User login
Rheumatic diseases and assisted reproductive technology: Things to consider
The field of “reproductive rheumatology” has received growing attention in recent years as we learn more about how autoimmune rheumatic diseases and their treatment affect women of reproductive age. In 2020, the American College of Rheumatology published a comprehensive guideline that includes recommendations and supporting evidence for managing issues related to reproductive health in patients with rheumatic diseases and has since launched an ongoing Reproductive Health Initiative, with the goal of translating established guidelines into practice through various education and awareness campaigns. One area addressed by the guideline that comes up commonly in practice but receives less attention and research is the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Literature is conflicting regarding whether patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases are inherently at increased risk for infertility, defined as failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected intercourse, or subfertility, defined as a delay in conception. Regardless, several factors indirectly contribute to a disproportionate risk for infertility or subfertility in this patient population, including active inflammatory disease, reduced ovarian reserve, and medications.
Patients with subfertility or infertility who desire pregnancy may pursue ovulation induction with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization (IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection with either embryo transfer, or gestational surrogacy. Those who require treatment with cyclophosphamide or who plan to defer pregnancy for whatever reason can opt for oocyte cryopreservation (colloquially known as “egg freezing”). For IVF and oocyte cryopreservation, controlled ovarian stimulation is typically the first step (except in unstimulated, or “natural cycle,” IVF).
Various protocols are used for ovarian stimulation and ovulation induction, the nuances of which are beyond the scope of this article. In general, ovarian stimulation involves gonadotropin therapy (follicle-stimulating hormone and/or human menopausal gonadotropin) administered via scheduled subcutaneous injections to stimulate follicular growth, as well as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists or antagonists to suppress luteinizing hormone, preventing ovulation. Adjunctive oral therapy (clomiphene citrate or letrozole, an aromatase inhibitor) may be used as well. The patient has frequent lab monitoring of hormone levels and transvaginal ultrasounds to measure follicle number and size and, when the timing is right, receives an “ovulation trigger” – either human chorionic gonadotropin or GnRH agonist, depending on the protocol. At this point, transvaginal ultrasound–guided egg retrieval is done under sedation. Recovered oocytes are then either frozen for later use or fertilized in the lab for embryo transfer. Lastly, exogenous hormones are often used: estrogen to support frozen embryo transfers and progesterone for so-called luteal phase support.
ART is not contraindicated in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, but there may be additional factors to consider, particularly for those with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), and antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) without clinical APS.
Ovarian stimulation elevates estrogen levels to varying degrees depending on the patient and the medications used. In all cases, though, peak levels are significantly lower than levels reached during pregnancy. It is well established that elevated estrogen – whether from hormone therapies or pregnancy – significantly increases thrombotic risk, even in healthy people. High-risk patients should receive low-molecular-weight heparin – a prophylactic dose for patients with either positive aPL without clinical APS (including those with SLE) or with obstetric APS, and a therapeutic dose for those with thrombotic APS – during ART procedures.
In patients with SLE, another concern is that increased estrogen will cause disease flare. One case series published in 2017 reported 37 patients with SLE and/or APS who underwent 97 IVF cycles, of which 8% were complicated by flare or thrombotic events. Notably, half of these complications occurred in patients who stopped prescribed therapies (immunomodulatory therapy in two patients with SLE, anticoagulation in two patients with APS) after failure to conceive. In a separate study from 2000 including 19 patients with SLE, APS, or high-titer aPL who underwent 68 IVF cycles, 19% of cycles in patients with SLE were complicated by flare, and no thrombotic events occurred in the cohort. The authors concluded that ovulation induction does not exacerbate SLE or APS. In these studies, the overall pregnancy rates were felt to be consistent with those achieved by the general population through IVF. Although obstetric complications, such as preeclampsia and preterm delivery, were reported in about half of the pregnancies described, these are known to occur more frequently in those with SLE and APS, especially when active disease or other risk factors are present. There are no large-scale, controlled studies evaluating ART outcomes in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases to date.
Finally, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is an increasingly rare but severe complication of ovarian stimulation. OHSS is characterized by capillary leak, fluid overload, and cytokine release syndrome and can lead to thromboembolic events. Comorbidities like hypertension and renal failure, which can go along with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, are risk factors for OHSS. The use of human chorionic gonadotropin to trigger ovulation is also associated with an increased risk for OHSS, so a GnRH agonist trigger may be preferable.
The ACR guideline recommends that individuals with any of these underlying conditions undergo ART only in expert centers. The ovarian stimulation protocol needs to be tailored to the individual patient to minimize risk and optimize outcomes. The overall goal when managing patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases during ART is to establish and maintain disease control with pregnancy-compatible medications (when pregnancy is the goal). With adequate planning, appropriate treatment, and collaboration between obstetricians and rheumatologists, individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases can safely pursue ART and go on to have successful pregnancies.
Dr. Siegel is a 2022-2023 UCB Women’s Health rheumatology fellow in the rheumatology reproductive health program of the Barbara Volcker Center for Women and Rheumatic Diseases at Hospital for Special Surgery/Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. Her clinical and research focus is on reproductive health issues in individuals with rheumatic disease. Dr. Chan is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for a monthly rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice. Follow Dr Chan on Twitter. Dr. Siegel and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article – an editorial collaboration between Medscape and the Hospital for Special Surgery – first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of “reproductive rheumatology” has received growing attention in recent years as we learn more about how autoimmune rheumatic diseases and their treatment affect women of reproductive age. In 2020, the American College of Rheumatology published a comprehensive guideline that includes recommendations and supporting evidence for managing issues related to reproductive health in patients with rheumatic diseases and has since launched an ongoing Reproductive Health Initiative, with the goal of translating established guidelines into practice through various education and awareness campaigns. One area addressed by the guideline that comes up commonly in practice but receives less attention and research is the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Literature is conflicting regarding whether patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases are inherently at increased risk for infertility, defined as failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected intercourse, or subfertility, defined as a delay in conception. Regardless, several factors indirectly contribute to a disproportionate risk for infertility or subfertility in this patient population, including active inflammatory disease, reduced ovarian reserve, and medications.
Patients with subfertility or infertility who desire pregnancy may pursue ovulation induction with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization (IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection with either embryo transfer, or gestational surrogacy. Those who require treatment with cyclophosphamide or who plan to defer pregnancy for whatever reason can opt for oocyte cryopreservation (colloquially known as “egg freezing”). For IVF and oocyte cryopreservation, controlled ovarian stimulation is typically the first step (except in unstimulated, or “natural cycle,” IVF).
Various protocols are used for ovarian stimulation and ovulation induction, the nuances of which are beyond the scope of this article. In general, ovarian stimulation involves gonadotropin therapy (follicle-stimulating hormone and/or human menopausal gonadotropin) administered via scheduled subcutaneous injections to stimulate follicular growth, as well as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists or antagonists to suppress luteinizing hormone, preventing ovulation. Adjunctive oral therapy (clomiphene citrate or letrozole, an aromatase inhibitor) may be used as well. The patient has frequent lab monitoring of hormone levels and transvaginal ultrasounds to measure follicle number and size and, when the timing is right, receives an “ovulation trigger” – either human chorionic gonadotropin or GnRH agonist, depending on the protocol. At this point, transvaginal ultrasound–guided egg retrieval is done under sedation. Recovered oocytes are then either frozen for later use or fertilized in the lab for embryo transfer. Lastly, exogenous hormones are often used: estrogen to support frozen embryo transfers and progesterone for so-called luteal phase support.
ART is not contraindicated in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, but there may be additional factors to consider, particularly for those with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), and antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) without clinical APS.
Ovarian stimulation elevates estrogen levels to varying degrees depending on the patient and the medications used. In all cases, though, peak levels are significantly lower than levels reached during pregnancy. It is well established that elevated estrogen – whether from hormone therapies or pregnancy – significantly increases thrombotic risk, even in healthy people. High-risk patients should receive low-molecular-weight heparin – a prophylactic dose for patients with either positive aPL without clinical APS (including those with SLE) or with obstetric APS, and a therapeutic dose for those with thrombotic APS – during ART procedures.
In patients with SLE, another concern is that increased estrogen will cause disease flare. One case series published in 2017 reported 37 patients with SLE and/or APS who underwent 97 IVF cycles, of which 8% were complicated by flare or thrombotic events. Notably, half of these complications occurred in patients who stopped prescribed therapies (immunomodulatory therapy in two patients with SLE, anticoagulation in two patients with APS) after failure to conceive. In a separate study from 2000 including 19 patients with SLE, APS, or high-titer aPL who underwent 68 IVF cycles, 19% of cycles in patients with SLE were complicated by flare, and no thrombotic events occurred in the cohort. The authors concluded that ovulation induction does not exacerbate SLE or APS. In these studies, the overall pregnancy rates were felt to be consistent with those achieved by the general population through IVF. Although obstetric complications, such as preeclampsia and preterm delivery, were reported in about half of the pregnancies described, these are known to occur more frequently in those with SLE and APS, especially when active disease or other risk factors are present. There are no large-scale, controlled studies evaluating ART outcomes in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases to date.
Finally, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is an increasingly rare but severe complication of ovarian stimulation. OHSS is characterized by capillary leak, fluid overload, and cytokine release syndrome and can lead to thromboembolic events. Comorbidities like hypertension and renal failure, which can go along with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, are risk factors for OHSS. The use of human chorionic gonadotropin to trigger ovulation is also associated with an increased risk for OHSS, so a GnRH agonist trigger may be preferable.
The ACR guideline recommends that individuals with any of these underlying conditions undergo ART only in expert centers. The ovarian stimulation protocol needs to be tailored to the individual patient to minimize risk and optimize outcomes. The overall goal when managing patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases during ART is to establish and maintain disease control with pregnancy-compatible medications (when pregnancy is the goal). With adequate planning, appropriate treatment, and collaboration between obstetricians and rheumatologists, individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases can safely pursue ART and go on to have successful pregnancies.
Dr. Siegel is a 2022-2023 UCB Women’s Health rheumatology fellow in the rheumatology reproductive health program of the Barbara Volcker Center for Women and Rheumatic Diseases at Hospital for Special Surgery/Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. Her clinical and research focus is on reproductive health issues in individuals with rheumatic disease. Dr. Chan is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for a monthly rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice. Follow Dr Chan on Twitter. Dr. Siegel and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article – an editorial collaboration between Medscape and the Hospital for Special Surgery – first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of “reproductive rheumatology” has received growing attention in recent years as we learn more about how autoimmune rheumatic diseases and their treatment affect women of reproductive age. In 2020, the American College of Rheumatology published a comprehensive guideline that includes recommendations and supporting evidence for managing issues related to reproductive health in patients with rheumatic diseases and has since launched an ongoing Reproductive Health Initiative, with the goal of translating established guidelines into practice through various education and awareness campaigns. One area addressed by the guideline that comes up commonly in practice but receives less attention and research is the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Literature is conflicting regarding whether patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases are inherently at increased risk for infertility, defined as failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected intercourse, or subfertility, defined as a delay in conception. Regardless, several factors indirectly contribute to a disproportionate risk for infertility or subfertility in this patient population, including active inflammatory disease, reduced ovarian reserve, and medications.
Patients with subfertility or infertility who desire pregnancy may pursue ovulation induction with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization (IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection with either embryo transfer, or gestational surrogacy. Those who require treatment with cyclophosphamide or who plan to defer pregnancy for whatever reason can opt for oocyte cryopreservation (colloquially known as “egg freezing”). For IVF and oocyte cryopreservation, controlled ovarian stimulation is typically the first step (except in unstimulated, or “natural cycle,” IVF).
Various protocols are used for ovarian stimulation and ovulation induction, the nuances of which are beyond the scope of this article. In general, ovarian stimulation involves gonadotropin therapy (follicle-stimulating hormone and/or human menopausal gonadotropin) administered via scheduled subcutaneous injections to stimulate follicular growth, as well as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists or antagonists to suppress luteinizing hormone, preventing ovulation. Adjunctive oral therapy (clomiphene citrate or letrozole, an aromatase inhibitor) may be used as well. The patient has frequent lab monitoring of hormone levels and transvaginal ultrasounds to measure follicle number and size and, when the timing is right, receives an “ovulation trigger” – either human chorionic gonadotropin or GnRH agonist, depending on the protocol. At this point, transvaginal ultrasound–guided egg retrieval is done under sedation. Recovered oocytes are then either frozen for later use or fertilized in the lab for embryo transfer. Lastly, exogenous hormones are often used: estrogen to support frozen embryo transfers and progesterone for so-called luteal phase support.
ART is not contraindicated in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, but there may be additional factors to consider, particularly for those with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), and antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) without clinical APS.
Ovarian stimulation elevates estrogen levels to varying degrees depending on the patient and the medications used. In all cases, though, peak levels are significantly lower than levels reached during pregnancy. It is well established that elevated estrogen – whether from hormone therapies or pregnancy – significantly increases thrombotic risk, even in healthy people. High-risk patients should receive low-molecular-weight heparin – a prophylactic dose for patients with either positive aPL without clinical APS (including those with SLE) or with obstetric APS, and a therapeutic dose for those with thrombotic APS – during ART procedures.
In patients with SLE, another concern is that increased estrogen will cause disease flare. One case series published in 2017 reported 37 patients with SLE and/or APS who underwent 97 IVF cycles, of which 8% were complicated by flare or thrombotic events. Notably, half of these complications occurred in patients who stopped prescribed therapies (immunomodulatory therapy in two patients with SLE, anticoagulation in two patients with APS) after failure to conceive. In a separate study from 2000 including 19 patients with SLE, APS, or high-titer aPL who underwent 68 IVF cycles, 19% of cycles in patients with SLE were complicated by flare, and no thrombotic events occurred in the cohort. The authors concluded that ovulation induction does not exacerbate SLE or APS. In these studies, the overall pregnancy rates were felt to be consistent with those achieved by the general population through IVF. Although obstetric complications, such as preeclampsia and preterm delivery, were reported in about half of the pregnancies described, these are known to occur more frequently in those with SLE and APS, especially when active disease or other risk factors are present. There are no large-scale, controlled studies evaluating ART outcomes in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases to date.
Finally, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is an increasingly rare but severe complication of ovarian stimulation. OHSS is characterized by capillary leak, fluid overload, and cytokine release syndrome and can lead to thromboembolic events. Comorbidities like hypertension and renal failure, which can go along with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, are risk factors for OHSS. The use of human chorionic gonadotropin to trigger ovulation is also associated with an increased risk for OHSS, so a GnRH agonist trigger may be preferable.
The ACR guideline recommends that individuals with any of these underlying conditions undergo ART only in expert centers. The ovarian stimulation protocol needs to be tailored to the individual patient to minimize risk and optimize outcomes. The overall goal when managing patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases during ART is to establish and maintain disease control with pregnancy-compatible medications (when pregnancy is the goal). With adequate planning, appropriate treatment, and collaboration between obstetricians and rheumatologists, individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases can safely pursue ART and go on to have successful pregnancies.
Dr. Siegel is a 2022-2023 UCB Women’s Health rheumatology fellow in the rheumatology reproductive health program of the Barbara Volcker Center for Women and Rheumatic Diseases at Hospital for Special Surgery/Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. Her clinical and research focus is on reproductive health issues in individuals with rheumatic disease. Dr. Chan is an assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and an attending physician at Hospital for Special Surgery and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. Before moving to New York City, she spent 7 years in private practice in Rhode Island and was a columnist for a monthly rheumatology publication, writing about the challenges of starting life as a full-fledged rheumatologist in a private practice. Follow Dr Chan on Twitter. Dr. Siegel and Dr. Chan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article – an editorial collaboration between Medscape and the Hospital for Special Surgery – first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is evolution’s greatest triumph its worst blunder?
Of all the dazzling achievements of evolution, the most glorious by far is the emergence of the advanced human brain, especially the prefrontal cortex. Homo sapiens (the wise humans) are without doubt the most transformative development in the consequential annals of evolution. It was evolution’s spectacular “moonshot.” Ironically, it may also have been the seed of its destruction.
The unprecedented growth of the human brain over the past 7 million years (tripling in size) was a monumental tipping point in evolution that ultimately disrupted the entire orderly cascade of evolution on Planet Earth. Because of their superior intelligence, Homo sapiens have substantially “tinkered” with the foundations of evolution, such as “natural selection” and “survival of the fittest,” and may eventually change the course of evolution, or even reverse it. It should also be recognized that 20% of the human genome is Neanderthal, and the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Svante Pääbo, the founder of the field of paleogenetics, who demonstrated genetically that Homo sapiens interbred with Homo neanderthalensis (who disappeared 30,000 years ago).
The majestic evolution of the human brain, in both size and complexity, led to monumental changes in the history of humankind compared to their primitive predecessors. Thanks to a superior cerebral cortex, humans developed traits and abilities that were nonexistent, even unimaginable, in the rest of animal kingdom, including primates and other mammals. These include thoughts; speech (hundreds of languages), spoken and written, to communicate among themselves; composed music and created numerous instruments to play it; invented mathematics, physics, and chemistry; developed agriculture to sustain and feed the masses; built homes, palaces, and pyramids, with water and sewage systems; hatched hundreds of religions and built thousands of houses of worship; built machines to transport themselves (cars, trains, ships, planes, and space shuttles); paved airports and countless miles of roads and railways; established companies, universities, hospitals, and research laboratories; built sports facilities such as stadiums for Olympic games and all its athletics; created hotels, restaurants, coffee shops, newspapers, and magazines; discovered the amazing DNA double helix and its genome with 23,000 coding genes containing instructions to build the brain and 200 other body tissues; developed surgeries and invented medications for diseases that would have killed millions every year; and established paper money to replace gold and silver coins. Humans established governments that included monarchies, dictatorships, democracies, and pseudodemocracies; stipulated constitutions, laws, and regulations to maintain various societies; and created several civilizations around the world that thrived and then faded. Over the past century, the advanced human brain elevated human existence to a higher sophistication with technologies such as electricity, phones, computers, internet, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Using powerful rockets and space stations, humans have begun to expand their influence to the moon and planets of the solar system. Humans are very likely to continue achieving what evolution could never have done without evolving the human brain to become the most powerful force in nature.
The key ingredient of the brain that has enabled humans to achieve so much is the development of an advanced cognition, with superior functions that far exceed those of other living organisms. These include neurocognitive functions such as memory and attention, and executive functions that include planning, problem-solving, decision-making, abstract thinking, and insight. Those cognitive functions generate lofty prose, splendiferous poetry, and heavenly symphonies that inspire those who create it and others. The human brain also developed social cognition, with empathy, theory of mind, recognition of facial expressions, and courtship rituals that can trigger infatuation and love. Homo sapiens can experience a wide range of emotions in addition to love and attachment (necessary for procreation), including shame, guilt, surprise, embarrassment, disgust, and indifference, and a unique sense of right and wrong.
Perhaps the most distinctive human attribute, generated by an advanced prefrontal cortex, is a belief system that includes philosophy, politics, religion, and faith. Hundreds of different religions sprouted throughout human history (each claiming a monopoly on “the truth”), mandating rituals and behaviors, but also promoting a profound and unshakable belief in a divine “higher being” and an afterlife that mitigates the fear of death. Humans, unlike other animals, are painfully aware of mortality and the inevitability of death. Faith is an antidote for thanatophobia. Unfortunately, religious beliefs often generated severe and protracted schisms and warfare, with fatal consequences for their followers.
The anti-evolution aspect of the advanced brain
Despite remarkable talents and achievements, the unprecedented evolutionary expansion of the human brain also has a detrimental downside. The same intellectual power that led to astonishing positive accomplishments has a wicked side as well. While most animals have a predator, humans have become the “omni-predator” that preys on all living things. The balanced ecosystems of animals and plants has been dominated and disrupted by humans. Thousands of species that evolution had so ingeniously spawned became extinct because of human actions. The rainforests, jewels of nature’s plantation system, were victimized by human indifference to the deleterious effects on nature and climate. The excavation of coal and oil, exploited as necessary sources of energy for societal infrastructure, came back to haunt humans with climate consequences. In many ways, human “progress” corrupted evolution and dismantled its components. Survival of the fittest among various species was whittled down to “survival of humans” (and their domesticated animals) at the expense of all other organisms, animals, or plants.
Among Homo sapiens, momentous scientific, medical, and technological advances completely undermined the principle of survival of the fittest. Very premature infants, who would have certainly died, were kept alive. Children with disabling genetic disorders who would have perished in childhood were kept alive into the age of procreation, perpetuating the genetic mutations. The discovery of antibiotic and antiviral medications, and especially vaccines, ensured the survival of millions of humans who would have succumbed to infections. With evolution’s natural selection, humans who survived severe infections without medications would have passed on their “infection-resistant genes” to their progeny. The triumph of human medical progress can be conceptualized as a setback for the principles of evolution.
Continue to: The most malignant...
The most malignant consequence of the exceptional human brain is the evil of which it is capable. Human ingenuity led to the development of weapons of individual killing (guns), large-scale murder (machine guns), and massive destruction (nuclear weapons). And because aggression and warfare are an inherent part of human nature, the most potent predator for a human is another human. The history of humans is riddled with conflict and death on a large scale. Ironically, many wars were instigated by various religious groups around the world, who developed intense hostility towards one another.
There are other downsides to the advanced human brain. It can channel its talents and skills into unimaginably wicked and depraved behaviors, such as premeditated and well-planned murder, slavery, cults, child abuse, domestic abuse, pornography, fascism, dictatorships, and political corruption. Astonishingly, the same brain that can be loving, kind, friendly, and empathetic can suddenly become hateful, vengeful, cruel, vile, sinister, vicious, diabolical, and capable of unimaginable violence and atrocities. The advanced human brain definitely has a very dark side.
Finally, unlike other members of the animal kingdom, the human brain generates its virtual counterpart: the highly complex human mind, which is prone to various maladies, labeled as “psychiatric disorders.” No other animal species develops delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, melancholia, mania, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety, panic attacks, posttraumatic stress disorder, psychopathy, narcissistic and borderline personality disorders, alcohol addiction, and drug abuse. Homo sapiens are the only species whose members decide to end their own life in large numbers. About 25% of human minds are afflicted with one or more of those psychiatric ailments.1,2 The redeeming grace of the large human brain is that it led to the development of pharmacologic and somatic treatments for most of them, including psychotherapy, which is a uniquely human treatment strategy that can mend many psychiatric disorders.
Evolution may not realize what it hath wrought when it evolved the dramatically expanded human brain, with its extraordinary cognition. This awe-inspiring “biological computer” can be creative and adaptive, with superlative survival abilities, but it can also degenerate and become nefarious, villainous, murderous, and even demonic. The human brain has essentially brought evolution to a screeching halt and may at some point end up destroying Earth and all of its Homo sapien inhabitants, who may foolishly use their weapons of mass destruction. The historic achievement of evolution has become the ultimate example of “the law of unintended consequences.”
1. Robin LN, Regier DA. Psychiatric Disorders in America: The Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. Free Press; 1990.
2. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Mental Health Disorder Statistics. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/mental-health-disorder-statistics
Of all the dazzling achievements of evolution, the most glorious by far is the emergence of the advanced human brain, especially the prefrontal cortex. Homo sapiens (the wise humans) are without doubt the most transformative development in the consequential annals of evolution. It was evolution’s spectacular “moonshot.” Ironically, it may also have been the seed of its destruction.
The unprecedented growth of the human brain over the past 7 million years (tripling in size) was a monumental tipping point in evolution that ultimately disrupted the entire orderly cascade of evolution on Planet Earth. Because of their superior intelligence, Homo sapiens have substantially “tinkered” with the foundations of evolution, such as “natural selection” and “survival of the fittest,” and may eventually change the course of evolution, or even reverse it. It should also be recognized that 20% of the human genome is Neanderthal, and the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Svante Pääbo, the founder of the field of paleogenetics, who demonstrated genetically that Homo sapiens interbred with Homo neanderthalensis (who disappeared 30,000 years ago).
The majestic evolution of the human brain, in both size and complexity, led to monumental changes in the history of humankind compared to their primitive predecessors. Thanks to a superior cerebral cortex, humans developed traits and abilities that were nonexistent, even unimaginable, in the rest of animal kingdom, including primates and other mammals. These include thoughts; speech (hundreds of languages), spoken and written, to communicate among themselves; composed music and created numerous instruments to play it; invented mathematics, physics, and chemistry; developed agriculture to sustain and feed the masses; built homes, palaces, and pyramids, with water and sewage systems; hatched hundreds of religions and built thousands of houses of worship; built machines to transport themselves (cars, trains, ships, planes, and space shuttles); paved airports and countless miles of roads and railways; established companies, universities, hospitals, and research laboratories; built sports facilities such as stadiums for Olympic games and all its athletics; created hotels, restaurants, coffee shops, newspapers, and magazines; discovered the amazing DNA double helix and its genome with 23,000 coding genes containing instructions to build the brain and 200 other body tissues; developed surgeries and invented medications for diseases that would have killed millions every year; and established paper money to replace gold and silver coins. Humans established governments that included monarchies, dictatorships, democracies, and pseudodemocracies; stipulated constitutions, laws, and regulations to maintain various societies; and created several civilizations around the world that thrived and then faded. Over the past century, the advanced human brain elevated human existence to a higher sophistication with technologies such as electricity, phones, computers, internet, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Using powerful rockets and space stations, humans have begun to expand their influence to the moon and planets of the solar system. Humans are very likely to continue achieving what evolution could never have done without evolving the human brain to become the most powerful force in nature.
The key ingredient of the brain that has enabled humans to achieve so much is the development of an advanced cognition, with superior functions that far exceed those of other living organisms. These include neurocognitive functions such as memory and attention, and executive functions that include planning, problem-solving, decision-making, abstract thinking, and insight. Those cognitive functions generate lofty prose, splendiferous poetry, and heavenly symphonies that inspire those who create it and others. The human brain also developed social cognition, with empathy, theory of mind, recognition of facial expressions, and courtship rituals that can trigger infatuation and love. Homo sapiens can experience a wide range of emotions in addition to love and attachment (necessary for procreation), including shame, guilt, surprise, embarrassment, disgust, and indifference, and a unique sense of right and wrong.
Perhaps the most distinctive human attribute, generated by an advanced prefrontal cortex, is a belief system that includes philosophy, politics, religion, and faith. Hundreds of different religions sprouted throughout human history (each claiming a monopoly on “the truth”), mandating rituals and behaviors, but also promoting a profound and unshakable belief in a divine “higher being” and an afterlife that mitigates the fear of death. Humans, unlike other animals, are painfully aware of mortality and the inevitability of death. Faith is an antidote for thanatophobia. Unfortunately, religious beliefs often generated severe and protracted schisms and warfare, with fatal consequences for their followers.
The anti-evolution aspect of the advanced brain
Despite remarkable talents and achievements, the unprecedented evolutionary expansion of the human brain also has a detrimental downside. The same intellectual power that led to astonishing positive accomplishments has a wicked side as well. While most animals have a predator, humans have become the “omni-predator” that preys on all living things. The balanced ecosystems of animals and plants has been dominated and disrupted by humans. Thousands of species that evolution had so ingeniously spawned became extinct because of human actions. The rainforests, jewels of nature’s plantation system, were victimized by human indifference to the deleterious effects on nature and climate. The excavation of coal and oil, exploited as necessary sources of energy for societal infrastructure, came back to haunt humans with climate consequences. In many ways, human “progress” corrupted evolution and dismantled its components. Survival of the fittest among various species was whittled down to “survival of humans” (and their domesticated animals) at the expense of all other organisms, animals, or plants.
Among Homo sapiens, momentous scientific, medical, and technological advances completely undermined the principle of survival of the fittest. Very premature infants, who would have certainly died, were kept alive. Children with disabling genetic disorders who would have perished in childhood were kept alive into the age of procreation, perpetuating the genetic mutations. The discovery of antibiotic and antiviral medications, and especially vaccines, ensured the survival of millions of humans who would have succumbed to infections. With evolution’s natural selection, humans who survived severe infections without medications would have passed on their “infection-resistant genes” to their progeny. The triumph of human medical progress can be conceptualized as a setback for the principles of evolution.
Continue to: The most malignant...
The most malignant consequence of the exceptional human brain is the evil of which it is capable. Human ingenuity led to the development of weapons of individual killing (guns), large-scale murder (machine guns), and massive destruction (nuclear weapons). And because aggression and warfare are an inherent part of human nature, the most potent predator for a human is another human. The history of humans is riddled with conflict and death on a large scale. Ironically, many wars were instigated by various religious groups around the world, who developed intense hostility towards one another.
There are other downsides to the advanced human brain. It can channel its talents and skills into unimaginably wicked and depraved behaviors, such as premeditated and well-planned murder, slavery, cults, child abuse, domestic abuse, pornography, fascism, dictatorships, and political corruption. Astonishingly, the same brain that can be loving, kind, friendly, and empathetic can suddenly become hateful, vengeful, cruel, vile, sinister, vicious, diabolical, and capable of unimaginable violence and atrocities. The advanced human brain definitely has a very dark side.
Finally, unlike other members of the animal kingdom, the human brain generates its virtual counterpart: the highly complex human mind, which is prone to various maladies, labeled as “psychiatric disorders.” No other animal species develops delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, melancholia, mania, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety, panic attacks, posttraumatic stress disorder, psychopathy, narcissistic and borderline personality disorders, alcohol addiction, and drug abuse. Homo sapiens are the only species whose members decide to end their own life in large numbers. About 25% of human minds are afflicted with one or more of those psychiatric ailments.1,2 The redeeming grace of the large human brain is that it led to the development of pharmacologic and somatic treatments for most of them, including psychotherapy, which is a uniquely human treatment strategy that can mend many psychiatric disorders.
Evolution may not realize what it hath wrought when it evolved the dramatically expanded human brain, with its extraordinary cognition. This awe-inspiring “biological computer” can be creative and adaptive, with superlative survival abilities, but it can also degenerate and become nefarious, villainous, murderous, and even demonic. The human brain has essentially brought evolution to a screeching halt and may at some point end up destroying Earth and all of its Homo sapien inhabitants, who may foolishly use their weapons of mass destruction. The historic achievement of evolution has become the ultimate example of “the law of unintended consequences.”
Of all the dazzling achievements of evolution, the most glorious by far is the emergence of the advanced human brain, especially the prefrontal cortex. Homo sapiens (the wise humans) are without doubt the most transformative development in the consequential annals of evolution. It was evolution’s spectacular “moonshot.” Ironically, it may also have been the seed of its destruction.
The unprecedented growth of the human brain over the past 7 million years (tripling in size) was a monumental tipping point in evolution that ultimately disrupted the entire orderly cascade of evolution on Planet Earth. Because of their superior intelligence, Homo sapiens have substantially “tinkered” with the foundations of evolution, such as “natural selection” and “survival of the fittest,” and may eventually change the course of evolution, or even reverse it. It should also be recognized that 20% of the human genome is Neanderthal, and the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Svante Pääbo, the founder of the field of paleogenetics, who demonstrated genetically that Homo sapiens interbred with Homo neanderthalensis (who disappeared 30,000 years ago).
The majestic evolution of the human brain, in both size and complexity, led to monumental changes in the history of humankind compared to their primitive predecessors. Thanks to a superior cerebral cortex, humans developed traits and abilities that were nonexistent, even unimaginable, in the rest of animal kingdom, including primates and other mammals. These include thoughts; speech (hundreds of languages), spoken and written, to communicate among themselves; composed music and created numerous instruments to play it; invented mathematics, physics, and chemistry; developed agriculture to sustain and feed the masses; built homes, palaces, and pyramids, with water and sewage systems; hatched hundreds of religions and built thousands of houses of worship; built machines to transport themselves (cars, trains, ships, planes, and space shuttles); paved airports and countless miles of roads and railways; established companies, universities, hospitals, and research laboratories; built sports facilities such as stadiums for Olympic games and all its athletics; created hotels, restaurants, coffee shops, newspapers, and magazines; discovered the amazing DNA double helix and its genome with 23,000 coding genes containing instructions to build the brain and 200 other body tissues; developed surgeries and invented medications for diseases that would have killed millions every year; and established paper money to replace gold and silver coins. Humans established governments that included monarchies, dictatorships, democracies, and pseudodemocracies; stipulated constitutions, laws, and regulations to maintain various societies; and created several civilizations around the world that thrived and then faded. Over the past century, the advanced human brain elevated human existence to a higher sophistication with technologies such as electricity, phones, computers, internet, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Using powerful rockets and space stations, humans have begun to expand their influence to the moon and planets of the solar system. Humans are very likely to continue achieving what evolution could never have done without evolving the human brain to become the most powerful force in nature.
The key ingredient of the brain that has enabled humans to achieve so much is the development of an advanced cognition, with superior functions that far exceed those of other living organisms. These include neurocognitive functions such as memory and attention, and executive functions that include planning, problem-solving, decision-making, abstract thinking, and insight. Those cognitive functions generate lofty prose, splendiferous poetry, and heavenly symphonies that inspire those who create it and others. The human brain also developed social cognition, with empathy, theory of mind, recognition of facial expressions, and courtship rituals that can trigger infatuation and love. Homo sapiens can experience a wide range of emotions in addition to love and attachment (necessary for procreation), including shame, guilt, surprise, embarrassment, disgust, and indifference, and a unique sense of right and wrong.
Perhaps the most distinctive human attribute, generated by an advanced prefrontal cortex, is a belief system that includes philosophy, politics, religion, and faith. Hundreds of different religions sprouted throughout human history (each claiming a monopoly on “the truth”), mandating rituals and behaviors, but also promoting a profound and unshakable belief in a divine “higher being” and an afterlife that mitigates the fear of death. Humans, unlike other animals, are painfully aware of mortality and the inevitability of death. Faith is an antidote for thanatophobia. Unfortunately, religious beliefs often generated severe and protracted schisms and warfare, with fatal consequences for their followers.
The anti-evolution aspect of the advanced brain
Despite remarkable talents and achievements, the unprecedented evolutionary expansion of the human brain also has a detrimental downside. The same intellectual power that led to astonishing positive accomplishments has a wicked side as well. While most animals have a predator, humans have become the “omni-predator” that preys on all living things. The balanced ecosystems of animals and plants has been dominated and disrupted by humans. Thousands of species that evolution had so ingeniously spawned became extinct because of human actions. The rainforests, jewels of nature’s plantation system, were victimized by human indifference to the deleterious effects on nature and climate. The excavation of coal and oil, exploited as necessary sources of energy for societal infrastructure, came back to haunt humans with climate consequences. In many ways, human “progress” corrupted evolution and dismantled its components. Survival of the fittest among various species was whittled down to “survival of humans” (and their domesticated animals) at the expense of all other organisms, animals, or plants.
Among Homo sapiens, momentous scientific, medical, and technological advances completely undermined the principle of survival of the fittest. Very premature infants, who would have certainly died, were kept alive. Children with disabling genetic disorders who would have perished in childhood were kept alive into the age of procreation, perpetuating the genetic mutations. The discovery of antibiotic and antiviral medications, and especially vaccines, ensured the survival of millions of humans who would have succumbed to infections. With evolution’s natural selection, humans who survived severe infections without medications would have passed on their “infection-resistant genes” to their progeny. The triumph of human medical progress can be conceptualized as a setback for the principles of evolution.
Continue to: The most malignant...
The most malignant consequence of the exceptional human brain is the evil of which it is capable. Human ingenuity led to the development of weapons of individual killing (guns), large-scale murder (machine guns), and massive destruction (nuclear weapons). And because aggression and warfare are an inherent part of human nature, the most potent predator for a human is another human. The history of humans is riddled with conflict and death on a large scale. Ironically, many wars were instigated by various religious groups around the world, who developed intense hostility towards one another.
There are other downsides to the advanced human brain. It can channel its talents and skills into unimaginably wicked and depraved behaviors, such as premeditated and well-planned murder, slavery, cults, child abuse, domestic abuse, pornography, fascism, dictatorships, and political corruption. Astonishingly, the same brain that can be loving, kind, friendly, and empathetic can suddenly become hateful, vengeful, cruel, vile, sinister, vicious, diabolical, and capable of unimaginable violence and atrocities. The advanced human brain definitely has a very dark side.
Finally, unlike other members of the animal kingdom, the human brain generates its virtual counterpart: the highly complex human mind, which is prone to various maladies, labeled as “psychiatric disorders.” No other animal species develops delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, melancholia, mania, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety, panic attacks, posttraumatic stress disorder, psychopathy, narcissistic and borderline personality disorders, alcohol addiction, and drug abuse. Homo sapiens are the only species whose members decide to end their own life in large numbers. About 25% of human minds are afflicted with one or more of those psychiatric ailments.1,2 The redeeming grace of the large human brain is that it led to the development of pharmacologic and somatic treatments for most of them, including psychotherapy, which is a uniquely human treatment strategy that can mend many psychiatric disorders.
Evolution may not realize what it hath wrought when it evolved the dramatically expanded human brain, with its extraordinary cognition. This awe-inspiring “biological computer” can be creative and adaptive, with superlative survival abilities, but it can also degenerate and become nefarious, villainous, murderous, and even demonic. The human brain has essentially brought evolution to a screeching halt and may at some point end up destroying Earth and all of its Homo sapien inhabitants, who may foolishly use their weapons of mass destruction. The historic achievement of evolution has become the ultimate example of “the law of unintended consequences.”
1. Robin LN, Regier DA. Psychiatric Disorders in America: The Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. Free Press; 1990.
2. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Mental Health Disorder Statistics. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/mental-health-disorder-statistics
1. Robin LN, Regier DA. Psychiatric Disorders in America: The Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. Free Press; 1990.
2. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Mental Health Disorder Statistics. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/mental-health-disorder-statistics
Innovation in GI: What’s the next big thing?
Dear colleagues,
Innovation is the livelihood of our field, driving major advances in endoscopy and attracting many of us to Gastroenterology. From the development of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography to the wide-spread adoption of third space endoscopy, we continue to push the boundaries of our practice. But what is the next big disruption in GI, and how will it impact us? Dr. Jeremy Glissen Brown discusses the application of artificial intelligence in GI highlighting its promise but also raising important questions. Dr. Raman Muthusamy elaborates on single-use endoscopes – are they the wave of the future in preventing infection and meeting patient preference? Or will their long-term cost and environmental impact limit their use? I welcome your own thoughts on disruptive innovation in Gastroenterology – share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN and by email at [email protected].
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is an associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
The AI revolution, with some important caveats
BY JEREMY R. GLISSEN BROWN, MD, MSC
In 2018, Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Agency approved the first artificial intelligence (AI)–based tool, a computer-aided diagnosis system (CADx) for use in clinical practice.1 Since that time, we have seen regulatory approval for a variety of deep learning and AI-based tools in endoscopy and beyond. In addition, there has been an enormous amount of commercial and research interest in AI-based tools in clinical medicine and gastroenterology, and it is almost impossible to open a major gastroenterology journal or go to an academic conference without encountering a slew of AI-based projects.
Many thought and industry leaders say that we are in the midst of an AI revolution in gastroenterology. Indeed, we are at a period of unprecedented growth for deep learning and AI for several reasons, including a recent shift toward data-driven approaches, advancement of machine-learning techniques, and increased computing power. There is, however, also an unprecedented amount of scrutiny and thoughtful conversation about the role AI might play in clinical practice and how we use and regulate these tools in the clinical setting. We are thus in a unique position to ask ourselves the essential question: “Are we on the cusp of an AI revolution in gastroenterology, or are we seeing the release of medical software that is perhaps at best useful in a niche environment and at worse a hype-driven novelty without much clinical benefit?” We will use the most popular use-case, computer aided detection (CADe) of polyps in the colon, to explore this question. In the end, I believe that deep-learning technology will fundamentally change the way we practice gastroenterology. However, this is the perfect time to explore what this means now, and what we can do to shape what it will mean for the future.
CADe: Promise and questions
CADe is a computer vision task that involves localization, such as finding a polyp during colonoscopy and highlighting it with a hollow box. CADe in colonoscopy is perhaps the most well-studied application of deep learning in GI endoscopy to date and is furthest along in the development-implementation pipeline. Because of this, it is an ideal use-case for examining both the evidence that currently supports its use as well as the questions that have come up as we are starting to see CADe algorithms deployed in clinical practice. It is honestly astounding to think that, just 5 years ago, we were talking about CADe as a research concept. While early efforts applying traditional machine learning date back at least to the 1990s, we started to see prospective studies of CADe systems with undetectable or nearly undetectable latency in 2019.2 Since that time we have seen the publication of at least 10 randomized clinical trials involving CADe.
CADe clearly has an impact on some of the conventional quality metrics we use for colonoscopy. While there is considerable heterogeneity in region and design among these trials, most show a significant increase in adenoma detection rate (ADR) and adenomas per colonoscopy. Tandem studies show decreases in adenoma miss rate, and at least one study showed a decrease in sessile serrated lesion miss rate as well. In one of the first randomized, controlled trials across multiple endoscopy centers in Italy, Repici and colleagues showed an increase in ADR from 40.4% in the control group to 54.8% in the CADe group (RR, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.45).3 Because of pioneering trials such as this one, there are currently several CADe systems that have received regulatory approval in Europe, Asia, and the United States and are being deployed commercially.
It is also clear that the technology is there. In clinical practice, the Food and Drug Administration–approved systems work smoothly, with little to no detectable latency and generally low false-positive and false-negative rates. With clinical deployment, however, we have seen the emergence of healthy debate surrounding every aspect of this task-specific AI. On the development side, important questions include transparency of development data, ensuring that algorithm development is ethical and equitable (as deep learning is susceptible to exacerbating human biases) and methods of data labeling. On the deployment level, important concerns include proper regulation of locked versus “open” algorithms and downstream effects on cost.
In addition, with CADe we have seen a variety of clinical questions crop up because of the novelty of the technology. These include the concern that the increase in ADR we have seen thus far is driven in large part by diminutive and small adenomas (with healthy debate in turn as to these entities’ influence on interval colorectal cancer rates), the effect CADe might have on fellowship training to detect polyps with the human eye, and whether the technology affects sessile serrated lesion detection rates or not. The great thing about such questions is that they have inspired novel research related to CADe in the clinical setting, including how CADe affects trainee ADR, how CADe affects gaze patterns, and how CADe affects recommended surveillance intervals.
CADx, novel applications, and the future
Though there is not space to expand in this particular forum, it is safe to say that with the advancement of CADx in endoscopy and colonoscopy, we have seen similar and novel questions come up. The beautiful thing about all of this is that we are just scratching the surface of what is achievable with deep learning. We have started to see novel projects utilizing deep-learning algorithms, from detecting cirrhosis on ECG to automatically classifying stool consistency on the Bristol Stool Scale from pictures of stool. I ultimately do think that the deployment of AI tools will fundamentally change the way we practice and think about gastroenterology. We are at an incredibly exciting time where we as physicians have the power to shape what that looks like, how we think about AI deployment and regulation and where we go from here.
Dr. Glissen Brown is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. He has served as a consultant for Medtronic.
References
1. Aisu N et al. PLOS Digital Health. 2021 Jan 18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000001.
2. Wang P et al. Gut. 2019 Oct;68(10):1813-9.
3. Repici A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Aug;159(2):512-20.e7.
What’s the future of single-use endoscopes?
BY V. RAMAN MUTHUSAMY, MD, MAS
Single-use endoscopes have been proposed as a definitive solution to the risk of endoscope-transmitted infections. While these infections have been reported for several decades, they have traditionally been associated with identified breaches in the reprocessing protocol. In 2015, numerous cases of duodenoscope-transmitted infections were reported after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures. Many, if not most, of these cases were not associated with identified deviations from standard high-level disinfection protocols and occurred at high-volume experienced facilities. A subsequent FDA postmarket surveillance study found contamination rates were linked with potentially pathogenic bacteria in approximately 5% of duodenoscopes. Thus, amid growing concerns about the ability to adequately clean these complex devices, these events prompted the development of single-use duodenoscopes. Given the multifactorial causes leading to contaminated duodenoscopes, the advantages of such single-use devices are their ability to ensure the elimination of the potential of infection transmission as these devices are never reused. In addition to this primary benefit, the ability to create single-use devices could lead to more easily available specialty scopes and allow variations in endoscope design that could improve ergonomics. Single-use devices may also expand the ability to provide endoscopic services by eliminating the need for device reprocessing equipment at low-volume sites. However, several concerns have been raised regarding their use, especially if it were to become widespread. These include issues of device quality and performance (potentially leading to more failed cases or adverse events), cost, their environmental impact and current uncertainty regarding their indications for use. Furthermore, new alternatives such as reusable devices with partially disposable components or future low-temperature sterilization options may minimize the need for such devices. We will briefly discuss these issues in more detail below.
Given that nearly all cases of GI device–transmitted infections where standard reprocessing protocols were followed have occurred in duodenoscopes, I will focus on single-use duodenoscopes in this article. It is important that we reassure our patients and colleagues that standard reprocessing appears to be extremely effective with all other types of devices, including elevator containing linear echoendoscopes. Studies investigating the causes of why duodenoscopes have primarily been associated with device-transmitted outbreaks have focused on the complexity of the elevator including its recesses, fixed end-cap and wire channels. However, culturing has shown that up to one-third of contamination may occur in the instrument channels or in the region of the biopsy cap, leading to some potential residual sites of infection even when newly developed reusable devices with disposable elevators/end-caps are utilized.1 Another challenge with reprocessing is the ability to prove residual contamination does not exist. While culturing the devices after reprocessing is most used, it should be noted many sites with outbreaks failed to culture the culprit bacteria from the devices as accessing the sites of contamination can be challenging. The use of other markers of residual contamination such as ATP and tests for residual blood/protein have yielded variable results. Specifically, ATP testing has not correlated well with culture results but may be helpful in assessing the quality of manual cleaning.2
These challenges have made the concept of single-use devices more appealing given the lack of a need reprocess devices or validate cleaning efficacy. Currently, there are two FDA-approved devices on the market, but the published literature to date has largely involved one of these devices. To date, in four published studies that have assessed the clinical performance of single-use duodenoscopes in over 400 patients, procedural success rates have ranged from 91% to 97% with adverse event rates and endoscopist satisfaction scores comparable to reusable devices. Most of these users were expert biliary endoscopists and more data are needed regarding the performance of the device in lower-volume and nonexpert users. While indications for use in these studies have varied, I feel that there are four potential scenarios to utilize these devices: in patients with known multidrug-resistant organisms undergoing ERCP; to facilitate logistics/operations when a reusable device is not available; in critically ill patients who would not tolerate a scope-acquired infection; and in procedures associated with a risk of bacteremia.
While preliminary data suggest single-use duodenoscopes are safe and effective in expert hands, concerns exist regarding their implementation more broadly into clinical practice. First, the devices cost between $1,500-3,000, making them impractical for many health systems. One study estimated the break-even cost of the device to be $800-1,300 based on variation in site volume and device contamination rates.3 However, it should be noted that current enhanced reprocessing protocols for reusable devices may add an additional $75,000-$400,000 per year based on center volume.4 In the United States, there is currently payment by federal and some commercial payors that cover part or all of the device cost, but whether this will continue long-term is unclear. In addition, there is significant concern regarding the environmental impact of a broader mover to single-use devices. Reprocessing programs do exist for these devices, but detailed analyses regarding the environmental effects of a strategy using single-use versus reusable devices and the waste generated from each are needed.
Finally, while primarily created to avoid device-related infection transmission, other benefits can be realized with single-use devices. The potential for ergonomic enhancements (variable handle sizes or shaft stiffness, R- and L-handed scopes) as well as the creation of specialty devices (extra-long or thin devices, devices with special optical or rotational capabilities) may become more feasible with a single-use platform. Finally, the pace of endoscopic innovation and refinement is likely to quicken with a single use platform, and new advancements can be incorporated in a timelier manner.
Conclusion
In summary, I believe single-use devices offer the potential to improve the safety of endoscopic procedures as well as improve procedural access, enhance ergonomics, and foster and expedite device innovation. However, reductions in cost, refining their indications, and developing recycling programs to minimize their environmental impact will be essential before more widespread adoption is achieved.
Dr. Muthusamy is a professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the medical director of endoscopy at the UCLA Health System. He reported relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Motus GI, Endogastric Solutions, and Capsovision.
References
1. Bartles RL et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Aug;88(2):306-13.e2.
2. Day LW et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Jan;93(1):11-33.e6.
3. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019 Nov;68(11):1915-7.
4. Bomman S et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Aug 23;9(9):E1404-12.
Dear colleagues,
Innovation is the livelihood of our field, driving major advances in endoscopy and attracting many of us to Gastroenterology. From the development of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography to the wide-spread adoption of third space endoscopy, we continue to push the boundaries of our practice. But what is the next big disruption in GI, and how will it impact us? Dr. Jeremy Glissen Brown discusses the application of artificial intelligence in GI highlighting its promise but also raising important questions. Dr. Raman Muthusamy elaborates on single-use endoscopes – are they the wave of the future in preventing infection and meeting patient preference? Or will their long-term cost and environmental impact limit their use? I welcome your own thoughts on disruptive innovation in Gastroenterology – share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN and by email at [email protected].
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is an associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
The AI revolution, with some important caveats
BY JEREMY R. GLISSEN BROWN, MD, MSC
In 2018, Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Agency approved the first artificial intelligence (AI)–based tool, a computer-aided diagnosis system (CADx) for use in clinical practice.1 Since that time, we have seen regulatory approval for a variety of deep learning and AI-based tools in endoscopy and beyond. In addition, there has been an enormous amount of commercial and research interest in AI-based tools in clinical medicine and gastroenterology, and it is almost impossible to open a major gastroenterology journal or go to an academic conference without encountering a slew of AI-based projects.
Many thought and industry leaders say that we are in the midst of an AI revolution in gastroenterology. Indeed, we are at a period of unprecedented growth for deep learning and AI for several reasons, including a recent shift toward data-driven approaches, advancement of machine-learning techniques, and increased computing power. There is, however, also an unprecedented amount of scrutiny and thoughtful conversation about the role AI might play in clinical practice and how we use and regulate these tools in the clinical setting. We are thus in a unique position to ask ourselves the essential question: “Are we on the cusp of an AI revolution in gastroenterology, or are we seeing the release of medical software that is perhaps at best useful in a niche environment and at worse a hype-driven novelty without much clinical benefit?” We will use the most popular use-case, computer aided detection (CADe) of polyps in the colon, to explore this question. In the end, I believe that deep-learning technology will fundamentally change the way we practice gastroenterology. However, this is the perfect time to explore what this means now, and what we can do to shape what it will mean for the future.
CADe: Promise and questions
CADe is a computer vision task that involves localization, such as finding a polyp during colonoscopy and highlighting it with a hollow box. CADe in colonoscopy is perhaps the most well-studied application of deep learning in GI endoscopy to date and is furthest along in the development-implementation pipeline. Because of this, it is an ideal use-case for examining both the evidence that currently supports its use as well as the questions that have come up as we are starting to see CADe algorithms deployed in clinical practice. It is honestly astounding to think that, just 5 years ago, we were talking about CADe as a research concept. While early efforts applying traditional machine learning date back at least to the 1990s, we started to see prospective studies of CADe systems with undetectable or nearly undetectable latency in 2019.2 Since that time we have seen the publication of at least 10 randomized clinical trials involving CADe.
CADe clearly has an impact on some of the conventional quality metrics we use for colonoscopy. While there is considerable heterogeneity in region and design among these trials, most show a significant increase in adenoma detection rate (ADR) and adenomas per colonoscopy. Tandem studies show decreases in adenoma miss rate, and at least one study showed a decrease in sessile serrated lesion miss rate as well. In one of the first randomized, controlled trials across multiple endoscopy centers in Italy, Repici and colleagues showed an increase in ADR from 40.4% in the control group to 54.8% in the CADe group (RR, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.45).3 Because of pioneering trials such as this one, there are currently several CADe systems that have received regulatory approval in Europe, Asia, and the United States and are being deployed commercially.
It is also clear that the technology is there. In clinical practice, the Food and Drug Administration–approved systems work smoothly, with little to no detectable latency and generally low false-positive and false-negative rates. With clinical deployment, however, we have seen the emergence of healthy debate surrounding every aspect of this task-specific AI. On the development side, important questions include transparency of development data, ensuring that algorithm development is ethical and equitable (as deep learning is susceptible to exacerbating human biases) and methods of data labeling. On the deployment level, important concerns include proper regulation of locked versus “open” algorithms and downstream effects on cost.
In addition, with CADe we have seen a variety of clinical questions crop up because of the novelty of the technology. These include the concern that the increase in ADR we have seen thus far is driven in large part by diminutive and small adenomas (with healthy debate in turn as to these entities’ influence on interval colorectal cancer rates), the effect CADe might have on fellowship training to detect polyps with the human eye, and whether the technology affects sessile serrated lesion detection rates or not. The great thing about such questions is that they have inspired novel research related to CADe in the clinical setting, including how CADe affects trainee ADR, how CADe affects gaze patterns, and how CADe affects recommended surveillance intervals.
CADx, novel applications, and the future
Though there is not space to expand in this particular forum, it is safe to say that with the advancement of CADx in endoscopy and colonoscopy, we have seen similar and novel questions come up. The beautiful thing about all of this is that we are just scratching the surface of what is achievable with deep learning. We have started to see novel projects utilizing deep-learning algorithms, from detecting cirrhosis on ECG to automatically classifying stool consistency on the Bristol Stool Scale from pictures of stool. I ultimately do think that the deployment of AI tools will fundamentally change the way we practice and think about gastroenterology. We are at an incredibly exciting time where we as physicians have the power to shape what that looks like, how we think about AI deployment and regulation and where we go from here.
Dr. Glissen Brown is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. He has served as a consultant for Medtronic.
References
1. Aisu N et al. PLOS Digital Health. 2021 Jan 18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000001.
2. Wang P et al. Gut. 2019 Oct;68(10):1813-9.
3. Repici A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Aug;159(2):512-20.e7.
What’s the future of single-use endoscopes?
BY V. RAMAN MUTHUSAMY, MD, MAS
Single-use endoscopes have been proposed as a definitive solution to the risk of endoscope-transmitted infections. While these infections have been reported for several decades, they have traditionally been associated with identified breaches in the reprocessing protocol. In 2015, numerous cases of duodenoscope-transmitted infections were reported after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures. Many, if not most, of these cases were not associated with identified deviations from standard high-level disinfection protocols and occurred at high-volume experienced facilities. A subsequent FDA postmarket surveillance study found contamination rates were linked with potentially pathogenic bacteria in approximately 5% of duodenoscopes. Thus, amid growing concerns about the ability to adequately clean these complex devices, these events prompted the development of single-use duodenoscopes. Given the multifactorial causes leading to contaminated duodenoscopes, the advantages of such single-use devices are their ability to ensure the elimination of the potential of infection transmission as these devices are never reused. In addition to this primary benefit, the ability to create single-use devices could lead to more easily available specialty scopes and allow variations in endoscope design that could improve ergonomics. Single-use devices may also expand the ability to provide endoscopic services by eliminating the need for device reprocessing equipment at low-volume sites. However, several concerns have been raised regarding their use, especially if it were to become widespread. These include issues of device quality and performance (potentially leading to more failed cases or adverse events), cost, their environmental impact and current uncertainty regarding their indications for use. Furthermore, new alternatives such as reusable devices with partially disposable components or future low-temperature sterilization options may minimize the need for such devices. We will briefly discuss these issues in more detail below.
Given that nearly all cases of GI device–transmitted infections where standard reprocessing protocols were followed have occurred in duodenoscopes, I will focus on single-use duodenoscopes in this article. It is important that we reassure our patients and colleagues that standard reprocessing appears to be extremely effective with all other types of devices, including elevator containing linear echoendoscopes. Studies investigating the causes of why duodenoscopes have primarily been associated with device-transmitted outbreaks have focused on the complexity of the elevator including its recesses, fixed end-cap and wire channels. However, culturing has shown that up to one-third of contamination may occur in the instrument channels or in the region of the biopsy cap, leading to some potential residual sites of infection even when newly developed reusable devices with disposable elevators/end-caps are utilized.1 Another challenge with reprocessing is the ability to prove residual contamination does not exist. While culturing the devices after reprocessing is most used, it should be noted many sites with outbreaks failed to culture the culprit bacteria from the devices as accessing the sites of contamination can be challenging. The use of other markers of residual contamination such as ATP and tests for residual blood/protein have yielded variable results. Specifically, ATP testing has not correlated well with culture results but may be helpful in assessing the quality of manual cleaning.2
These challenges have made the concept of single-use devices more appealing given the lack of a need reprocess devices or validate cleaning efficacy. Currently, there are two FDA-approved devices on the market, but the published literature to date has largely involved one of these devices. To date, in four published studies that have assessed the clinical performance of single-use duodenoscopes in over 400 patients, procedural success rates have ranged from 91% to 97% with adverse event rates and endoscopist satisfaction scores comparable to reusable devices. Most of these users were expert biliary endoscopists and more data are needed regarding the performance of the device in lower-volume and nonexpert users. While indications for use in these studies have varied, I feel that there are four potential scenarios to utilize these devices: in patients with known multidrug-resistant organisms undergoing ERCP; to facilitate logistics/operations when a reusable device is not available; in critically ill patients who would not tolerate a scope-acquired infection; and in procedures associated with a risk of bacteremia.
While preliminary data suggest single-use duodenoscopes are safe and effective in expert hands, concerns exist regarding their implementation more broadly into clinical practice. First, the devices cost between $1,500-3,000, making them impractical for many health systems. One study estimated the break-even cost of the device to be $800-1,300 based on variation in site volume and device contamination rates.3 However, it should be noted that current enhanced reprocessing protocols for reusable devices may add an additional $75,000-$400,000 per year based on center volume.4 In the United States, there is currently payment by federal and some commercial payors that cover part or all of the device cost, but whether this will continue long-term is unclear. In addition, there is significant concern regarding the environmental impact of a broader mover to single-use devices. Reprocessing programs do exist for these devices, but detailed analyses regarding the environmental effects of a strategy using single-use versus reusable devices and the waste generated from each are needed.
Finally, while primarily created to avoid device-related infection transmission, other benefits can be realized with single-use devices. The potential for ergonomic enhancements (variable handle sizes or shaft stiffness, R- and L-handed scopes) as well as the creation of specialty devices (extra-long or thin devices, devices with special optical or rotational capabilities) may become more feasible with a single-use platform. Finally, the pace of endoscopic innovation and refinement is likely to quicken with a single use platform, and new advancements can be incorporated in a timelier manner.
Conclusion
In summary, I believe single-use devices offer the potential to improve the safety of endoscopic procedures as well as improve procedural access, enhance ergonomics, and foster and expedite device innovation. However, reductions in cost, refining their indications, and developing recycling programs to minimize their environmental impact will be essential before more widespread adoption is achieved.
Dr. Muthusamy is a professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the medical director of endoscopy at the UCLA Health System. He reported relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Motus GI, Endogastric Solutions, and Capsovision.
References
1. Bartles RL et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Aug;88(2):306-13.e2.
2. Day LW et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Jan;93(1):11-33.e6.
3. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019 Nov;68(11):1915-7.
4. Bomman S et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Aug 23;9(9):E1404-12.
Dear colleagues,
Innovation is the livelihood of our field, driving major advances in endoscopy and attracting many of us to Gastroenterology. From the development of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography to the wide-spread adoption of third space endoscopy, we continue to push the boundaries of our practice. But what is the next big disruption in GI, and how will it impact us? Dr. Jeremy Glissen Brown discusses the application of artificial intelligence in GI highlighting its promise but also raising important questions. Dr. Raman Muthusamy elaborates on single-use endoscopes – are they the wave of the future in preventing infection and meeting patient preference? Or will their long-term cost and environmental impact limit their use? I welcome your own thoughts on disruptive innovation in Gastroenterology – share with us on Twitter @AGA_GIHN and by email at [email protected].
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is an associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and chief of endoscopy at West Haven (Conn.) VA Medical Center. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
The AI revolution, with some important caveats
BY JEREMY R. GLISSEN BROWN, MD, MSC
In 2018, Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Agency approved the first artificial intelligence (AI)–based tool, a computer-aided diagnosis system (CADx) for use in clinical practice.1 Since that time, we have seen regulatory approval for a variety of deep learning and AI-based tools in endoscopy and beyond. In addition, there has been an enormous amount of commercial and research interest in AI-based tools in clinical medicine and gastroenterology, and it is almost impossible to open a major gastroenterology journal or go to an academic conference without encountering a slew of AI-based projects.
Many thought and industry leaders say that we are in the midst of an AI revolution in gastroenterology. Indeed, we are at a period of unprecedented growth for deep learning and AI for several reasons, including a recent shift toward data-driven approaches, advancement of machine-learning techniques, and increased computing power. There is, however, also an unprecedented amount of scrutiny and thoughtful conversation about the role AI might play in clinical practice and how we use and regulate these tools in the clinical setting. We are thus in a unique position to ask ourselves the essential question: “Are we on the cusp of an AI revolution in gastroenterology, or are we seeing the release of medical software that is perhaps at best useful in a niche environment and at worse a hype-driven novelty without much clinical benefit?” We will use the most popular use-case, computer aided detection (CADe) of polyps in the colon, to explore this question. In the end, I believe that deep-learning technology will fundamentally change the way we practice gastroenterology. However, this is the perfect time to explore what this means now, and what we can do to shape what it will mean for the future.
CADe: Promise and questions
CADe is a computer vision task that involves localization, such as finding a polyp during colonoscopy and highlighting it with a hollow box. CADe in colonoscopy is perhaps the most well-studied application of deep learning in GI endoscopy to date and is furthest along in the development-implementation pipeline. Because of this, it is an ideal use-case for examining both the evidence that currently supports its use as well as the questions that have come up as we are starting to see CADe algorithms deployed in clinical practice. It is honestly astounding to think that, just 5 years ago, we were talking about CADe as a research concept. While early efforts applying traditional machine learning date back at least to the 1990s, we started to see prospective studies of CADe systems with undetectable or nearly undetectable latency in 2019.2 Since that time we have seen the publication of at least 10 randomized clinical trials involving CADe.
CADe clearly has an impact on some of the conventional quality metrics we use for colonoscopy. While there is considerable heterogeneity in region and design among these trials, most show a significant increase in adenoma detection rate (ADR) and adenomas per colonoscopy. Tandem studies show decreases in adenoma miss rate, and at least one study showed a decrease in sessile serrated lesion miss rate as well. In one of the first randomized, controlled trials across multiple endoscopy centers in Italy, Repici and colleagues showed an increase in ADR from 40.4% in the control group to 54.8% in the CADe group (RR, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.45).3 Because of pioneering trials such as this one, there are currently several CADe systems that have received regulatory approval in Europe, Asia, and the United States and are being deployed commercially.
It is also clear that the technology is there. In clinical practice, the Food and Drug Administration–approved systems work smoothly, with little to no detectable latency and generally low false-positive and false-negative rates. With clinical deployment, however, we have seen the emergence of healthy debate surrounding every aspect of this task-specific AI. On the development side, important questions include transparency of development data, ensuring that algorithm development is ethical and equitable (as deep learning is susceptible to exacerbating human biases) and methods of data labeling. On the deployment level, important concerns include proper regulation of locked versus “open” algorithms and downstream effects on cost.
In addition, with CADe we have seen a variety of clinical questions crop up because of the novelty of the technology. These include the concern that the increase in ADR we have seen thus far is driven in large part by diminutive and small adenomas (with healthy debate in turn as to these entities’ influence on interval colorectal cancer rates), the effect CADe might have on fellowship training to detect polyps with the human eye, and whether the technology affects sessile serrated lesion detection rates or not. The great thing about such questions is that they have inspired novel research related to CADe in the clinical setting, including how CADe affects trainee ADR, how CADe affects gaze patterns, and how CADe affects recommended surveillance intervals.
CADx, novel applications, and the future
Though there is not space to expand in this particular forum, it is safe to say that with the advancement of CADx in endoscopy and colonoscopy, we have seen similar and novel questions come up. The beautiful thing about all of this is that we are just scratching the surface of what is achievable with deep learning. We have started to see novel projects utilizing deep-learning algorithms, from detecting cirrhosis on ECG to automatically classifying stool consistency on the Bristol Stool Scale from pictures of stool. I ultimately do think that the deployment of AI tools will fundamentally change the way we practice and think about gastroenterology. We are at an incredibly exciting time where we as physicians have the power to shape what that looks like, how we think about AI deployment and regulation and where we go from here.
Dr. Glissen Brown is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. He has served as a consultant for Medtronic.
References
1. Aisu N et al. PLOS Digital Health. 2021 Jan 18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000001.
2. Wang P et al. Gut. 2019 Oct;68(10):1813-9.
3. Repici A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Aug;159(2):512-20.e7.
What’s the future of single-use endoscopes?
BY V. RAMAN MUTHUSAMY, MD, MAS
Single-use endoscopes have been proposed as a definitive solution to the risk of endoscope-transmitted infections. While these infections have been reported for several decades, they have traditionally been associated with identified breaches in the reprocessing protocol. In 2015, numerous cases of duodenoscope-transmitted infections were reported after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures. Many, if not most, of these cases were not associated with identified deviations from standard high-level disinfection protocols and occurred at high-volume experienced facilities. A subsequent FDA postmarket surveillance study found contamination rates were linked with potentially pathogenic bacteria in approximately 5% of duodenoscopes. Thus, amid growing concerns about the ability to adequately clean these complex devices, these events prompted the development of single-use duodenoscopes. Given the multifactorial causes leading to contaminated duodenoscopes, the advantages of such single-use devices are their ability to ensure the elimination of the potential of infection transmission as these devices are never reused. In addition to this primary benefit, the ability to create single-use devices could lead to more easily available specialty scopes and allow variations in endoscope design that could improve ergonomics. Single-use devices may also expand the ability to provide endoscopic services by eliminating the need for device reprocessing equipment at low-volume sites. However, several concerns have been raised regarding their use, especially if it were to become widespread. These include issues of device quality and performance (potentially leading to more failed cases or adverse events), cost, their environmental impact and current uncertainty regarding their indications for use. Furthermore, new alternatives such as reusable devices with partially disposable components or future low-temperature sterilization options may minimize the need for such devices. We will briefly discuss these issues in more detail below.
Given that nearly all cases of GI device–transmitted infections where standard reprocessing protocols were followed have occurred in duodenoscopes, I will focus on single-use duodenoscopes in this article. It is important that we reassure our patients and colleagues that standard reprocessing appears to be extremely effective with all other types of devices, including elevator containing linear echoendoscopes. Studies investigating the causes of why duodenoscopes have primarily been associated with device-transmitted outbreaks have focused on the complexity of the elevator including its recesses, fixed end-cap and wire channels. However, culturing has shown that up to one-third of contamination may occur in the instrument channels or in the region of the biopsy cap, leading to some potential residual sites of infection even when newly developed reusable devices with disposable elevators/end-caps are utilized.1 Another challenge with reprocessing is the ability to prove residual contamination does not exist. While culturing the devices after reprocessing is most used, it should be noted many sites with outbreaks failed to culture the culprit bacteria from the devices as accessing the sites of contamination can be challenging. The use of other markers of residual contamination such as ATP and tests for residual blood/protein have yielded variable results. Specifically, ATP testing has not correlated well with culture results but may be helpful in assessing the quality of manual cleaning.2
These challenges have made the concept of single-use devices more appealing given the lack of a need reprocess devices or validate cleaning efficacy. Currently, there are two FDA-approved devices on the market, but the published literature to date has largely involved one of these devices. To date, in four published studies that have assessed the clinical performance of single-use duodenoscopes in over 400 patients, procedural success rates have ranged from 91% to 97% with adverse event rates and endoscopist satisfaction scores comparable to reusable devices. Most of these users were expert biliary endoscopists and more data are needed regarding the performance of the device in lower-volume and nonexpert users. While indications for use in these studies have varied, I feel that there are four potential scenarios to utilize these devices: in patients with known multidrug-resistant organisms undergoing ERCP; to facilitate logistics/operations when a reusable device is not available; in critically ill patients who would not tolerate a scope-acquired infection; and in procedures associated with a risk of bacteremia.
While preliminary data suggest single-use duodenoscopes are safe and effective in expert hands, concerns exist regarding their implementation more broadly into clinical practice. First, the devices cost between $1,500-3,000, making them impractical for many health systems. One study estimated the break-even cost of the device to be $800-1,300 based on variation in site volume and device contamination rates.3 However, it should be noted that current enhanced reprocessing protocols for reusable devices may add an additional $75,000-$400,000 per year based on center volume.4 In the United States, there is currently payment by federal and some commercial payors that cover part or all of the device cost, but whether this will continue long-term is unclear. In addition, there is significant concern regarding the environmental impact of a broader mover to single-use devices. Reprocessing programs do exist for these devices, but detailed analyses regarding the environmental effects of a strategy using single-use versus reusable devices and the waste generated from each are needed.
Finally, while primarily created to avoid device-related infection transmission, other benefits can be realized with single-use devices. The potential for ergonomic enhancements (variable handle sizes or shaft stiffness, R- and L-handed scopes) as well as the creation of specialty devices (extra-long or thin devices, devices with special optical or rotational capabilities) may become more feasible with a single-use platform. Finally, the pace of endoscopic innovation and refinement is likely to quicken with a single use platform, and new advancements can be incorporated in a timelier manner.
Conclusion
In summary, I believe single-use devices offer the potential to improve the safety of endoscopic procedures as well as improve procedural access, enhance ergonomics, and foster and expedite device innovation. However, reductions in cost, refining their indications, and developing recycling programs to minimize their environmental impact will be essential before more widespread adoption is achieved.
Dr. Muthusamy is a professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the medical director of endoscopy at the UCLA Health System. He reported relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Motus GI, Endogastric Solutions, and Capsovision.
References
1. Bartles RL et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Aug;88(2):306-13.e2.
2. Day LW et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Jan;93(1):11-33.e6.
3. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019 Nov;68(11):1915-7.
4. Bomman S et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Aug 23;9(9):E1404-12.
I’m a physician battling long COVID. I can assure you it’s real
One in 5. It almost seems unimaginable that this is the real number of people who are struggling with long COVID, especially considering how many people in the United States have had COVID-19 at this point (more than 96 million).
Even more unimaginable at this time is that it’s happening to me. I’ve experienced not only the disabling effects of long COVID, but I’ve also seen, firsthand, the frustration of navigating diagnosis and treatment. It’s given me a taste of what millions of other patients are going through.
Vaxxed, masked, and (too) relaxed
I caught COVID-19 (probably Omicron BA.5) that presented as sniffles, making me think it was probably just allergies. However, my resting heart rate was up on my Garmin watch, so of course I got tested and was positive.
With my symptoms virtually nonexistent, it seemed, at the time, merely an inconvenience, because I was forced to isolate away from family and friends, who all stayed negative.
But 2 weeks later, I began to have urticaria – hives – after physical exertion. Did that mean my mast cells were angry? There’s some evidence these immune cells become overactivated in some patients with COVID. Next, I began to experience lightheadedness and the rapid heartbeat of tachycardia. The tachycardia was especially bad any time I physically exerted myself, including on a walk. Imagine me – a lover of all bargain shopping – cutting short a trip to the outlet mall on a particularly bad day when my heart rate was 140 after taking just a few steps. This was orthostatic intolerance.
Then came the severe worsening of my migraines – which are often vestibular, making me nauseated and dizzy on top of the throbbing.
I was of course familiar with these symptoms, as professor and chair of the department of rehabilitation medicine at the Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio. I developed a post-COVID recovery clinic to help patients.
So I knew about postexertional malaise (PEM) and postexertional symptom exacerbation (PESE), but I was now experiencing these distressing symptoms firsthand.
Clinicians really need to look for this cardinal sign of long COVID as well as evidence of myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). ME/CFS is marked by exacerbation of fatigue or symptoms after an activity that could previously be done without these aftereffects. In my case, as an All-American Masters miler with several marathons under my belt, running 5 miles is a walk in the park. But now, I pay for those 5 miles for the rest of the day on the couch or with palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue the following day. Busy clinic day full of procedures? I would have to be sitting by the end of it. Bed by 9 PM was not always early enough.
Becoming a statistic
Here I am, one of the leading experts in the country on caring for people with long COVID, featured in the national news and having testified in front of Congress, and now I am part of that lived experience. Me – a healthy athlete, with no comorbidities, a normal BMI, vaccinated and boosted, and after an almost asymptomatic bout of COVID-19, a victim to long COVID.
You just never know how your body is going to react. Neuroinflammation occurred in studies with mice with mild respiratory COVID and could be happening to me. I did not want a chronic immune-mediated vasculopathy.
So, I did what any other hyperaware physician-researcher would do. I enrolled in the RECOVER trial – a study my own institution is taking part in and one that I recommend to my own patients.
I also decided that I need to access care and not just ignore my symptoms or try to treat them myself.
That’s when things got difficult. There was a wait of at least a month to see my primary care provider – but I was able to use my privileged position as a physician to get in sooner.
My provider said that she had limited knowledge of long COVID, and she hesitated to order some of the tests and treatments that I recommended because they were not yet considered standard of care. I can understand the hesitation. It is engrained in medical education to follow evidence based on the highest-quality research studies. We are slowly learning more about long COVID, but acknowledging the learning curve offers little to patients who need help now.
This has made me realize that we cannot wait on an evidence-based approach – which can take decades to develop – while people are suffering. And it’s important that everyone on the front line learn about some of the manifestations and disease management of long COVID.
I left this first physician visit feeling more defeated than anything and decided to try to push through. That, I quickly realized, was not the right thing to do.
So again, after a couple of significant crashes and days of severe migraines, I phoned a friend: Ratna Bhavaraju-Sanka, MD, the amazing neurologist who treats patients with long COVID alongside me. She squeezed me in on a non-clinic day. Again, I had the privilege to see a specialist most people wait half a year to see. I was diagnosed with both autonomic dysfunction and intractable migraine.
She ordered some intravenous fluids and IV magnesium that would probably help both. But then another obstacle arose. My institution’s infusion center is focused on patients with cancer, and I was unable to schedule treatments there.
Luckily, I knew about the concierge mobile IV hydration therapy companies that come to your house – mostly offering a hangover treatment service. And I am thankful that I had the health literacy and financial ability to pay for some fluids at home.
On another particularly bad day, I phoned other friends – higher-ups at the hospital – who expedited a slot at the hospital infusion center and approval for the IV magnesium.
Thanks to my access, knowledge, and other privileges, I got fairly quick if imperfect care, enrolled in a research trial, and received medications. I knew to pace myself. The vast majority of others with long COVID lack these advantages.
The patient with long COVID
Things I have learned that others can learn, too:
- Acknowledge and recognize that long COVID is a disease that is affecting 1 in 5 Americans who catch COVID. Many look completely “normal on the outside.” Please listen to your patients.
- Autonomic dysfunction is a common manifestation of long COVID. A 10-minute stand test goes a long way in diagnosing this condition, from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. It is not just anxiety.
- “That’s only in research” is dismissive and harmful. Think outside the box. Follow guidelines. Consider encouraging patients to sign up for trials.
- Screen for PEM/PESE and teach your patients to pace themselves, because pushing through it or doing graded exercises will be harmful.
- We need to train more physicians to treat postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection () and other postinfectious conditions, such as ME/CFS.
If long COVID is hard for physicians to understand and deal with, imagine how difficult it is for patients with no expertise in this area.
It is exponentially harder for those with fewer resources, time, and health literacy. My lived experience with long COVID has shown me that being a patient is never easy. You put your body and fate into the hands of trusted professionals and expect validation and assistance, not gaslighting or gatekeeping.
Along with millions of others, I am tired of waiting.
Dr. Gutierrez is Professor and Distinguished Chair, department of rehabilitation medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. She reported receiving honoraria for lecturing on long COVID and receiving a research grant from Co-PI for the NIH RECOVER trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in 5. It almost seems unimaginable that this is the real number of people who are struggling with long COVID, especially considering how many people in the United States have had COVID-19 at this point (more than 96 million).
Even more unimaginable at this time is that it’s happening to me. I’ve experienced not only the disabling effects of long COVID, but I’ve also seen, firsthand, the frustration of navigating diagnosis and treatment. It’s given me a taste of what millions of other patients are going through.
Vaxxed, masked, and (too) relaxed
I caught COVID-19 (probably Omicron BA.5) that presented as sniffles, making me think it was probably just allergies. However, my resting heart rate was up on my Garmin watch, so of course I got tested and was positive.
With my symptoms virtually nonexistent, it seemed, at the time, merely an inconvenience, because I was forced to isolate away from family and friends, who all stayed negative.
But 2 weeks later, I began to have urticaria – hives – after physical exertion. Did that mean my mast cells were angry? There’s some evidence these immune cells become overactivated in some patients with COVID. Next, I began to experience lightheadedness and the rapid heartbeat of tachycardia. The tachycardia was especially bad any time I physically exerted myself, including on a walk. Imagine me – a lover of all bargain shopping – cutting short a trip to the outlet mall on a particularly bad day when my heart rate was 140 after taking just a few steps. This was orthostatic intolerance.
Then came the severe worsening of my migraines – which are often vestibular, making me nauseated and dizzy on top of the throbbing.
I was of course familiar with these symptoms, as professor and chair of the department of rehabilitation medicine at the Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio. I developed a post-COVID recovery clinic to help patients.
So I knew about postexertional malaise (PEM) and postexertional symptom exacerbation (PESE), but I was now experiencing these distressing symptoms firsthand.
Clinicians really need to look for this cardinal sign of long COVID as well as evidence of myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). ME/CFS is marked by exacerbation of fatigue or symptoms after an activity that could previously be done without these aftereffects. In my case, as an All-American Masters miler with several marathons under my belt, running 5 miles is a walk in the park. But now, I pay for those 5 miles for the rest of the day on the couch or with palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue the following day. Busy clinic day full of procedures? I would have to be sitting by the end of it. Bed by 9 PM was not always early enough.
Becoming a statistic
Here I am, one of the leading experts in the country on caring for people with long COVID, featured in the national news and having testified in front of Congress, and now I am part of that lived experience. Me – a healthy athlete, with no comorbidities, a normal BMI, vaccinated and boosted, and after an almost asymptomatic bout of COVID-19, a victim to long COVID.
You just never know how your body is going to react. Neuroinflammation occurred in studies with mice with mild respiratory COVID and could be happening to me. I did not want a chronic immune-mediated vasculopathy.
So, I did what any other hyperaware physician-researcher would do. I enrolled in the RECOVER trial – a study my own institution is taking part in and one that I recommend to my own patients.
I also decided that I need to access care and not just ignore my symptoms or try to treat them myself.
That’s when things got difficult. There was a wait of at least a month to see my primary care provider – but I was able to use my privileged position as a physician to get in sooner.
My provider said that she had limited knowledge of long COVID, and she hesitated to order some of the tests and treatments that I recommended because they were not yet considered standard of care. I can understand the hesitation. It is engrained in medical education to follow evidence based on the highest-quality research studies. We are slowly learning more about long COVID, but acknowledging the learning curve offers little to patients who need help now.
This has made me realize that we cannot wait on an evidence-based approach – which can take decades to develop – while people are suffering. And it’s important that everyone on the front line learn about some of the manifestations and disease management of long COVID.
I left this first physician visit feeling more defeated than anything and decided to try to push through. That, I quickly realized, was not the right thing to do.
So again, after a couple of significant crashes and days of severe migraines, I phoned a friend: Ratna Bhavaraju-Sanka, MD, the amazing neurologist who treats patients with long COVID alongside me. She squeezed me in on a non-clinic day. Again, I had the privilege to see a specialist most people wait half a year to see. I was diagnosed with both autonomic dysfunction and intractable migraine.
She ordered some intravenous fluids and IV magnesium that would probably help both. But then another obstacle arose. My institution’s infusion center is focused on patients with cancer, and I was unable to schedule treatments there.
Luckily, I knew about the concierge mobile IV hydration therapy companies that come to your house – mostly offering a hangover treatment service. And I am thankful that I had the health literacy and financial ability to pay for some fluids at home.
On another particularly bad day, I phoned other friends – higher-ups at the hospital – who expedited a slot at the hospital infusion center and approval for the IV magnesium.
Thanks to my access, knowledge, and other privileges, I got fairly quick if imperfect care, enrolled in a research trial, and received medications. I knew to pace myself. The vast majority of others with long COVID lack these advantages.
The patient with long COVID
Things I have learned that others can learn, too:
- Acknowledge and recognize that long COVID is a disease that is affecting 1 in 5 Americans who catch COVID. Many look completely “normal on the outside.” Please listen to your patients.
- Autonomic dysfunction is a common manifestation of long COVID. A 10-minute stand test goes a long way in diagnosing this condition, from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. It is not just anxiety.
- “That’s only in research” is dismissive and harmful. Think outside the box. Follow guidelines. Consider encouraging patients to sign up for trials.
- Screen for PEM/PESE and teach your patients to pace themselves, because pushing through it or doing graded exercises will be harmful.
- We need to train more physicians to treat postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection () and other postinfectious conditions, such as ME/CFS.
If long COVID is hard for physicians to understand and deal with, imagine how difficult it is for patients with no expertise in this area.
It is exponentially harder for those with fewer resources, time, and health literacy. My lived experience with long COVID has shown me that being a patient is never easy. You put your body and fate into the hands of trusted professionals and expect validation and assistance, not gaslighting or gatekeeping.
Along with millions of others, I am tired of waiting.
Dr. Gutierrez is Professor and Distinguished Chair, department of rehabilitation medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. She reported receiving honoraria for lecturing on long COVID and receiving a research grant from Co-PI for the NIH RECOVER trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in 5. It almost seems unimaginable that this is the real number of people who are struggling with long COVID, especially considering how many people in the United States have had COVID-19 at this point (more than 96 million).
Even more unimaginable at this time is that it’s happening to me. I’ve experienced not only the disabling effects of long COVID, but I’ve also seen, firsthand, the frustration of navigating diagnosis and treatment. It’s given me a taste of what millions of other patients are going through.
Vaxxed, masked, and (too) relaxed
I caught COVID-19 (probably Omicron BA.5) that presented as sniffles, making me think it was probably just allergies. However, my resting heart rate was up on my Garmin watch, so of course I got tested and was positive.
With my symptoms virtually nonexistent, it seemed, at the time, merely an inconvenience, because I was forced to isolate away from family and friends, who all stayed negative.
But 2 weeks later, I began to have urticaria – hives – after physical exertion. Did that mean my mast cells were angry? There’s some evidence these immune cells become overactivated in some patients with COVID. Next, I began to experience lightheadedness and the rapid heartbeat of tachycardia. The tachycardia was especially bad any time I physically exerted myself, including on a walk. Imagine me – a lover of all bargain shopping – cutting short a trip to the outlet mall on a particularly bad day when my heart rate was 140 after taking just a few steps. This was orthostatic intolerance.
Then came the severe worsening of my migraines – which are often vestibular, making me nauseated and dizzy on top of the throbbing.
I was of course familiar with these symptoms, as professor and chair of the department of rehabilitation medicine at the Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio. I developed a post-COVID recovery clinic to help patients.
So I knew about postexertional malaise (PEM) and postexertional symptom exacerbation (PESE), but I was now experiencing these distressing symptoms firsthand.
Clinicians really need to look for this cardinal sign of long COVID as well as evidence of myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). ME/CFS is marked by exacerbation of fatigue or symptoms after an activity that could previously be done without these aftereffects. In my case, as an All-American Masters miler with several marathons under my belt, running 5 miles is a walk in the park. But now, I pay for those 5 miles for the rest of the day on the couch or with palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue the following day. Busy clinic day full of procedures? I would have to be sitting by the end of it. Bed by 9 PM was not always early enough.
Becoming a statistic
Here I am, one of the leading experts in the country on caring for people with long COVID, featured in the national news and having testified in front of Congress, and now I am part of that lived experience. Me – a healthy athlete, with no comorbidities, a normal BMI, vaccinated and boosted, and after an almost asymptomatic bout of COVID-19, a victim to long COVID.
You just never know how your body is going to react. Neuroinflammation occurred in studies with mice with mild respiratory COVID and could be happening to me. I did not want a chronic immune-mediated vasculopathy.
So, I did what any other hyperaware physician-researcher would do. I enrolled in the RECOVER trial – a study my own institution is taking part in and one that I recommend to my own patients.
I also decided that I need to access care and not just ignore my symptoms or try to treat them myself.
That’s when things got difficult. There was a wait of at least a month to see my primary care provider – but I was able to use my privileged position as a physician to get in sooner.
My provider said that she had limited knowledge of long COVID, and she hesitated to order some of the tests and treatments that I recommended because they were not yet considered standard of care. I can understand the hesitation. It is engrained in medical education to follow evidence based on the highest-quality research studies. We are slowly learning more about long COVID, but acknowledging the learning curve offers little to patients who need help now.
This has made me realize that we cannot wait on an evidence-based approach – which can take decades to develop – while people are suffering. And it’s important that everyone on the front line learn about some of the manifestations and disease management of long COVID.
I left this first physician visit feeling more defeated than anything and decided to try to push through. That, I quickly realized, was not the right thing to do.
So again, after a couple of significant crashes and days of severe migraines, I phoned a friend: Ratna Bhavaraju-Sanka, MD, the amazing neurologist who treats patients with long COVID alongside me. She squeezed me in on a non-clinic day. Again, I had the privilege to see a specialist most people wait half a year to see. I was diagnosed with both autonomic dysfunction and intractable migraine.
She ordered some intravenous fluids and IV magnesium that would probably help both. But then another obstacle arose. My institution’s infusion center is focused on patients with cancer, and I was unable to schedule treatments there.
Luckily, I knew about the concierge mobile IV hydration therapy companies that come to your house – mostly offering a hangover treatment service. And I am thankful that I had the health literacy and financial ability to pay for some fluids at home.
On another particularly bad day, I phoned other friends – higher-ups at the hospital – who expedited a slot at the hospital infusion center and approval for the IV magnesium.
Thanks to my access, knowledge, and other privileges, I got fairly quick if imperfect care, enrolled in a research trial, and received medications. I knew to pace myself. The vast majority of others with long COVID lack these advantages.
The patient with long COVID
Things I have learned that others can learn, too:
- Acknowledge and recognize that long COVID is a disease that is affecting 1 in 5 Americans who catch COVID. Many look completely “normal on the outside.” Please listen to your patients.
- Autonomic dysfunction is a common manifestation of long COVID. A 10-minute stand test goes a long way in diagnosing this condition, from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. It is not just anxiety.
- “That’s only in research” is dismissive and harmful. Think outside the box. Follow guidelines. Consider encouraging patients to sign up for trials.
- Screen for PEM/PESE and teach your patients to pace themselves, because pushing through it or doing graded exercises will be harmful.
- We need to train more physicians to treat postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection () and other postinfectious conditions, such as ME/CFS.
If long COVID is hard for physicians to understand and deal with, imagine how difficult it is for patients with no expertise in this area.
It is exponentially harder for those with fewer resources, time, and health literacy. My lived experience with long COVID has shown me that being a patient is never easy. You put your body and fate into the hands of trusted professionals and expect validation and assistance, not gaslighting or gatekeeping.
Along with millions of others, I am tired of waiting.
Dr. Gutierrez is Professor and Distinguished Chair, department of rehabilitation medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. She reported receiving honoraria for lecturing on long COVID and receiving a research grant from Co-PI for the NIH RECOVER trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BMI and reproduction – weighing the evidence
Arguably, no topic during an infertility consultation generates more of an emotional reaction than discussing body mass index (BMI), particularly when it is high. Patients have become increasingly sensitive to weight discussions with their physicians because of concerns about body shaming. Among patients with an elevated BMI, criticism on social media of health care professionals’ counseling and a preemptive presentation of “Don’t Weigh Me” cards have become popular responses. Despite the medical evidence on impaired reproduction with an abnormal BMI, patients are choosing to forgo the topic. Research has demonstrated “extensive evidence [of] strong weight bias” in a wide range of health staff.1 A “viral” TikTok study revealed that medical “gaslighting” founded in weight stigma and bias is harmful, as reported on KevinMD.com.2 This month, we review the effect of abnormal BMI, both high and low, on reproduction and pregnancy.
A method to assess relative weight was first described in 1832 as its ratio in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters, or the Quetelet Index. The search for a functional assessment of relative body weight began after World War II when reports by actuaries noted the increased mortality of overweight policyholders. The relationship between weight and cardiovascular disease was further revealed in epidemiologic studies. The Quetelet Index became the BMI in 1972.3
Weight measurement is a mainstay in the assessment of a patient’s vital signs along with blood pressure, pulse rate, respiration rate, and temperature. Weight is vital to the calculation of medication dosage – for instance, administration of conscious sedative drugs, methotrexate, and gonadotropins. Some state boards of medicine, such as Florida, have a limitation on patient BMI at office-based surgery centers (40 kg/m2).
Obesity is a disease
As reported by the World Health Organization in 2022, the disease of obesity is an epidemic afflicting more than 1 billion people worldwide, or 1 in 8 individuals globally.4 The health implications of an elevated BMI include increased mortality, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, physical limitations to activities of daily living, and complications affecting reproduction.
Female obesity is related to poorer outcomes in natural and assisted conception, including an increased risk of miscarriage. Compared with normal-weight women, those with obesity are three times more likely to have ovulatory dysfunction,5 infertility,6 a lower chance for conception,7 higher rate of miscarriage, and low birth weight.8,9During pregnancy, women with obesity have three to four times higher rates of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia,10 as well as likelihood of delivering preterm,11 having a fetus with macrosomia and birth defects, and a 1.3- to 2.1-times higher risk of stillbirth.12
Obesity is present in 40%-80% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome,13 the most common cause of ovulatory dysfunction from dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. While PCOS is associated with reproductive and metabolic consequences, even in regularly ovulating women, increasing obesity appears to be associated with decreasing spontaneous pregnancy rates and increased time to pregnancy.14
Obesity and IVF
Women with obesity have reduced success with assisted reproductive technology, an increased number of canceled cycles, and poorer quality oocytes retrieved. A prospective cohort study of nearly 2,000 women reported that every 5 kg of body weight increase (from the patient’s baseline weight at age 18) was associated with a 5% increase in the mean duration of time required for conception (95% confidence interval, 3%-7%).15 Given that approximately 90% of these women had regular menstrual cycles, ovulatory dysfunction was not the suspected pathophysiology.
A meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies reported a lower likelihood of live birth following in vitro fertilization for women with obesity, compared with normal-weight women (risk ratio, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.82-0.87).16 A further subgroup analysis that evaluated only women with PCOS showed a reduction in the live birth rate following IVF for individuals with obesity, compared with normal-weight individuals (RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.74-0.82).
In a retrospective study of almost 500,000 fresh autologous IVF cycles, women with obesity had a 6% reduction in pregnancy rates and a 13% reduction in live birth rates, compared with normal-weight women. Both high and low BMI were associated with an increased risk of low birth weight and preterm delivery.17 The live birth rates per transfer for normal-weight and higher-weight women were 38% and 33%, respectively.
Contrarily, a randomized controlled trial showed that an intensive weight-reduction program resulted in a large weight loss but did not substantially affect live birth rates in women with obesity scheduled for IVF.18
Low BMI
A noteworthy cause of low BMI is functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA), a disorder with low energy availability either from decreased caloric intake and/or excessive energy expenditure associated with eating disorders, excessive exercise, and stress. Consequently, a reduced GnRH drive results in a decreased pulse frequency and amplitude leading to low levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, resulting in anovulation. Correction of lifestyle behaviors related to FHA can restore menstrual cycles. After normal weight is achieved, it appears unlikely that fertility is affected.19 In 47% of adolescent patients with anorexia, menses spontaneously returned within the first 12 months after admission, with an improved prognosis in secondary over primary amenorrhea.20,21 Interestingly, mildly and significantly underweight infertile women have pregnancy and live birth rates similar to normal-weight patients after IVF treatment.22
Pregnancy is complicated in underweight women, resulting in an increased risk of anemia, fetal growth retardation, and low birth weight, as well as preterm birth.21
Take-home message
The extremes of BMI both impair natural reproduction. Elevated BMI reduces success with IVF but rapid weight loss prior to IVF does not improve outcomes. A normal BMI is the goal for optimal reproductive and pregnancy health.
Dr. Trolice is director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Talumaa B et al. Obesity Rev. 2022;23:e13494.
2. https://bit.ly/3rHCivE.
3. Eknoyan G. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:47-51.
4. Wells JCK. Dis Models Mech. 2012;5:595-607.
5. Brewer CJ and Balen AH. Reproduction. 2010;140:347-64.
6. Silvestris E et al. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16:22.
7. Wise LA et al. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:253-64.
8. Bellver J. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:114-21.
9. Dickey RP et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:349.e1.
10. Alwash SM et al. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2021;15:425-30.
11. Cnattingius S et al. JAMA. 2013;309:2362-70.
12. Aune D et al. JAMA. 2014;311:1536-46.
13. Sam S. Obes Manag. 2007;3:69-73.
14. van der Steeg JW et al. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:324-8.
15. Gaskins AJ et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:850-8.
16. Sermondade N et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2019;25:439-519.
17. Kawwass JF et al. Fertil Steril. 2016;106[7]:1742-50.
18. Einarsson S et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32:1621-30.
19. Chaer R et al. Diseases. 2020;8:46.
20. Dempfle A et al. Psychiatry. 2013;13:308.
21. Verma A and Shrimali L. J Clin Diagn Res. 2012;6:1531-3.
22. Romanski PA et al. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020;42:366-74.
Arguably, no topic during an infertility consultation generates more of an emotional reaction than discussing body mass index (BMI), particularly when it is high. Patients have become increasingly sensitive to weight discussions with their physicians because of concerns about body shaming. Among patients with an elevated BMI, criticism on social media of health care professionals’ counseling and a preemptive presentation of “Don’t Weigh Me” cards have become popular responses. Despite the medical evidence on impaired reproduction with an abnormal BMI, patients are choosing to forgo the topic. Research has demonstrated “extensive evidence [of] strong weight bias” in a wide range of health staff.1 A “viral” TikTok study revealed that medical “gaslighting” founded in weight stigma and bias is harmful, as reported on KevinMD.com.2 This month, we review the effect of abnormal BMI, both high and low, on reproduction and pregnancy.
A method to assess relative weight was first described in 1832 as its ratio in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters, or the Quetelet Index. The search for a functional assessment of relative body weight began after World War II when reports by actuaries noted the increased mortality of overweight policyholders. The relationship between weight and cardiovascular disease was further revealed in epidemiologic studies. The Quetelet Index became the BMI in 1972.3
Weight measurement is a mainstay in the assessment of a patient’s vital signs along with blood pressure, pulse rate, respiration rate, and temperature. Weight is vital to the calculation of medication dosage – for instance, administration of conscious sedative drugs, methotrexate, and gonadotropins. Some state boards of medicine, such as Florida, have a limitation on patient BMI at office-based surgery centers (40 kg/m2).
Obesity is a disease
As reported by the World Health Organization in 2022, the disease of obesity is an epidemic afflicting more than 1 billion people worldwide, or 1 in 8 individuals globally.4 The health implications of an elevated BMI include increased mortality, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, physical limitations to activities of daily living, and complications affecting reproduction.
Female obesity is related to poorer outcomes in natural and assisted conception, including an increased risk of miscarriage. Compared with normal-weight women, those with obesity are three times more likely to have ovulatory dysfunction,5 infertility,6 a lower chance for conception,7 higher rate of miscarriage, and low birth weight.8,9During pregnancy, women with obesity have three to four times higher rates of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia,10 as well as likelihood of delivering preterm,11 having a fetus with macrosomia and birth defects, and a 1.3- to 2.1-times higher risk of stillbirth.12
Obesity is present in 40%-80% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome,13 the most common cause of ovulatory dysfunction from dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. While PCOS is associated with reproductive and metabolic consequences, even in regularly ovulating women, increasing obesity appears to be associated with decreasing spontaneous pregnancy rates and increased time to pregnancy.14
Obesity and IVF
Women with obesity have reduced success with assisted reproductive technology, an increased number of canceled cycles, and poorer quality oocytes retrieved. A prospective cohort study of nearly 2,000 women reported that every 5 kg of body weight increase (from the patient’s baseline weight at age 18) was associated with a 5% increase in the mean duration of time required for conception (95% confidence interval, 3%-7%).15 Given that approximately 90% of these women had regular menstrual cycles, ovulatory dysfunction was not the suspected pathophysiology.
A meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies reported a lower likelihood of live birth following in vitro fertilization for women with obesity, compared with normal-weight women (risk ratio, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.82-0.87).16 A further subgroup analysis that evaluated only women with PCOS showed a reduction in the live birth rate following IVF for individuals with obesity, compared with normal-weight individuals (RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.74-0.82).
In a retrospective study of almost 500,000 fresh autologous IVF cycles, women with obesity had a 6% reduction in pregnancy rates and a 13% reduction in live birth rates, compared with normal-weight women. Both high and low BMI were associated with an increased risk of low birth weight and preterm delivery.17 The live birth rates per transfer for normal-weight and higher-weight women were 38% and 33%, respectively.
Contrarily, a randomized controlled trial showed that an intensive weight-reduction program resulted in a large weight loss but did not substantially affect live birth rates in women with obesity scheduled for IVF.18
Low BMI
A noteworthy cause of low BMI is functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA), a disorder with low energy availability either from decreased caloric intake and/or excessive energy expenditure associated with eating disorders, excessive exercise, and stress. Consequently, a reduced GnRH drive results in a decreased pulse frequency and amplitude leading to low levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, resulting in anovulation. Correction of lifestyle behaviors related to FHA can restore menstrual cycles. After normal weight is achieved, it appears unlikely that fertility is affected.19 In 47% of adolescent patients with anorexia, menses spontaneously returned within the first 12 months after admission, with an improved prognosis in secondary over primary amenorrhea.20,21 Interestingly, mildly and significantly underweight infertile women have pregnancy and live birth rates similar to normal-weight patients after IVF treatment.22
Pregnancy is complicated in underweight women, resulting in an increased risk of anemia, fetal growth retardation, and low birth weight, as well as preterm birth.21
Take-home message
The extremes of BMI both impair natural reproduction. Elevated BMI reduces success with IVF but rapid weight loss prior to IVF does not improve outcomes. A normal BMI is the goal for optimal reproductive and pregnancy health.
Dr. Trolice is director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Talumaa B et al. Obesity Rev. 2022;23:e13494.
2. https://bit.ly/3rHCivE.
3. Eknoyan G. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:47-51.
4. Wells JCK. Dis Models Mech. 2012;5:595-607.
5. Brewer CJ and Balen AH. Reproduction. 2010;140:347-64.
6. Silvestris E et al. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16:22.
7. Wise LA et al. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:253-64.
8. Bellver J. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:114-21.
9. Dickey RP et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:349.e1.
10. Alwash SM et al. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2021;15:425-30.
11. Cnattingius S et al. JAMA. 2013;309:2362-70.
12. Aune D et al. JAMA. 2014;311:1536-46.
13. Sam S. Obes Manag. 2007;3:69-73.
14. van der Steeg JW et al. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:324-8.
15. Gaskins AJ et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:850-8.
16. Sermondade N et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2019;25:439-519.
17. Kawwass JF et al. Fertil Steril. 2016;106[7]:1742-50.
18. Einarsson S et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32:1621-30.
19. Chaer R et al. Diseases. 2020;8:46.
20. Dempfle A et al. Psychiatry. 2013;13:308.
21. Verma A and Shrimali L. J Clin Diagn Res. 2012;6:1531-3.
22. Romanski PA et al. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020;42:366-74.
Arguably, no topic during an infertility consultation generates more of an emotional reaction than discussing body mass index (BMI), particularly when it is high. Patients have become increasingly sensitive to weight discussions with their physicians because of concerns about body shaming. Among patients with an elevated BMI, criticism on social media of health care professionals’ counseling and a preemptive presentation of “Don’t Weigh Me” cards have become popular responses. Despite the medical evidence on impaired reproduction with an abnormal BMI, patients are choosing to forgo the topic. Research has demonstrated “extensive evidence [of] strong weight bias” in a wide range of health staff.1 A “viral” TikTok study revealed that medical “gaslighting” founded in weight stigma and bias is harmful, as reported on KevinMD.com.2 This month, we review the effect of abnormal BMI, both high and low, on reproduction and pregnancy.
A method to assess relative weight was first described in 1832 as its ratio in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters, or the Quetelet Index. The search for a functional assessment of relative body weight began after World War II when reports by actuaries noted the increased mortality of overweight policyholders. The relationship between weight and cardiovascular disease was further revealed in epidemiologic studies. The Quetelet Index became the BMI in 1972.3
Weight measurement is a mainstay in the assessment of a patient’s vital signs along with blood pressure, pulse rate, respiration rate, and temperature. Weight is vital to the calculation of medication dosage – for instance, administration of conscious sedative drugs, methotrexate, and gonadotropins. Some state boards of medicine, such as Florida, have a limitation on patient BMI at office-based surgery centers (40 kg/m2).
Obesity is a disease
As reported by the World Health Organization in 2022, the disease of obesity is an epidemic afflicting more than 1 billion people worldwide, or 1 in 8 individuals globally.4 The health implications of an elevated BMI include increased mortality, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, physical limitations to activities of daily living, and complications affecting reproduction.
Female obesity is related to poorer outcomes in natural and assisted conception, including an increased risk of miscarriage. Compared with normal-weight women, those with obesity are three times more likely to have ovulatory dysfunction,5 infertility,6 a lower chance for conception,7 higher rate of miscarriage, and low birth weight.8,9During pregnancy, women with obesity have three to four times higher rates of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia,10 as well as likelihood of delivering preterm,11 having a fetus with macrosomia and birth defects, and a 1.3- to 2.1-times higher risk of stillbirth.12
Obesity is present in 40%-80% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome,13 the most common cause of ovulatory dysfunction from dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. While PCOS is associated with reproductive and metabolic consequences, even in regularly ovulating women, increasing obesity appears to be associated with decreasing spontaneous pregnancy rates and increased time to pregnancy.14
Obesity and IVF
Women with obesity have reduced success with assisted reproductive technology, an increased number of canceled cycles, and poorer quality oocytes retrieved. A prospective cohort study of nearly 2,000 women reported that every 5 kg of body weight increase (from the patient’s baseline weight at age 18) was associated with a 5% increase in the mean duration of time required for conception (95% confidence interval, 3%-7%).15 Given that approximately 90% of these women had regular menstrual cycles, ovulatory dysfunction was not the suspected pathophysiology.
A meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies reported a lower likelihood of live birth following in vitro fertilization for women with obesity, compared with normal-weight women (risk ratio, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.82-0.87).16 A further subgroup analysis that evaluated only women with PCOS showed a reduction in the live birth rate following IVF for individuals with obesity, compared with normal-weight individuals (RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.74-0.82).
In a retrospective study of almost 500,000 fresh autologous IVF cycles, women with obesity had a 6% reduction in pregnancy rates and a 13% reduction in live birth rates, compared with normal-weight women. Both high and low BMI were associated with an increased risk of low birth weight and preterm delivery.17 The live birth rates per transfer for normal-weight and higher-weight women were 38% and 33%, respectively.
Contrarily, a randomized controlled trial showed that an intensive weight-reduction program resulted in a large weight loss but did not substantially affect live birth rates in women with obesity scheduled for IVF.18
Low BMI
A noteworthy cause of low BMI is functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA), a disorder with low energy availability either from decreased caloric intake and/or excessive energy expenditure associated with eating disorders, excessive exercise, and stress. Consequently, a reduced GnRH drive results in a decreased pulse frequency and amplitude leading to low levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, resulting in anovulation. Correction of lifestyle behaviors related to FHA can restore menstrual cycles. After normal weight is achieved, it appears unlikely that fertility is affected.19 In 47% of adolescent patients with anorexia, menses spontaneously returned within the first 12 months after admission, with an improved prognosis in secondary over primary amenorrhea.20,21 Interestingly, mildly and significantly underweight infertile women have pregnancy and live birth rates similar to normal-weight patients after IVF treatment.22
Pregnancy is complicated in underweight women, resulting in an increased risk of anemia, fetal growth retardation, and low birth weight, as well as preterm birth.21
Take-home message
The extremes of BMI both impair natural reproduction. Elevated BMI reduces success with IVF but rapid weight loss prior to IVF does not improve outcomes. A normal BMI is the goal for optimal reproductive and pregnancy health.
Dr. Trolice is director of the IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
References
1. Talumaa B et al. Obesity Rev. 2022;23:e13494.
2. https://bit.ly/3rHCivE.
3. Eknoyan G. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:47-51.
4. Wells JCK. Dis Models Mech. 2012;5:595-607.
5. Brewer CJ and Balen AH. Reproduction. 2010;140:347-64.
6. Silvestris E et al. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16:22.
7. Wise LA et al. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:253-64.
8. Bellver J. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:114-21.
9. Dickey RP et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:349.e1.
10. Alwash SM et al. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2021;15:425-30.
11. Cnattingius S et al. JAMA. 2013;309:2362-70.
12. Aune D et al. JAMA. 2014;311:1536-46.
13. Sam S. Obes Manag. 2007;3:69-73.
14. van der Steeg JW et al. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:324-8.
15. Gaskins AJ et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:850-8.
16. Sermondade N et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2019;25:439-519.
17. Kawwass JF et al. Fertil Steril. 2016;106[7]:1742-50.
18. Einarsson S et al. Hum Reprod. 2017;32:1621-30.
19. Chaer R et al. Diseases. 2020;8:46.
20. Dempfle A et al. Psychiatry. 2013;13:308.
21. Verma A and Shrimali L. J Clin Diagn Res. 2012;6:1531-3.
22. Romanski PA et al. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020;42:366-74.
Bugs, drugs, and the placenta
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
Ivermectin for COVID-19: Final nail in the coffin
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.
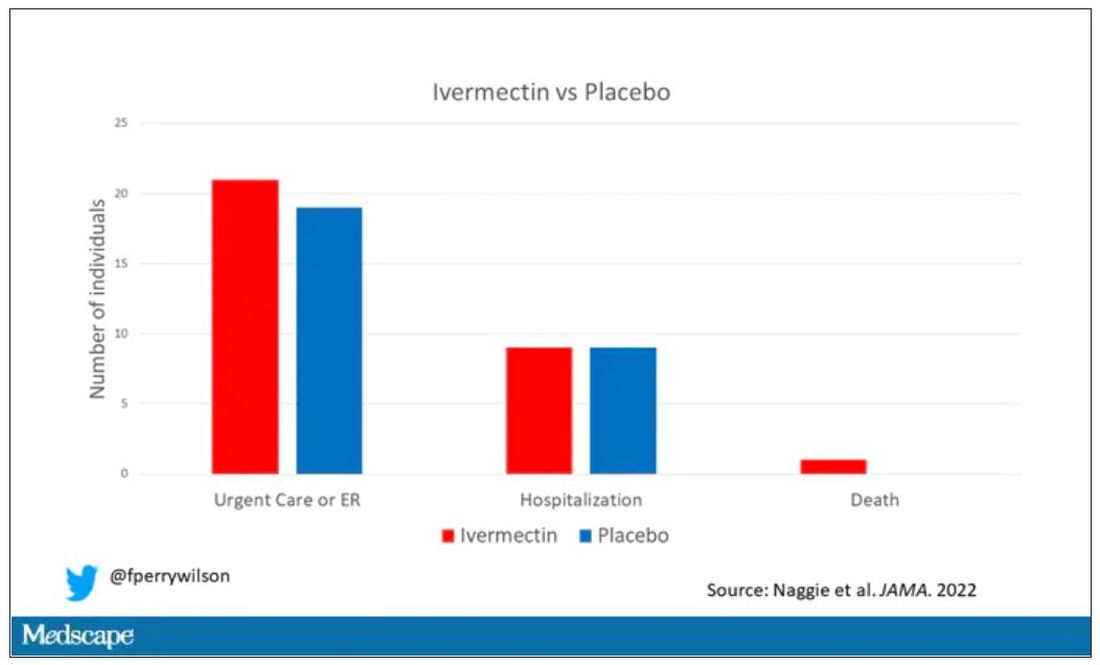
But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How can I keep from losing my mind?
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
The lives of drug users are more important than stopping drug use
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
The latest migraine therapies – some you might not know about
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.















