User login
‘Deeper dive’ into opioid overdose deaths during COVID pandemic
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EDs saw more benzodiazepine overdoses, but fewer patients overall, in 2020
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
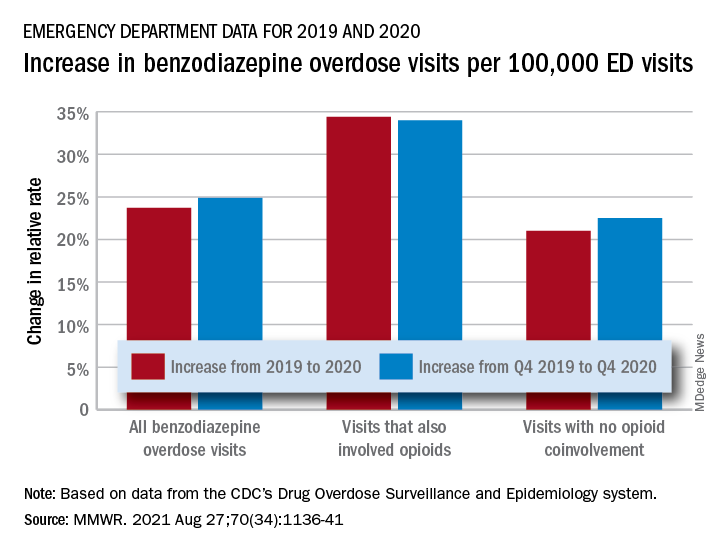
The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Self-described ‘assassin,’ now doctor, indicted for 1M illegal opioid doses
A according to the U.S. Department of Justice. The substances include oxycodone and morphine.
Adrian Dexter Talbot, MD, 55, of Slidell, La., is also charged with maintaining a medical clinic for the purpose of illegally distributing controlled substances, per the indictment.
Because the opioid prescriptions were filled using beneficiaries’ health insurance, Dr. Talbot is also charged with defrauding Medicare, Medicaid, and Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana of more than $5.1 million.
When contacted by this news organization for comment on the case via Twitter, Dr. Talbot or a representative responded with a link to his self-published book on Amazon. In his author bio, Dr. Talbot refers to himself as “a former assassin,” “retired military commander,” and “leader of the Medellin Cartel’s New York operations at the age of 16.” The Medellin Cartel is a notorious drug distribution empire.
Dr. Talbot is listed as the author of another book on Google Books detailing his time as a “former teenage assassin” and leader of the cartel, told as he struggles with early onset Alzheimer’s.
Dr. Talbot could spend decades in prison
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, 444 residents of the Bayou State lost their lives because of an opioid-related drug overdose in 2018. During that year, the state’s health care providers wrote more than 79.4 opioid prescriptions for every 100 persons, which puts the state in the top five in the United States in 2018, when the average U.S. rate was 51.4 prescriptions per 100 persons.
Charged with one count each of conspiracy to unlawfully distribute and dispense controlled substances and maintaining drug-involved premises and conspiracy to commit health care fraud, Dr. Talbot is also charged with four counts of unlawfully distributing and dispensing controlled substances. He is scheduled for a federal court appearance on September 10.
In addition to presigning prescriptions for individuals he didn’t meet or examine, federal officials allege Dr. Talbot hired another health care provider to similarly presign prescriptions for people who weren’t examined at a medical practice in Slidell, where Dr. Talbot was employed. The DOJ says Dr. Talbot took a full-time job in Pineville, La., and presigned prescriptions while no longer physically present at the Slidell clinic.
A speaker’s bio for Dr. Talbot indicates he worked as chief of medical services for the Alexandria Veterans Affairs Health Care System in Pineville.
According to the DOJ’s indictment, Dr. Talbot was aware that patients were filling the prescriptions that were provided outside the scope of professional practice and not for a legitimate medical purpose. This is what triggered the DOJ’s fraudulent billing claim.
Dr. Talbot faces a maximum penalty of 10 years for conspiracy to commit health care fraud and 20 years each for the other counts, if convicted.
Dr. Talbot was candidate for local coroner
In February 2015, Dr. Talbot announced his candidacy for coroner for St. Tammany Parish, about an hour’s drive south of New Orleans, reported the Times Picayune. The seat was open because the previous coroner had resigned and ultimately pleaded guilty to a federal corruption charge.
The Times Picayune reported at the time that Dr. Talbot was a U.S. Navy veteran, in addition to serving as medical director and a primary care physician at the Medical Care Center in Slidell. Among the services provided to his patients were evaluations and treatment for substance use and mental health disorders, according to a press release issued by Dr. Talbot’s campaign.
Dr. Talbot’s medical license was issued in 1999 and inactive as of 2017, per the Louisiana State Board of Medical Examiners.
Louisiana expects $325M in multistate settlement with opioid companies
Louisiana is a party to a multistate and multijurisdictional lawsuit where the state is expected to receive more than $325 million in a settlement reached with drug distributors Cardinal, McKesson, and AmerisourceBergen, and drug manufacturer Johnson & Johnson, reported the Louisiana Illuminator in July. The total settlement may reach $26 billion dollars.
The Associated Press reported in July that there have been at least $40 billion in completed or proposed settlements, penalties, and fines between governments as a result of the opioid epidemic since 2007.
That total doesn’t include a proposed settlement involving members of the Sackler family, who own Purdue Pharmaceuticals, which manufactured and marketed the opioid painkiller OxyContin. The Sackler family have agreed to pay approximately $4.3 billion and surrender ownership of their bankrupt company, reported NPR. The family’s proposed settlement is part of a deal involving Purdue Pharmaceuticals worth more than $10 billion, reported Reuters.
In 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths, the highest number recorded in a 12-month period, per the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fentanyl, an illicitly manufactured synthetic opioid, was the lead driver of those deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A according to the U.S. Department of Justice. The substances include oxycodone and morphine.
Adrian Dexter Talbot, MD, 55, of Slidell, La., is also charged with maintaining a medical clinic for the purpose of illegally distributing controlled substances, per the indictment.
Because the opioid prescriptions were filled using beneficiaries’ health insurance, Dr. Talbot is also charged with defrauding Medicare, Medicaid, and Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana of more than $5.1 million.
When contacted by this news organization for comment on the case via Twitter, Dr. Talbot or a representative responded with a link to his self-published book on Amazon. In his author bio, Dr. Talbot refers to himself as “a former assassin,” “retired military commander,” and “leader of the Medellin Cartel’s New York operations at the age of 16.” The Medellin Cartel is a notorious drug distribution empire.
Dr. Talbot is listed as the author of another book on Google Books detailing his time as a “former teenage assassin” and leader of the cartel, told as he struggles with early onset Alzheimer’s.
Dr. Talbot could spend decades in prison
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, 444 residents of the Bayou State lost their lives because of an opioid-related drug overdose in 2018. During that year, the state’s health care providers wrote more than 79.4 opioid prescriptions for every 100 persons, which puts the state in the top five in the United States in 2018, when the average U.S. rate was 51.4 prescriptions per 100 persons.
Charged with one count each of conspiracy to unlawfully distribute and dispense controlled substances and maintaining drug-involved premises and conspiracy to commit health care fraud, Dr. Talbot is also charged with four counts of unlawfully distributing and dispensing controlled substances. He is scheduled for a federal court appearance on September 10.
In addition to presigning prescriptions for individuals he didn’t meet or examine, federal officials allege Dr. Talbot hired another health care provider to similarly presign prescriptions for people who weren’t examined at a medical practice in Slidell, where Dr. Talbot was employed. The DOJ says Dr. Talbot took a full-time job in Pineville, La., and presigned prescriptions while no longer physically present at the Slidell clinic.
A speaker’s bio for Dr. Talbot indicates he worked as chief of medical services for the Alexandria Veterans Affairs Health Care System in Pineville.
According to the DOJ’s indictment, Dr. Talbot was aware that patients were filling the prescriptions that were provided outside the scope of professional practice and not for a legitimate medical purpose. This is what triggered the DOJ’s fraudulent billing claim.
Dr. Talbot faces a maximum penalty of 10 years for conspiracy to commit health care fraud and 20 years each for the other counts, if convicted.
Dr. Talbot was candidate for local coroner
In February 2015, Dr. Talbot announced his candidacy for coroner for St. Tammany Parish, about an hour’s drive south of New Orleans, reported the Times Picayune. The seat was open because the previous coroner had resigned and ultimately pleaded guilty to a federal corruption charge.
The Times Picayune reported at the time that Dr. Talbot was a U.S. Navy veteran, in addition to serving as medical director and a primary care physician at the Medical Care Center in Slidell. Among the services provided to his patients were evaluations and treatment for substance use and mental health disorders, according to a press release issued by Dr. Talbot’s campaign.
Dr. Talbot’s medical license was issued in 1999 and inactive as of 2017, per the Louisiana State Board of Medical Examiners.
Louisiana expects $325M in multistate settlement with opioid companies
Louisiana is a party to a multistate and multijurisdictional lawsuit where the state is expected to receive more than $325 million in a settlement reached with drug distributors Cardinal, McKesson, and AmerisourceBergen, and drug manufacturer Johnson & Johnson, reported the Louisiana Illuminator in July. The total settlement may reach $26 billion dollars.
The Associated Press reported in July that there have been at least $40 billion in completed or proposed settlements, penalties, and fines between governments as a result of the opioid epidemic since 2007.
That total doesn’t include a proposed settlement involving members of the Sackler family, who own Purdue Pharmaceuticals, which manufactured and marketed the opioid painkiller OxyContin. The Sackler family have agreed to pay approximately $4.3 billion and surrender ownership of their bankrupt company, reported NPR. The family’s proposed settlement is part of a deal involving Purdue Pharmaceuticals worth more than $10 billion, reported Reuters.
In 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths, the highest number recorded in a 12-month period, per the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fentanyl, an illicitly manufactured synthetic opioid, was the lead driver of those deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A according to the U.S. Department of Justice. The substances include oxycodone and morphine.
Adrian Dexter Talbot, MD, 55, of Slidell, La., is also charged with maintaining a medical clinic for the purpose of illegally distributing controlled substances, per the indictment.
Because the opioid prescriptions were filled using beneficiaries’ health insurance, Dr. Talbot is also charged with defrauding Medicare, Medicaid, and Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana of more than $5.1 million.
When contacted by this news organization for comment on the case via Twitter, Dr. Talbot or a representative responded with a link to his self-published book on Amazon. In his author bio, Dr. Talbot refers to himself as “a former assassin,” “retired military commander,” and “leader of the Medellin Cartel’s New York operations at the age of 16.” The Medellin Cartel is a notorious drug distribution empire.
Dr. Talbot is listed as the author of another book on Google Books detailing his time as a “former teenage assassin” and leader of the cartel, told as he struggles with early onset Alzheimer’s.
Dr. Talbot could spend decades in prison
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, 444 residents of the Bayou State lost their lives because of an opioid-related drug overdose in 2018. During that year, the state’s health care providers wrote more than 79.4 opioid prescriptions for every 100 persons, which puts the state in the top five in the United States in 2018, when the average U.S. rate was 51.4 prescriptions per 100 persons.
Charged with one count each of conspiracy to unlawfully distribute and dispense controlled substances and maintaining drug-involved premises and conspiracy to commit health care fraud, Dr. Talbot is also charged with four counts of unlawfully distributing and dispensing controlled substances. He is scheduled for a federal court appearance on September 10.
In addition to presigning prescriptions for individuals he didn’t meet or examine, federal officials allege Dr. Talbot hired another health care provider to similarly presign prescriptions for people who weren’t examined at a medical practice in Slidell, where Dr. Talbot was employed. The DOJ says Dr. Talbot took a full-time job in Pineville, La., and presigned prescriptions while no longer physically present at the Slidell clinic.
A speaker’s bio for Dr. Talbot indicates he worked as chief of medical services for the Alexandria Veterans Affairs Health Care System in Pineville.
According to the DOJ’s indictment, Dr. Talbot was aware that patients were filling the prescriptions that were provided outside the scope of professional practice and not for a legitimate medical purpose. This is what triggered the DOJ’s fraudulent billing claim.
Dr. Talbot faces a maximum penalty of 10 years for conspiracy to commit health care fraud and 20 years each for the other counts, if convicted.
Dr. Talbot was candidate for local coroner
In February 2015, Dr. Talbot announced his candidacy for coroner for St. Tammany Parish, about an hour’s drive south of New Orleans, reported the Times Picayune. The seat was open because the previous coroner had resigned and ultimately pleaded guilty to a federal corruption charge.
The Times Picayune reported at the time that Dr. Talbot was a U.S. Navy veteran, in addition to serving as medical director and a primary care physician at the Medical Care Center in Slidell. Among the services provided to his patients were evaluations and treatment for substance use and mental health disorders, according to a press release issued by Dr. Talbot’s campaign.
Dr. Talbot’s medical license was issued in 1999 and inactive as of 2017, per the Louisiana State Board of Medical Examiners.
Louisiana expects $325M in multistate settlement with opioid companies
Louisiana is a party to a multistate and multijurisdictional lawsuit where the state is expected to receive more than $325 million in a settlement reached with drug distributors Cardinal, McKesson, and AmerisourceBergen, and drug manufacturer Johnson & Johnson, reported the Louisiana Illuminator in July. The total settlement may reach $26 billion dollars.
The Associated Press reported in July that there have been at least $40 billion in completed or proposed settlements, penalties, and fines between governments as a result of the opioid epidemic since 2007.
That total doesn’t include a proposed settlement involving members of the Sackler family, who own Purdue Pharmaceuticals, which manufactured and marketed the opioid painkiller OxyContin. The Sackler family have agreed to pay approximately $4.3 billion and surrender ownership of their bankrupt company, reported NPR. The family’s proposed settlement is part of a deal involving Purdue Pharmaceuticals worth more than $10 billion, reported Reuters.
In 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths, the highest number recorded in a 12-month period, per the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fentanyl, an illicitly manufactured synthetic opioid, was the lead driver of those deaths.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alcohol use by young adolescents drops during pandemic
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic altered patterns of substance use by early adolescents to less alcohol use and greater use and misuse of nicotine and prescription drugs, based on data from more than 7,000 youth aged 10-14 years.
Substance use in early adolescence is a function of many environmental factors including substance availability, parent and peer use, and family function, as well as macroeconomic factors, William E. Pelham III, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, it is critical to evaluate how substance use during early adolescence has been impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a source of large and sustained disruptions to adolescents’ daily lives in terms of education, contact with family/friends, and health behaviors.”
In a prospective, community-based cohort study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, the researchers conducted a three-wave assessment of substance use between May 2020 and August 2020, and reviewed prepandemic assessments from 2018 to 2019. The participants included 7,842 adolescents with an average age of 12 years who were initially enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study at age 9-10 years. At the start of the study, 48% of the participants were female, 20% were Hispanic, 15% were Black, and 2% were Asian. Participants completed three online surveys between May 2020 and August 2020.
Each survey included the number of days in the past 30 days in which the adolescents drank alcohol; smoked cigarettes; used electronic nicotine delivery systems; smoked a cigar, hookah, or pipe; used smokeless tobacco products; used a cannabis product; abused prescription drugs; used inhalants; or used any other drugs. The response scale was 0 days to 10-plus days.
The overall prevalence of substance use among young adolescents was similar between prepandemic and pandemic periods; however fewer respondents reported using alcohol, but more reported using nicotine or misusing prescription medications.
Across all three survey periods, 7.4% of youth reported any substance use, 3.4% reported ever using alcohol, and 3.2% reported ever using nicotine. Of those who reported substance use, 79% reported 1-2 days of use in the past month, and 87% reported using a single substance.
In comparing prepandemic and pandemic substance use, the prevalence of alcohol use in the past 30 days decreased significantly, from 2.1% to 0.8%. However, use of nicotine increased significantly from 0% to 1.3%, and misuse of prescription drugs increased significantly from 0% to 0.6%. “Changes in the rates of use of any substance, cannabis, or inhalants were not statistically significant,” the researchers wrote.
Sex and ethnicity were not associated with substance use during the pandemic, but rates of substance use were higher among youth whose parents were unmarried or had lower levels of education, and among those with preexisting externalizing and internalizing behaviors. Youth who reported higher levels of uncertainty related to COVID-19 were significantly more likely to report substance use; additionally, stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were positively association with any substance use during the pandemic survey periods. Youth whose parents experienced hardship or whose parents used alcohol or drugs also were more likely to report substance use.
“Stability in the overall rate of substance use in this cohort is reassuring given that the pandemic has brought increases in teens’ unoccupied time, stress, and loneliness, reduced access to support services, and disruptions to routines and family/parenting practices, all of which might be expected to have increased youth substance use,” the researchers noted. The findings do not explain the decreased alcohol use, but the researchers cited possible reasons for reduced alcohol use including lack of contact with friends and social activities, and greater supervision by parents.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the comparison of prepandemic and pandemic substance use in younger adolescents, which may not reflect changes in substance use in older adolescents. The study also could not establish causality, and did not account for the intensity of substance use, such as number of drinks, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal design and large, diverse study population, and the use of prepandemic assessments that allowed evaluation of changes over time.
Overall, the results highlight the importance of preexisting and acute risk protective factors in mitigating substance use in young adolescents, and suggest the potential of economic support for families and emotional support for youth as ways to reduce risk, the researchers concluded.
Predicting use and identifying risk factors
“It was important to conduct research at this time so we know how trends have changed during the pandemic,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview. The research helps clinicians “so we can better predict which substances our patients may be using, especially those with preexisting psychological conditions and those at socioeconomic disadvantage.
“I was surprised by the increased prescription drug use, but it make sense, as adolescents are at home more and may be illicitly using their parents medications,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “I think as they go back to school, trends will shift back to where they were as they will be spending more time with friends.” The take-home message to clinicians is the increased use of nicotine and prescription drugs during the pandemic, and future research should focus on substance use trends in 14- to 20-year-olds.
The ABCD study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, and the current study also received support from the National Science Foundation and Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ADOLESCENT HEALTH
Four police suicides in the aftermath of the Capitol siege: What can we learn?
Officer Scott Davis is a passionate man who thinks and talks quickly. As a member of the Special Events Team for Montgomery County, Maryland, he was already staging in Rockville, outside of Washington, D.C., when the call came in last Jan. 6 to move their unit to the U.S. Capitol.
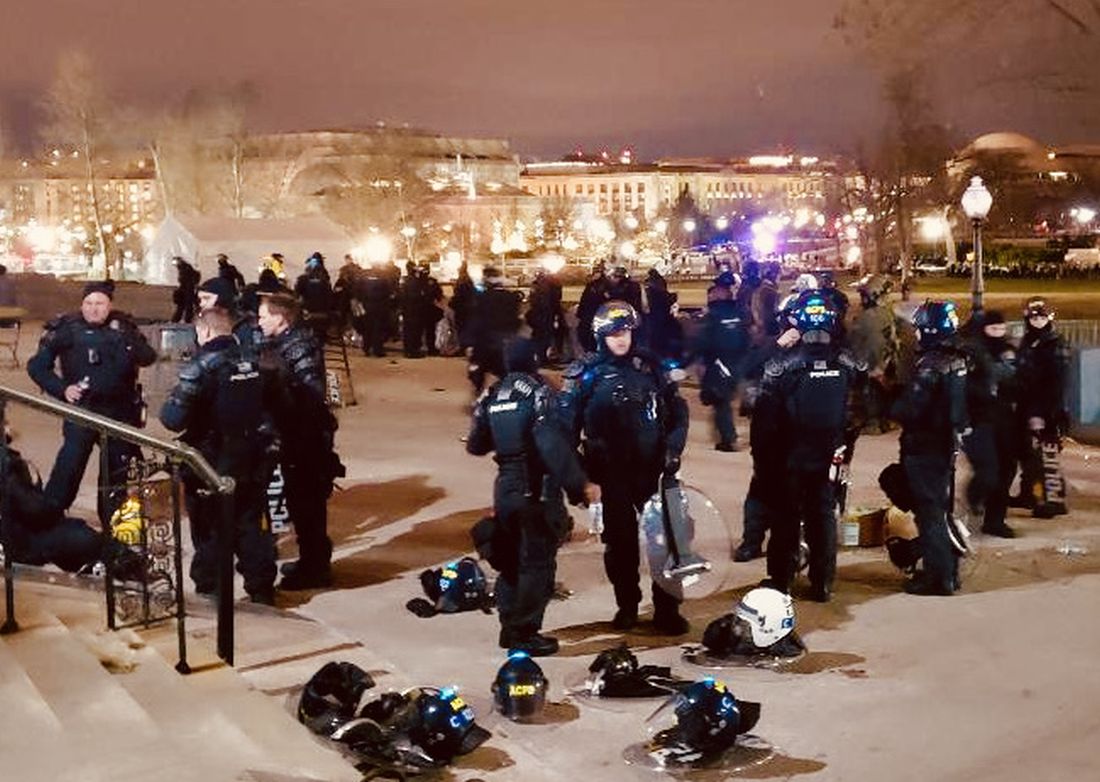
“It was surreal,” said Mr. Davis. “There were people from all different groups at the Capitol that day. Many people were trying to get out, but others surrounded us. They called us ‘human race traitors.’ And then I heard someone say, ‘It’s good you brought your shields, we’ll carry your bodies out on them.’”
Mr. Davis described hours of mayhem during which he was hit with bear spray, a brick, a chair, and a metal rod. One of the members of Mr. Davis’ unit remains on leave with a head injury nearly 9 months after the siege.
“It went on for 3 hours, but it felt like 15 minutes. Then, all of a sudden, it was over.”
For the members of law enforcement at the Capitol that day, the repercussions are still being felt, perhaps most notably in the case of the four officers who subsequently died of suicide. Three of the officers were with the Metropolitan Police Department of the District of Columbia and one worked for the Capitol Police Department.
Police officers are subjected to traumas on a regular basis and often placed in circumstances where their lives are in danger. Yet four suicides within a short time – all connected to a single event – is particularly shocking and tragic, even more so for how little attention it has garnered to date.
What contributes to the high rate of suicide among officers?
Scott Silverii, PhD, a former police officer and author of Broken and Blue: A Policeman’s Guide to Health, Hope, and Healing, commented that he “wouldn’t be surprised if there are more suicides to come.” This stems not only from the experiences of that day but also the elevated risk for suicide that law enforcement officers already experienced prior to the Capitol riots. Suicide remains a rare event, with a national all-population average of 13.9 per 100,000 citizens. But as Dr. Silverii noted, more officers die by suicide each year than are killed in the line of duty.
“Suicide is a big part of police culture – officers are doers and fixers, and it is seen as being more honorable to take yourself out of the equation than it is to ask for help,” he said. “Most officers come in with past pain, and this is a situation where they are being overwhelmed and under-respected. At the same time, police culture is a closed culture, and it is not friendly to researchers.”
Another contributor is the frequency with which law enforcement officers are exposed to trauma, according to Vernon Herron, Director of Officer Safety and Wellness for the Baltimore City Police.
Mr. Herron said, citing the psychiatric and addiction issues that officers commonly experience.
Protecting the protectors
Mr. Herron and others are working to address these problems head-on.
“We are trying to identify employees exposed to trauma and to offer counseling and intervention,” he said, “Otherwise, everything else will fall short.”
Yet implementing such measures is no easy task, given the lack of a central oversight organization for law enforcement, said Sheldon Greenberg, PhD, a former police officer and professor of management in the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“In the United States there is no such thing as ‘The Police.’ There is no one in a position to set policy, standards, or training mandates nationally,” he said. “There are approximately 18,000 police and sheriff departments in the country, and many of them are small. No one can compel law enforcement agencies to implement officer wellness and suicide prevention programs, make counseling available to officers, or train supervisors and peers to identify suicide ideation.”
Dr. Greenberg said a further barrier to helping police officers considering self-harm is posed by the fact that even if they do seek out counseling, there is no guarantee that it will remain confidential.
“Support personnel have an obligation to report an officer who is thinking about committing suicide,” he said. “Many officers are concerned about this lack of confidentiality and that they may be branded if they seek help.”
Although Dr. Greenberg said many police officers are self-professed “action junkies,” even their unusually high capacity for stress is often tested by the realities of the job.
“Increasing demands for service, shortages of personnel, misinformation about police, COVID-19, talk about restructuring policing with little concrete direction, increased exposure to violence, greater numbers of vulnerable people, and more take a toll over time,” he lamented. “In addition, we are in a recruiting crisis in law enforcement, and there are no standards to ensure the quality of psychological screening provided to applicants. Many officers will go through their entire career and never be screened again. We know little about the stresses and strains that officers bring to the job.”
After the siege
It is not clear how many police officers were present at the Capitol on Jan. 6. During the chaos of the day, reinforcements to the Capitol Police Department arrived from Washington D.C., Maryland, and Virginia, but no official numbers on responders were obtained; Mr. Davis thought it was likely that there were at least 1,000 law enforcement officers present. Those who did respond sustained an estimated 100 injuries, including an officer who died the next day. Of the officers who died by suicide, one died 3 days after, another died 9 days later, and two more died in July – numbers that contradict the notion that this is some coincidence. Officer Alexander Kettering, a colleague of Mr. Davis who has been with Montgomery County Police for 15 years, was among those tasked with protecting the Capitol on Jan. 6. The chaos, violence, and destruction of the day has stuck with him and continues to occupy his thoughts.
“I had a front-row seat to the whole thing. It was overwhelming, and I’ve never seen people this angry,” said Mr. Kettering. “There were people up on the veranda and on the scaffolding set up for the inauguration. They were smashing windows and throwing things into the crowd. It was insane. There were decent people coming up to us and saying they would pray for us, then others calling us traitors, telling us to stand down and join them.”
In the aftermath of the Capitol siege, Mr. Kettering watched in dismay as the narrative of the day’s events began to warp.
“At first there was a consensus that what happened was so wrong, and then the politics took over. People were saying it wasn’t as bad as the media said, that it really wasn’t that violent and those speaking out are traitors or political operatives. I relive it every day, and it’s hard to escape, even in casual conversation.”
He added that the days’ events were compounded by the already heightened tensions surrounding the national debate around policing.
“It’s been 18 months of stress, of anti-police movements, and there is a fine line between addressing police brutality and being anti-police,” Mr. Kettering said, noting that the aforementioned issues have all contributed to the ongoing struggles his fellow officers are experiencing.
“It’s not a thing for cops to talk about how an event affected them,” he said. “A lot of officers have just shut down. People have careers and pensions to protect, and every time we stop a motorist, something could go wrong, even if we do everything right. There are mixed signals: They tell us, ‘Defend but don’t defend.’”
His colleague, Mr. Davis, said that officers “need more support from politicians,” noting that he felt particularly insulted by a comment made by a Montgomery County public official who accused the officers present at the Capitol of racism. “And finally, we feel a little betrayed by the public.”
More questions than answers from the Capitol’s day of chaos
What about the events of Jan. 6 led to the suicides of four law enforcement officers and what can be done to prevent more deaths in the future? There are the individual factors of each man’s personal history, circumstances, and vulnerabilities, including the sense of being personally endangered, witnessing trauma, and direct injury – one officer who died of suicide had sustained a head injury that day.
We don’t know if the officers went into the event with preexisting mental illness or addiction or if the day’s events precipitated psychiatric episodes. And with all the partisan anger surrounding the presidential election, we don’t know if each officer’s political beliefs amplified his distress over what occurred in a social media climate where police are being faulted by all sides.
When multiple suicides occur in a community, there is always concern about a “copycat” phenomena. These concerns are made more difficult to address, however, given the police culture of taboo and stigma associated with getting professional help, difficulty accessing care, and career repercussions for speaking openly about suicidal thoughts and mental health issues.
Finally, there is the current political agenda that leaves officers feeling unsupported, fearful of negative outcomes, and unappreciated. The Capitol siege in particular embodied a great deal of national distress and confusion over basic issues of truth, justice, and perceptions of reality in our polarized society.
Can we move to a place where those who enforce laws have easy access to treatment, free from stigma? Can we encourage a culture that does not tolerate brutality or racism, while also refusing to label all police as bad and lending support to their mission? Can we be more attuned to the repercussions of circumstances where officers are witnesses to trauma, are endangered themselves, and would benefit from acknowledgment of their distress?
Time will tell if our anti-police pendulum swings back. In the meantime, these four suicides among people defending our country remain tragically overlooked.
Dinah Miller, MD, is coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Officer Scott Davis is a passionate man who thinks and talks quickly. As a member of the Special Events Team for Montgomery County, Maryland, he was already staging in Rockville, outside of Washington, D.C., when the call came in last Jan. 6 to move their unit to the U.S. Capitol.
“It was surreal,” said Mr. Davis. “There were people from all different groups at the Capitol that day. Many people were trying to get out, but others surrounded us. They called us ‘human race traitors.’ And then I heard someone say, ‘It’s good you brought your shields, we’ll carry your bodies out on them.’”
Mr. Davis described hours of mayhem during which he was hit with bear spray, a brick, a chair, and a metal rod. One of the members of Mr. Davis’ unit remains on leave with a head injury nearly 9 months after the siege.
“It went on for 3 hours, but it felt like 15 minutes. Then, all of a sudden, it was over.”
For the members of law enforcement at the Capitol that day, the repercussions are still being felt, perhaps most notably in the case of the four officers who subsequently died of suicide. Three of the officers were with the Metropolitan Police Department of the District of Columbia and one worked for the Capitol Police Department.
Police officers are subjected to traumas on a regular basis and often placed in circumstances where their lives are in danger. Yet four suicides within a short time – all connected to a single event – is particularly shocking and tragic, even more so for how little attention it has garnered to date.
What contributes to the high rate of suicide among officers?
Scott Silverii, PhD, a former police officer and author of Broken and Blue: A Policeman’s Guide to Health, Hope, and Healing, commented that he “wouldn’t be surprised if there are more suicides to come.” This stems not only from the experiences of that day but also the elevated risk for suicide that law enforcement officers already experienced prior to the Capitol riots. Suicide remains a rare event, with a national all-population average of 13.9 per 100,000 citizens. But as Dr. Silverii noted, more officers die by suicide each year than are killed in the line of duty.
“Suicide is a big part of police culture – officers are doers and fixers, and it is seen as being more honorable to take yourself out of the equation than it is to ask for help,” he said. “Most officers come in with past pain, and this is a situation where they are being overwhelmed and under-respected. At the same time, police culture is a closed culture, and it is not friendly to researchers.”
Another contributor is the frequency with which law enforcement officers are exposed to trauma, according to Vernon Herron, Director of Officer Safety and Wellness for the Baltimore City Police.
Mr. Herron said, citing the psychiatric and addiction issues that officers commonly experience.
Protecting the protectors
Mr. Herron and others are working to address these problems head-on.
“We are trying to identify employees exposed to trauma and to offer counseling and intervention,” he said, “Otherwise, everything else will fall short.”
Yet implementing such measures is no easy task, given the lack of a central oversight organization for law enforcement, said Sheldon Greenberg, PhD, a former police officer and professor of management in the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“In the United States there is no such thing as ‘The Police.’ There is no one in a position to set policy, standards, or training mandates nationally,” he said. “There are approximately 18,000 police and sheriff departments in the country, and many of them are small. No one can compel law enforcement agencies to implement officer wellness and suicide prevention programs, make counseling available to officers, or train supervisors and peers to identify suicide ideation.”
Dr. Greenberg said a further barrier to helping police officers considering self-harm is posed by the fact that even if they do seek out counseling, there is no guarantee that it will remain confidential.
“Support personnel have an obligation to report an officer who is thinking about committing suicide,” he said. “Many officers are concerned about this lack of confidentiality and that they may be branded if they seek help.”
Although Dr. Greenberg said many police officers are self-professed “action junkies,” even their unusually high capacity for stress is often tested by the realities of the job.
“Increasing demands for service, shortages of personnel, misinformation about police, COVID-19, talk about restructuring policing with little concrete direction, increased exposure to violence, greater numbers of vulnerable people, and more take a toll over time,” he lamented. “In addition, we are in a recruiting crisis in law enforcement, and there are no standards to ensure the quality of psychological screening provided to applicants. Many officers will go through their entire career and never be screened again. We know little about the stresses and strains that officers bring to the job.”
After the siege
It is not clear how many police officers were present at the Capitol on Jan. 6. During the chaos of the day, reinforcements to the Capitol Police Department arrived from Washington D.C., Maryland, and Virginia, but no official numbers on responders were obtained; Mr. Davis thought it was likely that there were at least 1,000 law enforcement officers present. Those who did respond sustained an estimated 100 injuries, including an officer who died the next day. Of the officers who died by suicide, one died 3 days after, another died 9 days later, and two more died in July – numbers that contradict the notion that this is some coincidence. Officer Alexander Kettering, a colleague of Mr. Davis who has been with Montgomery County Police for 15 years, was among those tasked with protecting the Capitol on Jan. 6. The chaos, violence, and destruction of the day has stuck with him and continues to occupy his thoughts.
“I had a front-row seat to the whole thing. It was overwhelming, and I’ve never seen people this angry,” said Mr. Kettering. “There were people up on the veranda and on the scaffolding set up for the inauguration. They were smashing windows and throwing things into the crowd. It was insane. There were decent people coming up to us and saying they would pray for us, then others calling us traitors, telling us to stand down and join them.”
In the aftermath of the Capitol siege, Mr. Kettering watched in dismay as the narrative of the day’s events began to warp.
“At first there was a consensus that what happened was so wrong, and then the politics took over. People were saying it wasn’t as bad as the media said, that it really wasn’t that violent and those speaking out are traitors or political operatives. I relive it every day, and it’s hard to escape, even in casual conversation.”
He added that the days’ events were compounded by the already heightened tensions surrounding the national debate around policing.
“It’s been 18 months of stress, of anti-police movements, and there is a fine line between addressing police brutality and being anti-police,” Mr. Kettering said, noting that the aforementioned issues have all contributed to the ongoing struggles his fellow officers are experiencing.
“It’s not a thing for cops to talk about how an event affected them,” he said. “A lot of officers have just shut down. People have careers and pensions to protect, and every time we stop a motorist, something could go wrong, even if we do everything right. There are mixed signals: They tell us, ‘Defend but don’t defend.’”
His colleague, Mr. Davis, said that officers “need more support from politicians,” noting that he felt particularly insulted by a comment made by a Montgomery County public official who accused the officers present at the Capitol of racism. “And finally, we feel a little betrayed by the public.”
More questions than answers from the Capitol’s day of chaos
What about the events of Jan. 6 led to the suicides of four law enforcement officers and what can be done to prevent more deaths in the future? There are the individual factors of each man’s personal history, circumstances, and vulnerabilities, including the sense of being personally endangered, witnessing trauma, and direct injury – one officer who died of suicide had sustained a head injury that day.
We don’t know if the officers went into the event with preexisting mental illness or addiction or if the day’s events precipitated psychiatric episodes. And with all the partisan anger surrounding the presidential election, we don’t know if each officer’s political beliefs amplified his distress over what occurred in a social media climate where police are being faulted by all sides.
When multiple suicides occur in a community, there is always concern about a “copycat” phenomena. These concerns are made more difficult to address, however, given the police culture of taboo and stigma associated with getting professional help, difficulty accessing care, and career repercussions for speaking openly about suicidal thoughts and mental health issues.
Finally, there is the current political agenda that leaves officers feeling unsupported, fearful of negative outcomes, and unappreciated. The Capitol siege in particular embodied a great deal of national distress and confusion over basic issues of truth, justice, and perceptions of reality in our polarized society.
Can we move to a place where those who enforce laws have easy access to treatment, free from stigma? Can we encourage a culture that does not tolerate brutality or racism, while also refusing to label all police as bad and lending support to their mission? Can we be more attuned to the repercussions of circumstances where officers are witnesses to trauma, are endangered themselves, and would benefit from acknowledgment of their distress?
Time will tell if our anti-police pendulum swings back. In the meantime, these four suicides among people defending our country remain tragically overlooked.
Dinah Miller, MD, is coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Officer Scott Davis is a passionate man who thinks and talks quickly. As a member of the Special Events Team for Montgomery County, Maryland, he was already staging in Rockville, outside of Washington, D.C., when the call came in last Jan. 6 to move their unit to the U.S. Capitol.
“It was surreal,” said Mr. Davis. “There were people from all different groups at the Capitol that day. Many people were trying to get out, but others surrounded us. They called us ‘human race traitors.’ And then I heard someone say, ‘It’s good you brought your shields, we’ll carry your bodies out on them.’”
Mr. Davis described hours of mayhem during which he was hit with bear spray, a brick, a chair, and a metal rod. One of the members of Mr. Davis’ unit remains on leave with a head injury nearly 9 months after the siege.
“It went on for 3 hours, but it felt like 15 minutes. Then, all of a sudden, it was over.”
For the members of law enforcement at the Capitol that day, the repercussions are still being felt, perhaps most notably in the case of the four officers who subsequently died of suicide. Three of the officers were with the Metropolitan Police Department of the District of Columbia and one worked for the Capitol Police Department.
Police officers are subjected to traumas on a regular basis and often placed in circumstances where their lives are in danger. Yet four suicides within a short time – all connected to a single event – is particularly shocking and tragic, even more so for how little attention it has garnered to date.
What contributes to the high rate of suicide among officers?
Scott Silverii, PhD, a former police officer and author of Broken and Blue: A Policeman’s Guide to Health, Hope, and Healing, commented that he “wouldn’t be surprised if there are more suicides to come.” This stems not only from the experiences of that day but also the elevated risk for suicide that law enforcement officers already experienced prior to the Capitol riots. Suicide remains a rare event, with a national all-population average of 13.9 per 100,000 citizens. But as Dr. Silverii noted, more officers die by suicide each year than are killed in the line of duty.
“Suicide is a big part of police culture – officers are doers and fixers, and it is seen as being more honorable to take yourself out of the equation than it is to ask for help,” he said. “Most officers come in with past pain, and this is a situation where they are being overwhelmed and under-respected. At the same time, police culture is a closed culture, and it is not friendly to researchers.”
Another contributor is the frequency with which law enforcement officers are exposed to trauma, according to Vernon Herron, Director of Officer Safety and Wellness for the Baltimore City Police.
Mr. Herron said, citing the psychiatric and addiction issues that officers commonly experience.
Protecting the protectors
Mr. Herron and others are working to address these problems head-on.
“We are trying to identify employees exposed to trauma and to offer counseling and intervention,” he said, “Otherwise, everything else will fall short.”
Yet implementing such measures is no easy task, given the lack of a central oversight organization for law enforcement, said Sheldon Greenberg, PhD, a former police officer and professor of management in the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“In the United States there is no such thing as ‘The Police.’ There is no one in a position to set policy, standards, or training mandates nationally,” he said. “There are approximately 18,000 police and sheriff departments in the country, and many of them are small. No one can compel law enforcement agencies to implement officer wellness and suicide prevention programs, make counseling available to officers, or train supervisors and peers to identify suicide ideation.”
Dr. Greenberg said a further barrier to helping police officers considering self-harm is posed by the fact that even if they do seek out counseling, there is no guarantee that it will remain confidential.
“Support personnel have an obligation to report an officer who is thinking about committing suicide,” he said. “Many officers are concerned about this lack of confidentiality and that they may be branded if they seek help.”
Although Dr. Greenberg said many police officers are self-professed “action junkies,” even their unusually high capacity for stress is often tested by the realities of the job.
“Increasing demands for service, shortages of personnel, misinformation about police, COVID-19, talk about restructuring policing with little concrete direction, increased exposure to violence, greater numbers of vulnerable people, and more take a toll over time,” he lamented. “In addition, we are in a recruiting crisis in law enforcement, and there are no standards to ensure the quality of psychological screening provided to applicants. Many officers will go through their entire career and never be screened again. We know little about the stresses and strains that officers bring to the job.”
After the siege
It is not clear how many police officers were present at the Capitol on Jan. 6. During the chaos of the day, reinforcements to the Capitol Police Department arrived from Washington D.C., Maryland, and Virginia, but no official numbers on responders were obtained; Mr. Davis thought it was likely that there were at least 1,000 law enforcement officers present. Those who did respond sustained an estimated 100 injuries, including an officer who died the next day. Of the officers who died by suicide, one died 3 days after, another died 9 days later, and two more died in July – numbers that contradict the notion that this is some coincidence. Officer Alexander Kettering, a colleague of Mr. Davis who has been with Montgomery County Police for 15 years, was among those tasked with protecting the Capitol on Jan. 6. The chaos, violence, and destruction of the day has stuck with him and continues to occupy his thoughts.
“I had a front-row seat to the whole thing. It was overwhelming, and I’ve never seen people this angry,” said Mr. Kettering. “There were people up on the veranda and on the scaffolding set up for the inauguration. They were smashing windows and throwing things into the crowd. It was insane. There were decent people coming up to us and saying they would pray for us, then others calling us traitors, telling us to stand down and join them.”
In the aftermath of the Capitol siege, Mr. Kettering watched in dismay as the narrative of the day’s events began to warp.
“At first there was a consensus that what happened was so wrong, and then the politics took over. People were saying it wasn’t as bad as the media said, that it really wasn’t that violent and those speaking out are traitors or political operatives. I relive it every day, and it’s hard to escape, even in casual conversation.”
He added that the days’ events were compounded by the already heightened tensions surrounding the national debate around policing.
“It’s been 18 months of stress, of anti-police movements, and there is a fine line between addressing police brutality and being anti-police,” Mr. Kettering said, noting that the aforementioned issues have all contributed to the ongoing struggles his fellow officers are experiencing.
“It’s not a thing for cops to talk about how an event affected them,” he said. “A lot of officers have just shut down. People have careers and pensions to protect, and every time we stop a motorist, something could go wrong, even if we do everything right. There are mixed signals: They tell us, ‘Defend but don’t defend.’”
His colleague, Mr. Davis, said that officers “need more support from politicians,” noting that he felt particularly insulted by a comment made by a Montgomery County public official who accused the officers present at the Capitol of racism. “And finally, we feel a little betrayed by the public.”
More questions than answers from the Capitol’s day of chaos
What about the events of Jan. 6 led to the suicides of four law enforcement officers and what can be done to prevent more deaths in the future? There are the individual factors of each man’s personal history, circumstances, and vulnerabilities, including the sense of being personally endangered, witnessing trauma, and direct injury – one officer who died of suicide had sustained a head injury that day.
We don’t know if the officers went into the event with preexisting mental illness or addiction or if the day’s events precipitated psychiatric episodes. And with all the partisan anger surrounding the presidential election, we don’t know if each officer’s political beliefs amplified his distress over what occurred in a social media climate where police are being faulted by all sides.
When multiple suicides occur in a community, there is always concern about a “copycat” phenomena. These concerns are made more difficult to address, however, given the police culture of taboo and stigma associated with getting professional help, difficulty accessing care, and career repercussions for speaking openly about suicidal thoughts and mental health issues.
Finally, there is the current political agenda that leaves officers feeling unsupported, fearful of negative outcomes, and unappreciated. The Capitol siege in particular embodied a great deal of national distress and confusion over basic issues of truth, justice, and perceptions of reality in our polarized society.
Can we move to a place where those who enforce laws have easy access to treatment, free from stigma? Can we encourage a culture that does not tolerate brutality or racism, while also refusing to label all police as bad and lending support to their mission? Can we be more attuned to the repercussions of circumstances where officers are witnesses to trauma, are endangered themselves, and would benefit from acknowledgment of their distress?
Time will tell if our anti-police pendulum swings back. In the meantime, these four suicides among people defending our country remain tragically overlooked.
Dinah Miller, MD, is coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pups for veterans with PTSD: Biden signs PAWS act into law
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Service members with posttraumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions may eventually have expanded access to service dogs through legislation recently signed into law by President Joseph R. Biden.
The Puppies Assisting Wounded Servicemembers (PAWS) for Veterans Therapy Act (HR 1448) orders the Department of Veterans Affairs to begin a pilot program that over the course of 5 years will examine the utility and effectiveness of service dogs for improving the mental health of military veterans.
The legislation does not set a specific start date for the pilot program, but Rory Diamond, CEO of K9s for Warriors, a nonprofit organization based in Ponte Vedra, Fla., noted that K9s for Warriors and other organizations will be pushing the VA to start in 2022.
“We commend the White House for supporting this bill as a critical step in combating veteran suicide, and we’re confident in the path ahead for service dogs ultimately becoming a covered VA benefit to veterans with PTSD,” Mr. Diamond said in a statement provided to this news organization.
“For servicemembers relying on task-trained service dogs for PTSD, the HR 1448 is a giant leap towards supporting veterans and their service dogs in an equitable way,” Canine Companions, a national nonprofit organization that trains and provides service dogs, said in its own statement.
“It might mean the difference between having a veteran who won’t be here tomorrow and having one that will,” the group added.
Invisible wounds of war
In another statement, Bill McCabe, legislative affairs director at the Enlisted Association, said that “now, more than ever, veterans suffering from invisible wounds of war need access to trained service dogs, which have been scientifically proven to help alleviate symptoms of posttraumatic stress,” as well as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) and military sexual trauma.
“We thank President Biden for recognizing veterans need every possible option when seeking mental health treatments, and look forward to working with the Department of Veterans Affairs to implement this important program,” Mr. McCabe said.
A recent VA report showed that in 2014, 40% of veterans had mental health conditions such as PTSD and substance use. An average of 20 veterans per day died by suicide that year.
Veterans with problems regarding mobility, hearing, and sight, as well as some mental health problems, have been eligible to have costs of veterinary care for service dogs paid by the VA, although the VA has not paid for the training of the animals.
The PAWS Act, which was bipartisan legislation introduced by U.S. Senators Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Kyrsten Sinema (D-Ariz.), Kevin Cramer (R-N.D.), and Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), aims to expand eligibility to those with any mental health problems.
For at least a decade, various service dog and veterans’ organizations have pushed to have the VA expand the service dog benefit. This new law is a “first step,” said Mr. Diamond. “We had to kick open the door,” he said, adding that “the VA has essentially said no for almost 15 years.”
Mr. Diamond noted that there is “overwhelming” evidence showing that service dogs improve quality of life and reduce distress for veterans with PTSD and other diagnoses.
‘No excuse’
Results from a VA study showed that suicidal ideation was reduced in veterans who were paired with service dogs, compared with veterans paired with emotional support dogs. The study, which was made public in March, found no reduction in overall disability, according to a report by Military.com.
K9s for Warriors cites numerous other studies, published in peer-reviewed journals, that have shown that service dogs reduce PTSD symptoms, especially hypervigilance.
“There really is no excuse not to have the VA engaged in helping veterans suffering from posttraumatic stress who are extremely high risk of suicide to get a lifesaving service dog,” Mr. Diamond said.
His organization has paired 700 veterans suffering from TBI, PTSD, or military sexual trauma with a service dog. The organization provides a 3-week training program for the veteran and his or her dog.
Although about 200 of the graduates have been eligible to receive coverage from the VA for veterinary care for the dogs, it requires a lot of paperwork, and the criteria for who can be certified to receive that benefit are somewhat vague, Mr. Diamond noted.
Under current policy, the dog and veteran must have successfully completed a training program offered by an organization accredited by Assistance Dogs International or the International Guide Dog Federation.
The new pilot program will enable eligible veterans to receive dog training instruction from accredited nonprofit service dog training organizations, and it will give them the opportunity to adopt a dog that they actively assisted in training.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic link may tie cannabis use disorder to severe COVID-19
The same genetic variations may boost susceptibility to both severe COVID-19 and cannabis use disorder (CUD), a new study suggests. The research does not confirm a genetic link, but the lead author said the signs of an association are still “troubling.”
“Reducing cannabis use among heavy users may potentially provide protection against severe COVID-19 presentations,” Alexander S. Hatoum, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview. “Outside of individual risk, these data also have important implications for policy regarding vaccination as well as treatment prioritization in an overly taxed medical system.”
The study was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science.
Dr. Hatoum and colleagues launched the study to gain insight into whether CUD might be a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations.
As defined by the DSM-5, people with CUD suffer from impairment or distress because of their cannabis use and meet at least 2 of 11 criteria over a 12-month period, such as cravings, cannabis tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. According to a 2020 study that examined 2008-2016 data, 2.72% of children aged 12-17 showed signs of CUD, as did 1.23% of those aged over 26.
The primary reasons for hospitalization and death related to COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms. “And we have observed that genetic vulnerability to CUD is shared with respiratory disease, even after tobacco use is considered,” Dr. Hatoum said.
He and his colleagues examined data from genomewide association studies and searched for genetic correlations between CUD (14,080 cases, 343,726 controls) and COVID-19 hospitalization (9,373 cases, 1,197,256 controls). “Genetic vulnerability to COVID-19 was correlated with genetic liability to CUD (P = 1.33e–6),” the researchers wrote. “This association remained when accounting for genetic liability to related risk factors and covariates (P = .012-.049).”
According to Dr. Hatoum, the researchers found inconclusive evidence that CUD might worsen COVID-19 cases. “We applied statistical causal models, which found an effect consistent with causality, but it was nonsignificant,” he said.
Despite the absence of causality, the study findings could prove useful for clinicians and policy makers.
“Those struggling with CUD may be prioritized for vaccination and vaccination boosters to mitigate their higher likelihood of a severe COVID-19 presentation,” Dr. Hatoum said. “When testing positive for COVID-19, they may also be prioritized for earlier treatment.”
The study authors also added that the findings “urge caution” in regard to the wave of U.S. states legalizing cannabis. “Our data suggest that heavy cannabis use, but not lifetime cannabis use, represents a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations,” Dr. Hatoum said.
In an interview, Danielle Dick, PhD, who was not involved with the study, said it applies “cutting-edge methods to an important research question” and offers a “hint” of a genetic risk factor that makes some people more likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, “the study does not tell us what those underlying genetically influenced processes might be,” added Dr. Dick, professor of psychology, and human and molecular genetics at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “And it’s an important caveat to point out that the results from this study are limited in that they are based on data from people from European descent – so they can’t necessarily be applied to address the harm experienced by so many people of color from the COVID pandemic. That’s an unfortunate limitation.”
As for the idea that the study findings should prompt caution about marijuana legalization, Dr. Dick said it’s true that increased acceptability of drug use “increases the likelihood that individuals who are genetically vulnerable will develop problems. There is robust evidence of this.”
However, Dr. Dick said, “the legalization of marijuana is a complex topic because the health consequences aren’t the only consideration when it comes to legalization. The other side of the coin is the huge harm that has been caused to communities of color through marijuana criminalization. Legalization will hopefully lead to decreased harm on that front. So it’s a double-edged sword.”
Dr. Hatoum, his colleagues, and Dr. Dick reported no relevant disclosures.
The same genetic variations may boost susceptibility to both severe COVID-19 and cannabis use disorder (CUD), a new study suggests. The research does not confirm a genetic link, but the lead author said the signs of an association are still “troubling.”
“Reducing cannabis use among heavy users may potentially provide protection against severe COVID-19 presentations,” Alexander S. Hatoum, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview. “Outside of individual risk, these data also have important implications for policy regarding vaccination as well as treatment prioritization in an overly taxed medical system.”
The study was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science.
Dr. Hatoum and colleagues launched the study to gain insight into whether CUD might be a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations.
As defined by the DSM-5, people with CUD suffer from impairment or distress because of their cannabis use and meet at least 2 of 11 criteria over a 12-month period, such as cravings, cannabis tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. According to a 2020 study that examined 2008-2016 data, 2.72% of children aged 12-17 showed signs of CUD, as did 1.23% of those aged over 26.
The primary reasons for hospitalization and death related to COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms. “And we have observed that genetic vulnerability to CUD is shared with respiratory disease, even after tobacco use is considered,” Dr. Hatoum said.
He and his colleagues examined data from genomewide association studies and searched for genetic correlations between CUD (14,080 cases, 343,726 controls) and COVID-19 hospitalization (9,373 cases, 1,197,256 controls). “Genetic vulnerability to COVID-19 was correlated with genetic liability to CUD (P = 1.33e–6),” the researchers wrote. “This association remained when accounting for genetic liability to related risk factors and covariates (P = .012-.049).”
According to Dr. Hatoum, the researchers found inconclusive evidence that CUD might worsen COVID-19 cases. “We applied statistical causal models, which found an effect consistent with causality, but it was nonsignificant,” he said.
Despite the absence of causality, the study findings could prove useful for clinicians and policy makers.
“Those struggling with CUD may be prioritized for vaccination and vaccination boosters to mitigate their higher likelihood of a severe COVID-19 presentation,” Dr. Hatoum said. “When testing positive for COVID-19, they may also be prioritized for earlier treatment.”
The study authors also added that the findings “urge caution” in regard to the wave of U.S. states legalizing cannabis. “Our data suggest that heavy cannabis use, but not lifetime cannabis use, represents a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations,” Dr. Hatoum said.
In an interview, Danielle Dick, PhD, who was not involved with the study, said it applies “cutting-edge methods to an important research question” and offers a “hint” of a genetic risk factor that makes some people more likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, “the study does not tell us what those underlying genetically influenced processes might be,” added Dr. Dick, professor of psychology, and human and molecular genetics at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “And it’s an important caveat to point out that the results from this study are limited in that they are based on data from people from European descent – so they can’t necessarily be applied to address the harm experienced by so many people of color from the COVID pandemic. That’s an unfortunate limitation.”
As for the idea that the study findings should prompt caution about marijuana legalization, Dr. Dick said it’s true that increased acceptability of drug use “increases the likelihood that individuals who are genetically vulnerable will develop problems. There is robust evidence of this.”
However, Dr. Dick said, “the legalization of marijuana is a complex topic because the health consequences aren’t the only consideration when it comes to legalization. The other side of the coin is the huge harm that has been caused to communities of color through marijuana criminalization. Legalization will hopefully lead to decreased harm on that front. So it’s a double-edged sword.”
Dr. Hatoum, his colleagues, and Dr. Dick reported no relevant disclosures.
The same genetic variations may boost susceptibility to both severe COVID-19 and cannabis use disorder (CUD), a new study suggests. The research does not confirm a genetic link, but the lead author said the signs of an association are still “troubling.”
“Reducing cannabis use among heavy users may potentially provide protection against severe COVID-19 presentations,” Alexander S. Hatoum, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview. “Outside of individual risk, these data also have important implications for policy regarding vaccination as well as treatment prioritization in an overly taxed medical system.”
The study was published in the journal Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science.
Dr. Hatoum and colleagues launched the study to gain insight into whether CUD might be a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations.
As defined by the DSM-5, people with CUD suffer from impairment or distress because of their cannabis use and meet at least 2 of 11 criteria over a 12-month period, such as cravings, cannabis tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. According to a 2020 study that examined 2008-2016 data, 2.72% of children aged 12-17 showed signs of CUD, as did 1.23% of those aged over 26.
The primary reasons for hospitalization and death related to COVID-19 are respiratory symptoms. “And we have observed that genetic vulnerability to CUD is shared with respiratory disease, even after tobacco use is considered,” Dr. Hatoum said.
He and his colleagues examined data from genomewide association studies and searched for genetic correlations between CUD (14,080 cases, 343,726 controls) and COVID-19 hospitalization (9,373 cases, 1,197,256 controls). “Genetic vulnerability to COVID-19 was correlated with genetic liability to CUD (P = 1.33e–6),” the researchers wrote. “This association remained when accounting for genetic liability to related risk factors and covariates (P = .012-.049).”
According to Dr. Hatoum, the researchers found inconclusive evidence that CUD might worsen COVID-19 cases. “We applied statistical causal models, which found an effect consistent with causality, but it was nonsignificant,” he said.
Despite the absence of causality, the study findings could prove useful for clinicians and policy makers.
“Those struggling with CUD may be prioritized for vaccination and vaccination boosters to mitigate their higher likelihood of a severe COVID-19 presentation,” Dr. Hatoum said. “When testing positive for COVID-19, they may also be prioritized for earlier treatment.”
The study authors also added that the findings “urge caution” in regard to the wave of U.S. states legalizing cannabis. “Our data suggest that heavy cannabis use, but not lifetime cannabis use, represents a risk factor for severe COVID-19 presentations,” Dr. Hatoum said.
In an interview, Danielle Dick, PhD, who was not involved with the study, said it applies “cutting-edge methods to an important research question” and offers a “hint” of a genetic risk factor that makes some people more likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, “the study does not tell us what those underlying genetically influenced processes might be,” added Dr. Dick, professor of psychology, and human and molecular genetics at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond. “And it’s an important caveat to point out that the results from this study are limited in that they are based on data from people from European descent – so they can’t necessarily be applied to address the harm experienced by so many people of color from the COVID pandemic. That’s an unfortunate limitation.”
As for the idea that the study findings should prompt caution about marijuana legalization, Dr. Dick said it’s true that increased acceptability of drug use “increases the likelihood that individuals who are genetically vulnerable will develop problems. There is robust evidence of this.”
However, Dr. Dick said, “the legalization of marijuana is a complex topic because the health consequences aren’t the only consideration when it comes to legalization. The other side of the coin is the huge harm that has been caused to communities of color through marijuana criminalization. Legalization will hopefully lead to decreased harm on that front. So it’s a double-edged sword.”
Dr. Hatoum, his colleagues, and Dr. Dick reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY GLOBAL OPEN SCIENCE
Explosive aggression may be neurologic
Aggression is an underappreciated mental health issue, and biological mechanisms might help explain more extreme forms like intermittent explosive disorder (IED), which is characterized by episodes of sudden impulses and inappropriate aggression, violence, or even verbal outbursts. IED can lead to road rage, domestic abuse, in addition to throwing objects and engaging in other destructive behaviors.
Despite those consequences, aggression hasn’t gained the same level of attention as other psychiatric conditions, according to Emil F. Coccaro, MD, who spoke about the topic at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“People seem to think that aggressive behavior is bad behavior, and therefore people just need an attitude adjustment. So there’s this sort of stigma, and there are no advocacy groups for it. There are no poster children for it. But there’s a whole lot of biology and neuroscience behind it,” said Dr. Coccaro, in an interview. He is a professor and vice chair of research in psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University, Columbus.
, who spoke at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There is a general view that psychiatric conditions may lead to increased aggression, but there is little evidence of that. “As a general statement, having a psychological [illness] in and of itself does not really increase the risk of being aggressive. What does is being aggressive in general, and substance use disorder. And the thing with [people who have] substance use disorders is that they only get aggressive when they are aggressive to begin with,” said Dr. Coccaro, noting that the strongest case for the relationship surrounds alcohol abuse.
The DSM-5 criteria for IED include: verbal or physical aggression without destruction, at least twice per week, or three or more episodes of assault or physical destruction within a year. The behavior must be out of proportion to the provocation, cause distress or impairment, and not be accountable by other diagnoses. “If they’re blowing up twice a week, for a few months, and usually they’re doing it for a long time, then that’s different than just blowing up very occasionally. Healthy people, nonaggressive people, maybe they blow up once a year, or even less frequently than that,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging studies consistently show differences associated with aggression.
“The IEDs really do distinguish themselves from the psychiatric controls. They also have other stuff going on with them; they have a hostile attribution. And they’re kind of irritable at baseline. They’re not walking around irritable all the time, but the people around them may be walking on eggshells,” Dr. Coccaro said.
The results from these sorts of studies aren’t fully conclusive and can’t be used for diagnosis, in part because of a lack of power. “It’s hard to do these MRI studies and lots and lots of subjects, because they’re kind of expensive,” Dr. Coccaro said. “We’re just not there yet.”
Other, less expensive imaging techniques like near-infrared spectroscopy may improve matters. “That might be something down the road that could lead to something (diagnostic). Right now, most imaging studies are being done to really understand mechanisms,” said Dr. Coccaro.
Those mechanistic studies suggest that the culprit for IED may be a combination of too much drive from subcortical structures like the amygdala and insufficient inhibitor function in the frontal part of the brain. The frontal cortex may suffer a loss of gray matter, according to Dr. Coccaro, and there may be insufficient connectivity, which could weaken signals coming from the frontal areas that might otherwise inhibit lower centers of the brain.
Treatment for IED could be aimed at improving that connectivity and signaling. Ketamine and other anesthetic agents like nitrous oxide may increase connectivity to nerve cells by increasing branching at synaptic dendrites.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have the potential to treat IED, but their utility is limited because they bind to the presynaptic transporter for serotonin, and more aggressive people have fewer of those transporters. “You only get so much bang for your buck,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy that focuses on anger management and relaxation shows promise. “CBT does help people deal with what’s coming at them. So it’s like, ‘oh, I’m getting angry, I better start doing those relaxation (techniques).’ It teaches them to rethink things.”
During the Q&A session following the presentation, Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who moderated the session, pointed out that misattribution can occur, leading an affected individual to misread someone’s facial expression and react aggressively, which is a problem also seen in psychosis.
“There are studies showing [that if] you show them a series of faces with different affects, many times paranoid patients read a normal facial expression as threatening. So it may be that it’s the same thing with aggression,” said Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
In the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it’s also possible that mask-wearing could improve or worsen such misunderstandings. “There is expression in the eyes that you can see, but you miss a lot,” Dr. Coccaro said.
For now, the effects of masks remain largely unknown. But that will change. “Sooner or later we will have a bunch of papers coming out about how masks have changed a lot of behaviors,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Coccaro has consulted for Avanir, Azevan, and Brackett. Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, IntraCellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim. Dr. Nasrallah has been on a speaker’s bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
Aggression is an underappreciated mental health issue, and biological mechanisms might help explain more extreme forms like intermittent explosive disorder (IED), which is characterized by episodes of sudden impulses and inappropriate aggression, violence, or even verbal outbursts. IED can lead to road rage, domestic abuse, in addition to throwing objects and engaging in other destructive behaviors.
Despite those consequences, aggression hasn’t gained the same level of attention as other psychiatric conditions, according to Emil F. Coccaro, MD, who spoke about the topic at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“People seem to think that aggressive behavior is bad behavior, and therefore people just need an attitude adjustment. So there’s this sort of stigma, and there are no advocacy groups for it. There are no poster children for it. But there’s a whole lot of biology and neuroscience behind it,” said Dr. Coccaro, in an interview. He is a professor and vice chair of research in psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University, Columbus.
, who spoke at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There is a general view that psychiatric conditions may lead to increased aggression, but there is little evidence of that. “As a general statement, having a psychological [illness] in and of itself does not really increase the risk of being aggressive. What does is being aggressive in general, and substance use disorder. And the thing with [people who have] substance use disorders is that they only get aggressive when they are aggressive to begin with,” said Dr. Coccaro, noting that the strongest case for the relationship surrounds alcohol abuse.
The DSM-5 criteria for IED include: verbal or physical aggression without destruction, at least twice per week, or three or more episodes of assault or physical destruction within a year. The behavior must be out of proportion to the provocation, cause distress or impairment, and not be accountable by other diagnoses. “If they’re blowing up twice a week, for a few months, and usually they’re doing it for a long time, then that’s different than just blowing up very occasionally. Healthy people, nonaggressive people, maybe they blow up once a year, or even less frequently than that,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging studies consistently show differences associated with aggression.
“The IEDs really do distinguish themselves from the psychiatric controls. They also have other stuff going on with them; they have a hostile attribution. And they’re kind of irritable at baseline. They’re not walking around irritable all the time, but the people around them may be walking on eggshells,” Dr. Coccaro said.
The results from these sorts of studies aren’t fully conclusive and can’t be used for diagnosis, in part because of a lack of power. “It’s hard to do these MRI studies and lots and lots of subjects, because they’re kind of expensive,” Dr. Coccaro said. “We’re just not there yet.”
Other, less expensive imaging techniques like near-infrared spectroscopy may improve matters. “That might be something down the road that could lead to something (diagnostic). Right now, most imaging studies are being done to really understand mechanisms,” said Dr. Coccaro.
Those mechanistic studies suggest that the culprit for IED may be a combination of too much drive from subcortical structures like the amygdala and insufficient inhibitor function in the frontal part of the brain. The frontal cortex may suffer a loss of gray matter, according to Dr. Coccaro, and there may be insufficient connectivity, which could weaken signals coming from the frontal areas that might otherwise inhibit lower centers of the brain.
Treatment for IED could be aimed at improving that connectivity and signaling. Ketamine and other anesthetic agents like nitrous oxide may increase connectivity to nerve cells by increasing branching at synaptic dendrites.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have the potential to treat IED, but their utility is limited because they bind to the presynaptic transporter for serotonin, and more aggressive people have fewer of those transporters. “You only get so much bang for your buck,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy that focuses on anger management and relaxation shows promise. “CBT does help people deal with what’s coming at them. So it’s like, ‘oh, I’m getting angry, I better start doing those relaxation (techniques).’ It teaches them to rethink things.”
During the Q&A session following the presentation, Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who moderated the session, pointed out that misattribution can occur, leading an affected individual to misread someone’s facial expression and react aggressively, which is a problem also seen in psychosis.
“There are studies showing [that if] you show them a series of faces with different affects, many times paranoid patients read a normal facial expression as threatening. So it may be that it’s the same thing with aggression,” said Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
In the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it’s also possible that mask-wearing could improve or worsen such misunderstandings. “There is expression in the eyes that you can see, but you miss a lot,” Dr. Coccaro said.
For now, the effects of masks remain largely unknown. But that will change. “Sooner or later we will have a bunch of papers coming out about how masks have changed a lot of behaviors,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Coccaro has consulted for Avanir, Azevan, and Brackett. Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, IntraCellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim. Dr. Nasrallah has been on a speaker’s bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
Aggression is an underappreciated mental health issue, and biological mechanisms might help explain more extreme forms like intermittent explosive disorder (IED), which is characterized by episodes of sudden impulses and inappropriate aggression, violence, or even verbal outbursts. IED can lead to road rage, domestic abuse, in addition to throwing objects and engaging in other destructive behaviors.
Despite those consequences, aggression hasn’t gained the same level of attention as other psychiatric conditions, according to Emil F. Coccaro, MD, who spoke about the topic at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“People seem to think that aggressive behavior is bad behavior, and therefore people just need an attitude adjustment. So there’s this sort of stigma, and there are no advocacy groups for it. There are no poster children for it. But there’s a whole lot of biology and neuroscience behind it,” said Dr. Coccaro, in an interview. He is a professor and vice chair of research in psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University, Columbus.
, who spoke at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There is a general view that psychiatric conditions may lead to increased aggression, but there is little evidence of that. “As a general statement, having a psychological [illness] in and of itself does not really increase the risk of being aggressive. What does is being aggressive in general, and substance use disorder. And the thing with [people who have] substance use disorders is that they only get aggressive when they are aggressive to begin with,” said Dr. Coccaro, noting that the strongest case for the relationship surrounds alcohol abuse.
The DSM-5 criteria for IED include: verbal or physical aggression without destruction, at least twice per week, or three or more episodes of assault or physical destruction within a year. The behavior must be out of proportion to the provocation, cause distress or impairment, and not be accountable by other diagnoses. “If they’re blowing up twice a week, for a few months, and usually they’re doing it for a long time, then that’s different than just blowing up very occasionally. Healthy people, nonaggressive people, maybe they blow up once a year, or even less frequently than that,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging studies consistently show differences associated with aggression.
“The IEDs really do distinguish themselves from the psychiatric controls. They also have other stuff going on with them; they have a hostile attribution. And they’re kind of irritable at baseline. They’re not walking around irritable all the time, but the people around them may be walking on eggshells,” Dr. Coccaro said.
The results from these sorts of studies aren’t fully conclusive and can’t be used for diagnosis, in part because of a lack of power. “It’s hard to do these MRI studies and lots and lots of subjects, because they’re kind of expensive,” Dr. Coccaro said. “We’re just not there yet.”
Other, less expensive imaging techniques like near-infrared spectroscopy may improve matters. “That might be something down the road that could lead to something (diagnostic). Right now, most imaging studies are being done to really understand mechanisms,” said Dr. Coccaro.
Those mechanistic studies suggest that the culprit for IED may be a combination of too much drive from subcortical structures like the amygdala and insufficient inhibitor function in the frontal part of the brain. The frontal cortex may suffer a loss of gray matter, according to Dr. Coccaro, and there may be insufficient connectivity, which could weaken signals coming from the frontal areas that might otherwise inhibit lower centers of the brain.
Treatment for IED could be aimed at improving that connectivity and signaling. Ketamine and other anesthetic agents like nitrous oxide may increase connectivity to nerve cells by increasing branching at synaptic dendrites.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have the potential to treat IED, but their utility is limited because they bind to the presynaptic transporter for serotonin, and more aggressive people have fewer of those transporters. “You only get so much bang for your buck,” Dr. Coccaro said.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy that focuses on anger management and relaxation shows promise. “CBT does help people deal with what’s coming at them. So it’s like, ‘oh, I’m getting angry, I better start doing those relaxation (techniques).’ It teaches them to rethink things.”
During the Q&A session following the presentation, Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who moderated the session, pointed out that misattribution can occur, leading an affected individual to misread someone’s facial expression and react aggressively, which is a problem also seen in psychosis.
“There are studies showing [that if] you show them a series of faces with different affects, many times paranoid patients read a normal facial expression as threatening. So it may be that it’s the same thing with aggression,” said Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
In the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it’s also possible that mask-wearing could improve or worsen such misunderstandings. “There is expression in the eyes that you can see, but you miss a lot,” Dr. Coccaro said.
For now, the effects of masks remain largely unknown. But that will change. “Sooner or later we will have a bunch of papers coming out about how masks have changed a lot of behaviors,” Dr. Nasrallah said.
Dr. Coccaro has consulted for Avanir, Azevan, and Brackett. Dr. Nasrallah has consulted for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, IntraCellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim. Dr. Nasrallah has been on a speaker’s bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
REPORTING FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2021
Pfizer recalls four more lots of smoking cessation drug Chantix
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid prescribing laws having an impact
State laws capping initial opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less have led to a reduction in opioid prescribing, a new analysis of Medicare data shows.
While overall opioid prescribing has decreased, the reduction in states with legislation restricting opioid prescribing was “significantly greater than in states without such legislation,” study investigator Michael Brenner, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published online August 9 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Significant but limited effect
Because of rising concern around the opioid crisis, 23 states representing 43% of the U.S. population passed laws from 2016 through 2018 limiting initial opioid prescription to 7 days or less.
Using Medicare data from 2013 through 2018, Dr. Brenner and colleagues conducted a before-and-after study to assess the effect of these laws.
They found that on average, the number of days an opioid was prescribed for each Medicare beneficiary decreased by 11.6 days (from 44.2 days in 2013 to 32.7 days in 2018) in states that imposed duration limits, compared with 10.1 days in states without these laws (from 43.4 days in 2013 to 33.3 days in 2018).
Prior to the start of duration limits in 2016, days an opioid was prescribed were comparable among states.
After adjusting for state-level differences in race, urbanization, median income, tobacco and alcohol use, serious mental illness, and other factors, state laws limiting opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less were associated with a reduction in prescribing of 1.7 days per enrollee, “suggesting a significant but limited outcome” for these laws, the researchers note.
, but this was not significantly different in states with limit laws versus those without. However, state laws limiting duration led to a significant reduction in days of opioid prescribed among surgeons, dentists, pain specialists, and other specialists.
Inadequate pain control?
The researchers note the study was limited to Medicare beneficiaries; however, excess opioid prescribing is prevalent across all patient populations.
In addition, it’s not possible to tell from the data whether acute pain was adequately controlled with fewer pills.
“The question of adequacy of pain control is a crucial one that has been investigated extensively in prior work but was not possible to evaluate in this particular study,” said Dr. Brenner.
However, “ample evidence supports a role for reducing opioid prescribing and that such reduction can be achieved while ensuring that pain is adequately controlled with fewer pills,” he noted.
“A persistent misconception is that opioids are uniquely powerful and effective for controlling pain. Patients may perceive that effective analgesia is being withheld when opioids are not included in a regimen,” Dr. Brenner added.
“Yet, the evidence from meta-analyses derived from large numbers of randomized clinical trials finds that [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] NSAIDS combined with acetaminophen provide similar or improved acute pain when compared to commonly prescribed opioid regimens, based on number-needed-to-treat analyses,” he added.
In a related editorial, Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, with University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell H. Katz, MD, president and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals, say the decrease in opioid prescribing with duration limits was “small but probably meaningful.”
Restricting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “reasonable because patients with new onset of pain should be re-evaluated in a week if the pain continues,” they write.
However, Dr. Grady and Dr. Katz “worry” that restricting initial prescriptions to shorter periods, such as 3 or 5 days, as has occurred in six states, “may result in patients with acute pain going untreated or having to go to extraordinary effort to obtain adequate pain relief.”
In their view, the data from this study suggest that limiting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “helpful, but we would not restrict any further given that we do not know how it affected patients with acute pain.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Brenner, Dr. Grady, and Dr. Katz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
State laws capping initial opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less have led to a reduction in opioid prescribing, a new analysis of Medicare data shows.
While overall opioid prescribing has decreased, the reduction in states with legislation restricting opioid prescribing was “significantly greater than in states without such legislation,” study investigator Michael Brenner, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published online August 9 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Significant but limited effect
Because of rising concern around the opioid crisis, 23 states representing 43% of the U.S. population passed laws from 2016 through 2018 limiting initial opioid prescription to 7 days or less.
Using Medicare data from 2013 through 2018, Dr. Brenner and colleagues conducted a before-and-after study to assess the effect of these laws.
They found that on average, the number of days an opioid was prescribed for each Medicare beneficiary decreased by 11.6 days (from 44.2 days in 2013 to 32.7 days in 2018) in states that imposed duration limits, compared with 10.1 days in states without these laws (from 43.4 days in 2013 to 33.3 days in 2018).
Prior to the start of duration limits in 2016, days an opioid was prescribed were comparable among states.
After adjusting for state-level differences in race, urbanization, median income, tobacco and alcohol use, serious mental illness, and other factors, state laws limiting opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less were associated with a reduction in prescribing of 1.7 days per enrollee, “suggesting a significant but limited outcome” for these laws, the researchers note.
, but this was not significantly different in states with limit laws versus those without. However, state laws limiting duration led to a significant reduction in days of opioid prescribed among surgeons, dentists, pain specialists, and other specialists.
Inadequate pain control?
The researchers note the study was limited to Medicare beneficiaries; however, excess opioid prescribing is prevalent across all patient populations.
In addition, it’s not possible to tell from the data whether acute pain was adequately controlled with fewer pills.
“The question of adequacy of pain control is a crucial one that has been investigated extensively in prior work but was not possible to evaluate in this particular study,” said Dr. Brenner.
However, “ample evidence supports a role for reducing opioid prescribing and that such reduction can be achieved while ensuring that pain is adequately controlled with fewer pills,” he noted.
“A persistent misconception is that opioids are uniquely powerful and effective for controlling pain. Patients may perceive that effective analgesia is being withheld when opioids are not included in a regimen,” Dr. Brenner added.
“Yet, the evidence from meta-analyses derived from large numbers of randomized clinical trials finds that [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] NSAIDS combined with acetaminophen provide similar or improved acute pain when compared to commonly prescribed opioid regimens, based on number-needed-to-treat analyses,” he added.
In a related editorial, Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, with University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell H. Katz, MD, president and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals, say the decrease in opioid prescribing with duration limits was “small but probably meaningful.”
Restricting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “reasonable because patients with new onset of pain should be re-evaluated in a week if the pain continues,” they write.
However, Dr. Grady and Dr. Katz “worry” that restricting initial prescriptions to shorter periods, such as 3 or 5 days, as has occurred in six states, “may result in patients with acute pain going untreated or having to go to extraordinary effort to obtain adequate pain relief.”
In their view, the data from this study suggest that limiting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “helpful, but we would not restrict any further given that we do not know how it affected patients with acute pain.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Brenner, Dr. Grady, and Dr. Katz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
State laws capping initial opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less have led to a reduction in opioid prescribing, a new analysis of Medicare data shows.
While overall opioid prescribing has decreased, the reduction in states with legislation restricting opioid prescribing was “significantly greater than in states without such legislation,” study investigator Michael Brenner, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published online August 9 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Significant but limited effect
Because of rising concern around the opioid crisis, 23 states representing 43% of the U.S. population passed laws from 2016 through 2018 limiting initial opioid prescription to 7 days or less.
Using Medicare data from 2013 through 2018, Dr. Brenner and colleagues conducted a before-and-after study to assess the effect of these laws.
They found that on average, the number of days an opioid was prescribed for each Medicare beneficiary decreased by 11.6 days (from 44.2 days in 2013 to 32.7 days in 2018) in states that imposed duration limits, compared with 10.1 days in states without these laws (from 43.4 days in 2013 to 33.3 days in 2018).
Prior to the start of duration limits in 2016, days an opioid was prescribed were comparable among states.
After adjusting for state-level differences in race, urbanization, median income, tobacco and alcohol use, serious mental illness, and other factors, state laws limiting opioid prescriptions to 7 days or less were associated with a reduction in prescribing of 1.7 days per enrollee, “suggesting a significant but limited outcome” for these laws, the researchers note.
, but this was not significantly different in states with limit laws versus those without. However, state laws limiting duration led to a significant reduction in days of opioid prescribed among surgeons, dentists, pain specialists, and other specialists.
Inadequate pain control?
The researchers note the study was limited to Medicare beneficiaries; however, excess opioid prescribing is prevalent across all patient populations.
In addition, it’s not possible to tell from the data whether acute pain was adequately controlled with fewer pills.
“The question of adequacy of pain control is a crucial one that has been investigated extensively in prior work but was not possible to evaluate in this particular study,” said Dr. Brenner.
However, “ample evidence supports a role for reducing opioid prescribing and that such reduction can be achieved while ensuring that pain is adequately controlled with fewer pills,” he noted.
“A persistent misconception is that opioids are uniquely powerful and effective for controlling pain. Patients may perceive that effective analgesia is being withheld when opioids are not included in a regimen,” Dr. Brenner added.
“Yet, the evidence from meta-analyses derived from large numbers of randomized clinical trials finds that [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs] NSAIDS combined with acetaminophen provide similar or improved acute pain when compared to commonly prescribed opioid regimens, based on number-needed-to-treat analyses,” he added.
In a related editorial, Deborah Grady, MD, MPH, with University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell H. Katz, MD, president and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals, say the decrease in opioid prescribing with duration limits was “small but probably meaningful.”
Restricting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “reasonable because patients with new onset of pain should be re-evaluated in a week if the pain continues,” they write.
However, Dr. Grady and Dr. Katz “worry” that restricting initial prescriptions to shorter periods, such as 3 or 5 days, as has occurred in six states, “may result in patients with acute pain going untreated or having to go to extraordinary effort to obtain adequate pain relief.”
In their view, the data from this study suggest that limiting initial prescriptions to seven or fewer days is “helpful, but we would not restrict any further given that we do not know how it affected patients with acute pain.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Brenner, Dr. Grady, and Dr. Katz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.











