User login
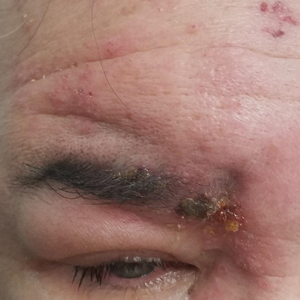
Periorbital Swelling and Rash Following Trauma
The Diagnosis: Herpes Zoster Opthalmicus
Due to the potential concern of vision loss, the patient was directed to a local emergency department for immediate ophthalmologic evaluation. He was diagnosed with herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) and treated with oral acyclovir and prednisone. The rash and periorbital swelling resolved within 2 weeks of treatment, and he remained asymptomatic at follow-up 3 months later.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus presents with an erythematous and vesicular rash in the distribution of cranial nerve V1. The herpetiform grouping of lesions on the forehead is diagnostic of HZO. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection presents in 2 distinct forms. Primary infection (commonly known as chickenpox) presents clinically as a vesicular rash usually located on the face, arms, and trunk. Although the initial presentation usually occurs in childhood and is self-limited, the virus becomes latent in the dorsal root ganglia of sensory neurons. Varicella-zoster virus may become reactivated later in life and is termed herpes zoster (commonly known as shingles). It most often presents as a painful vesicular rash that may later form pustules.
Zoster outbreaks typically do not cross the midline but may in disseminated disease. Patients may experience a prodrome in the form of pain or less commonly pruritus or paresthesia along the dermatome between 1 and 10 days before the rash appears. Triggers for herpes zoster include illness, medications, malnutrition, surgery, or the natural decline in immune function due to aging. Trauma is another important precipitating event for VZV reactivation; one case-control study showed that zoster patients were 3.4 times more likely than controls to have had trauma the week prior.1 Patients with cranial zoster are more than 25 times more likely to have experienced trauma in the preceding week. Local trauma may predispose these patients to VZV reactivation by stimulating local sensory nerves or by disrupting local cutaneous immunity.2
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus occurs when zoster presents in the ophthalmic division of the fifth cranial nerve. It is a serious, vision-threatening condition with a presentation that can include conjunctivitis, scleritis, keratitis, optic neuritis, exophthalmos, lid retraction, ptosis, and extraocular muscle palsies. Treatment includes antiviral medication (eg, acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir) and prompt ophthalmologic consultation due to potential vision-threatening complications, such as acute retinal necrosis. Acute pain control may be necessary with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, steroids, tricyclic antidepressants, or anticonvulsants.3 Wet-to-dry dressings with sterile saline or Burow solution and/or calamine lotion can provide symptomatic relief of itching.
Periorbital and preseptal cellulitis typically present with more erythema of the skin surrounding the eye and without the accompanying rash. Periorbital cellulitis is the more serious infection and may be clinically distinguished by the presence of pain with extraocular muscle movement. Contact dermatitis and pemphigus vulgaris are possibilities, but both were less likely than HZO in this case presentation given the distribution of the rash and the patient history. Contact dermatitis typically presents with no prodrome with a main concern of pruritus. Pemphigus vulgaris nearly always includes involvement of the oral mucous membranes.
- Goh CL, Khoo L. A retrospective study of the clinical presentation and outcome of herpes zoster in a tertiary dermatology outpatient referral clinic. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:667-672.
- Zhang JX, Joesoef RM, Bialek S, et al. Association of physical trauma with risk of herpes zoster among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:1007-1011.
- Rousseau A, Bourcier T, Colin J, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus--diagnosis and management. US Ophthalm Rev. 2013;6:119-124.
The Diagnosis: Herpes Zoster Opthalmicus
Due to the potential concern of vision loss, the patient was directed to a local emergency department for immediate ophthalmologic evaluation. He was diagnosed with herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) and treated with oral acyclovir and prednisone. The rash and periorbital swelling resolved within 2 weeks of treatment, and he remained asymptomatic at follow-up 3 months later.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus presents with an erythematous and vesicular rash in the distribution of cranial nerve V1. The herpetiform grouping of lesions on the forehead is diagnostic of HZO. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection presents in 2 distinct forms. Primary infection (commonly known as chickenpox) presents clinically as a vesicular rash usually located on the face, arms, and trunk. Although the initial presentation usually occurs in childhood and is self-limited, the virus becomes latent in the dorsal root ganglia of sensory neurons. Varicella-zoster virus may become reactivated later in life and is termed herpes zoster (commonly known as shingles). It most often presents as a painful vesicular rash that may later form pustules.
Zoster outbreaks typically do not cross the midline but may in disseminated disease. Patients may experience a prodrome in the form of pain or less commonly pruritus or paresthesia along the dermatome between 1 and 10 days before the rash appears. Triggers for herpes zoster include illness, medications, malnutrition, surgery, or the natural decline in immune function due to aging. Trauma is another important precipitating event for VZV reactivation; one case-control study showed that zoster patients were 3.4 times more likely than controls to have had trauma the week prior.1 Patients with cranial zoster are more than 25 times more likely to have experienced trauma in the preceding week. Local trauma may predispose these patients to VZV reactivation by stimulating local sensory nerves or by disrupting local cutaneous immunity.2
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus occurs when zoster presents in the ophthalmic division of the fifth cranial nerve. It is a serious, vision-threatening condition with a presentation that can include conjunctivitis, scleritis, keratitis, optic neuritis, exophthalmos, lid retraction, ptosis, and extraocular muscle palsies. Treatment includes antiviral medication (eg, acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir) and prompt ophthalmologic consultation due to potential vision-threatening complications, such as acute retinal necrosis. Acute pain control may be necessary with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, steroids, tricyclic antidepressants, or anticonvulsants.3 Wet-to-dry dressings with sterile saline or Burow solution and/or calamine lotion can provide symptomatic relief of itching.
Periorbital and preseptal cellulitis typically present with more erythema of the skin surrounding the eye and without the accompanying rash. Periorbital cellulitis is the more serious infection and may be clinically distinguished by the presence of pain with extraocular muscle movement. Contact dermatitis and pemphigus vulgaris are possibilities, but both were less likely than HZO in this case presentation given the distribution of the rash and the patient history. Contact dermatitis typically presents with no prodrome with a main concern of pruritus. Pemphigus vulgaris nearly always includes involvement of the oral mucous membranes.
The Diagnosis: Herpes Zoster Opthalmicus
Due to the potential concern of vision loss, the patient was directed to a local emergency department for immediate ophthalmologic evaluation. He was diagnosed with herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) and treated with oral acyclovir and prednisone. The rash and periorbital swelling resolved within 2 weeks of treatment, and he remained asymptomatic at follow-up 3 months later.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus presents with an erythematous and vesicular rash in the distribution of cranial nerve V1. The herpetiform grouping of lesions on the forehead is diagnostic of HZO. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection presents in 2 distinct forms. Primary infection (commonly known as chickenpox) presents clinically as a vesicular rash usually located on the face, arms, and trunk. Although the initial presentation usually occurs in childhood and is self-limited, the virus becomes latent in the dorsal root ganglia of sensory neurons. Varicella-zoster virus may become reactivated later in life and is termed herpes zoster (commonly known as shingles). It most often presents as a painful vesicular rash that may later form pustules.
Zoster outbreaks typically do not cross the midline but may in disseminated disease. Patients may experience a prodrome in the form of pain or less commonly pruritus or paresthesia along the dermatome between 1 and 10 days before the rash appears. Triggers for herpes zoster include illness, medications, malnutrition, surgery, or the natural decline in immune function due to aging. Trauma is another important precipitating event for VZV reactivation; one case-control study showed that zoster patients were 3.4 times more likely than controls to have had trauma the week prior.1 Patients with cranial zoster are more than 25 times more likely to have experienced trauma in the preceding week. Local trauma may predispose these patients to VZV reactivation by stimulating local sensory nerves or by disrupting local cutaneous immunity.2
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus occurs when zoster presents in the ophthalmic division of the fifth cranial nerve. It is a serious, vision-threatening condition with a presentation that can include conjunctivitis, scleritis, keratitis, optic neuritis, exophthalmos, lid retraction, ptosis, and extraocular muscle palsies. Treatment includes antiviral medication (eg, acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir) and prompt ophthalmologic consultation due to potential vision-threatening complications, such as acute retinal necrosis. Acute pain control may be necessary with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, steroids, tricyclic antidepressants, or anticonvulsants.3 Wet-to-dry dressings with sterile saline or Burow solution and/or calamine lotion can provide symptomatic relief of itching.
Periorbital and preseptal cellulitis typically present with more erythema of the skin surrounding the eye and without the accompanying rash. Periorbital cellulitis is the more serious infection and may be clinically distinguished by the presence of pain with extraocular muscle movement. Contact dermatitis and pemphigus vulgaris are possibilities, but both were less likely than HZO in this case presentation given the distribution of the rash and the patient history. Contact dermatitis typically presents with no prodrome with a main concern of pruritus. Pemphigus vulgaris nearly always includes involvement of the oral mucous membranes.
- Goh CL, Khoo L. A retrospective study of the clinical presentation and outcome of herpes zoster in a tertiary dermatology outpatient referral clinic. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:667-672.
- Zhang JX, Joesoef RM, Bialek S, et al. Association of physical trauma with risk of herpes zoster among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:1007-1011.
- Rousseau A, Bourcier T, Colin J, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus--diagnosis and management. US Ophthalm Rev. 2013;6:119-124.
- Goh CL, Khoo L. A retrospective study of the clinical presentation and outcome of herpes zoster in a tertiary dermatology outpatient referral clinic. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:667-672.
- Zhang JX, Joesoef RM, Bialek S, et al. Association of physical trauma with risk of herpes zoster among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:1007-1011.
- Rousseau A, Bourcier T, Colin J, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus--diagnosis and management. US Ophthalm Rev. 2013;6:119-124.
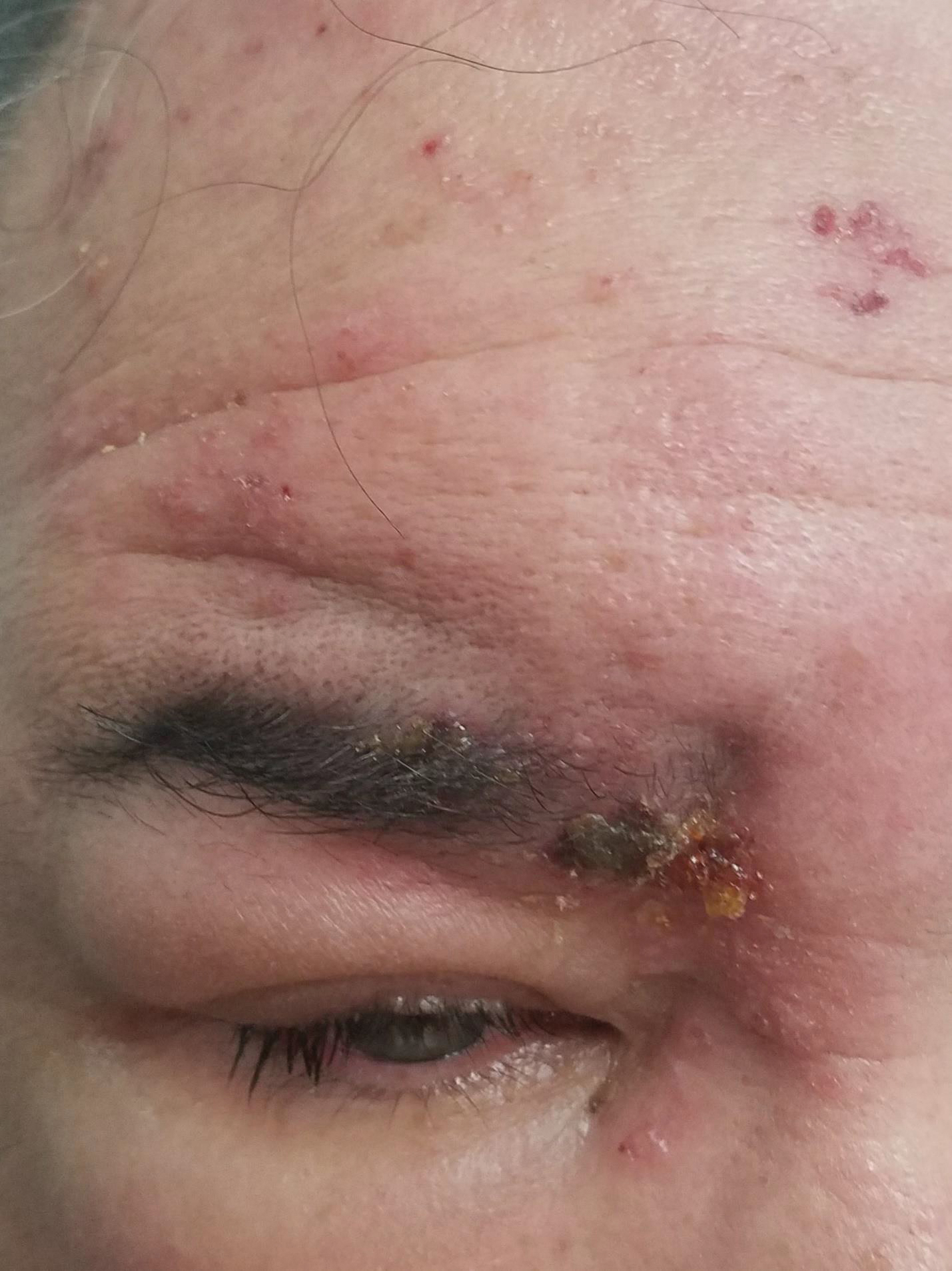
A 56-year-old man presented to an urgent care clinic with right periorbital swelling. He reported hitting his head on the door to a storage unit 2 days prior but did not lose consciousness. The swelling presented 2 days later. He reported mild headache and swelling around the right eye that coincided with an uncomfortable rash on the face and scalp. He also reported visual disruption due to the swelling but denied any eye pain, discharge from the eye, or painful eye movements. He had no lesions on the lips or inside the mouth. He denied any history of skin conditions. He further denied fever, joint pain, or any other systemic symptoms. His chronic medical conditions included diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia that were stable on metformin, carvedilol, amlodipine, enalapril, and simvastatin, which he had taken for several years. He had not started any new medications, and there were no recent changes in the dosing of his medications.
WHO declares public health emergency for novel coronavirus
Amid the rising spread of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV),
The declaration was made during a press briefing on Jan. 30 after a week of growing concern and pressure on WHO to designate the virus at a higher emergency level. WHO’s Emergency Committee made the nearly unanimous decision after considering the increasing number of coronavirus cases in China, the rising infections outside of China, and the questionable measures some countries are taking regarding travel, said committee chair Didier Houssin, MD, said during the press conference.
As of Jan. 30, there were 8,236 confirmed cases of the coronavirus in China and 171 deaths, with another 112 cases identified outside of China in 21 other countries.
“Declaring a Public Health Emergency of International Concern is likely to facilitate [WHO’s] leadership role for public health measures, holding countries to account concerning additional measures they may take regarding travel, trade, quarantine or screening, research efforts, global coordination and anticipation of economic impact [and] support to vulnerable states,” Dr. Houssin said during the press conference. “Declaring a PHEIC should certainly not be seen as manifestation of distrust in the Chinese authorities and people which are doing tremendous efforts on the frontlines of this outbreak, with transparency, and let us hope, with success.”
What happens next?
Once a PHEIC is declared, WHO launches a series of steps, including the release of temporary recommendations for the affected country on health measures to implement and guidance for other countries on preventing and reducing the international spread of the disease, WHO spokesman Tarik Jasarevic said in an interview.
“The purpose of declaring a PHEIC is to advise the world on what measures need to be taken to enhance global health security by preventing international transmission of an infectious hazard,” he said.
Following the Jan. 30 press conference, WHO released temporary guidance for China and for other countries regarding identifying, managing, containing, and preventing the virus. China is advised to continue updating the population about the outbreak, continue enhancing its public health measures for containment and surveillance of cases, and to continue collaboration with WHO and other partners to investigate the epidemiology and evolution of the outbreak and share data on all human cases.
Other countries should be prepared for containment, including the active surveillance, early detection, isolation, case management, and prevention of virus transmission and to share full data with WHO, according to the recommendations.
Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), countries are required to share information and data with WHO. Additionally, WHO leaders advised the global community to support low- and middle-income countries with their response to the coronavirus and to facilitate diagnostics, potential vaccines, and therapeutics in these areas.
The IHR requires that countries implementing health measures that go beyond what WHO recommends must send to WHO the public health rationale and justification within 48 hours of their implementation for WHO review, Mr. Jasarevic noted.
“WHO is obliged to share the information about measures and the justification received with other countries involved,” he said.
PHEIC travel and resource impact
Declaration of a PHEIC means WHO will now oversee any travel restrictions made by other countries in response to 2019-nCoV. The agency recommends that countries conduct a risk and cost-benefit analysis before enacting travel restrictions and other countries are required to inform WHO about any travel measures taken.
“Countries will be asked to provide public health justification for any travel or trade measures that are not scientifically based, such as refusal of entry of suspect cases or unaffected persons to affected areas,” Mr. Jasarevic said in an interview.
As far as resources, the PHEIC mechanism is not a fundraising mechanism, but some donors might consider a PHEIC declaration as a trigger for releasing additional funding to respond to the health threat, he said.
Allison T. Chamberlain, PhD, acting director for the Emory Center for Public Health Preparedness and Research at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, said national governments and nongovernmental aid organizations are among the most affected by a PHEIC because they are looked at to provide assistance to the most heavily affected areas and to bolster public health preparedness within their own borders.
“In terms of resources that are deployed, a Public Health Emergency of International Concern raises levels of international support and commitment to stopping the emergency,” Dr. Chamberlain said in an interview. “By doing so, it gives countries the needed flexibility to release financial resources of their own accord to support things like response teams that might go into heavily affected areas to assist, for instance.”
WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus stressed that cooperation among countries is key during the PHEIC.
“We can only stop it together,” he said during the press conference. “This is the time for facts, not fear. This is the time for science, not rumors. This is the time for solidarity, not stigma.”
This is the sixth PHEIC declared by WHO in the last 10 years. Such declarations were made for the 2009 H1NI influenza pandemic, the 2014 polio resurgence, the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, the 2016 Zika virus, and the 2019 Kivu Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Amid the rising spread of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV),
The declaration was made during a press briefing on Jan. 30 after a week of growing concern and pressure on WHO to designate the virus at a higher emergency level. WHO’s Emergency Committee made the nearly unanimous decision after considering the increasing number of coronavirus cases in China, the rising infections outside of China, and the questionable measures some countries are taking regarding travel, said committee chair Didier Houssin, MD, said during the press conference.
As of Jan. 30, there were 8,236 confirmed cases of the coronavirus in China and 171 deaths, with another 112 cases identified outside of China in 21 other countries.
“Declaring a Public Health Emergency of International Concern is likely to facilitate [WHO’s] leadership role for public health measures, holding countries to account concerning additional measures they may take regarding travel, trade, quarantine or screening, research efforts, global coordination and anticipation of economic impact [and] support to vulnerable states,” Dr. Houssin said during the press conference. “Declaring a PHEIC should certainly not be seen as manifestation of distrust in the Chinese authorities and people which are doing tremendous efforts on the frontlines of this outbreak, with transparency, and let us hope, with success.”
What happens next?
Once a PHEIC is declared, WHO launches a series of steps, including the release of temporary recommendations for the affected country on health measures to implement and guidance for other countries on preventing and reducing the international spread of the disease, WHO spokesman Tarik Jasarevic said in an interview.
“The purpose of declaring a PHEIC is to advise the world on what measures need to be taken to enhance global health security by preventing international transmission of an infectious hazard,” he said.
Following the Jan. 30 press conference, WHO released temporary guidance for China and for other countries regarding identifying, managing, containing, and preventing the virus. China is advised to continue updating the population about the outbreak, continue enhancing its public health measures for containment and surveillance of cases, and to continue collaboration with WHO and other partners to investigate the epidemiology and evolution of the outbreak and share data on all human cases.
Other countries should be prepared for containment, including the active surveillance, early detection, isolation, case management, and prevention of virus transmission and to share full data with WHO, according to the recommendations.
Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), countries are required to share information and data with WHO. Additionally, WHO leaders advised the global community to support low- and middle-income countries with their response to the coronavirus and to facilitate diagnostics, potential vaccines, and therapeutics in these areas.
The IHR requires that countries implementing health measures that go beyond what WHO recommends must send to WHO the public health rationale and justification within 48 hours of their implementation for WHO review, Mr. Jasarevic noted.
“WHO is obliged to share the information about measures and the justification received with other countries involved,” he said.
PHEIC travel and resource impact
Declaration of a PHEIC means WHO will now oversee any travel restrictions made by other countries in response to 2019-nCoV. The agency recommends that countries conduct a risk and cost-benefit analysis before enacting travel restrictions and other countries are required to inform WHO about any travel measures taken.
“Countries will be asked to provide public health justification for any travel or trade measures that are not scientifically based, such as refusal of entry of suspect cases or unaffected persons to affected areas,” Mr. Jasarevic said in an interview.
As far as resources, the PHEIC mechanism is not a fundraising mechanism, but some donors might consider a PHEIC declaration as a trigger for releasing additional funding to respond to the health threat, he said.
Allison T. Chamberlain, PhD, acting director for the Emory Center for Public Health Preparedness and Research at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, said national governments and nongovernmental aid organizations are among the most affected by a PHEIC because they are looked at to provide assistance to the most heavily affected areas and to bolster public health preparedness within their own borders.
“In terms of resources that are deployed, a Public Health Emergency of International Concern raises levels of international support and commitment to stopping the emergency,” Dr. Chamberlain said in an interview. “By doing so, it gives countries the needed flexibility to release financial resources of their own accord to support things like response teams that might go into heavily affected areas to assist, for instance.”
WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus stressed that cooperation among countries is key during the PHEIC.
“We can only stop it together,” he said during the press conference. “This is the time for facts, not fear. This is the time for science, not rumors. This is the time for solidarity, not stigma.”
This is the sixth PHEIC declared by WHO in the last 10 years. Such declarations were made for the 2009 H1NI influenza pandemic, the 2014 polio resurgence, the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, the 2016 Zika virus, and the 2019 Kivu Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Amid the rising spread of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV),
The declaration was made during a press briefing on Jan. 30 after a week of growing concern and pressure on WHO to designate the virus at a higher emergency level. WHO’s Emergency Committee made the nearly unanimous decision after considering the increasing number of coronavirus cases in China, the rising infections outside of China, and the questionable measures some countries are taking regarding travel, said committee chair Didier Houssin, MD, said during the press conference.
As of Jan. 30, there were 8,236 confirmed cases of the coronavirus in China and 171 deaths, with another 112 cases identified outside of China in 21 other countries.
“Declaring a Public Health Emergency of International Concern is likely to facilitate [WHO’s] leadership role for public health measures, holding countries to account concerning additional measures they may take regarding travel, trade, quarantine or screening, research efforts, global coordination and anticipation of economic impact [and] support to vulnerable states,” Dr. Houssin said during the press conference. “Declaring a PHEIC should certainly not be seen as manifestation of distrust in the Chinese authorities and people which are doing tremendous efforts on the frontlines of this outbreak, with transparency, and let us hope, with success.”
What happens next?
Once a PHEIC is declared, WHO launches a series of steps, including the release of temporary recommendations for the affected country on health measures to implement and guidance for other countries on preventing and reducing the international spread of the disease, WHO spokesman Tarik Jasarevic said in an interview.
“The purpose of declaring a PHEIC is to advise the world on what measures need to be taken to enhance global health security by preventing international transmission of an infectious hazard,” he said.
Following the Jan. 30 press conference, WHO released temporary guidance for China and for other countries regarding identifying, managing, containing, and preventing the virus. China is advised to continue updating the population about the outbreak, continue enhancing its public health measures for containment and surveillance of cases, and to continue collaboration with WHO and other partners to investigate the epidemiology and evolution of the outbreak and share data on all human cases.
Other countries should be prepared for containment, including the active surveillance, early detection, isolation, case management, and prevention of virus transmission and to share full data with WHO, according to the recommendations.
Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), countries are required to share information and data with WHO. Additionally, WHO leaders advised the global community to support low- and middle-income countries with their response to the coronavirus and to facilitate diagnostics, potential vaccines, and therapeutics in these areas.
The IHR requires that countries implementing health measures that go beyond what WHO recommends must send to WHO the public health rationale and justification within 48 hours of their implementation for WHO review, Mr. Jasarevic noted.
“WHO is obliged to share the information about measures and the justification received with other countries involved,” he said.
PHEIC travel and resource impact
Declaration of a PHEIC means WHO will now oversee any travel restrictions made by other countries in response to 2019-nCoV. The agency recommends that countries conduct a risk and cost-benefit analysis before enacting travel restrictions and other countries are required to inform WHO about any travel measures taken.
“Countries will be asked to provide public health justification for any travel or trade measures that are not scientifically based, such as refusal of entry of suspect cases or unaffected persons to affected areas,” Mr. Jasarevic said in an interview.
As far as resources, the PHEIC mechanism is not a fundraising mechanism, but some donors might consider a PHEIC declaration as a trigger for releasing additional funding to respond to the health threat, he said.
Allison T. Chamberlain, PhD, acting director for the Emory Center for Public Health Preparedness and Research at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, said national governments and nongovernmental aid organizations are among the most affected by a PHEIC because they are looked at to provide assistance to the most heavily affected areas and to bolster public health preparedness within their own borders.
“In terms of resources that are deployed, a Public Health Emergency of International Concern raises levels of international support and commitment to stopping the emergency,” Dr. Chamberlain said in an interview. “By doing so, it gives countries the needed flexibility to release financial resources of their own accord to support things like response teams that might go into heavily affected areas to assist, for instance.”
WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus stressed that cooperation among countries is key during the PHEIC.
“We can only stop it together,” he said during the press conference. “This is the time for facts, not fear. This is the time for science, not rumors. This is the time for solidarity, not stigma.”
This is the sixth PHEIC declared by WHO in the last 10 years. Such declarations were made for the 2009 H1NI influenza pandemic, the 2014 polio resurgence, the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, the 2016 Zika virus, and the 2019 Kivu Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
2019 Novel Coronavirus: Frequently asked questions for clinicians
The 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak has unfolded so rapidly that many clinicians are scrambling to stay on top of it. Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions about how to prepare your clinic to respond to this outbreak.
Keep in mind that the outbreak is moving rapidly. Though scientific and epidemiologic knowledge has increased at unprecedented speed, there is much we don’t know, and some of what we think we know will change. Follow the links for the most up-to-date information.
What should our clinic do first?
Plan ahead with the following:
- Develop a plan for office staff to take travel histories from anyone with a respiratory illness and provide training for those who need it. Travel history at present should include asking about travel to China in the past 14 days, specifically Wuhan city or Hubei province.
- Review up-to-date infection control practices with all office staff and provide training for those who need it.
- Take an inventory of supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gowns, gloves, masks, eye protection, and N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), and order items that are missing or low in stock.
- Fit-test users of N95 masks for maximal effectiveness.
- Plan where a potential patient would be isolated while obtaining expert advice.
- Know whom to contact at the state or local health department if you have a patient with the appropriate travel history.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has prepared a toolkit to help frontline health care professionals prepare for this virus. Providers need to stay up to date on the latest recommendations, as the situation is changing rapidly.
When should I suspect 2019-nCoV illness, and what should I do?
Take the following steps to assess the concern and respond:
- If a patient with respiratory illness has traveled to China in the past 14 days, immediately put a mask on the patient and move the individual to a private room. Use a negative-pressure room if available.
- Put on appropriate PPE (including gloves, gown, eye protection, and mask) for contact, droplet, and airborne precautions. CDC recommends an N95 respirator mask if available, although we don’t know yet if there is true airborne spread.
- Obtain an accurate travel history, including dates and cities. (Tip: Get the correct spelling, as the English spelling of cities in China can cause confusion.)
- If the patient meets the current CDC definition of “person under investigation” or PUI, or if you need guidance on how to proceed, notify infection control (if you are in a facility that has it) and call your state or local health department immediately.
- Contact public health authorities who can help decide whether the patient should be admitted to airborne isolation or monitored at home with appropriate precautions.
What is the definition of a PUI?
The current definition of a PUI is a person who has fever and symptoms of a respiratory infection (cough, shortness of breath) AND who has EITHER been in Wuhan city or Hubei province in the past 14 days OR had close contact with a person either under investigation for 2019-nCoV infection or with confirmed infection. The definition of a PUI will change over time, so check this link.
How can I test for 2019-nCoV?
As of Jan. 30, 2020, testing is by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and is available in the United States only through the CDC in Atlanta. Testing should soon be available in state health department laboratories. If public health authorities decide that your patient should be tested, they will instruct you on which samples to obtain.
The full sequence of 2019-nCoV has been shared, so some reference laboratories may develop and validate tests, ideally with assistance from CDC. If testing becomes available, make certain that it is a reputable lab that has carefully validated the test.
Should I test for other viruses?
Because the symptoms of 2019-nCoV infection overlap with those of influenza and other respiratory viruses, PCR testing for other viruses should be considered if it will change management (i.e., change the decision to provide influenza antivirals). Use appropriate PPE while collecting specimens, including eye protection. If 2019-nCoV is a consideration, you may want to send the specimen to a hospital lab for testing, where the sample will be processed under a biosafety hood, rather than doing point-of-care testing in the office.
How dangerous is 2019-nCoV?
The current estimated mortality rate is 2%-3%. That is probably an overestimate, as those with severe disease and those who die are more likely to be tested and reported early in an epidemic.
Our current knowledge is based on preliminary reports from hospitalized patients and will probably change. From the speed of spread and a single family cluster, it seems likely that there are milder cases and perhaps asymptomatic infection.
What else do I need to know about coronaviruses?
Coronaviruses are a large and diverse group of viruses, many of which are animal viruses. Before the discovery of the 2019-nCoV, six coronaviruses were known to infect humans. Four of these (HKU1, NL63, OC43, and 229E) predominantly caused mild to moderate upper respiratory illness, and they are thought to be responsible for 10%-30% of colds. They occasionally cause viral pneumonia and can be detected by some commercial multiplex panels.
Two other coronaviruses have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory illness in people: SARS, which emerged in Southern China in 2002, and MERS in the Middle East, in 2012. Unlike SARS, sporadic cases of MERS continue to occur.
The current outbreak is caused by 2019-nCoV, a previously unknown beta coronavirus. It is most closely related (~96%) to a bat virus and shares about 80% sequence homology with SARS CoV.
Andrew T. Pavia, MD, is the George and Esther Gross Presidential Professor and chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease in the department of pediatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. He is also director of hospital epidemiology and associate director of antimicrobial stewardship at Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City. Dr. Pavia has disclosed that he has served as a consultant for Genentech, Merck, and Seqirus and that he has served as associate editor for The Sanford Guide.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak has unfolded so rapidly that many clinicians are scrambling to stay on top of it. Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions about how to prepare your clinic to respond to this outbreak.
Keep in mind that the outbreak is moving rapidly. Though scientific and epidemiologic knowledge has increased at unprecedented speed, there is much we don’t know, and some of what we think we know will change. Follow the links for the most up-to-date information.
What should our clinic do first?
Plan ahead with the following:
- Develop a plan for office staff to take travel histories from anyone with a respiratory illness and provide training for those who need it. Travel history at present should include asking about travel to China in the past 14 days, specifically Wuhan city or Hubei province.
- Review up-to-date infection control practices with all office staff and provide training for those who need it.
- Take an inventory of supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gowns, gloves, masks, eye protection, and N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), and order items that are missing or low in stock.
- Fit-test users of N95 masks for maximal effectiveness.
- Plan where a potential patient would be isolated while obtaining expert advice.
- Know whom to contact at the state or local health department if you have a patient with the appropriate travel history.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has prepared a toolkit to help frontline health care professionals prepare for this virus. Providers need to stay up to date on the latest recommendations, as the situation is changing rapidly.
When should I suspect 2019-nCoV illness, and what should I do?
Take the following steps to assess the concern and respond:
- If a patient with respiratory illness has traveled to China in the past 14 days, immediately put a mask on the patient and move the individual to a private room. Use a negative-pressure room if available.
- Put on appropriate PPE (including gloves, gown, eye protection, and mask) for contact, droplet, and airborne precautions. CDC recommends an N95 respirator mask if available, although we don’t know yet if there is true airborne spread.
- Obtain an accurate travel history, including dates and cities. (Tip: Get the correct spelling, as the English spelling of cities in China can cause confusion.)
- If the patient meets the current CDC definition of “person under investigation” or PUI, or if you need guidance on how to proceed, notify infection control (if you are in a facility that has it) and call your state or local health department immediately.
- Contact public health authorities who can help decide whether the patient should be admitted to airborne isolation or monitored at home with appropriate precautions.
What is the definition of a PUI?
The current definition of a PUI is a person who has fever and symptoms of a respiratory infection (cough, shortness of breath) AND who has EITHER been in Wuhan city or Hubei province in the past 14 days OR had close contact with a person either under investigation for 2019-nCoV infection or with confirmed infection. The definition of a PUI will change over time, so check this link.
How can I test for 2019-nCoV?
As of Jan. 30, 2020, testing is by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and is available in the United States only through the CDC in Atlanta. Testing should soon be available in state health department laboratories. If public health authorities decide that your patient should be tested, they will instruct you on which samples to obtain.
The full sequence of 2019-nCoV has been shared, so some reference laboratories may develop and validate tests, ideally with assistance from CDC. If testing becomes available, make certain that it is a reputable lab that has carefully validated the test.
Should I test for other viruses?
Because the symptoms of 2019-nCoV infection overlap with those of influenza and other respiratory viruses, PCR testing for other viruses should be considered if it will change management (i.e., change the decision to provide influenza antivirals). Use appropriate PPE while collecting specimens, including eye protection. If 2019-nCoV is a consideration, you may want to send the specimen to a hospital lab for testing, where the sample will be processed under a biosafety hood, rather than doing point-of-care testing in the office.
How dangerous is 2019-nCoV?
The current estimated mortality rate is 2%-3%. That is probably an overestimate, as those with severe disease and those who die are more likely to be tested and reported early in an epidemic.
Our current knowledge is based on preliminary reports from hospitalized patients and will probably change. From the speed of spread and a single family cluster, it seems likely that there are milder cases and perhaps asymptomatic infection.
What else do I need to know about coronaviruses?
Coronaviruses are a large and diverse group of viruses, many of which are animal viruses. Before the discovery of the 2019-nCoV, six coronaviruses were known to infect humans. Four of these (HKU1, NL63, OC43, and 229E) predominantly caused mild to moderate upper respiratory illness, and they are thought to be responsible for 10%-30% of colds. They occasionally cause viral pneumonia and can be detected by some commercial multiplex panels.
Two other coronaviruses have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory illness in people: SARS, which emerged in Southern China in 2002, and MERS in the Middle East, in 2012. Unlike SARS, sporadic cases of MERS continue to occur.
The current outbreak is caused by 2019-nCoV, a previously unknown beta coronavirus. It is most closely related (~96%) to a bat virus and shares about 80% sequence homology with SARS CoV.
Andrew T. Pavia, MD, is the George and Esther Gross Presidential Professor and chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease in the department of pediatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. He is also director of hospital epidemiology and associate director of antimicrobial stewardship at Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City. Dr. Pavia has disclosed that he has served as a consultant for Genentech, Merck, and Seqirus and that he has served as associate editor for The Sanford Guide.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak has unfolded so rapidly that many clinicians are scrambling to stay on top of it. Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions about how to prepare your clinic to respond to this outbreak.
Keep in mind that the outbreak is moving rapidly. Though scientific and epidemiologic knowledge has increased at unprecedented speed, there is much we don’t know, and some of what we think we know will change. Follow the links for the most up-to-date information.
What should our clinic do first?
Plan ahead with the following:
- Develop a plan for office staff to take travel histories from anyone with a respiratory illness and provide training for those who need it. Travel history at present should include asking about travel to China in the past 14 days, specifically Wuhan city or Hubei province.
- Review up-to-date infection control practices with all office staff and provide training for those who need it.
- Take an inventory of supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gowns, gloves, masks, eye protection, and N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), and order items that are missing or low in stock.
- Fit-test users of N95 masks for maximal effectiveness.
- Plan where a potential patient would be isolated while obtaining expert advice.
- Know whom to contact at the state or local health department if you have a patient with the appropriate travel history.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has prepared a toolkit to help frontline health care professionals prepare for this virus. Providers need to stay up to date on the latest recommendations, as the situation is changing rapidly.
When should I suspect 2019-nCoV illness, and what should I do?
Take the following steps to assess the concern and respond:
- If a patient with respiratory illness has traveled to China in the past 14 days, immediately put a mask on the patient and move the individual to a private room. Use a negative-pressure room if available.
- Put on appropriate PPE (including gloves, gown, eye protection, and mask) for contact, droplet, and airborne precautions. CDC recommends an N95 respirator mask if available, although we don’t know yet if there is true airborne spread.
- Obtain an accurate travel history, including dates and cities. (Tip: Get the correct spelling, as the English spelling of cities in China can cause confusion.)
- If the patient meets the current CDC definition of “person under investigation” or PUI, or if you need guidance on how to proceed, notify infection control (if you are in a facility that has it) and call your state or local health department immediately.
- Contact public health authorities who can help decide whether the patient should be admitted to airborne isolation or monitored at home with appropriate precautions.
What is the definition of a PUI?
The current definition of a PUI is a person who has fever and symptoms of a respiratory infection (cough, shortness of breath) AND who has EITHER been in Wuhan city or Hubei province in the past 14 days OR had close contact with a person either under investigation for 2019-nCoV infection or with confirmed infection. The definition of a PUI will change over time, so check this link.
How can I test for 2019-nCoV?
As of Jan. 30, 2020, testing is by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and is available in the United States only through the CDC in Atlanta. Testing should soon be available in state health department laboratories. If public health authorities decide that your patient should be tested, they will instruct you on which samples to obtain.
The full sequence of 2019-nCoV has been shared, so some reference laboratories may develop and validate tests, ideally with assistance from CDC. If testing becomes available, make certain that it is a reputable lab that has carefully validated the test.
Should I test for other viruses?
Because the symptoms of 2019-nCoV infection overlap with those of influenza and other respiratory viruses, PCR testing for other viruses should be considered if it will change management (i.e., change the decision to provide influenza antivirals). Use appropriate PPE while collecting specimens, including eye protection. If 2019-nCoV is a consideration, you may want to send the specimen to a hospital lab for testing, where the sample will be processed under a biosafety hood, rather than doing point-of-care testing in the office.
How dangerous is 2019-nCoV?
The current estimated mortality rate is 2%-3%. That is probably an overestimate, as those with severe disease and those who die are more likely to be tested and reported early in an epidemic.
Our current knowledge is based on preliminary reports from hospitalized patients and will probably change. From the speed of spread and a single family cluster, it seems likely that there are milder cases and perhaps asymptomatic infection.
What else do I need to know about coronaviruses?
Coronaviruses are a large and diverse group of viruses, many of which are animal viruses. Before the discovery of the 2019-nCoV, six coronaviruses were known to infect humans. Four of these (HKU1, NL63, OC43, and 229E) predominantly caused mild to moderate upper respiratory illness, and they are thought to be responsible for 10%-30% of colds. They occasionally cause viral pneumonia and can be detected by some commercial multiplex panels.
Two other coronaviruses have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory illness in people: SARS, which emerged in Southern China in 2002, and MERS in the Middle East, in 2012. Unlike SARS, sporadic cases of MERS continue to occur.
The current outbreak is caused by 2019-nCoV, a previously unknown beta coronavirus. It is most closely related (~96%) to a bat virus and shares about 80% sequence homology with SARS CoV.
Andrew T. Pavia, MD, is the George and Esther Gross Presidential Professor and chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease in the department of pediatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. He is also director of hospital epidemiology and associate director of antimicrobial stewardship at Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City. Dr. Pavia has disclosed that he has served as a consultant for Genentech, Merck, and Seqirus and that he has served as associate editor for The Sanford Guide.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC: First person-to-person spread of novel coronavirus in U.S.
A Chicago woman in her 60s who tested positive for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) after returning from Wuhan, China, earlier this month has infected her husband, becoming the first known instance of person-to-person transmission of the 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“Limited person-to-person spread of this new virus outside of China has already been seen in nine close contacts, where travelers were infected and transmitted the virus to someone else,” Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a press briefing on Jan. 30, 2020. “However, the full picture of how easy and how sustainable this virus can spread is unclear. Today’s news underscores the important risk-dependent exposure. The vast majority of Americans have not had recent travel to China, where sustained human-to-human transmission is occurring. Individuals who are close personal contacts of cases, though, could have a risk.”
The affected man, also in his 60s, is the spouse of the first confirmed travel-associated case of 2019-nCoV to be reported in the state of Illinois, according to Ngozi O. Ezike, MD, director of the Illinois Department of Public Health. The man had no history of recent travel to China. “This person-to-person spread was between two very close contacts: a wife and husband,” said Dr. Ezike, who added that 21 individuals in the state are under investigation for 2019-nCoV. “The virus is not spreading widely across the community. At this time, we are not recommending that people in the general public take additional precautions such as canceling activities or avoiding going out. While there is concern with this second case, public health officials are actively monitoring close contacts, including health care workers, and we believe that people in Illinois are at low risk.”
Jennifer Layden, MD, state epidemiologist at the Illinois Department of Public Health, said that the infected Chicago woman returned from Wuhan, China on Jan. 13, 2020. She is hospitalized in stable condition “and continues to do well,” Dr. Layden said. “Public health officials have been actively and closely monitoring individuals who had contacts with her, including her husband, who had close contact for symptoms. He recently began reporting symptoms and was immediately admitted to the hospital and placed in an isolation room, where he is in stable condition. We are actively monitoring individuals such as health care workers, household contacts, and others who were in contact with either of the confirmed cases in the goal to contain and reduce the risk of additional transmission.”
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, expects that more cases of 2019-nCoV will transpire in the United States.
“More cases means the potential for more person-to-person spread,” Dr. Messonnier said. “We’re trying to strike a balance in our response right now. We want to be aggressive, but we want our actions to be evidence-based and appropriate for the current circumstance. For example, CDC does not currently recommend use of face masks for the general public. The virus is not spreading in the general community.”
A Chicago woman in her 60s who tested positive for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) after returning from Wuhan, China, earlier this month has infected her husband, becoming the first known instance of person-to-person transmission of the 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“Limited person-to-person spread of this new virus outside of China has already been seen in nine close contacts, where travelers were infected and transmitted the virus to someone else,” Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a press briefing on Jan. 30, 2020. “However, the full picture of how easy and how sustainable this virus can spread is unclear. Today’s news underscores the important risk-dependent exposure. The vast majority of Americans have not had recent travel to China, where sustained human-to-human transmission is occurring. Individuals who are close personal contacts of cases, though, could have a risk.”
The affected man, also in his 60s, is the spouse of the first confirmed travel-associated case of 2019-nCoV to be reported in the state of Illinois, according to Ngozi O. Ezike, MD, director of the Illinois Department of Public Health. The man had no history of recent travel to China. “This person-to-person spread was between two very close contacts: a wife and husband,” said Dr. Ezike, who added that 21 individuals in the state are under investigation for 2019-nCoV. “The virus is not spreading widely across the community. At this time, we are not recommending that people in the general public take additional precautions such as canceling activities or avoiding going out. While there is concern with this second case, public health officials are actively monitoring close contacts, including health care workers, and we believe that people in Illinois are at low risk.”
Jennifer Layden, MD, state epidemiologist at the Illinois Department of Public Health, said that the infected Chicago woman returned from Wuhan, China on Jan. 13, 2020. She is hospitalized in stable condition “and continues to do well,” Dr. Layden said. “Public health officials have been actively and closely monitoring individuals who had contacts with her, including her husband, who had close contact for symptoms. He recently began reporting symptoms and was immediately admitted to the hospital and placed in an isolation room, where he is in stable condition. We are actively monitoring individuals such as health care workers, household contacts, and others who were in contact with either of the confirmed cases in the goal to contain and reduce the risk of additional transmission.”
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, expects that more cases of 2019-nCoV will transpire in the United States.
“More cases means the potential for more person-to-person spread,” Dr. Messonnier said. “We’re trying to strike a balance in our response right now. We want to be aggressive, but we want our actions to be evidence-based and appropriate for the current circumstance. For example, CDC does not currently recommend use of face masks for the general public. The virus is not spreading in the general community.”
A Chicago woman in her 60s who tested positive for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) after returning from Wuhan, China, earlier this month has infected her husband, becoming the first known instance of person-to-person transmission of the 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“Limited person-to-person spread of this new virus outside of China has already been seen in nine close contacts, where travelers were infected and transmitted the virus to someone else,” Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said during a press briefing on Jan. 30, 2020. “However, the full picture of how easy and how sustainable this virus can spread is unclear. Today’s news underscores the important risk-dependent exposure. The vast majority of Americans have not had recent travel to China, where sustained human-to-human transmission is occurring. Individuals who are close personal contacts of cases, though, could have a risk.”
The affected man, also in his 60s, is the spouse of the first confirmed travel-associated case of 2019-nCoV to be reported in the state of Illinois, according to Ngozi O. Ezike, MD, director of the Illinois Department of Public Health. The man had no history of recent travel to China. “This person-to-person spread was between two very close contacts: a wife and husband,” said Dr. Ezike, who added that 21 individuals in the state are under investigation for 2019-nCoV. “The virus is not spreading widely across the community. At this time, we are not recommending that people in the general public take additional precautions such as canceling activities or avoiding going out. While there is concern with this second case, public health officials are actively monitoring close contacts, including health care workers, and we believe that people in Illinois are at low risk.”
Jennifer Layden, MD, state epidemiologist at the Illinois Department of Public Health, said that the infected Chicago woman returned from Wuhan, China on Jan. 13, 2020. She is hospitalized in stable condition “and continues to do well,” Dr. Layden said. “Public health officials have been actively and closely monitoring individuals who had contacts with her, including her husband, who had close contact for symptoms. He recently began reporting symptoms and was immediately admitted to the hospital and placed in an isolation room, where he is in stable condition. We are actively monitoring individuals such as health care workers, household contacts, and others who were in contact with either of the confirmed cases in the goal to contain and reduce the risk of additional transmission.”
Nancy Messonnier, MD, director, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, expects that more cases of 2019-nCoV will transpire in the United States.
“More cases means the potential for more person-to-person spread,” Dr. Messonnier said. “We’re trying to strike a balance in our response right now. We want to be aggressive, but we want our actions to be evidence-based and appropriate for the current circumstance. For example, CDC does not currently recommend use of face masks for the general public. The virus is not spreading in the general community.”
Occult HCV infection is correlated to unfavorable genotypes in hemophilia patients
The presence of occult hepatitis C virus infection is determined by finding HCV RNA in the liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with no HCV RNA in the serum. Researchers have shown that the presence of occult HCV infection (OCI) was correlated with unfavorable polymorphisms near interferon lambda-3/4 (IFNL3/4), which has been associated with spontaneous HCV clearance.
This study was conducted to assess the frequency of OCI in 450 hemophilia patients in Iran with negative HCV markers, and to evaluate the association of three IFNL3 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs8099917, rs12979860, and rs12980275) and the IFNL4 ss469415590 SNP with OCI positivity.
The estimated OCI rate was 10.2%. Among the 46 OCI patients, 56.5%, 23.9%, and 19.6% were infected with HCV-1b, HCV-1a, and HCV-3a, respectively. The researchers found that, compared with patients without OCI, unfavorable IFNL3 rs12979860, IFNL3 rs8099917, IFNL3 rs12980275, and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were more frequently found in OCI patients. Multivariate analysis showed that ALT, cholesterol, triglyceride, as well as the aforementioned unfavorable interferon SNP geneotypes were associated with OCI positivity.
“10.2% of anti-HCV seronegative Iranian patients with hemophilia had OCI in our study; therefore, risk of this infection should be taken into consideration. We also showed that patients with unfavorable IFNL3 SNPs and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were exposed to a higher risk of OCI, compared to hemophilia patients with other genotypes,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nafari AH et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.104144.
The presence of occult hepatitis C virus infection is determined by finding HCV RNA in the liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with no HCV RNA in the serum. Researchers have shown that the presence of occult HCV infection (OCI) was correlated with unfavorable polymorphisms near interferon lambda-3/4 (IFNL3/4), which has been associated with spontaneous HCV clearance.
This study was conducted to assess the frequency of OCI in 450 hemophilia patients in Iran with negative HCV markers, and to evaluate the association of three IFNL3 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs8099917, rs12979860, and rs12980275) and the IFNL4 ss469415590 SNP with OCI positivity.
The estimated OCI rate was 10.2%. Among the 46 OCI patients, 56.5%, 23.9%, and 19.6% were infected with HCV-1b, HCV-1a, and HCV-3a, respectively. The researchers found that, compared with patients without OCI, unfavorable IFNL3 rs12979860, IFNL3 rs8099917, IFNL3 rs12980275, and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were more frequently found in OCI patients. Multivariate analysis showed that ALT, cholesterol, triglyceride, as well as the aforementioned unfavorable interferon SNP geneotypes were associated with OCI positivity.
“10.2% of anti-HCV seronegative Iranian patients with hemophilia had OCI in our study; therefore, risk of this infection should be taken into consideration. We also showed that patients with unfavorable IFNL3 SNPs and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were exposed to a higher risk of OCI, compared to hemophilia patients with other genotypes,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nafari AH et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.104144.
The presence of occult hepatitis C virus infection is determined by finding HCV RNA in the liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with no HCV RNA in the serum. Researchers have shown that the presence of occult HCV infection (OCI) was correlated with unfavorable polymorphisms near interferon lambda-3/4 (IFNL3/4), which has been associated with spontaneous HCV clearance.
This study was conducted to assess the frequency of OCI in 450 hemophilia patients in Iran with negative HCV markers, and to evaluate the association of three IFNL3 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs8099917, rs12979860, and rs12980275) and the IFNL4 ss469415590 SNP with OCI positivity.
The estimated OCI rate was 10.2%. Among the 46 OCI patients, 56.5%, 23.9%, and 19.6% were infected with HCV-1b, HCV-1a, and HCV-3a, respectively. The researchers found that, compared with patients without OCI, unfavorable IFNL3 rs12979860, IFNL3 rs8099917, IFNL3 rs12980275, and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were more frequently found in OCI patients. Multivariate analysis showed that ALT, cholesterol, triglyceride, as well as the aforementioned unfavorable interferon SNP geneotypes were associated with OCI positivity.
“10.2% of anti-HCV seronegative Iranian patients with hemophilia had OCI in our study; therefore, risk of this infection should be taken into consideration. We also showed that patients with unfavorable IFNL3 SNPs and IFNL4 ss469415590 genotypes were exposed to a higher risk of OCI, compared to hemophilia patients with other genotypes,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Nafari AH et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Dec 13. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.104144.
FROM INFECTION, GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
CDC: Risk in U.S. from 2019-nCoV remains low
A total of 165 persons in the United States are under investigation for infection with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), with 68 testing negative and only 5 confirming positive, according to data presented Jan. 29 during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) briefing.

The remaining samples are in transit or are being processed at the CDC for testing, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the briefing.
“The genetic sequence for all five viruses detected in the United States to date has been uploaded to the CDC website,” she said. “We are working quickly through the process to get the CDC-developed test into the hands of public health partners in the U.S. and internationally.”
Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is expanding screening efforts to U.S. ports of entry that house CDC quarantine stations. Also, in collaboration with U.S. Customs and Border Protection, the agency is expanding distribution of travel health education materials to all travelers from China.
“The good news here is that, despite an aggressive public health investigation to find new cases [of 2019-nCoV], we have not,” she said. “The situation in China is concerning, however, we are looking hard here in the U.S. We will continue to be proactive. I still expect that we will find additional cases.”
In another development, the federal government facilitated the return of a plane full of U.S. citizens living in Wuhan, China, to March Air Reserve Force Base in Riverside County, Calif. “We have taken every precaution to ensure their safety while also continuing to protect the health of our nation and the people around them,” Dr. Messonnier said.
All 195 passengers have been screened, monitored, and evaluated by medical personnel “every step of the way,” including before takeoff, during the flight, during a refueling stop in Alaska, and again upon landing at March Air Reserve Force Base on Jan. 28. “All 195 patients are without the symptoms of the novel coronavirus, and all have been assigned living quarters at the Air Force base,” Dr. Messonnier said.
The CDC has launched a second stage of further screening and information gathering from the passengers, who will be offered testing as part of a thorough risk assessment.
“I understand that many people in the U.S. are worried about this virus and whether it will affect them,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Outbreaks like this are always concerning, particularly when a new virus is emerging. But we are well prepared and working closely with federal, state, and local partners to protect our communities and others nationwide from this public health threat. At this time, we continue to believe that the immediate health risk from this new virus to the general American public is low.”
A total of 165 persons in the United States are under investigation for infection with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), with 68 testing negative and only 5 confirming positive, according to data presented Jan. 29 during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) briefing.

The remaining samples are in transit or are being processed at the CDC for testing, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the briefing.
“The genetic sequence for all five viruses detected in the United States to date has been uploaded to the CDC website,” she said. “We are working quickly through the process to get the CDC-developed test into the hands of public health partners in the U.S. and internationally.”
Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is expanding screening efforts to U.S. ports of entry that house CDC quarantine stations. Also, in collaboration with U.S. Customs and Border Protection, the agency is expanding distribution of travel health education materials to all travelers from China.
“The good news here is that, despite an aggressive public health investigation to find new cases [of 2019-nCoV], we have not,” she said. “The situation in China is concerning, however, we are looking hard here in the U.S. We will continue to be proactive. I still expect that we will find additional cases.”
In another development, the federal government facilitated the return of a plane full of U.S. citizens living in Wuhan, China, to March Air Reserve Force Base in Riverside County, Calif. “We have taken every precaution to ensure their safety while also continuing to protect the health of our nation and the people around them,” Dr. Messonnier said.
All 195 passengers have been screened, monitored, and evaluated by medical personnel “every step of the way,” including before takeoff, during the flight, during a refueling stop in Alaska, and again upon landing at March Air Reserve Force Base on Jan. 28. “All 195 patients are without the symptoms of the novel coronavirus, and all have been assigned living quarters at the Air Force base,” Dr. Messonnier said.
The CDC has launched a second stage of further screening and information gathering from the passengers, who will be offered testing as part of a thorough risk assessment.
“I understand that many people in the U.S. are worried about this virus and whether it will affect them,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Outbreaks like this are always concerning, particularly when a new virus is emerging. But we are well prepared and working closely with federal, state, and local partners to protect our communities and others nationwide from this public health threat. At this time, we continue to believe that the immediate health risk from this new virus to the general American public is low.”
A total of 165 persons in the United States are under investigation for infection with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), with 68 testing negative and only 5 confirming positive, according to data presented Jan. 29 during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) briefing.

The remaining samples are in transit or are being processed at the CDC for testing, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the briefing.
“The genetic sequence for all five viruses detected in the United States to date has been uploaded to the CDC website,” she said. “We are working quickly through the process to get the CDC-developed test into the hands of public health partners in the U.S. and internationally.”
Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is expanding screening efforts to U.S. ports of entry that house CDC quarantine stations. Also, in collaboration with U.S. Customs and Border Protection, the agency is expanding distribution of travel health education materials to all travelers from China.
“The good news here is that, despite an aggressive public health investigation to find new cases [of 2019-nCoV], we have not,” she said. “The situation in China is concerning, however, we are looking hard here in the U.S. We will continue to be proactive. I still expect that we will find additional cases.”
In another development, the federal government facilitated the return of a plane full of U.S. citizens living in Wuhan, China, to March Air Reserve Force Base in Riverside County, Calif. “We have taken every precaution to ensure their safety while also continuing to protect the health of our nation and the people around them,” Dr. Messonnier said.
All 195 passengers have been screened, monitored, and evaluated by medical personnel “every step of the way,” including before takeoff, during the flight, during a refueling stop in Alaska, and again upon landing at March Air Reserve Force Base on Jan. 28. “All 195 patients are without the symptoms of the novel coronavirus, and all have been assigned living quarters at the Air Force base,” Dr. Messonnier said.
The CDC has launched a second stage of further screening and information gathering from the passengers, who will be offered testing as part of a thorough risk assessment.
“I understand that many people in the U.S. are worried about this virus and whether it will affect them,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Outbreaks like this are always concerning, particularly when a new virus is emerging. But we are well prepared and working closely with federal, state, and local partners to protect our communities and others nationwide from this public health threat. At this time, we continue to believe that the immediate health risk from this new virus to the general American public is low.”
Wuhan coronavirus cluster suggests human-to-human spread
A Chinese man became ill from a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) 4 days after arriving in Vietnam to visit his 27-year-old son. Three days later the healthy young man was also stricken, according to a report published online Jan. 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This family cluster of 2019-nCoV infection that occurred outside China arouses concern regarding human-to-human transmission,” the authors wrote.
The father, age 65 years and with multiple comorbidities including hypertension, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease with stent placement, and lung cancer, flew to Hanoi with his wife on January 13; they traveled from the Wuchang district in Wuhan, China, where outbreaks of 2019-nCoV have been occurring.
On Jan. 17, the older man and his wife met their adult son in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and shared a hotel room with him for 3 days. The father developed a fever that same day and the son developed a dry cough, fever, diarrhea, and vomiting on Jan. 20. Both men went to a hospital ED on Jan. 22.
The authors say the timing of the son’s symptoms suggests the incubation period may have been 3 days or fewer.
Upon admission to the hospital, the father reported that he had not visited a “wet market” where live and dead animals are sold while he was in Wuhan. Throat swabs were positive for 2019-nCoV on real-time reverse-transcription–polymerase-chain-reaction assays.
The man was placed in isolation and “treated empirically with antiviral agents, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and supportive therapies,” wrote Lan T. Phan, PhD, from the Pasteur Institute Ho Chi Minh City and coauthors.
On admission, chest radiographs revealed an infiltrate in the upper lobe of his left lung; he developed worsening dyspnea with hypoxemia on Jan. 25 and required supplemental oxygen at 5 L/min by nasal cannula. Chest radiographs showed a progressive infiltrate and consolidation. His fever resolved on that day and he has progressively improved.
The man’s son had a fever of 39° C (102.2° F) when the two men arrived at the hospital on Jan. 22; hospital staff isolated the son, and chest radiographs and other laboratory tests were normal with the exception of an increased C-reactive protein level.
The son’s throat swab was positive for 2019-nCoV and he is believed to have been exposed from his father; however, the strains have not been ascertained.
“This family had traveled to four cities across Vietnam using various forms of transportation, including planes, trains, and taxis,” the authors wrote. A total of 28 close contacts were identified, none of whom have developed respiratory symptoms. The older man’s wife has been healthy as well.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Chinese man became ill from a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) 4 days after arriving in Vietnam to visit his 27-year-old son. Three days later the healthy young man was also stricken, according to a report published online Jan. 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This family cluster of 2019-nCoV infection that occurred outside China arouses concern regarding human-to-human transmission,” the authors wrote.
The father, age 65 years and with multiple comorbidities including hypertension, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease with stent placement, and lung cancer, flew to Hanoi with his wife on January 13; they traveled from the Wuchang district in Wuhan, China, where outbreaks of 2019-nCoV have been occurring.
On Jan. 17, the older man and his wife met their adult son in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and shared a hotel room with him for 3 days. The father developed a fever that same day and the son developed a dry cough, fever, diarrhea, and vomiting on Jan. 20. Both men went to a hospital ED on Jan. 22.
The authors say the timing of the son’s symptoms suggests the incubation period may have been 3 days or fewer.
Upon admission to the hospital, the father reported that he had not visited a “wet market” where live and dead animals are sold while he was in Wuhan. Throat swabs were positive for 2019-nCoV on real-time reverse-transcription–polymerase-chain-reaction assays.
The man was placed in isolation and “treated empirically with antiviral agents, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and supportive therapies,” wrote Lan T. Phan, PhD, from the Pasteur Institute Ho Chi Minh City and coauthors.
On admission, chest radiographs revealed an infiltrate in the upper lobe of his left lung; he developed worsening dyspnea with hypoxemia on Jan. 25 and required supplemental oxygen at 5 L/min by nasal cannula. Chest radiographs showed a progressive infiltrate and consolidation. His fever resolved on that day and he has progressively improved.
The man’s son had a fever of 39° C (102.2° F) when the two men arrived at the hospital on Jan. 22; hospital staff isolated the son, and chest radiographs and other laboratory tests were normal with the exception of an increased C-reactive protein level.
The son’s throat swab was positive for 2019-nCoV and he is believed to have been exposed from his father; however, the strains have not been ascertained.
“This family had traveled to four cities across Vietnam using various forms of transportation, including planes, trains, and taxis,” the authors wrote. A total of 28 close contacts were identified, none of whom have developed respiratory symptoms. The older man’s wife has been healthy as well.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Chinese man became ill from a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) 4 days after arriving in Vietnam to visit his 27-year-old son. Three days later the healthy young man was also stricken, according to a report published online Jan. 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This family cluster of 2019-nCoV infection that occurred outside China arouses concern regarding human-to-human transmission,” the authors wrote.
The father, age 65 years and with multiple comorbidities including hypertension, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease with stent placement, and lung cancer, flew to Hanoi with his wife on January 13; they traveled from the Wuchang district in Wuhan, China, where outbreaks of 2019-nCoV have been occurring.
On Jan. 17, the older man and his wife met their adult son in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and shared a hotel room with him for 3 days. The father developed a fever that same day and the son developed a dry cough, fever, diarrhea, and vomiting on Jan. 20. Both men went to a hospital ED on Jan. 22.
The authors say the timing of the son’s symptoms suggests the incubation period may have been 3 days or fewer.
Upon admission to the hospital, the father reported that he had not visited a “wet market” where live and dead animals are sold while he was in Wuhan. Throat swabs were positive for 2019-nCoV on real-time reverse-transcription–polymerase-chain-reaction assays.
The man was placed in isolation and “treated empirically with antiviral agents, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and supportive therapies,” wrote Lan T. Phan, PhD, from the Pasteur Institute Ho Chi Minh City and coauthors.
On admission, chest radiographs revealed an infiltrate in the upper lobe of his left lung; he developed worsening dyspnea with hypoxemia on Jan. 25 and required supplemental oxygen at 5 L/min by nasal cannula. Chest radiographs showed a progressive infiltrate and consolidation. His fever resolved on that day and he has progressively improved.
The man’s son had a fever of 39° C (102.2° F) when the two men arrived at the hospital on Jan. 22; hospital staff isolated the son, and chest radiographs and other laboratory tests were normal with the exception of an increased C-reactive protein level.
The son’s throat swab was positive for 2019-nCoV and he is believed to have been exposed from his father; however, the strains have not been ascertained.
“This family had traveled to four cities across Vietnam using various forms of transportation, including planes, trains, and taxis,” the authors wrote. A total of 28 close contacts were identified, none of whom have developed respiratory symptoms. The older man’s wife has been healthy as well.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HHS: Coronavirus risk low in U.S., vaccine development underway
U.S. public health officials attempted to stymie concerns about the coronavirus during a press conference on Tuesday,

“Right now, there is no spread of this virus in our communities here at home,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Robert Redfield, MD, said during the Jan. 28 press conference. “This is why our current assessment is that the immediate health risk of this new virus to the general public is low in our nation. The coming days and weeks are likely to bring more confirmed cases here and around the world, including the possibility of some person-to-person spreading, but our goal of the ongoing U.S. public health response is to contain this outbreak and prevent sustained spread of the virus in our country.”
During the press conference, Department Health & Human Services Secretary Alex M. Azar II, reiterated there have been only five confirmed U.S. cases of the coronavirus thus far and all were associated with travel to Wuhan, China, where the virus first appeared. The number of confirmed cases in China, meanwhile, has risen to more than 4,500 with about 100 associated deaths.
U.S. health providers should be on the lookout for any patient who has traveled to China recently, particularly to Hubei province, and they should pay close attention to any relevant symptoms, Secretary Azar said during the press conference.
He defended the decision not to declare a public health emergency at this time, stressing that such a move is based on standards and requirements not yet met by the coronavirus.
“It’s important to remember where we are right now; we have five cases in the United States, each of those individuals with direct contact to Wuhan and no person-to-person transmission in the United States,” Secretary Azar said. “I won’t hesitate at all to invoke any authorities that I need to ensure that we’re taking all the steps to protect the American people, but I’ll do it when it’s appropriate under the standards that we have and the authorities that I need.”
In the meantime, a number of efforts are underway by U.S. agencies to assess the nation’s emergency preparedness stockpile, to assist American families in China with evacuation, and to pursue research into diagnostics and a potential vaccine for the virus, Secretary Azar said.
With regard to countermeasures, the CDC has rapidly developed a diagnostic based on the published sequence of the virus, said Anthony Fauci, MD, director for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). The National Institutes of Health and the CDC are now working on the development of next-generation diagnostics to better identify the virus in the United States and throughout the world, Dr. Fauci said during the press conference.
Currently, there are no proven therapeutics for the coronavirus infection, Dr. Fauci said. Based on experiences with SARS and MERS, however, researchers are studying certain antiviral drugs that could potentially treat the virus, he said. This includes the antiviral drug remdesivir, which was developed for the treatment of the Ebola virus, and lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), a combination therapy commonly used to treat HIV. In addition, monoclonal antibodies developed during the SARS outbreak are also being studied.
“Given the somewhat close homology between SARS and the new novel coronavirus, there could be some cross reactivity there that could be utilized,” he said.
Most importantly, he said, vaccine development is underway. Since China isolated the virus and published its sequence, U.S. researchers have already analyzed the components and determined an immunogen to be used in a vaccine, Dr. Fauci said. He anticipates moving to a Phase 1 trial within the next 3 months. The trial would then move to Phase 2 after another few more months for safety data.
“What we do from that point will be determined by what has happened with the outbreak over those months,” he said. “We are proceeding as if we will have to deploy a vaccine. In other words, we’re looking at the worst scenario that this becomes a bigger outbreak.”
Federal health officials, however, stressed that more data about infected patients in China is needed for research. HHS has repeatedly offered to send a CDC team to China to help with public health efforts, research, and response, but China has so far declined the offer, Secretary Azar added.
In addition, the CDC has updated its travel advisory in response to the illness. The latest travel guidance recommends that travelers avoid all nonessential travel to all parts of China.
U.S. public health officials attempted to stymie concerns about the coronavirus during a press conference on Tuesday,

“Right now, there is no spread of this virus in our communities here at home,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Robert Redfield, MD, said during the Jan. 28 press conference. “This is why our current assessment is that the immediate health risk of this new virus to the general public is low in our nation. The coming days and weeks are likely to bring more confirmed cases here and around the world, including the possibility of some person-to-person spreading, but our goal of the ongoing U.S. public health response is to contain this outbreak and prevent sustained spread of the virus in our country.”
During the press conference, Department Health & Human Services Secretary Alex M. Azar II, reiterated there have been only five confirmed U.S. cases of the coronavirus thus far and all were associated with travel to Wuhan, China, where the virus first appeared. The number of confirmed cases in China, meanwhile, has risen to more than 4,500 with about 100 associated deaths.
U.S. health providers should be on the lookout for any patient who has traveled to China recently, particularly to Hubei province, and they should pay close attention to any relevant symptoms, Secretary Azar said during the press conference.
He defended the decision not to declare a public health emergency at this time, stressing that such a move is based on standards and requirements not yet met by the coronavirus.
“It’s important to remember where we are right now; we have five cases in the United States, each of those individuals with direct contact to Wuhan and no person-to-person transmission in the United States,” Secretary Azar said. “I won’t hesitate at all to invoke any authorities that I need to ensure that we’re taking all the steps to protect the American people, but I’ll do it when it’s appropriate under the standards that we have and the authorities that I need.”
In the meantime, a number of efforts are underway by U.S. agencies to assess the nation’s emergency preparedness stockpile, to assist American families in China with evacuation, and to pursue research into diagnostics and a potential vaccine for the virus, Secretary Azar said.
With regard to countermeasures, the CDC has rapidly developed a diagnostic based on the published sequence of the virus, said Anthony Fauci, MD, director for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). The National Institutes of Health and the CDC are now working on the development of next-generation diagnostics to better identify the virus in the United States and throughout the world, Dr. Fauci said during the press conference.
Currently, there are no proven therapeutics for the coronavirus infection, Dr. Fauci said. Based on experiences with SARS and MERS, however, researchers are studying certain antiviral drugs that could potentially treat the virus, he said. This includes the antiviral drug remdesivir, which was developed for the treatment of the Ebola virus, and lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), a combination therapy commonly used to treat HIV. In addition, monoclonal antibodies developed during the SARS outbreak are also being studied.
“Given the somewhat close homology between SARS and the new novel coronavirus, there could be some cross reactivity there that could be utilized,” he said.
Most importantly, he said, vaccine development is underway. Since China isolated the virus and published its sequence, U.S. researchers have already analyzed the components and determined an immunogen to be used in a vaccine, Dr. Fauci said. He anticipates moving to a Phase 1 trial within the next 3 months. The trial would then move to Phase 2 after another few more months for safety data.
“What we do from that point will be determined by what has happened with the outbreak over those months,” he said. “We are proceeding as if we will have to deploy a vaccine. In other words, we’re looking at the worst scenario that this becomes a bigger outbreak.”
Federal health officials, however, stressed that more data about infected patients in China is needed for research. HHS has repeatedly offered to send a CDC team to China to help with public health efforts, research, and response, but China has so far declined the offer, Secretary Azar added.
In addition, the CDC has updated its travel advisory in response to the illness. The latest travel guidance recommends that travelers avoid all nonessential travel to all parts of China.
U.S. public health officials attempted to stymie concerns about the coronavirus during a press conference on Tuesday,

“Right now, there is no spread of this virus in our communities here at home,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Robert Redfield, MD, said during the Jan. 28 press conference. “This is why our current assessment is that the immediate health risk of this new virus to the general public is low in our nation. The coming days and weeks are likely to bring more confirmed cases here and around the world, including the possibility of some person-to-person spreading, but our goal of the ongoing U.S. public health response is to contain this outbreak and prevent sustained spread of the virus in our country.”
During the press conference, Department Health & Human Services Secretary Alex M. Azar II, reiterated there have been only five confirmed U.S. cases of the coronavirus thus far and all were associated with travel to Wuhan, China, where the virus first appeared. The number of confirmed cases in China, meanwhile, has risen to more than 4,500 with about 100 associated deaths.
U.S. health providers should be on the lookout for any patient who has traveled to China recently, particularly to Hubei province, and they should pay close attention to any relevant symptoms, Secretary Azar said during the press conference.
He defended the decision not to declare a public health emergency at this time, stressing that such a move is based on standards and requirements not yet met by the coronavirus.
“It’s important to remember where we are right now; we have five cases in the United States, each of those individuals with direct contact to Wuhan and no person-to-person transmission in the United States,” Secretary Azar said. “I won’t hesitate at all to invoke any authorities that I need to ensure that we’re taking all the steps to protect the American people, but I’ll do it when it’s appropriate under the standards that we have and the authorities that I need.”
In the meantime, a number of efforts are underway by U.S. agencies to assess the nation’s emergency preparedness stockpile, to assist American families in China with evacuation, and to pursue research into diagnostics and a potential vaccine for the virus, Secretary Azar said.
With regard to countermeasures, the CDC has rapidly developed a diagnostic based on the published sequence of the virus, said Anthony Fauci, MD, director for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). The National Institutes of Health and the CDC are now working on the development of next-generation diagnostics to better identify the virus in the United States and throughout the world, Dr. Fauci said during the press conference.
Currently, there are no proven therapeutics for the coronavirus infection, Dr. Fauci said. Based on experiences with SARS and MERS, however, researchers are studying certain antiviral drugs that could potentially treat the virus, he said. This includes the antiviral drug remdesivir, which was developed for the treatment of the Ebola virus, and lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), a combination therapy commonly used to treat HIV. In addition, monoclonal antibodies developed during the SARS outbreak are also being studied.
“Given the somewhat close homology between SARS and the new novel coronavirus, there could be some cross reactivity there that could be utilized,” he said.
Most importantly, he said, vaccine development is underway. Since China isolated the virus and published its sequence, U.S. researchers have already analyzed the components and determined an immunogen to be used in a vaccine, Dr. Fauci said. He anticipates moving to a Phase 1 trial within the next 3 months. The trial would then move to Phase 2 after another few more months for safety data.
“What we do from that point will be determined by what has happened with the outbreak over those months,” he said. “We are proceeding as if we will have to deploy a vaccine. In other words, we’re looking at the worst scenario that this becomes a bigger outbreak.”
Federal health officials, however, stressed that more data about infected patients in China is needed for research. HHS has repeatedly offered to send a CDC team to China to help with public health efforts, research, and response, but China has so far declined the offer, Secretary Azar added.
In addition, the CDC has updated its travel advisory in response to the illness. The latest travel guidance recommends that travelers avoid all nonessential travel to all parts of China.
Echoes of SARS mark 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak
The current outbreak of severe respiratory infections caused by the 2019 novel coronarvirus (2019-nCoV) has a clinical presentation resembling the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) outbreak that began in 2002, Chinese investigators caution.

By Jan. 2, 2020, 41 patients with confirmed 2019-nCoV had been admitted to a designated hospital in the city of Wuhan, Hubei Province, in central China. Thirteen required ICU admission and six died, reported Chaolin Huang, MD, from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, and colleagues.
“2019-nCoV still needs to be studied deeply in case it becomes a global health threat. Reliable quick pathogen tests and feasible differential diagnosis based on clinical description are crucial for clinicians in their first contact with suspected patients. Because of the pandemic potential of 2019-nCoV, careful surveillance is essential to monitor its future host adaption, viral evolution, infectivity, transmissibility, and pathogenicity,” they wrote in a review published online by The Lancet.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Jan. 28, 2020, the total number of 2019-nCoV cases reported in the United States stood at five, but further cases of the infection – which Chinese health officials have confirmed can be transmitted person-to-person – are expected.
Dr. Huang and colleagues note that although most human coronavirus infections are mild, SARS-CoV and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) were responsible for more than 10,000 infections, with mortality rates ranging from 10% with SARS to 37% with MERS. To date, 2019-nCoV has “caused clusters of fatal pneumonia greatly resembling SARS-CoV,” they write.
The authors studied the epidemiological, clinical, laboratory, and radiological characteristics as well as treatments and clinical outcomes of 41 patients admitted or transferred to the Jin Yin-tan Hospital with laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV infections.
The median patient age was 49 years. Thirty of the 41 patients (73%) were male. Comorbid conditions included diabetes in 13 of the 41 patients (32%), hypertension in 6 (15%), and cardiovascular disease in 6.
In all 27 of the 41 patients had been exposed to the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, the suspected epicenter of the outbreak that was shut down by health authorities on Jan. 1 of this year.
The most common symptoms at the onset of the illness were fever in all but one of the 41 patients, cough in 31, and myalgia or fatigue in 18. Other, less frequent symptoms included sputum production in 11, headache in three, hemoptysis in two, and diarrhea in one.
“In this cohort, most patients presented with fever, dry cough, dyspnoea, and bilateral ground-glass opacities on chest CT scans. These features of 2019-nCoV infection bear some resemblance to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infections. However, few patients with 2019-nCoV infection had prominent upper respiratory tract signs and symptoms (e.g., rhinorrhoea, sneezing, or sore throat), indicating that the target cells might be located in the lower airway. Furthermore, 2019-nCoV patients rarely developed intestinal signs and symptoms (e.g., diarrhoea), whereas about 20%-25% of patients with MERS-CoV or SARS-CoV infection had diarrhoea.”
In all, 22 patients developed dyspnea, with a median time from illness onset to dyspnea of 8 days. The median time from illness onset to admission was 7 days, median time to shortness of breath was 8 days, median time to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was 9 days, and median time to both mechanical ventilation and ICU admission was 10.5 days.
All of the patients developed pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT scan. In addition, 12 patients developed ARDS, six had RNAaemia, five developed acute cardiac injury, and four developed a secondary infection. As noted before, 13 of the 14 patients were admitted to an ICU, and six died. RNAaemia is a positive result for real-time polymerase chain reaction in plasma samples. Patients admitted to the ICU had higher initial concentrations of multiple inflammatory cytokines than patients who did not need ICU care, “suggesting that the cytokine storm was associated with disease severity.”
All of the patients received empirical antibiotics, 38 were treated with oseltamivir (Tamiflu), and 9 received systemic corticosteroids.
The investigators have initiated a randomized controlled trial of the antiviral agents lopinavir and ritonavir for patients hospitalized with 2019-nCoV infection.
The study was funded by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. All authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Huang C et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5.
The current outbreak of severe respiratory infections caused by the 2019 novel coronarvirus (2019-nCoV) has a clinical presentation resembling the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) outbreak that began in 2002, Chinese investigators caution.

By Jan. 2, 2020, 41 patients with confirmed 2019-nCoV had been admitted to a designated hospital in the city of Wuhan, Hubei Province, in central China. Thirteen required ICU admission and six died, reported Chaolin Huang, MD, from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, and colleagues.
“2019-nCoV still needs to be studied deeply in case it becomes a global health threat. Reliable quick pathogen tests and feasible differential diagnosis based on clinical description are crucial for clinicians in their first contact with suspected patients. Because of the pandemic potential of 2019-nCoV, careful surveillance is essential to monitor its future host adaption, viral evolution, infectivity, transmissibility, and pathogenicity,” they wrote in a review published online by The Lancet.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Jan. 28, 2020, the total number of 2019-nCoV cases reported in the United States stood at five, but further cases of the infection – which Chinese health officials have confirmed can be transmitted person-to-person – are expected.
Dr. Huang and colleagues note that although most human coronavirus infections are mild, SARS-CoV and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) were responsible for more than 10,000 infections, with mortality rates ranging from 10% with SARS to 37% with MERS. To date, 2019-nCoV has “caused clusters of fatal pneumonia greatly resembling SARS-CoV,” they write.
The authors studied the epidemiological, clinical, laboratory, and radiological characteristics as well as treatments and clinical outcomes of 41 patients admitted or transferred to the Jin Yin-tan Hospital with laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV infections.
The median patient age was 49 years. Thirty of the 41 patients (73%) were male. Comorbid conditions included diabetes in 13 of the 41 patients (32%), hypertension in 6 (15%), and cardiovascular disease in 6.
In all 27 of the 41 patients had been exposed to the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, the suspected epicenter of the outbreak that was shut down by health authorities on Jan. 1 of this year.
The most common symptoms at the onset of the illness were fever in all but one of the 41 patients, cough in 31, and myalgia or fatigue in 18. Other, less frequent symptoms included sputum production in 11, headache in three, hemoptysis in two, and diarrhea in one.
“In this cohort, most patients presented with fever, dry cough, dyspnoea, and bilateral ground-glass opacities on chest CT scans. These features of 2019-nCoV infection bear some resemblance to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infections. However, few patients with 2019-nCoV infection had prominent upper respiratory tract signs and symptoms (e.g., rhinorrhoea, sneezing, or sore throat), indicating that the target cells might be located in the lower airway. Furthermore, 2019-nCoV patients rarely developed intestinal signs and symptoms (e.g., diarrhoea), whereas about 20%-25% of patients with MERS-CoV or SARS-CoV infection had diarrhoea.”
In all, 22 patients developed dyspnea, with a median time from illness onset to dyspnea of 8 days. The median time from illness onset to admission was 7 days, median time to shortness of breath was 8 days, median time to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was 9 days, and median time to both mechanical ventilation and ICU admission was 10.5 days.
All of the patients developed pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT scan. In addition, 12 patients developed ARDS, six had RNAaemia, five developed acute cardiac injury, and four developed a secondary infection. As noted before, 13 of the 14 patients were admitted to an ICU, and six died. RNAaemia is a positive result for real-time polymerase chain reaction in plasma samples. Patients admitted to the ICU had higher initial concentrations of multiple inflammatory cytokines than patients who did not need ICU care, “suggesting that the cytokine storm was associated with disease severity.”
All of the patients received empirical antibiotics, 38 were treated with oseltamivir (Tamiflu), and 9 received systemic corticosteroids.
The investigators have initiated a randomized controlled trial of the antiviral agents lopinavir and ritonavir for patients hospitalized with 2019-nCoV infection.
The study was funded by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. All authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Huang C et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5.
The current outbreak of severe respiratory infections caused by the 2019 novel coronarvirus (2019-nCoV) has a clinical presentation resembling the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) outbreak that began in 2002, Chinese investigators caution.

By Jan. 2, 2020, 41 patients with confirmed 2019-nCoV had been admitted to a designated hospital in the city of Wuhan, Hubei Province, in central China. Thirteen required ICU admission and six died, reported Chaolin Huang, MD, from Jin Yin-tan Hospital in Wuhan, and colleagues.
“2019-nCoV still needs to be studied deeply in case it becomes a global health threat. Reliable quick pathogen tests and feasible differential diagnosis based on clinical description are crucial for clinicians in their first contact with suspected patients. Because of the pandemic potential of 2019-nCoV, careful surveillance is essential to monitor its future host adaption, viral evolution, infectivity, transmissibility, and pathogenicity,” they wrote in a review published online by The Lancet.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Jan. 28, 2020, the total number of 2019-nCoV cases reported in the United States stood at five, but further cases of the infection – which Chinese health officials have confirmed can be transmitted person-to-person – are expected.
Dr. Huang and colleagues note that although most human coronavirus infections are mild, SARS-CoV and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) were responsible for more than 10,000 infections, with mortality rates ranging from 10% with SARS to 37% with MERS. To date, 2019-nCoV has “caused clusters of fatal pneumonia greatly resembling SARS-CoV,” they write.
The authors studied the epidemiological, clinical, laboratory, and radiological characteristics as well as treatments and clinical outcomes of 41 patients admitted or transferred to the Jin Yin-tan Hospital with laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV infections.
The median patient age was 49 years. Thirty of the 41 patients (73%) were male. Comorbid conditions included diabetes in 13 of the 41 patients (32%), hypertension in 6 (15%), and cardiovascular disease in 6.
In all 27 of the 41 patients had been exposed to the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, the suspected epicenter of the outbreak that was shut down by health authorities on Jan. 1 of this year.
The most common symptoms at the onset of the illness were fever in all but one of the 41 patients, cough in 31, and myalgia or fatigue in 18. Other, less frequent symptoms included sputum production in 11, headache in three, hemoptysis in two, and diarrhea in one.
“In this cohort, most patients presented with fever, dry cough, dyspnoea, and bilateral ground-glass opacities on chest CT scans. These features of 2019-nCoV infection bear some resemblance to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infections. However, few patients with 2019-nCoV infection had prominent upper respiratory tract signs and symptoms (e.g., rhinorrhoea, sneezing, or sore throat), indicating that the target cells might be located in the lower airway. Furthermore, 2019-nCoV patients rarely developed intestinal signs and symptoms (e.g., diarrhoea), whereas about 20%-25% of patients with MERS-CoV or SARS-CoV infection had diarrhoea.”
In all, 22 patients developed dyspnea, with a median time from illness onset to dyspnea of 8 days. The median time from illness onset to admission was 7 days, median time to shortness of breath was 8 days, median time to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was 9 days, and median time to both mechanical ventilation and ICU admission was 10.5 days.
All of the patients developed pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT scan. In addition, 12 patients developed ARDS, six had RNAaemia, five developed acute cardiac injury, and four developed a secondary infection. As noted before, 13 of the 14 patients were admitted to an ICU, and six died. RNAaemia is a positive result for real-time polymerase chain reaction in plasma samples. Patients admitted to the ICU had higher initial concentrations of multiple inflammatory cytokines than patients who did not need ICU care, “suggesting that the cytokine storm was associated with disease severity.”
All of the patients received empirical antibiotics, 38 were treated with oseltamivir (Tamiflu), and 9 received systemic corticosteroids.
The investigators have initiated a randomized controlled trial of the antiviral agents lopinavir and ritonavir for patients hospitalized with 2019-nCoV infection.
The study was funded by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. All authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Huang C et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5.
FROM THE LANCET
A better approach to preventing active TB?
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 27-year-old daycare worker was tested for tuberculosis (TB) as part of a recent work physical. She presents to your office for follow-up for her positive purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test. You confirm the result with a quantiferon gold test and ensure she does not have active TB. What medication should you prescribe to treat her latent TB infection (LTBI)?
In 2017, there were 9093 cases of new active TB in the United States.2 It’s estimated that one-fourth of the world’s population has latent TB.3 Identifying and treating latent TB infection is vital to achieving TB’s elimination.4,5
Primary care clinicians are at the forefront of screening high-risk populations for TB. Once identified, treating LTBI can be challenging for providers and patients. Treatment guidelines recommend 4 to 9 months of daily isoniazid.5-8 Shorter treatment regimens were recommended previously; they tended to be rigorous, to involve multiple drugs, and to require high adherence rates. As such, they included directly observed therapy, which prevented widespread adoption.
Consequently, the mainstay for treating LTBI has been 9 months of daily isoniazid. However, isoniazid use is limited by hepatoxicity and by suboptimal treatment completion rates. A 2018 retrospective analysis of patients treated for LTBI reported a completion rate of only 49% for 9 months of isoniazid.9 Additionally, a Cochrane review last updated in 2013 suggests that shorter courses of rifampin are similar in efficacy to isoniazid (although with a wide confidence interval [CI]), and likely have higher adherence rates.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Rifampin is as effective as isoniazid with fewer adverse effects
The study by Menzies et al1 was a multisite, 9-country, open-label, randomized controlled trial (RCT) that compared 4 months of daily rifampin to 9 months of daily isoniazid for the treatment of LTBI in adults. Participants were eligible if they had a positive tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma-release assay, were ≥ 18 years of age, had an increased risk for reactivation of active TB, and if their health care provider had recommended treatment with isoniazid. Exclusion criteria included current pregnancy or plans to become pregnant, exposure to a patient with TB whose isolates were resistant to either trial drug, an allergy to either of the trial drugs, use of a medication with serious potential interactions with the trial drugs, or current active TB.
Method, outcomes, patient characteristics. Patients received either isoniazid 5 mg/kg body weight (maximum dose 300 mg) daily for 9 months or rifampin 10 mg/kg (maximum dose 600 mg) daily for 4 months and were followed for 28 months. Patients in the isoniazid group also received pyridoxine (vitamin B6) if they were at risk for neuropathy. The primary outcome was the rate of active TB. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, medication regimen completion rate, and drug resistance, among others.
A total of 2989 patients were treated with isoniazid; 3023 patients were treated with rifampin. The mean age of the participants was 38.4 years, 41% of the population was male, and 71% of the groups had confirmed active TB in close contacts.
Continue to: Results
Results. Overall, rates of active TB were low with 9 cases in the isoniazid group and 8 in the rifampin group. In the intention-to-treat analysis, the rate difference for confirmed active TB was < 0.01 cases per 100 person-years (95% CI; −0.14 to 0.16). This met the prespecified noninferiority endpoint, but did not show superiority. A total of 79% of patients treated with rifampin vs 63% treated with isoniazid completed their respective medication courses (difference of 15.1 percentage points; 95% CI, 12.7-17.4; P < .001). Compared with patients in the isoniazid group, those taking rifampin had fewer adverse events, leading to discontinuation (5.6% vs 2.8%).
WHAT’S NEW?
First high-quality study to show that less is more
This is the first large, high-quality study to show that a shorter (4 month) rifampin-based regimen is not inferior to a longer (9 months) isoniazid-based regimen for the treatment of LTBI, and that rifampin is associated with improved adherence and fewer adverse events.
CAVEATS
Low rate of active TB infection and potential bias
The current study had lower-than-anticipated rates of active TB infection, which made the study’s conclusions less compelling. This may have been because of a small number of patients with human immunodeficiency virus enrolled in the study and/or that even participants who discontinued treatment received a median of 3 months of partial treatment.
In addition, the study was an open-label RCT, subjecting it to potential bias. However, the diagnosis of active TB and attribution of adverse events were made by an independent, blinded review panel.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No challenges to speak of
We see no challenges to implementing this recommendation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Menzies D, Adjobimey M, Ruslami R, et al. Four months of rifampin or nine months of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis in adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:440-453.
2. Stewart RJ, Tsang CA, Pratt RH, et al. Tuberculosis — United States, 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:317-323.
3. Houben RM, Dodd PJ. The global burden of latent tuberculosis infection: a re-estimation using mathematical modeling. PLoS Med. 2016;13:e1002152.
4. Lönnroth K, Migliori GB, Abubakar I, et al. Towards tuberculosis elimination: an action framework for low-incidence countries. Eur Respir J. 2015;45:928-952.
5. Uplekar M, Weil D, Lonnroth K, et al. WHO’s new end TB strategy. Lancet. 2015;385:1799-1801.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treatment regimens for latent TB infection (LTBI). Last reviewed April 5, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/ltbi.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
7. World Health Organization. Latent TB infection: updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. 2018. Publication no. WHO/CDS/TB/2018.4. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2018/latent-tuberculosis-infection/en/. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Borisov AS, Bamrah Morris S, Njie GJ, et al. Update of recommendations for use of once-weekly isoniazid-rifapentine regimen to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:723-726.
9. Macaraig MM, Jalees M, Lam C, et al. Improved treatment completion with shorter treatment regimens for latent tuberculous infection. Int J Tuber Lung Dis. 2018;22:1344-1349. 10. Sharma SK, Sharma A, Kadhiravan T, et al. Rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine) compared to isoniazid for preventing tuberculosis in HIV-negative people at risk of active TB. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD007545.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 27-year-old daycare worker was tested for tuberculosis (TB) as part of a recent work physical. She presents to your office for follow-up for her positive purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test. You confirm the result with a quantiferon gold test and ensure she does not have active TB. What medication should you prescribe to treat her latent TB infection (LTBI)?
In 2017, there were 9093 cases of new active TB in the United States.2 It’s estimated that one-fourth of the world’s population has latent TB.3 Identifying and treating latent TB infection is vital to achieving TB’s elimination.4,5
Primary care clinicians are at the forefront of screening high-risk populations for TB. Once identified, treating LTBI can be challenging for providers and patients. Treatment guidelines recommend 4 to 9 months of daily isoniazid.5-8 Shorter treatment regimens were recommended previously; they tended to be rigorous, to involve multiple drugs, and to require high adherence rates. As such, they included directly observed therapy, which prevented widespread adoption.
Consequently, the mainstay for treating LTBI has been 9 months of daily isoniazid. However, isoniazid use is limited by hepatoxicity and by suboptimal treatment completion rates. A 2018 retrospective analysis of patients treated for LTBI reported a completion rate of only 49% for 9 months of isoniazid.9 Additionally, a Cochrane review last updated in 2013 suggests that shorter courses of rifampin are similar in efficacy to isoniazid (although with a wide confidence interval [CI]), and likely have higher adherence rates.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Rifampin is as effective as isoniazid with fewer adverse effects
The study by Menzies et al1 was a multisite, 9-country, open-label, randomized controlled trial (RCT) that compared 4 months of daily rifampin to 9 months of daily isoniazid for the treatment of LTBI in adults. Participants were eligible if they had a positive tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma-release assay, were ≥ 18 years of age, had an increased risk for reactivation of active TB, and if their health care provider had recommended treatment with isoniazid. Exclusion criteria included current pregnancy or plans to become pregnant, exposure to a patient with TB whose isolates were resistant to either trial drug, an allergy to either of the trial drugs, use of a medication with serious potential interactions with the trial drugs, or current active TB.
Method, outcomes, patient characteristics. Patients received either isoniazid 5 mg/kg body weight (maximum dose 300 mg) daily for 9 months or rifampin 10 mg/kg (maximum dose 600 mg) daily for 4 months and were followed for 28 months. Patients in the isoniazid group also received pyridoxine (vitamin B6) if they were at risk for neuropathy. The primary outcome was the rate of active TB. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, medication regimen completion rate, and drug resistance, among others.
A total of 2989 patients were treated with isoniazid; 3023 patients were treated with rifampin. The mean age of the participants was 38.4 years, 41% of the population was male, and 71% of the groups had confirmed active TB in close contacts.
Continue to: Results
Results. Overall, rates of active TB were low with 9 cases in the isoniazid group and 8 in the rifampin group. In the intention-to-treat analysis, the rate difference for confirmed active TB was < 0.01 cases per 100 person-years (95% CI; −0.14 to 0.16). This met the prespecified noninferiority endpoint, but did not show superiority. A total of 79% of patients treated with rifampin vs 63% treated with isoniazid completed their respective medication courses (difference of 15.1 percentage points; 95% CI, 12.7-17.4; P < .001). Compared with patients in the isoniazid group, those taking rifampin had fewer adverse events, leading to discontinuation (5.6% vs 2.8%).
WHAT’S NEW?
First high-quality study to show that less is more
This is the first large, high-quality study to show that a shorter (4 month) rifampin-based regimen is not inferior to a longer (9 months) isoniazid-based regimen for the treatment of LTBI, and that rifampin is associated with improved adherence and fewer adverse events.
CAVEATS
Low rate of active TB infection and potential bias
The current study had lower-than-anticipated rates of active TB infection, which made the study’s conclusions less compelling. This may have been because of a small number of patients with human immunodeficiency virus enrolled in the study and/or that even participants who discontinued treatment received a median of 3 months of partial treatment.
In addition, the study was an open-label RCT, subjecting it to potential bias. However, the diagnosis of active TB and attribution of adverse events were made by an independent, blinded review panel.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No challenges to speak of
We see no challenges to implementing this recommendation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 27-year-old daycare worker was tested for tuberculosis (TB) as part of a recent work physical. She presents to your office for follow-up for her positive purified protein derivative (PPD) skin test. You confirm the result with a quantiferon gold test and ensure she does not have active TB. What medication should you prescribe to treat her latent TB infection (LTBI)?
In 2017, there were 9093 cases of new active TB in the United States.2 It’s estimated that one-fourth of the world’s population has latent TB.3 Identifying and treating latent TB infection is vital to achieving TB’s elimination.4,5
Primary care clinicians are at the forefront of screening high-risk populations for TB. Once identified, treating LTBI can be challenging for providers and patients. Treatment guidelines recommend 4 to 9 months of daily isoniazid.5-8 Shorter treatment regimens were recommended previously; they tended to be rigorous, to involve multiple drugs, and to require high adherence rates. As such, they included directly observed therapy, which prevented widespread adoption.
Consequently, the mainstay for treating LTBI has been 9 months of daily isoniazid. However, isoniazid use is limited by hepatoxicity and by suboptimal treatment completion rates. A 2018 retrospective analysis of patients treated for LTBI reported a completion rate of only 49% for 9 months of isoniazid.9 Additionally, a Cochrane review last updated in 2013 suggests that shorter courses of rifampin are similar in efficacy to isoniazid (although with a wide confidence interval [CI]), and likely have higher adherence rates.10
STUDY SUMMARY
Rifampin is as effective as isoniazid with fewer adverse effects
The study by Menzies et al1 was a multisite, 9-country, open-label, randomized controlled trial (RCT) that compared 4 months of daily rifampin to 9 months of daily isoniazid for the treatment of LTBI in adults. Participants were eligible if they had a positive tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma-release assay, were ≥ 18 years of age, had an increased risk for reactivation of active TB, and if their health care provider had recommended treatment with isoniazid. Exclusion criteria included current pregnancy or plans to become pregnant, exposure to a patient with TB whose isolates were resistant to either trial drug, an allergy to either of the trial drugs, use of a medication with serious potential interactions with the trial drugs, or current active TB.
Method, outcomes, patient characteristics. Patients received either isoniazid 5 mg/kg body weight (maximum dose 300 mg) daily for 9 months or rifampin 10 mg/kg (maximum dose 600 mg) daily for 4 months and were followed for 28 months. Patients in the isoniazid group also received pyridoxine (vitamin B6) if they were at risk for neuropathy. The primary outcome was the rate of active TB. Secondary outcomes included adverse events, medication regimen completion rate, and drug resistance, among others.
A total of 2989 patients were treated with isoniazid; 3023 patients were treated with rifampin. The mean age of the participants was 38.4 years, 41% of the population was male, and 71% of the groups had confirmed active TB in close contacts.
Continue to: Results
Results. Overall, rates of active TB were low with 9 cases in the isoniazid group and 8 in the rifampin group. In the intention-to-treat analysis, the rate difference for confirmed active TB was < 0.01 cases per 100 person-years (95% CI; −0.14 to 0.16). This met the prespecified noninferiority endpoint, but did not show superiority. A total of 79% of patients treated with rifampin vs 63% treated with isoniazid completed their respective medication courses (difference of 15.1 percentage points; 95% CI, 12.7-17.4; P < .001). Compared with patients in the isoniazid group, those taking rifampin had fewer adverse events, leading to discontinuation (5.6% vs 2.8%).
WHAT’S NEW?
First high-quality study to show that less is more
This is the first large, high-quality study to show that a shorter (4 month) rifampin-based regimen is not inferior to a longer (9 months) isoniazid-based regimen for the treatment of LTBI, and that rifampin is associated with improved adherence and fewer adverse events.
CAVEATS
Low rate of active TB infection and potential bias
The current study had lower-than-anticipated rates of active TB infection, which made the study’s conclusions less compelling. This may have been because of a small number of patients with human immunodeficiency virus enrolled in the study and/or that even participants who discontinued treatment received a median of 3 months of partial treatment.
In addition, the study was an open-label RCT, subjecting it to potential bias. However, the diagnosis of active TB and attribution of adverse events were made by an independent, blinded review panel.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
No challenges to speak of
We see no challenges to implementing this recommendation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Menzies D, Adjobimey M, Ruslami R, et al. Four months of rifampin or nine months of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis in adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:440-453.
2. Stewart RJ, Tsang CA, Pratt RH, et al. Tuberculosis — United States, 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:317-323.
3. Houben RM, Dodd PJ. The global burden of latent tuberculosis infection: a re-estimation using mathematical modeling. PLoS Med. 2016;13:e1002152.
4. Lönnroth K, Migliori GB, Abubakar I, et al. Towards tuberculosis elimination: an action framework for low-incidence countries. Eur Respir J. 2015;45:928-952.
5. Uplekar M, Weil D, Lonnroth K, et al. WHO’s new end TB strategy. Lancet. 2015;385:1799-1801.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treatment regimens for latent TB infection (LTBI). Last reviewed April 5, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/ltbi.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
7. World Health Organization. Latent TB infection: updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. 2018. Publication no. WHO/CDS/TB/2018.4. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2018/latent-tuberculosis-infection/en/. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Borisov AS, Bamrah Morris S, Njie GJ, et al. Update of recommendations for use of once-weekly isoniazid-rifapentine regimen to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:723-726.
9. Macaraig MM, Jalees M, Lam C, et al. Improved treatment completion with shorter treatment regimens for latent tuberculous infection. Int J Tuber Lung Dis. 2018;22:1344-1349. 10. Sharma SK, Sharma A, Kadhiravan T, et al. Rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine) compared to isoniazid for preventing tuberculosis in HIV-negative people at risk of active TB. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD007545.
1. Menzies D, Adjobimey M, Ruslami R, et al. Four months of rifampin or nine months of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis in adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:440-453.
2. Stewart RJ, Tsang CA, Pratt RH, et al. Tuberculosis — United States, 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:317-323.
3. Houben RM, Dodd PJ. The global burden of latent tuberculosis infection: a re-estimation using mathematical modeling. PLoS Med. 2016;13:e1002152.
4. Lönnroth K, Migliori GB, Abubakar I, et al. Towards tuberculosis elimination: an action framework for low-incidence countries. Eur Respir J. 2015;45:928-952.
5. Uplekar M, Weil D, Lonnroth K, et al. WHO’s new end TB strategy. Lancet. 2015;385:1799-1801.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treatment regimens for latent TB infection (LTBI). Last reviewed April 5, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/treatment/ltbi.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
7. World Health Organization. Latent TB infection: updated and consolidated guidelines for programmatic management. 2018. Publication no. WHO/CDS/TB/2018.4. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2018/latent-tuberculosis-infection/en/. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Borisov AS, Bamrah Morris S, Njie GJ, et al. Update of recommendations for use of once-weekly isoniazid-rifapentine regimen to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:723-726.
9. Macaraig MM, Jalees M, Lam C, et al. Improved treatment completion with shorter treatment regimens for latent tuberculous infection. Int J Tuber Lung Dis. 2018;22:1344-1349. 10. Sharma SK, Sharma A, Kadhiravan T, et al. Rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine) compared to isoniazid for preventing tuberculosis in HIV-negative people at risk of active TB. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD007545.
PRACTICE CHANGER
Use 4 months of rifampin instead of 9 months of isoniazid to treat adults with latent tuberculosis; rifampin is associated with fewer adverse events and higher completion rates.
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
A: Based on a randomized controlled trial and a previous Cochrane review.
Menzies D, Adjobimey M, Ruslami R, et al. Four months of rifampin or nine months of isoniazid for latent tuberculosis in adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:440-453.