User login
Pharmacist-based strategy places more patients on statins
Visit-based strategy has more modest effect
PHILADELPHIA – In two studies run in parallel fashion to test different strategies, one that employed automatic referral to a pharmacist appeared to be superior to one using alerts from the electronic health record (EHR) in increasing the number of at-risk patients receiving a prescription for statins.
, reported Alexander C. Faranoff, MD, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia.
The parallel studies were part of the SUPER LIPID program, created to generate evidence-based strategies for increasing the proportion of at-risk patients on statins. Dr. Faranoff said current data show that at least 50% of patients indicated for high-intensity statins in the United States are not taking them.
The two studies were presented together in a late breaking presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
EHR algorithm identifies statin candidates
The candidates for statin therapy were identified through an EHR algorithm for both studies. Both compared the impact of the intervention against a baseline period of usual care, although the study of EHR alerts also randomized physicians to provide usual care for 3 months or 6 months prior to intervention.
Dr. Faranoff described these interventions as non–visit related and visit related.
In the study of the non–visit-related strategy, referrals were generated by EHR and sent directly to the pharmacist. Upon receipt, the pharmacist verified the order was appropriate and called the patient directly to discuss starting therapy. Patients agreeing to start a statin were provided with a prescription and followed by the pharmacist.
In the study of the patient-visit approach, physicians seeing EHR-identified candidates received interruptive pop-up alerts during patient encounters. The physicians were randomized to provide usual care for 3 or 6 months before they began receiving alerts. The alerts recommended referral to a pharmacist.
During usual care in the non–visit-related study, only 15.2% of the 975 candidates for statins received a prescription. During the intervention period, the rate climbed to 31.6%. Statistically, the intervention more than doubled the odds ratio (OR) of receiving a statin prescription relative to usual care (OR 2.22; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.47-3.37).
In addition, the proportion of patients receiving an appropriate dose of statins climbed from 7.7% in the period of usual care to 24.8% in the intervention period (OR 6.79; 95% CI 4.00-11.53).
Visit-based study also randomized
In the study evaluating a visit-based intervention, 16 physicians were randomized to deliver usual care for 3 or 6 months. Of physicians randomized to 3 months, 970 candidates for statins were treated during the 6-month intervention period. The physicians randomized to usual care for 6 months treated 672 candidates for statins during a 3-month intervention period,
More than 3,000 alerts were sent to both groups of physicians over the intervention period. Only 165 (4.6%) were associated with a prescription.
For the group randomized to 3 months of usual care, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from 14.9% during the period of usual care to 17.6% in the first 3 months of intervention and then fell slightly to 15.5% in the second 3 months.
For the group randomized to usual care for 6 months, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from about 11% during the period of usual care to 14.6%. Combining data from both arms, the small gain in prescriptions was significant but modest (OR 1.43; 95% CI 1.02-2.00).
In addition, the visit-based EHR notifications failed to yield a significant gain in the proportion of patients on an appropriate statin dose. During the intervention period, this proportion was only about 9% of patients treated by either of the two groups of randomized physicians,
The SUPER LIPID program involved 11 internal medicine and family medicine clinics in rural Pennsylvania. In the visit-based intervention, 16 primary care physicians (PCPs) were randomized. In the asynchronous intervention, 10 primary care practices participated. The EHR identified a total of 1,950 candidates for a statin.
Although the gain in statin prescriptions was disappointing for the visit-based intervention, the strategy of using the EHR to refer statin-eligible patients to pharmacists “could be an effective adjunct to visit-based clinical interactions in increasing statin prescribing for high-risk patients,” Dr. Faranoff maintained.
Overcoming clinical inertia a challenge
The greater efficacy of a pharmacist-based approach did not surprise the AHA-invited discussant, Benjamin M. Scirica, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Pointing out that the pharmacist-based strategy of increasing statin prescriptions is more complicated and more costly, he said, “You get what you pay for.” In his opinion, simple solutions are unlikely ever to be effective due to the complex reasons for clinical inertia. Overall, he thinks a multifaceted approach to placing more patients who need statins on therapy is essential.
“Implementation science is hard,” Dr. Scirica said. Even though the referral-to-a-pharmacist approach ended up putting more patients on statins and putting them on an appropriate dose, he said even this more effective strategy “is still not getting to the majority of patients.”
This does not mean that this approach is without merit or should not be one of many strategies employed, but Dr. Scirica said “there is so much more to be done,” and that it should be employed along with other initiatives.
Faranoff reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Scirica reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Aktiia, AstraZeneca, Better Therapeutics, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Hanmi, Lexicon, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
Visit-based strategy has more modest effect
Visit-based strategy has more modest effect
PHILADELPHIA – In two studies run in parallel fashion to test different strategies, one that employed automatic referral to a pharmacist appeared to be superior to one using alerts from the electronic health record (EHR) in increasing the number of at-risk patients receiving a prescription for statins.
, reported Alexander C. Faranoff, MD, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia.
The parallel studies were part of the SUPER LIPID program, created to generate evidence-based strategies for increasing the proportion of at-risk patients on statins. Dr. Faranoff said current data show that at least 50% of patients indicated for high-intensity statins in the United States are not taking them.
The two studies were presented together in a late breaking presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
EHR algorithm identifies statin candidates
The candidates for statin therapy were identified through an EHR algorithm for both studies. Both compared the impact of the intervention against a baseline period of usual care, although the study of EHR alerts also randomized physicians to provide usual care for 3 months or 6 months prior to intervention.
Dr. Faranoff described these interventions as non–visit related and visit related.
In the study of the non–visit-related strategy, referrals were generated by EHR and sent directly to the pharmacist. Upon receipt, the pharmacist verified the order was appropriate and called the patient directly to discuss starting therapy. Patients agreeing to start a statin were provided with a prescription and followed by the pharmacist.
In the study of the patient-visit approach, physicians seeing EHR-identified candidates received interruptive pop-up alerts during patient encounters. The physicians were randomized to provide usual care for 3 or 6 months before they began receiving alerts. The alerts recommended referral to a pharmacist.
During usual care in the non–visit-related study, only 15.2% of the 975 candidates for statins received a prescription. During the intervention period, the rate climbed to 31.6%. Statistically, the intervention more than doubled the odds ratio (OR) of receiving a statin prescription relative to usual care (OR 2.22; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.47-3.37).
In addition, the proportion of patients receiving an appropriate dose of statins climbed from 7.7% in the period of usual care to 24.8% in the intervention period (OR 6.79; 95% CI 4.00-11.53).
Visit-based study also randomized
In the study evaluating a visit-based intervention, 16 physicians were randomized to deliver usual care for 3 or 6 months. Of physicians randomized to 3 months, 970 candidates for statins were treated during the 6-month intervention period. The physicians randomized to usual care for 6 months treated 672 candidates for statins during a 3-month intervention period,
More than 3,000 alerts were sent to both groups of physicians over the intervention period. Only 165 (4.6%) were associated with a prescription.
For the group randomized to 3 months of usual care, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from 14.9% during the period of usual care to 17.6% in the first 3 months of intervention and then fell slightly to 15.5% in the second 3 months.
For the group randomized to usual care for 6 months, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from about 11% during the period of usual care to 14.6%. Combining data from both arms, the small gain in prescriptions was significant but modest (OR 1.43; 95% CI 1.02-2.00).
In addition, the visit-based EHR notifications failed to yield a significant gain in the proportion of patients on an appropriate statin dose. During the intervention period, this proportion was only about 9% of patients treated by either of the two groups of randomized physicians,
The SUPER LIPID program involved 11 internal medicine and family medicine clinics in rural Pennsylvania. In the visit-based intervention, 16 primary care physicians (PCPs) were randomized. In the asynchronous intervention, 10 primary care practices participated. The EHR identified a total of 1,950 candidates for a statin.
Although the gain in statin prescriptions was disappointing for the visit-based intervention, the strategy of using the EHR to refer statin-eligible patients to pharmacists “could be an effective adjunct to visit-based clinical interactions in increasing statin prescribing for high-risk patients,” Dr. Faranoff maintained.
Overcoming clinical inertia a challenge
The greater efficacy of a pharmacist-based approach did not surprise the AHA-invited discussant, Benjamin M. Scirica, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Pointing out that the pharmacist-based strategy of increasing statin prescriptions is more complicated and more costly, he said, “You get what you pay for.” In his opinion, simple solutions are unlikely ever to be effective due to the complex reasons for clinical inertia. Overall, he thinks a multifaceted approach to placing more patients who need statins on therapy is essential.
“Implementation science is hard,” Dr. Scirica said. Even though the referral-to-a-pharmacist approach ended up putting more patients on statins and putting them on an appropriate dose, he said even this more effective strategy “is still not getting to the majority of patients.”
This does not mean that this approach is without merit or should not be one of many strategies employed, but Dr. Scirica said “there is so much more to be done,” and that it should be employed along with other initiatives.
Faranoff reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Scirica reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Aktiia, AstraZeneca, Better Therapeutics, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Hanmi, Lexicon, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
PHILADELPHIA – In two studies run in parallel fashion to test different strategies, one that employed automatic referral to a pharmacist appeared to be superior to one using alerts from the electronic health record (EHR) in increasing the number of at-risk patients receiving a prescription for statins.
, reported Alexander C. Faranoff, MD, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine at Penn Medicine, Philadelphia.
The parallel studies were part of the SUPER LIPID program, created to generate evidence-based strategies for increasing the proportion of at-risk patients on statins. Dr. Faranoff said current data show that at least 50% of patients indicated for high-intensity statins in the United States are not taking them.
The two studies were presented together in a late breaking presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
EHR algorithm identifies statin candidates
The candidates for statin therapy were identified through an EHR algorithm for both studies. Both compared the impact of the intervention against a baseline period of usual care, although the study of EHR alerts also randomized physicians to provide usual care for 3 months or 6 months prior to intervention.
Dr. Faranoff described these interventions as non–visit related and visit related.
In the study of the non–visit-related strategy, referrals were generated by EHR and sent directly to the pharmacist. Upon receipt, the pharmacist verified the order was appropriate and called the patient directly to discuss starting therapy. Patients agreeing to start a statin were provided with a prescription and followed by the pharmacist.
In the study of the patient-visit approach, physicians seeing EHR-identified candidates received interruptive pop-up alerts during patient encounters. The physicians were randomized to provide usual care for 3 or 6 months before they began receiving alerts. The alerts recommended referral to a pharmacist.
During usual care in the non–visit-related study, only 15.2% of the 975 candidates for statins received a prescription. During the intervention period, the rate climbed to 31.6%. Statistically, the intervention more than doubled the odds ratio (OR) of receiving a statin prescription relative to usual care (OR 2.22; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.47-3.37).
In addition, the proportion of patients receiving an appropriate dose of statins climbed from 7.7% in the period of usual care to 24.8% in the intervention period (OR 6.79; 95% CI 4.00-11.53).
Visit-based study also randomized
In the study evaluating a visit-based intervention, 16 physicians were randomized to deliver usual care for 3 or 6 months. Of physicians randomized to 3 months, 970 candidates for statins were treated during the 6-month intervention period. The physicians randomized to usual care for 6 months treated 672 candidates for statins during a 3-month intervention period,
More than 3,000 alerts were sent to both groups of physicians over the intervention period. Only 165 (4.6%) were associated with a prescription.
For the group randomized to 3 months of usual care, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from 14.9% during the period of usual care to 17.6% in the first 3 months of intervention and then fell slightly to 15.5% in the second 3 months.
For the group randomized to usual care for 6 months, the proportion of candidates for statins who received a prescription rose from about 11% during the period of usual care to 14.6%. Combining data from both arms, the small gain in prescriptions was significant but modest (OR 1.43; 95% CI 1.02-2.00).
In addition, the visit-based EHR notifications failed to yield a significant gain in the proportion of patients on an appropriate statin dose. During the intervention period, this proportion was only about 9% of patients treated by either of the two groups of randomized physicians,
The SUPER LIPID program involved 11 internal medicine and family medicine clinics in rural Pennsylvania. In the visit-based intervention, 16 primary care physicians (PCPs) were randomized. In the asynchronous intervention, 10 primary care practices participated. The EHR identified a total of 1,950 candidates for a statin.
Although the gain in statin prescriptions was disappointing for the visit-based intervention, the strategy of using the EHR to refer statin-eligible patients to pharmacists “could be an effective adjunct to visit-based clinical interactions in increasing statin prescribing for high-risk patients,” Dr. Faranoff maintained.
Overcoming clinical inertia a challenge
The greater efficacy of a pharmacist-based approach did not surprise the AHA-invited discussant, Benjamin M. Scirica, MD, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
Pointing out that the pharmacist-based strategy of increasing statin prescriptions is more complicated and more costly, he said, “You get what you pay for.” In his opinion, simple solutions are unlikely ever to be effective due to the complex reasons for clinical inertia. Overall, he thinks a multifaceted approach to placing more patients who need statins on therapy is essential.
“Implementation science is hard,” Dr. Scirica said. Even though the referral-to-a-pharmacist approach ended up putting more patients on statins and putting them on an appropriate dose, he said even this more effective strategy “is still not getting to the majority of patients.”
This does not mean that this approach is without merit or should not be one of many strategies employed, but Dr. Scirica said “there is so much more to be done,” and that it should be employed along with other initiatives.
Faranoff reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Scirica reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Aktiia, AstraZeneca, Better Therapeutics, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Hanmi, Lexicon, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
AT AHA 2023
Low-salt diet cut BP by 6 mm Hg in 1 week: CARDIA-SSBP
The CARDIA-SSBP trial involved 213 individuals aged 50-75 years, including those with and those without hypertension, and showed that the decline in blood pressure brought about by a low-salt diet was independent of hypertension status and antihypertensive medication use. It was also generally consistent across subgroups and did not result in excess adverse events.
“The blood pressure reduction we see here is meaningful, and comparable to that produced by one antihypertensive medication,” lead investigator Deepak Gupta, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta presented the CARDIA-SSBP study on Nov. 11 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, held in Philadelphia. The study was published online in JAMA. The exact menus used in the study are available in a supplement to the JAMA paper.
“In order to live a healthy lifestyle, understanding what we eat has important health effects. Raised blood pressure contributes to one out of every eight deaths worldwide,” Dr. Gupta noted. “If people want to lower their blood pressure, attention to dietary sodium is one part of that. If individuals can stick with a low sodium diet, they may be able to stop taking one of their antihypertensive medications, and those who are normotensive will be less likely to develop hypertension.”
Commentators said the study had significant implications for public health, but they pointed out that maintaining a low-sodium diet over the long term is challenging, given the high salt content of generally available foods.
Dr. Gupta noted that the study did use commercially available products in the low-sodium diets and the menus are available for people to follow, making it more accessible than some diets used in previous studies.
“What may also be attractive to people is that you don’t have to wait for months to see an effect. If you start to consume a low-sodium diet, you can see results on blood pressure rapidly, within a week,” he said.
The diet in this study brought about a large reduction in dietary sodium, but Dr. Gupta says any reduction in dietary sodium is likely to be beneficial.
“If you go to the level that we got to, you could expect to see a reduction of around 6 mm Hg. But it’s like walking – you don’t necessarily need to get to 10,000 steps every day. Any amount of walking or physical activity is of benefit. The same is probably true for salt: Any reduction that you can make is probably of benefit.”
For the study, participants had their blood pressure measured by 24-hour ambulatory monitoring while on their usual diets. They were then randomly assigned to either a high-sodium diet or a low-sodium diet for 1 week. Participants then crossed over to the opposite diet for 1 week, with blood pressure measured over a 24-hour period on the last day of each diet.
As assessed by 24-hour urine excretion, the usual diet of participants was found to already be high in sodium (median, 4.45 g/d). This increased to a median of 5.00 g/d when on the high-sodium diet in the study and decreased to 1.27 g/d while on the low-sodium diet.
Results found participants had a median systolic blood pressure of 125 mm Hg on their usual diets. This was raised to 126 mm Hg on the high-sodium diet and lowered to 119 mm Hg on the low-sodium diet.
The researchers also reported that 75% of individuals showed a blood pressure reduction on the low-sodium diet and are thus defined as “salt-sensitive.” This is a higher percentage than found in previous studies.
“Of those that didn’t show a blood pressure reduction with a low-sodium diet in this study, it appears that they may not have been so adherent to the diet as those who did show a blood pressure reduction,” Dr. Gupta said.
He noted that hypertension is the most common chronic disease condition worldwide, with about 1.3 billion people affected, and although it has been known for some time that dietary sodium affects blood pressure, there have been some gaps in previous studies.
For example, many studies have excluded individuals who were already taking antihypertensive medications and people with diabetes, and they have generally not included many older individuals. The current study found that all of these groups showed significant blood pressure reductions by reducing dietary sodium.
Large effect in people with diabetes
Subgroup analysis largely showed consistent results across the population, regardless of age, sex, race, and body mass index and whether participants were taking antihypertensive medication or not, but there were a couple of exceptions. Individuals with higher blood pressure at baseline seemed to have a greater effect of lowering dietary sodium, although those who were normotensive at baseline still showed significant blood pressure reduction, Dr. Gupta reported.
The researchers found a particularly large reduction in blood pressure from lowering sodium intake in people with diabetes, who made up about 21% of the overall cohort. Their average reduction in systolic blood pressure between the high and low sodium diet was close to 17 mm Hg rather than the 7-8 mm Hg in the whole cohort.
Dr. Gupta said that the results are applicable to most of the population.
“The people who will be most motivated to follow a low-sodium diet are those with hypertension. But even in normotensive individuals, there is likely to be benefit.”
To help people follow a low-sodium diet, Dr. Gupta says education campaigns are needed “to show people that they can do it and make it work.” But there are bigger structural issues that need to be addressed at policy and governmental levels.
“Most of our food available in grocery stores and restaurants is high in salt. We now have a preponderance of evidence showing us that we need to change what’s available in the food supply,” he said. “There is a push going on for this now, and the U.S. has introduced some guidelines for the food industry on sodium content of foods. These are voluntary at this point, but it’s a start.”
Difficult to maintain long term
Commenting on the study, Paul Whelton, MD, chair in global public health at Tulane University, New Orleans, noted that sodium reduction is known to reduce blood pressure, with greater sodium reductions giving greater blood pressure decreases, and that some people are more sensitive to the effects of sodium than others.
He described CARDIA-SSBP as a “well-done study.”
“They managed to get a very low sodium intake and a large difference between the two groups, which translated into a big reduction in systolic blood pressure,” Dr. Whelton said. “However, the problem with these sorts of trials where the diets are provided to the participants is that although they show proof of concept, it is difficult to generalize because we can’t normally provide patients with their meals. In this type of ‘feeding’ study, we find it difficult to maintain people on their behavioral intervention over the long term.”
Dr. Whelton said that he was more excited about this trial knowing that the food given was commercially available. “That makes it more practical, but you still have to be quite motivated to follow a diet like this. Buying low-sodium products in the supermarket does require quite a lot of work to read the labels, and sometimes the low-sodium foods are specialty products and are more expensive.”
He pointed out that older people in higher socioeconomic classes are more likely to attempt this and do better from behavioral interventions in general. “Unfortunately, people who don’t do well from behavioral interventions like this are those from lower socioeconomic groups, who are ones at most at risk for cardiovascular disease.”
Dr. Whelton noted that the food industry has been reluctant to lower sodium content because high-salt foods sell better. “Unfortunately, foods high in saturated fat and salt taste good to most people. We are generally attuned to a high salt intake. But when people have been following a low-salt diet for a while, they generally don’t like high-salt foods anymore. They become attuned to lower-sodium diet,” he added.
New U.S. sodium reduction guidelines
Discussant of the CARDIA-SSBP study at the AHA meeting, Cheryl Anderson, MD, University of California, San Diego, said that the findings were important and consistent with prior studies.
“These studies have global implications because salt is ubiquitous in the food supply in much of the world,” she noted, adding that, “Americans consume almost 50% more sodium than recommended, and there has been a persistent lack of adherence to healthy diet recommendations for reductions in salt, sugar, and fats.”
Dr. Anderson pointed out that in 2021, the Food and Drug Administration issued guidance for voluntary sodium reduction, which uses a gradual approach, with targets to reach a population goal of 3,000 mg/d of sodium by 2023 and 2,300 mg/d by 2031.
“These targets apply to 150 categories of food that are sales-weighted to focus on dominant sellers in each category. They apply to food manufacturers, restaurants and food service operations,” she concluded. “These targets serve as a basis for continued dialogue. The research community eagerly awaits the review of population-based data to help refine this approach and goals.”
This study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial involved 213 individuals aged 50-75 years, including those with and those without hypertension, and showed that the decline in blood pressure brought about by a low-salt diet was independent of hypertension status and antihypertensive medication use. It was also generally consistent across subgroups and did not result in excess adverse events.
“The blood pressure reduction we see here is meaningful, and comparable to that produced by one antihypertensive medication,” lead investigator Deepak Gupta, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta presented the CARDIA-SSBP study on Nov. 11 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, held in Philadelphia. The study was published online in JAMA. The exact menus used in the study are available in a supplement to the JAMA paper.
“In order to live a healthy lifestyle, understanding what we eat has important health effects. Raised blood pressure contributes to one out of every eight deaths worldwide,” Dr. Gupta noted. “If people want to lower their blood pressure, attention to dietary sodium is one part of that. If individuals can stick with a low sodium diet, they may be able to stop taking one of their antihypertensive medications, and those who are normotensive will be less likely to develop hypertension.”
Commentators said the study had significant implications for public health, but they pointed out that maintaining a low-sodium diet over the long term is challenging, given the high salt content of generally available foods.
Dr. Gupta noted that the study did use commercially available products in the low-sodium diets and the menus are available for people to follow, making it more accessible than some diets used in previous studies.
“What may also be attractive to people is that you don’t have to wait for months to see an effect. If you start to consume a low-sodium diet, you can see results on blood pressure rapidly, within a week,” he said.
The diet in this study brought about a large reduction in dietary sodium, but Dr. Gupta says any reduction in dietary sodium is likely to be beneficial.
“If you go to the level that we got to, you could expect to see a reduction of around 6 mm Hg. But it’s like walking – you don’t necessarily need to get to 10,000 steps every day. Any amount of walking or physical activity is of benefit. The same is probably true for salt: Any reduction that you can make is probably of benefit.”
For the study, participants had their blood pressure measured by 24-hour ambulatory monitoring while on their usual diets. They were then randomly assigned to either a high-sodium diet or a low-sodium diet for 1 week. Participants then crossed over to the opposite diet for 1 week, with blood pressure measured over a 24-hour period on the last day of each diet.
As assessed by 24-hour urine excretion, the usual diet of participants was found to already be high in sodium (median, 4.45 g/d). This increased to a median of 5.00 g/d when on the high-sodium diet in the study and decreased to 1.27 g/d while on the low-sodium diet.
Results found participants had a median systolic blood pressure of 125 mm Hg on their usual diets. This was raised to 126 mm Hg on the high-sodium diet and lowered to 119 mm Hg on the low-sodium diet.
The researchers also reported that 75% of individuals showed a blood pressure reduction on the low-sodium diet and are thus defined as “salt-sensitive.” This is a higher percentage than found in previous studies.
“Of those that didn’t show a blood pressure reduction with a low-sodium diet in this study, it appears that they may not have been so adherent to the diet as those who did show a blood pressure reduction,” Dr. Gupta said.
He noted that hypertension is the most common chronic disease condition worldwide, with about 1.3 billion people affected, and although it has been known for some time that dietary sodium affects blood pressure, there have been some gaps in previous studies.
For example, many studies have excluded individuals who were already taking antihypertensive medications and people with diabetes, and they have generally not included many older individuals. The current study found that all of these groups showed significant blood pressure reductions by reducing dietary sodium.
Large effect in people with diabetes
Subgroup analysis largely showed consistent results across the population, regardless of age, sex, race, and body mass index and whether participants were taking antihypertensive medication or not, but there were a couple of exceptions. Individuals with higher blood pressure at baseline seemed to have a greater effect of lowering dietary sodium, although those who were normotensive at baseline still showed significant blood pressure reduction, Dr. Gupta reported.
The researchers found a particularly large reduction in blood pressure from lowering sodium intake in people with diabetes, who made up about 21% of the overall cohort. Their average reduction in systolic blood pressure between the high and low sodium diet was close to 17 mm Hg rather than the 7-8 mm Hg in the whole cohort.
Dr. Gupta said that the results are applicable to most of the population.
“The people who will be most motivated to follow a low-sodium diet are those with hypertension. But even in normotensive individuals, there is likely to be benefit.”
To help people follow a low-sodium diet, Dr. Gupta says education campaigns are needed “to show people that they can do it and make it work.” But there are bigger structural issues that need to be addressed at policy and governmental levels.
“Most of our food available in grocery stores and restaurants is high in salt. We now have a preponderance of evidence showing us that we need to change what’s available in the food supply,” he said. “There is a push going on for this now, and the U.S. has introduced some guidelines for the food industry on sodium content of foods. These are voluntary at this point, but it’s a start.”
Difficult to maintain long term
Commenting on the study, Paul Whelton, MD, chair in global public health at Tulane University, New Orleans, noted that sodium reduction is known to reduce blood pressure, with greater sodium reductions giving greater blood pressure decreases, and that some people are more sensitive to the effects of sodium than others.
He described CARDIA-SSBP as a “well-done study.”
“They managed to get a very low sodium intake and a large difference between the two groups, which translated into a big reduction in systolic blood pressure,” Dr. Whelton said. “However, the problem with these sorts of trials where the diets are provided to the participants is that although they show proof of concept, it is difficult to generalize because we can’t normally provide patients with their meals. In this type of ‘feeding’ study, we find it difficult to maintain people on their behavioral intervention over the long term.”
Dr. Whelton said that he was more excited about this trial knowing that the food given was commercially available. “That makes it more practical, but you still have to be quite motivated to follow a diet like this. Buying low-sodium products in the supermarket does require quite a lot of work to read the labels, and sometimes the low-sodium foods are specialty products and are more expensive.”
He pointed out that older people in higher socioeconomic classes are more likely to attempt this and do better from behavioral interventions in general. “Unfortunately, people who don’t do well from behavioral interventions like this are those from lower socioeconomic groups, who are ones at most at risk for cardiovascular disease.”
Dr. Whelton noted that the food industry has been reluctant to lower sodium content because high-salt foods sell better. “Unfortunately, foods high in saturated fat and salt taste good to most people. We are generally attuned to a high salt intake. But when people have been following a low-salt diet for a while, they generally don’t like high-salt foods anymore. They become attuned to lower-sodium diet,” he added.
New U.S. sodium reduction guidelines
Discussant of the CARDIA-SSBP study at the AHA meeting, Cheryl Anderson, MD, University of California, San Diego, said that the findings were important and consistent with prior studies.
“These studies have global implications because salt is ubiquitous in the food supply in much of the world,” she noted, adding that, “Americans consume almost 50% more sodium than recommended, and there has been a persistent lack of adherence to healthy diet recommendations for reductions in salt, sugar, and fats.”
Dr. Anderson pointed out that in 2021, the Food and Drug Administration issued guidance for voluntary sodium reduction, which uses a gradual approach, with targets to reach a population goal of 3,000 mg/d of sodium by 2023 and 2,300 mg/d by 2031.
“These targets apply to 150 categories of food that are sales-weighted to focus on dominant sellers in each category. They apply to food manufacturers, restaurants and food service operations,” she concluded. “These targets serve as a basis for continued dialogue. The research community eagerly awaits the review of population-based data to help refine this approach and goals.”
This study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial involved 213 individuals aged 50-75 years, including those with and those without hypertension, and showed that the decline in blood pressure brought about by a low-salt diet was independent of hypertension status and antihypertensive medication use. It was also generally consistent across subgroups and did not result in excess adverse events.
“The blood pressure reduction we see here is meaningful, and comparable to that produced by one antihypertensive medication,” lead investigator Deepak Gupta, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta presented the CARDIA-SSBP study on Nov. 11 at the American Heart Association scientific sessions, held in Philadelphia. The study was published online in JAMA. The exact menus used in the study are available in a supplement to the JAMA paper.
“In order to live a healthy lifestyle, understanding what we eat has important health effects. Raised blood pressure contributes to one out of every eight deaths worldwide,” Dr. Gupta noted. “If people want to lower their blood pressure, attention to dietary sodium is one part of that. If individuals can stick with a low sodium diet, they may be able to stop taking one of their antihypertensive medications, and those who are normotensive will be less likely to develop hypertension.”
Commentators said the study had significant implications for public health, but they pointed out that maintaining a low-sodium diet over the long term is challenging, given the high salt content of generally available foods.
Dr. Gupta noted that the study did use commercially available products in the low-sodium diets and the menus are available for people to follow, making it more accessible than some diets used in previous studies.
“What may also be attractive to people is that you don’t have to wait for months to see an effect. If you start to consume a low-sodium diet, you can see results on blood pressure rapidly, within a week,” he said.
The diet in this study brought about a large reduction in dietary sodium, but Dr. Gupta says any reduction in dietary sodium is likely to be beneficial.
“If you go to the level that we got to, you could expect to see a reduction of around 6 mm Hg. But it’s like walking – you don’t necessarily need to get to 10,000 steps every day. Any amount of walking or physical activity is of benefit. The same is probably true for salt: Any reduction that you can make is probably of benefit.”
For the study, participants had their blood pressure measured by 24-hour ambulatory monitoring while on their usual diets. They were then randomly assigned to either a high-sodium diet or a low-sodium diet for 1 week. Participants then crossed over to the opposite diet for 1 week, with blood pressure measured over a 24-hour period on the last day of each diet.
As assessed by 24-hour urine excretion, the usual diet of participants was found to already be high in sodium (median, 4.45 g/d). This increased to a median of 5.00 g/d when on the high-sodium diet in the study and decreased to 1.27 g/d while on the low-sodium diet.
Results found participants had a median systolic blood pressure of 125 mm Hg on their usual diets. This was raised to 126 mm Hg on the high-sodium diet and lowered to 119 mm Hg on the low-sodium diet.
The researchers also reported that 75% of individuals showed a blood pressure reduction on the low-sodium diet and are thus defined as “salt-sensitive.” This is a higher percentage than found in previous studies.
“Of those that didn’t show a blood pressure reduction with a low-sodium diet in this study, it appears that they may not have been so adherent to the diet as those who did show a blood pressure reduction,” Dr. Gupta said.
He noted that hypertension is the most common chronic disease condition worldwide, with about 1.3 billion people affected, and although it has been known for some time that dietary sodium affects blood pressure, there have been some gaps in previous studies.
For example, many studies have excluded individuals who were already taking antihypertensive medications and people with diabetes, and they have generally not included many older individuals. The current study found that all of these groups showed significant blood pressure reductions by reducing dietary sodium.
Large effect in people with diabetes
Subgroup analysis largely showed consistent results across the population, regardless of age, sex, race, and body mass index and whether participants were taking antihypertensive medication or not, but there were a couple of exceptions. Individuals with higher blood pressure at baseline seemed to have a greater effect of lowering dietary sodium, although those who were normotensive at baseline still showed significant blood pressure reduction, Dr. Gupta reported.
The researchers found a particularly large reduction in blood pressure from lowering sodium intake in people with diabetes, who made up about 21% of the overall cohort. Their average reduction in systolic blood pressure between the high and low sodium diet was close to 17 mm Hg rather than the 7-8 mm Hg in the whole cohort.
Dr. Gupta said that the results are applicable to most of the population.
“The people who will be most motivated to follow a low-sodium diet are those with hypertension. But even in normotensive individuals, there is likely to be benefit.”
To help people follow a low-sodium diet, Dr. Gupta says education campaigns are needed “to show people that they can do it and make it work.” But there are bigger structural issues that need to be addressed at policy and governmental levels.
“Most of our food available in grocery stores and restaurants is high in salt. We now have a preponderance of evidence showing us that we need to change what’s available in the food supply,” he said. “There is a push going on for this now, and the U.S. has introduced some guidelines for the food industry on sodium content of foods. These are voluntary at this point, but it’s a start.”
Difficult to maintain long term
Commenting on the study, Paul Whelton, MD, chair in global public health at Tulane University, New Orleans, noted that sodium reduction is known to reduce blood pressure, with greater sodium reductions giving greater blood pressure decreases, and that some people are more sensitive to the effects of sodium than others.
He described CARDIA-SSBP as a “well-done study.”
“They managed to get a very low sodium intake and a large difference between the two groups, which translated into a big reduction in systolic blood pressure,” Dr. Whelton said. “However, the problem with these sorts of trials where the diets are provided to the participants is that although they show proof of concept, it is difficult to generalize because we can’t normally provide patients with their meals. In this type of ‘feeding’ study, we find it difficult to maintain people on their behavioral intervention over the long term.”
Dr. Whelton said that he was more excited about this trial knowing that the food given was commercially available. “That makes it more practical, but you still have to be quite motivated to follow a diet like this. Buying low-sodium products in the supermarket does require quite a lot of work to read the labels, and sometimes the low-sodium foods are specialty products and are more expensive.”
He pointed out that older people in higher socioeconomic classes are more likely to attempt this and do better from behavioral interventions in general. “Unfortunately, people who don’t do well from behavioral interventions like this are those from lower socioeconomic groups, who are ones at most at risk for cardiovascular disease.”
Dr. Whelton noted that the food industry has been reluctant to lower sodium content because high-salt foods sell better. “Unfortunately, foods high in saturated fat and salt taste good to most people. We are generally attuned to a high salt intake. But when people have been following a low-salt diet for a while, they generally don’t like high-salt foods anymore. They become attuned to lower-sodium diet,” he added.
New U.S. sodium reduction guidelines
Discussant of the CARDIA-SSBP study at the AHA meeting, Cheryl Anderson, MD, University of California, San Diego, said that the findings were important and consistent with prior studies.
“These studies have global implications because salt is ubiquitous in the food supply in much of the world,” she noted, adding that, “Americans consume almost 50% more sodium than recommended, and there has been a persistent lack of adherence to healthy diet recommendations for reductions in salt, sugar, and fats.”
Dr. Anderson pointed out that in 2021, the Food and Drug Administration issued guidance for voluntary sodium reduction, which uses a gradual approach, with targets to reach a population goal of 3,000 mg/d of sodium by 2023 and 2,300 mg/d by 2031.
“These targets apply to 150 categories of food that are sales-weighted to focus on dominant sellers in each category. They apply to food manufacturers, restaurants and food service operations,” she concluded. “These targets serve as a basis for continued dialogue. The research community eagerly awaits the review of population-based data to help refine this approach and goals.”
This study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. The authors report no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Study takes fine-grained look at MACE risk with glucocorticoids in RA
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
AT ACR 2023
Better postpartum BP control with self-monitoring: POP-HT
, new research suggests.
In a randomized trial of 220 women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension, those who took daily postpartum BP readings and received clinician-guided advice for titrating antihypertensives had a 5 mm Hg–lower average diastolic BP at 9 months, compared with those receiving usual care.
Jamie Kitt, DPhil, from the University of Oxford (England) presented these findings from the Physicians Optimized Postpartum Hypertension Treatment (POP-HT, NCT04273854) clinical trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA, and a cardiac imaging substudy was published online in Circulation.
“This trial identifies a potential need for a paradigm shift in the way women affected by hypertensive pregnancy are managed postnatally,” Dr. Kitt said. “If a 5–mm Hg improvement in BP is maintained longer term, it can result in about a 20% reduction in lifetime cardiovascular risk.”
The imaging substudy suggests that short-term postnatal optimization of BP control following hypertensive pregnancy through self-monitoring and physician-guided antihypertensive titration is linked with better cardiac remodeling changes seen by cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiography.
POP-HT “proves for the first time that the first few weeks after delivery are a critical time that can determine the long-term cardiovascular health of the mother,” senior author Paul Leeson, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, who presented the findings in a press briefing, said in an interview.
“Interventions during this period can have long-term beneficial impacts on cardiovascular health,” he said. “These findings rewrite the textbook on our understanding of how and why hypertensive pregnancies associate with later cardiovascular disease in the mother.”
Next, Dr. Leeson said, “We need to work out the best ways to implement these interventions “at scale. Then we can ensure all women who have hypertensive pregnancies can get access to the long-term cardiovascular benefits we have demonstrated are possible through improving postpartum cardiac care,” he said, adding that “this is entirely achievable using current available technologies.”
Hypertension in pregnancy
About 1 in 10 pregnant women develop hypertension in pregnancy (preeclampsia or gestational hypertension), and 1 in 3 such women go on to develop chronic hypertension within 10 years, “when they are usually still in their 30s or 40s,” Dr. Leeson said.
During pregnancy, the heart remodels to cope with pregnancy, and it undergoes more severe changes if BP is high. Then during the 6 weeks after giving birth, this remodeling rapidly reverses.
Higher blood pressure in young adulthood is associated with a twofold higher risk of subsequent myocardial infarction and stroke. And abnormal cardiac remodeling postpartum is also linked with higher cardiovascular risk.
Self-monitoring blood pressure during the postpartum period may be a “critical window” for intervention.
Previously, the research group performed a pilot study, the Self-Management of Postnatal Antihypertensive Treatment (SNAP-HT) trial and the SNAP-extension trial, which compared a BP self-monitoring intervention with usual care in 91 women with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia requiring postnatal antihypertensive treatment.
Diastolic BP, which drives cardiovascular risk in younger populations, was 4.5–mm Hg lower at 6 months postpartum and 7–mm Hg lower at 4 years post partum in patients randomly assigned to BP self-management vs. usual care – even after they were no longer taking antihypertensives.
Building on these findings, the POP-HT trial enrolled 220 pregnant women seen at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom who were age 18 years or older, had either gestational hypertension or preeclampsia, and still required antihypertensives when they were being discharged from hospital after giving birth.
Following a baseline visit at day 1-6 after delivery, while in the postnatal ward, the patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to the intervention group (112 women) or usual-care group (108 women).
They had an average age of 32.6 years; 40% had gestational hypertension, and 60% had preeclampsia.
Women in the usual-care group typically received a BP review at 7-10 days after hospital discharge with a community midwife, and another at 6-8 weeks with their general practitioner.
The women in the intervention group were given and taught to use a Bluetooth-enabled OMRON Evolv BP monitor (Omron Healthcare Europe) while on the postnatal ward, and they installed a smartphone app on their mobile phones that transmitted self-monitored BP readings to a National Health Service-hosted, web-based platform.
They were instructed to take daily BP measurements (twice daily if out of target range). Dose titration of antihypertensives after hospital discharge was guided remotely by research clinicians, according to a guideline-based algorithm.
Patients in both groups had four study visits when their BP was measured: visit 1 (baseline) between days 1 and 6 post partum; visit 2 at week 1; visit 3 at week 6; and visit 4 between months 6 and 9 post partum.
Similar antihypertensive classes were prescribed in each group (enalapril 57%, nifedipine 27%, and labetalol 30% for intervention vs. enalapril 43%, nifedipine 30%, and labetalol 27% for control).
At 6 weeks, approximately 30% of participants in each group were still taking medication; this dropped to approximately 12% by visit 4.
The primary outcome – the mean 24-hour diastolic BP at visit 4 (roughly 9 months post partum), adjusted for baseline postnatal diastolic blood pressure – was 5.8–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (71.2 mm Hg vs. 76.6 mm Hg; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes – between-group differences in systolic BP at 9 months, BP-related postnatal admission, and cardiac remodeling assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance – were all better in the intervention group.
The mean 24-hour average systolic BP at 9 months post partum, adjusted for baseline postnatal systolic BP was 6.5–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (114.0 mm Hg vs. 120.3 mm Hg; P < .001).
There was an absolute risk reduction of 20% and a relative risk reduction of 73.5% in postnatal readmission. The number needed to treat to avoid one postnatal readmission was five, which “has potential for big cost savings,” said Dr. Leeson.
Blood pressure post partum can be improved with self-monitoring and physician-guided medication adjustment, Dr. Leeson summarized. The blood pressure remains low for at least 9 months, even when medication is stopped, and the intervention leads to beneficial cardiac remodeling.
U.S. pilot study
Non-Hispanic Black adults have a high hypertension and cardiovascular disease burden, and a related small U.S. study showed benefits of BP self-monitoring in a population comprising mainly Black women, Keith Ferdinand, MD, discussant of the POP-HT trial in the press briefing, said in an interview.
Dr. Ferdinand, from Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana, was lead author of the Text My Hypertension BP Meds NOLA pilot study that was published in February in the American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.
The study showed that text-messaging and social support increased hypertension medication adherence.
They enrolled 36 individuals, of whom 32 (89%) were non-Hispanic Black, and 23 (64%) were women. The participants received validated Bluetooth-enabled BP-monitoring devices that were synced to smartphones via a secured cloud-based application. The participants could send and receive messages to health care practitioners.
This intervention significantly improved medication adherence and systolic BP without modifying pharmacotherapy.
‘Need to be passionate about monitoring BP’
“The take-home messages from these exciting findings is that physicians and women who have had high BP during pregnancy need to be passionate about monitoring and controlling their blood pressure and not ignore it,” Anastasia Mihailidou, PhD, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, the assigned discussant in the late-breaking trial session, said in an interview.
“It also resulted in fewer postpartum hospital readmissions for high blood pressure and benefit at 9 months in the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels of the women,” she said.
“While we need to see further studies in ethnically diverse women to see that they are reproducible, there are simple measures that clinicians can implement, and women can ask to have their BP monitored more frequently than the current practice. In the U.K. it is 5-10 days after delivery and then at 6-8 weeks after giving birth when changes in heart structure have already started,” Dr. Mihailidou noted.
“The procedure will need to be modified if there are no telemedicine facilities, but that should not stop having close monitoring of BP and treating it adequately. Monitoring requires an accurate BP monitor. There also has to be monitoring BP for the children.”
The trial was funded by a BHF Clinical Research Training Fellowship to Dr. Kitt, with additional support from the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre and Oxford BHF Centre for Research Excellence.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a randomized trial of 220 women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension, those who took daily postpartum BP readings and received clinician-guided advice for titrating antihypertensives had a 5 mm Hg–lower average diastolic BP at 9 months, compared with those receiving usual care.
Jamie Kitt, DPhil, from the University of Oxford (England) presented these findings from the Physicians Optimized Postpartum Hypertension Treatment (POP-HT, NCT04273854) clinical trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA, and a cardiac imaging substudy was published online in Circulation.
“This trial identifies a potential need for a paradigm shift in the way women affected by hypertensive pregnancy are managed postnatally,” Dr. Kitt said. “If a 5–mm Hg improvement in BP is maintained longer term, it can result in about a 20% reduction in lifetime cardiovascular risk.”
The imaging substudy suggests that short-term postnatal optimization of BP control following hypertensive pregnancy through self-monitoring and physician-guided antihypertensive titration is linked with better cardiac remodeling changes seen by cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiography.
POP-HT “proves for the first time that the first few weeks after delivery are a critical time that can determine the long-term cardiovascular health of the mother,” senior author Paul Leeson, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, who presented the findings in a press briefing, said in an interview.
“Interventions during this period can have long-term beneficial impacts on cardiovascular health,” he said. “These findings rewrite the textbook on our understanding of how and why hypertensive pregnancies associate with later cardiovascular disease in the mother.”
Next, Dr. Leeson said, “We need to work out the best ways to implement these interventions “at scale. Then we can ensure all women who have hypertensive pregnancies can get access to the long-term cardiovascular benefits we have demonstrated are possible through improving postpartum cardiac care,” he said, adding that “this is entirely achievable using current available technologies.”
Hypertension in pregnancy
About 1 in 10 pregnant women develop hypertension in pregnancy (preeclampsia or gestational hypertension), and 1 in 3 such women go on to develop chronic hypertension within 10 years, “when they are usually still in their 30s or 40s,” Dr. Leeson said.
During pregnancy, the heart remodels to cope with pregnancy, and it undergoes more severe changes if BP is high. Then during the 6 weeks after giving birth, this remodeling rapidly reverses.
Higher blood pressure in young adulthood is associated with a twofold higher risk of subsequent myocardial infarction and stroke. And abnormal cardiac remodeling postpartum is also linked with higher cardiovascular risk.
Self-monitoring blood pressure during the postpartum period may be a “critical window” for intervention.
Previously, the research group performed a pilot study, the Self-Management of Postnatal Antihypertensive Treatment (SNAP-HT) trial and the SNAP-extension trial, which compared a BP self-monitoring intervention with usual care in 91 women with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia requiring postnatal antihypertensive treatment.
Diastolic BP, which drives cardiovascular risk in younger populations, was 4.5–mm Hg lower at 6 months postpartum and 7–mm Hg lower at 4 years post partum in patients randomly assigned to BP self-management vs. usual care – even after they were no longer taking antihypertensives.
Building on these findings, the POP-HT trial enrolled 220 pregnant women seen at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom who were age 18 years or older, had either gestational hypertension or preeclampsia, and still required antihypertensives when they were being discharged from hospital after giving birth.
Following a baseline visit at day 1-6 after delivery, while in the postnatal ward, the patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to the intervention group (112 women) or usual-care group (108 women).
They had an average age of 32.6 years; 40% had gestational hypertension, and 60% had preeclampsia.
Women in the usual-care group typically received a BP review at 7-10 days after hospital discharge with a community midwife, and another at 6-8 weeks with their general practitioner.
The women in the intervention group were given and taught to use a Bluetooth-enabled OMRON Evolv BP monitor (Omron Healthcare Europe) while on the postnatal ward, and they installed a smartphone app on their mobile phones that transmitted self-monitored BP readings to a National Health Service-hosted, web-based platform.
They were instructed to take daily BP measurements (twice daily if out of target range). Dose titration of antihypertensives after hospital discharge was guided remotely by research clinicians, according to a guideline-based algorithm.
Patients in both groups had four study visits when their BP was measured: visit 1 (baseline) between days 1 and 6 post partum; visit 2 at week 1; visit 3 at week 6; and visit 4 between months 6 and 9 post partum.
Similar antihypertensive classes were prescribed in each group (enalapril 57%, nifedipine 27%, and labetalol 30% for intervention vs. enalapril 43%, nifedipine 30%, and labetalol 27% for control).
At 6 weeks, approximately 30% of participants in each group were still taking medication; this dropped to approximately 12% by visit 4.
The primary outcome – the mean 24-hour diastolic BP at visit 4 (roughly 9 months post partum), adjusted for baseline postnatal diastolic blood pressure – was 5.8–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (71.2 mm Hg vs. 76.6 mm Hg; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes – between-group differences in systolic BP at 9 months, BP-related postnatal admission, and cardiac remodeling assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance – were all better in the intervention group.
The mean 24-hour average systolic BP at 9 months post partum, adjusted for baseline postnatal systolic BP was 6.5–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (114.0 mm Hg vs. 120.3 mm Hg; P < .001).
There was an absolute risk reduction of 20% and a relative risk reduction of 73.5% in postnatal readmission. The number needed to treat to avoid one postnatal readmission was five, which “has potential for big cost savings,” said Dr. Leeson.
Blood pressure post partum can be improved with self-monitoring and physician-guided medication adjustment, Dr. Leeson summarized. The blood pressure remains low for at least 9 months, even when medication is stopped, and the intervention leads to beneficial cardiac remodeling.
U.S. pilot study
Non-Hispanic Black adults have a high hypertension and cardiovascular disease burden, and a related small U.S. study showed benefits of BP self-monitoring in a population comprising mainly Black women, Keith Ferdinand, MD, discussant of the POP-HT trial in the press briefing, said in an interview.
Dr. Ferdinand, from Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana, was lead author of the Text My Hypertension BP Meds NOLA pilot study that was published in February in the American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.
The study showed that text-messaging and social support increased hypertension medication adherence.
They enrolled 36 individuals, of whom 32 (89%) were non-Hispanic Black, and 23 (64%) were women. The participants received validated Bluetooth-enabled BP-monitoring devices that were synced to smartphones via a secured cloud-based application. The participants could send and receive messages to health care practitioners.
This intervention significantly improved medication adherence and systolic BP without modifying pharmacotherapy.
‘Need to be passionate about monitoring BP’
“The take-home messages from these exciting findings is that physicians and women who have had high BP during pregnancy need to be passionate about monitoring and controlling their blood pressure and not ignore it,” Anastasia Mihailidou, PhD, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, the assigned discussant in the late-breaking trial session, said in an interview.
“It also resulted in fewer postpartum hospital readmissions for high blood pressure and benefit at 9 months in the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels of the women,” she said.
“While we need to see further studies in ethnically diverse women to see that they are reproducible, there are simple measures that clinicians can implement, and women can ask to have their BP monitored more frequently than the current practice. In the U.K. it is 5-10 days after delivery and then at 6-8 weeks after giving birth when changes in heart structure have already started,” Dr. Mihailidou noted.
“The procedure will need to be modified if there are no telemedicine facilities, but that should not stop having close monitoring of BP and treating it adequately. Monitoring requires an accurate BP monitor. There also has to be monitoring BP for the children.”
The trial was funded by a BHF Clinical Research Training Fellowship to Dr. Kitt, with additional support from the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre and Oxford BHF Centre for Research Excellence.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
In a randomized trial of 220 women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension, those who took daily postpartum BP readings and received clinician-guided advice for titrating antihypertensives had a 5 mm Hg–lower average diastolic BP at 9 months, compared with those receiving usual care.
Jamie Kitt, DPhil, from the University of Oxford (England) presented these findings from the Physicians Optimized Postpartum Hypertension Treatment (POP-HT, NCT04273854) clinical trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The study was simultaneously published online in JAMA, and a cardiac imaging substudy was published online in Circulation.
“This trial identifies a potential need for a paradigm shift in the way women affected by hypertensive pregnancy are managed postnatally,” Dr. Kitt said. “If a 5–mm Hg improvement in BP is maintained longer term, it can result in about a 20% reduction in lifetime cardiovascular risk.”
The imaging substudy suggests that short-term postnatal optimization of BP control following hypertensive pregnancy through self-monitoring and physician-guided antihypertensive titration is linked with better cardiac remodeling changes seen by cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiography.
POP-HT “proves for the first time that the first few weeks after delivery are a critical time that can determine the long-term cardiovascular health of the mother,” senior author Paul Leeson, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, who presented the findings in a press briefing, said in an interview.
“Interventions during this period can have long-term beneficial impacts on cardiovascular health,” he said. “These findings rewrite the textbook on our understanding of how and why hypertensive pregnancies associate with later cardiovascular disease in the mother.”
Next, Dr. Leeson said, “We need to work out the best ways to implement these interventions “at scale. Then we can ensure all women who have hypertensive pregnancies can get access to the long-term cardiovascular benefits we have demonstrated are possible through improving postpartum cardiac care,” he said, adding that “this is entirely achievable using current available technologies.”
Hypertension in pregnancy
About 1 in 10 pregnant women develop hypertension in pregnancy (preeclampsia or gestational hypertension), and 1 in 3 such women go on to develop chronic hypertension within 10 years, “when they are usually still in their 30s or 40s,” Dr. Leeson said.
During pregnancy, the heart remodels to cope with pregnancy, and it undergoes more severe changes if BP is high. Then during the 6 weeks after giving birth, this remodeling rapidly reverses.
Higher blood pressure in young adulthood is associated with a twofold higher risk of subsequent myocardial infarction and stroke. And abnormal cardiac remodeling postpartum is also linked with higher cardiovascular risk.
Self-monitoring blood pressure during the postpartum period may be a “critical window” for intervention.
Previously, the research group performed a pilot study, the Self-Management of Postnatal Antihypertensive Treatment (SNAP-HT) trial and the SNAP-extension trial, which compared a BP self-monitoring intervention with usual care in 91 women with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia requiring postnatal antihypertensive treatment.
Diastolic BP, which drives cardiovascular risk in younger populations, was 4.5–mm Hg lower at 6 months postpartum and 7–mm Hg lower at 4 years post partum in patients randomly assigned to BP self-management vs. usual care – even after they were no longer taking antihypertensives.
Building on these findings, the POP-HT trial enrolled 220 pregnant women seen at Oxford University Hospitals in the United Kingdom who were age 18 years or older, had either gestational hypertension or preeclampsia, and still required antihypertensives when they were being discharged from hospital after giving birth.
Following a baseline visit at day 1-6 after delivery, while in the postnatal ward, the patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to the intervention group (112 women) or usual-care group (108 women).
They had an average age of 32.6 years; 40% had gestational hypertension, and 60% had preeclampsia.
Women in the usual-care group typically received a BP review at 7-10 days after hospital discharge with a community midwife, and another at 6-8 weeks with their general practitioner.
The women in the intervention group were given and taught to use a Bluetooth-enabled OMRON Evolv BP monitor (Omron Healthcare Europe) while on the postnatal ward, and they installed a smartphone app on their mobile phones that transmitted self-monitored BP readings to a National Health Service-hosted, web-based platform.
They were instructed to take daily BP measurements (twice daily if out of target range). Dose titration of antihypertensives after hospital discharge was guided remotely by research clinicians, according to a guideline-based algorithm.
Patients in both groups had four study visits when their BP was measured: visit 1 (baseline) between days 1 and 6 post partum; visit 2 at week 1; visit 3 at week 6; and visit 4 between months 6 and 9 post partum.
Similar antihypertensive classes were prescribed in each group (enalapril 57%, nifedipine 27%, and labetalol 30% for intervention vs. enalapril 43%, nifedipine 30%, and labetalol 27% for control).
At 6 weeks, approximately 30% of participants in each group were still taking medication; this dropped to approximately 12% by visit 4.
The primary outcome – the mean 24-hour diastolic BP at visit 4 (roughly 9 months post partum), adjusted for baseline postnatal diastolic blood pressure – was 5.8–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (71.2 mm Hg vs. 76.6 mm Hg; P < .001).
Secondary outcomes – between-group differences in systolic BP at 9 months, BP-related postnatal admission, and cardiac remodeling assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance – were all better in the intervention group.
The mean 24-hour average systolic BP at 9 months post partum, adjusted for baseline postnatal systolic BP was 6.5–mm Hg lower in the intervention group than in the control group (114.0 mm Hg vs. 120.3 mm Hg; P < .001).
There was an absolute risk reduction of 20% and a relative risk reduction of 73.5% in postnatal readmission. The number needed to treat to avoid one postnatal readmission was five, which “has potential for big cost savings,” said Dr. Leeson.
Blood pressure post partum can be improved with self-monitoring and physician-guided medication adjustment, Dr. Leeson summarized. The blood pressure remains low for at least 9 months, even when medication is stopped, and the intervention leads to beneficial cardiac remodeling.
U.S. pilot study
Non-Hispanic Black adults have a high hypertension and cardiovascular disease burden, and a related small U.S. study showed benefits of BP self-monitoring in a population comprising mainly Black women, Keith Ferdinand, MD, discussant of the POP-HT trial in the press briefing, said in an interview.
Dr. Ferdinand, from Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana, was lead author of the Text My Hypertension BP Meds NOLA pilot study that was published in February in the American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.
The study showed that text-messaging and social support increased hypertension medication adherence.
They enrolled 36 individuals, of whom 32 (89%) were non-Hispanic Black, and 23 (64%) were women. The participants received validated Bluetooth-enabled BP-monitoring devices that were synced to smartphones via a secured cloud-based application. The participants could send and receive messages to health care practitioners.
This intervention significantly improved medication adherence and systolic BP without modifying pharmacotherapy.
‘Need to be passionate about monitoring BP’
“The take-home messages from these exciting findings is that physicians and women who have had high BP during pregnancy need to be passionate about monitoring and controlling their blood pressure and not ignore it,” Anastasia Mihailidou, PhD, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, the assigned discussant in the late-breaking trial session, said in an interview.
“It also resulted in fewer postpartum hospital readmissions for high blood pressure and benefit at 9 months in the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels of the women,” she said.
“While we need to see further studies in ethnically diverse women to see that they are reproducible, there are simple measures that clinicians can implement, and women can ask to have their BP monitored more frequently than the current practice. In the U.K. it is 5-10 days after delivery and then at 6-8 weeks after giving birth when changes in heart structure have already started,” Dr. Mihailidou noted.
“The procedure will need to be modified if there are no telemedicine facilities, but that should not stop having close monitoring of BP and treating it adequately. Monitoring requires an accurate BP monitor. There also has to be monitoring BP for the children.”
The trial was funded by a BHF Clinical Research Training Fellowship to Dr. Kitt, with additional support from the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre and Oxford BHF Centre for Research Excellence.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Apixaban cuts stroke but ups bleeding in subclinical AFib: ARTESIA
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Does taking BP medicine at night (vs morning) result in fewer cardiovascular events?
Evidence summary
Recent UK study shows no difference by timing
A 2022 UK prospective, randomized, multicenter trial assigned 21,104 predominantly White adults (58% men) with hypertension to take their usual antihypertensive medication either in the morning (6
All patient baseline characteristics were equivalent between groups. If troubled by nocturia, patients in the evening group taking diuretics were told to take only the diuretic earlier (6
The median follow-up was 5.2 years. Data were collected at regular intervals through patient completion of online questionnaires and researcher analysis of National Health Service data on hospitalization and death. The intention-to-treat analysis showed no difference in the primary outcome (a composite of vascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) between the evening and morning administration groups (0.69 events vs 0.72 events per 100 person-years; hazard ratio [HR] = 0.95; 95% CI, 0.83-1.10; P = .53).
The controversial Hygia Project favored evening
Prior to the UK study was the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial, a prospective, controlled, multicenter study conducted within the primary care setting in Spain. Caucasian Spanish adults (N = 19,168; mean age, 61 years; 56% men) with hypertension were randomly assigned to take all prescribed antihypertensive medication either at bedtime or upon waking.2
The Hygia Project initially sought to establish the value of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) compared to office blood pressure (BP) monitoring and to explore the prognostic value of sleeping BP.3 The study objectives evolved over time. The randomization process was not clearly described,2,3 but multiple randomizations were alluded to. The authors stated that “for any of these chronotherapy trials” randomizations were done separately for “each participating center” and “randomization of participants to treatment-time regimen is done separately for each hypertension medication or combination being tested.”
The baseline characteristics of patients in the evening and morning administration groups were similar, but statistically significant differences existed in BMI (29.6 vs 29.7; P = .030) and sleep-time systolic BP percent decline (9.3 vs 9.0; P < .001). Mean baseline 48-hour BP was 132/77 mm Hg. Hypertension was defined as an awake systolic BP ≥
Prescribers were free to prescribe medicines from 5 classes (diuretic, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or beta-blocker) as they thought appropriate, were encouraged to use fixed-dose combination pills, and were told not to use split (eg, twice per day) dosing. Annual 48-hour ABPM was completed, and patients’ electronic health records were analyzed by blinded investigators. Median follow-up was 6.3 years, and only 84 participants failed to complete the minimum 1-year participation requirement.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome—a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, heart failure, or stroke—occurred in 1752 patients, favoring the bedtime group (HR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.50-0.61; P < .001). The calculated number of events was 1130 in the morning administration group and 622 in the evening administration group; the authors did not explicitly report the event numbers in each group. Each component of the composite outcome also favored evening administration (P < .001 for all): cardiovascular death (HR = 0.44; 95% CI, 0.34-0.56), myocardial infarction (HR = 0.66; 95% CI, 0.52-0.84), coronary revascularization (HR = 0.60; 95% CI, 0.47-0.75), heart failure (HR = 0.58; 95% CI, 0.49-0.70), and stroke (HR = 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
The complicated, layered study design and randomization methods limit the ability to critically appraise the study.
Smaller Spanish study also supported evening administration
A prior, smaller, prospective randomized trial conducted by the same researchers as the Hygia Project found even greater benefits to evening BP medication administration.4 The 2156 Spanish patients (52% men; average age, 55 years) from multiple primary care offices were randomized 1:1 to BP medication administration either upon awakening or at bedtime. Dozens of baseline characteristics were evenly distributed except for age (55.0 vs 56.3; P = .021) and creatinine (0.96 vs 0.98; P = .028), both of which were lower in the evening group.
After a median follow-up of 5.6 years, the bedtime group had significantly lower total events (187 events in the morning group vs 68 in the evening group; relative risk [RR] = 0.39; 95% CI, 0.29-0.51; P < .001). Individual cardiovascular outcomes also dramatically favored the evening group: total deaths (12 vs 28; P = .008), cardiovascular deaths (3 vs 14; P = .006), cardiovascular disease events (30 vs 74; P < .001), stroke (7 vs 24; P = .001), and heart failure (8 vs 33; P < .001).
Limits of both the UK trial and the Hygia Project trial included single countries of study with a lack of racial and ethnic diversity, and greater nonadherence to the evening administration of the medications.
Recommendations from others
A 2022 consensus statement from the International Society of Hypertension, published before the UK trial, recommended against bedtime dosing until more high-quality data became available. They pointed to evidence showing higher medication adherence with morning dosing, risk for asleep BP dropping, and worsening daytime BP control as reasons to continue morning administration.5 Other reviewers have questioned the Hygia Project results due to their reported implausibly large effects on cardiovascular outcomes, noting that independent attempts to verify the methods and the data have proven challenging and are not completed.6
Editor’s takeaway
I confess that I was swayed by the results of the Hygia Project; for a year or so, I advised my patients to take at least 1 BP pill at night. But after the UK study came out, I needed to reconsider. I began to worry that the great outcomes of nocturnal therapy may have been a mirage. I have returned to counseling patients to take their BP medications in whichever way fosters consistency while minimizing adverse effects for them.
1. Mackenzie IS, Rogers A, Poulter NR, et al; TIME Study Group. Cardiovascular outcomes in adults with hypertension with evening versus morning dosing of usual antihypertensives in the UK (TIME study): a prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoint clinical trial. Lancet. 2022;400:1417-1425. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01786-X
2. Hermida RC, Crespo JJ, Domínguez-Sardiña M, et al; Hygia Project Investigators. Bedtime hypertension treatment improves cardiovascular risk reduction: the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:4565-4576. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz754
3. Hermida RC. Sleep-time ambulatory blood pressure as a prognostic marker of vascular and other risks and therapeutic target for prevention by hypertension chronotherapy: rationale and design of the Hygia Project. Chronobiol Int. 2016;33:906-936. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2016.1181078
4. Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, et al. Influence of circadian time of hypertension treatment on cardiovascular risk: results of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27:1629-1651. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2010.510230
5. Stergiou G, Brunström M, MacDonald T, et al. Bedtime dosing of antihypertensive medications: systematic review and consensus statement: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2022;40:1847-1858. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003240
6. Brunström M, Kjeldsen SE, Kreutz R, et al. Missing verification of source data in hypertension research: The HYGIA PROJECT in Perspective. Hypertension. 2021;78:555-558. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17356
Evidence summary
Recent UK study shows no difference by timing
A 2022 UK prospective, randomized, multicenter trial assigned 21,104 predominantly White adults (58% men) with hypertension to take their usual antihypertensive medication either in the morning (6
All patient baseline characteristics were equivalent between groups. If troubled by nocturia, patients in the evening group taking diuretics were told to take only the diuretic earlier (6
The median follow-up was 5.2 years. Data were collected at regular intervals through patient completion of online questionnaires and researcher analysis of National Health Service data on hospitalization and death. The intention-to-treat analysis showed no difference in the primary outcome (a composite of vascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) between the evening and morning administration groups (0.69 events vs 0.72 events per 100 person-years; hazard ratio [HR] = 0.95; 95% CI, 0.83-1.10; P = .53).
The controversial Hygia Project favored evening
Prior to the UK study was the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial, a prospective, controlled, multicenter study conducted within the primary care setting in Spain. Caucasian Spanish adults (N = 19,168; mean age, 61 years; 56% men) with hypertension were randomly assigned to take all prescribed antihypertensive medication either at bedtime or upon waking.2
The Hygia Project initially sought to establish the value of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) compared to office blood pressure (BP) monitoring and to explore the prognostic value of sleeping BP.3 The study objectives evolved over time. The randomization process was not clearly described,2,3 but multiple randomizations were alluded to. The authors stated that “for any of these chronotherapy trials” randomizations were done separately for “each participating center” and “randomization of participants to treatment-time regimen is done separately for each hypertension medication or combination being tested.”
The baseline characteristics of patients in the evening and morning administration groups were similar, but statistically significant differences existed in BMI (29.6 vs 29.7; P = .030) and sleep-time systolic BP percent decline (9.3 vs 9.0; P < .001). Mean baseline 48-hour BP was 132/77 mm Hg. Hypertension was defined as an awake systolic BP ≥
Prescribers were free to prescribe medicines from 5 classes (diuretic, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or beta-blocker) as they thought appropriate, were encouraged to use fixed-dose combination pills, and were told not to use split (eg, twice per day) dosing. Annual 48-hour ABPM was completed, and patients’ electronic health records were analyzed by blinded investigators. Median follow-up was 6.3 years, and only 84 participants failed to complete the minimum 1-year participation requirement.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome—a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, heart failure, or stroke—occurred in 1752 patients, favoring the bedtime group (HR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.50-0.61; P < .001). The calculated number of events was 1130 in the morning administration group and 622 in the evening administration group; the authors did not explicitly report the event numbers in each group. Each component of the composite outcome also favored evening administration (P < .001 for all): cardiovascular death (HR = 0.44; 95% CI, 0.34-0.56), myocardial infarction (HR = 0.66; 95% CI, 0.52-0.84), coronary revascularization (HR = 0.60; 95% CI, 0.47-0.75), heart failure (HR = 0.58; 95% CI, 0.49-0.70), and stroke (HR = 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
The complicated, layered study design and randomization methods limit the ability to critically appraise the study.
Smaller Spanish study also supported evening administration
A prior, smaller, prospective randomized trial conducted by the same researchers as the Hygia Project found even greater benefits to evening BP medication administration.4 The 2156 Spanish patients (52% men; average age, 55 years) from multiple primary care offices were randomized 1:1 to BP medication administration either upon awakening or at bedtime. Dozens of baseline characteristics were evenly distributed except for age (55.0 vs 56.3; P = .021) and creatinine (0.96 vs 0.98; P = .028), both of which were lower in the evening group.
After a median follow-up of 5.6 years, the bedtime group had significantly lower total events (187 events in the morning group vs 68 in the evening group; relative risk [RR] = 0.39; 95% CI, 0.29-0.51; P < .001). Individual cardiovascular outcomes also dramatically favored the evening group: total deaths (12 vs 28; P = .008), cardiovascular deaths (3 vs 14; P = .006), cardiovascular disease events (30 vs 74; P < .001), stroke (7 vs 24; P = .001), and heart failure (8 vs 33; P < .001).
Limits of both the UK trial and the Hygia Project trial included single countries of study with a lack of racial and ethnic diversity, and greater nonadherence to the evening administration of the medications.
Recommendations from others
A 2022 consensus statement from the International Society of Hypertension, published before the UK trial, recommended against bedtime dosing until more high-quality data became available. They pointed to evidence showing higher medication adherence with morning dosing, risk for asleep BP dropping, and worsening daytime BP control as reasons to continue morning administration.5 Other reviewers have questioned the Hygia Project results due to their reported implausibly large effects on cardiovascular outcomes, noting that independent attempts to verify the methods and the data have proven challenging and are not completed.6
Editor’s takeaway
I confess that I was swayed by the results of the Hygia Project; for a year or so, I advised my patients to take at least 1 BP pill at night. But after the UK study came out, I needed to reconsider. I began to worry that the great outcomes of nocturnal therapy may have been a mirage. I have returned to counseling patients to take their BP medications in whichever way fosters consistency while minimizing adverse effects for them.
Evidence summary
Recent UK study shows no difference by timing
A 2022 UK prospective, randomized, multicenter trial assigned 21,104 predominantly White adults (58% men) with hypertension to take their usual antihypertensive medication either in the morning (6
All patient baseline characteristics were equivalent between groups. If troubled by nocturia, patients in the evening group taking diuretics were told to take only the diuretic earlier (6
The median follow-up was 5.2 years. Data were collected at regular intervals through patient completion of online questionnaires and researcher analysis of National Health Service data on hospitalization and death. The intention-to-treat analysis showed no difference in the primary outcome (a composite of vascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) between the evening and morning administration groups (0.69 events vs 0.72 events per 100 person-years; hazard ratio [HR] = 0.95; 95% CI, 0.83-1.10; P = .53).
The controversial Hygia Project favored evening
Prior to the UK study was the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial, a prospective, controlled, multicenter study conducted within the primary care setting in Spain. Caucasian Spanish adults (N = 19,168; mean age, 61 years; 56% men) with hypertension were randomly assigned to take all prescribed antihypertensive medication either at bedtime or upon waking.2
The Hygia Project initially sought to establish the value of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) compared to office blood pressure (BP) monitoring and to explore the prognostic value of sleeping BP.3 The study objectives evolved over time. The randomization process was not clearly described,2,3 but multiple randomizations were alluded to. The authors stated that “for any of these chronotherapy trials” randomizations were done separately for “each participating center” and “randomization of participants to treatment-time regimen is done separately for each hypertension medication or combination being tested.”
The baseline characteristics of patients in the evening and morning administration groups were similar, but statistically significant differences existed in BMI (29.6 vs 29.7; P = .030) and sleep-time systolic BP percent decline (9.3 vs 9.0; P < .001). Mean baseline 48-hour BP was 132/77 mm Hg. Hypertension was defined as an awake systolic BP ≥
Prescribers were free to prescribe medicines from 5 classes (diuretic, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or beta-blocker) as they thought appropriate, were encouraged to use fixed-dose combination pills, and were told not to use split (eg, twice per day) dosing. Annual 48-hour ABPM was completed, and patients’ electronic health records were analyzed by blinded investigators. Median follow-up was 6.3 years, and only 84 participants failed to complete the minimum 1-year participation requirement.
Continue to: The primary outcome...
The primary outcome—a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, heart failure, or stroke—occurred in 1752 patients, favoring the bedtime group (HR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.50-0.61; P < .001). The calculated number of events was 1130 in the morning administration group and 622 in the evening administration group; the authors did not explicitly report the event numbers in each group. Each component of the composite outcome also favored evening administration (P < .001 for all): cardiovascular death (HR = 0.44; 95% CI, 0.34-0.56), myocardial infarction (HR = 0.66; 95% CI, 0.52-0.84), coronary revascularization (HR = 0.60; 95% CI, 0.47-0.75), heart failure (HR = 0.58; 95% CI, 0.49-0.70), and stroke (HR = 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41-0.63).
The complicated, layered study design and randomization methods limit the ability to critically appraise the study.
Smaller Spanish study also supported evening administration
A prior, smaller, prospective randomized trial conducted by the same researchers as the Hygia Project found even greater benefits to evening BP medication administration.4 The 2156 Spanish patients (52% men; average age, 55 years) from multiple primary care offices were randomized 1:1 to BP medication administration either upon awakening or at bedtime. Dozens of baseline characteristics were evenly distributed except for age (55.0 vs 56.3; P = .021) and creatinine (0.96 vs 0.98; P = .028), both of which were lower in the evening group.
After a median follow-up of 5.6 years, the bedtime group had significantly lower total events (187 events in the morning group vs 68 in the evening group; relative risk [RR] = 0.39; 95% CI, 0.29-0.51; P < .001). Individual cardiovascular outcomes also dramatically favored the evening group: total deaths (12 vs 28; P = .008), cardiovascular deaths (3 vs 14; P = .006), cardiovascular disease events (30 vs 74; P < .001), stroke (7 vs 24; P = .001), and heart failure (8 vs 33; P < .001).
Limits of both the UK trial and the Hygia Project trial included single countries of study with a lack of racial and ethnic diversity, and greater nonadherence to the evening administration of the medications.
Recommendations from others
A 2022 consensus statement from the International Society of Hypertension, published before the UK trial, recommended against bedtime dosing until more high-quality data became available. They pointed to evidence showing higher medication adherence with morning dosing, risk for asleep BP dropping, and worsening daytime BP control as reasons to continue morning administration.5 Other reviewers have questioned the Hygia Project results due to their reported implausibly large effects on cardiovascular outcomes, noting that independent attempts to verify the methods and the data have proven challenging and are not completed.6
Editor’s takeaway
I confess that I was swayed by the results of the Hygia Project; for a year or so, I advised my patients to take at least 1 BP pill at night. But after the UK study came out, I needed to reconsider. I began to worry that the great outcomes of nocturnal therapy may have been a mirage. I have returned to counseling patients to take their BP medications in whichever way fosters consistency while minimizing adverse effects for them.
1. Mackenzie IS, Rogers A, Poulter NR, et al; TIME Study Group. Cardiovascular outcomes in adults with hypertension with evening versus morning dosing of usual antihypertensives in the UK (TIME study): a prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoint clinical trial. Lancet. 2022;400:1417-1425. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01786-X
2. Hermida RC, Crespo JJ, Domínguez-Sardiña M, et al; Hygia Project Investigators. Bedtime hypertension treatment improves cardiovascular risk reduction: the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:4565-4576. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz754
3. Hermida RC. Sleep-time ambulatory blood pressure as a prognostic marker of vascular and other risks and therapeutic target for prevention by hypertension chronotherapy: rationale and design of the Hygia Project. Chronobiol Int. 2016;33:906-936. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2016.1181078
4. Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, et al. Influence of circadian time of hypertension treatment on cardiovascular risk: results of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27:1629-1651. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2010.510230
5. Stergiou G, Brunström M, MacDonald T, et al. Bedtime dosing of antihypertensive medications: systematic review and consensus statement: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2022;40:1847-1858. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003240
6. Brunström M, Kjeldsen SE, Kreutz R, et al. Missing verification of source data in hypertension research: The HYGIA PROJECT in Perspective. Hypertension. 2021;78:555-558. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17356
1. Mackenzie IS, Rogers A, Poulter NR, et al; TIME Study Group. Cardiovascular outcomes in adults with hypertension with evening versus morning dosing of usual antihypertensives in the UK (TIME study): a prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoint clinical trial. Lancet. 2022;400:1417-1425. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01786-X
2. Hermida RC, Crespo JJ, Domínguez-Sardiña M, et al; Hygia Project Investigators. Bedtime hypertension treatment improves cardiovascular risk reduction: the Hygia Chronotherapy Trial. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:4565-4576. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz754
3. Hermida RC. Sleep-time ambulatory blood pressure as a prognostic marker of vascular and other risks and therapeutic target for prevention by hypertension chronotherapy: rationale and design of the Hygia Project. Chronobiol Int. 2016;33:906-936. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2016.1181078
4. Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, et al. Influence of circadian time of hypertension treatment on cardiovascular risk: results of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27:1629-1651. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2010.510230
5. Stergiou G, Brunström M, MacDonald T, et al. Bedtime dosing of antihypertensive medications: systematic review and consensus statement: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by World Hypertension League and European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2022;40:1847-1858. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003240
6. Brunström M, Kjeldsen SE, Kreutz R, et al. Missing verification of source data in hypertension research: The HYGIA PROJECT in Perspective. Hypertension. 2021;78:555-558. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17356
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Impressive bleeding profile with factor XI inhibitor in AFib: AZALEA
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.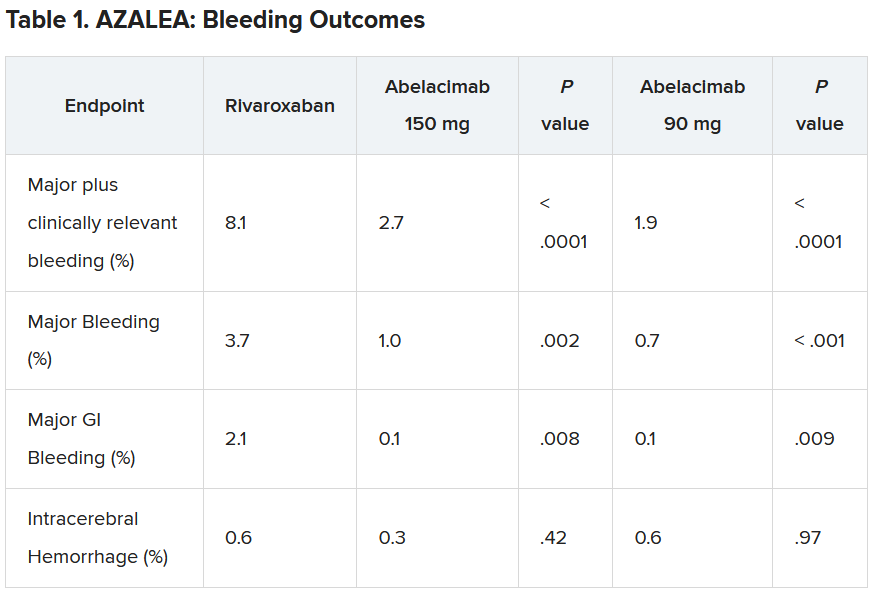
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.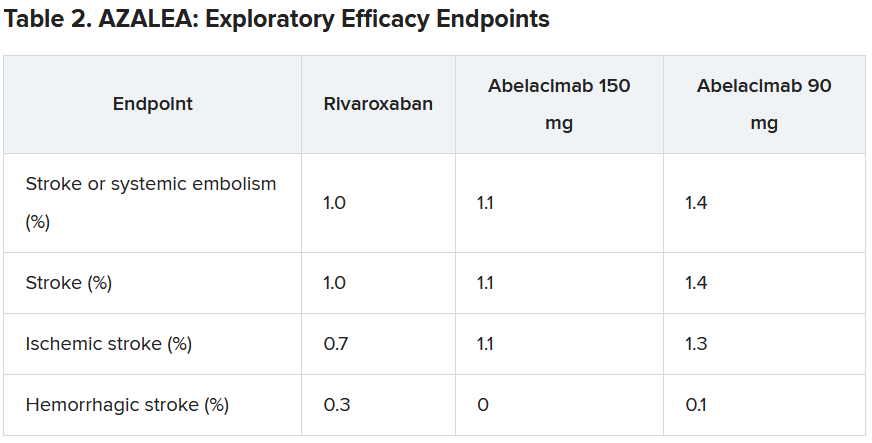
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Atrial fibrillation linked to dementia, especially when diagnosed before age 65 years
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Blood pressure lowering reduces dementia risk
Results of a trial using an intensive, 4-year program aimed at blood pressure lowering showed that intervention reduced not only blood pressure, but also significantly reduced the risk of total dementia over that period.
and cognitive impairment no dementia (CIND), a secondary outcome, was also significantly reduced by 16%.
“Blood pressure reduction is effective in reducing the risk of dementia in patients with hypertension,” concluded Jiang He, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology and medicine and director of Tulane University’s Translational Science Institute, New Orleans. “This proven, effective intervention should be widely scaled up to reduce the global burden of dementia.”
He presented these results from the China Rural Hypertension Control Project (CRHCP) at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Target organ damage
Keith Ferdinand, MD, also from Tulane University, commented on the findings during a press conference at the meeting, noting that the result “opens our opportunity to recognize that the target organ damage of hypertension also now includes dementia.”
The researchers were able to “rigorously lower blood pressure from 157 to 127.6 in the intervention, 155 to 147 in the controls – 22 mg Hg – and if you look at the P values for all the various outcomes, they were very robust,” Dr. Ferdinand said.
Another interesting feature about the strategy used in this trial is that “this was true team-based care,” he pointed out. The trained interventionists in the study, called village doctors, collaborated with primary care physicians and initiated medications. “They stayed on a simple treatment protocol, and they were able to assist patients to ensure they had free medications, health coaching for lifestyle, home blood pressure measurement, and ensuring adherence.”
So, Dr. Ferdinand added, “one of the questions is whether this is a model we can use in other places around the globe, in places with low resources, and in the United States in disadvantaged populations.”
Public health priority
It’s estimated that the global number of those living with dementia will increase from 57.4 million in 2019 to 152.8 million by 2050, Dr. He said. “In the absence of curative treatment, the primary prevention of dementia through risk factor reduction, such as blood pressure lowering, becomes a public health priority.”
Previous randomized trials have lacked sample size and duration but have reported a nonsignificant reduction in dementia associated with antihypertensive treatment in patients with hypertension or a history of stroke, Dr. He noted.
This new trial aimed to test the effectiveness of intensive BP intervention to reduce the risk of all-cause dementia and cognitive impairment over a 48-month intervention period versus usual care.
It was an open-label, blinded-endpoint, cluster-randomized trial, and included 33,995 individual patients from 325 villages in China, aged 40 years and older, with untreated hypertension. The villages were randomly assigned to an intervention group or usual care, stratified by province, county, and township.
Patients were eligible if they had mean untreated systolic BP greater than 140 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 90 mm Hg or mean treated systolic BP of greater than 130 and/or diastolic greater than 80 mm Hg. Patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes and a mean systolic BP greater than 130 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 80 mm Hg from six measures on two different days were also eligible.
All were enrolled in the China New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme, which covers 99% of rural residents for health care services, Dr. He noted.
The intervention was a simple stepped-care protocol for hypertension treatment, aimed at achieving a target systolic BP of less than 130 mm Hg and diastolic of less than 80 mm Hg.
Village doctors started and titrated antihypertensive treatment based on a protocol and were able to deliver discounted and free medications to patients. They also did health coaching on lifestyle modification and adherence to medication, and instructed patients on home BP monitoring.
Patients were provided training, supervision, and consultation by primary care physicians and hypertension specialists.
At the month 48 follow-up visit, the participants were assessed by neurologists who were blinded to randomization assignments. Neurologists did a variety of tests and assessments including collecting data on the patient’s medical and psychiatric history and risk factors for dementia, as well as neurologic assessment using the Mini-Mental State Examination, the Functional Activities Questionnaire, and the Quick Dementia Rating System.
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia, defined according to recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association work groups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease.
Secondary outcomes included CIND, a composite outcome of dementia or CIND, and a composite of dementia or deaths.
The final diagnosis of all-cause dementia or CIND was made by an expert adjudication panel blinded to the intervention assignment.
At 48 months, 91.3% of patients completed the follow-up for clinical outcomes. Participants were an average of 63 years of age, 61% were female, and 23% had less than a primary school education, Dr. He noted.
The net group differences in systolic and diastolic BP reduction were 22 and 9.3 mm Hg, respectively (P < .0001).
Significant differences were also seen between the groups in the primary outcome of all-cause dementia, as well as secondary outcomes of CIND, dementia or cognitive impairment, or dementia or deaths.
Serious adverse events were more common in the usual care group, and there was no difference between groups in the occurrence of falls or syncope.
The effect was consistent across subgroups, Dr. He said, including age, sex, education, cigarette smoking, body mass index, systolic BP, and fasting plasma glucose at baseline.
First definitive evidence
Invited discussant for the trial, Daniel W. Jones, MD, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and past president of the AHA, pointed out that previous results from CRHCP on cardiovascular outcomes, reported earlier in 2023 in The Lancet, showed that, similar to results of the large SPRINT trial, lowering systolic BP to a goal of less than 130 mm Hg reduced a composite endpoint of MI, stroke, heart failure requiring hospitalization, and cardiovascular disease death over the 36-month follow-up.
The SPRINT findings also suggested a possible reduction in dementia, Dr. Jones said.
Now, in these new CRHCP results, “there was a clear benefit for intensive BP control in reducing risk for dementia and cognitive dysfunction,” he said. “This is, importantly, the first definitive evidence of dementia risk reduction demonstrated in a randomized controlled clinical trial. This outcome supports observational data that shows a strong relationship between BP and dementia.”
Since it is the first of its kind though, replication of the results will be important, he noted.
The study also showed that the intervention, using minimally trained village doctors, sustained BP control for 48 months. “This model could be used in any setting with modifications, including in the United States,” Dr. Jones said.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; U.S. investigators did not receive financial support from this study. The researchers and Dr. Jones disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a trial using an intensive, 4-year program aimed at blood pressure lowering showed that intervention reduced not only blood pressure, but also significantly reduced the risk of total dementia over that period.
and cognitive impairment no dementia (CIND), a secondary outcome, was also significantly reduced by 16%.
“Blood pressure reduction is effective in reducing the risk of dementia in patients with hypertension,” concluded Jiang He, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology and medicine and director of Tulane University’s Translational Science Institute, New Orleans. “This proven, effective intervention should be widely scaled up to reduce the global burden of dementia.”
He presented these results from the China Rural Hypertension Control Project (CRHCP) at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Target organ damage
Keith Ferdinand, MD, also from Tulane University, commented on the findings during a press conference at the meeting, noting that the result “opens our opportunity to recognize that the target organ damage of hypertension also now includes dementia.”
The researchers were able to “rigorously lower blood pressure from 157 to 127.6 in the intervention, 155 to 147 in the controls – 22 mg Hg – and if you look at the P values for all the various outcomes, they were very robust,” Dr. Ferdinand said.
Another interesting feature about the strategy used in this trial is that “this was true team-based care,” he pointed out. The trained interventionists in the study, called village doctors, collaborated with primary care physicians and initiated medications. “They stayed on a simple treatment protocol, and they were able to assist patients to ensure they had free medications, health coaching for lifestyle, home blood pressure measurement, and ensuring adherence.”
So, Dr. Ferdinand added, “one of the questions is whether this is a model we can use in other places around the globe, in places with low resources, and in the United States in disadvantaged populations.”
Public health priority
It’s estimated that the global number of those living with dementia will increase from 57.4 million in 2019 to 152.8 million by 2050, Dr. He said. “In the absence of curative treatment, the primary prevention of dementia through risk factor reduction, such as blood pressure lowering, becomes a public health priority.”
Previous randomized trials have lacked sample size and duration but have reported a nonsignificant reduction in dementia associated with antihypertensive treatment in patients with hypertension or a history of stroke, Dr. He noted.
This new trial aimed to test the effectiveness of intensive BP intervention to reduce the risk of all-cause dementia and cognitive impairment over a 48-month intervention period versus usual care.
It was an open-label, blinded-endpoint, cluster-randomized trial, and included 33,995 individual patients from 325 villages in China, aged 40 years and older, with untreated hypertension. The villages were randomly assigned to an intervention group or usual care, stratified by province, county, and township.
Patients were eligible if they had mean untreated systolic BP greater than 140 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 90 mm Hg or mean treated systolic BP of greater than 130 and/or diastolic greater than 80 mm Hg. Patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes and a mean systolic BP greater than 130 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 80 mm Hg from six measures on two different days were also eligible.
All were enrolled in the China New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme, which covers 99% of rural residents for health care services, Dr. He noted.
The intervention was a simple stepped-care protocol for hypertension treatment, aimed at achieving a target systolic BP of less than 130 mm Hg and diastolic of less than 80 mm Hg.
Village doctors started and titrated antihypertensive treatment based on a protocol and were able to deliver discounted and free medications to patients. They also did health coaching on lifestyle modification and adherence to medication, and instructed patients on home BP monitoring.
Patients were provided training, supervision, and consultation by primary care physicians and hypertension specialists.
At the month 48 follow-up visit, the participants were assessed by neurologists who were blinded to randomization assignments. Neurologists did a variety of tests and assessments including collecting data on the patient’s medical and psychiatric history and risk factors for dementia, as well as neurologic assessment using the Mini-Mental State Examination, the Functional Activities Questionnaire, and the Quick Dementia Rating System.
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia, defined according to recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association work groups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease.
Secondary outcomes included CIND, a composite outcome of dementia or CIND, and a composite of dementia or deaths.
The final diagnosis of all-cause dementia or CIND was made by an expert adjudication panel blinded to the intervention assignment.
At 48 months, 91.3% of patients completed the follow-up for clinical outcomes. Participants were an average of 63 years of age, 61% were female, and 23% had less than a primary school education, Dr. He noted.
The net group differences in systolic and diastolic BP reduction were 22 and 9.3 mm Hg, respectively (P < .0001).
Significant differences were also seen between the groups in the primary outcome of all-cause dementia, as well as secondary outcomes of CIND, dementia or cognitive impairment, or dementia or deaths.
Serious adverse events were more common in the usual care group, and there was no difference between groups in the occurrence of falls or syncope.
The effect was consistent across subgroups, Dr. He said, including age, sex, education, cigarette smoking, body mass index, systolic BP, and fasting plasma glucose at baseline.
First definitive evidence
Invited discussant for the trial, Daniel W. Jones, MD, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and past president of the AHA, pointed out that previous results from CRHCP on cardiovascular outcomes, reported earlier in 2023 in The Lancet, showed that, similar to results of the large SPRINT trial, lowering systolic BP to a goal of less than 130 mm Hg reduced a composite endpoint of MI, stroke, heart failure requiring hospitalization, and cardiovascular disease death over the 36-month follow-up.
The SPRINT findings also suggested a possible reduction in dementia, Dr. Jones said.
Now, in these new CRHCP results, “there was a clear benefit for intensive BP control in reducing risk for dementia and cognitive dysfunction,” he said. “This is, importantly, the first definitive evidence of dementia risk reduction demonstrated in a randomized controlled clinical trial. This outcome supports observational data that shows a strong relationship between BP and dementia.”
Since it is the first of its kind though, replication of the results will be important, he noted.
The study also showed that the intervention, using minimally trained village doctors, sustained BP control for 48 months. “This model could be used in any setting with modifications, including in the United States,” Dr. Jones said.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; U.S. investigators did not receive financial support from this study. The researchers and Dr. Jones disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a trial using an intensive, 4-year program aimed at blood pressure lowering showed that intervention reduced not only blood pressure, but also significantly reduced the risk of total dementia over that period.
and cognitive impairment no dementia (CIND), a secondary outcome, was also significantly reduced by 16%.
“Blood pressure reduction is effective in reducing the risk of dementia in patients with hypertension,” concluded Jiang He, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology and medicine and director of Tulane University’s Translational Science Institute, New Orleans. “This proven, effective intervention should be widely scaled up to reduce the global burden of dementia.”
He presented these results from the China Rural Hypertension Control Project (CRHCP) at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Target organ damage
Keith Ferdinand, MD, also from Tulane University, commented on the findings during a press conference at the meeting, noting that the result “opens our opportunity to recognize that the target organ damage of hypertension also now includes dementia.”
The researchers were able to “rigorously lower blood pressure from 157 to 127.6 in the intervention, 155 to 147 in the controls – 22 mg Hg – and if you look at the P values for all the various outcomes, they were very robust,” Dr. Ferdinand said.
Another interesting feature about the strategy used in this trial is that “this was true team-based care,” he pointed out. The trained interventionists in the study, called village doctors, collaborated with primary care physicians and initiated medications. “They stayed on a simple treatment protocol, and they were able to assist patients to ensure they had free medications, health coaching for lifestyle, home blood pressure measurement, and ensuring adherence.”
So, Dr. Ferdinand added, “one of the questions is whether this is a model we can use in other places around the globe, in places with low resources, and in the United States in disadvantaged populations.”
Public health priority
It’s estimated that the global number of those living with dementia will increase from 57.4 million in 2019 to 152.8 million by 2050, Dr. He said. “In the absence of curative treatment, the primary prevention of dementia through risk factor reduction, such as blood pressure lowering, becomes a public health priority.”
Previous randomized trials have lacked sample size and duration but have reported a nonsignificant reduction in dementia associated with antihypertensive treatment in patients with hypertension or a history of stroke, Dr. He noted.
This new trial aimed to test the effectiveness of intensive BP intervention to reduce the risk of all-cause dementia and cognitive impairment over a 48-month intervention period versus usual care.
It was an open-label, blinded-endpoint, cluster-randomized trial, and included 33,995 individual patients from 325 villages in China, aged 40 years and older, with untreated hypertension. The villages were randomly assigned to an intervention group or usual care, stratified by province, county, and township.
Patients were eligible if they had mean untreated systolic BP greater than 140 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 90 mm Hg or mean treated systolic BP of greater than 130 and/or diastolic greater than 80 mm Hg. Patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes and a mean systolic BP greater than 130 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP greater than 80 mm Hg from six measures on two different days were also eligible.
All were enrolled in the China New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme, which covers 99% of rural residents for health care services, Dr. He noted.
The intervention was a simple stepped-care protocol for hypertension treatment, aimed at achieving a target systolic BP of less than 130 mm Hg and diastolic of less than 80 mm Hg.
Village doctors started and titrated antihypertensive treatment based on a protocol and were able to deliver discounted and free medications to patients. They also did health coaching on lifestyle modification and adherence to medication, and instructed patients on home BP monitoring.
Patients were provided training, supervision, and consultation by primary care physicians and hypertension specialists.
At the month 48 follow-up visit, the participants were assessed by neurologists who were blinded to randomization assignments. Neurologists did a variety of tests and assessments including collecting data on the patient’s medical and psychiatric history and risk factors for dementia, as well as neurologic assessment using the Mini-Mental State Examination, the Functional Activities Questionnaire, and the Quick Dementia Rating System.
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia, defined according to recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association work groups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease.
Secondary outcomes included CIND, a composite outcome of dementia or CIND, and a composite of dementia or deaths.
The final diagnosis of all-cause dementia or CIND was made by an expert adjudication panel blinded to the intervention assignment.
At 48 months, 91.3% of patients completed the follow-up for clinical outcomes. Participants were an average of 63 years of age, 61% were female, and 23% had less than a primary school education, Dr. He noted.
The net group differences in systolic and diastolic BP reduction were 22 and 9.3 mm Hg, respectively (P < .0001).
Significant differences were also seen between the groups in the primary outcome of all-cause dementia, as well as secondary outcomes of CIND, dementia or cognitive impairment, or dementia or deaths.
Serious adverse events were more common in the usual care group, and there was no difference between groups in the occurrence of falls or syncope.
The effect was consistent across subgroups, Dr. He said, including age, sex, education, cigarette smoking, body mass index, systolic BP, and fasting plasma glucose at baseline.
First definitive evidence
Invited discussant for the trial, Daniel W. Jones, MD, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and past president of the AHA, pointed out that previous results from CRHCP on cardiovascular outcomes, reported earlier in 2023 in The Lancet, showed that, similar to results of the large SPRINT trial, lowering systolic BP to a goal of less than 130 mm Hg reduced a composite endpoint of MI, stroke, heart failure requiring hospitalization, and cardiovascular disease death over the 36-month follow-up.
The SPRINT findings also suggested a possible reduction in dementia, Dr. Jones said.
Now, in these new CRHCP results, “there was a clear benefit for intensive BP control in reducing risk for dementia and cognitive dysfunction,” he said. “This is, importantly, the first definitive evidence of dementia risk reduction demonstrated in a randomized controlled clinical trial. This outcome supports observational data that shows a strong relationship between BP and dementia.”
Since it is the first of its kind though, replication of the results will be important, he noted.
The study also showed that the intervention, using minimally trained village doctors, sustained BP control for 48 months. “This model could be used in any setting with modifications, including in the United States,” Dr. Jones said.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; U.S. investigators did not receive financial support from this study. The researchers and Dr. Jones disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Classification identifies four stages of heart attack
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY



