User login
‘Reform School’ for Pharmacy Benefit Managers: How Might Legislation Help Patients?
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).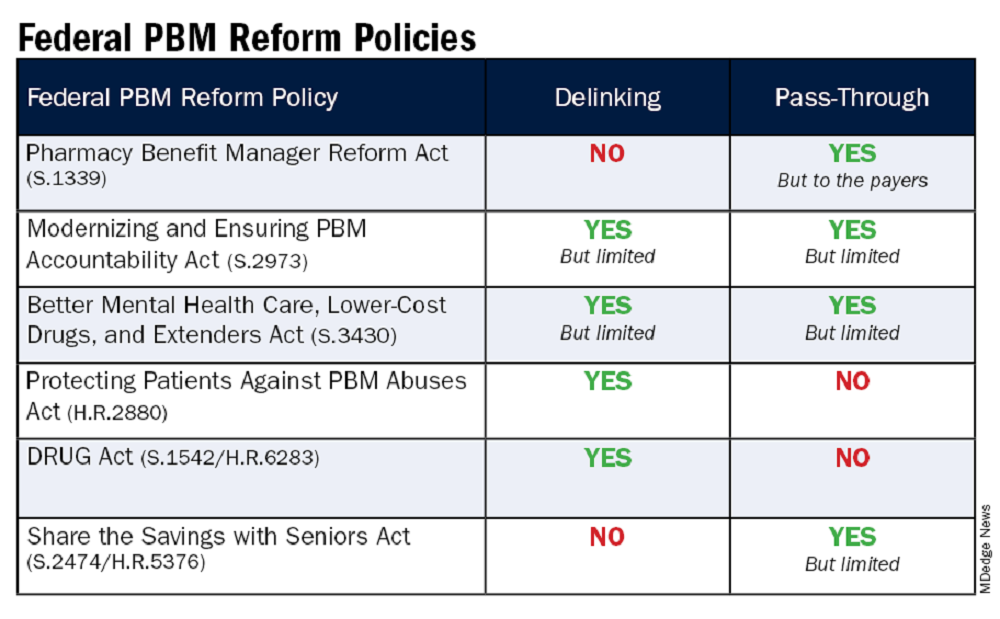
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
AI-Powered Clinical Documentation Tool Reduces EHR Time for Clinicians
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An artificial intelligence (AI)-powered clinical documentation tool helped reduce time spent on electronic health records (EHR) at home for almost 48% physicians, and nearly 45% reported less weekly time spent on EHR tasks outside of normal work hours.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers recruited 112 clinicians from family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics in North Carolina and Georgia.
- Patients were divided into an intervention group (n = 85) and control group (n = 55), with the intervention group receiving a 1-hour training program on a commercially available AI tool.
- A seven-question survey was administered to participants before and 5 weeks after the intervention to evaluate their experience.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers found 47.1% of clinicians in the intervention group reported spending less time on the EHR at home compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001); 44.7% reported decreased weekly time on the EHR outside normal work hours compared with 20% in the control group (P = .003).
- The study revealed 43.5% of physicians who used the AI instrument reported spending less time on documentation after visits compared with 18.2% in the control group (P = .002).
- Further, 44.7% reported less frustration when using the EHR compared with 14.5% in the control group (P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Approximately half of clinicians using the AI-powered clinical documentation tool based on interest reported a positive outcome, potentially reducing burnout. However, a significant subset did not find time-saving benefits or improved EHR experience,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tsai-Ling Liu, PhD, Center for Health System Sciences, Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers reported potential selection and recall bias in both groups. Additional research is needed to find areas of improvement and assess the effects on clinician groups and health systems, they said.
DISCLOSURES:
Andrew McWilliams, MD, MPH, reported receiving grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, the National Institutes of Health, and the Duke Endowment unrelated to this work. Ajay Dharod, MD, reported his role as an electronic health record consultant for the Association of American Medical College CORE program. Jeffrey Cleveland, MD, disclosed his participation on the Executive Client Council, a noncompensated advisory group, for Nuance/Microsoft.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Playing the ‘Doctor’ Card: A Lesson in Three Hypotheticals
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Montana Hospital to Pay $10.8M to Settle False Claims Oncology Suit
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the deadline nears for a Montana healthcare system to pay what has been called a “jaw-dropping” settlement of nearly $11 million dollars to resolve an alleged violation of the False Claims Act, the legal troubles for the oncologist at the center of the case are ongoing and escalating.
On August 26, the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Montana and other agencies announced the settlement agreement with St. Peter’s Health, a nonprofit healthcare system in Helena, to resolve allegations that it submitted “false claims for payments to federal health care programs for services performed by an oncology doctor.”
“This settlement would not have been possible without the cooperation of St. Peter’s Health, who voluntarily disclosed the misconduct and cooperated with federal investigators to identify the problem and amount of false billing,” said US Attorney Jesse Laslovich in a press release announcing the settlement.
On the same day, the US Attorney’s Office also filed a civil complaint against the oncologist Thomas Weiner, MD, accusing him of “false health care claims and improper prescribing of controlled substances.” Among the numerous allegations, the civil complaint specifies that Dr. Weiner used his position as the chief medical oncologist at St. Peter’s Health “to order medically unnecessary treatment,” including chemotherapy, blood tests, and imaging, as well as “knowingly falsified records” to double bill for office visits.
When It Began
The legal troubles for Dr. Weiner, now 61, started about 4 years ago. Dr. Weiner, who was the sole oncologist at St. Peter’s Health and worked there for 24 years, was suspended in October 2020 and then fired in November 2020 for allegedly providing unnecessary treatments and failing to refer patients to other specialists for care, among other claims.
“The magnitude of Dr. Weiner’s violations is staggering,” St. Peter’s CEO, Wade Johnson, had said in a December 2020 press statement.
At the time, Dr. Weiner had filed a lawsuit against St. Peter’s Health, claiming he was denied due process and seeking damages and a jury trial. Dr. Weiner’s lead lawyer, J. Devlan Geddes, said it was hard to believe that Dr. Weiner had suddenly become a danger to patients after more than 2 decades on the job.
Before 2020, Dr. Weiner had a clean record with Montana’s Board of Medical Examiners and had never been the subject of an internal investigation related to quality of care, according to his lawyers. He also served on St. Peter’s board of directors and as chief of medical staff.
Dr. Weiner’s exit from St. Peter’s in 2020 led to an outpouring of support from former patients and community members who formed the Facebook group, “ We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner.” The group soon grew to almost 4000 people.
Four years later, despite the new legal developments, community support for Dr. Weiner has held strong. Supporters continue to have regular rallies outside St. Peter’s Health as well as post messages and personal stories on two Facebook groups now devoted to the cause.
John Larson, 76, a Helena resident who was treated by Dr. Weiner, echoed a common sentiment from supporters. “I’m completely certain that Tom Weiner is not guilty of what the government is now involved in charging him with,” Dr. Larson said in an interview.
$10.8 Million: ‘It’s a Big Number’
At the press conference announcing the recent settlement, Mr. Laslovich recalled a participant describe the total as jaw-dropping, he said in an interview. While there haven’t been many such recent cases in the district, he agreed it’s a big number. The only other recent case he could remember was a 2018 settlement in Kalispell for $24 million.
The current settlement contends that St. Peter’s Health submitted false claims for payments to federal health care programs related to services performed and referred by Weiner. The infractions allegedly occurred between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2020.
According to the Department of Justice (DOJ), St. Peter Health’s “knew, or should have known,” that the oncologist submitted claims for office visits that were coded at a higher level of service than was performed — ie upcoded claims — or did not meet the requirements of a significant, separately identifiable service when performed on the same day chemotherapy was administered — ie non-payable claims.
The DOJ contended that the healthcare system violated the False Claims Act “by knowingly submitting the upcoded and non-payable” claims to the Federal Health Care Programs. And, as a result, St. Peter’s compensated the oncologist with a salary based on the false claims.
“We had documents showing some of the claims that were being submitted were being done because the doctor wanted more in compensation and of course you can’t do that,” Laslovich said. “For me, the message to providers, and I said this during our press conference, is that coding is critical.”
“The claims resolved by the settlement are allegations only,” the US Attorney’s Office press release clarified, and “there has been no determination of liability.”
The leadership at St. Peter’s Health issued a press release on August 27, stating it relied on Dr. Weiner’s medical record documentation and billing certification, though declined to comment further on the settlement
Bob Wade, a partner at Nelson Mullins, Nashville, Tennessee, and lead outside counsel representing St. Peter’s Health on the settlement, said in an interview that the quality issue was first identified in fall 2020.
“I first conducted a fair market value review for their entire system and noted that he [Weiner] was an extreme outlier with regard to his productivity,” Mr. Wade said.
In a separate statement, Mr. Wade praised the integrity of the health system, saying, “when the medical record documentation and medical necessity issues related to Dr. Weiner were identified, my client, St. Peter’s Health, through the Board and Executive Leadership took decisive action and authorized me to self-report to the Office of Inspector General and Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services and fully cooperated with the Department of Justice to reach an amicable settlement.”
Dr. Weiner still faces legal issues. According to the recent civil complaint filed against Weiner, the oncologist allegedly ordered “medically unnecessary treatments” for patients, “knowingly falsified records to double bill for patient office visits,” and “directed these false claims to increase his personal income, with little regard for the potential patient harm his conduct created.”
The complaint goes on to note that Dr. Weiner saw 50-70 patients a day — about four to five times more than most oncologists see in a given day. He allegedly wanted this schedule, the civil complaint said, “because it maximized his income.”
The civil complaint seeks treble damages, which is triple the actual damages awarded to the plaintiff, as well as civil penalties.
The Montana Board of Medical Examiners shows Dr. Weiner’s license as active, expiring March 31, 2025.
A Community’s Support
Over the past 4 years, Dr. Weiner has encountered strong, continued support from the community.
Rhonda Good, a Helena resident since 2002, is one of the nearly 4000 members of the “We Stand With Dr. Tom Weiner” public Facebook group. Her son was treated for cancer by Dr. Weiner and is doing well.
Like other residents, she has strong opinions about the settlement.
“My feeling was, St. Peter’s Health, by settling, basically admitted that if they went to court, they wouldn’t be able to defend their billing procedures and so they settled out of court and that probably saved them money,” she said. “Since I have lived here, St. Peter’s Health billing has been a topic of conversation. And it is not a good conversation.”
Dayna Schwartz, 58, founded a private Facebook support group for Weiner, which she said has about 730 members.
Ms. Schwartz believes the doctor was set up and she plans to continue the weekly rallies. Those who show up, she said, are only a fraction of the supporters.
“A lot of the staunch supporters maintain a low profile,” she said, as the healthcare system employs more than 1700 residents.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Investigates Tampons for Potential Lead and Metal Risks
The FDA has launched an investigation of the potential exposure to heavy metals when using tampons, the agency announced.
The move follows the publication earlier this year of concerning laboratory test results that detected the presence of more than a dozen metals in a variety of popular nonorganic and organic tampon products. That small study was a combined effort by researchers from Columbia University, Michigan State University, and the University of California, Berkeley.
“We want the public to know that before tampons can be legally sold in the US, they must meet FDA requirements for safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must test the product and its component materials before, during, and after manufacturing,” the FDA wrote in the announcement of its own upcoming study. “Before a product is allowed onto the market, biocompatibility testing is undertaken by the manufacturing company, which is part of safety testing, and is reviewed by the FDA prior to market authorization.”
There will be two studies, the FDA said. One of the studies will involve laboratory tests to evaluate metals in tampons and potential exposure people may experience when using them. The other study will be a review of current research regarding the health effects of metals that may be found in tampons.
The earlier study, published by the journal Environment International, found levels of lead in every product the researchers tested and detectable levels of more than a dozen other metals like arsenic and cadmium.
The researchers tested 24 tampon products from a range of major brands as well as store brands. The tampons were purchased at stores and online between September 2022 and March 2023. Metal content tended to differ by whether or not a product was labeled as organic, the researchers reported. Lead concentrations were higher in nonorganic tampons, and organic tampons had higher levels of arsenic.
There is no safe level of lead exposure, the US Environmental Protection Agency says, and the effects are cumulative throughout the course of life. The study authors noted that the average age that girls begin menstruation is 12 years old, and the onset of menopause occurs, on average, at age 51. One study mentioned by the researchers estimated that between 52% and 86% of people who menstruate use tampons.
The FDA plans a more expansive set of analyses than the earlier study, the agency announced.
“While the study found metals in some tampons, the study did not test whether metals are released from tampons when used. It also did not test for metals being released, absorbed into the vaginal lining, and getting into the bloodstream during tampon use,” the FDA announcement stated. “The FDA’s laboratory study will measure the amount of metals that come out of tampons under conditions that more closely mimic normal use.”
The absorbent materials in tampons, like cotton, rayon, and viscose, are potential sources of the metals. Cotton plants are particularly known to readily take up metals from the soil, although there are other ways that metals may enter the products, like during the manufacturing process.
Exposure to metals found in the initial analysis can affect a range of body systems and processes, including the brain, the kidneys, the heart, blood, and the reproductive and immune systems.
The vagina, the researchers noted, is highly permeable and substances absorbed there do not get filtered for toxins, such as by being metabolized or passing through the liver, before entering the body’s circulatory system.
The FDA announcement did not specify a timeframe for the completion of its investigation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.
The FDA has launched an investigation of the potential exposure to heavy metals when using tampons, the agency announced.
The move follows the publication earlier this year of concerning laboratory test results that detected the presence of more than a dozen metals in a variety of popular nonorganic and organic tampon products. That small study was a combined effort by researchers from Columbia University, Michigan State University, and the University of California, Berkeley.
“We want the public to know that before tampons can be legally sold in the US, they must meet FDA requirements for safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must test the product and its component materials before, during, and after manufacturing,” the FDA wrote in the announcement of its own upcoming study. “Before a product is allowed onto the market, biocompatibility testing is undertaken by the manufacturing company, which is part of safety testing, and is reviewed by the FDA prior to market authorization.”
There will be two studies, the FDA said. One of the studies will involve laboratory tests to evaluate metals in tampons and potential exposure people may experience when using them. The other study will be a review of current research regarding the health effects of metals that may be found in tampons.
The earlier study, published by the journal Environment International, found levels of lead in every product the researchers tested and detectable levels of more than a dozen other metals like arsenic and cadmium.
The researchers tested 24 tampon products from a range of major brands as well as store brands. The tampons were purchased at stores and online between September 2022 and March 2023. Metal content tended to differ by whether or not a product was labeled as organic, the researchers reported. Lead concentrations were higher in nonorganic tampons, and organic tampons had higher levels of arsenic.
There is no safe level of lead exposure, the US Environmental Protection Agency says, and the effects are cumulative throughout the course of life. The study authors noted that the average age that girls begin menstruation is 12 years old, and the onset of menopause occurs, on average, at age 51. One study mentioned by the researchers estimated that between 52% and 86% of people who menstruate use tampons.
The FDA plans a more expansive set of analyses than the earlier study, the agency announced.
“While the study found metals in some tampons, the study did not test whether metals are released from tampons when used. It also did not test for metals being released, absorbed into the vaginal lining, and getting into the bloodstream during tampon use,” the FDA announcement stated. “The FDA’s laboratory study will measure the amount of metals that come out of tampons under conditions that more closely mimic normal use.”
The absorbent materials in tampons, like cotton, rayon, and viscose, are potential sources of the metals. Cotton plants are particularly known to readily take up metals from the soil, although there are other ways that metals may enter the products, like during the manufacturing process.
Exposure to metals found in the initial analysis can affect a range of body systems and processes, including the brain, the kidneys, the heart, blood, and the reproductive and immune systems.
The vagina, the researchers noted, is highly permeable and substances absorbed there do not get filtered for toxins, such as by being metabolized or passing through the liver, before entering the body’s circulatory system.
The FDA announcement did not specify a timeframe for the completion of its investigation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.
The FDA has launched an investigation of the potential exposure to heavy metals when using tampons, the agency announced.
The move follows the publication earlier this year of concerning laboratory test results that detected the presence of more than a dozen metals in a variety of popular nonorganic and organic tampon products. That small study was a combined effort by researchers from Columbia University, Michigan State University, and the University of California, Berkeley.
“We want the public to know that before tampons can be legally sold in the US, they must meet FDA requirements for safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must test the product and its component materials before, during, and after manufacturing,” the FDA wrote in the announcement of its own upcoming study. “Before a product is allowed onto the market, biocompatibility testing is undertaken by the manufacturing company, which is part of safety testing, and is reviewed by the FDA prior to market authorization.”
There will be two studies, the FDA said. One of the studies will involve laboratory tests to evaluate metals in tampons and potential exposure people may experience when using them. The other study will be a review of current research regarding the health effects of metals that may be found in tampons.
The earlier study, published by the journal Environment International, found levels of lead in every product the researchers tested and detectable levels of more than a dozen other metals like arsenic and cadmium.
The researchers tested 24 tampon products from a range of major brands as well as store brands. The tampons were purchased at stores and online between September 2022 and March 2023. Metal content tended to differ by whether or not a product was labeled as organic, the researchers reported. Lead concentrations were higher in nonorganic tampons, and organic tampons had higher levels of arsenic.
There is no safe level of lead exposure, the US Environmental Protection Agency says, and the effects are cumulative throughout the course of life. The study authors noted that the average age that girls begin menstruation is 12 years old, and the onset of menopause occurs, on average, at age 51. One study mentioned by the researchers estimated that between 52% and 86% of people who menstruate use tampons.
The FDA plans a more expansive set of analyses than the earlier study, the agency announced.
“While the study found metals in some tampons, the study did not test whether metals are released from tampons when used. It also did not test for metals being released, absorbed into the vaginal lining, and getting into the bloodstream during tampon use,” the FDA announcement stated. “The FDA’s laboratory study will measure the amount of metals that come out of tampons under conditions that more closely mimic normal use.”
The absorbent materials in tampons, like cotton, rayon, and viscose, are potential sources of the metals. Cotton plants are particularly known to readily take up metals from the soil, although there are other ways that metals may enter the products, like during the manufacturing process.
Exposure to metals found in the initial analysis can affect a range of body systems and processes, including the brain, the kidneys, the heart, blood, and the reproductive and immune systems.
The vagina, the researchers noted, is highly permeable and substances absorbed there do not get filtered for toxins, such as by being metabolized or passing through the liver, before entering the body’s circulatory system.
The FDA announcement did not specify a timeframe for the completion of its investigation.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.
Are Pharmacy Deserts Worsening Health Disparities?
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
UVA Defends Medical School Dean, Hospital CEO After Docs Call for Their Removal
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Silent Exodus: Are Nurse Practitioners and Physician Assistants Quiet Quitting?
While she cared deeply about her work, Melissa Adams*, a family nurse practitioner (NP) in Madison, Alabama, was being frequently triple-booked, didn’t feel respected by her office manager, and started to worry about becoming burned out. When she sought help, “the administration was tone-deaf,” she said. “When I asked about what I could do to prevent burnout, they sent me an article about it. It was clear to me that asking for respite from triple-booking and asking to be respected by my office manager wasn’t being heard ... so I thought, ‘how do I fly under the radar and get by with what I can?’ ” That meant focusing on patient care and refusing to take on additional responsibilities, like training new hires or working with students.
“You’re overworked and underpaid, and you start giving less and less of yourself,” Ms. Adams said in an interview.
Quiet quitting, defined as performing only the assigned tasks of the job without making any extra effort or going the proverbial extra mile, has gained attention in the press in recent years. A Gallup poll found that about 50% of the workforce were “quiet quitters” or disengaged.
It may be even more prevalent in healthcare, where a recent survey found that 57% of frontline medical staff, including NPs and physician assistants (PAs), report being disengaged at work.
The Causes of Quiet Quitting
Potential causes of quiet quitting among PAs and NPs include:
- Unrealistic care expectations. Ms. Adams said.
- Lack of trust or respect. Physicians don’t always respect the role that PAs and NPs play in a practice.
- Dissatisfaction with leadership or administration. There’s often a feeling that the PA or NP isn’t “heard” or appreciated.
- Dissatisfaction with pay or working conditions.
- Moral injury. “There’s no way to escape being morally injured when you work with an at-risk population,” said Ms. Adams. “You may see someone who has 20-24 determinants of health, and you’re expected to schlep them through in 8 minutes — you know you’re not able to do what they need.”
What Quiet Quitting Looks Like
Terri Smith*, an NP at an academic medical center outpatient clinic in rural Vermont, said that, while she feels appreciated by her patients and her team, there’s poor communication from the administration, which has caused her to quietly quit.
“I stopped saying ‘yes’ to all the normal committee work and the extra stuff that used to add a lot to my professional enjoyment,” she said. “The last couple of years, my whole motto is to nod and smile when administration says to do something — to put your head down and take care of your patients.”
While the term “quiet quitting” may be new, the issue is not, said Bridget Roberts, PhD, a healthcare executive who ran a large physician’s group of 100 healthcare providers in Jacksonville, Florida, for a decade. “Quiet quitting is a fancy title for employees who are completely disengaged,” said Dr. Roberts. “When they’re on the way out, they ‘check the box’. That’s not a new thing.”
“Typically, the first thing you see is a lot of frustration in that they aren’t able to complete the tasks they have at hand,” said Rebecca Day, PMNHP, a doctoral-educated NP and director of nursing practice at a Federally Qualified Health Center in Corbin, Kentucky. “Staff may be overworked and not have enough time to do what’s required of them with patient care as well as the paperwork required behind the scenes. It [quiet quitting] is doing just enough to get by, but shortcutting as much as they can to try to save some time.”
Addressing Quiet Quitting
Those kinds of shortcuts may affect patients, admits Ms. Smith. “I do think it starts to seep into patient care,” she said. “And that really doesn’t feel good ... at our institution, I’m not just an NP — I’m the nurse, the doctor, the secretary — I’m everybody, and for the last year, almost every single day in clinic, I’m apologizing [to a patient] because we can’t do something.”
Watching for this frustration can help alert administrators to NPs and PAs who may be “checking out” at work. Open lines of communication can help you address the issue. “Ask questions like ‘What could we do differently to make your day easier?’” said Dr. Roberts. Understanding the day-to-day issues NPs and PAs face at work can help in developing a plan to address disengagement.
When Dr. Day sees quiet quitting at her practice, she talks with the advance practice provider about what’s causing the issue. “’Are you overworked? Are you understaffed? Are there problems at home? Do you feel you’re receiving inadequate pay?’ ” she said. “The first thing to do is address that and find mutual ground on the issues…deal with the person as a person and then go back and deal with the person as an employee. If your staff isn’t happy, your clinic isn’t going to be productive.”
Finally, while reasons for quiet quitting may vary, cultivating a collaborative atmosphere where NPs and PAs feel appreciated and valued can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting. “Get to know your advanced practice providers,” said Ms. Adams. “Understand their strengths and what they’re about. It’s not an ‘us vs them’ ... there is a lot more commonality when we approach it that way.” Respect for the integral role that NPs and PAs play in your practice can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting — and help provide better patient care.
*Names have been changed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While she cared deeply about her work, Melissa Adams*, a family nurse practitioner (NP) in Madison, Alabama, was being frequently triple-booked, didn’t feel respected by her office manager, and started to worry about becoming burned out. When she sought help, “the administration was tone-deaf,” she said. “When I asked about what I could do to prevent burnout, they sent me an article about it. It was clear to me that asking for respite from triple-booking and asking to be respected by my office manager wasn’t being heard ... so I thought, ‘how do I fly under the radar and get by with what I can?’ ” That meant focusing on patient care and refusing to take on additional responsibilities, like training new hires or working with students.
“You’re overworked and underpaid, and you start giving less and less of yourself,” Ms. Adams said in an interview.
Quiet quitting, defined as performing only the assigned tasks of the job without making any extra effort or going the proverbial extra mile, has gained attention in the press in recent years. A Gallup poll found that about 50% of the workforce were “quiet quitters” or disengaged.
It may be even more prevalent in healthcare, where a recent survey found that 57% of frontline medical staff, including NPs and physician assistants (PAs), report being disengaged at work.
The Causes of Quiet Quitting
Potential causes of quiet quitting among PAs and NPs include:
- Unrealistic care expectations. Ms. Adams said.
- Lack of trust or respect. Physicians don’t always respect the role that PAs and NPs play in a practice.
- Dissatisfaction with leadership or administration. There’s often a feeling that the PA or NP isn’t “heard” or appreciated.
- Dissatisfaction with pay or working conditions.
- Moral injury. “There’s no way to escape being morally injured when you work with an at-risk population,” said Ms. Adams. “You may see someone who has 20-24 determinants of health, and you’re expected to schlep them through in 8 minutes — you know you’re not able to do what they need.”
What Quiet Quitting Looks Like
Terri Smith*, an NP at an academic medical center outpatient clinic in rural Vermont, said that, while she feels appreciated by her patients and her team, there’s poor communication from the administration, which has caused her to quietly quit.
“I stopped saying ‘yes’ to all the normal committee work and the extra stuff that used to add a lot to my professional enjoyment,” she said. “The last couple of years, my whole motto is to nod and smile when administration says to do something — to put your head down and take care of your patients.”
While the term “quiet quitting” may be new, the issue is not, said Bridget Roberts, PhD, a healthcare executive who ran a large physician’s group of 100 healthcare providers in Jacksonville, Florida, for a decade. “Quiet quitting is a fancy title for employees who are completely disengaged,” said Dr. Roberts. “When they’re on the way out, they ‘check the box’. That’s not a new thing.”
“Typically, the first thing you see is a lot of frustration in that they aren’t able to complete the tasks they have at hand,” said Rebecca Day, PMNHP, a doctoral-educated NP and director of nursing practice at a Federally Qualified Health Center in Corbin, Kentucky. “Staff may be overworked and not have enough time to do what’s required of them with patient care as well as the paperwork required behind the scenes. It [quiet quitting] is doing just enough to get by, but shortcutting as much as they can to try to save some time.”
Addressing Quiet Quitting
Those kinds of shortcuts may affect patients, admits Ms. Smith. “I do think it starts to seep into patient care,” she said. “And that really doesn’t feel good ... at our institution, I’m not just an NP — I’m the nurse, the doctor, the secretary — I’m everybody, and for the last year, almost every single day in clinic, I’m apologizing [to a patient] because we can’t do something.”
Watching for this frustration can help alert administrators to NPs and PAs who may be “checking out” at work. Open lines of communication can help you address the issue. “Ask questions like ‘What could we do differently to make your day easier?’” said Dr. Roberts. Understanding the day-to-day issues NPs and PAs face at work can help in developing a plan to address disengagement.
When Dr. Day sees quiet quitting at her practice, she talks with the advance practice provider about what’s causing the issue. “’Are you overworked? Are you understaffed? Are there problems at home? Do you feel you’re receiving inadequate pay?’ ” she said. “The first thing to do is address that and find mutual ground on the issues…deal with the person as a person and then go back and deal with the person as an employee. If your staff isn’t happy, your clinic isn’t going to be productive.”
Finally, while reasons for quiet quitting may vary, cultivating a collaborative atmosphere where NPs and PAs feel appreciated and valued can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting. “Get to know your advanced practice providers,” said Ms. Adams. “Understand their strengths and what they’re about. It’s not an ‘us vs them’ ... there is a lot more commonality when we approach it that way.” Respect for the integral role that NPs and PAs play in your practice can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting — and help provide better patient care.
*Names have been changed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While she cared deeply about her work, Melissa Adams*, a family nurse practitioner (NP) in Madison, Alabama, was being frequently triple-booked, didn’t feel respected by her office manager, and started to worry about becoming burned out. When she sought help, “the administration was tone-deaf,” she said. “When I asked about what I could do to prevent burnout, they sent me an article about it. It was clear to me that asking for respite from triple-booking and asking to be respected by my office manager wasn’t being heard ... so I thought, ‘how do I fly under the radar and get by with what I can?’ ” That meant focusing on patient care and refusing to take on additional responsibilities, like training new hires or working with students.
“You’re overworked and underpaid, and you start giving less and less of yourself,” Ms. Adams said in an interview.
Quiet quitting, defined as performing only the assigned tasks of the job without making any extra effort or going the proverbial extra mile, has gained attention in the press in recent years. A Gallup poll found that about 50% of the workforce were “quiet quitters” or disengaged.
It may be even more prevalent in healthcare, where a recent survey found that 57% of frontline medical staff, including NPs and physician assistants (PAs), report being disengaged at work.
The Causes of Quiet Quitting
Potential causes of quiet quitting among PAs and NPs include:
- Unrealistic care expectations. Ms. Adams said.
- Lack of trust or respect. Physicians don’t always respect the role that PAs and NPs play in a practice.
- Dissatisfaction with leadership or administration. There’s often a feeling that the PA or NP isn’t “heard” or appreciated.
- Dissatisfaction with pay or working conditions.
- Moral injury. “There’s no way to escape being morally injured when you work with an at-risk population,” said Ms. Adams. “You may see someone who has 20-24 determinants of health, and you’re expected to schlep them through in 8 minutes — you know you’re not able to do what they need.”
What Quiet Quitting Looks Like
Terri Smith*, an NP at an academic medical center outpatient clinic in rural Vermont, said that, while she feels appreciated by her patients and her team, there’s poor communication from the administration, which has caused her to quietly quit.
“I stopped saying ‘yes’ to all the normal committee work and the extra stuff that used to add a lot to my professional enjoyment,” she said. “The last couple of years, my whole motto is to nod and smile when administration says to do something — to put your head down and take care of your patients.”
While the term “quiet quitting” may be new, the issue is not, said Bridget Roberts, PhD, a healthcare executive who ran a large physician’s group of 100 healthcare providers in Jacksonville, Florida, for a decade. “Quiet quitting is a fancy title for employees who are completely disengaged,” said Dr. Roberts. “When they’re on the way out, they ‘check the box’. That’s not a new thing.”
“Typically, the first thing you see is a lot of frustration in that they aren’t able to complete the tasks they have at hand,” said Rebecca Day, PMNHP, a doctoral-educated NP and director of nursing practice at a Federally Qualified Health Center in Corbin, Kentucky. “Staff may be overworked and not have enough time to do what’s required of them with patient care as well as the paperwork required behind the scenes. It [quiet quitting] is doing just enough to get by, but shortcutting as much as they can to try to save some time.”
Addressing Quiet Quitting
Those kinds of shortcuts may affect patients, admits Ms. Smith. “I do think it starts to seep into patient care,” she said. “And that really doesn’t feel good ... at our institution, I’m not just an NP — I’m the nurse, the doctor, the secretary — I’m everybody, and for the last year, almost every single day in clinic, I’m apologizing [to a patient] because we can’t do something.”
Watching for this frustration can help alert administrators to NPs and PAs who may be “checking out” at work. Open lines of communication can help you address the issue. “Ask questions like ‘What could we do differently to make your day easier?’” said Dr. Roberts. Understanding the day-to-day issues NPs and PAs face at work can help in developing a plan to address disengagement.
When Dr. Day sees quiet quitting at her practice, she talks with the advance practice provider about what’s causing the issue. “’Are you overworked? Are you understaffed? Are there problems at home? Do you feel you’re receiving inadequate pay?’ ” she said. “The first thing to do is address that and find mutual ground on the issues…deal with the person as a person and then go back and deal with the person as an employee. If your staff isn’t happy, your clinic isn’t going to be productive.”
Finally, while reasons for quiet quitting may vary, cultivating a collaborative atmosphere where NPs and PAs feel appreciated and valued can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting. “Get to know your advanced practice providers,” said Ms. Adams. “Understand their strengths and what they’re about. It’s not an ‘us vs them’ ... there is a lot more commonality when we approach it that way.” Respect for the integral role that NPs and PAs play in your practice can help reduce the risk for quiet quitting — and help provide better patient care.
*Names have been changed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baby-Led Weaning
I first heard the term “baby-led weaning” about 20 years ago, which turns out was just a few years after the concept was introduced to the public by a public health/midwife in Britain. Starting infants on solid foods when they could feed themselves didn’t sound as off-the-wall to me as it did to most other folks, but I chose not to include it in my list of standard recommendations at the 4- and 6-month well child visits. If any parent had asked me my opinion I would have told them to give it a try with a few specific cautions about what and how. But, I don’t recall any parents asking me. The ones who knew me well or had read, or at least heard about, my book on picky eating must have already figured out what my answer would be. The parents who didn’t know me may have been afraid I would tell them it was a crazy idea.
Twelve years ago I retired from office practice and hadn’t heard a peep about baby-led weaning until last week when I encountered a story in The New York Times. It appears that while I have been reveling in my post-practice existence, baby-led weaning has become a “thing.” As the author of the article observed: “The concept seems to appeal to millennials who favor parenting philosophies that prioritize child autonomy.”
Baby-led weaning’s traction has been so robust that the largest manufacturer of baby food in this country has been labeling some of its products “baby-led friendly since 2021.” There are several online businesses that have tapped into the growing market. One offers a very detailed free directory that lists almost any edible you can imagine with recommendations of when and how they can be presented in a safe and appealing matter to little hand feeders. Of course the company has also figured out a way to monetize the product.
Not surprisingly the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has remained silent on baby-led weaning. However, in The New York Times article, Dr. Mark R. Corkins, chair of the AAP nutrition committee, is quoted as describing baby-led weaning is “a social media–driven invention.”
While I was interested to learn about the concept’s growth and commercialization, I was troubled to find that like co-sleeping, sleep training, and exclusive breastfeeding, baby-led weaning has become one of those angst-producing topics that is torturing new parents who live every day in fear that they “aren’t doing it right.” We pediatricians might deserve a small dose of blame for not vigorously emphasizing that there are numerous ways to skin that cat known as parenting. However, social media websites and Mom chat rooms are probably more responsible for creating an atmosphere in which parents are afraid of being ostracized for the decisions they have made in good faith whether it is about weaning or when to start toilet training.
In isolated cultures, weaning a baby to solids was probably never a topic for discussion or debate. New parents did what their parents did, or more likely a child’s grandmother advised or took over the process herself. The child was fed what the rest of the family ate. If it was something the infant could handle himself you gave it to him. If not you mashed it up or maybe you chewed it for him into a consistency he could manage.
However, most new parents have become so distanced from their own parents’ childrearing practices geographically, temporally, and philosophically, that they must rely on folks like us and others whom they believe are, or at least claim to be, experts. Young adults are no longer hesitant to cross ethnic thresholds when they decide to be co-parents, meaning that any remnant of family tradition is either diluted or lost outright. In the void created by this abandonment of tradition, corporations were happy to step in with easy-to-prepare baby food that lacks in nutritional and dietary variety. Baby-led weaning is just one more logical step in the metamorphosis of our society’s infant feeding patterns.
I still have no problem with baby-led weaning as an option for parents, particularly if with just a click of a mouse they can access safe and healthy advice to make up for generations of grandmotherly experience acquired over hundreds of years. However,
It is one thing when parents hoping to encourage the process of self-feeding offer their infants an edible that may not be in the family’s usual diet. However, it is a totally different matter when a family allows itself to become dietary contortionists to a accommodate a 4-year-old whose diet consists of a monotonous rotation of three pasta shapes topped with grated Parmesan cheese, and on a good day a raw carrot slice or two. Parents living in this nutritional wasteland may have given up on managing their children’s pickiness, and may find it is less stressful to join the child and eat a few forkfuls of pasta to preserve some semblance of a family dinner. Then after the child has been put to bed they have their own balanced meal.
Almost by definition family meals are a compromise. Even adults without children negotiate often unspoken menu patterns with their partners. “This evening we’ll have your favorite, I may have my favorite next week.”
Most parents of young children understand that their diet may be a bit heavier on pasta than they might prefer and a little less varied when it comes to vegetables. It is just part of the deal. However, when mealtimes become totally dictated by the pickiness of a child there is a problem. While a poorly structured child-led family diet may be nutritionally deficient, the bigger problem is that it is expensive in time and labor, two resources usually in short supply in young families.
Theoretically, infants who have led their own weaning are more likely to have been introduced to a broad variety of flavors and textures and this may carry them into childhood as more adventuresome eaters. Picky eating can be managed successfully and result in a family that can enjoy the psychological and emotional benefits of nutritionally balanced family meals, but it requires a combination of parental courage and patience.
It is unclear exactly how we got into a situation in which a generation of parents makes things more difficult for themselves by favoring practices that overemphasize child autonomy. It may be that the parents had suffered under autocratic parents themselves, or more likely they have read too many novels or watched too many movies and TV shows in which the parents were portrayed as overbearing or controlling. Or, it may simply be that they haven’t had enough exposure to young children to realize that they all benefit from clear limits to a varying degree.
In the process of watching tens of thousands of parents, it has become clear to me that those who are the most successful are leaders and that they lead primarily by example. They have learned to be masters in the art of deception by creating a safe environment with sensible limits while at the same time fostering an atmosphere in which the child sees himself as participating in the process.
The biblical prophet Isaiah (11:6-9) in his description of how things will be different after the Lord acts to help his people predicts: “and a little child shall lead them.” This prediction fits nicely as the last in a string of crazy situations that includes a wolf living with a lamb and a leopard lying down with a calf.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I first heard the term “baby-led weaning” about 20 years ago, which turns out was just a few years after the concept was introduced to the public by a public health/midwife in Britain. Starting infants on solid foods when they could feed themselves didn’t sound as off-the-wall to me as it did to most other folks, but I chose not to include it in my list of standard recommendations at the 4- and 6-month well child visits. If any parent had asked me my opinion I would have told them to give it a try with a few specific cautions about what and how. But, I don’t recall any parents asking me. The ones who knew me well or had read, or at least heard about, my book on picky eating must have already figured out what my answer would be. The parents who didn’t know me may have been afraid I would tell them it was a crazy idea.
Twelve years ago I retired from office practice and hadn’t heard a peep about baby-led weaning until last week when I encountered a story in The New York Times. It appears that while I have been reveling in my post-practice existence, baby-led weaning has become a “thing.” As the author of the article observed: “The concept seems to appeal to millennials who favor parenting philosophies that prioritize child autonomy.”
Baby-led weaning’s traction has been so robust that the largest manufacturer of baby food in this country has been labeling some of its products “baby-led friendly since 2021.” There are several online businesses that have tapped into the growing market. One offers a very detailed free directory that lists almost any edible you can imagine with recommendations of when and how they can be presented in a safe and appealing matter to little hand feeders. Of course the company has also figured out a way to monetize the product.
Not surprisingly the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has remained silent on baby-led weaning. However, in The New York Times article, Dr. Mark R. Corkins, chair of the AAP nutrition committee, is quoted as describing baby-led weaning is “a social media–driven invention.”
While I was interested to learn about the concept’s growth and commercialization, I was troubled to find that like co-sleeping, sleep training, and exclusive breastfeeding, baby-led weaning has become one of those angst-producing topics that is torturing new parents who live every day in fear that they “aren’t doing it right.” We pediatricians might deserve a small dose of blame for not vigorously emphasizing that there are numerous ways to skin that cat known as parenting. However, social media websites and Mom chat rooms are probably more responsible for creating an atmosphere in which parents are afraid of being ostracized for the decisions they have made in good faith whether it is about weaning or when to start toilet training.
In isolated cultures, weaning a baby to solids was probably never a topic for discussion or debate. New parents did what their parents did, or more likely a child’s grandmother advised or took over the process herself. The child was fed what the rest of the family ate. If it was something the infant could handle himself you gave it to him. If not you mashed it up or maybe you chewed it for him into a consistency he could manage.
However, most new parents have become so distanced from their own parents’ childrearing practices geographically, temporally, and philosophically, that they must rely on folks like us and others whom they believe are, or at least claim to be, experts. Young adults are no longer hesitant to cross ethnic thresholds when they decide to be co-parents, meaning that any remnant of family tradition is either diluted or lost outright. In the void created by this abandonment of tradition, corporations were happy to step in with easy-to-prepare baby food that lacks in nutritional and dietary variety. Baby-led weaning is just one more logical step in the metamorphosis of our society’s infant feeding patterns.
I still have no problem with baby-led weaning as an option for parents, particularly if with just a click of a mouse they can access safe and healthy advice to make up for generations of grandmotherly experience acquired over hundreds of years. However,
It is one thing when parents hoping to encourage the process of self-feeding offer their infants an edible that may not be in the family’s usual diet. However, it is a totally different matter when a family allows itself to become dietary contortionists to a accommodate a 4-year-old whose diet consists of a monotonous rotation of three pasta shapes topped with grated Parmesan cheese, and on a good day a raw carrot slice or two. Parents living in this nutritional wasteland may have given up on managing their children’s pickiness, and may find it is less stressful to join the child and eat a few forkfuls of pasta to preserve some semblance of a family dinner. Then after the child has been put to bed they have their own balanced meal.
Almost by definition family meals are a compromise. Even adults without children negotiate often unspoken menu patterns with their partners. “This evening we’ll have your favorite, I may have my favorite next week.”
Most parents of young children understand that their diet may be a bit heavier on pasta than they might prefer and a little less varied when it comes to vegetables. It is just part of the deal. However, when mealtimes become totally dictated by the pickiness of a child there is a problem. While a poorly structured child-led family diet may be nutritionally deficient, the bigger problem is that it is expensive in time and labor, two resources usually in short supply in young families.
Theoretically, infants who have led their own weaning are more likely to have been introduced to a broad variety of flavors and textures and this may carry them into childhood as more adventuresome eaters. Picky eating can be managed successfully and result in a family that can enjoy the psychological and emotional benefits of nutritionally balanced family meals, but it requires a combination of parental courage and patience.
It is unclear exactly how we got into a situation in which a generation of parents makes things more difficult for themselves by favoring practices that overemphasize child autonomy. It may be that the parents had suffered under autocratic parents themselves, or more likely they have read too many novels or watched too many movies and TV shows in which the parents were portrayed as overbearing or controlling. Or, it may simply be that they haven’t had enough exposure to young children to realize that they all benefit from clear limits to a varying degree.
In the process of watching tens of thousands of parents, it has become clear to me that those who are the most successful are leaders and that they lead primarily by example. They have learned to be masters in the art of deception by creating a safe environment with sensible limits while at the same time fostering an atmosphere in which the child sees himself as participating in the process.
The biblical prophet Isaiah (11:6-9) in his description of how things will be different after the Lord acts to help his people predicts: “and a little child shall lead them.” This prediction fits nicely as the last in a string of crazy situations that includes a wolf living with a lamb and a leopard lying down with a calf.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I first heard the term “baby-led weaning” about 20 years ago, which turns out was just a few years after the concept was introduced to the public by a public health/midwife in Britain. Starting infants on solid foods when they could feed themselves didn’t sound as off-the-wall to me as it did to most other folks, but I chose not to include it in my list of standard recommendations at the 4- and 6-month well child visits. If any parent had asked me my opinion I would have told them to give it a try with a few specific cautions about what and how. But, I don’t recall any parents asking me. The ones who knew me well or had read, or at least heard about, my book on picky eating must have already figured out what my answer would be. The parents who didn’t know me may have been afraid I would tell them it was a crazy idea.
Twelve years ago I retired from office practice and hadn’t heard a peep about baby-led weaning until last week when I encountered a story in The New York Times. It appears that while I have been reveling in my post-practice existence, baby-led weaning has become a “thing.” As the author of the article observed: “The concept seems to appeal to millennials who favor parenting philosophies that prioritize child autonomy.”
Baby-led weaning’s traction has been so robust that the largest manufacturer of baby food in this country has been labeling some of its products “baby-led friendly since 2021.” There are several online businesses that have tapped into the growing market. One offers a very detailed free directory that lists almost any edible you can imagine with recommendations of when and how they can be presented in a safe and appealing matter to little hand feeders. Of course the company has also figured out a way to monetize the product.
Not surprisingly the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has remained silent on baby-led weaning. However, in The New York Times article, Dr. Mark R. Corkins, chair of the AAP nutrition committee, is quoted as describing baby-led weaning is “a social media–driven invention.”
While I was interested to learn about the concept’s growth and commercialization, I was troubled to find that like co-sleeping, sleep training, and exclusive breastfeeding, baby-led weaning has become one of those angst-producing topics that is torturing new parents who live every day in fear that they “aren’t doing it right.” We pediatricians might deserve a small dose of blame for not vigorously emphasizing that there are numerous ways to skin that cat known as parenting. However, social media websites and Mom chat rooms are probably more responsible for creating an atmosphere in which parents are afraid of being ostracized for the decisions they have made in good faith whether it is about weaning or when to start toilet training.
In isolated cultures, weaning a baby to solids was probably never a topic for discussion or debate. New parents did what their parents did, or more likely a child’s grandmother advised or took over the process herself. The child was fed what the rest of the family ate. If it was something the infant could handle himself you gave it to him. If not you mashed it up or maybe you chewed it for him into a consistency he could manage.
However, most new parents have become so distanced from their own parents’ childrearing practices geographically, temporally, and philosophically, that they must rely on folks like us and others whom they believe are, or at least claim to be, experts. Young adults are no longer hesitant to cross ethnic thresholds when they decide to be co-parents, meaning that any remnant of family tradition is either diluted or lost outright. In the void created by this abandonment of tradition, corporations were happy to step in with easy-to-prepare baby food that lacks in nutritional and dietary variety. Baby-led weaning is just one more logical step in the metamorphosis of our society’s infant feeding patterns.
I still have no problem with baby-led weaning as an option for parents, particularly if with just a click of a mouse they can access safe and healthy advice to make up for generations of grandmotherly experience acquired over hundreds of years. However,
It is one thing when parents hoping to encourage the process of self-feeding offer their infants an edible that may not be in the family’s usual diet. However, it is a totally different matter when a family allows itself to become dietary contortionists to a accommodate a 4-year-old whose diet consists of a monotonous rotation of three pasta shapes topped with grated Parmesan cheese, and on a good day a raw carrot slice or two. Parents living in this nutritional wasteland may have given up on managing their children’s pickiness, and may find it is less stressful to join the child and eat a few forkfuls of pasta to preserve some semblance of a family dinner. Then after the child has been put to bed they have their own balanced meal.
Almost by definition family meals are a compromise. Even adults without children negotiate often unspoken menu patterns with their partners. “This evening we’ll have your favorite, I may have my favorite next week.”
Most parents of young children understand that their diet may be a bit heavier on pasta than they might prefer and a little less varied when it comes to vegetables. It is just part of the deal. However, when mealtimes become totally dictated by the pickiness of a child there is a problem. While a poorly structured child-led family diet may be nutritionally deficient, the bigger problem is that it is expensive in time and labor, two resources usually in short supply in young families.
Theoretically, infants who have led their own weaning are more likely to have been introduced to a broad variety of flavors and textures and this may carry them into childhood as more adventuresome eaters. Picky eating can be managed successfully and result in a family that can enjoy the psychological and emotional benefits of nutritionally balanced family meals, but it requires a combination of parental courage and patience.
It is unclear exactly how we got into a situation in which a generation of parents makes things more difficult for themselves by favoring practices that overemphasize child autonomy. It may be that the parents had suffered under autocratic parents themselves, or more likely they have read too many novels or watched too many movies and TV shows in which the parents were portrayed as overbearing or controlling. Or, it may simply be that they haven’t had enough exposure to young children to realize that they all benefit from clear limits to a varying degree.
In the process of watching tens of thousands of parents, it has become clear to me that those who are the most successful are leaders and that they lead primarily by example. They have learned to be masters in the art of deception by creating a safe environment with sensible limits while at the same time fostering an atmosphere in which the child sees himself as participating in the process.
The biblical prophet Isaiah (11:6-9) in his description of how things will be different after the Lord acts to help his people predicts: “and a little child shall lead them.” This prediction fits nicely as the last in a string of crazy situations that includes a wolf living with a lamb and a leopard lying down with a calf.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
AI in Medicine Sparks Excitement, Concerns From Experts
VIENNA — At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress, experts discussed the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine and explored ethical implications and practical challenges.
Joshua Hatherley, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the School of Philosophy and History of Ideas at Aarhus University in Denmark, said the traditional bioethical principles — autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice — remain a crucial framework for assessing ethics regarding the use of AI tools in medicine. However, he said the emerging fifth principle of “explainability” has gained attention due to the unique characteristics of AI systems.
“Everyone is excited about AI right now, but there are many open questions about how much we can trust it and to what extent we can use it,” Ana Catalina Hernandez Padilla, a clinical researcher at the Université de Limoges, France, told this news organization.
Joseph Alderman, MBChB, an AI and digital health clinical research fellow at the Institute of Inflammation and Ageing at the University of Birmingham, UK, said these are undoubtedly exciting times to work in AI and health, but he believes clinicians should be “part of the story” and advocate for AI that is safe, effective, and equitable.
The Pros
Dr. Alderman said AI has huge potential to improve healthcare and patients’ experiences.
One interesting area in which AI is being applied is the informed consent process. Conversational AI models, like large language models, can provide patients with a time-unlimited platform to discuss risks, benefits, and recommendations, potentially improving understanding and patient engagement. AI systems can also predict the preferences of noncommunicative patients by analyzing their social media and medical data, which may improve surrogate decision-making and ensure treatment aligns with patient preferences, Dr. Hatherley explained.
Another significant benefit is AI’s capacity to improve patient outcomes through better resource allocation. For example, AI can help optimize the allocation of hospital beds, leading to more efficient use of resources and improved patient health outcomes.
AI systems can reduce medical errors and enhance diagnosis or treatment plans through large-scale data analysis, leading to faster and more accurate decision-making. It can handle administrative tasks, reducing clinician burnout and allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
AI also promises to advance health equity by improving access to quality care in underserved areas. In rural hospitals or developing countries, AI can help fill gaps in clinical expertise, potentially leveling the playing field in access to healthcare.
The Cons
Despite its potential, AI in medicine presents several risks that require careful ethical considerations. One primary concern is the possibility of embedded bias in AI systems.
For example, AI-driven advice from an AI agent may prioritize certain outcomes, such as survival, based on broad standards rather than unique patient values, potentially misaligning with the preferences of patients who value quality of life over longevity. “That may interfere with patients’ autonomous decisions,” Dr. Hatherley said.
AI systems also have limited generalizability. Models trained on a specific patient population may perform poorly when applied to different groups due to changes in demographic or clinical characteristics. This can result in less accurate or inappropriate recommendations in real-world settings. “These technologies work on the very narrow population on which the tool was developed but might not necessarily work in the real world,” said Dr. Alderman.
Another significant risk is algorithmic bias, which can worsen health disparities. AI models trained on biased datasets may perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequities in healthcare delivery, leading to suboptimal care for marginalized populations. “We have evidence of algorithms directly discriminating against people with certain characteristics,” Dr. Alderman said.
AI’s Black Box
AI systems, particularly those utilizing deep learning, often function as “black boxes,” meaning their internal decision-making processes are opaque and difficult to interpret. Dr. Hatherley said this lack of transparency raises significant concerns about trust and accountability in clinical decision-making.
While Explainable AI methods have been developed to offer insights into how these systems generate their recommendations, these explanations frequently fail to capture the reasoning process entirely. Dr. Hatherley explained that this is similar to using a pharmaceutical medicine without a clear understanding of the mechanisms for which it works.
This opacity in AI decision-making can lead to mistrust among clinicians and patients, limiting its effective use in healthcare. “We don’t really know how to interpret the information it provides,” Ms. Hernandez said.
She said while younger clinicians might be more open to testing the waters with AI tools, older practitioners still prefer to trust their own senses while looking at a patient as a whole and observing the evolution of their disease. “They are not just ticking boxes. They interpret all these variables together to make a medical decision,” she said.
“I am really optimistic about the future of AI,” Dr. Hatherley concluded. “There are still many challenges to overcome, but, ultimately, it’s not enough to talk about how AI should be adapted to human beings. We also need to talk about how humans should adapt to AI.”
Dr. Hatherley, Dr. Alderman, and Ms. Hernandez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress, experts discussed the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine and explored ethical implications and practical challenges.
Joshua Hatherley, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the School of Philosophy and History of Ideas at Aarhus University in Denmark, said the traditional bioethical principles — autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice — remain a crucial framework for assessing ethics regarding the use of AI tools in medicine. However, he said the emerging fifth principle of “explainability” has gained attention due to the unique characteristics of AI systems.
“Everyone is excited about AI right now, but there are many open questions about how much we can trust it and to what extent we can use it,” Ana Catalina Hernandez Padilla, a clinical researcher at the Université de Limoges, France, told this news organization.
Joseph Alderman, MBChB, an AI and digital health clinical research fellow at the Institute of Inflammation and Ageing at the University of Birmingham, UK, said these are undoubtedly exciting times to work in AI and health, but he believes clinicians should be “part of the story” and advocate for AI that is safe, effective, and equitable.
The Pros
Dr. Alderman said AI has huge potential to improve healthcare and patients’ experiences.
One interesting area in which AI is being applied is the informed consent process. Conversational AI models, like large language models, can provide patients with a time-unlimited platform to discuss risks, benefits, and recommendations, potentially improving understanding and patient engagement. AI systems can also predict the preferences of noncommunicative patients by analyzing their social media and medical data, which may improve surrogate decision-making and ensure treatment aligns with patient preferences, Dr. Hatherley explained.
Another significant benefit is AI’s capacity to improve patient outcomes through better resource allocation. For example, AI can help optimize the allocation of hospital beds, leading to more efficient use of resources and improved patient health outcomes.
AI systems can reduce medical errors and enhance diagnosis or treatment plans through large-scale data analysis, leading to faster and more accurate decision-making. It can handle administrative tasks, reducing clinician burnout and allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
AI also promises to advance health equity by improving access to quality care in underserved areas. In rural hospitals or developing countries, AI can help fill gaps in clinical expertise, potentially leveling the playing field in access to healthcare.
The Cons
Despite its potential, AI in medicine presents several risks that require careful ethical considerations. One primary concern is the possibility of embedded bias in AI systems.
For example, AI-driven advice from an AI agent may prioritize certain outcomes, such as survival, based on broad standards rather than unique patient values, potentially misaligning with the preferences of patients who value quality of life over longevity. “That may interfere with patients’ autonomous decisions,” Dr. Hatherley said.
AI systems also have limited generalizability. Models trained on a specific patient population may perform poorly when applied to different groups due to changes in demographic or clinical characteristics. This can result in less accurate or inappropriate recommendations in real-world settings. “These technologies work on the very narrow population on which the tool was developed but might not necessarily work in the real world,” said Dr. Alderman.
Another significant risk is algorithmic bias, which can worsen health disparities. AI models trained on biased datasets may perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequities in healthcare delivery, leading to suboptimal care for marginalized populations. “We have evidence of algorithms directly discriminating against people with certain characteristics,” Dr. Alderman said.
AI’s Black Box
AI systems, particularly those utilizing deep learning, often function as “black boxes,” meaning their internal decision-making processes are opaque and difficult to interpret. Dr. Hatherley said this lack of transparency raises significant concerns about trust and accountability in clinical decision-making.
While Explainable AI methods have been developed to offer insights into how these systems generate their recommendations, these explanations frequently fail to capture the reasoning process entirely. Dr. Hatherley explained that this is similar to using a pharmaceutical medicine without a clear understanding of the mechanisms for which it works.
This opacity in AI decision-making can lead to mistrust among clinicians and patients, limiting its effective use in healthcare. “We don’t really know how to interpret the information it provides,” Ms. Hernandez said.
She said while younger clinicians might be more open to testing the waters with AI tools, older practitioners still prefer to trust their own senses while looking at a patient as a whole and observing the evolution of their disease. “They are not just ticking boxes. They interpret all these variables together to make a medical decision,” she said.
“I am really optimistic about the future of AI,” Dr. Hatherley concluded. “There are still many challenges to overcome, but, ultimately, it’s not enough to talk about how AI should be adapted to human beings. We also need to talk about how humans should adapt to AI.”
Dr. Hatherley, Dr. Alderman, and Ms. Hernandez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress, experts discussed the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine and explored ethical implications and practical challenges.
Joshua Hatherley, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the School of Philosophy and History of Ideas at Aarhus University in Denmark, said the traditional bioethical principles — autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice — remain a crucial framework for assessing ethics regarding the use of AI tools in medicine. However, he said the emerging fifth principle of “explainability” has gained attention due to the unique characteristics of AI systems.
“Everyone is excited about AI right now, but there are many open questions about how much we can trust it and to what extent we can use it,” Ana Catalina Hernandez Padilla, a clinical researcher at the Université de Limoges, France, told this news organization.
Joseph Alderman, MBChB, an AI and digital health clinical research fellow at the Institute of Inflammation and Ageing at the University of Birmingham, UK, said these are undoubtedly exciting times to work in AI and health, but he believes clinicians should be “part of the story” and advocate for AI that is safe, effective, and equitable.
The Pros
Dr. Alderman said AI has huge potential to improve healthcare and patients’ experiences.
One interesting area in which AI is being applied is the informed consent process. Conversational AI models, like large language models, can provide patients with a time-unlimited platform to discuss risks, benefits, and recommendations, potentially improving understanding and patient engagement. AI systems can also predict the preferences of noncommunicative patients by analyzing their social media and medical data, which may improve surrogate decision-making and ensure treatment aligns with patient preferences, Dr. Hatherley explained.
Another significant benefit is AI’s capacity to improve patient outcomes through better resource allocation. For example, AI can help optimize the allocation of hospital beds, leading to more efficient use of resources and improved patient health outcomes.
AI systems can reduce medical errors and enhance diagnosis or treatment plans through large-scale data analysis, leading to faster and more accurate decision-making. It can handle administrative tasks, reducing clinician burnout and allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
AI also promises to advance health equity by improving access to quality care in underserved areas. In rural hospitals or developing countries, AI can help fill gaps in clinical expertise, potentially leveling the playing field in access to healthcare.
The Cons
Despite its potential, AI in medicine presents several risks that require careful ethical considerations. One primary concern is the possibility of embedded bias in AI systems.
For example, AI-driven advice from an AI agent may prioritize certain outcomes, such as survival, based on broad standards rather than unique patient values, potentially misaligning with the preferences of patients who value quality of life over longevity. “That may interfere with patients’ autonomous decisions,” Dr. Hatherley said.
AI systems also have limited generalizability. Models trained on a specific patient population may perform poorly when applied to different groups due to changes in demographic or clinical characteristics. This can result in less accurate or inappropriate recommendations in real-world settings. “These technologies work on the very narrow population on which the tool was developed but might not necessarily work in the real world,” said Dr. Alderman.
Another significant risk is algorithmic bias, which can worsen health disparities. AI models trained on biased datasets may perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequities in healthcare delivery, leading to suboptimal care for marginalized populations. “We have evidence of algorithms directly discriminating against people with certain characteristics,” Dr. Alderman said.
AI’s Black Box
AI systems, particularly those utilizing deep learning, often function as “black boxes,” meaning their internal decision-making processes are opaque and difficult to interpret. Dr. Hatherley said this lack of transparency raises significant concerns about trust and accountability in clinical decision-making.
While Explainable AI methods have been developed to offer insights into how these systems generate their recommendations, these explanations frequently fail to capture the reasoning process entirely. Dr. Hatherley explained that this is similar to using a pharmaceutical medicine without a clear understanding of the mechanisms for which it works.
This opacity in AI decision-making can lead to mistrust among clinicians and patients, limiting its effective use in healthcare. “We don’t really know how to interpret the information it provides,” Ms. Hernandez said.
She said while younger clinicians might be more open to testing the waters with AI tools, older practitioners still prefer to trust their own senses while looking at a patient as a whole and observing the evolution of their disease. “They are not just ticking boxes. They interpret all these variables together to make a medical decision,” she said.
“I am really optimistic about the future of AI,” Dr. Hatherley concluded. “There are still many challenges to overcome, but, ultimately, it’s not enough to talk about how AI should be adapted to human beings. We also need to talk about how humans should adapt to AI.”
Dr. Hatherley, Dr. Alderman, and Ms. Hernandez have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.



