User login
Shunt diameter predicts liver function after obliteration procedure
Patients with cirrhosis and larger spontaneous shunt diameters showed a significantly greater increase in hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) following balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration compared to patients with smaller shunt diameters, based on data from 34 adults.
Portal hypertension remains a key source of complications that greatly impact quality of life in patients with cirrhosis, wrote Akihisa Tatsumi, MD, of the University of Yamanashi, Japan, and colleagues. These patients sometimes develop spontaneous portosystemic shunts (SPSS) to lower portal pressure, but these natural shunts are an incomplete solution – one that may contribute to liver dysfunction by reducing hepatic portal blood flow. However, the association of SPSS with liver functional reserve remains unclear, the researchers said.
Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) is gaining popularity as a treatment for SPSS in patients with cirrhosis but determining the patients who will benefit from this procedure remains a challenge, the researchers wrote. “Apart from BRTO, some recent studies have reported the impact of the SPSS diameter on the future pathological state of the liver,” which prompted the question of whether SPSS diameter plays a role in predicting portal hypertension–related liver function at baseline and after BRTO, the researchers explained.
In their study, published in JGH Open, the researchers identified 34 cirrhotic patients with SPSS who underwent BRTO at a single center in Japan between 2006 and 2018; all of the patients were available for follow-up at least 6 months after the procedure.
The reasons for BRTO were intractable gastric varices in 18 patients and refractory hepatic encephalopathy with shunt in 16 patients; the mean observation period was 1,182 days (3.24 years). The median age of the patients was 66.5 years, and 53% were male. A majority (76%) of the patients had decompensated cirrhosis with Child-Pugh (CP) scores of B or C, and the maximum diameter of SPSS increased significantly with increased in CP scores (P < .001), the researchers noted.
Overall, at 6 months after BRTO, patients showed significant improvements in liver function from baseline. However, the improvement rate was lower in patients whose shunt diameter was 10 mm or less, and improvement was greatest when the shunt diameter was between 10 mm and 20 mm. “Because the CP score is a significant cofounding factor of the SPSS diameter, we next evaluated the changes in liver function classified by CP scores,” the researchers wrote. In this analysis, the post-BRTO changes in liver function in patients with CP scores of A or B still showed an association between improvement in liver function and larger shunt diameter, but this relationship did not extend to patients with CP scores of C, the researchers said.
A larger shunt diameter also was significantly associated with a greater increase in HVPG after balloon occlusion (P = .005).
“Considering that patients with large SPSS diameters might gain higher portal flow following elevation of HVPG after BRTO, it is natural that the larger the SPSS diameter, the greater the improvements in liver function,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “However, such a clear correlation was evident only when the baseline CP scores were within A or B, and not in C, indicating that the improvement of liver function might not parallel HVPG increase in some CP C patients,” they noted.
The study was limited by several factors including the retrospective design from a single center and its small sample size, the researchers noted. Other limitations included selecting and measuring only the largest SPSS of each patient and lack of data on the impact of SPSS diameter on overall survival, they said.
However, the results suggest that SPSS diameter may serve not only as an indicator of portal hypertension involvement at baseline, but also as a useful clinical predictor of liver function after BRTO, they concluded.
Study supports potential benefits of BRTO
“While the association between SPSS and complications of portal hypertension such as variceal bleeding and hepatic encephalopathy have been known, data are lacking in regard to characteristics of SPSS that are most dysfunctional, and whether certain patients may benefit from BRTO to occlude these shunts,” Khashayar Farsad, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview.
“The results are in many ways expected based on anticipated impact of larger versus smaller SPSS in overall liver function,” Dr. Farsad noted. “The study, however, does show a nice correlation between several factors involved in liver function and their changes depending on shunt diameter, correlated with changes in the relative venous pressure gradient across the liver,” he said. “Furthermore, the finding that changes were most evident in those with relatively preserved liver function [Child-Turcotte-Pugh grades A and B] suggests less of a relationship between SPSS and liver function in those with more decompensated liver disease,” he added.
“The impact of the study is significantly limited by its retrospective design, small numbers with potential patient heterogeneity, and lack of a control cohort,” said Dr. Farsad. However, “The major take-home message for clinicians is a potential signal that the size of the SPSS at baseline may predict the impact of the SPSS on liver function, and therefore, the potential benefit of a procedure such as BRTO to positively influence this,” he said. “Additional research with larger cohorts and a prospective study design would be warranted, however, before this information would be meaningful in daily clinical decision making,” he emphasized.
The study was supported by the Research Program on Hepatitis of the Japanese Agency for Medical Research and Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farsad disclosed research support from W.L. Gore & Associates, Guerbet LLC, Boston Scientific, and Exelixis; serving as a consultant for NeuWave Medical, Cook Medical, Guerbet LLC, and Eisai, and holding equity in Auxetics Inc.
Patients with cirrhosis and larger spontaneous shunt diameters showed a significantly greater increase in hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) following balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration compared to patients with smaller shunt diameters, based on data from 34 adults.
Portal hypertension remains a key source of complications that greatly impact quality of life in patients with cirrhosis, wrote Akihisa Tatsumi, MD, of the University of Yamanashi, Japan, and colleagues. These patients sometimes develop spontaneous portosystemic shunts (SPSS) to lower portal pressure, but these natural shunts are an incomplete solution – one that may contribute to liver dysfunction by reducing hepatic portal blood flow. However, the association of SPSS with liver functional reserve remains unclear, the researchers said.
Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) is gaining popularity as a treatment for SPSS in patients with cirrhosis but determining the patients who will benefit from this procedure remains a challenge, the researchers wrote. “Apart from BRTO, some recent studies have reported the impact of the SPSS diameter on the future pathological state of the liver,” which prompted the question of whether SPSS diameter plays a role in predicting portal hypertension–related liver function at baseline and after BRTO, the researchers explained.
In their study, published in JGH Open, the researchers identified 34 cirrhotic patients with SPSS who underwent BRTO at a single center in Japan between 2006 and 2018; all of the patients were available for follow-up at least 6 months after the procedure.
The reasons for BRTO were intractable gastric varices in 18 patients and refractory hepatic encephalopathy with shunt in 16 patients; the mean observation period was 1,182 days (3.24 years). The median age of the patients was 66.5 years, and 53% were male. A majority (76%) of the patients had decompensated cirrhosis with Child-Pugh (CP) scores of B or C, and the maximum diameter of SPSS increased significantly with increased in CP scores (P < .001), the researchers noted.
Overall, at 6 months after BRTO, patients showed significant improvements in liver function from baseline. However, the improvement rate was lower in patients whose shunt diameter was 10 mm or less, and improvement was greatest when the shunt diameter was between 10 mm and 20 mm. “Because the CP score is a significant cofounding factor of the SPSS diameter, we next evaluated the changes in liver function classified by CP scores,” the researchers wrote. In this analysis, the post-BRTO changes in liver function in patients with CP scores of A or B still showed an association between improvement in liver function and larger shunt diameter, but this relationship did not extend to patients with CP scores of C, the researchers said.
A larger shunt diameter also was significantly associated with a greater increase in HVPG after balloon occlusion (P = .005).
“Considering that patients with large SPSS diameters might gain higher portal flow following elevation of HVPG after BRTO, it is natural that the larger the SPSS diameter, the greater the improvements in liver function,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “However, such a clear correlation was evident only when the baseline CP scores were within A or B, and not in C, indicating that the improvement of liver function might not parallel HVPG increase in some CP C patients,” they noted.
The study was limited by several factors including the retrospective design from a single center and its small sample size, the researchers noted. Other limitations included selecting and measuring only the largest SPSS of each patient and lack of data on the impact of SPSS diameter on overall survival, they said.
However, the results suggest that SPSS diameter may serve not only as an indicator of portal hypertension involvement at baseline, but also as a useful clinical predictor of liver function after BRTO, they concluded.
Study supports potential benefits of BRTO
“While the association between SPSS and complications of portal hypertension such as variceal bleeding and hepatic encephalopathy have been known, data are lacking in regard to characteristics of SPSS that are most dysfunctional, and whether certain patients may benefit from BRTO to occlude these shunts,” Khashayar Farsad, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview.
“The results are in many ways expected based on anticipated impact of larger versus smaller SPSS in overall liver function,” Dr. Farsad noted. “The study, however, does show a nice correlation between several factors involved in liver function and their changes depending on shunt diameter, correlated with changes in the relative venous pressure gradient across the liver,” he said. “Furthermore, the finding that changes were most evident in those with relatively preserved liver function [Child-Turcotte-Pugh grades A and B] suggests less of a relationship between SPSS and liver function in those with more decompensated liver disease,” he added.
“The impact of the study is significantly limited by its retrospective design, small numbers with potential patient heterogeneity, and lack of a control cohort,” said Dr. Farsad. However, “The major take-home message for clinicians is a potential signal that the size of the SPSS at baseline may predict the impact of the SPSS on liver function, and therefore, the potential benefit of a procedure such as BRTO to positively influence this,” he said. “Additional research with larger cohorts and a prospective study design would be warranted, however, before this information would be meaningful in daily clinical decision making,” he emphasized.
The study was supported by the Research Program on Hepatitis of the Japanese Agency for Medical Research and Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farsad disclosed research support from W.L. Gore & Associates, Guerbet LLC, Boston Scientific, and Exelixis; serving as a consultant for NeuWave Medical, Cook Medical, Guerbet LLC, and Eisai, and holding equity in Auxetics Inc.
Patients with cirrhosis and larger spontaneous shunt diameters showed a significantly greater increase in hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) following balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration compared to patients with smaller shunt diameters, based on data from 34 adults.
Portal hypertension remains a key source of complications that greatly impact quality of life in patients with cirrhosis, wrote Akihisa Tatsumi, MD, of the University of Yamanashi, Japan, and colleagues. These patients sometimes develop spontaneous portosystemic shunts (SPSS) to lower portal pressure, but these natural shunts are an incomplete solution – one that may contribute to liver dysfunction by reducing hepatic portal blood flow. However, the association of SPSS with liver functional reserve remains unclear, the researchers said.
Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) is gaining popularity as a treatment for SPSS in patients with cirrhosis but determining the patients who will benefit from this procedure remains a challenge, the researchers wrote. “Apart from BRTO, some recent studies have reported the impact of the SPSS diameter on the future pathological state of the liver,” which prompted the question of whether SPSS diameter plays a role in predicting portal hypertension–related liver function at baseline and after BRTO, the researchers explained.
In their study, published in JGH Open, the researchers identified 34 cirrhotic patients with SPSS who underwent BRTO at a single center in Japan between 2006 and 2018; all of the patients were available for follow-up at least 6 months after the procedure.
The reasons for BRTO were intractable gastric varices in 18 patients and refractory hepatic encephalopathy with shunt in 16 patients; the mean observation period was 1,182 days (3.24 years). The median age of the patients was 66.5 years, and 53% were male. A majority (76%) of the patients had decompensated cirrhosis with Child-Pugh (CP) scores of B or C, and the maximum diameter of SPSS increased significantly with increased in CP scores (P < .001), the researchers noted.
Overall, at 6 months after BRTO, patients showed significant improvements in liver function from baseline. However, the improvement rate was lower in patients whose shunt diameter was 10 mm or less, and improvement was greatest when the shunt diameter was between 10 mm and 20 mm. “Because the CP score is a significant cofounding factor of the SPSS diameter, we next evaluated the changes in liver function classified by CP scores,” the researchers wrote. In this analysis, the post-BRTO changes in liver function in patients with CP scores of A or B still showed an association between improvement in liver function and larger shunt diameter, but this relationship did not extend to patients with CP scores of C, the researchers said.
A larger shunt diameter also was significantly associated with a greater increase in HVPG after balloon occlusion (P = .005).
“Considering that patients with large SPSS diameters might gain higher portal flow following elevation of HVPG after BRTO, it is natural that the larger the SPSS diameter, the greater the improvements in liver function,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “However, such a clear correlation was evident only when the baseline CP scores were within A or B, and not in C, indicating that the improvement of liver function might not parallel HVPG increase in some CP C patients,” they noted.
The study was limited by several factors including the retrospective design from a single center and its small sample size, the researchers noted. Other limitations included selecting and measuring only the largest SPSS of each patient and lack of data on the impact of SPSS diameter on overall survival, they said.
However, the results suggest that SPSS diameter may serve not only as an indicator of portal hypertension involvement at baseline, but also as a useful clinical predictor of liver function after BRTO, they concluded.
Study supports potential benefits of BRTO
“While the association between SPSS and complications of portal hypertension such as variceal bleeding and hepatic encephalopathy have been known, data are lacking in regard to characteristics of SPSS that are most dysfunctional, and whether certain patients may benefit from BRTO to occlude these shunts,” Khashayar Farsad, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview.
“The results are in many ways expected based on anticipated impact of larger versus smaller SPSS in overall liver function,” Dr. Farsad noted. “The study, however, does show a nice correlation between several factors involved in liver function and their changes depending on shunt diameter, correlated with changes in the relative venous pressure gradient across the liver,” he said. “Furthermore, the finding that changes were most evident in those with relatively preserved liver function [Child-Turcotte-Pugh grades A and B] suggests less of a relationship between SPSS and liver function in those with more decompensated liver disease,” he added.
“The impact of the study is significantly limited by its retrospective design, small numbers with potential patient heterogeneity, and lack of a control cohort,” said Dr. Farsad. However, “The major take-home message for clinicians is a potential signal that the size of the SPSS at baseline may predict the impact of the SPSS on liver function, and therefore, the potential benefit of a procedure such as BRTO to positively influence this,” he said. “Additional research with larger cohorts and a prospective study design would be warranted, however, before this information would be meaningful in daily clinical decision making,” he emphasized.
The study was supported by the Research Program on Hepatitis of the Japanese Agency for Medical Research and Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farsad disclosed research support from W.L. Gore & Associates, Guerbet LLC, Boston Scientific, and Exelixis; serving as a consultant for NeuWave Medical, Cook Medical, Guerbet LLC, and Eisai, and holding equity in Auxetics Inc.
FROM JGH OPEN
Weekend catch-up sleep may help fatty liver
People who don’t get enough sleep during the week may be able to reduce their risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by catching up on the weekends, researchers say.
“Our study revealed that people who get enough sleep have a lower risk of developing NAFLD than those who get insufficient sleep,” Sangheun Lee, MD, PhD, from Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Hepatology.
However, they cautioned that further research is needed to verify their finding.
Previous studies have associated insufficient sleep with obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease, as well as liver fibrosis.
A busy weekday schedule can make it harder to get enough sleep, and some people try to compensate by sleeping longer on weekends. Studies so far have produced mixed findings on this strategy, with some showing that more sleep on the weekend reduces the risk for obesity, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome, and others showing no effect on metabolic dysregulation or energy balance.
Accessing a nation’s sleep data
To explore the relationship between sleep patterns and NAFLD, Dr. Lee and colleagues analyzed data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys collected from 2008 to 2019. They excluded people aged less than 20 years, those with hepatitis B or C infections, liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, shift workers and others who “slept irregularly,” and those who consumed alcohol excessively, leaving a cohort of 101,138 participants.
The survey didn’t distinguish between sleep on weekdays and weekends until 2016, so the researchers divided their findings into two: 68,759 people surveyed from 2008 to 2015 (set 1) and 32,379 surveyed from 2016 to 2019 (set 2).
Set 1 was further divided into those who averaged more than 7 hours of sleep per day and those who slept less than that. Set 2 was divided into three groups: one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did not catch up on weekends, one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did catch up on weekends, and one that averaged more than 7 hours of sleep throughout the week.
The researchers used the hepatic steatosis index (HSI) to determine the presence of a fatty liver, calculated as 8 x (ratio of serum ALT to serum AST) + body mass index (+ 2 for female, + 2 in case of diabetes). An HSI of at least36 was considered an indicator of fatty liver.
Less sleep, more risk
Participants in set 1 slept for a mean of 6.8 hours, with 58.6% sleeping more than 7 hours a day. Those in set 2 slept a mean of 6.9 hours during weekdays, with 59.9% sleeping more than 7 hours. They also slept a mean of 7.7 hours on weekends.
In set 1, sleeping at least7 hours was associated with a 16% lower risk for NAFLD (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.89).
In set 2, sleeping at least 7 hours on weekdays was associated with a 19% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.74-0.89). Sleeping at least 7 hours on the weekend was associated with a 22% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.70-0.87). Compared with those who slept less than 7 hours throughout the week, those who slept less than 7 hours on weekdays and more than 7 hours on weekends had a 20% lower rate of NAFLD (OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.70-0.92).
All these associations held true for both men and women.
Why getting your Z’s may have hepatic advantages
One explanation for the link between sleep patterns and NAFLD is that dysregulation of cortisol, inflammatory cytokines, and norepinephrine are associated with both variations in sleep and NAFLD onset, Dr. Lee and colleagues wrote.
They also pointed out that a lack of sleep can reduce the secretion of two hormones that promote satiety: leptin and glucagonlike peptide–1. As a result, people who sleep less may eat more and gain weight, which increases the risk for NAFLD.
Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, a professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota, Vermillion, who was not involved in the study, noted that it was based on comparing a cross section of a population instead of following the participants over time.
“So, I think it’s an association rather than a cause and effect,” he said in an interview.
The authors don’t report a multivariate analysis to determine whether comorbidities or other characteristics of the patients could explain the association, he pointed out, noting that obesity, for example, can increase the risk for both NAFLD and sleep apnea.
Still, Dr. Singal said, the paper will influence him to mention sleep in the context of lifestyle factors that can affect fatty liver disease. “I’m going to tell my patients, and tell the community physicians to tell their patients, to follow a good sleep hygiene and make sure that they sleep at least 5-7 hours.”
Dr. Singal and the study authors all reported no relevant financial relationships. The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who don’t get enough sleep during the week may be able to reduce their risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by catching up on the weekends, researchers say.
“Our study revealed that people who get enough sleep have a lower risk of developing NAFLD than those who get insufficient sleep,” Sangheun Lee, MD, PhD, from Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Hepatology.
However, they cautioned that further research is needed to verify their finding.
Previous studies have associated insufficient sleep with obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease, as well as liver fibrosis.
A busy weekday schedule can make it harder to get enough sleep, and some people try to compensate by sleeping longer on weekends. Studies so far have produced mixed findings on this strategy, with some showing that more sleep on the weekend reduces the risk for obesity, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome, and others showing no effect on metabolic dysregulation or energy balance.
Accessing a nation’s sleep data
To explore the relationship between sleep patterns and NAFLD, Dr. Lee and colleagues analyzed data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys collected from 2008 to 2019. They excluded people aged less than 20 years, those with hepatitis B or C infections, liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, shift workers and others who “slept irregularly,” and those who consumed alcohol excessively, leaving a cohort of 101,138 participants.
The survey didn’t distinguish between sleep on weekdays and weekends until 2016, so the researchers divided their findings into two: 68,759 people surveyed from 2008 to 2015 (set 1) and 32,379 surveyed from 2016 to 2019 (set 2).
Set 1 was further divided into those who averaged more than 7 hours of sleep per day and those who slept less than that. Set 2 was divided into three groups: one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did not catch up on weekends, one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did catch up on weekends, and one that averaged more than 7 hours of sleep throughout the week.
The researchers used the hepatic steatosis index (HSI) to determine the presence of a fatty liver, calculated as 8 x (ratio of serum ALT to serum AST) + body mass index (+ 2 for female, + 2 in case of diabetes). An HSI of at least36 was considered an indicator of fatty liver.
Less sleep, more risk
Participants in set 1 slept for a mean of 6.8 hours, with 58.6% sleeping more than 7 hours a day. Those in set 2 slept a mean of 6.9 hours during weekdays, with 59.9% sleeping more than 7 hours. They also slept a mean of 7.7 hours on weekends.
In set 1, sleeping at least7 hours was associated with a 16% lower risk for NAFLD (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.89).
In set 2, sleeping at least 7 hours on weekdays was associated with a 19% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.74-0.89). Sleeping at least 7 hours on the weekend was associated with a 22% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.70-0.87). Compared with those who slept less than 7 hours throughout the week, those who slept less than 7 hours on weekdays and more than 7 hours on weekends had a 20% lower rate of NAFLD (OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.70-0.92).
All these associations held true for both men and women.
Why getting your Z’s may have hepatic advantages
One explanation for the link between sleep patterns and NAFLD is that dysregulation of cortisol, inflammatory cytokines, and norepinephrine are associated with both variations in sleep and NAFLD onset, Dr. Lee and colleagues wrote.
They also pointed out that a lack of sleep can reduce the secretion of two hormones that promote satiety: leptin and glucagonlike peptide–1. As a result, people who sleep less may eat more and gain weight, which increases the risk for NAFLD.
Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, a professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota, Vermillion, who was not involved in the study, noted that it was based on comparing a cross section of a population instead of following the participants over time.
“So, I think it’s an association rather than a cause and effect,” he said in an interview.
The authors don’t report a multivariate analysis to determine whether comorbidities or other characteristics of the patients could explain the association, he pointed out, noting that obesity, for example, can increase the risk for both NAFLD and sleep apnea.
Still, Dr. Singal said, the paper will influence him to mention sleep in the context of lifestyle factors that can affect fatty liver disease. “I’m going to tell my patients, and tell the community physicians to tell their patients, to follow a good sleep hygiene and make sure that they sleep at least 5-7 hours.”
Dr. Singal and the study authors all reported no relevant financial relationships. The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who don’t get enough sleep during the week may be able to reduce their risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by catching up on the weekends, researchers say.
“Our study revealed that people who get enough sleep have a lower risk of developing NAFLD than those who get insufficient sleep,” Sangheun Lee, MD, PhD, from Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Hepatology.
However, they cautioned that further research is needed to verify their finding.
Previous studies have associated insufficient sleep with obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease, as well as liver fibrosis.
A busy weekday schedule can make it harder to get enough sleep, and some people try to compensate by sleeping longer on weekends. Studies so far have produced mixed findings on this strategy, with some showing that more sleep on the weekend reduces the risk for obesity, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome, and others showing no effect on metabolic dysregulation or energy balance.
Accessing a nation’s sleep data
To explore the relationship between sleep patterns and NAFLD, Dr. Lee and colleagues analyzed data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys collected from 2008 to 2019. They excluded people aged less than 20 years, those with hepatitis B or C infections, liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, shift workers and others who “slept irregularly,” and those who consumed alcohol excessively, leaving a cohort of 101,138 participants.
The survey didn’t distinguish between sleep on weekdays and weekends until 2016, so the researchers divided their findings into two: 68,759 people surveyed from 2008 to 2015 (set 1) and 32,379 surveyed from 2016 to 2019 (set 2).
Set 1 was further divided into those who averaged more than 7 hours of sleep per day and those who slept less than that. Set 2 was divided into three groups: one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did not catch up on weekends, one that averaged less than 7 hours of sleep per day and did catch up on weekends, and one that averaged more than 7 hours of sleep throughout the week.
The researchers used the hepatic steatosis index (HSI) to determine the presence of a fatty liver, calculated as 8 x (ratio of serum ALT to serum AST) + body mass index (+ 2 for female, + 2 in case of diabetes). An HSI of at least36 was considered an indicator of fatty liver.
Less sleep, more risk
Participants in set 1 slept for a mean of 6.8 hours, with 58.6% sleeping more than 7 hours a day. Those in set 2 slept a mean of 6.9 hours during weekdays, with 59.9% sleeping more than 7 hours. They also slept a mean of 7.7 hours on weekends.
In set 1, sleeping at least7 hours was associated with a 16% lower risk for NAFLD (odds ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval, 0.79-0.89).
In set 2, sleeping at least 7 hours on weekdays was associated with a 19% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.74-0.89). Sleeping at least 7 hours on the weekend was associated with a 22% reduced risk for NAFLD (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.70-0.87). Compared with those who slept less than 7 hours throughout the week, those who slept less than 7 hours on weekdays and more than 7 hours on weekends had a 20% lower rate of NAFLD (OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.70-0.92).
All these associations held true for both men and women.
Why getting your Z’s may have hepatic advantages
One explanation for the link between sleep patterns and NAFLD is that dysregulation of cortisol, inflammatory cytokines, and norepinephrine are associated with both variations in sleep and NAFLD onset, Dr. Lee and colleagues wrote.
They also pointed out that a lack of sleep can reduce the secretion of two hormones that promote satiety: leptin and glucagonlike peptide–1. As a result, people who sleep less may eat more and gain weight, which increases the risk for NAFLD.
Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, a professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota, Vermillion, who was not involved in the study, noted that it was based on comparing a cross section of a population instead of following the participants over time.
“So, I think it’s an association rather than a cause and effect,” he said in an interview.
The authors don’t report a multivariate analysis to determine whether comorbidities or other characteristics of the patients could explain the association, he pointed out, noting that obesity, for example, can increase the risk for both NAFLD and sleep apnea.
Still, Dr. Singal said, the paper will influence him to mention sleep in the context of lifestyle factors that can affect fatty liver disease. “I’m going to tell my patients, and tell the community physicians to tell their patients, to follow a good sleep hygiene and make sure that they sleep at least 5-7 hours.”
Dr. Singal and the study authors all reported no relevant financial relationships. The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF HEPATOLOGY
Freiburg index accurately predicts survival in liver procedure
A new prognostic score is more accurate than the commonly used Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) in predicting post–transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) survival, researchers say.
The Freiburg Index of Post-TIPS Survival (FIPS) could help patients and doctors weigh the benefits and risks of the procedure, said Chongtu Yang, MD, a postgraduate fellow at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
“For patients defined as high risk, the TIPS procedure may not be the optimal choice, and transplantation may be better,” Dr. Yang told this news organization. He cautioned that FIPS needs further validation before being applied in clinical practice.
The study by Dr. Yang and his colleagues was published online Feb. 9 in the American Journal of Roentgenology. To their knowledge, this is the first study to validate FIPS in a cohort of Asian patients.
Decompensated cirrhosis can cause variceal bleeding and refractory ascites and may be life threatening. TIPS can manage these complications but comes with its own risks.
To determine which patients can best benefit from the procedure, researchers have proposed a variety of prognostic scoring systems. Some were developed for other purposes, such as predicting survival following hospitalization, rather than specifically for TIPS. Additionally, few studies have compared these approaches to each other.
A four-way comparison
To fill that gap, Dr. Yang and his colleagues compared four predictive models: the MELD, the sodium MELD (MELD-Na), the Chronic Liver Failure–Consortium Acute Decompensation (CLIF-CAD), and FIPS.
The MELD score uses serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time. MELD-Na adds sodium to this algorithm. The CLIF-CAD score is calculated using age, serum creatinine, INR, white blood count, and sodium level. FIPS, which was recently devised to predict results with TIPS, uses age, bilirubin, albumin, and creatinine.
To see which yielded more accurate predictions, Dr. Yang and his colleagues followed 383 patients with cirrhosis (mean age, 55 years; 341 with variceal bleeding and 42 with refractory ascites) who underwent TIPS placement at Wuhan Union Hospital between January 2016 and August 2021.
The most common cause of cirrhosis was hepatitis B infection (58.2% of patients), followed by hepatitis C infection (11.7%) and alcohol use (13.6%).
The researchers followed the patients for a median of 23.4 months. They lost track of 31 patients over that time, and another 72 died. The survival rate after TIPS placement was 92.3% at 6 months, 87.8% at 12 months, and 81.2% at 24 months. Thirty-seven patients received a TIPS revision.
In their first measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used a concordance index, which compares actual results with predicted results. The number of concordant pairs are divided by the total number of possible evaluation pairs. A score of 1 represents 100% accuracy.
By this measure, the prediction of survival at 6 months was highest for FIPS followed by CLIF-CAD, MELD, and MELD-Na. However, the confidence intervals overlapped.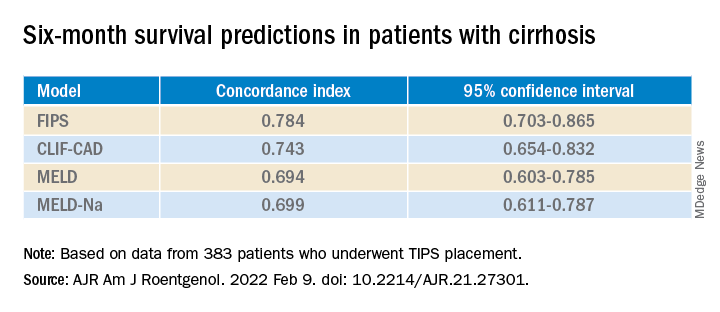
FIPS also scored highest in the concordance index at 12 and 24 months.
In a second measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used Brier scores, which calculate the mean squared error between predicted probabilities and actual values. Like the concordance index, Brier scores range from 0.0 to 1.0 but differ in that the lowest Brier score number represents the highest accuracy.
At 6 months, the CLIF-CAD score was the best, at 0.074. MELD and FIPS were equivalent at 0.075, with MELD-Na coming in at 0.077. However, FIPS attained slightly better scores than the other systems at 12 and 24 months.
Is FIPS worth implementing?
With scores this close, it may not be worth changing the predictive model clinicians use for choosing TIPS candidates, said Nancy Reau, MD, chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, who was not involved in the study.
MELD scores are already programmed into many electronic medical record systems in the United States, and clinicians are familiar with using that system to aid in further decisions, such as decisions regarding other kinds of surgery, she told this news organization.
“If you’re going to try to advocate for a new system, you really have to show that the performance of the predictive score is monumentally better than the tried and true,” she said.
Dr. Yang and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new prognostic score is more accurate than the commonly used Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) in predicting post–transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) survival, researchers say.
The Freiburg Index of Post-TIPS Survival (FIPS) could help patients and doctors weigh the benefits and risks of the procedure, said Chongtu Yang, MD, a postgraduate fellow at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
“For patients defined as high risk, the TIPS procedure may not be the optimal choice, and transplantation may be better,” Dr. Yang told this news organization. He cautioned that FIPS needs further validation before being applied in clinical practice.
The study by Dr. Yang and his colleagues was published online Feb. 9 in the American Journal of Roentgenology. To their knowledge, this is the first study to validate FIPS in a cohort of Asian patients.
Decompensated cirrhosis can cause variceal bleeding and refractory ascites and may be life threatening. TIPS can manage these complications but comes with its own risks.
To determine which patients can best benefit from the procedure, researchers have proposed a variety of prognostic scoring systems. Some were developed for other purposes, such as predicting survival following hospitalization, rather than specifically for TIPS. Additionally, few studies have compared these approaches to each other.
A four-way comparison
To fill that gap, Dr. Yang and his colleagues compared four predictive models: the MELD, the sodium MELD (MELD-Na), the Chronic Liver Failure–Consortium Acute Decompensation (CLIF-CAD), and FIPS.
The MELD score uses serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time. MELD-Na adds sodium to this algorithm. The CLIF-CAD score is calculated using age, serum creatinine, INR, white blood count, and sodium level. FIPS, which was recently devised to predict results with TIPS, uses age, bilirubin, albumin, and creatinine.
To see which yielded more accurate predictions, Dr. Yang and his colleagues followed 383 patients with cirrhosis (mean age, 55 years; 341 with variceal bleeding and 42 with refractory ascites) who underwent TIPS placement at Wuhan Union Hospital between January 2016 and August 2021.
The most common cause of cirrhosis was hepatitis B infection (58.2% of patients), followed by hepatitis C infection (11.7%) and alcohol use (13.6%).
The researchers followed the patients for a median of 23.4 months. They lost track of 31 patients over that time, and another 72 died. The survival rate after TIPS placement was 92.3% at 6 months, 87.8% at 12 months, and 81.2% at 24 months. Thirty-seven patients received a TIPS revision.
In their first measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used a concordance index, which compares actual results with predicted results. The number of concordant pairs are divided by the total number of possible evaluation pairs. A score of 1 represents 100% accuracy.
By this measure, the prediction of survival at 6 months was highest for FIPS followed by CLIF-CAD, MELD, and MELD-Na. However, the confidence intervals overlapped.
FIPS also scored highest in the concordance index at 12 and 24 months.
In a second measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used Brier scores, which calculate the mean squared error between predicted probabilities and actual values. Like the concordance index, Brier scores range from 0.0 to 1.0 but differ in that the lowest Brier score number represents the highest accuracy.
At 6 months, the CLIF-CAD score was the best, at 0.074. MELD and FIPS were equivalent at 0.075, with MELD-Na coming in at 0.077. However, FIPS attained slightly better scores than the other systems at 12 and 24 months.
Is FIPS worth implementing?
With scores this close, it may not be worth changing the predictive model clinicians use for choosing TIPS candidates, said Nancy Reau, MD, chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, who was not involved in the study.
MELD scores are already programmed into many electronic medical record systems in the United States, and clinicians are familiar with using that system to aid in further decisions, such as decisions regarding other kinds of surgery, she told this news organization.
“If you’re going to try to advocate for a new system, you really have to show that the performance of the predictive score is monumentally better than the tried and true,” she said.
Dr. Yang and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new prognostic score is more accurate than the commonly used Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) in predicting post–transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) survival, researchers say.
The Freiburg Index of Post-TIPS Survival (FIPS) could help patients and doctors weigh the benefits and risks of the procedure, said Chongtu Yang, MD, a postgraduate fellow at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
“For patients defined as high risk, the TIPS procedure may not be the optimal choice, and transplantation may be better,” Dr. Yang told this news organization. He cautioned that FIPS needs further validation before being applied in clinical practice.
The study by Dr. Yang and his colleagues was published online Feb. 9 in the American Journal of Roentgenology. To their knowledge, this is the first study to validate FIPS in a cohort of Asian patients.
Decompensated cirrhosis can cause variceal bleeding and refractory ascites and may be life threatening. TIPS can manage these complications but comes with its own risks.
To determine which patients can best benefit from the procedure, researchers have proposed a variety of prognostic scoring systems. Some were developed for other purposes, such as predicting survival following hospitalization, rather than specifically for TIPS. Additionally, few studies have compared these approaches to each other.
A four-way comparison
To fill that gap, Dr. Yang and his colleagues compared four predictive models: the MELD, the sodium MELD (MELD-Na), the Chronic Liver Failure–Consortium Acute Decompensation (CLIF-CAD), and FIPS.
The MELD score uses serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the international normalized ratio (INR) of prothrombin time. MELD-Na adds sodium to this algorithm. The CLIF-CAD score is calculated using age, serum creatinine, INR, white blood count, and sodium level. FIPS, which was recently devised to predict results with TIPS, uses age, bilirubin, albumin, and creatinine.
To see which yielded more accurate predictions, Dr. Yang and his colleagues followed 383 patients with cirrhosis (mean age, 55 years; 341 with variceal bleeding and 42 with refractory ascites) who underwent TIPS placement at Wuhan Union Hospital between January 2016 and August 2021.
The most common cause of cirrhosis was hepatitis B infection (58.2% of patients), followed by hepatitis C infection (11.7%) and alcohol use (13.6%).
The researchers followed the patients for a median of 23.4 months. They lost track of 31 patients over that time, and another 72 died. The survival rate after TIPS placement was 92.3% at 6 months, 87.8% at 12 months, and 81.2% at 24 months. Thirty-seven patients received a TIPS revision.
In their first measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used a concordance index, which compares actual results with predicted results. The number of concordant pairs are divided by the total number of possible evaluation pairs. A score of 1 represents 100% accuracy.
By this measure, the prediction of survival at 6 months was highest for FIPS followed by CLIF-CAD, MELD, and MELD-Na. However, the confidence intervals overlapped.
FIPS also scored highest in the concordance index at 12 and 24 months.
In a second measure of the models’ accuracy, the researchers used Brier scores, which calculate the mean squared error between predicted probabilities and actual values. Like the concordance index, Brier scores range from 0.0 to 1.0 but differ in that the lowest Brier score number represents the highest accuracy.
At 6 months, the CLIF-CAD score was the best, at 0.074. MELD and FIPS were equivalent at 0.075, with MELD-Na coming in at 0.077. However, FIPS attained slightly better scores than the other systems at 12 and 24 months.
Is FIPS worth implementing?
With scores this close, it may not be worth changing the predictive model clinicians use for choosing TIPS candidates, said Nancy Reau, MD, chief of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, who was not involved in the study.
MELD scores are already programmed into many electronic medical record systems in the United States, and clinicians are familiar with using that system to aid in further decisions, such as decisions regarding other kinds of surgery, she told this news organization.
“If you’re going to try to advocate for a new system, you really have to show that the performance of the predictive score is monumentally better than the tried and true,” she said.
Dr. Yang and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF ROENTGENOLOGY
Novel scoring system emerges for alcoholic hepatitis mortality
A new scoring system proved more accurate than several other available models at predicting the 30-day mortality risk for patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH), according to new data.
The system, called the Mortality Index for Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis (MIAAH), was created by a team of Mayo Clinic researchers, who published their results in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the currently available prognostic models for assessing AH severity are the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD); the Age, serum Bilirubin, International normalized ratio, and serum Creatinine (ABIC) score; the Maddrey Discriminant Function (MDF); and the Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score (GAHS). However, these models have poor accuracy, with the area under the curve between 0.71 and 0.77.
By comparison, the new model has an accuracy of 86% in predicting 30-day mortality for AH, said coauthor Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota Sanford School of Medicine, Sioux Falls.
“It’s a better predictor of the outcome, and that’s what sets it apart,” he told this news organization. “I think providers and patients will benefit.”
He said accuracy in determining the likelihood of death can help clinicians better determine treatment options and prepare patients and their families.
Camille Kezer, MD, a Mayo Clinic resident internist and first author of the paper, said in a statement, “MIAAH also has the advantage of performing well in patients, regardless of whether they’ve been treated with steroids, which makes it generalizable.”
Creating and validating the MIAAH
Researchers analyzed the health records of 266 eligible patients diagnosed with AH between 1998 and 2018 at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The patients collectively had a 30-day mortality rate of 19.2%.
They then studied the effect of several variables, of which the following were found to be significantly associated with mortality: age (P = .002), blood urea nitrogen (P = .003), albumin (P = .01), bilirubin (P = .02), and international normalized ratio (P = .001).
Mayo researchers built the MIAAH model using these variables and found that it was able to achieve a C statistic of 0.86, which translates into its being able to accurately predict mortality more than 86% of the time. When tested in the initial cohort of 266 patients, MIAAH had a significantly superior C statistic compared with several other available models, such as the MELD, MDF, and GAHS, although not for the ABIC.
The researchers then tested the MIAAH model in a validation cohort of 249 patients from health care centers at the University of South Dakota, Sioux Falls, and the University of Kansas, Lawrence. In this cohort, the MIAAH’s C statistic decreased to 0.73, which remained significantly more accurate than the MDF but was comparable to that found with the MELD.
Helping with transplant decisions
There are no pharmacologic treatments that can reduce 90-day mortality in severe cases of AH, and only a small survival benefit at 30 days has been reported with prednisolone use.
With a shortage of liver donors, many centers still require 6 months of alcohol abstinence for transplant consideration, although exceptions are sometimes made for cases of early transplant.
A model that more accurately predicts who is at the highest risk of dying within a month can help clinicians decide how best to proceed, Dr. Singal said.
Paul Martin, MD, chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in gastroenterology, and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, told this news organization that the model is potentially important in light of the rising prevalence of AH.
“The numbers of patients with AH are unequivocally increasing and often in young patients,” he noted, presenting difficult choices of who to treat with steroids and who to refer for a transplant.
“This model is certainly timely,” he said. “We need more accuracy in predicting which patients will recover with medical therapy and which patients won’t in the absence of a liver transplant.”
He noted, however, that the study’s retrospective design requires that it’s validated prospectively: “not only looking at the outcome in terms of mortality of patients, but its potential utility in identifying candidates for liver transplantation who are not going to recover on their own.”
He said it was unlikely that the model would replace others, particularly MELD, which is ingrained in practices in the United States and other countries, but may instead have a complementary role.
Dr. Singal, Dr. Kezer, and Dr. Martin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scoring system proved more accurate than several other available models at predicting the 30-day mortality risk for patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH), according to new data.
The system, called the Mortality Index for Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis (MIAAH), was created by a team of Mayo Clinic researchers, who published their results in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the currently available prognostic models for assessing AH severity are the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD); the Age, serum Bilirubin, International normalized ratio, and serum Creatinine (ABIC) score; the Maddrey Discriminant Function (MDF); and the Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score (GAHS). However, these models have poor accuracy, with the area under the curve between 0.71 and 0.77.
By comparison, the new model has an accuracy of 86% in predicting 30-day mortality for AH, said coauthor Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota Sanford School of Medicine, Sioux Falls.
“It’s a better predictor of the outcome, and that’s what sets it apart,” he told this news organization. “I think providers and patients will benefit.”
He said accuracy in determining the likelihood of death can help clinicians better determine treatment options and prepare patients and their families.
Camille Kezer, MD, a Mayo Clinic resident internist and first author of the paper, said in a statement, “MIAAH also has the advantage of performing well in patients, regardless of whether they’ve been treated with steroids, which makes it generalizable.”
Creating and validating the MIAAH
Researchers analyzed the health records of 266 eligible patients diagnosed with AH between 1998 and 2018 at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The patients collectively had a 30-day mortality rate of 19.2%.
They then studied the effect of several variables, of which the following were found to be significantly associated with mortality: age (P = .002), blood urea nitrogen (P = .003), albumin (P = .01), bilirubin (P = .02), and international normalized ratio (P = .001).
Mayo researchers built the MIAAH model using these variables and found that it was able to achieve a C statistic of 0.86, which translates into its being able to accurately predict mortality more than 86% of the time. When tested in the initial cohort of 266 patients, MIAAH had a significantly superior C statistic compared with several other available models, such as the MELD, MDF, and GAHS, although not for the ABIC.
The researchers then tested the MIAAH model in a validation cohort of 249 patients from health care centers at the University of South Dakota, Sioux Falls, and the University of Kansas, Lawrence. In this cohort, the MIAAH’s C statistic decreased to 0.73, which remained significantly more accurate than the MDF but was comparable to that found with the MELD.
Helping with transplant decisions
There are no pharmacologic treatments that can reduce 90-day mortality in severe cases of AH, and only a small survival benefit at 30 days has been reported with prednisolone use.
With a shortage of liver donors, many centers still require 6 months of alcohol abstinence for transplant consideration, although exceptions are sometimes made for cases of early transplant.
A model that more accurately predicts who is at the highest risk of dying within a month can help clinicians decide how best to proceed, Dr. Singal said.
Paul Martin, MD, chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in gastroenterology, and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, told this news organization that the model is potentially important in light of the rising prevalence of AH.
“The numbers of patients with AH are unequivocally increasing and often in young patients,” he noted, presenting difficult choices of who to treat with steroids and who to refer for a transplant.
“This model is certainly timely,” he said. “We need more accuracy in predicting which patients will recover with medical therapy and which patients won’t in the absence of a liver transplant.”
He noted, however, that the study’s retrospective design requires that it’s validated prospectively: “not only looking at the outcome in terms of mortality of patients, but its potential utility in identifying candidates for liver transplantation who are not going to recover on their own.”
He said it was unlikely that the model would replace others, particularly MELD, which is ingrained in practices in the United States and other countries, but may instead have a complementary role.
Dr. Singal, Dr. Kezer, and Dr. Martin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scoring system proved more accurate than several other available models at predicting the 30-day mortality risk for patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH), according to new data.
The system, called the Mortality Index for Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis (MIAAH), was created by a team of Mayo Clinic researchers, who published their results in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the currently available prognostic models for assessing AH severity are the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD); the Age, serum Bilirubin, International normalized ratio, and serum Creatinine (ABIC) score; the Maddrey Discriminant Function (MDF); and the Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score (GAHS). However, these models have poor accuracy, with the area under the curve between 0.71 and 0.77.
By comparison, the new model has an accuracy of 86% in predicting 30-day mortality for AH, said coauthor Ashwani K. Singal, MD, MS, professor of medicine at the University of South Dakota Sanford School of Medicine, Sioux Falls.
“It’s a better predictor of the outcome, and that’s what sets it apart,” he told this news organization. “I think providers and patients will benefit.”
He said accuracy in determining the likelihood of death can help clinicians better determine treatment options and prepare patients and their families.
Camille Kezer, MD, a Mayo Clinic resident internist and first author of the paper, said in a statement, “MIAAH also has the advantage of performing well in patients, regardless of whether they’ve been treated with steroids, which makes it generalizable.”
Creating and validating the MIAAH
Researchers analyzed the health records of 266 eligible patients diagnosed with AH between 1998 and 2018 at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. The patients collectively had a 30-day mortality rate of 19.2%.
They then studied the effect of several variables, of which the following were found to be significantly associated with mortality: age (P = .002), blood urea nitrogen (P = .003), albumin (P = .01), bilirubin (P = .02), and international normalized ratio (P = .001).
Mayo researchers built the MIAAH model using these variables and found that it was able to achieve a C statistic of 0.86, which translates into its being able to accurately predict mortality more than 86% of the time. When tested in the initial cohort of 266 patients, MIAAH had a significantly superior C statistic compared with several other available models, such as the MELD, MDF, and GAHS, although not for the ABIC.
The researchers then tested the MIAAH model in a validation cohort of 249 patients from health care centers at the University of South Dakota, Sioux Falls, and the University of Kansas, Lawrence. In this cohort, the MIAAH’s C statistic decreased to 0.73, which remained significantly more accurate than the MDF but was comparable to that found with the MELD.
Helping with transplant decisions
There are no pharmacologic treatments that can reduce 90-day mortality in severe cases of AH, and only a small survival benefit at 30 days has been reported with prednisolone use.
With a shortage of liver donors, many centers still require 6 months of alcohol abstinence for transplant consideration, although exceptions are sometimes made for cases of early transplant.
A model that more accurately predicts who is at the highest risk of dying within a month can help clinicians decide how best to proceed, Dr. Singal said.
Paul Martin, MD, chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in gastroenterology, and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, told this news organization that the model is potentially important in light of the rising prevalence of AH.
“The numbers of patients with AH are unequivocally increasing and often in young patients,” he noted, presenting difficult choices of who to treat with steroids and who to refer for a transplant.
“This model is certainly timely,” he said. “We need more accuracy in predicting which patients will recover with medical therapy and which patients won’t in the absence of a liver transplant.”
He noted, however, that the study’s retrospective design requires that it’s validated prospectively: “not only looking at the outcome in terms of mortality of patients, but its potential utility in identifying candidates for liver transplantation who are not going to recover on their own.”
He said it was unlikely that the model would replace others, particularly MELD, which is ingrained in practices in the United States and other countries, but may instead have a complementary role.
Dr. Singal, Dr. Kezer, and Dr. Martin report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS
Universal hepatitis B screening, vaccination deemed cost effective for pregnant women
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
RECAM vs. RUCAM: Finding a better way to diagnose DILI
Researchers looking for a better way to diagnose drug-induced liver injury (DILI) have found evidence to support the use of the Revised Electronic Causality Assessment Method (RECAM).
The broadly used Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM), introduced in 1993, “has been a valuable clinical framework for DILI diagnosis,” but it has been clouded by subjectivity and poor reliability, wrote the authors, led by Paul H. Hayashi, MD, MPH, with the Food and Drug Administration, in Hepatology. Citing a review from the Journal of Hepatology, Dr. Hayashi and colleagues noted three major problems: “(1) unclear operating instructions and subjectivity leading to poor reliability and usability, (2) unclear validity due to lack of an accepted gold standard and (3) domain criteria that are not evidence-based.”
Currently, a diagnosis of DILI is primarily based on clinicians’ judgment and ruling out alternative diagnoses, the authors of this study wrote. The lack of an evidence-based and reliable diagnostic tool is a significant obstacle in clinical care and research .
Reaching a new method
The researchers used classification tree analysis to set diagnostic cut-offs for RECAM and then compared RECAM with RUCAM for correlation with expert opinion diagnostic categories in 194 DILI cases (98 from the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network, 96 from the Spanish DILI Registry).
The area under receiver operator curves for identifying at least probable DILI were the same at 0.89 for both RECAM and RUCAM.
The authors wrote, “However, RECAM diagnostic categories have better observed overall agreement with expert opinion (0.62 vs. 0.56 weighted kappa, P = .14), and had better sensitivity to detect extreme diagnostic categories (73 vs. 54 for highly likely or high probable, P = .02; 65 vs. 48 for unlikely/excluded, P = .08) than RUCAM diagnostic categories.”
They concluded that RECAM “is at least as capable as RUCAM in diagnosing DILI compared to expert opinion but is better than RUCAM at the diagnostic extremes.”
RECAM appears to add objectivity and clarity that can improve precision and reliability when diagnosing DILI and improve diagnostic standardization, according to authors. It has automated scoring, which reduces subjective input and should lead to better reliability among raters, something that has limited RUCAM’s adaptation in clinical practice and research.
RECAM has automatic warnings for data inconsistencies, which DILI and RUCAM do not. In RUCAM, a different diagnosis or other data could rule out DILI, but the case would still gain points in other criteria.
The authors explained, “Even when data clearly diagnose acute viral hepatitis or autoimmune hepatitis by simplified autoimmune hepatitis score, points are still given for latency, dechallenge, or underlying hepatotoxicity risk of the drug. In these situations of highly implausible DILI, RECAM gives warnings to stop with an imputed total score of –6. One can over-ride these warnings, if one believes DILI may be concurrent with the non-DILI diagnosis. However, –6 points are still assessed.”
Diagnosis of exclusion
Paul Martin, MD, chief, division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in Gastroenterology and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, said in an interview that he hopes RECAM will become widely used and better address a condition that sometimes doesn’t get enough attention. DILI remains underappreciated, he said, despite it being a major cause of morbidity and mortality in some patients.
“Any algorithm or criteria that can improve diagnostic accuracy is useful because typically it is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Dr. Martin said. “This new system seems to be as good as any other prior algorithms to diagnose drug-induced liver injury.”
He added, “This should help clinicians with individual patients with unexplained liver disease.”
The authors noted some limitations. RECAM was developed in U.S. and Spanish cohorts, so its performance in other regions is unclear. Both registries have minimum enrollment requirements for liver enzyme and bilirubin elevation, so it is not known how effective RECAM is in less severe cases. It also needs to be tested by other clinicians, including nonhepatologists.
The authors also added, “It is currently limited to single-agent medication cases leaving the user to score each medication individually in multidrug cases. However, any competing medication causing loss of points in the RUCAM, probably deserves its own RECAM score.”
The DILIN is structured as a cooperative agreement with funds provided by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Dr. Hayashi is employed by the FDA, but the conclusions of this paper do not reflect any opinion of the FDA. One coauthor has advised Pfizer, GSK, and NuCANA through Nottingham University Consultants, and another has received support from Gilead and AbbVie and consulted for Sanofi. The remaining authors have no conflicts. Dr. Martin reports no relevant financial relationships.
Researchers looking for a better way to diagnose drug-induced liver injury (DILI) have found evidence to support the use of the Revised Electronic Causality Assessment Method (RECAM).
The broadly used Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM), introduced in 1993, “has been a valuable clinical framework for DILI diagnosis,” but it has been clouded by subjectivity and poor reliability, wrote the authors, led by Paul H. Hayashi, MD, MPH, with the Food and Drug Administration, in Hepatology. Citing a review from the Journal of Hepatology, Dr. Hayashi and colleagues noted three major problems: “(1) unclear operating instructions and subjectivity leading to poor reliability and usability, (2) unclear validity due to lack of an accepted gold standard and (3) domain criteria that are not evidence-based.”
Currently, a diagnosis of DILI is primarily based on clinicians’ judgment and ruling out alternative diagnoses, the authors of this study wrote. The lack of an evidence-based and reliable diagnostic tool is a significant obstacle in clinical care and research .
Reaching a new method
The researchers used classification tree analysis to set diagnostic cut-offs for RECAM and then compared RECAM with RUCAM for correlation with expert opinion diagnostic categories in 194 DILI cases (98 from the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network, 96 from the Spanish DILI Registry).
The area under receiver operator curves for identifying at least probable DILI were the same at 0.89 for both RECAM and RUCAM.
The authors wrote, “However, RECAM diagnostic categories have better observed overall agreement with expert opinion (0.62 vs. 0.56 weighted kappa, P = .14), and had better sensitivity to detect extreme diagnostic categories (73 vs. 54 for highly likely or high probable, P = .02; 65 vs. 48 for unlikely/excluded, P = .08) than RUCAM diagnostic categories.”
They concluded that RECAM “is at least as capable as RUCAM in diagnosing DILI compared to expert opinion but is better than RUCAM at the diagnostic extremes.”
RECAM appears to add objectivity and clarity that can improve precision and reliability when diagnosing DILI and improve diagnostic standardization, according to authors. It has automated scoring, which reduces subjective input and should lead to better reliability among raters, something that has limited RUCAM’s adaptation in clinical practice and research.
RECAM has automatic warnings for data inconsistencies, which DILI and RUCAM do not. In RUCAM, a different diagnosis or other data could rule out DILI, but the case would still gain points in other criteria.
The authors explained, “Even when data clearly diagnose acute viral hepatitis or autoimmune hepatitis by simplified autoimmune hepatitis score, points are still given for latency, dechallenge, or underlying hepatotoxicity risk of the drug. In these situations of highly implausible DILI, RECAM gives warnings to stop with an imputed total score of –6. One can over-ride these warnings, if one believes DILI may be concurrent with the non-DILI diagnosis. However, –6 points are still assessed.”
Diagnosis of exclusion
Paul Martin, MD, chief, division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in Gastroenterology and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, said in an interview that he hopes RECAM will become widely used and better address a condition that sometimes doesn’t get enough attention. DILI remains underappreciated, he said, despite it being a major cause of morbidity and mortality in some patients.
“Any algorithm or criteria that can improve diagnostic accuracy is useful because typically it is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Dr. Martin said. “This new system seems to be as good as any other prior algorithms to diagnose drug-induced liver injury.”
He added, “This should help clinicians with individual patients with unexplained liver disease.”
The authors noted some limitations. RECAM was developed in U.S. and Spanish cohorts, so its performance in other regions is unclear. Both registries have minimum enrollment requirements for liver enzyme and bilirubin elevation, so it is not known how effective RECAM is in less severe cases. It also needs to be tested by other clinicians, including nonhepatologists.
The authors also added, “It is currently limited to single-agent medication cases leaving the user to score each medication individually in multidrug cases. However, any competing medication causing loss of points in the RUCAM, probably deserves its own RECAM score.”
The DILIN is structured as a cooperative agreement with funds provided by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Dr. Hayashi is employed by the FDA, but the conclusions of this paper do not reflect any opinion of the FDA. One coauthor has advised Pfizer, GSK, and NuCANA through Nottingham University Consultants, and another has received support from Gilead and AbbVie and consulted for Sanofi. The remaining authors have no conflicts. Dr. Martin reports no relevant financial relationships.
Researchers looking for a better way to diagnose drug-induced liver injury (DILI) have found evidence to support the use of the Revised Electronic Causality Assessment Method (RECAM).
The broadly used Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM), introduced in 1993, “has been a valuable clinical framework for DILI diagnosis,” but it has been clouded by subjectivity and poor reliability, wrote the authors, led by Paul H. Hayashi, MD, MPH, with the Food and Drug Administration, in Hepatology. Citing a review from the Journal of Hepatology, Dr. Hayashi and colleagues noted three major problems: “(1) unclear operating instructions and subjectivity leading to poor reliability and usability, (2) unclear validity due to lack of an accepted gold standard and (3) domain criteria that are not evidence-based.”
Currently, a diagnosis of DILI is primarily based on clinicians’ judgment and ruling out alternative diagnoses, the authors of this study wrote. The lack of an evidence-based and reliable diagnostic tool is a significant obstacle in clinical care and research .
Reaching a new method
The researchers used classification tree analysis to set diagnostic cut-offs for RECAM and then compared RECAM with RUCAM for correlation with expert opinion diagnostic categories in 194 DILI cases (98 from the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network, 96 from the Spanish DILI Registry).
The area under receiver operator curves for identifying at least probable DILI were the same at 0.89 for both RECAM and RUCAM.
The authors wrote, “However, RECAM diagnostic categories have better observed overall agreement with expert opinion (0.62 vs. 0.56 weighted kappa, P = .14), and had better sensitivity to detect extreme diagnostic categories (73 vs. 54 for highly likely or high probable, P = .02; 65 vs. 48 for unlikely/excluded, P = .08) than RUCAM diagnostic categories.”
They concluded that RECAM “is at least as capable as RUCAM in diagnosing DILI compared to expert opinion but is better than RUCAM at the diagnostic extremes.”
RECAM appears to add objectivity and clarity that can improve precision and reliability when diagnosing DILI and improve diagnostic standardization, according to authors. It has automated scoring, which reduces subjective input and should lead to better reliability among raters, something that has limited RUCAM’s adaptation in clinical practice and research.
RECAM has automatic warnings for data inconsistencies, which DILI and RUCAM do not. In RUCAM, a different diagnosis or other data could rule out DILI, but the case would still gain points in other criteria.
The authors explained, “Even when data clearly diagnose acute viral hepatitis or autoimmune hepatitis by simplified autoimmune hepatitis score, points are still given for latency, dechallenge, or underlying hepatotoxicity risk of the drug. In these situations of highly implausible DILI, RECAM gives warnings to stop with an imputed total score of –6. One can over-ride these warnings, if one believes DILI may be concurrent with the non-DILI diagnosis. However, –6 points are still assessed.”
Diagnosis of exclusion
Paul Martin, MD, chief, division of digestive health and liver diseases, Mandel Chair in Gastroenterology and professor of medicine at the University of Miami, said in an interview that he hopes RECAM will become widely used and better address a condition that sometimes doesn’t get enough attention. DILI remains underappreciated, he said, despite it being a major cause of morbidity and mortality in some patients.
“Any algorithm or criteria that can improve diagnostic accuracy is useful because typically it is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Dr. Martin said. “This new system seems to be as good as any other prior algorithms to diagnose drug-induced liver injury.”
He added, “This should help clinicians with individual patients with unexplained liver disease.”
The authors noted some limitations. RECAM was developed in U.S. and Spanish cohorts, so its performance in other regions is unclear. Both registries have minimum enrollment requirements for liver enzyme and bilirubin elevation, so it is not known how effective RECAM is in less severe cases. It also needs to be tested by other clinicians, including nonhepatologists.
The authors also added, “It is currently limited to single-agent medication cases leaving the user to score each medication individually in multidrug cases. However, any competing medication causing loss of points in the RUCAM, probably deserves its own RECAM score.”
The DILIN is structured as a cooperative agreement with funds provided by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Dr. Hayashi is employed by the FDA, but the conclusions of this paper do not reflect any opinion of the FDA. One coauthor has advised Pfizer, GSK, and NuCANA through Nottingham University Consultants, and another has received support from Gilead and AbbVie and consulted for Sanofi. The remaining authors have no conflicts. Dr. Martin reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM HEPATOLOGY
Long COVID associated with risk of metabolic liver disease
Postacute COVID syndrome (PACS), an ongoing inflammatory state following infection with SARS-CoV-2, is associated with greater risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), according to an analysis of patients at a single clinic in Canada published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases.
MAFLD, also known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is considered an indicator of general health and is in turn linked to greater risk of cardiovascular complications and mortality. It may be a multisystem disorder with various underlying causes.
PACS includes symptoms that affect various organ systems, with neurocognitive, autonomic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, musculoskeletal, psychological, sensory, and dermatologic clusters. An estimated 50%-80% of COVID-19 patients experience one or more clusters of symptoms 3 months after leaving the hospital.
But liver problems also appear in the acute phase, said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “Up to about half the patients during the acute illness may have elevated liver tests, but there seems to be a subset of patients in whom the abnormality persists. And then there are some reports in the literature of patients developing injury to their bile ducts in the liver over the long term, apparently as a consequence of COVID infection. What this paper suggests is that there may be some metabolic derangements associated with COVID infection, which in turn can accentuate or possibly cause fatty liver,” said Dr. Martin in an interview. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases and a professor of medicine at the University of Miami.
“It highlights the need to get vaccinated against COVID and to take appropriate precautions because contracting the infection may lead to all sorts of consequences quite apart from having a respiratory illness,” said Dr. Martin.
The researchers retrospectively identified 235 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between July 2020 and April 2021. Overall, 69% were men, and the median age was 61 years; 19.2% underwent mechanical ventilation and the mean duration of hospitalization was 11.7 days. They were seen for PACS symptoms a median 143 days after COVID-19 symptoms began, with 77.5% having symptoms of at least one PACS cluster. Of these clusters, 34.9% were neurocognitive, 53.2% were respiratory, 26.4% were musculoskeletal, 29.4% were psychological, 25.1% were dermatologic, and 17.5% were sensory.
At the later clinical visit for PACS symptoms, all patients underwent screening for MAFLD, which was defined as the presence of liver steatosis plus overweight/obesity or type 2 diabetes. Hepatic steatosis was determined from controlled attenuation parameter using transient elastrography. The analysis excluded patients with significant alcohol intake or hepatitis B or C. All patients with liver steatosis also had MAFLD, and this included 55.3% of the study population.
The hospital was able to obtain hepatic steatosis index (HSI) scores for 103 of 235 patients. Of these, 50% had MAFLD on admission for acute COVID-19, and 48.1% had MAFLD upon discharge based on this criterion. At the PACS follow-up visit, 71.3% were diagnosed with MAFLD. There was no statistically significant difference in the use of glucocorticoids or tocilizumab during hospitalization between those with and without MAFLD, and remdesivir use was insignificant in the patient population.
Given that the prevalence of MAFLD among the study population is more than double that in the general population, the authors suggest that MAFLD may be a new PACS cluster phenotype that could lead to long-term metabolic and cardiovascular complications. A potential explanation is loss of lean body mass during COVID-19 hospitalization followed by liver fat accumulation during recovery.
Other infections have also shown an association with increased MAFLD incidence, including HIV, Heliobacter pylori, and viral hepatitis. The authors worry that COVID-19 infection could exacerbate underlying conditions to a more severe MAFLD disease state.
The study is limited by a small sample size, limited follow-up, and the lack of a control group. Its retrospective nature leaves it vulnerable to biases.
“The natural history of MAFLD in the context of PACS is unknown at this time, and careful follow-up of these patients is needed to understand the clinical implications of this syndrome in the context of long COVID,” the authors wrote. “We speculate that [MAFLD] may be considered as an independent PACS-cluster phenotype, potentially affecting the metabolic and cardiovascular health of patients with PACS.”
One author has relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, but the remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Martin has no relevant financial disclosures.
Postacute COVID syndrome (PACS), an ongoing inflammatory state following infection with SARS-CoV-2, is associated with greater risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), according to an analysis of patients at a single clinic in Canada published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases.
MAFLD, also known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is considered an indicator of general health and is in turn linked to greater risk of cardiovascular complications and mortality. It may be a multisystem disorder with various underlying causes.
PACS includes symptoms that affect various organ systems, with neurocognitive, autonomic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, musculoskeletal, psychological, sensory, and dermatologic clusters. An estimated 50%-80% of COVID-19 patients experience one or more clusters of symptoms 3 months after leaving the hospital.
But liver problems also appear in the acute phase, said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “Up to about half the patients during the acute illness may have elevated liver tests, but there seems to be a subset of patients in whom the abnormality persists. And then there are some reports in the literature of patients developing injury to their bile ducts in the liver over the long term, apparently as a consequence of COVID infection. What this paper suggests is that there may be some metabolic derangements associated with COVID infection, which in turn can accentuate or possibly cause fatty liver,” said Dr. Martin in an interview. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases and a professor of medicine at the University of Miami.
“It highlights the need to get vaccinated against COVID and to take appropriate precautions because contracting the infection may lead to all sorts of consequences quite apart from having a respiratory illness,” said Dr. Martin.
The researchers retrospectively identified 235 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between July 2020 and April 2021. Overall, 69% were men, and the median age was 61 years; 19.2% underwent mechanical ventilation and the mean duration of hospitalization was 11.7 days. They were seen for PACS symptoms a median 143 days after COVID-19 symptoms began, with 77.5% having symptoms of at least one PACS cluster. Of these clusters, 34.9% were neurocognitive, 53.2% were respiratory, 26.4% were musculoskeletal, 29.4% were psychological, 25.1% were dermatologic, and 17.5% were sensory.
At the later clinical visit for PACS symptoms, all patients underwent screening for MAFLD, which was defined as the presence of liver steatosis plus overweight/obesity or type 2 diabetes. Hepatic steatosis was determined from controlled attenuation parameter using transient elastrography. The analysis excluded patients with significant alcohol intake or hepatitis B or C. All patients with liver steatosis also had MAFLD, and this included 55.3% of the study population.
The hospital was able to obtain hepatic steatosis index (HSI) scores for 103 of 235 patients. Of these, 50% had MAFLD on admission for acute COVID-19, and 48.1% had MAFLD upon discharge based on this criterion. At the PACS follow-up visit, 71.3% were diagnosed with MAFLD. There was no statistically significant difference in the use of glucocorticoids or tocilizumab during hospitalization between those with and without MAFLD, and remdesivir use was insignificant in the patient population.
Given that the prevalence of MAFLD among the study population is more than double that in the general population, the authors suggest that MAFLD may be a new PACS cluster phenotype that could lead to long-term metabolic and cardiovascular complications. A potential explanation is loss of lean body mass during COVID-19 hospitalization followed by liver fat accumulation during recovery.
Other infections have also shown an association with increased MAFLD incidence, including HIV, Heliobacter pylori, and viral hepatitis. The authors worry that COVID-19 infection could exacerbate underlying conditions to a more severe MAFLD disease state.
The study is limited by a small sample size, limited follow-up, and the lack of a control group. Its retrospective nature leaves it vulnerable to biases.
“The natural history of MAFLD in the context of PACS is unknown at this time, and careful follow-up of these patients is needed to understand the clinical implications of this syndrome in the context of long COVID,” the authors wrote. “We speculate that [MAFLD] may be considered as an independent PACS-cluster phenotype, potentially affecting the metabolic and cardiovascular health of patients with PACS.”
One author has relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, but the remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Martin has no relevant financial disclosures.
Postacute COVID syndrome (PACS), an ongoing inflammatory state following infection with SARS-CoV-2, is associated with greater risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), according to an analysis of patients at a single clinic in Canada published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases.
MAFLD, also known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is considered an indicator of general health and is in turn linked to greater risk of cardiovascular complications and mortality. It may be a multisystem disorder with various underlying causes.
PACS includes symptoms that affect various organ systems, with neurocognitive, autonomic, gastrointestinal, respiratory, musculoskeletal, psychological, sensory, and dermatologic clusters. An estimated 50%-80% of COVID-19 patients experience one or more clusters of symptoms 3 months after leaving the hospital.
But liver problems also appear in the acute phase, said Paul Martin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “Up to about half the patients during the acute illness may have elevated liver tests, but there seems to be a subset of patients in whom the abnormality persists. And then there are some reports in the literature of patients developing injury to their bile ducts in the liver over the long term, apparently as a consequence of COVID infection. What this paper suggests is that there may be some metabolic derangements associated with COVID infection, which in turn can accentuate or possibly cause fatty liver,” said Dr. Martin in an interview. He is chief of digestive health and liver diseases and a professor of medicine at the University of Miami.
“It highlights the need to get vaccinated against COVID and to take appropriate precautions because contracting the infection may lead to all sorts of consequences quite apart from having a respiratory illness,” said Dr. Martin.
The researchers retrospectively identified 235 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between July 2020 and April 2021. Overall, 69% were men, and the median age was 61 years; 19.2% underwent mechanical ventilation and the mean duration of hospitalization was 11.7 days. They were seen for PACS symptoms a median 143 days after COVID-19 symptoms began, with 77.5% having symptoms of at least one PACS cluster. Of these clusters, 34.9% were neurocognitive, 53.2% were respiratory, 26.4% were musculoskeletal, 29.4% were psychological, 25.1% were dermatologic, and 17.5% were sensory.
At the later clinical visit for PACS symptoms, all patients underwent screening for MAFLD, which was defined as the presence of liver steatosis plus overweight/obesity or type 2 diabetes. Hepatic steatosis was determined from controlled attenuation parameter using transient elastrography. The analysis excluded patients with significant alcohol intake or hepatitis B or C. All patients with liver steatosis also had MAFLD, and this included 55.3% of the study population.
The hospital was able to obtain hepatic steatosis index (HSI) scores for 103 of 235 patients. Of these, 50% had MAFLD on admission for acute COVID-19, and 48.1% had MAFLD upon discharge based on this criterion. At the PACS follow-up visit, 71.3% were diagnosed with MAFLD. There was no statistically significant difference in the use of glucocorticoids or tocilizumab during hospitalization between those with and without MAFLD, and remdesivir use was insignificant in the patient population.
Given that the prevalence of MAFLD among the study population is more than double that in the general population, the authors suggest that MAFLD may be a new PACS cluster phenotype that could lead to long-term metabolic and cardiovascular complications. A potential explanation is loss of lean body mass during COVID-19 hospitalization followed by liver fat accumulation during recovery.
Other infections have also shown an association with increased MAFLD incidence, including HIV, Heliobacter pylori, and viral hepatitis. The authors worry that COVID-19 infection could exacerbate underlying conditions to a more severe MAFLD disease state.
The study is limited by a small sample size, limited follow-up, and the lack of a control group. Its retrospective nature leaves it vulnerable to biases.
“The natural history of MAFLD in the context of PACS is unknown at this time, and careful follow-up of these patients is needed to understand the clinical implications of this syndrome in the context of long COVID,” the authors wrote. “We speculate that [MAFLD] may be considered as an independent PACS-cluster phenotype, potentially affecting the metabolic and cardiovascular health of patients with PACS.”
One author has relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, but the remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Martin has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM OPEN FORUM INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Sleeve, RYGB reduce liver fat in type 2 diabetes
Both Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy (SG) are effective at improving hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes patients, according to a new analysis of a randomized, controlled trial.
Both procedures resulted in near elimination of liver fat 1 year after the surgery, but the effect on liver fibrosis was less clear. The authors called for more research to examine longer-term effects on fibrosis.
“Both gastric bypass and the sleeve had complete resolution of the liver fat based on their MRI findings. That’s impressive,” said Ali Aminian, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Aminian is a professor of surgery and director of the Bariatric & Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
About 25% of the general population, and about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes and obesity have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can lead to liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic steatosis can combine with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation to heighten the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Moderate weight loss can clear liver fat and lead to histologic improvement of hepatic steatosis, and retrospective studies have suggested that RYGB may be more effective than SG and gastric banding in countering hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis.
In fact, Dr. Aminian recently coauthored a paper describing results from the SPLENDOR study, which looked at 650 adults with obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) who underwent bariatric surgery at U.S. hospitals between 2004 and 2016, and compared liver biopsy outcomes to 508 patients who went through nonsurgical weight loss protocols.
After a median follow-up of 7 years, 2.3% In the bariatric surgery group had major adverse liver outcomes, compared with 9.6% in the nonsurgical group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.12; P = .01). The cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was 8.5% in the bariatric surgery group and 15.7% in the nonsurgery group (aHR, 0.30; P = .007). 0.6% of the surgical group died within the first year after surgery from surgical complications.
Still, the question has not been tested in a randomized, controlled trial.
In the study published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers led by Kathrine Aglen Seeberg, MD, and Jens Kristoffer Hertel, PhD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of data from 100 patients (65% female, mean age, 47.5 years) with type 2 diabetes who had been randomized to undergo RYGB or SG between January 2013 and February 2018 at their center.
Prior to surgery, the mean liver fat fraction (LFF) was 19% (stand deviation, 12%). In the SG and RYGB groups, 24% and 26% of patients had no or low-grade steatosis (LFF ≤ 10%). LFF declined by 13% in both groups at 5 weeks, and by 20% and 22% at 1 year, respectively, with no significant difference between the two groups.
At 1 year, 100% of the RYGB group had no or low-grade steatosis, as did 94% in the SG group (no significant difference). At 1 year, both groups had similar percentage decreases in the NAFLD liver fat score (between group difference, –0.05) and NAFLD liver fat percentage (between-group difference, –0.3; no significant difference for either).
At baseline, 6% of the RYGB group and 8% of the SG group had severe fibrosis as measured by the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) test. At 1 year, the respective frequencies were 9% and 15%, which were not statistically significant changes.
There was much variation in ELF score changes between Individuals, but 18% moved to a higher ELF category and only 5% improved to a lower ELF category at 1 year.
Limitations of the study include the fact that it was conducted at a single center and in a predominantly White population. The study also did not use liver biopsy, which is the standard for measuring fibrosis. Individuals with type 2 diabetes may have more severe NAFLD, which could limit the applicability to individuals without type 2 diabetes.
Together, the studies produce a clear clinical message, according to Dr. Aminian. “It provides compelling evidence for patients and medical providers that, if we can help patients lose weight, we can reverse fatty liver disease,” he said.
The study was funded by the Southeastern Norway Regional Health Authority. Dr. Aminian has received research support from Medtronic.
Both Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy (SG) are effective at improving hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes patients, according to a new analysis of a randomized, controlled trial.
Both procedures resulted in near elimination of liver fat 1 year after the surgery, but the effect on liver fibrosis was less clear. The authors called for more research to examine longer-term effects on fibrosis.
“Both gastric bypass and the sleeve had complete resolution of the liver fat based on their MRI findings. That’s impressive,” said Ali Aminian, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Aminian is a professor of surgery and director of the Bariatric & Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
About 25% of the general population, and about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes and obesity have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can lead to liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic steatosis can combine with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation to heighten the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Moderate weight loss can clear liver fat and lead to histologic improvement of hepatic steatosis, and retrospective studies have suggested that RYGB may be more effective than SG and gastric banding in countering hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis.
In fact, Dr. Aminian recently coauthored a paper describing results from the SPLENDOR study, which looked at 650 adults with obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) who underwent bariatric surgery at U.S. hospitals between 2004 and 2016, and compared liver biopsy outcomes to 508 patients who went through nonsurgical weight loss protocols.
After a median follow-up of 7 years, 2.3% In the bariatric surgery group had major adverse liver outcomes, compared with 9.6% in the nonsurgical group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.12; P = .01). The cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was 8.5% in the bariatric surgery group and 15.7% in the nonsurgery group (aHR, 0.30; P = .007). 0.6% of the surgical group died within the first year after surgery from surgical complications.
Still, the question has not been tested in a randomized, controlled trial.
In the study published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers led by Kathrine Aglen Seeberg, MD, and Jens Kristoffer Hertel, PhD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of data from 100 patients (65% female, mean age, 47.5 years) with type 2 diabetes who had been randomized to undergo RYGB or SG between January 2013 and February 2018 at their center.
Prior to surgery, the mean liver fat fraction (LFF) was 19% (stand deviation, 12%). In the SG and RYGB groups, 24% and 26% of patients had no or low-grade steatosis (LFF ≤ 10%). LFF declined by 13% in both groups at 5 weeks, and by 20% and 22% at 1 year, respectively, with no significant difference between the two groups.
At 1 year, 100% of the RYGB group had no or low-grade steatosis, as did 94% in the SG group (no significant difference). At 1 year, both groups had similar percentage decreases in the NAFLD liver fat score (between group difference, –0.05) and NAFLD liver fat percentage (between-group difference, –0.3; no significant difference for either).
At baseline, 6% of the RYGB group and 8% of the SG group had severe fibrosis as measured by the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) test. At 1 year, the respective frequencies were 9% and 15%, which were not statistically significant changes.
There was much variation in ELF score changes between Individuals, but 18% moved to a higher ELF category and only 5% improved to a lower ELF category at 1 year.
Limitations of the study include the fact that it was conducted at a single center and in a predominantly White population. The study also did not use liver biopsy, which is the standard for measuring fibrosis. Individuals with type 2 diabetes may have more severe NAFLD, which could limit the applicability to individuals without type 2 diabetes.
Together, the studies produce a clear clinical message, according to Dr. Aminian. “It provides compelling evidence for patients and medical providers that, if we can help patients lose weight, we can reverse fatty liver disease,” he said.
The study was funded by the Southeastern Norway Regional Health Authority. Dr. Aminian has received research support from Medtronic.
Both Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy (SG) are effective at improving hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes patients, according to a new analysis of a randomized, controlled trial.
Both procedures resulted in near elimination of liver fat 1 year after the surgery, but the effect on liver fibrosis was less clear. The authors called for more research to examine longer-term effects on fibrosis.
“Both gastric bypass and the sleeve had complete resolution of the liver fat based on their MRI findings. That’s impressive,” said Ali Aminian, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Aminian is a professor of surgery and director of the Bariatric & Metabolic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic.
About 25% of the general population, and about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes and obesity have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can lead to liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic steatosis can combine with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation to heighten the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Moderate weight loss can clear liver fat and lead to histologic improvement of hepatic steatosis, and retrospective studies have suggested that RYGB may be more effective than SG and gastric banding in countering hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis.
In fact, Dr. Aminian recently coauthored a paper describing results from the SPLENDOR study, which looked at 650 adults with obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) who underwent bariatric surgery at U.S. hospitals between 2004 and 2016, and compared liver biopsy outcomes to 508 patients who went through nonsurgical weight loss protocols.
After a median follow-up of 7 years, 2.3% In the bariatric surgery group had major adverse liver outcomes, compared with 9.6% in the nonsurgical group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.12; P = .01). The cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was 8.5% in the bariatric surgery group and 15.7% in the nonsurgery group (aHR, 0.30; P = .007). 0.6% of the surgical group died within the first year after surgery from surgical complications.
Still, the question has not been tested in a randomized, controlled trial.
In the study published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, researchers led by Kathrine Aglen Seeberg, MD, and Jens Kristoffer Hertel, PhD, of Vestfold Hospital Trust, Tønsberg, Norway, conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of data from 100 patients (65% female, mean age, 47.5 years) with type 2 diabetes who had been randomized to undergo RYGB or SG between January 2013 and February 2018 at their center.
Prior to surgery, the mean liver fat fraction (LFF) was 19% (stand deviation, 12%). In the SG and RYGB groups, 24% and 26% of patients had no or low-grade steatosis (LFF ≤ 10%). LFF declined by 13% in both groups at 5 weeks, and by 20% and 22% at 1 year, respectively, with no significant difference between the two groups.
At 1 year, 100% of the RYGB group had no or low-grade steatosis, as did 94% in the SG group (no significant difference). At 1 year, both groups had similar percentage decreases in the NAFLD liver fat score (between group difference, –0.05) and NAFLD liver fat percentage (between-group difference, –0.3; no significant difference for either).
At baseline, 6% of the RYGB group and 8% of the SG group had severe fibrosis as measured by the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) test. At 1 year, the respective frequencies were 9% and 15%, which were not statistically significant changes.
There was much variation in ELF score changes between Individuals, but 18% moved to a higher ELF category and only 5% improved to a lower ELF category at 1 year.
Limitations of the study include the fact that it was conducted at a single center and in a predominantly White population. The study also did not use liver biopsy, which is the standard for measuring fibrosis. Individuals with type 2 diabetes may have more severe NAFLD, which could limit the applicability to individuals without type 2 diabetes.
Together, the studies produce a clear clinical message, according to Dr. Aminian. “It provides compelling evidence for patients and medical providers that, if we can help patients lose weight, we can reverse fatty liver disease,” he said.
The study was funded by the Southeastern Norway Regional Health Authority. Dr. Aminian has received research support from Medtronic.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
New hepatitis B vaccination recommendations praised amid low awareness
An updated recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) calling for universal hepatitis B vaccination of all adults aged 59 and younger has boosted the call to improve clinicians’ awareness of the increasing infection and low vaccination rates – and raise the issue with patients.
“This new recommendation from [the] ACIP will be instrumental [in] raising adult hepatitis B vaccination rates in the U.S. to levels that will allow us to finally eliminate hepatitis B in this country,” said Rita K. Kuwahara, MD, a primary care internal medicine physician and health policy fellow at Georgetown University, in Washington, D.C., in addressing the issue at the U.S. Conference on HIV/AIDS (USCHA) this month.
“We have the tools to prevent hepatitis B, and since we have such safe and highly effective vaccines to protect against community [spread], we should not have a single new infection in our nation,” she asserted.
The unanimously approved updated ACIP recommendation was issued in November and still requires adoption by the CDC director. The ACIP specifically recommends that adults aged 19 to 59 and those 60 years and older with risk factors for infection “should” receive the hepatitis B vaccine, and it further stipulates that those 60 years and older without known risk factors for hepatitis B “may” receive the vaccine.
The recommendation was previously only for adults at risk for hepatitis B infection due to a variety of factors, including sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, and HIV infection.
“The number of risk factors was long, and for a busy primary care provider to have to go through a lengthy risk-based protocol like that, it may not happen,” Dr. Kuwahara told this news organization.
“Now we have a really helpful new recommendation that is simply age based, and clinicians can just tell patients that if they were born before this certain period, a hepatitis B vaccination is recommended.”
The change comes amid a troubling trajectory of hepatitis B, with up to 2.4 million individuals currently having chronic hepatitis B in the U.S. and infection rates soaring by 100% to more than 400% in states with high opioid use, such as West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Maine, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Notably, hepatitis B is the leading cause of liver disease, and one in four individuals with unmanaged chronic hepatitis B goes on to develop liver failure and/or cirrhosis or liver cancer, which has a 5-year survival rate of only 18%.
Despite the rising infection rates, only 25%-30% of adults in the U.S. are reported to be currently vaccinated for hepatitis B, even though safe and highly effective vaccines are available, notably including a new two-dose vaccine (Heplisav-B) that can be provided over just a month (vs. other hepatitis B vaccines requiring 3 doses over 6 months).
Clinician awareness of low vaccination rates lacking
Dr. Kuwahara noted that awareness among clinicians of the issues surrounding hepatitis B appears low, with one small survey that she and her colleagues conducted of 30 primary care physicians showing that not one of the respondents was aware of the low vaccination rate.
Dr. Kuwahara says a key reason for the low awareness to discuss the hepatitis B vaccination with adults is the common impression that the responsibility for the vaccination lies in the hands of pediatricians.
But that’s only half correct – universal vaccination for hepatitis B in all infants and children is indeed currently the policy in the U.S. – but that was not implemented in all states until the mid-to-late ‘90s, meaning the millions of adults over the age of about 25 to 30, born before that period, are likely not fully vaccinated against hepatitis B.
“When I was in medical school, there wasn’t a lot of discussion of how low the hepatitis B vaccination rate was because everyone knew there was universal childhood vaccination, and I think there was an assumption that it had been going on for a long time,” Dr. Kuwahara said. “So I think it’s clearly a misconception, and it’s really important to improve clinician awareness around the issue.”
Opioid use a key factor in rising infection rates
Importantly, a large proportion of opioid users are among the population of patients born before the mid-’90s – and those adults have a particularly high risk of transmission, with data indicating that 36% of new hepatitis B infections are the result of the opioid epidemic, Dr. Kuwahara noted.
“In the opioid epidemic, we have seen some of the greatest increases in acute hepatitis B presenting in adults aged 30 to 49 years old, as most adults in this age range would not have been vaccinated as children in the U.S.,” she said.
Approximately two-thirds of individuals with chronic hepatitis B are reportedly not even aware of their infection status due to ineffective prevention and vaccination programs, adding to the spread of infection, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 has only exacerbated the problem, with record-high instances of overdoses and overdose-related deaths during the pandemic, she explained.
However, the pandemic, and specifically the sweeping innovations that have been implemented in desperate efforts to bring COVID-19 vaccines to the public, could in fact represent a critical opportunity for hepatitis B prevention, Dr. Kuwahara said.
“Significant resources and federal funding have already been invested to develop a robust infrastructure for multi-dose COVID-19 vaccine administration during the pandemic, which has resulted in millions of people across the U.S. receiving the COVID-19 vaccine in easily accessible settings within their communities,” she said.
“It is essential that we expand the infrastructure development ... so that we may use this infrastructure to administer other vaccines such as the hepatitis B vaccine to adults throughout the nation and prevent additional outbreaks.”
Implementation of vaccine recommendations key
Dr. Kuwahara outlined key measures that will be important in implementing the hepatitis B vaccine recommendations:
- Awareness of the hepatitis B vaccination recommendations at the primary care level: “The first step in implementing universal [guidelines] will be to ensure that health care providers, particularly in primary care, are aware of the new ACIP guidelines so that they can speak with their patients about this and appropriately order hepatitis B testing and vaccination,” she said.
- Availability of vaccines: In addition to making sure primary care clinics are well stocked with hepatitis B vaccines, the vaccines should also be available in pharmacies and other convenient nonclinical settings through community outreach, similar to COVID-19 vaccines.
- Follow-up: Systems should be established to remind patients to receive follow-up doses.
- Public funding for vaccines: Policy changes will need to occur to allocate appropriate Section 317 funding to provide hepatitis B vaccines to adults without health insurance coverage, Dr. Kuwahara said, underscoring concerns about health equity in vaccination.
- Track vaccinations: Communication should be established between places administering vaccines and primary care providers to make sure that vaccination status can be documented in a reliable setting.
Dr. Kuwahara also noted that a federal immunization information system will be essential to track vaccines across a lifespan, providing one integrated vaccine record that can be accessed even when patients travel or move to different states.
Commenting on the issue, Frank Hood, manager of hepatitis advocacy for The AIDS Institute in Washington, D.C., added that, in addition to simplifying the process, the new age-based recommendation removes the issue of perceived judgement from the advice.
“The previous recommendations were more risk based, and patients may tend to say ‘oh, I don’t have any of those behaviors,’ and there can be some stigma,” he said. “But having something that says everyone in these age groups should be or may be vaccinated just makes it much easier and covers a greater number of individuals.”
Mr. Hood further underscored the need for continued diligence in improving measures to prevent and eradicate HBV as well as other infectious diseases.
“It is imperative that the systems being built now to respond to future infectious disease outbreaks are done so in a way to equitably support the efforts and end goal of eliminating current infectious disease epidemics like viral hepatitis and HIV,” he emphasized.“Elimination can’t be achieved if we leave people behind.”
Dr. Kuwahara and Mr. Hood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An updated recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) calling for universal hepatitis B vaccination of all adults aged 59 and younger has boosted the call to improve clinicians’ awareness of the increasing infection and low vaccination rates – and raise the issue with patients.
“This new recommendation from [the] ACIP will be instrumental [in] raising adult hepatitis B vaccination rates in the U.S. to levels that will allow us to finally eliminate hepatitis B in this country,” said Rita K. Kuwahara, MD, a primary care internal medicine physician and health policy fellow at Georgetown University, in Washington, D.C., in addressing the issue at the U.S. Conference on HIV/AIDS (USCHA) this month.
“We have the tools to prevent hepatitis B, and since we have such safe and highly effective vaccines to protect against community [spread], we should not have a single new infection in our nation,” she asserted.
The unanimously approved updated ACIP recommendation was issued in November and still requires adoption by the CDC director. The ACIP specifically recommends that adults aged 19 to 59 and those 60 years and older with risk factors for infection “should” receive the hepatitis B vaccine, and it further stipulates that those 60 years and older without known risk factors for hepatitis B “may” receive the vaccine.
The recommendation was previously only for adults at risk for hepatitis B infection due to a variety of factors, including sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, and HIV infection.
“The number of risk factors was long, and for a busy primary care provider to have to go through a lengthy risk-based protocol like that, it may not happen,” Dr. Kuwahara told this news organization.
“Now we have a really helpful new recommendation that is simply age based, and clinicians can just tell patients that if they were born before this certain period, a hepatitis B vaccination is recommended.”
The change comes amid a troubling trajectory of hepatitis B, with up to 2.4 million individuals currently having chronic hepatitis B in the U.S. and infection rates soaring by 100% to more than 400% in states with high opioid use, such as West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Maine, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Notably, hepatitis B is the leading cause of liver disease, and one in four individuals with unmanaged chronic hepatitis B goes on to develop liver failure and/or cirrhosis or liver cancer, which has a 5-year survival rate of only 18%.
Despite the rising infection rates, only 25%-30% of adults in the U.S. are reported to be currently vaccinated for hepatitis B, even though safe and highly effective vaccines are available, notably including a new two-dose vaccine (Heplisav-B) that can be provided over just a month (vs. other hepatitis B vaccines requiring 3 doses over 6 months).
Clinician awareness of low vaccination rates lacking
Dr. Kuwahara noted that awareness among clinicians of the issues surrounding hepatitis B appears low, with one small survey that she and her colleagues conducted of 30 primary care physicians showing that not one of the respondents was aware of the low vaccination rate.
Dr. Kuwahara says a key reason for the low awareness to discuss the hepatitis B vaccination with adults is the common impression that the responsibility for the vaccination lies in the hands of pediatricians.
But that’s only half correct – universal vaccination for hepatitis B in all infants and children is indeed currently the policy in the U.S. – but that was not implemented in all states until the mid-to-late ‘90s, meaning the millions of adults over the age of about 25 to 30, born before that period, are likely not fully vaccinated against hepatitis B.
“When I was in medical school, there wasn’t a lot of discussion of how low the hepatitis B vaccination rate was because everyone knew there was universal childhood vaccination, and I think there was an assumption that it had been going on for a long time,” Dr. Kuwahara said. “So I think it’s clearly a misconception, and it’s really important to improve clinician awareness around the issue.”
Opioid use a key factor in rising infection rates
Importantly, a large proportion of opioid users are among the population of patients born before the mid-’90s – and those adults have a particularly high risk of transmission, with data indicating that 36% of new hepatitis B infections are the result of the opioid epidemic, Dr. Kuwahara noted.
“In the opioid epidemic, we have seen some of the greatest increases in acute hepatitis B presenting in adults aged 30 to 49 years old, as most adults in this age range would not have been vaccinated as children in the U.S.,” she said.
Approximately two-thirds of individuals with chronic hepatitis B are reportedly not even aware of their infection status due to ineffective prevention and vaccination programs, adding to the spread of infection, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 has only exacerbated the problem, with record-high instances of overdoses and overdose-related deaths during the pandemic, she explained.
However, the pandemic, and specifically the sweeping innovations that have been implemented in desperate efforts to bring COVID-19 vaccines to the public, could in fact represent a critical opportunity for hepatitis B prevention, Dr. Kuwahara said.
“Significant resources and federal funding have already been invested to develop a robust infrastructure for multi-dose COVID-19 vaccine administration during the pandemic, which has resulted in millions of people across the U.S. receiving the COVID-19 vaccine in easily accessible settings within their communities,” she said.
“It is essential that we expand the infrastructure development ... so that we may use this infrastructure to administer other vaccines such as the hepatitis B vaccine to adults throughout the nation and prevent additional outbreaks.”
Implementation of vaccine recommendations key
Dr. Kuwahara outlined key measures that will be important in implementing the hepatitis B vaccine recommendations:
- Awareness of the hepatitis B vaccination recommendations at the primary care level: “The first step in implementing universal [guidelines] will be to ensure that health care providers, particularly in primary care, are aware of the new ACIP guidelines so that they can speak with their patients about this and appropriately order hepatitis B testing and vaccination,” she said.
- Availability of vaccines: In addition to making sure primary care clinics are well stocked with hepatitis B vaccines, the vaccines should also be available in pharmacies and other convenient nonclinical settings through community outreach, similar to COVID-19 vaccines.
- Follow-up: Systems should be established to remind patients to receive follow-up doses.
- Public funding for vaccines: Policy changes will need to occur to allocate appropriate Section 317 funding to provide hepatitis B vaccines to adults without health insurance coverage, Dr. Kuwahara said, underscoring concerns about health equity in vaccination.
- Track vaccinations: Communication should be established between places administering vaccines and primary care providers to make sure that vaccination status can be documented in a reliable setting.
Dr. Kuwahara also noted that a federal immunization information system will be essential to track vaccines across a lifespan, providing one integrated vaccine record that can be accessed even when patients travel or move to different states.
Commenting on the issue, Frank Hood, manager of hepatitis advocacy for The AIDS Institute in Washington, D.C., added that, in addition to simplifying the process, the new age-based recommendation removes the issue of perceived judgement from the advice.
“The previous recommendations were more risk based, and patients may tend to say ‘oh, I don’t have any of those behaviors,’ and there can be some stigma,” he said. “But having something that says everyone in these age groups should be or may be vaccinated just makes it much easier and covers a greater number of individuals.”
Mr. Hood further underscored the need for continued diligence in improving measures to prevent and eradicate HBV as well as other infectious diseases.
“It is imperative that the systems being built now to respond to future infectious disease outbreaks are done so in a way to equitably support the efforts and end goal of eliminating current infectious disease epidemics like viral hepatitis and HIV,” he emphasized.“Elimination can’t be achieved if we leave people behind.”
Dr. Kuwahara and Mr. Hood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An updated recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) calling for universal hepatitis B vaccination of all adults aged 59 and younger has boosted the call to improve clinicians’ awareness of the increasing infection and low vaccination rates – and raise the issue with patients.
“This new recommendation from [the] ACIP will be instrumental [in] raising adult hepatitis B vaccination rates in the U.S. to levels that will allow us to finally eliminate hepatitis B in this country,” said Rita K. Kuwahara, MD, a primary care internal medicine physician and health policy fellow at Georgetown University, in Washington, D.C., in addressing the issue at the U.S. Conference on HIV/AIDS (USCHA) this month.
“We have the tools to prevent hepatitis B, and since we have such safe and highly effective vaccines to protect against community [spread], we should not have a single new infection in our nation,” she asserted.
The unanimously approved updated ACIP recommendation was issued in November and still requires adoption by the CDC director. The ACIP specifically recommends that adults aged 19 to 59 and those 60 years and older with risk factors for infection “should” receive the hepatitis B vaccine, and it further stipulates that those 60 years and older without known risk factors for hepatitis B “may” receive the vaccine.
The recommendation was previously only for adults at risk for hepatitis B infection due to a variety of factors, including sexual exposure, percutaneous or mucosal exposure to blood, hepatitis C infection, chronic liver disease, end-stage renal disease, and HIV infection.
“The number of risk factors was long, and for a busy primary care provider to have to go through a lengthy risk-based protocol like that, it may not happen,” Dr. Kuwahara told this news organization.
“Now we have a really helpful new recommendation that is simply age based, and clinicians can just tell patients that if they were born before this certain period, a hepatitis B vaccination is recommended.”
The change comes amid a troubling trajectory of hepatitis B, with up to 2.4 million individuals currently having chronic hepatitis B in the U.S. and infection rates soaring by 100% to more than 400% in states with high opioid use, such as West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Maine, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Notably, hepatitis B is the leading cause of liver disease, and one in four individuals with unmanaged chronic hepatitis B goes on to develop liver failure and/or cirrhosis or liver cancer, which has a 5-year survival rate of only 18%.
Despite the rising infection rates, only 25%-30% of adults in the U.S. are reported to be currently vaccinated for hepatitis B, even though safe and highly effective vaccines are available, notably including a new two-dose vaccine (Heplisav-B) that can be provided over just a month (vs. other hepatitis B vaccines requiring 3 doses over 6 months).
Clinician awareness of low vaccination rates lacking
Dr. Kuwahara noted that awareness among clinicians of the issues surrounding hepatitis B appears low, with one small survey that she and her colleagues conducted of 30 primary care physicians showing that not one of the respondents was aware of the low vaccination rate.
Dr. Kuwahara says a key reason for the low awareness to discuss the hepatitis B vaccination with adults is the common impression that the responsibility for the vaccination lies in the hands of pediatricians.
But that’s only half correct – universal vaccination for hepatitis B in all infants and children is indeed currently the policy in the U.S. – but that was not implemented in all states until the mid-to-late ‘90s, meaning the millions of adults over the age of about 25 to 30, born before that period, are likely not fully vaccinated against hepatitis B.
“When I was in medical school, there wasn’t a lot of discussion of how low the hepatitis B vaccination rate was because everyone knew there was universal childhood vaccination, and I think there was an assumption that it had been going on for a long time,” Dr. Kuwahara said. “So I think it’s clearly a misconception, and it’s really important to improve clinician awareness around the issue.”
Opioid use a key factor in rising infection rates
Importantly, a large proportion of opioid users are among the population of patients born before the mid-’90s – and those adults have a particularly high risk of transmission, with data indicating that 36% of new hepatitis B infections are the result of the opioid epidemic, Dr. Kuwahara noted.
“In the opioid epidemic, we have seen some of the greatest increases in acute hepatitis B presenting in adults aged 30 to 49 years old, as most adults in this age range would not have been vaccinated as children in the U.S.,” she said.
Approximately two-thirds of individuals with chronic hepatitis B are reportedly not even aware of their infection status due to ineffective prevention and vaccination programs, adding to the spread of infection, Dr. Kuwahara said.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 has only exacerbated the problem, with record-high instances of overdoses and overdose-related deaths during the pandemic, she explained.
However, the pandemic, and specifically the sweeping innovations that have been implemented in desperate efforts to bring COVID-19 vaccines to the public, could in fact represent a critical opportunity for hepatitis B prevention, Dr. Kuwahara said.
“Significant resources and federal funding have already been invested to develop a robust infrastructure for multi-dose COVID-19 vaccine administration during the pandemic, which has resulted in millions of people across the U.S. receiving the COVID-19 vaccine in easily accessible settings within their communities,” she said.
“It is essential that we expand the infrastructure development ... so that we may use this infrastructure to administer other vaccines such as the hepatitis B vaccine to adults throughout the nation and prevent additional outbreaks.”
Implementation of vaccine recommendations key
Dr. Kuwahara outlined key measures that will be important in implementing the hepatitis B vaccine recommendations:
- Awareness of the hepatitis B vaccination recommendations at the primary care level: “The first step in implementing universal [guidelines] will be to ensure that health care providers, particularly in primary care, are aware of the new ACIP guidelines so that they can speak with their patients about this and appropriately order hepatitis B testing and vaccination,” she said.
- Availability of vaccines: In addition to making sure primary care clinics are well stocked with hepatitis B vaccines, the vaccines should also be available in pharmacies and other convenient nonclinical settings through community outreach, similar to COVID-19 vaccines.
- Follow-up: Systems should be established to remind patients to receive follow-up doses.
- Public funding for vaccines: Policy changes will need to occur to allocate appropriate Section 317 funding to provide hepatitis B vaccines to adults without health insurance coverage, Dr. Kuwahara said, underscoring concerns about health equity in vaccination.
- Track vaccinations: Communication should be established between places administering vaccines and primary care providers to make sure that vaccination status can be documented in a reliable setting.
Dr. Kuwahara also noted that a federal immunization information system will be essential to track vaccines across a lifespan, providing one integrated vaccine record that can be accessed even when patients travel or move to different states.
Commenting on the issue, Frank Hood, manager of hepatitis advocacy for The AIDS Institute in Washington, D.C., added that, in addition to simplifying the process, the new age-based recommendation removes the issue of perceived judgement from the advice.
“The previous recommendations were more risk based, and patients may tend to say ‘oh, I don’t have any of those behaviors,’ and there can be some stigma,” he said. “But having something that says everyone in these age groups should be or may be vaccinated just makes it much easier and covers a greater number of individuals.”
Mr. Hood further underscored the need for continued diligence in improving measures to prevent and eradicate HBV as well as other infectious diseases.
“It is imperative that the systems being built now to respond to future infectious disease outbreaks are done so in a way to equitably support the efforts and end goal of eliminating current infectious disease epidemics like viral hepatitis and HIV,” he emphasized.“Elimination can’t be achieved if we leave people behind.”
Dr. Kuwahara and Mr. Hood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Home-based system relieves refractory ascites in cirrhosis
A home-based tunneled peritoneal catheter (PeCa) drainage system provided significant relief for patients with refractory ascites who were not candidates for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
For these patients, the current standard of care is repeated large volume paracentesis, but this can require frequent hospital trips that can be costly and onerous.
The PeCa system consists of one part that lays in the peritoneal cavity, then a tunnel through subcutaneous tissue and an external port where the patient can connect drainage bags. It has been tested and found to provide relief for patients with malignant ascites, but there is little data available for patients with cirrhosis, according to Tammo Lambert Tergast, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Dr. Tergast is a resident in the department of gastroenterology, hepatology, and endocrinology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Patients with refractory ascites have a very high risk for rehospitalization, AKI [acute kidney injury], and death. Our data indicate that PeCa could be a valuable new treatment option for patients with refractory ascites and contraindication for TIPS. However, the risk for hyponatremia and AKI has to be considered and further explored,” said Dr. Tergast during his presentation.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed outcomes in 152 patients with refractory ascites who received a PeCa implant and 71 patients who received standard of care (SOC), which included repeated large volume paracentesis and albumin. The median explant-free survival was 74 days, and just under 50% were explant free at 90 days.
52 patients had the PeCa system removed: 54% because of an infection, 15% because of liver transplant, 12% because of dysfunction, and 10% because of accidental removal.
Factors associated with 90-day survival included PeCa (hazard ratio, 0.52; P = .05) and each point of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (HR, 1.16; P = .001). There was a trend toward a higher incidence of hyponatremia in the PeCa group (P = .09).
Hospitalizations were more common in the PeCa group (P = .035), but there was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups. Reasons for hospitalization included spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP; 18% in PeCa vs. 8% of SOC), hyponatremia (10% vs. 0%), and infections other than SBP (4% and 16%).
A propensity score–matched analysis that included age, history of SBP, platelet count, serum albumin levels, and MELD score found no significant differences between the two groups, but there were trends in the PeCa group towards higher 90-day survival (P = .16) and a higher frequency of acute kidney injury (P = .08).
Although the appropriate patient population for the system would be small, “once you get to refractory ascites, management of these individuals is really, really challenging, especially people that had contraindications to a TIPS procedure. Anything that you can do to improve their quality of life and help with management is definitely desired,” said Nancy Reau, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Reau is chief of the section of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
The study found little difference in infection risk between the PeCa and standard of care group, but there was a trend toward more hyponatremia in the PeCa group. That could be caused by reduced contact with the health system, according to Dr. Reau, since physicians may be keeping an eye on electrolytes, diuretics, and other factors during paracentesis visits. “But as long as you’re setting up home nursing or some other way to make sure that you’re managing them appropriately, that should be something that is overcome with awareness,” said Dr. Reau.
During the question-and-answer following the presentation, Dr. Tergast was asked about the heightened frequency of hospitalizations in the PeCa group. He posited that the observation may be caused by the retrospective nature of the study. His center is a tertiary care center, which accepts referrals from all over Germany. When a problem occurs with a PeCa, patients often get referred back to the tertiary center, leading to a higher number of hospitalizations observed in that group. “So this might be a bias in the analysis,” he said.
“I think if we can optimize the treatment after discharge, we can also minimize the rehospitalization in these patients. Rehospitalization rate because of ascites was quite low,” said Dr. Tergast.
Dr. Tergast and Dr. Reau have no relevant financial disclosures.
A home-based tunneled peritoneal catheter (PeCa) drainage system provided significant relief for patients with refractory ascites who were not candidates for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
For these patients, the current standard of care is repeated large volume paracentesis, but this can require frequent hospital trips that can be costly and onerous.
The PeCa system consists of one part that lays in the peritoneal cavity, then a tunnel through subcutaneous tissue and an external port where the patient can connect drainage bags. It has been tested and found to provide relief for patients with malignant ascites, but there is little data available for patients with cirrhosis, according to Tammo Lambert Tergast, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Dr. Tergast is a resident in the department of gastroenterology, hepatology, and endocrinology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Patients with refractory ascites have a very high risk for rehospitalization, AKI [acute kidney injury], and death. Our data indicate that PeCa could be a valuable new treatment option for patients with refractory ascites and contraindication for TIPS. However, the risk for hyponatremia and AKI has to be considered and further explored,” said Dr. Tergast during his presentation.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed outcomes in 152 patients with refractory ascites who received a PeCa implant and 71 patients who received standard of care (SOC), which included repeated large volume paracentesis and albumin. The median explant-free survival was 74 days, and just under 50% were explant free at 90 days.
52 patients had the PeCa system removed: 54% because of an infection, 15% because of liver transplant, 12% because of dysfunction, and 10% because of accidental removal.
Factors associated with 90-day survival included PeCa (hazard ratio, 0.52; P = .05) and each point of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (HR, 1.16; P = .001). There was a trend toward a higher incidence of hyponatremia in the PeCa group (P = .09).
Hospitalizations were more common in the PeCa group (P = .035), but there was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups. Reasons for hospitalization included spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP; 18% in PeCa vs. 8% of SOC), hyponatremia (10% vs. 0%), and infections other than SBP (4% and 16%).
A propensity score–matched analysis that included age, history of SBP, platelet count, serum albumin levels, and MELD score found no significant differences between the two groups, but there were trends in the PeCa group towards higher 90-day survival (P = .16) and a higher frequency of acute kidney injury (P = .08).
Although the appropriate patient population for the system would be small, “once you get to refractory ascites, management of these individuals is really, really challenging, especially people that had contraindications to a TIPS procedure. Anything that you can do to improve their quality of life and help with management is definitely desired,” said Nancy Reau, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Reau is chief of the section of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
The study found little difference in infection risk between the PeCa and standard of care group, but there was a trend toward more hyponatremia in the PeCa group. That could be caused by reduced contact with the health system, according to Dr. Reau, since physicians may be keeping an eye on electrolytes, diuretics, and other factors during paracentesis visits. “But as long as you’re setting up home nursing or some other way to make sure that you’re managing them appropriately, that should be something that is overcome with awareness,” said Dr. Reau.
During the question-and-answer following the presentation, Dr. Tergast was asked about the heightened frequency of hospitalizations in the PeCa group. He posited that the observation may be caused by the retrospective nature of the study. His center is a tertiary care center, which accepts referrals from all over Germany. When a problem occurs with a PeCa, patients often get referred back to the tertiary center, leading to a higher number of hospitalizations observed in that group. “So this might be a bias in the analysis,” he said.
“I think if we can optimize the treatment after discharge, we can also minimize the rehospitalization in these patients. Rehospitalization rate because of ascites was quite low,” said Dr. Tergast.
Dr. Tergast and Dr. Reau have no relevant financial disclosures.
A home-based tunneled peritoneal catheter (PeCa) drainage system provided significant relief for patients with refractory ascites who were not candidates for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
For these patients, the current standard of care is repeated large volume paracentesis, but this can require frequent hospital trips that can be costly and onerous.
The PeCa system consists of one part that lays in the peritoneal cavity, then a tunnel through subcutaneous tissue and an external port where the patient can connect drainage bags. It has been tested and found to provide relief for patients with malignant ascites, but there is little data available for patients with cirrhosis, according to Tammo Lambert Tergast, MD, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Dr. Tergast is a resident in the department of gastroenterology, hepatology, and endocrinology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Patients with refractory ascites have a very high risk for rehospitalization, AKI [acute kidney injury], and death. Our data indicate that PeCa could be a valuable new treatment option for patients with refractory ascites and contraindication for TIPS. However, the risk for hyponatremia and AKI has to be considered and further explored,” said Dr. Tergast during his presentation.
The researchers retrospectively analyzed outcomes in 152 patients with refractory ascites who received a PeCa implant and 71 patients who received standard of care (SOC), which included repeated large volume paracentesis and albumin. The median explant-free survival was 74 days, and just under 50% were explant free at 90 days.
52 patients had the PeCa system removed: 54% because of an infection, 15% because of liver transplant, 12% because of dysfunction, and 10% because of accidental removal.
Factors associated with 90-day survival included PeCa (hazard ratio, 0.52; P = .05) and each point of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (HR, 1.16; P = .001). There was a trend toward a higher incidence of hyponatremia in the PeCa group (P = .09).
Hospitalizations were more common in the PeCa group (P = .035), but there was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups. Reasons for hospitalization included spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP; 18% in PeCa vs. 8% of SOC), hyponatremia (10% vs. 0%), and infections other than SBP (4% and 16%).
A propensity score–matched analysis that included age, history of SBP, platelet count, serum albumin levels, and MELD score found no significant differences between the two groups, but there were trends in the PeCa group towards higher 90-day survival (P = .16) and a higher frequency of acute kidney injury (P = .08).
Although the appropriate patient population for the system would be small, “once you get to refractory ascites, management of these individuals is really, really challenging, especially people that had contraindications to a TIPS procedure. Anything that you can do to improve their quality of life and help with management is definitely desired,” said Nancy Reau, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Reau is chief of the section of hepatology at Rush University Medical Center, Chicago.
The study found little difference in infection risk between the PeCa and standard of care group, but there was a trend toward more hyponatremia in the PeCa group. That could be caused by reduced contact with the health system, according to Dr. Reau, since physicians may be keeping an eye on electrolytes, diuretics, and other factors during paracentesis visits. “But as long as you’re setting up home nursing or some other way to make sure that you’re managing them appropriately, that should be something that is overcome with awareness,” said Dr. Reau.
During the question-and-answer following the presentation, Dr. Tergast was asked about the heightened frequency of hospitalizations in the PeCa group. He posited that the observation may be caused by the retrospective nature of the study. His center is a tertiary care center, which accepts referrals from all over Germany. When a problem occurs with a PeCa, patients often get referred back to the tertiary center, leading to a higher number of hospitalizations observed in that group. “So this might be a bias in the analysis,” he said.
“I think if we can optimize the treatment after discharge, we can also minimize the rehospitalization in these patients. Rehospitalization rate because of ascites was quite low,” said Dr. Tergast.
Dr. Tergast and Dr. Reau have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE LIVER MEETING