User login
Spiky Papules on the Dorsal Feet
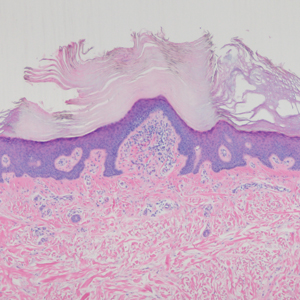
The Diagnosis: Hyperkeratosis Lenticularis Perstans (Flegel Disease)
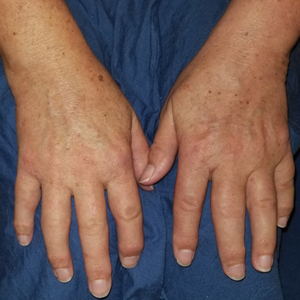
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, also known as Flegel disease, is a rare dermatosis first described by Flegel1 in 1958. This benign disorder is characterized by multiple asymptomatic 1- to 5-mm keratotic papules in a symmetric distribution favoring the dorsal aspects of the feet and distal extremities in adults. An autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern has been postulated, though many cases sporadically occur.2 The characteristic spiky papules typically appear during mid to late adulthood and tend to persist. Treatment options are lacking, with reports of partial or no response to topical calcipotriol, topical 5-fluorouracil, cryotherapy, and topical and oral retinoids.3,4
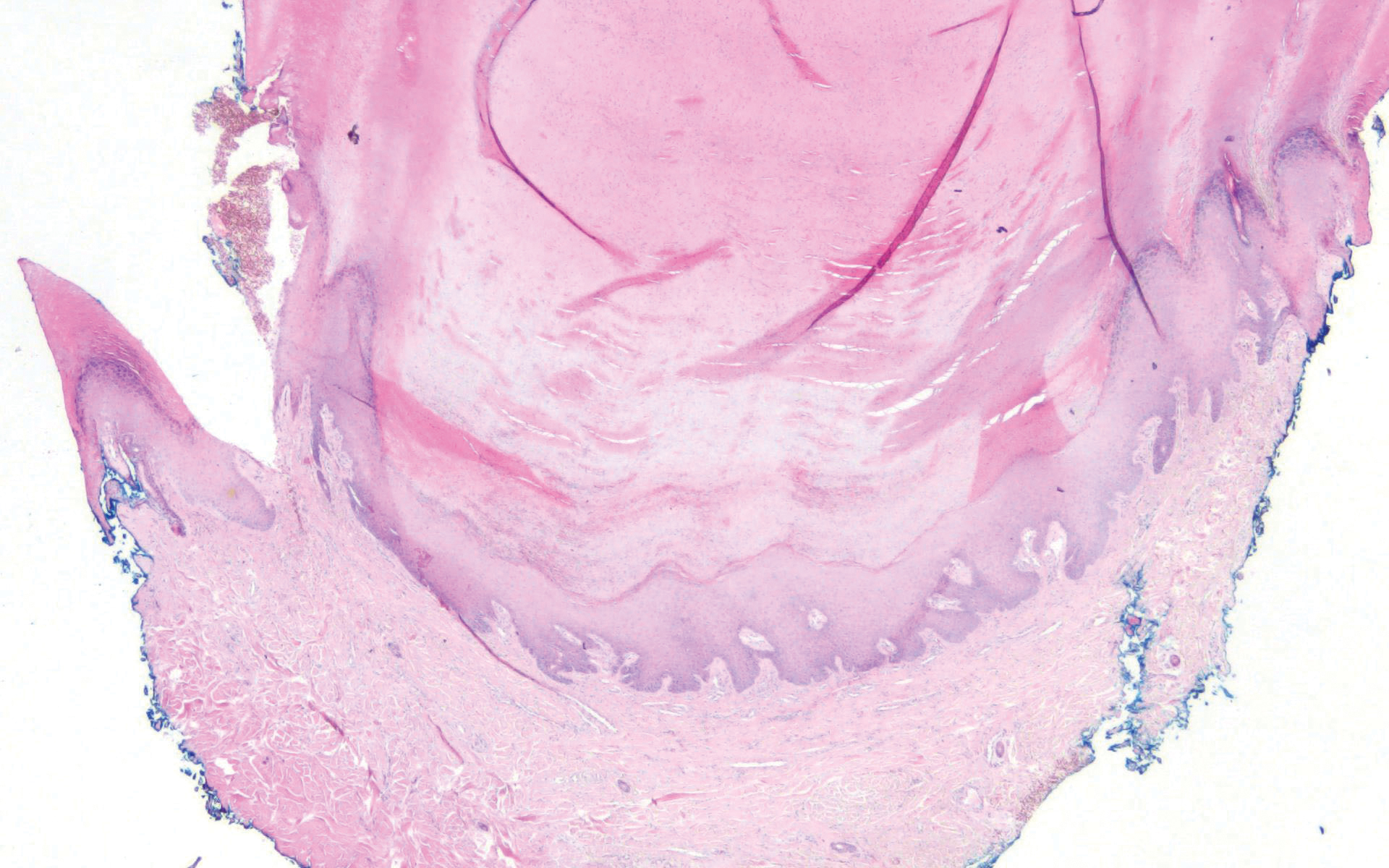
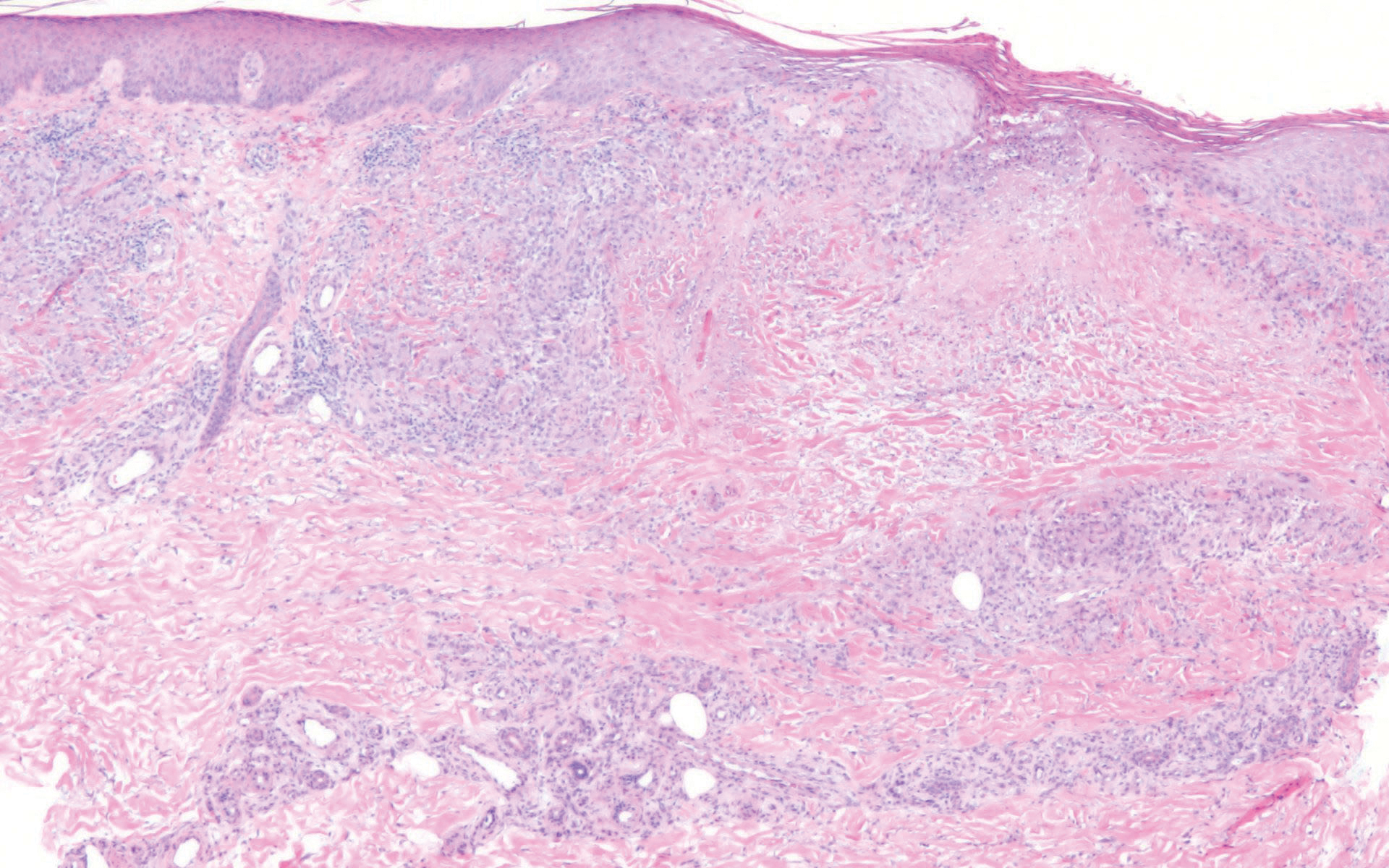
The histopathology of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is distinct, showing a central discrete area of orthohyperkeratosis with patchy parakeratosis flanked by a normal stratum corneum. The underlying epidermis typically shows effacement of the rete ridge pattern with subtle basal zone vacuolization and rare necrotic keratinocytes with an underlying lichenoid infiltrate within the papillary dermis comprised of lymphomononuclear cells.
In contrast, punctate porokeratosis clinically tends to involve the palms and soles, though the arms and legs also may be involved. This entity tends to occur during adolescence. A raised hyperkeratotic papule clinically is present. Histopathologically, the epidermis has a cup-shaped depression filled with hyperkeratosis and a column of parakeratosis (coronoid lamellae)(Figure 1).
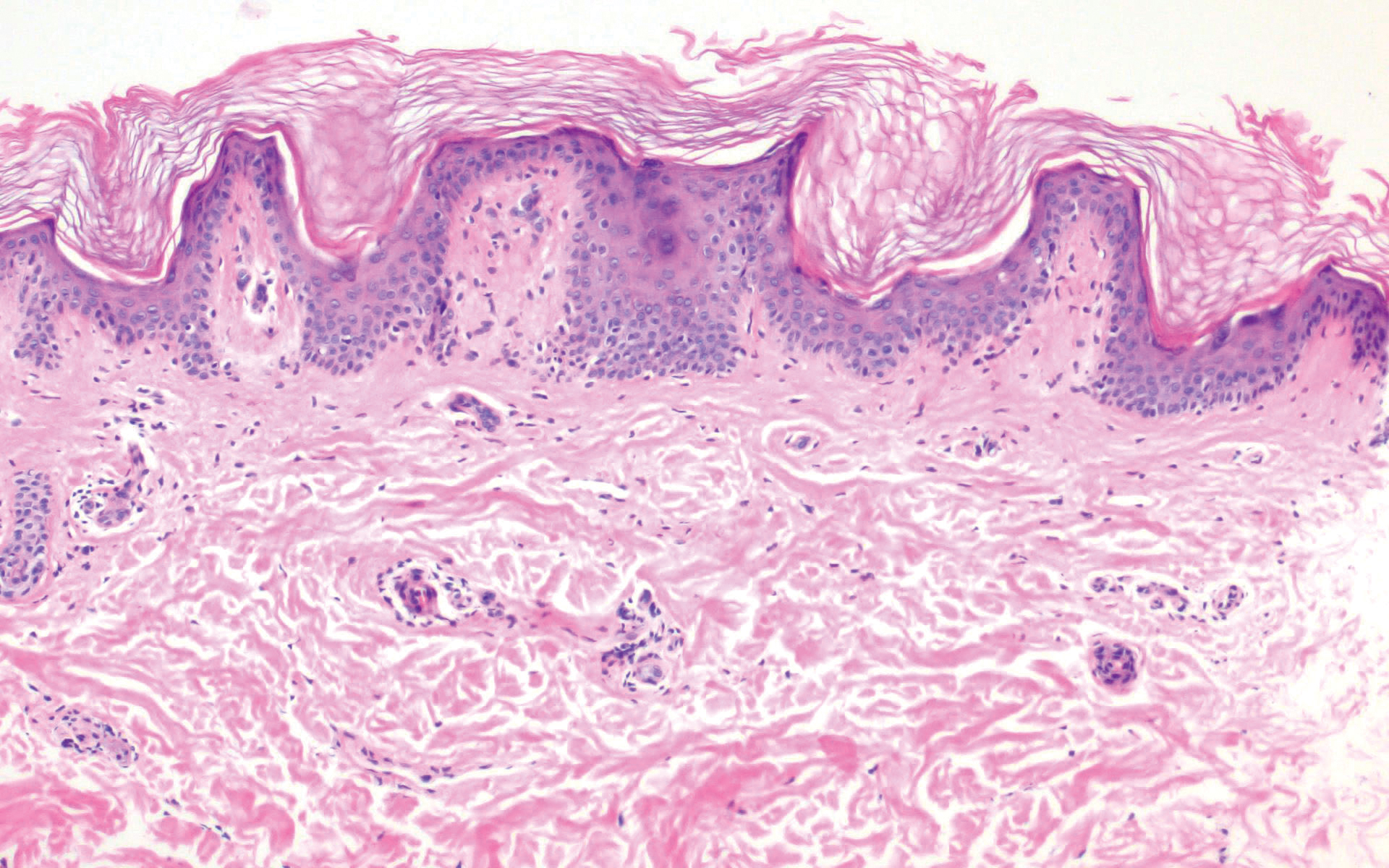
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf clinically appears on the dorsal aspects of the hands and feet as small warty papules in association with Darier disease. It typically presents during early childhood. Histopathology shows tiered hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2).
Perforating granuloma annulare presents on the dorsal aspects of the hands and fingers as scaly papules with either central umbilication or keratotic plugs. Histopathology shows transepidermal elimination of degenerated collagen (Figure 3).
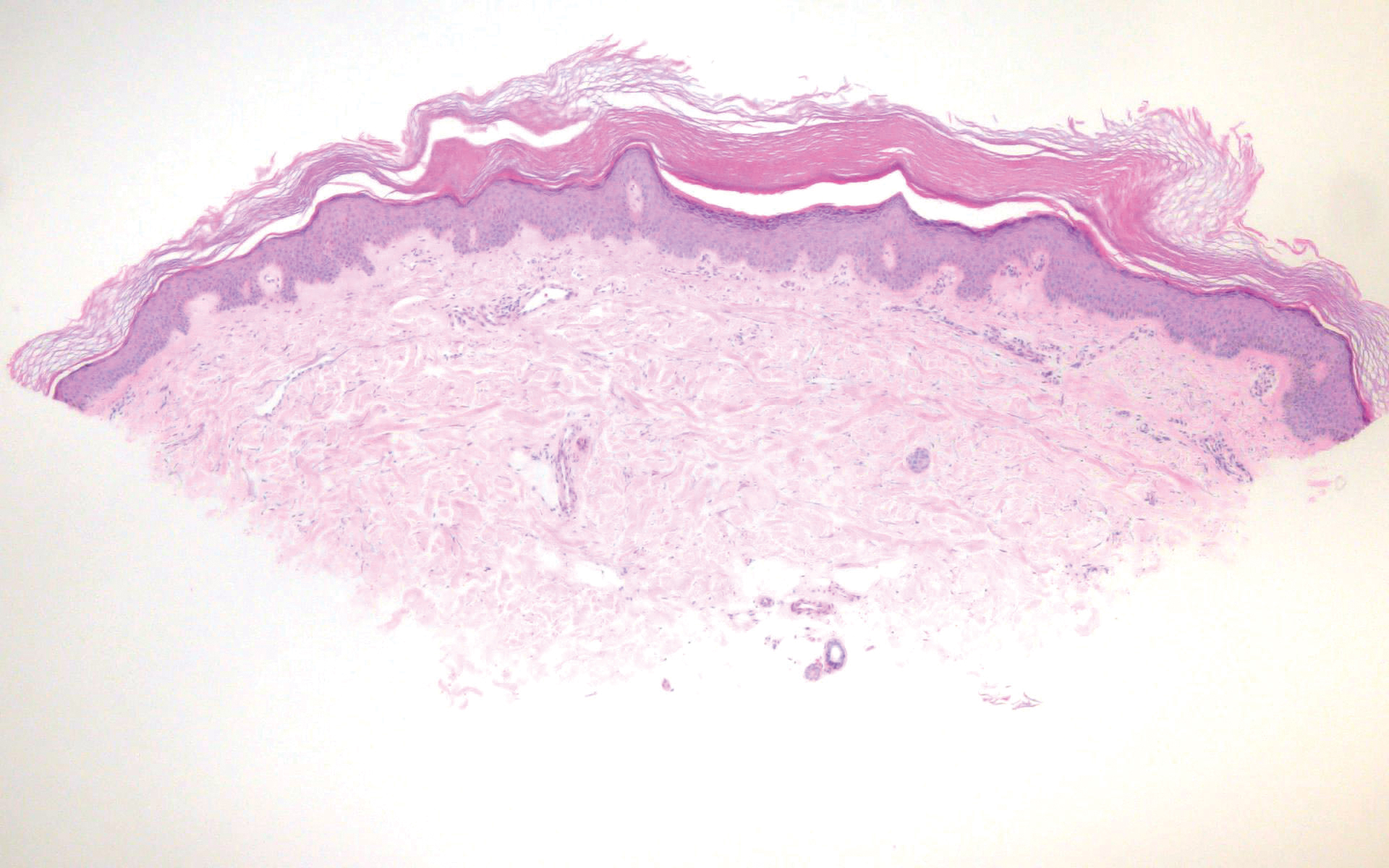
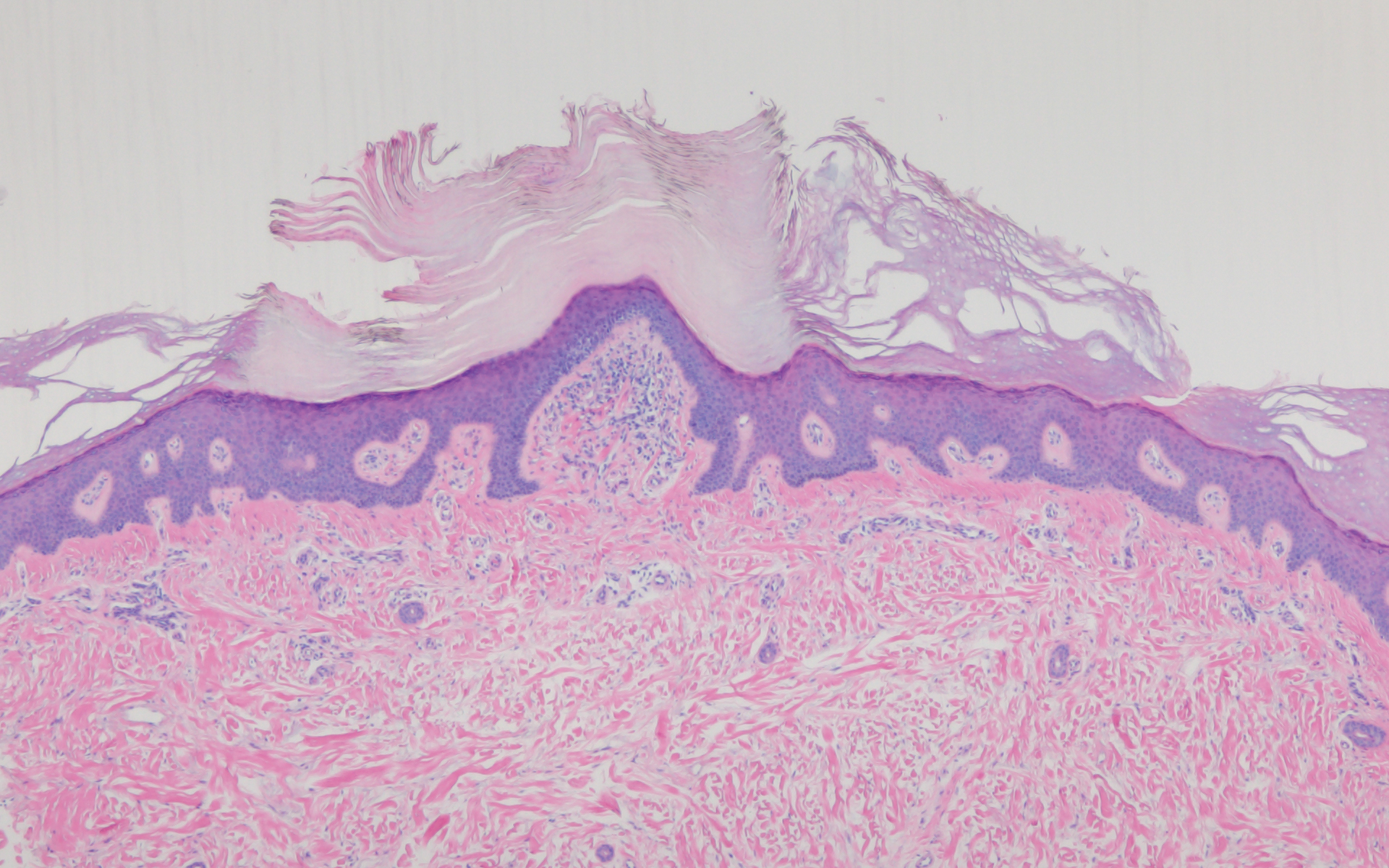
Stucco keratoses present on the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles but are waxy smooth papules as opposed to hyperkeratotic spiky papules. Histologically, they are characterized by retention hyperkeratosis with lack of parakeratosis and regular acanthosis with a "string sign" indicating that the lesion extends to a uniform depth. (Figure 4).
- Flegel H. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Hautzarzt. 1958;9:363-364.
- Ando K, Hattori H, Yamauchi Y. Histopathological differences between early and old lesions of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:122-126.
- Langer K, Zonzits E, Konrad K. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). ultrastructural study of lesional and perilesional skin and therapeutic trial of topical tretinoin versus 5-fluorouracil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:812-816.
- Blaheta HJ, Metzler G, Rassner G, et al. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease)--lack of response to treatment with tacalcitol and calcipotriol. Dermatology. 2001;202:255-258.
The Diagnosis: Hyperkeratosis Lenticularis Perstans (Flegel Disease)
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, also known as Flegel disease, is a rare dermatosis first described by Flegel1 in 1958. This benign disorder is characterized by multiple asymptomatic 1- to 5-mm keratotic papules in a symmetric distribution favoring the dorsal aspects of the feet and distal extremities in adults. An autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern has been postulated, though many cases sporadically occur.2 The characteristic spiky papules typically appear during mid to late adulthood and tend to persist. Treatment options are lacking, with reports of partial or no response to topical calcipotriol, topical 5-fluorouracil, cryotherapy, and topical and oral retinoids.3,4
The histopathology of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is distinct, showing a central discrete area of orthohyperkeratosis with patchy parakeratosis flanked by a normal stratum corneum. The underlying epidermis typically shows effacement of the rete ridge pattern with subtle basal zone vacuolization and rare necrotic keratinocytes with an underlying lichenoid infiltrate within the papillary dermis comprised of lymphomononuclear cells.
In contrast, punctate porokeratosis clinically tends to involve the palms and soles, though the arms and legs also may be involved. This entity tends to occur during adolescence. A raised hyperkeratotic papule clinically is present. Histopathologically, the epidermis has a cup-shaped depression filled with hyperkeratosis and a column of parakeratosis (coronoid lamellae)(Figure 1).

Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf clinically appears on the dorsal aspects of the hands and feet as small warty papules in association with Darier disease. It typically presents during early childhood. Histopathology shows tiered hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2).

Perforating granuloma annulare presents on the dorsal aspects of the hands and fingers as scaly papules with either central umbilication or keratotic plugs. Histopathology shows transepidermal elimination of degenerated collagen (Figure 3).

Stucco keratoses present on the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles but are waxy smooth papules as opposed to hyperkeratotic spiky papules. Histologically, they are characterized by retention hyperkeratosis with lack of parakeratosis and regular acanthosis with a "string sign" indicating that the lesion extends to a uniform depth. (Figure 4).

The Diagnosis: Hyperkeratosis Lenticularis Perstans (Flegel Disease)
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, also known as Flegel disease, is a rare dermatosis first described by Flegel1 in 1958. This benign disorder is characterized by multiple asymptomatic 1- to 5-mm keratotic papules in a symmetric distribution favoring the dorsal aspects of the feet and distal extremities in adults. An autosomal-dominant inheritance pattern has been postulated, though many cases sporadically occur.2 The characteristic spiky papules typically appear during mid to late adulthood and tend to persist. Treatment options are lacking, with reports of partial or no response to topical calcipotriol, topical 5-fluorouracil, cryotherapy, and topical and oral retinoids.3,4
The histopathology of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is distinct, showing a central discrete area of orthohyperkeratosis with patchy parakeratosis flanked by a normal stratum corneum. The underlying epidermis typically shows effacement of the rete ridge pattern with subtle basal zone vacuolization and rare necrotic keratinocytes with an underlying lichenoid infiltrate within the papillary dermis comprised of lymphomononuclear cells.
In contrast, punctate porokeratosis clinically tends to involve the palms and soles, though the arms and legs also may be involved. This entity tends to occur during adolescence. A raised hyperkeratotic papule clinically is present. Histopathologically, the epidermis has a cup-shaped depression filled with hyperkeratosis and a column of parakeratosis (coronoid lamellae)(Figure 1).

Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf clinically appears on the dorsal aspects of the hands and feet as small warty papules in association with Darier disease. It typically presents during early childhood. Histopathology shows tiered hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2).

Perforating granuloma annulare presents on the dorsal aspects of the hands and fingers as scaly papules with either central umbilication or keratotic plugs. Histopathology shows transepidermal elimination of degenerated collagen (Figure 3).

Stucco keratoses present on the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles but are waxy smooth papules as opposed to hyperkeratotic spiky papules. Histologically, they are characterized by retention hyperkeratosis with lack of parakeratosis and regular acanthosis with a "string sign" indicating that the lesion extends to a uniform depth. (Figure 4).

- Flegel H. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Hautzarzt. 1958;9:363-364.
- Ando K, Hattori H, Yamauchi Y. Histopathological differences between early and old lesions of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:122-126.
- Langer K, Zonzits E, Konrad K. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). ultrastructural study of lesional and perilesional skin and therapeutic trial of topical tretinoin versus 5-fluorouracil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:812-816.
- Blaheta HJ, Metzler G, Rassner G, et al. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease)--lack of response to treatment with tacalcitol and calcipotriol. Dermatology. 2001;202:255-258.
- Flegel H. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Hautzarzt. 1958;9:363-364.
- Ando K, Hattori H, Yamauchi Y. Histopathological differences between early and old lesions of hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:122-126.
- Langer K, Zonzits E, Konrad K. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease). ultrastructural study of lesional and perilesional skin and therapeutic trial of topical tretinoin versus 5-fluorouracil. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:812-816.
- Blaheta HJ, Metzler G, Rassner G, et al. Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans (Flegel's disease)--lack of response to treatment with tacalcitol and calcipotriol. Dermatology. 2001;202:255-258.
A 54-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with asymptomatic, discrete, rough, red-brown, hyperkeratotic papules on the dorsal aspects of the feet of several years' duration. The lesions spared the soles of the feet and hands. A diagnosis of eczema previously was made by his general practitioner, and he was using moisturizer. No prescription treatments were pursued, and no other rashes or lesions were noted on physical examination. A punch biopsy of a spiky papule was performed.
Cutaneous Collagenous Vasculopathy
To the Editor:
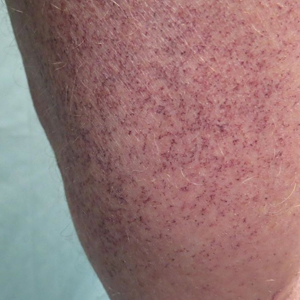
Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy (CCV) is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy characterized by diffuse blanchable telangiectases that usually develop in late adulthood. It appears morphologically identical to generalized essential telangiectasia (GET), but skin biopsy characteristically shows dilated superficial blood vessels in the papillary dermis that are surrounded by a thickened layer of type IV collagen.1 We report a case of CCV occurring in an elderly white man.
A 72-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic rash on the arms, legs, and abdomen of 3 years’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for hypothyroidism, hypertension, reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, coronary artery disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer. He denied any changes in medications or illnesses prior to onset of the rash. Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, blanchable telangiectases on the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1). No petechiae, atrophy, or epidermal changes were appreciated. Darier sign was negative.

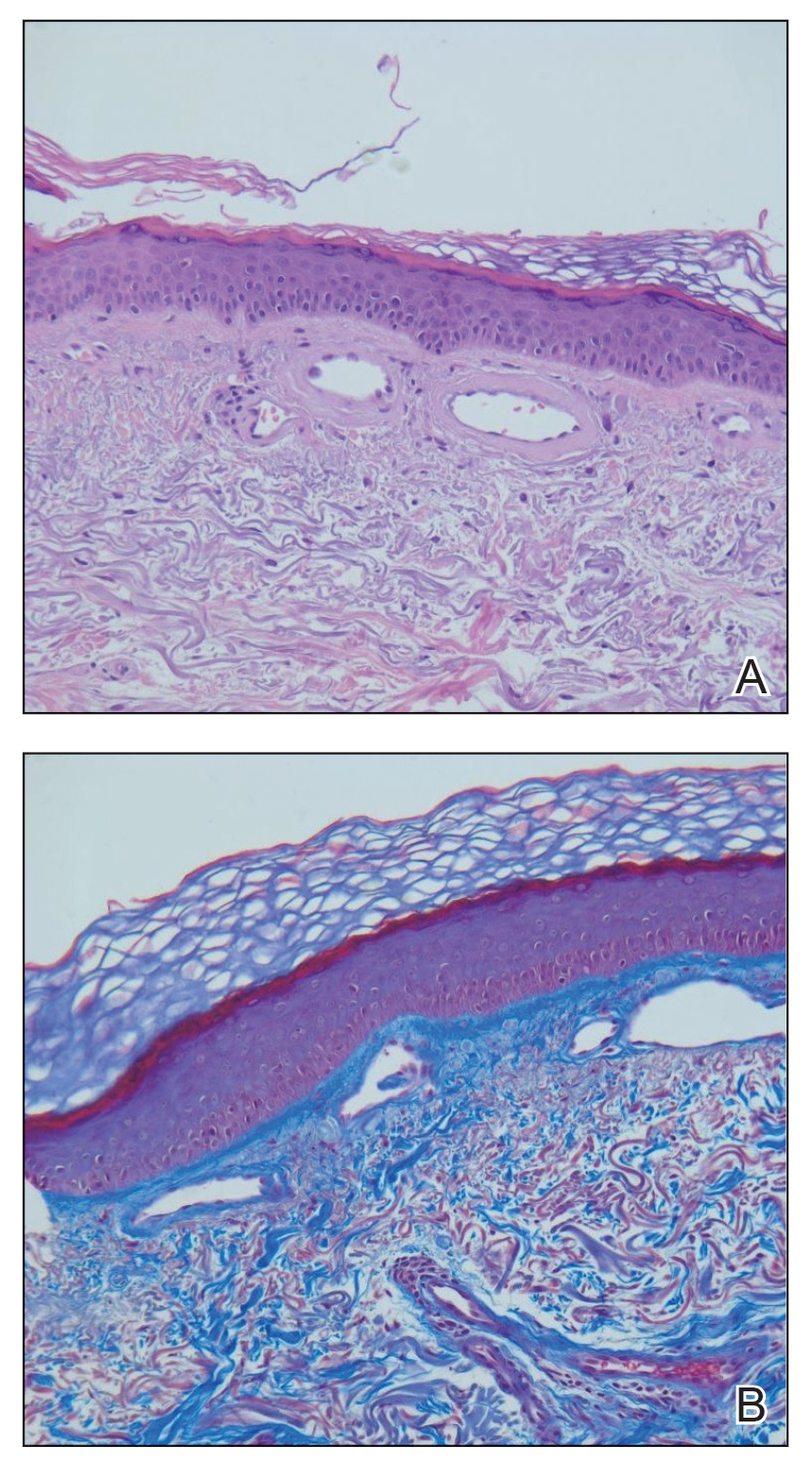
Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of skin from the abdomen showed an unremarkable epidermis overlying a superficial dermis with dilated blood vessels with thickened walls that contained eosinophilic amorphous hyaline material (Figure 2A). This material stained positive with Masson trichrome (Figure 2B), a finding that was consistent with increased collagen fiber deposition within the vessel walls. Phosphotungstic acid–hematoxylin and Congo red stains were negative. No histologic features of a vaso-occlusive disorder or vasculitis were identified. These histologic findings were consistent with the rare diagnosis of CCV.
Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy that was first reported by Salama and Rosenthal1 in 2000. They reported the case of a 54-year-old man with spreading, asymptomatic, generalized cutaneous telangiectases of 5 years’ duration. Similar to our patient, skin biopsy showed dilated superficial dermal vasculature with deposition of eosinophilic hyaline material, which stained positive with periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and exhibited immunoreactivity to type IV collagen.1
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search term cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy yielded 19 additional patients with biopsy-proven CCV.2-6 The condition has shown no gender prevalence but generally is seen in middle-aged or elderly white individuals, with the exception of a white pediatric patient.4 Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy usually presents as telangiectases on the legs that progress to involve the trunk and arms while sparing the head and neck, nail beds, and mucous membranes.5 However, it also has been described as first presenting on the bilateral breasts2 as well as a nonprogressive localization on the thigh.6
Skin biopsy is essential to differentiate CCV from GET, which appears morphologically identical. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy may be underreported as a result of clinician choice not to biopsy due to a presumptive diagnosis of GET.3 Successful treatment with a pulsed dye laser has been reported,7 though the extent of disease may make complete destruction of the lesions difficult to accomplish. Although it is theorized that CCV may be a marker for underlying systemic disease or even a genetic defect causing abnormal collagen deposition, its cause has yet to be ascertained.5 Previously reported patients have had a variety of comorbidities, including several cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus.6 Another patient was reported to have recently started treatment with an angiotensin receptor blocker prior to onset of CCV.5
Our case contributes to the small series of reported patients with this rare diagnosis and further suggests that it may be underreported at this time. Similar to previously reported cases, our patient was an elderly white individual. Although our patient had long-standing iatrogenic hypothyroidism, no recent medication changes or underlying comorbidities could be tied to the development of CCV. Further studies are needed to determine if this disease process is associated with any underlying systemic illnesses, medications, or family history.
- Salama S, Rosenthal D. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with generalized telangiectasia: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:40-48.
- Borroni RG, Derlino F, Agozzino M, et al. Hypothermic cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with centrifugal spreading [published online March 31, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1444-1446.
- Moulonguet I, Hershkovitch D, Fraitag S. Widespread cutaneous telangiectasias: challenge. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:661-662, 688-669.
- Lloyd BM, Pruden SJ 2nd, Lind AC, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: report of the first pediatric case. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:598-599.
- Kanitakis J, Faisant M, Wagschal D, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of a new case. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11:63-66.
- Davis TL, Mandal RV, Bevona C, et al. Collagenous vasculopathy: a report of three cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:967-970.
- Echeverría B, Sanmartín O, Botella-Estrada R, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy successfully treated with pulsed dye laser. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1359-1362.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy (CCV) is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy characterized by diffuse blanchable telangiectases that usually develop in late adulthood. It appears morphologically identical to generalized essential telangiectasia (GET), but skin biopsy characteristically shows dilated superficial blood vessels in the papillary dermis that are surrounded by a thickened layer of type IV collagen.1 We report a case of CCV occurring in an elderly white man.
A 72-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic rash on the arms, legs, and abdomen of 3 years’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for hypothyroidism, hypertension, reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, coronary artery disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer. He denied any changes in medications or illnesses prior to onset of the rash. Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, blanchable telangiectases on the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1). No petechiae, atrophy, or epidermal changes were appreciated. Darier sign was negative.

Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of skin from the abdomen showed an unremarkable epidermis overlying a superficial dermis with dilated blood vessels with thickened walls that contained eosinophilic amorphous hyaline material (Figure 2A). This material stained positive with Masson trichrome (Figure 2B), a finding that was consistent with increased collagen fiber deposition within the vessel walls. Phosphotungstic acid–hematoxylin and Congo red stains were negative. No histologic features of a vaso-occlusive disorder or vasculitis were identified. These histologic findings were consistent with the rare diagnosis of CCV.

Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy that was first reported by Salama and Rosenthal1 in 2000. They reported the case of a 54-year-old man with spreading, asymptomatic, generalized cutaneous telangiectases of 5 years’ duration. Similar to our patient, skin biopsy showed dilated superficial dermal vasculature with deposition of eosinophilic hyaline material, which stained positive with periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and exhibited immunoreactivity to type IV collagen.1
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search term cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy yielded 19 additional patients with biopsy-proven CCV.2-6 The condition has shown no gender prevalence but generally is seen in middle-aged or elderly white individuals, with the exception of a white pediatric patient.4 Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy usually presents as telangiectases on the legs that progress to involve the trunk and arms while sparing the head and neck, nail beds, and mucous membranes.5 However, it also has been described as first presenting on the bilateral breasts2 as well as a nonprogressive localization on the thigh.6
Skin biopsy is essential to differentiate CCV from GET, which appears morphologically identical. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy may be underreported as a result of clinician choice not to biopsy due to a presumptive diagnosis of GET.3 Successful treatment with a pulsed dye laser has been reported,7 though the extent of disease may make complete destruction of the lesions difficult to accomplish. Although it is theorized that CCV may be a marker for underlying systemic disease or even a genetic defect causing abnormal collagen deposition, its cause has yet to be ascertained.5 Previously reported patients have had a variety of comorbidities, including several cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus.6 Another patient was reported to have recently started treatment with an angiotensin receptor blocker prior to onset of CCV.5
Our case contributes to the small series of reported patients with this rare diagnosis and further suggests that it may be underreported at this time. Similar to previously reported cases, our patient was an elderly white individual. Although our patient had long-standing iatrogenic hypothyroidism, no recent medication changes or underlying comorbidities could be tied to the development of CCV. Further studies are needed to determine if this disease process is associated with any underlying systemic illnesses, medications, or family history.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy (CCV) is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy characterized by diffuse blanchable telangiectases that usually develop in late adulthood. It appears morphologically identical to generalized essential telangiectasia (GET), but skin biopsy characteristically shows dilated superficial blood vessels in the papillary dermis that are surrounded by a thickened layer of type IV collagen.1 We report a case of CCV occurring in an elderly white man.
A 72-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic rash on the arms, legs, and abdomen of 3 years’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for hypothyroidism, hypertension, reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, coronary artery disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer. He denied any changes in medications or illnesses prior to onset of the rash. Physical examination revealed diffuse, erythematous, blanchable telangiectases on the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1). No petechiae, atrophy, or epidermal changes were appreciated. Darier sign was negative.

Hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of skin from the abdomen showed an unremarkable epidermis overlying a superficial dermis with dilated blood vessels with thickened walls that contained eosinophilic amorphous hyaline material (Figure 2A). This material stained positive with Masson trichrome (Figure 2B), a finding that was consistent with increased collagen fiber deposition within the vessel walls. Phosphotungstic acid–hematoxylin and Congo red stains were negative. No histologic features of a vaso-occlusive disorder or vasculitis were identified. These histologic findings were consistent with the rare diagnosis of CCV.

Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy is a rare idiopathic microangiopathy that was first reported by Salama and Rosenthal1 in 2000. They reported the case of a 54-year-old man with spreading, asymptomatic, generalized cutaneous telangiectases of 5 years’ duration. Similar to our patient, skin biopsy showed dilated superficial dermal vasculature with deposition of eosinophilic hyaline material, which stained positive with periodic acid–Schiff with diastase and exhibited immunoreactivity to type IV collagen.1
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search term cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy yielded 19 additional patients with biopsy-proven CCV.2-6 The condition has shown no gender prevalence but generally is seen in middle-aged or elderly white individuals, with the exception of a white pediatric patient.4 Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy usually presents as telangiectases on the legs that progress to involve the trunk and arms while sparing the head and neck, nail beds, and mucous membranes.5 However, it also has been described as first presenting on the bilateral breasts2 as well as a nonprogressive localization on the thigh.6
Skin biopsy is essential to differentiate CCV from GET, which appears morphologically identical. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy may be underreported as a result of clinician choice not to biopsy due to a presumptive diagnosis of GET.3 Successful treatment with a pulsed dye laser has been reported,7 though the extent of disease may make complete destruction of the lesions difficult to accomplish. Although it is theorized that CCV may be a marker for underlying systemic disease or even a genetic defect causing abnormal collagen deposition, its cause has yet to be ascertained.5 Previously reported patients have had a variety of comorbidities, including several cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus.6 Another patient was reported to have recently started treatment with an angiotensin receptor blocker prior to onset of CCV.5
Our case contributes to the small series of reported patients with this rare diagnosis and further suggests that it may be underreported at this time. Similar to previously reported cases, our patient was an elderly white individual. Although our patient had long-standing iatrogenic hypothyroidism, no recent medication changes or underlying comorbidities could be tied to the development of CCV. Further studies are needed to determine if this disease process is associated with any underlying systemic illnesses, medications, or family history.
- Salama S, Rosenthal D. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with generalized telangiectasia: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:40-48.
- Borroni RG, Derlino F, Agozzino M, et al. Hypothermic cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with centrifugal spreading [published online March 31, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1444-1446.
- Moulonguet I, Hershkovitch D, Fraitag S. Widespread cutaneous telangiectasias: challenge. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:661-662, 688-669.
- Lloyd BM, Pruden SJ 2nd, Lind AC, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: report of the first pediatric case. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:598-599.
- Kanitakis J, Faisant M, Wagschal D, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of a new case. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11:63-66.
- Davis TL, Mandal RV, Bevona C, et al. Collagenous vasculopathy: a report of three cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:967-970.
- Echeverría B, Sanmartín O, Botella-Estrada R, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy successfully treated with pulsed dye laser. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1359-1362.
- Salama S, Rosenthal D. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with generalized telangiectasia: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:40-48.
- Borroni RG, Derlino F, Agozzino M, et al. Hypothermic cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy with centrifugal spreading [published online March 31, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1444-1446.
- Moulonguet I, Hershkovitch D, Fraitag S. Widespread cutaneous telangiectasias: challenge. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:661-662, 688-669.
- Lloyd BM, Pruden SJ 2nd, Lind AC, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: report of the first pediatric case. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:598-599.
- Kanitakis J, Faisant M, Wagschal D, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of a new case. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11:63-66.
- Davis TL, Mandal RV, Bevona C, et al. Collagenous vasculopathy: a report of three cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:967-970.
- Echeverría B, Sanmartín O, Botella-Estrada R, et al. Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy successfully treated with pulsed dye laser. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1359-1362.
Practice Points
- Cutaneous collagenous vasculopathy (CCV) should be in the differential diagnosis of widespread telangiectases.
- Biopsy is needed to differentiate between CCV and generalized essential telangiectasia because of their similar clinical features.
- There may be underlying comorbidities associated with CCV, but the exact cause of the condition has yet to be found.
Smooth Papules on the Left Hand
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).

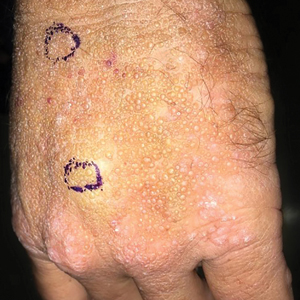
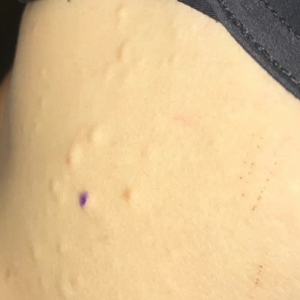
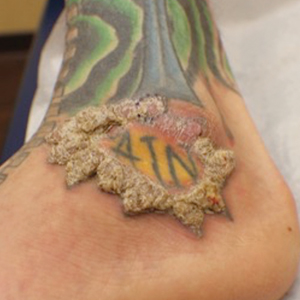
Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).
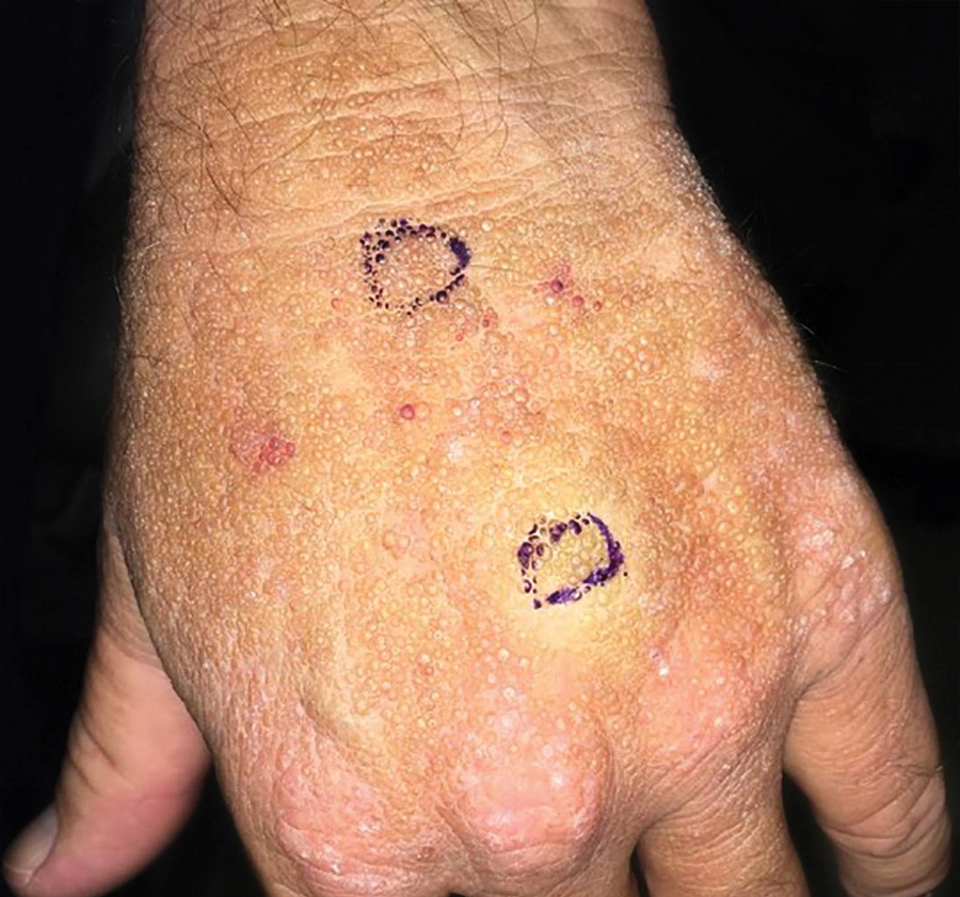
Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).

Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).

Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).

Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).

Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
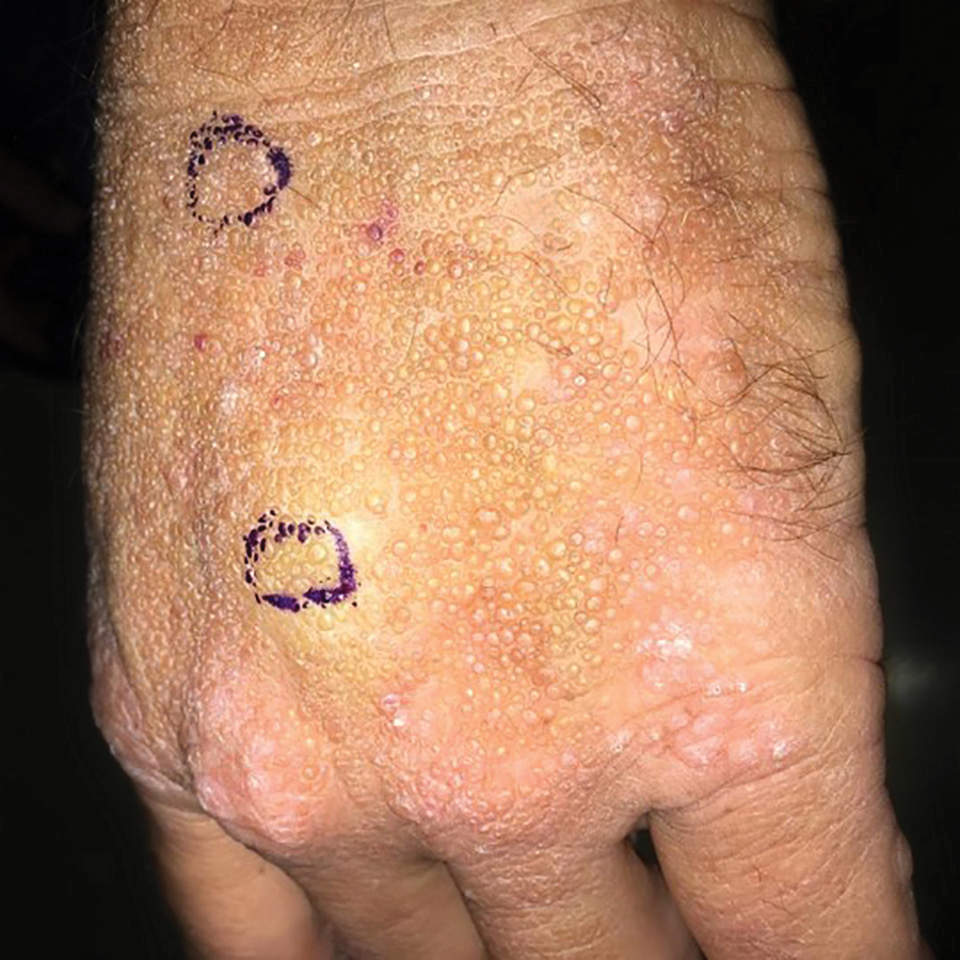
A 41-year-old man presented to the outpatient dermatology clinic with multiple smooth papules on the left hand of 7 years' duration. The papules had been steadily increasing in number, and the patient reported that they were frequently symptomatic with a burning itching sensation. Physical examination revealed multiple 1- to 3-mm, dome-shaped, translucent to flesh-colored papules on the left hand with a few scattered bright red papules. No similar lesions were present on the right hand or elsewhere on the body. He had a history of hypertension but was otherwise healthy with no other chronic medical conditions.
Pembrolizumab-Induced Lobular Panniculitis in the Setting of Metastatic Melanoma
To the Editor:
Pembrolizumab is an anti–programmed death receptor 1 humanized monoclonal antibody used for treating advanced or metastatic melanoma.1 It is associated with several immune-related adverse events because it blocks a T-cell receptor checkpoint.2 The most common dermatologic immune-related adverse event seen with anti–programmed death receptor 1 medications is a nonspecific morbilliform rash, usually seen after the second treatment cycle; however, pruritus, vitiligo, bullous disorders, and lichenoid reactions also have been reported.3 We report a case of pembrolizumab-induced, self-limited lobular panniculitis in a patient with metastatic melanoma.
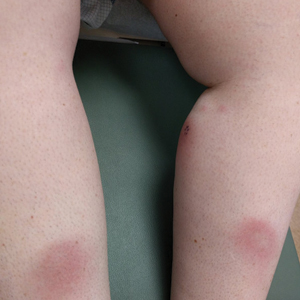
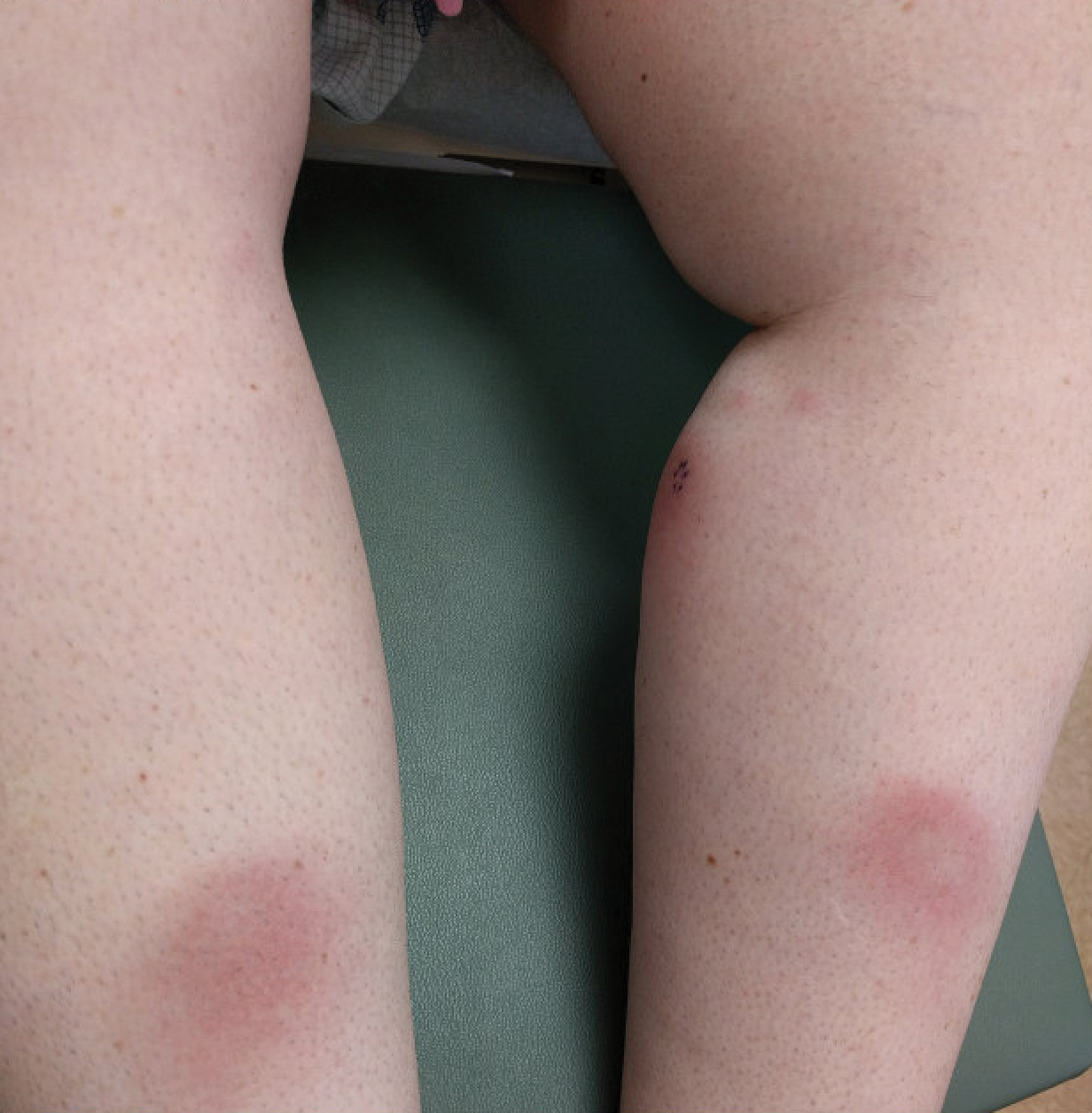
A 37-year-old woman with malignant melanoma presented with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules on the hips and legs of 2 weeks’ duration (Figure 1). Twelve years prior to the current presentation, she was diagnosed with metastases to the cecum, lung, and brain. A review of systems was otherwise negative. She had been receiving pembrolizumab infusions (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks) for the last 2.7 years as second-line therapy after previously undergoing chemotherapy, radiation, and resection. She was not taking oral contraceptives or other hormone-based medications and did not report any new medications.
Laboratory testing was negative for infectious processes including Lyme disease, tuberculosis, and Streptococcus due to recent upper respiratory infection. Punch biopsy of a left shin lesion revealed a lobular panniculitis with lymphohistiocytic inflammation, a focal lymphocytic vasculitis, and small granulomas (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff, Gram, and acid-fast bacilli stains were negative. After ruling out alternative causes, the etiology of the panniculitis was deemed to be a pembrolizumab side effect. The patient was treated conservatively with ibuprofen; pembrolizumab was not discontinued. Two weeks later, the panniculitis had resolved without additional treatment. She remains on pembrolizumab and is doing well.
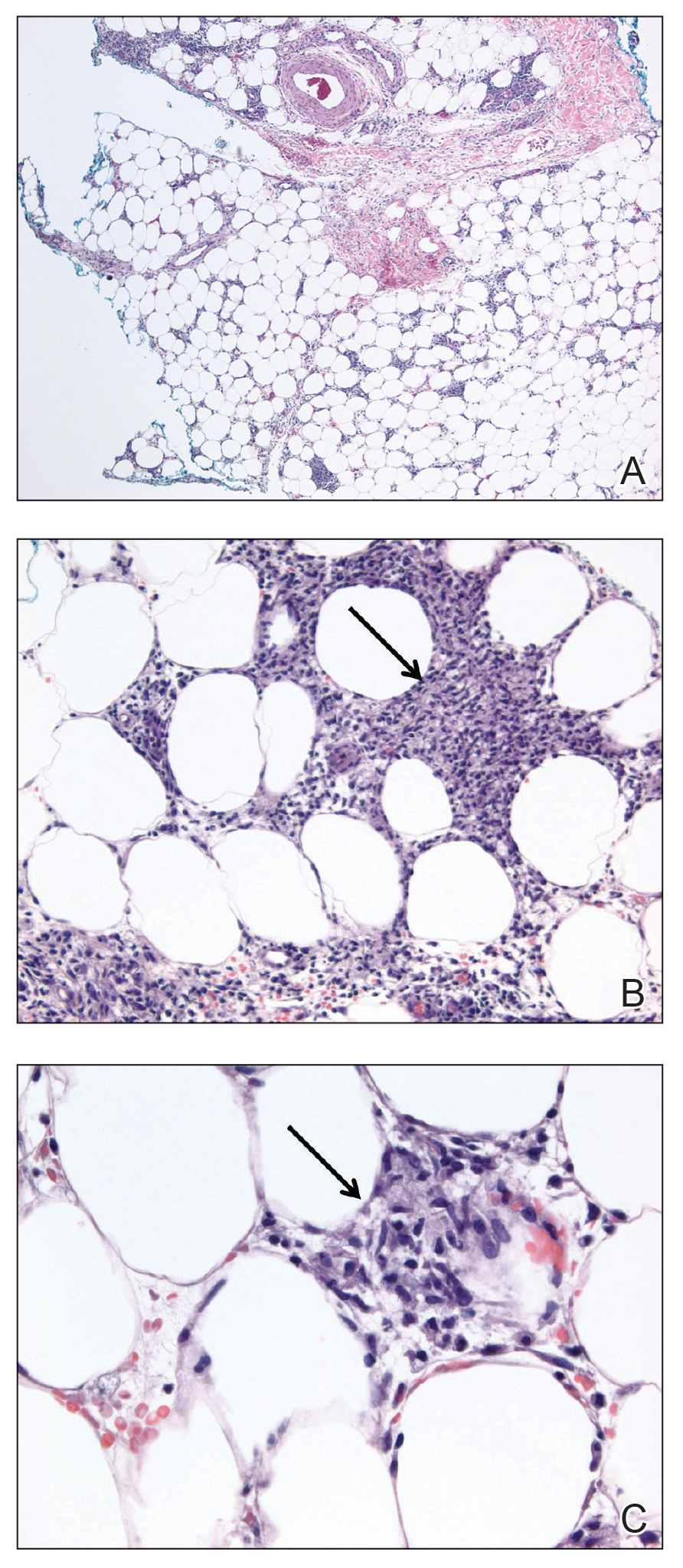
Panniculitis is known to be associated with certain BRAF inhibitors used for the treatment of melanoma positive for the BRAF V600E mutation, including vemurafenib and dabrafenib.4,5 Reports of panniculitis in the setting of pembrolizumab are limited and are seen within the larger context of sarcoidosis. One patient on pembrolizumab for metastatic melanoma developed granulomatous lobular panniculitis with oligoarthritis, high fever, and hilar/mediastinal adenopathy, consistent with pembrolizumab-induced sarcoidosis. It developed after her second pembrolizumab infusion and resolved with prednisone and temporary pembrolizumab cessation.6 In another case, pembrolizumab triggered a flare of sarcoidosis with similar granulomatous subcutaneous nodules in a patient with stage IV lymphoma who was previously diagnosed with sarcoidosis but lacked cutaneous manifestations. The lesions resolved with prednisone therapy.7
Chest computed tomography was normal in our patient, and she reported no systemic symptoms. Additional laboratory studies to evaluate for sarcoidosis were not obtained. Furthermore, the lesions quickly resolved despite continued use of pembrolizumab. We report this case to highlight that pembrolizumab may induce an isolated, self-limited lobular panniculitis years after medication initiation.
- Poole RM. Pembrolizumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74:1973-1981.
- Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S, et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: a comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer. 2016;54:139-148.
- Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, et al. Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1362.
- Boussemart L, Routier E, Mateus C, et al. Prospective study of cutaneous side-effects associated with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib: a study of 42 patients. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:1691-1697.
- Ramani NS, Curry JL, Kapil J, et al. Panniculitis with necrotizing granulomata in a patient on BRAF inhibitor (dabrafenib) therapy for metastatic melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:E96-E99.
- Burillo-Martinez S, Morales-Raya C, Prieto-Barrios M, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced extensive panniculitis and nevus regression: two novel cutaneous manifestations of the post-immunotherapy granulomatous reactions spectrum. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:721-722.
- Cotliar J, Querfeld C, Boswell WJ, et al. Pembrolizumab-associated sarcoidosis. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:290-293.
To the Editor:
Pembrolizumab is an anti–programmed death receptor 1 humanized monoclonal antibody used for treating advanced or metastatic melanoma.1 It is associated with several immune-related adverse events because it blocks a T-cell receptor checkpoint.2 The most common dermatologic immune-related adverse event seen with anti–programmed death receptor 1 medications is a nonspecific morbilliform rash, usually seen after the second treatment cycle; however, pruritus, vitiligo, bullous disorders, and lichenoid reactions also have been reported.3 We report a case of pembrolizumab-induced, self-limited lobular panniculitis in a patient with metastatic melanoma.
A 37-year-old woman with malignant melanoma presented with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules on the hips and legs of 2 weeks’ duration (Figure 1). Twelve years prior to the current presentation, she was diagnosed with metastases to the cecum, lung, and brain. A review of systems was otherwise negative. She had been receiving pembrolizumab infusions (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks) for the last 2.7 years as second-line therapy after previously undergoing chemotherapy, radiation, and resection. She was not taking oral contraceptives or other hormone-based medications and did not report any new medications.

Laboratory testing was negative for infectious processes including Lyme disease, tuberculosis, and Streptococcus due to recent upper respiratory infection. Punch biopsy of a left shin lesion revealed a lobular panniculitis with lymphohistiocytic inflammation, a focal lymphocytic vasculitis, and small granulomas (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff, Gram, and acid-fast bacilli stains were negative. After ruling out alternative causes, the etiology of the panniculitis was deemed to be a pembrolizumab side effect. The patient was treated conservatively with ibuprofen; pembrolizumab was not discontinued. Two weeks later, the panniculitis had resolved without additional treatment. She remains on pembrolizumab and is doing well.

Panniculitis is known to be associated with certain BRAF inhibitors used for the treatment of melanoma positive for the BRAF V600E mutation, including vemurafenib and dabrafenib.4,5 Reports of panniculitis in the setting of pembrolizumab are limited and are seen within the larger context of sarcoidosis. One patient on pembrolizumab for metastatic melanoma developed granulomatous lobular panniculitis with oligoarthritis, high fever, and hilar/mediastinal adenopathy, consistent with pembrolizumab-induced sarcoidosis. It developed after her second pembrolizumab infusion and resolved with prednisone and temporary pembrolizumab cessation.6 In another case, pembrolizumab triggered a flare of sarcoidosis with similar granulomatous subcutaneous nodules in a patient with stage IV lymphoma who was previously diagnosed with sarcoidosis but lacked cutaneous manifestations. The lesions resolved with prednisone therapy.7
Chest computed tomography was normal in our patient, and she reported no systemic symptoms. Additional laboratory studies to evaluate for sarcoidosis were not obtained. Furthermore, the lesions quickly resolved despite continued use of pembrolizumab. We report this case to highlight that pembrolizumab may induce an isolated, self-limited lobular panniculitis years after medication initiation.
To the Editor:
Pembrolizumab is an anti–programmed death receptor 1 humanized monoclonal antibody used for treating advanced or metastatic melanoma.1 It is associated with several immune-related adverse events because it blocks a T-cell receptor checkpoint.2 The most common dermatologic immune-related adverse event seen with anti–programmed death receptor 1 medications is a nonspecific morbilliform rash, usually seen after the second treatment cycle; however, pruritus, vitiligo, bullous disorders, and lichenoid reactions also have been reported.3 We report a case of pembrolizumab-induced, self-limited lobular panniculitis in a patient with metastatic melanoma.
A 37-year-old woman with malignant melanoma presented with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules on the hips and legs of 2 weeks’ duration (Figure 1). Twelve years prior to the current presentation, she was diagnosed with metastases to the cecum, lung, and brain. A review of systems was otherwise negative. She had been receiving pembrolizumab infusions (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks) for the last 2.7 years as second-line therapy after previously undergoing chemotherapy, radiation, and resection. She was not taking oral contraceptives or other hormone-based medications and did not report any new medications.

Laboratory testing was negative for infectious processes including Lyme disease, tuberculosis, and Streptococcus due to recent upper respiratory infection. Punch biopsy of a left shin lesion revealed a lobular panniculitis with lymphohistiocytic inflammation, a focal lymphocytic vasculitis, and small granulomas (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff, Gram, and acid-fast bacilli stains were negative. After ruling out alternative causes, the etiology of the panniculitis was deemed to be a pembrolizumab side effect. The patient was treated conservatively with ibuprofen; pembrolizumab was not discontinued. Two weeks later, the panniculitis had resolved without additional treatment. She remains on pembrolizumab and is doing well.

Panniculitis is known to be associated with certain BRAF inhibitors used for the treatment of melanoma positive for the BRAF V600E mutation, including vemurafenib and dabrafenib.4,5 Reports of panniculitis in the setting of pembrolizumab are limited and are seen within the larger context of sarcoidosis. One patient on pembrolizumab for metastatic melanoma developed granulomatous lobular panniculitis with oligoarthritis, high fever, and hilar/mediastinal adenopathy, consistent with pembrolizumab-induced sarcoidosis. It developed after her second pembrolizumab infusion and resolved with prednisone and temporary pembrolizumab cessation.6 In another case, pembrolizumab triggered a flare of sarcoidosis with similar granulomatous subcutaneous nodules in a patient with stage IV lymphoma who was previously diagnosed with sarcoidosis but lacked cutaneous manifestations. The lesions resolved with prednisone therapy.7
Chest computed tomography was normal in our patient, and she reported no systemic symptoms. Additional laboratory studies to evaluate for sarcoidosis were not obtained. Furthermore, the lesions quickly resolved despite continued use of pembrolizumab. We report this case to highlight that pembrolizumab may induce an isolated, self-limited lobular panniculitis years after medication initiation.
- Poole RM. Pembrolizumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74:1973-1981.
- Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S, et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: a comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer. 2016;54:139-148.
- Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, et al. Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1362.
- Boussemart L, Routier E, Mateus C, et al. Prospective study of cutaneous side-effects associated with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib: a study of 42 patients. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:1691-1697.
- Ramani NS, Curry JL, Kapil J, et al. Panniculitis with necrotizing granulomata in a patient on BRAF inhibitor (dabrafenib) therapy for metastatic melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:E96-E99.
- Burillo-Martinez S, Morales-Raya C, Prieto-Barrios M, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced extensive panniculitis and nevus regression: two novel cutaneous manifestations of the post-immunotherapy granulomatous reactions spectrum. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:721-722.
- Cotliar J, Querfeld C, Boswell WJ, et al. Pembrolizumab-associated sarcoidosis. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:290-293.
- Poole RM. Pembrolizumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74:1973-1981.
- Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S, et al. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: a comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer. 2016;54:139-148.
- Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, et al. Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1362.
- Boussemart L, Routier E, Mateus C, et al. Prospective study of cutaneous side-effects associated with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib: a study of 42 patients. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:1691-1697.
- Ramani NS, Curry JL, Kapil J, et al. Panniculitis with necrotizing granulomata in a patient on BRAF inhibitor (dabrafenib) therapy for metastatic melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:E96-E99.
- Burillo-Martinez S, Morales-Raya C, Prieto-Barrios M, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced extensive panniculitis and nevus regression: two novel cutaneous manifestations of the post-immunotherapy granulomatous reactions spectrum. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:721-722.
- Cotliar J, Querfeld C, Boswell WJ, et al. Pembrolizumab-associated sarcoidosis. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:290-293.
Practice Points
- Pembrolizumab may cause lobular panniculitis years after treatment initiation.
- Pembrolizumab-induced lobular panniculitis may self-resolve without discontinuing the medication.
Distinct Violaceous Plaques in Conjunction With Blisters
The Diagnosis: Lichen Planus Pemphigoides
Lichen planus pemphigoides (LPP) is a rare autoimmune subepithelial blistering disorder with clinical, pathologic, and immunologic features of lichen planus (LP) and bullous pemphigoid (BP).1 It mainly arises in adults and usually is idiopathic but has been associated with certain infections,2 drugs such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,3 phototherapy,4 and malignancy.5 Patients classically present with lichenoid lesions, tense vesiculobullae, and erosions.6 Vesiculobullae formation usually follows the development of lichenoid lesions, occurs on both lichenoid lesions and unaffected skin, and predominantly involves the lower extremities, as in our patient.1,6
The pathogenesis of LPP is not fully understood but likely represents a distinct entity rather than a subtype of BP or the simultaneous occurrence of LP and BP. Lichen planus pemphigoides generally has an earlier onset and better treatment response compared to BP.7 Further, autoantibodies in patients with LPP react to a novel epitope within the C-terminal portion of the BP-180 NC16A domain. Accordingly, it has been postulated that an inflammatory cutaneous process resulting from infection, phototherapy, or LP itself leads to damage of the epidermis and triggers a secondary blistering autoimmune dermatosis mediated by antibody formation against basement membrane (BM) antigens, such as BP-180.7
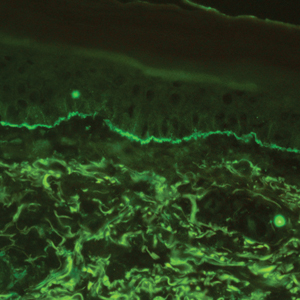
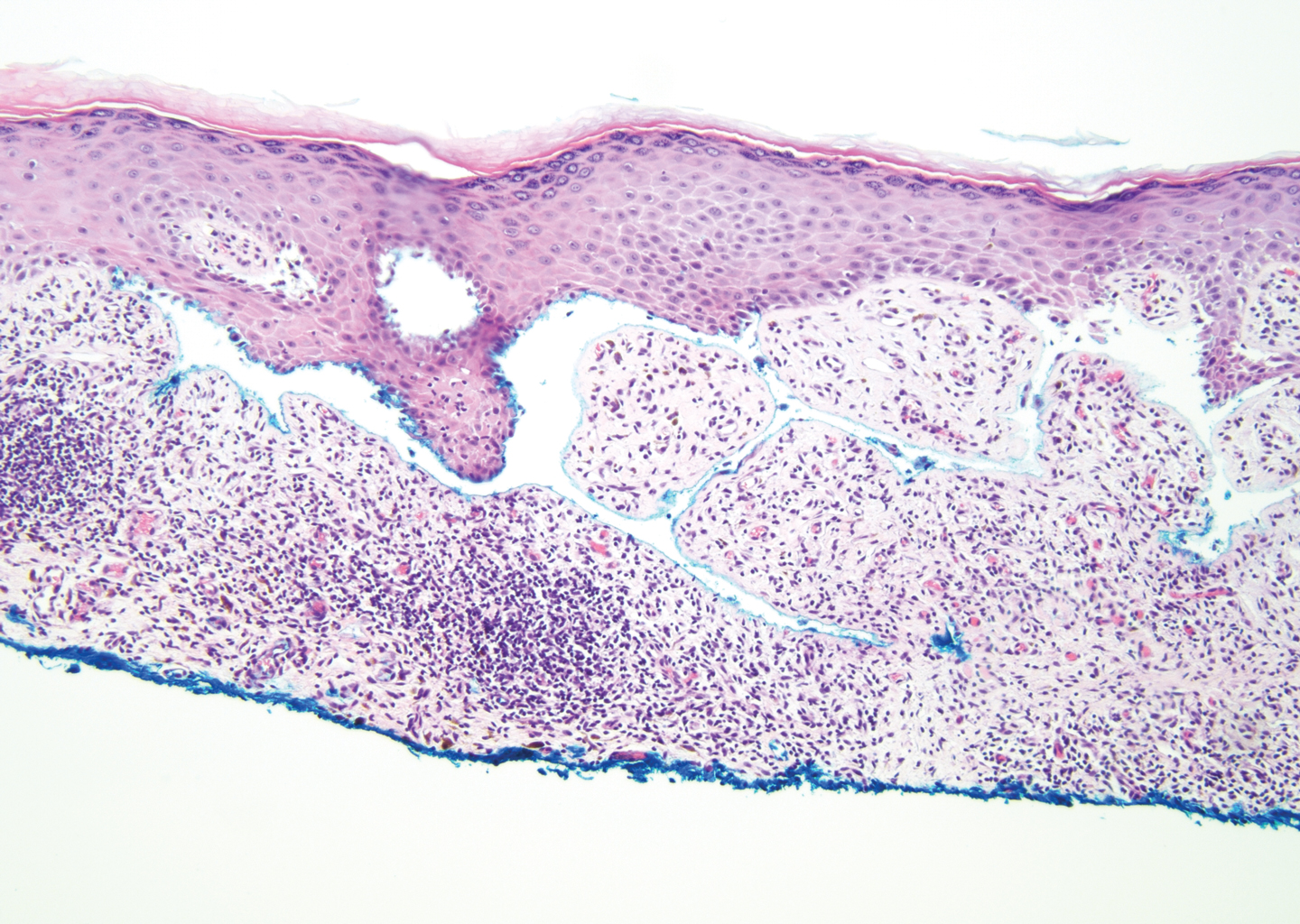
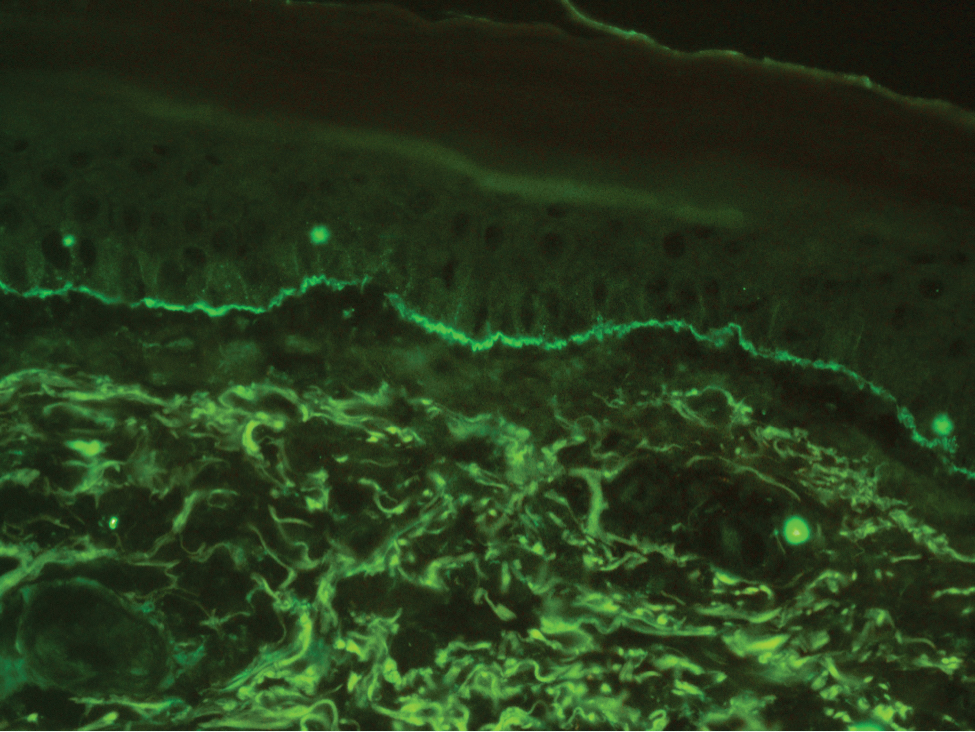
The diagnosis of LPP ultimately is confirmed with immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of LPP shows findings consistent with both LP and BP (quiz image [top]). In the lichenoid portion, biopsy reveals orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis; a bandlike infiltrate consisting primarily of lymphocytes in the upper dermis; and apoptotic keratinocytes (colloid bodies) and vacuolar degeneration at the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ).1 Biopsy of bullae reveals eosinophilic spongiosis, a subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils, and a mixed superficial inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence from perilesional skin reveals linear deposition of IgG and/or C3 at the DEJ (quiz image [bottom]).1 Measurement of anti-BM antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230 can be useful in suspected cases, as 50% to 60% of patients have circulating antibodies against these antigens.6 Remission usually is achieved with topical and systemic corticosteroids and/or steroid-sparing agents, with rare recurrence following lesion resolution.1 More recently, successful treatment with biologics such as ustekinumab has been reported.8
The predominant differential diagnosis for LPP is bullous LP, a variant of LP in which vesiculobullous disease occurs exclusively on preexisting LP lesions, commonly on the legs due to severe vacuolar degeneration at the DEJ. On histopathology, the characteristic features of LP (eg, orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate, colloid bodies) along with subepidermal clefting will be seen. However, in bullous LP (Figure 1) there is an absence of linear IgG and/or C3 deposition at the DEJ on direct immunofluorescence. Furthermore, patients lack circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230.9
Lichen planus pemphigoides also can be confused with BP. Bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disorder; typically arises in older adults; and is caused by autoantibody formation against hemidesmosomal proteins, particularly BP-180 and BP-230. Patients classically present with tense bullae and erosions on an erythematous, urticarial, or normal base. These lesions often are pruritic and concentrated on the trunk, axillary and inguinal folds, and extremity flexures. Histopathologic examination of a bulla edge reveals the classic findings seen in BP (eg, eosinophilic spongiosis, subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils)(Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin reveals linear IgG and/or C3 deposition along the DEJ. A large subset of patients also has circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230. In contrast to LPP, however, patients with BP do not develop lichenoid lesions clinically or a lichenoid tissue reaction histopathologically.10
Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a rare cutaneous manifestation of SLE, typically arises in young women of African descent and is due to autoantibody formation against type VII collagen and other BM-zone antigens. Patients generally present with acute onset of tense vesiculobullae on a normal or erythematous base, which often are transient and heal without milia or scarring. Common sites of involvement include the trunk, arms, neck, face, and vermilion border, as well as the oral mucosa. The diagnosis of bullous SLE requires that patients fulfill the criteria for SLE and is confirmed by immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of a bulla edge reveals a subepidermal blister containing neutrophils and increased mucin within the reticular dermis (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin most commonly reveals linear and/or granular deposition of IgG, IgA, C3, and IgM at the DEJ.11

Bullous tinea is a manifestation of cutaneous dermatophytosis that usually occurs in the setting of tinea pedis. Common causative dermatophytes include Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, and Epidermophyton floccosum. Diagnosis is made by demonstration of fungal hyphae on potassium hydroxide preparation of the blister roof, biopsy with periodic acid-Schiff stain, or fungal culture. If routine histopathologic analysis is performed, epidermal spongiosis with varying degrees of papillary dermal edema is seen, along with abundant fungal elements in the stratum corneum (Figure 4). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin usually is negative, but C3 deposition in a linear and/or granular pattern along the DEJ has been reported.12

Lichen planus pemphigoides is a rare disease entity and often presents a diagnostic challenge to clinicians. The differential for LPP includes bullous LP as well as other bullous disorders. Ultimately, the diagnosis is confirmed through immunohistologic analysis. Timely diagnosis of LPP is crucial, as most patients can achieve long-term remission with appropriate treatment.
- Zaraa I, Mahfoudh A, Sellami MK, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides: four new cases and a review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:406-412.
- Mohanarao TS, Kumar GA, Chennamsetty K, et al. Childhood lichen planus pemphigoides triggered by chickenpox. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:S98-S100.
- Onprasert W, Chanprapaph K. Lichen planus pemphigoides induced by enalapril: a case report and a review of literature. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:217-224.
- Kuramoto N, Kishimoto S, Shibagaki R, et al. PUVA-induced lichen planus pemphigoides. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:509-512.
- Shimada H, Shono T, Sakai T, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides concomitant with rectal adenocarcinoma: fortuitous or a true association? Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:501-503.
- Matos-Pires E, Campos S, Lencastre A, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:335-337.
- Zillikens D, Caux F, Mascaro JM, et al. Autoantibodies in lichen planus pemphigoides react with a novel epitope within the C-terminal NC16A domain of BP180. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113:117-121.
- Knisley RR, Petropolis AA, Mackey VT. Lichen planus pemphigoides treated with ustekinumab. Cutis. 2017;100:415-418.
- Wagner G, Rose C, Sachse MM. Clinical variants of lichen planus. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:309-319.
- Bagci IS, Horvath ON, Ruzicka T, et al. Bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:445-455.
- Contestable JJ, Edhegard KD, Meyerle JH. Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus: a review and update to diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:517-524.
- Miller DD, Bhawan J. Bullous tinea pedis with direct immunofluorescence positivity: when is a positive result not autoimmune bullous disease? Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:587-594.
The Diagnosis: Lichen Planus Pemphigoides
Lichen planus pemphigoides (LPP) is a rare autoimmune subepithelial blistering disorder with clinical, pathologic, and immunologic features of lichen planus (LP) and bullous pemphigoid (BP).1 It mainly arises in adults and usually is idiopathic but has been associated with certain infections,2 drugs such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,3 phototherapy,4 and malignancy.5 Patients classically present with lichenoid lesions, tense vesiculobullae, and erosions.6 Vesiculobullae formation usually follows the development of lichenoid lesions, occurs on both lichenoid lesions and unaffected skin, and predominantly involves the lower extremities, as in our patient.1,6
The pathogenesis of LPP is not fully understood but likely represents a distinct entity rather than a subtype of BP or the simultaneous occurrence of LP and BP. Lichen planus pemphigoides generally has an earlier onset and better treatment response compared to BP.7 Further, autoantibodies in patients with LPP react to a novel epitope within the C-terminal portion of the BP-180 NC16A domain. Accordingly, it has been postulated that an inflammatory cutaneous process resulting from infection, phototherapy, or LP itself leads to damage of the epidermis and triggers a secondary blistering autoimmune dermatosis mediated by antibody formation against basement membrane (BM) antigens, such as BP-180.7
The diagnosis of LPP ultimately is confirmed with immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of LPP shows findings consistent with both LP and BP (quiz image [top]). In the lichenoid portion, biopsy reveals orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis; a bandlike infiltrate consisting primarily of lymphocytes in the upper dermis; and apoptotic keratinocytes (colloid bodies) and vacuolar degeneration at the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ).1 Biopsy of bullae reveals eosinophilic spongiosis, a subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils, and a mixed superficial inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence from perilesional skin reveals linear deposition of IgG and/or C3 at the DEJ (quiz image [bottom]).1 Measurement of anti-BM antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230 can be useful in suspected cases, as 50% to 60% of patients have circulating antibodies against these antigens.6 Remission usually is achieved with topical and systemic corticosteroids and/or steroid-sparing agents, with rare recurrence following lesion resolution.1 More recently, successful treatment with biologics such as ustekinumab has been reported.8
The predominant differential diagnosis for LPP is bullous LP, a variant of LP in which vesiculobullous disease occurs exclusively on preexisting LP lesions, commonly on the legs due to severe vacuolar degeneration at the DEJ. On histopathology, the characteristic features of LP (eg, orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate, colloid bodies) along with subepidermal clefting will be seen. However, in bullous LP (Figure 1) there is an absence of linear IgG and/or C3 deposition at the DEJ on direct immunofluorescence. Furthermore, patients lack circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230.9

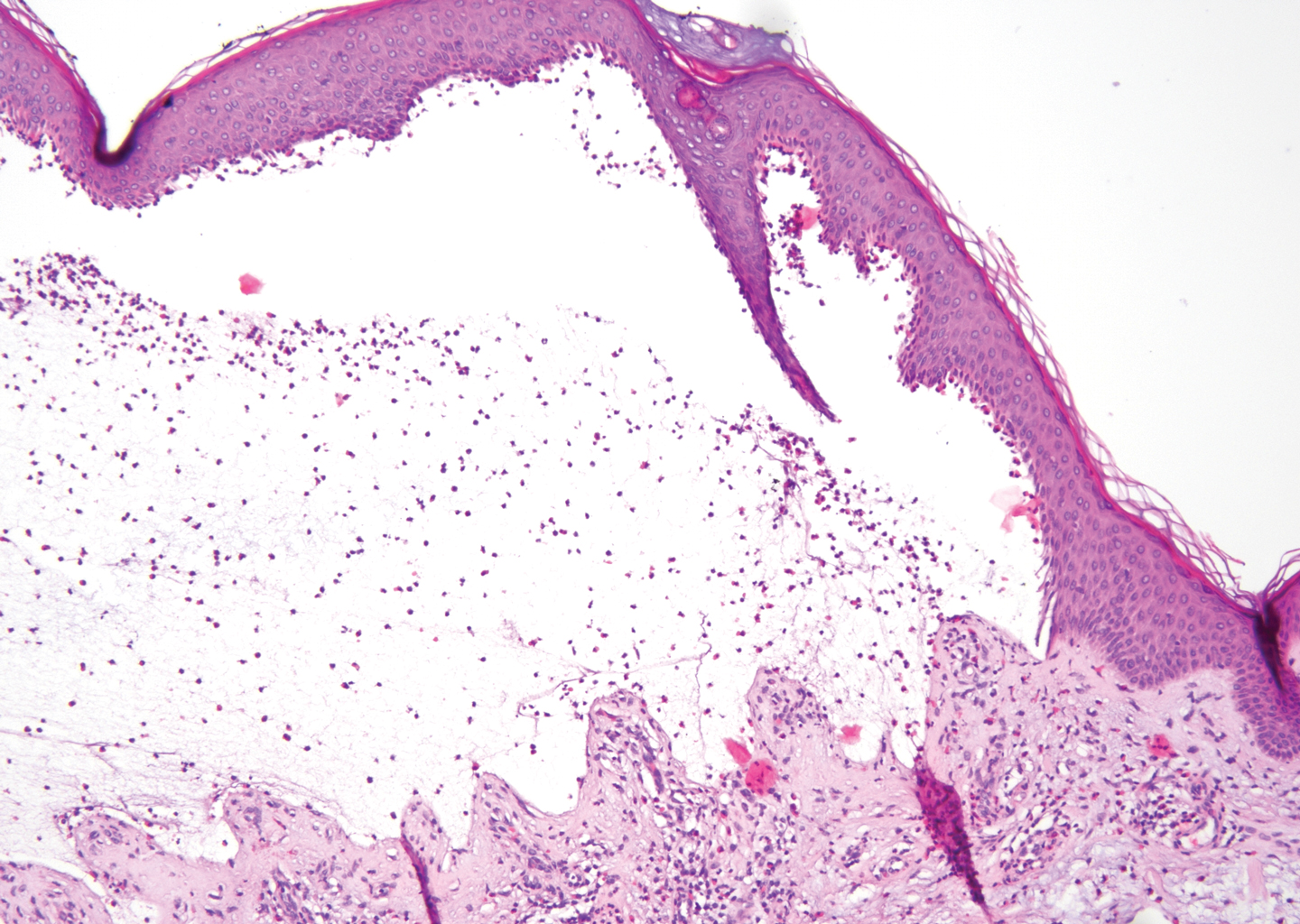
Lichen planus pemphigoides also can be confused with BP. Bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disorder; typically arises in older adults; and is caused by autoantibody formation against hemidesmosomal proteins, particularly BP-180 and BP-230. Patients classically present with tense bullae and erosions on an erythematous, urticarial, or normal base. These lesions often are pruritic and concentrated on the trunk, axillary and inguinal folds, and extremity flexures. Histopathologic examination of a bulla edge reveals the classic findings seen in BP (eg, eosinophilic spongiosis, subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils)(Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin reveals linear IgG and/or C3 deposition along the DEJ. A large subset of patients also has circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230. In contrast to LPP, however, patients with BP do not develop lichenoid lesions clinically or a lichenoid tissue reaction histopathologically.10

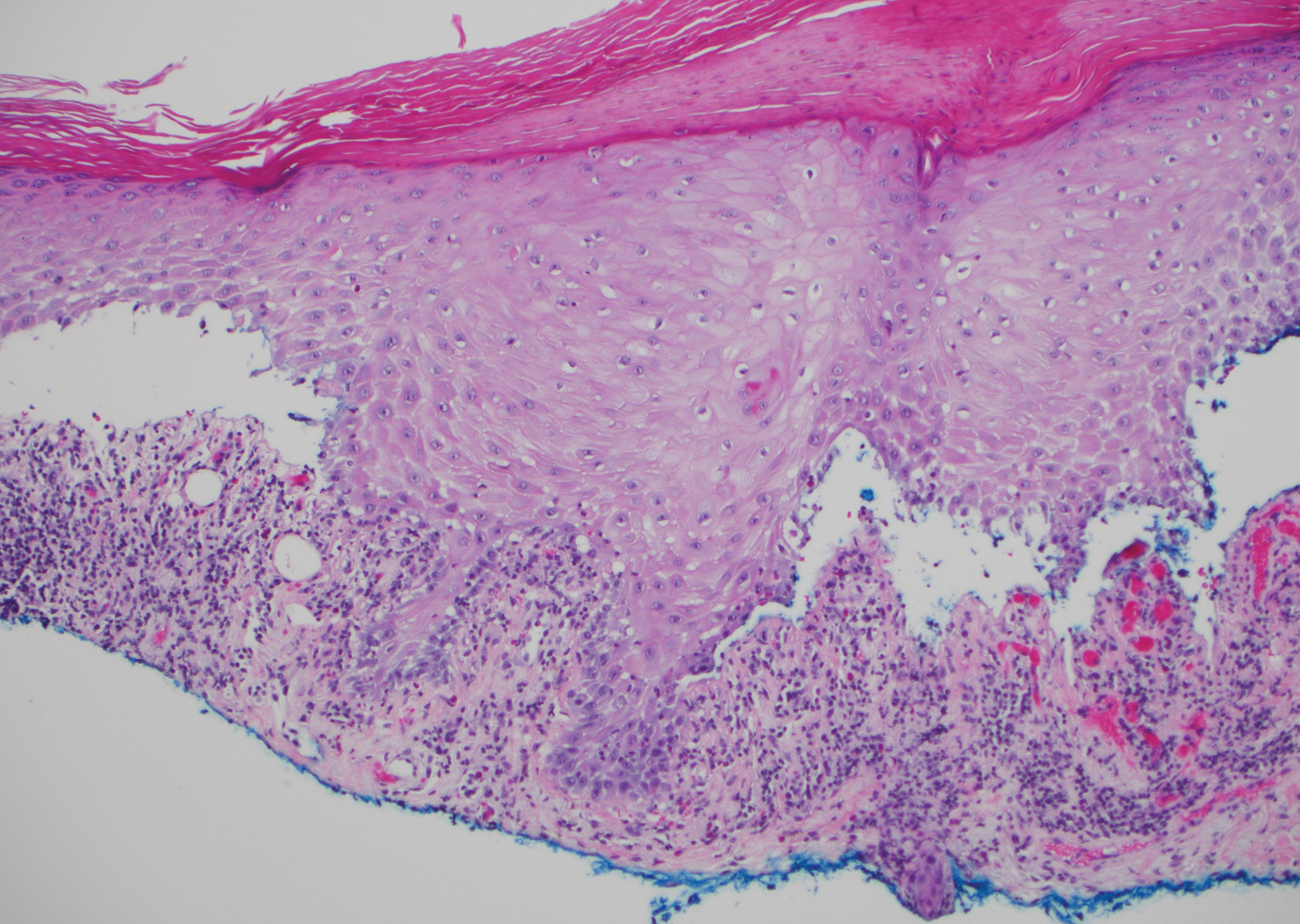
Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a rare cutaneous manifestation of SLE, typically arises in young women of African descent and is due to autoantibody formation against type VII collagen and other BM-zone antigens. Patients generally present with acute onset of tense vesiculobullae on a normal or erythematous base, which often are transient and heal without milia or scarring. Common sites of involvement include the trunk, arms, neck, face, and vermilion border, as well as the oral mucosa. The diagnosis of bullous SLE requires that patients fulfill the criteria for SLE and is confirmed by immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of a bulla edge reveals a subepidermal blister containing neutrophils and increased mucin within the reticular dermis (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin most commonly reveals linear and/or granular deposition of IgG, IgA, C3, and IgM at the DEJ.11

Bullous tinea is a manifestation of cutaneous dermatophytosis that usually occurs in the setting of tinea pedis. Common causative dermatophytes include Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, and Epidermophyton floccosum. Diagnosis is made by demonstration of fungal hyphae on potassium hydroxide preparation of the blister roof, biopsy with periodic acid-Schiff stain, or fungal culture. If routine histopathologic analysis is performed, epidermal spongiosis with varying degrees of papillary dermal edema is seen, along with abundant fungal elements in the stratum corneum (Figure 4). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin usually is negative, but C3 deposition in a linear and/or granular pattern along the DEJ has been reported.12

Lichen planus pemphigoides is a rare disease entity and often presents a diagnostic challenge to clinicians. The differential for LPP includes bullous LP as well as other bullous disorders. Ultimately, the diagnosis is confirmed through immunohistologic analysis. Timely diagnosis of LPP is crucial, as most patients can achieve long-term remission with appropriate treatment.
The Diagnosis: Lichen Planus Pemphigoides
Lichen planus pemphigoides (LPP) is a rare autoimmune subepithelial blistering disorder with clinical, pathologic, and immunologic features of lichen planus (LP) and bullous pemphigoid (BP).1 It mainly arises in adults and usually is idiopathic but has been associated with certain infections,2 drugs such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,3 phototherapy,4 and malignancy.5 Patients classically present with lichenoid lesions, tense vesiculobullae, and erosions.6 Vesiculobullae formation usually follows the development of lichenoid lesions, occurs on both lichenoid lesions and unaffected skin, and predominantly involves the lower extremities, as in our patient.1,6
The pathogenesis of LPP is not fully understood but likely represents a distinct entity rather than a subtype of BP or the simultaneous occurrence of LP and BP. Lichen planus pemphigoides generally has an earlier onset and better treatment response compared to BP.7 Further, autoantibodies in patients with LPP react to a novel epitope within the C-terminal portion of the BP-180 NC16A domain. Accordingly, it has been postulated that an inflammatory cutaneous process resulting from infection, phototherapy, or LP itself leads to damage of the epidermis and triggers a secondary blistering autoimmune dermatosis mediated by antibody formation against basement membrane (BM) antigens, such as BP-180.7
The diagnosis of LPP ultimately is confirmed with immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of LPP shows findings consistent with both LP and BP (quiz image [top]). In the lichenoid portion, biopsy reveals orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis; a bandlike infiltrate consisting primarily of lymphocytes in the upper dermis; and apoptotic keratinocytes (colloid bodies) and vacuolar degeneration at the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ).1 Biopsy of bullae reveals eosinophilic spongiosis, a subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils, and a mixed superficial inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence from perilesional skin reveals linear deposition of IgG and/or C3 at the DEJ (quiz image [bottom]).1 Measurement of anti-BM antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230 can be useful in suspected cases, as 50% to 60% of patients have circulating antibodies against these antigens.6 Remission usually is achieved with topical and systemic corticosteroids and/or steroid-sparing agents, with rare recurrence following lesion resolution.1 More recently, successful treatment with biologics such as ustekinumab has been reported.8
The predominant differential diagnosis for LPP is bullous LP, a variant of LP in which vesiculobullous disease occurs exclusively on preexisting LP lesions, commonly on the legs due to severe vacuolar degeneration at the DEJ. On histopathology, the characteristic features of LP (eg, orthohyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate, colloid bodies) along with subepidermal clefting will be seen. However, in bullous LP (Figure 1) there is an absence of linear IgG and/or C3 deposition at the DEJ on direct immunofluorescence. Furthermore, patients lack circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230.9

Lichen planus pemphigoides also can be confused with BP. Bullous pemphigoid is the most common autoimmune blistering disorder; typically arises in older adults; and is caused by autoantibody formation against hemidesmosomal proteins, particularly BP-180 and BP-230. Patients classically present with tense bullae and erosions on an erythematous, urticarial, or normal base. These lesions often are pruritic and concentrated on the trunk, axillary and inguinal folds, and extremity flexures. Histopathologic examination of a bulla edge reveals the classic findings seen in BP (eg, eosinophilic spongiosis, subepithelial blister plane with eosinophils)(Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin reveals linear IgG and/or C3 deposition along the DEJ. A large subset of patients also has circulating antibodies against BP-180 and BP-230. In contrast to LPP, however, patients with BP do not develop lichenoid lesions clinically or a lichenoid tissue reaction histopathologically.10

Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a rare cutaneous manifestation of SLE, typically arises in young women of African descent and is due to autoantibody formation against type VII collagen and other BM-zone antigens. Patients generally present with acute onset of tense vesiculobullae on a normal or erythematous base, which often are transient and heal without milia or scarring. Common sites of involvement include the trunk, arms, neck, face, and vermilion border, as well as the oral mucosa. The diagnosis of bullous SLE requires that patients fulfill the criteria for SLE and is confirmed by immunohistologic analysis. Biopsy of a bulla edge reveals a subepidermal blister containing neutrophils and increased mucin within the reticular dermis (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin most commonly reveals linear and/or granular deposition of IgG, IgA, C3, and IgM at the DEJ.11

Bullous tinea is a manifestation of cutaneous dermatophytosis that usually occurs in the setting of tinea pedis. Common causative dermatophytes include Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, and Epidermophyton floccosum. Diagnosis is made by demonstration of fungal hyphae on potassium hydroxide preparation of the blister roof, biopsy with periodic acid-Schiff stain, or fungal culture. If routine histopathologic analysis is performed, epidermal spongiosis with varying degrees of papillary dermal edema is seen, along with abundant fungal elements in the stratum corneum (Figure 4). Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin usually is negative, but C3 deposition in a linear and/or granular pattern along the DEJ has been reported.12

Lichen planus pemphigoides is a rare disease entity and often presents a diagnostic challenge to clinicians. The differential for LPP includes bullous LP as well as other bullous disorders. Ultimately, the diagnosis is confirmed through immunohistologic analysis. Timely diagnosis of LPP is crucial, as most patients can achieve long-term remission with appropriate treatment.
- Zaraa I, Mahfoudh A, Sellami MK, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides: four new cases and a review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:406-412.
- Mohanarao TS, Kumar GA, Chennamsetty K, et al. Childhood lichen planus pemphigoides triggered by chickenpox. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:S98-S100.
- Onprasert W, Chanprapaph K. Lichen planus pemphigoides induced by enalapril: a case report and a review of literature. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:217-224.
- Kuramoto N, Kishimoto S, Shibagaki R, et al. PUVA-induced lichen planus pemphigoides. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:509-512.
- Shimada H, Shono T, Sakai T, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides concomitant with rectal adenocarcinoma: fortuitous or a true association? Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:501-503.
- Matos-Pires E, Campos S, Lencastre A, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:335-337.
- Zillikens D, Caux F, Mascaro JM, et al. Autoantibodies in lichen planus pemphigoides react with a novel epitope within the C-terminal NC16A domain of BP180. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113:117-121.
- Knisley RR, Petropolis AA, Mackey VT. Lichen planus pemphigoides treated with ustekinumab. Cutis. 2017;100:415-418.
- Wagner G, Rose C, Sachse MM. Clinical variants of lichen planus. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:309-319.
- Bagci IS, Horvath ON, Ruzicka T, et al. Bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:445-455.
- Contestable JJ, Edhegard KD, Meyerle JH. Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus: a review and update to diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:517-524.
- Miller DD, Bhawan J. Bullous tinea pedis with direct immunofluorescence positivity: when is a positive result not autoimmune bullous disease? Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:587-594.
- Zaraa I, Mahfoudh A, Sellami MK, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides: four new cases and a review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:406-412.
- Mohanarao TS, Kumar GA, Chennamsetty K, et al. Childhood lichen planus pemphigoides triggered by chickenpox. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:S98-S100.
- Onprasert W, Chanprapaph K. Lichen planus pemphigoides induced by enalapril: a case report and a review of literature. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:217-224.
- Kuramoto N, Kishimoto S, Shibagaki R, et al. PUVA-induced lichen planus pemphigoides. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:509-512.
- Shimada H, Shono T, Sakai T, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides concomitant with rectal adenocarcinoma: fortuitous or a true association? Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:501-503.
- Matos-Pires E, Campos S, Lencastre A, et al. Lichen planus pemphigoides. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:335-337.
- Zillikens D, Caux F, Mascaro JM, et al. Autoantibodies in lichen planus pemphigoides react with a novel epitope within the C-terminal NC16A domain of BP180. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113:117-121.
- Knisley RR, Petropolis AA, Mackey VT. Lichen planus pemphigoides treated with ustekinumab. Cutis. 2017;100:415-418.
- Wagner G, Rose C, Sachse MM. Clinical variants of lichen planus. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:309-319.
- Bagci IS, Horvath ON, Ruzicka T, et al. Bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:445-455.
- Contestable JJ, Edhegard KD, Meyerle JH. Bullous systemic lupus erythematosus: a review and update to diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2014;15:517-524.
- Miller DD, Bhawan J. Bullous tinea pedis with direct immunofluorescence positivity: when is a positive result not autoimmune bullous disease? Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:587-594.
A 72-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a rash of several months' duration that began as itchy bumps on the wrists and spread to involve the legs. Approximately 2 months prior to presentation, she noted blisters on the feet and legs. She initially went to her primary care physician, who prescribed levofloxacin, cephalexin, and a 5-day course of prednisone. The prednisone initially helped; however the rash worsened on discontinuation. In our clinic, the patient had scattered tense bullae and numerous erosions with crust on the dorsum of the feet and legs, some of which were in conjunction with violaceous papules and plaques. There also was hypertrophic scale on the soles of the feet. A potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings from the feet was negative for fungal elements. Two shave biopsies of a violaceous plaque and bulla as well as a perilesional punch biopsy from the leg were obtained.
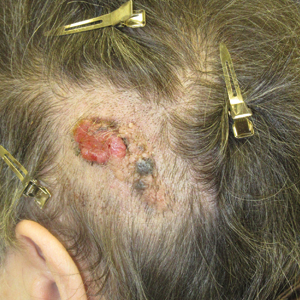
Friable Scalp Nodule
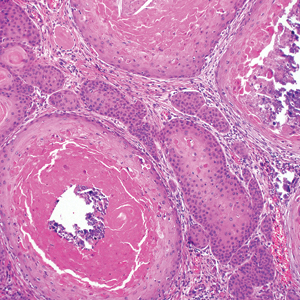
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).
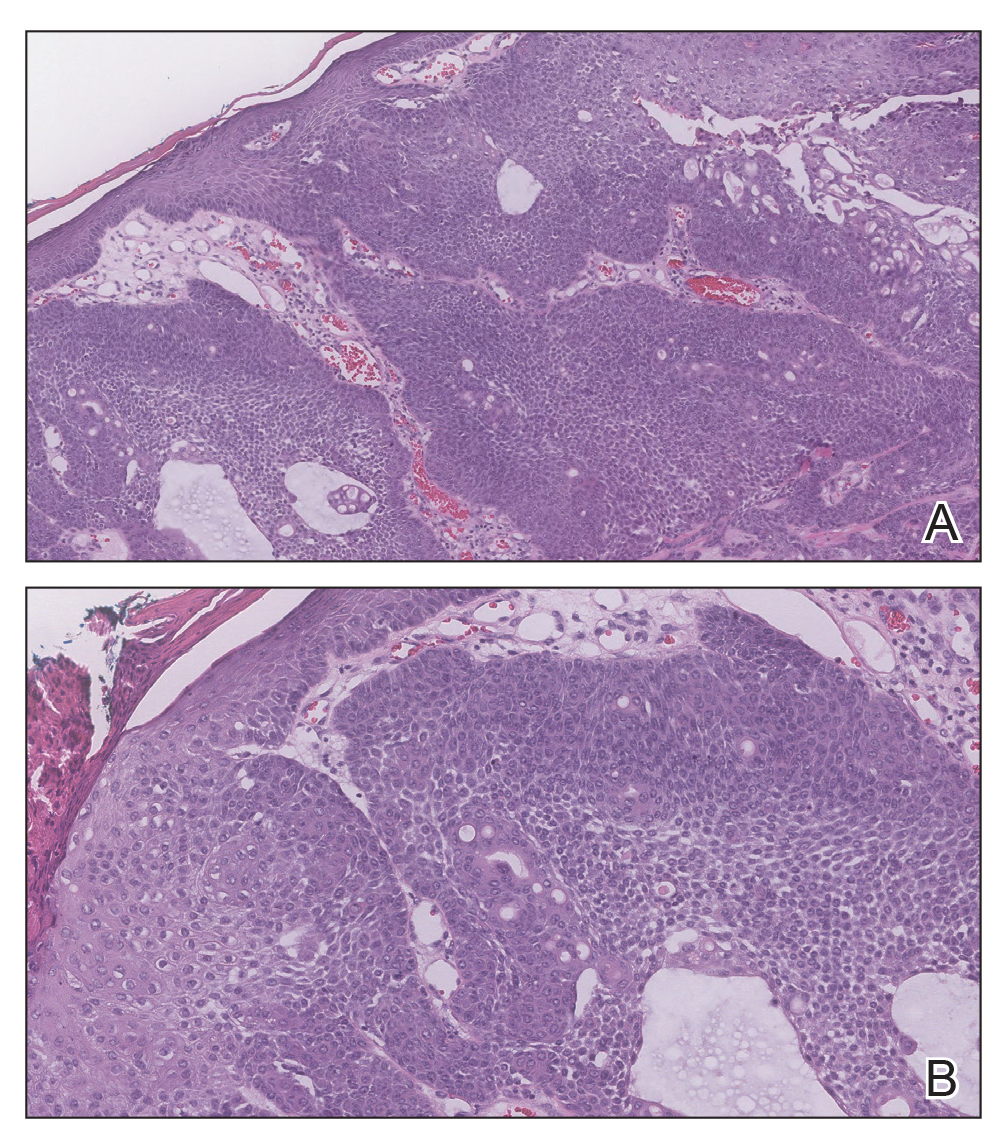
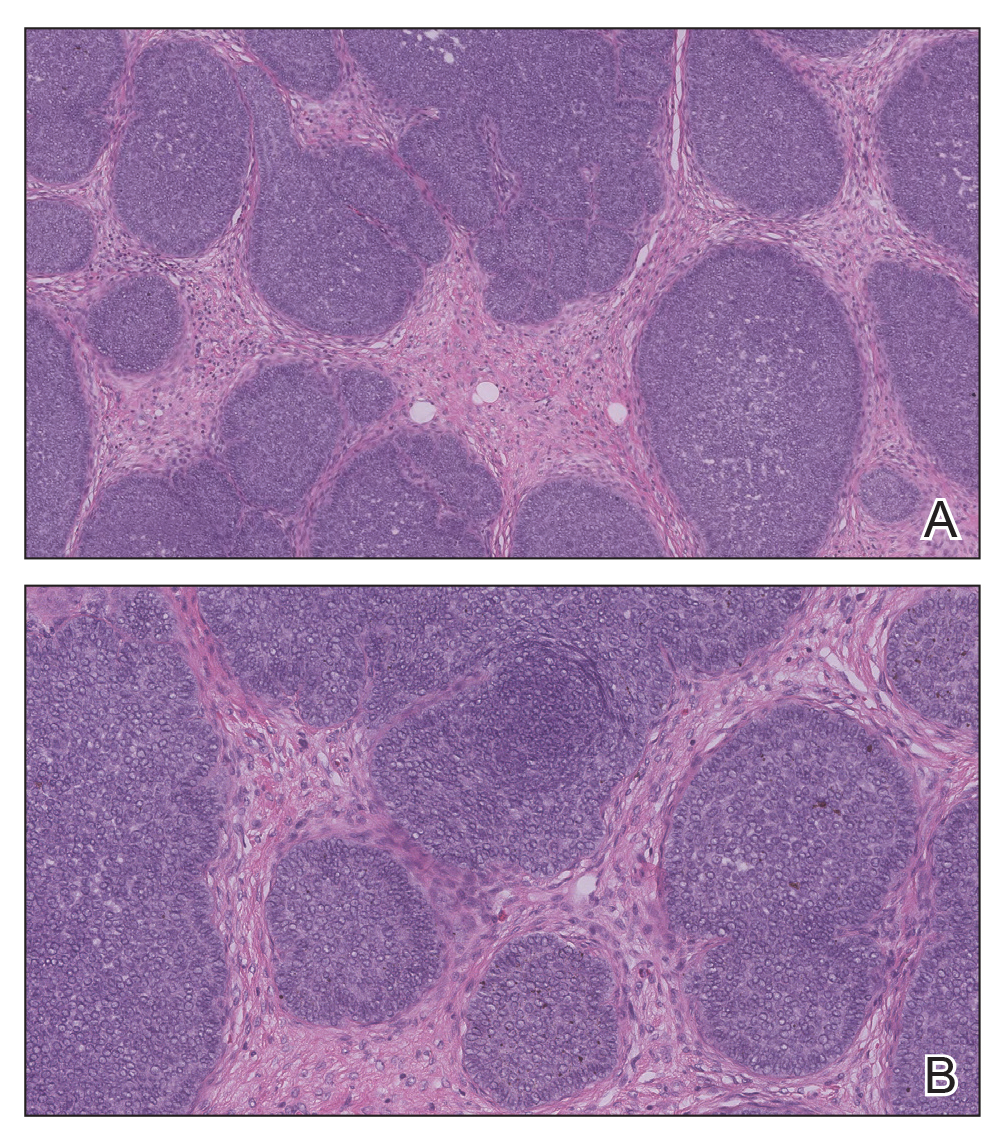
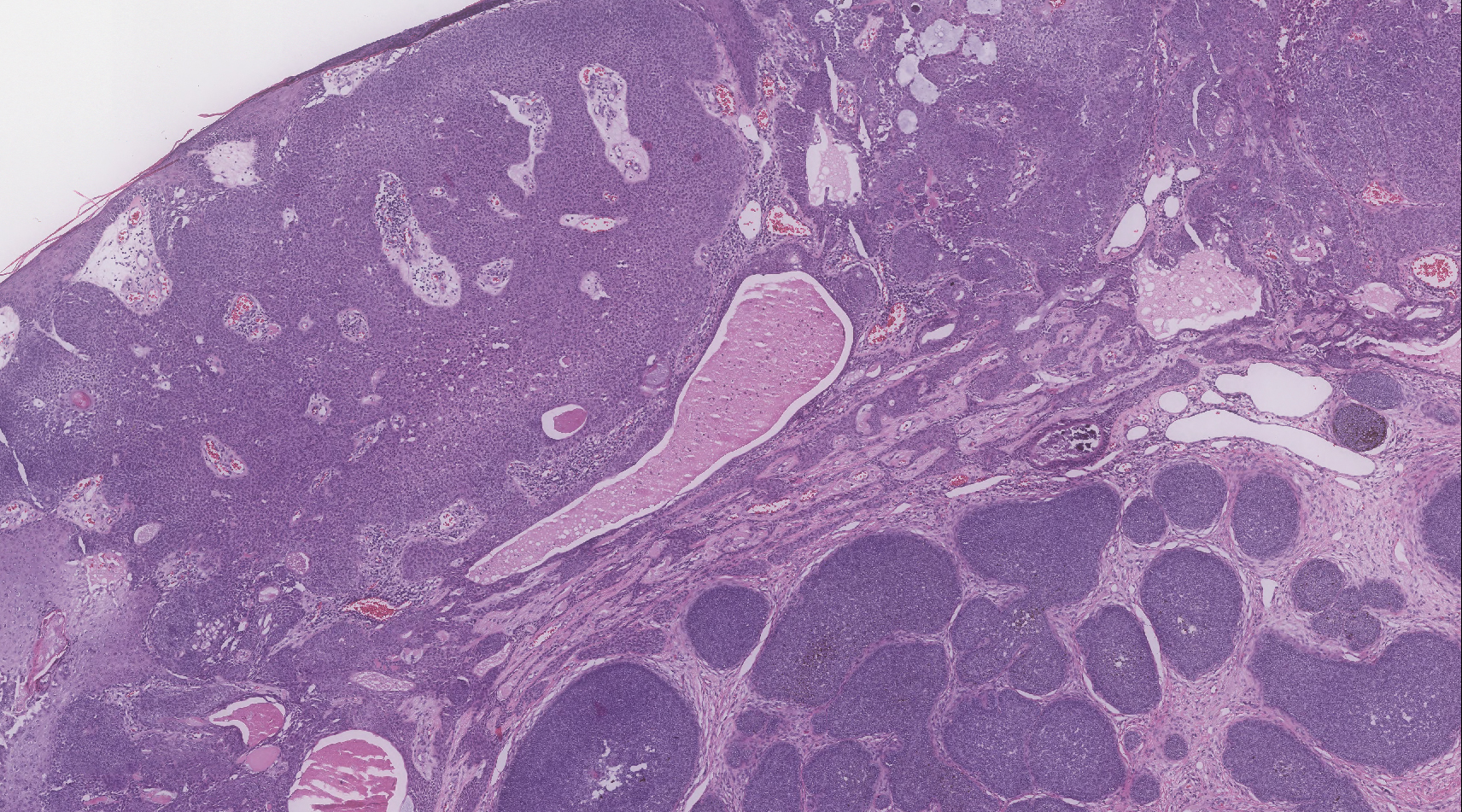
Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).



Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
The Diagnosis: Adnexal Neoplasm Arising in a Nevus Sebaceus
Biopsy of the lesion showed a proliferation of basaloid-appearing cells with focal ductal differentiation and ulceration consistent with poroma (Figure 1). Due to the superficial nature of the biopsy, the pathologist recommended excision to ensure complete removal and to rule out a well-differentiated porocarcinoma. Excision of the lesion showed large basaloid aggregates with a hypercellular stroma and a surrounding papillomatous epidermis with well-developed sebaceous lobules consistent with a trichoblastoma and a nevus sebaceus, respectively (Figure 2). There also was evidence of poroma; however, there were no findings concerning for porocarcinoma, which could lead to metastasis (Figure 3).



Nevus sebaceus is a benign, hamartomatous, congenital growth that occurs in approximately 1% of patients presenting to dermatology offices. It usually presents as a single asymptomatic plaque on the scalp (62.5%) or face (24.5%) that changes in morphology over its lifetime.1,2 In children, a nevus manifests as a yellowish, smooth, waxy skin lesion. As the sebaceous glands become more developed during adolescence, the lesion takes on more of a verrucous appearance and also can darken.
Although nevus sebaceus is benign, it may give rise to both benign and malignant neoplasms. In a 2014 study of 707 cases of nevus sebaceus, 21.4% developed secondary neoplasms, 88% of which were benign.2 The origins of these neoplasms can be epithelial, sebaceous, apocrine, and/or follicular. The 3 most common secondary neoplasms found in nevus sebaceus are trichoblastoma (34.7%), syringocystadenoma papilliferum (24.7%), and apocrine/eccrine adenoma (10%), all of which are benign.2 Trichoblastomas represent a type of hair follicle tumor. Malignant lesions manifest in approximately 2.5% of cases, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) being the most common (5.3% of all neoplasms), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (2.7% of all neoplasms).2 Differentiating BCC from trichoblastoma can be difficult, but histologically BCCs usually have tumor stromal clefting while trichoblastomas do not.3 The incidence of secondary tumors in nevus sebaceus displays a strong correlation with age; thus, the highest proportion of neoplasms occur in adults.
Treatment of nevus sebaceus depends on the patient's age. In children, because of the low probability of secondary neoplasms, observation in lieu of surgical excision is a common approach. In adults, the approach typically is surgical excision or close follow-up, as there is a concern for secondary neoplasm and the potential for malignant degeneration.
A nevus sebaceus leading to 2 or more tumors within the same lesion is rare (seen in only 4.2% of lesions). The most common combination is trichoblastoma with syringocystadenoma papilliferum (0.6% of all cases).2 Poromas represent sweat gland tumors that usually appear on the soles (65%) or palms (10%).4 It is uncommon for these neoplasms to manifest on the scalp or within a nevus sebaceus. Three independent studies (N=596; N=707; N=450) did not report any occurrences of eccrine poroma.1,2,5 Eccrine poroma in conjunction with nodular trichoblastoma arising in a nevus sebaceus is unusual, and definitive excision should be strongly considered because of the possibility to develop a porocarcinoma.6
Atypical fibroxanthoma presents on sun-exposed areas as an exophytic nodule or plaque that frequently ulcerates. Pathology of this tumor shows a spindled cell proliferation that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1. Basal cell carcinoma presents as a pearly papule or nodule displaying basaloid-appearing aggregates with tumor stromal clefting and can stain with Ber-EP4. Cylindromas typically present on the scalp as large rubbery-appearing plaques and nodules. Cylindromas usually present as a solitary tumor, but in the familial form there can be clusters of multiple nodules. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma frequently appears as a bleeding nodule on the scalp in patients with known renal cell cancer or as the initial presentation.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
- Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceus: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(pt 1):263-268.
- Idriss MH, Elston DM. Secondary neoplasms associated with nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn: a study of 707 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:332-337.
- Wang E, Lee JS, Kazakov DV. A rare combination of sebaceoma with carcinomatous change (sebaceous carcinoma), trichoblastoma, and poroma arising from a nevus sebaceus. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:676-682.
- Bae MI, Cho TH, Shin MK, et al. An unusual clinical presentation of eccrine poroma occurring on the auricle. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:523.
- Hsu MC, Liau JY, Hong JL, et al. Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: a retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan. J Dermatol. 2016;43:175-180.
- Takhan II, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:413-415.
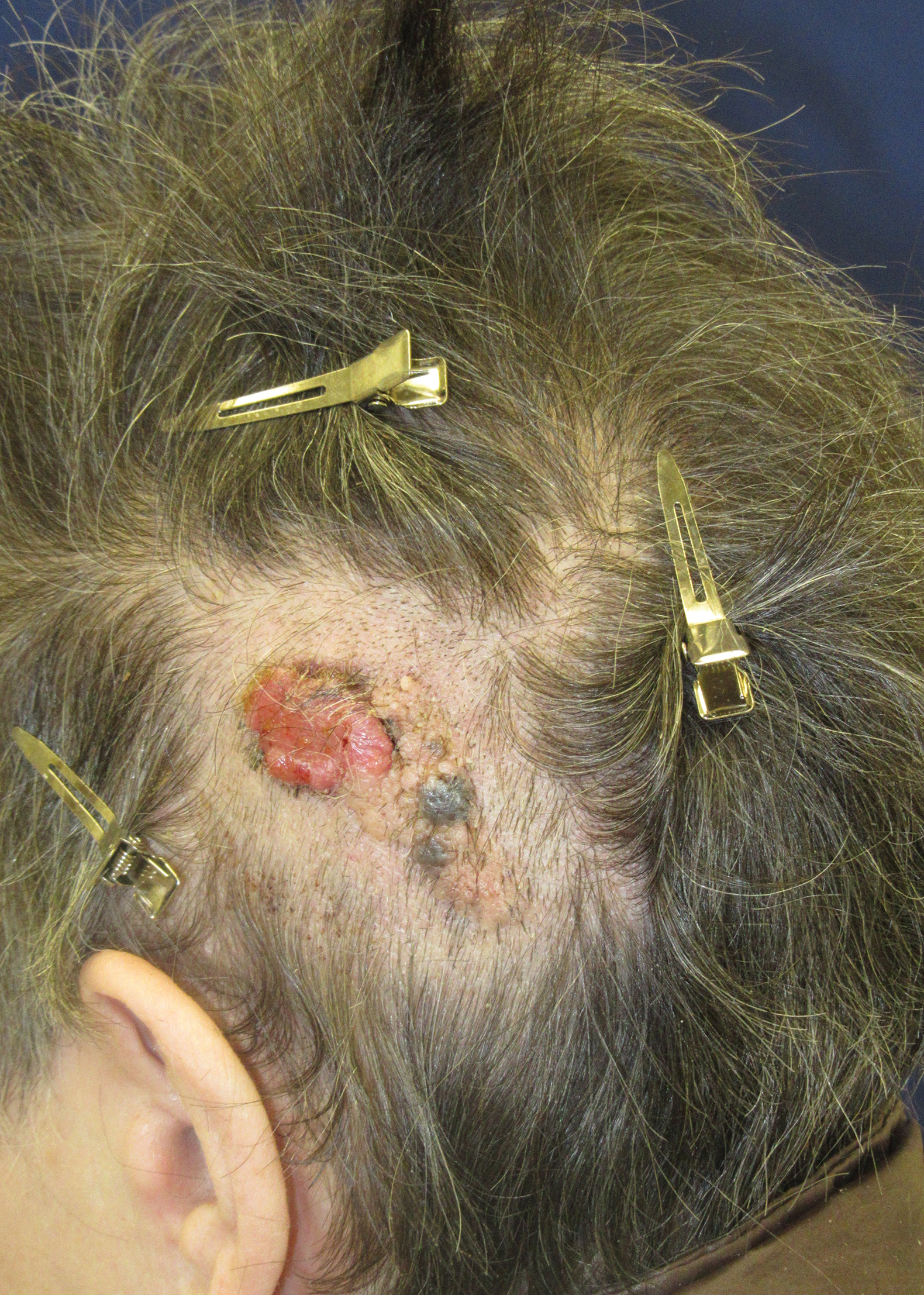
A 75-year-old woman presented with an enlarging plaque on the scalp of 5 years' duration. Physical examination revealed a 5.6.2 ×2.9-cm, tan-colored, verrucous plaque with an overlying pink friable nodule on the left occipital scalp. The lesion was not painful or pruritic, and the patient did not have any constitutional symptoms such as fever, night sweats, or weight loss. The patient denied prior tanning bed use and reported intermittent sun exposure over her lifetime. She denied any prior surgical intervention. There was no family history of similar lesions.
Ulcerated Nodule on the Scalp
The Diagnosis: Proliferating Pilar Tumor
Proliferating pilar tumor (PPT), or cyst, is a neoplasm of trichilemmal keratinization first described by Wilson-Jones1 in 1966. Proliferating pilar tumors lie on a spectrum with malignant PPT, which is a rare adnexal neoplasm first described by Saida et al2 in 1983. The incidence of PPT is unknown given the paucity of cases and the possible misdiagnosis as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Proliferating pilar tumors tend to present on the head and neck of older females as a multilobular and sometimes ulcerating nodule.3 Although PPT can occur de novo, the majority of cases are thought to develop progressively from a benign pilar cyst. Histopathologically, PPT is characterized by cords and nests of squamous cells that display trichilemmal keratinization (quiz images).
Classification of PPT as benign or malignant is challenging, though criteria have been proposed.3-7 Lesions with minimal infiltration into the surrounding dermis and scant mitosis typically behave in a benign manner, while lesions showing nuclear atypia, atypical mitosis, and irregular infiltration into the surrounding dermis can have up to a 50% locoregional recurrence rate.3 In addition, distinguishing a PPT from an SCC or trichilemmal carcinoma also can be difficult; however, SCC is favored when there is a lack of trichilemmal keratinization or when squamous atypia is present in the adjacent epidermis.8 Trichilemmal carcinoma is a rare tumor that has been questioned as a distinct entity.9-12
Pilomatricoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, is a benign pilar tumor that presents as a slowly growing nodule on the head or neck area or arms.13,14 Most pilomatricomas develop by the second decade of life. Multiple lesions may be present in association with myotonic dystrophy or Gardner syndrome among other syndromes.15-17 Similar to PPT, pilomatricomas present as large dermal nodules; however, they tend to be circumscribed and have a trabecular network that consists of basophilic cells and eosinophilic keratinized shadow cells (Figure 1).18 Calcification may be seen and bone formation subsequently may occur.19
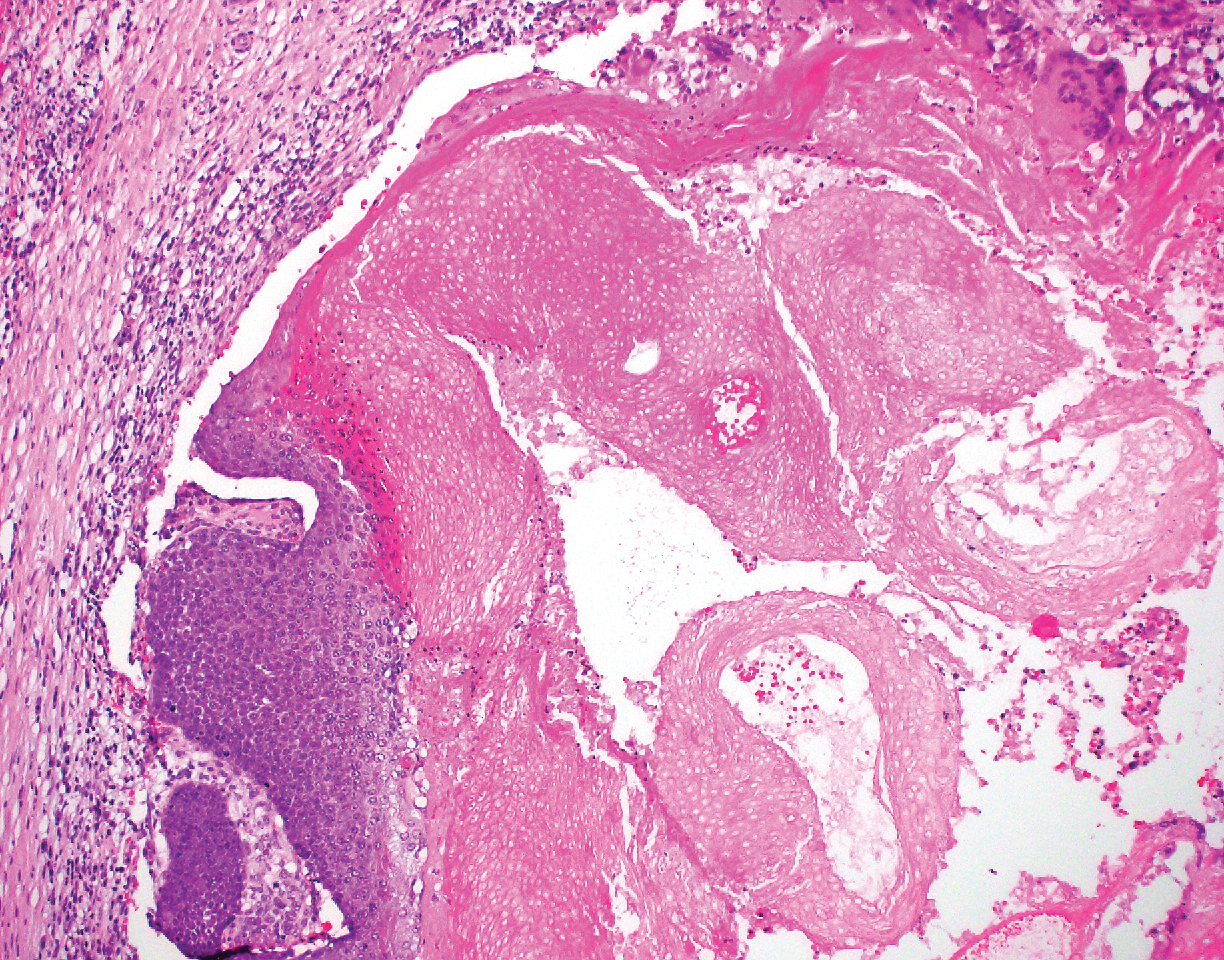
Most sources now consider keratoacanthoma (KA) as a well-differentiated SCC.20 The typical presentation consists of a rapidly growing erythematous to flesh-colored nodule with a central keratinous plug that develops over a period of weeks. If untreated, KAs may resolve over a period of months and leave a depressed scar. Local destruction can result from KAs, and they have the potential to transform into a more aggressive SCC. Accordingly, most clinicians use tissue destructive methods, excision, or Mohs micrographic surgery for treatment based on location. Histologically, a well-circumscribed proliferation of glassy cytoplasm is noted. A depressed keratin-filled center is surrounded by a lip of epithelium extending over the lesion (Figure 2).20,21 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia accompanied by hypergranulosis is seen in the center of KAs rather than at the periphery, which is typical of non-KA SCCs. Typical KAs lack acantholysis, a feature suggesting a non-KA type of SCC. Neutrophilic microabscesses and eosinophils commonly are seen in KAs.20,21
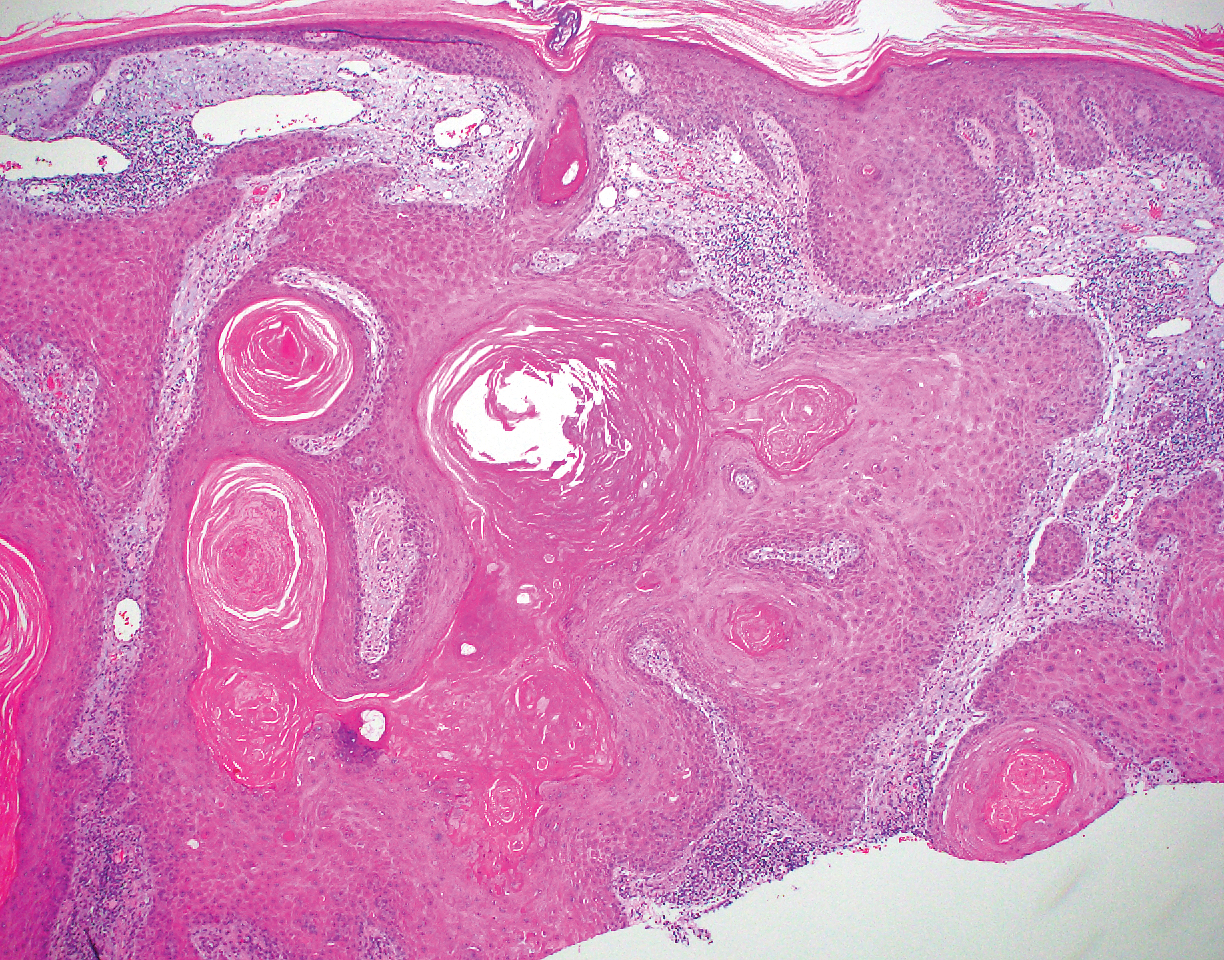
Inverted follicular keratosis is a benign tumor that gained traction as its own entity in the 1960s.22 These lesions typically develop from the follicular infundibulum, but some consider them a version of a wart or seborrheic keratosis.23 They generally are flesh-colored nodules on the upper cutaneous lip or face. Treatment usually consists of complete excision. There are many different growth patterns described, but they typically are endophytic tumors with eosinophilic squamous cells in the center and more basophilic cells at the periphery (Figure 3).24 Characteristically, there are squamous eddies throughout the tumor (Figure 3 [inset]). There also may be a scant lymphohistiocytic infiltrate within the dermis surrounding the lesion.
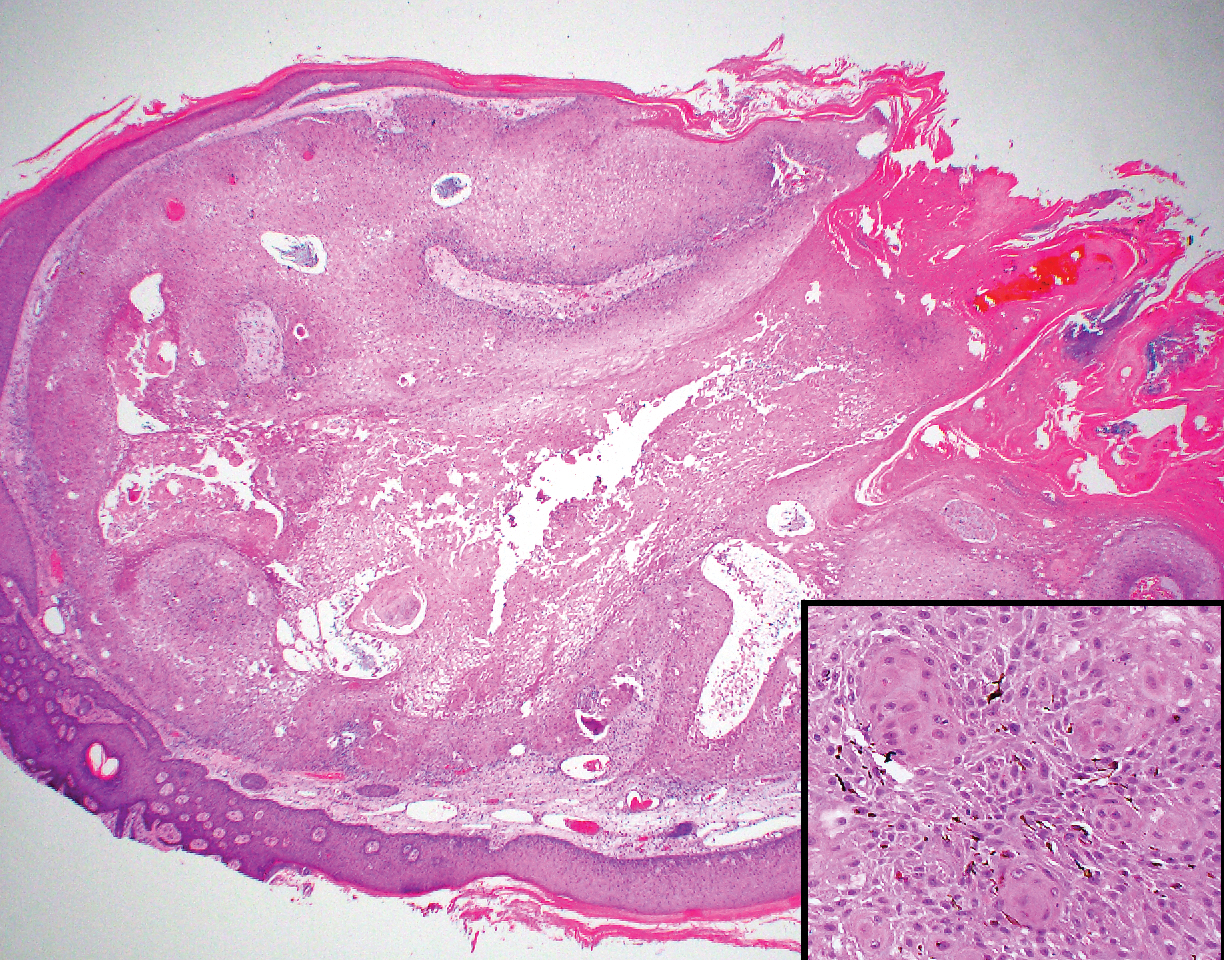
Trichilemmomas are flesh-colored adnexal neoplasms that may present as a solitary lesion or in clusters on the face. They have been reported to occur on all nonglabrous skin sites.25 Multiple lesions may occur in association with Cowden syndrome or with nevus sebaceous.26 A desmoplastic variant of trichilemmomas has been reported.27 Desmoplastic trichilemmomas appear as well-circumscribed tumors of outer root sheath differentiation with lobules extending down into the dermis.28 Vacuolated glycogen-filled keratinocytes are scattered throughout the lesion but are most prominent at the base. At the periphery of the lobules, peripheral palisading of basaloid cells is accompanied by a thickened eosinophilic basement membrane that is periodic acid-Schiff positive. Typical trichilemmomas also can display these features; however, the main differentiating feature of a desmoplastic trichilemmoma is the pink hyalinized stroma separating small islets of basophilic cells (Figure 4). Differentiation from an invasive malignant carcinoma sometimes can be challenging without a focus of typical trichilemmoma or if the biopsy specimen is too superficial.29

Pilar cysts are common tumors that typically arise on the scalp and sometimes are proliferating. Proliferating pilar tumor should be kept on the differential when secondary changes such as ulceration occur in the primary lesion of the scalp. Microscopically, and sometimes clinically, PPT can be difficult to differentiate from other mimickers.
- Wilson-Jones E. Proliferating epidermoid cysts. Arch Dermatol. 1966;94:11-19.
- Saida T, Oohara K, Hori Y, et al. Development of a malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst in a patient with multiple trichilemmal cysts. Dermatologica. 1983;166:203-208.
- Ye J, Nappi O, Swanson PE, et al. Proliferating pilar tumours: a clinicopathological study of 76 cases with a proposal for definition of benign and malignant variants. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:566-574.
- Garg PK, Dangi A, Khurana N, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a case report with review of literature. Malaysian J Pathol. 2009;31:71-76.
- Herrero J, Monteagudo C, Ruiz A, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal tumors: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study of three cases with DNA ploidy and morphometric evaluation. Histopathology. 1998;33:542-546.
- Haas N, Audring H, Sterry W. Carcinoma arising in a proliferating trichilemmal cyst expresses fetal and trichilemmal hair phenotype. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:340-344.
- Rutty GN, Richman PI, Laing JH. Malignant change in trichilemmal cysts: a study of cell proliferation and DNA content. Histopathology. 1992;21:465-468.
- Brownstein MH, Arluk DJ. Proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a simulant of squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1981;48:1207-1214.
- Misago N, Ackerman AB. Tricholemmal carcinoma? Dermatopathol Pract Concept. 1999;5:205-206.
- Misago N, Narisawa Y. Tricholemmal carcinoma in continuity with trichoblastoma within nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:149-155.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze TA, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
- Swanson PE, Marrogi AJ, Williams DJ, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma: clinicopathologic study of 10 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1992;19:100-109.
- Mehregan AH. Hair follicle tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:189-195.
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. A clinical review of 209 pilomatricomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:191-195.
- Marrogi AJ, Wick MR, Dehner LP. Pilomatrical neoplasms in children and young adults. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:87-94.
- Berberian BJ, Colonna TM, Battaglia M, et al. Multiple pilomatricomas in association with myotonic dystrophy and a family history of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:268-269.
- Cooper PH, Fechner RE. Pilomatricoma-like changes in the epidermal cysts of Gardner's syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:639-644.
- Kaddu S, Soyer HP, Cerroni L, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of pilomatricomas in adults. Int J Dermatol. 1994;33:705-708.
- Sano Y, Mihara M, Miyamoto T, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of calcification and amyloid deposit in pilomatricoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70:256-259.
- Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:1-19.
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1964;89:117-123.
- Spielvogel RL, Austin C, Ackerman AB. Inverted follicular keratosis is not a specific keratosis but a verruca vulgaris (or seborrheic keratosis) with squamous eddies. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:427-445.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis is a distinct follicular tumor. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:467-470.
- Brownstein MH. Trichilemmoma. benign follicular tumor or viral wart? Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:229-231.
- Brownstein MH. Multiple trichilemmomas in Cowden's syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:111.
- Roson E, Gomez Centeno P, Sanchez Aguilar D, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma arising within a nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:495-497.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Sharma R, Sirohi D, Sengupta P, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma of the facial region mimicking invasive carcinoma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010;10:71-73.
The Diagnosis: Proliferating Pilar Tumor
Proliferating pilar tumor (PPT), or cyst, is a neoplasm of trichilemmal keratinization first described by Wilson-Jones1 in 1966. Proliferating pilar tumors lie on a spectrum with malignant PPT, which is a rare adnexal neoplasm first described by Saida et al2 in 1983. The incidence of PPT is unknown given the paucity of cases and the possible misdiagnosis as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Proliferating pilar tumors tend to present on the head and neck of older females as a multilobular and sometimes ulcerating nodule.3 Although PPT can occur de novo, the majority of cases are thought to develop progressively from a benign pilar cyst. Histopathologically, PPT is characterized by cords and nests of squamous cells that display trichilemmal keratinization (quiz images).
Classification of PPT as benign or malignant is challenging, though criteria have been proposed.3-7 Lesions with minimal infiltration into the surrounding dermis and scant mitosis typically behave in a benign manner, while lesions showing nuclear atypia, atypical mitosis, and irregular infiltration into the surrounding dermis can have up to a 50% locoregional recurrence rate.3 In addition, distinguishing a PPT from an SCC or trichilemmal carcinoma also can be difficult; however, SCC is favored when there is a lack of trichilemmal keratinization or when squamous atypia is present in the adjacent epidermis.8 Trichilemmal carcinoma is a rare tumor that has been questioned as a distinct entity.9-12
Pilomatricoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, is a benign pilar tumor that presents as a slowly growing nodule on the head or neck area or arms.13,14 Most pilomatricomas develop by the second decade of life. Multiple lesions may be present in association with myotonic dystrophy or Gardner syndrome among other syndromes.15-17 Similar to PPT, pilomatricomas present as large dermal nodules; however, they tend to be circumscribed and have a trabecular network that consists of basophilic cells and eosinophilic keratinized shadow cells (Figure 1).18 Calcification may be seen and bone formation subsequently may occur.19

Most sources now consider keratoacanthoma (KA) as a well-differentiated SCC.20 The typical presentation consists of a rapidly growing erythematous to flesh-colored nodule with a central keratinous plug that develops over a period of weeks. If untreated, KAs may resolve over a period of months and leave a depressed scar. Local destruction can result from KAs, and they have the potential to transform into a more aggressive SCC. Accordingly, most clinicians use tissue destructive methods, excision, or Mohs micrographic surgery for treatment based on location. Histologically, a well-circumscribed proliferation of glassy cytoplasm is noted. A depressed keratin-filled center is surrounded by a lip of epithelium extending over the lesion (Figure 2).20,21 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia accompanied by hypergranulosis is seen in the center of KAs rather than at the periphery, which is typical of non-KA SCCs. Typical KAs lack acantholysis, a feature suggesting a non-KA type of SCC. Neutrophilic microabscesses and eosinophils commonly are seen in KAs.20,21

Inverted follicular keratosis is a benign tumor that gained traction as its own entity in the 1960s.22 These lesions typically develop from the follicular infundibulum, but some consider them a version of a wart or seborrheic keratosis.23 They generally are flesh-colored nodules on the upper cutaneous lip or face. Treatment usually consists of complete excision. There are many different growth patterns described, but they typically are endophytic tumors with eosinophilic squamous cells in the center and more basophilic cells at the periphery (Figure 3).24 Characteristically, there are squamous eddies throughout the tumor (Figure 3 [inset]). There also may be a scant lymphohistiocytic infiltrate within the dermis surrounding the lesion.

Trichilemmomas are flesh-colored adnexal neoplasms that may present as a solitary lesion or in clusters on the face. They have been reported to occur on all nonglabrous skin sites.25 Multiple lesions may occur in association with Cowden syndrome or with nevus sebaceous.26 A desmoplastic variant of trichilemmomas has been reported.27 Desmoplastic trichilemmomas appear as well-circumscribed tumors of outer root sheath differentiation with lobules extending down into the dermis.28 Vacuolated glycogen-filled keratinocytes are scattered throughout the lesion but are most prominent at the base. At the periphery of the lobules, peripheral palisading of basaloid cells is accompanied by a thickened eosinophilic basement membrane that is periodic acid-Schiff positive. Typical trichilemmomas also can display these features; however, the main differentiating feature of a desmoplastic trichilemmoma is the pink hyalinized stroma separating small islets of basophilic cells (Figure 4). Differentiation from an invasive malignant carcinoma sometimes can be challenging without a focus of typical trichilemmoma or if the biopsy specimen is too superficial.29

Pilar cysts are common tumors that typically arise on the scalp and sometimes are proliferating. Proliferating pilar tumor should be kept on the differential when secondary changes such as ulceration occur in the primary lesion of the scalp. Microscopically, and sometimes clinically, PPT can be difficult to differentiate from other mimickers.
The Diagnosis: Proliferating Pilar Tumor
Proliferating pilar tumor (PPT), or cyst, is a neoplasm of trichilemmal keratinization first described by Wilson-Jones1 in 1966. Proliferating pilar tumors lie on a spectrum with malignant PPT, which is a rare adnexal neoplasm first described by Saida et al2 in 1983. The incidence of PPT is unknown given the paucity of cases and the possible misdiagnosis as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Proliferating pilar tumors tend to present on the head and neck of older females as a multilobular and sometimes ulcerating nodule.3 Although PPT can occur de novo, the majority of cases are thought to develop progressively from a benign pilar cyst. Histopathologically, PPT is characterized by cords and nests of squamous cells that display trichilemmal keratinization (quiz images).
Classification of PPT as benign or malignant is challenging, though criteria have been proposed.3-7 Lesions with minimal infiltration into the surrounding dermis and scant mitosis typically behave in a benign manner, while lesions showing nuclear atypia, atypical mitosis, and irregular infiltration into the surrounding dermis can have up to a 50% locoregional recurrence rate.3 In addition, distinguishing a PPT from an SCC or trichilemmal carcinoma also can be difficult; however, SCC is favored when there is a lack of trichilemmal keratinization or when squamous atypia is present in the adjacent epidermis.8 Trichilemmal carcinoma is a rare tumor that has been questioned as a distinct entity.9-12
Pilomatricoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, is a benign pilar tumor that presents as a slowly growing nodule on the head or neck area or arms.13,14 Most pilomatricomas develop by the second decade of life. Multiple lesions may be present in association with myotonic dystrophy or Gardner syndrome among other syndromes.15-17 Similar to PPT, pilomatricomas present as large dermal nodules; however, they tend to be circumscribed and have a trabecular network that consists of basophilic cells and eosinophilic keratinized shadow cells (Figure 1).18 Calcification may be seen and bone formation subsequently may occur.19

Most sources now consider keratoacanthoma (KA) as a well-differentiated SCC.20 The typical presentation consists of a rapidly growing erythematous to flesh-colored nodule with a central keratinous plug that develops over a period of weeks. If untreated, KAs may resolve over a period of months and leave a depressed scar. Local destruction can result from KAs, and they have the potential to transform into a more aggressive SCC. Accordingly, most clinicians use tissue destructive methods, excision, or Mohs micrographic surgery for treatment based on location. Histologically, a well-circumscribed proliferation of glassy cytoplasm is noted. A depressed keratin-filled center is surrounded by a lip of epithelium extending over the lesion (Figure 2).20,21 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia accompanied by hypergranulosis is seen in the center of KAs rather than at the periphery, which is typical of non-KA SCCs. Typical KAs lack acantholysis, a feature suggesting a non-KA type of SCC. Neutrophilic microabscesses and eosinophils commonly are seen in KAs.20,21

Inverted follicular keratosis is a benign tumor that gained traction as its own entity in the 1960s.22 These lesions typically develop from the follicular infundibulum, but some consider them a version of a wart or seborrheic keratosis.23 They generally are flesh-colored nodules on the upper cutaneous lip or face. Treatment usually consists of complete excision. There are many different growth patterns described, but they typically are endophytic tumors with eosinophilic squamous cells in the center and more basophilic cells at the periphery (Figure 3).24 Characteristically, there are squamous eddies throughout the tumor (Figure 3 [inset]). There also may be a scant lymphohistiocytic infiltrate within the dermis surrounding the lesion.

Trichilemmomas are flesh-colored adnexal neoplasms that may present as a solitary lesion or in clusters on the face. They have been reported to occur on all nonglabrous skin sites.25 Multiple lesions may occur in association with Cowden syndrome or with nevus sebaceous.26 A desmoplastic variant of trichilemmomas has been reported.27 Desmoplastic trichilemmomas appear as well-circumscribed tumors of outer root sheath differentiation with lobules extending down into the dermis.28 Vacuolated glycogen-filled keratinocytes are scattered throughout the lesion but are most prominent at the base. At the periphery of the lobules, peripheral palisading of basaloid cells is accompanied by a thickened eosinophilic basement membrane that is periodic acid-Schiff positive. Typical trichilemmomas also can display these features; however, the main differentiating feature of a desmoplastic trichilemmoma is the pink hyalinized stroma separating small islets of basophilic cells (Figure 4). Differentiation from an invasive malignant carcinoma sometimes can be challenging without a focus of typical trichilemmoma or if the biopsy specimen is too superficial.29

Pilar cysts are common tumors that typically arise on the scalp and sometimes are proliferating. Proliferating pilar tumor should be kept on the differential when secondary changes such as ulceration occur in the primary lesion of the scalp. Microscopically, and sometimes clinically, PPT can be difficult to differentiate from other mimickers.
- Wilson-Jones E. Proliferating epidermoid cysts. Arch Dermatol. 1966;94:11-19.
- Saida T, Oohara K, Hori Y, et al. Development of a malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst in a patient with multiple trichilemmal cysts. Dermatologica. 1983;166:203-208.
- Ye J, Nappi O, Swanson PE, et al. Proliferating pilar tumours: a clinicopathological study of 76 cases with a proposal for definition of benign and malignant variants. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:566-574.
- Garg PK, Dangi A, Khurana N, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a case report with review of literature. Malaysian J Pathol. 2009;31:71-76.
- Herrero J, Monteagudo C, Ruiz A, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal tumors: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study of three cases with DNA ploidy and morphometric evaluation. Histopathology. 1998;33:542-546.
- Haas N, Audring H, Sterry W. Carcinoma arising in a proliferating trichilemmal cyst expresses fetal and trichilemmal hair phenotype. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:340-344.
- Rutty GN, Richman PI, Laing JH. Malignant change in trichilemmal cysts: a study of cell proliferation and DNA content. Histopathology. 1992;21:465-468.
- Brownstein MH, Arluk DJ. Proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a simulant of squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1981;48:1207-1214.
- Misago N, Ackerman AB. Tricholemmal carcinoma? Dermatopathol Pract Concept. 1999;5:205-206.
- Misago N, Narisawa Y. Tricholemmal carcinoma in continuity with trichoblastoma within nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:149-155.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze TA, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
- Swanson PE, Marrogi AJ, Williams DJ, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma: clinicopathologic study of 10 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1992;19:100-109.
- Mehregan AH. Hair follicle tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:189-195.
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. A clinical review of 209 pilomatricomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:191-195.
- Marrogi AJ, Wick MR, Dehner LP. Pilomatrical neoplasms in children and young adults. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:87-94.
- Berberian BJ, Colonna TM, Battaglia M, et al. Multiple pilomatricomas in association with myotonic dystrophy and a family history of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:268-269.
- Cooper PH, Fechner RE. Pilomatricoma-like changes in the epidermal cysts of Gardner's syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:639-644.
- Kaddu S, Soyer HP, Cerroni L, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of pilomatricomas in adults. Int J Dermatol. 1994;33:705-708.
- Sano Y, Mihara M, Miyamoto T, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of calcification and amyloid deposit in pilomatricoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70:256-259.
- Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:1-19.
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1964;89:117-123.
- Spielvogel RL, Austin C, Ackerman AB. Inverted follicular keratosis is not a specific keratosis but a verruca vulgaris (or seborrheic keratosis) with squamous eddies. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:427-445.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis is a distinct follicular tumor. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:467-470.
- Brownstein MH. Trichilemmoma. benign follicular tumor or viral wart? Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:229-231.
- Brownstein MH. Multiple trichilemmomas in Cowden's syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:111.
- Roson E, Gomez Centeno P, Sanchez Aguilar D, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma arising within a nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:495-497.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Sharma R, Sirohi D, Sengupta P, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma of the facial region mimicking invasive carcinoma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010;10:71-73.
- Wilson-Jones E. Proliferating epidermoid cysts. Arch Dermatol. 1966;94:11-19.
- Saida T, Oohara K, Hori Y, et al. Development of a malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst in a patient with multiple trichilemmal cysts. Dermatologica. 1983;166:203-208.
- Ye J, Nappi O, Swanson PE, et al. Proliferating pilar tumours: a clinicopathological study of 76 cases with a proposal for definition of benign and malignant variants. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:566-574.
- Garg PK, Dangi A, Khurana N, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a case report with review of literature. Malaysian J Pathol. 2009;31:71-76.
- Herrero J, Monteagudo C, Ruiz A, et al. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal tumors: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study of three cases with DNA ploidy and morphometric evaluation. Histopathology. 1998;33:542-546.
- Haas N, Audring H, Sterry W. Carcinoma arising in a proliferating trichilemmal cyst expresses fetal and trichilemmal hair phenotype. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:340-344.
- Rutty GN, Richman PI, Laing JH. Malignant change in trichilemmal cysts: a study of cell proliferation and DNA content. Histopathology. 1992;21:465-468.
- Brownstein MH, Arluk DJ. Proliferating trichilemmal cyst: a simulant of squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1981;48:1207-1214.
- Misago N, Ackerman AB. Tricholemmal carcinoma? Dermatopathol Pract Concept. 1999;5:205-206.
- Misago N, Narisawa Y. Tricholemmal carcinoma in continuity with trichoblastoma within nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002;24:149-155.
- Liang H, Wu H, Giorgadze TA, et al. Podoplanin is a highly sensitive and specific marker to distinguish primary skin adnexal carcinomas from adenocarcinomas metastatic to skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:304-310.
- Swanson PE, Marrogi AJ, Williams DJ, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma: clinicopathologic study of 10 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1992;19:100-109.
- Mehregan AH. Hair follicle tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:189-195.
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. A clinical review of 209 pilomatricomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:191-195.
- Marrogi AJ, Wick MR, Dehner LP. Pilomatrical neoplasms in children and young adults. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:87-94.
- Berberian BJ, Colonna TM, Battaglia M, et al. Multiple pilomatricomas in association with myotonic dystrophy and a family history of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:268-269.
- Cooper PH, Fechner RE. Pilomatricoma-like changes in the epidermal cysts of Gardner's syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:639-644.
- Kaddu S, Soyer HP, Cerroni L, et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of pilomatricomas in adults. Int J Dermatol. 1994;33:705-708.
- Sano Y, Mihara M, Miyamoto T, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of calcification and amyloid deposit in pilomatricoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70:256-259.
- Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:1-19.
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1964;89:117-123.
- Spielvogel RL, Austin C, Ackerman AB. Inverted follicular keratosis is not a specific keratosis but a verruca vulgaris (or seborrheic keratosis) with squamous eddies. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:427-445.
- Mehregan AH. Inverted follicular keratosis is a distinct follicular tumor. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983;5:467-470.
- Brownstein MH. Trichilemmoma. benign follicular tumor or viral wart? Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:229-231.
- Brownstein MH. Multiple trichilemmomas in Cowden's syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:111.
- Roson E, Gomez Centeno P, Sanchez Aguilar D, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma arising within a nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998;20:495-497.
- Tellechea O, Reis JP, Baptista AP. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992;14:107-114.
- Sharma R, Sirohi D, Sengupta P, et al. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma of the facial region mimicking invasive carcinoma. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010;10:71-73.
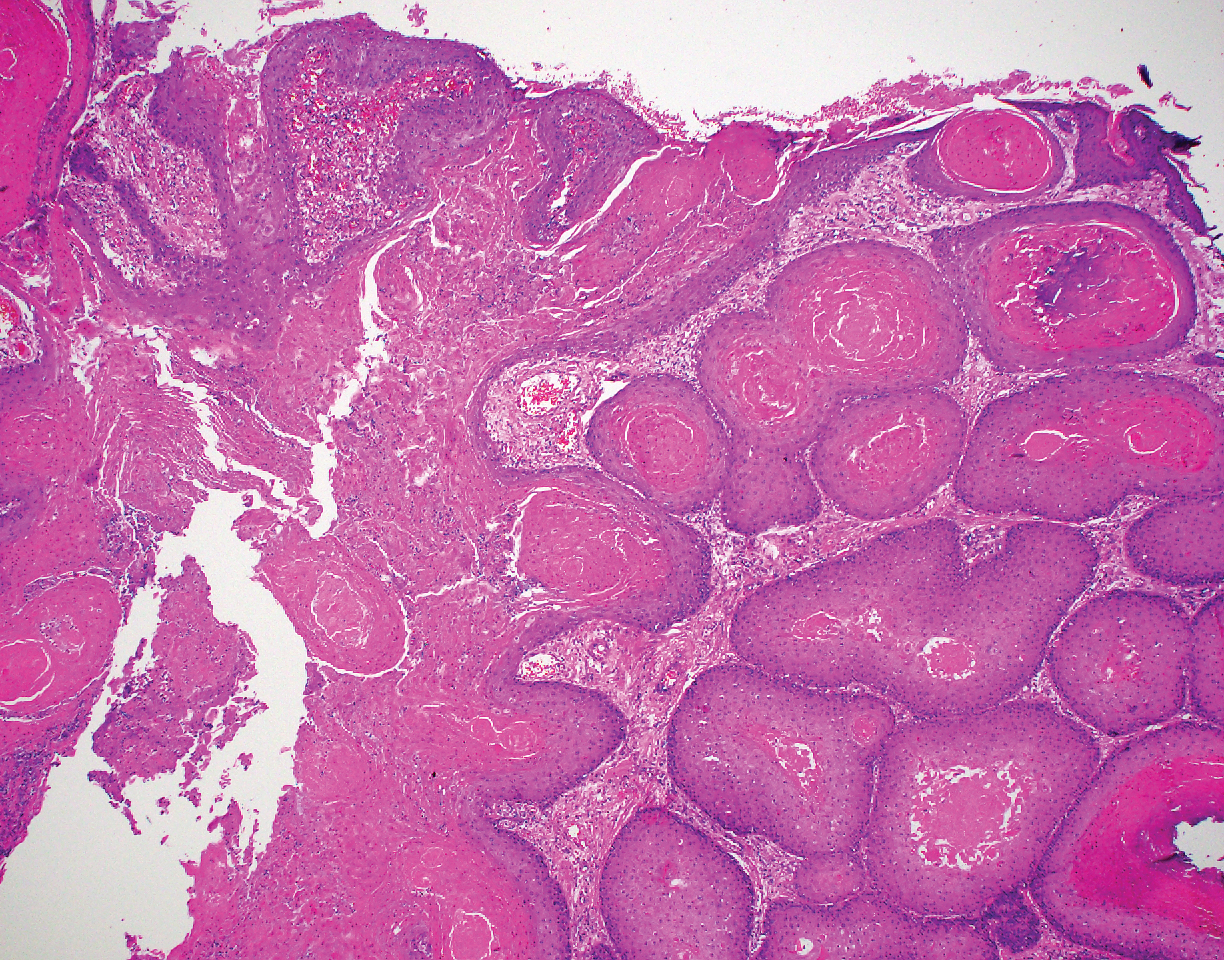
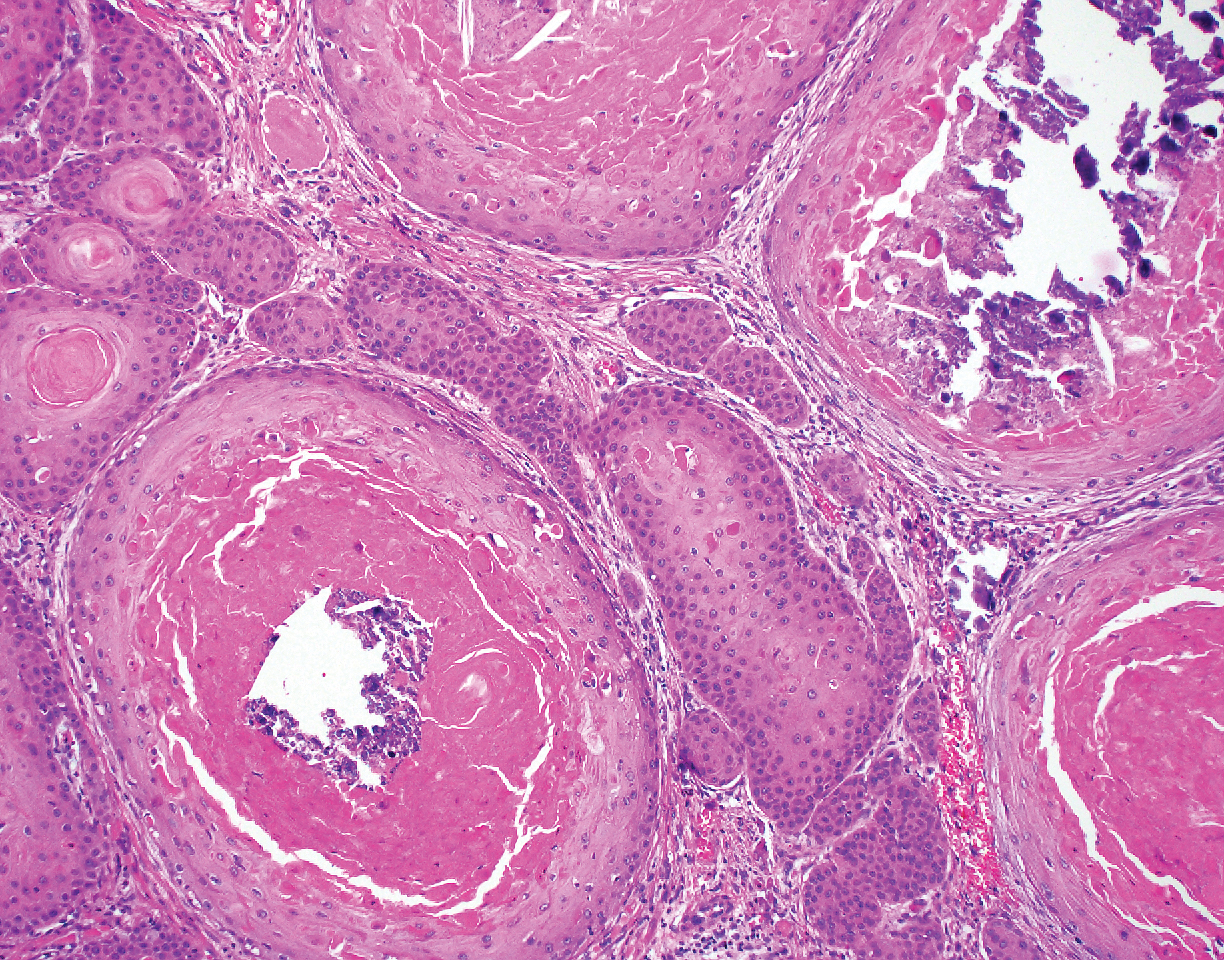
A 66-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with a rapidly enlarging, draining lesion on the scalp. The lesion seemed to enlarge over the last 3 months from a lesion that had been there for years. Physical examination revealed a 2.2-cm ulcerated nodule on the right parietal scalp. A shave biopsy was obtained.
Numerous Flesh-Colored Nodules on the Trunk
The Diagnosis: Steatocystoma Multiplex
The punch biopsy of an abdominal lesion demonstrated a folded cyst wall with a wavy eosinophilic cuticle (Figure), characteristics consistent with steatocystoma multiplex (SM).
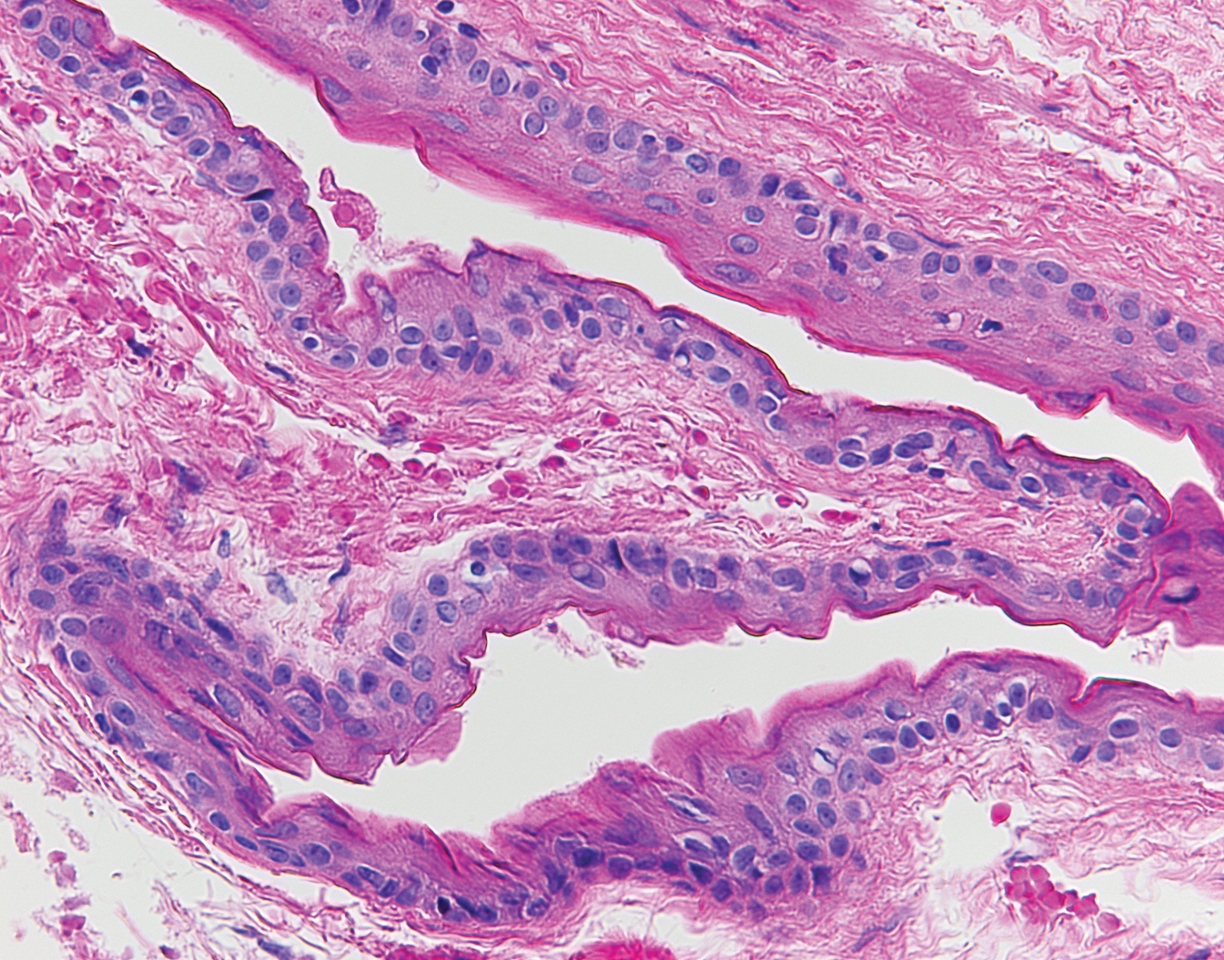
Also known as eruptive steatocystoma, SM consists of numerous flesh-colored, dome-shaped papules and nodules that most commonly arise during adolescence, with a median age of onset of 26 years.1 These hamartomatous nevoid malformations arise in areas with well-developed pilosebaceous units, such as the upper extremities, neck, axillae, and trunk.1,2 They occur less commonly on the scalp, face, and acral surfaces.2-5 The lesions range in size from 2 to 30 mm6 and usually are asymptomatic.1 Occasionally, steatocystomas become tender or can rupture.7
Steatocystoma multiplex may arise sporadically or may be inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion. Mutations in exon 1 of the keratin 17 gene, KRT17, have been identified in autosomal-dominant SM.6,8 KRT17 mutations also are responsible for pachyonychia congenita type 2, which is associated with SM.9 Some patients with pachyonychia congenita type 2 who have prominent SM and mild nail findings may be misdiagnosed as having pure SM.2
The histopathologic features of SM were described in a study by Cho and colleagues1 of 64 patients. Steatocystomas have cyst walls that may be either intricately folded or round/oval, comprised of an average of 4.9 epithelial cell layers. In most cases, the cyst wall contains sebaceous lobules. In all cases, an acellular eosinophilic cuticle was present, and no granular layer was seen. Few vellus hairs may be observed in the cystic cavity.1
The differential diagnosis of SM includes eruptive vellus hair cysts, lipomas, Muir-Torre syndrome, and Gardner syndrome. Some have suggested that eruptive vellus hair cysts and SM exist on a disease spectrum because of their similar clinical presentation.10 In contrast to SM, however, eruptive vellus hair cysts originate in the infundibulum of the hair shaft rather than the sebaceous duct, and more numerous vellus hair shafts are seen on histopathology.1
Various treatment modalities have been described, including isotretinoin for inflamed lesions,11 cryotherapy for noninflamed lesions,11 aspiration of lesions smallerthan 1 cm,12 and electrocautery combined with topical retinoids.13 Laser treatment has been described, with a 1450-nm diode laser used to target the abnormal sebaceous glands and a 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser used to target the dermal cysts.14 Carbon dioxide lasers also may be used to open the cyst for drainage.15 Surgical excision or mini-incision also may be performed.16,17
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his assistance with interpretation of the dermatopathology in this case.
- Cho S, Chang SE, Choi JH, et al. Clinical and histologic features of 64 cases of steatocystoma multiplex. J Dermatol. 2002;29:152-156.
- Rollins T, Levin RM, Heymann WR. Acral steatocystoma multiplex.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(2, pt 2):396-399.
- Setoyama M, Mizoguchi S, Usuki K, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex: a case with unusual clinical and histological manifestation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:89-92.
- Cole LA. Steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1437-1439.
- Marzano AV, Tavecchio S, Balice Y, et al. Acral subcutaneous steatocystoma multiplex: a distinct subtype of the disease? Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:198-201.
- Liu Q, Wu W, Lu J, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex is associated with the R94C mutation in the KRTl7 gene. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:5072-5076.
- Egbert BM, Price NM, Segal RJ. Steatocystoma multiplex. Report of a florid case and a review. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:334-335.
- Covello SP, Smith FJ, Sillevis Smitt JH, et al. Keratin 17 mutations cause either steatocystoma multiplex or pachyonychia congenita type 2. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139:475-480.
- McLean WH, Rugg EL, Lunny DP, et al. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995;9:273-278.
- Ohtake N, Kubota Y, Takayama O, et al. Relationship between steatocystoma multiplex and eruptive vellus hair cysts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(5, pt 2):876-878.
- Apaydin R, Bilen N, Bayramgurler D, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex suppurativum: oral isotretinoin treatment combined with cryotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:98-100.
- Sato K, Shibuya K, Taguchi H, et al. Aspiration therapy in steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:35-37.
- Papakonstantinou E, Franke I, Gollnick H. Facial steatocystoma multiplex combined with eruptive vellus hair cysts: a hybrid? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2051-2053.
- Moody MN, Landau JM, Goldberg LH, et al. 1,450-nm diode laser in combination with the 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser for the treatment of steatocystoma multiplex: a case report. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(7, pt 1):1104-1106.
- Rossi R, Cappugi P, Battini M, et al. CO2 laser therapy in a case of steatocystoma multiplex with prominent nodules on the face and neck. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:302-304.
- Schmook T, Burg G, Hafner J. Surgical pearl: mini-incisions for the extraction of steatocystoma multiplex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1041-1042.
- Adams BB, Mutasim DF, Nordlund JJ. Steatocystoma multiplex: a quick removal technique. Cutis. 1999;64:127-130.
The Diagnosis: Steatocystoma Multiplex
The punch biopsy of an abdominal lesion demonstrated a folded cyst wall with a wavy eosinophilic cuticle (Figure), characteristics consistent with steatocystoma multiplex (SM).

Also known as eruptive steatocystoma, SM consists of numerous flesh-colored, dome-shaped papules and nodules that most commonly arise during adolescence, with a median age of onset of 26 years.1 These hamartomatous nevoid malformations arise in areas with well-developed pilosebaceous units, such as the upper extremities, neck, axillae, and trunk.1,2 They occur less commonly on the scalp, face, and acral surfaces.2-5 The lesions range in size from 2 to 30 mm6 and usually are asymptomatic.1 Occasionally, steatocystomas become tender or can rupture.7
Steatocystoma multiplex may arise sporadically or may be inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion. Mutations in exon 1 of the keratin 17 gene, KRT17, have been identified in autosomal-dominant SM.6,8 KRT17 mutations also are responsible for pachyonychia congenita type 2, which is associated with SM.9 Some patients with pachyonychia congenita type 2 who have prominent SM and mild nail findings may be misdiagnosed as having pure SM.2
The histopathologic features of SM were described in a study by Cho and colleagues1 of 64 patients. Steatocystomas have cyst walls that may be either intricately folded or round/oval, comprised of an average of 4.9 epithelial cell layers. In most cases, the cyst wall contains sebaceous lobules. In all cases, an acellular eosinophilic cuticle was present, and no granular layer was seen. Few vellus hairs may be observed in the cystic cavity.1
The differential diagnosis of SM includes eruptive vellus hair cysts, lipomas, Muir-Torre syndrome, and Gardner syndrome. Some have suggested that eruptive vellus hair cysts and SM exist on a disease spectrum because of their similar clinical presentation.10 In contrast to SM, however, eruptive vellus hair cysts originate in the infundibulum of the hair shaft rather than the sebaceous duct, and more numerous vellus hair shafts are seen on histopathology.1
Various treatment modalities have been described, including isotretinoin for inflamed lesions,11 cryotherapy for noninflamed lesions,11 aspiration of lesions smallerthan 1 cm,12 and electrocautery combined with topical retinoids.13 Laser treatment has been described, with a 1450-nm diode laser used to target the abnormal sebaceous glands and a 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser used to target the dermal cysts.14 Carbon dioxide lasers also may be used to open the cyst for drainage.15 Surgical excision or mini-incision also may be performed.16,17
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his assistance with interpretation of the dermatopathology in this case.
The Diagnosis: Steatocystoma Multiplex
The punch biopsy of an abdominal lesion demonstrated a folded cyst wall with a wavy eosinophilic cuticle (Figure), characteristics consistent with steatocystoma multiplex (SM).

Also known as eruptive steatocystoma, SM consists of numerous flesh-colored, dome-shaped papules and nodules that most commonly arise during adolescence, with a median age of onset of 26 years.1 These hamartomatous nevoid malformations arise in areas with well-developed pilosebaceous units, such as the upper extremities, neck, axillae, and trunk.1,2 They occur less commonly on the scalp, face, and acral surfaces.2-5 The lesions range in size from 2 to 30 mm6 and usually are asymptomatic.1 Occasionally, steatocystomas become tender or can rupture.7
Steatocystoma multiplex may arise sporadically or may be inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion. Mutations in exon 1 of the keratin 17 gene, KRT17, have been identified in autosomal-dominant SM.6,8 KRT17 mutations also are responsible for pachyonychia congenita type 2, which is associated with SM.9 Some patients with pachyonychia congenita type 2 who have prominent SM and mild nail findings may be misdiagnosed as having pure SM.2
The histopathologic features of SM were described in a study by Cho and colleagues1 of 64 patients. Steatocystomas have cyst walls that may be either intricately folded or round/oval, comprised of an average of 4.9 epithelial cell layers. In most cases, the cyst wall contains sebaceous lobules. In all cases, an acellular eosinophilic cuticle was present, and no granular layer was seen. Few vellus hairs may be observed in the cystic cavity.1
The differential diagnosis of SM includes eruptive vellus hair cysts, lipomas, Muir-Torre syndrome, and Gardner syndrome. Some have suggested that eruptive vellus hair cysts and SM exist on a disease spectrum because of their similar clinical presentation.10 In contrast to SM, however, eruptive vellus hair cysts originate in the infundibulum of the hair shaft rather than the sebaceous duct, and more numerous vellus hair shafts are seen on histopathology.1
Various treatment modalities have been described, including isotretinoin for inflamed lesions,11 cryotherapy for noninflamed lesions,11 aspiration of lesions smallerthan 1 cm,12 and electrocautery combined with topical retinoids.13 Laser treatment has been described, with a 1450-nm diode laser used to target the abnormal sebaceous glands and a 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser used to target the dermal cysts.14 Carbon dioxide lasers also may be used to open the cyst for drainage.15 Surgical excision or mini-incision also may be performed.16,17
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his assistance with interpretation of the dermatopathology in this case.
- Cho S, Chang SE, Choi JH, et al. Clinical and histologic features of 64 cases of steatocystoma multiplex. J Dermatol. 2002;29:152-156.
- Rollins T, Levin RM, Heymann WR. Acral steatocystoma multiplex.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(2, pt 2):396-399.
- Setoyama M, Mizoguchi S, Usuki K, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex: a case with unusual clinical and histological manifestation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:89-92.
- Cole LA. Steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1437-1439.
- Marzano AV, Tavecchio S, Balice Y, et al. Acral subcutaneous steatocystoma multiplex: a distinct subtype of the disease? Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:198-201.
- Liu Q, Wu W, Lu J, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex is associated with the R94C mutation in the KRTl7 gene. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:5072-5076.
- Egbert BM, Price NM, Segal RJ. Steatocystoma multiplex. Report of a florid case and a review. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:334-335.
- Covello SP, Smith FJ, Sillevis Smitt JH, et al. Keratin 17 mutations cause either steatocystoma multiplex or pachyonychia congenita type 2. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139:475-480.
- McLean WH, Rugg EL, Lunny DP, et al. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995;9:273-278.
- Ohtake N, Kubota Y, Takayama O, et al. Relationship between steatocystoma multiplex and eruptive vellus hair cysts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(5, pt 2):876-878.
- Apaydin R, Bilen N, Bayramgurler D, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex suppurativum: oral isotretinoin treatment combined with cryotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:98-100.
- Sato K, Shibuya K, Taguchi H, et al. Aspiration therapy in steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:35-37.
- Papakonstantinou E, Franke I, Gollnick H. Facial steatocystoma multiplex combined with eruptive vellus hair cysts: a hybrid? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2051-2053.
- Moody MN, Landau JM, Goldberg LH, et al. 1,450-nm diode laser in combination with the 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser for the treatment of steatocystoma multiplex: a case report. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(7, pt 1):1104-1106.
- Rossi R, Cappugi P, Battini M, et al. CO2 laser therapy in a case of steatocystoma multiplex with prominent nodules on the face and neck. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:302-304.
- Schmook T, Burg G, Hafner J. Surgical pearl: mini-incisions for the extraction of steatocystoma multiplex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1041-1042.
- Adams BB, Mutasim DF, Nordlund JJ. Steatocystoma multiplex: a quick removal technique. Cutis. 1999;64:127-130.
- Cho S, Chang SE, Choi JH, et al. Clinical and histologic features of 64 cases of steatocystoma multiplex. J Dermatol. 2002;29:152-156.
- Rollins T, Levin RM, Heymann WR. Acral steatocystoma multiplex.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43(2, pt 2):396-399.
- Setoyama M, Mizoguchi S, Usuki K, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex: a case with unusual clinical and histological manifestation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:89-92.
- Cole LA. Steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1437-1439.
- Marzano AV, Tavecchio S, Balice Y, et al. Acral subcutaneous steatocystoma multiplex: a distinct subtype of the disease? Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:198-201.
- Liu Q, Wu W, Lu J, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex is associated with the R94C mutation in the KRTl7 gene. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:5072-5076.
- Egbert BM, Price NM, Segal RJ. Steatocystoma multiplex. Report of a florid case and a review. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:334-335.
- Covello SP, Smith FJ, Sillevis Smitt JH, et al. Keratin 17 mutations cause either steatocystoma multiplex or pachyonychia congenita type 2. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139:475-480.
- McLean WH, Rugg EL, Lunny DP, et al. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat Genet. 1995;9:273-278.
- Ohtake N, Kubota Y, Takayama O, et al. Relationship between steatocystoma multiplex and eruptive vellus hair cysts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(5, pt 2):876-878.
- Apaydin R, Bilen N, Bayramgurler D, et al. Steatocystoma multiplex suppurativum: oral isotretinoin treatment combined with cryotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2000;41:98-100.
- Sato K, Shibuya K, Taguchi H, et al. Aspiration therapy in steatocystoma multiplex. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:35-37.
- Papakonstantinou E, Franke I, Gollnick H. Facial steatocystoma multiplex combined with eruptive vellus hair cysts: a hybrid? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:2051-2053.
- Moody MN, Landau JM, Goldberg LH, et al. 1,450-nm diode laser in combination with the 1550-nm fractionated erbium-doped fiber laser for the treatment of steatocystoma multiplex: a case report. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(7, pt 1):1104-1106.
- Rossi R, Cappugi P, Battini M, et al. CO2 laser therapy in a case of steatocystoma multiplex with prominent nodules on the face and neck. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:302-304.
- Schmook T, Burg G, Hafner J. Surgical pearl: mini-incisions for the extraction of steatocystoma multiplex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1041-1042.
- Adams BB, Mutasim DF, Nordlund JJ. Steatocystoma multiplex: a quick removal technique. Cutis. 1999;64:127-130.

A 33-year-old woman presented with numerous firm, noncompressible, flesh-colored nodules that measured 3 to 4 mm and were distributed across the abdomen, chest, back, and neck. The lesions had been present for approximately 10 years. The patient denied any lesion-associated pain, itching, or bleeding, and there was no family history of similar lesions. A punch biopsy of a lesion on the central abdomen was obtained.
Widespread Skin Thickening
The Diagnosis: Scleromyxedema
Scleromyxedema is a rare skin disorder characterized by a diffuse eruption of small waxy papules that are linearly arranged and closely spaced together. As the papular lesions coalesce, the skin thickens. Firm induration of the skin is widespread and--unlike the distribution in scleroderma and scleredema--amplified over the facial convexities, especially the glabella and ears. Histopathology reveals the classic triad of mucin accumulation, proliferation of fibroblasts, and collagen deposition with associated fibrotic changes.1
In this case, the patient exhibited the characteristic doughnut sign over the second interphalangeal joint of the right hand due to thickening and dimpling of the skin (quiz image). Histopathology from the right second finger showed the dermis with a spindled histiocytic infiltrate, fibroblasts, fibrosis, and increased interstitial mucin deposition highlighted with colloidal iron stain (Figures 1 and 2). Multinucleated giant cells also were seen in the dermis (Figure 3), and a Shikata orcein stain illustrated decreased elastic fibers (stained black) in the superficial dermis within areas of increased collagen deposition (Figure 4).
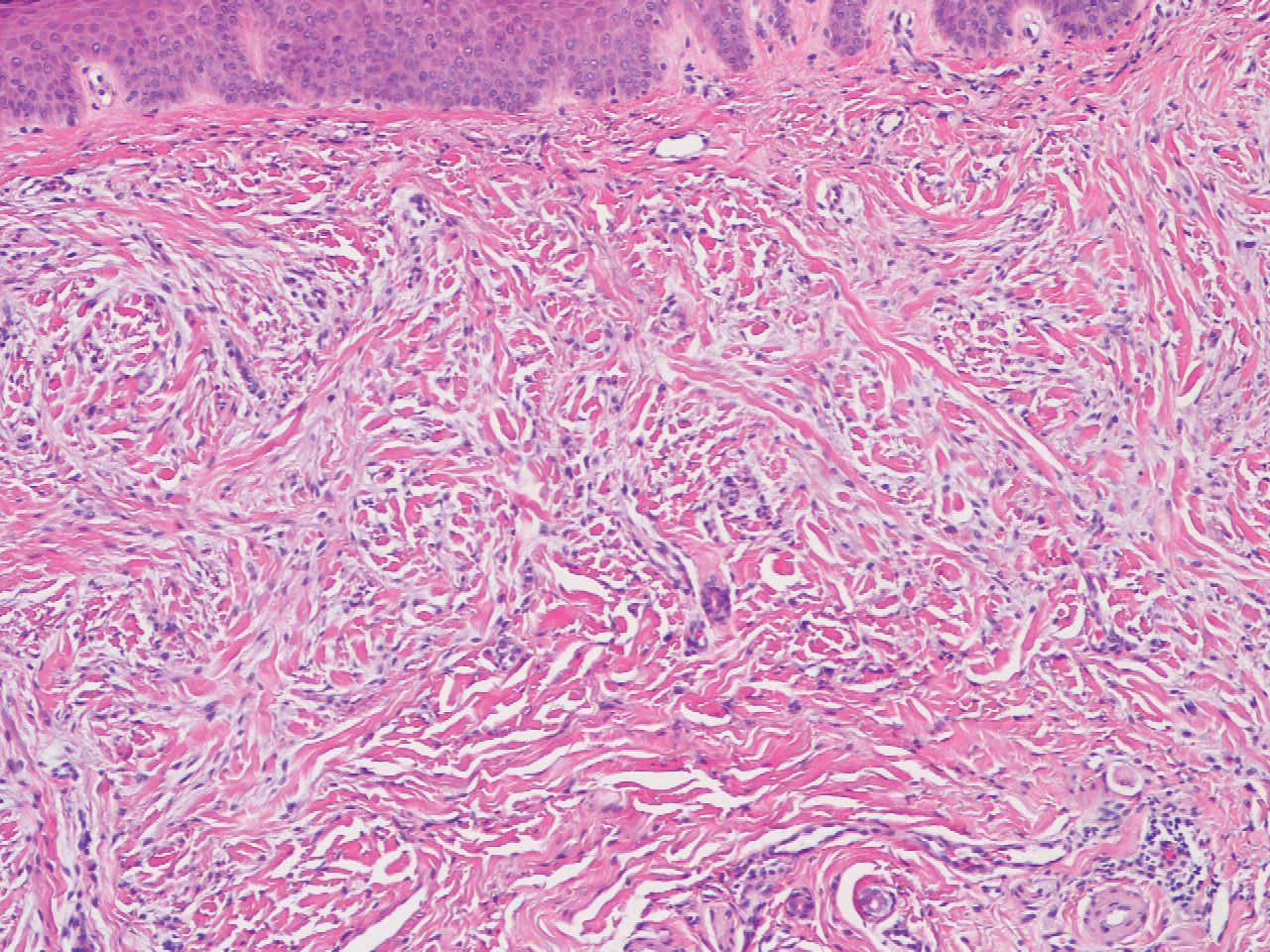
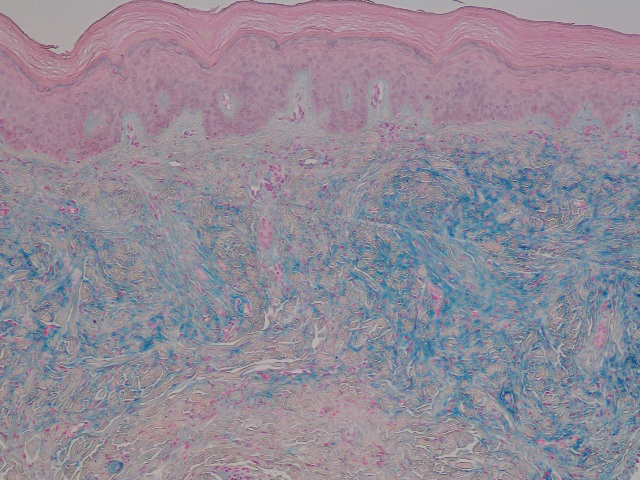
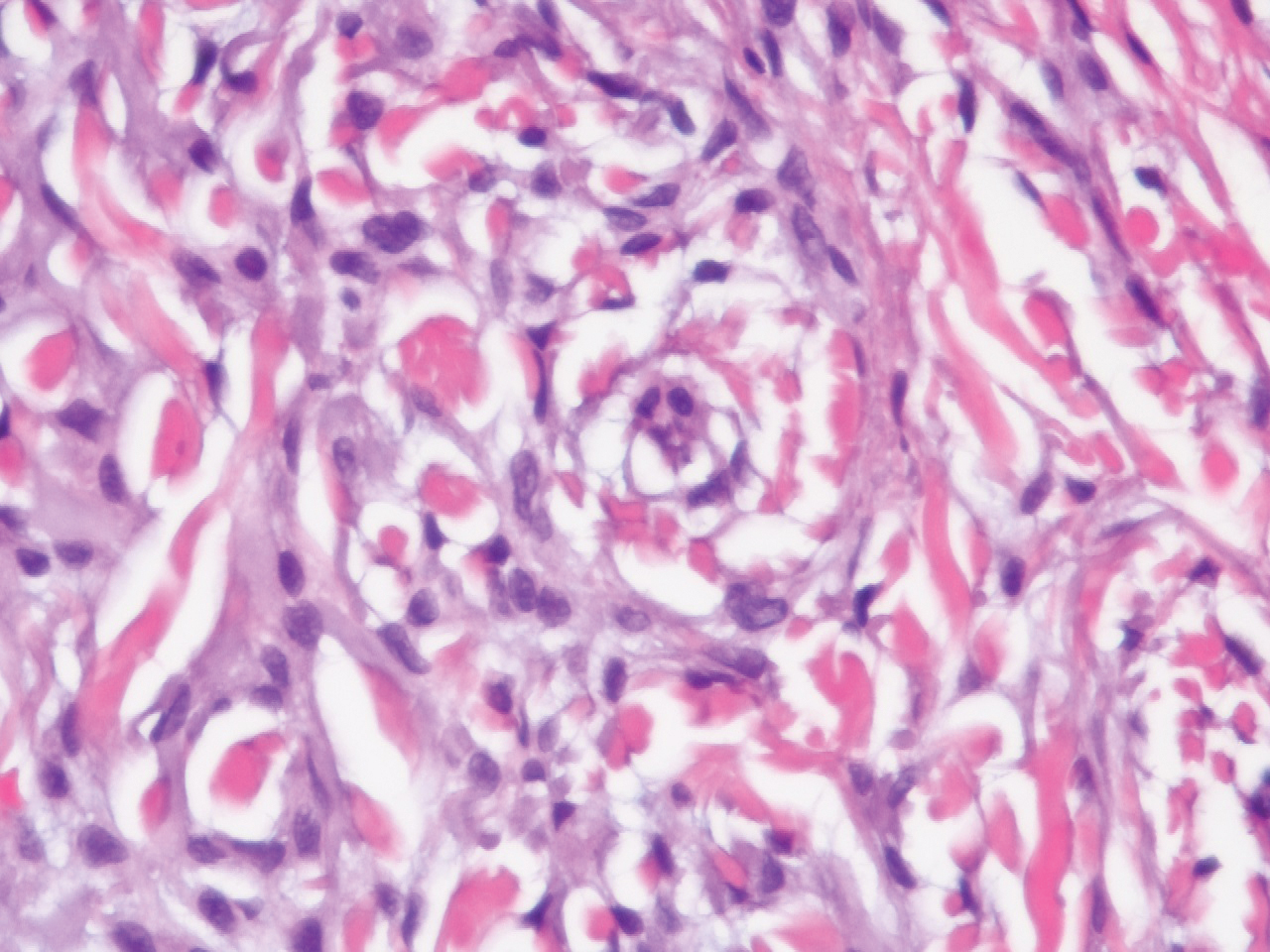
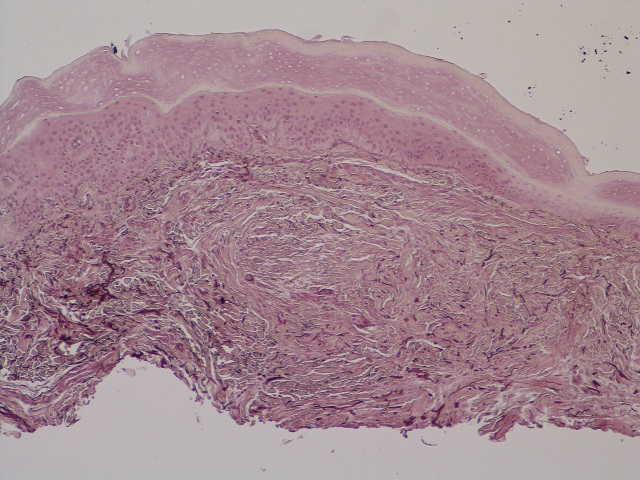
Scleromyxedema is strongly associated with a monoclonal gammopathy, which is generally mild and, in almost 80% of cases, related to λ IgG. However, the clinical implications are unclear.2,3 Scleromyxedema also is accompanied by systemic features, most commonly dysphagia, myalgias, and arthralgias, which distinguishes it from other cutaneous mucinoses. Notable morbidity and mortality are associated with involvement of the central nervous system, which can manifest as encephalopathy, seizures, or coma. Mucin deposition may be found in the myocardium and the coronary and pulmonary vasculature, resulting in rare cases of cardiac and pulmonary disease.4,5
Clinically, scleroderma also demonstrates progressive generalized skin tightening. Histopathology reveals hyalinization and thickening of the connective tissue of the deep dermis, subcutaneous fat, and muscular fascia. These changes are accompanied by a perivascular and focal interstitial lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrate with prominent myofibroblast proliferation. In this case, the normal nail fold capillaries and absence of Raynaud phenomenon help to distinguish the diagnosis from scleroderma. In limited scleroderma, common findings include calcinosis, esophageal dysmotility, telangiectasia, and pulmonary hypertension, while systemic sclerosis can involve the internal organs, with the greatest morbidity stemming from interstitial lung disease.3,6,7
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is another disorder of skin thickening that involves the extremities and trunk. It is a rare complication of exposure to gadolinium contrast media in patients with advanced renal disease and those undergoing dialysis; use of gadolinium is now strictly avoided in patients with at least moderately impaired glomerular filtration rate.8 Although nephrogenic systemic fibrosis histologically looks similar to scleromyxedema, it involves deeper tissues. There is fibrosis with haphazard collagen bundle deposition in the deep dermis and subcutaneous septa. Fibroblasts and histiocytes are increased between the collagen bundles, with surrounding edema and mucin buildup. Multinucleated giant cells may or may not be present.9
Patients with scleredema present with nonpitting edema and dermal hardening over the neck, face, upper trunk, and arms. Lesional skin appears shiny and indurated. The skin is characteristically difficult to wrinkle, and the face may appear expressionless. Skin biopsy will show a thickened reticular dermis with mucin deposition and eccrine glands appearing in the upper third or mid dermis. Fibroblasts are normal in number. Scleredema generally is associated with poorly controlled diabetes, a monoclonal gammopathy, or as the aftermath of an acute infection, especially streptococcal pharyngitis. The condition may develop at any age, though nearly 50% of cases occur in children and adolescents.3,10
Interstitial granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, benign, and self-limiting dermatosis. Distinct from other skin-thickening disorders, GA is composed of smooth annular papules and plaques that do not result in skin hardening. Although GA may manifest in a generalized distribution, it is more frequently localized to the distal extremities.11 The presence of an inflammatory infiltrate surrounded by abundant mucin and collagen resembles scleromyxedema. However, GA is distinguished by palisading granulomas of histiocytes, fibroblasts, and lymphocytes lining a necrobiotic center of collagen, mucin, and fibrin.12
This patient's skin showed an immediate and marked response to intravenous immunoglobulin with dramatic softening. Such a response is well reported in the literature, and intravenous immunoglobulin is considered first-line therapy for scleromyxedema, typically in conjunction with steroids.5 Other immunosuppressive agents have been employed with reported efficacy, as have several treatments used for multiple myeloma, including thalidomide and lenalidomide.
Although spontaneous improvement infrequently occurs, a chronic progressive course is far more common with scleromyxedema. Studies are ongoing to elucidate the etiopathogenesis of scleromyxedema, scleroderma, and similar disorders to uncover the triggers that provoke the underlying dysregulation of dermal fibroblast activation and proliferation, which could offer a more precise target for effective treatments.5,13-15
- Crowe DR. Scleromyxedema. In: Crowe DR, Morgan M, Somach S, Trapp K, eds. Deadly Dermatologic Diseases: Clinicopathologic Atlas and Text. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:139-142.
- Farmer ER, Hambrick GW Jr, Shulman LE. Papular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic study of four patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:9-13.
- Rongioletti F. Mucinoses. In: Smoller BR, Rongioletti F, eds. Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Skin Diseases in Endocrine, Metabolic, Nutritional and Deposition Disease. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2010:139-152.
- Gabriel PH, Oleson GB, Bowles GA. Scleromyxoedema: a scleroderma-like disorder with systemic manifestations. Medicine. 1988;67:58-65.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Hamodat M. Scleroderma. PathologyOutlines.com. http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorscleroderma.html. Published August 1, 2011. Updated March 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2019.
- Van Praet JT, Smith V, Haspeslagh M, et al. Histopathological cutaneous alterations in systemic sclerosis: a clinicopathological study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R35.
- Swartz RD, Crofford LJ, Phan SH, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: a novel cutaneous fibrosing disorder in patients with renal failure. Am J Med. 2003;114:563-572.
- Cowper SE, Rabach M, Girardi M. Clinical and histological findings in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur J Radiol. 2008;66:191-199.
- Boin F, Hummers LK. Scleroderma-like fibrosing disorders. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34:199-ix.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Conditions. In: Modern Surgical Pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2009:1843-1889.
- Muhlbauer JE. Granuloma annulare. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:217-230.
- Blum M, Wigley FM, Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema: a case series highlighting long-term outcomes of treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Medicine. 2008;87:10-20.
- Caradonna S, Jacobe H. Thalidomide as a potential treatment for scleromyxedema. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:277-280.
- Yeung CK, Loong F, Kwong YL. Scleromyxoedema due to a plasma cell neoplasm: rapid remission with bortezomib, thalidomide and dexamethasone. Br J Haematol. 2012;157:411.
The Diagnosis: Scleromyxedema
Scleromyxedema is a rare skin disorder characterized by a diffuse eruption of small waxy papules that are linearly arranged and closely spaced together. As the papular lesions coalesce, the skin thickens. Firm induration of the skin is widespread and--unlike the distribution in scleroderma and scleredema--amplified over the facial convexities, especially the glabella and ears. Histopathology reveals the classic triad of mucin accumulation, proliferation of fibroblasts, and collagen deposition with associated fibrotic changes.1
In this case, the patient exhibited the characteristic doughnut sign over the second interphalangeal joint of the right hand due to thickening and dimpling of the skin (quiz image). Histopathology from the right second finger showed the dermis with a spindled histiocytic infiltrate, fibroblasts, fibrosis, and increased interstitial mucin deposition highlighted with colloidal iron stain (Figures 1 and 2). Multinucleated giant cells also were seen in the dermis (Figure 3), and a Shikata orcein stain illustrated decreased elastic fibers (stained black) in the superficial dermis within areas of increased collagen deposition (Figure 4).




Scleromyxedema is strongly associated with a monoclonal gammopathy, which is generally mild and, in almost 80% of cases, related to λ IgG. However, the clinical implications are unclear.2,3 Scleromyxedema also is accompanied by systemic features, most commonly dysphagia, myalgias, and arthralgias, which distinguishes it from other cutaneous mucinoses. Notable morbidity and mortality are associated with involvement of the central nervous system, which can manifest as encephalopathy, seizures, or coma. Mucin deposition may be found in the myocardium and the coronary and pulmonary vasculature, resulting in rare cases of cardiac and pulmonary disease.4,5
Clinically, scleroderma also demonstrates progressive generalized skin tightening. Histopathology reveals hyalinization and thickening of the connective tissue of the deep dermis, subcutaneous fat, and muscular fascia. These changes are accompanied by a perivascular and focal interstitial lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrate with prominent myofibroblast proliferation. In this case, the normal nail fold capillaries and absence of Raynaud phenomenon help to distinguish the diagnosis from scleroderma. In limited scleroderma, common findings include calcinosis, esophageal dysmotility, telangiectasia, and pulmonary hypertension, while systemic sclerosis can involve the internal organs, with the greatest morbidity stemming from interstitial lung disease.3,6,7
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is another disorder of skin thickening that involves the extremities and trunk. It is a rare complication of exposure to gadolinium contrast media in patients with advanced renal disease and those undergoing dialysis; use of gadolinium is now strictly avoided in patients with at least moderately impaired glomerular filtration rate.8 Although nephrogenic systemic fibrosis histologically looks similar to scleromyxedema, it involves deeper tissues. There is fibrosis with haphazard collagen bundle deposition in the deep dermis and subcutaneous septa. Fibroblasts and histiocytes are increased between the collagen bundles, with surrounding edema and mucin buildup. Multinucleated giant cells may or may not be present.9
Patients with scleredema present with nonpitting edema and dermal hardening over the neck, face, upper trunk, and arms. Lesional skin appears shiny and indurated. The skin is characteristically difficult to wrinkle, and the face may appear expressionless. Skin biopsy will show a thickened reticular dermis with mucin deposition and eccrine glands appearing in the upper third or mid dermis. Fibroblasts are normal in number. Scleredema generally is associated with poorly controlled diabetes, a monoclonal gammopathy, or as the aftermath of an acute infection, especially streptococcal pharyngitis. The condition may develop at any age, though nearly 50% of cases occur in children and adolescents.3,10
Interstitial granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, benign, and self-limiting dermatosis. Distinct from other skin-thickening disorders, GA is composed of smooth annular papules and plaques that do not result in skin hardening. Although GA may manifest in a generalized distribution, it is more frequently localized to the distal extremities.11 The presence of an inflammatory infiltrate surrounded by abundant mucin and collagen resembles scleromyxedema. However, GA is distinguished by palisading granulomas of histiocytes, fibroblasts, and lymphocytes lining a necrobiotic center of collagen, mucin, and fibrin.12
This patient's skin showed an immediate and marked response to intravenous immunoglobulin with dramatic softening. Such a response is well reported in the literature, and intravenous immunoglobulin is considered first-line therapy for scleromyxedema, typically in conjunction with steroids.5 Other immunosuppressive agents have been employed with reported efficacy, as have several treatments used for multiple myeloma, including thalidomide and lenalidomide.
Although spontaneous improvement infrequently occurs, a chronic progressive course is far more common with scleromyxedema. Studies are ongoing to elucidate the etiopathogenesis of scleromyxedema, scleroderma, and similar disorders to uncover the triggers that provoke the underlying dysregulation of dermal fibroblast activation and proliferation, which could offer a more precise target for effective treatments.5,13-15
The Diagnosis: Scleromyxedema
Scleromyxedema is a rare skin disorder characterized by a diffuse eruption of small waxy papules that are linearly arranged and closely spaced together. As the papular lesions coalesce, the skin thickens. Firm induration of the skin is widespread and--unlike the distribution in scleroderma and scleredema--amplified over the facial convexities, especially the glabella and ears. Histopathology reveals the classic triad of mucin accumulation, proliferation of fibroblasts, and collagen deposition with associated fibrotic changes.1
In this case, the patient exhibited the characteristic doughnut sign over the second interphalangeal joint of the right hand due to thickening and dimpling of the skin (quiz image). Histopathology from the right second finger showed the dermis with a spindled histiocytic infiltrate, fibroblasts, fibrosis, and increased interstitial mucin deposition highlighted with colloidal iron stain (Figures 1 and 2). Multinucleated giant cells also were seen in the dermis (Figure 3), and a Shikata orcein stain illustrated decreased elastic fibers (stained black) in the superficial dermis within areas of increased collagen deposition (Figure 4).




Scleromyxedema is strongly associated with a monoclonal gammopathy, which is generally mild and, in almost 80% of cases, related to λ IgG. However, the clinical implications are unclear.2,3 Scleromyxedema also is accompanied by systemic features, most commonly dysphagia, myalgias, and arthralgias, which distinguishes it from other cutaneous mucinoses. Notable morbidity and mortality are associated with involvement of the central nervous system, which can manifest as encephalopathy, seizures, or coma. Mucin deposition may be found in the myocardium and the coronary and pulmonary vasculature, resulting in rare cases of cardiac and pulmonary disease.4,5
Clinically, scleroderma also demonstrates progressive generalized skin tightening. Histopathology reveals hyalinization and thickening of the connective tissue of the deep dermis, subcutaneous fat, and muscular fascia. These changes are accompanied by a perivascular and focal interstitial lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrate with prominent myofibroblast proliferation. In this case, the normal nail fold capillaries and absence of Raynaud phenomenon help to distinguish the diagnosis from scleroderma. In limited scleroderma, common findings include calcinosis, esophageal dysmotility, telangiectasia, and pulmonary hypertension, while systemic sclerosis can involve the internal organs, with the greatest morbidity stemming from interstitial lung disease.3,6,7
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is another disorder of skin thickening that involves the extremities and trunk. It is a rare complication of exposure to gadolinium contrast media in patients with advanced renal disease and those undergoing dialysis; use of gadolinium is now strictly avoided in patients with at least moderately impaired glomerular filtration rate.8 Although nephrogenic systemic fibrosis histologically looks similar to scleromyxedema, it involves deeper tissues. There is fibrosis with haphazard collagen bundle deposition in the deep dermis and subcutaneous septa. Fibroblasts and histiocytes are increased between the collagen bundles, with surrounding edema and mucin buildup. Multinucleated giant cells may or may not be present.9
Patients with scleredema present with nonpitting edema and dermal hardening over the neck, face, upper trunk, and arms. Lesional skin appears shiny and indurated. The skin is characteristically difficult to wrinkle, and the face may appear expressionless. Skin biopsy will show a thickened reticular dermis with mucin deposition and eccrine glands appearing in the upper third or mid dermis. Fibroblasts are normal in number. Scleredema generally is associated with poorly controlled diabetes, a monoclonal gammopathy, or as the aftermath of an acute infection, especially streptococcal pharyngitis. The condition may develop at any age, though nearly 50% of cases occur in children and adolescents.3,10
Interstitial granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, benign, and self-limiting dermatosis. Distinct from other skin-thickening disorders, GA is composed of smooth annular papules and plaques that do not result in skin hardening. Although GA may manifest in a generalized distribution, it is more frequently localized to the distal extremities.11 The presence of an inflammatory infiltrate surrounded by abundant mucin and collagen resembles scleromyxedema. However, GA is distinguished by palisading granulomas of histiocytes, fibroblasts, and lymphocytes lining a necrobiotic center of collagen, mucin, and fibrin.12
This patient's skin showed an immediate and marked response to intravenous immunoglobulin with dramatic softening. Such a response is well reported in the literature, and intravenous immunoglobulin is considered first-line therapy for scleromyxedema, typically in conjunction with steroids.5 Other immunosuppressive agents have been employed with reported efficacy, as have several treatments used for multiple myeloma, including thalidomide and lenalidomide.
Although spontaneous improvement infrequently occurs, a chronic progressive course is far more common with scleromyxedema. Studies are ongoing to elucidate the etiopathogenesis of scleromyxedema, scleroderma, and similar disorders to uncover the triggers that provoke the underlying dysregulation of dermal fibroblast activation and proliferation, which could offer a more precise target for effective treatments.5,13-15
- Crowe DR. Scleromyxedema. In: Crowe DR, Morgan M, Somach S, Trapp K, eds. Deadly Dermatologic Diseases: Clinicopathologic Atlas and Text. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:139-142.
- Farmer ER, Hambrick GW Jr, Shulman LE. Papular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic study of four patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:9-13.
- Rongioletti F. Mucinoses. In: Smoller BR, Rongioletti F, eds. Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Skin Diseases in Endocrine, Metabolic, Nutritional and Deposition Disease. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2010:139-152.
- Gabriel PH, Oleson GB, Bowles GA. Scleromyxoedema: a scleroderma-like disorder with systemic manifestations. Medicine. 1988;67:58-65.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Hamodat M. Scleroderma. PathologyOutlines.com. http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorscleroderma.html. Published August 1, 2011. Updated March 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2019.
- Van Praet JT, Smith V, Haspeslagh M, et al. Histopathological cutaneous alterations in systemic sclerosis: a clinicopathological study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R35.
- Swartz RD, Crofford LJ, Phan SH, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: a novel cutaneous fibrosing disorder in patients with renal failure. Am J Med. 2003;114:563-572.
- Cowper SE, Rabach M, Girardi M. Clinical and histological findings in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur J Radiol. 2008;66:191-199.
- Boin F, Hummers LK. Scleroderma-like fibrosing disorders. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34:199-ix.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Conditions. In: Modern Surgical Pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2009:1843-1889.
- Muhlbauer JE. Granuloma annulare. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:217-230.
- Blum M, Wigley FM, Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema: a case series highlighting long-term outcomes of treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Medicine. 2008;87:10-20.
- Caradonna S, Jacobe H. Thalidomide as a potential treatment for scleromyxedema. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:277-280.
- Yeung CK, Loong F, Kwong YL. Scleromyxoedema due to a plasma cell neoplasm: rapid remission with bortezomib, thalidomide and dexamethasone. Br J Haematol. 2012;157:411.
- Crowe DR. Scleromyxedema. In: Crowe DR, Morgan M, Somach S, Trapp K, eds. Deadly Dermatologic Diseases: Clinicopathologic Atlas and Text. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:139-142.
- Farmer ER, Hambrick GW Jr, Shulman LE. Papular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic study of four patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:9-13.
- Rongioletti F. Mucinoses. In: Smoller BR, Rongioletti F, eds. Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Skin Diseases in Endocrine, Metabolic, Nutritional and Deposition Disease. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2010:139-152.
- Gabriel PH, Oleson GB, Bowles GA. Scleromyxoedema: a scleroderma-like disorder with systemic manifestations. Medicine. 1988;67:58-65.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Hamodat M. Scleroderma. PathologyOutlines.com. http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorscleroderma.html. Published August 1, 2011. Updated March 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2019.
- Van Praet JT, Smith V, Haspeslagh M, et al. Histopathological cutaneous alterations in systemic sclerosis: a clinicopathological study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R35.
- Swartz RD, Crofford LJ, Phan SH, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: a novel cutaneous fibrosing disorder in patients with renal failure. Am J Med. 2003;114:563-572.
- Cowper SE, Rabach M, Girardi M. Clinical and histological findings in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur J Radiol. 2008;66:191-199.
- Boin F, Hummers LK. Scleroderma-like fibrosing disorders. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34:199-ix.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Conditions. In: Modern Surgical Pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2009:1843-1889.
- Muhlbauer JE. Granuloma annulare. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:217-230.
- Blum M, Wigley FM, Hummers LK. Scleromyxedema: a case series highlighting long-term outcomes of treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Medicine. 2008;87:10-20.
- Caradonna S, Jacobe H. Thalidomide as a potential treatment for scleromyxedema. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:277-280.
- Yeung CK, Loong F, Kwong YL. Scleromyxoedema due to a plasma cell neoplasm: rapid remission with bortezomib, thalidomide and dexamethasone. Br J Haematol. 2012;157:411.

A 62-year-old woman presented with widespread skin thickening and tightness that progressed over 2 months. Physical examination showed generalized, nonpruritic, nonpainful, flesh-colored papules along the fingers, bilateral arms and legs, chest, neck, forehead, chin, and ears. She reported mild acid reflux on review of systems. She denied a history of Raynaud phenomenon and had normal-appearing nail beds on capillaroscopy. Laboratory studies including autoimmune serologies were normal, aside from a mildly elevated monoclonal IgG spike.
Verruciform Plaques Within a Tattoo of an HIV-Positive Patient
The Diagnosis: Lichenoid Reaction With Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia
A shave biopsy of the left ankle and a punch biopsy of the left medial calf were performed and sent for histologic examination and acid-fast stain. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures also were sent for testing. The findings from direct examination were negative, and tissue cultures exhibited no growth. The shave and punch biopsies and histology revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH) with keratinocyte necrosis, satellitosis, and areas of acute folliculitis (Figure 1). A lichenoid hypersensitivity mixed infiltrate that included histiocytes admixed with anthracotic and red-orange pigment, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, and rare eosinophils was noted in the dermis. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with red-pigment tattoo lichenoid reaction with PEH.
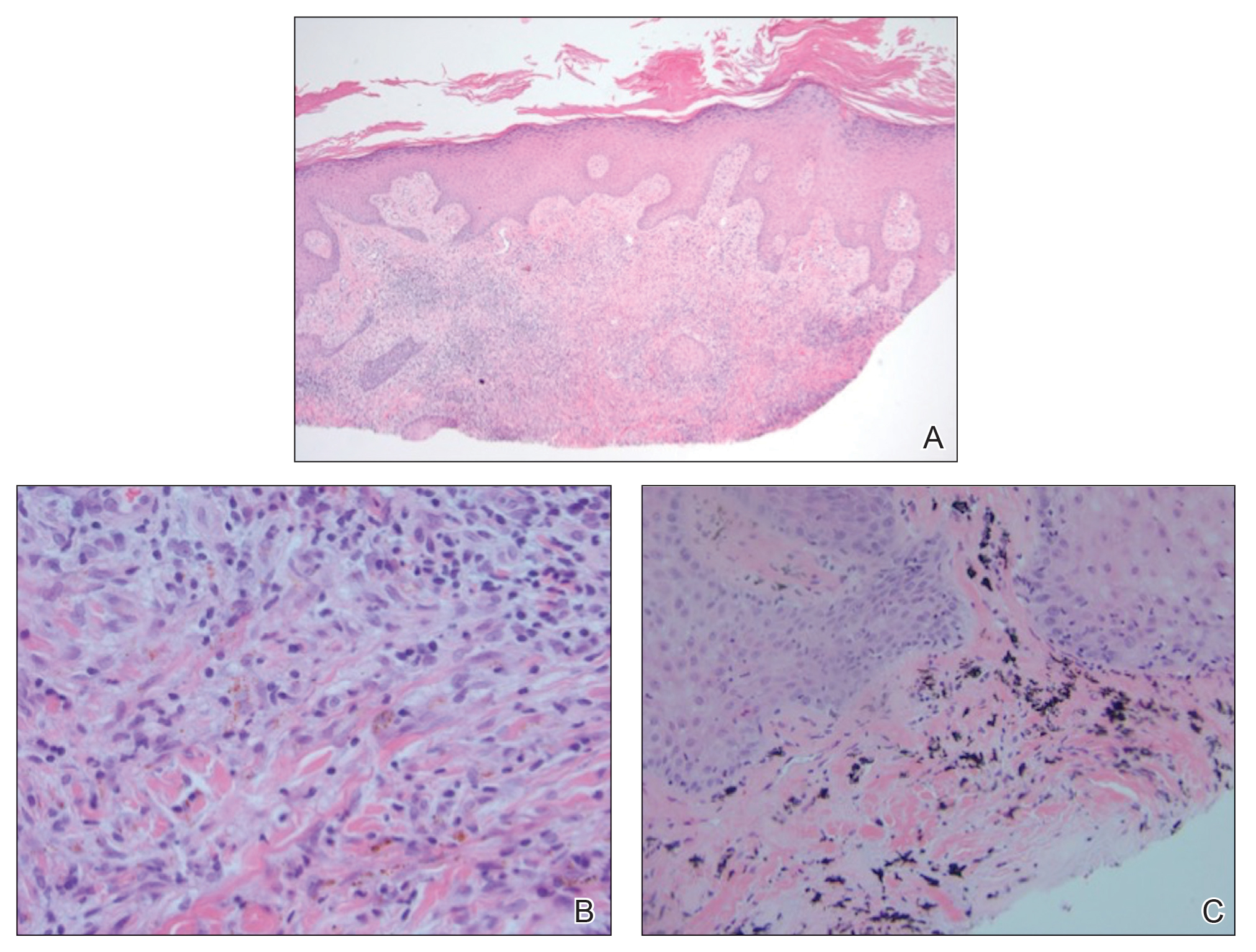
Tattoo-related inflammatory reactions can manifest clinically as allergic contact dermatitis, photodermatitis, infection, malignancy, foreign body granulomas, and delayed hypersensitivity reactions with myriad associated histopathologic patterns including spongiotic, psoriasiform, granulomatous, and lichenoid (as seen in our patient). Lichenoid tattoo reactions are the most common histopathologic variants of delayed hypersensitivity seen, mostly with cinnabar or red dye.1 However, there is a paucity of cases in the literature of PEH following tattooing with red dye. Interestingly, lichenoid tissue reaction accompanies PEH in all reported cases.2
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia can mimic squamous cell carcinoma and keratoacanthoma (KA) both clinically and histologically. All 3 conditions may exhibit epithelial hyperplasia with prominent dilated hyperplastic infundibula. In a case series of 11 presumed KAs within tattoos, Fraga and Prossick2 reported 82% (9/11) of the lesions were located strictly in areas with red pigment, and many were associated with a lichenoid tissue reaction. Kazlouskaya and Junkins-Hopkins3 previously described cases of KAs in tattoos that may represent PEH.
When treating lesions with this histologic appearance, consider the clinical and histologic overlap between KAs and PEH. Our patient was managed with clobetasol ointment 0.05% under occlusion followed by intralesional triamcinolone acetonide with notable improvement of the verrucous plaques on the left lateral malleolus (Figure 2). He also noted near resolution of the papules on the pretibial shin and complete resolution of all associated pruritus and burning. Calcineurin inhibitors, photochemotherapy, CO2 laser, excimer laser, and surgical removal with interval grafting also were considered.
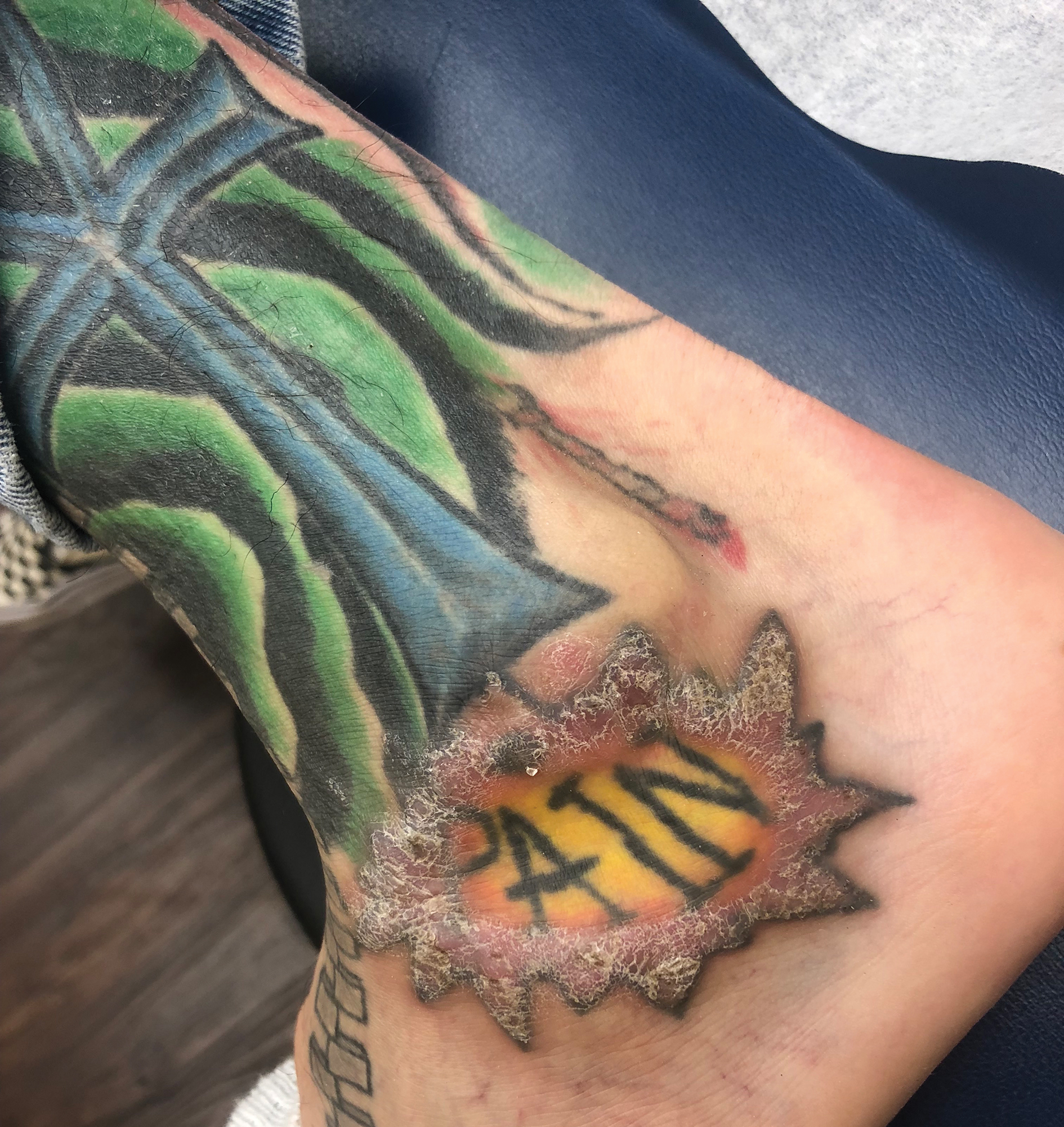

It is important to recognize PEH in the differential of eruptions occurring within tattoos to avoid unnecessary invasive surgical procedures such as complete surgical excision of a KA to avoid malignant transformation.
- Mortimer NJ, Chave TA, Johnston GA. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Fraga GR, Prossick TA. Tattoo-associated keratoacanthomas: a series of 8 patients with 11 keratoacanthomas. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:85-90.
- Kazlouskaya V, Junkins-Hopkins JM. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in a red pigment tattoo: a separate entity or hypertrophic lichen planus-like reaction? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:48-52.
The Diagnosis: Lichenoid Reaction With Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia
A shave biopsy of the left ankle and a punch biopsy of the left medial calf were performed and sent for histologic examination and acid-fast stain. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures also were sent for testing. The findings from direct examination were negative, and tissue cultures exhibited no growth. The shave and punch biopsies and histology revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH) with keratinocyte necrosis, satellitosis, and areas of acute folliculitis (Figure 1). A lichenoid hypersensitivity mixed infiltrate that included histiocytes admixed with anthracotic and red-orange pigment, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, and rare eosinophils was noted in the dermis. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with red-pigment tattoo lichenoid reaction with PEH.

Tattoo-related inflammatory reactions can manifest clinically as allergic contact dermatitis, photodermatitis, infection, malignancy, foreign body granulomas, and delayed hypersensitivity reactions with myriad associated histopathologic patterns including spongiotic, psoriasiform, granulomatous, and lichenoid (as seen in our patient). Lichenoid tattoo reactions are the most common histopathologic variants of delayed hypersensitivity seen, mostly with cinnabar or red dye.1 However, there is a paucity of cases in the literature of PEH following tattooing with red dye. Interestingly, lichenoid tissue reaction accompanies PEH in all reported cases.2
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia can mimic squamous cell carcinoma and keratoacanthoma (KA) both clinically and histologically. All 3 conditions may exhibit epithelial hyperplasia with prominent dilated hyperplastic infundibula. In a case series of 11 presumed KAs within tattoos, Fraga and Prossick2 reported 82% (9/11) of the lesions were located strictly in areas with red pigment, and many were associated with a lichenoid tissue reaction. Kazlouskaya and Junkins-Hopkins3 previously described cases of KAs in tattoos that may represent PEH.
When treating lesions with this histologic appearance, consider the clinical and histologic overlap between KAs and PEH. Our patient was managed with clobetasol ointment 0.05% under occlusion followed by intralesional triamcinolone acetonide with notable improvement of the verrucous plaques on the left lateral malleolus (Figure 2). He also noted near resolution of the papules on the pretibial shin and complete resolution of all associated pruritus and burning. Calcineurin inhibitors, photochemotherapy, CO2 laser, excimer laser, and surgical removal with interval grafting also were considered.

It is important to recognize PEH in the differential of eruptions occurring within tattoos to avoid unnecessary invasive surgical procedures such as complete surgical excision of a KA to avoid malignant transformation.
The Diagnosis: Lichenoid Reaction With Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia
A shave biopsy of the left ankle and a punch biopsy of the left medial calf were performed and sent for histologic examination and acid-fast stain. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures also were sent for testing. The findings from direct examination were negative, and tissue cultures exhibited no growth. The shave and punch biopsies and histology revealed pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH) with keratinocyte necrosis, satellitosis, and areas of acute folliculitis (Figure 1). A lichenoid hypersensitivity mixed infiltrate that included histiocytes admixed with anthracotic and red-orange pigment, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, and rare eosinophils was noted in the dermis. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with red-pigment tattoo lichenoid reaction with PEH.

Tattoo-related inflammatory reactions can manifest clinically as allergic contact dermatitis, photodermatitis, infection, malignancy, foreign body granulomas, and delayed hypersensitivity reactions with myriad associated histopathologic patterns including spongiotic, psoriasiform, granulomatous, and lichenoid (as seen in our patient). Lichenoid tattoo reactions are the most common histopathologic variants of delayed hypersensitivity seen, mostly with cinnabar or red dye.1 However, there is a paucity of cases in the literature of PEH following tattooing with red dye. Interestingly, lichenoid tissue reaction accompanies PEH in all reported cases.2
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia can mimic squamous cell carcinoma and keratoacanthoma (KA) both clinically and histologically. All 3 conditions may exhibit epithelial hyperplasia with prominent dilated hyperplastic infundibula. In a case series of 11 presumed KAs within tattoos, Fraga and Prossick2 reported 82% (9/11) of the lesions were located strictly in areas with red pigment, and many were associated with a lichenoid tissue reaction. Kazlouskaya and Junkins-Hopkins3 previously described cases of KAs in tattoos that may represent PEH.
When treating lesions with this histologic appearance, consider the clinical and histologic overlap between KAs and PEH. Our patient was managed with clobetasol ointment 0.05% under occlusion followed by intralesional triamcinolone acetonide with notable improvement of the verrucous plaques on the left lateral malleolus (Figure 2). He also noted near resolution of the papules on the pretibial shin and complete resolution of all associated pruritus and burning. Calcineurin inhibitors, photochemotherapy, CO2 laser, excimer laser, and surgical removal with interval grafting also were considered.

It is important to recognize PEH in the differential of eruptions occurring within tattoos to avoid unnecessary invasive surgical procedures such as complete surgical excision of a KA to avoid malignant transformation.
- Mortimer NJ, Chave TA, Johnston GA. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Fraga GR, Prossick TA. Tattoo-associated keratoacanthomas: a series of 8 patients with 11 keratoacanthomas. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:85-90.
- Kazlouskaya V, Junkins-Hopkins JM. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in a red pigment tattoo: a separate entity or hypertrophic lichen planus-like reaction? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:48-52.
- Mortimer NJ, Chave TA, Johnston GA. Red tattoo reactions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:508-510.
- Fraga GR, Prossick TA. Tattoo-associated keratoacanthomas: a series of 8 patients with 11 keratoacanthomas. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:85-90.
- Kazlouskaya V, Junkins-Hopkins JM. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in a red pigment tattoo: a separate entity or hypertrophic lichen planus-like reaction? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:48-52.
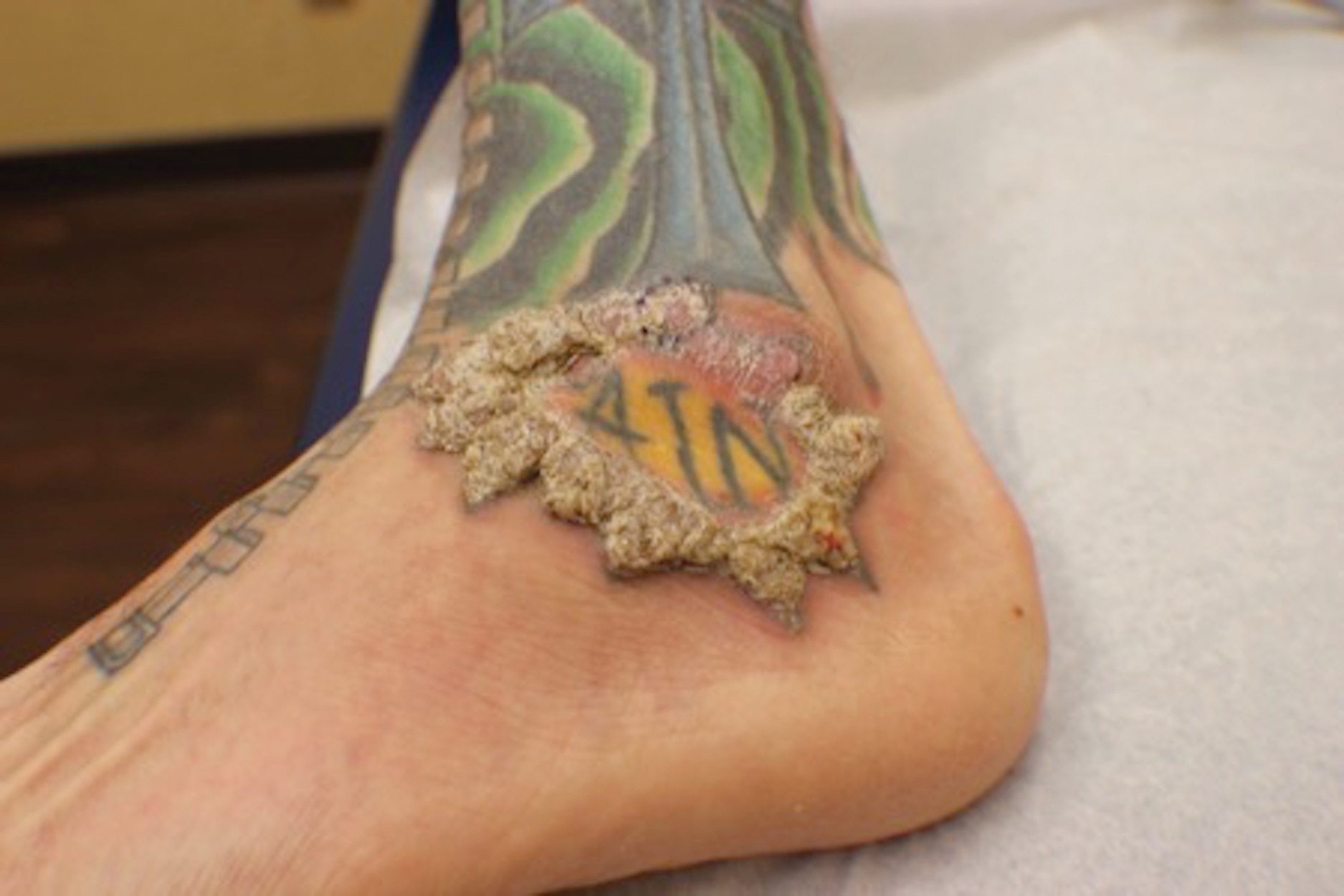
A 40-year-old man with a medical history of human immunodeficiency virus infection managed with highly active antiretroviral therapy (CD4 count, 888 cells/mm3 and an undetectable viral load), psoriasis, and recurrent condyloma acuminatum presented with exophytic, annular, hyperkeratotic, verrucous plaques on the left lateral malleolus with multiple erythematous hyperkeratotic papules on the pretibial shin of the left leg of 6 months' duration. These plaques and papules were localized to areas where red dye was used in a tattoo the patient had received 2 years prior to presentation. There was no associated fluctuance or drainage. The patient reported paroxysmal pruritus and burning pain.