User login
Children and COVID: New cases hold steady in nonholiday week
The new-case count for the most recent reporting week – 87,644 for June 3-9 – did go up from the previous week, but by only 270 cases, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That’s just 0.31% higher than a week ago and probably is affected by reduced testing and reporting because of Memorial Day, as the AAP and CHA noted earlier.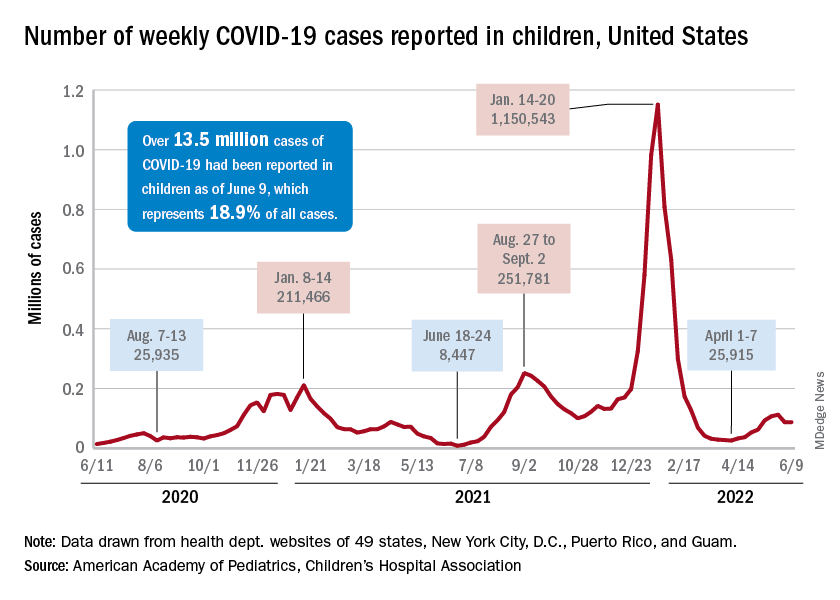
That hint of a continued decline accompanies the latest trend for new cases for all age groups: They have leveled out over the last month, with the moving 7-day daily average hovering around 100,000-110,000 since mid-May, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The Food and Drug Administration, meanwhile, is in the news this week as two of its advisory panels take the next steps toward pediatric approvals of vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTtech and Moderna. The panels could advance the approvals of the Pfizer vaccine for children under the age of 5 years and the Moderna vaccine for children aged 6 months to 17 years.
Matthew Harris, MD, medical director of the COVID-19 vaccination program for Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., emphasized the importance of vaccinations, as well as the continued challenge of convincing parents to get the shots for eligible children. “We still have a long way to go for primary vaccines and boosters for children 5 years and above,” he said in an interview.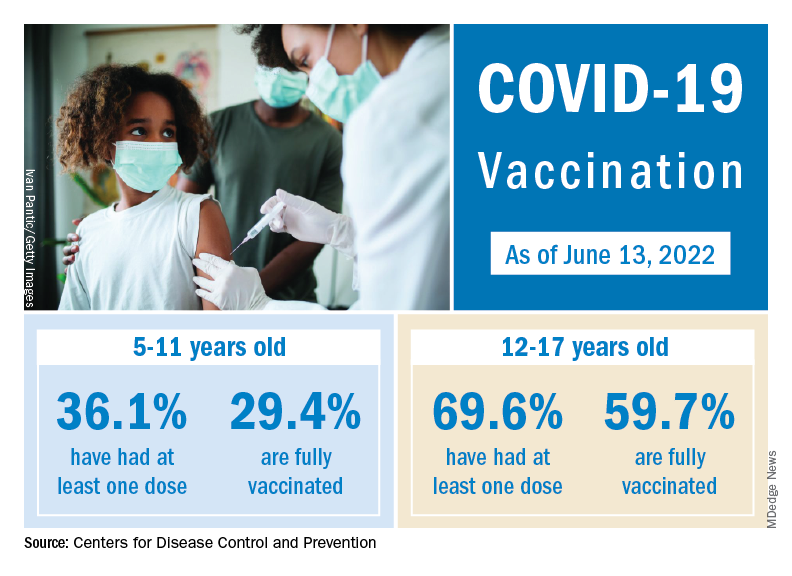
The vaccination effort against COVID-19 has stalled somewhat as interest has waned since the Omicron surge. Weekly initial vaccinations for children aged 5-11 years, which topped 100,000 as recently as mid-March, have been about 43,000 a week for the last 3 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds had around 27,000 or 28,000 initial vaccinations per week over that span, the AAP said in a separate report.
The latest data available from the CDC show that overall vaccine coverage levels for the younger group are only about half those of the 12- to 17-year-olds, both in terms of initial doses and completions. The 5- to 11-year-olds are not eligible for boosters yet, but 26.5% of the older children had received one as of June 13, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The new-case count for the most recent reporting week – 87,644 for June 3-9 – did go up from the previous week, but by only 270 cases, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That’s just 0.31% higher than a week ago and probably is affected by reduced testing and reporting because of Memorial Day, as the AAP and CHA noted earlier.
That hint of a continued decline accompanies the latest trend for new cases for all age groups: They have leveled out over the last month, with the moving 7-day daily average hovering around 100,000-110,000 since mid-May, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The Food and Drug Administration, meanwhile, is in the news this week as two of its advisory panels take the next steps toward pediatric approvals of vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTtech and Moderna. The panels could advance the approvals of the Pfizer vaccine for children under the age of 5 years and the Moderna vaccine for children aged 6 months to 17 years.
Matthew Harris, MD, medical director of the COVID-19 vaccination program for Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., emphasized the importance of vaccinations, as well as the continued challenge of convincing parents to get the shots for eligible children. “We still have a long way to go for primary vaccines and boosters for children 5 years and above,” he said in an interview.
The vaccination effort against COVID-19 has stalled somewhat as interest has waned since the Omicron surge. Weekly initial vaccinations for children aged 5-11 years, which topped 100,000 as recently as mid-March, have been about 43,000 a week for the last 3 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds had around 27,000 or 28,000 initial vaccinations per week over that span, the AAP said in a separate report.
The latest data available from the CDC show that overall vaccine coverage levels for the younger group are only about half those of the 12- to 17-year-olds, both in terms of initial doses and completions. The 5- to 11-year-olds are not eligible for boosters yet, but 26.5% of the older children had received one as of June 13, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The new-case count for the most recent reporting week – 87,644 for June 3-9 – did go up from the previous week, but by only 270 cases, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That’s just 0.31% higher than a week ago and probably is affected by reduced testing and reporting because of Memorial Day, as the AAP and CHA noted earlier.
That hint of a continued decline accompanies the latest trend for new cases for all age groups: They have leveled out over the last month, with the moving 7-day daily average hovering around 100,000-110,000 since mid-May, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show.
The Food and Drug Administration, meanwhile, is in the news this week as two of its advisory panels take the next steps toward pediatric approvals of vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTtech and Moderna. The panels could advance the approvals of the Pfizer vaccine for children under the age of 5 years and the Moderna vaccine for children aged 6 months to 17 years.
Matthew Harris, MD, medical director of the COVID-19 vaccination program for Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, N.Y., emphasized the importance of vaccinations, as well as the continued challenge of convincing parents to get the shots for eligible children. “We still have a long way to go for primary vaccines and boosters for children 5 years and above,” he said in an interview.
The vaccination effort against COVID-19 has stalled somewhat as interest has waned since the Omicron surge. Weekly initial vaccinations for children aged 5-11 years, which topped 100,000 as recently as mid-March, have been about 43,000 a week for the last 3 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds had around 27,000 or 28,000 initial vaccinations per week over that span, the AAP said in a separate report.
The latest data available from the CDC show that overall vaccine coverage levels for the younger group are only about half those of the 12- to 17-year-olds, both in terms of initial doses and completions. The 5- to 11-year-olds are not eligible for boosters yet, but 26.5% of the older children had received one as of June 13, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Surgery during a pandemic? COVID vaccination status matters – or not
An online survey captured mixed information about people’s willingness to undergo surgery during a viral pandemic in relation to the vaccine status of the patient and staff. The findings showcase opportunities for public education and “skillful messaging,” researchers report.
In survey scenarios that asked people to imagine their vaccination status, people were more willing to undergo surgery if it was lifesaving, rather than elective, especially if vaccinated. The prospect of no hospital stay tipped the scales further toward surgery. The vaccination status of hospital staff played only a minor role in decision making, according to the study, which was published in Vaccine.
But as a post hoc analysis revealed, it was participants who were not vaccinated against COVID-19 in real life who were more willing to undergo surgery, compared with those who had one or two shots.
In either case, too many people were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery, even though the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 is low. “Making this choice for an actual health problem would result in an unacceptably high rate of potential morbidity attributable to pandemic-related fears, the authors wrote.
In an unusual approach, the researchers used Amazon’s Mechanical Turk to electronically recruit 2,006 adults. The participants answered a 26-item survey about a hypothetical surgery in an unnamed pandemic with different combinations of vaccine status for patient and staff.
Coauthor and anesthesiologist Keith J. Ruskin, MD, of the University of Chicago, told this news organization that they “wanted to make this timeless” and independent of COVID “so that when the next thing came about, the paper would still be relevant.”
The researchers were surprised by the findings at the extreme ends of attitudes toward surgery. Some were still willing to have elective surgery with (hypothetically) unvaccinated patients and staff.
“And people at the other end, even though they are vaccinated, the hospital staff is vaccinated, and the surgery is lifesaving, they absolutely won’t have surgery,” Dr. Ruskin said.
He viewed these two groups as opportunities for education. “You can present information in the most positive light to get them to do the right thing with what’s best for themselves,” he said.
As an example, Dr. Ruskin pointed to an ad in Illinois. “It’s not only people saying I’m getting vaccinated for myself and my family, but there are people who said I got vaccinated and I still got COVID, but it could have been much worse. Please, if you’re on the fence, just get vaccinated,” he said.
Coauthor Anna Clebone Ruskin, MD, an anesthesiologist at the University of Chicago, said, “Humans are programmed to see things in extremes. With surgery, people tend to think of surgery as a monolith – surgery is all good, or surgery is all bad, where there is a huge in between. So we saw those extremes. ... Seeing that dichotomy with people on either end was pretty surprising.
“Getting surgery is not always good. Getting surgery is not always bad. It’s a risk-versus-benefit analysis and educating the public to consider the risks and benefits of medical decisions, in general, would be enormously beneficial,” she said.
A post hoc analysis found that “participants who were not actually vaccinated against COVID-19 were generally more willing to undergo surgery compared to those who had one vaccination or two vaccinations,” the authors wrote.
In a second post hoc finding, participants who reported high wariness of vaccines were generally more likely to be willing to undergo surgery. Notably, 15% of participants “were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery during a pandemic even when they and the health care staff were vaccinated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Keith J. Ruskin hypothesized about this result, saying, “What we think is that potentially actually getting vaccinated against COVID-19 may indicate that you have a lower risk tolerance. So you may be less likely to do anything you perceive to be risky if you’re vaccinated against COVID-19.”
The authors stated that “the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 even prior to vaccination is vanishingly small.” The risk of nosocomial COVID varies among different studies. An EPIC-based study between April 2020 and October 2021 found the risk to be 1.8%; EPIC describes the fears of a patient catching COVID at a hospital as “likely unfounded.”
In the United Kingdom, the risk was as high as 24% earlier in the pandemic and then declined to approximately 5% a year ago. Omicron also brought more infections. Rates varied significantly among hospitals – and, notably, the risk of death from a nosocomial COVID infection was 21% in April-September 2020.
Emily Landon, MD, an epidemiologist and executive medical director for infection prevention and control at the University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization that the study’s data were collected during Delta, a “time when we thought that this was a pandemic of the unvaccinated. But there was serious politicization of the vaccine.”
Dr. Landon said one of the study’s strengths was the large number of participants. A limitation was, “You’re going to have less participants who are generally poor and indigent, and fewer old participants, probably because they’re less likely to respond to an online survey.
“But the most interesting results are that people who were wary of vaccines or who hadn’t been vaccinated, were much more willing to undergo surgical procedures in the time of a pandemic, regardless of status, which reflects the fact that not being vaccinated correlates with not worrying much about COVID. Vaccinated individuals had a lot more wariness about undergoing surgical procedures during a pandemic.”
It appeared “individuals who were vaccinated in real life [were] worried about staff vaccination,” Dr. Landon noted. She concluded, “I think it supports the need for mandatory vaccinations in health care workers.”
The study has implications for hospital vaccination policies and practices. In Cumberland, Md., when COVID was high and vaccines first became available, the Maryland Hospital Association said that all health care staff should be vaccinated. The local hospital, UPMC–Western Maryland Hospital, refused.
Two months later, the local news reporter, Teresa McMinn, wrote, “While Maryland’s largest hospital systems have ‘led by example by mandating vaccines for all of their hospital staff,’ other facilities – including UPMC Western Maryland and Garrett Regional Medical Center – have taken no such action even though it’s been 8 months since vaccines were made available to health care workers.”
The hospital would not tell patients whether staff were vaccinated, either. An ongoing concern for members of the community is the lack of communication with UPMC, which erodes trust in the health system – the only hospital available in this rural community.
This vaccine study supports that the vaccination status of the staff may influence some patients’ decision on whether to have surgery.
The Ruskins and Dr. Landon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An online survey captured mixed information about people’s willingness to undergo surgery during a viral pandemic in relation to the vaccine status of the patient and staff. The findings showcase opportunities for public education and “skillful messaging,” researchers report.
In survey scenarios that asked people to imagine their vaccination status, people were more willing to undergo surgery if it was lifesaving, rather than elective, especially if vaccinated. The prospect of no hospital stay tipped the scales further toward surgery. The vaccination status of hospital staff played only a minor role in decision making, according to the study, which was published in Vaccine.
But as a post hoc analysis revealed, it was participants who were not vaccinated against COVID-19 in real life who were more willing to undergo surgery, compared with those who had one or two shots.
In either case, too many people were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery, even though the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 is low. “Making this choice for an actual health problem would result in an unacceptably high rate of potential morbidity attributable to pandemic-related fears, the authors wrote.
In an unusual approach, the researchers used Amazon’s Mechanical Turk to electronically recruit 2,006 adults. The participants answered a 26-item survey about a hypothetical surgery in an unnamed pandemic with different combinations of vaccine status for patient and staff.
Coauthor and anesthesiologist Keith J. Ruskin, MD, of the University of Chicago, told this news organization that they “wanted to make this timeless” and independent of COVID “so that when the next thing came about, the paper would still be relevant.”
The researchers were surprised by the findings at the extreme ends of attitudes toward surgery. Some were still willing to have elective surgery with (hypothetically) unvaccinated patients and staff.
“And people at the other end, even though they are vaccinated, the hospital staff is vaccinated, and the surgery is lifesaving, they absolutely won’t have surgery,” Dr. Ruskin said.
He viewed these two groups as opportunities for education. “You can present information in the most positive light to get them to do the right thing with what’s best for themselves,” he said.
As an example, Dr. Ruskin pointed to an ad in Illinois. “It’s not only people saying I’m getting vaccinated for myself and my family, but there are people who said I got vaccinated and I still got COVID, but it could have been much worse. Please, if you’re on the fence, just get vaccinated,” he said.
Coauthor Anna Clebone Ruskin, MD, an anesthesiologist at the University of Chicago, said, “Humans are programmed to see things in extremes. With surgery, people tend to think of surgery as a monolith – surgery is all good, or surgery is all bad, where there is a huge in between. So we saw those extremes. ... Seeing that dichotomy with people on either end was pretty surprising.
“Getting surgery is not always good. Getting surgery is not always bad. It’s a risk-versus-benefit analysis and educating the public to consider the risks and benefits of medical decisions, in general, would be enormously beneficial,” she said.
A post hoc analysis found that “participants who were not actually vaccinated against COVID-19 were generally more willing to undergo surgery compared to those who had one vaccination or two vaccinations,” the authors wrote.
In a second post hoc finding, participants who reported high wariness of vaccines were generally more likely to be willing to undergo surgery. Notably, 15% of participants “were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery during a pandemic even when they and the health care staff were vaccinated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Keith J. Ruskin hypothesized about this result, saying, “What we think is that potentially actually getting vaccinated against COVID-19 may indicate that you have a lower risk tolerance. So you may be less likely to do anything you perceive to be risky if you’re vaccinated against COVID-19.”
The authors stated that “the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 even prior to vaccination is vanishingly small.” The risk of nosocomial COVID varies among different studies. An EPIC-based study between April 2020 and October 2021 found the risk to be 1.8%; EPIC describes the fears of a patient catching COVID at a hospital as “likely unfounded.”
In the United Kingdom, the risk was as high as 24% earlier in the pandemic and then declined to approximately 5% a year ago. Omicron also brought more infections. Rates varied significantly among hospitals – and, notably, the risk of death from a nosocomial COVID infection was 21% in April-September 2020.
Emily Landon, MD, an epidemiologist and executive medical director for infection prevention and control at the University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization that the study’s data were collected during Delta, a “time when we thought that this was a pandemic of the unvaccinated. But there was serious politicization of the vaccine.”
Dr. Landon said one of the study’s strengths was the large number of participants. A limitation was, “You’re going to have less participants who are generally poor and indigent, and fewer old participants, probably because they’re less likely to respond to an online survey.
“But the most interesting results are that people who were wary of vaccines or who hadn’t been vaccinated, were much more willing to undergo surgical procedures in the time of a pandemic, regardless of status, which reflects the fact that not being vaccinated correlates with not worrying much about COVID. Vaccinated individuals had a lot more wariness about undergoing surgical procedures during a pandemic.”
It appeared “individuals who were vaccinated in real life [were] worried about staff vaccination,” Dr. Landon noted. She concluded, “I think it supports the need for mandatory vaccinations in health care workers.”
The study has implications for hospital vaccination policies and practices. In Cumberland, Md., when COVID was high and vaccines first became available, the Maryland Hospital Association said that all health care staff should be vaccinated. The local hospital, UPMC–Western Maryland Hospital, refused.
Two months later, the local news reporter, Teresa McMinn, wrote, “While Maryland’s largest hospital systems have ‘led by example by mandating vaccines for all of their hospital staff,’ other facilities – including UPMC Western Maryland and Garrett Regional Medical Center – have taken no such action even though it’s been 8 months since vaccines were made available to health care workers.”
The hospital would not tell patients whether staff were vaccinated, either. An ongoing concern for members of the community is the lack of communication with UPMC, which erodes trust in the health system – the only hospital available in this rural community.
This vaccine study supports that the vaccination status of the staff may influence some patients’ decision on whether to have surgery.
The Ruskins and Dr. Landon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An online survey captured mixed information about people’s willingness to undergo surgery during a viral pandemic in relation to the vaccine status of the patient and staff. The findings showcase opportunities for public education and “skillful messaging,” researchers report.
In survey scenarios that asked people to imagine their vaccination status, people were more willing to undergo surgery if it was lifesaving, rather than elective, especially if vaccinated. The prospect of no hospital stay tipped the scales further toward surgery. The vaccination status of hospital staff played only a minor role in decision making, according to the study, which was published in Vaccine.
But as a post hoc analysis revealed, it was participants who were not vaccinated against COVID-19 in real life who were more willing to undergo surgery, compared with those who had one or two shots.
In either case, too many people were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery, even though the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 is low. “Making this choice for an actual health problem would result in an unacceptably high rate of potential morbidity attributable to pandemic-related fears, the authors wrote.
In an unusual approach, the researchers used Amazon’s Mechanical Turk to electronically recruit 2,006 adults. The participants answered a 26-item survey about a hypothetical surgery in an unnamed pandemic with different combinations of vaccine status for patient and staff.
Coauthor and anesthesiologist Keith J. Ruskin, MD, of the University of Chicago, told this news organization that they “wanted to make this timeless” and independent of COVID “so that when the next thing came about, the paper would still be relevant.”
The researchers were surprised by the findings at the extreme ends of attitudes toward surgery. Some were still willing to have elective surgery with (hypothetically) unvaccinated patients and staff.
“And people at the other end, even though they are vaccinated, the hospital staff is vaccinated, and the surgery is lifesaving, they absolutely won’t have surgery,” Dr. Ruskin said.
He viewed these two groups as opportunities for education. “You can present information in the most positive light to get them to do the right thing with what’s best for themselves,” he said.
As an example, Dr. Ruskin pointed to an ad in Illinois. “It’s not only people saying I’m getting vaccinated for myself and my family, but there are people who said I got vaccinated and I still got COVID, but it could have been much worse. Please, if you’re on the fence, just get vaccinated,” he said.
Coauthor Anna Clebone Ruskin, MD, an anesthesiologist at the University of Chicago, said, “Humans are programmed to see things in extremes. With surgery, people tend to think of surgery as a monolith – surgery is all good, or surgery is all bad, where there is a huge in between. So we saw those extremes. ... Seeing that dichotomy with people on either end was pretty surprising.
“Getting surgery is not always good. Getting surgery is not always bad. It’s a risk-versus-benefit analysis and educating the public to consider the risks and benefits of medical decisions, in general, would be enormously beneficial,” she said.
A post hoc analysis found that “participants who were not actually vaccinated against COVID-19 were generally more willing to undergo surgery compared to those who had one vaccination or two vaccinations,” the authors wrote.
In a second post hoc finding, participants who reported high wariness of vaccines were generally more likely to be willing to undergo surgery. Notably, 15% of participants “were unwilling to undergo lifesaving surgery during a pandemic even when they and the health care staff were vaccinated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Keith J. Ruskin hypothesized about this result, saying, “What we think is that potentially actually getting vaccinated against COVID-19 may indicate that you have a lower risk tolerance. So you may be less likely to do anything you perceive to be risky if you’re vaccinated against COVID-19.”
The authors stated that “the risk of hospital-acquired COVID-19 even prior to vaccination is vanishingly small.” The risk of nosocomial COVID varies among different studies. An EPIC-based study between April 2020 and October 2021 found the risk to be 1.8%; EPIC describes the fears of a patient catching COVID at a hospital as “likely unfounded.”
In the United Kingdom, the risk was as high as 24% earlier in the pandemic and then declined to approximately 5% a year ago. Omicron also brought more infections. Rates varied significantly among hospitals – and, notably, the risk of death from a nosocomial COVID infection was 21% in April-September 2020.
Emily Landon, MD, an epidemiologist and executive medical director for infection prevention and control at the University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization that the study’s data were collected during Delta, a “time when we thought that this was a pandemic of the unvaccinated. But there was serious politicization of the vaccine.”
Dr. Landon said one of the study’s strengths was the large number of participants. A limitation was, “You’re going to have less participants who are generally poor and indigent, and fewer old participants, probably because they’re less likely to respond to an online survey.
“But the most interesting results are that people who were wary of vaccines or who hadn’t been vaccinated, were much more willing to undergo surgical procedures in the time of a pandemic, regardless of status, which reflects the fact that not being vaccinated correlates with not worrying much about COVID. Vaccinated individuals had a lot more wariness about undergoing surgical procedures during a pandemic.”
It appeared “individuals who were vaccinated in real life [were] worried about staff vaccination,” Dr. Landon noted. She concluded, “I think it supports the need for mandatory vaccinations in health care workers.”
The study has implications for hospital vaccination policies and practices. In Cumberland, Md., when COVID was high and vaccines first became available, the Maryland Hospital Association said that all health care staff should be vaccinated. The local hospital, UPMC–Western Maryland Hospital, refused.
Two months later, the local news reporter, Teresa McMinn, wrote, “While Maryland’s largest hospital systems have ‘led by example by mandating vaccines for all of their hospital staff,’ other facilities – including UPMC Western Maryland and Garrett Regional Medical Center – have taken no such action even though it’s been 8 months since vaccines were made available to health care workers.”
The hospital would not tell patients whether staff were vaccinated, either. An ongoing concern for members of the community is the lack of communication with UPMC, which erodes trust in the health system – the only hospital available in this rural community.
This vaccine study supports that the vaccination status of the staff may influence some patients’ decision on whether to have surgery.
The Ruskins and Dr. Landon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In utero COVID exposure tied to neurodevelopmental disorders at 1 year
Infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero are at increased risk for neurodevelopmental disorders in the first year of life, new research suggests.
But whether it is exposure to the pandemic or maternal exposure to the virus itself that may harm early childhood neurodevelopment is unclear, caution investigators, led by Roy Perlis, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“In this analysis of 222 offspring of mothers infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with the offspring of 7,550 mothers in the control group (not infected) delivered during the same period, we observed neurodevelopmental diagnoses to be significantly more common among exposed offspring, particularly those exposed to third-trimester maternal infection,” they write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Speech and language disorders
The study included 7,772 mostly singleton live births across six hospitals in Massachusetts between March and September 2020, including 222 (2.9%) births to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed by polymerase chain reaction testing during pregnancy.
In all, 14 of 222 children born to SARS-CoV-2–infected mothers (6.3%) were diagnosed with a neurodevelopmental disorder in the first year of life versus 227 of 7,550 unexposed offspring (3%) (unadjusted odds ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-3.79; P = .006).
In models adjusted for preterm delivery, as well as race, ethnicity, insurance status, child sex, and maternal age, COVID-exposed offspring were significantly more likely to receive a neurodevelopmental diagnosis in the first year of life (adjusted OR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.36; P = .04).
The magnitude of the association with neurodevelopmental disorders was greater with third-trimester SARS-CoV-2 infection (aOR, 2.34; 95% CI, 1.23-4.44; P = .01).
The majority of these diagnoses reflected developmental disorders of motor function or speech and language.
The researchers noted that the finding of an association between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months is in line with a “large body of literature” linking maternal viral infection and maternal immune activation with offspring neurodevelopmental disorders later in life.
They cautioned, however, that whether a definitive connection exists between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and adverse neurodevelopment in offspring is not yet known, in part because children born to women infected in the first wave of the pandemic haven’t reached their second birthday – a time when neurodevelopment disorders such as autism are typically diagnosed.
There is also the risk for ascertainment bias arising from greater concern for offspring of infected mothers who were ill during pregnancy. These parents may be more inclined to seek evaluation, and clinicians may be more inclined to diagnose or refer for evaluation, the researchers noted.
Nonetheless, as reported by this news organization, the study results support those of research released at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress; those results also showed an association between maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and impaired neurodevelopment in 6-week-old infants.
Hypothesis generating
In an accompanying commentary, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, with University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said the preliminary findings of Dr. Perlis and colleagues are “critically important, yet many questions remain.”
“Essentially all of what we know now about the effects of in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection is from children who were exposed to the early and Alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2, as those are the only children now old enough to undergo rigorous neurodevelopmental assessments,” Dr. Metz pointed out.
Ultimately, Dr. Metz said it’s not surprising that the pandemic and in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in young children.
Yet, as a retrospective cohort study, the study can only demonstrate associations, not causality.
“This type of work is intended to be hypothesis generating, and that goal has been accomplished as these preliminary findings generate numerous additional research questions to explore,” Dr. Metz wrote.
Among them: Are there genetic predispositions to adverse outcomes? Will we observe differential effects by SARS-CoV-2 variant, by severity of infection, and by trimester of infection? Is it the virus itself or all of the societal changes that occurred during this period, including differences in how those changes were experienced among those with and without SARS-CoV-2?
“Perhaps the most important question is how do we intervene to help mitigate the adverse effects of the pandemic on young children,” Dr. Metz noted.
“Prospective studies to validate these findings, tease out some of the nuance, and identify those at highest risk will help health care practitioners appropriately dedicate resources to improve outcomes as we follow the life course of this generation of children born during the COVID-19 pandemic,” she added.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Perlis is an associate editor for JAMA Network Open but was not involved in the editorial review or decision for the study. Dr. Metz reported receiving personal fees and grants from Pfizer and grants from GestVision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero are at increased risk for neurodevelopmental disorders in the first year of life, new research suggests.
But whether it is exposure to the pandemic or maternal exposure to the virus itself that may harm early childhood neurodevelopment is unclear, caution investigators, led by Roy Perlis, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“In this analysis of 222 offspring of mothers infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with the offspring of 7,550 mothers in the control group (not infected) delivered during the same period, we observed neurodevelopmental diagnoses to be significantly more common among exposed offspring, particularly those exposed to third-trimester maternal infection,” they write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Speech and language disorders
The study included 7,772 mostly singleton live births across six hospitals in Massachusetts between March and September 2020, including 222 (2.9%) births to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed by polymerase chain reaction testing during pregnancy.
In all, 14 of 222 children born to SARS-CoV-2–infected mothers (6.3%) were diagnosed with a neurodevelopmental disorder in the first year of life versus 227 of 7,550 unexposed offspring (3%) (unadjusted odds ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-3.79; P = .006).
In models adjusted for preterm delivery, as well as race, ethnicity, insurance status, child sex, and maternal age, COVID-exposed offspring were significantly more likely to receive a neurodevelopmental diagnosis in the first year of life (adjusted OR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.36; P = .04).
The magnitude of the association with neurodevelopmental disorders was greater with third-trimester SARS-CoV-2 infection (aOR, 2.34; 95% CI, 1.23-4.44; P = .01).
The majority of these diagnoses reflected developmental disorders of motor function or speech and language.
The researchers noted that the finding of an association between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months is in line with a “large body of literature” linking maternal viral infection and maternal immune activation with offspring neurodevelopmental disorders later in life.
They cautioned, however, that whether a definitive connection exists between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and adverse neurodevelopment in offspring is not yet known, in part because children born to women infected in the first wave of the pandemic haven’t reached their second birthday – a time when neurodevelopment disorders such as autism are typically diagnosed.
There is also the risk for ascertainment bias arising from greater concern for offspring of infected mothers who were ill during pregnancy. These parents may be more inclined to seek evaluation, and clinicians may be more inclined to diagnose or refer for evaluation, the researchers noted.
Nonetheless, as reported by this news organization, the study results support those of research released at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress; those results also showed an association between maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and impaired neurodevelopment in 6-week-old infants.
Hypothesis generating
In an accompanying commentary, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, with University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said the preliminary findings of Dr. Perlis and colleagues are “critically important, yet many questions remain.”
“Essentially all of what we know now about the effects of in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection is from children who were exposed to the early and Alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2, as those are the only children now old enough to undergo rigorous neurodevelopmental assessments,” Dr. Metz pointed out.
Ultimately, Dr. Metz said it’s not surprising that the pandemic and in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in young children.
Yet, as a retrospective cohort study, the study can only demonstrate associations, not causality.
“This type of work is intended to be hypothesis generating, and that goal has been accomplished as these preliminary findings generate numerous additional research questions to explore,” Dr. Metz wrote.
Among them: Are there genetic predispositions to adverse outcomes? Will we observe differential effects by SARS-CoV-2 variant, by severity of infection, and by trimester of infection? Is it the virus itself or all of the societal changes that occurred during this period, including differences in how those changes were experienced among those with and without SARS-CoV-2?
“Perhaps the most important question is how do we intervene to help mitigate the adverse effects of the pandemic on young children,” Dr. Metz noted.
“Prospective studies to validate these findings, tease out some of the nuance, and identify those at highest risk will help health care practitioners appropriately dedicate resources to improve outcomes as we follow the life course of this generation of children born during the COVID-19 pandemic,” she added.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Perlis is an associate editor for JAMA Network Open but was not involved in the editorial review or decision for the study. Dr. Metz reported receiving personal fees and grants from Pfizer and grants from GestVision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero are at increased risk for neurodevelopmental disorders in the first year of life, new research suggests.
But whether it is exposure to the pandemic or maternal exposure to the virus itself that may harm early childhood neurodevelopment is unclear, caution investigators, led by Roy Perlis, MD, MSc, with Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“In this analysis of 222 offspring of mothers infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with the offspring of 7,550 mothers in the control group (not infected) delivered during the same period, we observed neurodevelopmental diagnoses to be significantly more common among exposed offspring, particularly those exposed to third-trimester maternal infection,” they write.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Speech and language disorders
The study included 7,772 mostly singleton live births across six hospitals in Massachusetts between March and September 2020, including 222 (2.9%) births to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed by polymerase chain reaction testing during pregnancy.
In all, 14 of 222 children born to SARS-CoV-2–infected mothers (6.3%) were diagnosed with a neurodevelopmental disorder in the first year of life versus 227 of 7,550 unexposed offspring (3%) (unadjusted odds ratio, 2.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.24-3.79; P = .006).
In models adjusted for preterm delivery, as well as race, ethnicity, insurance status, child sex, and maternal age, COVID-exposed offspring were significantly more likely to receive a neurodevelopmental diagnosis in the first year of life (adjusted OR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.36; P = .04).
The magnitude of the association with neurodevelopmental disorders was greater with third-trimester SARS-CoV-2 infection (aOR, 2.34; 95% CI, 1.23-4.44; P = .01).
The majority of these diagnoses reflected developmental disorders of motor function or speech and language.
The researchers noted that the finding of an association between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and neurodevelopmental diagnoses at 12 months is in line with a “large body of literature” linking maternal viral infection and maternal immune activation with offspring neurodevelopmental disorders later in life.
They cautioned, however, that whether a definitive connection exists between prenatal SARS-CoV-2 exposure and adverse neurodevelopment in offspring is not yet known, in part because children born to women infected in the first wave of the pandemic haven’t reached their second birthday – a time when neurodevelopment disorders such as autism are typically diagnosed.
There is also the risk for ascertainment bias arising from greater concern for offspring of infected mothers who were ill during pregnancy. These parents may be more inclined to seek evaluation, and clinicians may be more inclined to diagnose or refer for evaluation, the researchers noted.
Nonetheless, as reported by this news organization, the study results support those of research released at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress; those results also showed an association between maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and impaired neurodevelopment in 6-week-old infants.
Hypothesis generating
In an accompanying commentary, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, with University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, said the preliminary findings of Dr. Perlis and colleagues are “critically important, yet many questions remain.”
“Essentially all of what we know now about the effects of in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection is from children who were exposed to the early and Alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2, as those are the only children now old enough to undergo rigorous neurodevelopmental assessments,” Dr. Metz pointed out.
Ultimately, Dr. Metz said it’s not surprising that the pandemic and in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in young children.
Yet, as a retrospective cohort study, the study can only demonstrate associations, not causality.
“This type of work is intended to be hypothesis generating, and that goal has been accomplished as these preliminary findings generate numerous additional research questions to explore,” Dr. Metz wrote.
Among them: Are there genetic predispositions to adverse outcomes? Will we observe differential effects by SARS-CoV-2 variant, by severity of infection, and by trimester of infection? Is it the virus itself or all of the societal changes that occurred during this period, including differences in how those changes were experienced among those with and without SARS-CoV-2?
“Perhaps the most important question is how do we intervene to help mitigate the adverse effects of the pandemic on young children,” Dr. Metz noted.
“Prospective studies to validate these findings, tease out some of the nuance, and identify those at highest risk will help health care practitioners appropriately dedicate resources to improve outcomes as we follow the life course of this generation of children born during the COVID-19 pandemic,” she added.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Perlis is an associate editor for JAMA Network Open but was not involved in the editorial review or decision for the study. Dr. Metz reported receiving personal fees and grants from Pfizer and grants from GestVision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Severe COVID-19 and blood cancer: Plasma therapy may help
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
The study demonstrated that “plasma from convalescent or vaccinated individuals shortens the time to improvement in hematological and solid cancer patients with severe COVID-19” and “prolongs overall survival,” said study coauthor Maike Janssen, MD, of the department of internal medicine at Heidelberg (Germany) University Hospital.
Dr. Janssen presented the study findings at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association held in Vienna.
Although people with COVID-19 do not appear to benefit from treatment with convalescent plasma, some data indicate that certain patients who cannot mount a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection may benefit.
In this recent multicenter study, 134 patients with confirmed COVID-19 whose oxygen saturation was 94% or lower were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma (n = 68) or to receive standard of care (n = 66). Patients fell into four clinical groups: those with a hematologic malignancy or who had undergone active cancer therapy for any cancer within the past 24 months; those with chronic immunosuppression; those between the ages of 50 and 75 with lymphopenia and/or elevated D-dimer levels; and those older than 75 years.
The convalescent or vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 plasma was administered in two bags (238-337 mL plasma each) from different donors on days 1 and 2. Only plasma from donors with high levels of neutralizing activity (titers above 1:80) were included. The primary endpoint was time to improvement by 2 points on a 7-point scale or discharge from the hospital. The secondary endpoint was improvement in overall survival.
The authors found that overall, patients in the plasma group demonstrated a shorter time to improvement – median of 12.5 days, vs. 18 days – but the difference was not significant (P = .29).
However, for the subgroup of 56 patients with hematologic/solid cancers, the time to improvement was significantly shorter: 13 days vs. 31 days (hazard ratio [HR], 2.5; P = .003).
Similarly, plasma therapy did not improve overall survival in the study population overall – there were 12 deaths in the plasma group over 80 days, vs. 15 in the control group (P = .80). Patients in the hematologic/solid cancer subgroup who received plasma therapy did demonstrate significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.28; P = .042).
No similar significant differences in time to improvement or overall survival were observed in the other three groups. “We found that plasma did not improve outcomes in immune-competent patients with other risk factors and/or older age,” Dr. Janssen said.
Although study enrollment ended when the Omicron variant began surging, Dr. Janssen noted that plasma from Omicron patients may also be of benefit to those with hematologic cancers.
“We have treated some patients in individual cases using plasma from Omicron patients who were already vaccinated or with breakthrough infections, and we did see benefits in those cases,” she noted.
The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany. Dr. Janssen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EHA 2022
People with HIV may need an additional COVID vaccine dose
People with HIV have an increased risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections, a new study finds, and the authors say an additional primary vaccine dose should be considered for all who are living with the disease.
Currently, an additional primary dose administered 28 days after a second dose of the mRNA (Moderna or Pfizer) vaccines or after the first dose of the Johnson & Johnson (J&J) vaccine is recommended only for those with advanced or untreated HIV.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends boosters for all adults with or without HIV.
Sally B. Coburn, PhD, of the department of epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open. In their study, the researchers estimate the risk of breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated adults on the basis of HIV status in the United States.
Adults with HIV who were fully vaccinated before June 30, 2021, were matched with adults without HIV with regard to date of full vaccination, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. All were followed through Dec. 31, 2021.
Patients were considered fully vaccinated either 14 days after the second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna shots or 14 days after the single dose of the J&J shot.
Breakthrough risk 28% higher
In the study of 113,994 patients, researchers found that risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection was low overall (3.8%) but was 28% higher among people with HIV in comparison with people without HIV (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-1.37).
The breakthrough rate was also higher in the HIV group (55 cases per 1,000 person-years, vs. 43 cases per 1,000 person-years in people without HIV).
Patients were drawn from the Corona-Infectious-Virus Epidemiology Team (CIVET)–II of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), which is part of the International Epidemiology Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) collaboration involving four cohorts.
Among people with HIV, those younger than 45 years (vs. those aged 45-54) and those with a history of COVID-19 were more likely to experience breakthrough infections. Those who did not get any additional shots after the primary vaccination were more likely to have breakthrough infections, amplifying the need to get boosters, the authors wrote.
There was no link between breakthrough infections and HIV viral load suppression, but high CD4 counts (> 500 cells/mm3) were associated with fewer breakthrough cases among people with HIV, they noted.
Monica Gandhi, MD, professor of medicine and associate division chief of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, praised the study, noting that until now, large studies have not examined the rate of breakthrough infections among vaccinated people with HIV and people without HIV in the United States.
She told this news organization she agrees with the authors that a third dose for all who are living with HIV is needed because rates of breakthrough infections were high across all populations during the Omicron surge (which largely occurred after the period of this study).
She said she was not convinced the third shot was needed before Omicron, because breakthrough rates in both HIV and non-HIV groups were low.
“However, the most interesting part of this study for me was how well the vaccines worked in people with HIV with generally higher CD4 counts and virologic suppression, again telling us as HIV providers how well the HIV medicines work and how our patients with HIV have relatively normal immune systems if treated,” she said.
One limitation was that the study population was 92% male. Also, those without regular access to health care (who may be at greater risk for COVID-19) were less likely to be included in the study. People engaged in care may seek more frequent COVID-19 testing, which could lead to higher detection of breakthrough infections than in the general population.
“Future analyses should account for testing practices and include a larger proportion of women with HIV,” the authors wrote. “Ultimately, policy makers must determine the appropriate balance between preventing further COVID-19 infections and possibly unnecessary additional vaccinations.”
Coauthor Keri N. Althoff, PhD, told this news organization that there’s one unanswered question that would strengthen the call to action by the CDC: Do people with HIV have more severe postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness?
“We have a second paper that is a preprint and currently under peer review,” she said. “In this paper, we found that people with HIV with a CD4 count less than 350 cells/mm3 were more likely to be hospitalized with postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness compared to similar people without HIV. “
At a minimum, Dr. Althoff said, policymakers should consider including people with HIV with a CD4 less than 350 cells/mm3 (loosening the restriction to less than 200 cells/mm3) in their recommendations for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised.
The research was funded with supplemental funds to the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design. Dr. Coburn reports no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, and University of Calgary/Alberta Health Services outside the submitted work. One coauthor reports serving as a consultant to Trio Health, Kennedy Dundas, and MedIQ outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with HIV have an increased risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections, a new study finds, and the authors say an additional primary vaccine dose should be considered for all who are living with the disease.
Currently, an additional primary dose administered 28 days after a second dose of the mRNA (Moderna or Pfizer) vaccines or after the first dose of the Johnson & Johnson (J&J) vaccine is recommended only for those with advanced or untreated HIV.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends boosters for all adults with or without HIV.
Sally B. Coburn, PhD, of the department of epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open. In their study, the researchers estimate the risk of breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated adults on the basis of HIV status in the United States.
Adults with HIV who were fully vaccinated before June 30, 2021, were matched with adults without HIV with regard to date of full vaccination, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. All were followed through Dec. 31, 2021.
Patients were considered fully vaccinated either 14 days after the second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna shots or 14 days after the single dose of the J&J shot.
Breakthrough risk 28% higher
In the study of 113,994 patients, researchers found that risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection was low overall (3.8%) but was 28% higher among people with HIV in comparison with people without HIV (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-1.37).
The breakthrough rate was also higher in the HIV group (55 cases per 1,000 person-years, vs. 43 cases per 1,000 person-years in people without HIV).
Patients were drawn from the Corona-Infectious-Virus Epidemiology Team (CIVET)–II of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), which is part of the International Epidemiology Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) collaboration involving four cohorts.
Among people with HIV, those younger than 45 years (vs. those aged 45-54) and those with a history of COVID-19 were more likely to experience breakthrough infections. Those who did not get any additional shots after the primary vaccination were more likely to have breakthrough infections, amplifying the need to get boosters, the authors wrote.
There was no link between breakthrough infections and HIV viral load suppression, but high CD4 counts (> 500 cells/mm3) were associated with fewer breakthrough cases among people with HIV, they noted.
Monica Gandhi, MD, professor of medicine and associate division chief of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, praised the study, noting that until now, large studies have not examined the rate of breakthrough infections among vaccinated people with HIV and people without HIV in the United States.
She told this news organization she agrees with the authors that a third dose for all who are living with HIV is needed because rates of breakthrough infections were high across all populations during the Omicron surge (which largely occurred after the period of this study).
She said she was not convinced the third shot was needed before Omicron, because breakthrough rates in both HIV and non-HIV groups were low.
“However, the most interesting part of this study for me was how well the vaccines worked in people with HIV with generally higher CD4 counts and virologic suppression, again telling us as HIV providers how well the HIV medicines work and how our patients with HIV have relatively normal immune systems if treated,” she said.
One limitation was that the study population was 92% male. Also, those without regular access to health care (who may be at greater risk for COVID-19) were less likely to be included in the study. People engaged in care may seek more frequent COVID-19 testing, which could lead to higher detection of breakthrough infections than in the general population.
“Future analyses should account for testing practices and include a larger proportion of women with HIV,” the authors wrote. “Ultimately, policy makers must determine the appropriate balance between preventing further COVID-19 infections and possibly unnecessary additional vaccinations.”
Coauthor Keri N. Althoff, PhD, told this news organization that there’s one unanswered question that would strengthen the call to action by the CDC: Do people with HIV have more severe postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness?
“We have a second paper that is a preprint and currently under peer review,” she said. “In this paper, we found that people with HIV with a CD4 count less than 350 cells/mm3 were more likely to be hospitalized with postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness compared to similar people without HIV. “
At a minimum, Dr. Althoff said, policymakers should consider including people with HIV with a CD4 less than 350 cells/mm3 (loosening the restriction to less than 200 cells/mm3) in their recommendations for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised.
The research was funded with supplemental funds to the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design. Dr. Coburn reports no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, and University of Calgary/Alberta Health Services outside the submitted work. One coauthor reports serving as a consultant to Trio Health, Kennedy Dundas, and MedIQ outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with HIV have an increased risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections, a new study finds, and the authors say an additional primary vaccine dose should be considered for all who are living with the disease.
Currently, an additional primary dose administered 28 days after a second dose of the mRNA (Moderna or Pfizer) vaccines or after the first dose of the Johnson & Johnson (J&J) vaccine is recommended only for those with advanced or untreated HIV.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends boosters for all adults with or without HIV.
Sally B. Coburn, PhD, of the department of epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open. In their study, the researchers estimate the risk of breakthrough infections among fully vaccinated adults on the basis of HIV status in the United States.
Adults with HIV who were fully vaccinated before June 30, 2021, were matched with adults without HIV with regard to date of full vaccination, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. All were followed through Dec. 31, 2021.
Patients were considered fully vaccinated either 14 days after the second dose of the Pfizer or Moderna shots or 14 days after the single dose of the J&J shot.
Breakthrough risk 28% higher
In the study of 113,994 patients, researchers found that risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection was low overall (3.8%) but was 28% higher among people with HIV in comparison with people without HIV (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-1.37).
The breakthrough rate was also higher in the HIV group (55 cases per 1,000 person-years, vs. 43 cases per 1,000 person-years in people without HIV).
Patients were drawn from the Corona-Infectious-Virus Epidemiology Team (CIVET)–II of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), which is part of the International Epidemiology Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) collaboration involving four cohorts.
Among people with HIV, those younger than 45 years (vs. those aged 45-54) and those with a history of COVID-19 were more likely to experience breakthrough infections. Those who did not get any additional shots after the primary vaccination were more likely to have breakthrough infections, amplifying the need to get boosters, the authors wrote.
There was no link between breakthrough infections and HIV viral load suppression, but high CD4 counts (> 500 cells/mm3) were associated with fewer breakthrough cases among people with HIV, they noted.
Monica Gandhi, MD, professor of medicine and associate division chief of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, praised the study, noting that until now, large studies have not examined the rate of breakthrough infections among vaccinated people with HIV and people without HIV in the United States.
She told this news organization she agrees with the authors that a third dose for all who are living with HIV is needed because rates of breakthrough infections were high across all populations during the Omicron surge (which largely occurred after the period of this study).
She said she was not convinced the third shot was needed before Omicron, because breakthrough rates in both HIV and non-HIV groups were low.
“However, the most interesting part of this study for me was how well the vaccines worked in people with HIV with generally higher CD4 counts and virologic suppression, again telling us as HIV providers how well the HIV medicines work and how our patients with HIV have relatively normal immune systems if treated,” she said.
One limitation was that the study population was 92% male. Also, those without regular access to health care (who may be at greater risk for COVID-19) were less likely to be included in the study. People engaged in care may seek more frequent COVID-19 testing, which could lead to higher detection of breakthrough infections than in the general population.
“Future analyses should account for testing practices and include a larger proportion of women with HIV,” the authors wrote. “Ultimately, policy makers must determine the appropriate balance between preventing further COVID-19 infections and possibly unnecessary additional vaccinations.”
Coauthor Keri N. Althoff, PhD, told this news organization that there’s one unanswered question that would strengthen the call to action by the CDC: Do people with HIV have more severe postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness?
“We have a second paper that is a preprint and currently under peer review,” she said. “In this paper, we found that people with HIV with a CD4 count less than 350 cells/mm3 were more likely to be hospitalized with postvaccination COVID-19 breakthrough illness compared to similar people without HIV. “
At a minimum, Dr. Althoff said, policymakers should consider including people with HIV with a CD4 less than 350 cells/mm3 (loosening the restriction to less than 200 cells/mm3) in their recommendations for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised.
The research was funded with supplemental funds to the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design. Dr. Coburn reports no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, and University of Calgary/Alberta Health Services outside the submitted work. One coauthor reports serving as a consultant to Trio Health, Kennedy Dundas, and MedIQ outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
COVID tied to a profound impact on children’s sleep
During the first year of the pandemic, profound changes in screen use and sleep timing occurred among U.S. adolescents as a result of spending more time using electronic devices, going to bed later, and getting up later, compared with before the pandemic, new research indicates.
The excessive screen time negatively affected sleep, said lead investigator Orsolya Kiss, PhD, with the Center for Health Sciences at SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif.
And what’s “concerning,” she told this news organization, is that there is no indication of any spontaneous decline in screen use in 2021, when there were fewer restrictions.
Dr. Kiss said she is “very much interested to see what future studies will show.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Sleep takes a pandemic hit
“Adolescents and families have turned to online activities and social platforms more than ever before to maintain wellbeing, [to] connect with friends and family, and for online schooling,” Dr. Kiss said in a conference statement.
She and her colleagues examined longitudinal data from 5,027 adolescents aged 11-14 years who are participating in the ongoing Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
As part of the study, participants reported sleep and daily screen time use prior to and at six time points during the first year of the pandemic (May 2020 to March 2021).
During the first year of the pandemic, relative to before the pandemic, recreational screen time was dramatically higher, with adolescents spending about 45 minutes more on social media and 20 minutes more playing video games, Dr. Kiss reported.
The jump in screen time was coupled with changes in sleep patterns.
Adolescents’ wake up times were delayed about 1.5 hours during May and August 2020, relative to prepandemic levels. The delay was partly due to summer break; wake-up times returned to earlier times in the fall of 2020.
During all pandemic assessments, bedtimes were delayed by about 1 hour, even when the new school year started. This was particularly the case in older adolescents and girls.
The findings highlight the need to promote “balanced and informed use of social media platforms, video games, and other digital technology to ensure adequate opportunity to sleep and maintain other healthy behaviors during this critical period of developmental change,” the authors wrote in their conference abstract.
Mental illness risk
In an interview, Ruth Benca, MD, PhD, co-chair of the Alliance for Sleep, noted that “during adolescence, the tendency to become more of a night owl naturally worsens, and when kids have no sleep schedule imposed on them, these patterns become exacerbated.”
Dr. Benca, who was not involved in the study, also noted that altered sleep patterns are risk factors for psychiatric illness.
“Adolescence, in particular, is so critical for brain development, and it really raises the question of whether sleep disturbances in adolescence or poor sleep patterns are contributing to the increase psychiatric epidemic we’re seeing in adolescents and children these days,” said Dr. Benca, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Also weighing in on the study, journalist and author Lisa Lewis, MS, based in Southern California, said, “It’s not surprising that tech use and social media – which is such an important part of their social worlds – went up during the pandemic.”
Ms. Lewis, a parent of two teenagers, played a key role in California’s new healthy school start times law, the first of its kind in the nation, and is the author of the newly released book, The Sleep-Deprived Teen (Mango Publishing).
“Far too many adolescents aren’t getting anywhere close to the 8-10 hours of nightly sleep they need,” Ms. Lewis said in an interview.
She noted that the the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no tech use an hour before bed.
“And there are other house rules parents can implement, such as charging all devices in a central location, like the kitchen. Making sleep a priority helps teens, but it helps parents too: No one functions well when they’re sleep-deprived,” Ms. Lewis added.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Benca is a consultant for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Ms. Lewis has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During the first year of the pandemic, profound changes in screen use and sleep timing occurred among U.S. adolescents as a result of spending more time using electronic devices, going to bed later, and getting up later, compared with before the pandemic, new research indicates.
The excessive screen time negatively affected sleep, said lead investigator Orsolya Kiss, PhD, with the Center for Health Sciences at SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif.
And what’s “concerning,” she told this news organization, is that there is no indication of any spontaneous decline in screen use in 2021, when there were fewer restrictions.
Dr. Kiss said she is “very much interested to see what future studies will show.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Sleep takes a pandemic hit
“Adolescents and families have turned to online activities and social platforms more than ever before to maintain wellbeing, [to] connect with friends and family, and for online schooling,” Dr. Kiss said in a conference statement.
She and her colleagues examined longitudinal data from 5,027 adolescents aged 11-14 years who are participating in the ongoing Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
As part of the study, participants reported sleep and daily screen time use prior to and at six time points during the first year of the pandemic (May 2020 to March 2021).
During the first year of the pandemic, relative to before the pandemic, recreational screen time was dramatically higher, with adolescents spending about 45 minutes more on social media and 20 minutes more playing video games, Dr. Kiss reported.
The jump in screen time was coupled with changes in sleep patterns.
Adolescents’ wake up times were delayed about 1.5 hours during May and August 2020, relative to prepandemic levels. The delay was partly due to summer break; wake-up times returned to earlier times in the fall of 2020.
During all pandemic assessments, bedtimes were delayed by about 1 hour, even when the new school year started. This was particularly the case in older adolescents and girls.
The findings highlight the need to promote “balanced and informed use of social media platforms, video games, and other digital technology to ensure adequate opportunity to sleep and maintain other healthy behaviors during this critical period of developmental change,” the authors wrote in their conference abstract.
Mental illness risk
In an interview, Ruth Benca, MD, PhD, co-chair of the Alliance for Sleep, noted that “during adolescence, the tendency to become more of a night owl naturally worsens, and when kids have no sleep schedule imposed on them, these patterns become exacerbated.”
Dr. Benca, who was not involved in the study, also noted that altered sleep patterns are risk factors for psychiatric illness.
“Adolescence, in particular, is so critical for brain development, and it really raises the question of whether sleep disturbances in adolescence or poor sleep patterns are contributing to the increase psychiatric epidemic we’re seeing in adolescents and children these days,” said Dr. Benca, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Also weighing in on the study, journalist and author Lisa Lewis, MS, based in Southern California, said, “It’s not surprising that tech use and social media – which is such an important part of their social worlds – went up during the pandemic.”
Ms. Lewis, a parent of two teenagers, played a key role in California’s new healthy school start times law, the first of its kind in the nation, and is the author of the newly released book, The Sleep-Deprived Teen (Mango Publishing).
“Far too many adolescents aren’t getting anywhere close to the 8-10 hours of nightly sleep they need,” Ms. Lewis said in an interview.
She noted that the the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no tech use an hour before bed.
“And there are other house rules parents can implement, such as charging all devices in a central location, like the kitchen. Making sleep a priority helps teens, but it helps parents too: No one functions well when they’re sleep-deprived,” Ms. Lewis added.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Benca is a consultant for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Ms. Lewis has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During the first year of the pandemic, profound changes in screen use and sleep timing occurred among U.S. adolescents as a result of spending more time using electronic devices, going to bed later, and getting up later, compared with before the pandemic, new research indicates.
The excessive screen time negatively affected sleep, said lead investigator Orsolya Kiss, PhD, with the Center for Health Sciences at SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif.
And what’s “concerning,” she told this news organization, is that there is no indication of any spontaneous decline in screen use in 2021, when there were fewer restrictions.
Dr. Kiss said she is “very much interested to see what future studies will show.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
Sleep takes a pandemic hit
“Adolescents and families have turned to online activities and social platforms more than ever before to maintain wellbeing, [to] connect with friends and family, and for online schooling,” Dr. Kiss said in a conference statement.
She and her colleagues examined longitudinal data from 5,027 adolescents aged 11-14 years who are participating in the ongoing Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
As part of the study, participants reported sleep and daily screen time use prior to and at six time points during the first year of the pandemic (May 2020 to March 2021).
During the first year of the pandemic, relative to before the pandemic, recreational screen time was dramatically higher, with adolescents spending about 45 minutes more on social media and 20 minutes more playing video games, Dr. Kiss reported.
The jump in screen time was coupled with changes in sleep patterns.
Adolescents’ wake up times were delayed about 1.5 hours during May and August 2020, relative to prepandemic levels. The delay was partly due to summer break; wake-up times returned to earlier times in the fall of 2020.
During all pandemic assessments, bedtimes were delayed by about 1 hour, even when the new school year started. This was particularly the case in older adolescents and girls.
The findings highlight the need to promote “balanced and informed use of social media platforms, video games, and other digital technology to ensure adequate opportunity to sleep and maintain other healthy behaviors during this critical period of developmental change,” the authors wrote in their conference abstract.
Mental illness risk
In an interview, Ruth Benca, MD, PhD, co-chair of the Alliance for Sleep, noted that “during adolescence, the tendency to become more of a night owl naturally worsens, and when kids have no sleep schedule imposed on them, these patterns become exacerbated.”
Dr. Benca, who was not involved in the study, also noted that altered sleep patterns are risk factors for psychiatric illness.
“Adolescence, in particular, is so critical for brain development, and it really raises the question of whether sleep disturbances in adolescence or poor sleep patterns are contributing to the increase psychiatric epidemic we’re seeing in adolescents and children these days,” said Dr. Benca, with Wake Forest University School of Medicine and Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, Winston-Salem, N.C.
Also weighing in on the study, journalist and author Lisa Lewis, MS, based in Southern California, said, “It’s not surprising that tech use and social media – which is such an important part of their social worlds – went up during the pandemic.”
Ms. Lewis, a parent of two teenagers, played a key role in California’s new healthy school start times law, the first of its kind in the nation, and is the author of the newly released book, The Sleep-Deprived Teen (Mango Publishing).
“Far too many adolescents aren’t getting anywhere close to the 8-10 hours of nightly sleep they need,” Ms. Lewis said in an interview.
She noted that the the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no tech use an hour before bed.
“And there are other house rules parents can implement, such as charging all devices in a central location, like the kitchen. Making sleep a priority helps teens, but it helps parents too: No one functions well when they’re sleep-deprived,” Ms. Lewis added.
Support for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Benca is a consultant for Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Ms. Lewis has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SLEEP 2022
In utero COVID exposure tied to developmental differences in infants
suggests a small-scale analysis that points to the need for further study and monitoring during pregnancy.
The study included 24 pregnant women, half of whom had COVID-19 during pregnancy, and their offspring. It showed impairments at 6 weeks of age on the social interactive dimension of a neonatal assessment.
“Not all babies born to mothers infected with COVID show neurodevelopmental differences, but our data show that their risk is increased in comparison to those not exposed to COVID in the womb. We need a bigger study to confirm the exact extent of the difference,” said lead researcher Rosa Ayesa Arriola, PhD, Valdecilla Research Institute (IDIVAL), Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, in a release.
The findings were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Differing responses to cuddling
Coauthor Águeda Castro Quintas, PhD student, Network Centre for Biomedical Research in Mental Health, University of Barcelona, explained that the tests showed the children born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy reacted “slightly differently to being held, or cuddled.”
“We need to note that these are preliminary results, but this is part of a project following a larger sample of 100 mothers and their babies,” she added. The authors plan to compare their results with those from a similar study.
The group will also monitor infant language and motor development aged between 18 and 42 months.
“This is an ongoing project, and we are at an early stage,” Ms. Castro Quintas said. “We don’t know if these effects will result in any longer-term issues,” but longer-term observation “may help us understand this.”
“Of course, in babies who are so young, there are several things we just can’t measure, such as language skills or cognition,” added coinvestigator Nerea San Martín González, department of evolutionary biology, ecology and environmental sciences, University of Barcelona.
While emphasizing the need for larger sample sizes, she said that “in the meantime, we need to stress the importance of medical monitoring to facilitate a healthy pregnancy.”
The researchers note that the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic for the newborns of affected mothers remain “unknown.”
However, previous studies of other infections during pregnancy suggest that offspring could be “especially vulnerable,”as the pathophysiological mechanisms of the infection, such as cytokine storms and microcoagulation, “could clearly compromise fetal neurodevelopment.”
To investigate further, they examined the neurodevelopment of infants born both immediately before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, from 2017 to 2021.
Twenty-one women who had COVID-19 during pregnancy were matched with 21 healthy controls. They were studied both during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, completing hormonal and other biochemical tests, salivary tests, movement assessments, and psychological questionnaires, adjusted for various factors.
The team also administered the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale (NBAS) to the offspring at 6 weeks of age to evaluate neurologic, social, and behavioral aspects of function.
“We have been especially sensitive in how we have conducted these tests,” said Ms. Castro Quintas. “Each mother and baby were closely examined by clinicians with expert training in the field and in the tests.”
Among those offspring exposed to COVID-19 during pregnancy, there was a significant decrease in scores on the social interactive dimension of the NBAS, particularly if infection occurred before week 20 of gestation.
Other NBAS subscales were not associated with maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy.
More research needed
Commenting on the findings, Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist and researcher in developmental psychobiology at the University of Pavia (Italy), noted there is a “great need” to study the direct and indirect effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on parents and their children. “Pregnancy is a period of life which shapes much of our subsequent development, and exposure to adversity in pregnancy can leave long-lasting biological footprints.”
Dr. Provenzi, who was not involved in the study, added in the release that the findings reinforce “evidence of epigenetic alterations in infants born from mothers exposed to pandemic-related stress during pregnancy.
“It shows we need more large-scale, international research to allow us to understand the developmental effects of this health emergency and to deliver better quality of care to parents and infants.”
The study was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the University of Barcelona multicenter project and the Government of Cantabria. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a small-scale analysis that points to the need for further study and monitoring during pregnancy.
The study included 24 pregnant women, half of whom had COVID-19 during pregnancy, and their offspring. It showed impairments at 6 weeks of age on the social interactive dimension of a neonatal assessment.
“Not all babies born to mothers infected with COVID show neurodevelopmental differences, but our data show that their risk is increased in comparison to those not exposed to COVID in the womb. We need a bigger study to confirm the exact extent of the difference,” said lead researcher Rosa Ayesa Arriola, PhD, Valdecilla Research Institute (IDIVAL), Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, in a release.
The findings were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Differing responses to cuddling
Coauthor Águeda Castro Quintas, PhD student, Network Centre for Biomedical Research in Mental Health, University of Barcelona, explained that the tests showed the children born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy reacted “slightly differently to being held, or cuddled.”
“We need to note that these are preliminary results, but this is part of a project following a larger sample of 100 mothers and their babies,” she added. The authors plan to compare their results with those from a similar study.
The group will also monitor infant language and motor development aged between 18 and 42 months.
“This is an ongoing project, and we are at an early stage,” Ms. Castro Quintas said. “We don’t know if these effects will result in any longer-term issues,” but longer-term observation “may help us understand this.”
“Of course, in babies who are so young, there are several things we just can’t measure, such as language skills or cognition,” added coinvestigator Nerea San Martín González, department of evolutionary biology, ecology and environmental sciences, University of Barcelona.
While emphasizing the need for larger sample sizes, she said that “in the meantime, we need to stress the importance of medical monitoring to facilitate a healthy pregnancy.”
The researchers note that the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic for the newborns of affected mothers remain “unknown.”
However, previous studies of other infections during pregnancy suggest that offspring could be “especially vulnerable,”as the pathophysiological mechanisms of the infection, such as cytokine storms and microcoagulation, “could clearly compromise fetal neurodevelopment.”
To investigate further, they examined the neurodevelopment of infants born both immediately before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, from 2017 to 2021.
Twenty-one women who had COVID-19 during pregnancy were matched with 21 healthy controls. They were studied both during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, completing hormonal and other biochemical tests, salivary tests, movement assessments, and psychological questionnaires, adjusted for various factors.
The team also administered the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale (NBAS) to the offspring at 6 weeks of age to evaluate neurologic, social, and behavioral aspects of function.
“We have been especially sensitive in how we have conducted these tests,” said Ms. Castro Quintas. “Each mother and baby were closely examined by clinicians with expert training in the field and in the tests.”
Among those offspring exposed to COVID-19 during pregnancy, there was a significant decrease in scores on the social interactive dimension of the NBAS, particularly if infection occurred before week 20 of gestation.
Other NBAS subscales were not associated with maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy.
More research needed
Commenting on the findings, Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist and researcher in developmental psychobiology at the University of Pavia (Italy), noted there is a “great need” to study the direct and indirect effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on parents and their children. “Pregnancy is a period of life which shapes much of our subsequent development, and exposure to adversity in pregnancy can leave long-lasting biological footprints.”
Dr. Provenzi, who was not involved in the study, added in the release that the findings reinforce “evidence of epigenetic alterations in infants born from mothers exposed to pandemic-related stress during pregnancy.
“It shows we need more large-scale, international research to allow us to understand the developmental effects of this health emergency and to deliver better quality of care to parents and infants.”
The study was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the University of Barcelona multicenter project and the Government of Cantabria. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a small-scale analysis that points to the need for further study and monitoring during pregnancy.
The study included 24 pregnant women, half of whom had COVID-19 during pregnancy, and their offspring. It showed impairments at 6 weeks of age on the social interactive dimension of a neonatal assessment.
“Not all babies born to mothers infected with COVID show neurodevelopmental differences, but our data show that their risk is increased in comparison to those not exposed to COVID in the womb. We need a bigger study to confirm the exact extent of the difference,” said lead researcher Rosa Ayesa Arriola, PhD, Valdecilla Research Institute (IDIVAL), Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, in a release.
The findings were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Differing responses to cuddling
Coauthor Águeda Castro Quintas, PhD student, Network Centre for Biomedical Research in Mental Health, University of Barcelona, explained that the tests showed the children born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy reacted “slightly differently to being held, or cuddled.”
“We need to note that these are preliminary results, but this is part of a project following a larger sample of 100 mothers and their babies,” she added. The authors plan to compare their results with those from a similar study.
The group will also monitor infant language and motor development aged between 18 and 42 months.
“This is an ongoing project, and we are at an early stage,” Ms. Castro Quintas said. “We don’t know if these effects will result in any longer-term issues,” but longer-term observation “may help us understand this.”
“Of course, in babies who are so young, there are several things we just can’t measure, such as language skills or cognition,” added coinvestigator Nerea San Martín González, department of evolutionary biology, ecology and environmental sciences, University of Barcelona.
While emphasizing the need for larger sample sizes, she said that “in the meantime, we need to stress the importance of medical monitoring to facilitate a healthy pregnancy.”
The researchers note that the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic for the newborns of affected mothers remain “unknown.”
However, previous studies of other infections during pregnancy suggest that offspring could be “especially vulnerable,”as the pathophysiological mechanisms of the infection, such as cytokine storms and microcoagulation, “could clearly compromise fetal neurodevelopment.”
To investigate further, they examined the neurodevelopment of infants born both immediately before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, from 2017 to 2021.
Twenty-one women who had COVID-19 during pregnancy were matched with 21 healthy controls. They were studied both during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, completing hormonal and other biochemical tests, salivary tests, movement assessments, and psychological questionnaires, adjusted for various factors.
The team also administered the Brazelton Neonatal Behavioural Assessment Scale (NBAS) to the offspring at 6 weeks of age to evaluate neurologic, social, and behavioral aspects of function.
“We have been especially sensitive in how we have conducted these tests,” said Ms. Castro Quintas. “Each mother and baby were closely examined by clinicians with expert training in the field and in the tests.”
Among those offspring exposed to COVID-19 during pregnancy, there was a significant decrease in scores on the social interactive dimension of the NBAS, particularly if infection occurred before week 20 of gestation.
Other NBAS subscales were not associated with maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy.
More research needed
Commenting on the findings, Livio Provenzi, PhD, a psychologist and researcher in developmental psychobiology at the University of Pavia (Italy), noted there is a “great need” to study the direct and indirect effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on parents and their children. “Pregnancy is a period of life which shapes much of our subsequent development, and exposure to adversity in pregnancy can leave long-lasting biological footprints.”
Dr. Provenzi, who was not involved in the study, added in the release that the findings reinforce “evidence of epigenetic alterations in infants born from mothers exposed to pandemic-related stress during pregnancy.
“It shows we need more large-scale, international research to allow us to understand the developmental effects of this health emergency and to deliver better quality of care to parents and infants.”
The study was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the University of Barcelona multicenter project and the Government of Cantabria. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EPA 2022
FDA panel strongly backs protein-based Novavax COVID-19 vaccine
than the cutting-edge technology used in mRNA-based shots.
The Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration voted almost unanimously June 7 in favor of Novavax’s two-dose COVID-19 vaccine for those 18 or older – despite some concerns over rare events of myocarditis and pericarditis.
The tally was 21 “yes” votes, without any “no” votes, but one abstention from a panelist who then offered a largely positive take on this vaccine.
Panelist Bruce Gellin, MD, explained at the end of the meeting that he would have cast a conditional vote in favor of the Novavax vaccine, called NVX-CoV2373, had that been an option. Dr. Gellin, chief of global public health strategy for the Rockefeller Foundation and a vaccine expert, said he didn’t want his abstention to be considered as signaling opposition to the Novavax shot.
Instead, he said, he expects FDA officials will gather more data and evidence about the Novavax vaccine, especially in relation to certain manufacturing issues, before making its decision on the company’s application.
Earlier in the day, a top FDA vaccine reviewer, Doran Fink, MD, PhD, noted that there were important manufacturing differences between the Novavax vaccine supply used in different projects, complicating efforts to assess the company’s application for emergency use authorization (EUA).
But Dr. Fink noted that the FDA staff already had made a convincing case in its briefing document, with enough evidence for an initial conditional clearance to be found in available data.
The FDA is not bound to follow the suggestions of its advisory committees but it often does.
Using the ‘bully pulpit’
At the beginning of the meeting, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said he was seizing the “bully pulpit” in addressing the need to persuade more people in the United States to take shots against COVID-19.
About 67% of people in the United States aged 18 and older are fully vaccinated, but only about 50% of those in this group have had a first booster, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The two-dose mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna have been the subject of intense misinformation campaigns on social media, despite efforts by the FDA and other public health officials to convey the message about their strong benefit-risk profile. The FDA in May limited the authorized use of Johnson & Johnson’s single-dose COVID-19 shot, which is based on a different technology, because of concerns about rare and potentially life-threatening blood clots.
Novavax has been described as a more traditional vaccine – a protein subunit shot similar to one people have long received for protection against influenza, pertussis (whooping cough), diphtheria, and tetanus.
“Having a protein-based alternative may be more comfortable for some in terms of their acceptance of vaccines,” Dr. Marks said. “We do have a problem with vaccine uptake that is very serious in the United States. And anything we can do to get people more comfortable to be able to accept these potentially life-saving medical products is something that we feel we are compelled to do.”
Dr. Marks offered these remarks in answer to an FDA panelist’s question about the need to consider an EUA for yet another vaccine.
EUAs are special clearances the FDA can grant in connection with public health emergencies such as the pandemic. The FDA used EUAs for the initial December 2020 clearances of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. It has since granted normal approvals for both of these mRNA-based vaccines, based on larger bodies of evidence gathered and submitted by their developers.
During the meeting, the FDA panelists in general appeared comfortable with the idea of granting another EUA for a vaccine. There was agreement that the shot appeared to work in key tests, although these were done before the rise of the Omicron variant.
In a key test, known as study 301, the Novavax vaccine was judged to be 90.4% effective. In the study, 17 of the 17,272 people who got the Novavax vaccine developed COVID-19, compared with 79 of the 8,385 in the placebo group.
Panelists expressed disappointment with the lack of information about how the shot would work now.
“We’re looking at the efficacy against strains that don’t exist any longer,” said panelist Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, a Harvard professor and editor of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Still, Dr. Rubin added that he agreed with the argument the FDA’s Dr. Marks had made earlier for an EUA for the Novavax vaccine.
“If there really is a population of patients who are willing to take this and not willing to take the existing vaccines, I think it’s pretty compelling,” Dr. Rubin said.
Other FDA panelists were skeptical of this argument. Jay Portnoy, MD, who was listed on the FDA roster as the panel’s consumer representative, said he has close friends who are vaccine skeptics.
“Their hesitancy is more ideological than technological,” said Dr. Portnoy of Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo. “So I really doubt that this vaccine is going to crack that nut, but perhaps some individuals would get this when they wouldn’t get the other ones.”
Myocarditis, pericarditis
The Novavax vaccine is already authorized in other countries, including Canada. Novavax in February announced that it had begun shipping its first doses of the vaccine to European Union member states. The vaccine can be moved through existing vaccine supply and cold chain channels instead of requiring complex new delivery procedures.
That could prove an advantage in time, said FDA panelist Michael Nelson, MD, PhD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Who knows even with supply chain challenges down the road, it will be nice to have options going forward,” Dr. Nelson said.
As with other COVID-19 vaccines, clinicians and researchers are still working to understand the potential risk for inflammation of heart muscle and nearby tissue with vaccination. Most patients with myocarditis or pericarditis who sought medical care for these conditions responded well to medicine and rest and felt better quickly, the CDC says on its website. They usually return to their normal daily activities after their symptoms improve.
At the June 7 meeting, Dr. Nelson said there may be cases of myocarditis that go undetected.
“Our signals are those who get admitted to the emergency room and the hospital,” he said. “I’m quite convinced that there are others who are experiencing cardiac events of lesser severity that are worthy of being studied, both from mechanistic and outcomes standpoints. So we have a lot of work to do.”
In looking at results for an initial pool of 40,000 people who received the Novavax vaccine, there were five reported cases of myocarditis or pericarditis developing within 20 days of people getting the shot, the FDA staff said in its presentation on safety.
In a briefing document released ahead of the advisory committee meeting, the FDA staff flagged this number of cases in a relatively small database as a concern, noting it “could be higher than reported during postauthorization use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (for which no cases were identified in preauthorization evaluation).”
Novavax officials took a somewhat unusual step of responding in public. The Gaithersburg, Md.–based company on June 3 issued a statement saying researchers had come to “expect to see natural background events of myocarditis in any sufficiently large database, and that young males are at higher risk.”
The data from the company’s placebo-controlled studies show that, overall, in its clinical development program, the rate of myocarditis was balanced between the vaccine and placebo arms (0.007% and 0.005%), Novavax said.
At the June 7 meeting, FDA panelists including Dr. Nelson, and Paul A. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, urged continued study to try to determine whether and how the vaccines could trigger myocarditis. Investments made now in pursuing these questions related to COVID-19 shots may pay off later, Dr. Offit said.
“We can use that knowledge to make safer vaccines for a disease that is going to be with us for decades, if not longer,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
than the cutting-edge technology used in mRNA-based shots.
The Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration voted almost unanimously June 7 in favor of Novavax’s two-dose COVID-19 vaccine for those 18 or older – despite some concerns over rare events of myocarditis and pericarditis.
The tally was 21 “yes” votes, without any “no” votes, but one abstention from a panelist who then offered a largely positive take on this vaccine.
Panelist Bruce Gellin, MD, explained at the end of the meeting that he would have cast a conditional vote in favor of the Novavax vaccine, called NVX-CoV2373, had that been an option. Dr. Gellin, chief of global public health strategy for the Rockefeller Foundation and a vaccine expert, said he didn’t want his abstention to be considered as signaling opposition to the Novavax shot.
Instead, he said, he expects FDA officials will gather more data and evidence about the Novavax vaccine, especially in relation to certain manufacturing issues, before making its decision on the company’s application.
Earlier in the day, a top FDA vaccine reviewer, Doran Fink, MD, PhD, noted that there were important manufacturing differences between the Novavax vaccine supply used in different projects, complicating efforts to assess the company’s application for emergency use authorization (EUA).
But Dr. Fink noted that the FDA staff already had made a convincing case in its briefing document, with enough evidence for an initial conditional clearance to be found in available data.
The FDA is not bound to follow the suggestions of its advisory committees but it often does.
Using the ‘bully pulpit’
At the beginning of the meeting, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said he was seizing the “bully pulpit” in addressing the need to persuade more people in the United States to take shots against COVID-19.
About 67% of people in the United States aged 18 and older are fully vaccinated, but only about 50% of those in this group have had a first booster, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The two-dose mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna have been the subject of intense misinformation campaigns on social media, despite efforts by the FDA and other public health officials to convey the message about their strong benefit-risk profile. The FDA in May limited the authorized use of Johnson & Johnson’s single-dose COVID-19 shot, which is based on a different technology, because of concerns about rare and potentially life-threatening blood clots.
Novavax has been described as a more traditional vaccine – a protein subunit shot similar to one people have long received for protection against influenza, pertussis (whooping cough), diphtheria, and tetanus.
“Having a protein-based alternative may be more comfortable for some in terms of their acceptance of vaccines,” Dr. Marks said. “We do have a problem with vaccine uptake that is very serious in the United States. And anything we can do to get people more comfortable to be able to accept these potentially life-saving medical products is something that we feel we are compelled to do.”
Dr. Marks offered these remarks in answer to an FDA panelist’s question about the need to consider an EUA for yet another vaccine.
EUAs are special clearances the FDA can grant in connection with public health emergencies such as the pandemic. The FDA used EUAs for the initial December 2020 clearances of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. It has since granted normal approvals for both of these mRNA-based vaccines, based on larger bodies of evidence gathered and submitted by their developers.
During the meeting, the FDA panelists in general appeared comfortable with the idea of granting another EUA for a vaccine. There was agreement that the shot appeared to work in key tests, although these were done before the rise of the Omicron variant.
In a key test, known as study 301, the Novavax vaccine was judged to be 90.4% effective. In the study, 17 of the 17,272 people who got the Novavax vaccine developed COVID-19, compared with 79 of the 8,385 in the placebo group.
Panelists expressed disappointment with the lack of information about how the shot would work now.
“We’re looking at the efficacy against strains that don’t exist any longer,” said panelist Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, a Harvard professor and editor of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Still, Dr. Rubin added that he agreed with the argument the FDA’s Dr. Marks had made earlier for an EUA for the Novavax vaccine.
“If there really is a population of patients who are willing to take this and not willing to take the existing vaccines, I think it’s pretty compelling,” Dr. Rubin said.
Other FDA panelists were skeptical of this argument. Jay Portnoy, MD, who was listed on the FDA roster as the panel’s consumer representative, said he has close friends who are vaccine skeptics.
“Their hesitancy is more ideological than technological,” said Dr. Portnoy of Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo. “So I really doubt that this vaccine is going to crack that nut, but perhaps some individuals would get this when they wouldn’t get the other ones.”
Myocarditis, pericarditis
The Novavax vaccine is already authorized in other countries, including Canada. Novavax in February announced that it had begun shipping its first doses of the vaccine to European Union member states. The vaccine can be moved through existing vaccine supply and cold chain channels instead of requiring complex new delivery procedures.
That could prove an advantage in time, said FDA panelist Michael Nelson, MD, PhD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Who knows even with supply chain challenges down the road, it will be nice to have options going forward,” Dr. Nelson said.
As with other COVID-19 vaccines, clinicians and researchers are still working to understand the potential risk for inflammation of heart muscle and nearby tissue with vaccination. Most patients with myocarditis or pericarditis who sought medical care for these conditions responded well to medicine and rest and felt better quickly, the CDC says on its website. They usually return to their normal daily activities after their symptoms improve.
At the June 7 meeting, Dr. Nelson said there may be cases of myocarditis that go undetected.
“Our signals are those who get admitted to the emergency room and the hospital,” he said. “I’m quite convinced that there are others who are experiencing cardiac events of lesser severity that are worthy of being studied, both from mechanistic and outcomes standpoints. So we have a lot of work to do.”
In looking at results for an initial pool of 40,000 people who received the Novavax vaccine, there were five reported cases of myocarditis or pericarditis developing within 20 days of people getting the shot, the FDA staff said in its presentation on safety.
In a briefing document released ahead of the advisory committee meeting, the FDA staff flagged this number of cases in a relatively small database as a concern, noting it “could be higher than reported during postauthorization use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (for which no cases were identified in preauthorization evaluation).”
Novavax officials took a somewhat unusual step of responding in public. The Gaithersburg, Md.–based company on June 3 issued a statement saying researchers had come to “expect to see natural background events of myocarditis in any sufficiently large database, and that young males are at higher risk.”
The data from the company’s placebo-controlled studies show that, overall, in its clinical development program, the rate of myocarditis was balanced between the vaccine and placebo arms (0.007% and 0.005%), Novavax said.
At the June 7 meeting, FDA panelists including Dr. Nelson, and Paul A. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, urged continued study to try to determine whether and how the vaccines could trigger myocarditis. Investments made now in pursuing these questions related to COVID-19 shots may pay off later, Dr. Offit said.
“We can use that knowledge to make safer vaccines for a disease that is going to be with us for decades, if not longer,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
than the cutting-edge technology used in mRNA-based shots.
The Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration voted almost unanimously June 7 in favor of Novavax’s two-dose COVID-19 vaccine for those 18 or older – despite some concerns over rare events of myocarditis and pericarditis.
The tally was 21 “yes” votes, without any “no” votes, but one abstention from a panelist who then offered a largely positive take on this vaccine.
Panelist Bruce Gellin, MD, explained at the end of the meeting that he would have cast a conditional vote in favor of the Novavax vaccine, called NVX-CoV2373, had that been an option. Dr. Gellin, chief of global public health strategy for the Rockefeller Foundation and a vaccine expert, said he didn’t want his abstention to be considered as signaling opposition to the Novavax shot.
Instead, he said, he expects FDA officials will gather more data and evidence about the Novavax vaccine, especially in relation to certain manufacturing issues, before making its decision on the company’s application.
Earlier in the day, a top FDA vaccine reviewer, Doran Fink, MD, PhD, noted that there were important manufacturing differences between the Novavax vaccine supply used in different projects, complicating efforts to assess the company’s application for emergency use authorization (EUA).
But Dr. Fink noted that the FDA staff already had made a convincing case in its briefing document, with enough evidence for an initial conditional clearance to be found in available data.
The FDA is not bound to follow the suggestions of its advisory committees but it often does.
Using the ‘bully pulpit’
At the beginning of the meeting, Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said he was seizing the “bully pulpit” in addressing the need to persuade more people in the United States to take shots against COVID-19.
About 67% of people in the United States aged 18 and older are fully vaccinated, but only about 50% of those in this group have had a first booster, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The two-dose mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna have been the subject of intense misinformation campaigns on social media, despite efforts by the FDA and other public health officials to convey the message about their strong benefit-risk profile. The FDA in May limited the authorized use of Johnson & Johnson’s single-dose COVID-19 shot, which is based on a different technology, because of concerns about rare and potentially life-threatening blood clots.
Novavax has been described as a more traditional vaccine – a protein subunit shot similar to one people have long received for protection against influenza, pertussis (whooping cough), diphtheria, and tetanus.
“Having a protein-based alternative may be more comfortable for some in terms of their acceptance of vaccines,” Dr. Marks said. “We do have a problem with vaccine uptake that is very serious in the United States. And anything we can do to get people more comfortable to be able to accept these potentially life-saving medical products is something that we feel we are compelled to do.”
Dr. Marks offered these remarks in answer to an FDA panelist’s question about the need to consider an EUA for yet another vaccine.
EUAs are special clearances the FDA can grant in connection with public health emergencies such as the pandemic. The FDA used EUAs for the initial December 2020 clearances of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. It has since granted normal approvals for both of these mRNA-based vaccines, based on larger bodies of evidence gathered and submitted by their developers.
During the meeting, the FDA panelists in general appeared comfortable with the idea of granting another EUA for a vaccine. There was agreement that the shot appeared to work in key tests, although these were done before the rise of the Omicron variant.
In a key test, known as study 301, the Novavax vaccine was judged to be 90.4% effective. In the study, 17 of the 17,272 people who got the Novavax vaccine developed COVID-19, compared with 79 of the 8,385 in the placebo group.
Panelists expressed disappointment with the lack of information about how the shot would work now.
“We’re looking at the efficacy against strains that don’t exist any longer,” said panelist Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, a Harvard professor and editor of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Still, Dr. Rubin added that he agreed with the argument the FDA’s Dr. Marks had made earlier for an EUA for the Novavax vaccine.
“If there really is a population of patients who are willing to take this and not willing to take the existing vaccines, I think it’s pretty compelling,” Dr. Rubin said.
Other FDA panelists were skeptical of this argument. Jay Portnoy, MD, who was listed on the FDA roster as the panel’s consumer representative, said he has close friends who are vaccine skeptics.
“Their hesitancy is more ideological than technological,” said Dr. Portnoy of Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo. “So I really doubt that this vaccine is going to crack that nut, but perhaps some individuals would get this when they wouldn’t get the other ones.”
Myocarditis, pericarditis
The Novavax vaccine is already authorized in other countries, including Canada. Novavax in February announced that it had begun shipping its first doses of the vaccine to European Union member states. The vaccine can be moved through existing vaccine supply and cold chain channels instead of requiring complex new delivery procedures.
That could prove an advantage in time, said FDA panelist Michael Nelson, MD, PhD, of the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Who knows even with supply chain challenges down the road, it will be nice to have options going forward,” Dr. Nelson said.
As with other COVID-19 vaccines, clinicians and researchers are still working to understand the potential risk for inflammation of heart muscle and nearby tissue with vaccination. Most patients with myocarditis or pericarditis who sought medical care for these conditions responded well to medicine and rest and felt better quickly, the CDC says on its website. They usually return to their normal daily activities after their symptoms improve.
At the June 7 meeting, Dr. Nelson said there may be cases of myocarditis that go undetected.
“Our signals are those who get admitted to the emergency room and the hospital,” he said. “I’m quite convinced that there are others who are experiencing cardiac events of lesser severity that are worthy of being studied, both from mechanistic and outcomes standpoints. So we have a lot of work to do.”
In looking at results for an initial pool of 40,000 people who received the Novavax vaccine, there were five reported cases of myocarditis or pericarditis developing within 20 days of people getting the shot, the FDA staff said in its presentation on safety.
In a briefing document released ahead of the advisory committee meeting, the FDA staff flagged this number of cases in a relatively small database as a concern, noting it “could be higher than reported during postauthorization use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (for which no cases were identified in preauthorization evaluation).”
Novavax officials took a somewhat unusual step of responding in public. The Gaithersburg, Md.–based company on June 3 issued a statement saying researchers had come to “expect to see natural background events of myocarditis in any sufficiently large database, and that young males are at higher risk.”
The data from the company’s placebo-controlled studies show that, overall, in its clinical development program, the rate of myocarditis was balanced between the vaccine and placebo arms (0.007% and 0.005%), Novavax said.
At the June 7 meeting, FDA panelists including Dr. Nelson, and Paul A. Offit, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, urged continued study to try to determine whether and how the vaccines could trigger myocarditis. Investments made now in pursuing these questions related to COVID-19 shots may pay off later, Dr. Offit said.
“We can use that knowledge to make safer vaccines for a disease that is going to be with us for decades, if not longer,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Cases down, start of vaccinations near
The first decline in COVID-19 cases among children since early April may have been holiday related, but the shortened week also brought news about vaccination for the youngest children.
The Food and Drug Administration has accepted Pfizer’s application for a COVID-19 vaccine for children under age 5, so vaccination could begin as early as June 21, according to White House COVID-19 response coordinator Ashish Jha, MD.
“We know that many, many parents are eager to vaccinate their youngest kids and it’s important to do this right,” Dr. Jha said at a White House press briefing June 2. “We expect that vaccinations will begin in earnest as early as June 21 and really roll on throughout that week.”
Decline may just be underreporting
Over on the incidence side of the pandemic, “Testing and reporting may have been affected by the holiday weekend [since] states may change their reporting schedules, which may cause irregularities in trends,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital association said in their latest COVID report.
The decline in new cases was not spread uniformly across the four major regions of the United States. The count actually went up in the West for the week of May 27 to June 2, while the South saw the largest decline. The Midwest and Northeast, meanwhile, saw new cases drop for the second straight week, the AAP and CHA said.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was up to 13.45 million as of June 2, with children representing 18.9% of all cases since the start of the pandemic, according to the two organizations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported figures of 13.14 million and 17.5% on June 6.
The AAP/CHA estimates, however, are based on state data that have become increasingly hard to obtain and subject to inconsistency. “Shortages of COVID-19 tests during surges and the increasing use of COVID-19 home tests likely affect the undercounting of COVID-19 cases,” they noted, and “at times when COVID-19 transmission is low, states might reduce the frequency information is updated.”
Vaccinations held steady over the holiday
The ongoing vaccination effort in children aged 5 years and older did not show a Memorial Day drop-off, as initial vaccinations held at 43,000 in 5- to 11-year-olds and at 27,000 in 12- to 17-year-olds for a second consecutive week. That number has ranged from 34,000 to 70,000 for the younger children and from 25,000 to 47,000 for the older group since mid-March, the AAP said in a separate weekly report.
Despite weekly vaccine initiations that have been roughly double those of the older children for months, the 5- to 11-year-olds are still only at 36.0% coverage with at least one dose, compared with 69.5% for the 12- to-17-year-olds. Full vaccination for the two age groups comes in at 29.3% and 59.6%, respectively, as of June 6, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The first decline in COVID-19 cases among children since early April may have been holiday related, but the shortened week also brought news about vaccination for the youngest children.
The Food and Drug Administration has accepted Pfizer’s application for a COVID-19 vaccine for children under age 5, so vaccination could begin as early as June 21, according to White House COVID-19 response coordinator Ashish Jha, MD.
“We know that many, many parents are eager to vaccinate their youngest kids and it’s important to do this right,” Dr. Jha said at a White House press briefing June 2. “We expect that vaccinations will begin in earnest as early as June 21 and really roll on throughout that week.”
Decline may just be underreporting
Over on the incidence side of the pandemic, “Testing and reporting may have been affected by the holiday weekend [since] states may change their reporting schedules, which may cause irregularities in trends,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital association said in their latest COVID report.
The decline in new cases was not spread uniformly across the four major regions of the United States. The count actually went up in the West for the week of May 27 to June 2, while the South saw the largest decline. The Midwest and Northeast, meanwhile, saw new cases drop for the second straight week, the AAP and CHA said.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was up to 13.45 million as of June 2, with children representing 18.9% of all cases since the start of the pandemic, according to the two organizations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported figures of 13.14 million and 17.5% on June 6.
The AAP/CHA estimates, however, are based on state data that have become increasingly hard to obtain and subject to inconsistency. “Shortages of COVID-19 tests during surges and the increasing use of COVID-19 home tests likely affect the undercounting of COVID-19 cases,” they noted, and “at times when COVID-19 transmission is low, states might reduce the frequency information is updated.”
Vaccinations held steady over the holiday
The ongoing vaccination effort in children aged 5 years and older did not show a Memorial Day drop-off, as initial vaccinations held at 43,000 in 5- to 11-year-olds and at 27,000 in 12- to 17-year-olds for a second consecutive week. That number has ranged from 34,000 to 70,000 for the younger children and from 25,000 to 47,000 for the older group since mid-March, the AAP said in a separate weekly report.
Despite weekly vaccine initiations that have been roughly double those of the older children for months, the 5- to 11-year-olds are still only at 36.0% coverage with at least one dose, compared with 69.5% for the 12- to-17-year-olds. Full vaccination for the two age groups comes in at 29.3% and 59.6%, respectively, as of June 6, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The first decline in COVID-19 cases among children since early April may have been holiday related, but the shortened week also brought news about vaccination for the youngest children.
The Food and Drug Administration has accepted Pfizer’s application for a COVID-19 vaccine for children under age 5, so vaccination could begin as early as June 21, according to White House COVID-19 response coordinator Ashish Jha, MD.
“We know that many, many parents are eager to vaccinate their youngest kids and it’s important to do this right,” Dr. Jha said at a White House press briefing June 2. “We expect that vaccinations will begin in earnest as early as June 21 and really roll on throughout that week.”
Decline may just be underreporting
Over on the incidence side of the pandemic, “Testing and reporting may have been affected by the holiday weekend [since] states may change their reporting schedules, which may cause irregularities in trends,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital association said in their latest COVID report.
The decline in new cases was not spread uniformly across the four major regions of the United States. The count actually went up in the West for the week of May 27 to June 2, while the South saw the largest decline. The Midwest and Northeast, meanwhile, saw new cases drop for the second straight week, the AAP and CHA said.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was up to 13.45 million as of June 2, with children representing 18.9% of all cases since the start of the pandemic, according to the two organizations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported figures of 13.14 million and 17.5% on June 6.
The AAP/CHA estimates, however, are based on state data that have become increasingly hard to obtain and subject to inconsistency. “Shortages of COVID-19 tests during surges and the increasing use of COVID-19 home tests likely affect the undercounting of COVID-19 cases,” they noted, and “at times when COVID-19 transmission is low, states might reduce the frequency information is updated.”
Vaccinations held steady over the holiday
The ongoing vaccination effort in children aged 5 years and older did not show a Memorial Day drop-off, as initial vaccinations held at 43,000 in 5- to 11-year-olds and at 27,000 in 12- to 17-year-olds for a second consecutive week. That number has ranged from 34,000 to 70,000 for the younger children and from 25,000 to 47,000 for the older group since mid-March, the AAP said in a separate weekly report.
Despite weekly vaccine initiations that have been roughly double those of the older children for months, the 5- to 11-year-olds are still only at 36.0% coverage with at least one dose, compared with 69.5% for the 12- to-17-year-olds. Full vaccination for the two age groups comes in at 29.3% and 59.6%, respectively, as of June 6, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Immunosuppressed rheumatic patients not at high risk of breakthrough COVID-19
COPENHAGEN – Most patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) should not be considered at high risk for severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections, but those on anti-CD20 therapy are the exception, data from a large prospective, cohort study show.
“Overall, the data are reassuring, with conventional risk factors, such as age, and comorbidities seeming to be more important regarding risk of severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections than rheumatic disease or immunosuppressant medication,” said Laura Boekel, MD, from Amsterdam UMC, who presented the study at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
But, she added, there was an exception for anti-CD20 therapy. “This is especially relevant for patients with conventional risk factors that might accumulate, and rheumatologists might want to consider alternative treatment options if possible. It is important to inform patients about the risks of anti-CD20.”
Another study, presented during the same session at the congress by Rebecca Hasseli, MD, from the University of Giessen (Germany) saw no deaths and no COVID-19 related complications in a cohort of triple-vaccinated patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases, despite a higher median age and a higher rate of comorbidities compared to double-vaccinated and unvaccinated cohorts.
Ingrid Jyssum, MD, from Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, who presented results of the Nor-vaC study investigating the impact of different DMARDs on the immunogenicity of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose, welcomed the research by Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli.
“The findings of Hasseli are interesting in the light of our data on serological response after the third dose, with a lack of breakthrough infections after three doses corresponding well to the robust antibody response that we found in our cohort,” she remarked. “This is very reassuring for our patients. Our own work together with the findings of Hasseli and Boekel demonstrate that additional vaccine doses are important to keep this population well protected against severe COVID-19 infections.”
The Nor-vaC study was conducted with a cohort of 1,100 patients with inflammatory joint and bowel diseases. “These patients had attenuated antibody responses after two vaccine doses; however, we found that a third vaccine dose brought the humoral response in patients up to the antibody levels that healthy controls had after two doses,” said Dr. Jyssum. “In addition, we found that the decline in antibodies after the third dose was less than the decline seen after the second dose. Importantly, the third dose was safe in our patients, with no new safety issues.”
Breakthrough infections and immunosuppressants
“Like the rest of the world, we were wondering if our patients were at increased risk of COVID-19, and if the immunosuppressants used by these patients influenced their risk,” said Dr. Boekel.
The researchers compared both the incidence and severity of COVID-19 breakthrough infections with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a population of fully vaccinated IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls (IMID patients not taking immunosuppressants and healthy controls).
Two large ongoing, prospective, multicenter cohort studies provided pooled data collected between February and December 2021 using digital questionnaires, standardized electronic case record forms, and medical files.
Finger-prick tests were used to collect blood samples that were analyzed after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 for anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) antibodies, and antinucleocapsid antibodies to identify asymptomatic breakthrough infections. Any associations between antibodies and the incidence of breakthrough infections were generated, and results were adjusted for sex, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, obesity, and vaccine type.
The analysis included 3,207 IMID patients taking immunosuppressants, and 1,810 controls (985 IMID patients not on immunosuppressants and 825 healthy controls).
Initially, Dr. Boekel and her colleagues looked at incidence of infections and hospitalizations prior to vaccination, and then after vaccination, which was the main aim of the study.
Prior to vaccination, hospitalization risk for COVID-19 was somewhat higher for IMID patients overall compared with controls, reported Dr. Boekel. “But those treated with anti-CD20 therapy, demonstrated much greater risk for severe disease.”
After the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination campaign began, the researchers then looked at how immunosuppressants influenced humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
“Anti-CD20 therapy showed the greatest impact on humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” said Dr. Boekel. Other immunosuppressant drugs had variable effects on humoral and cellular immunity.
Once they had established that immunosuppressant drugs impaired immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the researchers wanted to determine if this affected clinical outcomes. Blood samples taken 28 days after the second vaccination enabled Dr. Boekel and her colleagues to see if antibody production was associated with breakthrough infections.
Breakthrough infections were seen in 5% of patients on immunosuppressants, 5% of patients not on immunosuppressants, and 4% of healthy controls. Also, asymptomatic COVID-19 breakthrough cases were comparable between IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls, at 10% in each group.
“We saw that the incidence [of getting COVID-19] was comparable between groups, independent of whether they were receiving immunosuppressants or not, or healthy controls. However, if they developed antibodies against the two vaccinations the chance of getting infected was lower,” reported Dr. Boekel.
Hospitalization (severe disease) rates were also comparable between groups. “Patients with rheumatic diseases, even when treated with immunosuppressants were not at increased risk of severe disease from Delta breakthrough infections,” added the researcher. “Cases that were hospitalized were mainly elderly and those with comorbidities, for example cardiovascular disease and cardiopulmonary disease.”
Hospital admissions were 5.4% in patients on immunosuppressants, 5.7% in those not on immunosuppressants, and 6% in health controls.
However, once again, there was one exception, Dr. Boekel stressed. “Patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy were at increased risk of severe disease and hospitalization.”
Omicron variant has a different transmissibility than Delta, so the researchers continued the study looking at the Omicron variant. The data “were mostly reassuring,” said Dr. Boekel. “As expected, hospitalization rates decreased overall, with the exception of patients on anti-CD20 therapy where, despite overall reduced pathogenicity, patients remain at increased risk.”
She said that they were awaiting long-term data so the data reflect only short-term immunity against Omicron. “However, we included many elderly and patients with comorbidities, so this made the analysis very sensitive to detect severe cases,” she added.
Breakthrough infection among double- and triple-vaccinated patients
A lower rate of COVID-19 related complications and deaths were seen in patients who were triple-vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, than in double-vaccinated or unvaccinated patients, despite the former having more comorbidities and use of rituximab (Rituxan), said Dr. Hasseli.
“These data support the recommendation of booster vaccination to reduce COVID-19-related mortality in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRDs],” she said.
“A small number of COVID-19 cases were seen in patients with IRD after vaccinations, and in a few cases, hospitalizations were required. Breakthrough infections were mostly seen in patients on B-cell depletion therapy,” she added.
Dr. Hasseli and her colleagues looked at the characteristics and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among double- and triple-vaccinated patients with IRD.
“We wanted to understand if patients with IRD are protected in the same way as the general population following vaccination, given that these patients receive drugs that might impair the immune response,” she explained.
Data for analysis were drawn from the German COVID-19-IRD registry covering February 2021 and January 2022, and patients who were double- or triple- vaccinated against COVID-19 either 14 days or more prior to a SARS-CoV-2 infection were included. Type of IRD, vaccine, immunomodulation, comorbidities, and outcome of the infection were compared with 737 unvaccinated IRD patients with COVID-19. Those with prior COVID-19 were excluded.
Cases were stratified by vaccinations status: unvaccinated (1,388 patients, median age 57 years); double vaccinated (462, 56 years) and triple vaccinated (301, 53 years). Body mass index was similar across groups (25-26 kg/m2), and time between SARS-CoV-2 infection and last vaccination was 156 days in double-vaccinated patients, and 62 days in triple-vaccinated patients.
Patients had rheumatoid arthritis in 44.7% and 44.4% of unvaccinated and double-vaccinated patients respectively, but fewer triple-vaccinated patients had RA (37.2%). Triple vaccination was seen in 32.2% of patients with spondyloarthritis, 16.6% connective tissue diseases, 5.3% other vasculitis, and 3.3% ANCA-associated vasculitis. Of triple-vaccinated patients, 26.2% were treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, and 6.3% with rituximab, while 5.3% were not on immunomodulation. At least 25% were treated with glucocorticoids, reported Dr. Hasseli.
“Arterial hypertension and diabetes, that might be risk factors for COVID-19, were less frequently reported in triple-vaccinated patients. More patients in the double-vaccinated group [42.9%] than the triple-vaccinated [23.8%] reported absence of relevant comorbidities,” she said.
COVID-19 related complications were less often reported in double- and triple-vaccinated groups with hospitalizations at 9.5% and 4.3% in double and triple-vaccinated people respectively.
Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli report no relevant conflicts of interest.
COPENHAGEN – Most patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) should not be considered at high risk for severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections, but those on anti-CD20 therapy are the exception, data from a large prospective, cohort study show.
“Overall, the data are reassuring, with conventional risk factors, such as age, and comorbidities seeming to be more important regarding risk of severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections than rheumatic disease or immunosuppressant medication,” said Laura Boekel, MD, from Amsterdam UMC, who presented the study at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
But, she added, there was an exception for anti-CD20 therapy. “This is especially relevant for patients with conventional risk factors that might accumulate, and rheumatologists might want to consider alternative treatment options if possible. It is important to inform patients about the risks of anti-CD20.”
Another study, presented during the same session at the congress by Rebecca Hasseli, MD, from the University of Giessen (Germany) saw no deaths and no COVID-19 related complications in a cohort of triple-vaccinated patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases, despite a higher median age and a higher rate of comorbidities compared to double-vaccinated and unvaccinated cohorts.
Ingrid Jyssum, MD, from Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, who presented results of the Nor-vaC study investigating the impact of different DMARDs on the immunogenicity of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose, welcomed the research by Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli.
“The findings of Hasseli are interesting in the light of our data on serological response after the third dose, with a lack of breakthrough infections after three doses corresponding well to the robust antibody response that we found in our cohort,” she remarked. “This is very reassuring for our patients. Our own work together with the findings of Hasseli and Boekel demonstrate that additional vaccine doses are important to keep this population well protected against severe COVID-19 infections.”
The Nor-vaC study was conducted with a cohort of 1,100 patients with inflammatory joint and bowel diseases. “These patients had attenuated antibody responses after two vaccine doses; however, we found that a third vaccine dose brought the humoral response in patients up to the antibody levels that healthy controls had after two doses,” said Dr. Jyssum. “In addition, we found that the decline in antibodies after the third dose was less than the decline seen after the second dose. Importantly, the third dose was safe in our patients, with no new safety issues.”
Breakthrough infections and immunosuppressants
“Like the rest of the world, we were wondering if our patients were at increased risk of COVID-19, and if the immunosuppressants used by these patients influenced their risk,” said Dr. Boekel.
The researchers compared both the incidence and severity of COVID-19 breakthrough infections with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a population of fully vaccinated IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls (IMID patients not taking immunosuppressants and healthy controls).
Two large ongoing, prospective, multicenter cohort studies provided pooled data collected between February and December 2021 using digital questionnaires, standardized electronic case record forms, and medical files.
Finger-prick tests were used to collect blood samples that were analyzed after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 for anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) antibodies, and antinucleocapsid antibodies to identify asymptomatic breakthrough infections. Any associations between antibodies and the incidence of breakthrough infections were generated, and results were adjusted for sex, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, obesity, and vaccine type.
The analysis included 3,207 IMID patients taking immunosuppressants, and 1,810 controls (985 IMID patients not on immunosuppressants and 825 healthy controls).
Initially, Dr. Boekel and her colleagues looked at incidence of infections and hospitalizations prior to vaccination, and then after vaccination, which was the main aim of the study.
Prior to vaccination, hospitalization risk for COVID-19 was somewhat higher for IMID patients overall compared with controls, reported Dr. Boekel. “But those treated with anti-CD20 therapy, demonstrated much greater risk for severe disease.”
After the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination campaign began, the researchers then looked at how immunosuppressants influenced humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
“Anti-CD20 therapy showed the greatest impact on humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” said Dr. Boekel. Other immunosuppressant drugs had variable effects on humoral and cellular immunity.
Once they had established that immunosuppressant drugs impaired immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the researchers wanted to determine if this affected clinical outcomes. Blood samples taken 28 days after the second vaccination enabled Dr. Boekel and her colleagues to see if antibody production was associated with breakthrough infections.
Breakthrough infections were seen in 5% of patients on immunosuppressants, 5% of patients not on immunosuppressants, and 4% of healthy controls. Also, asymptomatic COVID-19 breakthrough cases were comparable between IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls, at 10% in each group.
“We saw that the incidence [of getting COVID-19] was comparable between groups, independent of whether they were receiving immunosuppressants or not, or healthy controls. However, if they developed antibodies against the two vaccinations the chance of getting infected was lower,” reported Dr. Boekel.
Hospitalization (severe disease) rates were also comparable between groups. “Patients with rheumatic diseases, even when treated with immunosuppressants were not at increased risk of severe disease from Delta breakthrough infections,” added the researcher. “Cases that were hospitalized were mainly elderly and those with comorbidities, for example cardiovascular disease and cardiopulmonary disease.”
Hospital admissions were 5.4% in patients on immunosuppressants, 5.7% in those not on immunosuppressants, and 6% in health controls.
However, once again, there was one exception, Dr. Boekel stressed. “Patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy were at increased risk of severe disease and hospitalization.”
Omicron variant has a different transmissibility than Delta, so the researchers continued the study looking at the Omicron variant. The data “were mostly reassuring,” said Dr. Boekel. “As expected, hospitalization rates decreased overall, with the exception of patients on anti-CD20 therapy where, despite overall reduced pathogenicity, patients remain at increased risk.”
She said that they were awaiting long-term data so the data reflect only short-term immunity against Omicron. “However, we included many elderly and patients with comorbidities, so this made the analysis very sensitive to detect severe cases,” she added.
Breakthrough infection among double- and triple-vaccinated patients
A lower rate of COVID-19 related complications and deaths were seen in patients who were triple-vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, than in double-vaccinated or unvaccinated patients, despite the former having more comorbidities and use of rituximab (Rituxan), said Dr. Hasseli.
“These data support the recommendation of booster vaccination to reduce COVID-19-related mortality in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRDs],” she said.
“A small number of COVID-19 cases were seen in patients with IRD after vaccinations, and in a few cases, hospitalizations were required. Breakthrough infections were mostly seen in patients on B-cell depletion therapy,” she added.
Dr. Hasseli and her colleagues looked at the characteristics and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among double- and triple-vaccinated patients with IRD.
“We wanted to understand if patients with IRD are protected in the same way as the general population following vaccination, given that these patients receive drugs that might impair the immune response,” she explained.
Data for analysis were drawn from the German COVID-19-IRD registry covering February 2021 and January 2022, and patients who were double- or triple- vaccinated against COVID-19 either 14 days or more prior to a SARS-CoV-2 infection were included. Type of IRD, vaccine, immunomodulation, comorbidities, and outcome of the infection were compared with 737 unvaccinated IRD patients with COVID-19. Those with prior COVID-19 were excluded.
Cases were stratified by vaccinations status: unvaccinated (1,388 patients, median age 57 years); double vaccinated (462, 56 years) and triple vaccinated (301, 53 years). Body mass index was similar across groups (25-26 kg/m2), and time between SARS-CoV-2 infection and last vaccination was 156 days in double-vaccinated patients, and 62 days in triple-vaccinated patients.
Patients had rheumatoid arthritis in 44.7% and 44.4% of unvaccinated and double-vaccinated patients respectively, but fewer triple-vaccinated patients had RA (37.2%). Triple vaccination was seen in 32.2% of patients with spondyloarthritis, 16.6% connective tissue diseases, 5.3% other vasculitis, and 3.3% ANCA-associated vasculitis. Of triple-vaccinated patients, 26.2% were treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, and 6.3% with rituximab, while 5.3% were not on immunomodulation. At least 25% were treated with glucocorticoids, reported Dr. Hasseli.
“Arterial hypertension and diabetes, that might be risk factors for COVID-19, were less frequently reported in triple-vaccinated patients. More patients in the double-vaccinated group [42.9%] than the triple-vaccinated [23.8%] reported absence of relevant comorbidities,” she said.
COVID-19 related complications were less often reported in double- and triple-vaccinated groups with hospitalizations at 9.5% and 4.3% in double and triple-vaccinated people respectively.
Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli report no relevant conflicts of interest.
COPENHAGEN – Most patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) should not be considered at high risk for severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections, but those on anti-CD20 therapy are the exception, data from a large prospective, cohort study show.
“Overall, the data are reassuring, with conventional risk factors, such as age, and comorbidities seeming to be more important regarding risk of severe COVID-19 breakthrough infections than rheumatic disease or immunosuppressant medication,” said Laura Boekel, MD, from Amsterdam UMC, who presented the study at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
But, she added, there was an exception for anti-CD20 therapy. “This is especially relevant for patients with conventional risk factors that might accumulate, and rheumatologists might want to consider alternative treatment options if possible. It is important to inform patients about the risks of anti-CD20.”
Another study, presented during the same session at the congress by Rebecca Hasseli, MD, from the University of Giessen (Germany) saw no deaths and no COVID-19 related complications in a cohort of triple-vaccinated patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases, despite a higher median age and a higher rate of comorbidities compared to double-vaccinated and unvaccinated cohorts.
Ingrid Jyssum, MD, from Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, who presented results of the Nor-vaC study investigating the impact of different DMARDs on the immunogenicity of a third COVID-19 vaccine dose, welcomed the research by Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli.
“The findings of Hasseli are interesting in the light of our data on serological response after the third dose, with a lack of breakthrough infections after three doses corresponding well to the robust antibody response that we found in our cohort,” she remarked. “This is very reassuring for our patients. Our own work together with the findings of Hasseli and Boekel demonstrate that additional vaccine doses are important to keep this population well protected against severe COVID-19 infections.”
The Nor-vaC study was conducted with a cohort of 1,100 patients with inflammatory joint and bowel diseases. “These patients had attenuated antibody responses after two vaccine doses; however, we found that a third vaccine dose brought the humoral response in patients up to the antibody levels that healthy controls had after two doses,” said Dr. Jyssum. “In addition, we found that the decline in antibodies after the third dose was less than the decline seen after the second dose. Importantly, the third dose was safe in our patients, with no new safety issues.”
Breakthrough infections and immunosuppressants
“Like the rest of the world, we were wondering if our patients were at increased risk of COVID-19, and if the immunosuppressants used by these patients influenced their risk,” said Dr. Boekel.
The researchers compared both the incidence and severity of COVID-19 breakthrough infections with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a population of fully vaccinated IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls (IMID patients not taking immunosuppressants and healthy controls).
Two large ongoing, prospective, multicenter cohort studies provided pooled data collected between February and December 2021 using digital questionnaires, standardized electronic case record forms, and medical files.
Finger-prick tests were used to collect blood samples that were analyzed after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 for anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) antibodies, and antinucleocapsid antibodies to identify asymptomatic breakthrough infections. Any associations between antibodies and the incidence of breakthrough infections were generated, and results were adjusted for sex, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, obesity, and vaccine type.
The analysis included 3,207 IMID patients taking immunosuppressants, and 1,810 controls (985 IMID patients not on immunosuppressants and 825 healthy controls).
Initially, Dr. Boekel and her colleagues looked at incidence of infections and hospitalizations prior to vaccination, and then after vaccination, which was the main aim of the study.
Prior to vaccination, hospitalization risk for COVID-19 was somewhat higher for IMID patients overall compared with controls, reported Dr. Boekel. “But those treated with anti-CD20 therapy, demonstrated much greater risk for severe disease.”
After the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination campaign began, the researchers then looked at how immunosuppressants influenced humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
“Anti-CD20 therapy showed the greatest impact on humoral immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” said Dr. Boekel. Other immunosuppressant drugs had variable effects on humoral and cellular immunity.
Once they had established that immunosuppressant drugs impaired immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the researchers wanted to determine if this affected clinical outcomes. Blood samples taken 28 days after the second vaccination enabled Dr. Boekel and her colleagues to see if antibody production was associated with breakthrough infections.
Breakthrough infections were seen in 5% of patients on immunosuppressants, 5% of patients not on immunosuppressants, and 4% of healthy controls. Also, asymptomatic COVID-19 breakthrough cases were comparable between IMID patients taking immunosuppressants and controls, at 10% in each group.
“We saw that the incidence [of getting COVID-19] was comparable between groups, independent of whether they were receiving immunosuppressants or not, or healthy controls. However, if they developed antibodies against the two vaccinations the chance of getting infected was lower,” reported Dr. Boekel.
Hospitalization (severe disease) rates were also comparable between groups. “Patients with rheumatic diseases, even when treated with immunosuppressants were not at increased risk of severe disease from Delta breakthrough infections,” added the researcher. “Cases that were hospitalized were mainly elderly and those with comorbidities, for example cardiovascular disease and cardiopulmonary disease.”
Hospital admissions were 5.4% in patients on immunosuppressants, 5.7% in those not on immunosuppressants, and 6% in health controls.
However, once again, there was one exception, Dr. Boekel stressed. “Patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy were at increased risk of severe disease and hospitalization.”
Omicron variant has a different transmissibility than Delta, so the researchers continued the study looking at the Omicron variant. The data “were mostly reassuring,” said Dr. Boekel. “As expected, hospitalization rates decreased overall, with the exception of patients on anti-CD20 therapy where, despite overall reduced pathogenicity, patients remain at increased risk.”
She said that they were awaiting long-term data so the data reflect only short-term immunity against Omicron. “However, we included many elderly and patients with comorbidities, so this made the analysis very sensitive to detect severe cases,” she added.
Breakthrough infection among double- and triple-vaccinated patients
A lower rate of COVID-19 related complications and deaths were seen in patients who were triple-vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, than in double-vaccinated or unvaccinated patients, despite the former having more comorbidities and use of rituximab (Rituxan), said Dr. Hasseli.
“These data support the recommendation of booster vaccination to reduce COVID-19-related mortality in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [IRDs],” she said.
“A small number of COVID-19 cases were seen in patients with IRD after vaccinations, and in a few cases, hospitalizations were required. Breakthrough infections were mostly seen in patients on B-cell depletion therapy,” she added.
Dr. Hasseli and her colleagues looked at the characteristics and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections among double- and triple-vaccinated patients with IRD.
“We wanted to understand if patients with IRD are protected in the same way as the general population following vaccination, given that these patients receive drugs that might impair the immune response,” she explained.
Data for analysis were drawn from the German COVID-19-IRD registry covering February 2021 and January 2022, and patients who were double- or triple- vaccinated against COVID-19 either 14 days or more prior to a SARS-CoV-2 infection were included. Type of IRD, vaccine, immunomodulation, comorbidities, and outcome of the infection were compared with 737 unvaccinated IRD patients with COVID-19. Those with prior COVID-19 were excluded.
Cases were stratified by vaccinations status: unvaccinated (1,388 patients, median age 57 years); double vaccinated (462, 56 years) and triple vaccinated (301, 53 years). Body mass index was similar across groups (25-26 kg/m2), and time between SARS-CoV-2 infection and last vaccination was 156 days in double-vaccinated patients, and 62 days in triple-vaccinated patients.
Patients had rheumatoid arthritis in 44.7% and 44.4% of unvaccinated and double-vaccinated patients respectively, but fewer triple-vaccinated patients had RA (37.2%). Triple vaccination was seen in 32.2% of patients with spondyloarthritis, 16.6% connective tissue diseases, 5.3% other vasculitis, and 3.3% ANCA-associated vasculitis. Of triple-vaccinated patients, 26.2% were treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, and 6.3% with rituximab, while 5.3% were not on immunomodulation. At least 25% were treated with glucocorticoids, reported Dr. Hasseli.
“Arterial hypertension and diabetes, that might be risk factors for COVID-19, were less frequently reported in triple-vaccinated patients. More patients in the double-vaccinated group [42.9%] than the triple-vaccinated [23.8%] reported absence of relevant comorbidities,” she said.
COVID-19 related complications were less often reported in double- and triple-vaccinated groups with hospitalizations at 9.5% and 4.3% in double and triple-vaccinated people respectively.
Dr. Boekel and Dr. Hasseli report no relevant conflicts of interest.
AT THE EULAR 2022 CONGRESS