User login
Fecal Immunochemical Test Performance for CRC Screening Varies Widely
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a comparative performance analysis of five commonly used FITs for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening, researchers found statistically significant differences in positivity rates, sensitivity, and specificity, as well as important differences in rates of unusable tests.
“Our findings have practical importance for FIT-based screening programs as these differences affect the need for repeated FIT, the yield of ACN detection, and the number of diagnostic colonoscopies that would be required to follow-up on abnormal findings,” wrote the researchers, led by Barcey T. Levy, MD, PhD, with University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Wide Variation Found
Despite widespread use of FITs for CRC screening, there is limited data to help guide test selection. Understanding the comparative performance of different FITs is “crucial” for a successful FIT-based screening program, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Levy and colleagues directly compared the performance of five commercially available FITs — including four qualitative tests (Hemoccult ICT, Hemosure iFOB, OC-Light S FIT, and QuickVue iFOB) and one quantitative test (OC-Auto FIT) — using colonoscopy as the reference standard.
Participants included a diverse group of 3761 adults (mean age, 62 years; 63% women). Each participant was given all five tests and completed them using the same stool sample. They sent the tests by first class mail to a central location, where FITs were analyzed by a trained professional on the day of receipt.
The primary outcome was test performance (sensitivity and specificity) for ACN, defined as advanced polyps or CRC.
A total of 320 participants (8.5%) were found to have ACN based on colonoscopy results, including nine with CRC (0.2%) — rates that are similar to those found in other studies.
The sensitivity for detecting ACN ranged from 10.1% (Hemoccult ICT) to 36.7% (OC-Light S FIT), and specificity varied from 85.5% (OC-Light S FIT) to 96.6% (Hemoccult ICT).
“Given the variation in FIT cutoffs reported by manufacturers, it is not surprising that tests with lower cutoffs (such as OC-Light S FIT) had higher sensitivity than tests with higher cutoffs (such as Hemoccult ICT),” Dr. Levy and colleagues wrote.
Test positivity rates varied fourfold across FITs, from 3.9% for Hemoccult ICT to 16.4% for OC-Light S FIT.
The rates of tests deemed unevaluable (due to factors such as indeterminant results or user mistakes) ranged from 0.2% for OC-Auto FIT to 2.5% for QuickVue iFOB.
The highest positive predictive value (PPV) was observed with OC-Auto FIT (28.9%) and the lowest with Hemosure iFOB (18.2%). The negative predictive value was similar across tests, ranging from 92.2% to 93.3%, indicating consistent performance in ruling out disease.
The study also identified significant differences in test sensitivity based on factors such as the location of neoplasia (higher sensitivity for distal lesions) and patient characteristics (higher sensitivity in people with higher body mass index and lower income).
Dr. Levy and colleagues said their findings have implications both in terms of clinical benefits and cost-effectiveness of CRC screening using FITs.
“Tests with lower sensitivity will miss more patients with CRC and advanced polyps, and tests with higher sensitivity and lower PPV will require more colonoscopies to detect patients with actionable findings,” they wrote.
‘Jaw-Dropping’ Results
The sensitivity results are “jaw-dropping,” Robert Smith, PhD, senior vice-president for cancer screening at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “A patient should have at least a 50/50 chance of having their colorectal cancer detected with a stool test at the time of testing.”
“What these numbers show is that the level that the manufacturers believe their test is performing is not reproduced,” Dr. Smith added.
This study adds to “concerns that have been raised about the inherent limitations and the performance of these tests that have been cleared for use and that are supposed to be lifesaving,” he said.
Clearance by the US Food and Drug Administration should mean that there’s essentially “no risk to using the test in terms of the test itself being harmful,” Dr. Smith said. But that’s not the case with FITs “because it’s harmful if you have cancer and your test doesn’t find it.”
By way of study limitations, Dr. Levy and colleagues said it’s important to note that they did not evaluate the “programmatic” sensitivity of repeating FIT testing every 1-2 years, as is generally recommended in screening guidelines. Therefore, the sensitivity of a single FIT may be lower than that of a repeated FIT. Also, variability in the FIT collection process by participants might have affected the results.
The study had no commercial funding. Disclosures for authors are available with the original article. Dr. Smith had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Short Interval Repeat Colonoscopy After Inadequate Bowel Preparation Is Low Among Veterans
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
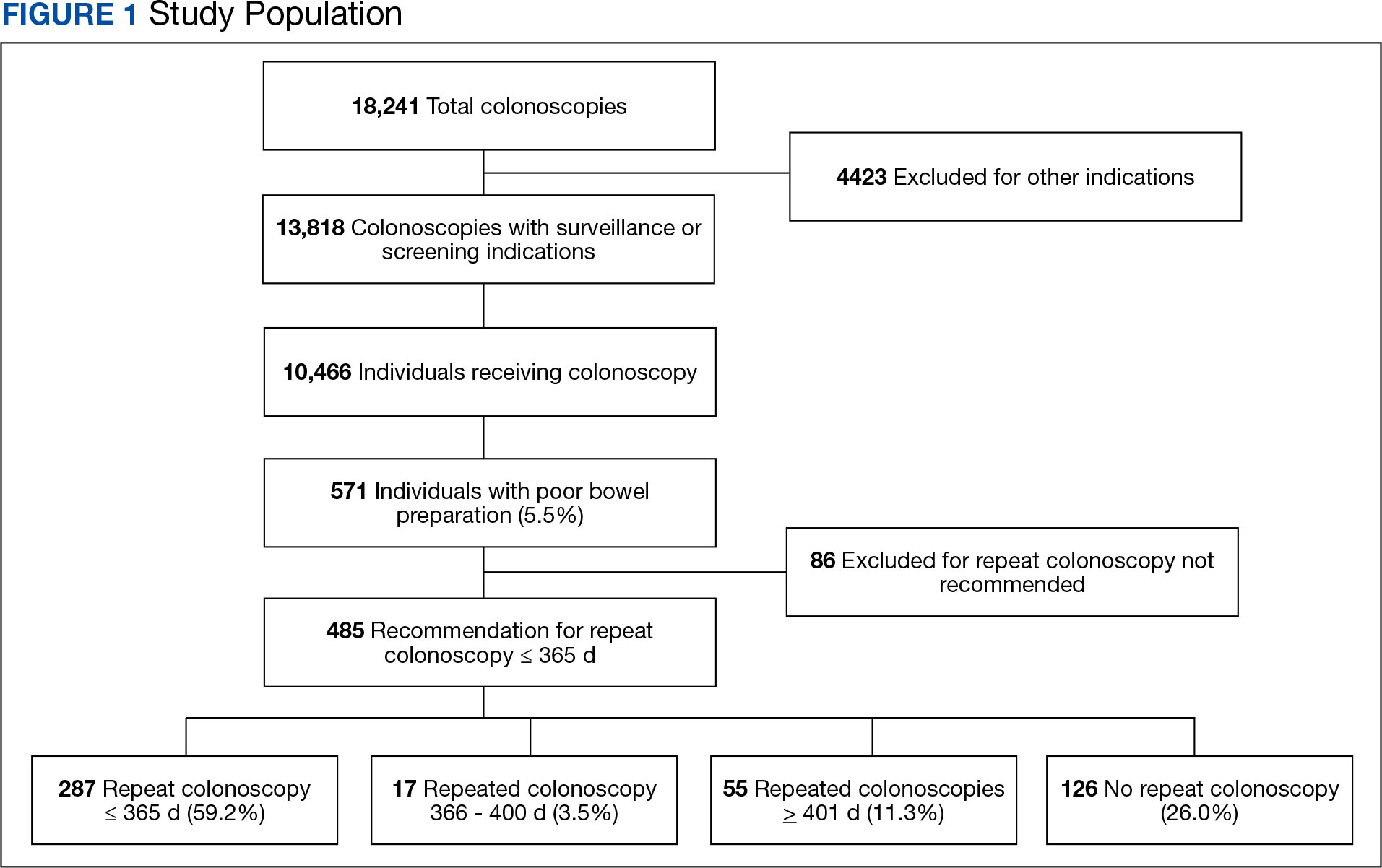
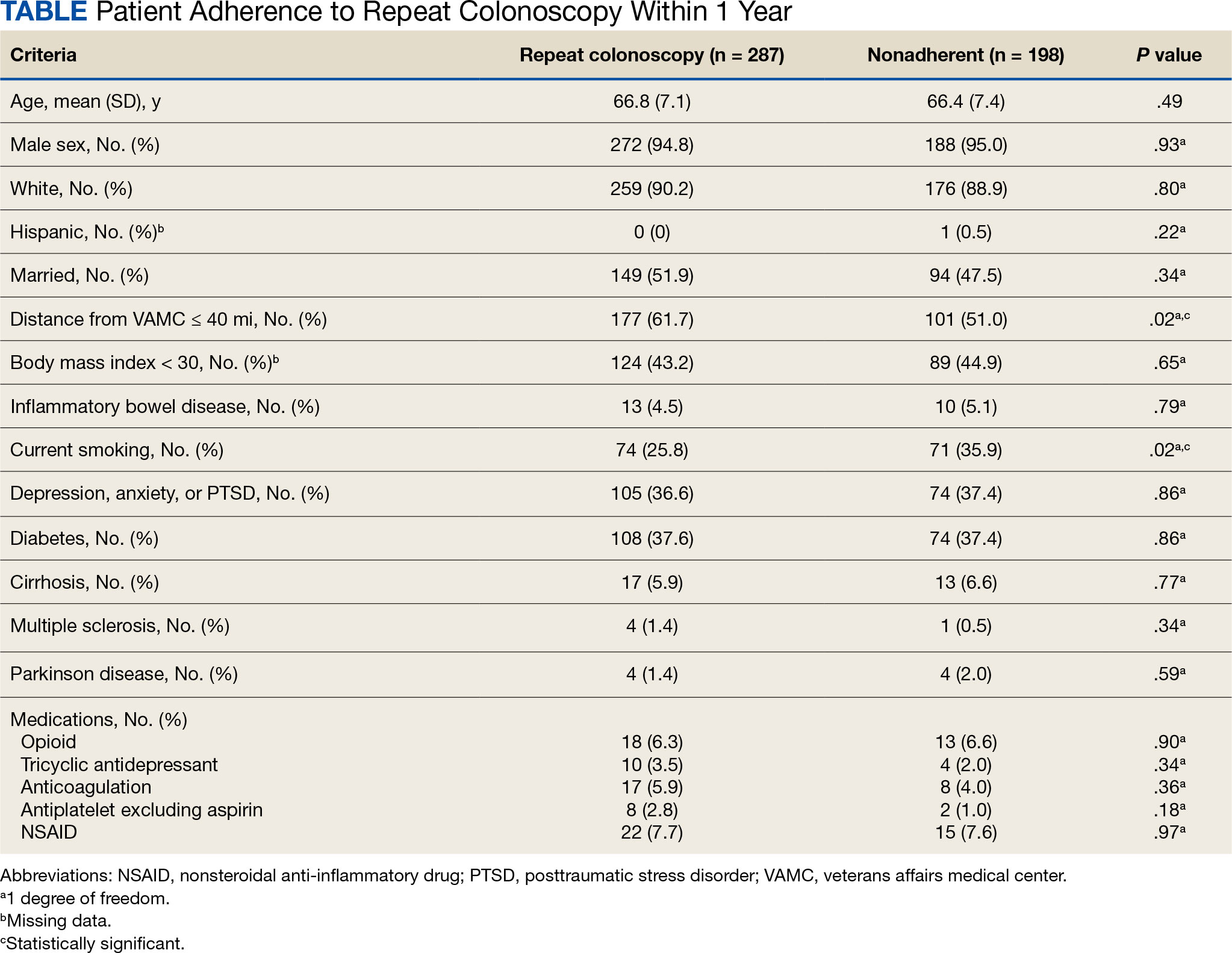
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.
Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
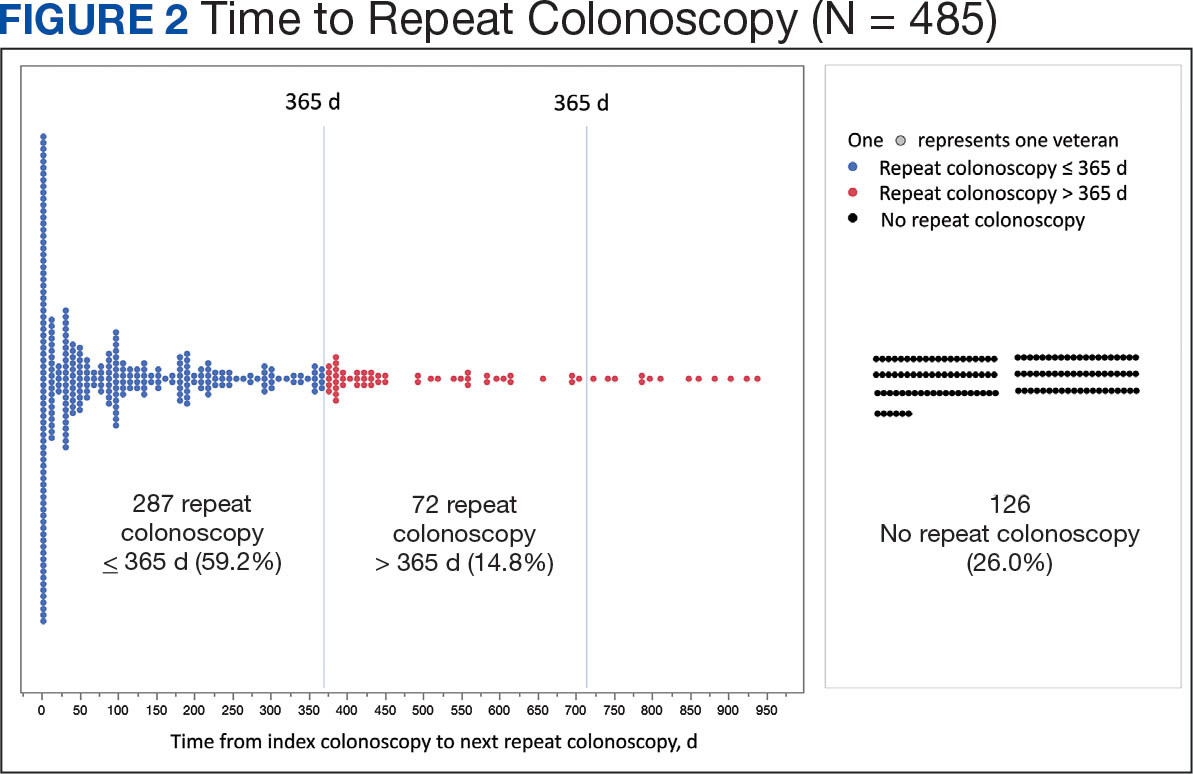
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).
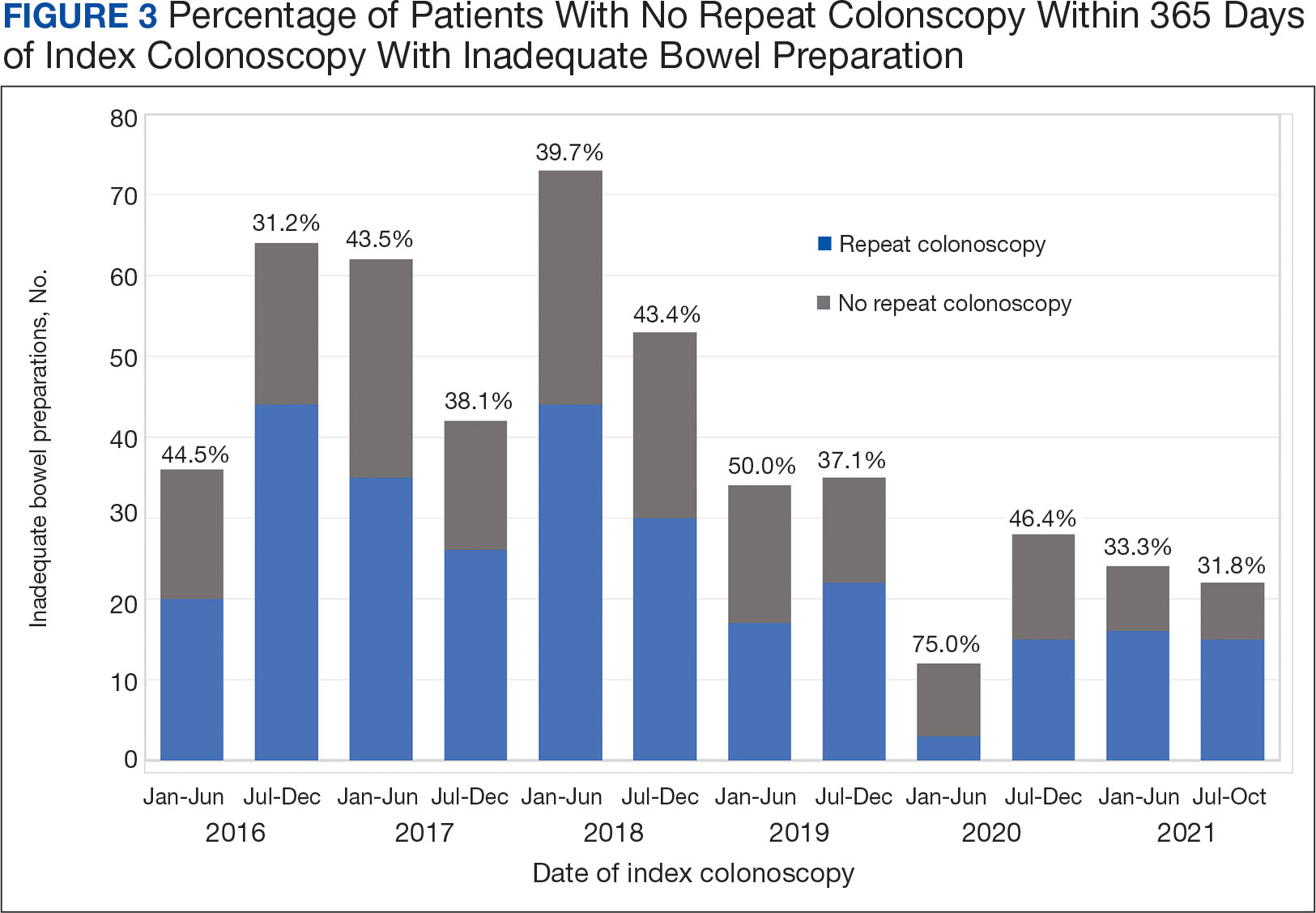
To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).
Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
PHASER Testing Initiative for Patients Newly Diagnosed With a GI Malignancy
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Mortality Risk From Early-Onset CRC Higher in Rural, Poor Areas
TOPLINE:
Patients with early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) living in rural and impoverished areas face a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous research has shown that patients living in impoverished and rural areas have an increased risk of dying from CRC, but it is unclear if this trend applies to patients with early-onset CRC.
- Researchers analyzed 58,200 patients with early-onset CRC from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program between 2006 and 2015.
- Of these patients, 1346 (21%) lived in rural areas with persistent poverty. Persistent poverty was defined as having 20% or more of the population living below the poverty level for about 30 years, and rural locations were identified using specific US Department of Agriculture codes.
- The primary outcome was cancer-specific survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cancer-specific survival at 5 years was highest for patients who lived in neither poverty-stricken nor rural areas (72%) and the lowest for those who lived in impoverished areas irrespective of rural status (67%).
- Patients who lived in rural areas had a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC than those living in nonrural areas, with younger individuals facing the highest risk. More specifically, patients aged between 20 and 29 years had a 35% higher risk of dying from CRC, those aged between 30 and 39 years had a 26% higher risk, and those aged between 40 and 49 years had a 12% higher risk.
- Patients who lived in poverty and rural areas had a 29% increased risk of dying from CRC compared with those in nonrural areas — with the highest 51% greater risk for those aged between 30 and 39 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results can be used to inform health system policies for ongoing investments in cancer diagnosis and treatment resources in rural or impoverished areas for younger CRC patients and their communities,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Meng-Han Tsai, PhD, Georgia Prevention Institute, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Confounders, such as lifestyle factors, comorbidities, and structural barriers, could affect the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Georgia Cancer Center Paceline funding mechanism at Augusta University. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) living in rural and impoverished areas face a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous research has shown that patients living in impoverished and rural areas have an increased risk of dying from CRC, but it is unclear if this trend applies to patients with early-onset CRC.
- Researchers analyzed 58,200 patients with early-onset CRC from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program between 2006 and 2015.
- Of these patients, 1346 (21%) lived in rural areas with persistent poverty. Persistent poverty was defined as having 20% or more of the population living below the poverty level for about 30 years, and rural locations were identified using specific US Department of Agriculture codes.
- The primary outcome was cancer-specific survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cancer-specific survival at 5 years was highest for patients who lived in neither poverty-stricken nor rural areas (72%) and the lowest for those who lived in impoverished areas irrespective of rural status (67%).
- Patients who lived in rural areas had a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC than those living in nonrural areas, with younger individuals facing the highest risk. More specifically, patients aged between 20 and 29 years had a 35% higher risk of dying from CRC, those aged between 30 and 39 years had a 26% higher risk, and those aged between 40 and 49 years had a 12% higher risk.
- Patients who lived in poverty and rural areas had a 29% increased risk of dying from CRC compared with those in nonrural areas — with the highest 51% greater risk for those aged between 30 and 39 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results can be used to inform health system policies for ongoing investments in cancer diagnosis and treatment resources in rural or impoverished areas for younger CRC patients and their communities,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Meng-Han Tsai, PhD, Georgia Prevention Institute, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Confounders, such as lifestyle factors, comorbidities, and structural barriers, could affect the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Georgia Cancer Center Paceline funding mechanism at Augusta University. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) living in rural and impoverished areas face a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous research has shown that patients living in impoverished and rural areas have an increased risk of dying from CRC, but it is unclear if this trend applies to patients with early-onset CRC.
- Researchers analyzed 58,200 patients with early-onset CRC from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program between 2006 and 2015.
- Of these patients, 1346 (21%) lived in rural areas with persistent poverty. Persistent poverty was defined as having 20% or more of the population living below the poverty level for about 30 years, and rural locations were identified using specific US Department of Agriculture codes.
- The primary outcome was cancer-specific survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cancer-specific survival at 5 years was highest for patients who lived in neither poverty-stricken nor rural areas (72%) and the lowest for those who lived in impoverished areas irrespective of rural status (67%).
- Patients who lived in rural areas had a significantly higher risk of dying from CRC than those living in nonrural areas, with younger individuals facing the highest risk. More specifically, patients aged between 20 and 29 years had a 35% higher risk of dying from CRC, those aged between 30 and 39 years had a 26% higher risk, and those aged between 40 and 49 years had a 12% higher risk.
- Patients who lived in poverty and rural areas had a 29% increased risk of dying from CRC compared with those in nonrural areas — with the highest 51% greater risk for those aged between 30 and 39 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results can be used to inform health system policies for ongoing investments in cancer diagnosis and treatment resources in rural or impoverished areas for younger CRC patients and their communities,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Meng-Han Tsai, PhD, Georgia Prevention Institute, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Confounders, such as lifestyle factors, comorbidities, and structural barriers, could affect the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Georgia Cancer Center Paceline funding mechanism at Augusta University. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five Key Measures to Ensure a Quality Colonoscopy
, a list that, for the first time, includes adequate bowel preparation and sessile serrated lesion detection rate (SSLDR).
“Endoscopy teams now have an updated set of guidelines which can be used to enhance the quality of their colonoscopies and should certainly use these current quality measures to ‘raise the bar’ on behalf of their patients,” task force member Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in a statement.
The task force published the recommendations online August 21 in The American Journal of Gastroenterology and in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. It represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on colonoscopy recommendations and incorporates new evidence published since 2015.
“The last set of quality indicators from this group was 9 years ago. Since then, there has been a tremendous amount of new data published in colonoscopy quality,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
“Keeping up with that data is a challenge, and so guidelines such as these are important in helping clinicians synthesize data on quality of care and implement best practices,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved with the task force.
Two New Priority Indicators
The task force identified 15 quality indicators, divided into preprocedure, intraprocedure, and postprocedure. It includes five “priority” indicators — two of which are new.
One is the rate of adequate bowel preparation, preferably defined as a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale score ≥ 2 in each of three colon segments or by description of the preparation as excellent, good, or adequate. It has a performance target > 90%.
“Inadequate bowel preparation substantially increases the cost of colonoscopy delivery and creates risk and inconvenience for patients, thus warranting a ranking as a priority indicator,” the task force wrote.
Dr. Gellad explained that the addition of this priority indicator is “notable because it highlights the importance of bowel prep in high-quality colonoscopy. It also shifts more of the responsibility of bowel prep from the patient to the practice.”
The second new quality indicator is the SSLDR, which was selected due to its ability to contribute to cancer prevention.
Based on available evidence, the task force recommends a current minimum threshold for the SSLDR of 6%. “This is expected to be revised upward as evidence of increasing detection occurs,” they wrote.
Dr. Gellad said the addition of SSLDR is “an important advance in these recommendations. We know that serrated adenomas are a precursor for colorectal cancer and that the detection of these subtle lesions is variable.
“Providing a benchmark encourages practices to measure the detection of serrated adenomas and intervene when rates are below benchmarks. Prior to these benchmarks, it was difficult to know where to peg our expectations,” Dr. Gellad added.
Changes to the Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR)
The ADR remains a priority indicator in the update, albeit with changes.
To keep the ADR measurement consistent with current screening guidelines, the task force now recommends that the ADR be measured starting at age 45 rather than 50 years.
“ADR plays a critical role in evaluating the performance of the colonoscopists,” task force lead Douglas K. Rex, MD, a gastroenterologist at Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, said in the statement.
“It is recommended that ADR calculations include screening, surveillance, and diagnostic colonoscopy but exclude indications of a positive noncolonoscopy screening test and therapeutic procedures for resection or treatment of known neoplasia, genetic cancer syndromes, and inflammatory bowel disease,” Dr. Rex explained.
The task force recommends a minimum ADR threshold of 35% (40% in men and 30% in women) and that colonoscopists with ADRs below 35% “undertake remedial measures to improve and to achieve acceptable performance.”
Additional Priorities
The cecal intubation rate (CIR) — the percentage of patients undergoing colonoscopy with intact colons who have full intubation of the cecum with photo documentation of cecal landmarks — remains a priority quality indicator and has a performance target ≥ 95%.
“A trained colonoscopist should achieve a high CIR with a very high level of safety,” the task force wrote. “Low CIRs have been associated with higher PCCRC [postcolonoscopy colorectal cancer] rates.”
The final priority indicator is the rate of using recommended screening and surveillance intervals, which carries a performance target ≥ 90%.
“We recommend that quality improvement efforts initially focus on high-priority indicators and then progress to other indicators once it is ascertained that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions,” the task force wrote.
“The priority indicators are absolutely important for practices to implement,” Dr. Gellad said.
“There is compelling evidence that these measures are correlated with clinically important outcomes, particularly ADR,” he added. “Many practices already capture this data, and the changes in ADR calculation make measurement less burdensome. Hopefully, this will encourage more practices to collect and report these measures.”
Dr. Rex is a consultant for Olympus, Boston Scientific, Braintree Laboratories, Norgine, GI Supply, Medtronic, and Acacia Pharmaceuticals; receives research support from Olympus, Medivators, Erbe USA, and Braintree Laboratories; and is a shareholder in Satisfai Health. Dr. Shaheen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Gellad has consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a cofounder of Higgs Boson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a list that, for the first time, includes adequate bowel preparation and sessile serrated lesion detection rate (SSLDR).
“Endoscopy teams now have an updated set of guidelines which can be used to enhance the quality of their colonoscopies and should certainly use these current quality measures to ‘raise the bar’ on behalf of their patients,” task force member Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in a statement.
The task force published the recommendations online August 21 in The American Journal of Gastroenterology and in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. It represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on colonoscopy recommendations and incorporates new evidence published since 2015.
“The last set of quality indicators from this group was 9 years ago. Since then, there has been a tremendous amount of new data published in colonoscopy quality,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
“Keeping up with that data is a challenge, and so guidelines such as these are important in helping clinicians synthesize data on quality of care and implement best practices,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved with the task force.
Two New Priority Indicators
The task force identified 15 quality indicators, divided into preprocedure, intraprocedure, and postprocedure. It includes five “priority” indicators — two of which are new.
One is the rate of adequate bowel preparation, preferably defined as a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale score ≥ 2 in each of three colon segments or by description of the preparation as excellent, good, or adequate. It has a performance target > 90%.
“Inadequate bowel preparation substantially increases the cost of colonoscopy delivery and creates risk and inconvenience for patients, thus warranting a ranking as a priority indicator,” the task force wrote.
Dr. Gellad explained that the addition of this priority indicator is “notable because it highlights the importance of bowel prep in high-quality colonoscopy. It also shifts more of the responsibility of bowel prep from the patient to the practice.”
The second new quality indicator is the SSLDR, which was selected due to its ability to contribute to cancer prevention.
Based on available evidence, the task force recommends a current minimum threshold for the SSLDR of 6%. “This is expected to be revised upward as evidence of increasing detection occurs,” they wrote.
Dr. Gellad said the addition of SSLDR is “an important advance in these recommendations. We know that serrated adenomas are a precursor for colorectal cancer and that the detection of these subtle lesions is variable.
“Providing a benchmark encourages practices to measure the detection of serrated adenomas and intervene when rates are below benchmarks. Prior to these benchmarks, it was difficult to know where to peg our expectations,” Dr. Gellad added.
Changes to the Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR)
The ADR remains a priority indicator in the update, albeit with changes.
To keep the ADR measurement consistent with current screening guidelines, the task force now recommends that the ADR be measured starting at age 45 rather than 50 years.
“ADR plays a critical role in evaluating the performance of the colonoscopists,” task force lead Douglas K. Rex, MD, a gastroenterologist at Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, said in the statement.
“It is recommended that ADR calculations include screening, surveillance, and diagnostic colonoscopy but exclude indications of a positive noncolonoscopy screening test and therapeutic procedures for resection or treatment of known neoplasia, genetic cancer syndromes, and inflammatory bowel disease,” Dr. Rex explained.
The task force recommends a minimum ADR threshold of 35% (40% in men and 30% in women) and that colonoscopists with ADRs below 35% “undertake remedial measures to improve and to achieve acceptable performance.”
Additional Priorities
The cecal intubation rate (CIR) — the percentage of patients undergoing colonoscopy with intact colons who have full intubation of the cecum with photo documentation of cecal landmarks — remains a priority quality indicator and has a performance target ≥ 95%.
“A trained colonoscopist should achieve a high CIR with a very high level of safety,” the task force wrote. “Low CIRs have been associated with higher PCCRC [postcolonoscopy colorectal cancer] rates.”
The final priority indicator is the rate of using recommended screening and surveillance intervals, which carries a performance target ≥ 90%.
“We recommend that quality improvement efforts initially focus on high-priority indicators and then progress to other indicators once it is ascertained that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions,” the task force wrote.
“The priority indicators are absolutely important for practices to implement,” Dr. Gellad said.
“There is compelling evidence that these measures are correlated with clinically important outcomes, particularly ADR,” he added. “Many practices already capture this data, and the changes in ADR calculation make measurement less burdensome. Hopefully, this will encourage more practices to collect and report these measures.”
Dr. Rex is a consultant for Olympus, Boston Scientific, Braintree Laboratories, Norgine, GI Supply, Medtronic, and Acacia Pharmaceuticals; receives research support from Olympus, Medivators, Erbe USA, and Braintree Laboratories; and is a shareholder in Satisfai Health. Dr. Shaheen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Gellad has consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a cofounder of Higgs Boson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a list that, for the first time, includes adequate bowel preparation and sessile serrated lesion detection rate (SSLDR).
“Endoscopy teams now have an updated set of guidelines which can be used to enhance the quality of their colonoscopies and should certainly use these current quality measures to ‘raise the bar’ on behalf of their patients,” task force member Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in a statement.
The task force published the recommendations online August 21 in The American Journal of Gastroenterology and in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. It represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on colonoscopy recommendations and incorporates new evidence published since 2015.
“The last set of quality indicators from this group was 9 years ago. Since then, there has been a tremendous amount of new data published in colonoscopy quality,” Ziad F. Gellad, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
“Keeping up with that data is a challenge, and so guidelines such as these are important in helping clinicians synthesize data on quality of care and implement best practices,” said Dr. Gellad, who was not involved with the task force.
Two New Priority Indicators
The task force identified 15 quality indicators, divided into preprocedure, intraprocedure, and postprocedure. It includes five “priority” indicators — two of which are new.
One is the rate of adequate bowel preparation, preferably defined as a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale score ≥ 2 in each of three colon segments or by description of the preparation as excellent, good, or adequate. It has a performance target > 90%.
“Inadequate bowel preparation substantially increases the cost of colonoscopy delivery and creates risk and inconvenience for patients, thus warranting a ranking as a priority indicator,” the task force wrote.
Dr. Gellad explained that the addition of this priority indicator is “notable because it highlights the importance of bowel prep in high-quality colonoscopy. It also shifts more of the responsibility of bowel prep from the patient to the practice.”
The second new quality indicator is the SSLDR, which was selected due to its ability to contribute to cancer prevention.
Based on available evidence, the task force recommends a current minimum threshold for the SSLDR of 6%. “This is expected to be revised upward as evidence of increasing detection occurs,” they wrote.
Dr. Gellad said the addition of SSLDR is “an important advance in these recommendations. We know that serrated adenomas are a precursor for colorectal cancer and that the detection of these subtle lesions is variable.
“Providing a benchmark encourages practices to measure the detection of serrated adenomas and intervene when rates are below benchmarks. Prior to these benchmarks, it was difficult to know where to peg our expectations,” Dr. Gellad added.
Changes to the Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR)
The ADR remains a priority indicator in the update, albeit with changes.
To keep the ADR measurement consistent with current screening guidelines, the task force now recommends that the ADR be measured starting at age 45 rather than 50 years.
“ADR plays a critical role in evaluating the performance of the colonoscopists,” task force lead Douglas K. Rex, MD, a gastroenterologist at Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, said in the statement.
“It is recommended that ADR calculations include screening, surveillance, and diagnostic colonoscopy but exclude indications of a positive noncolonoscopy screening test and therapeutic procedures for resection or treatment of known neoplasia, genetic cancer syndromes, and inflammatory bowel disease,” Dr. Rex explained.
The task force recommends a minimum ADR threshold of 35% (40% in men and 30% in women) and that colonoscopists with ADRs below 35% “undertake remedial measures to improve and to achieve acceptable performance.”
Additional Priorities
The cecal intubation rate (CIR) — the percentage of patients undergoing colonoscopy with intact colons who have full intubation of the cecum with photo documentation of cecal landmarks — remains a priority quality indicator and has a performance target ≥ 95%.
“A trained colonoscopist should achieve a high CIR with a very high level of safety,” the task force wrote. “Low CIRs have been associated with higher PCCRC [postcolonoscopy colorectal cancer] rates.”
The final priority indicator is the rate of using recommended screening and surveillance intervals, which carries a performance target ≥ 90%.
“We recommend that quality improvement efforts initially focus on high-priority indicators and then progress to other indicators once it is ascertained that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions,” the task force wrote.
“The priority indicators are absolutely important for practices to implement,” Dr. Gellad said.
“There is compelling evidence that these measures are correlated with clinically important outcomes, particularly ADR,” he added. “Many practices already capture this data, and the changes in ADR calculation make measurement less burdensome. Hopefully, this will encourage more practices to collect and report these measures.”
Dr. Rex is a consultant for Olympus, Boston Scientific, Braintree Laboratories, Norgine, GI Supply, Medtronic, and Acacia Pharmaceuticals; receives research support from Olympus, Medivators, Erbe USA, and Braintree Laboratories; and is a shareholder in Satisfai Health. Dr. Shaheen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Gellad has consulted for Merck & Co. and Novo Nordisk and is a cofounder of Higgs Boson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In Colorectal Cancer, Donating Half a Liver Could Save Lives
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD: Dr. Dib is the director of the Hepatobiliary Surgery and Living Donor Program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center here in Boston, and a Harvard Medical School faculty member.
He was previously at the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, a leading international institution investigating the role of liver transplant in colorectal cancer, among other diseases. Dr. Dib, before we move to our discussion, I’d like to hear a bit about your pathway to becoming a transplant surgeon. How did you end up working on colorectal cancer and liver transplants in this field?
Martin J. Dib, MD: Thank you so much, Dr. Schlechter. I am originally from Chile. I had an opportunity to come to Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center after medical school and I did liver regeneration research at the transplant center. After that, I was lucky enough to match as a general surgery resident at Beth Israel Deaconess.
This is my alma mater and I was able to graduate as a surgeon here. You and I had some paths together. After graduating from Harvard as a surgeon, I was trained in liver transplant, abdominal transplant, surgical oncology, and hepatobiliary surgery at the University of Toronto.
I have been developing this passion for being able to transplant cancer patients and use organ transplant techniques to be able to do complex resections for cancer.
Dr. Schlechter: Let’s talk about the topic for today, which is liver transplant and colorectal cancer. I’ll be honest — this is not a very familiar topic for a lot of oncologists. There are a lot of details that I think are new to us as oncologists. We need to expand this conversation to get access to patients for this.
First and foremost, can you talk about some of the parameters for a resectable liver metastasis vs unresectable disease that would be an indication for a liver transplant?
Dr. Dib: I think this is a very interesting topic because liver transplantation for cancer is not new. Liver transplantation started in the 1960s when people started doing liver transplants for advanced liver tumors. The problem is that they were selecting patients who had very advanced — and poor tumor biology — tumors. The outcomes were not good.
It was only in 1996 when the Milan criteria started. Mazzaferro and colleagues, using strict patient selection, were able to do liver transplant for selected hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Having those excellent outcomes in selecting patients opened the field for what we now call transplant oncology, which is using selection criteria and using other methods to be able to select which patients will do well after transplantation, even with immunosuppression.
Liver transplantation for colorectal metastasis was used at the very beginning of the era of liver transplantation, but with very poor outcomes. It was abandoned because of the outcomes. It is exciting to see that after 20 years of not doing it, there was a group in Norway that started again. They are doing liver transplants for colorectal metastases (mets), but with very selected patients.
In Norway, they had a very unusual setting where they had more liver donors than patients on the list waiting for liver transplant. So they can’t share these livers and we’re all jealous, right? Every single country in the West struggles because we don’t have enough livers for the rest of the list. And they had a lot of livers to be able to transplant people.
They decided to transplant some selected patients with colorectal mets that were unresectable. And the surprise was that they found that they were able to get a 60% survival at 5 years. And so that was new. After that, in Norway, they started showing this data to other centers in the world. It wasn’t until this year that we could see not only the long-term data and long-term outcomes of using liver transplantation for unresectable colorectal mets, but also we’re now having data from a prospective clinical trial from France.
It was three countries in the prospective clinical trial: France, Belgium, and Italy. We now see that we have a little stronger data to support the use of liver transplants for unresectable colorectal mets.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s the TRANSMET study you’re referencing that was presented at ASCO in the late-breaking abstract session in 2024, and then more recently in The Lancet’s eClinicalMedicine. Both of those papers were led by René Adam. That was a cool presentation to sit through. I was in the room, and I was taking a ton of notes and there was a lot of info that came out of that.
First of all, it showed that patients who had received chemotherapy and were responding could then go on to liver transplant in that population. Impressively, 81% of the patients who were randomized to transplant received it. Frankly, that’s a big number, especially compared with the West, as you said, and in particular the US and here in New England where livers are a very precious commodity.
And even accounting for that, if you look at the intention-to-treat analysis, the 5-year overall survival in that population was 57% compared with 13% with chemotherapy. And that feels like a real number for chemotherapy. If you look at the per-protocol analysis, frankly, the numbers are higher.
It’s always a challenging assessment. What was also interesting to me was the pattern of recurrence, which in general was that recurrences were extrahepatic. So not only were patients rendered disease-free, but in general, the liver remained disease-free and only 3% of patients had liver-only recurrence and 11% had widespread metastatic disease.
The biggest group was lung metastases, at about 40%. Ultimately, they reported a progression-free survival of 17. 4 months for transplant compared with 6. 4 months with chemotherapy. On every parameter, it looks like liver transplant wins for these people. Help me out. Who are these people? How do we find these people?
What are the inclusions and exclusions for this population?
Dr. Dib: I think that’s very important. This is not a therapy that will be for every patient. These are selected patients who have liver-only unresectable colorectal mets. These are patients that don’t have any extrahepatic disease and that either the primary has been taken out already or that they have the primary present, but the plan is to take the primary and then do a liver transplantation after 3 months, hopefully after 6 months, of removing the primary.
These are patients who meet all the criteria that we have seen in terms of the best outcomes — patients that have Oslo scores of less than three. The Oslo trial, which included the SECA (Secondary Cancer)-I and SECA-II trials, basically showed that patients with a maximal tumor diameter of less than 5.5 with a pretransplant CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) of less than 80 that do not have progression on chemotherapy, among other variables, do better. But the concept is that this is a therapy that will apply only to selected patients. That way we can continue to have adequate overall survival post-transplant that would be comparable to other diseases that we do liver transplants for.
Dr. Schlechter: Were there other biomarkers, any mutations that were included or excluded?
Dr. Dib: Yes. If you look at SECA-I, SECA-II trial outcomes, and also TRANSMET, they all say patients with BRAF mutations shouldn’t be transplanted. There are other parameters, including, for example, the site of the primary tumor. Patients with a left-sided colon primary tumor do much better than patients who have a right-sided primary tumor.
That’s not a complete contraindication, but if you look at the most updated inclusion criteria of programs, like the ones that the one that we have here at Beth Israel Deaconess and many others, the inclusion criteria protocols include patients who have only hepatic disease.
So, if there are no extrahepatic mets, the resection of the primary has been done or will be done after a multidisciplinary discussion. We want to make sure they have the absence of BRAF mutation, and that they don’t have disease progression while on chemotherapy. So hopefully we have data from enough months to be able to make sure that there’s no intrahepatic or extrahepatic progression while on chemotherapy.
And that’s including CEA and also looking at the imaging.
Dr. Schlechter: When you’re seeing a patient, how much chemo do you think they should have? What’s a good run chemotherapy-wise for these patients? Let’s say, before I refer a patient to you, how much chemo should they have? And then what should I do? Do I get a PET scan? Do I get MRI? What’s the right scanning I should do to prove there’s no extrahepatic disease before sending a patient in for consideration?
Dr. Dib: First, we need to confirm unresectability. Referring patients early is always a good measure to make sure that we’re all in agreement that it’s an unresectable patient. Having a PET scan from the very beginning is helpful because it shows the disease before doing chemotherapy.
In terms of the lines of chemotherapy, ideally in the TRANSMET trial, for example, the idea was to show tumor control for at least 3 months, with less than three lines of chemotherapy. Some patients will do that with FOLFIRI. It depends on the case.
I think some of those evaluations will need a multidisciplinary discussion. In our case, we are connected to the Norway team. We frequently talk with the Oslo team and an international community of transplant centers to get opinions on particular cases.
But I think referring patients early is a good measure. If we don’t think that they qualify, we will let the team know. We’re strictly looking at patients who have unresectable liver mets that don’t have extrahepatic disease. The idea is to do a primary tumor resection, and then get to transplantation, hopefully after 6 months. In some cases that have some concerns in terms of tumor biology, we may even extend the time from diagnosis to transplant to over 1.5 years.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And what’s the experience like for these patients? In training as a resident many years ago, I saw patients with cirrhosis who went on to have a liver transplant, and that was sort of trading one disease for another. What is the posttransplant, or the remission, experience of a liver transplant for colorectal cancer like for the patient?
Dr. Dib: That’s a very important point. I think that transplantation has gotten better and better, as has chemotherapy systemic therapy. The liver transplantation experience from 20 years ago has improved dramatically. I think the quality of life of liver transplant patients after transplantation has increased quite a bit.
At Beth Israel Deaconess, we have a liver transplant program that is doing over a 100 livers a year. And when you have a high-volume center, usually the experience gets better. The time in the hospital post-transplant decreases.
In general, when we’re doing liver transplants, patients are getting extubated in the OR 30% of the time. The vast majority of patients are going home within 1 or 2 weeks. They need to have immunosuppression for the rest of their lives. We have a very good program of transplant coordinators that will help the family and the patient to live with immunosuppression and live with a transplanted organ.
But I would say that we have many, many patients, especially these patients who are not patients with cirrhosis. Their health is not as deteriorated as patients who have low MELD (model for end-stage liver disease) scores. They don’t have liver disease. They have cancer. So usually patients like that, many of them can go back to work and live a quality of life that is fairly reasonable.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s good to hear. When we hear statements like liver transplant for colon cancer, a lot of us have this picture of a much sicker population, but it’s interesting and true that the colorectal cancer population as a candidate for liver transplant is a much healthier population than the population with cirrhosis.
Let’s talk about organs and donors. Largely in the TRANSMET study, for example, that was cadaveric donors. Those were not living donors and you’ve done a lot of work on living donors. If the answer in the United States, because of limited access to organs, is going to be living donors, who are those donors?
What is that like? How do you identify them?
Dr. Dib: There’s a lot of advantages to using living donors for these patients. In any type of patient that needs a liver transplant, cadaveric donors or deceased donors is the same concept. There are two types of deceased donors: the brain-dead donors and donors after cardiac death. Those are hard to come by.
We still have 15%-20% mortality on the waiting list in the United States. We’re already still struggling to get enough donors to transplant the patients that are on the list. Now, if you add a new indication, which is unresectable colorectal mets, we need to make sure that the outcomes are equivalent to the patients who are going to be transplanted for other reasons.
Right now, for example, the 5-year overall survival of a patient with cirrhosis, or a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma, is over 80% 5-year survival. In the SECA trials and TRANSMET trial, if we do a good selection, I think we can get to 70% 5-year survival. But until we have more data, I think it’s a cautious measure to, as a field, try to use living donors and not compete with the rest of the list of patients who are already dying on the list for liver transplants.
Once we get more data, it’s going to be something that, in the transplant community, we may be able to use deceased donors. Especially deceased donors with maybe extended criteria that are not going to be used for other patients. We can do living-unrelated or living-related donations. Family members or also friends or neighbors or part of the community, even altruistic donors, can donate to a potential recipient. And that enables us to not only time the transplant in an adequate manner, because we’re able to transplant the patient early, but also time it so we can give the number of chemotherapy cycles that we want to give.
That’s a huge advantage. You don’t compete for a liver with the cadaveric waiting list of patients that are waiting for other reasons, and you can select the tumor biology very well because you know exactly when the surgery is going to be. For instance, we can say, okay, this patient has KRAS mutation, left-sided colon cancer, and has been having good tumor biology with no progression. We will wait 6 months from the primary tumor to the transplant, which is going to be 1 year from diagnosis to transplant. And we can see during that time whether they continue to have good tumor biology.
But if you have a deceased donor liver transplant, sometimes you can’t time that well and schedule it. It becomes a bit more tricky in terms of patient selection and making sure that we do this for the people who are going to benefit.
Dr. Schlechter: And how does donor matching work? Is it HLA (human leukocyte antigen) matched or ABO-matched? Who can donate when you say a living-related? For example, when we think about bone marrow transplantation, which we’re all familiar with in the oncology population, it’s an incredibly complex match process. Is this the same challenge?
Dr. Dib: No, it’s a little bit simpler. Living donors for liver transplants need to be between the ages of 18 and 60. They need to be relatively healthy, relatively fit, with a BMI hopefully less than 30, definitely less than 35. The compatibility is ABO compatibility. So, if they’re ABO-compatible, relatively young, relatively healthy, they would be a potential donor and we will go ahead and do a CT scan.
If the CT scan shows that they have a good, adequate anatomy, more than 90% of those will be good donors. I would say that out of 100 people who want to be donors, 25 of them will be adequate. One out of four people who want to save their family member and want to have this operation are able to donate half of their liver to their family member or loved one.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And it’s helpful to know that the matching process is simpler. During his discussion, René Adam unequivocally stated that liver transplants are a new standard of care for colorectal cancer. And I guess my question is, do you agree with this statement? How do we balance the demand for living donors and the demand for deceased donors? Especially in a time of increasing fatty liver disease and obesity, other indications for liver transplant, causes of cirrhosis, and also in an era of young-onset colorectal cancer. Patients are younger. Is this a new standard of care? Do you agree with that statement?
Dr. Dib: I do agree with that statement. I think it’s important to understand that not all patients with colorectal mets are the same. Of the number of patients in the United States who have colorectal cancer, let’s say 50% of them will have liver metastasis. Only 15%-20% of them will have liver-only metastasis.
This is only for patients who have liver-only metastasis without extrahepatic disease. And only maybe 15%-20% of them will meet all the criteria to be able to undergo liver transplantation. I think it’s for a very selective subset of patients who have very good tumor biology, generally young patients who don’t have any other alternative to having even a complex liver resection and are not able to get R0 resection. That is when we could think about doing liver transplantation.
It’s one more of the skills that we can have. It doesn’t mean that it will be the only skill, or the best skill, for all of the patients.
Dr. Schlechter: When a patient volunteers to be a living donor for a loved one or a family member, and they go through all the screening and they’re found to be a candidate, what is the surgical experience for that patient?
How long are they in the hospital? What sort of operation is that?
Dr. Dib: Living donors are very special patients. These are patients who do not need an operation. And the only reason they’re doing this is to save the life of their loved one. Donor safety is our priority number one, two, three, and four. The donor operation needs to be perfect.
And so we take good care of, first of all, selecting the living donors, making sure that they’re young and they don’t have any big contraindications. We also ensure that they are well informed of the process. The living donor surgery that we’re now doing is laparoscopic and minimally invasive. Here at Beth Israel Deaconess, we have done it laparoscopically with very good results.
I think that experience before and after the surgery gets so much better because of the better recovery. They’re able to go home, in general, within 4 or 5 days, and they get on with their normal life within 6-8 weeks. I think it’s important for them to know all the processes and the actual risks and benefits for the recipient.
Among those risks, I think it’s important for them to understand that this is a complex operation. Even if we do it laparoscopically or robotically, so that the scar is less, inside we’re still taking out half of the liver. That is a surgery that needs to be undertaken very meticulously, with a focus on minimizing any bleeding.
It’s a surgery that takes a long time. It takes about 6 hours. We do our best to try to minimize any risks.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. Thanks for that. Today we had Dr. Martin Dib joining us to discuss liver transplant for metastatic colorectal cancer. We discussed the various important criteria. We discussed that early referral to multidisciplinary centers that manage these is important to help get patients set up.
We discussed the fact that there are certain inclusion and exclusion criteria to consider. Obviously, unresectable disease is a critical determination that should be made by a liver surgeon. The absence of extrahepatic disease is important in staging with PET or other imaging. We discussed certain other biological exclusions.
There’s a relative contraindication of right-sided vs left-sided cancers, but right-sided cancers can be transplanted. We discussed that an elevated CEA greater than 80 is a contraindication, as are mutations in BRAF. We reviewed data from both the TRANSMET trial recently published in The Lancet and presented at ASCO in 2024, as well as the older Oslo criteria and Oslo trials and SECA trials.
And finally, we heard that donors can now come as living donors, a laparoscopic robotic surgery with a better safety profile, and greater access to organs that are ABO matched and not HLA matched because of the nature of the biology. Thank you again for joining us.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD, is senior physician, Gastrointestinal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Martin J. Dib, MD, is member of the faculty, Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School; director of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Division of Transplantation, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this transcript appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD: Dr. Dib is the director of the Hepatobiliary Surgery and Living Donor Program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center here in Boston, and a Harvard Medical School faculty member.
He was previously at the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, a leading international institution investigating the role of liver transplant in colorectal cancer, among other diseases. Dr. Dib, before we move to our discussion, I’d like to hear a bit about your pathway to becoming a transplant surgeon. How did you end up working on colorectal cancer and liver transplants in this field?
Martin J. Dib, MD: Thank you so much, Dr. Schlechter. I am originally from Chile. I had an opportunity to come to Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center after medical school and I did liver regeneration research at the transplant center. After that, I was lucky enough to match as a general surgery resident at Beth Israel Deaconess.
This is my alma mater and I was able to graduate as a surgeon here. You and I had some paths together. After graduating from Harvard as a surgeon, I was trained in liver transplant, abdominal transplant, surgical oncology, and hepatobiliary surgery at the University of Toronto.
I have been developing this passion for being able to transplant cancer patients and use organ transplant techniques to be able to do complex resections for cancer.
Dr. Schlechter: Let’s talk about the topic for today, which is liver transplant and colorectal cancer. I’ll be honest — this is not a very familiar topic for a lot of oncologists. There are a lot of details that I think are new to us as oncologists. We need to expand this conversation to get access to patients for this.
First and foremost, can you talk about some of the parameters for a resectable liver metastasis vs unresectable disease that would be an indication for a liver transplant?
Dr. Dib: I think this is a very interesting topic because liver transplantation for cancer is not new. Liver transplantation started in the 1960s when people started doing liver transplants for advanced liver tumors. The problem is that they were selecting patients who had very advanced — and poor tumor biology — tumors. The outcomes were not good.
It was only in 1996 when the Milan criteria started. Mazzaferro and colleagues, using strict patient selection, were able to do liver transplant for selected hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Having those excellent outcomes in selecting patients opened the field for what we now call transplant oncology, which is using selection criteria and using other methods to be able to select which patients will do well after transplantation, even with immunosuppression.
Liver transplantation for colorectal metastasis was used at the very beginning of the era of liver transplantation, but with very poor outcomes. It was abandoned because of the outcomes. It is exciting to see that after 20 years of not doing it, there was a group in Norway that started again. They are doing liver transplants for colorectal metastases (mets), but with very selected patients.
In Norway, they had a very unusual setting where they had more liver donors than patients on the list waiting for liver transplant. So they can’t share these livers and we’re all jealous, right? Every single country in the West struggles because we don’t have enough livers for the rest of the list. And they had a lot of livers to be able to transplant people.
They decided to transplant some selected patients with colorectal mets that were unresectable. And the surprise was that they found that they were able to get a 60% survival at 5 years. And so that was new. After that, in Norway, they started showing this data to other centers in the world. It wasn’t until this year that we could see not only the long-term data and long-term outcomes of using liver transplantation for unresectable colorectal mets, but also we’re now having data from a prospective clinical trial from France.
It was three countries in the prospective clinical trial: France, Belgium, and Italy. We now see that we have a little stronger data to support the use of liver transplants for unresectable colorectal mets.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s the TRANSMET study you’re referencing that was presented at ASCO in the late-breaking abstract session in 2024, and then more recently in The Lancet’s eClinicalMedicine. Both of those papers were led by René Adam. That was a cool presentation to sit through. I was in the room, and I was taking a ton of notes and there was a lot of info that came out of that.
First of all, it showed that patients who had received chemotherapy and were responding could then go on to liver transplant in that population. Impressively, 81% of the patients who were randomized to transplant received it. Frankly, that’s a big number, especially compared with the West, as you said, and in particular the US and here in New England where livers are a very precious commodity.
And even accounting for that, if you look at the intention-to-treat analysis, the 5-year overall survival in that population was 57% compared with 13% with chemotherapy. And that feels like a real number for chemotherapy. If you look at the per-protocol analysis, frankly, the numbers are higher.
It’s always a challenging assessment. What was also interesting to me was the pattern of recurrence, which in general was that recurrences were extrahepatic. So not only were patients rendered disease-free, but in general, the liver remained disease-free and only 3% of patients had liver-only recurrence and 11% had widespread metastatic disease.
The biggest group was lung metastases, at about 40%. Ultimately, they reported a progression-free survival of 17. 4 months for transplant compared with 6. 4 months with chemotherapy. On every parameter, it looks like liver transplant wins for these people. Help me out. Who are these people? How do we find these people?
What are the inclusions and exclusions for this population?
Dr. Dib: I think that’s very important. This is not a therapy that will be for every patient. These are selected patients who have liver-only unresectable colorectal mets. These are patients that don’t have any extrahepatic disease and that either the primary has been taken out already or that they have the primary present, but the plan is to take the primary and then do a liver transplantation after 3 months, hopefully after 6 months, of removing the primary.
These are patients who meet all the criteria that we have seen in terms of the best outcomes — patients that have Oslo scores of less than three. The Oslo trial, which included the SECA (Secondary Cancer)-I and SECA-II trials, basically showed that patients with a maximal tumor diameter of less than 5.5 with a pretransplant CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) of less than 80 that do not have progression on chemotherapy, among other variables, do better. But the concept is that this is a therapy that will apply only to selected patients. That way we can continue to have adequate overall survival post-transplant that would be comparable to other diseases that we do liver transplants for.
Dr. Schlechter: Were there other biomarkers, any mutations that were included or excluded?
Dr. Dib: Yes. If you look at SECA-I, SECA-II trial outcomes, and also TRANSMET, they all say patients with BRAF mutations shouldn’t be transplanted. There are other parameters, including, for example, the site of the primary tumor. Patients with a left-sided colon primary tumor do much better than patients who have a right-sided primary tumor.
That’s not a complete contraindication, but if you look at the most updated inclusion criteria of programs, like the ones that the one that we have here at Beth Israel Deaconess and many others, the inclusion criteria protocols include patients who have only hepatic disease.
So, if there are no extrahepatic mets, the resection of the primary has been done or will be done after a multidisciplinary discussion. We want to make sure they have the absence of BRAF mutation, and that they don’t have disease progression while on chemotherapy. So hopefully we have data from enough months to be able to make sure that there’s no intrahepatic or extrahepatic progression while on chemotherapy.
And that’s including CEA and also looking at the imaging.
Dr. Schlechter: When you’re seeing a patient, how much chemo do you think they should have? What’s a good run chemotherapy-wise for these patients? Let’s say, before I refer a patient to you, how much chemo should they have? And then what should I do? Do I get a PET scan? Do I get MRI? What’s the right scanning I should do to prove there’s no extrahepatic disease before sending a patient in for consideration?
Dr. Dib: First, we need to confirm unresectability. Referring patients early is always a good measure to make sure that we’re all in agreement that it’s an unresectable patient. Having a PET scan from the very beginning is helpful because it shows the disease before doing chemotherapy.
In terms of the lines of chemotherapy, ideally in the TRANSMET trial, for example, the idea was to show tumor control for at least 3 months, with less than three lines of chemotherapy. Some patients will do that with FOLFIRI. It depends on the case.
I think some of those evaluations will need a multidisciplinary discussion. In our case, we are connected to the Norway team. We frequently talk with the Oslo team and an international community of transplant centers to get opinions on particular cases.
But I think referring patients early is a good measure. If we don’t think that they qualify, we will let the team know. We’re strictly looking at patients who have unresectable liver mets that don’t have extrahepatic disease. The idea is to do a primary tumor resection, and then get to transplantation, hopefully after 6 months. In some cases that have some concerns in terms of tumor biology, we may even extend the time from diagnosis to transplant to over 1.5 years.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And what’s the experience like for these patients? In training as a resident many years ago, I saw patients with cirrhosis who went on to have a liver transplant, and that was sort of trading one disease for another. What is the posttransplant, or the remission, experience of a liver transplant for colorectal cancer like for the patient?
Dr. Dib: That’s a very important point. I think that transplantation has gotten better and better, as has chemotherapy systemic therapy. The liver transplantation experience from 20 years ago has improved dramatically. I think the quality of life of liver transplant patients after transplantation has increased quite a bit.
At Beth Israel Deaconess, we have a liver transplant program that is doing over a 100 livers a year. And when you have a high-volume center, usually the experience gets better. The time in the hospital post-transplant decreases.
In general, when we’re doing liver transplants, patients are getting extubated in the OR 30% of the time. The vast majority of patients are going home within 1 or 2 weeks. They need to have immunosuppression for the rest of their lives. We have a very good program of transplant coordinators that will help the family and the patient to live with immunosuppression and live with a transplanted organ.
But I would say that we have many, many patients, especially these patients who are not patients with cirrhosis. Their health is not as deteriorated as patients who have low MELD (model for end-stage liver disease) scores. They don’t have liver disease. They have cancer. So usually patients like that, many of them can go back to work and live a quality of life that is fairly reasonable.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s good to hear. When we hear statements like liver transplant for colon cancer, a lot of us have this picture of a much sicker population, but it’s interesting and true that the colorectal cancer population as a candidate for liver transplant is a much healthier population than the population with cirrhosis.
Let’s talk about organs and donors. Largely in the TRANSMET study, for example, that was cadaveric donors. Those were not living donors and you’ve done a lot of work on living donors. If the answer in the United States, because of limited access to organs, is going to be living donors, who are those donors?
What is that like? How do you identify them?
Dr. Dib: There’s a lot of advantages to using living donors for these patients. In any type of patient that needs a liver transplant, cadaveric donors or deceased donors is the same concept. There are two types of deceased donors: the brain-dead donors and donors after cardiac death. Those are hard to come by.
We still have 15%-20% mortality on the waiting list in the United States. We’re already still struggling to get enough donors to transplant the patients that are on the list. Now, if you add a new indication, which is unresectable colorectal mets, we need to make sure that the outcomes are equivalent to the patients who are going to be transplanted for other reasons.
Right now, for example, the 5-year overall survival of a patient with cirrhosis, or a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma, is over 80% 5-year survival. In the SECA trials and TRANSMET trial, if we do a good selection, I think we can get to 70% 5-year survival. But until we have more data, I think it’s a cautious measure to, as a field, try to use living donors and not compete with the rest of the list of patients who are already dying on the list for liver transplants.
Once we get more data, it’s going to be something that, in the transplant community, we may be able to use deceased donors. Especially deceased donors with maybe extended criteria that are not going to be used for other patients. We can do living-unrelated or living-related donations. Family members or also friends or neighbors or part of the community, even altruistic donors, can donate to a potential recipient. And that enables us to not only time the transplant in an adequate manner, because we’re able to transplant the patient early, but also time it so we can give the number of chemotherapy cycles that we want to give.
That’s a huge advantage. You don’t compete for a liver with the cadaveric waiting list of patients that are waiting for other reasons, and you can select the tumor biology very well because you know exactly when the surgery is going to be. For instance, we can say, okay, this patient has KRAS mutation, left-sided colon cancer, and has been having good tumor biology with no progression. We will wait 6 months from the primary tumor to the transplant, which is going to be 1 year from diagnosis to transplant. And we can see during that time whether they continue to have good tumor biology.
But if you have a deceased donor liver transplant, sometimes you can’t time that well and schedule it. It becomes a bit more tricky in terms of patient selection and making sure that we do this for the people who are going to benefit.
Dr. Schlechter: And how does donor matching work? Is it HLA (human leukocyte antigen) matched or ABO-matched? Who can donate when you say a living-related? For example, when we think about bone marrow transplantation, which we’re all familiar with in the oncology population, it’s an incredibly complex match process. Is this the same challenge?
Dr. Dib: No, it’s a little bit simpler. Living donors for liver transplants need to be between the ages of 18 and 60. They need to be relatively healthy, relatively fit, with a BMI hopefully less than 30, definitely less than 35. The compatibility is ABO compatibility. So, if they’re ABO-compatible, relatively young, relatively healthy, they would be a potential donor and we will go ahead and do a CT scan.
If the CT scan shows that they have a good, adequate anatomy, more than 90% of those will be good donors. I would say that out of 100 people who want to be donors, 25 of them will be adequate. One out of four people who want to save their family member and want to have this operation are able to donate half of their liver to their family member or loved one.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And it’s helpful to know that the matching process is simpler. During his discussion, René Adam unequivocally stated that liver transplants are a new standard of care for colorectal cancer. And I guess my question is, do you agree with this statement? How do we balance the demand for living donors and the demand for deceased donors? Especially in a time of increasing fatty liver disease and obesity, other indications for liver transplant, causes of cirrhosis, and also in an era of young-onset colorectal cancer. Patients are younger. Is this a new standard of care? Do you agree with that statement?
Dr. Dib: I do agree with that statement. I think it’s important to understand that not all patients with colorectal mets are the same. Of the number of patients in the United States who have colorectal cancer, let’s say 50% of them will have liver metastasis. Only 15%-20% of them will have liver-only metastasis.
This is only for patients who have liver-only metastasis without extrahepatic disease. And only maybe 15%-20% of them will meet all the criteria to be able to undergo liver transplantation. I think it’s for a very selective subset of patients who have very good tumor biology, generally young patients who don’t have any other alternative to having even a complex liver resection and are not able to get R0 resection. That is when we could think about doing liver transplantation.
It’s one more of the skills that we can have. It doesn’t mean that it will be the only skill, or the best skill, for all of the patients.
Dr. Schlechter: When a patient volunteers to be a living donor for a loved one or a family member, and they go through all the screening and they’re found to be a candidate, what is the surgical experience for that patient?
How long are they in the hospital? What sort of operation is that?
Dr. Dib: Living donors are very special patients. These are patients who do not need an operation. And the only reason they’re doing this is to save the life of their loved one. Donor safety is our priority number one, two, three, and four. The donor operation needs to be perfect.
And so we take good care of, first of all, selecting the living donors, making sure that they’re young and they don’t have any big contraindications. We also ensure that they are well informed of the process. The living donor surgery that we’re now doing is laparoscopic and minimally invasive. Here at Beth Israel Deaconess, we have done it laparoscopically with very good results.
I think that experience before and after the surgery gets so much better because of the better recovery. They’re able to go home, in general, within 4 or 5 days, and they get on with their normal life within 6-8 weeks. I think it’s important for them to know all the processes and the actual risks and benefits for the recipient.
Among those risks, I think it’s important for them to understand that this is a complex operation. Even if we do it laparoscopically or robotically, so that the scar is less, inside we’re still taking out half of the liver. That is a surgery that needs to be undertaken very meticulously, with a focus on minimizing any bleeding.
It’s a surgery that takes a long time. It takes about 6 hours. We do our best to try to minimize any risks.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. Thanks for that. Today we had Dr. Martin Dib joining us to discuss liver transplant for metastatic colorectal cancer. We discussed the various important criteria. We discussed that early referral to multidisciplinary centers that manage these is important to help get patients set up.
We discussed the fact that there are certain inclusion and exclusion criteria to consider. Obviously, unresectable disease is a critical determination that should be made by a liver surgeon. The absence of extrahepatic disease is important in staging with PET or other imaging. We discussed certain other biological exclusions.
There’s a relative contraindication of right-sided vs left-sided cancers, but right-sided cancers can be transplanted. We discussed that an elevated CEA greater than 80 is a contraindication, as are mutations in BRAF. We reviewed data from both the TRANSMET trial recently published in The Lancet and presented at ASCO in 2024, as well as the older Oslo criteria and Oslo trials and SECA trials.
And finally, we heard that donors can now come as living donors, a laparoscopic robotic surgery with a better safety profile, and greater access to organs that are ABO matched and not HLA matched because of the nature of the biology. Thank you again for joining us.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD, is senior physician, Gastrointestinal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Martin J. Dib, MD, is member of the faculty, Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School; director of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Division of Transplantation, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this transcript appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD: Dr. Dib is the director of the Hepatobiliary Surgery and Living Donor Program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center here in Boston, and a Harvard Medical School faculty member.
He was previously at the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, a leading international institution investigating the role of liver transplant in colorectal cancer, among other diseases. Dr. Dib, before we move to our discussion, I’d like to hear a bit about your pathway to becoming a transplant surgeon. How did you end up working on colorectal cancer and liver transplants in this field?
Martin J. Dib, MD: Thank you so much, Dr. Schlechter. I am originally from Chile. I had an opportunity to come to Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center after medical school and I did liver regeneration research at the transplant center. After that, I was lucky enough to match as a general surgery resident at Beth Israel Deaconess.
This is my alma mater and I was able to graduate as a surgeon here. You and I had some paths together. After graduating from Harvard as a surgeon, I was trained in liver transplant, abdominal transplant, surgical oncology, and hepatobiliary surgery at the University of Toronto.
I have been developing this passion for being able to transplant cancer patients and use organ transplant techniques to be able to do complex resections for cancer.
Dr. Schlechter: Let’s talk about the topic for today, which is liver transplant and colorectal cancer. I’ll be honest — this is not a very familiar topic for a lot of oncologists. There are a lot of details that I think are new to us as oncologists. We need to expand this conversation to get access to patients for this.
First and foremost, can you talk about some of the parameters for a resectable liver metastasis vs unresectable disease that would be an indication for a liver transplant?
Dr. Dib: I think this is a very interesting topic because liver transplantation for cancer is not new. Liver transplantation started in the 1960s when people started doing liver transplants for advanced liver tumors. The problem is that they were selecting patients who had very advanced — and poor tumor biology — tumors. The outcomes were not good.
It was only in 1996 when the Milan criteria started. Mazzaferro and colleagues, using strict patient selection, were able to do liver transplant for selected hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Having those excellent outcomes in selecting patients opened the field for what we now call transplant oncology, which is using selection criteria and using other methods to be able to select which patients will do well after transplantation, even with immunosuppression.
Liver transplantation for colorectal metastasis was used at the very beginning of the era of liver transplantation, but with very poor outcomes. It was abandoned because of the outcomes. It is exciting to see that after 20 years of not doing it, there was a group in Norway that started again. They are doing liver transplants for colorectal metastases (mets), but with very selected patients.
In Norway, they had a very unusual setting where they had more liver donors than patients on the list waiting for liver transplant. So they can’t share these livers and we’re all jealous, right? Every single country in the West struggles because we don’t have enough livers for the rest of the list. And they had a lot of livers to be able to transplant people.
They decided to transplant some selected patients with colorectal mets that were unresectable. And the surprise was that they found that they were able to get a 60% survival at 5 years. And so that was new. After that, in Norway, they started showing this data to other centers in the world. It wasn’t until this year that we could see not only the long-term data and long-term outcomes of using liver transplantation for unresectable colorectal mets, but also we’re now having data from a prospective clinical trial from France.
It was three countries in the prospective clinical trial: France, Belgium, and Italy. We now see that we have a little stronger data to support the use of liver transplants for unresectable colorectal mets.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s the TRANSMET study you’re referencing that was presented at ASCO in the late-breaking abstract session in 2024, and then more recently in The Lancet’s eClinicalMedicine. Both of those papers were led by René Adam. That was a cool presentation to sit through. I was in the room, and I was taking a ton of notes and there was a lot of info that came out of that.
First of all, it showed that patients who had received chemotherapy and were responding could then go on to liver transplant in that population. Impressively, 81% of the patients who were randomized to transplant received it. Frankly, that’s a big number, especially compared with the West, as you said, and in particular the US and here in New England where livers are a very precious commodity.
And even accounting for that, if you look at the intention-to-treat analysis, the 5-year overall survival in that population was 57% compared with 13% with chemotherapy. And that feels like a real number for chemotherapy. If you look at the per-protocol analysis, frankly, the numbers are higher.
It’s always a challenging assessment. What was also interesting to me was the pattern of recurrence, which in general was that recurrences were extrahepatic. So not only were patients rendered disease-free, but in general, the liver remained disease-free and only 3% of patients had liver-only recurrence and 11% had widespread metastatic disease.
The biggest group was lung metastases, at about 40%. Ultimately, they reported a progression-free survival of 17. 4 months for transplant compared with 6. 4 months with chemotherapy. On every parameter, it looks like liver transplant wins for these people. Help me out. Who are these people? How do we find these people?
What are the inclusions and exclusions for this population?
Dr. Dib: I think that’s very important. This is not a therapy that will be for every patient. These are selected patients who have liver-only unresectable colorectal mets. These are patients that don’t have any extrahepatic disease and that either the primary has been taken out already or that they have the primary present, but the plan is to take the primary and then do a liver transplantation after 3 months, hopefully after 6 months, of removing the primary.
These are patients who meet all the criteria that we have seen in terms of the best outcomes — patients that have Oslo scores of less than three. The Oslo trial, which included the SECA (Secondary Cancer)-I and SECA-II trials, basically showed that patients with a maximal tumor diameter of less than 5.5 with a pretransplant CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) of less than 80 that do not have progression on chemotherapy, among other variables, do better. But the concept is that this is a therapy that will apply only to selected patients. That way we can continue to have adequate overall survival post-transplant that would be comparable to other diseases that we do liver transplants for.
Dr. Schlechter: Were there other biomarkers, any mutations that were included or excluded?
Dr. Dib: Yes. If you look at SECA-I, SECA-II trial outcomes, and also TRANSMET, they all say patients with BRAF mutations shouldn’t be transplanted. There are other parameters, including, for example, the site of the primary tumor. Patients with a left-sided colon primary tumor do much better than patients who have a right-sided primary tumor.
That’s not a complete contraindication, but if you look at the most updated inclusion criteria of programs, like the ones that the one that we have here at Beth Israel Deaconess and many others, the inclusion criteria protocols include patients who have only hepatic disease.
So, if there are no extrahepatic mets, the resection of the primary has been done or will be done after a multidisciplinary discussion. We want to make sure they have the absence of BRAF mutation, and that they don’t have disease progression while on chemotherapy. So hopefully we have data from enough months to be able to make sure that there’s no intrahepatic or extrahepatic progression while on chemotherapy.
And that’s including CEA and also looking at the imaging.
Dr. Schlechter: When you’re seeing a patient, how much chemo do you think they should have? What’s a good run chemotherapy-wise for these patients? Let’s say, before I refer a patient to you, how much chemo should they have? And then what should I do? Do I get a PET scan? Do I get MRI? What’s the right scanning I should do to prove there’s no extrahepatic disease before sending a patient in for consideration?
Dr. Dib: First, we need to confirm unresectability. Referring patients early is always a good measure to make sure that we’re all in agreement that it’s an unresectable patient. Having a PET scan from the very beginning is helpful because it shows the disease before doing chemotherapy.
In terms of the lines of chemotherapy, ideally in the TRANSMET trial, for example, the idea was to show tumor control for at least 3 months, with less than three lines of chemotherapy. Some patients will do that with FOLFIRI. It depends on the case.
I think some of those evaluations will need a multidisciplinary discussion. In our case, we are connected to the Norway team. We frequently talk with the Oslo team and an international community of transplant centers to get opinions on particular cases.
But I think referring patients early is a good measure. If we don’t think that they qualify, we will let the team know. We’re strictly looking at patients who have unresectable liver mets that don’t have extrahepatic disease. The idea is to do a primary tumor resection, and then get to transplantation, hopefully after 6 months. In some cases that have some concerns in terms of tumor biology, we may even extend the time from diagnosis to transplant to over 1.5 years.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And what’s the experience like for these patients? In training as a resident many years ago, I saw patients with cirrhosis who went on to have a liver transplant, and that was sort of trading one disease for another. What is the posttransplant, or the remission, experience of a liver transplant for colorectal cancer like for the patient?
Dr. Dib: That’s a very important point. I think that transplantation has gotten better and better, as has chemotherapy systemic therapy. The liver transplantation experience from 20 years ago has improved dramatically. I think the quality of life of liver transplant patients after transplantation has increased quite a bit.
At Beth Israel Deaconess, we have a liver transplant program that is doing over a 100 livers a year. And when you have a high-volume center, usually the experience gets better. The time in the hospital post-transplant decreases.
In general, when we’re doing liver transplants, patients are getting extubated in the OR 30% of the time. The vast majority of patients are going home within 1 or 2 weeks. They need to have immunosuppression for the rest of their lives. We have a very good program of transplant coordinators that will help the family and the patient to live with immunosuppression and live with a transplanted organ.
But I would say that we have many, many patients, especially these patients who are not patients with cirrhosis. Their health is not as deteriorated as patients who have low MELD (model for end-stage liver disease) scores. They don’t have liver disease. They have cancer. So usually patients like that, many of them can go back to work and live a quality of life that is fairly reasonable.
Dr. Schlechter: That’s good to hear. When we hear statements like liver transplant for colon cancer, a lot of us have this picture of a much sicker population, but it’s interesting and true that the colorectal cancer population as a candidate for liver transplant is a much healthier population than the population with cirrhosis.
Let’s talk about organs and donors. Largely in the TRANSMET study, for example, that was cadaveric donors. Those were not living donors and you’ve done a lot of work on living donors. If the answer in the United States, because of limited access to organs, is going to be living donors, who are those donors?
What is that like? How do you identify them?
Dr. Dib: There’s a lot of advantages to using living donors for these patients. In any type of patient that needs a liver transplant, cadaveric donors or deceased donors is the same concept. There are two types of deceased donors: the brain-dead donors and donors after cardiac death. Those are hard to come by.
We still have 15%-20% mortality on the waiting list in the United States. We’re already still struggling to get enough donors to transplant the patients that are on the list. Now, if you add a new indication, which is unresectable colorectal mets, we need to make sure that the outcomes are equivalent to the patients who are going to be transplanted for other reasons.
Right now, for example, the 5-year overall survival of a patient with cirrhosis, or a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma, is over 80% 5-year survival. In the SECA trials and TRANSMET trial, if we do a good selection, I think we can get to 70% 5-year survival. But until we have more data, I think it’s a cautious measure to, as a field, try to use living donors and not compete with the rest of the list of patients who are already dying on the list for liver transplants.
Once we get more data, it’s going to be something that, in the transplant community, we may be able to use deceased donors. Especially deceased donors with maybe extended criteria that are not going to be used for other patients. We can do living-unrelated or living-related donations. Family members or also friends or neighbors or part of the community, even altruistic donors, can donate to a potential recipient. And that enables us to not only time the transplant in an adequate manner, because we’re able to transplant the patient early, but also time it so we can give the number of chemotherapy cycles that we want to give.
That’s a huge advantage. You don’t compete for a liver with the cadaveric waiting list of patients that are waiting for other reasons, and you can select the tumor biology very well because you know exactly when the surgery is going to be. For instance, we can say, okay, this patient has KRAS mutation, left-sided colon cancer, and has been having good tumor biology with no progression. We will wait 6 months from the primary tumor to the transplant, which is going to be 1 year from diagnosis to transplant. And we can see during that time whether they continue to have good tumor biology.
But if you have a deceased donor liver transplant, sometimes you can’t time that well and schedule it. It becomes a bit more tricky in terms of patient selection and making sure that we do this for the people who are going to benefit.
Dr. Schlechter: And how does donor matching work? Is it HLA (human leukocyte antigen) matched or ABO-matched? Who can donate when you say a living-related? For example, when we think about bone marrow transplantation, which we’re all familiar with in the oncology population, it’s an incredibly complex match process. Is this the same challenge?
Dr. Dib: No, it’s a little bit simpler. Living donors for liver transplants need to be between the ages of 18 and 60. They need to be relatively healthy, relatively fit, with a BMI hopefully less than 30, definitely less than 35. The compatibility is ABO compatibility. So, if they’re ABO-compatible, relatively young, relatively healthy, they would be a potential donor and we will go ahead and do a CT scan.
If the CT scan shows that they have a good, adequate anatomy, more than 90% of those will be good donors. I would say that out of 100 people who want to be donors, 25 of them will be adequate. One out of four people who want to save their family member and want to have this operation are able to donate half of their liver to their family member or loved one.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. And it’s helpful to know that the matching process is simpler. During his discussion, René Adam unequivocally stated that liver transplants are a new standard of care for colorectal cancer. And I guess my question is, do you agree with this statement? How do we balance the demand for living donors and the demand for deceased donors? Especially in a time of increasing fatty liver disease and obesity, other indications for liver transplant, causes of cirrhosis, and also in an era of young-onset colorectal cancer. Patients are younger. Is this a new standard of care? Do you agree with that statement?
Dr. Dib: I do agree with that statement. I think it’s important to understand that not all patients with colorectal mets are the same. Of the number of patients in the United States who have colorectal cancer, let’s say 50% of them will have liver metastasis. Only 15%-20% of them will have liver-only metastasis.
This is only for patients who have liver-only metastasis without extrahepatic disease. And only maybe 15%-20% of them will meet all the criteria to be able to undergo liver transplantation. I think it’s for a very selective subset of patients who have very good tumor biology, generally young patients who don’t have any other alternative to having even a complex liver resection and are not able to get R0 resection. That is when we could think about doing liver transplantation.
It’s one more of the skills that we can have. It doesn’t mean that it will be the only skill, or the best skill, for all of the patients.
Dr. Schlechter: When a patient volunteers to be a living donor for a loved one or a family member, and they go through all the screening and they’re found to be a candidate, what is the surgical experience for that patient?
How long are they in the hospital? What sort of operation is that?
Dr. Dib: Living donors are very special patients. These are patients who do not need an operation. And the only reason they’re doing this is to save the life of their loved one. Donor safety is our priority number one, two, three, and four. The donor operation needs to be perfect.
And so we take good care of, first of all, selecting the living donors, making sure that they’re young and they don’t have any big contraindications. We also ensure that they are well informed of the process. The living donor surgery that we’re now doing is laparoscopic and minimally invasive. Here at Beth Israel Deaconess, we have done it laparoscopically with very good results.
I think that experience before and after the surgery gets so much better because of the better recovery. They’re able to go home, in general, within 4 or 5 days, and they get on with their normal life within 6-8 weeks. I think it’s important for them to know all the processes and the actual risks and benefits for the recipient.
Among those risks, I think it’s important for them to understand that this is a complex operation. Even if we do it laparoscopically or robotically, so that the scar is less, inside we’re still taking out half of the liver. That is a surgery that needs to be undertaken very meticulously, with a focus on minimizing any bleeding.
It’s a surgery that takes a long time. It takes about 6 hours. We do our best to try to minimize any risks.
Dr. Schlechter: Excellent. Thanks for that. Today we had Dr. Martin Dib joining us to discuss liver transplant for metastatic colorectal cancer. We discussed the various important criteria. We discussed that early referral to multidisciplinary centers that manage these is important to help get patients set up.
We discussed the fact that there are certain inclusion and exclusion criteria to consider. Obviously, unresectable disease is a critical determination that should be made by a liver surgeon. The absence of extrahepatic disease is important in staging with PET or other imaging. We discussed certain other biological exclusions.
There’s a relative contraindication of right-sided vs left-sided cancers, but right-sided cancers can be transplanted. We discussed that an elevated CEA greater than 80 is a contraindication, as are mutations in BRAF. We reviewed data from both the TRANSMET trial recently published in The Lancet and presented at ASCO in 2024, as well as the older Oslo criteria and Oslo trials and SECA trials.
And finally, we heard that donors can now come as living donors, a laparoscopic robotic surgery with a better safety profile, and greater access to organs that are ABO matched and not HLA matched because of the nature of the biology. Thank you again for joining us.
Benjamin L. Schlechter, MD, is senior physician, Gastrointestinal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Martin J. Dib, MD, is member of the faculty, Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School; director of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Division of Transplantation, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this transcript appeared on Medscape.com.
Diet Rich in Processed Foods Linked to Elevated Risk for Colorectal Cancer
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no known studies have investigated how a dietary pattern (rather than just individual foods or nutrients) specifically directed at CRC-related microbes may contribute to an increased CRC risk.
- Using stool metagenomes and dietary information from 307 men and 212 women, researchers identified and then validated a dietary pattern specifically linked to an established CRC-related gut microbial signature, which they termed the CRC Microbial Dietary Score (CMDS).
- They then investigated the association between CMDS and the risk for CRC in 259,200 participants (50,637 men and 208,563 women) from three large US cohorts where health professionals provided detailed information on various lifestyle factors over long follow-up periods.
- Researchers also analyzed the risk for CRC on the basis of the presence of gut bacteria, such as F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, in the tumor tissues of the participants who underwent surgical resection for CRC.
TAKEAWAY:
- The CMDS was characterized by high intake of processed foods and low intake of fiber-rich foods.
- Over 6,467,378 person-years assessed in the three US cohorts, 3854 cases of incident CRC were documented, with 1172, 1096, and 1119 cases measured for F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, respectively.
- A higher CMDS was associated with an increased risk for CRC after adjusting for putative CRC risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; Ptrend < .001).
- The association between CMDS and the risk for CRC was stronger for tumors with detectable levels of F nucleatum (HR, 2.51; Ptrend < .001), pks+ E coli (HR, 1.68; Ptrend = .005), and ETBF (HR, 2.06; Ptrend = .016).
IN PRACTICE:
“A dietary pattern with a low consumption of processed foods may help prevent colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiome. The dietary pattern modulating the colorectal cancer–related gut microbial signature may particularly help prevent tumoral microbial positive colorectal cancer, which tends to have a worse prognosis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Kai Wang and Chun-Han Lo, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design may have limited the ability to establish causality between dietary patterns and the risk for CRC. The inclusion of participants who were all health professionals from a predominantly White US population may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations. The reliance on self-reported dietary data may have introduced recall bias and affected the accuracy of the dietary pattern assessed.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by various sources, including the National Institutes of Health and the Cancer Research UK Grand Challenge Award. One author served as a consultant for some pharmaceutical companies, and another received funding from various sources, both unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no known studies have investigated how a dietary pattern (rather than just individual foods or nutrients) specifically directed at CRC-related microbes may contribute to an increased CRC risk.
- Using stool metagenomes and dietary information from 307 men and 212 women, researchers identified and then validated a dietary pattern specifically linked to an established CRC-related gut microbial signature, which they termed the CRC Microbial Dietary Score (CMDS).
- They then investigated the association between CMDS and the risk for CRC in 259,200 participants (50,637 men and 208,563 women) from three large US cohorts where health professionals provided detailed information on various lifestyle factors over long follow-up periods.
- Researchers also analyzed the risk for CRC on the basis of the presence of gut bacteria, such as F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, in the tumor tissues of the participants who underwent surgical resection for CRC.
TAKEAWAY:
- The CMDS was characterized by high intake of processed foods and low intake of fiber-rich foods.
- Over 6,467,378 person-years assessed in the three US cohorts, 3854 cases of incident CRC were documented, with 1172, 1096, and 1119 cases measured for F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, respectively.
- A higher CMDS was associated with an increased risk for CRC after adjusting for putative CRC risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; Ptrend < .001).
- The association between CMDS and the risk for CRC was stronger for tumors with detectable levels of F nucleatum (HR, 2.51; Ptrend < .001), pks+ E coli (HR, 1.68; Ptrend = .005), and ETBF (HR, 2.06; Ptrend = .016).
IN PRACTICE:
“A dietary pattern with a low consumption of processed foods may help prevent colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiome. The dietary pattern modulating the colorectal cancer–related gut microbial signature may particularly help prevent tumoral microbial positive colorectal cancer, which tends to have a worse prognosis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Kai Wang and Chun-Han Lo, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design may have limited the ability to establish causality between dietary patterns and the risk for CRC. The inclusion of participants who were all health professionals from a predominantly White US population may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations. The reliance on self-reported dietary data may have introduced recall bias and affected the accuracy of the dietary pattern assessed.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by various sources, including the National Institutes of Health and the Cancer Research UK Grand Challenge Award. One author served as a consultant for some pharmaceutical companies, and another received funding from various sources, both unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no known studies have investigated how a dietary pattern (rather than just individual foods or nutrients) specifically directed at CRC-related microbes may contribute to an increased CRC risk.
- Using stool metagenomes and dietary information from 307 men and 212 women, researchers identified and then validated a dietary pattern specifically linked to an established CRC-related gut microbial signature, which they termed the CRC Microbial Dietary Score (CMDS).
- They then investigated the association between CMDS and the risk for CRC in 259,200 participants (50,637 men and 208,563 women) from three large US cohorts where health professionals provided detailed information on various lifestyle factors over long follow-up periods.
- Researchers also analyzed the risk for CRC on the basis of the presence of gut bacteria, such as F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, in the tumor tissues of the participants who underwent surgical resection for CRC.
TAKEAWAY:
- The CMDS was characterized by high intake of processed foods and low intake of fiber-rich foods.
- Over 6,467,378 person-years assessed in the three US cohorts, 3854 cases of incident CRC were documented, with 1172, 1096, and 1119 cases measured for F nucleatum, pks+ E coli, and ETBF, respectively.
- A higher CMDS was associated with an increased risk for CRC after adjusting for putative CRC risk factors (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; Ptrend < .001).
- The association between CMDS and the risk for CRC was stronger for tumors with detectable levels of F nucleatum (HR, 2.51; Ptrend < .001), pks+ E coli (HR, 1.68; Ptrend = .005), and ETBF (HR, 2.06; Ptrend = .016).
IN PRACTICE:
“A dietary pattern with a low consumption of processed foods may help prevent colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiome. The dietary pattern modulating the colorectal cancer–related gut microbial signature may particularly help prevent tumoral microbial positive colorectal cancer, which tends to have a worse prognosis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Kai Wang and Chun-Han Lo, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design may have limited the ability to establish causality between dietary patterns and the risk for CRC. The inclusion of participants who were all health professionals from a predominantly White US population may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations. The reliance on self-reported dietary data may have introduced recall bias and affected the accuracy of the dietary pattern assessed.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by various sources, including the National Institutes of Health and the Cancer Research UK Grand Challenge Award. One author served as a consultant for some pharmaceutical companies, and another received funding from various sources, both unrelated to this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SBRT vs Surgery in CRC Lung Metastases: Which Is Better?
TOPLINE:
However, those who received surgery had significantly better progression-free and disease-free survival rates, as well as a longer time to intrathoracic progression.
METHODOLOGY:
- SBRT has been shown to provide effective local control and improve short-term survival for patients with pulmonary oligometastases from CRC and has become an alternative for these patients who are ineligible or reluctant to undergo surgery. It’s unclear, however, whether SBRT should be prioritized over surgery in patients with CRC pulmonary metastases, largely because of a lack of prospective data.
- In the current analysis, researchers compared outcomes among 335 patients (median age, 61 years) with lung metastases from CRC who underwent surgery or SBRT, using data from the Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute between March 2011 and September 2022.
- A total of 251 patients were included in the final analysis after propensity score matching, 173 (68.9%) underwent surgery and 78 (31.1%) received SBRT. The median follow-up was 61.6 months in the surgery group and 54.4 months in the SBRT group.
- The study outcomes were freedom from intrathoracic progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 5 years, rates of freedom from intrathoracic progression were more than twofold higher in the surgery group than in the SBRT group (53% vs 23.4%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.46; P < .001). Progression-free survival rates were also more than twofold higher in the surgery group vs the SBRT group (43.8% vs 18.5%; HR, 0.47; P < .001), respectively. In the SBRT group, a higher percentage of patients had a disease-free interval of less than 12 months compared with the surgery group, with rates of 48.7% and 32.9%, respectively (P = 0.025).
- Overall survival, however, was not significantly different between the two groups at 5 years (72.5% in the surgery group vs 63.7% in the SBRT group; P = .260). The number of pulmonary metastases (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.11-3.14, P = .019 and tumor size (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.05, P = .023) were significant prognostic factors for overall survival.
- Local recurrence was more prevalent after SBRT (33.3%) than surgery (16.9%), while new intrathoracic tumors occurred more frequently after surgery than SBRT (71.8% vs 43.1%). Repeated local treatments were common among patients with intrathoracic progression, which might have contributed to favorable survival outcomes in both groups.
- Both treatments were well-tolerated with no treatment-related mortality or grade ≥ 3 toxicities. In the surgery group, 14 patients experienced complications, including atrial fibrillation (n = 4) and prolonged air leaks (n = 7). In the SBRT group, radiation pneumonitis was the most common adverse event (n = 21).
IN PRACTICE:
SBRT yielded overall survival benefits similar to surgery despite a “higher likelihood of prior extrapulmonary metastases, a shorter disease-free interval, and a greater number of metastatic lesions,” the authors wrote. Still, SBRT should be regarded as an “effective alternative in cases in which surgical intervention is either unviable or declined by the patient,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was co-led by Yaqi Wang and Xin Dong, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China, and was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
This single-center retrospective study had an inherent selection bias. The lack of balanced sample sizes of the surgery and SBRT groups might have affected the robustness of the statistical analyses. Detailed data on adverse events were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Beijing Natural Science Foundation, and Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospital’s Ascent Plan. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
However, those who received surgery had significantly better progression-free and disease-free survival rates, as well as a longer time to intrathoracic progression.
METHODOLOGY:
- SBRT has been shown to provide effective local control and improve short-term survival for patients with pulmonary oligometastases from CRC and has become an alternative for these patients who are ineligible or reluctant to undergo surgery. It’s unclear, however, whether SBRT should be prioritized over surgery in patients with CRC pulmonary metastases, largely because of a lack of prospective data.
- In the current analysis, researchers compared outcomes among 335 patients (median age, 61 years) with lung metastases from CRC who underwent surgery or SBRT, using data from the Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute between March 2011 and September 2022.
- A total of 251 patients were included in the final analysis after propensity score matching, 173 (68.9%) underwent surgery and 78 (31.1%) received SBRT. The median follow-up was 61.6 months in the surgery group and 54.4 months in the SBRT group.
- The study outcomes were freedom from intrathoracic progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 5 years, rates of freedom from intrathoracic progression were more than twofold higher in the surgery group than in the SBRT group (53% vs 23.4%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.46; P < .001). Progression-free survival rates were also more than twofold higher in the surgery group vs the SBRT group (43.8% vs 18.5%; HR, 0.47; P < .001), respectively. In the SBRT group, a higher percentage of patients had a disease-free interval of less than 12 months compared with the surgery group, with rates of 48.7% and 32.9%, respectively (P = 0.025).
- Overall survival, however, was not significantly different between the two groups at 5 years (72.5% in the surgery group vs 63.7% in the SBRT group; P = .260). The number of pulmonary metastases (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.11-3.14, P = .019 and tumor size (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.05, P = .023) were significant prognostic factors for overall survival.
- Local recurrence was more prevalent after SBRT (33.3%) than surgery (16.9%), while new intrathoracic tumors occurred more frequently after surgery than SBRT (71.8% vs 43.1%). Repeated local treatments were common among patients with intrathoracic progression, which might have contributed to favorable survival outcomes in both groups.
- Both treatments were well-tolerated with no treatment-related mortality or grade ≥ 3 toxicities. In the surgery group, 14 patients experienced complications, including atrial fibrillation (n = 4) and prolonged air leaks (n = 7). In the SBRT group, radiation pneumonitis was the most common adverse event (n = 21).
IN PRACTICE:
SBRT yielded overall survival benefits similar to surgery despite a “higher likelihood of prior extrapulmonary metastases, a shorter disease-free interval, and a greater number of metastatic lesions,” the authors wrote. Still, SBRT should be regarded as an “effective alternative in cases in which surgical intervention is either unviable or declined by the patient,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was co-led by Yaqi Wang and Xin Dong, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China, and was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
This single-center retrospective study had an inherent selection bias. The lack of balanced sample sizes of the surgery and SBRT groups might have affected the robustness of the statistical analyses. Detailed data on adverse events were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Beijing Natural Science Foundation, and Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospital’s Ascent Plan. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
However, those who received surgery had significantly better progression-free and disease-free survival rates, as well as a longer time to intrathoracic progression.
METHODOLOGY:
- SBRT has been shown to provide effective local control and improve short-term survival for patients with pulmonary oligometastases from CRC and has become an alternative for these patients who are ineligible or reluctant to undergo surgery. It’s unclear, however, whether SBRT should be prioritized over surgery in patients with CRC pulmonary metastases, largely because of a lack of prospective data.
- In the current analysis, researchers compared outcomes among 335 patients (median age, 61 years) with lung metastases from CRC who underwent surgery or SBRT, using data from the Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute between March 2011 and September 2022.
- A total of 251 patients were included in the final analysis after propensity score matching, 173 (68.9%) underwent surgery and 78 (31.1%) received SBRT. The median follow-up was 61.6 months in the surgery group and 54.4 months in the SBRT group.
- The study outcomes were freedom from intrathoracic progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 5 years, rates of freedom from intrathoracic progression were more than twofold higher in the surgery group than in the SBRT group (53% vs 23.4%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.46; P < .001). Progression-free survival rates were also more than twofold higher in the surgery group vs the SBRT group (43.8% vs 18.5%; HR, 0.47; P < .001), respectively. In the SBRT group, a higher percentage of patients had a disease-free interval of less than 12 months compared with the surgery group, with rates of 48.7% and 32.9%, respectively (P = 0.025).
- Overall survival, however, was not significantly different between the two groups at 5 years (72.5% in the surgery group vs 63.7% in the SBRT group; P = .260). The number of pulmonary metastases (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.11-3.14, P = .019 and tumor size (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.05, P = .023) were significant prognostic factors for overall survival.
- Local recurrence was more prevalent after SBRT (33.3%) than surgery (16.9%), while new intrathoracic tumors occurred more frequently after surgery than SBRT (71.8% vs 43.1%). Repeated local treatments were common among patients with intrathoracic progression, which might have contributed to favorable survival outcomes in both groups.
- Both treatments were well-tolerated with no treatment-related mortality or grade ≥ 3 toxicities. In the surgery group, 14 patients experienced complications, including atrial fibrillation (n = 4) and prolonged air leaks (n = 7). In the SBRT group, radiation pneumonitis was the most common adverse event (n = 21).
IN PRACTICE:
SBRT yielded overall survival benefits similar to surgery despite a “higher likelihood of prior extrapulmonary metastases, a shorter disease-free interval, and a greater number of metastatic lesions,” the authors wrote. Still, SBRT should be regarded as an “effective alternative in cases in which surgical intervention is either unviable or declined by the patient,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was co-led by Yaqi Wang and Xin Dong, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China, and was published online in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics.
LIMITATIONS:
This single-center retrospective study had an inherent selection bias. The lack of balanced sample sizes of the surgery and SBRT groups might have affected the robustness of the statistical analyses. Detailed data on adverse events were not available.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Beijing Natural Science Foundation, and Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospital’s Ascent Plan. The authors did not declare any conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Aspirin for CRC Prevention May Work Best in Adults With Unhealthy Lifestyles
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Closing the Gap: Priority Zones Identified for CRC Screening in Hispanic/Latino Populations
TOPLINE:
Researchers identified thousands of census tracts as priority zones where improving the screening of colorectal cancer (CRC) may benefit Hispanic or Latino communities.
METHODOLOGY:
- Hispanic or Latino individuals have the lowest rate of CRC screening among the six broader census-designated racial or ethnic groups in the United States, while they face a high proportion of cancer deaths due to CRC.
- Researchers performed a cross-sectional ecologic study using 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES and 2019 American Community Survey data to identify priority zones for CRC screening where intervention programs may be targeted.
- They analyzed a total of 72,136 US census tracts, representing 98.7% of all US census tracts.
- Nine race and ethnic groups were selected on the basis of the population size and categorizations used in prior research on health or cancer disparity: non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, Asian, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican, Central or South American, and “other race.”
- Geographically weighted regression and Getis-Ord Gi* hot spot procedures were used to identify the screening priority zones for all Hispanic or Latino groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analysis identified 6519 hot spot tracts for Mexican, 3477 for Puerto Rican, 3522 for Central or South American, 1069 for Dominican, and 1424 for Cuban individuals. The average rates of screening for CRC were 57.2%, 59.9%, 59.3%, 58.9%, and 60.4%, respectively.
- The percentage of Cuban individuals showed a positive association with the CRC screening rate, while the percentage of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Dominican, and Central or South American Hispanic or Latino individuals and of the uninsured showed a negative association with the CRC screening rate.
- The priority zones for Mexican communities were primarily located in Texas and southwestern United States, while those for Puerto Rican, Central or South American, and other populations were located in southern Florida and the metro areas of New York City and Texas.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings and interactive web map may serve as a translational tool for public health authorities, policymakers, clinicians, and other stakeholders to target investment and interventions to increase guideline-concordant CRC screening uptake benefiting specific H/L [Hispanic or Latino] communities in the United States,” the authors wrote. “These data can inform more precise neighborhood-level interventions to increase CRC screening considering unique characteristics important for these H/L [Hispanic or Latino] groups.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by R. Blake Buchalter, PhD, MPH, Center for Populations Health Research, Department of Quantitative Health Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, was published online in the American Journal of Public Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to infer causality. The use of census tract-level data did not capture individual-level screening behaviors. The study did not account for nativity status or years of migration owing to the lack of data. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES dataset may not represent the actual screening delivered as it is based on survey data.
DISCLOSURES:
The National Cancer Institute partially supported this study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Researchers identified thousands of census tracts as priority zones where improving the screening of colorectal cancer (CRC) may benefit Hispanic or Latino communities.
METHODOLOGY:
- Hispanic or Latino individuals have the lowest rate of CRC screening among the six broader census-designated racial or ethnic groups in the United States, while they face a high proportion of cancer deaths due to CRC.
- Researchers performed a cross-sectional ecologic study using 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES and 2019 American Community Survey data to identify priority zones for CRC screening where intervention programs may be targeted.
- They analyzed a total of 72,136 US census tracts, representing 98.7% of all US census tracts.
- Nine race and ethnic groups were selected on the basis of the population size and categorizations used in prior research on health or cancer disparity: non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, Asian, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican, Central or South American, and “other race.”
- Geographically weighted regression and Getis-Ord Gi* hot spot procedures were used to identify the screening priority zones for all Hispanic or Latino groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analysis identified 6519 hot spot tracts for Mexican, 3477 for Puerto Rican, 3522 for Central or South American, 1069 for Dominican, and 1424 for Cuban individuals. The average rates of screening for CRC were 57.2%, 59.9%, 59.3%, 58.9%, and 60.4%, respectively.
- The percentage of Cuban individuals showed a positive association with the CRC screening rate, while the percentage of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Dominican, and Central or South American Hispanic or Latino individuals and of the uninsured showed a negative association with the CRC screening rate.
- The priority zones for Mexican communities were primarily located in Texas and southwestern United States, while those for Puerto Rican, Central or South American, and other populations were located in southern Florida and the metro areas of New York City and Texas.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings and interactive web map may serve as a translational tool for public health authorities, policymakers, clinicians, and other stakeholders to target investment and interventions to increase guideline-concordant CRC screening uptake benefiting specific H/L [Hispanic or Latino] communities in the United States,” the authors wrote. “These data can inform more precise neighborhood-level interventions to increase CRC screening considering unique characteristics important for these H/L [Hispanic or Latino] groups.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by R. Blake Buchalter, PhD, MPH, Center for Populations Health Research, Department of Quantitative Health Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, was published online in the American Journal of Public Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to infer causality. The use of census tract-level data did not capture individual-level screening behaviors. The study did not account for nativity status or years of migration owing to the lack of data. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES dataset may not represent the actual screening delivered as it is based on survey data.
DISCLOSURES:
The National Cancer Institute partially supported this study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Researchers identified thousands of census tracts as priority zones where improving the screening of colorectal cancer (CRC) may benefit Hispanic or Latino communities.
METHODOLOGY:
- Hispanic or Latino individuals have the lowest rate of CRC screening among the six broader census-designated racial or ethnic groups in the United States, while they face a high proportion of cancer deaths due to CRC.
- Researchers performed a cross-sectional ecologic study using 2021 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES and 2019 American Community Survey data to identify priority zones for CRC screening where intervention programs may be targeted.
- They analyzed a total of 72,136 US census tracts, representing 98.7% of all US census tracts.
- Nine race and ethnic groups were selected on the basis of the population size and categorizations used in prior research on health or cancer disparity: non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, Asian, Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican, Central or South American, and “other race.”
- Geographically weighted regression and Getis-Ord Gi* hot spot procedures were used to identify the screening priority zones for all Hispanic or Latino groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analysis identified 6519 hot spot tracts for Mexican, 3477 for Puerto Rican, 3522 for Central or South American, 1069 for Dominican, and 1424 for Cuban individuals. The average rates of screening for CRC were 57.2%, 59.9%, 59.3%, 58.9%, and 60.4%, respectively.
- The percentage of Cuban individuals showed a positive association with the CRC screening rate, while the percentage of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Dominican, and Central or South American Hispanic or Latino individuals and of the uninsured showed a negative association with the CRC screening rate.
- The priority zones for Mexican communities were primarily located in Texas and southwestern United States, while those for Puerto Rican, Central or South American, and other populations were located in southern Florida and the metro areas of New York City and Texas.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings and interactive web map may serve as a translational tool for public health authorities, policymakers, clinicians, and other stakeholders to target investment and interventions to increase guideline-concordant CRC screening uptake benefiting specific H/L [Hispanic or Latino] communities in the United States,” the authors wrote. “These data can inform more precise neighborhood-level interventions to increase CRC screening considering unique characteristics important for these H/L [Hispanic or Latino] groups.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by R. Blake Buchalter, PhD, MPH, Center for Populations Health Research, Department of Quantitative Health Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, was published online in the American Journal of Public Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to infer causality. The use of census tract-level data did not capture individual-level screening behaviors. The study did not account for nativity status or years of migration owing to the lack of data. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention PLACES dataset may not represent the actual screening delivered as it is based on survey data.
DISCLOSURES:
The National Cancer Institute partially supported this study. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



