHA class III or IV heart failure with a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg.
Of note, Desai said, only two patients in each group elected to undergo SRT during the study. “The primary endpoint was driven by reduction in guideline eligibility for SRT, but 95% of patients in the study chose to continue with medical therapy.”
Speaking as a panelist after Dr. Desai’s presentation, Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, lauded the phase 3 trial’s “brave design,” which featured a highly unusual subjective primary endpoint and framed it as an advantage.
That the trial showed a significant mavacamten effect for that endpoint “answered, in one step, the question of what does this actually mean to the patient – which often takes much longer,” observed Dr. Stevenson, from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Even so, she added, whether patients still qualified for SRT in the trial at least had to be supported by objective measures of LVOT gradient and NT-proBNP levels.
“My perspective is that of a cardiac surgeon who performs septal myectomies,” said John Cleveland, MD, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who said he was impressed at how few patients receiving mavacamten went on to undergo SRT, while the rest were able to at least defer that decision.
Current recommendations are that patients who go to SRT “should be maximally medically treated and still symptomatic,” Dr. Cleveland observed at a press conference on VALOR-HCM. Should mavacamten be added to the list of agents to use before resorting to invasive therapy? “My answer would be yes,” he said, and patients who remain symptomatic even while receiving the myosin inhibitor and other medications should proceed to SRT.
The trial’s patients had documented OHCM, severe symptoms, and a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of at least 50 mm Hg despite maximally tolerated medications – which could include disopyramide, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. About half the study population was female, and 89% were White. All had been referred for SRT.
Active therapy consisted of mavacamten initiated at 5 mg/day, with up-titrations at 8 and 12 weeks as tolerated, guided by echocardiographic left ventricular ejection fraction and LVOT gradient.
Most secondary endpoints improved significantly in patients receiving the drug, compared with placebo. They included measures of quality of life, symptom status, ventricular function, natriuretic peptides, and troponin I.

The secondary outcomes are consistent with what was observed in the EXPLORER-HCM trial, which in 2020 suggested that mavacamten could improve measures of quality of life, NYHA functional class, LVOT gradient, peak VO2, and other metrics in patients with OHCM.
Dr. Desai said mavacamten was well tolerated. “There were two patients who had a transient drop in ejection fraction to less than 50%, so the drug was temporarily discontinued, but resumed at a lower dose and they were able to complete the study.”
Dr. Stevenson commented on the “pretty quick” up-titration of mavacamten dosages in a study lasting only 4 months, which could have been a concern given the drug’s limited track record and its mechanism of action targeting contractility. “Fortunately, no serious safety signals” were observed.
Dr. Desai emphasized that mavacamten up-titrations were strictly guided by regular echocardiographic monitoring and assessment of LVOT gradients, in addition to clinical responses. And that, he said, is likely how up-titrations should be carried out if mavacamten is approved for OHCM.
VALOR-HCM was supported by MyoKardia. Dr. Desai disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Caristo Diagnostics, Medtronic, and MyoKardia. Dr. Stevenson disclosed receiving honoraria or consulting fees from Novartis; serving on a data safety monitoring board for Livanova; and other relationships with Abbott Medical, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Endotronic, Gore Medical, and Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Cleveland had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022
FAME 3 subanalysis adds twist to negative primary results
A new subanalysis of the FAME 3 trial, which failed to show that percutaneous intervention (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) is noninferior to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for treating three-vessel coronary artery disease, has associated PCI with early quality of life (QOL) advantages, according to findings presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a modestly greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) at the end of 12 months’ follow-up among those treated with FFR-guided PCI, the greater QOL early after the procedure might be relevant to patients weighing these options, according to Frederik M. Zimmerman, MD, of Catharina Hospital in Eindhoven, the Netherlands.
“FFR-guided PCI results in a faster improvement in quality of life than CABG during the first year after revascularization, and it improved working status in patients younger than 65 years of age,” Dr. Zimmermann said.
The primary results of FAME 3 were presented at the 2021 Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting by lead author William F. Fearon, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Rather than confirming the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI is comparable with CABG for the primary composite MACE outcome death from any cause, myocardial infarction, stroke, or revascularization, the incidence of MACE at 12 months was 10.6% in those randomized to PCI and 6.9% in the group assigned to CABG.
This translated into a hazard ratio for MACE of 1.5, signifying a 50% increase in risk for FFR-guided PCI relative to CABG for the primary outcome, a difference that negated the study definition of noninferiority (P = .35).
In this new health-related subanalysis, which was published simultaneously with his ACC presentation, the groups were compared over 12 months for QOL as measured with European Quality of Life–5 dimensions (EQ-5D) scale, angina as measured with the Canadian Cardiovascular Classification (CCC) system, and employment.
Outcomes data available in >85% of patients
Of the 1,500 patients enrolled and randomized in FAME 3 (757 to FFR-guided PCI and 743 to CABG), this health outcomes subanalysis was performed with complete data at 12 months from 89% of those in the PCI group and 88% of those in the CABG group.
Ultimately, the study did not show differences in any of these measures at the end of 12 months, but there were significant differences in QOL and employment at earlier time points. In particular, the significantly different (P < .001) trajectory for QOL improvement at 1 and 6 months favored FFR-guided PCI whether evaluated with the EQ-5D instrument or an EQ visual analog scale.
Rates of angina defined by as CCC class of at least 2 were low after revascularization in both arms of the study, negating any opportunity for differences, but patients aged younger than 65 years were almost twice as likely to have returned to full- or part-time work 1 month after revascularization (60.2% vs. 33.1%), and they remained at higher odds for working at 12 months (68.1% vs. 57.4%).
In patients aged older than 65 years, return-to-work rates did not differ significantly at any time point.
These results suggest potentially clinically meaningful early advantages for FFR-guided PCI, but some experts questioned the rationale for reporting positive secondary findings from a negative trial.
“This subanalysis is curious,” said Allen Jeremias, MD, director of interventional cardiology research, Saint Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y. He pointed out that reporting these data is an anomaly.
Subanalyses uncommon in negative trials
“CABG was found to be better, so why look at QOL,” said Dr. Jeremias, who was an ACC-invited expert to discuss the results. However, he went on to say, “this could be an exception to the rule.”
The reason, according to Dr. Jeremias, is that the absolute difference at 12 months between FFR-guided PCI and CABG for the MACE events of greatest concern – death, MI, or stroke – was only about 2% greater in the FFR-guided PCI group (7.3% vs. 5.2%). The biggest contributor to the difference in MACE in FAME 3 at 12 months was the higher rate of repeat revascularization (5.9% vs. 3.9%).
Moreover, patients randomized to FFR-guided PCI had lower rates of many adverse events. This included risk of bleeding (1.6% vs. 3.8%; P = .009 as defined by type ≥3 Bleeding Academic Research Consortium , acute kidney injury (0.1% vs. 0.9%; P = .04), atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%; P < .001) and rehospitalization within 30 days (5.5% vs. 10.2%; P < .001).
In the context of a modest increase in risk of MACE and the lower rate of several important treatment-related adverse events, the QOL advantages identified in this subanalysis “might be a reasonable topic for patient-shared decision-making,” Dr. Jeremias suggested.
New data might inform patient decision-making
He granted the possibility that well-informed patients might accept the modestly increased risk of MACE for one or more of the outcomes, such as a higher likelihood of an early return to work, that favored FFR-guided PCI.
This is the point of this subanalysis, agreed Dr. Zimmermann.
“It is all about shared decision-making,” he said. Also emphasizing that the negative trial endpoint of FAME 3 “was driven largely by an increased risk of revascularization,” he believes that these new data might be a basis for discussions with patients weighing relative risks and benefits.
There are more data to come, according to Dr. Zimmermann, who said that follow-up of up to 5 years is planned. The 3-year data will be made available in 2023.
Dr. Zimmermann reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Jeremias reported financial relationships with Abbott, ACIST, Boston Scientific, and Volcano. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Abbott Vascular and Medtronic.
A new subanalysis of the FAME 3 trial, which failed to show that percutaneous intervention (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) is noninferior to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for treating three-vessel coronary artery disease, has associated PCI with early quality of life (QOL) advantages, according to findings presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a modestly greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) at the end of 12 months’ follow-up among those treated with FFR-guided PCI, the greater QOL early after the procedure might be relevant to patients weighing these options, according to Frederik M. Zimmerman, MD, of Catharina Hospital in Eindhoven, the Netherlands.
“FFR-guided PCI results in a faster improvement in quality of life than CABG during the first year after revascularization, and it improved working status in patients younger than 65 years of age,” Dr. Zimmermann said.
The primary results of FAME 3 were presented at the 2021 Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting by lead author William F. Fearon, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Rather than confirming the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI is comparable with CABG for the primary composite MACE outcome death from any cause, myocardial infarction, stroke, or revascularization, the incidence of MACE at 12 months was 10.6% in those randomized to PCI and 6.9% in the group assigned to CABG.
This translated into a hazard ratio for MACE of 1.5, signifying a 50% increase in risk for FFR-guided PCI relative to CABG for the primary outcome, a difference that negated the study definition of noninferiority (P = .35).
In this new health-related subanalysis, which was published simultaneously with his ACC presentation, the groups were compared over 12 months for QOL as measured with European Quality of Life–5 dimensions (EQ-5D) scale, angina as measured with the Canadian Cardiovascular Classification (CCC) system, and employment.
Outcomes data available in >85% of patients
Of the 1,500 patients enrolled and randomized in FAME 3 (757 to FFR-guided PCI and 743 to CABG), this health outcomes subanalysis was performed with complete data at 12 months from 89% of those in the PCI group and 88% of those in the CABG group.
Ultimately, the study did not show differences in any of these measures at the end of 12 months, but there were significant differences in QOL and employment at earlier time points. In particular, the significantly different (P < .001) trajectory for QOL improvement at 1 and 6 months favored FFR-guided PCI whether evaluated with the EQ-5D instrument or an EQ visual analog scale.
Rates of angina defined by as CCC class of at least 2 were low after revascularization in both arms of the study, negating any opportunity for differences, but patients aged younger than 65 years were almost twice as likely to have returned to full- or part-time work 1 month after revascularization (60.2% vs. 33.1%), and they remained at higher odds for working at 12 months (68.1% vs. 57.4%).
In patients aged older than 65 years, return-to-work rates did not differ significantly at any time point.
These results suggest potentially clinically meaningful early advantages for FFR-guided PCI, but some experts questioned the rationale for reporting positive secondary findings from a negative trial.
“This subanalysis is curious,” said Allen Jeremias, MD, director of interventional cardiology research, Saint Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y. He pointed out that reporting these data is an anomaly.
Subanalyses uncommon in negative trials
“CABG was found to be better, so why look at QOL,” said Dr. Jeremias, who was an ACC-invited expert to discuss the results. However, he went on to say, “this could be an exception to the rule.”
The reason, according to Dr. Jeremias, is that the absolute difference at 12 months between FFR-guided PCI and CABG for the MACE events of greatest concern – death, MI, or stroke – was only about 2% greater in the FFR-guided PCI group (7.3% vs. 5.2%). The biggest contributor to the difference in MACE in FAME 3 at 12 months was the higher rate of repeat revascularization (5.9% vs. 3.9%).
Moreover, patients randomized to FFR-guided PCI had lower rates of many adverse events. This included risk of bleeding (1.6% vs. 3.8%; P = .009 as defined by type ≥3 Bleeding Academic Research Consortium , acute kidney injury (0.1% vs. 0.9%; P = .04), atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%; P < .001) and rehospitalization within 30 days (5.5% vs. 10.2%; P < .001).
In the context of a modest increase in risk of MACE and the lower rate of several important treatment-related adverse events, the QOL advantages identified in this subanalysis “might be a reasonable topic for patient-shared decision-making,” Dr. Jeremias suggested.
New data might inform patient decision-making
He granted the possibility that well-informed patients might accept the modestly increased risk of MACE for one or more of the outcomes, such as a higher likelihood of an early return to work, that favored FFR-guided PCI.
This is the point of this subanalysis, agreed Dr. Zimmermann.
“It is all about shared decision-making,” he said. Also emphasizing that the negative trial endpoint of FAME 3 “was driven largely by an increased risk of revascularization,” he believes that these new data might be a basis for discussions with patients weighing relative risks and benefits.
There are more data to come, according to Dr. Zimmermann, who said that follow-up of up to 5 years is planned. The 3-year data will be made available in 2023.
Dr. Zimmermann reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Jeremias reported financial relationships with Abbott, ACIST, Boston Scientific, and Volcano. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Abbott Vascular and Medtronic.
A new subanalysis of the FAME 3 trial, which failed to show that percutaneous intervention (PCI) guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) is noninferior to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for treating three-vessel coronary artery disease, has associated PCI with early quality of life (QOL) advantages, according to findings presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Despite a modestly greater risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) at the end of 12 months’ follow-up among those treated with FFR-guided PCI, the greater QOL early after the procedure might be relevant to patients weighing these options, according to Frederik M. Zimmerman, MD, of Catharina Hospital in Eindhoven, the Netherlands.
“FFR-guided PCI results in a faster improvement in quality of life than CABG during the first year after revascularization, and it improved working status in patients younger than 65 years of age,” Dr. Zimmermann said.
The primary results of FAME 3 were presented at the 2021 Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting by lead author William F. Fearon, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Rather than confirming the hypothesis that FFR-guided PCI is comparable with CABG for the primary composite MACE outcome death from any cause, myocardial infarction, stroke, or revascularization, the incidence of MACE at 12 months was 10.6% in those randomized to PCI and 6.9% in the group assigned to CABG.
This translated into a hazard ratio for MACE of 1.5, signifying a 50% increase in risk for FFR-guided PCI relative to CABG for the primary outcome, a difference that negated the study definition of noninferiority (P = .35).
In this new health-related subanalysis, which was published simultaneously with his ACC presentation, the groups were compared over 12 months for QOL as measured with European Quality of Life–5 dimensions (EQ-5D) scale, angina as measured with the Canadian Cardiovascular Classification (CCC) system, and employment.
Outcomes data available in >85% of patients
Of the 1,500 patients enrolled and randomized in FAME 3 (757 to FFR-guided PCI and 743 to CABG), this health outcomes subanalysis was performed with complete data at 12 months from 89% of those in the PCI group and 88% of those in the CABG group.
Ultimately, the study did not show differences in any of these measures at the end of 12 months, but there were significant differences in QOL and employment at earlier time points. In particular, the significantly different (P < .001) trajectory for QOL improvement at 1 and 6 months favored FFR-guided PCI whether evaluated with the EQ-5D instrument or an EQ visual analog scale.
Rates of angina defined by as CCC class of at least 2 were low after revascularization in both arms of the study, negating any opportunity for differences, but patients aged younger than 65 years were almost twice as likely to have returned to full- or part-time work 1 month after revascularization (60.2% vs. 33.1%), and they remained at higher odds for working at 12 months (68.1% vs. 57.4%).
In patients aged older than 65 years, return-to-work rates did not differ significantly at any time point.
These results suggest potentially clinically meaningful early advantages for FFR-guided PCI, but some experts questioned the rationale for reporting positive secondary findings from a negative trial.
“This subanalysis is curious,” said Allen Jeremias, MD, director of interventional cardiology research, Saint Francis Hospital, Roslyn, N.Y. He pointed out that reporting these data is an anomaly.
Subanalyses uncommon in negative trials
“CABG was found to be better, so why look at QOL,” said Dr. Jeremias, who was an ACC-invited expert to discuss the results. However, he went on to say, “this could be an exception to the rule.”
The reason, according to Dr. Jeremias, is that the absolute difference at 12 months between FFR-guided PCI and CABG for the MACE events of greatest concern – death, MI, or stroke – was only about 2% greater in the FFR-guided PCI group (7.3% vs. 5.2%). The biggest contributor to the difference in MACE in FAME 3 at 12 months was the higher rate of repeat revascularization (5.9% vs. 3.9%).
Moreover, patients randomized to FFR-guided PCI had lower rates of many adverse events. This included risk of bleeding (1.6% vs. 3.8%; P = .009 as defined by type ≥3 Bleeding Academic Research Consortium , acute kidney injury (0.1% vs. 0.9%; P = .04), atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%; P < .001) and rehospitalization within 30 days (5.5% vs. 10.2%; P < .001).
In the context of a modest increase in risk of MACE and the lower rate of several important treatment-related adverse events, the QOL advantages identified in this subanalysis “might be a reasonable topic for patient-shared decision-making,” Dr. Jeremias suggested.
New data might inform patient decision-making
He granted the possibility that well-informed patients might accept the modestly increased risk of MACE for one or more of the outcomes, such as a higher likelihood of an early return to work, that favored FFR-guided PCI.
This is the point of this subanalysis, agreed Dr. Zimmermann.
“It is all about shared decision-making,” he said. Also emphasizing that the negative trial endpoint of FAME 3 “was driven largely by an increased risk of revascularization,” he believes that these new data might be a basis for discussions with patients weighing relative risks and benefits.
There are more data to come, according to Dr. Zimmermann, who said that follow-up of up to 5 years is planned. The 3-year data will be made available in 2023.
Dr. Zimmermann reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Jeremias reported financial relationships with Abbott, ACIST, Boston Scientific, and Volcano. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Abbott Vascular and Medtronic.
FROM ACC 2021
POISE-3 backs wider use of tranexamic acid in noncardiac surgery
The antifibrinolytic tranexamic acid (TXA) reduced serious bleeding without a significant effect on major vascular outcomes in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery at risk for these complications in the POISE-3 trial.
TXA cut the primary efficacy outcome of life-threatening, major, and critical organ bleeding at 30 days by 24% compared with placebo (9.1% vs. 11.7%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P < .0001).
The primary safety outcome of myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS), nonhemorrhagic stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal venous thromboembolism (VTE) at 30 days occurred in 14.2% vs.. 13.9% of patients, respectively (HR, 1.023). This failed, however, to meet the study›s threshold to prove TXA noninferior to placebo (one-sided P = .044).
There was no increased risk for death or stroke with TXA, according to results published April 2 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Principal investigator P.J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, Population Health Research Institute and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, pointed out that there is only a 4.4% probability that the composite vascular outcome hazard ratio was above the noninferiority margin and that just 10 events separated the two groups (649 vs.. 639).
“Healthcare providers and patients will have to weigh a clear beneficial reduction in the composite bleeding outcome, which is an absolute difference of 2.7%, a result that was highly statistically significant, versus a low probability of a small increase in risk of the composite vascular endpoint, with an absolute difference of 0.3%,” a nonsignificant result, Dr. Devereaux said during the formal presentation of the results at the hybrid annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings, he said, should also be put in the context that 300 million adults have a major surgery each year worldwide and most don’t receive TXA. At the same time, there’s an annual global shortage of 30 million blood product units, and surgical bleeding accounts for up to 40% of all transfusions.
“POISE-3 identifies that use of TXA could avoid upwards of 8 million bleeding events resulting in transfusion on an annual basis, indicating potential for large public health and clinical benefit if TXA become standard practice in noncardiac surgery,” Dr. Devereaux said during the late-breaking trial session.
TXA is indicated for heavy menstrual bleeding and hemophilia and has been used in cardiac surgery, but it is increasingly being used in noncardiac surgeries. As previously reported, POISE showed that the beta-blocker metoprolol lowered the risk for myocardial infarction (MI) but increased the risk for severe stroke and overall death, whereas in POISE-2, perioperative low-dose aspirin lowered the risk for MI but was linked to more major bleeding.
The cumulative data have not shown an increased risk for thrombotic events in other settings, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
“I’m a cardiologist, and I think that we’ve been guilty at times of always only focusing on the thrombotic side of the equation and ignoring that bleeding is a very important aspect of the circulatory system,” he said. “And I think this shows for the first time clear unequivocal evidence that there’s a cheap, very encouraging, safe way to prevent this.”
“An important point is that if you can give tranexamic acid and prevent bleeding in your cardiac patients having noncardiac surgery, then you can prevent the delay of reinitiating their anticoagulants and their antiplatelets after surgery and getting them back on the medications that are important for them to prevent their cardiovascular event,” Dr. Devereaux added.
Discussant Michael J. Mack, MD, commented that TXA, widely used in cardiac surgery, is an old, inexpensive drug that “should be more widely used in noncardiac surgery.” Dr. Mack, from Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, added that he would limit it to major noncardiac surgery.
International trial
PeriOperative ISchemic Evaluation-3 (POISE-3) investigators at 114 hospitals in 22 countries (including countries in North and South America, Europe, and Africa; Russia; India; and Australia) randomly assigned 9,535 patients, aged 45 years or older, with or at risk for cardiovascular and bleeding complications to receive a TXA 1-g intravenous bolus or placebo at the start and end of inpatient noncardiac surgery.
Patients taking at least one long-term antihypertensive medication were also randomly assigned to a perioperative hypotension- or hypertension-avoidance strategy, which differ in the use of antihypertensives on the morning of surgery and the first 2 days after surgery, and in the target mean arterial pressure during surgery. Results from these cohorts will be presented in a separate session on April 4.
The study had planned to enroll 10,000 patients but was stopped early by the steering committee because of financial constraints resulting from slow enrollment during the pandemic. The decision was made without knowledge of the trial results but with knowledge that aggregate composite bleeding and vascular outcomes were higher than originally estimated, Dr. Devereaux noted.
Among all participants, the mean age was 70 years, 56% were male, almost a third had coronary artery disease, 15% had peripheral artery disease, and 8% had a prior stroke. About 80% were undergoing major surgery. Adherence to the study medications was 96.3% in both groups.
Secondary bleeding outcomes were lower in the TXA and placebo groups, including bleeding independently associated with mortality after surgery (8.7% vs. 11.3%), life-threatening bleeding (1.6% vs. 1.7%), major bleeding (7.6% vs. 10.4%), and critical organ bleeding (0.3% vs. 0.4%).
Importantly, the TXA group had significantly lower rates of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis major bleeding (6.6% vs. 8.7%; P = .0001) and the need for transfusion of 1 or more units of packed red blood cells (9.4% vs. 12.0%; P <.0001), Dr. Devereaux noted.
In terms of secondary vascular outcomes, there were no significant differences between the TXA and placebo groups in rates of MINS (12.8% vs. 12.6%), MINS not fulfilling definition of MI (both 11.5%), MI (1.4% vs. 1.1%), and the net risk-benefit outcome (a composite of vascular death and nonfatal life-threatening, major, or critical organ bleeding, MINS, stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal VTE; 20.7% vs. 21.9%).
The two groups had similar rates of all-cause (1.1% vs. 1.2%) and vascular (0.5% vs. 0.6%) mortality.
There also were no significant differences in other tertiary outcomes, such as acute kidney injury (14.1% vs. 13.7%), rehospitalization for vascular reasons (1.8% vs. 1.6%), or seizures (0.2% vs. <0.1%). The latter has been a concern, with the risk reported to increase with higher doses.
Subgroup analyses
Preplanned subgroup analyses showed a benefit for TXA over placebo for the primary efficacy outcome in orthopedic and nonorthopedic surgery and in patients with hemoglobin level below 120 g/L or 120 g/L or higher, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or higher, or with an N-terminal pro– B-type natriuretic peptide level below 200 ng/L or 200 ng/L or higher.
For the primary safety outcome, the benefit favored placebo but the interaction was not statistically significant for any of the four subgroups.
A post hoc subgroup analysis also showed similar results across the major categories of surgery, including general, vascular, urologic, and gynecologic, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
Although TXA is commonly used in orthopedic procedures, Dr. Devereaux noted, in other types of surgeries, “it’s not used at all.” But because TXA “is so cheap, and we can apply it to a broad population, even at an economic level it looks like it’s a winner to give to almost all patients having noncardiac surgery.”
The team also recently published a risk prediction tool that can help estimate a patient’s baseline risk for bleeding.
“So just using a model, which will bring together the patient’s type of surgery and their risk factors, you can look to see, okay, this is enough risk of bleeding, I’m just going to give tranexamic acid,” he said. “We will also be doing economic analyses because blood is also not cheap.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia), and the Research Grant Council (Hong Kong). Dr. Devereaux reports research/research grants from Abbott Diagnostics, Philips Healthcare, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens. Dr. Mack reports receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The antifibrinolytic tranexamic acid (TXA) reduced serious bleeding without a significant effect on major vascular outcomes in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery at risk for these complications in the POISE-3 trial.
TXA cut the primary efficacy outcome of life-threatening, major, and critical organ bleeding at 30 days by 24% compared with placebo (9.1% vs. 11.7%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P < .0001).
The primary safety outcome of myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS), nonhemorrhagic stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal venous thromboembolism (VTE) at 30 days occurred in 14.2% vs.. 13.9% of patients, respectively (HR, 1.023). This failed, however, to meet the study›s threshold to prove TXA noninferior to placebo (one-sided P = .044).
There was no increased risk for death or stroke with TXA, according to results published April 2 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Principal investigator P.J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, Population Health Research Institute and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, pointed out that there is only a 4.4% probability that the composite vascular outcome hazard ratio was above the noninferiority margin and that just 10 events separated the two groups (649 vs.. 639).
“Healthcare providers and patients will have to weigh a clear beneficial reduction in the composite bleeding outcome, which is an absolute difference of 2.7%, a result that was highly statistically significant, versus a low probability of a small increase in risk of the composite vascular endpoint, with an absolute difference of 0.3%,” a nonsignificant result, Dr. Devereaux said during the formal presentation of the results at the hybrid annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings, he said, should also be put in the context that 300 million adults have a major surgery each year worldwide and most don’t receive TXA. At the same time, there’s an annual global shortage of 30 million blood product units, and surgical bleeding accounts for up to 40% of all transfusions.
“POISE-3 identifies that use of TXA could avoid upwards of 8 million bleeding events resulting in transfusion on an annual basis, indicating potential for large public health and clinical benefit if TXA become standard practice in noncardiac surgery,” Dr. Devereaux said during the late-breaking trial session.
TXA is indicated for heavy menstrual bleeding and hemophilia and has been used in cardiac surgery, but it is increasingly being used in noncardiac surgeries. As previously reported, POISE showed that the beta-blocker metoprolol lowered the risk for myocardial infarction (MI) but increased the risk for severe stroke and overall death, whereas in POISE-2, perioperative low-dose aspirin lowered the risk for MI but was linked to more major bleeding.
The cumulative data have not shown an increased risk for thrombotic events in other settings, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
“I’m a cardiologist, and I think that we’ve been guilty at times of always only focusing on the thrombotic side of the equation and ignoring that bleeding is a very important aspect of the circulatory system,” he said. “And I think this shows for the first time clear unequivocal evidence that there’s a cheap, very encouraging, safe way to prevent this.”
“An important point is that if you can give tranexamic acid and prevent bleeding in your cardiac patients having noncardiac surgery, then you can prevent the delay of reinitiating their anticoagulants and their antiplatelets after surgery and getting them back on the medications that are important for them to prevent their cardiovascular event,” Dr. Devereaux added.
Discussant Michael J. Mack, MD, commented that TXA, widely used in cardiac surgery, is an old, inexpensive drug that “should be more widely used in noncardiac surgery.” Dr. Mack, from Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, added that he would limit it to major noncardiac surgery.
International trial
PeriOperative ISchemic Evaluation-3 (POISE-3) investigators at 114 hospitals in 22 countries (including countries in North and South America, Europe, and Africa; Russia; India; and Australia) randomly assigned 9,535 patients, aged 45 years or older, with or at risk for cardiovascular and bleeding complications to receive a TXA 1-g intravenous bolus or placebo at the start and end of inpatient noncardiac surgery.
Patients taking at least one long-term antihypertensive medication were also randomly assigned to a perioperative hypotension- or hypertension-avoidance strategy, which differ in the use of antihypertensives on the morning of surgery and the first 2 days after surgery, and in the target mean arterial pressure during surgery. Results from these cohorts will be presented in a separate session on April 4.
The study had planned to enroll 10,000 patients but was stopped early by the steering committee because of financial constraints resulting from slow enrollment during the pandemic. The decision was made without knowledge of the trial results but with knowledge that aggregate composite bleeding and vascular outcomes were higher than originally estimated, Dr. Devereaux noted.
Among all participants, the mean age was 70 years, 56% were male, almost a third had coronary artery disease, 15% had peripheral artery disease, and 8% had a prior stroke. About 80% were undergoing major surgery. Adherence to the study medications was 96.3% in both groups.
Secondary bleeding outcomes were lower in the TXA and placebo groups, including bleeding independently associated with mortality after surgery (8.7% vs. 11.3%), life-threatening bleeding (1.6% vs. 1.7%), major bleeding (7.6% vs. 10.4%), and critical organ bleeding (0.3% vs. 0.4%).
Importantly, the TXA group had significantly lower rates of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis major bleeding (6.6% vs. 8.7%; P = .0001) and the need for transfusion of 1 or more units of packed red blood cells (9.4% vs. 12.0%; P <.0001), Dr. Devereaux noted.
In terms of secondary vascular outcomes, there were no significant differences between the TXA and placebo groups in rates of MINS (12.8% vs. 12.6%), MINS not fulfilling definition of MI (both 11.5%), MI (1.4% vs. 1.1%), and the net risk-benefit outcome (a composite of vascular death and nonfatal life-threatening, major, or critical organ bleeding, MINS, stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal VTE; 20.7% vs. 21.9%).
The two groups had similar rates of all-cause (1.1% vs. 1.2%) and vascular (0.5% vs. 0.6%) mortality.
There also were no significant differences in other tertiary outcomes, such as acute kidney injury (14.1% vs. 13.7%), rehospitalization for vascular reasons (1.8% vs. 1.6%), or seizures (0.2% vs. <0.1%). The latter has been a concern, with the risk reported to increase with higher doses.
Subgroup analyses
Preplanned subgroup analyses showed a benefit for TXA over placebo for the primary efficacy outcome in orthopedic and nonorthopedic surgery and in patients with hemoglobin level below 120 g/L or 120 g/L or higher, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or higher, or with an N-terminal pro– B-type natriuretic peptide level below 200 ng/L or 200 ng/L or higher.
For the primary safety outcome, the benefit favored placebo but the interaction was not statistically significant for any of the four subgroups.
A post hoc subgroup analysis also showed similar results across the major categories of surgery, including general, vascular, urologic, and gynecologic, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
Although TXA is commonly used in orthopedic procedures, Dr. Devereaux noted, in other types of surgeries, “it’s not used at all.” But because TXA “is so cheap, and we can apply it to a broad population, even at an economic level it looks like it’s a winner to give to almost all patients having noncardiac surgery.”
The team also recently published a risk prediction tool that can help estimate a patient’s baseline risk for bleeding.
“So just using a model, which will bring together the patient’s type of surgery and their risk factors, you can look to see, okay, this is enough risk of bleeding, I’m just going to give tranexamic acid,” he said. “We will also be doing economic analyses because blood is also not cheap.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia), and the Research Grant Council (Hong Kong). Dr. Devereaux reports research/research grants from Abbott Diagnostics, Philips Healthcare, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens. Dr. Mack reports receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The antifibrinolytic tranexamic acid (TXA) reduced serious bleeding without a significant effect on major vascular outcomes in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery at risk for these complications in the POISE-3 trial.
TXA cut the primary efficacy outcome of life-threatening, major, and critical organ bleeding at 30 days by 24% compared with placebo (9.1% vs. 11.7%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P < .0001).
The primary safety outcome of myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS), nonhemorrhagic stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal venous thromboembolism (VTE) at 30 days occurred in 14.2% vs.. 13.9% of patients, respectively (HR, 1.023). This failed, however, to meet the study›s threshold to prove TXA noninferior to placebo (one-sided P = .044).
There was no increased risk for death or stroke with TXA, according to results published April 2 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Principal investigator P.J. Devereaux, MD, PhD, Population Health Research Institute and McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, pointed out that there is only a 4.4% probability that the composite vascular outcome hazard ratio was above the noninferiority margin and that just 10 events separated the two groups (649 vs.. 639).
“Healthcare providers and patients will have to weigh a clear beneficial reduction in the composite bleeding outcome, which is an absolute difference of 2.7%, a result that was highly statistically significant, versus a low probability of a small increase in risk of the composite vascular endpoint, with an absolute difference of 0.3%,” a nonsignificant result, Dr. Devereaux said during the formal presentation of the results at the hybrid annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings, he said, should also be put in the context that 300 million adults have a major surgery each year worldwide and most don’t receive TXA. At the same time, there’s an annual global shortage of 30 million blood product units, and surgical bleeding accounts for up to 40% of all transfusions.
“POISE-3 identifies that use of TXA could avoid upwards of 8 million bleeding events resulting in transfusion on an annual basis, indicating potential for large public health and clinical benefit if TXA become standard practice in noncardiac surgery,” Dr. Devereaux said during the late-breaking trial session.
TXA is indicated for heavy menstrual bleeding and hemophilia and has been used in cardiac surgery, but it is increasingly being used in noncardiac surgeries. As previously reported, POISE showed that the beta-blocker metoprolol lowered the risk for myocardial infarction (MI) but increased the risk for severe stroke and overall death, whereas in POISE-2, perioperative low-dose aspirin lowered the risk for MI but was linked to more major bleeding.
The cumulative data have not shown an increased risk for thrombotic events in other settings, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
“I’m a cardiologist, and I think that we’ve been guilty at times of always only focusing on the thrombotic side of the equation and ignoring that bleeding is a very important aspect of the circulatory system,” he said. “And I think this shows for the first time clear unequivocal evidence that there’s a cheap, very encouraging, safe way to prevent this.”
“An important point is that if you can give tranexamic acid and prevent bleeding in your cardiac patients having noncardiac surgery, then you can prevent the delay of reinitiating their anticoagulants and their antiplatelets after surgery and getting them back on the medications that are important for them to prevent their cardiovascular event,” Dr. Devereaux added.
Discussant Michael J. Mack, MD, commented that TXA, widely used in cardiac surgery, is an old, inexpensive drug that “should be more widely used in noncardiac surgery.” Dr. Mack, from Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, added that he would limit it to major noncardiac surgery.
International trial
PeriOperative ISchemic Evaluation-3 (POISE-3) investigators at 114 hospitals in 22 countries (including countries in North and South America, Europe, and Africa; Russia; India; and Australia) randomly assigned 9,535 patients, aged 45 years or older, with or at risk for cardiovascular and bleeding complications to receive a TXA 1-g intravenous bolus or placebo at the start and end of inpatient noncardiac surgery.
Patients taking at least one long-term antihypertensive medication were also randomly assigned to a perioperative hypotension- or hypertension-avoidance strategy, which differ in the use of antihypertensives on the morning of surgery and the first 2 days after surgery, and in the target mean arterial pressure during surgery. Results from these cohorts will be presented in a separate session on April 4.
The study had planned to enroll 10,000 patients but was stopped early by the steering committee because of financial constraints resulting from slow enrollment during the pandemic. The decision was made without knowledge of the trial results but with knowledge that aggregate composite bleeding and vascular outcomes were higher than originally estimated, Dr. Devereaux noted.
Among all participants, the mean age was 70 years, 56% were male, almost a third had coronary artery disease, 15% had peripheral artery disease, and 8% had a prior stroke. About 80% were undergoing major surgery. Adherence to the study medications was 96.3% in both groups.
Secondary bleeding outcomes were lower in the TXA and placebo groups, including bleeding independently associated with mortality after surgery (8.7% vs. 11.3%), life-threatening bleeding (1.6% vs. 1.7%), major bleeding (7.6% vs. 10.4%), and critical organ bleeding (0.3% vs. 0.4%).
Importantly, the TXA group had significantly lower rates of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis major bleeding (6.6% vs. 8.7%; P = .0001) and the need for transfusion of 1 or more units of packed red blood cells (9.4% vs. 12.0%; P <.0001), Dr. Devereaux noted.
In terms of secondary vascular outcomes, there were no significant differences between the TXA and placebo groups in rates of MINS (12.8% vs. 12.6%), MINS not fulfilling definition of MI (both 11.5%), MI (1.4% vs. 1.1%), and the net risk-benefit outcome (a composite of vascular death and nonfatal life-threatening, major, or critical organ bleeding, MINS, stroke, peripheral arterial thrombosis, and symptomatic proximal VTE; 20.7% vs. 21.9%).
The two groups had similar rates of all-cause (1.1% vs. 1.2%) and vascular (0.5% vs. 0.6%) mortality.
There also were no significant differences in other tertiary outcomes, such as acute kidney injury (14.1% vs. 13.7%), rehospitalization for vascular reasons (1.8% vs. 1.6%), or seizures (0.2% vs. <0.1%). The latter has been a concern, with the risk reported to increase with higher doses.
Subgroup analyses
Preplanned subgroup analyses showed a benefit for TXA over placebo for the primary efficacy outcome in orthopedic and nonorthopedic surgery and in patients with hemoglobin level below 120 g/L or 120 g/L or higher, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or higher, or with an N-terminal pro– B-type natriuretic peptide level below 200 ng/L or 200 ng/L or higher.
For the primary safety outcome, the benefit favored placebo but the interaction was not statistically significant for any of the four subgroups.
A post hoc subgroup analysis also showed similar results across the major categories of surgery, including general, vascular, urologic, and gynecologic, Dr. Devereaux told this news organization.
Although TXA is commonly used in orthopedic procedures, Dr. Devereaux noted, in other types of surgeries, “it’s not used at all.” But because TXA “is so cheap, and we can apply it to a broad population, even at an economic level it looks like it’s a winner to give to almost all patients having noncardiac surgery.”
The team also recently published a risk prediction tool that can help estimate a patient’s baseline risk for bleeding.
“So just using a model, which will bring together the patient’s type of surgery and their risk factors, you can look to see, okay, this is enough risk of bleeding, I’m just going to give tranexamic acid,” he said. “We will also be doing economic analyses because blood is also not cheap.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia), and the Research Grant Council (Hong Kong). Dr. Devereaux reports research/research grants from Abbott Diagnostics, Philips Healthcare, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens. Dr. Mack reports receiving research grants from Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022







