User login
Statins might protect against rectal anastomotic leaks
SEATTLE – Statins appeared to decrease the risk of sepsis after colorectal surgery and of anastomotic leak after rectal resection in a review of 7,285 elective colorectal surgery patients at 64 Michigan hospitals.
Overall, 2,515 patients (34.5%) were on statins preoperatively and received at least one dose while in the hospital post op. Their outcomes were compared with those of the 4,770 patients (65.5%) who were not on statins.
Statin patients were older (mean, 68 vs. 59 years) with more comorbidities (mean, 2.4 vs. 1.1), including diabetes (34% vs.12%) and hypertension (78% vs. 41%). The majority of statin patients were American Society of Anesthesiologists class 3, and the majority of nonstatin patients were class 1 or 2. The investigators controlled for those and other confounders by multivariate logistic regression and propensity scoring.
“We believe that statin medications can reduce sepsis in the colorectal patient population and may improve anastomotic leak rates for rectal resections,” concluded investigators led by David Disbrow, MD, a colorectal surgery fellow at St. Joseph Mercy Hospital in Ann Arbor, Mich.
The immediate take-home from the study is to make sure that patients who should be on statins for hypercholesterolemia or other reasons are actually taking the drugs prior to colorectal surgery. It just might improve their surgical outcomes. “I think that would be a good way to start,” Dr. Disbrow said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
If statins truly do help reduce postop sepsis and rectal anastomotic leaks, he said, it’s probably because of their anti-inflammatory effects, which have been demonstrated in previous studies. New Zealand investigators, for instance, randomized 65 patients to 40 mg oral simvastatin for up to a week before elective colorectal resections or Hartmann’s procedure reversals and for 2 weeks afterwards; 67 patients were randomized to placebo. The simvastatin group had significantly lower postop plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha (J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Aug;223[2]:308-20.e1).
Even so, there were no between-group differences in postoperative complications in that study, and, in general, the impact of statins on postop complications has been mixed in the literature. Some studies have shown benefits, others have suggested harm, and a few have shown nothing either way.
It’s the same situation with prior looks at anastomotic leaks. A Danish review of 2,766 patients who had colorectal anastomoses – 496 (19%) treated perioperatively with statins, some in high-dose – found no difference in leakage rates (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.84-2.05; P = 0.23)(Dis Colon Rectum. 2013 Aug;56[8]:980-6). On the other hand, a more recent British review of 144 patients – 45 (39.4%) on preoperative statins – found that “although patients taking statins did not have a significantly reduced leak risk, compared to nonstatin users, high-risk patients taking statins had the same leak risk as non–high risk patients; therefore, it is plausible that statins normalize the risk of anastomotic leak in high-risk patients” (Gut. 2015;64:A162-3).
In the new Michigan study, there were no differences in surgical site infections or 30-day mortality between statin and nonstatin patients, but patients on statins were less likely to get pneumonia, which might help account for their lower sepsis risk, Dr. Disbrow said.
Data for the study came from the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative database.
Dr. Disbrow had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Statins appeared to decrease the risk of sepsis after colorectal surgery and of anastomotic leak after rectal resection in a review of 7,285 elective colorectal surgery patients at 64 Michigan hospitals.
Overall, 2,515 patients (34.5%) were on statins preoperatively and received at least one dose while in the hospital post op. Their outcomes were compared with those of the 4,770 patients (65.5%) who were not on statins.
Statin patients were older (mean, 68 vs. 59 years) with more comorbidities (mean, 2.4 vs. 1.1), including diabetes (34% vs.12%) and hypertension (78% vs. 41%). The majority of statin patients were American Society of Anesthesiologists class 3, and the majority of nonstatin patients were class 1 or 2. The investigators controlled for those and other confounders by multivariate logistic regression and propensity scoring.
“We believe that statin medications can reduce sepsis in the colorectal patient population and may improve anastomotic leak rates for rectal resections,” concluded investigators led by David Disbrow, MD, a colorectal surgery fellow at St. Joseph Mercy Hospital in Ann Arbor, Mich.
The immediate take-home from the study is to make sure that patients who should be on statins for hypercholesterolemia or other reasons are actually taking the drugs prior to colorectal surgery. It just might improve their surgical outcomes. “I think that would be a good way to start,” Dr. Disbrow said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
If statins truly do help reduce postop sepsis and rectal anastomotic leaks, he said, it’s probably because of their anti-inflammatory effects, which have been demonstrated in previous studies. New Zealand investigators, for instance, randomized 65 patients to 40 mg oral simvastatin for up to a week before elective colorectal resections or Hartmann’s procedure reversals and for 2 weeks afterwards; 67 patients were randomized to placebo. The simvastatin group had significantly lower postop plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha (J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Aug;223[2]:308-20.e1).
Even so, there were no between-group differences in postoperative complications in that study, and, in general, the impact of statins on postop complications has been mixed in the literature. Some studies have shown benefits, others have suggested harm, and a few have shown nothing either way.
It’s the same situation with prior looks at anastomotic leaks. A Danish review of 2,766 patients who had colorectal anastomoses – 496 (19%) treated perioperatively with statins, some in high-dose – found no difference in leakage rates (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.84-2.05; P = 0.23)(Dis Colon Rectum. 2013 Aug;56[8]:980-6). On the other hand, a more recent British review of 144 patients – 45 (39.4%) on preoperative statins – found that “although patients taking statins did not have a significantly reduced leak risk, compared to nonstatin users, high-risk patients taking statins had the same leak risk as non–high risk patients; therefore, it is plausible that statins normalize the risk of anastomotic leak in high-risk patients” (Gut. 2015;64:A162-3).
In the new Michigan study, there were no differences in surgical site infections or 30-day mortality between statin and nonstatin patients, but patients on statins were less likely to get pneumonia, which might help account for their lower sepsis risk, Dr. Disbrow said.
Data for the study came from the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative database.
Dr. Disbrow had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Statins appeared to decrease the risk of sepsis after colorectal surgery and of anastomotic leak after rectal resection in a review of 7,285 elective colorectal surgery patients at 64 Michigan hospitals.
Overall, 2,515 patients (34.5%) were on statins preoperatively and received at least one dose while in the hospital post op. Their outcomes were compared with those of the 4,770 patients (65.5%) who were not on statins.
Statin patients were older (mean, 68 vs. 59 years) with more comorbidities (mean, 2.4 vs. 1.1), including diabetes (34% vs.12%) and hypertension (78% vs. 41%). The majority of statin patients were American Society of Anesthesiologists class 3, and the majority of nonstatin patients were class 1 or 2. The investigators controlled for those and other confounders by multivariate logistic regression and propensity scoring.
“We believe that statin medications can reduce sepsis in the colorectal patient population and may improve anastomotic leak rates for rectal resections,” concluded investigators led by David Disbrow, MD, a colorectal surgery fellow at St. Joseph Mercy Hospital in Ann Arbor, Mich.
The immediate take-home from the study is to make sure that patients who should be on statins for hypercholesterolemia or other reasons are actually taking the drugs prior to colorectal surgery. It just might improve their surgical outcomes. “I think that would be a good way to start,” Dr. Disbrow said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
If statins truly do help reduce postop sepsis and rectal anastomotic leaks, he said, it’s probably because of their anti-inflammatory effects, which have been demonstrated in previous studies. New Zealand investigators, for instance, randomized 65 patients to 40 mg oral simvastatin for up to a week before elective colorectal resections or Hartmann’s procedure reversals and for 2 weeks afterwards; 67 patients were randomized to placebo. The simvastatin group had significantly lower postop plasma concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha (J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Aug;223[2]:308-20.e1).
Even so, there were no between-group differences in postoperative complications in that study, and, in general, the impact of statins on postop complications has been mixed in the literature. Some studies have shown benefits, others have suggested harm, and a few have shown nothing either way.
It’s the same situation with prior looks at anastomotic leaks. A Danish review of 2,766 patients who had colorectal anastomoses – 496 (19%) treated perioperatively with statins, some in high-dose – found no difference in leakage rates (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.84-2.05; P = 0.23)(Dis Colon Rectum. 2013 Aug;56[8]:980-6). On the other hand, a more recent British review of 144 patients – 45 (39.4%) on preoperative statins – found that “although patients taking statins did not have a significantly reduced leak risk, compared to nonstatin users, high-risk patients taking statins had the same leak risk as non–high risk patients; therefore, it is plausible that statins normalize the risk of anastomotic leak in high-risk patients” (Gut. 2015;64:A162-3).
In the new Michigan study, there were no differences in surgical site infections or 30-day mortality between statin and nonstatin patients, but patients on statins were less likely to get pneumonia, which might help account for their lower sepsis risk, Dr. Disbrow said.
Data for the study came from the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative database.
Dr. Disbrow had no disclosures.
AT ASCRS 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The statin group had a reduced risk of sepsis (OR, 0.712; 95% CI, 0.535-0.948; P = .020), and, while statins were not associated with a reduction in anastomotic leaks overall, they were protective in subgroup analysis of patients who had rectal resections, which are especially prone to leakage (OR, 0.260; 95% CI, 0.112-0.605, P = .002).
Data source: A review of 7,285 elective colorectal surgery patients.
Disclosures: The lead investigator had no disclosures.
Colonoscopy patients prefer propofol over fentanyl/midazolam
SEATTLE – As patient satisfaction becomes increasingly important for reimbursements, it might be a good idea to switch to propofol for colonoscopies.
The reason is because patients prefer propofol over standard-of-care fentanyl/midazolam as their anesthetic for outpatient colonoscopies, according to a randomized, blinded trial at a single center. Importantly, clinical assessment also showed that propofol outperformed fentanyl/midazolam in terms of hypoxia, pain, nausea, and procedural difficulties.
“Our study demonstrated the superiority of propofol over fentanyl/midazolam in an outpatient setting from both a patient satisfaction standpoint and from a provider prospective,” said lead investigator Anantha Padmanabhan, MD, a colorectal surgeon with Mount Carmel Health, Columbus, Ohio.
The short duration of action and quick turnaround time have led to an increase in the use of propofol for outpatient procedures. It’s been studied extensively for safety and efficacy, but patient preference has not been well documented. The investigators wanted to look into the issue because patient satisfaction has become an important metric for reimbursement, Dr. Padmanabhan said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, where the study was presented.
Patients were randomly assigned to propofol or fentanyl/midazolam in the colonoscopy suite at the Taylor Station Surgical Center in Columbus. Anesthesia personnel administered the assigned anesthetic, and circulating nurses rated the difficulty of the procedure. Patients were surveyed after they came to, and again over the phone at least 24 hours after discharge.
Fewer propofol patients reported pain greater than zero during the procedure (2% versus 6%); fewer remembered being awake (2% versus 17%); and fewer had complications (2.7% versus 11.7%); 21 patients in the fentanyl/midazolam group had intraoperative hypoxia, versus 1 in the propofol group. Eleven fentanyl/midazolam patients had postprocedure nausea and vomiting, versus one propofol patient.
Nurses rated 26% of fentanyl/midazolam procedures as “difficult,” compared to 4.7% in the propofol group. Mean induction time was 2.1 minutes with propofol and 3.2 minutes with fentanyl/midazolam; mean procedure time was about 13 minutes in both groups. The cecal intubation rate was 100% in both groups, and there were no perforations.
Propofol patients reacted less during the procedure; an audience member wondered if the loss of feedback was a problem for Dr. Padmanabhan.
“We use propofol in a very light sedation, and sometimes we do get feedback, but more importantly we feel the technique of colonoscopy is as much by feel as it is by vision. If you feel that the scope is not going in correctly, you should pull back then try the loop reduction maneuvers,” he said.
The most common indication for colonoscopy was a history of polyps, followed by general colon screening. Patients in both groups were a mean of 61 years old, and about evenly split between the sexes. Body mass index was a mean of 30 kg/m2 in both groups. There were no between-group differences in comorbidities; hypertension and diabetes were the most common.
There was no external funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – As patient satisfaction becomes increasingly important for reimbursements, it might be a good idea to switch to propofol for colonoscopies.
The reason is because patients prefer propofol over standard-of-care fentanyl/midazolam as their anesthetic for outpatient colonoscopies, according to a randomized, blinded trial at a single center. Importantly, clinical assessment also showed that propofol outperformed fentanyl/midazolam in terms of hypoxia, pain, nausea, and procedural difficulties.
“Our study demonstrated the superiority of propofol over fentanyl/midazolam in an outpatient setting from both a patient satisfaction standpoint and from a provider prospective,” said lead investigator Anantha Padmanabhan, MD, a colorectal surgeon with Mount Carmel Health, Columbus, Ohio.
The short duration of action and quick turnaround time have led to an increase in the use of propofol for outpatient procedures. It’s been studied extensively for safety and efficacy, but patient preference has not been well documented. The investigators wanted to look into the issue because patient satisfaction has become an important metric for reimbursement, Dr. Padmanabhan said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, where the study was presented.
Patients were randomly assigned to propofol or fentanyl/midazolam in the colonoscopy suite at the Taylor Station Surgical Center in Columbus. Anesthesia personnel administered the assigned anesthetic, and circulating nurses rated the difficulty of the procedure. Patients were surveyed after they came to, and again over the phone at least 24 hours after discharge.
Fewer propofol patients reported pain greater than zero during the procedure (2% versus 6%); fewer remembered being awake (2% versus 17%); and fewer had complications (2.7% versus 11.7%); 21 patients in the fentanyl/midazolam group had intraoperative hypoxia, versus 1 in the propofol group. Eleven fentanyl/midazolam patients had postprocedure nausea and vomiting, versus one propofol patient.
Nurses rated 26% of fentanyl/midazolam procedures as “difficult,” compared to 4.7% in the propofol group. Mean induction time was 2.1 minutes with propofol and 3.2 minutes with fentanyl/midazolam; mean procedure time was about 13 minutes in both groups. The cecal intubation rate was 100% in both groups, and there were no perforations.
Propofol patients reacted less during the procedure; an audience member wondered if the loss of feedback was a problem for Dr. Padmanabhan.
“We use propofol in a very light sedation, and sometimes we do get feedback, but more importantly we feel the technique of colonoscopy is as much by feel as it is by vision. If you feel that the scope is not going in correctly, you should pull back then try the loop reduction maneuvers,” he said.
The most common indication for colonoscopy was a history of polyps, followed by general colon screening. Patients in both groups were a mean of 61 years old, and about evenly split between the sexes. Body mass index was a mean of 30 kg/m2 in both groups. There were no between-group differences in comorbidities; hypertension and diabetes were the most common.
There was no external funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – As patient satisfaction becomes increasingly important for reimbursements, it might be a good idea to switch to propofol for colonoscopies.
The reason is because patients prefer propofol over standard-of-care fentanyl/midazolam as their anesthetic for outpatient colonoscopies, according to a randomized, blinded trial at a single center. Importantly, clinical assessment also showed that propofol outperformed fentanyl/midazolam in terms of hypoxia, pain, nausea, and procedural difficulties.
“Our study demonstrated the superiority of propofol over fentanyl/midazolam in an outpatient setting from both a patient satisfaction standpoint and from a provider prospective,” said lead investigator Anantha Padmanabhan, MD, a colorectal surgeon with Mount Carmel Health, Columbus, Ohio.
The short duration of action and quick turnaround time have led to an increase in the use of propofol for outpatient procedures. It’s been studied extensively for safety and efficacy, but patient preference has not been well documented. The investigators wanted to look into the issue because patient satisfaction has become an important metric for reimbursement, Dr. Padmanabhan said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, where the study was presented.
Patients were randomly assigned to propofol or fentanyl/midazolam in the colonoscopy suite at the Taylor Station Surgical Center in Columbus. Anesthesia personnel administered the assigned anesthetic, and circulating nurses rated the difficulty of the procedure. Patients were surveyed after they came to, and again over the phone at least 24 hours after discharge.
Fewer propofol patients reported pain greater than zero during the procedure (2% versus 6%); fewer remembered being awake (2% versus 17%); and fewer had complications (2.7% versus 11.7%); 21 patients in the fentanyl/midazolam group had intraoperative hypoxia, versus 1 in the propofol group. Eleven fentanyl/midazolam patients had postprocedure nausea and vomiting, versus one propofol patient.
Nurses rated 26% of fentanyl/midazolam procedures as “difficult,” compared to 4.7% in the propofol group. Mean induction time was 2.1 minutes with propofol and 3.2 minutes with fentanyl/midazolam; mean procedure time was about 13 minutes in both groups. The cecal intubation rate was 100% in both groups, and there were no perforations.
Propofol patients reacted less during the procedure; an audience member wondered if the loss of feedback was a problem for Dr. Padmanabhan.
“We use propofol in a very light sedation, and sometimes we do get feedback, but more importantly we feel the technique of colonoscopy is as much by feel as it is by vision. If you feel that the scope is not going in correctly, you should pull back then try the loop reduction maneuvers,” he said.
The most common indication for colonoscopy was a history of polyps, followed by general colon screening. Patients in both groups were a mean of 61 years old, and about evenly split between the sexes. Body mass index was a mean of 30 kg/m2 in both groups. There were no between-group differences in comorbidities; hypertension and diabetes were the most common.
There was no external funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
AT THE ASCRS ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 300 patients randomized to propofol were more likely than were the 300 randomized to standard-of-care fentanyl/midazolam to state that they were “very satisfied” with their anesthesia during the procedure (86.3% versus 74%).
Data source: Randomized, blinded trial of 600 patients at a single center.
Disclosures: There was no external funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
NSAIDs remain a concern in colorectal ERAS protocols
SEATTLE – Nonselective NSAIDs increase the risk of anastomotic leaks after colorectal surgery, according to a meta-analysis from the University of Sydney, Australia.
After combing results from six randomized, controlled trials and seven retrospective studies involving a total of 23,508 patients, investigators found that postop nonselective NSAIDs (odds ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.43-0.67; P less than .00001), and especially diclofenac (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55; P less than .00001), were both associated with an increased risk of leakage.
There was an increased risk with all NSAIDs compared to patients who did not receive them after surgery, but the risk was statistically significant only for nonselective options like diclofenac on subgroup analysis. There was a trend for increased leakage with the nonselective agent ketorolac, as well, but it was not significant (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.35-1.43; P = .34).
“I’m not going to say we need to wait for more studies; there’s something here. We have to be aware there could be a high risk of leakage with nonsteroidals, and we have to be mindful of that with our ERAS [Enhanced Recovery after Surgery] protocols. I don’t think you should be using nonsteroidals unless you are using them in a trial” and collecting data, “because of the uncertainty,” lead investigator and colorectal surgeon Christopher Young, MD, a clinical associate professor of surgery at the University of Sydney, said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
NSAIDS are a routine part of colorectal ERAS protocols in some places to limit opioid use and hasten recovery and hospital discharge, but there’s been concern for some time that they might also increase the risk of anastomotic leakage. The new Australian findings fit in with previous investigations that raised concerns.
A 2016 review, for instance, found that among 856 patients undergoing an elective colon or rectal resection for cancer, the anastomotic leakage rate was significantly higher in the group that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs compared to patients who did not (9.2% versus 5.3%). The higher rate was only seen in patients receiving diclofenac. “The use of diclofenac in colorectal surgery can no longer be recommended. Alternatives for postoperative analgesia need to be explored within an enhanced recovery program,” the investigators concluded (J Gastrointest Surg. 2016 Apr;20[4]:776-82. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-3010-1).
A review of 13,082 bariatric and colorectal surgery patients in Washington State found that NSAIDs beginning within 24 hours after surgery were associated with a 70% increased risk of anastomotic leaks in nonelective colorectal surgery, with a leak rate of 12.3% in the NSAID group and 8.3% in the non-NSAID group (OR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.11–2.68; P = .01). Although it was unclear which nonsteroidals patients received, intravenous ketorolac or ibuprofen were likely the most common (JAMA Surg. 2015 Mar 1;150[3]: 223–8).
It’s unknown why, exactly, NSAIDs impair healing and anastomotic strength, but it’s thought to be related to effects on prostaglandin synthesis, Dr. Young noted.
Dr. Young had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Nonselective NSAIDs increase the risk of anastomotic leaks after colorectal surgery, according to a meta-analysis from the University of Sydney, Australia.
After combing results from six randomized, controlled trials and seven retrospective studies involving a total of 23,508 patients, investigators found that postop nonselective NSAIDs (odds ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.43-0.67; P less than .00001), and especially diclofenac (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55; P less than .00001), were both associated with an increased risk of leakage.
There was an increased risk with all NSAIDs compared to patients who did not receive them after surgery, but the risk was statistically significant only for nonselective options like diclofenac on subgroup analysis. There was a trend for increased leakage with the nonselective agent ketorolac, as well, but it was not significant (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.35-1.43; P = .34).
“I’m not going to say we need to wait for more studies; there’s something here. We have to be aware there could be a high risk of leakage with nonsteroidals, and we have to be mindful of that with our ERAS [Enhanced Recovery after Surgery] protocols. I don’t think you should be using nonsteroidals unless you are using them in a trial” and collecting data, “because of the uncertainty,” lead investigator and colorectal surgeon Christopher Young, MD, a clinical associate professor of surgery at the University of Sydney, said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
NSAIDS are a routine part of colorectal ERAS protocols in some places to limit opioid use and hasten recovery and hospital discharge, but there’s been concern for some time that they might also increase the risk of anastomotic leakage. The new Australian findings fit in with previous investigations that raised concerns.
A 2016 review, for instance, found that among 856 patients undergoing an elective colon or rectal resection for cancer, the anastomotic leakage rate was significantly higher in the group that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs compared to patients who did not (9.2% versus 5.3%). The higher rate was only seen in patients receiving diclofenac. “The use of diclofenac in colorectal surgery can no longer be recommended. Alternatives for postoperative analgesia need to be explored within an enhanced recovery program,” the investigators concluded (J Gastrointest Surg. 2016 Apr;20[4]:776-82. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-3010-1).
A review of 13,082 bariatric and colorectal surgery patients in Washington State found that NSAIDs beginning within 24 hours after surgery were associated with a 70% increased risk of anastomotic leaks in nonelective colorectal surgery, with a leak rate of 12.3% in the NSAID group and 8.3% in the non-NSAID group (OR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.11–2.68; P = .01). Although it was unclear which nonsteroidals patients received, intravenous ketorolac or ibuprofen were likely the most common (JAMA Surg. 2015 Mar 1;150[3]: 223–8).
It’s unknown why, exactly, NSAIDs impair healing and anastomotic strength, but it’s thought to be related to effects on prostaglandin synthesis, Dr. Young noted.
Dr. Young had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Nonselective NSAIDs increase the risk of anastomotic leaks after colorectal surgery, according to a meta-analysis from the University of Sydney, Australia.
After combing results from six randomized, controlled trials and seven retrospective studies involving a total of 23,508 patients, investigators found that postop nonselective NSAIDs (odds ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.43-0.67; P less than .00001), and especially diclofenac (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55; P less than .00001), were both associated with an increased risk of leakage.
There was an increased risk with all NSAIDs compared to patients who did not receive them after surgery, but the risk was statistically significant only for nonselective options like diclofenac on subgroup analysis. There was a trend for increased leakage with the nonselective agent ketorolac, as well, but it was not significant (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.35-1.43; P = .34).
“I’m not going to say we need to wait for more studies; there’s something here. We have to be aware there could be a high risk of leakage with nonsteroidals, and we have to be mindful of that with our ERAS [Enhanced Recovery after Surgery] protocols. I don’t think you should be using nonsteroidals unless you are using them in a trial” and collecting data, “because of the uncertainty,” lead investigator and colorectal surgeon Christopher Young, MD, a clinical associate professor of surgery at the University of Sydney, said at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
NSAIDS are a routine part of colorectal ERAS protocols in some places to limit opioid use and hasten recovery and hospital discharge, but there’s been concern for some time that they might also increase the risk of anastomotic leakage. The new Australian findings fit in with previous investigations that raised concerns.
A 2016 review, for instance, found that among 856 patients undergoing an elective colon or rectal resection for cancer, the anastomotic leakage rate was significantly higher in the group that received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs compared to patients who did not (9.2% versus 5.3%). The higher rate was only seen in patients receiving diclofenac. “The use of diclofenac in colorectal surgery can no longer be recommended. Alternatives for postoperative analgesia need to be explored within an enhanced recovery program,” the investigators concluded (J Gastrointest Surg. 2016 Apr;20[4]:776-82. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-3010-1).
A review of 13,082 bariatric and colorectal surgery patients in Washington State found that NSAIDs beginning within 24 hours after surgery were associated with a 70% increased risk of anastomotic leaks in nonelective colorectal surgery, with a leak rate of 12.3% in the NSAID group and 8.3% in the non-NSAID group (OR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.11–2.68; P = .01). Although it was unclear which nonsteroidals patients received, intravenous ketorolac or ibuprofen were likely the most common (JAMA Surg. 2015 Mar 1;150[3]: 223–8).
It’s unknown why, exactly, NSAIDs impair healing and anastomotic strength, but it’s thought to be related to effects on prostaglandin synthesis, Dr. Young noted.
Dr. Young had no disclosures.
AT ASCRS 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Postop nonselective NSAIDs (OR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.43-0.67; P less than .00001), and especially diclofenac (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.28-0.55; P less than .00001), were both associated with an increased risk of leakage.
Data source: Meta-analysis involving 23,508 patients
Disclosures: The presenter had no disclosures.
Consider intraperitoneal ropivacaine for colectomy ERAS
SEATTLE – Intraperitoneal ropivacaine decreases postoperative pain and improves functional recovery after laparoscopic colectomy, according to randomized, blinded trial from the Royal Adelaide (Australia) Hospital.
“We recommend routine inclusion of IPLA [intraperitoneal local anesthetic] in the multimodal analgesia component of ERAS [enhanced-recovery-after-surgery] programs for laparoscopic colectomy,” the investigators concluded.
Recovery was smoother in the ropivacaine group. On a 90-point surgical recovery scale assessing fatigue, mental function, and the ability to do normal daily activities, ropivacaine patients were a few points ahead on days 1 and 3; the gap widened to about 10 points on days 7, 30, and 45. Ropivacaine might have helped reduced inflammation, accounting for the extended benefit, Dr. Lewis said.
Pain control was better with ropivacaine, as well. Ropivacaine patients were about 15-20 points lower on 50-point scales assessing both visceral and abdominal pain at postop hours 3 and 24, and day 7. The findings were statistically significant.
Several trends also favored ropivacaine. Ropivacaine patients had their first bowel movement at around 70 hours postop, versus about 82 hours in the control group. They were also discharged almost a day sooner, and had less postop vomiting. Just one patient in the ropivacaine group was diagnosed with ileus, versus four in the control arm.
There was also a trend for less opioid use in the ropivacaine group, which Dr. Lewis suspected would have been statistically significant if the trial had more patients.
Ropivacaine patients were a mean of 67 years old, versus 62 years old in the control group. There were slightly more men than women in each arm. The mean body mass index in the ropivacaine group was 28.5 kg/m2, and in the control group 26.4 kg/m2. Ropivacaine was discontinued in two patients due to possible toxicity.
An audience member noted that intravenous lidocaine has shown similar benefits in abdominal surgery.
The investigators had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Intraperitoneal ropivacaine decreases postoperative pain and improves functional recovery after laparoscopic colectomy, according to randomized, blinded trial from the Royal Adelaide (Australia) Hospital.
“We recommend routine inclusion of IPLA [intraperitoneal local anesthetic] in the multimodal analgesia component of ERAS [enhanced-recovery-after-surgery] programs for laparoscopic colectomy,” the investigators concluded.
Recovery was smoother in the ropivacaine group. On a 90-point surgical recovery scale assessing fatigue, mental function, and the ability to do normal daily activities, ropivacaine patients were a few points ahead on days 1 and 3; the gap widened to about 10 points on days 7, 30, and 45. Ropivacaine might have helped reduced inflammation, accounting for the extended benefit, Dr. Lewis said.
Pain control was better with ropivacaine, as well. Ropivacaine patients were about 15-20 points lower on 50-point scales assessing both visceral and abdominal pain at postop hours 3 and 24, and day 7. The findings were statistically significant.
Several trends also favored ropivacaine. Ropivacaine patients had their first bowel movement at around 70 hours postop, versus about 82 hours in the control group. They were also discharged almost a day sooner, and had less postop vomiting. Just one patient in the ropivacaine group was diagnosed with ileus, versus four in the control arm.
There was also a trend for less opioid use in the ropivacaine group, which Dr. Lewis suspected would have been statistically significant if the trial had more patients.
Ropivacaine patients were a mean of 67 years old, versus 62 years old in the control group. There were slightly more men than women in each arm. The mean body mass index in the ropivacaine group was 28.5 kg/m2, and in the control group 26.4 kg/m2. Ropivacaine was discontinued in two patients due to possible toxicity.
An audience member noted that intravenous lidocaine has shown similar benefits in abdominal surgery.
The investigators had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Intraperitoneal ropivacaine decreases postoperative pain and improves functional recovery after laparoscopic colectomy, according to randomized, blinded trial from the Royal Adelaide (Australia) Hospital.
“We recommend routine inclusion of IPLA [intraperitoneal local anesthetic] in the multimodal analgesia component of ERAS [enhanced-recovery-after-surgery] programs for laparoscopic colectomy,” the investigators concluded.
Recovery was smoother in the ropivacaine group. On a 90-point surgical recovery scale assessing fatigue, mental function, and the ability to do normal daily activities, ropivacaine patients were a few points ahead on days 1 and 3; the gap widened to about 10 points on days 7, 30, and 45. Ropivacaine might have helped reduced inflammation, accounting for the extended benefit, Dr. Lewis said.
Pain control was better with ropivacaine, as well. Ropivacaine patients were about 15-20 points lower on 50-point scales assessing both visceral and abdominal pain at postop hours 3 and 24, and day 7. The findings were statistically significant.
Several trends also favored ropivacaine. Ropivacaine patients had their first bowel movement at around 70 hours postop, versus about 82 hours in the control group. They were also discharged almost a day sooner, and had less postop vomiting. Just one patient in the ropivacaine group was diagnosed with ileus, versus four in the control arm.
There was also a trend for less opioid use in the ropivacaine group, which Dr. Lewis suspected would have been statistically significant if the trial had more patients.
Ropivacaine patients were a mean of 67 years old, versus 62 years old in the control group. There were slightly more men than women in each arm. The mean body mass index in the ropivacaine group was 28.5 kg/m2, and in the control group 26.4 kg/m2. Ropivacaine was discontinued in two patients due to possible toxicity.
An audience member noted that intravenous lidocaine has shown similar benefits in abdominal surgery.
The investigators had no disclosures.
AT ASCRS 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: On a 90-point surgical recovery scale assessing fatigue, mental function, and the ability to do normal daily activities, ropivacaine patients were a few points ahead of saline controls on postop days 1 and 3; the gap widened to about 10 points on days 7, 30, and 45.
Data source: Randomized, blinded trial with 51 patients
Disclosures: The investigators had no disclosures.
Proper catheter removal promotes colorectal surgery recovery
Adherence to guidelines for urinary catheter removal significantly reduced rates of urinary tract infection and length of hospital stay, based on data from almost 3,000 patients.
UTIs occurred in 0.8% of colonic surgery patients who were guideline compliant, compared with 4.1% of noncompliant patients. Similarly, UTIs were significantly less likely in rectal surgery patients who complied with guidelines, compared with those who did not (3.5% vs. 9.6%).
The Implementation of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (iERAS) program involved 15 academic hospitals in Ontario, Canada. The guidelines include prompt removal of catheters from colonic and rectal surgery patients. Recommended removal times ranged from 24 hours to 72 hours, depending on the procedure.
“Although numerous reports have documented the overall effectiveness of bundled ERAS interventions improving outcome, the contribution of individual components of the pathway in the context of an ERAS implementation program is uncertain,” wrote Allan Okrainec, MD, of the University of Toronto, and his colleagues.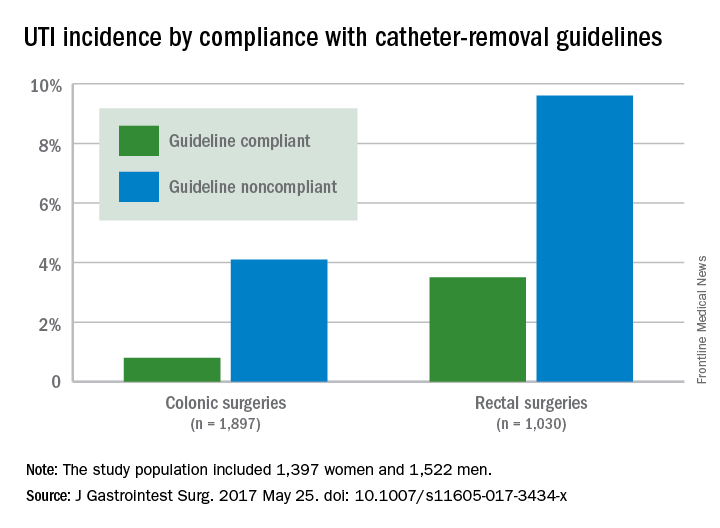
Overall, 53% of patients had catheters removed in compliance with the guidelines, including 47.2% of those with colonic resections and 69.5% of those with rectal resections.
The average length of hospital stay for colonic surgery patients who complied with the urinary catheter guideline was 4 days, compared with 5 days for noncompliant patients, a statistically significant difference. Similarly, the average length of stay was significantly shorter for compliant rectal surgery patients, compared with noncompliant patients (5 days vs. 8 days, respectively).
Reinsertion of the urinary catheter was needed for 6% of the patients, including 122 patients with suspected or confirmed urinary retention and 36 patients who had other indications for reinsertion.
“One of the concerns about early removal of catheters is that it might lead to an increased need for reinsertion,” the researchers noted. “In our study, guideline compliance was associated with an increased rate of catheter reinsertion, but [it] only increased the risk by 2%-3% in patients having rectal or colonic procedures,” the investigators said.
The study results were limited by a lack of information about reasons for noncompliance with the guidelines, the researchers added. However, the data support the value of early catheter removal for surgical patients. “It is noteworthy that, in our study, as well as others, urinary retention rates are relatively low,” they said.
The Council of Academic Hospitals of Ontario funded the study. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adherence to guidelines for urinary catheter removal significantly reduced rates of urinary tract infection and length of hospital stay, based on data from almost 3,000 patients.
UTIs occurred in 0.8% of colonic surgery patients who were guideline compliant, compared with 4.1% of noncompliant patients. Similarly, UTIs were significantly less likely in rectal surgery patients who complied with guidelines, compared with those who did not (3.5% vs. 9.6%).
The Implementation of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (iERAS) program involved 15 academic hospitals in Ontario, Canada. The guidelines include prompt removal of catheters from colonic and rectal surgery patients. Recommended removal times ranged from 24 hours to 72 hours, depending on the procedure.
“Although numerous reports have documented the overall effectiveness of bundled ERAS interventions improving outcome, the contribution of individual components of the pathway in the context of an ERAS implementation program is uncertain,” wrote Allan Okrainec, MD, of the University of Toronto, and his colleagues.
Overall, 53% of patients had catheters removed in compliance with the guidelines, including 47.2% of those with colonic resections and 69.5% of those with rectal resections.
The average length of hospital stay for colonic surgery patients who complied with the urinary catheter guideline was 4 days, compared with 5 days for noncompliant patients, a statistically significant difference. Similarly, the average length of stay was significantly shorter for compliant rectal surgery patients, compared with noncompliant patients (5 days vs. 8 days, respectively).
Reinsertion of the urinary catheter was needed for 6% of the patients, including 122 patients with suspected or confirmed urinary retention and 36 patients who had other indications for reinsertion.
“One of the concerns about early removal of catheters is that it might lead to an increased need for reinsertion,” the researchers noted. “In our study, guideline compliance was associated with an increased rate of catheter reinsertion, but [it] only increased the risk by 2%-3% in patients having rectal or colonic procedures,” the investigators said.
The study results were limited by a lack of information about reasons for noncompliance with the guidelines, the researchers added. However, the data support the value of early catheter removal for surgical patients. “It is noteworthy that, in our study, as well as others, urinary retention rates are relatively low,” they said.
The Council of Academic Hospitals of Ontario funded the study. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adherence to guidelines for urinary catheter removal significantly reduced rates of urinary tract infection and length of hospital stay, based on data from almost 3,000 patients.
UTIs occurred in 0.8% of colonic surgery patients who were guideline compliant, compared with 4.1% of noncompliant patients. Similarly, UTIs were significantly less likely in rectal surgery patients who complied with guidelines, compared with those who did not (3.5% vs. 9.6%).
The Implementation of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (iERAS) program involved 15 academic hospitals in Ontario, Canada. The guidelines include prompt removal of catheters from colonic and rectal surgery patients. Recommended removal times ranged from 24 hours to 72 hours, depending on the procedure.
“Although numerous reports have documented the overall effectiveness of bundled ERAS interventions improving outcome, the contribution of individual components of the pathway in the context of an ERAS implementation program is uncertain,” wrote Allan Okrainec, MD, of the University of Toronto, and his colleagues.
Overall, 53% of patients had catheters removed in compliance with the guidelines, including 47.2% of those with colonic resections and 69.5% of those with rectal resections.
The average length of hospital stay for colonic surgery patients who complied with the urinary catheter guideline was 4 days, compared with 5 days for noncompliant patients, a statistically significant difference. Similarly, the average length of stay was significantly shorter for compliant rectal surgery patients, compared with noncompliant patients (5 days vs. 8 days, respectively).
Reinsertion of the urinary catheter was needed for 6% of the patients, including 122 patients with suspected or confirmed urinary retention and 36 patients who had other indications for reinsertion.
“One of the concerns about early removal of catheters is that it might lead to an increased need for reinsertion,” the researchers noted. “In our study, guideline compliance was associated with an increased rate of catheter reinsertion, but [it] only increased the risk by 2%-3% in patients having rectal or colonic procedures,” the investigators said.
The study results were limited by a lack of information about reasons for noncompliance with the guidelines, the researchers added. However, the data support the value of early catheter removal for surgical patients. “It is noteworthy that, in our study, as well as others, urinary retention rates are relatively low,” they said.
The Council of Academic Hospitals of Ontario funded the study. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GASTROINTESTINAL SURGERY
Key clinical point: Compliance with guidelines for urinary catheter removal significantly reduced hospital stay and UTI rates in colon and rectal surgery patients.
Major finding: UTI rates in colonic surgery patients were 0.8% and 4.1%, respectively, for those who were compliant and noncompliant with the guidelines. Rates were 3.5% and 9.6%, respectively, for compliant and noncompliant rectal surgery patients.
Data source: A prospective study of 2,927 adults who underwent colonic or rectal surgery between September 2012 and April 2015.
Disclosures: The Council of Academic Hospitals of Ontario funded the study. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Sooner is better than later for acute UC surgery
SEATTLE – Postponing surgery for acute ulcerative colitis more than a day increases postoperative complications, lengths of stay, and hospital costs, according to a review by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, of almost 2,000 patients.
It’s not uncommon to wait 5 or even 10 days to give biologics a chance to work when patients are admitted for acute ulcerative colitis (UC). Based on the review, however, “we believe that the need for prolonged medical therapy and resuscitation in this patient population prior to colectomy may be overstated,” and that “the lasting effects of persistent inflammation cascade are underestimated.”
The team reviewed 1,953 index UC admissions with emergent non-elective abdominal surgery in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database from 2008-13; 546 patients (28%) had early operations - within 24 hours of admission – and the other 1,407 had operations after that time.
Although it’s impossible to say for sure given the limits of administrative data in the NIS, patients who had surgery soon after admission were probably sicker. Even so, they were less likely to have complications than patients in the delayed surgery group (55% versus 43%), and they had shorter hospital stays, with just 8% in the hospital past 21 days, versus 29% of patients who had delayed operations. The findings were similar for both overall length of stay and post-op length of stay.
Renal complications (8% versus 14%), pulmonary complications (20% versus 25%), and thromboembolic events (4% versus 6%) were also less common in the early surgery group. On multivariable analysis, delayed surgery increased the complication rate by 64%.
With fewer complications and shorter hospital stays, early operations were also less expensive, with a mean total hospitalization cost of $19,985 versus $34,258. The findings were all statistically significant.
Dr. Leeds noted the limits of the study; medical management regimes and the reasons for variations in surgical timing are unknown, among other things. “This is not the final answer on what to do with patients like this, but it opens the door to prospective studies that could control” for such variables, he said.
Early surgery patients were more likely to be male (57% versus 51%) and from households with incomes higher than the national median. There were no difference in age, race, comorbidities, region, or hospital type between the two groups.
Dr. Leeds said he had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Postponing surgery for acute ulcerative colitis more than a day increases postoperative complications, lengths of stay, and hospital costs, according to a review by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, of almost 2,000 patients.
It’s not uncommon to wait 5 or even 10 days to give biologics a chance to work when patients are admitted for acute ulcerative colitis (UC). Based on the review, however, “we believe that the need for prolonged medical therapy and resuscitation in this patient population prior to colectomy may be overstated,” and that “the lasting effects of persistent inflammation cascade are underestimated.”
The team reviewed 1,953 index UC admissions with emergent non-elective abdominal surgery in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database from 2008-13; 546 patients (28%) had early operations - within 24 hours of admission – and the other 1,407 had operations after that time.
Although it’s impossible to say for sure given the limits of administrative data in the NIS, patients who had surgery soon after admission were probably sicker. Even so, they were less likely to have complications than patients in the delayed surgery group (55% versus 43%), and they had shorter hospital stays, with just 8% in the hospital past 21 days, versus 29% of patients who had delayed operations. The findings were similar for both overall length of stay and post-op length of stay.
Renal complications (8% versus 14%), pulmonary complications (20% versus 25%), and thromboembolic events (4% versus 6%) were also less common in the early surgery group. On multivariable analysis, delayed surgery increased the complication rate by 64%.
With fewer complications and shorter hospital stays, early operations were also less expensive, with a mean total hospitalization cost of $19,985 versus $34,258. The findings were all statistically significant.
Dr. Leeds noted the limits of the study; medical management regimes and the reasons for variations in surgical timing are unknown, among other things. “This is not the final answer on what to do with patients like this, but it opens the door to prospective studies that could control” for such variables, he said.
Early surgery patients were more likely to be male (57% versus 51%) and from households with incomes higher than the national median. There were no difference in age, race, comorbidities, region, or hospital type between the two groups.
Dr. Leeds said he had no disclosures.
SEATTLE – Postponing surgery for acute ulcerative colitis more than a day increases postoperative complications, lengths of stay, and hospital costs, according to a review by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, of almost 2,000 patients.
It’s not uncommon to wait 5 or even 10 days to give biologics a chance to work when patients are admitted for acute ulcerative colitis (UC). Based on the review, however, “we believe that the need for prolonged medical therapy and resuscitation in this patient population prior to colectomy may be overstated,” and that “the lasting effects of persistent inflammation cascade are underestimated.”
The team reviewed 1,953 index UC admissions with emergent non-elective abdominal surgery in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database from 2008-13; 546 patients (28%) had early operations - within 24 hours of admission – and the other 1,407 had operations after that time.
Although it’s impossible to say for sure given the limits of administrative data in the NIS, patients who had surgery soon after admission were probably sicker. Even so, they were less likely to have complications than patients in the delayed surgery group (55% versus 43%), and they had shorter hospital stays, with just 8% in the hospital past 21 days, versus 29% of patients who had delayed operations. The findings were similar for both overall length of stay and post-op length of stay.
Renal complications (8% versus 14%), pulmonary complications (20% versus 25%), and thromboembolic events (4% versus 6%) were also less common in the early surgery group. On multivariable analysis, delayed surgery increased the complication rate by 64%.
With fewer complications and shorter hospital stays, early operations were also less expensive, with a mean total hospitalization cost of $19,985 versus $34,258. The findings were all statistically significant.
Dr. Leeds noted the limits of the study; medical management regimes and the reasons for variations in surgical timing are unknown, among other things. “This is not the final answer on what to do with patients like this, but it opens the door to prospective studies that could control” for such variables, he said.
Early surgery patients were more likely to be male (57% versus 51%) and from households with incomes higher than the national median. There were no difference in age, race, comorbidities, region, or hospital type between the two groups.
Dr. Leeds said he had no disclosures.
AT ASCRS 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients who had surgery soon after admission were probably sicker. Even so, they were less likely to have complications than patients in the delayed surgery group (55% versus 43%), and they had shorter hospital stays, with just 8% in the hospital past 21 days, versus 29% of patients who had delayed operations.
Data source: Review of almost 2,000 patients in the National Inpatient Sample
Disclosures: The lead investigator had no disclosures.
Anal dysplasia surveillance called into question
SEATTLE – Aggressive screening and treatment of HPV anal dysplasia probably doesn’t decrease the incidence of anal cancer, even in high-risk groups, according to investigators from Kaiser Permanente of Southern California.
The increase in anal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) over the past 20 years has led to surveillance programs for anal dysplasia in many institutions, based on the assumption that finding and destroying the lesions will prevent anal cancer, similar to the reason why polyps are removed during colonoscopy to prevent colon cancer, said lead investigator Marco Tomassi, MD, a general surgeon with Kaiser in San Diego.
Kaiser in Southern California doesn’t have an intensive surveillance program for anal HPV. Instead, high risk patients – those with HIV, past cervical cancer, anogenital warts, among others – are screened with digital rectal exams and anoscopy every 3-12 months, and only anal warts and other grossly abnormal growths are removed.
Physicians there do not routinely use high resolution anoscopy (HRA), Pap smears, and other techniques to identify and destroy microscopic foci of dysplasia, as in more intensive programs.
To see how the approach has worked, Dr. Tomassi and his colleagues reviewed the incidence of anal SCC among almost 6 million Kaiser patients from 2005 through 2015.
The cumulative incidence in all groups of patients, even those at risk for the disease, was less than 1%; 425 of the 460 anal cancers (92%) were in the general population, among patients who would not have been part of a high risk surveillance program.
Even without an aggressive surveillance program, high grade anal dysplasia was identified in 377 patients; their incidence of anal SCC was 0.8%, the highest found in the study.
There were no incident cases of SCC among the 133 HIV patients with anal dysplasia. Among over 5,000 HIV patients in the study, the anal SCC incidence was 0.09%. In the general population of 5.86 million, it was 0.01%.
“The cumulative incidence in our group, despite not performing ablative techniques for dysplasia, was comparable to those institutions that routinely perform high resolution anoscopy and destruction of dysplasia. The low rate of malignant conversion suggests that aggressive surveillance regimens, such as HRA, may lead to unnecessary procedures even in high risk patients,” Dr. Tomassi said.
Intensive surveillance doesn’t seem to make much difference because “the incidence of anal cancer is very low even in very high risk populations,” and “most SCC cases develop in the general population,” so “regimens dedicated to identifying cancer in high risk groups will ultimate miss the majority of patients who will succumb to this disease,” he said.
“It’s rare that I come to a meeting and hear a paper that’s going to change my practice. Thank you for that,” an audience member said after Dr. Tomassi presented his findings at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
Dr. Tomassi did not have any disclosures.
SEATTLE – Aggressive screening and treatment of HPV anal dysplasia probably doesn’t decrease the incidence of anal cancer, even in high-risk groups, according to investigators from Kaiser Permanente of Southern California.
The increase in anal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) over the past 20 years has led to surveillance programs for anal dysplasia in many institutions, based on the assumption that finding and destroying the lesions will prevent anal cancer, similar to the reason why polyps are removed during colonoscopy to prevent colon cancer, said lead investigator Marco Tomassi, MD, a general surgeon with Kaiser in San Diego.
Kaiser in Southern California doesn’t have an intensive surveillance program for anal HPV. Instead, high risk patients – those with HIV, past cervical cancer, anogenital warts, among others – are screened with digital rectal exams and anoscopy every 3-12 months, and only anal warts and other grossly abnormal growths are removed.
Physicians there do not routinely use high resolution anoscopy (HRA), Pap smears, and other techniques to identify and destroy microscopic foci of dysplasia, as in more intensive programs.
To see how the approach has worked, Dr. Tomassi and his colleagues reviewed the incidence of anal SCC among almost 6 million Kaiser patients from 2005 through 2015.
The cumulative incidence in all groups of patients, even those at risk for the disease, was less than 1%; 425 of the 460 anal cancers (92%) were in the general population, among patients who would not have been part of a high risk surveillance program.
Even without an aggressive surveillance program, high grade anal dysplasia was identified in 377 patients; their incidence of anal SCC was 0.8%, the highest found in the study.
There were no incident cases of SCC among the 133 HIV patients with anal dysplasia. Among over 5,000 HIV patients in the study, the anal SCC incidence was 0.09%. In the general population of 5.86 million, it was 0.01%.
“The cumulative incidence in our group, despite not performing ablative techniques for dysplasia, was comparable to those institutions that routinely perform high resolution anoscopy and destruction of dysplasia. The low rate of malignant conversion suggests that aggressive surveillance regimens, such as HRA, may lead to unnecessary procedures even in high risk patients,” Dr. Tomassi said.
Intensive surveillance doesn’t seem to make much difference because “the incidence of anal cancer is very low even in very high risk populations,” and “most SCC cases develop in the general population,” so “regimens dedicated to identifying cancer in high risk groups will ultimate miss the majority of patients who will succumb to this disease,” he said.
“It’s rare that I come to a meeting and hear a paper that’s going to change my practice. Thank you for that,” an audience member said after Dr. Tomassi presented his findings at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
Dr. Tomassi did not have any disclosures.
SEATTLE – Aggressive screening and treatment of HPV anal dysplasia probably doesn’t decrease the incidence of anal cancer, even in high-risk groups, according to investigators from Kaiser Permanente of Southern California.
The increase in anal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) over the past 20 years has led to surveillance programs for anal dysplasia in many institutions, based on the assumption that finding and destroying the lesions will prevent anal cancer, similar to the reason why polyps are removed during colonoscopy to prevent colon cancer, said lead investigator Marco Tomassi, MD, a general surgeon with Kaiser in San Diego.
Kaiser in Southern California doesn’t have an intensive surveillance program for anal HPV. Instead, high risk patients – those with HIV, past cervical cancer, anogenital warts, among others – are screened with digital rectal exams and anoscopy every 3-12 months, and only anal warts and other grossly abnormal growths are removed.
Physicians there do not routinely use high resolution anoscopy (HRA), Pap smears, and other techniques to identify and destroy microscopic foci of dysplasia, as in more intensive programs.
To see how the approach has worked, Dr. Tomassi and his colleagues reviewed the incidence of anal SCC among almost 6 million Kaiser patients from 2005 through 2015.
The cumulative incidence in all groups of patients, even those at risk for the disease, was less than 1%; 425 of the 460 anal cancers (92%) were in the general population, among patients who would not have been part of a high risk surveillance program.
Even without an aggressive surveillance program, high grade anal dysplasia was identified in 377 patients; their incidence of anal SCC was 0.8%, the highest found in the study.
There were no incident cases of SCC among the 133 HIV patients with anal dysplasia. Among over 5,000 HIV patients in the study, the anal SCC incidence was 0.09%. In the general population of 5.86 million, it was 0.01%.
“The cumulative incidence in our group, despite not performing ablative techniques for dysplasia, was comparable to those institutions that routinely perform high resolution anoscopy and destruction of dysplasia. The low rate of malignant conversion suggests that aggressive surveillance regimens, such as HRA, may lead to unnecessary procedures even in high risk patients,” Dr. Tomassi said.
Intensive surveillance doesn’t seem to make much difference because “the incidence of anal cancer is very low even in very high risk populations,” and “most SCC cases develop in the general population,” so “regimens dedicated to identifying cancer in high risk groups will ultimate miss the majority of patients who will succumb to this disease,” he said.
“It’s rare that I come to a meeting and hear a paper that’s going to change my practice. Thank you for that,” an audience member said after Dr. Tomassi presented his findings at the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons annual meeting.
Dr. Tomassi did not have any disclosures.
AT ASCRS 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: When high risk patients were not screened and treated for anal dysplasia, the cumulative incidence of anal squamous cell carcinoma was 0.8% or less, similar to programs that target and treat the lesions.
Data source: Review of almost 6 million patients at Kaiser Permanente of Southern California
Disclosures: The lead investigator had no disclosures.
Large-scale ERAS program reduces postoperative LOS, complications
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS), a program implemented by Kaiser Permanente Northern California – a multihospital integrated health system – significantly reduced length of stay and complication rates, according to a report published in JAMA Surgery.
Beginning in 2014, when the ERAS program was implemented in 20 Kaiser hospitals, progress was made on the goal of improving inpatient safety, as well as improvements in-hospital mortality, rates of early ambulation, patient nutrition, and reduced opioid use, said Vincent X. Liu, MD, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Oakland, and his associates. Those outcomes were studied in the context of a similar group of patients in other, non-ERAS hospitals to determine the degree of change in each area.
ERAS aimed to reduce opioid use by encouraging multimodal analgesia, which included pre- and postoperative IV acetaminophen and NSAIDs, perioperative IV lidocaine, or peripheral nerve blocks. It encouraged ambulation within 12 hours of surgery completion and a daily goal of walking at least 21 feet during the first 3 postoperative days.
The program enhanced patient nutrition by reducing prolonged preoperative fasting, providing a high-carbohydrate beverage 2-4 hours before surgery, and allowing solids 8-12 hours before surgery. It also provided food within 12 hours of completing surgery. ERAS also encouraged patient engagement in care by use of educational materials and a calendar that detailed what the care process would entail. For clinicians, ERAS provided new electronic tools such as electronic medical record order sets to facilitate standardized practice.
In the first phase of their study, Dr. Liu and his associates assessed changes over time in patient safety outcomes among 3,768 patients undergoing elective colorectal resection and 5,002 undergoing emergency hip fracture repair.
Hospital length of stay decreased significantly after implementation of ERAS, from 5.1 to 4.2 days in the colorectal resection group and from 3.6 to 3.2 days in the hip fracture group. Complication rates decreased from 18.1% to 14.7% and from 30.8% to 24.9%, respectively. Early ambulation rates increased substantially, from 22.3% to 56.5% and from 2.8% to 21.2%, respectively.
The rate of improved nutrition rose from 13.0% to 39.2% in the colorectal resection group and from 45.6% to 57.1% in the hip repair group. And the total dose of morphine equivalents dropped from 52.4 to 30.6 and from 38.9 to 27.0, respectively (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1032).
In the second phase of the study, the investigators compared these changes against the outcomes of two comparator groups who underwent similar surgeries (5,556 resection comparators and 1,523 hip repair comparators) during the same time frame but in hospitals that did not implement the ERAS program.
In this analysis, LOS was significantly shorter and complication rates were significantly lower for both procedures at the hospitals where the intervention was implemented, compared with the other hospitals. In-hospital mortality, opioid use, early ambulation, and discharge to home rather than a rehabilitation facility also favored the intervention groups.
“This study demonstrates the effectiveness of a systems-level approach to ERAS program implementation, even across widely divergent target populations,” Dr. Liu and his associates said.
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Permanente Medical Group, the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, and the National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Liu and his associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Findings from Liu et al. have clinical, research, and policy relevance. First, they went beyond select surgical procedures from single hospitals. The investigators have robustly taken implementation science to the next level, thus showing that thoughtfully planned quality-improvement endeavors that are integrated with robust research evaluation measures can positively affect our surgical patients. In a similar vein, these results underscore the value proposition of research conducted in large health care systems that goes beyond the limitation of traditional stand-alone hospitals, such as small sample size and referral and practice biases. [In addition,] this investigation raises many and exciting future research opportunities to an eager audience of stakeholders. What are the cost implications of such efforts? How can we better leverage electronic health records with smart tools to better implement and measure the effects of the ERAS program and other quality and safety initiatives? [We also] need to be mindful of its unintended consequences on vulnerable populations and financially strained hospitals.
Mohammed Bayasi, MD, FACS, and Waddah Al-Refaie, MD, FACS, are with the department of surgery, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington. Their comments are from an editorial (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1051). They had no disclosures.
Findings from Liu et al. have clinical, research, and policy relevance. First, they went beyond select surgical procedures from single hospitals. The investigators have robustly taken implementation science to the next level, thus showing that thoughtfully planned quality-improvement endeavors that are integrated with robust research evaluation measures can positively affect our surgical patients. In a similar vein, these results underscore the value proposition of research conducted in large health care systems that goes beyond the limitation of traditional stand-alone hospitals, such as small sample size and referral and practice biases. [In addition,] this investigation raises many and exciting future research opportunities to an eager audience of stakeholders. What are the cost implications of such efforts? How can we better leverage electronic health records with smart tools to better implement and measure the effects of the ERAS program and other quality and safety initiatives? [We also] need to be mindful of its unintended consequences on vulnerable populations and financially strained hospitals.
Mohammed Bayasi, MD, FACS, and Waddah Al-Refaie, MD, FACS, are with the department of surgery, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington. Their comments are from an editorial (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1051). They had no disclosures.
Findings from Liu et al. have clinical, research, and policy relevance. First, they went beyond select surgical procedures from single hospitals. The investigators have robustly taken implementation science to the next level, thus showing that thoughtfully planned quality-improvement endeavors that are integrated with robust research evaluation measures can positively affect our surgical patients. In a similar vein, these results underscore the value proposition of research conducted in large health care systems that goes beyond the limitation of traditional stand-alone hospitals, such as small sample size and referral and practice biases. [In addition,] this investigation raises many and exciting future research opportunities to an eager audience of stakeholders. What are the cost implications of such efforts? How can we better leverage electronic health records with smart tools to better implement and measure the effects of the ERAS program and other quality and safety initiatives? [We also] need to be mindful of its unintended consequences on vulnerable populations and financially strained hospitals.
Mohammed Bayasi, MD, FACS, and Waddah Al-Refaie, MD, FACS, are with the department of surgery, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington. Their comments are from an editorial (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1051). They had no disclosures.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS), a program implemented by Kaiser Permanente Northern California – a multihospital integrated health system – significantly reduced length of stay and complication rates, according to a report published in JAMA Surgery.
Beginning in 2014, when the ERAS program was implemented in 20 Kaiser hospitals, progress was made on the goal of improving inpatient safety, as well as improvements in-hospital mortality, rates of early ambulation, patient nutrition, and reduced opioid use, said Vincent X. Liu, MD, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Oakland, and his associates. Those outcomes were studied in the context of a similar group of patients in other, non-ERAS hospitals to determine the degree of change in each area.
ERAS aimed to reduce opioid use by encouraging multimodal analgesia, which included pre- and postoperative IV acetaminophen and NSAIDs, perioperative IV lidocaine, or peripheral nerve blocks. It encouraged ambulation within 12 hours of surgery completion and a daily goal of walking at least 21 feet during the first 3 postoperative days.
The program enhanced patient nutrition by reducing prolonged preoperative fasting, providing a high-carbohydrate beverage 2-4 hours before surgery, and allowing solids 8-12 hours before surgery. It also provided food within 12 hours of completing surgery. ERAS also encouraged patient engagement in care by use of educational materials and a calendar that detailed what the care process would entail. For clinicians, ERAS provided new electronic tools such as electronic medical record order sets to facilitate standardized practice.
In the first phase of their study, Dr. Liu and his associates assessed changes over time in patient safety outcomes among 3,768 patients undergoing elective colorectal resection and 5,002 undergoing emergency hip fracture repair.
Hospital length of stay decreased significantly after implementation of ERAS, from 5.1 to 4.2 days in the colorectal resection group and from 3.6 to 3.2 days in the hip fracture group. Complication rates decreased from 18.1% to 14.7% and from 30.8% to 24.9%, respectively. Early ambulation rates increased substantially, from 22.3% to 56.5% and from 2.8% to 21.2%, respectively.
The rate of improved nutrition rose from 13.0% to 39.2% in the colorectal resection group and from 45.6% to 57.1% in the hip repair group. And the total dose of morphine equivalents dropped from 52.4 to 30.6 and from 38.9 to 27.0, respectively (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1032).
In the second phase of the study, the investigators compared these changes against the outcomes of two comparator groups who underwent similar surgeries (5,556 resection comparators and 1,523 hip repair comparators) during the same time frame but in hospitals that did not implement the ERAS program.
In this analysis, LOS was significantly shorter and complication rates were significantly lower for both procedures at the hospitals where the intervention was implemented, compared with the other hospitals. In-hospital mortality, opioid use, early ambulation, and discharge to home rather than a rehabilitation facility also favored the intervention groups.
“This study demonstrates the effectiveness of a systems-level approach to ERAS program implementation, even across widely divergent target populations,” Dr. Liu and his associates said.
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Permanente Medical Group, the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, and the National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Liu and his associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS), a program implemented by Kaiser Permanente Northern California – a multihospital integrated health system – significantly reduced length of stay and complication rates, according to a report published in JAMA Surgery.
Beginning in 2014, when the ERAS program was implemented in 20 Kaiser hospitals, progress was made on the goal of improving inpatient safety, as well as improvements in-hospital mortality, rates of early ambulation, patient nutrition, and reduced opioid use, said Vincent X. Liu, MD, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Oakland, and his associates. Those outcomes were studied in the context of a similar group of patients in other, non-ERAS hospitals to determine the degree of change in each area.
ERAS aimed to reduce opioid use by encouraging multimodal analgesia, which included pre- and postoperative IV acetaminophen and NSAIDs, perioperative IV lidocaine, or peripheral nerve blocks. It encouraged ambulation within 12 hours of surgery completion and a daily goal of walking at least 21 feet during the first 3 postoperative days.
The program enhanced patient nutrition by reducing prolonged preoperative fasting, providing a high-carbohydrate beverage 2-4 hours before surgery, and allowing solids 8-12 hours before surgery. It also provided food within 12 hours of completing surgery. ERAS also encouraged patient engagement in care by use of educational materials and a calendar that detailed what the care process would entail. For clinicians, ERAS provided new electronic tools such as electronic medical record order sets to facilitate standardized practice.
In the first phase of their study, Dr. Liu and his associates assessed changes over time in patient safety outcomes among 3,768 patients undergoing elective colorectal resection and 5,002 undergoing emergency hip fracture repair.
Hospital length of stay decreased significantly after implementation of ERAS, from 5.1 to 4.2 days in the colorectal resection group and from 3.6 to 3.2 days in the hip fracture group. Complication rates decreased from 18.1% to 14.7% and from 30.8% to 24.9%, respectively. Early ambulation rates increased substantially, from 22.3% to 56.5% and from 2.8% to 21.2%, respectively.
The rate of improved nutrition rose from 13.0% to 39.2% in the colorectal resection group and from 45.6% to 57.1% in the hip repair group. And the total dose of morphine equivalents dropped from 52.4 to 30.6 and from 38.9 to 27.0, respectively (JAMA Surg. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1032).
In the second phase of the study, the investigators compared these changes against the outcomes of two comparator groups who underwent similar surgeries (5,556 resection comparators and 1,523 hip repair comparators) during the same time frame but in hospitals that did not implement the ERAS program.
In this analysis, LOS was significantly shorter and complication rates were significantly lower for both procedures at the hospitals where the intervention was implemented, compared with the other hospitals. In-hospital mortality, opioid use, early ambulation, and discharge to home rather than a rehabilitation facility also favored the intervention groups.
“This study demonstrates the effectiveness of a systems-level approach to ERAS program implementation, even across widely divergent target populations,” Dr. Liu and his associates said.
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Permanente Medical Group, the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, and the National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Liu and his associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Key clinical point: An Enhanced Recovery After Surgery program aimed at improving inpatient safety significantly reduced length of stay and complication rates at 20 California hospitals.
Major finding: After the ERAS program was implemented, hospital LOS decreased from 5.1 to 4.2 days in the colorectal resection group and from 3.6 to 3.2 days in the hip fracture group, and complication rates decreased from 18.1% to 14.7% and from 30.8% to 24.9%, respectively.
Data source: A “pre-post” comparison study of patients’ safety outcomes after implementation of an ERAS program, which involved 15,849 surgical patients at 20 hospitals.
Disclosures: The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Permanente Medical Group, the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, and the National Institutes of Health funded the study. Dr. Liu and his associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
It Pays to Get Screened for Colon Cancer
Although cancer death rates have been decreasing for the general population, they’ve been increasing for American Indians, according to the American Indian Cancer Foundation (AICAF). The AICAF cites a number of barriers to prevention and care, such as low awareness of risks, distrust of medical systems and research, health beliefs that may conflict with prevention practices, and low awareness of screening options.
The Northern Plains region has some of the highest rates of cancer diagnoses and death in the U.S. Colon cancer, for example, is 53% higher in Northern Plains American Indians, AICAF says. Although screening rates are improving, fewer than half of Northern Plains American Indians aged ≥ 50 years have had a colorectal cancer screening, according to the Association of American Indian Physicians.
The cancer mortality rates are the result of a “complex set of factors” that the AICAF is beginning to address with a comprehensive set of approaches. For instance, in addition to educating the public, AICAF, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Health and Get Your Rear in Gear Colon Cancer Coalition is putting money where its mouth is, with the “Refer-a-Relative” program.
“We are all related,” the campaign says: “Help your community and end colon cancer!” Refer-a-Relative encourages Native Americans in the Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area to get screened, and then to refer up to 5 relatives aged ≥ 50 years for screening. Patients receive a $20 gift card for completing screening, and $10 for each relative who completes screening. The relatives receive a $20 gift card and can refer more people.
The screening project is 1 branch of the AICAF’s interest in innovating clinical systems at IHS, Tribal, and Urban (ITU) clinics. Much of the work is based on the Improving Northern Plains American Indian Colorectal Cancer Screening (INPACS) project with ITU clinics. The AICAF invites interested ITU clinics to join the Clinical Cancer Screening Network. For more information, infographics, and other patient education materials, visit www.americanindiancancer.org.
Although cancer death rates have been decreasing for the general population, they’ve been increasing for American Indians, according to the American Indian Cancer Foundation (AICAF). The AICAF cites a number of barriers to prevention and care, such as low awareness of risks, distrust of medical systems and research, health beliefs that may conflict with prevention practices, and low awareness of screening options.
The Northern Plains region has some of the highest rates of cancer diagnoses and death in the U.S. Colon cancer, for example, is 53% higher in Northern Plains American Indians, AICAF says. Although screening rates are improving, fewer than half of Northern Plains American Indians aged ≥ 50 years have had a colorectal cancer screening, according to the Association of American Indian Physicians.
The cancer mortality rates are the result of a “complex set of factors” that the AICAF is beginning to address with a comprehensive set of approaches. For instance, in addition to educating the public, AICAF, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Health and Get Your Rear in Gear Colon Cancer Coalition is putting money where its mouth is, with the “Refer-a-Relative” program.
“We are all related,” the campaign says: “Help your community and end colon cancer!” Refer-a-Relative encourages Native Americans in the Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area to get screened, and then to refer up to 5 relatives aged ≥ 50 years for screening. Patients receive a $20 gift card for completing screening, and $10 for each relative who completes screening. The relatives receive a $20 gift card and can refer more people.
The screening project is 1 branch of the AICAF’s interest in innovating clinical systems at IHS, Tribal, and Urban (ITU) clinics. Much of the work is based on the Improving Northern Plains American Indian Colorectal Cancer Screening (INPACS) project with ITU clinics. The AICAF invites interested ITU clinics to join the Clinical Cancer Screening Network. For more information, infographics, and other patient education materials, visit www.americanindiancancer.org.
Although cancer death rates have been decreasing for the general population, they’ve been increasing for American Indians, according to the American Indian Cancer Foundation (AICAF). The AICAF cites a number of barriers to prevention and care, such as low awareness of risks, distrust of medical systems and research, health beliefs that may conflict with prevention practices, and low awareness of screening options.
The Northern Plains region has some of the highest rates of cancer diagnoses and death in the U.S. Colon cancer, for example, is 53% higher in Northern Plains American Indians, AICAF says. Although screening rates are improving, fewer than half of Northern Plains American Indians aged ≥ 50 years have had a colorectal cancer screening, according to the Association of American Indian Physicians.
The cancer mortality rates are the result of a “complex set of factors” that the AICAF is beginning to address with a comprehensive set of approaches. For instance, in addition to educating the public, AICAF, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Health and Get Your Rear in Gear Colon Cancer Coalition is putting money where its mouth is, with the “Refer-a-Relative” program.
“We are all related,” the campaign says: “Help your community and end colon cancer!” Refer-a-Relative encourages Native Americans in the Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area to get screened, and then to refer up to 5 relatives aged ≥ 50 years for screening. Patients receive a $20 gift card for completing screening, and $10 for each relative who completes screening. The relatives receive a $20 gift card and can refer more people.
The screening project is 1 branch of the AICAF’s interest in innovating clinical systems at IHS, Tribal, and Urban (ITU) clinics. Much of the work is based on the Improving Northern Plains American Indian Colorectal Cancer Screening (INPACS) project with ITU clinics. The AICAF invites interested ITU clinics to join the Clinical Cancer Screening Network. For more information, infographics, and other patient education materials, visit www.americanindiancancer.org.
Novel robotic camera photographs colon
A novel robotically driven capsule successfully navigated a colon in a pig model in 100% of 30 retroflexion maneuvers, setting the stage for further study of robotics in colonoscopy. The data were presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Although capsule technology has expanded exploration of the GI tract, current capsules are limited by passive movement and lack therapeutic capability, said Keith L. Obstein, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
The researchers developed a capsule with an 18-mm head and interior permanent magnets designed to be automatically controlled by an external robotic arm in difficult areas.
“Retroflexion is a common but mechanically complex maneuver during colonoscopy, and therefore serves as an excellent subject for autonomous control,” the researchers noted.
Logistically, the capsule is soft-tethered after it is introduced through the rectum, which allows the potential for therapeutic procedures such as biopsies and polyp removal. In addition, the use of an external magnet to pull the robot with the tether may reduce the pressure on the colon that typically created when a physician pushes the colonoscope from behind. Therefore, use of a robotic capsule may help reduce patients’ discomfort and make them more amenable to the procedure, Dr. Obstein said.
In the study, an endoscopist performed the first retroflexion with a standard colonoscope at 15 cm from the anal sphincter, and these parameters were used to set the robotic system for autonomous retroflexion at 15 cm from the anal sphincter.
The success rate was 100% for both the standard endoscope and the automatically controlled robot for each of 30 maneuvers. The average time for a robotic maneuver was 12 seconds, and no leaks or histologic abnormalities were noted.
Studies to evaluate additional control algorithms are in progress, and the robot capsule may be ready for human trials in 2018, Dr. Obstein said.
This study was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01EB018992. Dr. Obstein had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Digestive Disease Week® is jointly sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT).
A novel robotically driven capsule successfully navigated a colon in a pig model in 100% of 30 retroflexion maneuvers, setting the stage for further study of robotics in colonoscopy. The data were presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Although capsule technology has expanded exploration of the GI tract, current capsules are limited by passive movement and lack therapeutic capability, said Keith L. Obstein, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
The researchers developed a capsule with an 18-mm head and interior permanent magnets designed to be automatically controlled by an external robotic arm in difficult areas.
“Retroflexion is a common but mechanically complex maneuver during colonoscopy, and therefore serves as an excellent subject for autonomous control,” the researchers noted.
Logistically, the capsule is soft-tethered after it is introduced through the rectum, which allows the potential for therapeutic procedures such as biopsies and polyp removal. In addition, the use of an external magnet to pull the robot with the tether may reduce the pressure on the colon that typically created when a physician pushes the colonoscope from behind. Therefore, use of a robotic capsule may help reduce patients’ discomfort and make them more amenable to the procedure, Dr. Obstein said.
In the study, an endoscopist performed the first retroflexion with a standard colonoscope at 15 cm from the anal sphincter, and these parameters were used to set the robotic system for autonomous retroflexion at 15 cm from the anal sphincter.
The success rate was 100% for both the standard endoscope and the automatically controlled robot for each of 30 maneuvers. The average time for a robotic maneuver was 12 seconds, and no leaks or histologic abnormalities were noted.
Studies to evaluate additional control algorithms are in progress, and the robot capsule may be ready for human trials in 2018, Dr. Obstein said.
This study was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01EB018992. Dr. Obstein had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Digestive Disease Week® is jointly sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT).
A novel robotically driven capsule successfully navigated a colon in a pig model in 100% of 30 retroflexion maneuvers, setting the stage for further study of robotics in colonoscopy. The data were presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Although capsule technology has expanded exploration of the GI tract, current capsules are limited by passive movement and lack therapeutic capability, said Keith L. Obstein, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
The researchers developed a capsule with an 18-mm head and interior permanent magnets designed to be automatically controlled by an external robotic arm in difficult areas.
“Retroflexion is a common but mechanically complex maneuver during colonoscopy, and therefore serves as an excellent subject for autonomous control,” the researchers noted.
Logistically, the capsule is soft-tethered after it is introduced through the rectum, which allows the potential for therapeutic procedures such as biopsies and polyp removal. In addition, the use of an external magnet to pull the robot with the tether may reduce the pressure on the colon that typically created when a physician pushes the colonoscope from behind. Therefore, use of a robotic capsule may help reduce patients’ discomfort and make them more amenable to the procedure, Dr. Obstein said.
In the study, an endoscopist performed the first retroflexion with a standard colonoscope at 15 cm from the anal sphincter, and these parameters were used to set the robotic system for autonomous retroflexion at 15 cm from the anal sphincter.
The success rate was 100% for both the standard endoscope and the automatically controlled robot for each of 30 maneuvers. The average time for a robotic maneuver was 12 seconds, and no leaks or histologic abnormalities were noted.
Studies to evaluate additional control algorithms are in progress, and the robot capsule may be ready for human trials in 2018, Dr. Obstein said.
This study was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01EB018992. Dr. Obstein had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Digestive Disease Week® is jointly sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT).
FROM DDW
Key clinical point: An 18-mm magnetized capsule colonoscope successfully navigated a pig colon, and researchers are planning human trials for 2018.
Major finding: An automated robot capsule successfully completed 30 retroflexion maneuvers in a pig colon with an average time of 12 seconds.
Data source: The data come from a test of 30 maneuvers.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01EB018992. Dr. Obstein had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.