User login
Kratom: What we know, what to tell your patients
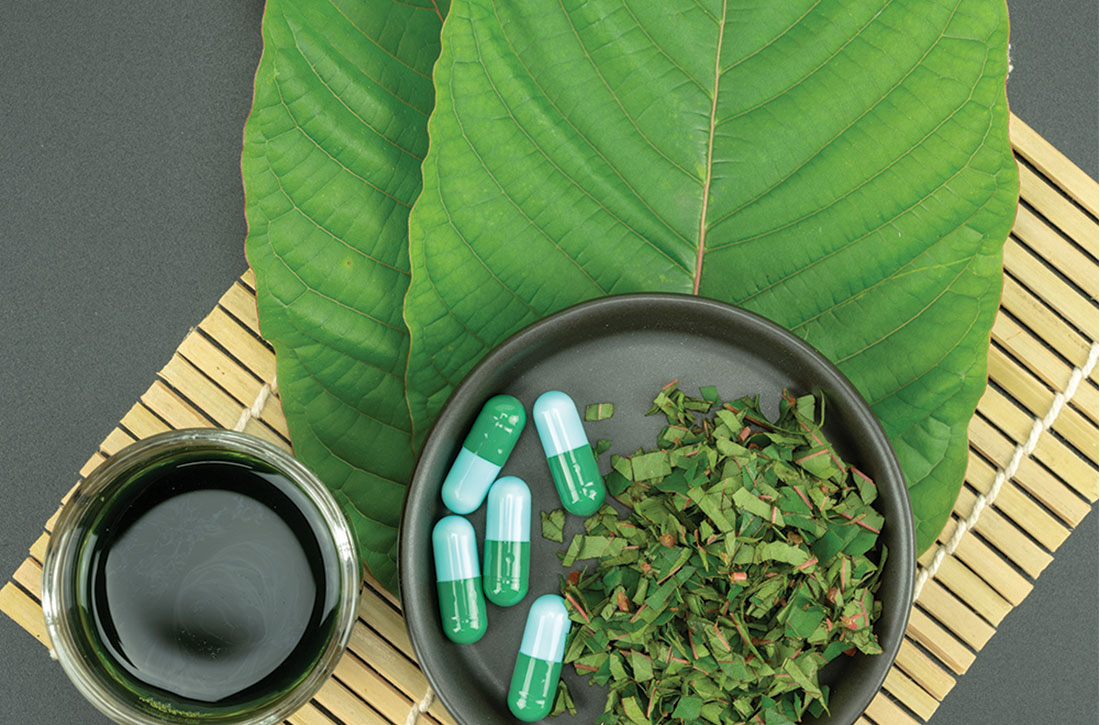
Mitragyna speciosa, better known as kratom, is a tropical evergreen tree that is native to Southeast Asia. Botanically, it is a member of the Rubiaceae family, as is the coffee plant, and physical laborers among indigenous populations have historically chewed the leaves or brewed them as a tea to improve endurance and reduce fatigue.1 Kratom is psychoactive; small amounts (up to 5 g of plant material) possess stimulant properties, while larger doses (>5 g) produce opioid-like, sedative, euphoric, and antinociceptive effects.2
In recent years, kratom has gained popularity in Western parts of the world due to its unique properties and perceived safety as a botanical product. Individuals may use kratom to boost their energy, relieve pain, or treat a wide range of physical or mood problems. Increasingly, kratom is being used by people who abuse opioids to self-manage opioid withdrawal, or for its euphoric effects. But kratom carries several important risks, including addiction, serious adverse effects, and possibly death. In this article, we review the epidemiology and pharmacology of kratom, and provide some guidance for educating patients about this substance.
Widely used but not FDA approved
Although kratom is not regulated or approved by the FDA, 3 to 5 million Americans use it regularly.3 According to an internet survey, kratom users are mostly college-educated, employed white men, age 31 to 50, who take the substance to manage pain or to treat general anxiety and mood disorders.4 Some individuals use kratom as an opioid substitute to reduce symptoms of opioid withdrawal.4
Kratom is available from a wide range of manufacturers in various formulations, including powders, tablets, liquids, and gum. It is sometimes sold in combination with other agents as a single product. Low-cost, over-the-counter kratom products are available as “dietary supplements” in retail stores or online. Although the product packaging sometimes recommends a specific dose, the amount of active ingredients (as well as other agents) is unknown. Kratom is illegal in several states (Box5).
Box
The use and sale of kratom is illegal in several countries, including Australia, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Malaysia, and Vietnam. In the United States, kratom was legal to grow and purchase in all 50 states until 2015, when the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) identified kratom as a “substance of concern.” In August 2016, the DEA submitted a notice of intent to place mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, 2 alkaloids of kratom that have opioid-like properties, into Schedule I of the Controlled Substance Act; however, due to significant public pressure, the DEA withdrew the request in October 2016.
As of February 2020, kratom was illegal to buy, sell, or use in Wisconsin, Rhode Island, Vermont, Indiana, Arkansas, Alabama, specific counties of some states, and the District of Columbia. Legislation was pending in New York, Missouri, and Louisiana.
Source: Reference 5
The 2 alkaloids of interest
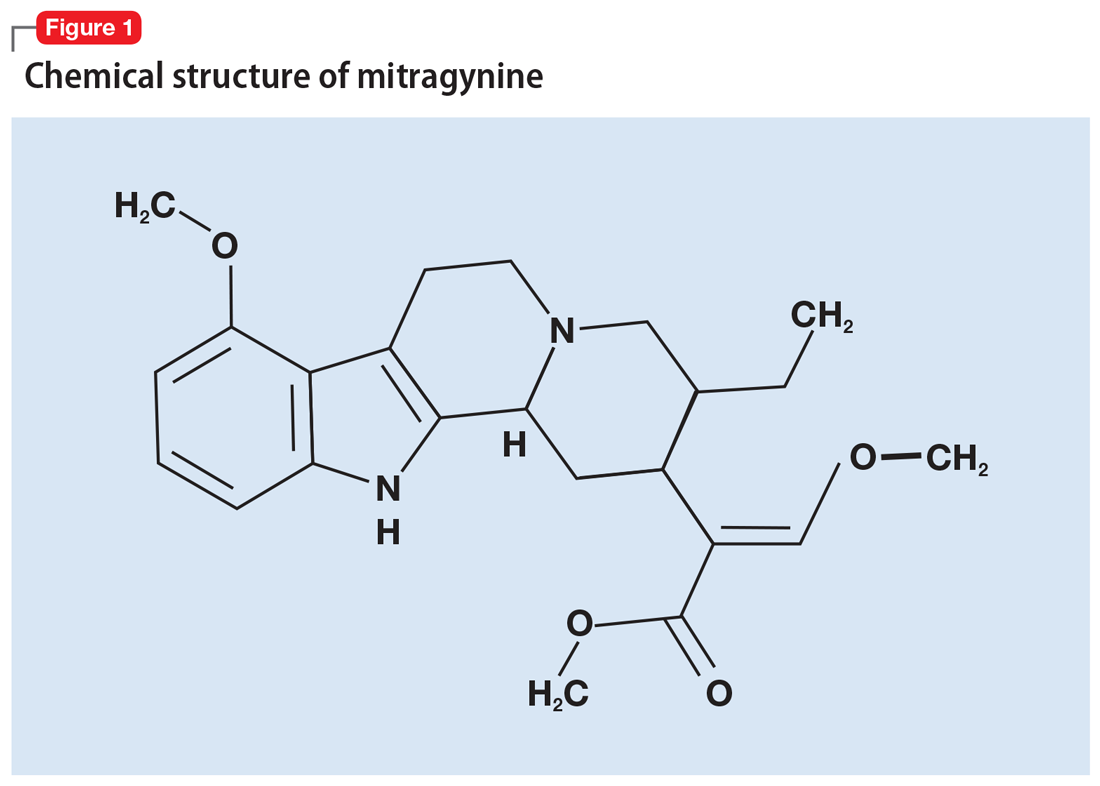
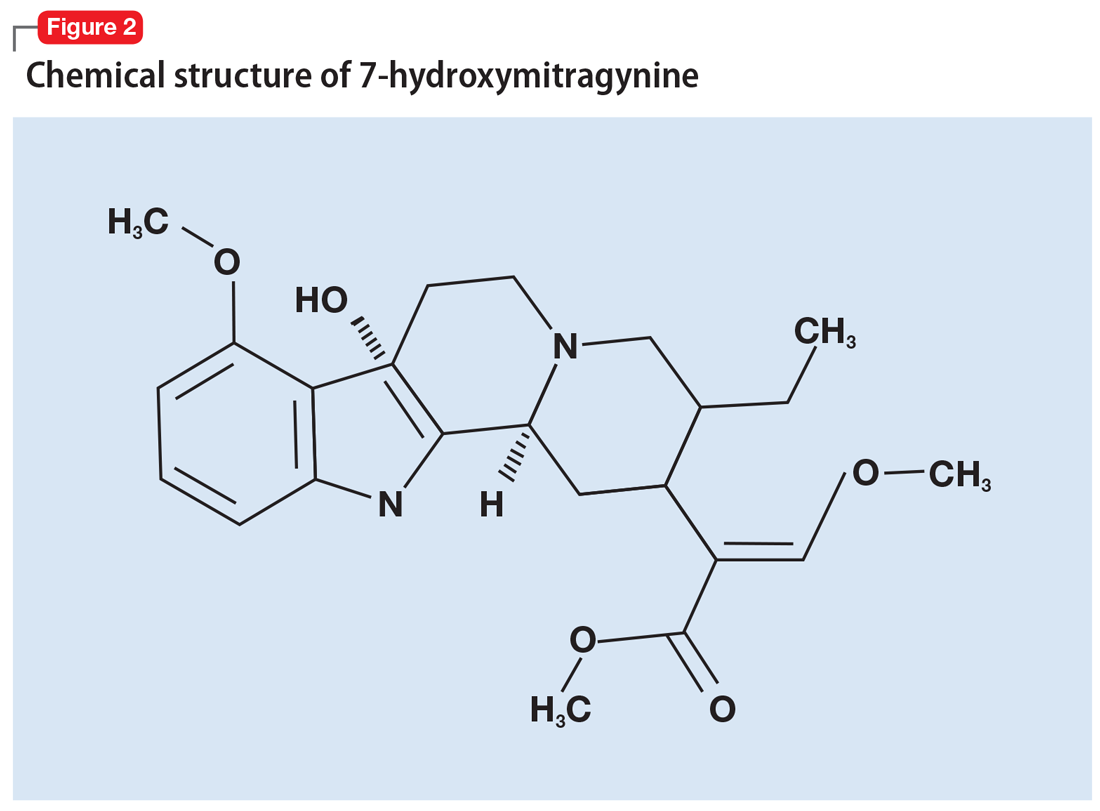
More than 40 alkaloids have been isolated from kratom leaves. The proportions of these alkaloids vary significantly depending on the environment in which the plant is grown, the breeding and harvesting techniques, and the age of the plant.6 Two alkaloids of significant interest are mitragynine (Figure 1) and 7-hydroxymitragynine (Figure 2), both of which are unique to M. speciosa and have opioid-like properties. Administering these alkaloids to morphine-dependent rats resulted in cross-tolerance and precipitated withdrawal when the rats were given naloxone.7 The potency of kratom at the mu opioid receptor has been found to exceed that of morphine.
Competitive binding studies that examined the affinity of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine at the various opioid receptor subtypes found a preference for the kappa receptors (antagonism), followed by mu (partial agonism), and lastly delta. This profile of mitragynine is very similar to that of buprenorphine.8 The affinity of 7-hydroxymitragynine for the mu receptor (agonism) is significantly greater than that of mitragynine.9 Mitragynine also interacts with noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways by stimulating postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and inhibiting 5-HT2A receptors.9 These properties are responsible for kratom’s ability to manage opioid withdrawal symptoms, which are generally attributed to a hyperactive noradrenergic system. There also is evidence that the hepatic metabolite 7-hydroxymitragynine is important in mediating the analgesic component of mitragynine.10
The initial effects of kratom typically begin within 10 to 20 minutes of consumption, and the full effects are experienced in 30 to 60 minutes.1 The half-life of mitragynine in humans has not yet been determined, but is believed to be relatively short.11 In rats, the half-life of mitragynine is 2 to 3 hours.12 Individuals who use kratom to prevent opioid withdrawal have reported taking it as often as every 6 to 12 hours.13
Continue to: Metabolism of mitragynine...
Metabolism of mitragynine is predominantly carried out through cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4, with minor contributions by 2D6 and 2C9. A total of 13 metabolites are produced, including 7-hydroxymitragynine.14 Kratom’s constituents also interact with the CYP system, inhibiting 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4 isoenzymes, and to some extent, 1A2.
Adverse effects can be fatal
An animal study revealed that when administered intravenously, mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine have a similar toxicity profile to heroin.15 When these alkaloids were administered in ascending doses, increases in blood pressure and elevations in liver function tests and creatinine levels from baseline were observed.
Chronic kratom use can result in weight loss, insomnia, constipation, dehydration, skin hyperpigmentation, and extreme fatigue.16 There have also been reports of seizures, delusions, hallucinations, respiratory depression, hepatotoxicity, coma, and death.17,18 An emerging concern is the potential development of fatty liver infiltrates leading to cholestatic liver damage.19-25 One case report described a young man who developed a serum aspartate aminotransferase level of 1,300 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 45 IU/L) and a serum alanine aminotransaminase level of 3,700 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 60 IU/L) after he ingested a kratom product.26 Histologically, the pattern of liver injury mimics primary biliary cholangitis.27
In recent years, calls to poison control centers in the United States related to kratom exposure have risen. Between 2011 and 2017, the number of calls increased from 1 a month to 2 each day.28 The US National Poison Data System has also noted an increase in the number of calls in reference to kratom. It received 2,312 calls from January 2011 through July 2018, with 18 calls occurring in 2011, and 357 within the first 7 months of 2018.29
As of February 2018, the FDA had received reports of 44 deaths associated with kratom.30 There have been reports of fatal overdoses involving kratom, particularly when kratom is co-ingested or used with adulterated and/or combination agents, including one case that involved quetiapine.31-33 There have been reports of deaths believed to be attributed to the use of kratom alone; in one such case, a 35-year-old man experienced a fatal cardiac arrest due to kratom use with no other coingestants.34 Among the reports of deaths in which kratom was the only substance consumed, the mitragynine blood levels of the deceased individuals were found to be higher than the levels associated with individuals who had consumed traditional kratom teas.29
Continue to: There is a lack of quality control...
There is a lack of quality control of commercially available kratom preparations. The FDA has found kratom products that exceeded the level of safe exposure to nickel and lead.35 There have also been reports of Salmonella outbreaks associated with kratom products.36
Detecting kratom use
Mitragynine is a lipophilic alkaloid that is poorly soluble in water37 and eliminated primarily in urine.12 Based on data from treatment center admissions, kratom can be detected in urine samples for 5 to 6 days after use.24,38,39 However, kratom is not detectable by a standard urine toxicology screen; therefore, a high degree of suspicion and special confirmatory testing are necessary. The breakdown products of mitragynine can be detected through gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS), liquid chromatography with linear ion trap mass spectrometry, or electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.40-42
A familiar withdrawal syndrome
Abrupt discontinuation of high-dose, long-term kratom use can produce withdrawal symptoms.13 Symptoms of kratom withdrawal resemble those of opioid withdrawal. These include physiological symptoms (mydriasis, nausea, sweating and chills, muscle and body aches, tremors and twitches, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, and lacrimation) and psychological symptoms (insomnia, restlessness, irritability/hostility, fatigue, anxiety, mood disturbances, and hallucinations).13 Symptoms are first noted starting 12 hours after the last use of kratom, and can last up to 7 days.43 Withdrawal intensity has been positively correlated with the daily amount of kratom consumed, as well as the duration and frequency of use.13,16
In 2 case reports, the newborns of women who used kratom during pregnancy experienced neonatal abstinence syndrome.44,45 In these 2 reports, symptoms such as jitteriness, irritability, feeding intolerance, and vomiting emerged on postpartum Day 2. The newborns were admitted to a neonatal ICU and started on a standard opioid protocol with IV morphine and subsequently tapered with an oral formulation over 5 days.44,45
Helping patients who use kratom
The best approach to treating a patient who is experiencing kratom withdrawal is symptomatic management, as would be appropriate for a patient experiencing opioid withdrawal.13 However, the use of agents such as methadone or buprenorphine for patients undergoing kratom withdrawal has not been thoroughly evaluated; very few reports have been published.46,47
Continue to: Similarly, while the standard of care...
Similarly, while the standard of care for treating a patient with opioid use disorder is medication-assisted treatment in combination with counseling and behavioral therapies, there is little evidence on the efficacy of such treatments for patients who use kratom. There are no specific guidelines, and the risk of relapsing to kratom use is high.48,49 Nonetheless, some clinicians have used the same protocol for patients with opioid use disorder to treat patients using kratom, and several published case reports describe this approach.50,51 Because administering buprenorphine/naltrexone to a patient who is dependent on kratom can precipitate withdrawal, clinicians should follow a similar initiation protocol as for opioid dependence when starting a patient on these agents (ie, a washout period with a challenge test would be prudent prior to starting naltrexone).
In cases of kratom overdose, naloxone has been shown to reverse the analgesic effects of mitragynine in rats. However, in a case report of an individual who accidently overdosed on a kratom product, naloxone had a modest effect.52
Bottom Line
Kratom is a botanical substance that acts like a stimulant at low doses and an opioid at higher doses. Patients might use it to treat mood-related symptoms, relieve pain, or manage opioid withdrawal. Kratom use has been associated with the development of addiction as well as a multitude of serious adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity and overdose. Long-term management may be required for a patient who uses kratom.
Related Resources
- White CM. Pharmacologic and clinical assessment of kratom: an update. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(23):1915-1925.
- Smith KE, Lawson T. Prevalence and motivations for kratom use in a sample of substance users enrolled in a residential treatment program. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:340-348.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naltrexone • Suboxone
Methadone • Methadose
Naltrexone • Revia
Naloxone • Narcan
Quetiapine • Seroquel
1. Henningfield JE, Fant RV, Wang DW. The abuse potential of kratom according the 8 factors of the controlled substances act: implications for regulation and research. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):573-589.
2. Chang-Chien GC, Odonkor CA, Amorapanth P, et al. Is kratom the new ‘legal high’ on the block?: the case of an emerging opioid receptor agonist with substance abuse potential. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E195-E198.
3. Penders T, Jones WB. Kratom, a substance of increasing concern [PCSS webinar]. Providers Clinical Support System. November 28, 2018. https://pcssnow.org/event/kratom-a-substance-of-increasing-concern. Accessed January 29, 2020.
4. Grundmann O. Patterns of kratom use and health impact in the US-results from an online survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;176:63-70.
5. US Drug Enforcement Administration. Drugs of concern. https://www.dea.gov/sites/default/files/sites/getsmartaboutdrugs.com/files/publications/DoA_2017Ed_Updated_6.16.17.pdf#page=84. Updated June 16, 2017. Accessed January 29, 2020.
6. Matsumoto K, Horie S, Ishikawa H, et al. Antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxymitragynine in mice: discovery of an orally active opioid analgesic from the Thai medicinal herb Mitragyna speciosa. Life Sciences. 2004;74(17):2143-2155.
7. Takayama H. Chemistry and pharmacology of analgesic indole alkaloids from the rubiaceous plant, Mitragyna speciosa. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2004;52(8):916-928.
8. Suhaimi FW, Yusoff NH, Hassan R, et al. Neurobiology of kratom and its main alkaloid mitragynine. Brain Res Bull. 2016;126(pt 1):29-40.
9. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
10. Kruegel AC, Uprety R, Grinnell SG, et al. 7-hydroxymitragynine is an active metabolite of mitragynine and a key mediator of its analgesic effects. ACS Cent Sci. 2019;5(6):992-1001.
11. Trakulsrichai S, Sathirakul K, Auparakkitanon S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of mitragynine in man. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015:9:2421-2429.
12. Warner ML, Kaufman NC, Grundmann O, et al. The pharmacology and toxicology of kratom: from traditional herb to drug of abuse. Intl J Legal Med. 2016;130(1):127-138.
13. Stanciu CN, Gnanasegaram SA, Ahmed S, et al. Kratom withdrawal: a systematic review with case series. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):12-18.
14. Kamble SH, Sharma A, King TI, et al. Metabolite profiling and identification of enzymes responsible for the metabolism of mitragynine, the major alkaloid of Mitragyna speciosa (kratom). Xenobiotica. 2019;49(11):1279-1288.
15. Smith LC, Lin L, Hwang CS, et al. Lateral flow assessment and unanticipated toxicity of kratom. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(1):113-121.
16. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Factor analytical investigation of Krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) withdrawal syndrome in Thailand. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2016;48(2):76-85.
17. Vicknasingam B, Narayanan S, Beng GT, et al. The informal use of ketum (Mitragyna speciosa) for opioid withdrawal in the northern states of peninsular Malaysia and implications for drug substitution therapy. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(4):283-288.
18. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Pattern and consequences of krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) use among male villagers in southern Thailand: a qualitative study. Int J Drug Policy. 2013;24(4):351-358.
19. Fernandes CT, Iqbal U, Tighe SP, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury and its conservative management. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619836138. doi: 10.1177/2324709619836138.
20. Dorman C, Wong M, Khan A. Cholestatic hepatitis from prolonged kratom use: a case report. Hepatology. 2015;61(3):1086-1087.
21. Osborne CS, Overstreet AN, Rockey DC, et al. Drug-induced liver injury caused by kratom use as an alternative pain treatment amid an ongoing opioid epidemic. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619826167. doi: 10.1177/2324709619826167.
22. Mousa MS, Sephien A, Gutierrez J, et al. N-acetylcysteine for acute hepatitis induced by kratom herbal tea. Am J Ther. 2018;25(5):e550-e551.
23. Riverso M, Chang M, Soldevila-Pico C, et al. Histologic characterization of kratom use-associated liver injury. Gastroenterology Res. 2018;11(1):79-82.
24. Kapp FG, Maurer HH, Auwärter V, et al. Intrahepatic cholestasis following abuse of powdered kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). J Med Toxicol. 2011;7(3):227-231.
25. Antony A, Lee TP. Herb-induced liver injury with cholestasis and renal injury secondary to short-term use of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). Am J Ther. 2019;26(4):e546-e547.
26. Palasamudram Shekar S, Rojas EE, D’Angelo CC, et al. Legally lethal kratom: a herbal supplement with overdose potential. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):28-30.
27. Aldyab M, Ells PF, Bui R, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury mimicking anti-mitochondrial antibody-negative primary biliary cholangitis: a case report and review of literature. Gastroenterology Res. 2019;12(4):211-215.
28. Post S, Spiller HA, Chounthirath T. Kratom exposures reported to United States poison control centers: 2011-2017. Clinical Toxicol (Phila). 2019;57(10):847-854.
29. Eggleston W, Stoppacher R, Suen K, et al. Kratom use and toxicities in the United States. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(7):775-777.
30. US Food & Drug Administration. Statement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D., on the agency’s scientific evidence on the presence of opioid compounds in kratom , underscoring its potential for abuse. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/statement-fda-commissioner-scott-gottlieb-md-agencys-scientific-evidence-presence-opioid-compounds. Published February 6, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
31. Gershman K, Timm K, Frank M, et al. Deaths in Colorado attributed to kratom. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):97-98.
32. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, et al. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
33. Hughes RL. Fatal combination of mitragynine and quetiapine - a case report with discussion of a potential herb-drug interaction. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019;15(1):110-113.
34. Abdullah HMA, Haq I, Lamfers R. Cardiac arrest in a young healthy male patient secondary to kratom ingestion: is this ‘legal high’ substance more dangerous than initially thought? BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(7):pii: e229778. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229778.
35. Laboratory analysis of kratom products for heavy metals. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/laboratory-analysis-kratom-products-heavy-metals. Updated April 3, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
36. FDA investigated multistate outbreak of salmonella infections linked to products reported to contain kratom. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/fda-investigated-multistate-outbreak-salmonella-infections-linked-products-reported-contain-kratom. Updated June 29, 2018. Accessed January 14, 2020.
37. Aggarwal G, Robertson E, McKinlay J, et a., Death from kratom toxicity and the possible role of intralipid. J Intensive Care Soc. 2018;19(1):61-63.
38. Drug Facts. Kratom. Confirm Biosciences. https://www.confirmbiosciences.com/knowledge/drug-facts/kratom/. Accessed January 14, 2020.
39. Grinspoon P. How long does kratom stay in the system? Addiction Resource. https://addictionresource.com/drugs/kratom/how-long-kratom-stay-in-your-system/. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
40. Kaewklum D, Kaewklum M, Pootrakronchai R, et al. Detection of mitragynine and its metaboilite in urine following ingestion of leaves of Mitragyna speciosa korth. Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (13). Proceedings of the Manfred Donike Workshop, 23rd Cologne Workshop on Dope Analysis. 2005:403-406.
41. Lu S, Tran BN, Nelsen JL, et al. Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009;877(24):2499-2505.
42. Philipp AA, Wissenbach DK, Zoerntlein SW, et al. Studies on the metabolism of mitragynine, the main alkaloid of the herbal drug kratom, in rat and human urine using liquid chromatography-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2009;44(8):1249-1261.
43. Manda VK, Bharathi A, Ali Z, et al. Evaluation of in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and mitraphylline. Planta Med. 2014;80(7):568-576.
44. Davidson L, Rawat M, Stojanovski S, et al. Natural drugs, not so natural effects: neonatal abstinence syndrome secondary to ‘kratom‘. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2019;12(1):109-112.
45. Mackay L, Abrahams R. Novel case of maternal and neonatal kratom dependence and withdrawal. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64(2):121-122.
46. McWhirter L, Morris S. A case report of inpatient detoxification after kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) dependence. Eur Addict Res. 2010;16(4):229-231.
47. Galbis-Reig David. A case report of kratom addiction and withdrawal. WMJ. 2016;115(1):49-52; quiz 53.
48. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam BK. Kratom (Mitragyna speciose) dependence, withdrawal symptoms and craving in regular users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;139:132-137.
49. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam, et al. Social functioning of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) users in Malaysia. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2015;47(2):125-131.
50. Khazaeli A, Jerry JM, Vazirian M. Treatment of kratom withdrawal and addiction with buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):493-495.
51. Buresh M. Treatment of kratom dependence with buprenorphine-naloxone maintenance. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):481-483.
52. Overbeek DL, Abraham J, Munzer BW. Kratom (mitragynine) ingestion requiring naloxone reversal. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2019;3(1):24-26.
Mitragyna speciosa, better known as kratom, is a tropical evergreen tree that is native to Southeast Asia. Botanically, it is a member of the Rubiaceae family, as is the coffee plant, and physical laborers among indigenous populations have historically chewed the leaves or brewed them as a tea to improve endurance and reduce fatigue.1 Kratom is psychoactive; small amounts (up to 5 g of plant material) possess stimulant properties, while larger doses (>5 g) produce opioid-like, sedative, euphoric, and antinociceptive effects.2
In recent years, kratom has gained popularity in Western parts of the world due to its unique properties and perceived safety as a botanical product. Individuals may use kratom to boost their energy, relieve pain, or treat a wide range of physical or mood problems. Increasingly, kratom is being used by people who abuse opioids to self-manage opioid withdrawal, or for its euphoric effects. But kratom carries several important risks, including addiction, serious adverse effects, and possibly death. In this article, we review the epidemiology and pharmacology of kratom, and provide some guidance for educating patients about this substance.
Widely used but not FDA approved
Although kratom is not regulated or approved by the FDA, 3 to 5 million Americans use it regularly.3 According to an internet survey, kratom users are mostly college-educated, employed white men, age 31 to 50, who take the substance to manage pain or to treat general anxiety and mood disorders.4 Some individuals use kratom as an opioid substitute to reduce symptoms of opioid withdrawal.4
Kratom is available from a wide range of manufacturers in various formulations, including powders, tablets, liquids, and gum. It is sometimes sold in combination with other agents as a single product. Low-cost, over-the-counter kratom products are available as “dietary supplements” in retail stores or online. Although the product packaging sometimes recommends a specific dose, the amount of active ingredients (as well as other agents) is unknown. Kratom is illegal in several states (Box5).
Box
The use and sale of kratom is illegal in several countries, including Australia, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Malaysia, and Vietnam. In the United States, kratom was legal to grow and purchase in all 50 states until 2015, when the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) identified kratom as a “substance of concern.” In August 2016, the DEA submitted a notice of intent to place mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, 2 alkaloids of kratom that have opioid-like properties, into Schedule I of the Controlled Substance Act; however, due to significant public pressure, the DEA withdrew the request in October 2016.
As of February 2020, kratom was illegal to buy, sell, or use in Wisconsin, Rhode Island, Vermont, Indiana, Arkansas, Alabama, specific counties of some states, and the District of Columbia. Legislation was pending in New York, Missouri, and Louisiana.
Source: Reference 5
The 2 alkaloids of interest
More than 40 alkaloids have been isolated from kratom leaves. The proportions of these alkaloids vary significantly depending on the environment in which the plant is grown, the breeding and harvesting techniques, and the age of the plant.6 Two alkaloids of significant interest are mitragynine (Figure 1) and 7-hydroxymitragynine (Figure 2), both of which are unique to M. speciosa and have opioid-like properties. Administering these alkaloids to morphine-dependent rats resulted in cross-tolerance and precipitated withdrawal when the rats were given naloxone.7 The potency of kratom at the mu opioid receptor has been found to exceed that of morphine.

Competitive binding studies that examined the affinity of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine at the various opioid receptor subtypes found a preference for the kappa receptors (antagonism), followed by mu (partial agonism), and lastly delta. This profile of mitragynine is very similar to that of buprenorphine.8 The affinity of 7-hydroxymitragynine for the mu receptor (agonism) is significantly greater than that of mitragynine.9 Mitragynine also interacts with noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways by stimulating postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and inhibiting 5-HT2A receptors.9 These properties are responsible for kratom’s ability to manage opioid withdrawal symptoms, which are generally attributed to a hyperactive noradrenergic system. There also is evidence that the hepatic metabolite 7-hydroxymitragynine is important in mediating the analgesic component of mitragynine.10

The initial effects of kratom typically begin within 10 to 20 minutes of consumption, and the full effects are experienced in 30 to 60 minutes.1 The half-life of mitragynine in humans has not yet been determined, but is believed to be relatively short.11 In rats, the half-life of mitragynine is 2 to 3 hours.12 Individuals who use kratom to prevent opioid withdrawal have reported taking it as often as every 6 to 12 hours.13
Continue to: Metabolism of mitragynine...
Metabolism of mitragynine is predominantly carried out through cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4, with minor contributions by 2D6 and 2C9. A total of 13 metabolites are produced, including 7-hydroxymitragynine.14 Kratom’s constituents also interact with the CYP system, inhibiting 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4 isoenzymes, and to some extent, 1A2.
Adverse effects can be fatal
An animal study revealed that when administered intravenously, mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine have a similar toxicity profile to heroin.15 When these alkaloids were administered in ascending doses, increases in blood pressure and elevations in liver function tests and creatinine levels from baseline were observed.
Chronic kratom use can result in weight loss, insomnia, constipation, dehydration, skin hyperpigmentation, and extreme fatigue.16 There have also been reports of seizures, delusions, hallucinations, respiratory depression, hepatotoxicity, coma, and death.17,18 An emerging concern is the potential development of fatty liver infiltrates leading to cholestatic liver damage.19-25 One case report described a young man who developed a serum aspartate aminotransferase level of 1,300 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 45 IU/L) and a serum alanine aminotransaminase level of 3,700 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 60 IU/L) after he ingested a kratom product.26 Histologically, the pattern of liver injury mimics primary biliary cholangitis.27
In recent years, calls to poison control centers in the United States related to kratom exposure have risen. Between 2011 and 2017, the number of calls increased from 1 a month to 2 each day.28 The US National Poison Data System has also noted an increase in the number of calls in reference to kratom. It received 2,312 calls from January 2011 through July 2018, with 18 calls occurring in 2011, and 357 within the first 7 months of 2018.29
As of February 2018, the FDA had received reports of 44 deaths associated with kratom.30 There have been reports of fatal overdoses involving kratom, particularly when kratom is co-ingested or used with adulterated and/or combination agents, including one case that involved quetiapine.31-33 There have been reports of deaths believed to be attributed to the use of kratom alone; in one such case, a 35-year-old man experienced a fatal cardiac arrest due to kratom use with no other coingestants.34 Among the reports of deaths in which kratom was the only substance consumed, the mitragynine blood levels of the deceased individuals were found to be higher than the levels associated with individuals who had consumed traditional kratom teas.29
Continue to: There is a lack of quality control...
There is a lack of quality control of commercially available kratom preparations. The FDA has found kratom products that exceeded the level of safe exposure to nickel and lead.35 There have also been reports of Salmonella outbreaks associated with kratom products.36
Detecting kratom use
Mitragynine is a lipophilic alkaloid that is poorly soluble in water37 and eliminated primarily in urine.12 Based on data from treatment center admissions, kratom can be detected in urine samples for 5 to 6 days after use.24,38,39 However, kratom is not detectable by a standard urine toxicology screen; therefore, a high degree of suspicion and special confirmatory testing are necessary. The breakdown products of mitragynine can be detected through gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS), liquid chromatography with linear ion trap mass spectrometry, or electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.40-42
A familiar withdrawal syndrome
Abrupt discontinuation of high-dose, long-term kratom use can produce withdrawal symptoms.13 Symptoms of kratom withdrawal resemble those of opioid withdrawal. These include physiological symptoms (mydriasis, nausea, sweating and chills, muscle and body aches, tremors and twitches, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, and lacrimation) and psychological symptoms (insomnia, restlessness, irritability/hostility, fatigue, anxiety, mood disturbances, and hallucinations).13 Symptoms are first noted starting 12 hours after the last use of kratom, and can last up to 7 days.43 Withdrawal intensity has been positively correlated with the daily amount of kratom consumed, as well as the duration and frequency of use.13,16
In 2 case reports, the newborns of women who used kratom during pregnancy experienced neonatal abstinence syndrome.44,45 In these 2 reports, symptoms such as jitteriness, irritability, feeding intolerance, and vomiting emerged on postpartum Day 2. The newborns were admitted to a neonatal ICU and started on a standard opioid protocol with IV morphine and subsequently tapered with an oral formulation over 5 days.44,45
Helping patients who use kratom
The best approach to treating a patient who is experiencing kratom withdrawal is symptomatic management, as would be appropriate for a patient experiencing opioid withdrawal.13 However, the use of agents such as methadone or buprenorphine for patients undergoing kratom withdrawal has not been thoroughly evaluated; very few reports have been published.46,47
Continue to: Similarly, while the standard of care...
Similarly, while the standard of care for treating a patient with opioid use disorder is medication-assisted treatment in combination with counseling and behavioral therapies, there is little evidence on the efficacy of such treatments for patients who use kratom. There are no specific guidelines, and the risk of relapsing to kratom use is high.48,49 Nonetheless, some clinicians have used the same protocol for patients with opioid use disorder to treat patients using kratom, and several published case reports describe this approach.50,51 Because administering buprenorphine/naltrexone to a patient who is dependent on kratom can precipitate withdrawal, clinicians should follow a similar initiation protocol as for opioid dependence when starting a patient on these agents (ie, a washout period with a challenge test would be prudent prior to starting naltrexone).
In cases of kratom overdose, naloxone has been shown to reverse the analgesic effects of mitragynine in rats. However, in a case report of an individual who accidently overdosed on a kratom product, naloxone had a modest effect.52
Bottom Line
Kratom is a botanical substance that acts like a stimulant at low doses and an opioid at higher doses. Patients might use it to treat mood-related symptoms, relieve pain, or manage opioid withdrawal. Kratom use has been associated with the development of addiction as well as a multitude of serious adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity and overdose. Long-term management may be required for a patient who uses kratom.
Related Resources
- White CM. Pharmacologic and clinical assessment of kratom: an update. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(23):1915-1925.
- Smith KE, Lawson T. Prevalence and motivations for kratom use in a sample of substance users enrolled in a residential treatment program. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:340-348.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naltrexone • Suboxone
Methadone • Methadose
Naltrexone • Revia
Naloxone • Narcan
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Mitragyna speciosa, better known as kratom, is a tropical evergreen tree that is native to Southeast Asia. Botanically, it is a member of the Rubiaceae family, as is the coffee plant, and physical laborers among indigenous populations have historically chewed the leaves or brewed them as a tea to improve endurance and reduce fatigue.1 Kratom is psychoactive; small amounts (up to 5 g of plant material) possess stimulant properties, while larger doses (>5 g) produce opioid-like, sedative, euphoric, and antinociceptive effects.2
In recent years, kratom has gained popularity in Western parts of the world due to its unique properties and perceived safety as a botanical product. Individuals may use kratom to boost their energy, relieve pain, or treat a wide range of physical or mood problems. Increasingly, kratom is being used by people who abuse opioids to self-manage opioid withdrawal, or for its euphoric effects. But kratom carries several important risks, including addiction, serious adverse effects, and possibly death. In this article, we review the epidemiology and pharmacology of kratom, and provide some guidance for educating patients about this substance.
Widely used but not FDA approved
Although kratom is not regulated or approved by the FDA, 3 to 5 million Americans use it regularly.3 According to an internet survey, kratom users are mostly college-educated, employed white men, age 31 to 50, who take the substance to manage pain or to treat general anxiety and mood disorders.4 Some individuals use kratom as an opioid substitute to reduce symptoms of opioid withdrawal.4
Kratom is available from a wide range of manufacturers in various formulations, including powders, tablets, liquids, and gum. It is sometimes sold in combination with other agents as a single product. Low-cost, over-the-counter kratom products are available as “dietary supplements” in retail stores or online. Although the product packaging sometimes recommends a specific dose, the amount of active ingredients (as well as other agents) is unknown. Kratom is illegal in several states (Box5).
Box
The use and sale of kratom is illegal in several countries, including Australia, Poland, Denmark, Sweden, Malaysia, and Vietnam. In the United States, kratom was legal to grow and purchase in all 50 states until 2015, when the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) identified kratom as a “substance of concern.” In August 2016, the DEA submitted a notice of intent to place mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, 2 alkaloids of kratom that have opioid-like properties, into Schedule I of the Controlled Substance Act; however, due to significant public pressure, the DEA withdrew the request in October 2016.
As of February 2020, kratom was illegal to buy, sell, or use in Wisconsin, Rhode Island, Vermont, Indiana, Arkansas, Alabama, specific counties of some states, and the District of Columbia. Legislation was pending in New York, Missouri, and Louisiana.
Source: Reference 5
The 2 alkaloids of interest
More than 40 alkaloids have been isolated from kratom leaves. The proportions of these alkaloids vary significantly depending on the environment in which the plant is grown, the breeding and harvesting techniques, and the age of the plant.6 Two alkaloids of significant interest are mitragynine (Figure 1) and 7-hydroxymitragynine (Figure 2), both of which are unique to M. speciosa and have opioid-like properties. Administering these alkaloids to morphine-dependent rats resulted in cross-tolerance and precipitated withdrawal when the rats were given naloxone.7 The potency of kratom at the mu opioid receptor has been found to exceed that of morphine.

Competitive binding studies that examined the affinity of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine at the various opioid receptor subtypes found a preference for the kappa receptors (antagonism), followed by mu (partial agonism), and lastly delta. This profile of mitragynine is very similar to that of buprenorphine.8 The affinity of 7-hydroxymitragynine for the mu receptor (agonism) is significantly greater than that of mitragynine.9 Mitragynine also interacts with noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways by stimulating postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and inhibiting 5-HT2A receptors.9 These properties are responsible for kratom’s ability to manage opioid withdrawal symptoms, which are generally attributed to a hyperactive noradrenergic system. There also is evidence that the hepatic metabolite 7-hydroxymitragynine is important in mediating the analgesic component of mitragynine.10

The initial effects of kratom typically begin within 10 to 20 minutes of consumption, and the full effects are experienced in 30 to 60 minutes.1 The half-life of mitragynine in humans has not yet been determined, but is believed to be relatively short.11 In rats, the half-life of mitragynine is 2 to 3 hours.12 Individuals who use kratom to prevent opioid withdrawal have reported taking it as often as every 6 to 12 hours.13
Continue to: Metabolism of mitragynine...
Metabolism of mitragynine is predominantly carried out through cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4, with minor contributions by 2D6 and 2C9. A total of 13 metabolites are produced, including 7-hydroxymitragynine.14 Kratom’s constituents also interact with the CYP system, inhibiting 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4 isoenzymes, and to some extent, 1A2.
Adverse effects can be fatal
An animal study revealed that when administered intravenously, mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine have a similar toxicity profile to heroin.15 When these alkaloids were administered in ascending doses, increases in blood pressure and elevations in liver function tests and creatinine levels from baseline were observed.
Chronic kratom use can result in weight loss, insomnia, constipation, dehydration, skin hyperpigmentation, and extreme fatigue.16 There have also been reports of seizures, delusions, hallucinations, respiratory depression, hepatotoxicity, coma, and death.17,18 An emerging concern is the potential development of fatty liver infiltrates leading to cholestatic liver damage.19-25 One case report described a young man who developed a serum aspartate aminotransferase level of 1,300 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 45 IU/L) and a serum alanine aminotransaminase level of 3,700 IU/L (reference range: 5 to 60 IU/L) after he ingested a kratom product.26 Histologically, the pattern of liver injury mimics primary biliary cholangitis.27
In recent years, calls to poison control centers in the United States related to kratom exposure have risen. Between 2011 and 2017, the number of calls increased from 1 a month to 2 each day.28 The US National Poison Data System has also noted an increase in the number of calls in reference to kratom. It received 2,312 calls from January 2011 through July 2018, with 18 calls occurring in 2011, and 357 within the first 7 months of 2018.29
As of February 2018, the FDA had received reports of 44 deaths associated with kratom.30 There have been reports of fatal overdoses involving kratom, particularly when kratom is co-ingested or used with adulterated and/or combination agents, including one case that involved quetiapine.31-33 There have been reports of deaths believed to be attributed to the use of kratom alone; in one such case, a 35-year-old man experienced a fatal cardiac arrest due to kratom use with no other coingestants.34 Among the reports of deaths in which kratom was the only substance consumed, the mitragynine blood levels of the deceased individuals were found to be higher than the levels associated with individuals who had consumed traditional kratom teas.29
Continue to: There is a lack of quality control...
There is a lack of quality control of commercially available kratom preparations. The FDA has found kratom products that exceeded the level of safe exposure to nickel and lead.35 There have also been reports of Salmonella outbreaks associated with kratom products.36
Detecting kratom use
Mitragynine is a lipophilic alkaloid that is poorly soluble in water37 and eliminated primarily in urine.12 Based on data from treatment center admissions, kratom can be detected in urine samples for 5 to 6 days after use.24,38,39 However, kratom is not detectable by a standard urine toxicology screen; therefore, a high degree of suspicion and special confirmatory testing are necessary. The breakdown products of mitragynine can be detected through gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS), liquid chromatography with linear ion trap mass spectrometry, or electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.40-42
A familiar withdrawal syndrome
Abrupt discontinuation of high-dose, long-term kratom use can produce withdrawal symptoms.13 Symptoms of kratom withdrawal resemble those of opioid withdrawal. These include physiological symptoms (mydriasis, nausea, sweating and chills, muscle and body aches, tremors and twitches, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, and lacrimation) and psychological symptoms (insomnia, restlessness, irritability/hostility, fatigue, anxiety, mood disturbances, and hallucinations).13 Symptoms are first noted starting 12 hours after the last use of kratom, and can last up to 7 days.43 Withdrawal intensity has been positively correlated with the daily amount of kratom consumed, as well as the duration and frequency of use.13,16
In 2 case reports, the newborns of women who used kratom during pregnancy experienced neonatal abstinence syndrome.44,45 In these 2 reports, symptoms such as jitteriness, irritability, feeding intolerance, and vomiting emerged on postpartum Day 2. The newborns were admitted to a neonatal ICU and started on a standard opioid protocol with IV morphine and subsequently tapered with an oral formulation over 5 days.44,45
Helping patients who use kratom
The best approach to treating a patient who is experiencing kratom withdrawal is symptomatic management, as would be appropriate for a patient experiencing opioid withdrawal.13 However, the use of agents such as methadone or buprenorphine for patients undergoing kratom withdrawal has not been thoroughly evaluated; very few reports have been published.46,47
Continue to: Similarly, while the standard of care...
Similarly, while the standard of care for treating a patient with opioid use disorder is medication-assisted treatment in combination with counseling and behavioral therapies, there is little evidence on the efficacy of such treatments for patients who use kratom. There are no specific guidelines, and the risk of relapsing to kratom use is high.48,49 Nonetheless, some clinicians have used the same protocol for patients with opioid use disorder to treat patients using kratom, and several published case reports describe this approach.50,51 Because administering buprenorphine/naltrexone to a patient who is dependent on kratom can precipitate withdrawal, clinicians should follow a similar initiation protocol as for opioid dependence when starting a patient on these agents (ie, a washout period with a challenge test would be prudent prior to starting naltrexone).
In cases of kratom overdose, naloxone has been shown to reverse the analgesic effects of mitragynine in rats. However, in a case report of an individual who accidently overdosed on a kratom product, naloxone had a modest effect.52
Bottom Line
Kratom is a botanical substance that acts like a stimulant at low doses and an opioid at higher doses. Patients might use it to treat mood-related symptoms, relieve pain, or manage opioid withdrawal. Kratom use has been associated with the development of addiction as well as a multitude of serious adverse effects, including hepatotoxicity and overdose. Long-term management may be required for a patient who uses kratom.
Related Resources
- White CM. Pharmacologic and clinical assessment of kratom: an update. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(23):1915-1925.
- Smith KE, Lawson T. Prevalence and motivations for kratom use in a sample of substance users enrolled in a residential treatment program. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:340-348.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naltrexone • Suboxone
Methadone • Methadose
Naltrexone • Revia
Naloxone • Narcan
Quetiapine • Seroquel
1. Henningfield JE, Fant RV, Wang DW. The abuse potential of kratom according the 8 factors of the controlled substances act: implications for regulation and research. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):573-589.
2. Chang-Chien GC, Odonkor CA, Amorapanth P, et al. Is kratom the new ‘legal high’ on the block?: the case of an emerging opioid receptor agonist with substance abuse potential. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E195-E198.
3. Penders T, Jones WB. Kratom, a substance of increasing concern [PCSS webinar]. Providers Clinical Support System. November 28, 2018. https://pcssnow.org/event/kratom-a-substance-of-increasing-concern. Accessed January 29, 2020.
4. Grundmann O. Patterns of kratom use and health impact in the US-results from an online survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;176:63-70.
5. US Drug Enforcement Administration. Drugs of concern. https://www.dea.gov/sites/default/files/sites/getsmartaboutdrugs.com/files/publications/DoA_2017Ed_Updated_6.16.17.pdf#page=84. Updated June 16, 2017. Accessed January 29, 2020.
6. Matsumoto K, Horie S, Ishikawa H, et al. Antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxymitragynine in mice: discovery of an orally active opioid analgesic from the Thai medicinal herb Mitragyna speciosa. Life Sciences. 2004;74(17):2143-2155.
7. Takayama H. Chemistry and pharmacology of analgesic indole alkaloids from the rubiaceous plant, Mitragyna speciosa. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2004;52(8):916-928.
8. Suhaimi FW, Yusoff NH, Hassan R, et al. Neurobiology of kratom and its main alkaloid mitragynine. Brain Res Bull. 2016;126(pt 1):29-40.
9. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
10. Kruegel AC, Uprety R, Grinnell SG, et al. 7-hydroxymitragynine is an active metabolite of mitragynine and a key mediator of its analgesic effects. ACS Cent Sci. 2019;5(6):992-1001.
11. Trakulsrichai S, Sathirakul K, Auparakkitanon S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of mitragynine in man. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015:9:2421-2429.
12. Warner ML, Kaufman NC, Grundmann O, et al. The pharmacology and toxicology of kratom: from traditional herb to drug of abuse. Intl J Legal Med. 2016;130(1):127-138.
13. Stanciu CN, Gnanasegaram SA, Ahmed S, et al. Kratom withdrawal: a systematic review with case series. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):12-18.
14. Kamble SH, Sharma A, King TI, et al. Metabolite profiling and identification of enzymes responsible for the metabolism of mitragynine, the major alkaloid of Mitragyna speciosa (kratom). Xenobiotica. 2019;49(11):1279-1288.
15. Smith LC, Lin L, Hwang CS, et al. Lateral flow assessment and unanticipated toxicity of kratom. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(1):113-121.
16. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Factor analytical investigation of Krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) withdrawal syndrome in Thailand. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2016;48(2):76-85.
17. Vicknasingam B, Narayanan S, Beng GT, et al. The informal use of ketum (Mitragyna speciosa) for opioid withdrawal in the northern states of peninsular Malaysia and implications for drug substitution therapy. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(4):283-288.
18. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Pattern and consequences of krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) use among male villagers in southern Thailand: a qualitative study. Int J Drug Policy. 2013;24(4):351-358.
19. Fernandes CT, Iqbal U, Tighe SP, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury and its conservative management. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619836138. doi: 10.1177/2324709619836138.
20. Dorman C, Wong M, Khan A. Cholestatic hepatitis from prolonged kratom use: a case report. Hepatology. 2015;61(3):1086-1087.
21. Osborne CS, Overstreet AN, Rockey DC, et al. Drug-induced liver injury caused by kratom use as an alternative pain treatment amid an ongoing opioid epidemic. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619826167. doi: 10.1177/2324709619826167.
22. Mousa MS, Sephien A, Gutierrez J, et al. N-acetylcysteine for acute hepatitis induced by kratom herbal tea. Am J Ther. 2018;25(5):e550-e551.
23. Riverso M, Chang M, Soldevila-Pico C, et al. Histologic characterization of kratom use-associated liver injury. Gastroenterology Res. 2018;11(1):79-82.
24. Kapp FG, Maurer HH, Auwärter V, et al. Intrahepatic cholestasis following abuse of powdered kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). J Med Toxicol. 2011;7(3):227-231.
25. Antony A, Lee TP. Herb-induced liver injury with cholestasis and renal injury secondary to short-term use of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). Am J Ther. 2019;26(4):e546-e547.
26. Palasamudram Shekar S, Rojas EE, D’Angelo CC, et al. Legally lethal kratom: a herbal supplement with overdose potential. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):28-30.
27. Aldyab M, Ells PF, Bui R, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury mimicking anti-mitochondrial antibody-negative primary biliary cholangitis: a case report and review of literature. Gastroenterology Res. 2019;12(4):211-215.
28. Post S, Spiller HA, Chounthirath T. Kratom exposures reported to United States poison control centers: 2011-2017. Clinical Toxicol (Phila). 2019;57(10):847-854.
29. Eggleston W, Stoppacher R, Suen K, et al. Kratom use and toxicities in the United States. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(7):775-777.
30. US Food & Drug Administration. Statement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D., on the agency’s scientific evidence on the presence of opioid compounds in kratom , underscoring its potential for abuse. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/statement-fda-commissioner-scott-gottlieb-md-agencys-scientific-evidence-presence-opioid-compounds. Published February 6, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
31. Gershman K, Timm K, Frank M, et al. Deaths in Colorado attributed to kratom. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):97-98.
32. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, et al. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
33. Hughes RL. Fatal combination of mitragynine and quetiapine - a case report with discussion of a potential herb-drug interaction. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019;15(1):110-113.
34. Abdullah HMA, Haq I, Lamfers R. Cardiac arrest in a young healthy male patient secondary to kratom ingestion: is this ‘legal high’ substance more dangerous than initially thought? BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(7):pii: e229778. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229778.
35. Laboratory analysis of kratom products for heavy metals. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/laboratory-analysis-kratom-products-heavy-metals. Updated April 3, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
36. FDA investigated multistate outbreak of salmonella infections linked to products reported to contain kratom. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/fda-investigated-multistate-outbreak-salmonella-infections-linked-products-reported-contain-kratom. Updated June 29, 2018. Accessed January 14, 2020.
37. Aggarwal G, Robertson E, McKinlay J, et a., Death from kratom toxicity and the possible role of intralipid. J Intensive Care Soc. 2018;19(1):61-63.
38. Drug Facts. Kratom. Confirm Biosciences. https://www.confirmbiosciences.com/knowledge/drug-facts/kratom/. Accessed January 14, 2020.
39. Grinspoon P. How long does kratom stay in the system? Addiction Resource. https://addictionresource.com/drugs/kratom/how-long-kratom-stay-in-your-system/. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
40. Kaewklum D, Kaewklum M, Pootrakronchai R, et al. Detection of mitragynine and its metaboilite in urine following ingestion of leaves of Mitragyna speciosa korth. Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (13). Proceedings of the Manfred Donike Workshop, 23rd Cologne Workshop on Dope Analysis. 2005:403-406.
41. Lu S, Tran BN, Nelsen JL, et al. Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009;877(24):2499-2505.
42. Philipp AA, Wissenbach DK, Zoerntlein SW, et al. Studies on the metabolism of mitragynine, the main alkaloid of the herbal drug kratom, in rat and human urine using liquid chromatography-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2009;44(8):1249-1261.
43. Manda VK, Bharathi A, Ali Z, et al. Evaluation of in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and mitraphylline. Planta Med. 2014;80(7):568-576.
44. Davidson L, Rawat M, Stojanovski S, et al. Natural drugs, not so natural effects: neonatal abstinence syndrome secondary to ‘kratom‘. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2019;12(1):109-112.
45. Mackay L, Abrahams R. Novel case of maternal and neonatal kratom dependence and withdrawal. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64(2):121-122.
46. McWhirter L, Morris S. A case report of inpatient detoxification after kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) dependence. Eur Addict Res. 2010;16(4):229-231.
47. Galbis-Reig David. A case report of kratom addiction and withdrawal. WMJ. 2016;115(1):49-52; quiz 53.
48. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam BK. Kratom (Mitragyna speciose) dependence, withdrawal symptoms and craving in regular users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;139:132-137.
49. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam, et al. Social functioning of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) users in Malaysia. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2015;47(2):125-131.
50. Khazaeli A, Jerry JM, Vazirian M. Treatment of kratom withdrawal and addiction with buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):493-495.
51. Buresh M. Treatment of kratom dependence with buprenorphine-naloxone maintenance. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):481-483.
52. Overbeek DL, Abraham J, Munzer BW. Kratom (mitragynine) ingestion requiring naloxone reversal. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2019;3(1):24-26.
1. Henningfield JE, Fant RV, Wang DW. The abuse potential of kratom according the 8 factors of the controlled substances act: implications for regulation and research. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):573-589.
2. Chang-Chien GC, Odonkor CA, Amorapanth P, et al. Is kratom the new ‘legal high’ on the block?: the case of an emerging opioid receptor agonist with substance abuse potential. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E195-E198.
3. Penders T, Jones WB. Kratom, a substance of increasing concern [PCSS webinar]. Providers Clinical Support System. November 28, 2018. https://pcssnow.org/event/kratom-a-substance-of-increasing-concern. Accessed January 29, 2020.
4. Grundmann O. Patterns of kratom use and health impact in the US-results from an online survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;176:63-70.
5. US Drug Enforcement Administration. Drugs of concern. https://www.dea.gov/sites/default/files/sites/getsmartaboutdrugs.com/files/publications/DoA_2017Ed_Updated_6.16.17.pdf#page=84. Updated June 16, 2017. Accessed January 29, 2020.
6. Matsumoto K, Horie S, Ishikawa H, et al. Antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxymitragynine in mice: discovery of an orally active opioid analgesic from the Thai medicinal herb Mitragyna speciosa. Life Sciences. 2004;74(17):2143-2155.
7. Takayama H. Chemistry and pharmacology of analgesic indole alkaloids from the rubiaceous plant, Mitragyna speciosa. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2004;52(8):916-928.
8. Suhaimi FW, Yusoff NH, Hassan R, et al. Neurobiology of kratom and its main alkaloid mitragynine. Brain Res Bull. 2016;126(pt 1):29-40.
9. Prozialeck WC, Jivan JK, Andurkar SV. Pharmacology of kratom: an emerging botanical agent with stimulant, analgesic and opioid-like effects. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(12):792-799.
10. Kruegel AC, Uprety R, Grinnell SG, et al. 7-hydroxymitragynine is an active metabolite of mitragynine and a key mediator of its analgesic effects. ACS Cent Sci. 2019;5(6):992-1001.
11. Trakulsrichai S, Sathirakul K, Auparakkitanon S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of mitragynine in man. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015:9:2421-2429.
12. Warner ML, Kaufman NC, Grundmann O, et al. The pharmacology and toxicology of kratom: from traditional herb to drug of abuse. Intl J Legal Med. 2016;130(1):127-138.
13. Stanciu CN, Gnanasegaram SA, Ahmed S, et al. Kratom withdrawal: a systematic review with case series. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):12-18.
14. Kamble SH, Sharma A, King TI, et al. Metabolite profiling and identification of enzymes responsible for the metabolism of mitragynine, the major alkaloid of Mitragyna speciosa (kratom). Xenobiotica. 2019;49(11):1279-1288.
15. Smith LC, Lin L, Hwang CS, et al. Lateral flow assessment and unanticipated toxicity of kratom. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(1):113-121.
16. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Factor analytical investigation of Krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) withdrawal syndrome in Thailand. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2016;48(2):76-85.
17. Vicknasingam B, Narayanan S, Beng GT, et al. The informal use of ketum (Mitragyna speciosa) for opioid withdrawal in the northern states of peninsular Malaysia and implications for drug substitution therapy. Int J Drug Policy. 2010;21(4):283-288.
18. Saingam D, Assanangkornchai S, Geater AF, et al. Pattern and consequences of krathom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) use among male villagers in southern Thailand: a qualitative study. Int J Drug Policy. 2013;24(4):351-358.
19. Fernandes CT, Iqbal U, Tighe SP, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury and its conservative management. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619836138. doi: 10.1177/2324709619836138.
20. Dorman C, Wong M, Khan A. Cholestatic hepatitis from prolonged kratom use: a case report. Hepatology. 2015;61(3):1086-1087.
21. Osborne CS, Overstreet AN, Rockey DC, et al. Drug-induced liver injury caused by kratom use as an alternative pain treatment amid an ongoing opioid epidemic. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2019;7:2324709619826167. doi: 10.1177/2324709619826167.
22. Mousa MS, Sephien A, Gutierrez J, et al. N-acetylcysteine for acute hepatitis induced by kratom herbal tea. Am J Ther. 2018;25(5):e550-e551.
23. Riverso M, Chang M, Soldevila-Pico C, et al. Histologic characterization of kratom use-associated liver injury. Gastroenterology Res. 2018;11(1):79-82.
24. Kapp FG, Maurer HH, Auwärter V, et al. Intrahepatic cholestasis following abuse of powdered kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). J Med Toxicol. 2011;7(3):227-231.
25. Antony A, Lee TP. Herb-induced liver injury with cholestasis and renal injury secondary to short-term use of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa). Am J Ther. 2019;26(4):e546-e547.
26. Palasamudram Shekar S, Rojas EE, D’Angelo CC, et al. Legally lethal kratom: a herbal supplement with overdose potential. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019;51(1):28-30.
27. Aldyab M, Ells PF, Bui R, et al. Kratom-induced cholestatic liver injury mimicking anti-mitochondrial antibody-negative primary biliary cholangitis: a case report and review of literature. Gastroenterology Res. 2019;12(4):211-215.
28. Post S, Spiller HA, Chounthirath T. Kratom exposures reported to United States poison control centers: 2011-2017. Clinical Toxicol (Phila). 2019;57(10):847-854.
29. Eggleston W, Stoppacher R, Suen K, et al. Kratom use and toxicities in the United States. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(7):775-777.
30. US Food & Drug Administration. Statement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D., on the agency’s scientific evidence on the presence of opioid compounds in kratom , underscoring its potential for abuse. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/statement-fda-commissioner-scott-gottlieb-md-agencys-scientific-evidence-presence-opioid-compounds. Published February 6, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
31. Gershman K, Timm K, Frank M, et al. Deaths in Colorado attributed to kratom. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):97-98.
32. Kronstrand R, Roman M, Thelander G, et al. Unintentional fatal intoxications with mitragynine and O-desmethyltramadol from the herbal blend krypton. J Anal Toxicol. 2011;35(4):242-247.
33. Hughes RL. Fatal combination of mitragynine and quetiapine - a case report with discussion of a potential herb-drug interaction. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019;15(1):110-113.
34. Abdullah HMA, Haq I, Lamfers R. Cardiac arrest in a young healthy male patient secondary to kratom ingestion: is this ‘legal high’ substance more dangerous than initially thought? BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(7):pii: e229778. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229778.
35. Laboratory analysis of kratom products for heavy metals. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/laboratory-analysis-kratom-products-heavy-metals. Updated April 3, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
36. FDA investigated multistate outbreak of salmonella infections linked to products reported to contain kratom. US FDA. https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/fda-investigated-multistate-outbreak-salmonella-infections-linked-products-reported-contain-kratom. Updated June 29, 2018. Accessed January 14, 2020.
37. Aggarwal G, Robertson E, McKinlay J, et a., Death from kratom toxicity and the possible role of intralipid. J Intensive Care Soc. 2018;19(1):61-63.
38. Drug Facts. Kratom. Confirm Biosciences. https://www.confirmbiosciences.com/knowledge/drug-facts/kratom/. Accessed January 14, 2020.
39. Grinspoon P. How long does kratom stay in the system? Addiction Resource. https://addictionresource.com/drugs/kratom/how-long-kratom-stay-in-your-system/. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
40. Kaewklum D, Kaewklum M, Pootrakronchai R, et al. Detection of mitragynine and its metaboilite in urine following ingestion of leaves of Mitragyna speciosa korth. Recent Advances in Doping Analysis (13). Proceedings of the Manfred Donike Workshop, 23rd Cologne Workshop on Dope Analysis. 2005:403-406.
41. Lu S, Tran BN, Nelsen JL, et al. Quantitative analysis of mitragynine in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009;877(24):2499-2505.
42. Philipp AA, Wissenbach DK, Zoerntlein SW, et al. Studies on the metabolism of mitragynine, the main alkaloid of the herbal drug kratom, in rat and human urine using liquid chromatography-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2009;44(8):1249-1261.
43. Manda VK, Bharathi A, Ali Z, et al. Evaluation of in vitro absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of mitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine, and mitraphylline. Planta Med. 2014;80(7):568-576.
44. Davidson L, Rawat M, Stojanovski S, et al. Natural drugs, not so natural effects: neonatal abstinence syndrome secondary to ‘kratom‘. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2019;12(1):109-112.
45. Mackay L, Abrahams R. Novel case of maternal and neonatal kratom dependence and withdrawal. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64(2):121-122.
46. McWhirter L, Morris S. A case report of inpatient detoxification after kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) dependence. Eur Addict Res. 2010;16(4):229-231.
47. Galbis-Reig David. A case report of kratom addiction and withdrawal. WMJ. 2016;115(1):49-52; quiz 53.
48. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam BK. Kratom (Mitragyna speciose) dependence, withdrawal symptoms and craving in regular users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;139:132-137.
49. Singh D, Müller CP, Vicknasingam, et al. Social functioning of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) users in Malaysia. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2015;47(2):125-131.
50. Khazaeli A, Jerry JM, Vazirian M. Treatment of kratom withdrawal and addiction with buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):493-495.
51. Buresh M. Treatment of kratom dependence with buprenorphine-naloxone maintenance. J Addict Med. 2018;12(6):481-483.
52. Overbeek DL, Abraham J, Munzer BW. Kratom (mitragynine) ingestion requiring naloxone reversal. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2019;3(1):24-26.
Expert: Eliminating HCV ‘sounds ambitious, but I think it’s possible’
LAS VEGAS – Between 2010 and 2017, the proportion of newly diagnosed cases of acute hepatitis C virus infection rose threefold, driven largely by the concomitant opioid epidemic.
That makes efforts to screen, diagnose, and cure high-risk populations more important than ever, Stevan A. Gonzalez, MD, said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association.
About 70% of HCV cases are related to injection drug use,” said Dr. Gonzalez, medical director of liver transplantation at the Baylor Simmons Transplant Institute at the Baylor Scott & White All Saints Medical Center in Fort Worth, Tex. “This is affecting whites as much as blacks and Hispanics, females as much as males, and in nonurban areas as much as in urban areas.”
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration indicate that during 2004-2014, the number of acute HCV cases among those aged 18-29 years increased 400%, and the use of injection opioids rose 600%.
At the same time, the number of HCV cases among those aged 30-39 years increased 325%, and the use of injection opioids rose 83%.
“We’re starting to see a pattern overlapping between HCV exposure and opioid injection,” Dr. Gonzalez said. Other high-risk populations include homeless and incarcerated individuals.
More than 70 million people worldwide have chronic HCV infection, Dr. Gonzalez noted, with possibly as many as 5 million cases in the United States. It remains the nation’s most common blood-borne infection.
Chronic disease develops in up to 85% of people who are exposed, infection is asymptomatic, and HCV remains one of the leading indications for liver transplantation and causes of liver cancer.
From a geographic standpoint, the prevalence of HCV in young adults is eclipsing that of Baby Boomers in several states in the Appalachian region and in Northeast, which have long been trouble spots for opioid use disorder (Gastroenterol. 2018 May;154[6]:1850-1).
Surprising exposure risk
The primary risk of transmission is through contaminated blood and the exposure through needles.
“It really doesn’t matter whether it’s a needle that has a small amount of dead space where a little bit of blood can remain or needles that have a larger amount of blood,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
“I’ve had patients who come to me and say, ‘I can’t believe I have HCV. It’s impossible. I always use my own needles. They’re always brand new; I’ve never shared with anybody,’” he continued.
“This is where education and awareness is so critical, because it’s not just the needles,” Dr. Gonzalez explained. “HCV can survive on inanimate objects. For example, on a tabletop surface or a water container, HCV can remain viable up to 3 weeks. In a syringe, 2 months. For that reason, HCV can also be transmitted through crack pipes and nasal drug use, where the prevalence can be up to 35%.”
The duration of a person’s HCV infection drives the transmission.
“That’s important to think about, because people who have chronic hepatitis C are infectious until they’re treated,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “If they don’t know that they have hepatitis C, they continue to transmit the virus to others.”
One study found that half of people living with HCV are unaware of their infection (PLoS One. 2014 Jul 2;9[7]:e101554). According to Dr. Gonzalez, forthcoming guidelines from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force are expected to recommend a one-time screening for HCV infection in all adults aged 18-79 years, a Grade B recommendation. “That’s a big deal,” he said. (The draft recommendations are available here.)
HCV infection disproportionately affects individuals in correctional institutions. In fact, an estimated one in three inmates in the United States has chronic HCV.
“This is sort of a forgotten population with a lot of substance use and mental illness,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “Injection drug use in that setting is the most common risk factor: It’s about 60% in terms of the risk of transmission within correctional settings. HCV-associated liver disease has now surpassed HIV as a cause of death within correctional settings.”
Weighing treatment options
The most common oral regimens for chronic HCV include sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir. They achieve cure in 93%-100% of cases.
“HCV can be cured; it can be eradicated from the body long term,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “The choice of regimen, treatment duration, and use of ribavirin depends on the presence/absence of cirrhosis, prior treatment experience, and the genotype.”
All six forms of the HCV genotype can be treated with oral medication, he added, and methadone, bupropion, and naloxone are safe to use during therapy.
Reinfection following HCV treatment occurs infrequently. Dr. Gonzalez cited a randomized, controlled trial presented as an abstract at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. That study’s researchers found that – among 199 patients on opioid-replacement therapy who were receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy, in whom greater than 50% were actively using drugs – the rate of reinfection at 3 years was 1.8 reinfections/100 person-years.
“That’s lower than people expect,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
How to boost screening
Electronic health record systems can be used as an important tool to increase HCV screening in health care settings.
In 2017, researchers published an analysis of three randomized trials carried out at three separate primary care settings to improve screening for HCV: repeated mailings, an EHR best practice alert (BPA), and patient solicitation (Hepatology 2017 Jan;65[1]:44-53). They evaluated HCV antibody testing, diagnosis, and costs for each of the interventions, compared with standard-of-care testing.
The investigators found that the BPA intervention had the lowest incremental cost per completed test – $24 with fixed start-up costs, including technical design and development of the BPA system; $3 without fixed start-up costs. The BPA intervention also had the lowest incremental cost per new case identified.
Other efforts to expand access to screening and treatment are underway.
In 2019, Louisiana health officials negotiated a one-time fee for unlimited access for 5 years to sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) to treat the estimated 30,000 patients on Louisiana Medicaid and in that state’s department of corrections who have HCV.
“The goal is 90% cure; the burden is on the state health department to screen, diagnose, and dispense medication,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
Also in 2019, the state of Washington used an open bidding process to negotiate access to glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) for the state’s Medicaid population who have HCV.
“Those states are setting the pace,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “They are showing examples of how we can start implementing a process to treat these vulnerable populations.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization set a goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030.
“That sounds ambitious, but I think it’s possible,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “It’s important to address these high-risk populations: the incarcerated, people who use drugs, and the homeless, because those are the groups that have a high prevalence of HCV – mainly through injection drug use.
“If we don’t address that population, and we only target the general population, we’re going to have a continual source of transmission,” Dr. Gonzalez warned. “In that case, we would never be able to achieve elimination.”
Dr. Gonzalez disclosed that he is a member of the speakers bureau for AbbVie and Salix.
LAS VEGAS – Between 2010 and 2017, the proportion of newly diagnosed cases of acute hepatitis C virus infection rose threefold, driven largely by the concomitant opioid epidemic.
That makes efforts to screen, diagnose, and cure high-risk populations more important than ever, Stevan A. Gonzalez, MD, said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association.
About 70% of HCV cases are related to injection drug use,” said Dr. Gonzalez, medical director of liver transplantation at the Baylor Simmons Transplant Institute at the Baylor Scott & White All Saints Medical Center in Fort Worth, Tex. “This is affecting whites as much as blacks and Hispanics, females as much as males, and in nonurban areas as much as in urban areas.”
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration indicate that during 2004-2014, the number of acute HCV cases among those aged 18-29 years increased 400%, and the use of injection opioids rose 600%.
At the same time, the number of HCV cases among those aged 30-39 years increased 325%, and the use of injection opioids rose 83%.
“We’re starting to see a pattern overlapping between HCV exposure and opioid injection,” Dr. Gonzalez said. Other high-risk populations include homeless and incarcerated individuals.
More than 70 million people worldwide have chronic HCV infection, Dr. Gonzalez noted, with possibly as many as 5 million cases in the United States. It remains the nation’s most common blood-borne infection.
Chronic disease develops in up to 85% of people who are exposed, infection is asymptomatic, and HCV remains one of the leading indications for liver transplantation and causes of liver cancer.
From a geographic standpoint, the prevalence of HCV in young adults is eclipsing that of Baby Boomers in several states in the Appalachian region and in Northeast, which have long been trouble spots for opioid use disorder (Gastroenterol. 2018 May;154[6]:1850-1).
Surprising exposure risk
The primary risk of transmission is through contaminated blood and the exposure through needles.
“It really doesn’t matter whether it’s a needle that has a small amount of dead space where a little bit of blood can remain or needles that have a larger amount of blood,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
“I’ve had patients who come to me and say, ‘I can’t believe I have HCV. It’s impossible. I always use my own needles. They’re always brand new; I’ve never shared with anybody,’” he continued.
“This is where education and awareness is so critical, because it’s not just the needles,” Dr. Gonzalez explained. “HCV can survive on inanimate objects. For example, on a tabletop surface or a water container, HCV can remain viable up to 3 weeks. In a syringe, 2 months. For that reason, HCV can also be transmitted through crack pipes and nasal drug use, where the prevalence can be up to 35%.”
The duration of a person’s HCV infection drives the transmission.
“That’s important to think about, because people who have chronic hepatitis C are infectious until they’re treated,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “If they don’t know that they have hepatitis C, they continue to transmit the virus to others.”
One study found that half of people living with HCV are unaware of their infection (PLoS One. 2014 Jul 2;9[7]:e101554). According to Dr. Gonzalez, forthcoming guidelines from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force are expected to recommend a one-time screening for HCV infection in all adults aged 18-79 years, a Grade B recommendation. “That’s a big deal,” he said. (The draft recommendations are available here.)
HCV infection disproportionately affects individuals in correctional institutions. In fact, an estimated one in three inmates in the United States has chronic HCV.
“This is sort of a forgotten population with a lot of substance use and mental illness,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “Injection drug use in that setting is the most common risk factor: It’s about 60% in terms of the risk of transmission within correctional settings. HCV-associated liver disease has now surpassed HIV as a cause of death within correctional settings.”
Weighing treatment options
The most common oral regimens for chronic HCV include sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir. They achieve cure in 93%-100% of cases.
“HCV can be cured; it can be eradicated from the body long term,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “The choice of regimen, treatment duration, and use of ribavirin depends on the presence/absence of cirrhosis, prior treatment experience, and the genotype.”
All six forms of the HCV genotype can be treated with oral medication, he added, and methadone, bupropion, and naloxone are safe to use during therapy.
Reinfection following HCV treatment occurs infrequently. Dr. Gonzalez cited a randomized, controlled trial presented as an abstract at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. That study’s researchers found that – among 199 patients on opioid-replacement therapy who were receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy, in whom greater than 50% were actively using drugs – the rate of reinfection at 3 years was 1.8 reinfections/100 person-years.
“That’s lower than people expect,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
How to boost screening
Electronic health record systems can be used as an important tool to increase HCV screening in health care settings.
In 2017, researchers published an analysis of three randomized trials carried out at three separate primary care settings to improve screening for HCV: repeated mailings, an EHR best practice alert (BPA), and patient solicitation (Hepatology 2017 Jan;65[1]:44-53). They evaluated HCV antibody testing, diagnosis, and costs for each of the interventions, compared with standard-of-care testing.
The investigators found that the BPA intervention had the lowest incremental cost per completed test – $24 with fixed start-up costs, including technical design and development of the BPA system; $3 without fixed start-up costs. The BPA intervention also had the lowest incremental cost per new case identified.
Other efforts to expand access to screening and treatment are underway.
In 2019, Louisiana health officials negotiated a one-time fee for unlimited access for 5 years to sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) to treat the estimated 30,000 patients on Louisiana Medicaid and in that state’s department of corrections who have HCV.
“The goal is 90% cure; the burden is on the state health department to screen, diagnose, and dispense medication,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
Also in 2019, the state of Washington used an open bidding process to negotiate access to glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) for the state’s Medicaid population who have HCV.
“Those states are setting the pace,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “They are showing examples of how we can start implementing a process to treat these vulnerable populations.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization set a goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030.
“That sounds ambitious, but I think it’s possible,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “It’s important to address these high-risk populations: the incarcerated, people who use drugs, and the homeless, because those are the groups that have a high prevalence of HCV – mainly through injection drug use.
“If we don’t address that population, and we only target the general population, we’re going to have a continual source of transmission,” Dr. Gonzalez warned. “In that case, we would never be able to achieve elimination.”
Dr. Gonzalez disclosed that he is a member of the speakers bureau for AbbVie and Salix.
LAS VEGAS – Between 2010 and 2017, the proportion of newly diagnosed cases of acute hepatitis C virus infection rose threefold, driven largely by the concomitant opioid epidemic.
That makes efforts to screen, diagnose, and cure high-risk populations more important than ever, Stevan A. Gonzalez, MD, said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association.
About 70% of HCV cases are related to injection drug use,” said Dr. Gonzalez, medical director of liver transplantation at the Baylor Simmons Transplant Institute at the Baylor Scott & White All Saints Medical Center in Fort Worth, Tex. “This is affecting whites as much as blacks and Hispanics, females as much as males, and in nonurban areas as much as in urban areas.”
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration indicate that during 2004-2014, the number of acute HCV cases among those aged 18-29 years increased 400%, and the use of injection opioids rose 600%.
At the same time, the number of HCV cases among those aged 30-39 years increased 325%, and the use of injection opioids rose 83%.
“We’re starting to see a pattern overlapping between HCV exposure and opioid injection,” Dr. Gonzalez said. Other high-risk populations include homeless and incarcerated individuals.
More than 70 million people worldwide have chronic HCV infection, Dr. Gonzalez noted, with possibly as many as 5 million cases in the United States. It remains the nation’s most common blood-borne infection.
Chronic disease develops in up to 85% of people who are exposed, infection is asymptomatic, and HCV remains one of the leading indications for liver transplantation and causes of liver cancer.
From a geographic standpoint, the prevalence of HCV in young adults is eclipsing that of Baby Boomers in several states in the Appalachian region and in Northeast, which have long been trouble spots for opioid use disorder (Gastroenterol. 2018 May;154[6]:1850-1).
Surprising exposure risk
The primary risk of transmission is through contaminated blood and the exposure through needles.
“It really doesn’t matter whether it’s a needle that has a small amount of dead space where a little bit of blood can remain or needles that have a larger amount of blood,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
“I’ve had patients who come to me and say, ‘I can’t believe I have HCV. It’s impossible. I always use my own needles. They’re always brand new; I’ve never shared with anybody,’” he continued.
“This is where education and awareness is so critical, because it’s not just the needles,” Dr. Gonzalez explained. “HCV can survive on inanimate objects. For example, on a tabletop surface or a water container, HCV can remain viable up to 3 weeks. In a syringe, 2 months. For that reason, HCV can also be transmitted through crack pipes and nasal drug use, where the prevalence can be up to 35%.”
The duration of a person’s HCV infection drives the transmission.
“That’s important to think about, because people who have chronic hepatitis C are infectious until they’re treated,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “If they don’t know that they have hepatitis C, they continue to transmit the virus to others.”
One study found that half of people living with HCV are unaware of their infection (PLoS One. 2014 Jul 2;9[7]:e101554). According to Dr. Gonzalez, forthcoming guidelines from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force are expected to recommend a one-time screening for HCV infection in all adults aged 18-79 years, a Grade B recommendation. “That’s a big deal,” he said. (The draft recommendations are available here.)
HCV infection disproportionately affects individuals in correctional institutions. In fact, an estimated one in three inmates in the United States has chronic HCV.
“This is sort of a forgotten population with a lot of substance use and mental illness,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “Injection drug use in that setting is the most common risk factor: It’s about 60% in terms of the risk of transmission within correctional settings. HCV-associated liver disease has now surpassed HIV as a cause of death within correctional settings.”
Weighing treatment options
The most common oral regimens for chronic HCV include sofosbuvir/ledipasvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir. They achieve cure in 93%-100% of cases.
“HCV can be cured; it can be eradicated from the body long term,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “The choice of regimen, treatment duration, and use of ribavirin depends on the presence/absence of cirrhosis, prior treatment experience, and the genotype.”
All six forms of the HCV genotype can be treated with oral medication, he added, and methadone, bupropion, and naloxone are safe to use during therapy.
Reinfection following HCV treatment occurs infrequently. Dr. Gonzalez cited a randomized, controlled trial presented as an abstract at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. That study’s researchers found that – among 199 patients on opioid-replacement therapy who were receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy, in whom greater than 50% were actively using drugs – the rate of reinfection at 3 years was 1.8 reinfections/100 person-years.
“That’s lower than people expect,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
How to boost screening
Electronic health record systems can be used as an important tool to increase HCV screening in health care settings.
In 2017, researchers published an analysis of three randomized trials carried out at three separate primary care settings to improve screening for HCV: repeated mailings, an EHR best practice alert (BPA), and patient solicitation (Hepatology 2017 Jan;65[1]:44-53). They evaluated HCV antibody testing, diagnosis, and costs for each of the interventions, compared with standard-of-care testing.
The investigators found that the BPA intervention had the lowest incremental cost per completed test – $24 with fixed start-up costs, including technical design and development of the BPA system; $3 without fixed start-up costs. The BPA intervention also had the lowest incremental cost per new case identified.
Other efforts to expand access to screening and treatment are underway.
In 2019, Louisiana health officials negotiated a one-time fee for unlimited access for 5 years to sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) to treat the estimated 30,000 patients on Louisiana Medicaid and in that state’s department of corrections who have HCV.
“The goal is 90% cure; the burden is on the state health department to screen, diagnose, and dispense medication,” Dr. Gonzalez said.
Also in 2019, the state of Washington used an open bidding process to negotiate access to glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) for the state’s Medicaid population who have HCV.
“Those states are setting the pace,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “They are showing examples of how we can start implementing a process to treat these vulnerable populations.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization set a goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a major public health threat by 2030.
“That sounds ambitious, but I think it’s possible,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “It’s important to address these high-risk populations: the incarcerated, people who use drugs, and the homeless, because those are the groups that have a high prevalence of HCV – mainly through injection drug use.
“If we don’t address that population, and we only target the general population, we’re going to have a continual source of transmission,” Dr. Gonzalez warned. “In that case, we would never be able to achieve elimination.”
Dr. Gonzalez disclosed that he is a member of the speakers bureau for AbbVie and Salix.
REPORTING FROM NPA 2020
Rising number of young people dying after heavy drinking
MAUI, HAWAII – Alcohol use and deaths related to alcohol-use disorders are increasing, and young adults might be the group to watch, said Norah Terrault, MD, MPH, professor at the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles.
“A lot of young people are drinking large amounts and they don’t know they’re at risk. They may not drink much during the week but then drink 30 drinks on the weekend,” Dr. Terrault told Medscape Medical News.
The largest relative increase in deaths from alcoholic cirrhosis – 10.5% from 2009 to 2016 – was in the 25- to 34-year age group, she reported here at the Gastroenterology Updates IBD Liver Disease Conference 2020.
This highlights the importance of asking for details about alcohol use during primary care visits; not only how much, but also what time of day, for instance, she explained.
Dr. Terrault’s team at Keck is part of the ACCELERATE-AH consortium, a group of 12 transplant centers looking at patterns of alcohol use before and after liver transplantation.
In their retrospective study of 147 consecutive transplant patients from 2006 to 2018, they found that young age, a history of multiple rehab attempts, and overt encephalopathy at time of transplantation were predictors of alcohol use after the procedure.
Corticosteroids remain the only proven therapy for alcoholic hepatitis. “We have not seen a new therapy in this arena in decades,” said Dr. Terrault. “We really have nothing to offer these patients, yet it’s an incredibly common presentation with a high mortality.”
More treatment options
The good news is that some phase 2 data look promising for new therapies, she reported.
“Some of them are targeting injury and regeneration primarily. Others are looking at the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. Some are also looking at how gut permeability and the microbiome are influencing outcomes,” she explained.
Transplantation has become very important for patients who do not respond to current therapy, and selection criteria have evolved over the years to take this into account, she pointed out.
In the early 1980s, alcoholic hepatitis was considered an inappropriate indication for liver transplantation. In the early 2000s, the guidance moved to setting 6 months of alcohol abstinence as a criterion for transplantation. The 6-month rule effectively eliminated patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, who, by the time they needed a new liver, would not have 6 months to live.
Recently, guidelines have added the option of transplantation for patients with alcoholic hepatitis. The option was always there for people who developed alcohol cirrhosis or liver cancer, but now alcoholic hepatitis is recognized as a potential indication for transplantation, Dr. Terrault explained.
Today, transplant centers are moving away from the 6-month rule for two main reasons, she said. One is that few data support the 6-month time period as the duration that makes a difference.
“There is nothing magical about 6 months vs. 3 months or 12 months,” she said, adding that studies have shown that other factors might be better indicators, such as family support and whether the person is employed.
Second, recent studies have shown that rates of 3-year survival are similar in people who did not abstain at all before the procedure and those who undergo transplantation for other reasons.
The ACCELERATE-AH consortium also found that 70% of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis remained abstinent up to 3 years after transplantation.
Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant.
The selection process remains complicated and controversial, Dr. Terrault acknowledged.
“Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant,” she said.
And there is concern that because patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis present with severe illness, they get moved to the top of the wait list. The rationale for that, she explained, is that it is done that way in other acute situations.
“We transplant individuals who have an acetaminophen overdose, for example. That’s common in many programs,” she said.
“My issue is that some patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis that have a very high severity score, but some of them, just with abstinence, will get better,” said Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
There are cases in which acute alcoholic hepatitis will resolve with abstinence, “and patients can return to an entirely compensated state of cirrhosis, in which they are entirely asymptomatic and they can live,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But it’s hard to know without a control group which patients would have that kind of success with just abstinence, she acknowledged.
Terrault said she agreed, and added that “our tools are not that good,” so determining which patients can be “pulled back from the brink” without transplantation is a challenge.
“There’s still a lot to learn about how we do this, and how we do it well,” she said.
Alcoholic hepatitis as an indication for liver transplantation is rare – less than 1% – but growing.
“This is a potential therapy for your patient who is sick in the ICU with a high severity of disease who has failed steroids. We should call out to see if there’s a transplant program that might be willing to evaluate them,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MAUI, HAWAII – Alcohol use and deaths related to alcohol-use disorders are increasing, and young adults might be the group to watch, said Norah Terrault, MD, MPH, professor at the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles.
“A lot of young people are drinking large amounts and they don’t know they’re at risk. They may not drink much during the week but then drink 30 drinks on the weekend,” Dr. Terrault told Medscape Medical News.
The largest relative increase in deaths from alcoholic cirrhosis – 10.5% from 2009 to 2016 – was in the 25- to 34-year age group, she reported here at the Gastroenterology Updates IBD Liver Disease Conference 2020.
This highlights the importance of asking for details about alcohol use during primary care visits; not only how much, but also what time of day, for instance, she explained.
Dr. Terrault’s team at Keck is part of the ACCELERATE-AH consortium, a group of 12 transplant centers looking at patterns of alcohol use before and after liver transplantation.
In their retrospective study of 147 consecutive transplant patients from 2006 to 2018, they found that young age, a history of multiple rehab attempts, and overt encephalopathy at time of transplantation were predictors of alcohol use after the procedure.
Corticosteroids remain the only proven therapy for alcoholic hepatitis. “We have not seen a new therapy in this arena in decades,” said Dr. Terrault. “We really have nothing to offer these patients, yet it’s an incredibly common presentation with a high mortality.”
More treatment options
The good news is that some phase 2 data look promising for new therapies, she reported.
“Some of them are targeting injury and regeneration primarily. Others are looking at the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. Some are also looking at how gut permeability and the microbiome are influencing outcomes,” she explained.
Transplantation has become very important for patients who do not respond to current therapy, and selection criteria have evolved over the years to take this into account, she pointed out.
In the early 1980s, alcoholic hepatitis was considered an inappropriate indication for liver transplantation. In the early 2000s, the guidance moved to setting 6 months of alcohol abstinence as a criterion for transplantation. The 6-month rule effectively eliminated patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, who, by the time they needed a new liver, would not have 6 months to live.
Recently, guidelines have added the option of transplantation for patients with alcoholic hepatitis. The option was always there for people who developed alcohol cirrhosis or liver cancer, but now alcoholic hepatitis is recognized as a potential indication for transplantation, Dr. Terrault explained.
Today, transplant centers are moving away from the 6-month rule for two main reasons, she said. One is that few data support the 6-month time period as the duration that makes a difference.
“There is nothing magical about 6 months vs. 3 months or 12 months,” she said, adding that studies have shown that other factors might be better indicators, such as family support and whether the person is employed.
Second, recent studies have shown that rates of 3-year survival are similar in people who did not abstain at all before the procedure and those who undergo transplantation for other reasons.
The ACCELERATE-AH consortium also found that 70% of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis remained abstinent up to 3 years after transplantation.
Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant.
The selection process remains complicated and controversial, Dr. Terrault acknowledged.
“Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant,” she said.
And there is concern that because patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis present with severe illness, they get moved to the top of the wait list. The rationale for that, she explained, is that it is done that way in other acute situations.
“We transplant individuals who have an acetaminophen overdose, for example. That’s common in many programs,” she said.
“My issue is that some patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis that have a very high severity score, but some of them, just with abstinence, will get better,” said Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
There are cases in which acute alcoholic hepatitis will resolve with abstinence, “and patients can return to an entirely compensated state of cirrhosis, in which they are entirely asymptomatic and they can live,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But it’s hard to know without a control group which patients would have that kind of success with just abstinence, she acknowledged.
Terrault said she agreed, and added that “our tools are not that good,” so determining which patients can be “pulled back from the brink” without transplantation is a challenge.
“There’s still a lot to learn about how we do this, and how we do it well,” she said.
Alcoholic hepatitis as an indication for liver transplantation is rare – less than 1% – but growing.
“This is a potential therapy for your patient who is sick in the ICU with a high severity of disease who has failed steroids. We should call out to see if there’s a transplant program that might be willing to evaluate them,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MAUI, HAWAII – Alcohol use and deaths related to alcohol-use disorders are increasing, and young adults might be the group to watch, said Norah Terrault, MD, MPH, professor at the Keck School of Medicine of USC in Los Angeles.
“A lot of young people are drinking large amounts and they don’t know they’re at risk. They may not drink much during the week but then drink 30 drinks on the weekend,” Dr. Terrault told Medscape Medical News.
The largest relative increase in deaths from alcoholic cirrhosis – 10.5% from 2009 to 2016 – was in the 25- to 34-year age group, she reported here at the Gastroenterology Updates IBD Liver Disease Conference 2020.
This highlights the importance of asking for details about alcohol use during primary care visits; not only how much, but also what time of day, for instance, she explained.
Dr. Terrault’s team at Keck is part of the ACCELERATE-AH consortium, a group of 12 transplant centers looking at patterns of alcohol use before and after liver transplantation.
In their retrospective study of 147 consecutive transplant patients from 2006 to 2018, they found that young age, a history of multiple rehab attempts, and overt encephalopathy at time of transplantation were predictors of alcohol use after the procedure.
Corticosteroids remain the only proven therapy for alcoholic hepatitis. “We have not seen a new therapy in this arena in decades,” said Dr. Terrault. “We really have nothing to offer these patients, yet it’s an incredibly common presentation with a high mortality.”
More treatment options
The good news is that some phase 2 data look promising for new therapies, she reported.
“Some of them are targeting injury and regeneration primarily. Others are looking at the anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. Some are also looking at how gut permeability and the microbiome are influencing outcomes,” she explained.
Transplantation has become very important for patients who do not respond to current therapy, and selection criteria have evolved over the years to take this into account, she pointed out.
In the early 1980s, alcoholic hepatitis was considered an inappropriate indication for liver transplantation. In the early 2000s, the guidance moved to setting 6 months of alcohol abstinence as a criterion for transplantation. The 6-month rule effectively eliminated patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, who, by the time they needed a new liver, would not have 6 months to live.
Recently, guidelines have added the option of transplantation for patients with alcoholic hepatitis. The option was always there for people who developed alcohol cirrhosis or liver cancer, but now alcoholic hepatitis is recognized as a potential indication for transplantation, Dr. Terrault explained.
Today, transplant centers are moving away from the 6-month rule for two main reasons, she said. One is that few data support the 6-month time period as the duration that makes a difference.
“There is nothing magical about 6 months vs. 3 months or 12 months,” she said, adding that studies have shown that other factors might be better indicators, such as family support and whether the person is employed.
Second, recent studies have shown that rates of 3-year survival are similar in people who did not abstain at all before the procedure and those who undergo transplantation for other reasons.
The ACCELERATE-AH consortium also found that 70% of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis remained abstinent up to 3 years after transplantation.
Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant.
The selection process remains complicated and controversial, Dr. Terrault acknowledged.
“Anytime we give an organ to anyone on the list, someone else may die without one. Every year, 20% of patients on the list die without a transplant,” she said.
And there is concern that because patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis present with severe illness, they get moved to the top of the wait list. The rationale for that, she explained, is that it is done that way in other acute situations.
“We transplant individuals who have an acetaminophen overdose, for example. That’s common in many programs,” she said.
“My issue is that some patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis that have a very high severity score, but some of them, just with abstinence, will get better,” said Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, MD, professor of medicine at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
There are cases in which acute alcoholic hepatitis will resolve with abstinence, “and patients can return to an entirely compensated state of cirrhosis, in which they are entirely asymptomatic and they can live,” she told Medscape Medical News.
But it’s hard to know without a control group which patients would have that kind of success with just abstinence, she acknowledged.
Terrault said she agreed, and added that “our tools are not that good,” so determining which patients can be “pulled back from the brink” without transplantation is a challenge.
“There’s still a lot to learn about how we do this, and how we do it well,” she said.
Alcoholic hepatitis as an indication for liver transplantation is rare – less than 1% – but growing.
“This is a potential therapy for your patient who is sick in the ICU with a high severity of disease who has failed steroids. We should call out to see if there’s a transplant program that might be willing to evaluate them,” she said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM GUILD 2020
Cigarette smoking is associated with prefrontal function in patients with schizophrenia
Patients with schizophrenia have decreased chronnectomic density in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, compared with healthy controls, and cigarette smoking in patients with schizophrenia may be associated with a degree of preserved function in that brain region, researchers reported. The results indicate that smoking may be associated with a preservation effect, but it “cannot restore patients’ prefrontal dysfunction to normal levels,” the researchers said.
The chronnectome depicts how brain functional connectivity patterns (i.e., the connectome) vary over time. “Therefore, the chronnectome may be an effective index to evaluate the smoking-related prefrontal functional changes in schizophrenia,” said Yun-Shuang Fan, a researcher at the Clinical Hospital of Chengdu Brain Science Institute in China, and colleagues in the report, which was published in Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry.
The investigators studied 49 patients with schizophrenia, including 22 smokers and 27 nonsmokers, and 43 healthy controls, including 22 smokers and 21 nonsmokers. Participants underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging, and the researchers analyzed chronnectomic density using a sliding-window method. The investigators examined interactions between smoking status and diagnosis.
Smoking was associated with reduced chronnectomic density in healthy controls, but increased density in patients with schizophrenia. The study provides a “framework to elaborate upon the self-medication hypothesis in schizophrenia” and sheds “some fresh light on the elevated rates of smoking in schizophrenia,” they said.
The study was relatively small, and patients’ use of antipsychotic medications, which can affect the connectome, may limit the results. In addition, the study’s cross-sectional design precludes knowing whether “smoking behavior is the cause or result of the prefrontal chronnectome alterations in schizophrenia,” the authors added.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program. The researchers had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fan YS et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109860.
Patients with schizophrenia have decreased chronnectomic density in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, compared with healthy controls, and cigarette smoking in patients with schizophrenia may be associated with a degree of preserved function in that brain region, researchers reported. The results indicate that smoking may be associated with a preservation effect, but it “cannot restore patients’ prefrontal dysfunction to normal levels,” the researchers said.
The chronnectome depicts how brain functional connectivity patterns (i.e., the connectome) vary over time. “Therefore, the chronnectome may be an effective index to evaluate the smoking-related prefrontal functional changes in schizophrenia,” said Yun-Shuang Fan, a researcher at the Clinical Hospital of Chengdu Brain Science Institute in China, and colleagues in the report, which was published in Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry.
The investigators studied 49 patients with schizophrenia, including 22 smokers and 27 nonsmokers, and 43 healthy controls, including 22 smokers and 21 nonsmokers. Participants underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging, and the researchers analyzed chronnectomic density using a sliding-window method. The investigators examined interactions between smoking status and diagnosis.
Smoking was associated with reduced chronnectomic density in healthy controls, but increased density in patients with schizophrenia. The study provides a “framework to elaborate upon the self-medication hypothesis in schizophrenia” and sheds “some fresh light on the elevated rates of smoking in schizophrenia,” they said.
The study was relatively small, and patients’ use of antipsychotic medications, which can affect the connectome, may limit the results. In addition, the study’s cross-sectional design precludes knowing whether “smoking behavior is the cause or result of the prefrontal chronnectome alterations in schizophrenia,” the authors added.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program. The researchers had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fan YS et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109860.
Patients with schizophrenia have decreased chronnectomic density in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, compared with healthy controls, and cigarette smoking in patients with schizophrenia may be associated with a degree of preserved function in that brain region, researchers reported. The results indicate that smoking may be associated with a preservation effect, but it “cannot restore patients’ prefrontal dysfunction to normal levels,” the researchers said.
The chronnectome depicts how brain functional connectivity patterns (i.e., the connectome) vary over time. “Therefore, the chronnectome may be an effective index to evaluate the smoking-related prefrontal functional changes in schizophrenia,” said Yun-Shuang Fan, a researcher at the Clinical Hospital of Chengdu Brain Science Institute in China, and colleagues in the report, which was published in Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry.
The investigators studied 49 patients with schizophrenia, including 22 smokers and 27 nonsmokers, and 43 healthy controls, including 22 smokers and 21 nonsmokers. Participants underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging, and the researchers analyzed chronnectomic density using a sliding-window method. The investigators examined interactions between smoking status and diagnosis.
Smoking was associated with reduced chronnectomic density in healthy controls, but increased density in patients with schizophrenia. The study provides a “framework to elaborate upon the self-medication hypothesis in schizophrenia” and sheds “some fresh light on the elevated rates of smoking in schizophrenia,” they said.
The study was relatively small, and patients’ use of antipsychotic medications, which can affect the connectome, may limit the results. In addition, the study’s cross-sectional design precludes knowing whether “smoking behavior is the cause or result of the prefrontal chronnectome alterations in schizophrenia,” the authors added.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program. The researchers had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Fan YS et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109860.
FROM PROGRESS IN NEURO-PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY & BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY
For OUD patients, ‘a lot of work to be done’
Most Americans who need medication-assisted treatment not getting it
LAS VEGAS – For Karen J. Hartwell, MD, few things in her clinical work bring more reward than providing medication-assisted treatment (MAT) to patients with opioid use disorder.
or to see a depression remit on your selection of an antidepressant,” she said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “We know that medication-assisted treatment is underused and, sadly, relapse rates remain high.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 70,237 drug-related overdose deaths in 2017 – 47,600 from prescription and illicit opioids. “This is being driven predominately by fentanyl and other high-potency synthetic opioids, followed by prescription opioids and heroin,” said Dr. Hartwell, an associate professor in the addiction sciences division in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
There were an estimated 2 million Americans with an opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2018, she said, and more than 10 million misused prescription opioids. At the same time, prescriptions for opioids have dropped to lowest level in 10 years from a peak in 2012 of 81.3 prescriptions per 100 persons to 58.7 prescriptions per 100 persons in 2017 – total of more than 191 million scripts. “There is a decline in the number of opioid prescriptions, but there is still a lot of diversion, and there are some prescription ‘hot spots’ in the Southeast,” Dr. Hartwell said. “Heroin is a very low cost, and we’re wrestling with the issue of fentanyl.”
To complicate matters, most Americans with opioid use disorder are not in treatment. “In many people, the disorder is never diagnosed, and even fewer engage in care,” she said. “There are challenges with treatment retention, and even fewer achieve remission. There’s a lot of work to be done. One of which is the availability of medication-assisted treatment.”
Dr. Hartwell said that she knows of physician colleagues who have obtained a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine but have yet to prescribe it. “Some people may prefer to avoid the dance [of buprenorphine prescribing],” she said. “I’m here to advise you to dance.” Clinicians can learn about MAT waiver training opportunities by visiting the website of the Providers Clinical Support System, a program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
Another option is to join a telementoring session on the topic facilitated by Project ECHO, or Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes, which is being used by the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. The goal of this model is to break down the walls between specialty and primary care by linking experts at an academic “hub” with primary care doctors and nurses in nearby communities.
“Our Project ECHO at the Medical University of South Carolina is twice a month on Fridays,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The first half is a case. The second half is a didactic [session], and you get a free hour of CME.”
The most common drugs used for medication-assisted treatment of opioid disorder are buprenorphine (a partial agonist), naltrexone (an antagonist), and methadone (a full agonist). Methadone retention generally is better than buprenorphine or naltrexone. The recommended treatment duration is 6-12 months, yet many studies demonstrate that many only stay on treatment for 30-60 days.
“You want to keep patients on treatment as long as they benefit from the medication,” Dr. Hartwell said. One large study of Medicaid claims data found that the risk of acute care service use and overdose were high following buprenorphine discontinuation, regardless of treatment duration. Superior outcomes became significant with treatment duration beyond 15 months, although rates of the primary adverse outcomes remained high (Am J Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 1;177[2]:117-24). About 5% of patients across all cohorts experienced one or more medically treated overdoses.
“One thing I don’t want is for people to drop out of treatment and not come back to see me,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is a time for us to use our shared decision-making skills. I like to use the Tapering Readiness Inventory, a list of 16 questions. It asks such things as ‘Are you able to cope with difficult situations without using?’ and ‘Do you have all of the [drug] paraphernalia out of the house?’ We then have a discussion. If the patient decides to go ahead and do a taper, I always leave the door open. So, as that taper persists and someone says, ‘I’m starting to think about using, Doctor,’ I’ll put them back on [buprenorphine]. Or, if they come off the drug and they find themselves at risk of relapsing, they come back in and see me.”
There’s also some evidence that contingency management might be helpful, both in terms of opioid negative urines, and retention and treatment. Meanwhile, extended-release forms of buprenorphine are emerging.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Sublocade, the first once-monthly injectable buprenorphine product for the treatment of moderate-to-severe OUD in adult patients who have initiated treatment with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product. “The recommendations are that you have about a 7-day lead-in of sublingual buprenorphine, and then 2 months of a 300-mg IV injection,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is followed by either 100-mg injections monthly or 300-mg maintenance in select cases. There is some pain at the injection site. Some clinicians are getting around this by using a little bit of lidocaine prior to giving the injection.”
Another product, Brixadi, is an extended-release weekly (8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, 32 mg) and monthly (64 mg, 96 mg, 128 mg) buprenorphine injection used for the treatment of moderate to severe OUD. It is expected to be available in December 2020.
In 2016, the FDA approved Probuphine, the first buprenorphine implant for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. Probuphine is designed to provide a constant, low-level dose of buprenorphine for 6 months in patients who are already stable on low to moderate doses of other forms of buprenorphine, as part of a complete treatment program. “The 6-month duration kind of takes the issue of adherence off the table,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The caveat with this is that you have to be stable on 8 mg of buprenorphine per day or less. The majority of my patients require much higher doses.”
Dr. Hartwell reported having no relevant disclosures.
Most Americans who need medication-assisted treatment not getting it
Most Americans who need medication-assisted treatment not getting it
LAS VEGAS – For Karen J. Hartwell, MD, few things in her clinical work bring more reward than providing medication-assisted treatment (MAT) to patients with opioid use disorder.
or to see a depression remit on your selection of an antidepressant,” she said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “We know that medication-assisted treatment is underused and, sadly, relapse rates remain high.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 70,237 drug-related overdose deaths in 2017 – 47,600 from prescription and illicit opioids. “This is being driven predominately by fentanyl and other high-potency synthetic opioids, followed by prescription opioids and heroin,” said Dr. Hartwell, an associate professor in the addiction sciences division in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
There were an estimated 2 million Americans with an opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2018, she said, and more than 10 million misused prescription opioids. At the same time, prescriptions for opioids have dropped to lowest level in 10 years from a peak in 2012 of 81.3 prescriptions per 100 persons to 58.7 prescriptions per 100 persons in 2017 – total of more than 191 million scripts. “There is a decline in the number of opioid prescriptions, but there is still a lot of diversion, and there are some prescription ‘hot spots’ in the Southeast,” Dr. Hartwell said. “Heroin is a very low cost, and we’re wrestling with the issue of fentanyl.”
To complicate matters, most Americans with opioid use disorder are not in treatment. “In many people, the disorder is never diagnosed, and even fewer engage in care,” she said. “There are challenges with treatment retention, and even fewer achieve remission. There’s a lot of work to be done. One of which is the availability of medication-assisted treatment.”
Dr. Hartwell said that she knows of physician colleagues who have obtained a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine but have yet to prescribe it. “Some people may prefer to avoid the dance [of buprenorphine prescribing],” she said. “I’m here to advise you to dance.” Clinicians can learn about MAT waiver training opportunities by visiting the website of the Providers Clinical Support System, a program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
Another option is to join a telementoring session on the topic facilitated by Project ECHO, or Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes, which is being used by the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. The goal of this model is to break down the walls between specialty and primary care by linking experts at an academic “hub” with primary care doctors and nurses in nearby communities.
“Our Project ECHO at the Medical University of South Carolina is twice a month on Fridays,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The first half is a case. The second half is a didactic [session], and you get a free hour of CME.”
The most common drugs used for medication-assisted treatment of opioid disorder are buprenorphine (a partial agonist), naltrexone (an antagonist), and methadone (a full agonist). Methadone retention generally is better than buprenorphine or naltrexone. The recommended treatment duration is 6-12 months, yet many studies demonstrate that many only stay on treatment for 30-60 days.
“You want to keep patients on treatment as long as they benefit from the medication,” Dr. Hartwell said. One large study of Medicaid claims data found that the risk of acute care service use and overdose were high following buprenorphine discontinuation, regardless of treatment duration. Superior outcomes became significant with treatment duration beyond 15 months, although rates of the primary adverse outcomes remained high (Am J Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 1;177[2]:117-24). About 5% of patients across all cohorts experienced one or more medically treated overdoses.
“One thing I don’t want is for people to drop out of treatment and not come back to see me,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is a time for us to use our shared decision-making skills. I like to use the Tapering Readiness Inventory, a list of 16 questions. It asks such things as ‘Are you able to cope with difficult situations without using?’ and ‘Do you have all of the [drug] paraphernalia out of the house?’ We then have a discussion. If the patient decides to go ahead and do a taper, I always leave the door open. So, as that taper persists and someone says, ‘I’m starting to think about using, Doctor,’ I’ll put them back on [buprenorphine]. Or, if they come off the drug and they find themselves at risk of relapsing, they come back in and see me.”
There’s also some evidence that contingency management might be helpful, both in terms of opioid negative urines, and retention and treatment. Meanwhile, extended-release forms of buprenorphine are emerging.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Sublocade, the first once-monthly injectable buprenorphine product for the treatment of moderate-to-severe OUD in adult patients who have initiated treatment with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product. “The recommendations are that you have about a 7-day lead-in of sublingual buprenorphine, and then 2 months of a 300-mg IV injection,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is followed by either 100-mg injections monthly or 300-mg maintenance in select cases. There is some pain at the injection site. Some clinicians are getting around this by using a little bit of lidocaine prior to giving the injection.”
Another product, Brixadi, is an extended-release weekly (8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, 32 mg) and monthly (64 mg, 96 mg, 128 mg) buprenorphine injection used for the treatment of moderate to severe OUD. It is expected to be available in December 2020.
In 2016, the FDA approved Probuphine, the first buprenorphine implant for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. Probuphine is designed to provide a constant, low-level dose of buprenorphine for 6 months in patients who are already stable on low to moderate doses of other forms of buprenorphine, as part of a complete treatment program. “The 6-month duration kind of takes the issue of adherence off the table,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The caveat with this is that you have to be stable on 8 mg of buprenorphine per day or less. The majority of my patients require much higher doses.”
Dr. Hartwell reported having no relevant disclosures.
LAS VEGAS – For Karen J. Hartwell, MD, few things in her clinical work bring more reward than providing medication-assisted treatment (MAT) to patients with opioid use disorder.
or to see a depression remit on your selection of an antidepressant,” she said at an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “We know that medication-assisted treatment is underused and, sadly, relapse rates remain high.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 70,237 drug-related overdose deaths in 2017 – 47,600 from prescription and illicit opioids. “This is being driven predominately by fentanyl and other high-potency synthetic opioids, followed by prescription opioids and heroin,” said Dr. Hartwell, an associate professor in the addiction sciences division in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
There were an estimated 2 million Americans with an opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2018, she said, and more than 10 million misused prescription opioids. At the same time, prescriptions for opioids have dropped to lowest level in 10 years from a peak in 2012 of 81.3 prescriptions per 100 persons to 58.7 prescriptions per 100 persons in 2017 – total of more than 191 million scripts. “There is a decline in the number of opioid prescriptions, but there is still a lot of diversion, and there are some prescription ‘hot spots’ in the Southeast,” Dr. Hartwell said. “Heroin is a very low cost, and we’re wrestling with the issue of fentanyl.”
To complicate matters, most Americans with opioid use disorder are not in treatment. “In many people, the disorder is never diagnosed, and even fewer engage in care,” she said. “There are challenges with treatment retention, and even fewer achieve remission. There’s a lot of work to be done. One of which is the availability of medication-assisted treatment.”
Dr. Hartwell said that she knows of physician colleagues who have obtained a waiver to prescribe buprenorphine but have yet to prescribe it. “Some people may prefer to avoid the dance [of buprenorphine prescribing],” she said. “I’m here to advise you to dance.” Clinicians can learn about MAT waiver training opportunities by visiting the website of the Providers Clinical Support System, a program funded by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
Another option is to join a telementoring session on the topic facilitated by Project ECHO, or Extension for Community Healthcare Outcomes, which is being used by the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. The goal of this model is to break down the walls between specialty and primary care by linking experts at an academic “hub” with primary care doctors and nurses in nearby communities.
“Our Project ECHO at the Medical University of South Carolina is twice a month on Fridays,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The first half is a case. The second half is a didactic [session], and you get a free hour of CME.”
The most common drugs used for medication-assisted treatment of opioid disorder are buprenorphine (a partial agonist), naltrexone (an antagonist), and methadone (a full agonist). Methadone retention generally is better than buprenorphine or naltrexone. The recommended treatment duration is 6-12 months, yet many studies demonstrate that many only stay on treatment for 30-60 days.
“You want to keep patients on treatment as long as they benefit from the medication,” Dr. Hartwell said. One large study of Medicaid claims data found that the risk of acute care service use and overdose were high following buprenorphine discontinuation, regardless of treatment duration. Superior outcomes became significant with treatment duration beyond 15 months, although rates of the primary adverse outcomes remained high (Am J Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 1;177[2]:117-24). About 5% of patients across all cohorts experienced one or more medically treated overdoses.
“One thing I don’t want is for people to drop out of treatment and not come back to see me,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is a time for us to use our shared decision-making skills. I like to use the Tapering Readiness Inventory, a list of 16 questions. It asks such things as ‘Are you able to cope with difficult situations without using?’ and ‘Do you have all of the [drug] paraphernalia out of the house?’ We then have a discussion. If the patient decides to go ahead and do a taper, I always leave the door open. So, as that taper persists and someone says, ‘I’m starting to think about using, Doctor,’ I’ll put them back on [buprenorphine]. Or, if they come off the drug and they find themselves at risk of relapsing, they come back in and see me.”
There’s also some evidence that contingency management might be helpful, both in terms of opioid negative urines, and retention and treatment. Meanwhile, extended-release forms of buprenorphine are emerging.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Sublocade, the first once-monthly injectable buprenorphine product for the treatment of moderate-to-severe OUD in adult patients who have initiated treatment with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product. “The recommendations are that you have about a 7-day lead-in of sublingual buprenorphine, and then 2 months of a 300-mg IV injection,” Dr. Hartwell said. “This is followed by either 100-mg injections monthly or 300-mg maintenance in select cases. There is some pain at the injection site. Some clinicians are getting around this by using a little bit of lidocaine prior to giving the injection.”
Another product, Brixadi, is an extended-release weekly (8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, 32 mg) and monthly (64 mg, 96 mg, 128 mg) buprenorphine injection used for the treatment of moderate to severe OUD. It is expected to be available in December 2020.
In 2016, the FDA approved Probuphine, the first buprenorphine implant for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. Probuphine is designed to provide a constant, low-level dose of buprenorphine for 6 months in patients who are already stable on low to moderate doses of other forms of buprenorphine, as part of a complete treatment program. “The 6-month duration kind of takes the issue of adherence off the table,” Dr. Hartwell said. “The caveat with this is that you have to be stable on 8 mg of buprenorphine per day or less. The majority of my patients require much higher doses.”
Dr. Hartwell reported having no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM NPA 2020
Another round of research shows ketamine may help alcoholism
More research suggests that a single infusion of ketamine combined with counseling may help alcohol-dependent patients curb their drinking.
In a pilot study of 40 participants, those who were randomly assigned to receive intravenous ketamine plus outpatient motivational enhancement therapy (MET) showed greater abstinence rates, longer time to relapse, and fewer heavy drinking days than did those who received MET plus midazolam.
The findings support a U.K. study published late last year showing that a single dose of intravenous ketamine plus therapy that focused on reactivating drinking-related “maladaptive reward memories” reduced drinking urges and alcohol intake more than just ketamine or a placebo infusion alone (Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 26;10[1]:5187).
of the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“It’s an important area of research to understand in order to make behavioral treatments more effective, and ketamine appears to have the properties to address those vulnerabilities,” Dr. Dakwar said.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry (2019 Dec 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19070684).
Real-world approach
Pathologic alcohol use is responsible for an estimated 3.8% of all deaths globally, yet current interventions for alcohol use disorder have limited efficacy, the researchers noted.
New treatments with innovative mechanisms would be valuable, they added.
Ketamine is a high-affinity N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist.
Previously, research offered “promising results” with the use of ketamine for cocaine use disorder, including increased motivation to quit and decreased craving, Dr. Dakwar noted.
“Those results led us to think about how ketamine might be helpful for other substance use disorders, especially given the overlap in clinical vulnerabilities and epidemiology,” he said.
The study from the U.K. researchers was conducted in 90 patients with harmful drinking behavior but who had not been diagnosed with alcohol use disorder.
Dr. Dakwar noted that this was “a nontreatment study. None of the people there had alcohol use disorder; they were heavy drinkers. Also, the effects there were fairly modest.
“My interest was how to integrate ketamine into a clinical, real-world framework that could be helpful for people,” he added.
The study included 40 participants (52.5% women; 70.3% white; mean age, 53 years) with alcohol dependence whose average consumption was five drinks per day.
All entered a 5-week outpatient program of MET, which involved engaging in strategies to promote motivation and self-directed change.
During the program’s second week, the participants were randomly assigned to received a 52-minute IV infusion of ketamine 0.71 mg/kg (n = 17) or the benzodiazepine midazolam 0.025 mg/kg (n = 23).
This ketamine dose was selected “because it was the highest dose tolerated by participants in preliminary studies,” the researchers reported.
“Midazolam was chosen as the active control because it alters consciousness without any known persistent ... effect on alcohol dependence,” they added.
The “timeline follow back method” was used to assess alcohol use after treatment. Abstinence was confirmed by measuring urine ethyl glucuronide levels with urine toxicology tests.
Other measures included use of a visual analogue scale, the Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment, and the modified Perceived Stress Scale.
Primary outcome met
Results showed that 47.1% of the ketamine group and 59.1% of the midazolam group used alcohol during the 21 days after treatment infusion; 17.6% and 40.9%, respectively, had a heavy drinking day.
For the primary outcome measure of alcohol abstinence, the “quadratic effect of time was significant” (P = .004), as was time-by-treatment interaction (P less than .001).
Although the model-estimated proportions of alcohol abstinence remained stable for the ketamine group for 21 days post infusion, the proportions decreased significantly for the control group.
The odds of having a heavy drinking day did not change significantly after treatment for the ketamine group (odds ratio, 0.98; P = .74) but increased significantly with each postinfusion day for the midazolam group (OR, 1.19; P less than .001).
For the ketamine group, time to relapse was also significantly longer (P = .04).
No significant differences were found between the groups in rates of withdrawal, craving, or stress sensitivity.
A new direction?
The most common adverse events after treatment were sedation, seen in 12 members of the midazolam group and in 8 members of the ketamine group, and headache, seen in four and six members, respectively.
Although two ketamine-group members experienced mild agitation for up to 1 hour post infusion, no incidents of persistent psychoactive effects were reported in either group.
No participants who received ketamine dropped out during the study period; among those who received midazolam, six dropped out.
“These preliminary data suggest new directions in integrated pharmacotherapy-behavioral treatments for alcohol use disorder,” the investigators wrote.
However, a larger patient population will be needed in future research in order to “replicate these promising results,” they added.
Dr. Dakwar noted that the time to first drink after treatment was comparable between the groups.
“But what was different in the ketamine group was that they didn’t continue drinking after that first drink. They didn’t initiate heavy drinking, they didn’t relapse, they were able to bounce back and stay with the program,” he said.
“It was surprising but still consistent with the central hypothesis that ketamine provides this opportunity for setting the foundation for the requisite commitment so that, once things become difficult, they’re still able to maintain recovery,” Dr. Dakwar said.
‘Provocative findings’
In an accompanying editorial, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and Rebecca B. Price, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh, noted that ketamine’s effects on abstinence “were robust” in this trial.
“It is also noteworthy that, in spite of recruiting from a population of patients with active and significant substance use history (a group that has routinely been excluded from ketamine trials in depression), no participant showed evidence of new drug-seeking behaviors,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price wrote.
“Overall, these findings are provocative and hypothesis generating but certainly not definitive because of the small sample size,” they add.
Other limitations cited include the short follow-up period and the fact that only half of the participants were available for a 6-month follow-up telephone interview. In addition, generalizability was limited because the population did not have additional medical or psychiatric illnesses or additional substance use disorders, the editorialists wrote.
Because of the limitations, the investigators “are appropriately circumspect about the immediate clinical implications of this small pilot study.”
Still, the results “affirm the potential of rational combinatorial approaches for a vexing medical and public health problem,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the New York State Psychiatric Institute. The study authors and Dr. Price reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr Mathew reported serving as a consultant to or having received research support from several companies, including Alkermes, Allergan, Clexio Biosciences, and Janssen. The original article includes a full list of his disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More research suggests that a single infusion of ketamine combined with counseling may help alcohol-dependent patients curb their drinking.
In a pilot study of 40 participants, those who were randomly assigned to receive intravenous ketamine plus outpatient motivational enhancement therapy (MET) showed greater abstinence rates, longer time to relapse, and fewer heavy drinking days than did those who received MET plus midazolam.
The findings support a U.K. study published late last year showing that a single dose of intravenous ketamine plus therapy that focused on reactivating drinking-related “maladaptive reward memories” reduced drinking urges and alcohol intake more than just ketamine or a placebo infusion alone (Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 26;10[1]:5187).
of the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“It’s an important area of research to understand in order to make behavioral treatments more effective, and ketamine appears to have the properties to address those vulnerabilities,” Dr. Dakwar said.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry (2019 Dec 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19070684).
Real-world approach
Pathologic alcohol use is responsible for an estimated 3.8% of all deaths globally, yet current interventions for alcohol use disorder have limited efficacy, the researchers noted.
New treatments with innovative mechanisms would be valuable, they added.
Ketamine is a high-affinity N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist.
Previously, research offered “promising results” with the use of ketamine for cocaine use disorder, including increased motivation to quit and decreased craving, Dr. Dakwar noted.
“Those results led us to think about how ketamine might be helpful for other substance use disorders, especially given the overlap in clinical vulnerabilities and epidemiology,” he said.
The study from the U.K. researchers was conducted in 90 patients with harmful drinking behavior but who had not been diagnosed with alcohol use disorder.
Dr. Dakwar noted that this was “a nontreatment study. None of the people there had alcohol use disorder; they were heavy drinkers. Also, the effects there were fairly modest.
“My interest was how to integrate ketamine into a clinical, real-world framework that could be helpful for people,” he added.
The study included 40 participants (52.5% women; 70.3% white; mean age, 53 years) with alcohol dependence whose average consumption was five drinks per day.
All entered a 5-week outpatient program of MET, which involved engaging in strategies to promote motivation and self-directed change.
During the program’s second week, the participants were randomly assigned to received a 52-minute IV infusion of ketamine 0.71 mg/kg (n = 17) or the benzodiazepine midazolam 0.025 mg/kg (n = 23).
This ketamine dose was selected “because it was the highest dose tolerated by participants in preliminary studies,” the researchers reported.
“Midazolam was chosen as the active control because it alters consciousness without any known persistent ... effect on alcohol dependence,” they added.
The “timeline follow back method” was used to assess alcohol use after treatment. Abstinence was confirmed by measuring urine ethyl glucuronide levels with urine toxicology tests.
Other measures included use of a visual analogue scale, the Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment, and the modified Perceived Stress Scale.
Primary outcome met
Results showed that 47.1% of the ketamine group and 59.1% of the midazolam group used alcohol during the 21 days after treatment infusion; 17.6% and 40.9%, respectively, had a heavy drinking day.
For the primary outcome measure of alcohol abstinence, the “quadratic effect of time was significant” (P = .004), as was time-by-treatment interaction (P less than .001).
Although the model-estimated proportions of alcohol abstinence remained stable for the ketamine group for 21 days post infusion, the proportions decreased significantly for the control group.
The odds of having a heavy drinking day did not change significantly after treatment for the ketamine group (odds ratio, 0.98; P = .74) but increased significantly with each postinfusion day for the midazolam group (OR, 1.19; P less than .001).
For the ketamine group, time to relapse was also significantly longer (P = .04).
No significant differences were found between the groups in rates of withdrawal, craving, or stress sensitivity.
A new direction?
The most common adverse events after treatment were sedation, seen in 12 members of the midazolam group and in 8 members of the ketamine group, and headache, seen in four and six members, respectively.
Although two ketamine-group members experienced mild agitation for up to 1 hour post infusion, no incidents of persistent psychoactive effects were reported in either group.
No participants who received ketamine dropped out during the study period; among those who received midazolam, six dropped out.
“These preliminary data suggest new directions in integrated pharmacotherapy-behavioral treatments for alcohol use disorder,” the investigators wrote.
However, a larger patient population will be needed in future research in order to “replicate these promising results,” they added.
Dr. Dakwar noted that the time to first drink after treatment was comparable between the groups.
“But what was different in the ketamine group was that they didn’t continue drinking after that first drink. They didn’t initiate heavy drinking, they didn’t relapse, they were able to bounce back and stay with the program,” he said.
“It was surprising but still consistent with the central hypothesis that ketamine provides this opportunity for setting the foundation for the requisite commitment so that, once things become difficult, they’re still able to maintain recovery,” Dr. Dakwar said.
‘Provocative findings’
In an accompanying editorial, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and Rebecca B. Price, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh, noted that ketamine’s effects on abstinence “were robust” in this trial.
“It is also noteworthy that, in spite of recruiting from a population of patients with active and significant substance use history (a group that has routinely been excluded from ketamine trials in depression), no participant showed evidence of new drug-seeking behaviors,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price wrote.
“Overall, these findings are provocative and hypothesis generating but certainly not definitive because of the small sample size,” they add.
Other limitations cited include the short follow-up period and the fact that only half of the participants were available for a 6-month follow-up telephone interview. In addition, generalizability was limited because the population did not have additional medical or psychiatric illnesses or additional substance use disorders, the editorialists wrote.
Because of the limitations, the investigators “are appropriately circumspect about the immediate clinical implications of this small pilot study.”
Still, the results “affirm the potential of rational combinatorial approaches for a vexing medical and public health problem,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the New York State Psychiatric Institute. The study authors and Dr. Price reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr Mathew reported serving as a consultant to or having received research support from several companies, including Alkermes, Allergan, Clexio Biosciences, and Janssen. The original article includes a full list of his disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More research suggests that a single infusion of ketamine combined with counseling may help alcohol-dependent patients curb their drinking.
In a pilot study of 40 participants, those who were randomly assigned to receive intravenous ketamine plus outpatient motivational enhancement therapy (MET) showed greater abstinence rates, longer time to relapse, and fewer heavy drinking days than did those who received MET plus midazolam.
The findings support a U.K. study published late last year showing that a single dose of intravenous ketamine plus therapy that focused on reactivating drinking-related “maladaptive reward memories” reduced drinking urges and alcohol intake more than just ketamine or a placebo infusion alone (Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 26;10[1]:5187).
of the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“It’s an important area of research to understand in order to make behavioral treatments more effective, and ketamine appears to have the properties to address those vulnerabilities,” Dr. Dakwar said.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry (2019 Dec 2. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19070684).
Real-world approach
Pathologic alcohol use is responsible for an estimated 3.8% of all deaths globally, yet current interventions for alcohol use disorder have limited efficacy, the researchers noted.
New treatments with innovative mechanisms would be valuable, they added.
Ketamine is a high-affinity N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist.
Previously, research offered “promising results” with the use of ketamine for cocaine use disorder, including increased motivation to quit and decreased craving, Dr. Dakwar noted.
“Those results led us to think about how ketamine might be helpful for other substance use disorders, especially given the overlap in clinical vulnerabilities and epidemiology,” he said.
The study from the U.K. researchers was conducted in 90 patients with harmful drinking behavior but who had not been diagnosed with alcohol use disorder.
Dr. Dakwar noted that this was “a nontreatment study. None of the people there had alcohol use disorder; they were heavy drinkers. Also, the effects there were fairly modest.
“My interest was how to integrate ketamine into a clinical, real-world framework that could be helpful for people,” he added.
The study included 40 participants (52.5% women; 70.3% white; mean age, 53 years) with alcohol dependence whose average consumption was five drinks per day.
All entered a 5-week outpatient program of MET, which involved engaging in strategies to promote motivation and self-directed change.
During the program’s second week, the participants were randomly assigned to received a 52-minute IV infusion of ketamine 0.71 mg/kg (n = 17) or the benzodiazepine midazolam 0.025 mg/kg (n = 23).
This ketamine dose was selected “because it was the highest dose tolerated by participants in preliminary studies,” the researchers reported.
“Midazolam was chosen as the active control because it alters consciousness without any known persistent ... effect on alcohol dependence,” they added.
The “timeline follow back method” was used to assess alcohol use after treatment. Abstinence was confirmed by measuring urine ethyl glucuronide levels with urine toxicology tests.
Other measures included use of a visual analogue scale, the Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment, and the modified Perceived Stress Scale.
Primary outcome met
Results showed that 47.1% of the ketamine group and 59.1% of the midazolam group used alcohol during the 21 days after treatment infusion; 17.6% and 40.9%, respectively, had a heavy drinking day.
For the primary outcome measure of alcohol abstinence, the “quadratic effect of time was significant” (P = .004), as was time-by-treatment interaction (P less than .001).
Although the model-estimated proportions of alcohol abstinence remained stable for the ketamine group for 21 days post infusion, the proportions decreased significantly for the control group.
The odds of having a heavy drinking day did not change significantly after treatment for the ketamine group (odds ratio, 0.98; P = .74) but increased significantly with each postinfusion day for the midazolam group (OR, 1.19; P less than .001).
For the ketamine group, time to relapse was also significantly longer (P = .04).
No significant differences were found between the groups in rates of withdrawal, craving, or stress sensitivity.
A new direction?
The most common adverse events after treatment were sedation, seen in 12 members of the midazolam group and in 8 members of the ketamine group, and headache, seen in four and six members, respectively.
Although two ketamine-group members experienced mild agitation for up to 1 hour post infusion, no incidents of persistent psychoactive effects were reported in either group.
No participants who received ketamine dropped out during the study period; among those who received midazolam, six dropped out.
“These preliminary data suggest new directions in integrated pharmacotherapy-behavioral treatments for alcohol use disorder,” the investigators wrote.
However, a larger patient population will be needed in future research in order to “replicate these promising results,” they added.
Dr. Dakwar noted that the time to first drink after treatment was comparable between the groups.
“But what was different in the ketamine group was that they didn’t continue drinking after that first drink. They didn’t initiate heavy drinking, they didn’t relapse, they were able to bounce back and stay with the program,” he said.
“It was surprising but still consistent with the central hypothesis that ketamine provides this opportunity for setting the foundation for the requisite commitment so that, once things become difficult, they’re still able to maintain recovery,” Dr. Dakwar said.
‘Provocative findings’
In an accompanying editorial, Sanjay J. Mathew, MD, of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and Rebecca B. Price, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh, noted that ketamine’s effects on abstinence “were robust” in this trial.
“It is also noteworthy that, in spite of recruiting from a population of patients with active and significant substance use history (a group that has routinely been excluded from ketamine trials in depression), no participant showed evidence of new drug-seeking behaviors,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price wrote.
“Overall, these findings are provocative and hypothesis generating but certainly not definitive because of the small sample size,” they add.
Other limitations cited include the short follow-up period and the fact that only half of the participants were available for a 6-month follow-up telephone interview. In addition, generalizability was limited because the population did not have additional medical or psychiatric illnesses or additional substance use disorders, the editorialists wrote.
Because of the limitations, the investigators “are appropriately circumspect about the immediate clinical implications of this small pilot study.”
Still, the results “affirm the potential of rational combinatorial approaches for a vexing medical and public health problem,” Dr. Mathew and Dr. Price concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the New York State Psychiatric Institute. The study authors and Dr. Price reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr Mathew reported serving as a consultant to or having received research support from several companies, including Alkermes, Allergan, Clexio Biosciences, and Janssen. The original article includes a full list of his disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. heroin use: Good news, bad news?
U.S. rates of heroin use, heroin use disorder, and heroin injections all increased overall among adults during a recent 17-year period, but rates have plateaued, new research shows.
Although on the face of it this may seem like good news, investigators at the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) note that the plateau in heroin use may simply reflect a switch to fentanyl.
“The recent leveling off of heroin use might reflect shifts from heroin to illicit fentanyl-related compounds,” wrote the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, MPH.
The study was published online Feb. 11 as a research letter in JAMA (2020;323[6]:568-71).
National data
For the study, researchers collected data from a nationally representative group of adults aged 18 years or older who participated in the 2002-2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH).
The analysis included 800,500 respondents during the study period. The mean age of respondents was 34.5 years, and 53.2% were women.
Results showed that the reported past-year prevalence of heroin use increased from 0.17% in 2002 to 0.32% in 2018 (average annual percentage change [AAPC], 5.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-10.5; P = .02). During 2002-2016, the APC was 7.6 (95% CI, 6.3-9.0; P less than .001) but then plateaued during 2016-2018 (APC, –7.1; 95% CI, –36.9 to 36.7; P = .69).
The prevalence of heroin use disorder increased from 0.10% in 2002 to 0.21% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.0; 95% CI, 3.2-8.8; P less than .001). The rate remained stable during 2002-2008, increased during 2008-2015, then plateaued during 2015-2018.
The prevalence of heroin injections increased from 0.09% in 2002 to 0.17% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.9; 95% CI, 5.7-8.0; P less than .001), although there was a dip from the previous year. This rate increased during the study period among both men and women, those aged 35-49 years, non-Hispanic whites, and those residing in the Northeast or West regions.
For individuals up to age 25 years and those living in the Midwest, the heroin injection rate stopped increasing and plateaued, but there was an overall increase during the study period.
In 2018, the rate of past-year heroin injection was highest in those in the Northeast, those up to age 49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
More infectious disease testing
Prevalence of heroin injection did not increase among adults who used heroin or who had heroin use disorder. This, the researchers note, “suggests that increases in heroin injection are related to overall increases in heroin use rather than increases in the propensity to inject.”
Future research should examine differences in heroin injection trends across subgroups, the authors wrote.
The researchers advocate for expanding HIV and hepatitis testing and treatment, the provision of sterile syringes, and use of Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for opioid use disorders, particularly among populations at greatest risk – adults in the Northeast, those aged 18-49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
“In parallel, interventions to prevent opioid misuse and opioid use disorder are needed to avert further increases in injection drug use,” they noted.
A limitation of the study was that the NSDUH excludes jail and prison populations and homeless people not in living shelters. In addition, the NSDUH is subject to recall bias.
The study was jointly sponsored by SAMHSA and the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. One author reports owning stock in General Electric Co, 3M Co, and Pfizer Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. rates of heroin use, heroin use disorder, and heroin injections all increased overall among adults during a recent 17-year period, but rates have plateaued, new research shows.
Although on the face of it this may seem like good news, investigators at the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) note that the plateau in heroin use may simply reflect a switch to fentanyl.
“The recent leveling off of heroin use might reflect shifts from heroin to illicit fentanyl-related compounds,” wrote the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, MPH.
The study was published online Feb. 11 as a research letter in JAMA (2020;323[6]:568-71).
National data
For the study, researchers collected data from a nationally representative group of adults aged 18 years or older who participated in the 2002-2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH).
The analysis included 800,500 respondents during the study period. The mean age of respondents was 34.5 years, and 53.2% were women.
Results showed that the reported past-year prevalence of heroin use increased from 0.17% in 2002 to 0.32% in 2018 (average annual percentage change [AAPC], 5.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-10.5; P = .02). During 2002-2016, the APC was 7.6 (95% CI, 6.3-9.0; P less than .001) but then plateaued during 2016-2018 (APC, –7.1; 95% CI, –36.9 to 36.7; P = .69).
The prevalence of heroin use disorder increased from 0.10% in 2002 to 0.21% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.0; 95% CI, 3.2-8.8; P less than .001). The rate remained stable during 2002-2008, increased during 2008-2015, then plateaued during 2015-2018.
The prevalence of heroin injections increased from 0.09% in 2002 to 0.17% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.9; 95% CI, 5.7-8.0; P less than .001), although there was a dip from the previous year. This rate increased during the study period among both men and women, those aged 35-49 years, non-Hispanic whites, and those residing in the Northeast or West regions.
For individuals up to age 25 years and those living in the Midwest, the heroin injection rate stopped increasing and plateaued, but there was an overall increase during the study period.
In 2018, the rate of past-year heroin injection was highest in those in the Northeast, those up to age 49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
More infectious disease testing
Prevalence of heroin injection did not increase among adults who used heroin or who had heroin use disorder. This, the researchers note, “suggests that increases in heroin injection are related to overall increases in heroin use rather than increases in the propensity to inject.”
Future research should examine differences in heroin injection trends across subgroups, the authors wrote.
The researchers advocate for expanding HIV and hepatitis testing and treatment, the provision of sterile syringes, and use of Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for opioid use disorders, particularly among populations at greatest risk – adults in the Northeast, those aged 18-49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
“In parallel, interventions to prevent opioid misuse and opioid use disorder are needed to avert further increases in injection drug use,” they noted.
A limitation of the study was that the NSDUH excludes jail and prison populations and homeless people not in living shelters. In addition, the NSDUH is subject to recall bias.
The study was jointly sponsored by SAMHSA and the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. One author reports owning stock in General Electric Co, 3M Co, and Pfizer Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. rates of heroin use, heroin use disorder, and heroin injections all increased overall among adults during a recent 17-year period, but rates have plateaued, new research shows.
Although on the face of it this may seem like good news, investigators at the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) note that the plateau in heroin use may simply reflect a switch to fentanyl.
“The recent leveling off of heroin use might reflect shifts from heroin to illicit fentanyl-related compounds,” wrote the investigators, led by Beth Han, MD, PhD, MPH.
The study was published online Feb. 11 as a research letter in JAMA (2020;323[6]:568-71).
National data
For the study, researchers collected data from a nationally representative group of adults aged 18 years or older who participated in the 2002-2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH).
The analysis included 800,500 respondents during the study period. The mean age of respondents was 34.5 years, and 53.2% were women.
Results showed that the reported past-year prevalence of heroin use increased from 0.17% in 2002 to 0.32% in 2018 (average annual percentage change [AAPC], 5.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-10.5; P = .02). During 2002-2016, the APC was 7.6 (95% CI, 6.3-9.0; P less than .001) but then plateaued during 2016-2018 (APC, –7.1; 95% CI, –36.9 to 36.7; P = .69).
The prevalence of heroin use disorder increased from 0.10% in 2002 to 0.21% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.0; 95% CI, 3.2-8.8; P less than .001). The rate remained stable during 2002-2008, increased during 2008-2015, then plateaued during 2015-2018.
The prevalence of heroin injections increased from 0.09% in 2002 to 0.17% in 2018 (AAPC, 6.9; 95% CI, 5.7-8.0; P less than .001), although there was a dip from the previous year. This rate increased during the study period among both men and women, those aged 35-49 years, non-Hispanic whites, and those residing in the Northeast or West regions.
For individuals up to age 25 years and those living in the Midwest, the heroin injection rate stopped increasing and plateaued, but there was an overall increase during the study period.
In 2018, the rate of past-year heroin injection was highest in those in the Northeast, those up to age 49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
More infectious disease testing
Prevalence of heroin injection did not increase among adults who used heroin or who had heroin use disorder. This, the researchers note, “suggests that increases in heroin injection are related to overall increases in heroin use rather than increases in the propensity to inject.”
Future research should examine differences in heroin injection trends across subgroups, the authors wrote.
The researchers advocate for expanding HIV and hepatitis testing and treatment, the provision of sterile syringes, and use of Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for opioid use disorders, particularly among populations at greatest risk – adults in the Northeast, those aged 18-49 years, men, and non-Hispanic whites.
“In parallel, interventions to prevent opioid misuse and opioid use disorder are needed to avert further increases in injection drug use,” they noted.
A limitation of the study was that the NSDUH excludes jail and prison populations and homeless people not in living shelters. In addition, the NSDUH is subject to recall bias.
The study was jointly sponsored by SAMHSA and the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health. One author reports owning stock in General Electric Co, 3M Co, and Pfizer Inc.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Funding failures: Tobacco prevention and cessation
When it comes to state funding for tobacco prevention and cessation, the American Lung Association grades on a curve. It did not help.

Each state’s annual funding for tobacco prevention and cessation was calculated and then compared with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommended spending level. That percentage became the grade, with any level of funding at 80% or more of the CDC’s recommendation getting an A and anything below 50% getting an F, the ALA explained.
The three A’s went to Alaska – which spent $10.14 million, or 99.4% of the CDC-recommended $10.2 million – California (96.0%), and Maine (83.5%). The lowest levels of spending came from Georgia, which spend just 2.8% of the CDC’s recommendation of $106 million, and Missouri, which spent 3.0%, the ALA reported.
States’ grades were generally better in the four other areas of tobacco-control policy: There were 24 A’s and 9 F’s for smoke-free air laws, 1 A and 35 F’s for tobacco excise taxes, 3 A’s and 17 F’s for access to cessation treatment, and 10 A’s and 30 F’s for laws to raise the tobacco sales age to 21 years, the ALA said in the report.
Despite an overall grade of F, the federal government managed to earn some praise in that last area: “In what could only be described as unimaginable even 2 years ago, in December 2019, Congress passed bipartisan legislation to raise the minimum age of sale for tobacco products to 21,” the ALA said.
The federal government was strongly criticized on the subject of e-cigarettes. “The Trump Administration failed to prioritize public health over the tobacco industry with its Jan. 2, 2020, announcement that will leave thousands of flavored e-cigarettes on the market,” the ALA said, while concluding that the rising use of e-cigarettes in recent years “is a real-world demonstration of the failure of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to properly oversee all tobacco products. … This failure places the lung health and lives of Americans at risk.”
When it comes to state funding for tobacco prevention and cessation, the American Lung Association grades on a curve. It did not help.

Each state’s annual funding for tobacco prevention and cessation was calculated and then compared with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommended spending level. That percentage became the grade, with any level of funding at 80% or more of the CDC’s recommendation getting an A and anything below 50% getting an F, the ALA explained.
The three A’s went to Alaska – which spent $10.14 million, or 99.4% of the CDC-recommended $10.2 million – California (96.0%), and Maine (83.5%). The lowest levels of spending came from Georgia, which spend just 2.8% of the CDC’s recommendation of $106 million, and Missouri, which spent 3.0%, the ALA reported.
States’ grades were generally better in the four other areas of tobacco-control policy: There were 24 A’s and 9 F’s for smoke-free air laws, 1 A and 35 F’s for tobacco excise taxes, 3 A’s and 17 F’s for access to cessation treatment, and 10 A’s and 30 F’s for laws to raise the tobacco sales age to 21 years, the ALA said in the report.
Despite an overall grade of F, the federal government managed to earn some praise in that last area: “In what could only be described as unimaginable even 2 years ago, in December 2019, Congress passed bipartisan legislation to raise the minimum age of sale for tobacco products to 21,” the ALA said.
The federal government was strongly criticized on the subject of e-cigarettes. “The Trump Administration failed to prioritize public health over the tobacco industry with its Jan. 2, 2020, announcement that will leave thousands of flavored e-cigarettes on the market,” the ALA said, while concluding that the rising use of e-cigarettes in recent years “is a real-world demonstration of the failure of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to properly oversee all tobacco products. … This failure places the lung health and lives of Americans at risk.”
When it comes to state funding for tobacco prevention and cessation, the American Lung Association grades on a curve. It did not help.

Each state’s annual funding for tobacco prevention and cessation was calculated and then compared with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommended spending level. That percentage became the grade, with any level of funding at 80% or more of the CDC’s recommendation getting an A and anything below 50% getting an F, the ALA explained.
The three A’s went to Alaska – which spent $10.14 million, or 99.4% of the CDC-recommended $10.2 million – California (96.0%), and Maine (83.5%). The lowest levels of spending came from Georgia, which spend just 2.8% of the CDC’s recommendation of $106 million, and Missouri, which spent 3.0%, the ALA reported.
States’ grades were generally better in the four other areas of tobacco-control policy: There were 24 A’s and 9 F’s for smoke-free air laws, 1 A and 35 F’s for tobacco excise taxes, 3 A’s and 17 F’s for access to cessation treatment, and 10 A’s and 30 F’s for laws to raise the tobacco sales age to 21 years, the ALA said in the report.
Despite an overall grade of F, the federal government managed to earn some praise in that last area: “In what could only be described as unimaginable even 2 years ago, in December 2019, Congress passed bipartisan legislation to raise the minimum age of sale for tobacco products to 21,” the ALA said.
The federal government was strongly criticized on the subject of e-cigarettes. “The Trump Administration failed to prioritize public health over the tobacco industry with its Jan. 2, 2020, announcement that will leave thousands of flavored e-cigarettes on the market,” the ALA said, while concluding that the rising use of e-cigarettes in recent years “is a real-world demonstration of the failure of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to properly oversee all tobacco products. … This failure places the lung health and lives of Americans at risk.”
Opioid use disorder in adolescents: An overview
Ms. L, age 17, seeks treatment because she has an ongoing struggle with multiple substances, including benzodiazepines, heroin, alcohol, cannabis, and prescription opioids.
She reports that she was 13 when she first used a prescription opioid that was not prescribed for her. She also reports engaging in unsafe sexual practices while using these substances, and has been diagnosed and treated for a sexually transmitted disease. She dropped out of school and is estranged from her family. She says that for a long time she has felt depressed and that she uses drugs to “self-medicate my emotions.” She endorses high anxiety and lack of motivation. Ms. L also reports having several criminal charges for theft, assault, and exchanging sex for drugs. She has undergone 3 admissions for detoxification, but promptly resumed using drugs, primarily heroin and oxycodone, immediately after discharge. Ms. L meets DSM-5 criteria for opioid use disorder (OUD).
Ms. L’s case illustrates a disturbing trend in the current opioid epidemic in the United States. Nearly 11.8 million individuals age ≥12 reported misuse of opioids in the last year.1 Adolescents who misuse prescription or illicit opioids are more likely to be involved with the legal system due to truancy, running away from home, physical altercations, prostitution, exchanging sex for drugs, robbery, and gang involvement. Adolescents who use opioids may also struggle with academic decline, drop out of school early, be unable to maintain a job, and have relationship difficulties, especially with family members.
In this article, I describe the scope of OUD among adolescents, including epidemiology, clinical manifestations, screening tools, and treatment approaches.
Scope of the problem
According to the most recent Monitoring the Future survey of more than 42,500 8th, 10th, and 12th grade students, 2.7% of 12th graders reported prescription opioid misuse (reported in the survey as “narcotics other than heroin”) in the past year.2 In addition, 0.4% of 12th graders reported heroin use over the same period.2 Although the prevalence of opioid use among adolescents has been declining over the past 5 years,2 it still represents a serious health crisis.
Part of the issue may relate to easier access to more potent opioids. For example, heroin available today can be >4 times purer than it was in the past. In 2002, t
Between 1997 and 2012, the annual incidence of youth (age 15 to 19) hospitalizations for prescription opioid poisoning increased >170%.5 Approximately 6% to 9% of youth involved in risky opioid use develop OUD 6 to 12 months after s
Continue to: In recent years...
In recent years, deaths from drug overdose have increased for all age groups; however, limited data is available regarding adolescent overdose deaths. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), from 2015 to 2016, drug overdose death rates for persons age 15 to 24 increased to 28%.9
How opioids work
Opioids activate specific transmembrane neurotransmitter receptors, including mu, kappa, and delta, in the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS). This leads to activation of G protein–mediated intracellular signal transduction. Mainly it is activation of endogenous mu opioid receptors that mediates the reward, withdrawal, and analgesic effects of opioids. These effects depend on the location of mu receptors. In the CNS, activation of mu opioid receptors may cause miosis, respiratory depression, euphoria, and analgesia.10
Different opioids vary in terms of their half-life; for most opioids, the half-life ranges from 2 to 4 hours.10 Heroin has a half-life of 30 minutes, but due to active metabolites its duration of action is 4 to 5 hours. Opioid metabolites can be detected in urine toxicology within approximately 1 to 2 days since last use.10
Chronic opioid use is associated with neurologic effects that change the function of areas of the brain that control pleasure/reward, stress, decision-making, and more. This leads to cravings, continued substance use, and dependence.11 After continued long-term use, patients report decreased euphoria, but typically they continue to use opioids to avoid withdrawal symptoms or worsening mood.
Criteria for opioid use disorder
In DSM-5, substance use disorders (SUDs)are no longer categorized as abuse or dependence.12 For opioids, the diagnosis is OUD. The Table12 outlines the DSM-5 criteria for OUD. Craving opioids is included for the first time in the OUD diagnosis. Having problems with the legal system is no longer considered a diagnostic criterion for OUD.
Continue to: A vulnerable population
A vulnerable population
As defined by Erik Erikson’s psychosocial stages of development, adolescents struggle between establishing their own identity vs role confusion.13 In an attempt to relate to peers or give in to peer pressure, some adolescents start by experimenting with nicotine, alcohol, and/or marijuana; however, some may move on to using other illicit drugs.14 Risk factors for the development of SUDs include early onset of substance use and a rapid progression through stages of substance use from experimentation to regular use, risky use, and dependence.15 In our case study, Ms. L’s substance use followed a similar pattern. Further, the comorbidity of SUDs and other psychiatric disorders may add a layer of complexity when caring for adolescents. Box 116-20 describes the relationship between comorbid psychiatric disorders and SUDs in adolescents.
Box 1
Disruptive behavior disorders are the most common coexisting psychiatric disorders in an adolescent with a substance use disorder (SUD), including opioid use disorder. These individuals typically present with aggression and other conduct disorder symptoms, and have early involvement with the legal system. Conversely, patients with conduct disorder are at high risk of early initiation of illicit substance use, including opioids. Early onset of substance use is a strong risk factor for developing an SUD.16
Mood disorders, particularly depression, can either precede or occur as a result of heavy and prolonged substance use.17 The estimated prevalence of major depressive disorder in individuals with an SUD is 24% to 50%. Among adolescents, an SUD is also a risk factor for suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and completed suicide.18-20
Anxiety disorders, especially social phobia, and posttraumatic stress disorder are common in individuals with SUD.
Adolescents with SUD should be carefully evaluated for comorbid psychiatric disorders and treated accordingly.
Clinical manifestations
Common clinical manifestations of opioid use vary depending on when the patient is seen. An individual with OUD may appear acutely intoxicated, be in withdrawal, or show no effects. Chronic/prolonged use can lead to tolerance, such that a user needs to ingest larger amounts of the opioid to produce the same effects.
Acute intoxication can cause sedation, slurring of speech, and pinpoint pupils. Fresh injection sites may be visible on physical examination of IV users. The effects of acute intoxication usually depend on the half-life of the specific opioid and the individual’s tolerance.10 Tolerance to heroin can occur in 10 days and withdrawal can manifest in 3 to 7 hours after last use, depending on dose and purity.3 Tolerance can lead to unintentional overdose and death.
Withdrawal. Individuals experiencing withdrawal from opioids present with flu-like physical symptoms, including generalized body ache, rhinorrhea, diarrhea, goose bumps, lacrimation, and vomiting. Individuals also may experience irritability, restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, and depression during withdrawal.
Other manifestations. Excessive and chronic/prolonged opioid use can adversely impact socio-occupational functioning and cause academic decline in adolescents and youth. Personal relationships are significantly affected. Opioid users may have legal difficulties as a result of committing crimes such as theft, prostitution, or robbery in order to obtain opioids.
Continue to: Screening for OUD
Screening for OUD
Several screening tools are available to assess adolescents for SUDs, including OUD.
CRAFFT is a 6-item, clinician-administered screening tool that has been approved by American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Substance Abuse for adolescents and young adults age <21.21-23 This commonly used tool can assess for alcohol, cannabis, and other drug use. A score ≥2 is considered positive for drug use, indicating that the individual would require further evaluation and assessment22,23 (Figure). There is also a self-administered CRAFFT questionnaire that can be completed by the patient.

NIDA-modified ASSIST. The American Psychiatric Association has adapted the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)-modified ASSIST. One version is designated for parents/guardians to administer to their children (age 6 to 17), and one is designated for adolescents (age 11 to 17) to self-administer.24,25 Each screening tool has 2 levels: Level 1 screens for substance use and other mental health symptoms, and Level 2 is more specific for substance use alone.
Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI) is a self-report questionnaire that has 149 items that assess the use of numerous drugs. It is designed to quantify the severity of consequences associated with drug and alcohol use.26,27
Problem-Oriented Screening Instrument for Teenagers (PO
Continue to: Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ)...
Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ) is a brief, 40-item, cost-effective, self-report questionnaire that can help identify adolescents (age 12 to 18) who should be referred for further evaluation.30
Addressing treatment expectations
For an adolescent with OUD, treatment should begin in the least restrictive environment that is perceived as safe for the patient. An adolescent’s readiness and motivation to achieve and maintain abstinence are crucial. Treatment planning should include the adolescent as well as his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Start with a definitive treatment plan that addresses an individual’s needs. The plan should provide structure and an understanding of treatment expectations. The treatment team should clarify the realistic plan and goals based on empirical and clinical evidence. Treatment goals should include interventions to strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation, such as establishing academic and/or vocational goals. Addressing readiness and working on a patient’s motivation is extremely important for most of these interventions.
In order for any intervention to be successful, clinicians need to establish and foster rapport with the adolescent. By law, substance use or behaviors related to substance use are not allowed to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship, unless the adolescent gives consent or there are concerns that such behaviors might put the patient or others at risk. It is important to prime the adolescent and help them understand that any information pertaining to their safety or the safety of others may need to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship.
Choosing an intervention
Less than 50% of a nationally representative sample of 345 addiction treatment programs serving adolescents and adults offer medications for treating OUD.31 Even in programs that offer pharmacotherapy, medications are significantly underutilized. Fewer than 30% of patients in addiction treatment programs receive medication, compared with 74% of patients receiving treatment for other mental health disorders.31 A
Psychotherapy may be used to treat OUD in adolescents. Several family therapies have been studied and are considered as critical psychotherapeutic interventions for treating SUDs, including structural family treatment and functional family therapy approaches.34 An integrated behavioral and family therapy model is also recommended for adolescent patients with SUDs. Cognitive distortions and use of self-deprecatory statements are common among adolescents.35 Therefore, using approaches of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), or CBT plus motivational enhancement therapy, also might be effective for this population.36 The adolescent community reinforcement approach (A-CRA) is a behavioral treatment designed to help adolescents and their families learn how to lead a healthy and happy life without the use of drugs or alcohol by increasing access to social, familial, and educational/vocational reinforcers. Support groups and peer and family support should be encouraged as adjuncts to other interventions. In some areas, sober housing options for adolescents are also available.
Continue to: Harm-reduction strategies
Harm-reduction strategies. Although the primary goal of treatment for adolescents with OUD is to achieve and maintain abstinence from opioid use, implicit and explicit goals can be set. Short-term implicit goals may include harm-reduction strategies that emphasize decreasing the duration, frequency, and amount of substance use and limiting the chances of adverse effects, while the long-term explicit goal should be abstinence from opioid use.
Naloxone nasal spray is used as a harm-reduction strategy. It is an FDA-approved formulation that can reverse the effects of unintentional opioid overdoses and potentially prevent death from respiratory depression.37 Other harm-reduction strategies include needle exchange programs, which provide sterile needles to individuals who inject drugs in an effort to prevent or reduce the transmission of human immunodeficiency virus and other bloodborne viruses that can be spread via shared injection equipment. Fentanyl testing strips allow opioid users to test for the presence fentanyl and fentanyl analogs in the unregulated “street” opioid supply.
Pharmacologic interventions. Because there is limited empirical evidence on the efficacy of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for adolescents with OUD, clinicians need to rely on evidence from research and experience with adults. Unfortunately, MAT is offered to adolescents considerably less often than it is to adults. Feder et al38 reported that only 2.4% of adolescents received MAT for heroin use and only 0.4% of adolescents received MAT for prescription opioid use, compared with 26.3% and 12% of adults, respectively.
Detoxification. Medications available for detoxification from opioids include opiates (such as methadone or buprenorphine) and clonidine (a central sympathomimetic). If the patient has used heroin for a short period (<1 year) and has no history of detoxification, consider a detoxification strategy with a longer-term taper (90 to 180 days) to allow for stabilization.
Maintenance treatment. Consider maintenance treatment for adolescents with a history of long-term opioid use and at least 2 prior short-term detoxification attempts or nonpharmacotherapy-based treatment within 12 months. Be sure to receive consent from a legal guardian and the patient. Maintenance treatment is usually recommended to continue for 1 to 6 years. Maintenance programs with longer durations have shown higher rates of abstinence, improved engagement, and retention in treatment.39
Continue to: According to guidelines from...
According to guidelines from the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM), adolescents age >16 should be offered MAT; the first-line treatment is buprenorphine.40 To avoid risks of abuse and diversion, a combination of buprenorphine/naloxone may be administered.
Maintenance with buprenorphine
In order to prescribe and dispense buprenorphine, clinicians need to obtain a waiver from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Before initiating buprenorphine, consider the type of opioid the individual used (short- or long-acting), the severity of the OUD, and the last reported use. The 3 phases of buprenorphine treatment are41:
- Induction phase. Buprenorphine can be initiated at 2 to 4 mg/d. Some patients may require up to 8 mg/d on the first day, which can be administered in divided doses.42 Evaluate and monitor patients carefully during the first few hours after the first dose. Patients should be in early withdrawal; otherwise, the buprenorphine might precipitate withdrawal. The induction phase can be completed in 2 to 4 days by titrating the dose so that the signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal are minimal, and the patient is able to continue treatment. It may be helpful to have the patient’s legal guardian nearby in case the patient does not tolerate the medication or experiences withdrawal. The initial target dose for buprenorphine is approximately 12 to 16 mg/d.
- Stabilization phase. Patients no longer experience withdrawal symptoms and no longer have cravings. This phase can last 6 to 8 weeks. During this phase, patients should be seen weekly and doses should be adjusted if necessary. As a partial mu agonist, buprenorphine does not activate mu receptors fully and reaches a ceiling effect. Hence, doses >24 mg/d have limited added agonist properties.
- Maintenance phase. Because discontinuation of buprenorphine is associated with high relapse rates, patients may need to be maintained long-term on their stabilization dose, and for some patients, the length of time could be indefinite.39 During this phase, patients continue to undergo follow-up, but do so less frequently.
Methadone maintenance is generally not recommended for individuals age <18.
Preventing opioid diversion
Prescription medications that are kept in the home are a substantial source of opioids for adolescents. In 2014, 56% of 12th graders who did not need medications for medical purposes were able to acquire them from their friends or relatives; 36% of 12th graders used their own prescriptions.21 Limiting adolescents’ access to prescription opioids is the first line of prevention. Box 2 describes interventions and strategies to limit adolescents’ access to opioids.
Box 2
Many adolescents obtain opioids for recreational use from medications that were legitimately prescribed to family or friends. Both clinicians and parents/ guardians can take steps to reduce or prevent this type of diversion
Health care facilities. Regulating the number of pills dispensed to patients is crucial. It is highly recommended to prescribe only the minimal number of opioids necessary. In most cases, 3 to 7 days’ worth of opioids at a time might be sufficient, especially after surgical procedures.
Home. Families can limit adolescents’ access to prescription opioids in the home by keeping all medications in a lock box.
Proper disposal. Various entities offer locations for patients to drop off their unused opioids and other medications for safe disposal. These include police or fire departments and retail pharmacies. The US Drug Enforcement Administration sponsors a National Prescription Drug Take Back Day; see https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_disposal/takeback/index.html. The FDA also offers information on where and how to dispose of unused medicines at https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/where-and-how-dispose-unused-medicines.
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. L is initially prescribed, clonidine, 0.1 mg every 6 hours, to address opioid withdrawal. Clonidine is then tapered and maintained at 0.1 mg twice a day for irritability and impulse control. She is also prescribed sertraline, 100 mg/d, for depression and anxiety, and trazodone, 75 mg as needed at night, to assist with sleep.
Continue to: Following inpatient hospitalization...
Following inpatient hospitalization, during 12 weeks of partial hospital treatment, Ms. L participates in individual psychotherapy sessions 5 days/week; family therapy sessions once a week; and experiential therapy along with group sessions with other peers. She undergoes medication evaluations and adjustments on a weekly basis. Ms. L is now working at a store and is pursuing a high school equivalency certificate. She manages to avoid high-risk behaviors, although she reports having occasional cravings. Ms. L is actively involved in Narcotics Anonymous and has a sponsor. She has reconciled with her mother and moved back home, so she can stay away from her former acquaintances who are still using.
Bottom Line
Adolescents with opioid use disorder can benefit from an individualized treatment plan that includes psychosocial interventions, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of the two. Treatment planning should include the adolescent and his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Treatment should focus on interventions that strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation. Ongoing follow-up care is necessary for maintaining abstinence.
Related Resource
- Patkar AA, Weisler RH. Opioid abuse and overdose: Keep your patients safe. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(8):8-12,14-16.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Clonidine • Clorpres
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Narcan
Oxycodone • OxyContin
Sertraline • Zoloft
Tramadol • Ultram
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
1. Davis JP, Prindle JJ, Eddie D, et al. Addressing the opioid epidemic with behavioral interventions for adolescents and young adults: a quasi-experimental design. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2019;87(10):941-951.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Monitoring the Future Survey: High School and Youth Trends. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/monitoring-future-survey-high-school-youth-trends. Updated December 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Hopfer CJ, Khuri E, Crowley TJ. Treating adolescent heroin use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003;42(5):609-611.
4. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency, Diversion Control Division. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/. Accessed January 21, 2020.
5. Gaither JR, Leventhal JM, Ryan SA, et al. National trends in hospitalizations for opioid poisonings among children and adolescents, 1997-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(12):1195-1201.
6. Parker MA, Anthony JC. Epidemiological evidence on extra-medical use of prescription pain relievers: transitions from newly incident use to dependence among 12-21 year olds in United States using meta-analysis, 2002-13. Peer J. 2015;3:e1340. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1340. eCollection 2015.
7. Subramaniam GA, Fishman MJ, Woody G. Treatment of opioid-dependent adolescents and young adults with buprenorphine. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009;11(5):360-363.
8. Borodovsky JT, Levy S, Fishman M. Buprenorphine treatment for adolescents and young adults with opioid use disorders: a narrative review. J Addict Med. 2018;12(3):170-183.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999-2016. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db294.htm. Published December 2017. Accessed January 15, 2020.
10. Strain E. Opioid use disorder: epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical manifestation, course, screening, assessment, diagnosis. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/opioid-use-disorder-epidemiology-pharmacology-clinical-manifestations-course-screening-assessment-and-diagnosis. Updated August 15, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
11. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Substance Use and Prevention. Policy statement: medication-assisted treatment of adolescents with opioid use disorder. Pediatrics. 2016;138(3):e20161893. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-1893.
12. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013:514.
13. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Chapter 6: Theories of personality and psychopathology. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, eds. Kaplan and Sadock’s synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007:209.
14. Kandel DB. Stages and pathways of drug involvement: examining the gateway hypothesis. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2002.
15. Robins LN, McEvoy L. Conduct problems as predictors of substance abuse. In: Robins LN, Rutter M, eds. Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 1990;182-204.
16. Hopfer C, Salomonsen-Sautel S, Mikulich-Gilbertson S, et al. Conduct disorder and initiation of substance use: a prospective longitudinal study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;52(5):511-518.e4.
17. Armstrong TD, Costello EJ. Community studies on adolescent substance use, abuse, or dependence and psychiatric comorbidity. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2002;70(6):1224-1239.
18. Crumley FE. Substance abuse and adolescent suicidal behavior. JAMA. 1990;263(22):3051-3056.
19. Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Seeley JR. Adolescent suicidal ideation and attempts: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 1996;3(1):25-46.
20. Kendler KS, Bulik CM, Silberg J, et al. Childhood sexual abuse and adult psychiatric and substance use disorder in women: an epidemiological and cotwin control analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(10):953-959.
21. Yule AM, Wilens TE, Rausch PK. The opioid epidemic: what a child psychiatrist is to do? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;56(7);541-543.
22. CRAFFT. https://crafft.org. Accessed January 21, 2020.
23. Knight JR, Sherritt L, Harris SK, et al. Validity of brief alcohol screening tests among adolescents: a comparison of the AUDIT, POSIT, CAGE, and CRAFFT. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27(1):67-73.
24. American Psychiatric Association. Online assessment measures. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm/educational-resources/assessment-measures. Accessed January 15, 2020.
25. National Institute of Drug Abuse. American Psychiatric Association adapted NIDA modified ASSIST tools. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/tool-resources-your-practice/screening-assessment-drug-testing-resources/american-psychiatric-association-adapted-nida. Updated November 15, 2015. Accessed January 21, 2020.
26. Canada’s Mental Health & Addiction Network. Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI). https://www.porticonetwork.ca/web/knowledgex-archive/amh-specialists/screening-for-cd-in-youth/screening-both-mh-sud/dusi. Published 2009. Accessed January 21, 2020.
27. Tarter RE. Evaluation and treatment of adolescent substance abuse: a decision tree method. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1990;16(1-2):1-46.
28. Klitzner M, Gruenwald PJ, Taff GA, et al. The adolescent assessment referral system-final report. National Institute on Drug Abuse; Rockville, MD: 1993. NIDA Contract No. 271-89-8252.
29. Slesnick N, Tonigan JS. Assessment of alcohol and other drug use by runaway youths: a test-retest study of the Form 90. Alcohol Treat Q. 2004;22(2):21-34.
30. Winters KC, Kaminer Y. Screening and assessing adolescent substance use disorders in clinical populations. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(7):740-744.
31. Knudsen HK, Abraham AJ, Roman PM. Adoption and implementation of medications in addiction treatment programs. J Addict Med. 2011;5(1):21-27.
32. Deas D, Thomas SE. An overview of controlled study of adolescent substance abuse treatment. Am J Addiction. 2001;10(2):178-189.
33. William RJ, Chang, SY. A comprehensive and comparative review of adolescent substance abuse treatment outcome. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2000;7(2):138-166.
34. Bukstein OG, Work Group on Quality Issues. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with substance use disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(6):609-621.
35. Van Hasselt VB, Null JA, Kempton T, et al. Social skills and depression in adolescent substance abusers. Addict Behav. 1993;18(1):9-18.
36. Dennis M, Godley SH, Diamond G, et al. The Cannabis Youth Treatment (CYT) study: main findings from two randomized trials. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2004;27(3):197-213.
37. US Food and Drug Administration. Information about naloxone. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/information-about-naloxone. Updated December 19, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
38. Feder KA, Krawcyzk N, Saloner, B. Medication-assisted treatment for adolescents in specialty treatment for opioid use disorder. J Adolesc Health. 2018;60(6):747-750.
39. Woody GE, Poole SA, Subramaniam G, et al. Extended vs short-term buprenorphine-naloxone for treatment of opioid-addicted youth: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300(17):2003-2011.
40. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Ser-vices Administration. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs: a treatment improvement protocol TIP 43. https://www.asam.org/docs/advocacy/samhsa_tip43_matforopioidaddiction.pdf?sfvrsn=0. Published 2005. Accessed January 15, 2020.
41. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT). https://www.samhsa.gov/medication-assisted-treatment. Updated September 9, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
42. Johnson RE, Strain EC, Amass L. Buprenorphine: how to use it right. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003;70(suppl 2):S59-S77.
Ms. L, age 17, seeks treatment because she has an ongoing struggle with multiple substances, including benzodiazepines, heroin, alcohol, cannabis, and prescription opioids.
She reports that she was 13 when she first used a prescription opioid that was not prescribed for her. She also reports engaging in unsafe sexual practices while using these substances, and has been diagnosed and treated for a sexually transmitted disease. She dropped out of school and is estranged from her family. She says that for a long time she has felt depressed and that she uses drugs to “self-medicate my emotions.” She endorses high anxiety and lack of motivation. Ms. L also reports having several criminal charges for theft, assault, and exchanging sex for drugs. She has undergone 3 admissions for detoxification, but promptly resumed using drugs, primarily heroin and oxycodone, immediately after discharge. Ms. L meets DSM-5 criteria for opioid use disorder (OUD).
Ms. L’s case illustrates a disturbing trend in the current opioid epidemic in the United States. Nearly 11.8 million individuals age ≥12 reported misuse of opioids in the last year.1 Adolescents who misuse prescription or illicit opioids are more likely to be involved with the legal system due to truancy, running away from home, physical altercations, prostitution, exchanging sex for drugs, robbery, and gang involvement. Adolescents who use opioids may also struggle with academic decline, drop out of school early, be unable to maintain a job, and have relationship difficulties, especially with family members.
In this article, I describe the scope of OUD among adolescents, including epidemiology, clinical manifestations, screening tools, and treatment approaches.
Scope of the problem
According to the most recent Monitoring the Future survey of more than 42,500 8th, 10th, and 12th grade students, 2.7% of 12th graders reported prescription opioid misuse (reported in the survey as “narcotics other than heroin”) in the past year.2 In addition, 0.4% of 12th graders reported heroin use over the same period.2 Although the prevalence of opioid use among adolescents has been declining over the past 5 years,2 it still represents a serious health crisis.
Part of the issue may relate to easier access to more potent opioids. For example, heroin available today can be >4 times purer than it was in the past. In 2002, t
Between 1997 and 2012, the annual incidence of youth (age 15 to 19) hospitalizations for prescription opioid poisoning increased >170%.5 Approximately 6% to 9% of youth involved in risky opioid use develop OUD 6 to 12 months after s
Continue to: In recent years...
In recent years, deaths from drug overdose have increased for all age groups; however, limited data is available regarding adolescent overdose deaths. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), from 2015 to 2016, drug overdose death rates for persons age 15 to 24 increased to 28%.9
How opioids work
Opioids activate specific transmembrane neurotransmitter receptors, including mu, kappa, and delta, in the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS). This leads to activation of G protein–mediated intracellular signal transduction. Mainly it is activation of endogenous mu opioid receptors that mediates the reward, withdrawal, and analgesic effects of opioids. These effects depend on the location of mu receptors. In the CNS, activation of mu opioid receptors may cause miosis, respiratory depression, euphoria, and analgesia.10
Different opioids vary in terms of their half-life; for most opioids, the half-life ranges from 2 to 4 hours.10 Heroin has a half-life of 30 minutes, but due to active metabolites its duration of action is 4 to 5 hours. Opioid metabolites can be detected in urine toxicology within approximately 1 to 2 days since last use.10
Chronic opioid use is associated with neurologic effects that change the function of areas of the brain that control pleasure/reward, stress, decision-making, and more. This leads to cravings, continued substance use, and dependence.11 After continued long-term use, patients report decreased euphoria, but typically they continue to use opioids to avoid withdrawal symptoms or worsening mood.
Criteria for opioid use disorder
In DSM-5, substance use disorders (SUDs)are no longer categorized as abuse or dependence.12 For opioids, the diagnosis is OUD. The Table12 outlines the DSM-5 criteria for OUD. Craving opioids is included for the first time in the OUD diagnosis. Having problems with the legal system is no longer considered a diagnostic criterion for OUD.
Continue to: A vulnerable population
A vulnerable population
As defined by Erik Erikson’s psychosocial stages of development, adolescents struggle between establishing their own identity vs role confusion.13 In an attempt to relate to peers or give in to peer pressure, some adolescents start by experimenting with nicotine, alcohol, and/or marijuana; however, some may move on to using other illicit drugs.14 Risk factors for the development of SUDs include early onset of substance use and a rapid progression through stages of substance use from experimentation to regular use, risky use, and dependence.15 In our case study, Ms. L’s substance use followed a similar pattern. Further, the comorbidity of SUDs and other psychiatric disorders may add a layer of complexity when caring for adolescents. Box 116-20 describes the relationship between comorbid psychiatric disorders and SUDs in adolescents.
Box 1
Disruptive behavior disorders are the most common coexisting psychiatric disorders in an adolescent with a substance use disorder (SUD), including opioid use disorder. These individuals typically present with aggression and other conduct disorder symptoms, and have early involvement with the legal system. Conversely, patients with conduct disorder are at high risk of early initiation of illicit substance use, including opioids. Early onset of substance use is a strong risk factor for developing an SUD.16
Mood disorders, particularly depression, can either precede or occur as a result of heavy and prolonged substance use.17 The estimated prevalence of major depressive disorder in individuals with an SUD is 24% to 50%. Among adolescents, an SUD is also a risk factor for suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and completed suicide.18-20
Anxiety disorders, especially social phobia, and posttraumatic stress disorder are common in individuals with SUD.
Adolescents with SUD should be carefully evaluated for comorbid psychiatric disorders and treated accordingly.
Clinical manifestations
Common clinical manifestations of opioid use vary depending on when the patient is seen. An individual with OUD may appear acutely intoxicated, be in withdrawal, or show no effects. Chronic/prolonged use can lead to tolerance, such that a user needs to ingest larger amounts of the opioid to produce the same effects.
Acute intoxication can cause sedation, slurring of speech, and pinpoint pupils. Fresh injection sites may be visible on physical examination of IV users. The effects of acute intoxication usually depend on the half-life of the specific opioid and the individual’s tolerance.10 Tolerance to heroin can occur in 10 days and withdrawal can manifest in 3 to 7 hours after last use, depending on dose and purity.3 Tolerance can lead to unintentional overdose and death.
Withdrawal. Individuals experiencing withdrawal from opioids present with flu-like physical symptoms, including generalized body ache, rhinorrhea, diarrhea, goose bumps, lacrimation, and vomiting. Individuals also may experience irritability, restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, and depression during withdrawal.
Other manifestations. Excessive and chronic/prolonged opioid use can adversely impact socio-occupational functioning and cause academic decline in adolescents and youth. Personal relationships are significantly affected. Opioid users may have legal difficulties as a result of committing crimes such as theft, prostitution, or robbery in order to obtain opioids.
Continue to: Screening for OUD
Screening for OUD
Several screening tools are available to assess adolescents for SUDs, including OUD.
CRAFFT is a 6-item, clinician-administered screening tool that has been approved by American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Substance Abuse for adolescents and young adults age <21.21-23 This commonly used tool can assess for alcohol, cannabis, and other drug use. A score ≥2 is considered positive for drug use, indicating that the individual would require further evaluation and assessment22,23 (Figure). There is also a self-administered CRAFFT questionnaire that can be completed by the patient.

NIDA-modified ASSIST. The American Psychiatric Association has adapted the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)-modified ASSIST. One version is designated for parents/guardians to administer to their children (age 6 to 17), and one is designated for adolescents (age 11 to 17) to self-administer.24,25 Each screening tool has 2 levels: Level 1 screens for substance use and other mental health symptoms, and Level 2 is more specific for substance use alone.
Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI) is a self-report questionnaire that has 149 items that assess the use of numerous drugs. It is designed to quantify the severity of consequences associated with drug and alcohol use.26,27
Problem-Oriented Screening Instrument for Teenagers (PO
Continue to: Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ)...
Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ) is a brief, 40-item, cost-effective, self-report questionnaire that can help identify adolescents (age 12 to 18) who should be referred for further evaluation.30
Addressing treatment expectations
For an adolescent with OUD, treatment should begin in the least restrictive environment that is perceived as safe for the patient. An adolescent’s readiness and motivation to achieve and maintain abstinence are crucial. Treatment planning should include the adolescent as well as his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Start with a definitive treatment plan that addresses an individual’s needs. The plan should provide structure and an understanding of treatment expectations. The treatment team should clarify the realistic plan and goals based on empirical and clinical evidence. Treatment goals should include interventions to strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation, such as establishing academic and/or vocational goals. Addressing readiness and working on a patient’s motivation is extremely important for most of these interventions.
In order for any intervention to be successful, clinicians need to establish and foster rapport with the adolescent. By law, substance use or behaviors related to substance use are not allowed to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship, unless the adolescent gives consent or there are concerns that such behaviors might put the patient or others at risk. It is important to prime the adolescent and help them understand that any information pertaining to their safety or the safety of others may need to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship.
Choosing an intervention
Less than 50% of a nationally representative sample of 345 addiction treatment programs serving adolescents and adults offer medications for treating OUD.31 Even in programs that offer pharmacotherapy, medications are significantly underutilized. Fewer than 30% of patients in addiction treatment programs receive medication, compared with 74% of patients receiving treatment for other mental health disorders.31 A
Psychotherapy may be used to treat OUD in adolescents. Several family therapies have been studied and are considered as critical psychotherapeutic interventions for treating SUDs, including structural family treatment and functional family therapy approaches.34 An integrated behavioral and family therapy model is also recommended for adolescent patients with SUDs. Cognitive distortions and use of self-deprecatory statements are common among adolescents.35 Therefore, using approaches of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), or CBT plus motivational enhancement therapy, also might be effective for this population.36 The adolescent community reinforcement approach (A-CRA) is a behavioral treatment designed to help adolescents and their families learn how to lead a healthy and happy life without the use of drugs or alcohol by increasing access to social, familial, and educational/vocational reinforcers. Support groups and peer and family support should be encouraged as adjuncts to other interventions. In some areas, sober housing options for adolescents are also available.
Continue to: Harm-reduction strategies
Harm-reduction strategies. Although the primary goal of treatment for adolescents with OUD is to achieve and maintain abstinence from opioid use, implicit and explicit goals can be set. Short-term implicit goals may include harm-reduction strategies that emphasize decreasing the duration, frequency, and amount of substance use and limiting the chances of adverse effects, while the long-term explicit goal should be abstinence from opioid use.
Naloxone nasal spray is used as a harm-reduction strategy. It is an FDA-approved formulation that can reverse the effects of unintentional opioid overdoses and potentially prevent death from respiratory depression.37 Other harm-reduction strategies include needle exchange programs, which provide sterile needles to individuals who inject drugs in an effort to prevent or reduce the transmission of human immunodeficiency virus and other bloodborne viruses that can be spread via shared injection equipment. Fentanyl testing strips allow opioid users to test for the presence fentanyl and fentanyl analogs in the unregulated “street” opioid supply.
Pharmacologic interventions. Because there is limited empirical evidence on the efficacy of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for adolescents with OUD, clinicians need to rely on evidence from research and experience with adults. Unfortunately, MAT is offered to adolescents considerably less often than it is to adults. Feder et al38 reported that only 2.4% of adolescents received MAT for heroin use and only 0.4% of adolescents received MAT for prescription opioid use, compared with 26.3% and 12% of adults, respectively.
Detoxification. Medications available for detoxification from opioids include opiates (such as methadone or buprenorphine) and clonidine (a central sympathomimetic). If the patient has used heroin for a short period (<1 year) and has no history of detoxification, consider a detoxification strategy with a longer-term taper (90 to 180 days) to allow for stabilization.
Maintenance treatment. Consider maintenance treatment for adolescents with a history of long-term opioid use and at least 2 prior short-term detoxification attempts or nonpharmacotherapy-based treatment within 12 months. Be sure to receive consent from a legal guardian and the patient. Maintenance treatment is usually recommended to continue for 1 to 6 years. Maintenance programs with longer durations have shown higher rates of abstinence, improved engagement, and retention in treatment.39
Continue to: According to guidelines from...
According to guidelines from the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM), adolescents age >16 should be offered MAT; the first-line treatment is buprenorphine.40 To avoid risks of abuse and diversion, a combination of buprenorphine/naloxone may be administered.
Maintenance with buprenorphine
In order to prescribe and dispense buprenorphine, clinicians need to obtain a waiver from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Before initiating buprenorphine, consider the type of opioid the individual used (short- or long-acting), the severity of the OUD, and the last reported use. The 3 phases of buprenorphine treatment are41:
- Induction phase. Buprenorphine can be initiated at 2 to 4 mg/d. Some patients may require up to 8 mg/d on the first day, which can be administered in divided doses.42 Evaluate and monitor patients carefully during the first few hours after the first dose. Patients should be in early withdrawal; otherwise, the buprenorphine might precipitate withdrawal. The induction phase can be completed in 2 to 4 days by titrating the dose so that the signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal are minimal, and the patient is able to continue treatment. It may be helpful to have the patient’s legal guardian nearby in case the patient does not tolerate the medication or experiences withdrawal. The initial target dose for buprenorphine is approximately 12 to 16 mg/d.
- Stabilization phase. Patients no longer experience withdrawal symptoms and no longer have cravings. This phase can last 6 to 8 weeks. During this phase, patients should be seen weekly and doses should be adjusted if necessary. As a partial mu agonist, buprenorphine does not activate mu receptors fully and reaches a ceiling effect. Hence, doses >24 mg/d have limited added agonist properties.
- Maintenance phase. Because discontinuation of buprenorphine is associated with high relapse rates, patients may need to be maintained long-term on their stabilization dose, and for some patients, the length of time could be indefinite.39 During this phase, patients continue to undergo follow-up, but do so less frequently.
Methadone maintenance is generally not recommended for individuals age <18.
Preventing opioid diversion
Prescription medications that are kept in the home are a substantial source of opioids for adolescents. In 2014, 56% of 12th graders who did not need medications for medical purposes were able to acquire them from their friends or relatives; 36% of 12th graders used their own prescriptions.21 Limiting adolescents’ access to prescription opioids is the first line of prevention. Box 2 describes interventions and strategies to limit adolescents’ access to opioids.
Box 2
Many adolescents obtain opioids for recreational use from medications that were legitimately prescribed to family or friends. Both clinicians and parents/ guardians can take steps to reduce or prevent this type of diversion
Health care facilities. Regulating the number of pills dispensed to patients is crucial. It is highly recommended to prescribe only the minimal number of opioids necessary. In most cases, 3 to 7 days’ worth of opioids at a time might be sufficient, especially after surgical procedures.
Home. Families can limit adolescents’ access to prescription opioids in the home by keeping all medications in a lock box.
Proper disposal. Various entities offer locations for patients to drop off their unused opioids and other medications for safe disposal. These include police or fire departments and retail pharmacies. The US Drug Enforcement Administration sponsors a National Prescription Drug Take Back Day; see https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_disposal/takeback/index.html. The FDA also offers information on where and how to dispose of unused medicines at https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/where-and-how-dispose-unused-medicines.
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. L is initially prescribed, clonidine, 0.1 mg every 6 hours, to address opioid withdrawal. Clonidine is then tapered and maintained at 0.1 mg twice a day for irritability and impulse control. She is also prescribed sertraline, 100 mg/d, for depression and anxiety, and trazodone, 75 mg as needed at night, to assist with sleep.
Continue to: Following inpatient hospitalization...
Following inpatient hospitalization, during 12 weeks of partial hospital treatment, Ms. L participates in individual psychotherapy sessions 5 days/week; family therapy sessions once a week; and experiential therapy along with group sessions with other peers. She undergoes medication evaluations and adjustments on a weekly basis. Ms. L is now working at a store and is pursuing a high school equivalency certificate. She manages to avoid high-risk behaviors, although she reports having occasional cravings. Ms. L is actively involved in Narcotics Anonymous and has a sponsor. She has reconciled with her mother and moved back home, so she can stay away from her former acquaintances who are still using.
Bottom Line
Adolescents with opioid use disorder can benefit from an individualized treatment plan that includes psychosocial interventions, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of the two. Treatment planning should include the adolescent and his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Treatment should focus on interventions that strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation. Ongoing follow-up care is necessary for maintaining abstinence.
Related Resource
- Patkar AA, Weisler RH. Opioid abuse and overdose: Keep your patients safe. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(8):8-12,14-16.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Clonidine • Clorpres
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Narcan
Oxycodone • OxyContin
Sertraline • Zoloft
Tramadol • Ultram
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
Ms. L, age 17, seeks treatment because she has an ongoing struggle with multiple substances, including benzodiazepines, heroin, alcohol, cannabis, and prescription opioids.
She reports that she was 13 when she first used a prescription opioid that was not prescribed for her. She also reports engaging in unsafe sexual practices while using these substances, and has been diagnosed and treated for a sexually transmitted disease. She dropped out of school and is estranged from her family. She says that for a long time she has felt depressed and that she uses drugs to “self-medicate my emotions.” She endorses high anxiety and lack of motivation. Ms. L also reports having several criminal charges for theft, assault, and exchanging sex for drugs. She has undergone 3 admissions for detoxification, but promptly resumed using drugs, primarily heroin and oxycodone, immediately after discharge. Ms. L meets DSM-5 criteria for opioid use disorder (OUD).
Ms. L’s case illustrates a disturbing trend in the current opioid epidemic in the United States. Nearly 11.8 million individuals age ≥12 reported misuse of opioids in the last year.1 Adolescents who misuse prescription or illicit opioids are more likely to be involved with the legal system due to truancy, running away from home, physical altercations, prostitution, exchanging sex for drugs, robbery, and gang involvement. Adolescents who use opioids may also struggle with academic decline, drop out of school early, be unable to maintain a job, and have relationship difficulties, especially with family members.
In this article, I describe the scope of OUD among adolescents, including epidemiology, clinical manifestations, screening tools, and treatment approaches.
Scope of the problem
According to the most recent Monitoring the Future survey of more than 42,500 8th, 10th, and 12th grade students, 2.7% of 12th graders reported prescription opioid misuse (reported in the survey as “narcotics other than heroin”) in the past year.2 In addition, 0.4% of 12th graders reported heroin use over the same period.2 Although the prevalence of opioid use among adolescents has been declining over the past 5 years,2 it still represents a serious health crisis.
Part of the issue may relate to easier access to more potent opioids. For example, heroin available today can be >4 times purer than it was in the past. In 2002, t
Between 1997 and 2012, the annual incidence of youth (age 15 to 19) hospitalizations for prescription opioid poisoning increased >170%.5 Approximately 6% to 9% of youth involved in risky opioid use develop OUD 6 to 12 months after s
Continue to: In recent years...
In recent years, deaths from drug overdose have increased for all age groups; however, limited data is available regarding adolescent overdose deaths. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), from 2015 to 2016, drug overdose death rates for persons age 15 to 24 increased to 28%.9
How opioids work
Opioids activate specific transmembrane neurotransmitter receptors, including mu, kappa, and delta, in the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS). This leads to activation of G protein–mediated intracellular signal transduction. Mainly it is activation of endogenous mu opioid receptors that mediates the reward, withdrawal, and analgesic effects of opioids. These effects depend on the location of mu receptors. In the CNS, activation of mu opioid receptors may cause miosis, respiratory depression, euphoria, and analgesia.10
Different opioids vary in terms of their half-life; for most opioids, the half-life ranges from 2 to 4 hours.10 Heroin has a half-life of 30 minutes, but due to active metabolites its duration of action is 4 to 5 hours. Opioid metabolites can be detected in urine toxicology within approximately 1 to 2 days since last use.10
Chronic opioid use is associated with neurologic effects that change the function of areas of the brain that control pleasure/reward, stress, decision-making, and more. This leads to cravings, continued substance use, and dependence.11 After continued long-term use, patients report decreased euphoria, but typically they continue to use opioids to avoid withdrawal symptoms or worsening mood.
Criteria for opioid use disorder
In DSM-5, substance use disorders (SUDs)are no longer categorized as abuse or dependence.12 For opioids, the diagnosis is OUD. The Table12 outlines the DSM-5 criteria for OUD. Craving opioids is included for the first time in the OUD diagnosis. Having problems with the legal system is no longer considered a diagnostic criterion for OUD.
Continue to: A vulnerable population
A vulnerable population
As defined by Erik Erikson’s psychosocial stages of development, adolescents struggle between establishing their own identity vs role confusion.13 In an attempt to relate to peers or give in to peer pressure, some adolescents start by experimenting with nicotine, alcohol, and/or marijuana; however, some may move on to using other illicit drugs.14 Risk factors for the development of SUDs include early onset of substance use and a rapid progression through stages of substance use from experimentation to regular use, risky use, and dependence.15 In our case study, Ms. L’s substance use followed a similar pattern. Further, the comorbidity of SUDs and other psychiatric disorders may add a layer of complexity when caring for adolescents. Box 116-20 describes the relationship between comorbid psychiatric disorders and SUDs in adolescents.
Box 1
Disruptive behavior disorders are the most common coexisting psychiatric disorders in an adolescent with a substance use disorder (SUD), including opioid use disorder. These individuals typically present with aggression and other conduct disorder symptoms, and have early involvement with the legal system. Conversely, patients with conduct disorder are at high risk of early initiation of illicit substance use, including opioids. Early onset of substance use is a strong risk factor for developing an SUD.16
Mood disorders, particularly depression, can either precede or occur as a result of heavy and prolonged substance use.17 The estimated prevalence of major depressive disorder in individuals with an SUD is 24% to 50%. Among adolescents, an SUD is also a risk factor for suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and completed suicide.18-20
Anxiety disorders, especially social phobia, and posttraumatic stress disorder are common in individuals with SUD.
Adolescents with SUD should be carefully evaluated for comorbid psychiatric disorders and treated accordingly.
Clinical manifestations
Common clinical manifestations of opioid use vary depending on when the patient is seen. An individual with OUD may appear acutely intoxicated, be in withdrawal, or show no effects. Chronic/prolonged use can lead to tolerance, such that a user needs to ingest larger amounts of the opioid to produce the same effects.
Acute intoxication can cause sedation, slurring of speech, and pinpoint pupils. Fresh injection sites may be visible on physical examination of IV users. The effects of acute intoxication usually depend on the half-life of the specific opioid and the individual’s tolerance.10 Tolerance to heroin can occur in 10 days and withdrawal can manifest in 3 to 7 hours after last use, depending on dose and purity.3 Tolerance can lead to unintentional overdose and death.
Withdrawal. Individuals experiencing withdrawal from opioids present with flu-like physical symptoms, including generalized body ache, rhinorrhea, diarrhea, goose bumps, lacrimation, and vomiting. Individuals also may experience irritability, restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, and depression during withdrawal.
Other manifestations. Excessive and chronic/prolonged opioid use can adversely impact socio-occupational functioning and cause academic decline in adolescents and youth. Personal relationships are significantly affected. Opioid users may have legal difficulties as a result of committing crimes such as theft, prostitution, or robbery in order to obtain opioids.
Continue to: Screening for OUD
Screening for OUD
Several screening tools are available to assess adolescents for SUDs, including OUD.
CRAFFT is a 6-item, clinician-administered screening tool that has been approved by American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Substance Abuse for adolescents and young adults age <21.21-23 This commonly used tool can assess for alcohol, cannabis, and other drug use. A score ≥2 is considered positive for drug use, indicating that the individual would require further evaluation and assessment22,23 (Figure). There is also a self-administered CRAFFT questionnaire that can be completed by the patient.

NIDA-modified ASSIST. The American Psychiatric Association has adapted the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)-modified ASSIST. One version is designated for parents/guardians to administer to their children (age 6 to 17), and one is designated for adolescents (age 11 to 17) to self-administer.24,25 Each screening tool has 2 levels: Level 1 screens for substance use and other mental health symptoms, and Level 2 is more specific for substance use alone.
Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI) is a self-report questionnaire that has 149 items that assess the use of numerous drugs. It is designed to quantify the severity of consequences associated with drug and alcohol use.26,27
Problem-Oriented Screening Instrument for Teenagers (PO
Continue to: Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ)...
Personal Experience Screening Questionnaire (PESQ) is a brief, 40-item, cost-effective, self-report questionnaire that can help identify adolescents (age 12 to 18) who should be referred for further evaluation.30
Addressing treatment expectations
For an adolescent with OUD, treatment should begin in the least restrictive environment that is perceived as safe for the patient. An adolescent’s readiness and motivation to achieve and maintain abstinence are crucial. Treatment planning should include the adolescent as well as his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Start with a definitive treatment plan that addresses an individual’s needs. The plan should provide structure and an understanding of treatment expectations. The treatment team should clarify the realistic plan and goals based on empirical and clinical evidence. Treatment goals should include interventions to strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation, such as establishing academic and/or vocational goals. Addressing readiness and working on a patient’s motivation is extremely important for most of these interventions.
In order for any intervention to be successful, clinicians need to establish and foster rapport with the adolescent. By law, substance use or behaviors related to substance use are not allowed to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship, unless the adolescent gives consent or there are concerns that such behaviors might put the patient or others at risk. It is important to prime the adolescent and help them understand that any information pertaining to their safety or the safety of others may need to be shared outside the patient-clinician relationship.
Choosing an intervention
Less than 50% of a nationally representative sample of 345 addiction treatment programs serving adolescents and adults offer medications for treating OUD.31 Even in programs that offer pharmacotherapy, medications are significantly underutilized. Fewer than 30% of patients in addiction treatment programs receive medication, compared with 74% of patients receiving treatment for other mental health disorders.31 A
Psychotherapy may be used to treat OUD in adolescents. Several family therapies have been studied and are considered as critical psychotherapeutic interventions for treating SUDs, including structural family treatment and functional family therapy approaches.34 An integrated behavioral and family therapy model is also recommended for adolescent patients with SUDs. Cognitive distortions and use of self-deprecatory statements are common among adolescents.35 Therefore, using approaches of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), or CBT plus motivational enhancement therapy, also might be effective for this population.36 The adolescent community reinforcement approach (A-CRA) is a behavioral treatment designed to help adolescents and their families learn how to lead a healthy and happy life without the use of drugs or alcohol by increasing access to social, familial, and educational/vocational reinforcers. Support groups and peer and family support should be encouraged as adjuncts to other interventions. In some areas, sober housing options for adolescents are also available.
Continue to: Harm-reduction strategies
Harm-reduction strategies. Although the primary goal of treatment for adolescents with OUD is to achieve and maintain abstinence from opioid use, implicit and explicit goals can be set. Short-term implicit goals may include harm-reduction strategies that emphasize decreasing the duration, frequency, and amount of substance use and limiting the chances of adverse effects, while the long-term explicit goal should be abstinence from opioid use.
Naloxone nasal spray is used as a harm-reduction strategy. It is an FDA-approved formulation that can reverse the effects of unintentional opioid overdoses and potentially prevent death from respiratory depression.37 Other harm-reduction strategies include needle exchange programs, which provide sterile needles to individuals who inject drugs in an effort to prevent or reduce the transmission of human immunodeficiency virus and other bloodborne viruses that can be spread via shared injection equipment. Fentanyl testing strips allow opioid users to test for the presence fentanyl and fentanyl analogs in the unregulated “street” opioid supply.
Pharmacologic interventions. Because there is limited empirical evidence on the efficacy of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for adolescents with OUD, clinicians need to rely on evidence from research and experience with adults. Unfortunately, MAT is offered to adolescents considerably less often than it is to adults. Feder et al38 reported that only 2.4% of adolescents received MAT for heroin use and only 0.4% of adolescents received MAT for prescription opioid use, compared with 26.3% and 12% of adults, respectively.
Detoxification. Medications available for detoxification from opioids include opiates (such as methadone or buprenorphine) and clonidine (a central sympathomimetic). If the patient has used heroin for a short period (<1 year) and has no history of detoxification, consider a detoxification strategy with a longer-term taper (90 to 180 days) to allow for stabilization.
Maintenance treatment. Consider maintenance treatment for adolescents with a history of long-term opioid use and at least 2 prior short-term detoxification attempts or nonpharmacotherapy-based treatment within 12 months. Be sure to receive consent from a legal guardian and the patient. Maintenance treatment is usually recommended to continue for 1 to 6 years. Maintenance programs with longer durations have shown higher rates of abstinence, improved engagement, and retention in treatment.39
Continue to: According to guidelines from...
According to guidelines from the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM), adolescents age >16 should be offered MAT; the first-line treatment is buprenorphine.40 To avoid risks of abuse and diversion, a combination of buprenorphine/naloxone may be administered.
Maintenance with buprenorphine
In order to prescribe and dispense buprenorphine, clinicians need to obtain a waiver from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Before initiating buprenorphine, consider the type of opioid the individual used (short- or long-acting), the severity of the OUD, and the last reported use. The 3 phases of buprenorphine treatment are41:
- Induction phase. Buprenorphine can be initiated at 2 to 4 mg/d. Some patients may require up to 8 mg/d on the first day, which can be administered in divided doses.42 Evaluate and monitor patients carefully during the first few hours after the first dose. Patients should be in early withdrawal; otherwise, the buprenorphine might precipitate withdrawal. The induction phase can be completed in 2 to 4 days by titrating the dose so that the signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal are minimal, and the patient is able to continue treatment. It may be helpful to have the patient’s legal guardian nearby in case the patient does not tolerate the medication or experiences withdrawal. The initial target dose for buprenorphine is approximately 12 to 16 mg/d.
- Stabilization phase. Patients no longer experience withdrawal symptoms and no longer have cravings. This phase can last 6 to 8 weeks. During this phase, patients should be seen weekly and doses should be adjusted if necessary. As a partial mu agonist, buprenorphine does not activate mu receptors fully and reaches a ceiling effect. Hence, doses >24 mg/d have limited added agonist properties.
- Maintenance phase. Because discontinuation of buprenorphine is associated with high relapse rates, patients may need to be maintained long-term on their stabilization dose, and for some patients, the length of time could be indefinite.39 During this phase, patients continue to undergo follow-up, but do so less frequently.
Methadone maintenance is generally not recommended for individuals age <18.
Preventing opioid diversion
Prescription medications that are kept in the home are a substantial source of opioids for adolescents. In 2014, 56% of 12th graders who did not need medications for medical purposes were able to acquire them from their friends or relatives; 36% of 12th graders used their own prescriptions.21 Limiting adolescents’ access to prescription opioids is the first line of prevention. Box 2 describes interventions and strategies to limit adolescents’ access to opioids.
Box 2
Many adolescents obtain opioids for recreational use from medications that were legitimately prescribed to family or friends. Both clinicians and parents/ guardians can take steps to reduce or prevent this type of diversion
Health care facilities. Regulating the number of pills dispensed to patients is crucial. It is highly recommended to prescribe only the minimal number of opioids necessary. In most cases, 3 to 7 days’ worth of opioids at a time might be sufficient, especially after surgical procedures.
Home. Families can limit adolescents’ access to prescription opioids in the home by keeping all medications in a lock box.
Proper disposal. Various entities offer locations for patients to drop off their unused opioids and other medications for safe disposal. These include police or fire departments and retail pharmacies. The US Drug Enforcement Administration sponsors a National Prescription Drug Take Back Day; see https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_disposal/takeback/index.html. The FDA also offers information on where and how to dispose of unused medicines at https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/where-and-how-dispose-unused-medicines.
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. L is initially prescribed, clonidine, 0.1 mg every 6 hours, to address opioid withdrawal. Clonidine is then tapered and maintained at 0.1 mg twice a day for irritability and impulse control. She is also prescribed sertraline, 100 mg/d, for depression and anxiety, and trazodone, 75 mg as needed at night, to assist with sleep.
Continue to: Following inpatient hospitalization...
Following inpatient hospitalization, during 12 weeks of partial hospital treatment, Ms. L participates in individual psychotherapy sessions 5 days/week; family therapy sessions once a week; and experiential therapy along with group sessions with other peers. She undergoes medication evaluations and adjustments on a weekly basis. Ms. L is now working at a store and is pursuing a high school equivalency certificate. She manages to avoid high-risk behaviors, although she reports having occasional cravings. Ms. L is actively involved in Narcotics Anonymous and has a sponsor. She has reconciled with her mother and moved back home, so she can stay away from her former acquaintances who are still using.
Bottom Line
Adolescents with opioid use disorder can benefit from an individualized treatment plan that includes psychosocial interventions, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of the two. Treatment planning should include the adolescent and his/her family to ensure they are able to verbalize their expectations. Treatment should focus on interventions that strengthen interpersonal relationships and assist with rehabilitation. Ongoing follow-up care is necessary for maintaining abstinence.
Related Resource
- Patkar AA, Weisler RH. Opioid abuse and overdose: Keep your patients safe. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(8):8-12,14-16.
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Clonidine • Clorpres
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Narcan
Oxycodone • OxyContin
Sertraline • Zoloft
Tramadol • Ultram
Trazodone • Desyrel, Oleptro
1. Davis JP, Prindle JJ, Eddie D, et al. Addressing the opioid epidemic with behavioral interventions for adolescents and young adults: a quasi-experimental design. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2019;87(10):941-951.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Monitoring the Future Survey: High School and Youth Trends. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/monitoring-future-survey-high-school-youth-trends. Updated December 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Hopfer CJ, Khuri E, Crowley TJ. Treating adolescent heroin use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003;42(5):609-611.
4. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency, Diversion Control Division. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/. Accessed January 21, 2020.
5. Gaither JR, Leventhal JM, Ryan SA, et al. National trends in hospitalizations for opioid poisonings among children and adolescents, 1997-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(12):1195-1201.
6. Parker MA, Anthony JC. Epidemiological evidence on extra-medical use of prescription pain relievers: transitions from newly incident use to dependence among 12-21 year olds in United States using meta-analysis, 2002-13. Peer J. 2015;3:e1340. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1340. eCollection 2015.
7. Subramaniam GA, Fishman MJ, Woody G. Treatment of opioid-dependent adolescents and young adults with buprenorphine. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009;11(5):360-363.
8. Borodovsky JT, Levy S, Fishman M. Buprenorphine treatment for adolescents and young adults with opioid use disorders: a narrative review. J Addict Med. 2018;12(3):170-183.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999-2016. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db294.htm. Published December 2017. Accessed January 15, 2020.
10. Strain E. Opioid use disorder: epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical manifestation, course, screening, assessment, diagnosis. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/opioid-use-disorder-epidemiology-pharmacology-clinical-manifestations-course-screening-assessment-and-diagnosis. Updated August 15, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
11. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Substance Use and Prevention. Policy statement: medication-assisted treatment of adolescents with opioid use disorder. Pediatrics. 2016;138(3):e20161893. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-1893.
12. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013:514.
13. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Chapter 6: Theories of personality and psychopathology. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, eds. Kaplan and Sadock’s synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007:209.
14. Kandel DB. Stages and pathways of drug involvement: examining the gateway hypothesis. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2002.
15. Robins LN, McEvoy L. Conduct problems as predictors of substance abuse. In: Robins LN, Rutter M, eds. Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 1990;182-204.
16. Hopfer C, Salomonsen-Sautel S, Mikulich-Gilbertson S, et al. Conduct disorder and initiation of substance use: a prospective longitudinal study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;52(5):511-518.e4.
17. Armstrong TD, Costello EJ. Community studies on adolescent substance use, abuse, or dependence and psychiatric comorbidity. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2002;70(6):1224-1239.
18. Crumley FE. Substance abuse and adolescent suicidal behavior. JAMA. 1990;263(22):3051-3056.
19. Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Seeley JR. Adolescent suicidal ideation and attempts: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 1996;3(1):25-46.
20. Kendler KS, Bulik CM, Silberg J, et al. Childhood sexual abuse and adult psychiatric and substance use disorder in women: an epidemiological and cotwin control analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(10):953-959.
21. Yule AM, Wilens TE, Rausch PK. The opioid epidemic: what a child psychiatrist is to do? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;56(7);541-543.
22. CRAFFT. https://crafft.org. Accessed January 21, 2020.
23. Knight JR, Sherritt L, Harris SK, et al. Validity of brief alcohol screening tests among adolescents: a comparison of the AUDIT, POSIT, CAGE, and CRAFFT. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27(1):67-73.
24. American Psychiatric Association. Online assessment measures. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm/educational-resources/assessment-measures. Accessed January 15, 2020.
25. National Institute of Drug Abuse. American Psychiatric Association adapted NIDA modified ASSIST tools. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/tool-resources-your-practice/screening-assessment-drug-testing-resources/american-psychiatric-association-adapted-nida. Updated November 15, 2015. Accessed January 21, 2020.
26. Canada’s Mental Health & Addiction Network. Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI). https://www.porticonetwork.ca/web/knowledgex-archive/amh-specialists/screening-for-cd-in-youth/screening-both-mh-sud/dusi. Published 2009. Accessed January 21, 2020.
27. Tarter RE. Evaluation and treatment of adolescent substance abuse: a decision tree method. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1990;16(1-2):1-46.
28. Klitzner M, Gruenwald PJ, Taff GA, et al. The adolescent assessment referral system-final report. National Institute on Drug Abuse; Rockville, MD: 1993. NIDA Contract No. 271-89-8252.
29. Slesnick N, Tonigan JS. Assessment of alcohol and other drug use by runaway youths: a test-retest study of the Form 90. Alcohol Treat Q. 2004;22(2):21-34.
30. Winters KC, Kaminer Y. Screening and assessing adolescent substance use disorders in clinical populations. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(7):740-744.
31. Knudsen HK, Abraham AJ, Roman PM. Adoption and implementation of medications in addiction treatment programs. J Addict Med. 2011;5(1):21-27.
32. Deas D, Thomas SE. An overview of controlled study of adolescent substance abuse treatment. Am J Addiction. 2001;10(2):178-189.
33. William RJ, Chang, SY. A comprehensive and comparative review of adolescent substance abuse treatment outcome. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2000;7(2):138-166.
34. Bukstein OG, Work Group on Quality Issues. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with substance use disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(6):609-621.
35. Van Hasselt VB, Null JA, Kempton T, et al. Social skills and depression in adolescent substance abusers. Addict Behav. 1993;18(1):9-18.
36. Dennis M, Godley SH, Diamond G, et al. The Cannabis Youth Treatment (CYT) study: main findings from two randomized trials. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2004;27(3):197-213.
37. US Food and Drug Administration. Information about naloxone. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/information-about-naloxone. Updated December 19, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
38. Feder KA, Krawcyzk N, Saloner, B. Medication-assisted treatment for adolescents in specialty treatment for opioid use disorder. J Adolesc Health. 2018;60(6):747-750.
39. Woody GE, Poole SA, Subramaniam G, et al. Extended vs short-term buprenorphine-naloxone for treatment of opioid-addicted youth: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300(17):2003-2011.
40. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Ser-vices Administration. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs: a treatment improvement protocol TIP 43. https://www.asam.org/docs/advocacy/samhsa_tip43_matforopioidaddiction.pdf?sfvrsn=0. Published 2005. Accessed January 15, 2020.
41. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT). https://www.samhsa.gov/medication-assisted-treatment. Updated September 9, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
42. Johnson RE, Strain EC, Amass L. Buprenorphine: how to use it right. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003;70(suppl 2):S59-S77.
1. Davis JP, Prindle JJ, Eddie D, et al. Addressing the opioid epidemic with behavioral interventions for adolescents and young adults: a quasi-experimental design. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2019;87(10):941-951.
2. National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Monitoring the Future Survey: High School and Youth Trends. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/monitoring-future-survey-high-school-youth-trends. Updated December 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Hopfer CJ, Khuri E, Crowley TJ. Treating adolescent heroin use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003;42(5):609-611.
4. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency, Diversion Control Division. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/. Accessed January 21, 2020.
5. Gaither JR, Leventhal JM, Ryan SA, et al. National trends in hospitalizations for opioid poisonings among children and adolescents, 1997-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(12):1195-1201.
6. Parker MA, Anthony JC. Epidemiological evidence on extra-medical use of prescription pain relievers: transitions from newly incident use to dependence among 12-21 year olds in United States using meta-analysis, 2002-13. Peer J. 2015;3:e1340. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1340. eCollection 2015.
7. Subramaniam GA, Fishman MJ, Woody G. Treatment of opioid-dependent adolescents and young adults with buprenorphine. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009;11(5):360-363.
8. Borodovsky JT, Levy S, Fishman M. Buprenorphine treatment for adolescents and young adults with opioid use disorders: a narrative review. J Addict Med. 2018;12(3):170-183.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Center for Health Statistics. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999-2016. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db294.htm. Published December 2017. Accessed January 15, 2020.
10. Strain E. Opioid use disorder: epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical manifestation, course, screening, assessment, diagnosis. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/opioid-use-disorder-epidemiology-pharmacology-clinical-manifestations-course-screening-assessment-and-diagnosis. Updated August 15, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
11. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Substance Use and Prevention. Policy statement: medication-assisted treatment of adolescents with opioid use disorder. Pediatrics. 2016;138(3):e20161893. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-1893.
12. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013:514.
13. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Chapter 6: Theories of personality and psychopathology. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, eds. Kaplan and Sadock’s synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007:209.
14. Kandel DB. Stages and pathways of drug involvement: examining the gateway hypothesis. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 2002.
15. Robins LN, McEvoy L. Conduct problems as predictors of substance abuse. In: Robins LN, Rutter M, eds. Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 1990;182-204.
16. Hopfer C, Salomonsen-Sautel S, Mikulich-Gilbertson S, et al. Conduct disorder and initiation of substance use: a prospective longitudinal study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;52(5):511-518.e4.
17. Armstrong TD, Costello EJ. Community studies on adolescent substance use, abuse, or dependence and psychiatric comorbidity. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2002;70(6):1224-1239.
18. Crumley FE. Substance abuse and adolescent suicidal behavior. JAMA. 1990;263(22):3051-3056.
19. Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Seeley JR. Adolescent suicidal ideation and attempts: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 1996;3(1):25-46.
20. Kendler KS, Bulik CM, Silberg J, et al. Childhood sexual abuse and adult psychiatric and substance use disorder in women: an epidemiological and cotwin control analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(10):953-959.
21. Yule AM, Wilens TE, Rausch PK. The opioid epidemic: what a child psychiatrist is to do? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;56(7);541-543.
22. CRAFFT. https://crafft.org. Accessed January 21, 2020.
23. Knight JR, Sherritt L, Harris SK, et al. Validity of brief alcohol screening tests among adolescents: a comparison of the AUDIT, POSIT, CAGE, and CRAFFT. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27(1):67-73.
24. American Psychiatric Association. Online assessment measures. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm/educational-resources/assessment-measures. Accessed January 15, 2020.
25. National Institute of Drug Abuse. American Psychiatric Association adapted NIDA modified ASSIST tools. https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/tool-resources-your-practice/screening-assessment-drug-testing-resources/american-psychiatric-association-adapted-nida. Updated November 15, 2015. Accessed January 21, 2020.
26. Canada’s Mental Health & Addiction Network. Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI). https://www.porticonetwork.ca/web/knowledgex-archive/amh-specialists/screening-for-cd-in-youth/screening-both-mh-sud/dusi. Published 2009. Accessed January 21, 2020.
27. Tarter RE. Evaluation and treatment of adolescent substance abuse: a decision tree method. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1990;16(1-2):1-46.
28. Klitzner M, Gruenwald PJ, Taff GA, et al. The adolescent assessment referral system-final report. National Institute on Drug Abuse; Rockville, MD: 1993. NIDA Contract No. 271-89-8252.
29. Slesnick N, Tonigan JS. Assessment of alcohol and other drug use by runaway youths: a test-retest study of the Form 90. Alcohol Treat Q. 2004;22(2):21-34.
30. Winters KC, Kaminer Y. Screening and assessing adolescent substance use disorders in clinical populations. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008;47(7):740-744.
31. Knudsen HK, Abraham AJ, Roman PM. Adoption and implementation of medications in addiction treatment programs. J Addict Med. 2011;5(1):21-27.
32. Deas D, Thomas SE. An overview of controlled study of adolescent substance abuse treatment. Am J Addiction. 2001;10(2):178-189.
33. William RJ, Chang, SY. A comprehensive and comparative review of adolescent substance abuse treatment outcome. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2000;7(2):138-166.
34. Bukstein OG, Work Group on Quality Issues. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with substance use disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(6):609-621.
35. Van Hasselt VB, Null JA, Kempton T, et al. Social skills and depression in adolescent substance abusers. Addict Behav. 1993;18(1):9-18.
36. Dennis M, Godley SH, Diamond G, et al. The Cannabis Youth Treatment (CYT) study: main findings from two randomized trials. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2004;27(3):197-213.
37. US Food and Drug Administration. Information about naloxone. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/information-about-naloxone. Updated December 19, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
38. Feder KA, Krawcyzk N, Saloner, B. Medication-assisted treatment for adolescents in specialty treatment for opioid use disorder. J Adolesc Health. 2018;60(6):747-750.
39. Woody GE, Poole SA, Subramaniam G, et al. Extended vs short-term buprenorphine-naloxone for treatment of opioid-addicted youth: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300(17):2003-2011.
40. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Ser-vices Administration. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs: a treatment improvement protocol TIP 43. https://www.asam.org/docs/advocacy/samhsa_tip43_matforopioidaddiction.pdf?sfvrsn=0. Published 2005. Accessed January 15, 2020.
41. US Department of Health and Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT). https://www.samhsa.gov/medication-assisted-treatment. Updated September 9, 2019. Accessed January 21, 2020.
42. Johnson RE, Strain EC, Amass L. Buprenorphine: how to use it right. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2003;70(suppl 2):S59-S77.
Legalization of marijuana and youths’ attitudes toward its use
The legal status of marijuana has changed a great deal during the last 4 decades. In the United States, several states have legalized the use of marijuana to treat several medical conditions. Some states have decriminalized marijuana possession, and several have legalized marijuana for recreational use by adults. These changes have contributed to a growing misperception among young people that marijuana is harmless or not as risky as other illicit
In this article, I explore the effect the legalization of marijuana has had on young peoples’ attitudes toward its use.
Marijuana use among adolescents
Among adolescents, marijuana is the most commonly used illicit substance, after alcohol.1 According to data from the 2019 Monitoring the Future Survey, while past month, past year, and lifetime marijuana use among 8th and 10th graders remained steady from 2018 to 2019, daily marijuana use among these adolescents increased.2 This survey also reported increases in adolescent marijuana vaping from 2018 to 2019.2 Further, the percentage of adolescents who think that the regular use of marijuana is risky has been trending down since the mid-2000s.2
Youth substance use rates depend on numerous factors, including legal status, availability, ease of access to the substance, and perception of harm.3 Although the legalization of marijuana for recreational use has been for adults only, based on rates of tobacco and alcohol use in adolescents (both of which are legal for adults), the legalization of marijuana is likely to have implications for adolescents.4
Adverse effects among adolescents
During adolescence, the brain is still developing, and marijuana use during this time could cause decreased cognitive functioning, especially executive fun
- an increased risk of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis, particularly among adolescents at higher risk, such as those with a family history of psychiatric illness
- a decline in school performance
- an increased school dropout rate
- an increased risk of marijuana dependence
- an elevated rate of engaging in risky behaviors.
Factors by which the legalization of marijuana might increase its use among adolescents include4:
- perceived decreased risk of marijuana use
- increased availability
- lower cost
- decreased fear of legal consequences of marijuana use.
Increased parental use is an indirect way in which legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use might increase use in youth.
Continue to: What the evidence says
What the evidence says
Colorado legalized marijuana for medical use in 2000, and for adult recreational use in 2014. A 2012 study of adolescents receiving substance abuse treatment in Colorado found diversion of medical marijuana to these adolescents was common.6 This study also reported that compared with those who did not use medical marijuana, adolescents who used medical marijuana had an earlier age of regular marijuana use, more marijuana use disorder symptoms, and more symptoms of conduct disorder.6 However, data from the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration7 and from the Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment8 suggest that marijuana use among adolescents has not increased since legalization in Colorado.
In 2012, voters in Washington state legalized marijuana for recreational use. In 2013, Moreno et al9 interviewed college students in Washington, where marijuana had just been legalized, and Wisconsin, where it had not. In both states, most participants indicated that legalization would not change their attitude towards use. A small proportion of students felt that legalization would signify an endorsement of marijuana, and they were likely to perceive it as safe to use.
In an analysis of data on more than 250,000 students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grade, Cerdá et al10 found that after legalization in Washington, the perceived harmfulness of marijuana decreased and marijuana use increased among 8th and 10th graders in Washington; however, there were no significant differences noted among adolescents in Colorado.
In 2010, voters in California passed legislation to decriminalize marijuana. In an analysis of data from 8th, 10th, and 12th graders in California, Miech et al11 found a positive correlation between decriminalization and increases in youth future marijuana use. They also found that compared with their peers in other states, 12thgraders in California were more likely to have used marijuana in the last 30 days, less likely to perceive marijuana use as a health risk, and less likely to disapprove of its use.11
Although some studies have suggested that legalization of marijuana might increase use among adolescents, limitations of these studies include that they relied on self-reported use by adolescents, and they did not evaluate adolescent populations outside of school settings.
Continue to: Addressing adolescents' marijuana use
Addressing adolescents’ marijuana use
Strategies for preventing or reducing marijuana use among adolescents might include imposing restrictions and passing stricter laws on the sale of marijuana to individuals age <21, regulating marijuana advertising, increasing adolescent substance use prevention program initiatives, and educating youth about the negative effects of marijuana. Further research is needed to clearly establish if the legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use will increase its use among adolescents.
1. US Department of Health & Human Services. Marijuana use in adolescence. https://www.hhs.gov/ash/oah/adolescent-development/substance-use/marijuana/index.html. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed January 15, 2020.
2. University of Michigan Institute for Social Research. National adolescent drug trends in 2019: Findings released. http://monitoringthefuture.org//pressreleases/19drugpr.pdf. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Ammerman S, Ryan S, William P; Committee on Substance Abuse, the Committee on Adolescence. The impact of marijuana policies on youth: clinical, research, and legal update. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):584-587.
4. Hopfer C. Implications of marijuana legalization for adolescent substance use. Subst Abus. 2014;35(4):331-335.
5. Silins E, Horwood LJ, Patton GC, et al. Young adult sequelae of adolescent cannabis use: an integrative analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(4):286-293.
6. Salomonsen-Sautel S, Sakai JT, Thurstone C, et al. Medical marijuana use among adolescents in substance abuse treatment. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):694-702.
7. US Department of Health & Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Comparison of 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 Population Percentages (50 States and the District of Columbia). https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment. Data Brief: Colorado youth marijuana use 2017. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AX_2RWWgygGXtGpAGoOMTe84Crzsv62T/view. Accessed January 15, 2020.
9. Moreno MA, Whitehill JM, Quach V, et al. Marijuana experiences, voting behaviors, and early perspectives regarding marijuana legalization among college students from 2 states. J Am Coll Health. 2016;64(1):9-18.
10. Cerdá M, Wall M, Feng T, et al. Association of state recreational marijuana laws with adolescent marijuana use. JAMA Pediatrics. 2017;171(2):142-149.
11. Miech RA, Johnston L, O’Malley PM, et al. Trends in use of marijuana and attitudes toward marijuana among youth before and after decriminalization: the case of California 2007-2013. Int J Drug Policy. 2015;26(4):336-344.
The legal status of marijuana has changed a great deal during the last 4 decades. In the United States, several states have legalized the use of marijuana to treat several medical conditions. Some states have decriminalized marijuana possession, and several have legalized marijuana for recreational use by adults. These changes have contributed to a growing misperception among young people that marijuana is harmless or not as risky as other illicit
In this article, I explore the effect the legalization of marijuana has had on young peoples’ attitudes toward its use.
Marijuana use among adolescents
Among adolescents, marijuana is the most commonly used illicit substance, after alcohol.1 According to data from the 2019 Monitoring the Future Survey, while past month, past year, and lifetime marijuana use among 8th and 10th graders remained steady from 2018 to 2019, daily marijuana use among these adolescents increased.2 This survey also reported increases in adolescent marijuana vaping from 2018 to 2019.2 Further, the percentage of adolescents who think that the regular use of marijuana is risky has been trending down since the mid-2000s.2
Youth substance use rates depend on numerous factors, including legal status, availability, ease of access to the substance, and perception of harm.3 Although the legalization of marijuana for recreational use has been for adults only, based on rates of tobacco and alcohol use in adolescents (both of which are legal for adults), the legalization of marijuana is likely to have implications for adolescents.4
Adverse effects among adolescents
During adolescence, the brain is still developing, and marijuana use during this time could cause decreased cognitive functioning, especially executive fun
- an increased risk of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis, particularly among adolescents at higher risk, such as those with a family history of psychiatric illness
- a decline in school performance
- an increased school dropout rate
- an increased risk of marijuana dependence
- an elevated rate of engaging in risky behaviors.
Factors by which the legalization of marijuana might increase its use among adolescents include4:
- perceived decreased risk of marijuana use
- increased availability
- lower cost
- decreased fear of legal consequences of marijuana use.
Increased parental use is an indirect way in which legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use might increase use in youth.
Continue to: What the evidence says
What the evidence says
Colorado legalized marijuana for medical use in 2000, and for adult recreational use in 2014. A 2012 study of adolescents receiving substance abuse treatment in Colorado found diversion of medical marijuana to these adolescents was common.6 This study also reported that compared with those who did not use medical marijuana, adolescents who used medical marijuana had an earlier age of regular marijuana use, more marijuana use disorder symptoms, and more symptoms of conduct disorder.6 However, data from the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration7 and from the Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment8 suggest that marijuana use among adolescents has not increased since legalization in Colorado.
In 2012, voters in Washington state legalized marijuana for recreational use. In 2013, Moreno et al9 interviewed college students in Washington, where marijuana had just been legalized, and Wisconsin, where it had not. In both states, most participants indicated that legalization would not change their attitude towards use. A small proportion of students felt that legalization would signify an endorsement of marijuana, and they were likely to perceive it as safe to use.
In an analysis of data on more than 250,000 students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grade, Cerdá et al10 found that after legalization in Washington, the perceived harmfulness of marijuana decreased and marijuana use increased among 8th and 10th graders in Washington; however, there were no significant differences noted among adolescents in Colorado.
In 2010, voters in California passed legislation to decriminalize marijuana. In an analysis of data from 8th, 10th, and 12th graders in California, Miech et al11 found a positive correlation between decriminalization and increases in youth future marijuana use. They also found that compared with their peers in other states, 12thgraders in California were more likely to have used marijuana in the last 30 days, less likely to perceive marijuana use as a health risk, and less likely to disapprove of its use.11
Although some studies have suggested that legalization of marijuana might increase use among adolescents, limitations of these studies include that they relied on self-reported use by adolescents, and they did not evaluate adolescent populations outside of school settings.
Continue to: Addressing adolescents' marijuana use
Addressing adolescents’ marijuana use
Strategies for preventing or reducing marijuana use among adolescents might include imposing restrictions and passing stricter laws on the sale of marijuana to individuals age <21, regulating marijuana advertising, increasing adolescent substance use prevention program initiatives, and educating youth about the negative effects of marijuana. Further research is needed to clearly establish if the legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use will increase its use among adolescents.
The legal status of marijuana has changed a great deal during the last 4 decades. In the United States, several states have legalized the use of marijuana to treat several medical conditions. Some states have decriminalized marijuana possession, and several have legalized marijuana for recreational use by adults. These changes have contributed to a growing misperception among young people that marijuana is harmless or not as risky as other illicit
In this article, I explore the effect the legalization of marijuana has had on young peoples’ attitudes toward its use.
Marijuana use among adolescents
Among adolescents, marijuana is the most commonly used illicit substance, after alcohol.1 According to data from the 2019 Monitoring the Future Survey, while past month, past year, and lifetime marijuana use among 8th and 10th graders remained steady from 2018 to 2019, daily marijuana use among these adolescents increased.2 This survey also reported increases in adolescent marijuana vaping from 2018 to 2019.2 Further, the percentage of adolescents who think that the regular use of marijuana is risky has been trending down since the mid-2000s.2
Youth substance use rates depend on numerous factors, including legal status, availability, ease of access to the substance, and perception of harm.3 Although the legalization of marijuana for recreational use has been for adults only, based on rates of tobacco and alcohol use in adolescents (both of which are legal for adults), the legalization of marijuana is likely to have implications for adolescents.4
Adverse effects among adolescents
During adolescence, the brain is still developing, and marijuana use during this time could cause decreased cognitive functioning, especially executive fun
- an increased risk of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis, particularly among adolescents at higher risk, such as those with a family history of psychiatric illness
- a decline in school performance
- an increased school dropout rate
- an increased risk of marijuana dependence
- an elevated rate of engaging in risky behaviors.
Factors by which the legalization of marijuana might increase its use among adolescents include4:
- perceived decreased risk of marijuana use
- increased availability
- lower cost
- decreased fear of legal consequences of marijuana use.
Increased parental use is an indirect way in which legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use might increase use in youth.
Continue to: What the evidence says
What the evidence says
Colorado legalized marijuana for medical use in 2000, and for adult recreational use in 2014. A 2012 study of adolescents receiving substance abuse treatment in Colorado found diversion of medical marijuana to these adolescents was common.6 This study also reported that compared with those who did not use medical marijuana, adolescents who used medical marijuana had an earlier age of regular marijuana use, more marijuana use disorder symptoms, and more symptoms of conduct disorder.6 However, data from the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration7 and from the Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment8 suggest that marijuana use among adolescents has not increased since legalization in Colorado.
In 2012, voters in Washington state legalized marijuana for recreational use. In 2013, Moreno et al9 interviewed college students in Washington, where marijuana had just been legalized, and Wisconsin, where it had not. In both states, most participants indicated that legalization would not change their attitude towards use. A small proportion of students felt that legalization would signify an endorsement of marijuana, and they were likely to perceive it as safe to use.
In an analysis of data on more than 250,000 students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grade, Cerdá et al10 found that after legalization in Washington, the perceived harmfulness of marijuana decreased and marijuana use increased among 8th and 10th graders in Washington; however, there were no significant differences noted among adolescents in Colorado.
In 2010, voters in California passed legislation to decriminalize marijuana. In an analysis of data from 8th, 10th, and 12th graders in California, Miech et al11 found a positive correlation between decriminalization and increases in youth future marijuana use. They also found that compared with their peers in other states, 12thgraders in California were more likely to have used marijuana in the last 30 days, less likely to perceive marijuana use as a health risk, and less likely to disapprove of its use.11
Although some studies have suggested that legalization of marijuana might increase use among adolescents, limitations of these studies include that they relied on self-reported use by adolescents, and they did not evaluate adolescent populations outside of school settings.
Continue to: Addressing adolescents' marijuana use
Addressing adolescents’ marijuana use
Strategies for preventing or reducing marijuana use among adolescents might include imposing restrictions and passing stricter laws on the sale of marijuana to individuals age <21, regulating marijuana advertising, increasing adolescent substance use prevention program initiatives, and educating youth about the negative effects of marijuana. Further research is needed to clearly establish if the legalization of marijuana for adult recreational use will increase its use among adolescents.
1. US Department of Health & Human Services. Marijuana use in adolescence. https://www.hhs.gov/ash/oah/adolescent-development/substance-use/marijuana/index.html. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed January 15, 2020.
2. University of Michigan Institute for Social Research. National adolescent drug trends in 2019: Findings released. http://monitoringthefuture.org//pressreleases/19drugpr.pdf. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Ammerman S, Ryan S, William P; Committee on Substance Abuse, the Committee on Adolescence. The impact of marijuana policies on youth: clinical, research, and legal update. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):584-587.
4. Hopfer C. Implications of marijuana legalization for adolescent substance use. Subst Abus. 2014;35(4):331-335.
5. Silins E, Horwood LJ, Patton GC, et al. Young adult sequelae of adolescent cannabis use: an integrative analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(4):286-293.
6. Salomonsen-Sautel S, Sakai JT, Thurstone C, et al. Medical marijuana use among adolescents in substance abuse treatment. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):694-702.
7. US Department of Health & Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Comparison of 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 Population Percentages (50 States and the District of Columbia). https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment. Data Brief: Colorado youth marijuana use 2017. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AX_2RWWgygGXtGpAGoOMTe84Crzsv62T/view. Accessed January 15, 2020.
9. Moreno MA, Whitehill JM, Quach V, et al. Marijuana experiences, voting behaviors, and early perspectives regarding marijuana legalization among college students from 2 states. J Am Coll Health. 2016;64(1):9-18.
10. Cerdá M, Wall M, Feng T, et al. Association of state recreational marijuana laws with adolescent marijuana use. JAMA Pediatrics. 2017;171(2):142-149.
11. Miech RA, Johnston L, O’Malley PM, et al. Trends in use of marijuana and attitudes toward marijuana among youth before and after decriminalization: the case of California 2007-2013. Int J Drug Policy. 2015;26(4):336-344.
1. US Department of Health & Human Services. Marijuana use in adolescence. https://www.hhs.gov/ash/oah/adolescent-development/substance-use/marijuana/index.html. Updated April 19, 2019. Accessed January 15, 2020.
2. University of Michigan Institute for Social Research. National adolescent drug trends in 2019: Findings released. http://monitoringthefuture.org//pressreleases/19drugpr.pdf. Updated December 18, 2019. Accessed January 13, 2020.
3. Ammerman S, Ryan S, William P; Committee on Substance Abuse, the Committee on Adolescence. The impact of marijuana policies on youth: clinical, research, and legal update. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):584-587.
4. Hopfer C. Implications of marijuana legalization for adolescent substance use. Subst Abus. 2014;35(4):331-335.
5. Silins E, Horwood LJ, Patton GC, et al. Young adult sequelae of adolescent cannabis use: an integrative analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(4):286-293.
6. Salomonsen-Sautel S, Sakai JT, Thurstone C, et al. Medical marijuana use among adolescents in substance abuse treatment. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(7):694-702.
7. US Department of Health & Human Services. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Comparison of 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 Population Percentages (50 States and the District of Columbia). https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016/NSDUHsaeShortTermCHG2016.htm. Accessed January 15, 2020.
8. Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment. Data Brief: Colorado youth marijuana use 2017. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AX_2RWWgygGXtGpAGoOMTe84Crzsv62T/view. Accessed January 15, 2020.
9. Moreno MA, Whitehill JM, Quach V, et al. Marijuana experiences, voting behaviors, and early perspectives regarding marijuana legalization among college students from 2 states. J Am Coll Health. 2016;64(1):9-18.
10. Cerdá M, Wall M, Feng T, et al. Association of state recreational marijuana laws with adolescent marijuana use. JAMA Pediatrics. 2017;171(2):142-149.
11. Miech RA, Johnston L, O’Malley PM, et al. Trends in use of marijuana and attitudes toward marijuana among youth before and after decriminalization: the case of California 2007-2013. Int J Drug Policy. 2015;26(4):336-344.