User login
Lifting the restrictions on mifepristone during COVID-19: A step in the right direction
Mifepristone is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated medication for managing miscarriage and for medical abortion when combined with misoprostol.1,2 Since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use in 2000, more than 4 million women have used this medication.3 The combination of mifepristone with misoprostol was used for 39% of all US abortions in 2017.4 Approximately 10% of all clinically recognized pregnancies end in miscarriages, and many are safely managed with either misoprostol alone or with the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol.5
The issue
The prescription and distribution of mifepristone is highly regulated by the FDA via requirements outlined in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) drug safety program. The FDA may determine a REMS is necessary for a specific drug to ensure the benefits of a drug outweigh the potential risks. A REMS may include an informative package insert for patients, follow-up communication to prescribers—including letters, safety protocols or recommended laboratory tests, or Elements to Assure Safe Use (ETASU). ETASU are types of REMS that are placed on medications that have significant potential for serious adverse effects, and without such restrictions FDA approval would be rescinded.
Are mifepristone requirements fairly applied?
The 3 ETASU restrictions on the distribution of mifepristone are in-person dispensation, prescriber certification, and patient signatures on special forms.6 The in-person dispensing requirement is applied to only 16 other medications (one of which is Mifeprex, the brand version of mifepristone), and Mifeprex/mifepristone are the only ones deemed safe for self-administration—meaning that patients receive the drug from a clinic but then may take it at a site of their choosing. The prescriber certification requirement places expectations on providers to account for distribution of doses and keep records of serial numbers (in effect, having clinicians act as both physician and pharmacist, as most medications are distributed and recorded in pharmacies). The patient form was recommended for elimination in 2016 due to its duplicative information and burden on patients—a recommendation that was then overruled by the FDA commissioner.7
These 3 requirements placed on mifepristone specifically target dosages for use related to abortions and miscarriages. Mifepristone is used to treat other medical conditions, with much higher doses, without the same restrictions—in fact, the FDA has allowed much higher doses of mifepristone to be mailed directly to a patient when prescribed for different disorders. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has long opposed the burdensome REMS requirements on mifepristone for reproductive health indications.8
Arguments regarding the safety of mifepristone must be understood in the context of how the medication is taken, and the unique difference with other medications that must be administered by physicians or in health care facilities. Mifepristone is self-administered, and the desired effect—evacuation of uterine contents—typically occurs after a patient takes the accompanying medication misoprostol, which is some 24 to 72 hours later. This timeframe makes it highly unlikely that any patient would be in the presence of their provider at the time of medication effect, thus an in-person dispensing requirement has no medical bearing on the outcome of the health of the patient.
REMS changes during the COVID-19 pandemic
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has necessarily changed the structure of REMS and ETASU requirements for many medications, with changes made in order to mitigate viral transmission through the limitation of unnecessary visits to clinics or hospitals. The FDA announced in March of 2020 that it would not enforce pre-prescription requirements, such as laboratory or magnetic resonance imaging results, for many medications (including those more toxic than mifepristone), and that it would lift the requirement for in-person dispensation of several medications.9 Also in March 2020 the Department of Health and Human Services Secretary (HHS) and the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) activated a “telemedicine exception” to allow physicians to use telemedicine to satisfy mandatory requirements for prescribing controlled substances, including opioids.10
Despite repeated pleas from organizations, individuals, and physician groups, the FDA continued to enforce the REMS/ETASU for mifepristone as the pandemic decimated communities. Importantly, the pandemic has not had an equal effect on all communities, and the disparities highlighted in outcomes as related to COVID-19 are also reflected in disparities to access to reproductive choices.11 By enforcing REMS/ETASU for mifepristone during a global pandemic, the FDA has placed additional burden on women and people who menstruate. As offices and clinics have closed, and as many jobs have evaporated, additional barriers have emerged, such as lack of childcare, fewer transportation options, and decreased clinic appointments.
As the pandemic continues to affect communities in the United States, ACOG has issued guidance recommending assessment for eligibility for medical abortion remotely, and has encouraged the use of telemedicine and other remote interactions for its members and patients to limit transmission of the virus.
The lawsuit
On May 27, 2020, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) (on behalf of ACOG, the Council of University Chairs of Obstetrics and Gynecology, New York State Academy of Family Physicians, SisterSong, and Honor MacNaughton, MD) filed a civil action against the FDA and HHS challenging the requirement for in-person dispensing of mifepristone and associated ETASU requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic. The plaintiffs sought this injunction based on the claim that these restrictions during the pandemic infringe on the constitutional rights to patients’ privacy and liberty and to equal protection of the law as protected by the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment. Additionally, the ACLU and other organizations said these unnecessary restrictions place patients, providers, and staff at unnecessary risk of viral exposure amidst a global pandemic.
The verdict
On July 13, 2020, a federal court granted the preliminary injunction to suspend FDA’s enforcement of the in-person requirements of mifepristone for abortion during the COVID-19 pandemic. The court denied the motion for suspension of in-person restrictions as applied to miscarriage management. The preliminary injunction applies nationwide without geographic limitation. It will remain in effect until the end of the litigation or for 30 days following the expiration of the public health emergency.
What the outcome means
This injunction is a step in the right direction for patients and providers to allow for autonomy and clinical practice guided by clinician expertise. However, this ruling remains narrow. Patients must be counseled about mifepristone via telemedicine and sign a Patient Agreement Form, which must be returned electronically or by mail. Patients must receive a copy of the mifepristone medication guide, and dispensing of mifepristone must still be conducted by or under the supervision of a certified provider. The medication may not be dispensed by retail pharmacies, thus requiring providers to arrange for mailing of prescriptions to patients. Given state-based legal statutes regarding mailing of medications, this injunction may not lead to an immediate increase in access to care. In addition, patients seeking management for miscarriage must go to clinic to have mifepristone dispensed and thus risk exposure to viral transmission.
What now?
The regulation of mifepristone—in spite of excellent safety and specifically for the narrow purpose of administration in the setting of abortion and miscarriage care—is by definition a discriminatory practice against patients and providers. As clinicians, we are duty-bound to speak out against injustices to our practices and our patients. At a local level, we can work to implement safe practices in the setting of this injunction and continue to work on a national level to ensure this injunction becomes permanent and with more broad scope to eliminate all of the REMS requirements for mifepristone.
ACTION ITEMS
- Act locally! Are you an abortion provider? Contact your local ACLU (find them here) or lawyer in your area for assistance navigating the legal landscape to prescribe after this injunction.
- Act statewide! Press candidates in your state to stand up for science and data. Support legislative acts and bills that address combating discriminatory regulations.
- Act nationally! The President is responsible for appointing the Commissioner of the FDA and the Secretary of Health and Human Services (with Senate advice and consent). Who we elect matters. Seek out opportunities to become involved in increasing access to and awareness of voter registration and Election Day, and speak out against voter suppression. Make sure you are registered to vote here and check your area to review new recommendations amidst the pandemic.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin number 143: medical management of first trimester abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:676-692.
- Schreiber CA, Crenin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Danco Laboratories. Mifeprex effectiveness and advantages. https://www.earlyoptionpill.com/is-mifeprex-right-for-me/effectiveness-advantages/ Accessed August 2, 2020.
- Jones RK, Witwer E, Jerman J. Abortion incidence and service availability in the United States, 2017. September 2019. https://www.guttmacher.org/report/abortion-incidence-service-availability-us-2017. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 150: early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1258-1267.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) single shared system for mifepristone 200 mg. April 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/rems/Mifepristone_2019_04_11_REMS_Full.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 2016 REMS Review, Summary Review 25. March 29, 2016. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2016/020687Orig1s020SumR.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Improving access to mifepristone for reproductive health indications. June 2018. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/policy-and-position-statements/position-statements/2018/improving-access-to-mifepristone-for-reproductive-health-indications. Accessed August 2, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Policy for certain REMS requirements during the COVID-19 public health emergency: guidance for industry and health care professionals. March 2020. https://www.fda.gov/media/136317/download. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Department of Justice. US Drug Enforcement Administration. COVID-19 Information Page, Telemedicine. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/coronavirus.html#TELE. Accessed May 25, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019: health equity considerations and racial and ethnic minority groups. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/health-equity/race-ethnicity.html. Updated July 24, 2020. Accessed September 10, 2020.
Mifepristone is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated medication for managing miscarriage and for medical abortion when combined with misoprostol.1,2 Since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use in 2000, more than 4 million women have used this medication.3 The combination of mifepristone with misoprostol was used for 39% of all US abortions in 2017.4 Approximately 10% of all clinically recognized pregnancies end in miscarriages, and many are safely managed with either misoprostol alone or with the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol.5
The issue
The prescription and distribution of mifepristone is highly regulated by the FDA via requirements outlined in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) drug safety program. The FDA may determine a REMS is necessary for a specific drug to ensure the benefits of a drug outweigh the potential risks. A REMS may include an informative package insert for patients, follow-up communication to prescribers—including letters, safety protocols or recommended laboratory tests, or Elements to Assure Safe Use (ETASU). ETASU are types of REMS that are placed on medications that have significant potential for serious adverse effects, and without such restrictions FDA approval would be rescinded.
Are mifepristone requirements fairly applied?
The 3 ETASU restrictions on the distribution of mifepristone are in-person dispensation, prescriber certification, and patient signatures on special forms.6 The in-person dispensing requirement is applied to only 16 other medications (one of which is Mifeprex, the brand version of mifepristone), and Mifeprex/mifepristone are the only ones deemed safe for self-administration—meaning that patients receive the drug from a clinic but then may take it at a site of their choosing. The prescriber certification requirement places expectations on providers to account for distribution of doses and keep records of serial numbers (in effect, having clinicians act as both physician and pharmacist, as most medications are distributed and recorded in pharmacies). The patient form was recommended for elimination in 2016 due to its duplicative information and burden on patients—a recommendation that was then overruled by the FDA commissioner.7
These 3 requirements placed on mifepristone specifically target dosages for use related to abortions and miscarriages. Mifepristone is used to treat other medical conditions, with much higher doses, without the same restrictions—in fact, the FDA has allowed much higher doses of mifepristone to be mailed directly to a patient when prescribed for different disorders. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has long opposed the burdensome REMS requirements on mifepristone for reproductive health indications.8
Arguments regarding the safety of mifepristone must be understood in the context of how the medication is taken, and the unique difference with other medications that must be administered by physicians or in health care facilities. Mifepristone is self-administered, and the desired effect—evacuation of uterine contents—typically occurs after a patient takes the accompanying medication misoprostol, which is some 24 to 72 hours later. This timeframe makes it highly unlikely that any patient would be in the presence of their provider at the time of medication effect, thus an in-person dispensing requirement has no medical bearing on the outcome of the health of the patient.
REMS changes during the COVID-19 pandemic
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has necessarily changed the structure of REMS and ETASU requirements for many medications, with changes made in order to mitigate viral transmission through the limitation of unnecessary visits to clinics or hospitals. The FDA announced in March of 2020 that it would not enforce pre-prescription requirements, such as laboratory or magnetic resonance imaging results, for many medications (including those more toxic than mifepristone), and that it would lift the requirement for in-person dispensation of several medications.9 Also in March 2020 the Department of Health and Human Services Secretary (HHS) and the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) activated a “telemedicine exception” to allow physicians to use telemedicine to satisfy mandatory requirements for prescribing controlled substances, including opioids.10
Despite repeated pleas from organizations, individuals, and physician groups, the FDA continued to enforce the REMS/ETASU for mifepristone as the pandemic decimated communities. Importantly, the pandemic has not had an equal effect on all communities, and the disparities highlighted in outcomes as related to COVID-19 are also reflected in disparities to access to reproductive choices.11 By enforcing REMS/ETASU for mifepristone during a global pandemic, the FDA has placed additional burden on women and people who menstruate. As offices and clinics have closed, and as many jobs have evaporated, additional barriers have emerged, such as lack of childcare, fewer transportation options, and decreased clinic appointments.
As the pandemic continues to affect communities in the United States, ACOG has issued guidance recommending assessment for eligibility for medical abortion remotely, and has encouraged the use of telemedicine and other remote interactions for its members and patients to limit transmission of the virus.
The lawsuit
On May 27, 2020, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) (on behalf of ACOG, the Council of University Chairs of Obstetrics and Gynecology, New York State Academy of Family Physicians, SisterSong, and Honor MacNaughton, MD) filed a civil action against the FDA and HHS challenging the requirement for in-person dispensing of mifepristone and associated ETASU requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic. The plaintiffs sought this injunction based on the claim that these restrictions during the pandemic infringe on the constitutional rights to patients’ privacy and liberty and to equal protection of the law as protected by the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment. Additionally, the ACLU and other organizations said these unnecessary restrictions place patients, providers, and staff at unnecessary risk of viral exposure amidst a global pandemic.
The verdict
On July 13, 2020, a federal court granted the preliminary injunction to suspend FDA’s enforcement of the in-person requirements of mifepristone for abortion during the COVID-19 pandemic. The court denied the motion for suspension of in-person restrictions as applied to miscarriage management. The preliminary injunction applies nationwide without geographic limitation. It will remain in effect until the end of the litigation or for 30 days following the expiration of the public health emergency.
What the outcome means
This injunction is a step in the right direction for patients and providers to allow for autonomy and clinical practice guided by clinician expertise. However, this ruling remains narrow. Patients must be counseled about mifepristone via telemedicine and sign a Patient Agreement Form, which must be returned electronically or by mail. Patients must receive a copy of the mifepristone medication guide, and dispensing of mifepristone must still be conducted by or under the supervision of a certified provider. The medication may not be dispensed by retail pharmacies, thus requiring providers to arrange for mailing of prescriptions to patients. Given state-based legal statutes regarding mailing of medications, this injunction may not lead to an immediate increase in access to care. In addition, patients seeking management for miscarriage must go to clinic to have mifepristone dispensed and thus risk exposure to viral transmission.
What now?
The regulation of mifepristone—in spite of excellent safety and specifically for the narrow purpose of administration in the setting of abortion and miscarriage care—is by definition a discriminatory practice against patients and providers. As clinicians, we are duty-bound to speak out against injustices to our practices and our patients. At a local level, we can work to implement safe practices in the setting of this injunction and continue to work on a national level to ensure this injunction becomes permanent and with more broad scope to eliminate all of the REMS requirements for mifepristone.
ACTION ITEMS
- Act locally! Are you an abortion provider? Contact your local ACLU (find them here) or lawyer in your area for assistance navigating the legal landscape to prescribe after this injunction.
- Act statewide! Press candidates in your state to stand up for science and data. Support legislative acts and bills that address combating discriminatory regulations.
- Act nationally! The President is responsible for appointing the Commissioner of the FDA and the Secretary of Health and Human Services (with Senate advice and consent). Who we elect matters. Seek out opportunities to become involved in increasing access to and awareness of voter registration and Election Day, and speak out against voter suppression. Make sure you are registered to vote here and check your area to review new recommendations amidst the pandemic.
Mifepristone is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated medication for managing miscarriage and for medical abortion when combined with misoprostol.1,2 Since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use in 2000, more than 4 million women have used this medication.3 The combination of mifepristone with misoprostol was used for 39% of all US abortions in 2017.4 Approximately 10% of all clinically recognized pregnancies end in miscarriages, and many are safely managed with either misoprostol alone or with the combination of mifepristone and misoprostol.5
The issue
The prescription and distribution of mifepristone is highly regulated by the FDA via requirements outlined in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) drug safety program. The FDA may determine a REMS is necessary for a specific drug to ensure the benefits of a drug outweigh the potential risks. A REMS may include an informative package insert for patients, follow-up communication to prescribers—including letters, safety protocols or recommended laboratory tests, or Elements to Assure Safe Use (ETASU). ETASU are types of REMS that are placed on medications that have significant potential for serious adverse effects, and without such restrictions FDA approval would be rescinded.
Are mifepristone requirements fairly applied?
The 3 ETASU restrictions on the distribution of mifepristone are in-person dispensation, prescriber certification, and patient signatures on special forms.6 The in-person dispensing requirement is applied to only 16 other medications (one of which is Mifeprex, the brand version of mifepristone), and Mifeprex/mifepristone are the only ones deemed safe for self-administration—meaning that patients receive the drug from a clinic but then may take it at a site of their choosing. The prescriber certification requirement places expectations on providers to account for distribution of doses and keep records of serial numbers (in effect, having clinicians act as both physician and pharmacist, as most medications are distributed and recorded in pharmacies). The patient form was recommended for elimination in 2016 due to its duplicative information and burden on patients—a recommendation that was then overruled by the FDA commissioner.7
These 3 requirements placed on mifepristone specifically target dosages for use related to abortions and miscarriages. Mifepristone is used to treat other medical conditions, with much higher doses, without the same restrictions—in fact, the FDA has allowed much higher doses of mifepristone to be mailed directly to a patient when prescribed for different disorders. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has long opposed the burdensome REMS requirements on mifepristone for reproductive health indications.8
Arguments regarding the safety of mifepristone must be understood in the context of how the medication is taken, and the unique difference with other medications that must be administered by physicians or in health care facilities. Mifepristone is self-administered, and the desired effect—evacuation of uterine contents—typically occurs after a patient takes the accompanying medication misoprostol, which is some 24 to 72 hours later. This timeframe makes it highly unlikely that any patient would be in the presence of their provider at the time of medication effect, thus an in-person dispensing requirement has no medical bearing on the outcome of the health of the patient.
REMS changes during the COVID-19 pandemic
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has necessarily changed the structure of REMS and ETASU requirements for many medications, with changes made in order to mitigate viral transmission through the limitation of unnecessary visits to clinics or hospitals. The FDA announced in March of 2020 that it would not enforce pre-prescription requirements, such as laboratory or magnetic resonance imaging results, for many medications (including those more toxic than mifepristone), and that it would lift the requirement for in-person dispensation of several medications.9 Also in March 2020 the Department of Health and Human Services Secretary (HHS) and the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) activated a “telemedicine exception” to allow physicians to use telemedicine to satisfy mandatory requirements for prescribing controlled substances, including opioids.10
Despite repeated pleas from organizations, individuals, and physician groups, the FDA continued to enforce the REMS/ETASU for mifepristone as the pandemic decimated communities. Importantly, the pandemic has not had an equal effect on all communities, and the disparities highlighted in outcomes as related to COVID-19 are also reflected in disparities to access to reproductive choices.11 By enforcing REMS/ETASU for mifepristone during a global pandemic, the FDA has placed additional burden on women and people who menstruate. As offices and clinics have closed, and as many jobs have evaporated, additional barriers have emerged, such as lack of childcare, fewer transportation options, and decreased clinic appointments.
As the pandemic continues to affect communities in the United States, ACOG has issued guidance recommending assessment for eligibility for medical abortion remotely, and has encouraged the use of telemedicine and other remote interactions for its members and patients to limit transmission of the virus.
The lawsuit
On May 27, 2020, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) (on behalf of ACOG, the Council of University Chairs of Obstetrics and Gynecology, New York State Academy of Family Physicians, SisterSong, and Honor MacNaughton, MD) filed a civil action against the FDA and HHS challenging the requirement for in-person dispensing of mifepristone and associated ETASU requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic. The plaintiffs sought this injunction based on the claim that these restrictions during the pandemic infringe on the constitutional rights to patients’ privacy and liberty and to equal protection of the law as protected by the Due Process Clause of the Fifth Amendment. Additionally, the ACLU and other organizations said these unnecessary restrictions place patients, providers, and staff at unnecessary risk of viral exposure amidst a global pandemic.
The verdict
On July 13, 2020, a federal court granted the preliminary injunction to suspend FDA’s enforcement of the in-person requirements of mifepristone for abortion during the COVID-19 pandemic. The court denied the motion for suspension of in-person restrictions as applied to miscarriage management. The preliminary injunction applies nationwide without geographic limitation. It will remain in effect until the end of the litigation or for 30 days following the expiration of the public health emergency.
What the outcome means
This injunction is a step in the right direction for patients and providers to allow for autonomy and clinical practice guided by clinician expertise. However, this ruling remains narrow. Patients must be counseled about mifepristone via telemedicine and sign a Patient Agreement Form, which must be returned electronically or by mail. Patients must receive a copy of the mifepristone medication guide, and dispensing of mifepristone must still be conducted by or under the supervision of a certified provider. The medication may not be dispensed by retail pharmacies, thus requiring providers to arrange for mailing of prescriptions to patients. Given state-based legal statutes regarding mailing of medications, this injunction may not lead to an immediate increase in access to care. In addition, patients seeking management for miscarriage must go to clinic to have mifepristone dispensed and thus risk exposure to viral transmission.
What now?
The regulation of mifepristone—in spite of excellent safety and specifically for the narrow purpose of administration in the setting of abortion and miscarriage care—is by definition a discriminatory practice against patients and providers. As clinicians, we are duty-bound to speak out against injustices to our practices and our patients. At a local level, we can work to implement safe practices in the setting of this injunction and continue to work on a national level to ensure this injunction becomes permanent and with more broad scope to eliminate all of the REMS requirements for mifepristone.
ACTION ITEMS
- Act locally! Are you an abortion provider? Contact your local ACLU (find them here) or lawyer in your area for assistance navigating the legal landscape to prescribe after this injunction.
- Act statewide! Press candidates in your state to stand up for science and data. Support legislative acts and bills that address combating discriminatory regulations.
- Act nationally! The President is responsible for appointing the Commissioner of the FDA and the Secretary of Health and Human Services (with Senate advice and consent). Who we elect matters. Seek out opportunities to become involved in increasing access to and awareness of voter registration and Election Day, and speak out against voter suppression. Make sure you are registered to vote here and check your area to review new recommendations amidst the pandemic.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin number 143: medical management of first trimester abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:676-692.
- Schreiber CA, Crenin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Danco Laboratories. Mifeprex effectiveness and advantages. https://www.earlyoptionpill.com/is-mifeprex-right-for-me/effectiveness-advantages/ Accessed August 2, 2020.
- Jones RK, Witwer E, Jerman J. Abortion incidence and service availability in the United States, 2017. September 2019. https://www.guttmacher.org/report/abortion-incidence-service-availability-us-2017. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 150: early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1258-1267.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) single shared system for mifepristone 200 mg. April 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/rems/Mifepristone_2019_04_11_REMS_Full.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 2016 REMS Review, Summary Review 25. March 29, 2016. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2016/020687Orig1s020SumR.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Improving access to mifepristone for reproductive health indications. June 2018. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/policy-and-position-statements/position-statements/2018/improving-access-to-mifepristone-for-reproductive-health-indications. Accessed August 2, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Policy for certain REMS requirements during the COVID-19 public health emergency: guidance for industry and health care professionals. March 2020. https://www.fda.gov/media/136317/download. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Department of Justice. US Drug Enforcement Administration. COVID-19 Information Page, Telemedicine. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/coronavirus.html#TELE. Accessed May 25, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019: health equity considerations and racial and ethnic minority groups. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/health-equity/race-ethnicity.html. Updated July 24, 2020. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin number 143: medical management of first trimester abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:676-692.
- Schreiber CA, Crenin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Danco Laboratories. Mifeprex effectiveness and advantages. https://www.earlyoptionpill.com/is-mifeprex-right-for-me/effectiveness-advantages/ Accessed August 2, 2020.
- Jones RK, Witwer E, Jerman J. Abortion incidence and service availability in the United States, 2017. September 2019. https://www.guttmacher.org/report/abortion-incidence-service-availability-us-2017. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 150: early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:1258-1267.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) single shared system for mifepristone 200 mg. April 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/rems/Mifepristone_2019_04_11_REMS_Full.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 2016 REMS Review, Summary Review 25. March 29, 2016. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2016/020687Orig1s020SumR.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Improving access to mifepristone for reproductive health indications. June 2018. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/policy-and-position-statements/position-statements/2018/improving-access-to-mifepristone-for-reproductive-health-indications. Accessed August 2, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Policy for certain REMS requirements during the COVID-19 public health emergency: guidance for industry and health care professionals. March 2020. https://www.fda.gov/media/136317/download. Accessed September 10, 2020.
- US Department of Justice. US Drug Enforcement Administration. COVID-19 Information Page, Telemedicine. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/coronavirus.html#TELE. Accessed May 25, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019: health equity considerations and racial and ethnic minority groups. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/health-equity/race-ethnicity.html. Updated July 24, 2020. Accessed September 10, 2020.
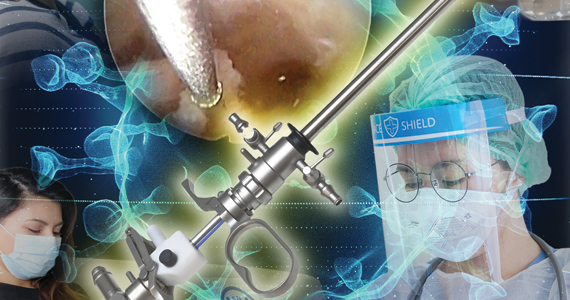
Hysteroscopy and COVID-19: Have recommended techniques changed due to the pandemic?
The emergence of the coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection (COVID-19) in December 2019, has resulted in a global pandemic that has challenged the medical community and will continue to represent a public health emergency for the next several months.1 It has rapidly spread globally, infecting many individuals in an unprecedented rate of infection and worldwide reach. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization designated COVID-19 as a pandemic. While the majority of infected individuals are asymptomatic or develop only mild symptoms, some have an unfortunate clinical course resulting in multi-organ failure and death.2
It is accepted that the virus mainly spreads during close contact and via respiratory droplets.3 The average time from infection to onset of symptoms ranges from 2 to 14 days, with an average of 5 days.4 Recommended measures to prevent the spread of the infection include social distancing (at least 6 feet from others), meticulous hand hygiene, and wearing a mask covering the mouth and nose when in public.5 Aiming to mitigate the risk of viral dissemination for patients and health care providers, and to preserve hospital resources, all nonessential medical interventions were initially suspended. Recently, the American College of Surgeons in a joint statement with 9 women’s health care societies have provided recommendations on how to resume clinical activities as we recover from the pandemic.6
As we reinitiate clinical activities, gynecologists have been alerted of the potential risk of viral dissemination during gynecologic minimally invasive surgical procedures due to the presence of the virus in blood, stool, and the potential risk of aerosolization of the virus, especially when using smoke-generating devices.7,8 This risk is not limited to intubation and extubation of the airway during anesthesia; the risk also presents itself during other aerosol-generating procedures, such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery.9,10
Hysteroscopy is considered the gold standard procedure for the diagnosis and management of intrauterine pathologies.11 It is frequently performed in an office setting without the use of anesthesia.11,12 It is usually well tolerated, with only a few patients reporting discomfort.12 It allows for immediate treatment (using the “see and treat” approach) while avoiding not only the risk of anesthesia, as stated, but also the need for intubation—which has a high risk of droplet contamination in COVID-19–infected individuals.13
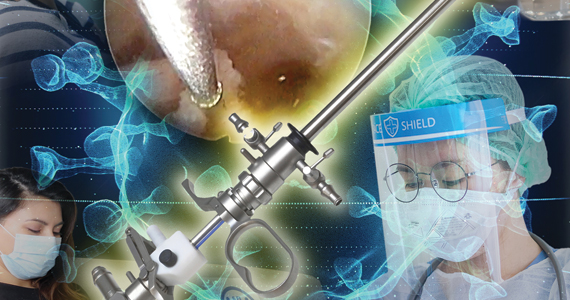
Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures?
The novel and rapidly changing nature of the COVID-19 pandemic present many challenges to the gynecologist. Significant concerns have been raised regarding potential risk of viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery due to aerosolization of viral particles and the presence of the virus in blood and the gastrointestinal tract of infected patients.7 Diagnostic, and some simple, hysteroscopic procedures are commonly performed in an outpatient setting, with the patient awake. Complex hysteroscopic interventions, however, are generally performed in the operating room, typically with the use of general anesthesia. Hysteroscopy has the theoretical risks of viral dissemination when performed in COVID-19–positive patients. Two important questions must be addressed to better understand the potential risk of COVID-19 viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures.
Continue to: 1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?...
1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?
Recent studies have confirmed the presence of viral particles in urine, feces, blood, and tears in addition to the respiratory tract in patients infected with COVID-19.3,14,15 The presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the female genital system is currently unknown. Previous studies, of other epidemic viral infections, have demonstrated the presence of the virus in the female genital tract in affected patients of Zika virus and Ebola.16,17 However, 2 recent studies have failed to demonstrate the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the vaginal fluid of pregnant14 and not pregnant18 women with severe COVID-19 infection.
2. Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopy if using electrosurgery?
There are significant concerns with possible risk of COVID-19 transmission to health care providers in direct contact with infected patients during minimally invasive gynecologic procedures due to direct contamination and aerosolization of the virus.10,19 Current data on COVID-19 transmission during surgery are limited. However, it is important to recognize that viral aerosolization has been documented with other viral diseases, such as human papillomavirus and hepatitis B.20 A recent report called for awareness in the surgical community about the potential risks of COVID-19 viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery. Among other recommendations, international experts advised minimizing the use of electrosurgery to reduce the creation of surgical plume, decreasing the pneumoperitoneum pressure to minimum levels, and using suction devices in a closed system.21 Although these preventive measures apply to laparoscopic surgery, it is important to consider that hysteroscopy is performed in a unique environment.
During hysteroscopy the uterine cavity is distended with a liquid medium (normal saline or electrolyte-free solutions); this is opposed to gynecologic laparoscopy, in which the peritoneal cavity is distended with carbon dioxide.22 The smoke produced with the use of hysteroscopic electrosurgical instruments generates bubbles that are immediately cooled down to the temperature of the distention media and subsequently dissolve into it. Therefore, there are no bubbles generated during hysteroscopic surgery that are subsequently released into the air. This results in a low risk for viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures. Nevertheless, the necessary precautions to minimize the risk of COVID-19 transmission during hysteroscopic intervention are extremely important.
Recommendations for hysteroscopic procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic
We provide our overall recommendations for hysteroscopy, as well as those specific to the office and hospital setting.
Recommendations: General
Limit hysteroscopic procedures to COVID-19–negative patients and to those patients in whom delaying the procedure could result in adverse clinical outcomes.23
Universally screen for potential COVID-19 infection. When possible, a phone interview to triage patients based on their symptoms and infection exposure status should take place before the patient arrives to the health care center. Patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection who require immediate evaluation should be directed to COVID-19–designated emergency areas.
Universally test for SARS-CoV-2 before procedures performed in the operating room (OR). Using nasopharyngeal swabs for the detection of viral RNA, employing molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), within 48 to 72 hours prior to all OR hysteroscopic procedures is strongly recommended. Adopting this testing strategy will aid to identify asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2‒infected patients, allowing to defer the procedure, if possible, among patients testing positive. If tests are limited, testing only patients scheduled for hysteroscopic procedures in which general or regional anesthesia will be required is acceptable.
Universal SARS-CoV-2 testing of patients undergoing in-office hysteroscopic diagnostic or minor operative procedures without the use of anesthesia is not required.
Limit the presence of a companion. It is understood that visitor policies may vary at the discretion of each institution’s guidelines. Children and individuals over the age of 60 years should not be granted access to the center. Companions will be subjected to the same screening criteria as patients.
Provide for social distancing and other precautionary measures. If more than one patient is scheduled to be at the facility at the same time, ensure that the facility provides adequate space to allow the appropriate social distancing recommendations between patients. Hand sanitizers and facemasks should be available for patients and companions.
Provide PPE for clinicians. All health care providers in close contact with the patient must wear personal protective equipment (PPE), which includes an apron and gown, a surgical mask, eye protection, and gloves. Health care providers should wear PPE deemed appropriate by their regulatory institutions following their local and national guidelines during clinical patient interactions.
Restrict surgical attendees to vital personnel. The participation of learners by physical presence in the office or operating room should be restricted.
Continue to: Recommendations: Office setting...
Recommendations: Office setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Advise patients to come to the office alone. If the patient requires a companion, a maximum of one adult companion under the age of 60 should be accepted.
- Limit the number of health care team members present in the procedure room.
Intraprocedural recommendations
- Choose the appropriate device(s) that will allow for an effective and fast procedure.
- Use the recommended PPE for all clinicians.
- Limit the movement of staff members in and out of the procedure room.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same procedure room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Allow for patients to recover from the procedure in the same room as the procedure took place in order to avoid potential contamination of multiple rooms.
- Expedite patient discharge.
- Follow up after the procedure by phone or telemedicine.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Continue to: Recommendations: Operating room setting...
Recommendations: Operating room setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Perform adequate patient screening for potential COVID-19 infection. (Screening should be independent of symptoms and not be limited to those with clinical symptoms.)
- Limit the number of health care team members in the operating procedure room.
- To minimize unnecessary staff exposure, have surgeons and staff not needed for intubation remain outside the OR until intubation is completed and leave the OR before extubation.
Intraprocedure recommendations
- Limit personnel in the OR to a minimum.
- Staff should not enter or leave the room during the procedure.
- When possible, use conscious sedation or regional anesthesia to avoid the risk of viral dissemination at the time of intubation/extubation.
- Choose the device that will allow an effective and fast procedure.
- Favor non–smoke-generating devices, such as hysteroscopic scissors, graspers, and tissue retrieval systems.
- Connect active suction to the outflow, especially when using smoke-generating instruments, to facilitate the extraction of surgical smoke.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Expedite postprocedure recovery and patient discharge.
- After completion of the procedure, staff should remove scrubs and change into clean clothing.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a global health emergency. Our knowledge of this devastating virus is constantly evolving as we continue to fight this overwhelming disease. Theoretical risk of “viral” dissemination is considered extremely low, or negligible, during hysterosocopy. Hysteroscopic procedures in COVID-19–positive patients with life-threatening conditions or in patients in whom delaying the procedure could worsen outcomes should be performed taking appropriate measures. Patients who test negative for COVID-19 (confirmed by PCR) and require hysteroscopic procedures, should be treated using universal precautions. ●
- Al-Shamsi HO, Alhazzani W, Alhuraiji A, et al. A practical approach to the management of cancer patients during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: an international collaborative group. Oncologist. 2020;25:e936-e945.
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. February 24, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
- Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA. 2020;323:1843-1844.
- Yu F, Yan L, Wang N, et al. Quantitative detection and viral load analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in infected patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:793-798.
- Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, et al; Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases COVID-19 Working Group. The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e261-e270.
- American College of Surgeons, American Society of Aesthesiologists, Association of periOperative Registered Nurses, American Hospital Association. Joint Statement: Roadmap for resuming elective surgery after COVID-19 pandemic. April 16, 2020. https://www.aorn.org/guidelines/aorn-support/roadmap-for-resuming-elective-surgery-after-covid-19. Accessed August 27, 2020.
- Zhang W, Du RH, Li B, et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:386-389.
- Mowbray NG, Ansell J, Horwood J, et al. Safe management of surgical smoke in the age of COVID-19. Br J Surg. May 3, 2020. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11679.
- Cohen SL, Liu G, Abrao M, et al. Perspectives on surgery in the time of COVID-19: safety first. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:792-793.
- COVID-19: protecting health-care workers. Lancet. 2020;395:922.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Cicinelli E. Hysteroscopy without anesthesia: review of recent literature. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:703-708.
- Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anaesth. 2020;67:568-576.
- Aslan MM, Yuvaci HU, Köse O, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not present in the vaginal fluid of pregnant women with COVID-19. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020:1-3. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1793318.
- Chen Y, Chen L, Deng Q, et al. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92:833-840.
- Prisant N, Bujan L, Benichou H, et al. Zika virus in the female genital tract. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:1000-1001.
- Rodriguez LL, De Roo A, Guimard Y, et al. Persistence and genetic stability of Ebola virus during the outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179 Suppl 1:S170-S176.
- Qiu L, Liu X, Xiao M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not detectable in the vaginal fluid of women with severe COVID-19 infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:813-817.
- Brat GA, Hersey S, Chhabra K, et al. Protecting surgical teams during the COVID-19 outbreak: a narrative review and clinical considerations. Ann Surg. April 17, 2020. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003926.
- Kwak HD, Kim SH, Seo YS, et al. Detecting hepatitis B virus in surgical smoke emitted during laparoscopic surgery. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73:857-863.
- Zheng MH, Boni L, Fingerhut A. Minimally invasive surgery and the novel coronavirus outbreak: lessons learned in China and Italy. Ann Surg. 2020;272:e5-e6.
- Catena U. Surgical smoke in hysteroscopic surgery: does it really matter in COVID-19 times? Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2020;12:67-68.
- Carugno J, Di Spiezio Sardo A, Alonso L, et al. COVID-19 pandemic. Impact on hysteroscopic procedures: a consensus statement from the Global Congress of Hysteroscopy Scientific Committee. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:988-992.
The emergence of the coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection (COVID-19) in December 2019, has resulted in a global pandemic that has challenged the medical community and will continue to represent a public health emergency for the next several months.1 It has rapidly spread globally, infecting many individuals in an unprecedented rate of infection and worldwide reach. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization designated COVID-19 as a pandemic. While the majority of infected individuals are asymptomatic or develop only mild symptoms, some have an unfortunate clinical course resulting in multi-organ failure and death.2
It is accepted that the virus mainly spreads during close contact and via respiratory droplets.3 The average time from infection to onset of symptoms ranges from 2 to 14 days, with an average of 5 days.4 Recommended measures to prevent the spread of the infection include social distancing (at least 6 feet from others), meticulous hand hygiene, and wearing a mask covering the mouth and nose when in public.5 Aiming to mitigate the risk of viral dissemination for patients and health care providers, and to preserve hospital resources, all nonessential medical interventions were initially suspended. Recently, the American College of Surgeons in a joint statement with 9 women’s health care societies have provided recommendations on how to resume clinical activities as we recover from the pandemic.6
As we reinitiate clinical activities, gynecologists have been alerted of the potential risk of viral dissemination during gynecologic minimally invasive surgical procedures due to the presence of the virus in blood, stool, and the potential risk of aerosolization of the virus, especially when using smoke-generating devices.7,8 This risk is not limited to intubation and extubation of the airway during anesthesia; the risk also presents itself during other aerosol-generating procedures, such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery.9,10
Hysteroscopy is considered the gold standard procedure for the diagnosis and management of intrauterine pathologies.11 It is frequently performed in an office setting without the use of anesthesia.11,12 It is usually well tolerated, with only a few patients reporting discomfort.12 It allows for immediate treatment (using the “see and treat” approach) while avoiding not only the risk of anesthesia, as stated, but also the need for intubation—which has a high risk of droplet contamination in COVID-19–infected individuals.13

Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures?
The novel and rapidly changing nature of the COVID-19 pandemic present many challenges to the gynecologist. Significant concerns have been raised regarding potential risk of viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery due to aerosolization of viral particles and the presence of the virus in blood and the gastrointestinal tract of infected patients.7 Diagnostic, and some simple, hysteroscopic procedures are commonly performed in an outpatient setting, with the patient awake. Complex hysteroscopic interventions, however, are generally performed in the operating room, typically with the use of general anesthesia. Hysteroscopy has the theoretical risks of viral dissemination when performed in COVID-19–positive patients. Two important questions must be addressed to better understand the potential risk of COVID-19 viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures.
Continue to: 1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?...
1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?
Recent studies have confirmed the presence of viral particles in urine, feces, blood, and tears in addition to the respiratory tract in patients infected with COVID-19.3,14,15 The presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the female genital system is currently unknown. Previous studies, of other epidemic viral infections, have demonstrated the presence of the virus in the female genital tract in affected patients of Zika virus and Ebola.16,17 However, 2 recent studies have failed to demonstrate the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the vaginal fluid of pregnant14 and not pregnant18 women with severe COVID-19 infection.
2. Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopy if using electrosurgery?
There are significant concerns with possible risk of COVID-19 transmission to health care providers in direct contact with infected patients during minimally invasive gynecologic procedures due to direct contamination and aerosolization of the virus.10,19 Current data on COVID-19 transmission during surgery are limited. However, it is important to recognize that viral aerosolization has been documented with other viral diseases, such as human papillomavirus and hepatitis B.20 A recent report called for awareness in the surgical community about the potential risks of COVID-19 viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery. Among other recommendations, international experts advised minimizing the use of electrosurgery to reduce the creation of surgical plume, decreasing the pneumoperitoneum pressure to minimum levels, and using suction devices in a closed system.21 Although these preventive measures apply to laparoscopic surgery, it is important to consider that hysteroscopy is performed in a unique environment.
During hysteroscopy the uterine cavity is distended with a liquid medium (normal saline or electrolyte-free solutions); this is opposed to gynecologic laparoscopy, in which the peritoneal cavity is distended with carbon dioxide.22 The smoke produced with the use of hysteroscopic electrosurgical instruments generates bubbles that are immediately cooled down to the temperature of the distention media and subsequently dissolve into it. Therefore, there are no bubbles generated during hysteroscopic surgery that are subsequently released into the air. This results in a low risk for viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures. Nevertheless, the necessary precautions to minimize the risk of COVID-19 transmission during hysteroscopic intervention are extremely important.
Recommendations for hysteroscopic procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic
We provide our overall recommendations for hysteroscopy, as well as those specific to the office and hospital setting.
Recommendations: General
Limit hysteroscopic procedures to COVID-19–negative patients and to those patients in whom delaying the procedure could result in adverse clinical outcomes.23
Universally screen for potential COVID-19 infection. When possible, a phone interview to triage patients based on their symptoms and infection exposure status should take place before the patient arrives to the health care center. Patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection who require immediate evaluation should be directed to COVID-19–designated emergency areas.
Universally test for SARS-CoV-2 before procedures performed in the operating room (OR). Using nasopharyngeal swabs for the detection of viral RNA, employing molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), within 48 to 72 hours prior to all OR hysteroscopic procedures is strongly recommended. Adopting this testing strategy will aid to identify asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2‒infected patients, allowing to defer the procedure, if possible, among patients testing positive. If tests are limited, testing only patients scheduled for hysteroscopic procedures in which general or regional anesthesia will be required is acceptable.
Universal SARS-CoV-2 testing of patients undergoing in-office hysteroscopic diagnostic or minor operative procedures without the use of anesthesia is not required.
Limit the presence of a companion. It is understood that visitor policies may vary at the discretion of each institution’s guidelines. Children and individuals over the age of 60 years should not be granted access to the center. Companions will be subjected to the same screening criteria as patients.
Provide for social distancing and other precautionary measures. If more than one patient is scheduled to be at the facility at the same time, ensure that the facility provides adequate space to allow the appropriate social distancing recommendations between patients. Hand sanitizers and facemasks should be available for patients and companions.
Provide PPE for clinicians. All health care providers in close contact with the patient must wear personal protective equipment (PPE), which includes an apron and gown, a surgical mask, eye protection, and gloves. Health care providers should wear PPE deemed appropriate by their regulatory institutions following their local and national guidelines during clinical patient interactions.
Restrict surgical attendees to vital personnel. The participation of learners by physical presence in the office or operating room should be restricted.
Continue to: Recommendations: Office setting...
Recommendations: Office setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Advise patients to come to the office alone. If the patient requires a companion, a maximum of one adult companion under the age of 60 should be accepted.
- Limit the number of health care team members present in the procedure room.
Intraprocedural recommendations
- Choose the appropriate device(s) that will allow for an effective and fast procedure.
- Use the recommended PPE for all clinicians.
- Limit the movement of staff members in and out of the procedure room.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same procedure room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Allow for patients to recover from the procedure in the same room as the procedure took place in order to avoid potential contamination of multiple rooms.
- Expedite patient discharge.
- Follow up after the procedure by phone or telemedicine.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Continue to: Recommendations: Operating room setting...
Recommendations: Operating room setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Perform adequate patient screening for potential COVID-19 infection. (Screening should be independent of symptoms and not be limited to those with clinical symptoms.)
- Limit the number of health care team members in the operating procedure room.
- To minimize unnecessary staff exposure, have surgeons and staff not needed for intubation remain outside the OR until intubation is completed and leave the OR before extubation.
Intraprocedure recommendations
- Limit personnel in the OR to a minimum.
- Staff should not enter or leave the room during the procedure.
- When possible, use conscious sedation or regional anesthesia to avoid the risk of viral dissemination at the time of intubation/extubation.
- Choose the device that will allow an effective and fast procedure.
- Favor non–smoke-generating devices, such as hysteroscopic scissors, graspers, and tissue retrieval systems.
- Connect active suction to the outflow, especially when using smoke-generating instruments, to facilitate the extraction of surgical smoke.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Expedite postprocedure recovery and patient discharge.
- After completion of the procedure, staff should remove scrubs and change into clean clothing.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a global health emergency. Our knowledge of this devastating virus is constantly evolving as we continue to fight this overwhelming disease. Theoretical risk of “viral” dissemination is considered extremely low, or negligible, during hysterosocopy. Hysteroscopic procedures in COVID-19–positive patients with life-threatening conditions or in patients in whom delaying the procedure could worsen outcomes should be performed taking appropriate measures. Patients who test negative for COVID-19 (confirmed by PCR) and require hysteroscopic procedures, should be treated using universal precautions. ●
The emergence of the coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection (COVID-19) in December 2019, has resulted in a global pandemic that has challenged the medical community and will continue to represent a public health emergency for the next several months.1 It has rapidly spread globally, infecting many individuals in an unprecedented rate of infection and worldwide reach. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization designated COVID-19 as a pandemic. While the majority of infected individuals are asymptomatic or develop only mild symptoms, some have an unfortunate clinical course resulting in multi-organ failure and death.2
It is accepted that the virus mainly spreads during close contact and via respiratory droplets.3 The average time from infection to onset of symptoms ranges from 2 to 14 days, with an average of 5 days.4 Recommended measures to prevent the spread of the infection include social distancing (at least 6 feet from others), meticulous hand hygiene, and wearing a mask covering the mouth and nose when in public.5 Aiming to mitigate the risk of viral dissemination for patients and health care providers, and to preserve hospital resources, all nonessential medical interventions were initially suspended. Recently, the American College of Surgeons in a joint statement with 9 women’s health care societies have provided recommendations on how to resume clinical activities as we recover from the pandemic.6
As we reinitiate clinical activities, gynecologists have been alerted of the potential risk of viral dissemination during gynecologic minimally invasive surgical procedures due to the presence of the virus in blood, stool, and the potential risk of aerosolization of the virus, especially when using smoke-generating devices.7,8 This risk is not limited to intubation and extubation of the airway during anesthesia; the risk also presents itself during other aerosol-generating procedures, such as laparoscopy or robotic surgery.9,10
Hysteroscopy is considered the gold standard procedure for the diagnosis and management of intrauterine pathologies.11 It is frequently performed in an office setting without the use of anesthesia.11,12 It is usually well tolerated, with only a few patients reporting discomfort.12 It allows for immediate treatment (using the “see and treat” approach) while avoiding not only the risk of anesthesia, as stated, but also the need for intubation—which has a high risk of droplet contamination in COVID-19–infected individuals.13

Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures?
The novel and rapidly changing nature of the COVID-19 pandemic present many challenges to the gynecologist. Significant concerns have been raised regarding potential risk of viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery due to aerosolization of viral particles and the presence of the virus in blood and the gastrointestinal tract of infected patients.7 Diagnostic, and some simple, hysteroscopic procedures are commonly performed in an outpatient setting, with the patient awake. Complex hysteroscopic interventions, however, are generally performed in the operating room, typically with the use of general anesthesia. Hysteroscopy has the theoretical risks of viral dissemination when performed in COVID-19–positive patients. Two important questions must be addressed to better understand the potential risk of COVID-19 viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures.
Continue to: 1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?...
1. Is the virus present in the vaginal fluid of women infected with COVID-19?
Recent studies have confirmed the presence of viral particles in urine, feces, blood, and tears in addition to the respiratory tract in patients infected with COVID-19.3,14,15 The presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the female genital system is currently unknown. Previous studies, of other epidemic viral infections, have demonstrated the presence of the virus in the female genital tract in affected patients of Zika virus and Ebola.16,17 However, 2 recent studies have failed to demonstrate the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the vaginal fluid of pregnant14 and not pregnant18 women with severe COVID-19 infection.
2. Is there risk of viral dissemination during hysteroscopy if using electrosurgery?
There are significant concerns with possible risk of COVID-19 transmission to health care providers in direct contact with infected patients during minimally invasive gynecologic procedures due to direct contamination and aerosolization of the virus.10,19 Current data on COVID-19 transmission during surgery are limited. However, it is important to recognize that viral aerosolization has been documented with other viral diseases, such as human papillomavirus and hepatitis B.20 A recent report called for awareness in the surgical community about the potential risks of COVID-19 viral dissemination during laparoscopic surgery. Among other recommendations, international experts advised minimizing the use of electrosurgery to reduce the creation of surgical plume, decreasing the pneumoperitoneum pressure to minimum levels, and using suction devices in a closed system.21 Although these preventive measures apply to laparoscopic surgery, it is important to consider that hysteroscopy is performed in a unique environment.
During hysteroscopy the uterine cavity is distended with a liquid medium (normal saline or electrolyte-free solutions); this is opposed to gynecologic laparoscopy, in which the peritoneal cavity is distended with carbon dioxide.22 The smoke produced with the use of hysteroscopic electrosurgical instruments generates bubbles that are immediately cooled down to the temperature of the distention media and subsequently dissolve into it. Therefore, there are no bubbles generated during hysteroscopic surgery that are subsequently released into the air. This results in a low risk for viral dissemination during hysteroscopic procedures. Nevertheless, the necessary precautions to minimize the risk of COVID-19 transmission during hysteroscopic intervention are extremely important.
Recommendations for hysteroscopic procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic
We provide our overall recommendations for hysteroscopy, as well as those specific to the office and hospital setting.
Recommendations: General
Limit hysteroscopic procedures to COVID-19–negative patients and to those patients in whom delaying the procedure could result in adverse clinical outcomes.23
Universally screen for potential COVID-19 infection. When possible, a phone interview to triage patients based on their symptoms and infection exposure status should take place before the patient arrives to the health care center. Patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection who require immediate evaluation should be directed to COVID-19–designated emergency areas.
Universally test for SARS-CoV-2 before procedures performed in the operating room (OR). Using nasopharyngeal swabs for the detection of viral RNA, employing molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), within 48 to 72 hours prior to all OR hysteroscopic procedures is strongly recommended. Adopting this testing strategy will aid to identify asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2‒infected patients, allowing to defer the procedure, if possible, among patients testing positive. If tests are limited, testing only patients scheduled for hysteroscopic procedures in which general or regional anesthesia will be required is acceptable.
Universal SARS-CoV-2 testing of patients undergoing in-office hysteroscopic diagnostic or minor operative procedures without the use of anesthesia is not required.
Limit the presence of a companion. It is understood that visitor policies may vary at the discretion of each institution’s guidelines. Children and individuals over the age of 60 years should not be granted access to the center. Companions will be subjected to the same screening criteria as patients.
Provide for social distancing and other precautionary measures. If more than one patient is scheduled to be at the facility at the same time, ensure that the facility provides adequate space to allow the appropriate social distancing recommendations between patients. Hand sanitizers and facemasks should be available for patients and companions.
Provide PPE for clinicians. All health care providers in close contact with the patient must wear personal protective equipment (PPE), which includes an apron and gown, a surgical mask, eye protection, and gloves. Health care providers should wear PPE deemed appropriate by their regulatory institutions following their local and national guidelines during clinical patient interactions.
Restrict surgical attendees to vital personnel. The participation of learners by physical presence in the office or operating room should be restricted.
Continue to: Recommendations: Office setting...
Recommendations: Office setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Advise patients to come to the office alone. If the patient requires a companion, a maximum of one adult companion under the age of 60 should be accepted.
- Limit the number of health care team members present in the procedure room.
Intraprocedural recommendations
- Choose the appropriate device(s) that will allow for an effective and fast procedure.
- Use the recommended PPE for all clinicians.
- Limit the movement of staff members in and out of the procedure room.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same procedure room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Allow for patients to recover from the procedure in the same room as the procedure took place in order to avoid potential contamination of multiple rooms.
- Expedite patient discharge.
- Follow up after the procedure by phone or telemedicine.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Continue to: Recommendations: Operating room setting...
Recommendations: Operating room setting
Preprocedural recommendations
- Perform adequate patient screening for potential COVID-19 infection. (Screening should be independent of symptoms and not be limited to those with clinical symptoms.)
- Limit the number of health care team members in the operating procedure room.
- To minimize unnecessary staff exposure, have surgeons and staff not needed for intubation remain outside the OR until intubation is completed and leave the OR before extubation.
Intraprocedure recommendations
- Limit personnel in the OR to a minimum.
- Staff should not enter or leave the room during the procedure.
- When possible, use conscious sedation or regional anesthesia to avoid the risk of viral dissemination at the time of intubation/extubation.
- Choose the device that will allow an effective and fast procedure.
- Favor non–smoke-generating devices, such as hysteroscopic scissors, graspers, and tissue retrieval systems.
- Connect active suction to the outflow, especially when using smoke-generating instruments, to facilitate the extraction of surgical smoke.
Postprocedure recommendations
- When more than one case is scheduled to be performed in the same room, allow enough time in between cases to grant a thorough OR decontamination.
- Expedite postprocedure recovery and patient discharge.
- After completion of the procedure, staff should remove scrubs and change into clean clothing.
- Use standard endoscope disinfection procedures, as they are effective and should not be modified.
Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a global health emergency. Our knowledge of this devastating virus is constantly evolving as we continue to fight this overwhelming disease. Theoretical risk of “viral” dissemination is considered extremely low, or negligible, during hysterosocopy. Hysteroscopic procedures in COVID-19–positive patients with life-threatening conditions or in patients in whom delaying the procedure could worsen outcomes should be performed taking appropriate measures. Patients who test negative for COVID-19 (confirmed by PCR) and require hysteroscopic procedures, should be treated using universal precautions. ●
- Al-Shamsi HO, Alhazzani W, Alhuraiji A, et al. A practical approach to the management of cancer patients during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: an international collaborative group. Oncologist. 2020;25:e936-e945.
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. February 24, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
- Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA. 2020;323:1843-1844.
- Yu F, Yan L, Wang N, et al. Quantitative detection and viral load analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in infected patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:793-798.
- Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, et al; Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases COVID-19 Working Group. The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e261-e270.
- American College of Surgeons, American Society of Aesthesiologists, Association of periOperative Registered Nurses, American Hospital Association. Joint Statement: Roadmap for resuming elective surgery after COVID-19 pandemic. April 16, 2020. https://www.aorn.org/guidelines/aorn-support/roadmap-for-resuming-elective-surgery-after-covid-19. Accessed August 27, 2020.
- Zhang W, Du RH, Li B, et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:386-389.
- Mowbray NG, Ansell J, Horwood J, et al. Safe management of surgical smoke in the age of COVID-19. Br J Surg. May 3, 2020. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11679.
- Cohen SL, Liu G, Abrao M, et al. Perspectives on surgery in the time of COVID-19: safety first. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:792-793.
- COVID-19: protecting health-care workers. Lancet. 2020;395:922.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Cicinelli E. Hysteroscopy without anesthesia: review of recent literature. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:703-708.
- Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anaesth. 2020;67:568-576.
- Aslan MM, Yuvaci HU, Köse O, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not present in the vaginal fluid of pregnant women with COVID-19. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020:1-3. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1793318.
- Chen Y, Chen L, Deng Q, et al. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92:833-840.
- Prisant N, Bujan L, Benichou H, et al. Zika virus in the female genital tract. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:1000-1001.
- Rodriguez LL, De Roo A, Guimard Y, et al. Persistence and genetic stability of Ebola virus during the outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179 Suppl 1:S170-S176.
- Qiu L, Liu X, Xiao M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not detectable in the vaginal fluid of women with severe COVID-19 infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:813-817.
- Brat GA, Hersey S, Chhabra K, et al. Protecting surgical teams during the COVID-19 outbreak: a narrative review and clinical considerations. Ann Surg. April 17, 2020. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003926.
- Kwak HD, Kim SH, Seo YS, et al. Detecting hepatitis B virus in surgical smoke emitted during laparoscopic surgery. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73:857-863.
- Zheng MH, Boni L, Fingerhut A. Minimally invasive surgery and the novel coronavirus outbreak: lessons learned in China and Italy. Ann Surg. 2020;272:e5-e6.
- Catena U. Surgical smoke in hysteroscopic surgery: does it really matter in COVID-19 times? Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2020;12:67-68.
- Carugno J, Di Spiezio Sardo A, Alonso L, et al. COVID-19 pandemic. Impact on hysteroscopic procedures: a consensus statement from the Global Congress of Hysteroscopy Scientific Committee. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:988-992.
- Al-Shamsi HO, Alhazzani W, Alhuraiji A, et al. A practical approach to the management of cancer patients during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: an international collaborative group. Oncologist. 2020;25:e936-e945.
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. February 24, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
- Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA. 2020;323:1843-1844.
- Yu F, Yan L, Wang N, et al. Quantitative detection and viral load analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in infected patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:793-798.
- Prem K, Liu Y, Russell TW, et al; Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases COVID-19 Working Group. The effect of control strategies to reduce social mixing on outcomes of the COVID-19 epidemic in Wuhan, China: a modelling study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e261-e270.
- American College of Surgeons, American Society of Aesthesiologists, Association of periOperative Registered Nurses, American Hospital Association. Joint Statement: Roadmap for resuming elective surgery after COVID-19 pandemic. April 16, 2020. https://www.aorn.org/guidelines/aorn-support/roadmap-for-resuming-elective-surgery-after-covid-19. Accessed August 27, 2020.
- Zhang W, Du RH, Li B, et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:386-389.
- Mowbray NG, Ansell J, Horwood J, et al. Safe management of surgical smoke in the age of COVID-19. Br J Surg. May 3, 2020. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11679.
- Cohen SL, Liu G, Abrao M, et al. Perspectives on surgery in the time of COVID-19: safety first. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:792-793.
- COVID-19: protecting health-care workers. Lancet. 2020;395:922.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Cicinelli E. Hysteroscopy without anesthesia: review of recent literature. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:703-708.
- Wax RS, Christian MD. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anaesth. 2020;67:568-576.
- Aslan MM, Yuvaci HU, Köse O, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not present in the vaginal fluid of pregnant women with COVID-19. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020:1-3. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1793318.
- Chen Y, Chen L, Deng Q, et al. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92:833-840.
- Prisant N, Bujan L, Benichou H, et al. Zika virus in the female genital tract. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:1000-1001.
- Rodriguez LL, De Roo A, Guimard Y, et al. Persistence and genetic stability of Ebola virus during the outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179 Suppl 1:S170-S176.
- Qiu L, Liu X, Xiao M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is not detectable in the vaginal fluid of women with severe COVID-19 infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:813-817.
- Brat GA, Hersey S, Chhabra K, et al. Protecting surgical teams during the COVID-19 outbreak: a narrative review and clinical considerations. Ann Surg. April 17, 2020. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003926.
- Kwak HD, Kim SH, Seo YS, et al. Detecting hepatitis B virus in surgical smoke emitted during laparoscopic surgery. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73:857-863.
- Zheng MH, Boni L, Fingerhut A. Minimally invasive surgery and the novel coronavirus outbreak: lessons learned in China and Italy. Ann Surg. 2020;272:e5-e6.
- Catena U. Surgical smoke in hysteroscopic surgery: does it really matter in COVID-19 times? Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2020;12:67-68.
- Carugno J, Di Spiezio Sardo A, Alonso L, et al. COVID-19 pandemic. Impact on hysteroscopic procedures: a consensus statement from the Global Congress of Hysteroscopy Scientific Committee. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:988-992.
Identifying ovarian malignancy is not so easy
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at [email protected].
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at [email protected].
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at [email protected].
How to evaluate a suspicious ovarian mass
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.
Patients may prefer retrograde-fill voiding trials after pelvic floor surgery
Voiding trials after female pelvic floor surgery may detect similar rates of voiding dysfunction regardless of whether voiding occurs spontaneously or after the bladder is retrograde-filled with saline, according to a randomized study.
Nevertheless, patients may prefer the more common retrograde-fill approach.
In the study of 109 patients, those who underwent retrograde fill reported significantly greater satisfaction with their method of voiding evaluation, compared with patients whose voiding trials occurred spontaneously. The increased satisfaction could relate to the fact that retrograde-fill trials take less time, study investigator Patrick Popiel, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. The exact reasons are unclear, however.
Voiding trials help identify patients who cannot sufficiently empty their bladder after surgery. Prior research has indicated that the incidence of voiding dysfunction after pelvic floor surgery is about 25%-35%. “Patients with voiding dysfunction are generally managed with an indwelling Foley catheter or clean intermittent self-catheterization,” Dr. Popiel said. “Catheterization increases the risk of urinary tract infection, increases anxiety, and decreases patient satisfaction. A large proportion of patients who are discharged home with a Foley catheter state that the catheter was the worst aspect of their experience.”
Dr. Popiel and colleagues conducted a randomized, prospective study to examine the rate of failed voiding trials that necessitate discharge home with an indwelling Foley catheter using spontaneous and retrograde-fill approaches. The study included women who required a voiding trial after surgery for pelvic organ prolapse or urinary incontinence. Patients who required prolonged catheterization after surgery, such as those with a urinary tract infection, bowel injury, or large amount of blood loss, were excluded.
Researchers analyzed data from 55 patients who were randomly assigned to the retrograde-fill group and 54 patients who were randomly assigned to the spontaneous trial group.
In the spontaneous group, patients were required to void at least 150 mL at one time within 6 hours of catheter removal to successfully complete the voiding trial.
In the retrograde-fill group, the bladder was filled in the postanesthesia care unit with 300 mL of saline or until the maximum volume tolerated by the patient (not exceeding 300 mL ) was reached. Patients in this group had to void at least 150 mL or 50% of the instilled volume at one time within 60 minutes of catheter removal to pass the trial.
The researchers documented postvoid residual (PVR) but did not use this measure to determine voiding function.
The baseline demographics of the two groups were similar, although prior hysterectomy was more common in the retrograde-fill group than in the spontaneous group (32.7% vs. 14.8%). The average age was 58.5 years in the retrograde-fill group and 61 years in the spontaneous group.
“There was no significant difference in our primary outcome,” Dr. Popiel said. “There was a 12.7% rate of failed voiding trial in the retrograde group versus 7.7% in the spontaneous group.”
No patients had urinary retention after initially passing their voiding trial. Force of stream did not differ between groups, and about 15% in each group had a postoperative urinary tract infection.
The study demonstrates that voiding assessment based on a spontaneous minimum void of 150 mL is safe and has similar pass rates, compared with the more commonly performed retrograde void trial, Dr. Popiel said. “If the voided amount is at least 150 mL, PVR is not critical to obtain. The study adds to the body of literature that supports less stringent criteria for evaluating voiding function and can limit postoperative urinary recatheterization.”
The investigators allowed patients with PVRs as high as 575 mL to return home without an alternative way to empty the bladder, C. Sage Claydon, MD, a urogynecologist who was not involved in the study, noted during a discussion after the presentation. In all, 6 patients who met the passing criteria for the spontaneous voiding trial had a PVR greater than 200 mL, with volumes ranging from 205-575 mL.
The patients received standardized counseling about postoperative voiding problems, said Dr. Popiel. “This is similar to the work done by Ingber et al. from 2011, where patients who reached a certain force of stream, greater than 5 out of 10, were discharged home regardless of PVR.”
Dr. Popiel had no relevant disclosures. Two coinvestigators disclosed ties to BlossomMed, Renovia, and ArmadaHealth.
SOURCE: Popiel P et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
Voiding trials after female pelvic floor surgery may detect similar rates of voiding dysfunction regardless of whether voiding occurs spontaneously or after the bladder is retrograde-filled with saline, according to a randomized study.
Nevertheless, patients may prefer the more common retrograde-fill approach.
In the study of 109 patients, those who underwent retrograde fill reported significantly greater satisfaction with their method of voiding evaluation, compared with patients whose voiding trials occurred spontaneously. The increased satisfaction could relate to the fact that retrograde-fill trials take less time, study investigator Patrick Popiel, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. The exact reasons are unclear, however.
Voiding trials help identify patients who cannot sufficiently empty their bladder after surgery. Prior research has indicated that the incidence of voiding dysfunction after pelvic floor surgery is about 25%-35%. “Patients with voiding dysfunction are generally managed with an indwelling Foley catheter or clean intermittent self-catheterization,” Dr. Popiel said. “Catheterization increases the risk of urinary tract infection, increases anxiety, and decreases patient satisfaction. A large proportion of patients who are discharged home with a Foley catheter state that the catheter was the worst aspect of their experience.”
Dr. Popiel and colleagues conducted a randomized, prospective study to examine the rate of failed voiding trials that necessitate discharge home with an indwelling Foley catheter using spontaneous and retrograde-fill approaches. The study included women who required a voiding trial after surgery for pelvic organ prolapse or urinary incontinence. Patients who required prolonged catheterization after surgery, such as those with a urinary tract infection, bowel injury, or large amount of blood loss, were excluded.
Researchers analyzed data from 55 patients who were randomly assigned to the retrograde-fill group and 54 patients who were randomly assigned to the spontaneous trial group.
In the spontaneous group, patients were required to void at least 150 mL at one time within 6 hours of catheter removal to successfully complete the voiding trial.
In the retrograde-fill group, the bladder was filled in the postanesthesia care unit with 300 mL of saline or until the maximum volume tolerated by the patient (not exceeding 300 mL ) was reached. Patients in this group had to void at least 150 mL or 50% of the instilled volume at one time within 60 minutes of catheter removal to pass the trial.
The researchers documented postvoid residual (PVR) but did not use this measure to determine voiding function.
The baseline demographics of the two groups were similar, although prior hysterectomy was more common in the retrograde-fill group than in the spontaneous group (32.7% vs. 14.8%). The average age was 58.5 years in the retrograde-fill group and 61 years in the spontaneous group.
“There was no significant difference in our primary outcome,” Dr. Popiel said. “There was a 12.7% rate of failed voiding trial in the retrograde group versus 7.7% in the spontaneous group.”
No patients had urinary retention after initially passing their voiding trial. Force of stream did not differ between groups, and about 15% in each group had a postoperative urinary tract infection.
The study demonstrates that voiding assessment based on a spontaneous minimum void of 150 mL is safe and has similar pass rates, compared with the more commonly performed retrograde void trial, Dr. Popiel said. “If the voided amount is at least 150 mL, PVR is not critical to obtain. The study adds to the body of literature that supports less stringent criteria for evaluating voiding function and can limit postoperative urinary recatheterization.”
The investigators allowed patients with PVRs as high as 575 mL to return home without an alternative way to empty the bladder, C. Sage Claydon, MD, a urogynecologist who was not involved in the study, noted during a discussion after the presentation. In all, 6 patients who met the passing criteria for the spontaneous voiding trial had a PVR greater than 200 mL, with volumes ranging from 205-575 mL.
The patients received standardized counseling about postoperative voiding problems, said Dr. Popiel. “This is similar to the work done by Ingber et al. from 2011, where patients who reached a certain force of stream, greater than 5 out of 10, were discharged home regardless of PVR.”
Dr. Popiel had no relevant disclosures. Two coinvestigators disclosed ties to BlossomMed, Renovia, and ArmadaHealth.
SOURCE: Popiel P et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
Voiding trials after female pelvic floor surgery may detect similar rates of voiding dysfunction regardless of whether voiding occurs spontaneously or after the bladder is retrograde-filled with saline, according to a randomized study.
Nevertheless, patients may prefer the more common retrograde-fill approach.
In the study of 109 patients, those who underwent retrograde fill reported significantly greater satisfaction with their method of voiding evaluation, compared with patients whose voiding trials occurred spontaneously. The increased satisfaction could relate to the fact that retrograde-fill trials take less time, study investigator Patrick Popiel, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. The exact reasons are unclear, however.
Voiding trials help identify patients who cannot sufficiently empty their bladder after surgery. Prior research has indicated that the incidence of voiding dysfunction after pelvic floor surgery is about 25%-35%. “Patients with voiding dysfunction are generally managed with an indwelling Foley catheter or clean intermittent self-catheterization,” Dr. Popiel said. “Catheterization increases the risk of urinary tract infection, increases anxiety, and decreases patient satisfaction. A large proportion of patients who are discharged home with a Foley catheter state that the catheter was the worst aspect of their experience.”
Dr. Popiel and colleagues conducted a randomized, prospective study to examine the rate of failed voiding trials that necessitate discharge home with an indwelling Foley catheter using spontaneous and retrograde-fill approaches. The study included women who required a voiding trial after surgery for pelvic organ prolapse or urinary incontinence. Patients who required prolonged catheterization after surgery, such as those with a urinary tract infection, bowel injury, or large amount of blood loss, were excluded.
Researchers analyzed data from 55 patients who were randomly assigned to the retrograde-fill group and 54 patients who were randomly assigned to the spontaneous trial group.
In the spontaneous group, patients were required to void at least 150 mL at one time within 6 hours of catheter removal to successfully complete the voiding trial.
In the retrograde-fill group, the bladder was filled in the postanesthesia care unit with 300 mL of saline or until the maximum volume tolerated by the patient (not exceeding 300 mL ) was reached. Patients in this group had to void at least 150 mL or 50% of the instilled volume at one time within 60 minutes of catheter removal to pass the trial.
The researchers documented postvoid residual (PVR) but did not use this measure to determine voiding function.
The baseline demographics of the two groups were similar, although prior hysterectomy was more common in the retrograde-fill group than in the spontaneous group (32.7% vs. 14.8%). The average age was 58.5 years in the retrograde-fill group and 61 years in the spontaneous group.
“There was no significant difference in our primary outcome,” Dr. Popiel said. “There was a 12.7% rate of failed voiding trial in the retrograde group versus 7.7% in the spontaneous group.”
No patients had urinary retention after initially passing their voiding trial. Force of stream did not differ between groups, and about 15% in each group had a postoperative urinary tract infection.
The study demonstrates that voiding assessment based on a spontaneous minimum void of 150 mL is safe and has similar pass rates, compared with the more commonly performed retrograde void trial, Dr. Popiel said. “If the voided amount is at least 150 mL, PVR is not critical to obtain. The study adds to the body of literature that supports less stringent criteria for evaluating voiding function and can limit postoperative urinary recatheterization.”
The investigators allowed patients with PVRs as high as 575 mL to return home without an alternative way to empty the bladder, C. Sage Claydon, MD, a urogynecologist who was not involved in the study, noted during a discussion after the presentation. In all, 6 patients who met the passing criteria for the spontaneous voiding trial had a PVR greater than 200 mL, with volumes ranging from 205-575 mL.
The patients received standardized counseling about postoperative voiding problems, said Dr. Popiel. “This is similar to the work done by Ingber et al. from 2011, where patients who reached a certain force of stream, greater than 5 out of 10, were discharged home regardless of PVR.”
Dr. Popiel had no relevant disclosures. Two coinvestigators disclosed ties to BlossomMed, Renovia, and ArmadaHealth.
SOURCE: Popiel P et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
FROM SGS 2020
New hormonal medical treatment is an important advance for AUB caused by uterine fibroids
Uterine leiomyomata (fibroids) are the most common pelvic tumor diagnosed in women.1 Women with symptomatic fibroids often report abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) and pelvic cramping, fullness, or pain. Fibroids also may cause frequency of urination and contribute to fertility and pregnancy problems. Treatment options for the AUB caused by fibroids include, but are not limited to, hysterectomy, myomectomy, uterine artery embolization, endometrial ablation, insertion of a levonorgestrel intrauterine device, focused ultrasound surgery, radiofrequency ablation, leuprolide acetate, and elagolix plus low-dose hormone add-back (Oriahnn; AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois).1 Oriahnn is the most recent addition to our treatment armamentarium for fibroids and represents the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved long-term hormonal option for AUB caused by fibroids.
Gene dysregulation contributes to fibroid development
Most uterine fibroids are clonal tumors, which develop following a somatic mutation in a precursor uterine myocyte. The somatic mutation causes gene dysregulation that stimulates cell growth resulting in a benign tumor mass. The majority of fibroids contain a mutation in one of the following 6 genes: mediator complex subunit 12 (MED12), high mobility group AT-hook (HMGA2 or HMGA1), RAD51B, fumarate hydratase (FH), collagen type IV, alpha 5 chain (COL4A5), or collagen type IV alpha 6 chain (COL4A6).2
Gene dysregulation in fibroids may arise following chromothripsis of the uterine myocyte genome
Chromothripsis is a catastrophic intracellular genetic event in which one or more chromosomes are broken and reassemble in a new nucleic acid sequence, producing a derivative chromosome that contains complex genetic rearrangements.3 Chromothripsis is believed to occur frequently in uterine myocytes. It is unknown why uterine myocytes are susceptible to chromothripsis,3 or why a catastrophic intracellular event such as chromothripsis results in preferential mutations in the 6 genes that are associated with myoma formation.
Estrogen and progesterone influence fibroid size and cell activity
Although uterine fibroids are clonal tumors containing broken genes, they are also exquisitely responsive to estradiol and progesterone. Estradiol and progesterone play an important role in regulating fibroid size and function.4 Estrogen stimulates uterine fibroids to increase in size. In a hypoestrogenic state, uterine fibroids decrease in size. In addition, a hypoestrogenic state results in an atrophic endometrium and thereby reduces AUB. For women with uterine fibroids and AUB, a reversible hypoestrogenic state can be induced either with a parenteral GnRH-agonist analogue (leuprolide) or an oral GnRH-antagonist (elagolix). Both leuprolide and elagolix are approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids (see below).
Surprisingly, progesterone stimulates cell division in normal uterine myocytes and fibroid cells.5 In the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, uterine myocyte mitoses are more frequent than in the follicular phase. In addition, synthetic progestins appear to maintain fibroid size in a hypoestrogenic environment. In one randomized trial, women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus a placebo pill for 24 weeks had a 51% reduction in uterine volume as measured by ultrasound.6 Women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus the synthetic progestin, oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily, had only a 15% reduction in uterine volume.6 This finding suggests that synthetic progestins partially block the decrease in uterine volume that occurs in a hypoestrogenic state.
Further evidence that progesterone plays a role in fibroid biology is the observation that treatment of women with uterine fibroids with the antiprogestin ulipristal decreases fibroid size and reduces AUB.7-9 Ulipristal was approved for the treatment of fibroids in many countries but not the United States. Reports of severe, life-threatening liver injury—some necessitating liver transplantation—among women using ulipristal prompted the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2020 to recommend that women stop taking ulipristal. In addition, the EMA recommended that no woman should initiate ulipristal treatment at this time.10
Continue to: Leuprolide acetate...
Leuprolide acetate
Leuprolide acetate is a peptide GnRH-agonist analogue. Initiation of leuprolide treatment stimulates gonadotropin release, but with chronic administration pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) decreases, resulting in reduced ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Leuprolide treatment concomitant with iron therapy is approved by the FDA for improving red blood cell volume prior to surgery in women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia.11 Among women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia, after 12 weeks of treatment, the hemoglobin concentration was ≥12 g/dL in 79% treated with leuprolide plus iron and 56% treated with iron alone.11 The FDA recommends limiting preoperative leuprolide treatment to no more than 3 months. The approved leuprolide regimens are a maximum of 3 monthly injections of leuprolide 3.75 mg or a single injection of leuprolide 11.25 mg. Leuprolide treatment prior to hysterectomy surgery for uterine fibroids usually will result in a decrease in uterine size and may facilitate vaginal hysterectomy.
Elagolix plus estradiol plus norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn)
GnRH analogues cause a hypoestrogenic state resulting in adverse effects, including moderate to severe hot flashes and a reduction in bone mineral density. One approach to reducing the unwanted effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density is to combine a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back therapy. Combining a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back permits long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids, with few hot flashes and a minimal decrease in bone mineral density. The FDA recently has approved the combination of elagolix plus low-dose estradiol and norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn) for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids.
Elagolix is a nonpeptide oral GnRH antagonist that reduces pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, resulting in a decrease in ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Unlike leuprolide, which causes an initial increase in LH and FSH secretion, the initiation of elagolix treatment causes an immediate and sustained reduction in LH and FSH secretion. Combining elagolix with a low dose of estradiol and norethindrone acetate reduces the side effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density. Clinical trials have reported that the combination of elagolix (300 mg) twice daily plus estradiol (1 mg) and norethindrone acetate (0.5 mg) once daily is an effective long-term treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids.
To study the efficacy of elagolix (alone or with estrogen-progestin add-back therapy) for the treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids, two identical trials were performed,12 in which 790 women participated. The participants had a mean age of 42 years and were documented to have heavy menstrual bleeding (>80 mL blood loss per cycle) and ultrasound-diagnosed uterine fibroids. The participants were randomized to one of 3 groups:
- elagolix (300 mg twice daily) plus low-dose steroid add-back (1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily),
- elagolix 300 mg twice daily with no steroid add-back (elagolix alone), or
- placebo for 6 months.12
Menstrual blood loss was quantified using the alkaline hematin method on collected sanitary products. The primary endpoint was menstrual blood loss <80 mL per cycle as well as a ≥50% reduction in quantified blood loss from baseline during the final month of treatment. At 6 months, the percentage of women achieving the primary endpoint in the first trial was 84% (elagolix alone), 69% (elagolix plus add-back), and 9% (placebo). Mean changes from baseline in lumbar spine bone density were −2.95% (elagolix alone), −0.76% (elagolix plus add-back), and −0.21% (placebo). The percentage of women reporting hot flashes was 64% in the elagolix group, 20% in the elagolix plus low-dose steroid add-back group, and 9% in the placebo group. Results were similar in the second trial.12
The initial trials were extended to 12 months with two groups: elagolix 300 mg twice daily plus low-dose hormone add-back with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily (n = 218) or elagolix 300 mg twice daily (elagolix alone) (n = 98).13 Following 12 months of treatment, heavy menstrual bleeding was controlled in 88% and 89% of women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Amenorrhea was reported by 65% of the women in the elagolix plus add-back group. Compared with baseline bone density, at the end of 12 months of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -1.5% and -4.8% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Compared with baseline bone density, at 1 year following completion of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -0.6% and -2.0% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Similar trends were observed in total hip and femoral neck bone density. During treatment with elagolix plus add-back, adverse effects were modest, including hot flushes (6%), night sweats (3.2%), headache (5.5%), and nausea (4.1%). Two women developed liver transaminase levels >3 times the upper limit of normal, resulting in one woman discontinuing treatment.13
Continue to: Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies...
Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies to the components of the medication (including the yellow dye tartrazine); high risk of arterial, venous thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders; pregnancy; known osteoporosis; current breast cancer or other hormonally-sensitive malignancies; known liver disease; and concurrent use of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 inhibitors, which includes many HIV antiviral medications.14 Undiagnosed AUB is a contraindication, and all women prescribed Oriahnn should have endometrial sampling before initiating treatment. Oriahnn should not be used for more than 24 months due to the risk of irreversible bone loss.14 Systemic estrogen and progestin combinations, a component of Oriahnn, increases the risk for pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, and myocardial infarction, especially in women at increased risk for these events (such as women >35 years who smoke cigarettes and women with uncontrolled hypertension).14 In two studies there was a higher incidence of depression, depressed mood, and/or tearfulness in women taking Oriahnn (3%) compared with those taking a placebo (1%).14 The FDA recommends promptly evaluating women with depressive symptoms to determine the risks of initiating and continuing Oriahnn therapy. In two studies there was a higher risk of reported alopecia among women taking Oriahnn (3.5%) compared with placebo (1%).14
It should be noted that elagolix is approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis at a dose of 150 mg daily for 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months. The elagolix dose for the treatment of AUB caused by fibroids is 300 mg twice daily for up to 24 months, necessitating the addition of low-dose estradiol-norethindrone add-back to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and minimize the loss of bone density. Norethindrone acetate also protects the endometrium from the stimulatory effect of estradiol, reducing the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Oriahnn is formulated as two different capsules. A yellow and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg plus estradiol 1 mg and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg to be taken in the morning, and a blue and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg to be taken in the evening.
AUB caused by fibroids is a common problem in gyn practice
There are many procedural interventions that are effective in reducing AUB caused by fibroids. However, prior to the approval of Oriahnn there were no hormonal medications that were FDA approved for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids. Hence, Oriahnn represents an important advance in the hormonal treatment of AUB caused by fibroids and expands the treatment options available to our patients. ●
Black women are more likely to develop fibroids and experience more severe fibroid symptoms. Obstetrician-gynecologists are experts in the diagnosis and treatment of fibroids. We play a key role in partnering with Black women to reduce fibroid disease burden.
Factors that increase the risk of developing fibroids include: increasing age, Black race, nulliparity, early menarche (<10 years of age), obesity, and consumption of red meat.1 The Nurses Health Study II is the largest prospective study of the factors that influence fibroid development.2 A total of 95,061 premenopausal nurses aged 25 to 44 years were followed from September 1989 through May 1993. Review of a sample of medical records demonstrated that the nurses participating in the study were reliable reporters of whether or not they had been diagnosed with fibroids. Based on a report of an ultrasound or hysterectomy diagnosis, the incidence rate for fibroids increased with age. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 4.3 (age 25 to 29 years), 9.0 (30 to 34 years), 14.7 (age 35 to 39 years), and 22.5 (40 to 44 years). Compared with White race, Black race (but not Hispanic ethnicity or Asian race) was associated with an increased incidence of fibroids. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 12.5 (White race), 37.9 (Black race), 14.5 (Hispanic ethnicity), and 10.4 (Asian race). The risk of developing fibroids was 3.25 times (95% CI, 2.71 to 3.88) greater among Black compared with White women after controlling for body mass index, age at first birth, years since last birth, history of infertility, age at first oral contraceptive use, marital status, and current alcohol use.2
Other epidemiology studies also report an increased incidence of fibroids among Black women.3,4 The size of the uterus, the size and number of fibroids, and the severity of fibroid symptoms are greater among Black versus White women.5,6 The molecular factors that increase fibroid incidence among Black women are unknown. Given the burden of fibroid disease among Black women, obstetrician-gynecologists are best positioned to ensure early diagnosis and to develop an effective follow-up and treatment plan for affected women.
References
1. Stewart EA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Catherino WH, et al. Uterine fibroids. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16043.
2. Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973.
3. Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
4. Brett KM, Marsh JV, Madans JH. Epidemiology of hysterectomy in the United States: demographic and reproductive factors in a nationally representative sample. J Womens Health. 1997;6:309-316.
5. Peddada SD, Laughlin SK, Miner K, et al. Growth of uterine leiomyomata among premenopausal black and white women. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1988719892.
6. Huyck KL, Panhuysen CI, Cuenco KT, et al. The impact of race as a risk factor for symptom severity and age at diagnosis of uterine leiomyomata among affected sisters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:168.e1-e9.
- Stewart EA. Uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1646-1655.
- Mehine M, Makinen N, Heinonen HR, et al. Genomics of uterine leiomyomas: insights from high-throughput sequencing. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:621-629.
- Mehine M, Kaasinen E, Makinen N, et al. Characterization of uterine leiomyomas by whole-genome sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:43-53.
- Moravek MB, Bulun SE. Endocrinology of uterine fibroids: steroid hormones, stem cells and genetic contribution. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;27:276-283.
- Rein MS. Advances in uterine leiomyoma research: the progesterone hypothesis. Environ Health Perspect. 2000;108(suppl 5):791-793.
- Friedman AJ, Barbieri RL, Doubilet PM, et al. A randomized double-blind trial of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of leiomyomata uteri. Fertil Steril. 1988;49:404-409.
- Donnez J, Hudecek R, Donnez O, et al. Efficacy and safety of repeated use of ulipristal acetate in uterine fibroids. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:519-527.
- Donnez J, Tatarchuk TF, Bouchard P, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus placebo for fibroid treatment before surgery. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:409-420.
- Donnez J, Tomaszewski J, Vazquez F, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus leuprolide acetate for uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:421-432.
- European Medicines Agency. Suspension of ulipristal acetate for uterine fibroids during ongoing EMA review of liver injury risk. March 13, 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/suspension-ulipristal-acetate-uterine-fibroids-during-ongoing-ema-review-liver-injury-risk#:~:text=EMA's%20safety%20committee%20(PRAC)%20has,the%20EU%20during%20the%20review. Accessed July 24, 2020.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. Osaka, Japan: Takeda; Revised March 2012.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie; 2020.
Uterine leiomyomata (fibroids) are the most common pelvic tumor diagnosed in women.1 Women with symptomatic fibroids often report abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) and pelvic cramping, fullness, or pain. Fibroids also may cause frequency of urination and contribute to fertility and pregnancy problems. Treatment options for the AUB caused by fibroids include, but are not limited to, hysterectomy, myomectomy, uterine artery embolization, endometrial ablation, insertion of a levonorgestrel intrauterine device, focused ultrasound surgery, radiofrequency ablation, leuprolide acetate, and elagolix plus low-dose hormone add-back (Oriahnn; AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois).1 Oriahnn is the most recent addition to our treatment armamentarium for fibroids and represents the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved long-term hormonal option for AUB caused by fibroids.
Gene dysregulation contributes to fibroid development
Most uterine fibroids are clonal tumors, which develop following a somatic mutation in a precursor uterine myocyte. The somatic mutation causes gene dysregulation that stimulates cell growth resulting in a benign tumor mass. The majority of fibroids contain a mutation in one of the following 6 genes: mediator complex subunit 12 (MED12), high mobility group AT-hook (HMGA2 or HMGA1), RAD51B, fumarate hydratase (FH), collagen type IV, alpha 5 chain (COL4A5), or collagen type IV alpha 6 chain (COL4A6).2
Gene dysregulation in fibroids may arise following chromothripsis of the uterine myocyte genome
Chromothripsis is a catastrophic intracellular genetic event in which one or more chromosomes are broken and reassemble in a new nucleic acid sequence, producing a derivative chromosome that contains complex genetic rearrangements.3 Chromothripsis is believed to occur frequently in uterine myocytes. It is unknown why uterine myocytes are susceptible to chromothripsis,3 or why a catastrophic intracellular event such as chromothripsis results in preferential mutations in the 6 genes that are associated with myoma formation.
Estrogen and progesterone influence fibroid size and cell activity
Although uterine fibroids are clonal tumors containing broken genes, they are also exquisitely responsive to estradiol and progesterone. Estradiol and progesterone play an important role in regulating fibroid size and function.4 Estrogen stimulates uterine fibroids to increase in size. In a hypoestrogenic state, uterine fibroids decrease in size. In addition, a hypoestrogenic state results in an atrophic endometrium and thereby reduces AUB. For women with uterine fibroids and AUB, a reversible hypoestrogenic state can be induced either with a parenteral GnRH-agonist analogue (leuprolide) or an oral GnRH-antagonist (elagolix). Both leuprolide and elagolix are approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids (see below).
Surprisingly, progesterone stimulates cell division in normal uterine myocytes and fibroid cells.5 In the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, uterine myocyte mitoses are more frequent than in the follicular phase. In addition, synthetic progestins appear to maintain fibroid size in a hypoestrogenic environment. In one randomized trial, women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus a placebo pill for 24 weeks had a 51% reduction in uterine volume as measured by ultrasound.6 Women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus the synthetic progestin, oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily, had only a 15% reduction in uterine volume.6 This finding suggests that synthetic progestins partially block the decrease in uterine volume that occurs in a hypoestrogenic state.
Further evidence that progesterone plays a role in fibroid biology is the observation that treatment of women with uterine fibroids with the antiprogestin ulipristal decreases fibroid size and reduces AUB.7-9 Ulipristal was approved for the treatment of fibroids in many countries but not the United States. Reports of severe, life-threatening liver injury—some necessitating liver transplantation—among women using ulipristal prompted the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2020 to recommend that women stop taking ulipristal. In addition, the EMA recommended that no woman should initiate ulipristal treatment at this time.10
Continue to: Leuprolide acetate...
Leuprolide acetate
Leuprolide acetate is a peptide GnRH-agonist analogue. Initiation of leuprolide treatment stimulates gonadotropin release, but with chronic administration pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) decreases, resulting in reduced ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Leuprolide treatment concomitant with iron therapy is approved by the FDA for improving red blood cell volume prior to surgery in women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia.11 Among women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia, after 12 weeks of treatment, the hemoglobin concentration was ≥12 g/dL in 79% treated with leuprolide plus iron and 56% treated with iron alone.11 The FDA recommends limiting preoperative leuprolide treatment to no more than 3 months. The approved leuprolide regimens are a maximum of 3 monthly injections of leuprolide 3.75 mg or a single injection of leuprolide 11.25 mg. Leuprolide treatment prior to hysterectomy surgery for uterine fibroids usually will result in a decrease in uterine size and may facilitate vaginal hysterectomy.
Elagolix plus estradiol plus norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn)
GnRH analogues cause a hypoestrogenic state resulting in adverse effects, including moderate to severe hot flashes and a reduction in bone mineral density. One approach to reducing the unwanted effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density is to combine a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back therapy. Combining a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back permits long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids, with few hot flashes and a minimal decrease in bone mineral density. The FDA recently has approved the combination of elagolix plus low-dose estradiol and norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn) for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids.
Elagolix is a nonpeptide oral GnRH antagonist that reduces pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, resulting in a decrease in ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Unlike leuprolide, which causes an initial increase in LH and FSH secretion, the initiation of elagolix treatment causes an immediate and sustained reduction in LH and FSH secretion. Combining elagolix with a low dose of estradiol and norethindrone acetate reduces the side effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density. Clinical trials have reported that the combination of elagolix (300 mg) twice daily plus estradiol (1 mg) and norethindrone acetate (0.5 mg) once daily is an effective long-term treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids.
To study the efficacy of elagolix (alone or with estrogen-progestin add-back therapy) for the treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids, two identical trials were performed,12 in which 790 women participated. The participants had a mean age of 42 years and were documented to have heavy menstrual bleeding (>80 mL blood loss per cycle) and ultrasound-diagnosed uterine fibroids. The participants were randomized to one of 3 groups:
- elagolix (300 mg twice daily) plus low-dose steroid add-back (1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily),
- elagolix 300 mg twice daily with no steroid add-back (elagolix alone), or
- placebo for 6 months.12
Menstrual blood loss was quantified using the alkaline hematin method on collected sanitary products. The primary endpoint was menstrual blood loss <80 mL per cycle as well as a ≥50% reduction in quantified blood loss from baseline during the final month of treatment. At 6 months, the percentage of women achieving the primary endpoint in the first trial was 84% (elagolix alone), 69% (elagolix plus add-back), and 9% (placebo). Mean changes from baseline in lumbar spine bone density were −2.95% (elagolix alone), −0.76% (elagolix plus add-back), and −0.21% (placebo). The percentage of women reporting hot flashes was 64% in the elagolix group, 20% in the elagolix plus low-dose steroid add-back group, and 9% in the placebo group. Results were similar in the second trial.12
The initial trials were extended to 12 months with two groups: elagolix 300 mg twice daily plus low-dose hormone add-back with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily (n = 218) or elagolix 300 mg twice daily (elagolix alone) (n = 98).13 Following 12 months of treatment, heavy menstrual bleeding was controlled in 88% and 89% of women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Amenorrhea was reported by 65% of the women in the elagolix plus add-back group. Compared with baseline bone density, at the end of 12 months of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -1.5% and -4.8% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Compared with baseline bone density, at 1 year following completion of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -0.6% and -2.0% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Similar trends were observed in total hip and femoral neck bone density. During treatment with elagolix plus add-back, adverse effects were modest, including hot flushes (6%), night sweats (3.2%), headache (5.5%), and nausea (4.1%). Two women developed liver transaminase levels >3 times the upper limit of normal, resulting in one woman discontinuing treatment.13
Continue to: Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies...
Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies to the components of the medication (including the yellow dye tartrazine); high risk of arterial, venous thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders; pregnancy; known osteoporosis; current breast cancer or other hormonally-sensitive malignancies; known liver disease; and concurrent use of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 inhibitors, which includes many HIV antiviral medications.14 Undiagnosed AUB is a contraindication, and all women prescribed Oriahnn should have endometrial sampling before initiating treatment. Oriahnn should not be used for more than 24 months due to the risk of irreversible bone loss.14 Systemic estrogen and progestin combinations, a component of Oriahnn, increases the risk for pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, and myocardial infarction, especially in women at increased risk for these events (such as women >35 years who smoke cigarettes and women with uncontrolled hypertension).14 In two studies there was a higher incidence of depression, depressed mood, and/or tearfulness in women taking Oriahnn (3%) compared with those taking a placebo (1%).14 The FDA recommends promptly evaluating women with depressive symptoms to determine the risks of initiating and continuing Oriahnn therapy. In two studies there was a higher risk of reported alopecia among women taking Oriahnn (3.5%) compared with placebo (1%).14
It should be noted that elagolix is approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis at a dose of 150 mg daily for 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months. The elagolix dose for the treatment of AUB caused by fibroids is 300 mg twice daily for up to 24 months, necessitating the addition of low-dose estradiol-norethindrone add-back to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and minimize the loss of bone density. Norethindrone acetate also protects the endometrium from the stimulatory effect of estradiol, reducing the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Oriahnn is formulated as two different capsules. A yellow and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg plus estradiol 1 mg and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg to be taken in the morning, and a blue and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg to be taken in the evening.
AUB caused by fibroids is a common problem in gyn practice
There are many procedural interventions that are effective in reducing AUB caused by fibroids. However, prior to the approval of Oriahnn there were no hormonal medications that were FDA approved for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids. Hence, Oriahnn represents an important advance in the hormonal treatment of AUB caused by fibroids and expands the treatment options available to our patients. ●
Black women are more likely to develop fibroids and experience more severe fibroid symptoms. Obstetrician-gynecologists are experts in the diagnosis and treatment of fibroids. We play a key role in partnering with Black women to reduce fibroid disease burden.
Factors that increase the risk of developing fibroids include: increasing age, Black race, nulliparity, early menarche (<10 years of age), obesity, and consumption of red meat.1 The Nurses Health Study II is the largest prospective study of the factors that influence fibroid development.2 A total of 95,061 premenopausal nurses aged 25 to 44 years were followed from September 1989 through May 1993. Review of a sample of medical records demonstrated that the nurses participating in the study were reliable reporters of whether or not they had been diagnosed with fibroids. Based on a report of an ultrasound or hysterectomy diagnosis, the incidence rate for fibroids increased with age. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 4.3 (age 25 to 29 years), 9.0 (30 to 34 years), 14.7 (age 35 to 39 years), and 22.5 (40 to 44 years). Compared with White race, Black race (but not Hispanic ethnicity or Asian race) was associated with an increased incidence of fibroids. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 12.5 (White race), 37.9 (Black race), 14.5 (Hispanic ethnicity), and 10.4 (Asian race). The risk of developing fibroids was 3.25 times (95% CI, 2.71 to 3.88) greater among Black compared with White women after controlling for body mass index, age at first birth, years since last birth, history of infertility, age at first oral contraceptive use, marital status, and current alcohol use.2
Other epidemiology studies also report an increased incidence of fibroids among Black women.3,4 The size of the uterus, the size and number of fibroids, and the severity of fibroid symptoms are greater among Black versus White women.5,6 The molecular factors that increase fibroid incidence among Black women are unknown. Given the burden of fibroid disease among Black women, obstetrician-gynecologists are best positioned to ensure early diagnosis and to develop an effective follow-up and treatment plan for affected women.
References
1. Stewart EA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Catherino WH, et al. Uterine fibroids. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16043.
2. Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973.
3. Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
4. Brett KM, Marsh JV, Madans JH. Epidemiology of hysterectomy in the United States: demographic and reproductive factors in a nationally representative sample. J Womens Health. 1997;6:309-316.
5. Peddada SD, Laughlin SK, Miner K, et al. Growth of uterine leiomyomata among premenopausal black and white women. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1988719892.
6. Huyck KL, Panhuysen CI, Cuenco KT, et al. The impact of race as a risk factor for symptom severity and age at diagnosis of uterine leiomyomata among affected sisters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:168.e1-e9.
Uterine leiomyomata (fibroids) are the most common pelvic tumor diagnosed in women.1 Women with symptomatic fibroids often report abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) and pelvic cramping, fullness, or pain. Fibroids also may cause frequency of urination and contribute to fertility and pregnancy problems. Treatment options for the AUB caused by fibroids include, but are not limited to, hysterectomy, myomectomy, uterine artery embolization, endometrial ablation, insertion of a levonorgestrel intrauterine device, focused ultrasound surgery, radiofrequency ablation, leuprolide acetate, and elagolix plus low-dose hormone add-back (Oriahnn; AbbVie, North Chicago, Illinois).1 Oriahnn is the most recent addition to our treatment armamentarium for fibroids and represents the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved long-term hormonal option for AUB caused by fibroids.
Gene dysregulation contributes to fibroid development
Most uterine fibroids are clonal tumors, which develop following a somatic mutation in a precursor uterine myocyte. The somatic mutation causes gene dysregulation that stimulates cell growth resulting in a benign tumor mass. The majority of fibroids contain a mutation in one of the following 6 genes: mediator complex subunit 12 (MED12), high mobility group AT-hook (HMGA2 or HMGA1), RAD51B, fumarate hydratase (FH), collagen type IV, alpha 5 chain (COL4A5), or collagen type IV alpha 6 chain (COL4A6).2
Gene dysregulation in fibroids may arise following chromothripsis of the uterine myocyte genome
Chromothripsis is a catastrophic intracellular genetic event in which one or more chromosomes are broken and reassemble in a new nucleic acid sequence, producing a derivative chromosome that contains complex genetic rearrangements.3 Chromothripsis is believed to occur frequently in uterine myocytes. It is unknown why uterine myocytes are susceptible to chromothripsis,3 or why a catastrophic intracellular event such as chromothripsis results in preferential mutations in the 6 genes that are associated with myoma formation.
Estrogen and progesterone influence fibroid size and cell activity
Although uterine fibroids are clonal tumors containing broken genes, they are also exquisitely responsive to estradiol and progesterone. Estradiol and progesterone play an important role in regulating fibroid size and function.4 Estrogen stimulates uterine fibroids to increase in size. In a hypoestrogenic state, uterine fibroids decrease in size. In addition, a hypoestrogenic state results in an atrophic endometrium and thereby reduces AUB. For women with uterine fibroids and AUB, a reversible hypoestrogenic state can be induced either with a parenteral GnRH-agonist analogue (leuprolide) or an oral GnRH-antagonist (elagolix). Both leuprolide and elagolix are approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids (see below).
Surprisingly, progesterone stimulates cell division in normal uterine myocytes and fibroid cells.5 In the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, uterine myocyte mitoses are more frequent than in the follicular phase. In addition, synthetic progestins appear to maintain fibroid size in a hypoestrogenic environment. In one randomized trial, women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus a placebo pill for 24 weeks had a 51% reduction in uterine volume as measured by ultrasound.6 Women with uterine fibroids treated with leuprolide acetate plus the synthetic progestin, oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg daily, had only a 15% reduction in uterine volume.6 This finding suggests that synthetic progestins partially block the decrease in uterine volume that occurs in a hypoestrogenic state.
Further evidence that progesterone plays a role in fibroid biology is the observation that treatment of women with uterine fibroids with the antiprogestin ulipristal decreases fibroid size and reduces AUB.7-9 Ulipristal was approved for the treatment of fibroids in many countries but not the United States. Reports of severe, life-threatening liver injury—some necessitating liver transplantation—among women using ulipristal prompted the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2020 to recommend that women stop taking ulipristal. In addition, the EMA recommended that no woman should initiate ulipristal treatment at this time.10
Continue to: Leuprolide acetate...
Leuprolide acetate
Leuprolide acetate is a peptide GnRH-agonist analogue. Initiation of leuprolide treatment stimulates gonadotropin release, but with chronic administration pituitary secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) decreases, resulting in reduced ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Leuprolide treatment concomitant with iron therapy is approved by the FDA for improving red blood cell volume prior to surgery in women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia.11 Among women with fibroids, AUB, and anemia, after 12 weeks of treatment, the hemoglobin concentration was ≥12 g/dL in 79% treated with leuprolide plus iron and 56% treated with iron alone.11 The FDA recommends limiting preoperative leuprolide treatment to no more than 3 months. The approved leuprolide regimens are a maximum of 3 monthly injections of leuprolide 3.75 mg or a single injection of leuprolide 11.25 mg. Leuprolide treatment prior to hysterectomy surgery for uterine fibroids usually will result in a decrease in uterine size and may facilitate vaginal hysterectomy.
Elagolix plus estradiol plus norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn)
GnRH analogues cause a hypoestrogenic state resulting in adverse effects, including moderate to severe hot flashes and a reduction in bone mineral density. One approach to reducing the unwanted effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density is to combine a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back therapy. Combining a GnRH analogue with low-dose steroid hormone add-back permits long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids, with few hot flashes and a minimal decrease in bone mineral density. The FDA recently has approved the combination of elagolix plus low-dose estradiol and norethindrone acetate (Oriahnn) for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids.
Elagolix is a nonpeptide oral GnRH antagonist that reduces pituitary secretion of LH and FSH, resulting in a decrease in ovarian follicular activity, anovulation, and low serum concentration of estradiol and progesterone. Unlike leuprolide, which causes an initial increase in LH and FSH secretion, the initiation of elagolix treatment causes an immediate and sustained reduction in LH and FSH secretion. Combining elagolix with a low dose of estradiol and norethindrone acetate reduces the side effects of hot flashes and decreased bone density. Clinical trials have reported that the combination of elagolix (300 mg) twice daily plus estradiol (1 mg) and norethindrone acetate (0.5 mg) once daily is an effective long-term treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids.
To study the efficacy of elagolix (alone or with estrogen-progestin add-back therapy) for the treatment of AUB caused by uterine fibroids, two identical trials were performed,12 in which 790 women participated. The participants had a mean age of 42 years and were documented to have heavy menstrual bleeding (>80 mL blood loss per cycle) and ultrasound-diagnosed uterine fibroids. The participants were randomized to one of 3 groups:
- elagolix (300 mg twice daily) plus low-dose steroid add-back (1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily),
- elagolix 300 mg twice daily with no steroid add-back (elagolix alone), or
- placebo for 6 months.12
Menstrual blood loss was quantified using the alkaline hematin method on collected sanitary products. The primary endpoint was menstrual blood loss <80 mL per cycle as well as a ≥50% reduction in quantified blood loss from baseline during the final month of treatment. At 6 months, the percentage of women achieving the primary endpoint in the first trial was 84% (elagolix alone), 69% (elagolix plus add-back), and 9% (placebo). Mean changes from baseline in lumbar spine bone density were −2.95% (elagolix alone), −0.76% (elagolix plus add-back), and −0.21% (placebo). The percentage of women reporting hot flashes was 64% in the elagolix group, 20% in the elagolix plus low-dose steroid add-back group, and 9% in the placebo group. Results were similar in the second trial.12
The initial trials were extended to 12 months with two groups: elagolix 300 mg twice daily plus low-dose hormone add-back with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate once daily (n = 218) or elagolix 300 mg twice daily (elagolix alone) (n = 98).13 Following 12 months of treatment, heavy menstrual bleeding was controlled in 88% and 89% of women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Amenorrhea was reported by 65% of the women in the elagolix plus add-back group. Compared with baseline bone density, at the end of 12 months of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -1.5% and -4.8% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Compared with baseline bone density, at 1 year following completion of treatment, bone mineral density in the lumbar spine was reduced by -0.6% and -2.0% in the women treated with elagolix plus add-back and elagolix alone, respectively. Similar trends were observed in total hip and femoral neck bone density. During treatment with elagolix plus add-back, adverse effects were modest, including hot flushes (6%), night sweats (3.2%), headache (5.5%), and nausea (4.1%). Two women developed liver transaminase levels >3 times the upper limit of normal, resulting in one woman discontinuing treatment.13
Continue to: Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies...
Contraindications to Oriahnn include known allergies to the components of the medication (including the yellow dye tartrazine); high risk of arterial, venous thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders; pregnancy; known osteoporosis; current breast cancer or other hormonally-sensitive malignancies; known liver disease; and concurrent use of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 inhibitors, which includes many HIV antiviral medications.14 Undiagnosed AUB is a contraindication, and all women prescribed Oriahnn should have endometrial sampling before initiating treatment. Oriahnn should not be used for more than 24 months due to the risk of irreversible bone loss.14 Systemic estrogen and progestin combinations, a component of Oriahnn, increases the risk for pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, and myocardial infarction, especially in women at increased risk for these events (such as women >35 years who smoke cigarettes and women with uncontrolled hypertension).14 In two studies there was a higher incidence of depression, depressed mood, and/or tearfulness in women taking Oriahnn (3%) compared with those taking a placebo (1%).14 The FDA recommends promptly evaluating women with depressive symptoms to determine the risks of initiating and continuing Oriahnn therapy. In two studies there was a higher risk of reported alopecia among women taking Oriahnn (3.5%) compared with placebo (1%).14
It should be noted that elagolix is approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis at a dose of 150 mg daily for 24 months or 200 mg twice daily for 6 months. The elagolix dose for the treatment of AUB caused by fibroids is 300 mg twice daily for up to 24 months, necessitating the addition of low-dose estradiol-norethindrone add-back to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and minimize the loss of bone density. Norethindrone acetate also protects the endometrium from the stimulatory effect of estradiol, reducing the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Oriahnn is formulated as two different capsules. A yellow and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg plus estradiol 1 mg and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg to be taken in the morning, and a blue and white capsule contains elagolix 300 mg to be taken in the evening.
AUB caused by fibroids is a common problem in gyn practice
There are many procedural interventions that are effective in reducing AUB caused by fibroids. However, prior to the approval of Oriahnn there were no hormonal medications that were FDA approved for the long-term treatment of AUB caused by fibroids. Hence, Oriahnn represents an important advance in the hormonal treatment of AUB caused by fibroids and expands the treatment options available to our patients. ●
Black women are more likely to develop fibroids and experience more severe fibroid symptoms. Obstetrician-gynecologists are experts in the diagnosis and treatment of fibroids. We play a key role in partnering with Black women to reduce fibroid disease burden.
Factors that increase the risk of developing fibroids include: increasing age, Black race, nulliparity, early menarche (<10 years of age), obesity, and consumption of red meat.1 The Nurses Health Study II is the largest prospective study of the factors that influence fibroid development.2 A total of 95,061 premenopausal nurses aged 25 to 44 years were followed from September 1989 through May 1993. Review of a sample of medical records demonstrated that the nurses participating in the study were reliable reporters of whether or not they had been diagnosed with fibroids. Based on a report of an ultrasound or hysterectomy diagnosis, the incidence rate for fibroids increased with age. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 4.3 (age 25 to 29 years), 9.0 (30 to 34 years), 14.7 (age 35 to 39 years), and 22.5 (40 to 44 years). Compared with White race, Black race (but not Hispanic ethnicity or Asian race) was associated with an increased incidence of fibroids. Incidence rate per 1,000 women-years was 12.5 (White race), 37.9 (Black race), 14.5 (Hispanic ethnicity), and 10.4 (Asian race). The risk of developing fibroids was 3.25 times (95% CI, 2.71 to 3.88) greater among Black compared with White women after controlling for body mass index, age at first birth, years since last birth, history of infertility, age at first oral contraceptive use, marital status, and current alcohol use.2
Other epidemiology studies also report an increased incidence of fibroids among Black women.3,4 The size of the uterus, the size and number of fibroids, and the severity of fibroid symptoms are greater among Black versus White women.5,6 The molecular factors that increase fibroid incidence among Black women are unknown. Given the burden of fibroid disease among Black women, obstetrician-gynecologists are best positioned to ensure early diagnosis and to develop an effective follow-up and treatment plan for affected women.
References
1. Stewart EA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Catherino WH, et al. Uterine fibroids. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16043.
2. Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973.
3. Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
4. Brett KM, Marsh JV, Madans JH. Epidemiology of hysterectomy in the United States: demographic and reproductive factors in a nationally representative sample. J Womens Health. 1997;6:309-316.
5. Peddada SD, Laughlin SK, Miner K, et al. Growth of uterine leiomyomata among premenopausal black and white women. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1988719892.
6. Huyck KL, Panhuysen CI, Cuenco KT, et al. The impact of race as a risk factor for symptom severity and age at diagnosis of uterine leiomyomata among affected sisters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:168.e1-e9.
- Stewart EA. Uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1646-1655.
- Mehine M, Makinen N, Heinonen HR, et al. Genomics of uterine leiomyomas: insights from high-throughput sequencing. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:621-629.
- Mehine M, Kaasinen E, Makinen N, et al. Characterization of uterine leiomyomas by whole-genome sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:43-53.
- Moravek MB, Bulun SE. Endocrinology of uterine fibroids: steroid hormones, stem cells and genetic contribution. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;27:276-283.
- Rein MS. Advances in uterine leiomyoma research: the progesterone hypothesis. Environ Health Perspect. 2000;108(suppl 5):791-793.
- Friedman AJ, Barbieri RL, Doubilet PM, et al. A randomized double-blind trial of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of leiomyomata uteri. Fertil Steril. 1988;49:404-409.
- Donnez J, Hudecek R, Donnez O, et al. Efficacy and safety of repeated use of ulipristal acetate in uterine fibroids. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:519-527.
- Donnez J, Tatarchuk TF, Bouchard P, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus placebo for fibroid treatment before surgery. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:409-420.
- Donnez J, Tomaszewski J, Vazquez F, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus leuprolide acetate for uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:421-432.
- European Medicines Agency. Suspension of ulipristal acetate for uterine fibroids during ongoing EMA review of liver injury risk. March 13, 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/suspension-ulipristal-acetate-uterine-fibroids-during-ongoing-ema-review-liver-injury-risk#:~:text=EMA's%20safety%20committee%20(PRAC)%20has,the%20EU%20during%20the%20review. Accessed July 24, 2020.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. Osaka, Japan: Takeda; Revised March 2012.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie; 2020.
- Stewart EA. Uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1646-1655.
- Mehine M, Makinen N, Heinonen HR, et al. Genomics of uterine leiomyomas: insights from high-throughput sequencing. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:621-629.
- Mehine M, Kaasinen E, Makinen N, et al. Characterization of uterine leiomyomas by whole-genome sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:43-53.
- Moravek MB, Bulun SE. Endocrinology of uterine fibroids: steroid hormones, stem cells and genetic contribution. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;27:276-283.
- Rein MS. Advances in uterine leiomyoma research: the progesterone hypothesis. Environ Health Perspect. 2000;108(suppl 5):791-793.
- Friedman AJ, Barbieri RL, Doubilet PM, et al. A randomized double-blind trial of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide) with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate in the treatment of leiomyomata uteri. Fertil Steril. 1988;49:404-409.
- Donnez J, Hudecek R, Donnez O, et al. Efficacy and safety of repeated use of ulipristal acetate in uterine fibroids. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:519-527.
- Donnez J, Tatarchuk TF, Bouchard P, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus placebo for fibroid treatment before surgery. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:409-420.
- Donnez J, Tomaszewski J, Vazquez F, et al. Ulipristal acetate versus leuprolide acetate for uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:421-432.
- European Medicines Agency. Suspension of ulipristal acetate for uterine fibroids during ongoing EMA review of liver injury risk. March 13, 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/suspension-ulipristal-acetate-uterine-fibroids-during-ongoing-ema-review-liver-injury-risk#:~:text=EMA's%20safety%20committee%20(PRAC)%20has,the%20EU%20during%20the%20review. Accessed July 24, 2020.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. Osaka, Japan: Takeda; Revised March 2012.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie; 2020.
Comment & Controversy
How do you feel about expectantly managing a well-dated pregnancy past 41 weeks’ gestation?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; FEBRUARY 2019)
Is it reasonable to choose the age of 40 for proposing an anticipation of labor induction?
In physiologic ongoing pregnancies (whether they are spontaneous or autologous in vitro fertilization [IVF] or heterologous IVF), the evidence for anticipating labor induction based upon the only factor of age (after 40 years) is missing. Nonetheless, the number of women becoming pregnant at an older age is expected to increase, and from my perspective, to induce all physiologic pregnancies at term by 41 weeks and 5 days’ gestation does not appear to be best practice. I favor the idea of all women aged 40 and older to start labor induction earlier (for instance, to offer labor induction, with proper informed consent, by 41+ 0 and not 41+ 5 through 42+ 0 weeks of pregnancy).
Luca Bernardini, MD
La Spezia, Italy
Dr. Barbieri responds
At Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, our approach is to offer women ≥40 years of age induction of labor (IOL) at 39 weeks’ gestation, unless there is an obstetric contraindication to IOL. We believe that IOL at 39 weeks’ gestation is associated with a reduced risk of both cesarean delivery and a new diagnosis of hypertension.1
Reference
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy, UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
What is the optimal hormonal treatment for women with polycystic ovary syndrome?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; JANUARY 2020)
OCs and spironolactone study
I often recommend oral contraceptives (OCs) containing drospirenone for patients with polycyctic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-associated mild acne and hirsutism—since OCs are already approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne, with similar effects as spironolactone. My patients seem to do well on an OC, and require only one medication. Of course, I would add spironolactone to the treatment regimen and switch OCs if she was not responding well.
Michael T. Cane, MD
Arlington, Texas
Dr. Barbieri responds
The Endocrine Society agrees with Dr. Cane’s approach, recommending the initiation of monotherapy with an estrogen-progestin followed by the addition of spironolactone if 6 months of monotherapy produces insufficient improvement in dermatologic symptoms of PCOS, including hirsutism and acne. Most contraceptives contain 3 mg or 4 mg of drospirenone, which is thought to have antiandrogenic effects similar to spironolactone 25 mg. I believe that spironolactone 100 mg provides more complete and rapid resolution of the dermatologic symptoms caused by PCOS. Hence, I initiate both an estrogen-progestin contraceptive with spironolactone.
How do you feel about expectantly managing a well-dated pregnancy past 41 weeks’ gestation?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; FEBRUARY 2019)
Is it reasonable to choose the age of 40 for proposing an anticipation of labor induction?
In physiologic ongoing pregnancies (whether they are spontaneous or autologous in vitro fertilization [IVF] or heterologous IVF), the evidence for anticipating labor induction based upon the only factor of age (after 40 years) is missing. Nonetheless, the number of women becoming pregnant at an older age is expected to increase, and from my perspective, to induce all physiologic pregnancies at term by 41 weeks and 5 days’ gestation does not appear to be best practice. I favor the idea of all women aged 40 and older to start labor induction earlier (for instance, to offer labor induction, with proper informed consent, by 41+ 0 and not 41+ 5 through 42+ 0 weeks of pregnancy).
Luca Bernardini, MD
La Spezia, Italy
Dr. Barbieri responds
At Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, our approach is to offer women ≥40 years of age induction of labor (IOL) at 39 weeks’ gestation, unless there is an obstetric contraindication to IOL. We believe that IOL at 39 weeks’ gestation is associated with a reduced risk of both cesarean delivery and a new diagnosis of hypertension.1
Reference
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy, UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
What is the optimal hormonal treatment for women with polycystic ovary syndrome?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; JANUARY 2020)
OCs and spironolactone study
I often recommend oral contraceptives (OCs) containing drospirenone for patients with polycyctic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-associated mild acne and hirsutism—since OCs are already approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne, with similar effects as spironolactone. My patients seem to do well on an OC, and require only one medication. Of course, I would add spironolactone to the treatment regimen and switch OCs if she was not responding well.
Michael T. Cane, MD
Arlington, Texas
Dr. Barbieri responds
The Endocrine Society agrees with Dr. Cane’s approach, recommending the initiation of monotherapy with an estrogen-progestin followed by the addition of spironolactone if 6 months of monotherapy produces insufficient improvement in dermatologic symptoms of PCOS, including hirsutism and acne. Most contraceptives contain 3 mg or 4 mg of drospirenone, which is thought to have antiandrogenic effects similar to spironolactone 25 mg. I believe that spironolactone 100 mg provides more complete and rapid resolution of the dermatologic symptoms caused by PCOS. Hence, I initiate both an estrogen-progestin contraceptive with spironolactone.
How do you feel about expectantly managing a well-dated pregnancy past 41 weeks’ gestation?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; FEBRUARY 2019)
Is it reasonable to choose the age of 40 for proposing an anticipation of labor induction?
In physiologic ongoing pregnancies (whether they are spontaneous or autologous in vitro fertilization [IVF] or heterologous IVF), the evidence for anticipating labor induction based upon the only factor of age (after 40 years) is missing. Nonetheless, the number of women becoming pregnant at an older age is expected to increase, and from my perspective, to induce all physiologic pregnancies at term by 41 weeks and 5 days’ gestation does not appear to be best practice. I favor the idea of all women aged 40 and older to start labor induction earlier (for instance, to offer labor induction, with proper informed consent, by 41+ 0 and not 41+ 5 through 42+ 0 weeks of pregnancy).
Luca Bernardini, MD
La Spezia, Italy
Dr. Barbieri responds
At Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, our approach is to offer women ≥40 years of age induction of labor (IOL) at 39 weeks’ gestation, unless there is an obstetric contraindication to IOL. We believe that IOL at 39 weeks’ gestation is associated with a reduced risk of both cesarean delivery and a new diagnosis of hypertension.1
Reference
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy, UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
What is the optimal hormonal treatment for women with polycystic ovary syndrome?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD
(EDITORIAL; JANUARY 2020)
OCs and spironolactone study
I often recommend oral contraceptives (OCs) containing drospirenone for patients with polycyctic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-associated mild acne and hirsutism—since OCs are already approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne, with similar effects as spironolactone. My patients seem to do well on an OC, and require only one medication. Of course, I would add spironolactone to the treatment regimen and switch OCs if she was not responding well.
Michael T. Cane, MD
Arlington, Texas
Dr. Barbieri responds
The Endocrine Society agrees with Dr. Cane’s approach, recommending the initiation of monotherapy with an estrogen-progestin followed by the addition of spironolactone if 6 months of monotherapy produces insufficient improvement in dermatologic symptoms of PCOS, including hirsutism and acne. Most contraceptives contain 3 mg or 4 mg of drospirenone, which is thought to have antiandrogenic effects similar to spironolactone 25 mg. I believe that spironolactone 100 mg provides more complete and rapid resolution of the dermatologic symptoms caused by PCOS. Hence, I initiate both an estrogen-progestin contraceptive with spironolactone.
Telemedicine meets menopause in customized patient care service
Women facing issues related to perimenopause and menopause can consult their primary care physicians or ob.gyns. through telemedicine visits, but
The Cusp doesn’t claim to replace routine gynecologic care. Rather, it focuses on perimenopause and menopause symptoms specifically, and states that its physicians, some of whom are certified by the North American Menopause Society, provide expertise in menopause beyond what patients might receive as part of a typical ob.gyn. visit.
The Cusp is a for-profit organization, a group of physicians, nurse practitioners, and technologists who focus on integrated care for women in perimenopause and beyond. The aim is to leverage technology as a way to connect women to the care platform to book physician and nurse practitioner visits virtually and to have all of the information about their care centralized in one place.
According to the website, most patients who sign up for a care plan check in with their providers at least once a month to monitor their symptoms and tweak treatment strategies. Patients who sign up are prompted to download an app, which then becomes the main tool for scheduling future visits, tracking symptoms, and communicating with providers.
The Cusp launched in early 2019, before the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the pandemic has accelerated the acceptance across medical specialties, suggesting that telemedicine is here to stay, according to Mindy Goldman, MD, professor of gynecology and gynecologic surgery at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Gynecology Center for Cancer Survivors and At-Risk Women at UCSF, who also serves as a medical adviser to the Cusp.
Partnering with technology companies allows opportunities to provide care in areas where there are gaps, such as menopause management, she said. Many clinicians in primary care and ob.gyn. care don’t have the time or training to discuss menopause management in depth with patients, and patient interviews conducted by the Cusp before launching the site showed that this was an area of need.
“One thing that is really unique about the Cusp is that we brought together experts to provide care in both in an evidence-based and holistic fashion,” Dr. Goldman emphasized.
The Cusp’s medical team includes physician and nurse practitioner menopause experts with backgrounds including not only ob.gyn. but also psychiatry, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine, with plans to add endocrinology and dermatology as well. This holistic approach allows the Cusp to tailor care based on what each woman is looking for, with evidence-based expertise to support treatment decisions, said Dr. Goldman, whose advisory role includes helping to develop patient treatment protocols and services.
If a woman wants to begin treating symptoms with a naturopathic approach, the team will provide protocols that take current guidelines into account. Regular visits, approximately once a month or as needed, allow for collaboration with the Cusp’s specialists to provide consistent care that is very comprehensive, she said.
One of the benefits of the Cusp is the opportunity for “frequent touchpoints” in which providers reach out to patients via text, email, or video. Although a traditional medical visit may include some initial discussion of menopause and treatment plans, the Cusp offers “a more seamless way to address needs on an ongoing basis,” to provide more complete patient care, Dr. Goldman said.
“We are constantly asking women what they are looking for in menopause care,” and a recurring question was about hormone testing, she said. Nontraditional practitioners may offer hormone testing as a way of individualizing care that also involves compounded formulations, and other treatments that are not standard of care. “In all of our protocols we follow what is recommended by standard organizations such as ACOG [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] and NAMS.”
The Cusp’s newest service is an at-home hormone test currently for women in New York and California, but the company plans to expand this service. The hormone test, while not essential, is another tool to guide menopause management, and having a sense of when menopause will occur “gives us a chance to talk to people about behavioral changes and time to personalize a treatment protocol,” Dr. Goldman said.
The test is based in part on the anti-Müllerian hormone, which recent studies have shown is useful in predicting time to menopause. This, in combination with other hormone tests and other clinical information, will allow the Cusp’s menopause specialists to help women in perimenopause gain perspective on their symptoms and design a treatment plan that can evolve as their needs change, she explained.
“The more information you know about when menopause is going to be happening, you can tailor your treatment plan,” Dr. Goldman said. For example, a woman who may be 2 years away from menopause might consider a naturopathic approach at first, and switch to a different therapy as menopause occurs. “We know that the risks of cardiovascular disease and bone loss increase after menopause, and knowing the time to menopause gives us more guidance when educating patients about healthy lifestyle habits such as exercise and dietary changes that can help reduce these risks.”
The Cusp allows patients to use money in flexible spending accounts or health savings accounts to pay for the program. If doctors require lab tests or other procedures, these are covered through the patients’ regular health insurance as they would be if requested by a primary care physician or other health care professional.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that part of the value in a telehealth site such as the Cusp is to serve as “a resource for reproductively aging women to understand what is happening to them.”
Any way to improve education on the topic of menopause is empowering to women, said Dr. Pal, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale. “This is an opportunity for patients to have access to a directed evaluation” of menopause-related symptoms. Then, when women visit their regular health care provider in person, they are well-equipped with knowledge to ask more informed questions and discuss a wide range of treatment options.
Dr. Pal noted that the hormone test is less valuable than the interaction between physicians and patients, whether online or in person.
“Menopause is a Monday morning quarterback diagnosis,” she said, emphasizing that, not only is a year without menses part of the diagnosis of menopause, many women in perimenopause can have wide fluctuations in hormone levels, so a test is more of a snapshot than a diagnostic tool, and that the results might cause unnecessary angst and concerns for patients.
However, part of the value of a telehealth site that focuses on menopause is that it gives women a place to learn more about their biology and to clarify their questions about symptoms and become aware of a range of treatment options. Telehealth consultations also can help women recognize how other factors such as lifestyle modifications can play a role in menopause symptoms, and how modifying these factors may provide some relief, she said.
Dr. Pal said she would be cautious about the idea of prescribing without seeing the patient in person, but noted that telehealth sites such as the Cusp can be a win-win to enhance women’s health when used in combination with regular in-person visits to an ob.gyn. The added value in patients’ being able to discuss their concerns and to learn more about their symptoms means that they will be better informed to develop a menopause management strategy in partnership with their providers, said Dr. Pal, who is not associated with the Cusp.
Dr. Goldman disclosed receiving compensation from the Cusp for her advisory work. She also holds stock options in the company. Dr. Pal, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board, had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Women facing issues related to perimenopause and menopause can consult their primary care physicians or ob.gyns. through telemedicine visits, but
The Cusp doesn’t claim to replace routine gynecologic care. Rather, it focuses on perimenopause and menopause symptoms specifically, and states that its physicians, some of whom are certified by the North American Menopause Society, provide expertise in menopause beyond what patients might receive as part of a typical ob.gyn. visit.
The Cusp is a for-profit organization, a group of physicians, nurse practitioners, and technologists who focus on integrated care for women in perimenopause and beyond. The aim is to leverage technology as a way to connect women to the care platform to book physician and nurse practitioner visits virtually and to have all of the information about their care centralized in one place.
According to the website, most patients who sign up for a care plan check in with their providers at least once a month to monitor their symptoms and tweak treatment strategies. Patients who sign up are prompted to download an app, which then becomes the main tool for scheduling future visits, tracking symptoms, and communicating with providers.
The Cusp launched in early 2019, before the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the pandemic has accelerated the acceptance across medical specialties, suggesting that telemedicine is here to stay, according to Mindy Goldman, MD, professor of gynecology and gynecologic surgery at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Gynecology Center for Cancer Survivors and At-Risk Women at UCSF, who also serves as a medical adviser to the Cusp.
Partnering with technology companies allows opportunities to provide care in areas where there are gaps, such as menopause management, she said. Many clinicians in primary care and ob.gyn. care don’t have the time or training to discuss menopause management in depth with patients, and patient interviews conducted by the Cusp before launching the site showed that this was an area of need.
“One thing that is really unique about the Cusp is that we brought together experts to provide care in both in an evidence-based and holistic fashion,” Dr. Goldman emphasized.
The Cusp’s medical team includes physician and nurse practitioner menopause experts with backgrounds including not only ob.gyn. but also psychiatry, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine, with plans to add endocrinology and dermatology as well. This holistic approach allows the Cusp to tailor care based on what each woman is looking for, with evidence-based expertise to support treatment decisions, said Dr. Goldman, whose advisory role includes helping to develop patient treatment protocols and services.
If a woman wants to begin treating symptoms with a naturopathic approach, the team will provide protocols that take current guidelines into account. Regular visits, approximately once a month or as needed, allow for collaboration with the Cusp’s specialists to provide consistent care that is very comprehensive, she said.
One of the benefits of the Cusp is the opportunity for “frequent touchpoints” in which providers reach out to patients via text, email, or video. Although a traditional medical visit may include some initial discussion of menopause and treatment plans, the Cusp offers “a more seamless way to address needs on an ongoing basis,” to provide more complete patient care, Dr. Goldman said.
“We are constantly asking women what they are looking for in menopause care,” and a recurring question was about hormone testing, she said. Nontraditional practitioners may offer hormone testing as a way of individualizing care that also involves compounded formulations, and other treatments that are not standard of care. “In all of our protocols we follow what is recommended by standard organizations such as ACOG [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] and NAMS.”
The Cusp’s newest service is an at-home hormone test currently for women in New York and California, but the company plans to expand this service. The hormone test, while not essential, is another tool to guide menopause management, and having a sense of when menopause will occur “gives us a chance to talk to people about behavioral changes and time to personalize a treatment protocol,” Dr. Goldman said.
The test is based in part on the anti-Müllerian hormone, which recent studies have shown is useful in predicting time to menopause. This, in combination with other hormone tests and other clinical information, will allow the Cusp’s menopause specialists to help women in perimenopause gain perspective on their symptoms and design a treatment plan that can evolve as their needs change, she explained.
“The more information you know about when menopause is going to be happening, you can tailor your treatment plan,” Dr. Goldman said. For example, a woman who may be 2 years away from menopause might consider a naturopathic approach at first, and switch to a different therapy as menopause occurs. “We know that the risks of cardiovascular disease and bone loss increase after menopause, and knowing the time to menopause gives us more guidance when educating patients about healthy lifestyle habits such as exercise and dietary changes that can help reduce these risks.”
The Cusp allows patients to use money in flexible spending accounts or health savings accounts to pay for the program. If doctors require lab tests or other procedures, these are covered through the patients’ regular health insurance as they would be if requested by a primary care physician or other health care professional.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that part of the value in a telehealth site such as the Cusp is to serve as “a resource for reproductively aging women to understand what is happening to them.”
Any way to improve education on the topic of menopause is empowering to women, said Dr. Pal, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale. “This is an opportunity for patients to have access to a directed evaluation” of menopause-related symptoms. Then, when women visit their regular health care provider in person, they are well-equipped with knowledge to ask more informed questions and discuss a wide range of treatment options.
Dr. Pal noted that the hormone test is less valuable than the interaction between physicians and patients, whether online or in person.
“Menopause is a Monday morning quarterback diagnosis,” she said, emphasizing that, not only is a year without menses part of the diagnosis of menopause, many women in perimenopause can have wide fluctuations in hormone levels, so a test is more of a snapshot than a diagnostic tool, and that the results might cause unnecessary angst and concerns for patients.
However, part of the value of a telehealth site that focuses on menopause is that it gives women a place to learn more about their biology and to clarify their questions about symptoms and become aware of a range of treatment options. Telehealth consultations also can help women recognize how other factors such as lifestyle modifications can play a role in menopause symptoms, and how modifying these factors may provide some relief, she said.
Dr. Pal said she would be cautious about the idea of prescribing without seeing the patient in person, but noted that telehealth sites such as the Cusp can be a win-win to enhance women’s health when used in combination with regular in-person visits to an ob.gyn. The added value in patients’ being able to discuss their concerns and to learn more about their symptoms means that they will be better informed to develop a menopause management strategy in partnership with their providers, said Dr. Pal, who is not associated with the Cusp.
Dr. Goldman disclosed receiving compensation from the Cusp for her advisory work. She also holds stock options in the company. Dr. Pal, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board, had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Women facing issues related to perimenopause and menopause can consult their primary care physicians or ob.gyns. through telemedicine visits, but
The Cusp doesn’t claim to replace routine gynecologic care. Rather, it focuses on perimenopause and menopause symptoms specifically, and states that its physicians, some of whom are certified by the North American Menopause Society, provide expertise in menopause beyond what patients might receive as part of a typical ob.gyn. visit.
The Cusp is a for-profit organization, a group of physicians, nurse practitioners, and technologists who focus on integrated care for women in perimenopause and beyond. The aim is to leverage technology as a way to connect women to the care platform to book physician and nurse practitioner visits virtually and to have all of the information about their care centralized in one place.
According to the website, most patients who sign up for a care plan check in with their providers at least once a month to monitor their symptoms and tweak treatment strategies. Patients who sign up are prompted to download an app, which then becomes the main tool for scheduling future visits, tracking symptoms, and communicating with providers.
The Cusp launched in early 2019, before the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the pandemic has accelerated the acceptance across medical specialties, suggesting that telemedicine is here to stay, according to Mindy Goldman, MD, professor of gynecology and gynecologic surgery at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the Gynecology Center for Cancer Survivors and At-Risk Women at UCSF, who also serves as a medical adviser to the Cusp.
Partnering with technology companies allows opportunities to provide care in areas where there are gaps, such as menopause management, she said. Many clinicians in primary care and ob.gyn. care don’t have the time or training to discuss menopause management in depth with patients, and patient interviews conducted by the Cusp before launching the site showed that this was an area of need.
“One thing that is really unique about the Cusp is that we brought together experts to provide care in both in an evidence-based and holistic fashion,” Dr. Goldman emphasized.
The Cusp’s medical team includes physician and nurse practitioner menopause experts with backgrounds including not only ob.gyn. but also psychiatry, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine, with plans to add endocrinology and dermatology as well. This holistic approach allows the Cusp to tailor care based on what each woman is looking for, with evidence-based expertise to support treatment decisions, said Dr. Goldman, whose advisory role includes helping to develop patient treatment protocols and services.
If a woman wants to begin treating symptoms with a naturopathic approach, the team will provide protocols that take current guidelines into account. Regular visits, approximately once a month or as needed, allow for collaboration with the Cusp’s specialists to provide consistent care that is very comprehensive, she said.
One of the benefits of the Cusp is the opportunity for “frequent touchpoints” in which providers reach out to patients via text, email, or video. Although a traditional medical visit may include some initial discussion of menopause and treatment plans, the Cusp offers “a more seamless way to address needs on an ongoing basis,” to provide more complete patient care, Dr. Goldman said.
“We are constantly asking women what they are looking for in menopause care,” and a recurring question was about hormone testing, she said. Nontraditional practitioners may offer hormone testing as a way of individualizing care that also involves compounded formulations, and other treatments that are not standard of care. “In all of our protocols we follow what is recommended by standard organizations such as ACOG [American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists] and NAMS.”
The Cusp’s newest service is an at-home hormone test currently for women in New York and California, but the company plans to expand this service. The hormone test, while not essential, is another tool to guide menopause management, and having a sense of when menopause will occur “gives us a chance to talk to people about behavioral changes and time to personalize a treatment protocol,” Dr. Goldman said.
The test is based in part on the anti-Müllerian hormone, which recent studies have shown is useful in predicting time to menopause. This, in combination with other hormone tests and other clinical information, will allow the Cusp’s menopause specialists to help women in perimenopause gain perspective on their symptoms and design a treatment plan that can evolve as their needs change, she explained.
“The more information you know about when menopause is going to be happening, you can tailor your treatment plan,” Dr. Goldman said. For example, a woman who may be 2 years away from menopause might consider a naturopathic approach at first, and switch to a different therapy as menopause occurs. “We know that the risks of cardiovascular disease and bone loss increase after menopause, and knowing the time to menopause gives us more guidance when educating patients about healthy lifestyle habits such as exercise and dietary changes that can help reduce these risks.”
The Cusp allows patients to use money in flexible spending accounts or health savings accounts to pay for the program. If doctors require lab tests or other procedures, these are covered through the patients’ regular health insurance as they would be if requested by a primary care physician or other health care professional.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented that part of the value in a telehealth site such as the Cusp is to serve as “a resource for reproductively aging women to understand what is happening to them.”
Any way to improve education on the topic of menopause is empowering to women, said Dr. Pal, professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale. “This is an opportunity for patients to have access to a directed evaluation” of menopause-related symptoms. Then, when women visit their regular health care provider in person, they are well-equipped with knowledge to ask more informed questions and discuss a wide range of treatment options.
Dr. Pal noted that the hormone test is less valuable than the interaction between physicians and patients, whether online or in person.
“Menopause is a Monday morning quarterback diagnosis,” she said, emphasizing that, not only is a year without menses part of the diagnosis of menopause, many women in perimenopause can have wide fluctuations in hormone levels, so a test is more of a snapshot than a diagnostic tool, and that the results might cause unnecessary angst and concerns for patients.
However, part of the value of a telehealth site that focuses on menopause is that it gives women a place to learn more about their biology and to clarify their questions about symptoms and become aware of a range of treatment options. Telehealth consultations also can help women recognize how other factors such as lifestyle modifications can play a role in menopause symptoms, and how modifying these factors may provide some relief, she said.
Dr. Pal said she would be cautious about the idea of prescribing without seeing the patient in person, but noted that telehealth sites such as the Cusp can be a win-win to enhance women’s health when used in combination with regular in-person visits to an ob.gyn. The added value in patients’ being able to discuss their concerns and to learn more about their symptoms means that they will be better informed to develop a menopause management strategy in partnership with their providers, said Dr. Pal, who is not associated with the Cusp.
Dr. Goldman disclosed receiving compensation from the Cusp for her advisory work. She also holds stock options in the company. Dr. Pal, who is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board, had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Appendix may be common site of endometriosis
Among women who have a coincidental appendectomy during surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, about 15% have appendiceal endometriosis confirmed by pathological examination, according to a study.
“In the women with appendiceal endometriosis, only 26% had an appendix that looked abnormal,” said Whitney T. Ross, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Penn State Health, Hershey.
The results, presented at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, indicate that “appendiceal endometriosis is common in women receiving surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis,” she said. “This study and multiple other studies have also demonstrated that coincidental appendectomy is safe.”
The long-term impact of coincidental appendectomy and its effect on quality of life are not known, however, which may make it difficult to weigh the costs and benefits of the procedure, Dr. Ross said. “It is important to talk to patients about this procedure and determine which approach is the right approach for your institution.”
The study of 609 coincidental appendectomies did not include patients with retrocecal appendices, which may confound the true rate of appendiceal endometriosis, commented Saifuddin T. Mama, MD, MPH, of Rowan University, Camden, N.J.
When the investigators started the study, they were not sure of the risks and benefits of the procedure in patients with retrocecal appendices. An anecdotal report from another research group suggests that outcomes with retrocecal appendices may not be significantly different. “But that is certainly an important question and one that we would like to address in a future prospective study,” Dr. Ross said.
Surgeons have debated the role of coincidental appendectomy during gynecologic surgery. Concerns about safety and questions about the prevalence of appendiceal pathology are reasons that coincidental appendectomy has not been more widely adopted. On the other hand, the procedure may benefit patients and aid diagnosis.
To evaluate the role of coincidental appendectomy in the surgical excision of endometriosis, Dr. Ross and colleagues analyzed data from consecutive coincidental appendectomies performed at one institution between 2013 and 2019. They identified cases in a prospectively maintained surgical database to assess safety and the prevalence of appendiceal pathology.
The indication for surgery was chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis for 42 patients, stage I-II endometriosis for 388 patients, and stage III-IV endometriosis for 179 patients.
Surgeries included laparoscopic hysterectomy (77.5%), operative laparoscopy (19.9%), and laparoscopic trachelectomy (2.6%). Pathological analysis of the appendices identified endometriosis in 14.9%, malignancy in 0.7%, polyps in 0.5%, and appendicitis in 0.3%.
Among women with chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis, 2.4% had appendiceal endometriosis. Among those with stage I-II endometriosis, 7% had appendiceal endometriosis, and in patients with stage III-IV endometriosis, the rate of appendiceal endometriosis was 35.2%.
In about 6% of patients with appendiceal endometriosis, the appendix was the only site of pathologically confirmed endometriosis.
Compared with chronic pelvic pain, stage III-IV endometriosis was associated with a significantly increased risk of appendiceal endometriosis (odds ratio, 22.2). The likelihood of appendiceal endometriosis also increased when the appendix looked abnormal (odds ratio, 6.5).
The probability of diagnosing appendiceal endometriosis also increases with the number of other locations of confirmed endometriosis.
“Our surgical decision making is based off of intraoperative findings. However, the final gold-standard diagnosis can’t take place until the pathologic specimen is analyzed,” she said. “We also know that there is a significant discordance, as high as 50%, in early-stage endometriosis between visual inspection and pathology findings.”
There were no complications related to the performance of a coincidental appendectomy during surgery or in the 12 weeks after.
Dr. Ross outlined surgeons’ three main options for performing coincidental appendectomy in patients undergoing surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis: universal coincidental appendectomy, targeted appendectomy based on operative findings, and performing the procedure based on the appearance of the appendix.
Basing the decision on appearance “is going to miss a lot of appendiceal endometriosis,” Dr. Ross said. In the present study, 67 of the 91 cases, about 74%, would have been missed.
Dr. Ross and Dr. Mama had no relevant financial disclosures. The study coauthors disclosed ties to Titan Medical, Merck, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Ross WT et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
Among women who have a coincidental appendectomy during surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, about 15% have appendiceal endometriosis confirmed by pathological examination, according to a study.
“In the women with appendiceal endometriosis, only 26% had an appendix that looked abnormal,” said Whitney T. Ross, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Penn State Health, Hershey.
The results, presented at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, indicate that “appendiceal endometriosis is common in women receiving surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis,” she said. “This study and multiple other studies have also demonstrated that coincidental appendectomy is safe.”
The long-term impact of coincidental appendectomy and its effect on quality of life are not known, however, which may make it difficult to weigh the costs and benefits of the procedure, Dr. Ross said. “It is important to talk to patients about this procedure and determine which approach is the right approach for your institution.”
The study of 609 coincidental appendectomies did not include patients with retrocecal appendices, which may confound the true rate of appendiceal endometriosis, commented Saifuddin T. Mama, MD, MPH, of Rowan University, Camden, N.J.
When the investigators started the study, they were not sure of the risks and benefits of the procedure in patients with retrocecal appendices. An anecdotal report from another research group suggests that outcomes with retrocecal appendices may not be significantly different. “But that is certainly an important question and one that we would like to address in a future prospective study,” Dr. Ross said.
Surgeons have debated the role of coincidental appendectomy during gynecologic surgery. Concerns about safety and questions about the prevalence of appendiceal pathology are reasons that coincidental appendectomy has not been more widely adopted. On the other hand, the procedure may benefit patients and aid diagnosis.
To evaluate the role of coincidental appendectomy in the surgical excision of endometriosis, Dr. Ross and colleagues analyzed data from consecutive coincidental appendectomies performed at one institution between 2013 and 2019. They identified cases in a prospectively maintained surgical database to assess safety and the prevalence of appendiceal pathology.
The indication for surgery was chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis for 42 patients, stage I-II endometriosis for 388 patients, and stage III-IV endometriosis for 179 patients.
Surgeries included laparoscopic hysterectomy (77.5%), operative laparoscopy (19.9%), and laparoscopic trachelectomy (2.6%). Pathological analysis of the appendices identified endometriosis in 14.9%, malignancy in 0.7%, polyps in 0.5%, and appendicitis in 0.3%.
Among women with chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis, 2.4% had appendiceal endometriosis. Among those with stage I-II endometriosis, 7% had appendiceal endometriosis, and in patients with stage III-IV endometriosis, the rate of appendiceal endometriosis was 35.2%.
In about 6% of patients with appendiceal endometriosis, the appendix was the only site of pathologically confirmed endometriosis.
Compared with chronic pelvic pain, stage III-IV endometriosis was associated with a significantly increased risk of appendiceal endometriosis (odds ratio, 22.2). The likelihood of appendiceal endometriosis also increased when the appendix looked abnormal (odds ratio, 6.5).
The probability of diagnosing appendiceal endometriosis also increases with the number of other locations of confirmed endometriosis.
“Our surgical decision making is based off of intraoperative findings. However, the final gold-standard diagnosis can’t take place until the pathologic specimen is analyzed,” she said. “We also know that there is a significant discordance, as high as 50%, in early-stage endometriosis between visual inspection and pathology findings.”
There were no complications related to the performance of a coincidental appendectomy during surgery or in the 12 weeks after.
Dr. Ross outlined surgeons’ three main options for performing coincidental appendectomy in patients undergoing surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis: universal coincidental appendectomy, targeted appendectomy based on operative findings, and performing the procedure based on the appearance of the appendix.
Basing the decision on appearance “is going to miss a lot of appendiceal endometriosis,” Dr. Ross said. In the present study, 67 of the 91 cases, about 74%, would have been missed.
Dr. Ross and Dr. Mama had no relevant financial disclosures. The study coauthors disclosed ties to Titan Medical, Merck, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Ross WT et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
Among women who have a coincidental appendectomy during surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis, about 15% have appendiceal endometriosis confirmed by pathological examination, according to a study.
“In the women with appendiceal endometriosis, only 26% had an appendix that looked abnormal,” said Whitney T. Ross, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Penn State Health, Hershey.
The results, presented at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, indicate that “appendiceal endometriosis is common in women receiving surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis,” she said. “This study and multiple other studies have also demonstrated that coincidental appendectomy is safe.”
The long-term impact of coincidental appendectomy and its effect on quality of life are not known, however, which may make it difficult to weigh the costs and benefits of the procedure, Dr. Ross said. “It is important to talk to patients about this procedure and determine which approach is the right approach for your institution.”
The study of 609 coincidental appendectomies did not include patients with retrocecal appendices, which may confound the true rate of appendiceal endometriosis, commented Saifuddin T. Mama, MD, MPH, of Rowan University, Camden, N.J.
When the investigators started the study, they were not sure of the risks and benefits of the procedure in patients with retrocecal appendices. An anecdotal report from another research group suggests that outcomes with retrocecal appendices may not be significantly different. “But that is certainly an important question and one that we would like to address in a future prospective study,” Dr. Ross said.
Surgeons have debated the role of coincidental appendectomy during gynecologic surgery. Concerns about safety and questions about the prevalence of appendiceal pathology are reasons that coincidental appendectomy has not been more widely adopted. On the other hand, the procedure may benefit patients and aid diagnosis.
To evaluate the role of coincidental appendectomy in the surgical excision of endometriosis, Dr. Ross and colleagues analyzed data from consecutive coincidental appendectomies performed at one institution between 2013 and 2019. They identified cases in a prospectively maintained surgical database to assess safety and the prevalence of appendiceal pathology.
The indication for surgery was chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis for 42 patients, stage I-II endometriosis for 388 patients, and stage III-IV endometriosis for 179 patients.
Surgeries included laparoscopic hysterectomy (77.5%), operative laparoscopy (19.9%), and laparoscopic trachelectomy (2.6%). Pathological analysis of the appendices identified endometriosis in 14.9%, malignancy in 0.7%, polyps in 0.5%, and appendicitis in 0.3%.
Among women with chronic pelvic pain but no visualized endometriosis, 2.4% had appendiceal endometriosis. Among those with stage I-II endometriosis, 7% had appendiceal endometriosis, and in patients with stage III-IV endometriosis, the rate of appendiceal endometriosis was 35.2%.
In about 6% of patients with appendiceal endometriosis, the appendix was the only site of pathologically confirmed endometriosis.
Compared with chronic pelvic pain, stage III-IV endometriosis was associated with a significantly increased risk of appendiceal endometriosis (odds ratio, 22.2). The likelihood of appendiceal endometriosis also increased when the appendix looked abnormal (odds ratio, 6.5).
The probability of diagnosing appendiceal endometriosis also increases with the number of other locations of confirmed endometriosis.
“Our surgical decision making is based off of intraoperative findings. However, the final gold-standard diagnosis can’t take place until the pathologic specimen is analyzed,” she said. “We also know that there is a significant discordance, as high as 50%, in early-stage endometriosis between visual inspection and pathology findings.”
There were no complications related to the performance of a coincidental appendectomy during surgery or in the 12 weeks after.
Dr. Ross outlined surgeons’ three main options for performing coincidental appendectomy in patients undergoing surgery for chronic pelvic pain or endometriosis: universal coincidental appendectomy, targeted appendectomy based on operative findings, and performing the procedure based on the appearance of the appendix.
Basing the decision on appearance “is going to miss a lot of appendiceal endometriosis,” Dr. Ross said. In the present study, 67 of the 91 cases, about 74%, would have been missed.
Dr. Ross and Dr. Mama had no relevant financial disclosures. The study coauthors disclosed ties to Titan Medical, Merck, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Ross WT et al. SGS 2020, Abstract 14.
FROM SGS 2020
Does stirrup choice influence vaginal surgery outcome?
according to the first randomized controlled trial comparing both types of lithotomy stirrups.
“Participants positioned in candy cane stirrups had greater hip abduction than those positioned in boot stirrups, which could provide a rationale for our findings,” suggested Ankita Gupta, MD, MPH, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), and colleagues. Their report is in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
But one expert questions this interpretation, calling it a major limitation of the study.
“The only difference between the two arms of the study is associated with the angles between the femurs,” said Rosanne M. Kho, MD, a gynecologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in the study. “The difference of the angles at the femur is not inherent to the type of stirrup but in the method in which the patients were positioned using the two different types of stirrups,” she said. “The same wide angle between the femurs can be attained with the boot stirrups if the patient is not positioned properly. To determine if the same benefit in physical function is achieved with a lesser angle between the femur, the investigators should use only one type of stirrup (whether the candy cane or the boot stirrups) and change only the angles of the femur.”
The study was a single-masked, randomized controlled trial of women undergoing vaginal surgery at the University of Louisville’s division of urogynecology between March 2018 and Oct. 2019. Surgeries included any combination of vaginal hysterectomy, vaginal vault suspension (uterosacral or sacrospinous ligament fixation), vaginectomy (partial or total), mid-urethral slings, or other surgeries such as urethral diverticulectomy, fistula repair, or mesh excision.
Among the 138 women included in the intention-to-treat analysis, 72 were randomized to candy cane, and 66 to boot (Yellofin) stirrups. They were positioned in the assigned stirrup by the attending surgeon, with assistance from the surgical team, after administration of anesthesia and were not informed of their allocation until the end of the study at 6 weeks post surgery.
On day 1 post surgery, a 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) questionnaire was administered for pain in the lower back, hips, buttocks, thighs, knees, calves, and feet, followed by a series of questionnaires at 6 weeks post surgery, including the PROMIS (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System) forms on physical function, pain intensity, and pain interference, as well as the Pelvic Floor Disability Index (PFDI-20) and the Patient Global Impression of Improvement forms.
While the authors acknowledged that neurologic injuries following vaginal surgery are rare, and therefore difficult to measure, physical function is a “prudent” alternative measurement.
Although the study was designed to compare lithotomy stirrups, patient positioning also was measured. Once the patient was anesthetized, the surgeon used a goniometer to measure flexion at the hip and knee joints, the angle of abduction and external rotation at the hip. The “angle between the femurs” was measured by placing the fulcrum of the goniometer at the anal opening.
While the angles of flexion at the hips and knees were similar between groups, the study found a significant difference between groups in the angle between the femurs (mean ± standard deviation, 88.7 ± 13.4 candy cane vs. 77.2 ± 13.3 boot, P < .01).
In addition, the primary outcome, change in physical function based on the PROMIS physical function shortform-20a, was significantly different between the two groups: While subjects in the candy cane group demonstrated a decline of 1.9 in mean physical function score at 6 weeks compared to baseline, those in the boot stirrup group showed an increase of 1.9 from baseline. The mean 6-week postoperative scores were 45.8 versus 49.8 for the candy cane and boot stirrup groups respectively (P < .01).
Although it was “well executed by a well-respected group of vaginal surgeons at a major academic institution,” the study has other limitations, noted Dr. Kho.
“Though the measurements were obtained with the goniometer at the beginning of the surgery, it does not appear that a repeat measurement was performed at the end of the case. Is it possible that positioning could have shifted and resulted in further change in the angle of the femur/hip/knees compared to the beginning of the surgery?” she asked.
In addition, “compared to the candy canes, the boot stirrup has bulky boots that could limit opportunities for bedside assistants who were standing next to the primary surgeon to lean against the patient’s thighs during the surgery. Were there measures done to ensure that assistants were not leaning against the [candy cane] patients?”
In terms of the 6-week outcome measure, Dr. Kho suggested PROMIS outcomes measured at 2 weeks and at 4 or 6 weeks “would have provided greater insight to the study question.
“The authors acknowledge that neuropathies due to patient positioning manifest soon after surgery and tend to be transient. Incidence of neuropathy is extremely low in both groups and is equivalent. Factors that could impair quick return to normal activity as a result of the neuromuscular effects due to patient positioning should have been measured earlier,” she suggested.
Finally, Dr. Kho noted that the authors “fail to provide any likely rationale for the impaired physical function measured at 6 weeks that can be attributed to the difference in the angles at the femur. The findings of decreased physical function at 6 weeks in the candy cane group may be incidental, and may be different if measured at an earlier time (which would be more pertinent for this study) or at a later time such as 3 months.”
Individual authors acknowledged personal funds from Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, Elsevier publishing, RBI Medical, and AMAG Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kho had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Gupta A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 July 8. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003954.
according to the first randomized controlled trial comparing both types of lithotomy stirrups.
“Participants positioned in candy cane stirrups had greater hip abduction than those positioned in boot stirrups, which could provide a rationale for our findings,” suggested Ankita Gupta, MD, MPH, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), and colleagues. Their report is in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
But one expert questions this interpretation, calling it a major limitation of the study.
“The only difference between the two arms of the study is associated with the angles between the femurs,” said Rosanne M. Kho, MD, a gynecologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in the study. “The difference of the angles at the femur is not inherent to the type of stirrup but in the method in which the patients were positioned using the two different types of stirrups,” she said. “The same wide angle between the femurs can be attained with the boot stirrups if the patient is not positioned properly. To determine if the same benefit in physical function is achieved with a lesser angle between the femur, the investigators should use only one type of stirrup (whether the candy cane or the boot stirrups) and change only the angles of the femur.”
The study was a single-masked, randomized controlled trial of women undergoing vaginal surgery at the University of Louisville’s division of urogynecology between March 2018 and Oct. 2019. Surgeries included any combination of vaginal hysterectomy, vaginal vault suspension (uterosacral or sacrospinous ligament fixation), vaginectomy (partial or total), mid-urethral slings, or other surgeries such as urethral diverticulectomy, fistula repair, or mesh excision.
Among the 138 women included in the intention-to-treat analysis, 72 were randomized to candy cane, and 66 to boot (Yellofin) stirrups. They were positioned in the assigned stirrup by the attending surgeon, with assistance from the surgical team, after administration of anesthesia and were not informed of their allocation until the end of the study at 6 weeks post surgery.
On day 1 post surgery, a 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) questionnaire was administered for pain in the lower back, hips, buttocks, thighs, knees, calves, and feet, followed by a series of questionnaires at 6 weeks post surgery, including the PROMIS (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System) forms on physical function, pain intensity, and pain interference, as well as the Pelvic Floor Disability Index (PFDI-20) and the Patient Global Impression of Improvement forms.
While the authors acknowledged that neurologic injuries following vaginal surgery are rare, and therefore difficult to measure, physical function is a “prudent” alternative measurement.
Although the study was designed to compare lithotomy stirrups, patient positioning also was measured. Once the patient was anesthetized, the surgeon used a goniometer to measure flexion at the hip and knee joints, the angle of abduction and external rotation at the hip. The “angle between the femurs” was measured by placing the fulcrum of the goniometer at the anal opening.
While the angles of flexion at the hips and knees were similar between groups, the study found a significant difference between groups in the angle between the femurs (mean ± standard deviation, 88.7 ± 13.4 candy cane vs. 77.2 ± 13.3 boot, P < .01).
In addition, the primary outcome, change in physical function based on the PROMIS physical function shortform-20a, was significantly different between the two groups: While subjects in the candy cane group demonstrated a decline of 1.9 in mean physical function score at 6 weeks compared to baseline, those in the boot stirrup group showed an increase of 1.9 from baseline. The mean 6-week postoperative scores were 45.8 versus 49.8 for the candy cane and boot stirrup groups respectively (P < .01).
Although it was “well executed by a well-respected group of vaginal surgeons at a major academic institution,” the study has other limitations, noted Dr. Kho.
“Though the measurements were obtained with the goniometer at the beginning of the surgery, it does not appear that a repeat measurement was performed at the end of the case. Is it possible that positioning could have shifted and resulted in further change in the angle of the femur/hip/knees compared to the beginning of the surgery?” she asked.
In addition, “compared to the candy canes, the boot stirrup has bulky boots that could limit opportunities for bedside assistants who were standing next to the primary surgeon to lean against the patient’s thighs during the surgery. Were there measures done to ensure that assistants were not leaning against the [candy cane] patients?”
In terms of the 6-week outcome measure, Dr. Kho suggested PROMIS outcomes measured at 2 weeks and at 4 or 6 weeks “would have provided greater insight to the study question.
“The authors acknowledge that neuropathies due to patient positioning manifest soon after surgery and tend to be transient. Incidence of neuropathy is extremely low in both groups and is equivalent. Factors that could impair quick return to normal activity as a result of the neuromuscular effects due to patient positioning should have been measured earlier,” she suggested.
Finally, Dr. Kho noted that the authors “fail to provide any likely rationale for the impaired physical function measured at 6 weeks that can be attributed to the difference in the angles at the femur. The findings of decreased physical function at 6 weeks in the candy cane group may be incidental, and may be different if measured at an earlier time (which would be more pertinent for this study) or at a later time such as 3 months.”
Individual authors acknowledged personal funds from Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, Elsevier publishing, RBI Medical, and AMAG Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kho had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Gupta A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 July 8. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003954.
according to the first randomized controlled trial comparing both types of lithotomy stirrups.
“Participants positioned in candy cane stirrups had greater hip abduction than those positioned in boot stirrups, which could provide a rationale for our findings,” suggested Ankita Gupta, MD, MPH, of the University of Louisville (Ky.), and colleagues. Their report is in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
But one expert questions this interpretation, calling it a major limitation of the study.
“The only difference between the two arms of the study is associated with the angles between the femurs,” said Rosanne M. Kho, MD, a gynecologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in the study. “The difference of the angles at the femur is not inherent to the type of stirrup but in the method in which the patients were positioned using the two different types of stirrups,” she said. “The same wide angle between the femurs can be attained with the boot stirrups if the patient is not positioned properly. To determine if the same benefit in physical function is achieved with a lesser angle between the femur, the investigators should use only one type of stirrup (whether the candy cane or the boot stirrups) and change only the angles of the femur.”
The study was a single-masked, randomized controlled trial of women undergoing vaginal surgery at the University of Louisville’s division of urogynecology between March 2018 and Oct. 2019. Surgeries included any combination of vaginal hysterectomy, vaginal vault suspension (uterosacral or sacrospinous ligament fixation), vaginectomy (partial or total), mid-urethral slings, or other surgeries such as urethral diverticulectomy, fistula repair, or mesh excision.
Among the 138 women included in the intention-to-treat analysis, 72 were randomized to candy cane, and 66 to boot (Yellofin) stirrups. They were positioned in the assigned stirrup by the attending surgeon, with assistance from the surgical team, after administration of anesthesia and were not informed of their allocation until the end of the study at 6 weeks post surgery.
On day 1 post surgery, a 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) questionnaire was administered for pain in the lower back, hips, buttocks, thighs, knees, calves, and feet, followed by a series of questionnaires at 6 weeks post surgery, including the PROMIS (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System) forms on physical function, pain intensity, and pain interference, as well as the Pelvic Floor Disability Index (PFDI-20) and the Patient Global Impression of Improvement forms.
While the authors acknowledged that neurologic injuries following vaginal surgery are rare, and therefore difficult to measure, physical function is a “prudent” alternative measurement.
Although the study was designed to compare lithotomy stirrups, patient positioning also was measured. Once the patient was anesthetized, the surgeon used a goniometer to measure flexion at the hip and knee joints, the angle of abduction and external rotation at the hip. The “angle between the femurs” was measured by placing the fulcrum of the goniometer at the anal opening.
While the angles of flexion at the hips and knees were similar between groups, the study found a significant difference between groups in the angle between the femurs (mean ± standard deviation, 88.7 ± 13.4 candy cane vs. 77.2 ± 13.3 boot, P < .01).
In addition, the primary outcome, change in physical function based on the PROMIS physical function shortform-20a, was significantly different between the two groups: While subjects in the candy cane group demonstrated a decline of 1.9 in mean physical function score at 6 weeks compared to baseline, those in the boot stirrup group showed an increase of 1.9 from baseline. The mean 6-week postoperative scores were 45.8 versus 49.8 for the candy cane and boot stirrup groups respectively (P < .01).
Although it was “well executed by a well-respected group of vaginal surgeons at a major academic institution,” the study has other limitations, noted Dr. Kho.
“Though the measurements were obtained with the goniometer at the beginning of the surgery, it does not appear that a repeat measurement was performed at the end of the case. Is it possible that positioning could have shifted and resulted in further change in the angle of the femur/hip/knees compared to the beginning of the surgery?” she asked.
In addition, “compared to the candy canes, the boot stirrup has bulky boots that could limit opportunities for bedside assistants who were standing next to the primary surgeon to lean against the patient’s thighs during the surgery. Were there measures done to ensure that assistants were not leaning against the [candy cane] patients?”
In terms of the 6-week outcome measure, Dr. Kho suggested PROMIS outcomes measured at 2 weeks and at 4 or 6 weeks “would have provided greater insight to the study question.
“The authors acknowledge that neuropathies due to patient positioning manifest soon after surgery and tend to be transient. Incidence of neuropathy is extremely low in both groups and is equivalent. Factors that could impair quick return to normal activity as a result of the neuromuscular effects due to patient positioning should have been measured earlier,” she suggested.
Finally, Dr. Kho noted that the authors “fail to provide any likely rationale for the impaired physical function measured at 6 weeks that can be attributed to the difference in the angles at the femur. The findings of decreased physical function at 6 weeks in the candy cane group may be incidental, and may be different if measured at an earlier time (which would be more pertinent for this study) or at a later time such as 3 months.”
Individual authors acknowledged personal funds from Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, Elsevier publishing, RBI Medical, and AMAG Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kho had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Gupta A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 July 8. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003954.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY