User login
New blood biomarker to detect early dementia?
Investigators found that plasma concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine could distinguish adults with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease from cognitively normal adults.
“Our biomarker for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease represents new thinking and is unique from the amyloid-beta and p-tau molecules that are currently being investigated to diagnose AD,” Sandra Banack, PhD, senior scientist, Brain Chemistry Labs, Jackson, Wyoming, told this news organization.
If further studies pan out, Dr. Banack said this biomarker could “easily be transformed into a test to aid clinical evaluations for Alzheimer’s disease.”
The study was published online in PLOS ONE.
New drug target?
The researchers measured concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine in blood plasma samples in 25 patients (21 men; mean age, 71) with a clinical diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s based on a Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) score of 0.5, suggesting very mild cognitive impairment, and 25 healthy controls (20 men; mean age, 39).
The concentration of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate, normalized by the concentration of taurine, reliably distinguished blood samples of early-stage Alzheimer’s patients from controls in a blinded analysis.
This biomarker “could lead to new understanding of [AD] and lead to new drug candidates,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The researchers note that 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate plays an important role in the structure and function of cellular membranes.
Physiologic effects of increased 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate concentrations in the blood are not known. However, in one study, concentrations of this molecule were found to be significantly lower in the temporal cortex, frontal cortex, and hippocampus (40%) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, compared with controls.
“New biomarkers take time before they can be implemented in the clinic. The next step will be to repeat the experiments using a large sample size of AD patient blood samples,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The study team is looking to source a larger sample size of AD blood samples to replicate these findings. They are also examining this biomarker relative to other neurodegenerative diseases.
“If verified with larger sample sizes, the quantification of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate could potentially assist in the diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s disease when used in conjunction with the patient’s CDR score and other potential AD biomarkers,” Dr. Banack and colleagues say.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on the findings, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific engagement, said the study is “interesting, though very small-scale and very preliminary.”
Dr. Edelmayer said one “major limitation” is that participants did not have their Alzheimer’s diagnosis confirmed with “gold standard biomarkers. They have been diagnosed based only on their cognitive and behavioral symptoms.”
She also cautioned that the study population is not representative – either of the general public or people living with Alzheimer’s disease.
For example, 41 out of all 50 samples are from men, “though we know women are disproportionately impacted by Alzheimer’s.”
“There is a mismatch in the age of the study groups,” Dr. Edelmayer noted. The mean age of controls in the study was 39 and the mean age of people with dementia was 71. Race or ethnicity and other demographic information is also unclear from the article.
“There is an urgent need for simple, inexpensive, noninvasive and easily available diagnostic tools for Alzheimer’s, such as a blood test. A simple blood test for Alzheimer’s would be a great advance for individuals with – and at risk for – the disease, families, doctors, and researchers,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
“Bottom line,” Dr. Edelmayer continued, “these results need to be further tested and verified in long-term, large-scale studies with diverse populations that are representative of those living with Alzheimer’s disease.”
This research was supported by the William Stamps Farish Fund and the Josephine P. & John J. Louis Foundation. Brain Chemistry Labs has applied for a patent related to this research. Dr. Edelmayer has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that plasma concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine could distinguish adults with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease from cognitively normal adults.
“Our biomarker for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease represents new thinking and is unique from the amyloid-beta and p-tau molecules that are currently being investigated to diagnose AD,” Sandra Banack, PhD, senior scientist, Brain Chemistry Labs, Jackson, Wyoming, told this news organization.
If further studies pan out, Dr. Banack said this biomarker could “easily be transformed into a test to aid clinical evaluations for Alzheimer’s disease.”
The study was published online in PLOS ONE.
New drug target?
The researchers measured concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine in blood plasma samples in 25 patients (21 men; mean age, 71) with a clinical diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s based on a Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) score of 0.5, suggesting very mild cognitive impairment, and 25 healthy controls (20 men; mean age, 39).
The concentration of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate, normalized by the concentration of taurine, reliably distinguished blood samples of early-stage Alzheimer’s patients from controls in a blinded analysis.
This biomarker “could lead to new understanding of [AD] and lead to new drug candidates,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The researchers note that 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate plays an important role in the structure and function of cellular membranes.
Physiologic effects of increased 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate concentrations in the blood are not known. However, in one study, concentrations of this molecule were found to be significantly lower in the temporal cortex, frontal cortex, and hippocampus (40%) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, compared with controls.
“New biomarkers take time before they can be implemented in the clinic. The next step will be to repeat the experiments using a large sample size of AD patient blood samples,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The study team is looking to source a larger sample size of AD blood samples to replicate these findings. They are also examining this biomarker relative to other neurodegenerative diseases.
“If verified with larger sample sizes, the quantification of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate could potentially assist in the diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s disease when used in conjunction with the patient’s CDR score and other potential AD biomarkers,” Dr. Banack and colleagues say.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on the findings, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific engagement, said the study is “interesting, though very small-scale and very preliminary.”
Dr. Edelmayer said one “major limitation” is that participants did not have their Alzheimer’s diagnosis confirmed with “gold standard biomarkers. They have been diagnosed based only on their cognitive and behavioral symptoms.”
She also cautioned that the study population is not representative – either of the general public or people living with Alzheimer’s disease.
For example, 41 out of all 50 samples are from men, “though we know women are disproportionately impacted by Alzheimer’s.”
“There is a mismatch in the age of the study groups,” Dr. Edelmayer noted. The mean age of controls in the study was 39 and the mean age of people with dementia was 71. Race or ethnicity and other demographic information is also unclear from the article.
“There is an urgent need for simple, inexpensive, noninvasive and easily available diagnostic tools for Alzheimer’s, such as a blood test. A simple blood test for Alzheimer’s would be a great advance for individuals with – and at risk for – the disease, families, doctors, and researchers,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
“Bottom line,” Dr. Edelmayer continued, “these results need to be further tested and verified in long-term, large-scale studies with diverse populations that are representative of those living with Alzheimer’s disease.”
This research was supported by the William Stamps Farish Fund and the Josephine P. & John J. Louis Foundation. Brain Chemistry Labs has applied for a patent related to this research. Dr. Edelmayer has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that plasma concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine could distinguish adults with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease from cognitively normal adults.
“Our biomarker for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease represents new thinking and is unique from the amyloid-beta and p-tau molecules that are currently being investigated to diagnose AD,” Sandra Banack, PhD, senior scientist, Brain Chemistry Labs, Jackson, Wyoming, told this news organization.
If further studies pan out, Dr. Banack said this biomarker could “easily be transformed into a test to aid clinical evaluations for Alzheimer’s disease.”
The study was published online in PLOS ONE.
New drug target?
The researchers measured concentrations of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate and taurine in blood plasma samples in 25 patients (21 men; mean age, 71) with a clinical diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s based on a Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) score of 0.5, suggesting very mild cognitive impairment, and 25 healthy controls (20 men; mean age, 39).
The concentration of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate, normalized by the concentration of taurine, reliably distinguished blood samples of early-stage Alzheimer’s patients from controls in a blinded analysis.
This biomarker “could lead to new understanding of [AD] and lead to new drug candidates,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The researchers note that 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate plays an important role in the structure and function of cellular membranes.
Physiologic effects of increased 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate concentrations in the blood are not known. However, in one study, concentrations of this molecule were found to be significantly lower in the temporal cortex, frontal cortex, and hippocampus (40%) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, compared with controls.
“New biomarkers take time before they can be implemented in the clinic. The next step will be to repeat the experiments using a large sample size of AD patient blood samples,” Dr. Banack told this news organization.
The study team is looking to source a larger sample size of AD blood samples to replicate these findings. They are also examining this biomarker relative to other neurodegenerative diseases.
“If verified with larger sample sizes, the quantification of 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate could potentially assist in the diagnosis of early-stage Alzheimer’s disease when used in conjunction with the patient’s CDR score and other potential AD biomarkers,” Dr. Banack and colleagues say.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on the findings, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific engagement, said the study is “interesting, though very small-scale and very preliminary.”
Dr. Edelmayer said one “major limitation” is that participants did not have their Alzheimer’s diagnosis confirmed with “gold standard biomarkers. They have been diagnosed based only on their cognitive and behavioral symptoms.”
She also cautioned that the study population is not representative – either of the general public or people living with Alzheimer’s disease.
For example, 41 out of all 50 samples are from men, “though we know women are disproportionately impacted by Alzheimer’s.”
“There is a mismatch in the age of the study groups,” Dr. Edelmayer noted. The mean age of controls in the study was 39 and the mean age of people with dementia was 71. Race or ethnicity and other demographic information is also unclear from the article.
“There is an urgent need for simple, inexpensive, noninvasive and easily available diagnostic tools for Alzheimer’s, such as a blood test. A simple blood test for Alzheimer’s would be a great advance for individuals with – and at risk for – the disease, families, doctors, and researchers,” Dr. Edelmayer said.
“Bottom line,” Dr. Edelmayer continued, “these results need to be further tested and verified in long-term, large-scale studies with diverse populations that are representative of those living with Alzheimer’s disease.”
This research was supported by the William Stamps Farish Fund and the Josephine P. & John J. Louis Foundation. Brain Chemistry Labs has applied for a patent related to this research. Dr. Edelmayer has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Impaired vision an overlooked dementia risk factor
Investigators analyzed estimated population attributable fractions (PAFs) associated with dementia in more than 16,000 older adults. A PAF represents the number of dementia cases that could be prevented if a given risk factor were eliminated.
Results showed the PAF of vision impairment was 1.8%, suggesting that healthy vision had the potential to prevent more than 100,000 cases of dementia in the United States.
“Vision impairment and blindness disproportionately impact older adults, yet vision impairment is often preventable or even correctable,” study investigator Joshua Ehrlich MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Poor vision affects not only how individuals see the world, but also their systemic health and well-being, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“Accordingly, ensuring that older adults receive appropriate eye care is vital to promoting health, independence, and optimal aging,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A surprising omission
There is an “urgent need to identify modifiable risk factors for dementia that can be targeted with interventions to slow cognitive decline and prevent dementia,” the investigators wrote.
In 2020, the Lancet Commission report on dementia prevention, intervention, and care proposed a life-course model of 12 potentially modifiable dementia risk factors. This included lower educational level, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, hypertension, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, smoking, depression, social isolation, physical inactivity, diabetes, and air pollution.
Together, these factors are associated with about 40% of dementia cases worldwide, the report notes.
Vision impairment was not included in this model, “despite considerable evidence that it is associated with an elevated risk of incident dementia and that it may operate through the same pathways as hearing loss,” the current researchers wrote.
“We have known for some time that vision impairment is a risk factor for dementia [and] we also know that a very large fraction of vision impairment, possibly in excess of 80%, is avoidable or has simply yet to be addressed,” Dr. Ehrlich said.
He and his colleagues found it “surprising that vision impairment had been ignored in key models of modifiable dementia risk factors that are used to shape health policy and resource allocation.” They set out to demonstrate that, “in fact, vision impairment is just as influential as a number of other long accepted modifiable dementia risk factors.”
The investigators assessed data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a panel study that surveys more than 20,000 U.S. adults aged 50 years or older every 2 years.
The investigators applied the same methods used by the Lancet Commission to the HRS dataset and added vision impairment to the Lancet life-course model. Air pollution was excluded in their model “because those data were not readily available in the HRS,” the researchers wrote.
They noted the PAF is “based on the population prevalence and relative risk of dementia for each risk factor” and is “weighted, based on a principal components analysis, to account for communality (clustering of risk factors).”
A missed prevention opportunity
The sample included 16,690 participants (54% were women, 51.5% were at least age 65, 80.2% were White, 10.6% were Black, 9.2% were other).
In total, the 12 potentially modifiable risk factors used in the researchers’ model were associated with an estimated 62.4% of dementia cases in the United States, with hypertension as the most prevalent risk factor with the highest weighted PAF.
A new focus for prevention
Commenting for this article, Suzann Pershing, MD, associate professor of ophthalmology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called the study “particularly important because, despite growing recognition of its importance in relation to cognition, visual impairment is often an underrecognized risk factor.”
The current research “builds on increasingly robust medical literature linking visual impairment and dementia, applying analogous methods to those used for the life course model recently presented by the Lancet Commission to evaluate potentially modifiable dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Pershing, who was not involved with the study.
The investigators “make a compelling argument for inclusion of visual impairment as one of the potentially modifiable risk factors; practicing clinicians and health care systems may consider screening and targeted therapies to address visual impairment, with a goal of population health and contributing to a reduction in future dementia disease burden,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial), Jennifer Deal, PhD, department of epidemiology and Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health, Baltimore, and Julio Rojas, MD, PhD, Memory and Aging Center, department of neurology, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, call the findings “an important reminder that dementia is a social problem in which potentially treatable risk factors, including visual impairment, are highly prevalent in disadvantaged populations.”
The editorialists noted that 90% of cases of vision impairment are “preventable or have yet to be treated. The two “highly cost-effective interventions” of eyeglasses and/or cataract surgery “remain underused both in the U.S. and globally, especially in disadvantaged communities,” they wrote.
They added that more research is needed to “test the effectiveness of interventions to preserve cognitive health by promoting healthy vision.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Deal reported having received grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rojas reported serving as site principal investigator on clinical trials for Eli Lilly and Eisai and receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Pershing is a consultant for Acumen, and Verana Health (as DigiSight Technologies).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed estimated population attributable fractions (PAFs) associated with dementia in more than 16,000 older adults. A PAF represents the number of dementia cases that could be prevented if a given risk factor were eliminated.
Results showed the PAF of vision impairment was 1.8%, suggesting that healthy vision had the potential to prevent more than 100,000 cases of dementia in the United States.
“Vision impairment and blindness disproportionately impact older adults, yet vision impairment is often preventable or even correctable,” study investigator Joshua Ehrlich MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Poor vision affects not only how individuals see the world, but also their systemic health and well-being, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“Accordingly, ensuring that older adults receive appropriate eye care is vital to promoting health, independence, and optimal aging,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A surprising omission
There is an “urgent need to identify modifiable risk factors for dementia that can be targeted with interventions to slow cognitive decline and prevent dementia,” the investigators wrote.
In 2020, the Lancet Commission report on dementia prevention, intervention, and care proposed a life-course model of 12 potentially modifiable dementia risk factors. This included lower educational level, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, hypertension, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, smoking, depression, social isolation, physical inactivity, diabetes, and air pollution.
Together, these factors are associated with about 40% of dementia cases worldwide, the report notes.
Vision impairment was not included in this model, “despite considerable evidence that it is associated with an elevated risk of incident dementia and that it may operate through the same pathways as hearing loss,” the current researchers wrote.
“We have known for some time that vision impairment is a risk factor for dementia [and] we also know that a very large fraction of vision impairment, possibly in excess of 80%, is avoidable or has simply yet to be addressed,” Dr. Ehrlich said.
He and his colleagues found it “surprising that vision impairment had been ignored in key models of modifiable dementia risk factors that are used to shape health policy and resource allocation.” They set out to demonstrate that, “in fact, vision impairment is just as influential as a number of other long accepted modifiable dementia risk factors.”
The investigators assessed data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a panel study that surveys more than 20,000 U.S. adults aged 50 years or older every 2 years.
The investigators applied the same methods used by the Lancet Commission to the HRS dataset and added vision impairment to the Lancet life-course model. Air pollution was excluded in their model “because those data were not readily available in the HRS,” the researchers wrote.
They noted the PAF is “based on the population prevalence and relative risk of dementia for each risk factor” and is “weighted, based on a principal components analysis, to account for communality (clustering of risk factors).”
A missed prevention opportunity
The sample included 16,690 participants (54% were women, 51.5% were at least age 65, 80.2% were White, 10.6% were Black, 9.2% were other).
In total, the 12 potentially modifiable risk factors used in the researchers’ model were associated with an estimated 62.4% of dementia cases in the United States, with hypertension as the most prevalent risk factor with the highest weighted PAF.
A new focus for prevention
Commenting for this article, Suzann Pershing, MD, associate professor of ophthalmology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called the study “particularly important because, despite growing recognition of its importance in relation to cognition, visual impairment is often an underrecognized risk factor.”
The current research “builds on increasingly robust medical literature linking visual impairment and dementia, applying analogous methods to those used for the life course model recently presented by the Lancet Commission to evaluate potentially modifiable dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Pershing, who was not involved with the study.
The investigators “make a compelling argument for inclusion of visual impairment as one of the potentially modifiable risk factors; practicing clinicians and health care systems may consider screening and targeted therapies to address visual impairment, with a goal of population health and contributing to a reduction in future dementia disease burden,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial), Jennifer Deal, PhD, department of epidemiology and Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health, Baltimore, and Julio Rojas, MD, PhD, Memory and Aging Center, department of neurology, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, call the findings “an important reminder that dementia is a social problem in which potentially treatable risk factors, including visual impairment, are highly prevalent in disadvantaged populations.”
The editorialists noted that 90% of cases of vision impairment are “preventable or have yet to be treated. The two “highly cost-effective interventions” of eyeglasses and/or cataract surgery “remain underused both in the U.S. and globally, especially in disadvantaged communities,” they wrote.
They added that more research is needed to “test the effectiveness of interventions to preserve cognitive health by promoting healthy vision.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Deal reported having received grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rojas reported serving as site principal investigator on clinical trials for Eli Lilly and Eisai and receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Pershing is a consultant for Acumen, and Verana Health (as DigiSight Technologies).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed estimated population attributable fractions (PAFs) associated with dementia in more than 16,000 older adults. A PAF represents the number of dementia cases that could be prevented if a given risk factor were eliminated.
Results showed the PAF of vision impairment was 1.8%, suggesting that healthy vision had the potential to prevent more than 100,000 cases of dementia in the United States.
“Vision impairment and blindness disproportionately impact older adults, yet vision impairment is often preventable or even correctable,” study investigator Joshua Ehrlich MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Poor vision affects not only how individuals see the world, but also their systemic health and well-being, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“Accordingly, ensuring that older adults receive appropriate eye care is vital to promoting health, independence, and optimal aging,” he added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A surprising omission
There is an “urgent need to identify modifiable risk factors for dementia that can be targeted with interventions to slow cognitive decline and prevent dementia,” the investigators wrote.
In 2020, the Lancet Commission report on dementia prevention, intervention, and care proposed a life-course model of 12 potentially modifiable dementia risk factors. This included lower educational level, hearing loss, traumatic brain injury, hypertension, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, smoking, depression, social isolation, physical inactivity, diabetes, and air pollution.
Together, these factors are associated with about 40% of dementia cases worldwide, the report notes.
Vision impairment was not included in this model, “despite considerable evidence that it is associated with an elevated risk of incident dementia and that it may operate through the same pathways as hearing loss,” the current researchers wrote.
“We have known for some time that vision impairment is a risk factor for dementia [and] we also know that a very large fraction of vision impairment, possibly in excess of 80%, is avoidable or has simply yet to be addressed,” Dr. Ehrlich said.
He and his colleagues found it “surprising that vision impairment had been ignored in key models of modifiable dementia risk factors that are used to shape health policy and resource allocation.” They set out to demonstrate that, “in fact, vision impairment is just as influential as a number of other long accepted modifiable dementia risk factors.”
The investigators assessed data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), a panel study that surveys more than 20,000 U.S. adults aged 50 years or older every 2 years.
The investigators applied the same methods used by the Lancet Commission to the HRS dataset and added vision impairment to the Lancet life-course model. Air pollution was excluded in their model “because those data were not readily available in the HRS,” the researchers wrote.
They noted the PAF is “based on the population prevalence and relative risk of dementia for each risk factor” and is “weighted, based on a principal components analysis, to account for communality (clustering of risk factors).”
A missed prevention opportunity
The sample included 16,690 participants (54% were women, 51.5% were at least age 65, 80.2% were White, 10.6% were Black, 9.2% were other).
In total, the 12 potentially modifiable risk factors used in the researchers’ model were associated with an estimated 62.4% of dementia cases in the United States, with hypertension as the most prevalent risk factor with the highest weighted PAF.
A new focus for prevention
Commenting for this article, Suzann Pershing, MD, associate professor of ophthalmology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called the study “particularly important because, despite growing recognition of its importance in relation to cognition, visual impairment is often an underrecognized risk factor.”
The current research “builds on increasingly robust medical literature linking visual impairment and dementia, applying analogous methods to those used for the life course model recently presented by the Lancet Commission to evaluate potentially modifiable dementia risk factors,” said Dr. Pershing, who was not involved with the study.
The investigators “make a compelling argument for inclusion of visual impairment as one of the potentially modifiable risk factors; practicing clinicians and health care systems may consider screening and targeted therapies to address visual impairment, with a goal of population health and contributing to a reduction in future dementia disease burden,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial), Jennifer Deal, PhD, department of epidemiology and Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health, Baltimore, and Julio Rojas, MD, PhD, Memory and Aging Center, department of neurology, Weill Institute for Neurosciences, University of California, San Francisco, call the findings “an important reminder that dementia is a social problem in which potentially treatable risk factors, including visual impairment, are highly prevalent in disadvantaged populations.”
The editorialists noted that 90% of cases of vision impairment are “preventable or have yet to be treated. The two “highly cost-effective interventions” of eyeglasses and/or cataract surgery “remain underused both in the U.S. and globally, especially in disadvantaged communities,” they wrote.
They added that more research is needed to “test the effectiveness of interventions to preserve cognitive health by promoting healthy vision.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and Research to Prevent Blindness. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Deal reported having received grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Rojas reported serving as site principal investigator on clinical trials for Eli Lilly and Eisai and receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Pershing is a consultant for Acumen, and Verana Health (as DigiSight Technologies).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Virtual reality an ‘exciting opportunity’ for geriatric psychiatry
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAGP 2022
Nap length linked to cognitive changes
No wonder we feel worse after naps
Some of us have hectic schedules that may make a nap feel more necessary. It’s common knowledge that naps shouldn’t be too long – maybe 20 minutes or so – but if you frequently take 3-hour naps and wake up thinking you’re late for school even though you’re 47 and have your PhD, this LOTME is for you.
Studies have shown that there is a link between napping during the day and Alzheimer’s/cognitive decline, but now we’ve got a double whammy for you: Longer and more frequent napping is linked to worse cognition after a year, and in turn, those with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s are known to nap longer and more frequently during the day.
“We now know that the pathology related to cognitive decline can cause other changes in function,” he said. “It’s really a multisystem disorder, also including difficulty sleeping, changes in movement, changes in body composition, depression symptoms, behavioral changes, etc.,” coauthor Aron Buchman, MD, said in a statement from Rush University Medical Center.
The investigators monitored 1,400 patients over the course of 14 years with wrist bracelets that recorded when a person was not active during the day and considered that a nap.
At the beginning of the study, 75% of the study subjects had no cognitive impairment, 19.5% had some cognitive impairment, and approximately 4% had Alzheimer’s. Napping during the day only increased about 11 minutes a year for those with no signs of cognitive impairment, but those who showed significantly more signs of cognitive decline doubled their nap time and those actually diagnosed with Alzheimer’s tripled theirs.
The investigators did not imply that napping causes Alzheimer’s, but they noted that people who are older and nap more than an hour a day are 40% more likely to be at risk. It is something to consider and monitor.
Sometimes, after all, a nap seems like the best idea ever, but more often than not we wake up feeling 10 times worse. Our bodies may be giving us a heads up.
Pokemon Go away depression
The summer of 2016 was a great time if you happened to be a fan of Pokemon. Which is quite a lot of people. For almost 20 years millions have enjoyed the games and animated series, but Pokemon Go brought the thrill of catching Pokemon to life in a whole new way. For the first time, you could go out into the world and pretend you were a real Pokemon trainer, and everywhere you went, there would be others like you.
The ability to chase after Pikachu and Charizard in real life (well, augmented reality, but close enough) seemed to bring people a lot of joy, but seemed is never good enough for science. Can’t have anecdotes, we need data! So researchers at the London School of Economics and Political Science conducted a study into how Pokemon Go affected local Internet search rates of depression as the game was released slowly around the world.
Through analyzing Google Trend data of words like “depression,” “anxiety,” and “stress,” the researchers found that the release of Pokemon Go was significantly associated with a noticeable, though short-term, drop in depression-related Internet searches. Location-based augmented reality games may alleviate symptoms of mild depression, the researchers said, as they encourage physical activity, face-to-face socialization, and exposure to nature, though they added that simply going outside is likely not enough to combat clinical cases of severe depression.
Still, augmented reality games represent a viable target for public health investment, since they’re easy to use and inexpensive to make. That said, we’re not sure we want the FDA or CDC making a new Pokemon Go game. They’d probably end up filling the streets with Mr. Mime. And no one would leave their house for that.
And now a word from our sponsor
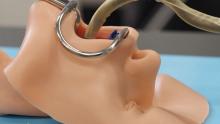
How many times has this happened to you? You need to repair a jet engine, inspect a nuclear reactor cooling system, AND perform bowel surgery, but you can’t carry around all the heavy, old-fashioned tools needed for those jobs.
Well, we’ve got one tool that can do it all! And that tool is a snake. No, it’s a robot.
It’s both! It’s the COntinuum roBot for Remote Applications. COBRA is the robot that looks like a snake! A snake that’s 5 meters long but only as thick as a pencil (about 9 mm in diameter). A robot with “extraordinary manoeuvrability and responsiveness due to … a compliant-joint structure and multiple continuous sections that enable it to bend at around 90 degrees,” according to the team at the University of Nottingham (England) that developed it.
COBRA comes equipped with a stereovision camera and a miniature cutting tool to perform complex industrial repair, but other devices can be interchanged for possible medical use.
COBRA and its joystick-like controller were designed to be easy to use. Dr. Oladejo Olaleye, the ear, nose, and throat and robotic surgeon at University Hospitals of Leicester who is directing its surgical development, was able to use COBRA on a dummy after just 5 minutes of training. He called it “the future of diagnostic endoscopy and therapeutic surgery.”
Don’t be the last aircraft engineer/nuclear technician/surgeon on your block to have this ultraslender, ultramaneuverable reptilian repair robot. Get your COBRA now! Operators are standing by.
Disclaimer: Robot is still under development and not yet on sale.
Rule, (worm) Britannia!
As long as there have been people, there have been parasitic worms living in their guts. Helminth infection is a continuing and largely ignored crisis in poor, tropical nations, though worm-based diseases have been basically eliminated from wealthier countries.
This wasn’t always the case, however, as a study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases (now there’s a specific topic) has found. The researchers detail the glorious history of helminth infestation in the United Kingdom from the Victorian era all the way back to prehistory, scouring hundreds of skeletons found in 17 sites across the country for eggs, which can remain intact for thousands of years.
The researchers found that two eras in particular had very high rates of infection. Unsurprisingly, the late medieval era was one of them, but the other is less obvious. The Romans were famous for their hygiene, their baths, and their plumbing, but maybe they also should be famous for the abundance of worms in their bellies. That doesn’t make sense at first: Shouldn’t good hygiene lower infection? The benefits of a good sewer system, however, are lessened when the waste containing said infectious organisms is used to fertilize crops. Recycling is generally a good thing, but less so when you’re recycling parasitic worms.
Curiously, of the three sites from the industrial age, only the one in London had high levels of worm infestation. Considering how dirty and cramped 19th-century British cities were, one might expect disease to run rampant (tuberculosis certainly did), but the sites in Oxford and Birmingham were almost devoid of worms. The researchers theorized that this was because of access to clean well water. Or maybe worms just have a thing for London. [Editor’s note: It’s probably not that.]
No wonder we feel worse after naps
Some of us have hectic schedules that may make a nap feel more necessary. It’s common knowledge that naps shouldn’t be too long – maybe 20 minutes or so – but if you frequently take 3-hour naps and wake up thinking you’re late for school even though you’re 47 and have your PhD, this LOTME is for you.
Studies have shown that there is a link between napping during the day and Alzheimer’s/cognitive decline, but now we’ve got a double whammy for you: Longer and more frequent napping is linked to worse cognition after a year, and in turn, those with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s are known to nap longer and more frequently during the day.
“We now know that the pathology related to cognitive decline can cause other changes in function,” he said. “It’s really a multisystem disorder, also including difficulty sleeping, changes in movement, changes in body composition, depression symptoms, behavioral changes, etc.,” coauthor Aron Buchman, MD, said in a statement from Rush University Medical Center.
The investigators monitored 1,400 patients over the course of 14 years with wrist bracelets that recorded when a person was not active during the day and considered that a nap.
At the beginning of the study, 75% of the study subjects had no cognitive impairment, 19.5% had some cognitive impairment, and approximately 4% had Alzheimer’s. Napping during the day only increased about 11 minutes a year for those with no signs of cognitive impairment, but those who showed significantly more signs of cognitive decline doubled their nap time and those actually diagnosed with Alzheimer’s tripled theirs.
The investigators did not imply that napping causes Alzheimer’s, but they noted that people who are older and nap more than an hour a day are 40% more likely to be at risk. It is something to consider and monitor.
Sometimes, after all, a nap seems like the best idea ever, but more often than not we wake up feeling 10 times worse. Our bodies may be giving us a heads up.
Pokemon Go away depression
The summer of 2016 was a great time if you happened to be a fan of Pokemon. Which is quite a lot of people. For almost 20 years millions have enjoyed the games and animated series, but Pokemon Go brought the thrill of catching Pokemon to life in a whole new way. For the first time, you could go out into the world and pretend you were a real Pokemon trainer, and everywhere you went, there would be others like you.
The ability to chase after Pikachu and Charizard in real life (well, augmented reality, but close enough) seemed to bring people a lot of joy, but seemed is never good enough for science. Can’t have anecdotes, we need data! So researchers at the London School of Economics and Political Science conducted a study into how Pokemon Go affected local Internet search rates of depression as the game was released slowly around the world.
Through analyzing Google Trend data of words like “depression,” “anxiety,” and “stress,” the researchers found that the release of Pokemon Go was significantly associated with a noticeable, though short-term, drop in depression-related Internet searches. Location-based augmented reality games may alleviate symptoms of mild depression, the researchers said, as they encourage physical activity, face-to-face socialization, and exposure to nature, though they added that simply going outside is likely not enough to combat clinical cases of severe depression.
Still, augmented reality games represent a viable target for public health investment, since they’re easy to use and inexpensive to make. That said, we’re not sure we want the FDA or CDC making a new Pokemon Go game. They’d probably end up filling the streets with Mr. Mime. And no one would leave their house for that.
And now a word from our sponsor
How many times has this happened to you? You need to repair a jet engine, inspect a nuclear reactor cooling system, AND perform bowel surgery, but you can’t carry around all the heavy, old-fashioned tools needed for those jobs.
Well, we’ve got one tool that can do it all! And that tool is a snake. No, it’s a robot.
It’s both! It’s the COntinuum roBot for Remote Applications. COBRA is the robot that looks like a snake! A snake that’s 5 meters long but only as thick as a pencil (about 9 mm in diameter). A robot with “extraordinary manoeuvrability and responsiveness due to … a compliant-joint structure and multiple continuous sections that enable it to bend at around 90 degrees,” according to the team at the University of Nottingham (England) that developed it.
COBRA comes equipped with a stereovision camera and a miniature cutting tool to perform complex industrial repair, but other devices can be interchanged for possible medical use.
COBRA and its joystick-like controller were designed to be easy to use. Dr. Oladejo Olaleye, the ear, nose, and throat and robotic surgeon at University Hospitals of Leicester who is directing its surgical development, was able to use COBRA on a dummy after just 5 minutes of training. He called it “the future of diagnostic endoscopy and therapeutic surgery.”
Don’t be the last aircraft engineer/nuclear technician/surgeon on your block to have this ultraslender, ultramaneuverable reptilian repair robot. Get your COBRA now! Operators are standing by.
Disclaimer: Robot is still under development and not yet on sale.
Rule, (worm) Britannia!
As long as there have been people, there have been parasitic worms living in their guts. Helminth infection is a continuing and largely ignored crisis in poor, tropical nations, though worm-based diseases have been basically eliminated from wealthier countries.
This wasn’t always the case, however, as a study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases (now there’s a specific topic) has found. The researchers detail the glorious history of helminth infestation in the United Kingdom from the Victorian era all the way back to prehistory, scouring hundreds of skeletons found in 17 sites across the country for eggs, which can remain intact for thousands of years.
The researchers found that two eras in particular had very high rates of infection. Unsurprisingly, the late medieval era was one of them, but the other is less obvious. The Romans were famous for their hygiene, their baths, and their plumbing, but maybe they also should be famous for the abundance of worms in their bellies. That doesn’t make sense at first: Shouldn’t good hygiene lower infection? The benefits of a good sewer system, however, are lessened when the waste containing said infectious organisms is used to fertilize crops. Recycling is generally a good thing, but less so when you’re recycling parasitic worms.
Curiously, of the three sites from the industrial age, only the one in London had high levels of worm infestation. Considering how dirty and cramped 19th-century British cities were, one might expect disease to run rampant (tuberculosis certainly did), but the sites in Oxford and Birmingham were almost devoid of worms. The researchers theorized that this was because of access to clean well water. Or maybe worms just have a thing for London. [Editor’s note: It’s probably not that.]
No wonder we feel worse after naps
Some of us have hectic schedules that may make a nap feel more necessary. It’s common knowledge that naps shouldn’t be too long – maybe 20 minutes or so – but if you frequently take 3-hour naps and wake up thinking you’re late for school even though you’re 47 and have your PhD, this LOTME is for you.
Studies have shown that there is a link between napping during the day and Alzheimer’s/cognitive decline, but now we’ve got a double whammy for you: Longer and more frequent napping is linked to worse cognition after a year, and in turn, those with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s are known to nap longer and more frequently during the day.
“We now know that the pathology related to cognitive decline can cause other changes in function,” he said. “It’s really a multisystem disorder, also including difficulty sleeping, changes in movement, changes in body composition, depression symptoms, behavioral changes, etc.,” coauthor Aron Buchman, MD, said in a statement from Rush University Medical Center.
The investigators monitored 1,400 patients over the course of 14 years with wrist bracelets that recorded when a person was not active during the day and considered that a nap.
At the beginning of the study, 75% of the study subjects had no cognitive impairment, 19.5% had some cognitive impairment, and approximately 4% had Alzheimer’s. Napping during the day only increased about 11 minutes a year for those with no signs of cognitive impairment, but those who showed significantly more signs of cognitive decline doubled their nap time and those actually diagnosed with Alzheimer’s tripled theirs.
The investigators did not imply that napping causes Alzheimer’s, but they noted that people who are older and nap more than an hour a day are 40% more likely to be at risk. It is something to consider and monitor.
Sometimes, after all, a nap seems like the best idea ever, but more often than not we wake up feeling 10 times worse. Our bodies may be giving us a heads up.
Pokemon Go away depression
The summer of 2016 was a great time if you happened to be a fan of Pokemon. Which is quite a lot of people. For almost 20 years millions have enjoyed the games and animated series, but Pokemon Go brought the thrill of catching Pokemon to life in a whole new way. For the first time, you could go out into the world and pretend you were a real Pokemon trainer, and everywhere you went, there would be others like you.
The ability to chase after Pikachu and Charizard in real life (well, augmented reality, but close enough) seemed to bring people a lot of joy, but seemed is never good enough for science. Can’t have anecdotes, we need data! So researchers at the London School of Economics and Political Science conducted a study into how Pokemon Go affected local Internet search rates of depression as the game was released slowly around the world.
Through analyzing Google Trend data of words like “depression,” “anxiety,” and “stress,” the researchers found that the release of Pokemon Go was significantly associated with a noticeable, though short-term, drop in depression-related Internet searches. Location-based augmented reality games may alleviate symptoms of mild depression, the researchers said, as they encourage physical activity, face-to-face socialization, and exposure to nature, though they added that simply going outside is likely not enough to combat clinical cases of severe depression.
Still, augmented reality games represent a viable target for public health investment, since they’re easy to use and inexpensive to make. That said, we’re not sure we want the FDA or CDC making a new Pokemon Go game. They’d probably end up filling the streets with Mr. Mime. And no one would leave their house for that.
And now a word from our sponsor
How many times has this happened to you? You need to repair a jet engine, inspect a nuclear reactor cooling system, AND perform bowel surgery, but you can’t carry around all the heavy, old-fashioned tools needed for those jobs.
Well, we’ve got one tool that can do it all! And that tool is a snake. No, it’s a robot.
It’s both! It’s the COntinuum roBot for Remote Applications. COBRA is the robot that looks like a snake! A snake that’s 5 meters long but only as thick as a pencil (about 9 mm in diameter). A robot with “extraordinary manoeuvrability and responsiveness due to … a compliant-joint structure and multiple continuous sections that enable it to bend at around 90 degrees,” according to the team at the University of Nottingham (England) that developed it.
COBRA comes equipped with a stereovision camera and a miniature cutting tool to perform complex industrial repair, but other devices can be interchanged for possible medical use.
COBRA and its joystick-like controller were designed to be easy to use. Dr. Oladejo Olaleye, the ear, nose, and throat and robotic surgeon at University Hospitals of Leicester who is directing its surgical development, was able to use COBRA on a dummy after just 5 minutes of training. He called it “the future of diagnostic endoscopy and therapeutic surgery.”
Don’t be the last aircraft engineer/nuclear technician/surgeon on your block to have this ultraslender, ultramaneuverable reptilian repair robot. Get your COBRA now! Operators are standing by.
Disclaimer: Robot is still under development and not yet on sale.
Rule, (worm) Britannia!
As long as there have been people, there have been parasitic worms living in their guts. Helminth infection is a continuing and largely ignored crisis in poor, tropical nations, though worm-based diseases have been basically eliminated from wealthier countries.
This wasn’t always the case, however, as a study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases (now there’s a specific topic) has found. The researchers detail the glorious history of helminth infestation in the United Kingdom from the Victorian era all the way back to prehistory, scouring hundreds of skeletons found in 17 sites across the country for eggs, which can remain intact for thousands of years.
The researchers found that two eras in particular had very high rates of infection. Unsurprisingly, the late medieval era was one of them, but the other is less obvious. The Romans were famous for their hygiene, their baths, and their plumbing, but maybe they also should be famous for the abundance of worms in their bellies. That doesn’t make sense at first: Shouldn’t good hygiene lower infection? The benefits of a good sewer system, however, are lessened when the waste containing said infectious organisms is used to fertilize crops. Recycling is generally a good thing, but less so when you’re recycling parasitic worms.
Curiously, of the three sites from the industrial age, only the one in London had high levels of worm infestation. Considering how dirty and cramped 19th-century British cities were, one might expect disease to run rampant (tuberculosis certainly did), but the sites in Oxford and Birmingham were almost devoid of worms. The researchers theorized that this was because of access to clean well water. Or maybe worms just have a thing for London. [Editor’s note: It’s probably not that.]
Do personality traits predict cognitive decline?
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PERSONALITY AND SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
Meta-analysis confirms neuroprotective benefit of metformin
Key takeaways
, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal data.
However, the heterogeneity between the available studies and the potential heterogeneity of diagnostic criteria may mean that validation studies are needed.
Why is this important?
Data suggest that metformin, the most commonly prescribed antidiabetic drug, may be neuroprotective, while diabetes is associated with an excess risk of neurodegenerative disease. Results of studies conducted specifically to investigate the benefit of the antidiabetic drug on cognitive prognosis have been unclear. A meta-analysis was published in 2020, but it included cross-sectional and case-control studies. Given the long observation period needed to measure such an outcome, only cohort studies conducted over several years can provide reliable results. This new meta-analysis attempts to circumvent this limitation.
Methods
The meta-analysis was conducted using studies published up to March 2021 that met the inclusion criteria (population-based cohort studies published in English in which the administration of metformin and associated risk of exposure were reported).
Main results
Twelve studies were included in this analysis, of which eight were retrospective and 11 were considered to be of good methodologic quality. In total, 194,792 patients were included.
Pooled data showed that the relative risk associated with onset of neurodegenerative disease was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.67-0.88) for patients with diabetes taking metformin versus those not taking metformin. However, heterogeneity between studies was high (I2; 78.8%; P < .001).
The effect was greater with longer metformin use, with an RR of 0.29 (95% CI, 0.13-0.44) for those who took metformin for 4 years or more. Similarly, the studies conducted in Asian countries versus other locations suggested an added benefit for this population (RR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.64-0.74).
Sensitivity analyses confirmed these results, and subtype analyses showed no difference according to the nature of the neurodegenerative disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
Key takeaways
, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal data.
However, the heterogeneity between the available studies and the potential heterogeneity of diagnostic criteria may mean that validation studies are needed.
Why is this important?
Data suggest that metformin, the most commonly prescribed antidiabetic drug, may be neuroprotective, while diabetes is associated with an excess risk of neurodegenerative disease. Results of studies conducted specifically to investigate the benefit of the antidiabetic drug on cognitive prognosis have been unclear. A meta-analysis was published in 2020, but it included cross-sectional and case-control studies. Given the long observation period needed to measure such an outcome, only cohort studies conducted over several years can provide reliable results. This new meta-analysis attempts to circumvent this limitation.
Methods
The meta-analysis was conducted using studies published up to March 2021 that met the inclusion criteria (population-based cohort studies published in English in which the administration of metformin and associated risk of exposure were reported).
Main results
Twelve studies were included in this analysis, of which eight were retrospective and 11 were considered to be of good methodologic quality. In total, 194,792 patients were included.
Pooled data showed that the relative risk associated with onset of neurodegenerative disease was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.67-0.88) for patients with diabetes taking metformin versus those not taking metformin. However, heterogeneity between studies was high (I2; 78.8%; P < .001).
The effect was greater with longer metformin use, with an RR of 0.29 (95% CI, 0.13-0.44) for those who took metformin for 4 years or more. Similarly, the studies conducted in Asian countries versus other locations suggested an added benefit for this population (RR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.64-0.74).
Sensitivity analyses confirmed these results, and subtype analyses showed no difference according to the nature of the neurodegenerative disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
Key takeaways
, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal data.
However, the heterogeneity between the available studies and the potential heterogeneity of diagnostic criteria may mean that validation studies are needed.
Why is this important?
Data suggest that metformin, the most commonly prescribed antidiabetic drug, may be neuroprotective, while diabetes is associated with an excess risk of neurodegenerative disease. Results of studies conducted specifically to investigate the benefit of the antidiabetic drug on cognitive prognosis have been unclear. A meta-analysis was published in 2020, but it included cross-sectional and case-control studies. Given the long observation period needed to measure such an outcome, only cohort studies conducted over several years can provide reliable results. This new meta-analysis attempts to circumvent this limitation.
Methods
The meta-analysis was conducted using studies published up to March 2021 that met the inclusion criteria (population-based cohort studies published in English in which the administration of metformin and associated risk of exposure were reported).
Main results
Twelve studies were included in this analysis, of which eight were retrospective and 11 were considered to be of good methodologic quality. In total, 194,792 patients were included.
Pooled data showed that the relative risk associated with onset of neurodegenerative disease was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.67-0.88) for patients with diabetes taking metformin versus those not taking metformin. However, heterogeneity between studies was high (I2; 78.8%; P < .001).
The effect was greater with longer metformin use, with an RR of 0.29 (95% CI, 0.13-0.44) for those who took metformin for 4 years or more. Similarly, the studies conducted in Asian countries versus other locations suggested an added benefit for this population (RR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.64-0.74).
Sensitivity analyses confirmed these results, and subtype analyses showed no difference according to the nature of the neurodegenerative disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
Long-term cannabis use linked to dementia risk factors
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
Antibody reduces amyloid, induces symptom decline
SEATTLE – The researchers identified two plasma biomarkers that correlate well with established amyloid PET standard uptake value ratio (SUVr) changes, potentially paving the way for monitoring lecanemab treatment effects. The researchers also found evidence that the plasma biomarker could be used to allow dose frequency reduction after initial reduction in amyloid plaques.
Lecanemab preferably targets aggregated species of amyloid called protofibrils, which is unique among anti-amyloid antibodies, and these are also among the most toxic manifestations of amyloid, according to Chad Swanson, PhD, who presented the study at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Are amyloid plaques a key driver of Alzheimer’s disease?
The study could help answer the question of whether amyloid plaques drive the cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease, in part because the antibody is so effective at what it was designed to do, according to Fernando Testai, MD, PhD, who comoderated the session where the study was presented. “The effect on amyloid content that they measured was persistent over a number of months. Cognition may follow along, so more studies have to be done, but the medication seems to be quite effective doing what it’s supposed to do. If it has something to do with disease, these treatments actually should give us the answer, because the effect on amyloid is pretty significant. After so many years of thinking amyloid probably has nothing to do (with Alzheimer’s symptoms, these results suggest) it may have something to do with the disease,” Dr. Testai said in an interview. He is a professor of neurology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
Dr. Swanson is confident that amyloid plaques are a key driver of disease. “I’d say a number of companies now with anti-amyloid agents have shown that targeting amyloid can produce some slowing of clinical decline, as well as a robust reduction in amyloid, supporting this idea that that amyloid is meaningful. And it’s very clear that amyloid [deposition] tends to trigger tau pathology,” said Dr. Swanson in an interview. He is executive director of the neurology business group at Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the anti-amyloid antibody, called lecanemab.
Searching for the best dose and dose frequency
Dr. Swanson noted that Eisai has already conducted a large phase 2b study which informed the current phase 3 ClarityAD study design. The phase 2b study utilized a Bayesian adaptive design, which allocated more patients in a fully blinded way to doses that had the most potential for slowing clinical decline. “The intent was to maximize the efficiency of the design so that more subjects would go to a dose that looks like it could be the best dose according to the Bayesian algorithm,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study also included a gap period that followed the randomized phase of the trial, where subjects were not being dosed with the antibody from 9 to 59 months (mean, 2 years), before reinitiation at the start of the open-label extension phase. “[That] allowed us to answer some really important questions about what happens when you remove lecanemab after reducing amyloid, and then what happens when you reintroduce lecanemab in the open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The researchers found that amyloid reaccumulated during the treatment gap, and soluble biomarkers were potentially the most sensitive to the change. “Taking all of this information together with clinical data that suggest potential disease-modifying effects, it suggests that we need to continue to treat these individuals, but we may be able to treat with a less-frequent dosing interval once amyloid is removed from the brain. It’s a biweekly infusion. Following 18 months of treatment, we may be able to go in once every month or once every 3 months to maintain low levels of amyloid. We’re going to be testing that soon in the current phase 2 open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study included 856 patients who were randomized to biweekly placebo or lecanemab 2.5 mg/kg biweekly, 5 mg/kg monthly, 5 mg/kg biweekly, 10 mg/kg monthly, or 10 mg/kg biweekly. The primary endpoint was the Alzheimer’s disease composite score at 12 months; secondary endpoints included ADCOMS and various biomarker levels at 18 months.
At 18 months, the 10-mg/kg biweekly group had an adjusted mean change from placebo in brain amyloid of –0.31 SUVr units, with more than 80% of the subjects converting from amyloid positive to amyloid negative by visual read. Most subjects remained amyloid negative at open-label extension baseline following the gap period despite a slow reaccumulation of amyloid plaque in the treated group. Out to 18 months in the core study, the same group had a 30% reduction in cognitive decline, compared with placebo, as measured by ADCOMS (P < .05).
There was a correlation between PET SUVr, clinical outcomes, and the Abeta42/40 ratio and plasma p-tau181. During the gap period, treatment discontinuation was associated with changes in the plasma biomarkers that echoed amyloid re-accumulation and clinical decline. Change from baseline in both plasma biomarkers were associated with a change from baseline in PET SUVr at 18 months.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities related to brain edema or sulcal effusion (ARIA-E) occurred in 9.9% of patients during the randomized phase of the trial, and 7.8% during the open-label extension phase. About 2% were symptomatic in both the randomization and open-label extension phases. The majority of ARIA-E cases appeared within 3 months of treatment initiation, and generally resolved in 4-16 weeks. 80% were mild to moderate by radiography.
Dr. Swanson is an employee of Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study. Dr. Testai has no relevant financial disclosures.
SEATTLE – The researchers identified two plasma biomarkers that correlate well with established amyloid PET standard uptake value ratio (SUVr) changes, potentially paving the way for monitoring lecanemab treatment effects. The researchers also found evidence that the plasma biomarker could be used to allow dose frequency reduction after initial reduction in amyloid plaques.
Lecanemab preferably targets aggregated species of amyloid called protofibrils, which is unique among anti-amyloid antibodies, and these are also among the most toxic manifestations of amyloid, according to Chad Swanson, PhD, who presented the study at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Are amyloid plaques a key driver of Alzheimer’s disease?
The study could help answer the question of whether amyloid plaques drive the cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease, in part because the antibody is so effective at what it was designed to do, according to Fernando Testai, MD, PhD, who comoderated the session where the study was presented. “The effect on amyloid content that they measured was persistent over a number of months. Cognition may follow along, so more studies have to be done, but the medication seems to be quite effective doing what it’s supposed to do. If it has something to do with disease, these treatments actually should give us the answer, because the effect on amyloid is pretty significant. After so many years of thinking amyloid probably has nothing to do (with Alzheimer’s symptoms, these results suggest) it may have something to do with the disease,” Dr. Testai said in an interview. He is a professor of neurology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
Dr. Swanson is confident that amyloid plaques are a key driver of disease. “I’d say a number of companies now with anti-amyloid agents have shown that targeting amyloid can produce some slowing of clinical decline, as well as a robust reduction in amyloid, supporting this idea that that amyloid is meaningful. And it’s very clear that amyloid [deposition] tends to trigger tau pathology,” said Dr. Swanson in an interview. He is executive director of the neurology business group at Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the anti-amyloid antibody, called lecanemab.
Searching for the best dose and dose frequency
Dr. Swanson noted that Eisai has already conducted a large phase 2b study which informed the current phase 3 ClarityAD study design. The phase 2b study utilized a Bayesian adaptive design, which allocated more patients in a fully blinded way to doses that had the most potential for slowing clinical decline. “The intent was to maximize the efficiency of the design so that more subjects would go to a dose that looks like it could be the best dose according to the Bayesian algorithm,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study also included a gap period that followed the randomized phase of the trial, where subjects were not being dosed with the antibody from 9 to 59 months (mean, 2 years), before reinitiation at the start of the open-label extension phase. “[That] allowed us to answer some really important questions about what happens when you remove lecanemab after reducing amyloid, and then what happens when you reintroduce lecanemab in the open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The researchers found that amyloid reaccumulated during the treatment gap, and soluble biomarkers were potentially the most sensitive to the change. “Taking all of this information together with clinical data that suggest potential disease-modifying effects, it suggests that we need to continue to treat these individuals, but we may be able to treat with a less-frequent dosing interval once amyloid is removed from the brain. It’s a biweekly infusion. Following 18 months of treatment, we may be able to go in once every month or once every 3 months to maintain low levels of amyloid. We’re going to be testing that soon in the current phase 2 open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study included 856 patients who were randomized to biweekly placebo or lecanemab 2.5 mg/kg biweekly, 5 mg/kg monthly, 5 mg/kg biweekly, 10 mg/kg monthly, or 10 mg/kg biweekly. The primary endpoint was the Alzheimer’s disease composite score at 12 months; secondary endpoints included ADCOMS and various biomarker levels at 18 months.
At 18 months, the 10-mg/kg biweekly group had an adjusted mean change from placebo in brain amyloid of –0.31 SUVr units, with more than 80% of the subjects converting from amyloid positive to amyloid negative by visual read. Most subjects remained amyloid negative at open-label extension baseline following the gap period despite a slow reaccumulation of amyloid plaque in the treated group. Out to 18 months in the core study, the same group had a 30% reduction in cognitive decline, compared with placebo, as measured by ADCOMS (P < .05).
There was a correlation between PET SUVr, clinical outcomes, and the Abeta42/40 ratio and plasma p-tau181. During the gap period, treatment discontinuation was associated with changes in the plasma biomarkers that echoed amyloid re-accumulation and clinical decline. Change from baseline in both plasma biomarkers were associated with a change from baseline in PET SUVr at 18 months.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities related to brain edema or sulcal effusion (ARIA-E) occurred in 9.9% of patients during the randomized phase of the trial, and 7.8% during the open-label extension phase. About 2% were symptomatic in both the randomization and open-label extension phases. The majority of ARIA-E cases appeared within 3 months of treatment initiation, and generally resolved in 4-16 weeks. 80% were mild to moderate by radiography.
Dr. Swanson is an employee of Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study. Dr. Testai has no relevant financial disclosures.
SEATTLE – The researchers identified two plasma biomarkers that correlate well with established amyloid PET standard uptake value ratio (SUVr) changes, potentially paving the way for monitoring lecanemab treatment effects. The researchers also found evidence that the plasma biomarker could be used to allow dose frequency reduction after initial reduction in amyloid plaques.
Lecanemab preferably targets aggregated species of amyloid called protofibrils, which is unique among anti-amyloid antibodies, and these are also among the most toxic manifestations of amyloid, according to Chad Swanson, PhD, who presented the study at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Are amyloid plaques a key driver of Alzheimer’s disease?
The study could help answer the question of whether amyloid plaques drive the cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer’s disease, in part because the antibody is so effective at what it was designed to do, according to Fernando Testai, MD, PhD, who comoderated the session where the study was presented. “The effect on amyloid content that they measured was persistent over a number of months. Cognition may follow along, so more studies have to be done, but the medication seems to be quite effective doing what it’s supposed to do. If it has something to do with disease, these treatments actually should give us the answer, because the effect on amyloid is pretty significant. After so many years of thinking amyloid probably has nothing to do (with Alzheimer’s symptoms, these results suggest) it may have something to do with the disease,” Dr. Testai said in an interview. He is a professor of neurology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
Dr. Swanson is confident that amyloid plaques are a key driver of disease. “I’d say a number of companies now with anti-amyloid agents have shown that targeting amyloid can produce some slowing of clinical decline, as well as a robust reduction in amyloid, supporting this idea that that amyloid is meaningful. And it’s very clear that amyloid [deposition] tends to trigger tau pathology,” said Dr. Swanson in an interview. He is executive director of the neurology business group at Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which is developing the anti-amyloid antibody, called lecanemab.
Searching for the best dose and dose frequency
Dr. Swanson noted that Eisai has already conducted a large phase 2b study which informed the current phase 3 ClarityAD study design. The phase 2b study utilized a Bayesian adaptive design, which allocated more patients in a fully blinded way to doses that had the most potential for slowing clinical decline. “The intent was to maximize the efficiency of the design so that more subjects would go to a dose that looks like it could be the best dose according to the Bayesian algorithm,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study also included a gap period that followed the randomized phase of the trial, where subjects were not being dosed with the antibody from 9 to 59 months (mean, 2 years), before reinitiation at the start of the open-label extension phase. “[That] allowed us to answer some really important questions about what happens when you remove lecanemab after reducing amyloid, and then what happens when you reintroduce lecanemab in the open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The researchers found that amyloid reaccumulated during the treatment gap, and soluble biomarkers were potentially the most sensitive to the change. “Taking all of this information together with clinical data that suggest potential disease-modifying effects, it suggests that we need to continue to treat these individuals, but we may be able to treat with a less-frequent dosing interval once amyloid is removed from the brain. It’s a biweekly infusion. Following 18 months of treatment, we may be able to go in once every month or once every 3 months to maintain low levels of amyloid. We’re going to be testing that soon in the current phase 2 open-label extension,” said Dr. Swanson.
The study included 856 patients who were randomized to biweekly placebo or lecanemab 2.5 mg/kg biweekly, 5 mg/kg monthly, 5 mg/kg biweekly, 10 mg/kg monthly, or 10 mg/kg biweekly. The primary endpoint was the Alzheimer’s disease composite score at 12 months; secondary endpoints included ADCOMS and various biomarker levels at 18 months.
At 18 months, the 10-mg/kg biweekly group had an adjusted mean change from placebo in brain amyloid of –0.31 SUVr units, with more than 80% of the subjects converting from amyloid positive to amyloid negative by visual read. Most subjects remained amyloid negative at open-label extension baseline following the gap period despite a slow reaccumulation of amyloid plaque in the treated group. Out to 18 months in the core study, the same group had a 30% reduction in cognitive decline, compared with placebo, as measured by ADCOMS (P < .05).
There was a correlation between PET SUVr, clinical outcomes, and the Abeta42/40 ratio and plasma p-tau181. During the gap period, treatment discontinuation was associated with changes in the plasma biomarkers that echoed amyloid re-accumulation and clinical decline. Change from baseline in both plasma biomarkers were associated with a change from baseline in PET SUVr at 18 months.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities related to brain edema or sulcal effusion (ARIA-E) occurred in 9.9% of patients during the randomized phase of the trial, and 7.8% during the open-label extension phase. About 2% were symptomatic in both the randomization and open-label extension phases. The majority of ARIA-E cases appeared within 3 months of treatment initiation, and generally resolved in 4-16 weeks. 80% were mild to moderate by radiography.
Dr. Swanson is an employee of Eisai Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study. Dr. Testai has no relevant financial disclosures.
AT AAN 2022
The EMR gets it wrong: SNAFU
The medical news is full of articles about the coming epidemic of dementia. How many people will have it in 10 years, 20 years, etc. It’s a very legitimate concern, and I am not going to make light of it, or disagree with the predictions.
In my everyday practice, though, I find there’s an epidemic of overdiagnosed dementia, in those who aren’t even close.
This occurs in a few ways:
Aricept is pretty inexpensive these days. Long off patent, insurance companies don’t bother to question its use anymore. So anyone older than 60 who complains of losing their car keys gets put on it. Why? Because patients want their doctors to DO SOMETHING. Even if the doctor knows that there’s really nothing of alarm going on, sometimes it’s easier to go with the placebo effect than argue. I think we’ve all done that before.
There are also a lot of nonneurologists in practice who still, after almost 30 years on the market, think Aricept improves memory, when in fact that’s far from the truth. The best it can claim to do is slow down the rate at which patients get worse, but nobody wants to hear that.
I’ve also seen Aricept used for pseudodementia due to depression. Actually, I’ve seen it used for depression, too. Sometimes it’s used to counteract the side effects dof drugs that can impair cognition, such as Topamax, even in patients who aren’t even remotely demented.
None of the above are a major issue on their own. Where the trouble really happens, as with so many other things, is when they collide with an EMR, or someone too rushed to take a history, or both.
Let’s say Mrs. Jones is on Aricept because she went into a room, then forgot why she did.
Then she gets admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. Or she changes doctors and, like many practices these days, her medications are put in the computer by an MA or secretary.
A lot of times , so that gets punched in as a diagnosis and the patient is now believed to be unable to provide a reliable history. Or the person entering the info looks up its indication and enters “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Even worse is that I’ve seen EMRs where, in an effort to save time, the computer automatically enters diagnoses as you type medications in, and it’s up to the doctor to review them for accuracy. How that saves time I have no idea. But, as above, in these cases it’s going to lead to an entry of dementia where there isn’t any.
That, in particular, is pretty scary. As I wrote here in January of this year, what happens in the EMR stays in the EMR (kind of like Las Vegas).
I’m not knocking off-label use of medications. I don’t know a doctor who doesn’t use some that way, including myself.
But when doing so leads to the wrong assumptions and diagnoses it creates a lot of problems.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The medical news is full of articles about the coming epidemic of dementia. How many people will have it in 10 years, 20 years, etc. It’s a very legitimate concern, and I am not going to make light of it, or disagree with the predictions.
In my everyday practice, though, I find there’s an epidemic of overdiagnosed dementia, in those who aren’t even close.
This occurs in a few ways:
Aricept is pretty inexpensive these days. Long off patent, insurance companies don’t bother to question its use anymore. So anyone older than 60 who complains of losing their car keys gets put on it. Why? Because patients want their doctors to DO SOMETHING. Even if the doctor knows that there’s really nothing of alarm going on, sometimes it’s easier to go with the placebo effect than argue. I think we’ve all done that before.
There are also a lot of nonneurologists in practice who still, after almost 30 years on the market, think Aricept improves memory, when in fact that’s far from the truth. The best it can claim to do is slow down the rate at which patients get worse, but nobody wants to hear that.
I’ve also seen Aricept used for pseudodementia due to depression. Actually, I’ve seen it used for depression, too. Sometimes it’s used to counteract the side effects dof drugs that can impair cognition, such as Topamax, even in patients who aren’t even remotely demented.
None of the above are a major issue on their own. Where the trouble really happens, as with so many other things, is when they collide with an EMR, or someone too rushed to take a history, or both.
Let’s say Mrs. Jones is on Aricept because she went into a room, then forgot why she did.
Then she gets admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. Or she changes doctors and, like many practices these days, her medications are put in the computer by an MA or secretary.
A lot of times , so that gets punched in as a diagnosis and the patient is now believed to be unable to provide a reliable history. Or the person entering the info looks up its indication and enters “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Even worse is that I’ve seen EMRs where, in an effort to save time, the computer automatically enters diagnoses as you type medications in, and it’s up to the doctor to review them for accuracy. How that saves time I have no idea. But, as above, in these cases it’s going to lead to an entry of dementia where there isn’t any.
That, in particular, is pretty scary. As I wrote here in January of this year, what happens in the EMR stays in the EMR (kind of like Las Vegas).
I’m not knocking off-label use of medications. I don’t know a doctor who doesn’t use some that way, including myself.
But when doing so leads to the wrong assumptions and diagnoses it creates a lot of problems.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The medical news is full of articles about the coming epidemic of dementia. How many people will have it in 10 years, 20 years, etc. It’s a very legitimate concern, and I am not going to make light of it, or disagree with the predictions.
In my everyday practice, though, I find there’s an epidemic of overdiagnosed dementia, in those who aren’t even close.
This occurs in a few ways:
Aricept is pretty inexpensive these days. Long off patent, insurance companies don’t bother to question its use anymore. So anyone older than 60 who complains of losing their car keys gets put on it. Why? Because patients want their doctors to DO SOMETHING. Even if the doctor knows that there’s really nothing of alarm going on, sometimes it’s easier to go with the placebo effect than argue. I think we’ve all done that before.
There are also a lot of nonneurologists in practice who still, after almost 30 years on the market, think Aricept improves memory, when in fact that’s far from the truth. The best it can claim to do is slow down the rate at which patients get worse, but nobody wants to hear that.
I’ve also seen Aricept used for pseudodementia due to depression. Actually, I’ve seen it used for depression, too. Sometimes it’s used to counteract the side effects dof drugs that can impair cognition, such as Topamax, even in patients who aren’t even remotely demented.
None of the above are a major issue on their own. Where the trouble really happens, as with so many other things, is when they collide with an EMR, or someone too rushed to take a history, or both.
Let’s say Mrs. Jones is on Aricept because she went into a room, then forgot why she did.
Then she gets admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. Or she changes doctors and, like many practices these days, her medications are put in the computer by an MA or secretary.
A lot of times , so that gets punched in as a diagnosis and the patient is now believed to be unable to provide a reliable history. Or the person entering the info looks up its indication and enters “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Even worse is that I’ve seen EMRs where, in an effort to save time, the computer automatically enters diagnoses as you type medications in, and it’s up to the doctor to review them for accuracy. How that saves time I have no idea. But, as above, in these cases it’s going to lead to an entry of dementia where there isn’t any.
That, in particular, is pretty scary. As I wrote here in January of this year, what happens in the EMR stays in the EMR (kind of like Las Vegas).
I’m not knocking off-label use of medications. I don’t know a doctor who doesn’t use some that way, including myself.
But when doing so leads to the wrong assumptions and diagnoses it creates a lot of problems.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Study: Physical fitness in children linked with concentration, quality of life
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MEDICINE