User login
CVD deaths rose, imaging declined during pandemic
While the direct toll of the COVID-19 pandemic is being tallied and shared on the nightly news, the indirect effects will undoubtedly take years to fully measure.
In two papers published online Jan. 11 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, researchers have started the process of quantifying the impact of the pandemic on the care of patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD).
In the first study, Rishi Wadhera, MD, MPP, MPhil, and colleagues from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School in Boston examined population-level data to determine how deaths from cardiovascular causes changed in the United States in the early months of the pandemic relative to the same periods in 2019.
In a second paper, Andrew J. Einstein, MD, PhD, from Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital and colleagues looked at the pandemic’s international impact on the diagnosis of heart disease.
Using data from the National Center for Health Statistics, Dr. Wadhera and colleagues compared death rates from cardiovascular causes in the United States from March 18, 2020, to June 2, 2020, (the first wave of the pandemic) and from Jan. 1, 2020, to March 17, 2020, (the period just before the pandemic started) and compared them to the same periods in 2019. ICD codes were used to identify underlying causes of death.
Relative to 2019, they found a significant increase in deaths from ischemic heart disease nationally (1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.18), as well as an increase in deaths caused by hypertensive disease (1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26). There was no apparent increase in deaths from heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, or other diseases of the circulatory system.
When they looked just at New York City, the area hit hardest during the early part of the pandemic, the relative increases in deaths from ischemic heart disease were more pronounced.
Deaths from ischemic heart disease or hypertensive diseases jumped 139% and 164%, respectively, between March 18, 2020, and June 2, 2020.
More modest increases in deaths were seen in the remainder of New York state, New Jersey, Michigan and Illinois, while Massachusetts and Louisiana did not see a change in cardiovascular deaths.
Several studies from different parts of the world have indicated a 40%-50% drop in hospitalization for myocardial infarction in the initial months of the pandemic, said Dr. Wadhera in an interview.
“We wanted to understand where did all the heart attacks go? And we worried that patients with urgent heart conditions were not seeking the medical care they needed. I think our data suggest that this may have been the case,” reported Dr. Wadhera.
“This very much reflects the reality of what we’re seeing on the ground,” he told this news organization. “After the initial surge ended, when hospital volumes began to return to normal, we saw patients come into the hospital who clearly had a heart attack during the surge months – and were now experiencing complications of that event – because they had initially not come into the hospital due to concerns about exposure to the virus.”
A limitation of their data, he stressed, is whether some deaths coded as CVD deaths were really deaths from undiagnosed COVID-19. “It’s possible that some portion of the increased deaths we observed really reflect the cardiovascular complications of undiagnosed COVID-19, because we know that testing was quite limited during the early first surge of cases.”
“I think that basically three factors – patients avoiding the health care system because of fear of getting COVID, health care systems being strained and overwhelmed leading to the deferral of cardiovascular care and semi-elective procedures, and the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 itself – all probably collectively contributed to the rise in cardiovascular deaths that we observed,” said Dr. Wadhera.
In an accompanying editorial, Michael N. Young, MD, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, N.H., and colleagues write that these data, taken together with an earlier study showing an increase in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests at the pandemic peak in New York City, “support the notion of excess fatalities due to unattended comorbid illnesses.” That said, attribution of death in the COVID era “remains problematic.”
In the second article, Andrew Einstein, MD, PhD, and the INCAPS COVID Investigators Group took a broader approach and looked at the impact of COVID-19 on cardiac diagnostic procedures in over 100 countries.
The INCAPS (International Atomic Energy Agency Noninvasive Cardiology Protocols Study) group has for the past decade conducted numerous studies addressing the use of best practices and worldwide practice variation in CVD diagnosis.
For this effort, they sent a survey link to INCAPS participants worldwide, ultimately including 909 survey responses from 108 countries in the final analysis.
Compared with March 2019, overall procedure volume decreased 42% in March 2020 and 64% in April 2020.
The greatest decreases were seen in stress testing (78%) and transesophageal echocardiography (76%), both procedures, noted Dr. Einstein, associated with a greater risk of aerosolization.
“Whether as we reset after COVID we return to the same place in terms of the use of cardiovascular diagnostic testing remains to be seen, but it certainly poses an opportunity to improve our utilization of various modes of testing,” said Dr. Einstein.
Using regression analysis, Dr. Einstein and colleagues were able to see that sites located in low-income and lower-middle-income countries saw an additional 22% reduction in cardiac procedures and less availability of personal protective equipment (PPE) and telehealth.
Fifty-two percent of survey respondents reported significant shortages of N95 masks early in the pandemic, with fewer issues in supplies of gloves, gowns, and face shields. Lower-income countries were more likely to face significant PPE shortages and less likely to be able to implement telehealth strategies to make up for reduced in-person care. PPE shortage itself, however, was not related to lower procedural volume on multivariable regression.
“It all really begs the question of whether there is more that the world can do to help out the developing world in terms of managing the pandemic in all its facets,” said Dr. Einstein in an interview, adding he was “shocked” to learn how difficult it was for some lower-income countries to get sufficient PPE.
Did shutdowns go too far?
Calling this a “remarkable study,” an editorial written by Darryl P. Leong, MBBS, PhD, John W. Eikelboom, MBBS, and Salim Yusuf, MBBS, DPhil, all from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., suggests that perhaps health systems in some places went too far in closing down during the first wave of the pandemic, naming specifically Canada, Eastern Europe, and Saudi Arabia as examples.
“Although these measures were taken to prepare for the worst, overwhelming numbers of patients with COVID-19 did not materialize during the first wave of the pandemic in these countries. It is possible that delaying so-called nonessential services may have been unnecessary and potentially harmful, because it likely led to delays in providing care for the treatment of serious non–COVID-19 illnesses.”
Since then, more experience and more data have largely allowed hospital systems to “tackle the ebb and flow” of COVID-19 cases in ways that limit shutdowns of important health services, they said.
Given the more pronounced effect in low- and middle-income countries, they stressed the need to focus resources on ways to promote prevention and treatment that do not rely on diagnostic procedures.
“This calls for more emphasis on developing efficient systems of telehealth, especially in poorer countries or in remote settings in all countries,” Dr. Leong and colleagues conclude.
Dr. Wadhera has reported research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, along with fellow senior author Robert W. Yeh, MD, MBA, who has also received personal fees and grants from several companies not related to the submitted work. Dr. Einstein, Dr. Leong, Dr. Eikelboom, and Dr. Yusuf have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While the direct toll of the COVID-19 pandemic is being tallied and shared on the nightly news, the indirect effects will undoubtedly take years to fully measure.
In two papers published online Jan. 11 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, researchers have started the process of quantifying the impact of the pandemic on the care of patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD).
In the first study, Rishi Wadhera, MD, MPP, MPhil, and colleagues from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School in Boston examined population-level data to determine how deaths from cardiovascular causes changed in the United States in the early months of the pandemic relative to the same periods in 2019.
In a second paper, Andrew J. Einstein, MD, PhD, from Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital and colleagues looked at the pandemic’s international impact on the diagnosis of heart disease.
Using data from the National Center for Health Statistics, Dr. Wadhera and colleagues compared death rates from cardiovascular causes in the United States from March 18, 2020, to June 2, 2020, (the first wave of the pandemic) and from Jan. 1, 2020, to March 17, 2020, (the period just before the pandemic started) and compared them to the same periods in 2019. ICD codes were used to identify underlying causes of death.
Relative to 2019, they found a significant increase in deaths from ischemic heart disease nationally (1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.18), as well as an increase in deaths caused by hypertensive disease (1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26). There was no apparent increase in deaths from heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, or other diseases of the circulatory system.
When they looked just at New York City, the area hit hardest during the early part of the pandemic, the relative increases in deaths from ischemic heart disease were more pronounced.
Deaths from ischemic heart disease or hypertensive diseases jumped 139% and 164%, respectively, between March 18, 2020, and June 2, 2020.
More modest increases in deaths were seen in the remainder of New York state, New Jersey, Michigan and Illinois, while Massachusetts and Louisiana did not see a change in cardiovascular deaths.
Several studies from different parts of the world have indicated a 40%-50% drop in hospitalization for myocardial infarction in the initial months of the pandemic, said Dr. Wadhera in an interview.
“We wanted to understand where did all the heart attacks go? And we worried that patients with urgent heart conditions were not seeking the medical care they needed. I think our data suggest that this may have been the case,” reported Dr. Wadhera.
“This very much reflects the reality of what we’re seeing on the ground,” he told this news organization. “After the initial surge ended, when hospital volumes began to return to normal, we saw patients come into the hospital who clearly had a heart attack during the surge months – and were now experiencing complications of that event – because they had initially not come into the hospital due to concerns about exposure to the virus.”
A limitation of their data, he stressed, is whether some deaths coded as CVD deaths were really deaths from undiagnosed COVID-19. “It’s possible that some portion of the increased deaths we observed really reflect the cardiovascular complications of undiagnosed COVID-19, because we know that testing was quite limited during the early first surge of cases.”
“I think that basically three factors – patients avoiding the health care system because of fear of getting COVID, health care systems being strained and overwhelmed leading to the deferral of cardiovascular care and semi-elective procedures, and the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 itself – all probably collectively contributed to the rise in cardiovascular deaths that we observed,” said Dr. Wadhera.
In an accompanying editorial, Michael N. Young, MD, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, N.H., and colleagues write that these data, taken together with an earlier study showing an increase in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests at the pandemic peak in New York City, “support the notion of excess fatalities due to unattended comorbid illnesses.” That said, attribution of death in the COVID era “remains problematic.”
In the second article, Andrew Einstein, MD, PhD, and the INCAPS COVID Investigators Group took a broader approach and looked at the impact of COVID-19 on cardiac diagnostic procedures in over 100 countries.
The INCAPS (International Atomic Energy Agency Noninvasive Cardiology Protocols Study) group has for the past decade conducted numerous studies addressing the use of best practices and worldwide practice variation in CVD diagnosis.
For this effort, they sent a survey link to INCAPS participants worldwide, ultimately including 909 survey responses from 108 countries in the final analysis.
Compared with March 2019, overall procedure volume decreased 42% in March 2020 and 64% in April 2020.
The greatest decreases were seen in stress testing (78%) and transesophageal echocardiography (76%), both procedures, noted Dr. Einstein, associated with a greater risk of aerosolization.
“Whether as we reset after COVID we return to the same place in terms of the use of cardiovascular diagnostic testing remains to be seen, but it certainly poses an opportunity to improve our utilization of various modes of testing,” said Dr. Einstein.
Using regression analysis, Dr. Einstein and colleagues were able to see that sites located in low-income and lower-middle-income countries saw an additional 22% reduction in cardiac procedures and less availability of personal protective equipment (PPE) and telehealth.
Fifty-two percent of survey respondents reported significant shortages of N95 masks early in the pandemic, with fewer issues in supplies of gloves, gowns, and face shields. Lower-income countries were more likely to face significant PPE shortages and less likely to be able to implement telehealth strategies to make up for reduced in-person care. PPE shortage itself, however, was not related to lower procedural volume on multivariable regression.
“It all really begs the question of whether there is more that the world can do to help out the developing world in terms of managing the pandemic in all its facets,” said Dr. Einstein in an interview, adding he was “shocked” to learn how difficult it was for some lower-income countries to get sufficient PPE.
Did shutdowns go too far?
Calling this a “remarkable study,” an editorial written by Darryl P. Leong, MBBS, PhD, John W. Eikelboom, MBBS, and Salim Yusuf, MBBS, DPhil, all from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., suggests that perhaps health systems in some places went too far in closing down during the first wave of the pandemic, naming specifically Canada, Eastern Europe, and Saudi Arabia as examples.
“Although these measures were taken to prepare for the worst, overwhelming numbers of patients with COVID-19 did not materialize during the first wave of the pandemic in these countries. It is possible that delaying so-called nonessential services may have been unnecessary and potentially harmful, because it likely led to delays in providing care for the treatment of serious non–COVID-19 illnesses.”
Since then, more experience and more data have largely allowed hospital systems to “tackle the ebb and flow” of COVID-19 cases in ways that limit shutdowns of important health services, they said.
Given the more pronounced effect in low- and middle-income countries, they stressed the need to focus resources on ways to promote prevention and treatment that do not rely on diagnostic procedures.
“This calls for more emphasis on developing efficient systems of telehealth, especially in poorer countries or in remote settings in all countries,” Dr. Leong and colleagues conclude.
Dr. Wadhera has reported research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, along with fellow senior author Robert W. Yeh, MD, MBA, who has also received personal fees and grants from several companies not related to the submitted work. Dr. Einstein, Dr. Leong, Dr. Eikelboom, and Dr. Yusuf have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While the direct toll of the COVID-19 pandemic is being tallied and shared on the nightly news, the indirect effects will undoubtedly take years to fully measure.
In two papers published online Jan. 11 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, researchers have started the process of quantifying the impact of the pandemic on the care of patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD).
In the first study, Rishi Wadhera, MD, MPP, MPhil, and colleagues from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School in Boston examined population-level data to determine how deaths from cardiovascular causes changed in the United States in the early months of the pandemic relative to the same periods in 2019.
In a second paper, Andrew J. Einstein, MD, PhD, from Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital and colleagues looked at the pandemic’s international impact on the diagnosis of heart disease.
Using data from the National Center for Health Statistics, Dr. Wadhera and colleagues compared death rates from cardiovascular causes in the United States from March 18, 2020, to June 2, 2020, (the first wave of the pandemic) and from Jan. 1, 2020, to March 17, 2020, (the period just before the pandemic started) and compared them to the same periods in 2019. ICD codes were used to identify underlying causes of death.
Relative to 2019, they found a significant increase in deaths from ischemic heart disease nationally (1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.18), as well as an increase in deaths caused by hypertensive disease (1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26). There was no apparent increase in deaths from heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, or other diseases of the circulatory system.
When they looked just at New York City, the area hit hardest during the early part of the pandemic, the relative increases in deaths from ischemic heart disease were more pronounced.
Deaths from ischemic heart disease or hypertensive diseases jumped 139% and 164%, respectively, between March 18, 2020, and June 2, 2020.
More modest increases in deaths were seen in the remainder of New York state, New Jersey, Michigan and Illinois, while Massachusetts and Louisiana did not see a change in cardiovascular deaths.
Several studies from different parts of the world have indicated a 40%-50% drop in hospitalization for myocardial infarction in the initial months of the pandemic, said Dr. Wadhera in an interview.
“We wanted to understand where did all the heart attacks go? And we worried that patients with urgent heart conditions were not seeking the medical care they needed. I think our data suggest that this may have been the case,” reported Dr. Wadhera.
“This very much reflects the reality of what we’re seeing on the ground,” he told this news organization. “After the initial surge ended, when hospital volumes began to return to normal, we saw patients come into the hospital who clearly had a heart attack during the surge months – and were now experiencing complications of that event – because they had initially not come into the hospital due to concerns about exposure to the virus.”
A limitation of their data, he stressed, is whether some deaths coded as CVD deaths were really deaths from undiagnosed COVID-19. “It’s possible that some portion of the increased deaths we observed really reflect the cardiovascular complications of undiagnosed COVID-19, because we know that testing was quite limited during the early first surge of cases.”
“I think that basically three factors – patients avoiding the health care system because of fear of getting COVID, health care systems being strained and overwhelmed leading to the deferral of cardiovascular care and semi-elective procedures, and the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 itself – all probably collectively contributed to the rise in cardiovascular deaths that we observed,” said Dr. Wadhera.
In an accompanying editorial, Michael N. Young, MD, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, N.H., and colleagues write that these data, taken together with an earlier study showing an increase in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests at the pandemic peak in New York City, “support the notion of excess fatalities due to unattended comorbid illnesses.” That said, attribution of death in the COVID era “remains problematic.”
In the second article, Andrew Einstein, MD, PhD, and the INCAPS COVID Investigators Group took a broader approach and looked at the impact of COVID-19 on cardiac diagnostic procedures in over 100 countries.
The INCAPS (International Atomic Energy Agency Noninvasive Cardiology Protocols Study) group has for the past decade conducted numerous studies addressing the use of best practices and worldwide practice variation in CVD diagnosis.
For this effort, they sent a survey link to INCAPS participants worldwide, ultimately including 909 survey responses from 108 countries in the final analysis.
Compared with March 2019, overall procedure volume decreased 42% in March 2020 and 64% in April 2020.
The greatest decreases were seen in stress testing (78%) and transesophageal echocardiography (76%), both procedures, noted Dr. Einstein, associated with a greater risk of aerosolization.
“Whether as we reset after COVID we return to the same place in terms of the use of cardiovascular diagnostic testing remains to be seen, but it certainly poses an opportunity to improve our utilization of various modes of testing,” said Dr. Einstein.
Using regression analysis, Dr. Einstein and colleagues were able to see that sites located in low-income and lower-middle-income countries saw an additional 22% reduction in cardiac procedures and less availability of personal protective equipment (PPE) and telehealth.
Fifty-two percent of survey respondents reported significant shortages of N95 masks early in the pandemic, with fewer issues in supplies of gloves, gowns, and face shields. Lower-income countries were more likely to face significant PPE shortages and less likely to be able to implement telehealth strategies to make up for reduced in-person care. PPE shortage itself, however, was not related to lower procedural volume on multivariable regression.
“It all really begs the question of whether there is more that the world can do to help out the developing world in terms of managing the pandemic in all its facets,” said Dr. Einstein in an interview, adding he was “shocked” to learn how difficult it was for some lower-income countries to get sufficient PPE.
Did shutdowns go too far?
Calling this a “remarkable study,” an editorial written by Darryl P. Leong, MBBS, PhD, John W. Eikelboom, MBBS, and Salim Yusuf, MBBS, DPhil, all from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., suggests that perhaps health systems in some places went too far in closing down during the first wave of the pandemic, naming specifically Canada, Eastern Europe, and Saudi Arabia as examples.
“Although these measures were taken to prepare for the worst, overwhelming numbers of patients with COVID-19 did not materialize during the first wave of the pandemic in these countries. It is possible that delaying so-called nonessential services may have been unnecessary and potentially harmful, because it likely led to delays in providing care for the treatment of serious non–COVID-19 illnesses.”
Since then, more experience and more data have largely allowed hospital systems to “tackle the ebb and flow” of COVID-19 cases in ways that limit shutdowns of important health services, they said.
Given the more pronounced effect in low- and middle-income countries, they stressed the need to focus resources on ways to promote prevention and treatment that do not rely on diagnostic procedures.
“This calls for more emphasis on developing efficient systems of telehealth, especially in poorer countries or in remote settings in all countries,” Dr. Leong and colleagues conclude.
Dr. Wadhera has reported research support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, along with fellow senior author Robert W. Yeh, MD, MBA, who has also received personal fees and grants from several companies not related to the submitted work. Dr. Einstein, Dr. Leong, Dr. Eikelboom, and Dr. Yusuf have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Calcium-induced autonomic denervation linked to lower post-op AF
Intraoperative injection of calcium chloride into the four major atrial ganglionated plexi (GPs) reduced the incidence of early postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, in a proof-of-concept study.
“[We] hypothesized that injecting [calcium chloride] into the major atrial GPs during isolated CABG can reduce the incidence of POAF by calcium-induced autonomic neurotoxicity,” wrote Huishan Wang, MD, of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command in Shenyang, China, and colleagues. Their report was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The single-center, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept study included 200 patients without a history of AF undergoing isolated, off-pump CABG surgery. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive an injection of either 5% calcium chloride or 0.9% sodium chloride into the four major GPs during CABG.
Post surgery, patients were monitored for the occurrence of POAF using routine 12-lead ECG and 7-day continuous telemetry and Holter monitoring. The primary endpoint was the incidence of POAF lasting 30 seconds or longer through 7 days. Various secondary outcomes, including POAF burden and length of hospitalization, were also measured.
After analysis, the researchers found that 15 patients in the calcium chloride arm and 36 patients in the sodium chloride arm developed POAF during the first 7 days post CABG, corresponding to a POAF hazard reduction of 63% (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.21-0.64; P = .001) with no significant adverse effects observed among study patients.
The calcium chloride injection also resulted in reduced AF burden and lower rates of amiodarone and esmolol use to treat POAF; however, there was no difference in the length of hospitalization between the two groups. The incidences of nonsustained atrial tachyarrhythmia (less than 30 seconds) and atrial couplets were also significantly reduced in the calcium chloride group.
“We selected the 4 major atrial GPs as our targets because [of] their role in the initiation and maintenance of AF is more established than other cardiac neural plexi,” the researchers explained. “Interruption of the atrial neural network by Ca-mediated GP neurotoxicity may underlie the therapeutic effects.”
Is ‘nuisance’ arrhythmia worth targeting?
In an editorial accompanying the report, John H. Alexander, MD, MHS, wrote that intraoperative calcium chloride atrial ganglionic ablation can now be considered as an effective intervention to prevent POAF in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. “These investigators should be congratulated for studying post-operative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery,” he stated.
“However, this trial has two significant limitations. Firstly, it was conducted in a single center in a very homogeneous population; secondly, POAF, in and of itself, is largely a nuisance arrhythmia and hardly worth preventing, but is associated with a higher risk of other adverse outcomes,” Dr. Alexander, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“The unanswered question is whether preventing perioperative AF will prevent stroke, heart failure, and death,” he further explained. “Answering these questions would require a larger trial (or trials) with longer term (months to years) follow-up.”
Dr. Wang and colleagues acknowledged that the current study was underpowered for some secondary outcomes, such as length of hospitalization. They explained that a large sample size is needed to detect a difference in length of hospitalization, as well as other outcomes.
“Further studies are needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of calcium-induced atrial autonomic denervation in patients undergoing on-pump CABG and surgery for valvular heart disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Provincial Key R & D Program in China. One author reported holding a U.S. patent related to the study. The remaining authors had no relevant relationships to disclose.
Intraoperative injection of calcium chloride into the four major atrial ganglionated plexi (GPs) reduced the incidence of early postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, in a proof-of-concept study.
“[We] hypothesized that injecting [calcium chloride] into the major atrial GPs during isolated CABG can reduce the incidence of POAF by calcium-induced autonomic neurotoxicity,” wrote Huishan Wang, MD, of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command in Shenyang, China, and colleagues. Their report was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The single-center, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept study included 200 patients without a history of AF undergoing isolated, off-pump CABG surgery. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive an injection of either 5% calcium chloride or 0.9% sodium chloride into the four major GPs during CABG.
Post surgery, patients were monitored for the occurrence of POAF using routine 12-lead ECG and 7-day continuous telemetry and Holter monitoring. The primary endpoint was the incidence of POAF lasting 30 seconds or longer through 7 days. Various secondary outcomes, including POAF burden and length of hospitalization, were also measured.
After analysis, the researchers found that 15 patients in the calcium chloride arm and 36 patients in the sodium chloride arm developed POAF during the first 7 days post CABG, corresponding to a POAF hazard reduction of 63% (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.21-0.64; P = .001) with no significant adverse effects observed among study patients.
The calcium chloride injection also resulted in reduced AF burden and lower rates of amiodarone and esmolol use to treat POAF; however, there was no difference in the length of hospitalization between the two groups. The incidences of nonsustained atrial tachyarrhythmia (less than 30 seconds) and atrial couplets were also significantly reduced in the calcium chloride group.
“We selected the 4 major atrial GPs as our targets because [of] their role in the initiation and maintenance of AF is more established than other cardiac neural plexi,” the researchers explained. “Interruption of the atrial neural network by Ca-mediated GP neurotoxicity may underlie the therapeutic effects.”
Is ‘nuisance’ arrhythmia worth targeting?
In an editorial accompanying the report, John H. Alexander, MD, MHS, wrote that intraoperative calcium chloride atrial ganglionic ablation can now be considered as an effective intervention to prevent POAF in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. “These investigators should be congratulated for studying post-operative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery,” he stated.
“However, this trial has two significant limitations. Firstly, it was conducted in a single center in a very homogeneous population; secondly, POAF, in and of itself, is largely a nuisance arrhythmia and hardly worth preventing, but is associated with a higher risk of other adverse outcomes,” Dr. Alexander, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“The unanswered question is whether preventing perioperative AF will prevent stroke, heart failure, and death,” he further explained. “Answering these questions would require a larger trial (or trials) with longer term (months to years) follow-up.”
Dr. Wang and colleagues acknowledged that the current study was underpowered for some secondary outcomes, such as length of hospitalization. They explained that a large sample size is needed to detect a difference in length of hospitalization, as well as other outcomes.
“Further studies are needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of calcium-induced atrial autonomic denervation in patients undergoing on-pump CABG and surgery for valvular heart disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Provincial Key R & D Program in China. One author reported holding a U.S. patent related to the study. The remaining authors had no relevant relationships to disclose.
Intraoperative injection of calcium chloride into the four major atrial ganglionated plexi (GPs) reduced the incidence of early postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, in a proof-of-concept study.
“[We] hypothesized that injecting [calcium chloride] into the major atrial GPs during isolated CABG can reduce the incidence of POAF by calcium-induced autonomic neurotoxicity,” wrote Huishan Wang, MD, of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command in Shenyang, China, and colleagues. Their report was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The single-center, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept study included 200 patients without a history of AF undergoing isolated, off-pump CABG surgery. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive an injection of either 5% calcium chloride or 0.9% sodium chloride into the four major GPs during CABG.
Post surgery, patients were monitored for the occurrence of POAF using routine 12-lead ECG and 7-day continuous telemetry and Holter monitoring. The primary endpoint was the incidence of POAF lasting 30 seconds or longer through 7 days. Various secondary outcomes, including POAF burden and length of hospitalization, were also measured.
After analysis, the researchers found that 15 patients in the calcium chloride arm and 36 patients in the sodium chloride arm developed POAF during the first 7 days post CABG, corresponding to a POAF hazard reduction of 63% (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.21-0.64; P = .001) with no significant adverse effects observed among study patients.
The calcium chloride injection also resulted in reduced AF burden and lower rates of amiodarone and esmolol use to treat POAF; however, there was no difference in the length of hospitalization between the two groups. The incidences of nonsustained atrial tachyarrhythmia (less than 30 seconds) and atrial couplets were also significantly reduced in the calcium chloride group.
“We selected the 4 major atrial GPs as our targets because [of] their role in the initiation and maintenance of AF is more established than other cardiac neural plexi,” the researchers explained. “Interruption of the atrial neural network by Ca-mediated GP neurotoxicity may underlie the therapeutic effects.”
Is ‘nuisance’ arrhythmia worth targeting?
In an editorial accompanying the report, John H. Alexander, MD, MHS, wrote that intraoperative calcium chloride atrial ganglionic ablation can now be considered as an effective intervention to prevent POAF in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. “These investigators should be congratulated for studying post-operative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery,” he stated.
“However, this trial has two significant limitations. Firstly, it was conducted in a single center in a very homogeneous population; secondly, POAF, in and of itself, is largely a nuisance arrhythmia and hardly worth preventing, but is associated with a higher risk of other adverse outcomes,” Dr. Alexander, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“The unanswered question is whether preventing perioperative AF will prevent stroke, heart failure, and death,” he further explained. “Answering these questions would require a larger trial (or trials) with longer term (months to years) follow-up.”
Dr. Wang and colleagues acknowledged that the current study was underpowered for some secondary outcomes, such as length of hospitalization. They explained that a large sample size is needed to detect a difference in length of hospitalization, as well as other outcomes.
“Further studies are needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of calcium-induced atrial autonomic denervation in patients undergoing on-pump CABG and surgery for valvular heart disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Provincial Key R & D Program in China. One author reported holding a U.S. patent related to the study. The remaining authors had no relevant relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Left atrial appendage occlusion, DOAC comparable for AFib
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) for high-risk atrial fibrillation seems to prevent stroke as well as direct oral anticoagulation (DOAC) with a lower risk of major bleeding, according to results of a European study.
And although some experts question the strength of the conclusions, a lead researcher contends the study may provide enough support for interventional cardiologists to consider LAAO in selected patients until randomized clinical trials yield stronger evidence.
“The results suggest LAAO to be superior to DOAC in AF patients who have a predicted high risk of stroke and bleeding and adds to the evidence that LAAO is a promising stroke prevention strategy in selected AF patients,” said lead investigator Jens Erik Nielsen-Kudsk, MD, DMSc, a cardiologist at Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk and colleagues wrote in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions that this is the largest comparative study of LAAO vs. DOAC to date, but they also acknowledged the study limitations: its observational design, unaccounted confounders, potential selection bias, and disparities in the nature of the comparative datasets (a multination cohort vs. a single national registry).
Observational registry study shows 43% reduction in primary outcome
The study compared outcomes of 1,078 patients from the Amulet Observational Study who had LAAO during June 2015–September 2016 with 1,184 patients on DOAC therapy selected by propensity score matching from two Danish national registries. The LAAO population was prospectively enrolled at 61 centers in 17 countries. The study population had a high risk of stroke and bleeding; about one-third had a previous stroke and about three-quarters had a prior bleeding episode. The average age was 75 years.
The LAAO group had almost half the rate of the primary outcome – either stroke, major bleeding, or all-cause death – 256 vs. 461 events in the DOAC group with median follow-up of 2 years. The annualized event rate was significantly lower for the LAAO group: 14.5 vs. 25.7 per 100 patient years in the DOAC group. The researchers calculated the LAAO group had a relative 43% reduction risk.
Of the LAAO group, 155 patients (14.5%) died in the follow-up period, 35% of them from a cardiovascular cause, whereas 308 (26%) of patients in the DOAC group died, with a similar percentage, 36%, from a cardiovascular cause.
Using data from the Danish Cause of Death Registry, the study determined cause of death in the DOAC patients on a more granular level: 9.5% of the deaths were from vascular disease and 4.5% from stroke (the remainder in both groups were from noncardiovascular events).
Stroke incidence was similar between the two groups: 39 in the LAAO group vs. 37 in DOAC patients, conferring an 11% greater risk in the former. The risk of major bleeding and all-cause mortality were significantly lower in LAAO patients, 37% and 47%, respectively. However, 50% of DOAC patients had discontinued therapy after a year of follow-up, and 58% had done so after 2 years.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk noted that the findings line up with those from the smaller PRAQUE-17 study comparing LAAO and DOAC. He added that his group is participating in two larger RCTs, CATALYST and CHAMPION-AF, evaluating LAAO and medical therapy in about 6,000 patients combined.
“It will take at least 2 to 5 years before we have data from these randomized LAAO trials,” Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk said. “Meanwhile, based on data from three prior randomized clinical trials, propensity-score matched studies and data from large registries, LAAO should be considered in clinical practice for patients who have a high risk of bleeding or who for any other reason are unsuitable for long-term DOAC treatment.”
Noncompliance to DOAC therapy a concern
In an invited commentary, Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, of the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., wrote, “These findings provide reassuring evidence supporting the efficacy of LAAO despite the remaining challenges with this therapy.”
However, Dr. Alkhouli pointed out that the high rate of noncompliance among AF patients on DOAC can be a confounding factor for interpreting the efficacy of therapy. “This highlights the challenges of comparing LAAO to DOAC, considering that many patients are actually not on effective anticoagulation, but also suggests a possible real important role for LAAO in addressing the unmet need in stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
“The study showed a very good safety profile for LAAO,” Dr. Alkhouli added. “However, we should remember that this was an observational study without routine temporal imaging and a relatively short-term follow- up.”
Methods ‘severely flawed’
John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist at Baptist Health in Louisville, Ky., said the study methodology was “severely flawed,” citing its nonrandomized nature and enrollment of only patients with successful implants in the LAAO group. “You have to take all patients who had attempted implants,” he said. Further, the study may be subject to selection bias based on how patients were recruited for the Ampulet Observational Study.
“Comparing LAAO to DOAC is a vital clinical question,” said Dr. Mandrola. “It simply cannot be answered with observational methods like this. It requires a properly powered RCT.”
Dr. Alkhouli said he’s looking forward to results from five large RCTS evaluating LAAO due in 3-5 years. “Until the results of those trials are out, careful patient selection and shared decision-making should continue to govern the rational dissipation of LAAO as a stroke prevention strategy,” he said.
Novo Nordisk Research Foundation supported the study and Abbott provided a grant. Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk disclosed financial relationships with Abbott and Boston Scientific. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Bayer Vital, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Medtronic, Pfizer, Portolo, and Sanofi.
Dr. Alkhouli disclosed a relationship with Boston Scientific. Dr. Mandrola has no relevant disclosures. He is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) for high-risk atrial fibrillation seems to prevent stroke as well as direct oral anticoagulation (DOAC) with a lower risk of major bleeding, according to results of a European study.
And although some experts question the strength of the conclusions, a lead researcher contends the study may provide enough support for interventional cardiologists to consider LAAO in selected patients until randomized clinical trials yield stronger evidence.
“The results suggest LAAO to be superior to DOAC in AF patients who have a predicted high risk of stroke and bleeding and adds to the evidence that LAAO is a promising stroke prevention strategy in selected AF patients,” said lead investigator Jens Erik Nielsen-Kudsk, MD, DMSc, a cardiologist at Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk and colleagues wrote in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions that this is the largest comparative study of LAAO vs. DOAC to date, but they also acknowledged the study limitations: its observational design, unaccounted confounders, potential selection bias, and disparities in the nature of the comparative datasets (a multination cohort vs. a single national registry).
Observational registry study shows 43% reduction in primary outcome
The study compared outcomes of 1,078 patients from the Amulet Observational Study who had LAAO during June 2015–September 2016 with 1,184 patients on DOAC therapy selected by propensity score matching from two Danish national registries. The LAAO population was prospectively enrolled at 61 centers in 17 countries. The study population had a high risk of stroke and bleeding; about one-third had a previous stroke and about three-quarters had a prior bleeding episode. The average age was 75 years.
The LAAO group had almost half the rate of the primary outcome – either stroke, major bleeding, or all-cause death – 256 vs. 461 events in the DOAC group with median follow-up of 2 years. The annualized event rate was significantly lower for the LAAO group: 14.5 vs. 25.7 per 100 patient years in the DOAC group. The researchers calculated the LAAO group had a relative 43% reduction risk.
Of the LAAO group, 155 patients (14.5%) died in the follow-up period, 35% of them from a cardiovascular cause, whereas 308 (26%) of patients in the DOAC group died, with a similar percentage, 36%, from a cardiovascular cause.
Using data from the Danish Cause of Death Registry, the study determined cause of death in the DOAC patients on a more granular level: 9.5% of the deaths were from vascular disease and 4.5% from stroke (the remainder in both groups were from noncardiovascular events).
Stroke incidence was similar between the two groups: 39 in the LAAO group vs. 37 in DOAC patients, conferring an 11% greater risk in the former. The risk of major bleeding and all-cause mortality were significantly lower in LAAO patients, 37% and 47%, respectively. However, 50% of DOAC patients had discontinued therapy after a year of follow-up, and 58% had done so after 2 years.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk noted that the findings line up with those from the smaller PRAQUE-17 study comparing LAAO and DOAC. He added that his group is participating in two larger RCTs, CATALYST and CHAMPION-AF, evaluating LAAO and medical therapy in about 6,000 patients combined.
“It will take at least 2 to 5 years before we have data from these randomized LAAO trials,” Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk said. “Meanwhile, based on data from three prior randomized clinical trials, propensity-score matched studies and data from large registries, LAAO should be considered in clinical practice for patients who have a high risk of bleeding or who for any other reason are unsuitable for long-term DOAC treatment.”
Noncompliance to DOAC therapy a concern
In an invited commentary, Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, of the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., wrote, “These findings provide reassuring evidence supporting the efficacy of LAAO despite the remaining challenges with this therapy.”
However, Dr. Alkhouli pointed out that the high rate of noncompliance among AF patients on DOAC can be a confounding factor for interpreting the efficacy of therapy. “This highlights the challenges of comparing LAAO to DOAC, considering that many patients are actually not on effective anticoagulation, but also suggests a possible real important role for LAAO in addressing the unmet need in stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
“The study showed a very good safety profile for LAAO,” Dr. Alkhouli added. “However, we should remember that this was an observational study without routine temporal imaging and a relatively short-term follow- up.”
Methods ‘severely flawed’
John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist at Baptist Health in Louisville, Ky., said the study methodology was “severely flawed,” citing its nonrandomized nature and enrollment of only patients with successful implants in the LAAO group. “You have to take all patients who had attempted implants,” he said. Further, the study may be subject to selection bias based on how patients were recruited for the Ampulet Observational Study.
“Comparing LAAO to DOAC is a vital clinical question,” said Dr. Mandrola. “It simply cannot be answered with observational methods like this. It requires a properly powered RCT.”
Dr. Alkhouli said he’s looking forward to results from five large RCTS evaluating LAAO due in 3-5 years. “Until the results of those trials are out, careful patient selection and shared decision-making should continue to govern the rational dissipation of LAAO as a stroke prevention strategy,” he said.
Novo Nordisk Research Foundation supported the study and Abbott provided a grant. Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk disclosed financial relationships with Abbott and Boston Scientific. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Bayer Vital, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Medtronic, Pfizer, Portolo, and Sanofi.
Dr. Alkhouli disclosed a relationship with Boston Scientific. Dr. Mandrola has no relevant disclosures. He is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) for high-risk atrial fibrillation seems to prevent stroke as well as direct oral anticoagulation (DOAC) with a lower risk of major bleeding, according to results of a European study.
And although some experts question the strength of the conclusions, a lead researcher contends the study may provide enough support for interventional cardiologists to consider LAAO in selected patients until randomized clinical trials yield stronger evidence.
“The results suggest LAAO to be superior to DOAC in AF patients who have a predicted high risk of stroke and bleeding and adds to the evidence that LAAO is a promising stroke prevention strategy in selected AF patients,” said lead investigator Jens Erik Nielsen-Kudsk, MD, DMSc, a cardiologist at Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk and colleagues wrote in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions that this is the largest comparative study of LAAO vs. DOAC to date, but they also acknowledged the study limitations: its observational design, unaccounted confounders, potential selection bias, and disparities in the nature of the comparative datasets (a multination cohort vs. a single national registry).
Observational registry study shows 43% reduction in primary outcome
The study compared outcomes of 1,078 patients from the Amulet Observational Study who had LAAO during June 2015–September 2016 with 1,184 patients on DOAC therapy selected by propensity score matching from two Danish national registries. The LAAO population was prospectively enrolled at 61 centers in 17 countries. The study population had a high risk of stroke and bleeding; about one-third had a previous stroke and about three-quarters had a prior bleeding episode. The average age was 75 years.
The LAAO group had almost half the rate of the primary outcome – either stroke, major bleeding, or all-cause death – 256 vs. 461 events in the DOAC group with median follow-up of 2 years. The annualized event rate was significantly lower for the LAAO group: 14.5 vs. 25.7 per 100 patient years in the DOAC group. The researchers calculated the LAAO group had a relative 43% reduction risk.
Of the LAAO group, 155 patients (14.5%) died in the follow-up period, 35% of them from a cardiovascular cause, whereas 308 (26%) of patients in the DOAC group died, with a similar percentage, 36%, from a cardiovascular cause.
Using data from the Danish Cause of Death Registry, the study determined cause of death in the DOAC patients on a more granular level: 9.5% of the deaths were from vascular disease and 4.5% from stroke (the remainder in both groups were from noncardiovascular events).
Stroke incidence was similar between the two groups: 39 in the LAAO group vs. 37 in DOAC patients, conferring an 11% greater risk in the former. The risk of major bleeding and all-cause mortality were significantly lower in LAAO patients, 37% and 47%, respectively. However, 50% of DOAC patients had discontinued therapy after a year of follow-up, and 58% had done so after 2 years.
Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk noted that the findings line up with those from the smaller PRAQUE-17 study comparing LAAO and DOAC. He added that his group is participating in two larger RCTs, CATALYST and CHAMPION-AF, evaluating LAAO and medical therapy in about 6,000 patients combined.
“It will take at least 2 to 5 years before we have data from these randomized LAAO trials,” Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk said. “Meanwhile, based on data from three prior randomized clinical trials, propensity-score matched studies and data from large registries, LAAO should be considered in clinical practice for patients who have a high risk of bleeding or who for any other reason are unsuitable for long-term DOAC treatment.”
Noncompliance to DOAC therapy a concern
In an invited commentary, Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, of the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., wrote, “These findings provide reassuring evidence supporting the efficacy of LAAO despite the remaining challenges with this therapy.”
However, Dr. Alkhouli pointed out that the high rate of noncompliance among AF patients on DOAC can be a confounding factor for interpreting the efficacy of therapy. “This highlights the challenges of comparing LAAO to DOAC, considering that many patients are actually not on effective anticoagulation, but also suggests a possible real important role for LAAO in addressing the unmet need in stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
“The study showed a very good safety profile for LAAO,” Dr. Alkhouli added. “However, we should remember that this was an observational study without routine temporal imaging and a relatively short-term follow- up.”
Methods ‘severely flawed’
John Mandrola, MD, an electrophysiologist at Baptist Health in Louisville, Ky., said the study methodology was “severely flawed,” citing its nonrandomized nature and enrollment of only patients with successful implants in the LAAO group. “You have to take all patients who had attempted implants,” he said. Further, the study may be subject to selection bias based on how patients were recruited for the Ampulet Observational Study.
“Comparing LAAO to DOAC is a vital clinical question,” said Dr. Mandrola. “It simply cannot be answered with observational methods like this. It requires a properly powered RCT.”
Dr. Alkhouli said he’s looking forward to results from five large RCTS evaluating LAAO due in 3-5 years. “Until the results of those trials are out, careful patient selection and shared decision-making should continue to govern the rational dissipation of LAAO as a stroke prevention strategy,” he said.
Novo Nordisk Research Foundation supported the study and Abbott provided a grant. Dr. Nielsen-Kudsk disclosed financial relationships with Abbott and Boston Scientific. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, Bayer Vital, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Medtronic, Pfizer, Portolo, and Sanofi.
Dr. Alkhouli disclosed a relationship with Boston Scientific. Dr. Mandrola has no relevant disclosures. He is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
FROM JACC CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTION
ACC/AHA update two atrial fibrillation performance measures
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 and risk of clotting: ‘Be proactive about prevention’
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.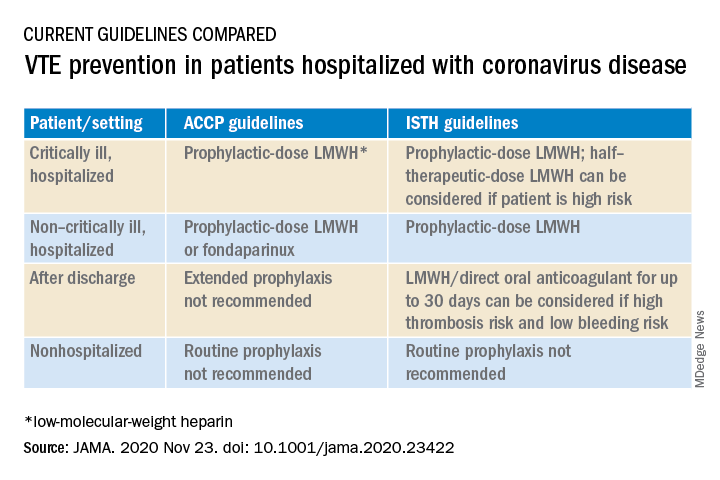
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of arterial and venous thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 has been a major issue throughout the pandemic, and how best to manage this risk is the subject of a new review article.
The article, by Gregory Dr. Piazza, MD, and David A. Morrow, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online in JAMA on Nov. 23.
“Basically we’re saying: ‘Be proactive about prevention,’” Dr. Piazza told this news organization.
There is growing recognition among those on the frontline that there is an increased risk of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients, Dr. Piazza said. The risk is highest in patients in the intensive care unit, but the risk is also increased in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, even those not in ICU.
“We don’t really know what the risk is in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but we think it’s much lower than in those who are hospitalized,” he said. “We are waiting for data on the optimal way of managing this increased risk of thrombosis in COVID patients, but for the time being, we believe a systematic way of addressing this risk is best, with every patient hospitalized with COVID-19 receiving some type of thromboprophylaxis. This would mainly be with anticoagulation, but in patients in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated, then mechanical methods could be used, such as pneumatic compression boots or compression stockings.”
The authors report thrombotic complication rates of 2.6% in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 35.3% in critically ill patients from a recent U.S. registry study.
Autopsy findings of microthrombi in multiple organ systems, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys, suggest that thrombosis may contribute to multisystem organ dysfunction in severe COVID-19, they note. Although the pathophysiology is not fully defined, prothrombotic abnormalities have been identified in patients with COVID-19, including elevated levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and factor VIII, they add.
“There are several major questions about which COVID-19 patients to treat with thromboprophylaxis, how to treat them in term of levels of anticoagulation, and there are many ongoing clinical trials to try and answer these questions,” Dr. Piazza commented. “We need results from these randomized trials to provide a better compass for COVID-19 patients at risk of clotting.”
At present, clinicians can follow two different sets of guidelines on the issue, one from the American College of Chest Physicians and the other from the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, the authors note.
“The ACCP guidelines are very conservative and basically follow the evidence base for medical patients, while the ISTH guidelines are more aggressive and recommend increased levels of anticoagulation in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients and also extend prophylaxis after discharge,” Dr. Piazza said.
“There is quite a difference between the two sets of guidelines, which can be a point of confusion,” he added.
Dr. Piazza notes that at his center every hospitalized COVID patient who does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation receives a standard prophylactic dose of a once-daily low-molecular-weight heparin (for example, enoxaparin 40 mg). A once-daily product is used to minimize infection risk to staff.
While all COVID patients in the ICU should automatically receive some anticoagulation, the optimal dose is an area of active investigation, he explained. “There were several early reports of ICU patients developing blood clots despite receiving standard thromboprophylaxis so perhaps we need to use higher doses. There are trials underway looking at this, and we would advise enrolling patients into these trials.”
If patients can’t be enrolled into trials, and clinicians feel higher anticoagulation levels are needed, Dr. Piazza advises following the ISTH guidance, which allows an intermediate dose of low-molecular-weight heparin (up to 1 mg/kg enoxaparin).
“Some experts are suggesting even higher doses may be needed in some ICU patients, such as the full therapeutic dose, but I worry about the risk of bleeding with such a strategy,” he said.
Dr. Piazza says they do not routinely give anticoagulation after discharge, but if this is desired then patients could be switched to an oral agent, and some of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants are approved for prophylactic use in medically ill patients.
Dr. Piazza points out that whether thromboprophylaxis should be used for nonhospitalized COVID patients who have risk factors for clotting such as a prior history of thrombosis or obesity is a pressing question, and he encourages clinicians to enroll these patients in clinical trials evaluating this issue, such as the PREVENT-HD trial.
“If they can’t enroll patents in a trial, then they have to make a decision whether the patient is high-enough risk to justify off-label use of anticoagulant. There is a case to be made for this, but there is no evidence for or against such action at present,” he noted.
At this time, neither the ISTH nor ACCP recommend measuring D-dimer to screen for venous thromboembolism or to determine intensity of prophylaxis or treatment, the authors note.
“Ongoing investigation will determine optimal preventive regimens in COVID-19 in the intensive care unit, at hospital discharge, and in nonhospitalized patients at high risk for thrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Piazza reported grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Janssen, and Portola, and personal fees from Agile, Amgen, Pfizer, and the Prairie Education and Research Cooperative outside the submitted work. Dr. Morrow reported grants from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, and The Medicines Company; grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics; and personal fees from Bayer Pharma and InCarda outside the submitted work.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac arrest in COVID-19 pandemic: ‘Survival is possible’
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2020
New-onset AFib common but unrecognized in the month after cardiac surgery
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
FROM AHA 2020
Omega-3 caps, vitamin D both fail for atrial fib primary prevention: VITAL-Rhythm
Clinical trials of omega-3 fatty acid or vitamin D supplements have followed a long and winding road in search of benefits in cardiovascular (CV) disease, with wildly mixed results. But the journey may be in vain in one of cardiology’s frontier research areas, primary prevention of atrial fibrillation (AF), suggest primary results of the VITAL-Rhythm trial, presented Nov. 13 during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 virtual meeting.
Neither marine-oil caps nor the vitamin D3 supplements made a difference to risk for incident AF, whether paroxysmal or persistent, over more than 5 years in the study, with more than 25,000 adults in the community. Nor did they seem to cause harm.
“To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale, long-term, randomized placebo-controlled trial to test the effect of any intervention on incident AF,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, said at a media briefing on VITAL-Rhythm before her formal presentation of the trial during the conference.
Its findings, she said, don’t support the use of marine-oil caps or vitamin D3 for primary prevention of incident AF. “Fortunately, they also do not show any increased risk in atrial fibrillation for patients who are using these supplements for other indications.”
Both agents are widely taken without physician supervision for their perceived benefits, and marine-oil caps in particular – often in special prescription formulations – may be used for reducing elevated triglyceride levels and, based on the results of REDUCE-IT, cutting cardiovascular risk.
“It’s pretty clear that there’s no evidence to suggest that either of these supplements is helpful for preventing atrial fibrillation. And I think that’s clear from the evidence these investigators presented,” said Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., who wasn’t part of the study.
“It’s also a little disappointing because atrial fibrillation is such a huge problem, and the inability to identify preventative strategies is a repeated theme,” he said in an interview.
VITAL-Rhythm is an ancillary study within the VITAL trial, which showed no benefit from either supplement regarding risk for incident cancer or CV events, as reported at the AHA sessions 2 years ago. In fact, their effects seem sweepingly negative throughout the trial; in another ancillary study, VITAL-DKD, neither supplement helped preserve renal function over 5 years in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The participants started VITAL without a history of AF, CV disease, or cancer; they were randomly assigned to take about a gram of omega-3 fatty acids, 2000 IU vitamin D3 daily, or their placebos, in a double randomization.
VITAL and its ancillary studies collectively undercut mechanistic theories about how omega-3 fatty acid and vitamin D supplements may affect AF risk, ideas derived from epidemiologic and dietary studies. They were thought perhaps “to have direct antiarrhythmic effects on myocytes through effects on ion channels, electrical remodeling, electrical stabilizing effects, and fluidity of the cell membranes,” observed Renate B. Schnabel, MD, MSc, University Heart Center, Hamburg, Germany, at the briefing. Or such effects might be related to beneficial effects on atherosclerosis, inflammation, or ischemic heart disease, she noted.
Neither idea is likely after VITAL and VITAL-Rhythm, said Dr. Schnabel, who spoke as an invited discussant after Albert’s formal presentation at AHA 2020.
That omega-3 fatty acid supplements may not improve AF incidence or risks has also been evident from many clinical trials and observational studies. Several, including REDUCE-IT, included some evidence for increasing risk for AF with marine-oil supplement intake. That may have happened in VITAL-Rhythm as well.
“While there was no evidence that the omega-3 three fatty acids prevented atrial fibrillation, there was a signal of perhaps more atrial fibrillation in the omega-3 fatty-acids group,” said Dr. Piccini, who directs his center’s electrophysiology clinical trials program.
A sensitivity analysis limited to participants who adhered to their assigned regimens, as opposed to the main intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, showed a nonsignificant 13% increased hazard ratio for incident AF for the marine-oil supplement group. It reached a P value of .09, which can be interpreted as a trend.
“There are a few studies that have now showed a trend or an increased incidence of arrhythmia in patients treated with omega-3 fatty acids,” Dr. Piccini noted. “I don’t think it’s definitive, but it’s certainly something to keep an eye on.”
VITAL-Rhythm included an electrocardiography (ECG) substudy, yet to be reported, that should yield more insights about any such effects of marine-oil or vitamin D supplements in the trial, Dr. Albert said at the briefing.
The ancillary study assigned its 25,119 patients (mean age, 67 years; 51% women) to take vitamin D3 at 2000 IU/day, marine-oil supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids at 840 mg per day – 460 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) plus 380 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Pronova BioPharma) – or their placebos in a 2 x 2 randomization.
Incident cases of AF were identified through annual questionnaires in which the participants self-reported whether they had received a physician diagnosis of the arrhythmia, supplemented by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data for AF hospital and clinical visits. Those led to a review of inpatient and outpatient records, from which AF events were adjudicated by an endpoint committee.
An electrocardiogram (72.9%) or physician’s report (27.1%) confirmed the AF diagnosis as the protocol required.
By those standards, 900 incident cases were identified, for a rate of 3.6% over a median of 5.3 years. They were paroxysmal in 58.4%, persistent in 38.4%, and indeterminant in 3.1%, Dr. Albert reported.
Of the 12,542 patients assigned to marine-oil caps by ITT, 469 (3.74%) developed incident AF in the ITT analysis, compared to 431 of 12,577 (3.43%) who received placebo, for an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.24; P = .19).
The results were similar in two sensitivity analyses, one of which omitted patients with AF who may have had symptoms before randomization and another excluding those whose incident AF was identified solely in CMS data. But in the third “on treatment” sensitivity analysis, the HR for events was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.98-1.30; P = .09).
Outcomes for the vitamin D randomization were nearly the same, for an HR of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.25; P = .19) by ITT; the results were similar in all three sensitivity analyses.
“It’s not a tremendous signal of risk,” said Piccini of the marine-oil on-treatment analysis. But it, along with consistent evidence from other studies, does give him pause. “If a patient came to me and said,
Doctor, I want to take omega-3 fish oil, because I want to reduce my risk of events, as an arrhythmia doctor I would say, ‘We don’t have great evidence to do that for preventing atrial fibrillation. And there’s actually some evidence that it could mildly increase your risk of developing it.’ ”
For those prescribed evidence-based marine-oil therapy for other indications, he said, “I think the take-home message certainly is, if they report palpitations or other signs or symptoms that could be due to atrial fibrillation, we should be aggressive about screening for atrial fibrillation,” and making the diagnosis as appropriate. If the incident AF resolves after stopping the treatment, “maybe it’s reasonable to refrain from prescribing the medication for that patient.”
VITAL-Rhythm and VITAL are supported by multiple grants from the National Institutes of Health. Albert discloses receiving grant support from St. Jude Medical, Abbott, and Roche. Schnabel reports receiving honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Piccini previously disclosed receiving research grants from Abbott, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serving as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, Sanofi, Philips, and UptoDate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials of omega-3 fatty acid or vitamin D supplements have followed a long and winding road in search of benefits in cardiovascular (CV) disease, with wildly mixed results. But the journey may be in vain in one of cardiology’s frontier research areas, primary prevention of atrial fibrillation (AF), suggest primary results of the VITAL-Rhythm trial, presented Nov. 13 during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 virtual meeting.
Neither marine-oil caps nor the vitamin D3 supplements made a difference to risk for incident AF, whether paroxysmal or persistent, over more than 5 years in the study, with more than 25,000 adults in the community. Nor did they seem to cause harm.
“To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale, long-term, randomized placebo-controlled trial to test the effect of any intervention on incident AF,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, said at a media briefing on VITAL-Rhythm before her formal presentation of the trial during the conference.
Its findings, she said, don’t support the use of marine-oil caps or vitamin D3 for primary prevention of incident AF. “Fortunately, they also do not show any increased risk in atrial fibrillation for patients who are using these supplements for other indications.”
Both agents are widely taken without physician supervision for their perceived benefits, and marine-oil caps in particular – often in special prescription formulations – may be used for reducing elevated triglyceride levels and, based on the results of REDUCE-IT, cutting cardiovascular risk.
“It’s pretty clear that there’s no evidence to suggest that either of these supplements is helpful for preventing atrial fibrillation. And I think that’s clear from the evidence these investigators presented,” said Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., who wasn’t part of the study.
“It’s also a little disappointing because atrial fibrillation is such a huge problem, and the inability to identify preventative strategies is a repeated theme,” he said in an interview.
VITAL-Rhythm is an ancillary study within the VITAL trial, which showed no benefit from either supplement regarding risk for incident cancer or CV events, as reported at the AHA sessions 2 years ago. In fact, their effects seem sweepingly negative throughout the trial; in another ancillary study, VITAL-DKD, neither supplement helped preserve renal function over 5 years in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The participants started VITAL without a history of AF, CV disease, or cancer; they were randomly assigned to take about a gram of omega-3 fatty acids, 2000 IU vitamin D3 daily, or their placebos, in a double randomization.
VITAL and its ancillary studies collectively undercut mechanistic theories about how omega-3 fatty acid and vitamin D supplements may affect AF risk, ideas derived from epidemiologic and dietary studies. They were thought perhaps “to have direct antiarrhythmic effects on myocytes through effects on ion channels, electrical remodeling, electrical stabilizing effects, and fluidity of the cell membranes,” observed Renate B. Schnabel, MD, MSc, University Heart Center, Hamburg, Germany, at the briefing. Or such effects might be related to beneficial effects on atherosclerosis, inflammation, or ischemic heart disease, she noted.
Neither idea is likely after VITAL and VITAL-Rhythm, said Dr. Schnabel, who spoke as an invited discussant after Albert’s formal presentation at AHA 2020.
That omega-3 fatty acid supplements may not improve AF incidence or risks has also been evident from many clinical trials and observational studies. Several, including REDUCE-IT, included some evidence for increasing risk for AF with marine-oil supplement intake. That may have happened in VITAL-Rhythm as well.
“While there was no evidence that the omega-3 three fatty acids prevented atrial fibrillation, there was a signal of perhaps more atrial fibrillation in the omega-3 fatty-acids group,” said Dr. Piccini, who directs his center’s electrophysiology clinical trials program.
A sensitivity analysis limited to participants who adhered to their assigned regimens, as opposed to the main intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, showed a nonsignificant 13% increased hazard ratio for incident AF for the marine-oil supplement group. It reached a P value of .09, which can be interpreted as a trend.
“There are a few studies that have now showed a trend or an increased incidence of arrhythmia in patients treated with omega-3 fatty acids,” Dr. Piccini noted. “I don’t think it’s definitive, but it’s certainly something to keep an eye on.”
VITAL-Rhythm included an electrocardiography (ECG) substudy, yet to be reported, that should yield more insights about any such effects of marine-oil or vitamin D supplements in the trial, Dr. Albert said at the briefing.
The ancillary study assigned its 25,119 patients (mean age, 67 years; 51% women) to take vitamin D3 at 2000 IU/day, marine-oil supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids at 840 mg per day – 460 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) plus 380 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Pronova BioPharma) – or their placebos in a 2 x 2 randomization.
Incident cases of AF were identified through annual questionnaires in which the participants self-reported whether they had received a physician diagnosis of the arrhythmia, supplemented by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data for AF hospital and clinical visits. Those led to a review of inpatient and outpatient records, from which AF events were adjudicated by an endpoint committee.
An electrocardiogram (72.9%) or physician’s report (27.1%) confirmed the AF diagnosis as the protocol required.
By those standards, 900 incident cases were identified, for a rate of 3.6% over a median of 5.3 years. They were paroxysmal in 58.4%, persistent in 38.4%, and indeterminant in 3.1%, Dr. Albert reported.
Of the 12,542 patients assigned to marine-oil caps by ITT, 469 (3.74%) developed incident AF in the ITT analysis, compared to 431 of 12,577 (3.43%) who received placebo, for an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.24; P = .19).
The results were similar in two sensitivity analyses, one of which omitted patients with AF who may have had symptoms before randomization and another excluding those whose incident AF was identified solely in CMS data. But in the third “on treatment” sensitivity analysis, the HR for events was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.98-1.30; P = .09).
Outcomes for the vitamin D randomization were nearly the same, for an HR of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.25; P = .19) by ITT; the results were similar in all three sensitivity analyses.
“It’s not a tremendous signal of risk,” said Piccini of the marine-oil on-treatment analysis. But it, along with consistent evidence from other studies, does give him pause. “If a patient came to me and said,
Doctor, I want to take omega-3 fish oil, because I want to reduce my risk of events, as an arrhythmia doctor I would say, ‘We don’t have great evidence to do that for preventing atrial fibrillation. And there’s actually some evidence that it could mildly increase your risk of developing it.’ ”
For those prescribed evidence-based marine-oil therapy for other indications, he said, “I think the take-home message certainly is, if they report palpitations or other signs or symptoms that could be due to atrial fibrillation, we should be aggressive about screening for atrial fibrillation,” and making the diagnosis as appropriate. If the incident AF resolves after stopping the treatment, “maybe it’s reasonable to refrain from prescribing the medication for that patient.”
VITAL-Rhythm and VITAL are supported by multiple grants from the National Institutes of Health. Albert discloses receiving grant support from St. Jude Medical, Abbott, and Roche. Schnabel reports receiving honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Piccini previously disclosed receiving research grants from Abbott, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serving as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, Sanofi, Philips, and UptoDate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials of omega-3 fatty acid or vitamin D supplements have followed a long and winding road in search of benefits in cardiovascular (CV) disease, with wildly mixed results. But the journey may be in vain in one of cardiology’s frontier research areas, primary prevention of atrial fibrillation (AF), suggest primary results of the VITAL-Rhythm trial, presented Nov. 13 during the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 virtual meeting.
Neither marine-oil caps nor the vitamin D3 supplements made a difference to risk for incident AF, whether paroxysmal or persistent, over more than 5 years in the study, with more than 25,000 adults in the community. Nor did they seem to cause harm.
“To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale, long-term, randomized placebo-controlled trial to test the effect of any intervention on incident AF,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, said at a media briefing on VITAL-Rhythm before her formal presentation of the trial during the conference.
Its findings, she said, don’t support the use of marine-oil caps or vitamin D3 for primary prevention of incident AF. “Fortunately, they also do not show any increased risk in atrial fibrillation for patients who are using these supplements for other indications.”
Both agents are widely taken without physician supervision for their perceived benefits, and marine-oil caps in particular – often in special prescription formulations – may be used for reducing elevated triglyceride levels and, based on the results of REDUCE-IT, cutting cardiovascular risk.
“It’s pretty clear that there’s no evidence to suggest that either of these supplements is helpful for preventing atrial fibrillation. And I think that’s clear from the evidence these investigators presented,” said Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., who wasn’t part of the study.
“It’s also a little disappointing because atrial fibrillation is such a huge problem, and the inability to identify preventative strategies is a repeated theme,” he said in an interview.
VITAL-Rhythm is an ancillary study within the VITAL trial, which showed no benefit from either supplement regarding risk for incident cancer or CV events, as reported at the AHA sessions 2 years ago. In fact, their effects seem sweepingly negative throughout the trial; in another ancillary study, VITAL-DKD, neither supplement helped preserve renal function over 5 years in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The participants started VITAL without a history of AF, CV disease, or cancer; they were randomly assigned to take about a gram of omega-3 fatty acids, 2000 IU vitamin D3 daily, or their placebos, in a double randomization.
VITAL and its ancillary studies collectively undercut mechanistic theories about how omega-3 fatty acid and vitamin D supplements may affect AF risk, ideas derived from epidemiologic and dietary studies. They were thought perhaps “to have direct antiarrhythmic effects on myocytes through effects on ion channels, electrical remodeling, electrical stabilizing effects, and fluidity of the cell membranes,” observed Renate B. Schnabel, MD, MSc, University Heart Center, Hamburg, Germany, at the briefing. Or such effects might be related to beneficial effects on atherosclerosis, inflammation, or ischemic heart disease, she noted.
Neither idea is likely after VITAL and VITAL-Rhythm, said Dr. Schnabel, who spoke as an invited discussant after Albert’s formal presentation at AHA 2020.
That omega-3 fatty acid supplements may not improve AF incidence or risks has also been evident from many clinical trials and observational studies. Several, including REDUCE-IT, included some evidence for increasing risk for AF with marine-oil supplement intake. That may have happened in VITAL-Rhythm as well.
“While there was no evidence that the omega-3 three fatty acids prevented atrial fibrillation, there was a signal of perhaps more atrial fibrillation in the omega-3 fatty-acids group,” said Dr. Piccini, who directs his center’s electrophysiology clinical trials program.
A sensitivity analysis limited to participants who adhered to their assigned regimens, as opposed to the main intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, showed a nonsignificant 13% increased hazard ratio for incident AF for the marine-oil supplement group. It reached a P value of .09, which can be interpreted as a trend.
“There are a few studies that have now showed a trend or an increased incidence of arrhythmia in patients treated with omega-3 fatty acids,” Dr. Piccini noted. “I don’t think it’s definitive, but it’s certainly something to keep an eye on.”
VITAL-Rhythm included an electrocardiography (ECG) substudy, yet to be reported, that should yield more insights about any such effects of marine-oil or vitamin D supplements in the trial, Dr. Albert said at the briefing.
The ancillary study assigned its 25,119 patients (mean age, 67 years; 51% women) to take vitamin D3 at 2000 IU/day, marine-oil supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids at 840 mg per day – 460 mg eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) plus 380 mg docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Pronova BioPharma) – or their placebos in a 2 x 2 randomization.
Incident cases of AF were identified through annual questionnaires in which the participants self-reported whether they had received a physician diagnosis of the arrhythmia, supplemented by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services claims data for AF hospital and clinical visits. Those led to a review of inpatient and outpatient records, from which AF events were adjudicated by an endpoint committee.
An electrocardiogram (72.9%) or physician’s report (27.1%) confirmed the AF diagnosis as the protocol required.
By those standards, 900 incident cases were identified, for a rate of 3.6% over a median of 5.3 years. They were paroxysmal in 58.4%, persistent in 38.4%, and indeterminant in 3.1%, Dr. Albert reported.
Of the 12,542 patients assigned to marine-oil caps by ITT, 469 (3.74%) developed incident AF in the ITT analysis, compared to 431 of 12,577 (3.43%) who received placebo, for an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.24; P = .19).
The results were similar in two sensitivity analyses, one of which omitted patients with AF who may have had symptoms before randomization and another excluding those whose incident AF was identified solely in CMS data. But in the third “on treatment” sensitivity analysis, the HR for events was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.98-1.30; P = .09).
Outcomes for the vitamin D randomization were nearly the same, for an HR of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.96-1.25; P = .19) by ITT; the results were similar in all three sensitivity analyses.
“It’s not a tremendous signal of risk,” said Piccini of the marine-oil on-treatment analysis. But it, along with consistent evidence from other studies, does give him pause. “If a patient came to me and said,
Doctor, I want to take omega-3 fish oil, because I want to reduce my risk of events, as an arrhythmia doctor I would say, ‘We don’t have great evidence to do that for preventing atrial fibrillation. And there’s actually some evidence that it could mildly increase your risk of developing it.’ ”
For those prescribed evidence-based marine-oil therapy for other indications, he said, “I think the take-home message certainly is, if they report palpitations or other signs or symptoms that could be due to atrial fibrillation, we should be aggressive about screening for atrial fibrillation,” and making the diagnosis as appropriate. If the incident AF resolves after stopping the treatment, “maybe it’s reasonable to refrain from prescribing the medication for that patient.”
VITAL-Rhythm and VITAL are supported by multiple grants from the National Institutes of Health. Albert discloses receiving grant support from St. Jude Medical, Abbott, and Roche. Schnabel reports receiving honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Piccini previously disclosed receiving research grants from Abbott, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Philips and serving as a consultant to Abbott, Allergan, ARCA Biopharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, Milestone, Sanofi, Philips, and UptoDate.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Virtual AHA 2020 may influence template for postpandemic scientific sessions
Cardiologists are already old hands at virtual meetings this year and are fast becoming experts on Zoom and other teleconferencing platforms, if not on how to unmute their microphones.
With expectations perhaps elevated and the new communications genre’s novelty on the wane, the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 has a chance to both innovate with familiar formats and captivate with the field’s latest research findings.
Although the virtual AHA 2020 might not satisfy longings for face-to-face networking, shop talk, or kidding around over coffee, it will feature many traditional elements of the live conferences adapted for ear buds and small screens. They include late-breaking science (LBS) presentations and panel discussions, poster and live oral abstract presentations, meet-the-trialist talks, fireside-chat discussion forums, early career events, and satellite symposia.
The event may well hold lessons for future iterations of AHA Scientific Sessions in the postpandemic world, which some foresee as, potentially, an amalgam of the time-honored live format and a robust, complementary online presence.
“I can’t commit to exactly what AHA sessions will look like next November; I think that’s still being looked at,” the organization’s president-elect Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of the AHA Committee on Scientific Sessions Programming, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
There’s no debating that a live conference is valuable “for career networking and other opportunities, so I don’t think we can do without it. That has to be an important part of it,” he said. “When we can safely, of course.”
Still, “the virtual platform democratizes, right? I mean, it just allows greater access for a broader audience, and I think that’s important, too,” said Lloyd-Jones, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago.
“I don’t think we’ll ever go completely back to it being all in-person,” he said. “I think the world has changed, and we’ll have to adapt our platforms to recognize that.”
Online, at least, meeting registrants will get a better look at Anthony Fauci, MD, than one might from the middle rows of a vast ballroom-turned-auditorium. Fauci is scheduled to speak on “Public Health and Scientific Challenges” during the Main Event Session “Latest Insights on COVID 19 and Cardiovascular Disease,” slated for the meeting’s final day.
Fauci has directed the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) since 1984, and has been celebrated for his leadership roles in the battles against AIDS and Ebola virus. Today, his name is close to a household word for his service as a prominent though embattled member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force.
The virtual AHA sessions will feature a core collection of LBS presentations from often high-profile clinical trials and other studies the organization deems worthy of special attention. There are nine such presentations arrayed across the meeting’s five days — from Friday, November 13 to Tuesday, November 17 — at times listed in this story and throughout the AHA Scientific Session program synched with the Central Standard Time (CST) zone of the AHA’s home office in Dallas.
Late-Breaking Science 1. Friday, November 13, 10:30 AM - 11:30 AM CST
The LBS sessions launch with the GALACTIC-HF trial, which — the world recently learned — may expand the burgeoning list of meds shown to improve clinical outcomes in chronic heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
In cursory top-line results announced last month, those in the trial of more than 8000 patients who were randomly assigned to receive omecamtiv mecarbil (Amgen/Cytokinetics/Servier) showed a slight but significant benefit for the primary end point of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF events. The hazard ratio (HR), compared with standard care, was 0.92 (95% CI, 0.86 - 0.99; P = .025), noted a press release from Amgen.
Among the announcement’s few other details was a short take on safety outcomes: no difference in risk for “adverse events, including major ischemic cardiac events,” between the active and control groups. The presentation is sure to provide further insights and caveats, if any, along with other information crucial to the study’s interpretation.
Next on the schedule is the closely watched AFFIRM-AHF, billed as the first major outcomes trial of iron administration to iron-deficient patients with acute HF. It randomly assigned more than 1000 such patients to receive IV ferric carboxymaltose or a placebo. The first dose was given in-hospital and subsequent doses at home for 24 weeks or until patients were no longer iron deficient. They were followed to 1 year for the primary end point of recurrent HF hospitalizations or CV death.
The session wraps with the VITAL Rhythm trial, a substudy of the doubly randomized VITAL trial that explored the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on CV and cancer risk in more than 25,000 patients in the community. The substudy explored the effects of two active therapies, a preparation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Reliant Pharmaceuticals) or vitamin D3 supplements, on new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) as the primary end point; it also looked at risk for sudden death.
Late-Breaking Science 2. Friday, November 13, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
Dominating the session in two presentations, the (TIPS)-3 trial explored a polypill primary-prevention strategy and daily aspirin with vitamin D supplementation in three separate placebo-controlled comparisons in more than 5700 “intermediate risk” participants 55 years and older, mostly in developing countries.
The daily polypill in this trial is a combination of hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, atenolol 100 mg, ramipril 10 mg, and simvastatin 40 mg; aspirin was given at 75 mg daily and vitamin D at 60,000 IU monthly.
The participants are followed for a primary end point composed of major CV disease, HF, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or ischemia-driven revascularization for the polypill comparison; CV events or cancer for the aspirin comparison; and fracture risk for the vitamin D component of the trial.
In the Swedish Cardiopulmonary Bioimage Study (SCAPIS), presented third in the session, a random sample of adults from throughout Sweden, projected at about 30,000, underwent a 2-day evaluation for metabolic risk factors plus ultrasound and coronary and lung CT scans. The group has been followed for risks for myocardial infarction (MI), sudden death, and other cardiac diseases; and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung disorders.
Late-Breaking Science 3. Saturday, November 14, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The field may learn more mechanistically about MI associated with nonobstructed coronary arteries (MINOCA) than ever before from the Heart Attack Research Program-Imaging Study (HARP). The observational study is enrolling a projected 450 patients with suspected MI and ischemic symptoms who were referred for cardiac catheterization.
Their evaluation includes coronary optical coherence tomographic (OCT) scanning and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging for evidence of coronary plaque disruption as the primary end point. The patients are to be followed for 10 years for a composite of death, unstable angina, stroke, recurrent MI, diagnostic or interventional catheterization, and cardiac hospitalization.
The major direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) comparisons with warfarin in atrial fibrillation (AF) didn’t include many patients with prosthetic valve implants. In contrast, the RIVER trial enrolled 1005 adults with either persistent or paroxysmal AF and bioprosthetic mitral valves and assigned them to rivaroxaban 20 mg or the vitamin K antagonist.
The presentation will include the noninferiority primary outcome of major clinical events, which is stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), major bleeding, death from any cause, valve thrombosis, other systemic embolism, or HF hospitalization over 12 months.
This session also includes ALPHEUS, a trial pitting ticagrelor (Brilinta/Brilique, AstraZeneca) against mainstay clopidogrel in a setting that is mostly uncharted for such comparisons, elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
About 1900 patients with stable coronary disease were randomly assigned to a month of treatment with either agent on top of continuous aspirin. The primary end point is PCI-related MI or myocardial injury within 48 hours of the procedure.
Late-Breaking Science 4. Sunday, November 15, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The Self-Assessment Method for Statin Side-effects Or Nocebo (SAMSON) trial may be one of the AHA 2020 frontrunners for early buzz and anticipation. So it’s with some irony that it’s also among the smallest of the LBS studies, at 60 patients, which was nonetheless considered sufficient due to its unusual design.
SAMSON is the latest and perhaps most rigorous attempt to clarify whether symptoms, especially muscle pain or discomfort, attributed to statins by many patients are pharmacologic in origin or, rather, a nocebo effect from negative expectations about statin side effects.
The study patients, all of whom had previously halted statins because of side effects, were assigned to follow three separate regimens, each for month, in a randomized order; they did that four times, for a total of 12 months. The regimens consisted of atorvastatin 20 mg daily, a placebo, or neither.
Patients kept daily logs of any perceived side effects. Parity between side effects experienced on the statin and the placebo would point to a nocebo effect, whereas a significant excess on atorvastatin would suggest they are direct drug effects.
The session also features two randomized trials each on a unique omega-3 fatty acid preparation for either secondary prevention or high-risk primary prevention, in both cases compared with a corn-oil placebo.
The Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Elderly Patients with Myocardial Infarction (OMEMI) trial randomly assigned more than 1000 elderly post-MI patients to take Pikasol (Orkla Care) at 1.8 g EPA and DHA per day or the placebo. It looked for all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, revascularization, or hospitalization for new or worsened HF over 24 months.
The STRENGTH trial, with a planned enrollment of about 13,000 high-vascular-risk patients, looked primarily at the effect of daily treatment with Epanova (AstraZeneca), which also contains DHA and EPA, on the composite of CV death, nonfatal MI or stroke, coronary revascularization, and hospitalization for unstable angina. The trial was halted early for low likelihood of benefit, AstraZeneca announced in January of this year.
Late-Breaking Science 5. Sunday, November 15, 7:15 PM - 8:30 PM CST
Slated for the session is the primary analysis of the PIONEER 3 trial, conducted in the United States, Europe, and Japan. It compared the BuMA Supreme biodegradable drug-coated stent (SinoMed) with the durable Xience (Abbott Vascular) and Promus (Boston Scientific) drug-eluting stents. The trial followed more than 1600 patients treated for chronic stable angina or acute coronary syndrome (ACS) for the 1-year composite of cardiac death, target-vessel-related MI, and clinically driven target-lesion revascularization.
Late-Breaking Science 6. Monday, November 16, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The EARLY-AF trial enrolled 303 patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AF suitable for catheter ablation, assigning them to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) by cryoablation using the Arctic Front (Medtronic) system or antiarrhythmic drug therapy for rhythm control. The primary end point is time to recurrence of AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic, as determined by implantable loop recorder. Patients will also be followed for symptoms and arrhythmia burden.
Also in the session, the SEARCH-AF study randomized almost 400 patients undergoing cardiac surgery who were engaged subacutely with one of two commercial portable cardiac rhythm monitoring devices (CardioSTAT, Icentia; or SEEQ, Medtronic) or, alternatively, to receive usual postoperative care
The patients, considered to be at high risk for stroke with no history of AF, were followed for the primary end point of cumulative burden of AF or atrial flutter exceeding 6 minutes or documentation of either arrhythmia by 12-lead ECG within 30 days.
Two other studies in the session look at different approaches to AF screening, one using a handheld ECG monitor in the primary care setting and the other wearable monitors in the form of a patch or wristband. The VITAL-AF presentation is titled “Screening for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults at Primary Care Visits Using Single Lead Electrocardiograms.” The other presentation, on the study mSToPS, is called “Three-Year Clinical Outcomes in a Nationwide, Randomized, Pragmatic Clinical Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Screening — Mhealth Screening to Prevent Strokes.”
Late-Breaking Science 7. Monday, November 16, 7:00 PM - 8:30 PM CST
In the randomized FIDELIO-DKD trial with more than 5700 patients with type 2 diabetes and associated kidney disease, those assigned to the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Bayer) showed an 18% drop in risk for adverse renal events, including death from renal causes (P = .001), over a median of 2.6 years. That primary outcome was previously presented in detail at a nephrology meeting and published in the New England Journal of Medicine in October.
Patients on the MRA showed a similar reduction in a composite CV-event end point, it was also reported at that time. A follow-up presentation at the AHA sessions promises to dive deeper into the trial’s CV outcomes.
In the RAPID-CTCA study, slated next for the session, 1749 patients with suspected or confirmed intermediate-risk ACS were randomly assigned to undergo computed tomographic coronary angiography (CTCA) for guiding treatment decisions or a standard-of-care strategy. It followed patients for the primary end point of death or nonfatal MI over 1 year.
Rilonacept (Arcalyst, Kiniksa/Regeneron) is an interleukin-1α and -1β inhibitor used in several autoinflammatory diseases that went unsuccessfully before regulators for the treatment of gout. The RHAPSODY trial has now explored its use against recurrent pericarditis in a randomized trial that entered 86 patients 12 years and older who had previously experienced at least three episodes.
In top-line results reported to investors in June, patients assigned to receive the drug instead of placebo in weekly injections showed a 96% drop in risk for pericarditis recurrence and “no or minimal pain” on more than 90% of days in the trial. A full presentation is expected during this LBS session.
Also on the schedule is the THALES study, which led the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expand indications for ticagrelor to include stroke prevention in patients with a history of acute ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA based on the trial’s primary results published in July.
In THALES, more than 11,000 patients with mild to moderate acute noncardiogenic ischemic stroke or TIA were randomly assigned within 24 hours to start on daily aspirin with or without ticagrelor given as a 180 mg loading dose followed by 90 mg twice daily for 30 days.
At the end of a month, it was reported, those on dual antiplatelet therapy showed a 17% risk reduction (P = .02) for the primary end point of stroke or death, at the cost of a slight but significant increase in “severe” bleeding (0.5% vs 0.1%; P = .001).
The session is to conclude with two related studies that fell victim in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, both of which explored sotagliflozin (Zynquista, Sanofi/Lexicon), an inhibitor of both sodium-glucose cotransporters 1 and 2 (SGLT1 and SGLT2, respectively) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
SOLOIST-WHF had entered 1222 such patients hospitalized with urgent or worsening HF at 466 centers and randomly assigned them to receive sotagliflozin or placebo; they were followed for the composite of CV death or HF events. SCORED reached an enrollment of 10,584 patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease at 754 hospitals, following them for the same primary end point.
Lexicon announced in March that the trials would be “closed out early” because of the unavailability of funding “together with uncertainties relating to the COVID-19 pandemic on the trials.” The LBS presentation is expected to include analyses of available data; SOLOIST-WHF launched in summer 2018 and SCORED began in November 2017.
Late-Breaking Science 8. Tuesday, November 17, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
Most of this LBS session is devoted to the AHA COVID-19 Cardiovascular Disease registry, which is looking at the hospital journey, clinical course, and outcomes of patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infections at centers participating in the organization’s Get With The Guidelines (GWTG) quality-improvement program. As of September, the registry included data from more than 15,000 patients.
Scheduled presentations include a summary of the registry’s design and initial results; an analysis of racial and ethnic variation in therapy and clinical outcomes; an exploration of how body mass index influenced outcomes, including death, use of mechanical ventilation, and cardiovascular end points, in patients with COVID-19; and a deep dive into the relation between CV disease and clinical outcomes in the cohort.
The last of this LBS block’s five talks will cover the randomized Influenza Vaccine to Effectively Stop Cardio Thoracic Events and Decompensated Heart Failure (INVESTED) trial, which compared vaccination with high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine or a standard-dose quadrivalent vaccine in 5388 adults with a history of hospitalization for either MI or HF. Patients were required to have at least one other CV risk factor, such as older age, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, or diabetes.
INVESTED tracked the patients at 190 centers across an initial pilot flu season and three subsequent flu seasons for the primary end point of death from any cause or cardiopulmonary hospitalization.
The trial is one of at least three that have been looking at the effect of flu vaccination on cardiovascular outcomes; results from the other two — IAMI, with more than 2500 participants, and RCT-IVVE, with an enrollment of 4871 — are planned for presentation in 2021, theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology recently reported.
Late-Breaking Science 9. Tuesday, November 17, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The conference’s concluding LBS session features three studies that relied on technologic strategies for modifying patient compliance and other care behaviors and one that used human-centered design principles to develop a group-care model aimed improving the management of diabetes, hypertension, and other noncommunicable diseases in economically disadvantaged regions of Kenya.
The EPIC-HF trial tested a strategy for improving HFrEF medication-plan engagement by use of a video and documents delivered to patients several times by email or text prior to their follow-up clinic appointments. The strategy was compared with usual care for its effect on HF-medication optimization over 1 month and 1 year in a total of 306 patients.
Following EPIC-HF on the schedule is the MYROAD trial, looking at the efficacy of discharge instructions provided to patients with acute HF as an audio recording that they and their physicians could replay on demand, the idea being to increase adherence to the instructions. The trial’s 1073 patients were assigned to the novel strategy or usual care and followed for HF rehospitalization within 30 days.
MYROAD is to be followed by a presentation entitled “Digital Care Transformation: One-Year Report of >5,000 Patients Enrolled in a Remote Algorithm-Based CV Risk Management Program to Achieve Optimal Lipid and Hypertension Control.”
Rounding out the LBS session: the Bridging Income Generation With Group Integrated Care (BIGPIC) program, a pilot study that developed and executed “a healthcare delivery model targeting health behaviors, medication adherence, and financial barriers to accessing healthcare” in four rural counties in Kenya.
The model features locally developed plans, tailored for regional needs, that are said to “combine the benefits of microfinance with the peer support available through group medical care to enhance management of hypertension and diabetes.” The microfinance component is aimed at improving household economies to alleviate the financial burden of care and clinic attendance, and for the health effects of improved quality of life.
The study randomized 2890 adults with diabetes or prediabetes to one of four groups: usual care plus microfinance group support, group medical visits only or combined with microfinance group support, or usual care only. They were followed for changes in systolic blood pressure and CV-risk score over 12 months.
Lloyd-Jones and Fauci declared no conflicts.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiologists are already old hands at virtual meetings this year and are fast becoming experts on Zoom and other teleconferencing platforms, if not on how to unmute their microphones.
With expectations perhaps elevated and the new communications genre’s novelty on the wane, the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 has a chance to both innovate with familiar formats and captivate with the field’s latest research findings.
Although the virtual AHA 2020 might not satisfy longings for face-to-face networking, shop talk, or kidding around over coffee, it will feature many traditional elements of the live conferences adapted for ear buds and small screens. They include late-breaking science (LBS) presentations and panel discussions, poster and live oral abstract presentations, meet-the-trialist talks, fireside-chat discussion forums, early career events, and satellite symposia.
The event may well hold lessons for future iterations of AHA Scientific Sessions in the postpandemic world, which some foresee as, potentially, an amalgam of the time-honored live format and a robust, complementary online presence.
“I can’t commit to exactly what AHA sessions will look like next November; I think that’s still being looked at,” the organization’s president-elect Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of the AHA Committee on Scientific Sessions Programming, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
There’s no debating that a live conference is valuable “for career networking and other opportunities, so I don’t think we can do without it. That has to be an important part of it,” he said. “When we can safely, of course.”
Still, “the virtual platform democratizes, right? I mean, it just allows greater access for a broader audience, and I think that’s important, too,” said Lloyd-Jones, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago.
“I don’t think we’ll ever go completely back to it being all in-person,” he said. “I think the world has changed, and we’ll have to adapt our platforms to recognize that.”
Online, at least, meeting registrants will get a better look at Anthony Fauci, MD, than one might from the middle rows of a vast ballroom-turned-auditorium. Fauci is scheduled to speak on “Public Health and Scientific Challenges” during the Main Event Session “Latest Insights on COVID 19 and Cardiovascular Disease,” slated for the meeting’s final day.
Fauci has directed the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) since 1984, and has been celebrated for his leadership roles in the battles against AIDS and Ebola virus. Today, his name is close to a household word for his service as a prominent though embattled member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force.
The virtual AHA sessions will feature a core collection of LBS presentations from often high-profile clinical trials and other studies the organization deems worthy of special attention. There are nine such presentations arrayed across the meeting’s five days — from Friday, November 13 to Tuesday, November 17 — at times listed in this story and throughout the AHA Scientific Session program synched with the Central Standard Time (CST) zone of the AHA’s home office in Dallas.
Late-Breaking Science 1. Friday, November 13, 10:30 AM - 11:30 AM CST
The LBS sessions launch with the GALACTIC-HF trial, which — the world recently learned — may expand the burgeoning list of meds shown to improve clinical outcomes in chronic heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
In cursory top-line results announced last month, those in the trial of more than 8000 patients who were randomly assigned to receive omecamtiv mecarbil (Amgen/Cytokinetics/Servier) showed a slight but significant benefit for the primary end point of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF events. The hazard ratio (HR), compared with standard care, was 0.92 (95% CI, 0.86 - 0.99; P = .025), noted a press release from Amgen.
Among the announcement’s few other details was a short take on safety outcomes: no difference in risk for “adverse events, including major ischemic cardiac events,” between the active and control groups. The presentation is sure to provide further insights and caveats, if any, along with other information crucial to the study’s interpretation.
Next on the schedule is the closely watched AFFIRM-AHF, billed as the first major outcomes trial of iron administration to iron-deficient patients with acute HF. It randomly assigned more than 1000 such patients to receive IV ferric carboxymaltose or a placebo. The first dose was given in-hospital and subsequent doses at home for 24 weeks or until patients were no longer iron deficient. They were followed to 1 year for the primary end point of recurrent HF hospitalizations or CV death.
The session wraps with the VITAL Rhythm trial, a substudy of the doubly randomized VITAL trial that explored the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on CV and cancer risk in more than 25,000 patients in the community. The substudy explored the effects of two active therapies, a preparation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Reliant Pharmaceuticals) or vitamin D3 supplements, on new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) as the primary end point; it also looked at risk for sudden death.
Late-Breaking Science 2. Friday, November 13, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
Dominating the session in two presentations, the (TIPS)-3 trial explored a polypill primary-prevention strategy and daily aspirin with vitamin D supplementation in three separate placebo-controlled comparisons in more than 5700 “intermediate risk” participants 55 years and older, mostly in developing countries.
The daily polypill in this trial is a combination of hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, atenolol 100 mg, ramipril 10 mg, and simvastatin 40 mg; aspirin was given at 75 mg daily and vitamin D at 60,000 IU monthly.
The participants are followed for a primary end point composed of major CV disease, HF, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or ischemia-driven revascularization for the polypill comparison; CV events or cancer for the aspirin comparison; and fracture risk for the vitamin D component of the trial.
In the Swedish Cardiopulmonary Bioimage Study (SCAPIS), presented third in the session, a random sample of adults from throughout Sweden, projected at about 30,000, underwent a 2-day evaluation for metabolic risk factors plus ultrasound and coronary and lung CT scans. The group has been followed for risks for myocardial infarction (MI), sudden death, and other cardiac diseases; and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung disorders.
Late-Breaking Science 3. Saturday, November 14, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The field may learn more mechanistically about MI associated with nonobstructed coronary arteries (MINOCA) than ever before from the Heart Attack Research Program-Imaging Study (HARP). The observational study is enrolling a projected 450 patients with suspected MI and ischemic symptoms who were referred for cardiac catheterization.
Their evaluation includes coronary optical coherence tomographic (OCT) scanning and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging for evidence of coronary plaque disruption as the primary end point. The patients are to be followed for 10 years for a composite of death, unstable angina, stroke, recurrent MI, diagnostic or interventional catheterization, and cardiac hospitalization.
The major direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) comparisons with warfarin in atrial fibrillation (AF) didn’t include many patients with prosthetic valve implants. In contrast, the RIVER trial enrolled 1005 adults with either persistent or paroxysmal AF and bioprosthetic mitral valves and assigned them to rivaroxaban 20 mg or the vitamin K antagonist.
The presentation will include the noninferiority primary outcome of major clinical events, which is stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), major bleeding, death from any cause, valve thrombosis, other systemic embolism, or HF hospitalization over 12 months.
This session also includes ALPHEUS, a trial pitting ticagrelor (Brilinta/Brilique, AstraZeneca) against mainstay clopidogrel in a setting that is mostly uncharted for such comparisons, elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
About 1900 patients with stable coronary disease were randomly assigned to a month of treatment with either agent on top of continuous aspirin. The primary end point is PCI-related MI or myocardial injury within 48 hours of the procedure.
Late-Breaking Science 4. Sunday, November 15, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The Self-Assessment Method for Statin Side-effects Or Nocebo (SAMSON) trial may be one of the AHA 2020 frontrunners for early buzz and anticipation. So it’s with some irony that it’s also among the smallest of the LBS studies, at 60 patients, which was nonetheless considered sufficient due to its unusual design.
SAMSON is the latest and perhaps most rigorous attempt to clarify whether symptoms, especially muscle pain or discomfort, attributed to statins by many patients are pharmacologic in origin or, rather, a nocebo effect from negative expectations about statin side effects.
The study patients, all of whom had previously halted statins because of side effects, were assigned to follow three separate regimens, each for month, in a randomized order; they did that four times, for a total of 12 months. The regimens consisted of atorvastatin 20 mg daily, a placebo, or neither.
Patients kept daily logs of any perceived side effects. Parity between side effects experienced on the statin and the placebo would point to a nocebo effect, whereas a significant excess on atorvastatin would suggest they are direct drug effects.
The session also features two randomized trials each on a unique omega-3 fatty acid preparation for either secondary prevention or high-risk primary prevention, in both cases compared with a corn-oil placebo.
The Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Elderly Patients with Myocardial Infarction (OMEMI) trial randomly assigned more than 1000 elderly post-MI patients to take Pikasol (Orkla Care) at 1.8 g EPA and DHA per day or the placebo. It looked for all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, revascularization, or hospitalization for new or worsened HF over 24 months.
The STRENGTH trial, with a planned enrollment of about 13,000 high-vascular-risk patients, looked primarily at the effect of daily treatment with Epanova (AstraZeneca), which also contains DHA and EPA, on the composite of CV death, nonfatal MI or stroke, coronary revascularization, and hospitalization for unstable angina. The trial was halted early for low likelihood of benefit, AstraZeneca announced in January of this year.
Late-Breaking Science 5. Sunday, November 15, 7:15 PM - 8:30 PM CST
Slated for the session is the primary analysis of the PIONEER 3 trial, conducted in the United States, Europe, and Japan. It compared the BuMA Supreme biodegradable drug-coated stent (SinoMed) with the durable Xience (Abbott Vascular) and Promus (Boston Scientific) drug-eluting stents. The trial followed more than 1600 patients treated for chronic stable angina or acute coronary syndrome (ACS) for the 1-year composite of cardiac death, target-vessel-related MI, and clinically driven target-lesion revascularization.
Late-Breaking Science 6. Monday, November 16, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The EARLY-AF trial enrolled 303 patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AF suitable for catheter ablation, assigning them to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) by cryoablation using the Arctic Front (Medtronic) system or antiarrhythmic drug therapy for rhythm control. The primary end point is time to recurrence of AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic, as determined by implantable loop recorder. Patients will also be followed for symptoms and arrhythmia burden.
Also in the session, the SEARCH-AF study randomized almost 400 patients undergoing cardiac surgery who were engaged subacutely with one of two commercial portable cardiac rhythm monitoring devices (CardioSTAT, Icentia; or SEEQ, Medtronic) or, alternatively, to receive usual postoperative care
The patients, considered to be at high risk for stroke with no history of AF, were followed for the primary end point of cumulative burden of AF or atrial flutter exceeding 6 minutes or documentation of either arrhythmia by 12-lead ECG within 30 days.
Two other studies in the session look at different approaches to AF screening, one using a handheld ECG monitor in the primary care setting and the other wearable monitors in the form of a patch or wristband. The VITAL-AF presentation is titled “Screening for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults at Primary Care Visits Using Single Lead Electrocardiograms.” The other presentation, on the study mSToPS, is called “Three-Year Clinical Outcomes in a Nationwide, Randomized, Pragmatic Clinical Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Screening — Mhealth Screening to Prevent Strokes.”
Late-Breaking Science 7. Monday, November 16, 7:00 PM - 8:30 PM CST
In the randomized FIDELIO-DKD trial with more than 5700 patients with type 2 diabetes and associated kidney disease, those assigned to the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Bayer) showed an 18% drop in risk for adverse renal events, including death from renal causes (P = .001), over a median of 2.6 years. That primary outcome was previously presented in detail at a nephrology meeting and published in the New England Journal of Medicine in October.
Patients on the MRA showed a similar reduction in a composite CV-event end point, it was also reported at that time. A follow-up presentation at the AHA sessions promises to dive deeper into the trial’s CV outcomes.
In the RAPID-CTCA study, slated next for the session, 1749 patients with suspected or confirmed intermediate-risk ACS were randomly assigned to undergo computed tomographic coronary angiography (CTCA) for guiding treatment decisions or a standard-of-care strategy. It followed patients for the primary end point of death or nonfatal MI over 1 year.
Rilonacept (Arcalyst, Kiniksa/Regeneron) is an interleukin-1α and -1β inhibitor used in several autoinflammatory diseases that went unsuccessfully before regulators for the treatment of gout. The RHAPSODY trial has now explored its use against recurrent pericarditis in a randomized trial that entered 86 patients 12 years and older who had previously experienced at least three episodes.
In top-line results reported to investors in June, patients assigned to receive the drug instead of placebo in weekly injections showed a 96% drop in risk for pericarditis recurrence and “no or minimal pain” on more than 90% of days in the trial. A full presentation is expected during this LBS session.
Also on the schedule is the THALES study, which led the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expand indications for ticagrelor to include stroke prevention in patients with a history of acute ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA based on the trial’s primary results published in July.
In THALES, more than 11,000 patients with mild to moderate acute noncardiogenic ischemic stroke or TIA were randomly assigned within 24 hours to start on daily aspirin with or without ticagrelor given as a 180 mg loading dose followed by 90 mg twice daily for 30 days.
At the end of a month, it was reported, those on dual antiplatelet therapy showed a 17% risk reduction (P = .02) for the primary end point of stroke or death, at the cost of a slight but significant increase in “severe” bleeding (0.5% vs 0.1%; P = .001).
The session is to conclude with two related studies that fell victim in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, both of which explored sotagliflozin (Zynquista, Sanofi/Lexicon), an inhibitor of both sodium-glucose cotransporters 1 and 2 (SGLT1 and SGLT2, respectively) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
SOLOIST-WHF had entered 1222 such patients hospitalized with urgent or worsening HF at 466 centers and randomly assigned them to receive sotagliflozin or placebo; they were followed for the composite of CV death or HF events. SCORED reached an enrollment of 10,584 patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease at 754 hospitals, following them for the same primary end point.
Lexicon announced in March that the trials would be “closed out early” because of the unavailability of funding “together with uncertainties relating to the COVID-19 pandemic on the trials.” The LBS presentation is expected to include analyses of available data; SOLOIST-WHF launched in summer 2018 and SCORED began in November 2017.
Late-Breaking Science 8. Tuesday, November 17, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
Most of this LBS session is devoted to the AHA COVID-19 Cardiovascular Disease registry, which is looking at the hospital journey, clinical course, and outcomes of patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infections at centers participating in the organization’s Get With The Guidelines (GWTG) quality-improvement program. As of September, the registry included data from more than 15,000 patients.
Scheduled presentations include a summary of the registry’s design and initial results; an analysis of racial and ethnic variation in therapy and clinical outcomes; an exploration of how body mass index influenced outcomes, including death, use of mechanical ventilation, and cardiovascular end points, in patients with COVID-19; and a deep dive into the relation between CV disease and clinical outcomes in the cohort.
The last of this LBS block’s five talks will cover the randomized Influenza Vaccine to Effectively Stop Cardio Thoracic Events and Decompensated Heart Failure (INVESTED) trial, which compared vaccination with high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine or a standard-dose quadrivalent vaccine in 5388 adults with a history of hospitalization for either MI or HF. Patients were required to have at least one other CV risk factor, such as older age, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, or diabetes.
INVESTED tracked the patients at 190 centers across an initial pilot flu season and three subsequent flu seasons for the primary end point of death from any cause or cardiopulmonary hospitalization.
The trial is one of at least three that have been looking at the effect of flu vaccination on cardiovascular outcomes; results from the other two — IAMI, with more than 2500 participants, and RCT-IVVE, with an enrollment of 4871 — are planned for presentation in 2021, theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology recently reported.
Late-Breaking Science 9. Tuesday, November 17, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The conference’s concluding LBS session features three studies that relied on technologic strategies for modifying patient compliance and other care behaviors and one that used human-centered design principles to develop a group-care model aimed improving the management of diabetes, hypertension, and other noncommunicable diseases in economically disadvantaged regions of Kenya.
The EPIC-HF trial tested a strategy for improving HFrEF medication-plan engagement by use of a video and documents delivered to patients several times by email or text prior to their follow-up clinic appointments. The strategy was compared with usual care for its effect on HF-medication optimization over 1 month and 1 year in a total of 306 patients.
Following EPIC-HF on the schedule is the MYROAD trial, looking at the efficacy of discharge instructions provided to patients with acute HF as an audio recording that they and their physicians could replay on demand, the idea being to increase adherence to the instructions. The trial’s 1073 patients were assigned to the novel strategy or usual care and followed for HF rehospitalization within 30 days.
MYROAD is to be followed by a presentation entitled “Digital Care Transformation: One-Year Report of >5,000 Patients Enrolled in a Remote Algorithm-Based CV Risk Management Program to Achieve Optimal Lipid and Hypertension Control.”
Rounding out the LBS session: the Bridging Income Generation With Group Integrated Care (BIGPIC) program, a pilot study that developed and executed “a healthcare delivery model targeting health behaviors, medication adherence, and financial barriers to accessing healthcare” in four rural counties in Kenya.
The model features locally developed plans, tailored for regional needs, that are said to “combine the benefits of microfinance with the peer support available through group medical care to enhance management of hypertension and diabetes.” The microfinance component is aimed at improving household economies to alleviate the financial burden of care and clinic attendance, and for the health effects of improved quality of life.
The study randomized 2890 adults with diabetes or prediabetes to one of four groups: usual care plus microfinance group support, group medical visits only or combined with microfinance group support, or usual care only. They were followed for changes in systolic blood pressure and CV-risk score over 12 months.
Lloyd-Jones and Fauci declared no conflicts.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiologists are already old hands at virtual meetings this year and are fast becoming experts on Zoom and other teleconferencing platforms, if not on how to unmute their microphones.
With expectations perhaps elevated and the new communications genre’s novelty on the wane, the American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 has a chance to both innovate with familiar formats and captivate with the field’s latest research findings.
Although the virtual AHA 2020 might not satisfy longings for face-to-face networking, shop talk, or kidding around over coffee, it will feature many traditional elements of the live conferences adapted for ear buds and small screens. They include late-breaking science (LBS) presentations and panel discussions, poster and live oral abstract presentations, meet-the-trialist talks, fireside-chat discussion forums, early career events, and satellite symposia.
The event may well hold lessons for future iterations of AHA Scientific Sessions in the postpandemic world, which some foresee as, potentially, an amalgam of the time-honored live format and a robust, complementary online presence.
“I can’t commit to exactly what AHA sessions will look like next November; I think that’s still being looked at,” the organization’s president-elect Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of the AHA Committee on Scientific Sessions Programming, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
There’s no debating that a live conference is valuable “for career networking and other opportunities, so I don’t think we can do without it. That has to be an important part of it,” he said. “When we can safely, of course.”
Still, “the virtual platform democratizes, right? I mean, it just allows greater access for a broader audience, and I think that’s important, too,” said Lloyd-Jones, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago.
“I don’t think we’ll ever go completely back to it being all in-person,” he said. “I think the world has changed, and we’ll have to adapt our platforms to recognize that.”
Online, at least, meeting registrants will get a better look at Anthony Fauci, MD, than one might from the middle rows of a vast ballroom-turned-auditorium. Fauci is scheduled to speak on “Public Health and Scientific Challenges” during the Main Event Session “Latest Insights on COVID 19 and Cardiovascular Disease,” slated for the meeting’s final day.
Fauci has directed the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) since 1984, and has been celebrated for his leadership roles in the battles against AIDS and Ebola virus. Today, his name is close to a household word for his service as a prominent though embattled member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force.
The virtual AHA sessions will feature a core collection of LBS presentations from often high-profile clinical trials and other studies the organization deems worthy of special attention. There are nine such presentations arrayed across the meeting’s five days — from Friday, November 13 to Tuesday, November 17 — at times listed in this story and throughout the AHA Scientific Session program synched with the Central Standard Time (CST) zone of the AHA’s home office in Dallas.
Late-Breaking Science 1. Friday, November 13, 10:30 AM - 11:30 AM CST
The LBS sessions launch with the GALACTIC-HF trial, which — the world recently learned — may expand the burgeoning list of meds shown to improve clinical outcomes in chronic heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
In cursory top-line results announced last month, those in the trial of more than 8000 patients who were randomly assigned to receive omecamtiv mecarbil (Amgen/Cytokinetics/Servier) showed a slight but significant benefit for the primary end point of cardiovascular (CV) death or HF events. The hazard ratio (HR), compared with standard care, was 0.92 (95% CI, 0.86 - 0.99; P = .025), noted a press release from Amgen.
Among the announcement’s few other details was a short take on safety outcomes: no difference in risk for “adverse events, including major ischemic cardiac events,” between the active and control groups. The presentation is sure to provide further insights and caveats, if any, along with other information crucial to the study’s interpretation.
Next on the schedule is the closely watched AFFIRM-AHF, billed as the first major outcomes trial of iron administration to iron-deficient patients with acute HF. It randomly assigned more than 1000 such patients to receive IV ferric carboxymaltose or a placebo. The first dose was given in-hospital and subsequent doses at home for 24 weeks or until patients were no longer iron deficient. They were followed to 1 year for the primary end point of recurrent HF hospitalizations or CV death.
The session wraps with the VITAL Rhythm trial, a substudy of the doubly randomized VITAL trial that explored the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on CV and cancer risk in more than 25,000 patients in the community. The substudy explored the effects of two active therapies, a preparation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Omacor, Reliant Pharmaceuticals) or vitamin D3 supplements, on new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) as the primary end point; it also looked at risk for sudden death.
Late-Breaking Science 2. Friday, November 13, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
Dominating the session in two presentations, the (TIPS)-3 trial explored a polypill primary-prevention strategy and daily aspirin with vitamin D supplementation in three separate placebo-controlled comparisons in more than 5700 “intermediate risk” participants 55 years and older, mostly in developing countries.
The daily polypill in this trial is a combination of hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, atenolol 100 mg, ramipril 10 mg, and simvastatin 40 mg; aspirin was given at 75 mg daily and vitamin D at 60,000 IU monthly.
The participants are followed for a primary end point composed of major CV disease, HF, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or ischemia-driven revascularization for the polypill comparison; CV events or cancer for the aspirin comparison; and fracture risk for the vitamin D component of the trial.
In the Swedish Cardiopulmonary Bioimage Study (SCAPIS), presented third in the session, a random sample of adults from throughout Sweden, projected at about 30,000, underwent a 2-day evaluation for metabolic risk factors plus ultrasound and coronary and lung CT scans. The group has been followed for risks for myocardial infarction (MI), sudden death, and other cardiac diseases; and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung disorders.
Late-Breaking Science 3. Saturday, November 14, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The field may learn more mechanistically about MI associated with nonobstructed coronary arteries (MINOCA) than ever before from the Heart Attack Research Program-Imaging Study (HARP). The observational study is enrolling a projected 450 patients with suspected MI and ischemic symptoms who were referred for cardiac catheterization.
Their evaluation includes coronary optical coherence tomographic (OCT) scanning and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging for evidence of coronary plaque disruption as the primary end point. The patients are to be followed for 10 years for a composite of death, unstable angina, stroke, recurrent MI, diagnostic or interventional catheterization, and cardiac hospitalization.
The major direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) comparisons with warfarin in atrial fibrillation (AF) didn’t include many patients with prosthetic valve implants. In contrast, the RIVER trial enrolled 1005 adults with either persistent or paroxysmal AF and bioprosthetic mitral valves and assigned them to rivaroxaban 20 mg or the vitamin K antagonist.
The presentation will include the noninferiority primary outcome of major clinical events, which is stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), major bleeding, death from any cause, valve thrombosis, other systemic embolism, or HF hospitalization over 12 months.
This session also includes ALPHEUS, a trial pitting ticagrelor (Brilinta/Brilique, AstraZeneca) against mainstay clopidogrel in a setting that is mostly uncharted for such comparisons, elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
About 1900 patients with stable coronary disease were randomly assigned to a month of treatment with either agent on top of continuous aspirin. The primary end point is PCI-related MI or myocardial injury within 48 hours of the procedure.
Late-Breaking Science 4. Sunday, November 15, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The Self-Assessment Method for Statin Side-effects Or Nocebo (SAMSON) trial may be one of the AHA 2020 frontrunners for early buzz and anticipation. So it’s with some irony that it’s also among the smallest of the LBS studies, at 60 patients, which was nonetheless considered sufficient due to its unusual design.
SAMSON is the latest and perhaps most rigorous attempt to clarify whether symptoms, especially muscle pain or discomfort, attributed to statins by many patients are pharmacologic in origin or, rather, a nocebo effect from negative expectations about statin side effects.
The study patients, all of whom had previously halted statins because of side effects, were assigned to follow three separate regimens, each for month, in a randomized order; they did that four times, for a total of 12 months. The regimens consisted of atorvastatin 20 mg daily, a placebo, or neither.
Patients kept daily logs of any perceived side effects. Parity between side effects experienced on the statin and the placebo would point to a nocebo effect, whereas a significant excess on atorvastatin would suggest they are direct drug effects.
The session also features two randomized trials each on a unique omega-3 fatty acid preparation for either secondary prevention or high-risk primary prevention, in both cases compared with a corn-oil placebo.
The Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Elderly Patients with Myocardial Infarction (OMEMI) trial randomly assigned more than 1000 elderly post-MI patients to take Pikasol (Orkla Care) at 1.8 g EPA and DHA per day or the placebo. It looked for all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, stroke, revascularization, or hospitalization for new or worsened HF over 24 months.
The STRENGTH trial, with a planned enrollment of about 13,000 high-vascular-risk patients, looked primarily at the effect of daily treatment with Epanova (AstraZeneca), which also contains DHA and EPA, on the composite of CV death, nonfatal MI or stroke, coronary revascularization, and hospitalization for unstable angina. The trial was halted early for low likelihood of benefit, AstraZeneca announced in January of this year.
Late-Breaking Science 5. Sunday, November 15, 7:15 PM - 8:30 PM CST
Slated for the session is the primary analysis of the PIONEER 3 trial, conducted in the United States, Europe, and Japan. It compared the BuMA Supreme biodegradable drug-coated stent (SinoMed) with the durable Xience (Abbott Vascular) and Promus (Boston Scientific) drug-eluting stents. The trial followed more than 1600 patients treated for chronic stable angina or acute coronary syndrome (ACS) for the 1-year composite of cardiac death, target-vessel-related MI, and clinically driven target-lesion revascularization.
Late-Breaking Science 6. Monday, November 16, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
The EARLY-AF trial enrolled 303 patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent AF suitable for catheter ablation, assigning them to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) by cryoablation using the Arctic Front (Medtronic) system or antiarrhythmic drug therapy for rhythm control. The primary end point is time to recurrence of AF, atrial flutter, or atrial tachycardia, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic, as determined by implantable loop recorder. Patients will also be followed for symptoms and arrhythmia burden.
Also in the session, the SEARCH-AF study randomized almost 400 patients undergoing cardiac surgery who were engaged subacutely with one of two commercial portable cardiac rhythm monitoring devices (CardioSTAT, Icentia; or SEEQ, Medtronic) or, alternatively, to receive usual postoperative care
The patients, considered to be at high risk for stroke with no history of AF, were followed for the primary end point of cumulative burden of AF or atrial flutter exceeding 6 minutes or documentation of either arrhythmia by 12-lead ECG within 30 days.
Two other studies in the session look at different approaches to AF screening, one using a handheld ECG monitor in the primary care setting and the other wearable monitors in the form of a patch or wristband. The VITAL-AF presentation is titled “Screening for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults at Primary Care Visits Using Single Lead Electrocardiograms.” The other presentation, on the study mSToPS, is called “Three-Year Clinical Outcomes in a Nationwide, Randomized, Pragmatic Clinical Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Screening — Mhealth Screening to Prevent Strokes.”
Late-Breaking Science 7. Monday, November 16, 7:00 PM - 8:30 PM CST
In the randomized FIDELIO-DKD trial with more than 5700 patients with type 2 diabetes and associated kidney disease, those assigned to the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Bayer) showed an 18% drop in risk for adverse renal events, including death from renal causes (P = .001), over a median of 2.6 years. That primary outcome was previously presented in detail at a nephrology meeting and published in the New England Journal of Medicine in October.
Patients on the MRA showed a similar reduction in a composite CV-event end point, it was also reported at that time. A follow-up presentation at the AHA sessions promises to dive deeper into the trial’s CV outcomes.
In the RAPID-CTCA study, slated next for the session, 1749 patients with suspected or confirmed intermediate-risk ACS were randomly assigned to undergo computed tomographic coronary angiography (CTCA) for guiding treatment decisions or a standard-of-care strategy. It followed patients for the primary end point of death or nonfatal MI over 1 year.
Rilonacept (Arcalyst, Kiniksa/Regeneron) is an interleukin-1α and -1β inhibitor used in several autoinflammatory diseases that went unsuccessfully before regulators for the treatment of gout. The RHAPSODY trial has now explored its use against recurrent pericarditis in a randomized trial that entered 86 patients 12 years and older who had previously experienced at least three episodes.
In top-line results reported to investors in June, patients assigned to receive the drug instead of placebo in weekly injections showed a 96% drop in risk for pericarditis recurrence and “no or minimal pain” on more than 90% of days in the trial. A full presentation is expected during this LBS session.
Also on the schedule is the THALES study, which led the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expand indications for ticagrelor to include stroke prevention in patients with a history of acute ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA based on the trial’s primary results published in July.
In THALES, more than 11,000 patients with mild to moderate acute noncardiogenic ischemic stroke or TIA were randomly assigned within 24 hours to start on daily aspirin with or without ticagrelor given as a 180 mg loading dose followed by 90 mg twice daily for 30 days.
At the end of a month, it was reported, those on dual antiplatelet therapy showed a 17% risk reduction (P = .02) for the primary end point of stroke or death, at the cost of a slight but significant increase in “severe” bleeding (0.5% vs 0.1%; P = .001).
The session is to conclude with two related studies that fell victim in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, both of which explored sotagliflozin (Zynquista, Sanofi/Lexicon), an inhibitor of both sodium-glucose cotransporters 1 and 2 (SGLT1 and SGLT2, respectively) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
SOLOIST-WHF had entered 1222 such patients hospitalized with urgent or worsening HF at 466 centers and randomly assigned them to receive sotagliflozin or placebo; they were followed for the composite of CV death or HF events. SCORED reached an enrollment of 10,584 patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease at 754 hospitals, following them for the same primary end point.
Lexicon announced in March that the trials would be “closed out early” because of the unavailability of funding “together with uncertainties relating to the COVID-19 pandemic on the trials.” The LBS presentation is expected to include analyses of available data; SOLOIST-WHF launched in summer 2018 and SCORED began in November 2017.
Late-Breaking Science 8. Tuesday, November 17, 9:00 AM - 10:00 AM CST
Most of this LBS session is devoted to the AHA COVID-19 Cardiovascular Disease registry, which is looking at the hospital journey, clinical course, and outcomes of patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infections at centers participating in the organization’s Get With The Guidelines (GWTG) quality-improvement program. As of September, the registry included data from more than 15,000 patients.
Scheduled presentations include a summary of the registry’s design and initial results; an analysis of racial and ethnic variation in therapy and clinical outcomes; an exploration of how body mass index influenced outcomes, including death, use of mechanical ventilation, and cardiovascular end points, in patients with COVID-19; and a deep dive into the relation between CV disease and clinical outcomes in the cohort.
The last of this LBS block’s five talks will cover the randomized Influenza Vaccine to Effectively Stop Cardio Thoracic Events and Decompensated Heart Failure (INVESTED) trial, which compared vaccination with high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine or a standard-dose quadrivalent vaccine in 5388 adults with a history of hospitalization for either MI or HF. Patients were required to have at least one other CV risk factor, such as older age, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, or diabetes.
INVESTED tracked the patients at 190 centers across an initial pilot flu season and three subsequent flu seasons for the primary end point of death from any cause or cardiopulmonary hospitalization.
The trial is one of at least three that have been looking at the effect of flu vaccination on cardiovascular outcomes; results from the other two — IAMI, with more than 2500 participants, and RCT-IVVE, with an enrollment of 4871 — are planned for presentation in 2021, theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology recently reported.
Late-Breaking Science 9. Tuesday, November 17, 12:00 PM - 1:00 PM CST
The conference’s concluding LBS session features three studies that relied on technologic strategies for modifying patient compliance and other care behaviors and one that used human-centered design principles to develop a group-care model aimed improving the management of diabetes, hypertension, and other noncommunicable diseases in economically disadvantaged regions of Kenya.
The EPIC-HF trial tested a strategy for improving HFrEF medication-plan engagement by use of a video and documents delivered to patients several times by email or text prior to their follow-up clinic appointments. The strategy was compared with usual care for its effect on HF-medication optimization over 1 month and 1 year in a total of 306 patients.
Following EPIC-HF on the schedule is the MYROAD trial, looking at the efficacy of discharge instructions provided to patients with acute HF as an audio recording that they and their physicians could replay on demand, the idea being to increase adherence to the instructions. The trial’s 1073 patients were assigned to the novel strategy or usual care and followed for HF rehospitalization within 30 days.
MYROAD is to be followed by a presentation entitled “Digital Care Transformation: One-Year Report of >5,000 Patients Enrolled in a Remote Algorithm-Based CV Risk Management Program to Achieve Optimal Lipid and Hypertension Control.”
Rounding out the LBS session: the Bridging Income Generation With Group Integrated Care (BIGPIC) program, a pilot study that developed and executed “a healthcare delivery model targeting health behaviors, medication adherence, and financial barriers to accessing healthcare” in four rural counties in Kenya.
The model features locally developed plans, tailored for regional needs, that are said to “combine the benefits of microfinance with the peer support available through group medical care to enhance management of hypertension and diabetes.” The microfinance component is aimed at improving household economies to alleviate the financial burden of care and clinic attendance, and for the health effects of improved quality of life.
The study randomized 2890 adults with diabetes or prediabetes to one of four groups: usual care plus microfinance group support, group medical visits only or combined with microfinance group support, or usual care only. They were followed for changes in systolic blood pressure and CV-risk score over 12 months.
Lloyd-Jones and Fauci declared no conflicts.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.