User login
Why getting a COVID-19 vaccine to children could take time
Testing COVID-19 vaccines in young children is going to be tricky. Deciding how to approve them and who should get them may be even more difficult.
So far, the vaccines available to Americans ages 12 and up have sailed through the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s regulatory checks, taking advantage of an accelerated clearance process called an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).
EUAs set a lower bar for effectiveness, saying the vaccines may be safe and effective based on just a few months of data.
But with COVID cases plummeting in the United States and children historically seeing far less serious disease than adults, a panel of expert advisors to the FDA was asked to deliberate on Thursday whether the agency could consider vaccines for this age group under the same standard.
Stated another way: Is COVID an emergency for kids?
There’s another wrinkle in the mix, too – heart inflammation, which appears to be a very rare emerging adverse event tied to vaccination. It seems to happen more often in teens and young adults. To date, cases of myocarditis and pericarditis appear to be happening in 16 to 30 people for every 1 million doses given.
But if it is conclusively linked to the shots, some wonder whether it might tip the balance between benefits and risks for kids.
That left some of the experts who sit on the FDA’s advisory committee for vaccines and related biological products urging the FDA to take its time and more thoroughly study the shots before they’re given to millions of children.
Vaccine studies different in children?
Clinical studies of the vaccines in teens and adults have thus far relied on some straightforward math. You take two groups of similar people. You give half the vaccine and half a placebo. Then you wait and see which group has more symptomatic infections. To date, the vaccines have dramatically cut the risk of getting severely ill with COVID for every age group tested.
But COVID infections are falling rapidly in the U.S., and that may make it more difficult for researchers to conduct a similar kind of experiment in children.
The FDA is considering different approaches to figure out whether a vaccine would be effective in kids, including something called an “immunobridging trial.”
In bridging trials, researchers don’t look for infections; rather, they look for proven signs that someone has developed immunity, like antibody levels. Those biomarkers are then compared to the immune responses of younger adults who have demonstrated good protection against infection.
The main advantage of bridging studies is speed. It’s possible to get a snapshot of how the immune system responds to a vaccine within weeks of the final dose.
The drawback is that researchers don’t know exactly what to look for to judge how well the shots are generating protection.
That’s made even more difficult because kids’ immune systems are still developing, so it may be tough to draw direct parallels to adults.
“We don’t know what the serologic correlate of immunity is now. We don’t know how much antibody you have to get in order to be protected. We don’t know what the role of T cells will be,” said H. Cody Meissner, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease at Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
“I have so much sympathy for the FDA because these are enormous problems, and you have to make a decision,” said Dr. Meissner, who is a member of the FDA’s vaccines and related biological products advisory committee.
Speed vaccines to market, or gather more data?
The plummeting rate of infections in the United States also means that it may be more difficult for the FDA to justify allowing a vaccine on the market for emergency use for children under age 12.
In its recent advisory committee meeting, the agency asked the panel whether it should consider COVID vaccines for children under an EUA or a biologics license application (BLA), aka full approval.
A BLA typically means the agency considers a year or two of data on a new product, rather than just 2 months’ worth. Emergency use also allows products on the market under a looser standard – they “may be” safe and effective, instead of has been proven to be safe and effective.
Several committee members said they didn’t feel the United States was still in an emergency with COVID and couldn’t see the FDA allowing a vaccine to be used in kids that wasn’t given the agency’s highest level of scrutiny, particularly with reports of adverse events like myocarditis coming to light.
“I just want to be sure the price we pay for vaccinating millions of children justifies the side effects, and I don’t think we know that yet,” Dr. Meissner said.
Others acknowledged that there was little risk to kids now with infections on the decline but said that picture could change as variants spread, schools reopen, and colder temperatures force people indoors.
The FDA must decide whether to act based on where we are now or where we could be in a few months.
“I think it’s the million-dollar question right now,” said Hannah Kirking, MD, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention who presented new and unpublished data on COVID’s impact in children to the FDA’s advisory committee.
She said prospective studies tracking the way COVID moves through a household with weekly testing from New York City and Utah had found that children catch and transmit COVID almost as readily as adults. But they don’t usually get as sick as adults do, so their cases are easy to miss.
She also presented the results of blood tests from samples around the country looking for evidence of past infection. In these seroprevalence studies, about 27% of children under age 17 had antibodies to COVID – the most of any age group. So more than 1 in 4 kids already has some natural immunity.
That means the main benefit of vaccinating children might be the protection of others, while they still bear the risks – however tiny.
Some experts felt that wasn’t enough reason to justify mass distribution of the vaccines to kids, and from a regulatory standpoint, it might not be permissible.
“FDA can only approve a medical product in a population if the benefits outweigh the risks in that population,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, assistant professor of pharmaceutical health services research in the University of Maryland’s school of pharmacy, Baltimore.
“If benefits don’t outweigh risks in children, it can’t be indicated for children. Full stop,” said Dr. Doshi, who is also an editor at the BMJ.
He said there’s another way to give children access to vaccines, through an expanded access or compassionate use program. Because most COVID deaths have been in children with underlying health conditions, Dr. Doshi and others said it might make sense to allow expanded access – which would get vaccines to children at high risk for complications – without turning them loose on millions before they are more thoroughly studied.
“It’s not a particularly attractive option for industry, because there’s no money to be made. Your medicine can’t be commercialized under expanded access. The most you can reap is manufacturing cost, which is not a lot,” he said.
Art Caplan, a professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone medical center, said the argument for vaccinating children for flu falls along the same lines. The benefit-to-risk ratio is finely balanced in children. The main value of protecting them is to protect others.
“Flu rarely kills young folks. But you’re really trying to protect old folks and that’s the classic example,” he said.
What’s more, he said the idea that children would take on some risk with a vaccine for little personal benefit is oversimplified.
“Yes, you might get vaccinated to prevent harm to others, but those others are providing benefits to you. It’s not a one-way street. I think that’s a little morally distorted,” Mr. Caplan said. “Being able to keep society open benefits kids and adults alike.”
Other committee members felt like it was too early to sound the all-clear on COVID and said the FDA should authorize vaccines for children as quickly as it had for other age groups.
“We are still, I believe, in an emergency situation. I think that when this virus goes into our children, which is what it’s going to do, that will give it an incubator to change,” said Oveta Fuller, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Fuller said that for the good of the world, Americans needed to vaccinate children to prevent the virus from mutating and creating new and potentially more dangerous variants.
Weighing risk over safety
Beth Thielen, MD, PhD, pediatric infectious disease specialist and virologist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said she had not followed the committee’s discussions, but about once a month she treats kids who are very sick because of the virus – either because of a COVID infection or because of multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C), an inflammatory reaction that strikes after infection.
She’s worried about how the virus has already changed. She said the kind of disease she’s seeing in kids now is different than what she saw in the early months of the pandemic.
“In the last couple of months, I’ve actually seen a few cases of severe pulmonary disease, more similar to adult disease in children,” Dr. Thielen said. “I see on the horizon that we could start seeing more significant disease in young people, and then the risks of being unvaccinated go up substantially.”
But she also knows nobody has a crystal ball, and right now, everything seems to be trending in the right direction with COVID. That makes the risk-to-benefit consideration murkier.
“The question in my mind is, what is the risk of side effects from the vaccine?” she said. “I think we really need to know what the safety profile of vaccine looks like in children because we do have a decent understanding now what risk from disease looks like, because it’s small, but we are seeing it.”
Dr. Thielen said she’ll be keeping an eye on the next meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for more answers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Testing COVID-19 vaccines in young children is going to be tricky. Deciding how to approve them and who should get them may be even more difficult.
So far, the vaccines available to Americans ages 12 and up have sailed through the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s regulatory checks, taking advantage of an accelerated clearance process called an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).
EUAs set a lower bar for effectiveness, saying the vaccines may be safe and effective based on just a few months of data.
But with COVID cases plummeting in the United States and children historically seeing far less serious disease than adults, a panel of expert advisors to the FDA was asked to deliberate on Thursday whether the agency could consider vaccines for this age group under the same standard.
Stated another way: Is COVID an emergency for kids?
There’s another wrinkle in the mix, too – heart inflammation, which appears to be a very rare emerging adverse event tied to vaccination. It seems to happen more often in teens and young adults. To date, cases of myocarditis and pericarditis appear to be happening in 16 to 30 people for every 1 million doses given.
But if it is conclusively linked to the shots, some wonder whether it might tip the balance between benefits and risks for kids.
That left some of the experts who sit on the FDA’s advisory committee for vaccines and related biological products urging the FDA to take its time and more thoroughly study the shots before they’re given to millions of children.
Vaccine studies different in children?
Clinical studies of the vaccines in teens and adults have thus far relied on some straightforward math. You take two groups of similar people. You give half the vaccine and half a placebo. Then you wait and see which group has more symptomatic infections. To date, the vaccines have dramatically cut the risk of getting severely ill with COVID for every age group tested.
But COVID infections are falling rapidly in the U.S., and that may make it more difficult for researchers to conduct a similar kind of experiment in children.
The FDA is considering different approaches to figure out whether a vaccine would be effective in kids, including something called an “immunobridging trial.”
In bridging trials, researchers don’t look for infections; rather, they look for proven signs that someone has developed immunity, like antibody levels. Those biomarkers are then compared to the immune responses of younger adults who have demonstrated good protection against infection.
The main advantage of bridging studies is speed. It’s possible to get a snapshot of how the immune system responds to a vaccine within weeks of the final dose.
The drawback is that researchers don’t know exactly what to look for to judge how well the shots are generating protection.
That’s made even more difficult because kids’ immune systems are still developing, so it may be tough to draw direct parallels to adults.
“We don’t know what the serologic correlate of immunity is now. We don’t know how much antibody you have to get in order to be protected. We don’t know what the role of T cells will be,” said H. Cody Meissner, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease at Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
“I have so much sympathy for the FDA because these are enormous problems, and you have to make a decision,” said Dr. Meissner, who is a member of the FDA’s vaccines and related biological products advisory committee.
Speed vaccines to market, or gather more data?
The plummeting rate of infections in the United States also means that it may be more difficult for the FDA to justify allowing a vaccine on the market for emergency use for children under age 12.
In its recent advisory committee meeting, the agency asked the panel whether it should consider COVID vaccines for children under an EUA or a biologics license application (BLA), aka full approval.
A BLA typically means the agency considers a year or two of data on a new product, rather than just 2 months’ worth. Emergency use also allows products on the market under a looser standard – they “may be” safe and effective, instead of has been proven to be safe and effective.
Several committee members said they didn’t feel the United States was still in an emergency with COVID and couldn’t see the FDA allowing a vaccine to be used in kids that wasn’t given the agency’s highest level of scrutiny, particularly with reports of adverse events like myocarditis coming to light.
“I just want to be sure the price we pay for vaccinating millions of children justifies the side effects, and I don’t think we know that yet,” Dr. Meissner said.
Others acknowledged that there was little risk to kids now with infections on the decline but said that picture could change as variants spread, schools reopen, and colder temperatures force people indoors.
The FDA must decide whether to act based on where we are now or where we could be in a few months.
“I think it’s the million-dollar question right now,” said Hannah Kirking, MD, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention who presented new and unpublished data on COVID’s impact in children to the FDA’s advisory committee.
She said prospective studies tracking the way COVID moves through a household with weekly testing from New York City and Utah had found that children catch and transmit COVID almost as readily as adults. But they don’t usually get as sick as adults do, so their cases are easy to miss.
She also presented the results of blood tests from samples around the country looking for evidence of past infection. In these seroprevalence studies, about 27% of children under age 17 had antibodies to COVID – the most of any age group. So more than 1 in 4 kids already has some natural immunity.
That means the main benefit of vaccinating children might be the protection of others, while they still bear the risks – however tiny.
Some experts felt that wasn’t enough reason to justify mass distribution of the vaccines to kids, and from a regulatory standpoint, it might not be permissible.
“FDA can only approve a medical product in a population if the benefits outweigh the risks in that population,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, assistant professor of pharmaceutical health services research in the University of Maryland’s school of pharmacy, Baltimore.
“If benefits don’t outweigh risks in children, it can’t be indicated for children. Full stop,” said Dr. Doshi, who is also an editor at the BMJ.
He said there’s another way to give children access to vaccines, through an expanded access or compassionate use program. Because most COVID deaths have been in children with underlying health conditions, Dr. Doshi and others said it might make sense to allow expanded access – which would get vaccines to children at high risk for complications – without turning them loose on millions before they are more thoroughly studied.
“It’s not a particularly attractive option for industry, because there’s no money to be made. Your medicine can’t be commercialized under expanded access. The most you can reap is manufacturing cost, which is not a lot,” he said.
Art Caplan, a professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone medical center, said the argument for vaccinating children for flu falls along the same lines. The benefit-to-risk ratio is finely balanced in children. The main value of protecting them is to protect others.
“Flu rarely kills young folks. But you’re really trying to protect old folks and that’s the classic example,” he said.
What’s more, he said the idea that children would take on some risk with a vaccine for little personal benefit is oversimplified.
“Yes, you might get vaccinated to prevent harm to others, but those others are providing benefits to you. It’s not a one-way street. I think that’s a little morally distorted,” Mr. Caplan said. “Being able to keep society open benefits kids and adults alike.”
Other committee members felt like it was too early to sound the all-clear on COVID and said the FDA should authorize vaccines for children as quickly as it had for other age groups.
“We are still, I believe, in an emergency situation. I think that when this virus goes into our children, which is what it’s going to do, that will give it an incubator to change,” said Oveta Fuller, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Fuller said that for the good of the world, Americans needed to vaccinate children to prevent the virus from mutating and creating new and potentially more dangerous variants.
Weighing risk over safety
Beth Thielen, MD, PhD, pediatric infectious disease specialist and virologist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said she had not followed the committee’s discussions, but about once a month she treats kids who are very sick because of the virus – either because of a COVID infection or because of multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C), an inflammatory reaction that strikes after infection.
She’s worried about how the virus has already changed. She said the kind of disease she’s seeing in kids now is different than what she saw in the early months of the pandemic.
“In the last couple of months, I’ve actually seen a few cases of severe pulmonary disease, more similar to adult disease in children,” Dr. Thielen said. “I see on the horizon that we could start seeing more significant disease in young people, and then the risks of being unvaccinated go up substantially.”
But she also knows nobody has a crystal ball, and right now, everything seems to be trending in the right direction with COVID. That makes the risk-to-benefit consideration murkier.
“The question in my mind is, what is the risk of side effects from the vaccine?” she said. “I think we really need to know what the safety profile of vaccine looks like in children because we do have a decent understanding now what risk from disease looks like, because it’s small, but we are seeing it.”
Dr. Thielen said she’ll be keeping an eye on the next meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for more answers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Testing COVID-19 vaccines in young children is going to be tricky. Deciding how to approve them and who should get them may be even more difficult.
So far, the vaccines available to Americans ages 12 and up have sailed through the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s regulatory checks, taking advantage of an accelerated clearance process called an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).
EUAs set a lower bar for effectiveness, saying the vaccines may be safe and effective based on just a few months of data.
But with COVID cases plummeting in the United States and children historically seeing far less serious disease than adults, a panel of expert advisors to the FDA was asked to deliberate on Thursday whether the agency could consider vaccines for this age group under the same standard.
Stated another way: Is COVID an emergency for kids?
There’s another wrinkle in the mix, too – heart inflammation, which appears to be a very rare emerging adverse event tied to vaccination. It seems to happen more often in teens and young adults. To date, cases of myocarditis and pericarditis appear to be happening in 16 to 30 people for every 1 million doses given.
But if it is conclusively linked to the shots, some wonder whether it might tip the balance between benefits and risks for kids.
That left some of the experts who sit on the FDA’s advisory committee for vaccines and related biological products urging the FDA to take its time and more thoroughly study the shots before they’re given to millions of children.
Vaccine studies different in children?
Clinical studies of the vaccines in teens and adults have thus far relied on some straightforward math. You take two groups of similar people. You give half the vaccine and half a placebo. Then you wait and see which group has more symptomatic infections. To date, the vaccines have dramatically cut the risk of getting severely ill with COVID for every age group tested.
But COVID infections are falling rapidly in the U.S., and that may make it more difficult for researchers to conduct a similar kind of experiment in children.
The FDA is considering different approaches to figure out whether a vaccine would be effective in kids, including something called an “immunobridging trial.”
In bridging trials, researchers don’t look for infections; rather, they look for proven signs that someone has developed immunity, like antibody levels. Those biomarkers are then compared to the immune responses of younger adults who have demonstrated good protection against infection.
The main advantage of bridging studies is speed. It’s possible to get a snapshot of how the immune system responds to a vaccine within weeks of the final dose.
The drawback is that researchers don’t know exactly what to look for to judge how well the shots are generating protection.
That’s made even more difficult because kids’ immune systems are still developing, so it may be tough to draw direct parallels to adults.
“We don’t know what the serologic correlate of immunity is now. We don’t know how much antibody you have to get in order to be protected. We don’t know what the role of T cells will be,” said H. Cody Meissner, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious disease at Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
“I have so much sympathy for the FDA because these are enormous problems, and you have to make a decision,” said Dr. Meissner, who is a member of the FDA’s vaccines and related biological products advisory committee.
Speed vaccines to market, or gather more data?
The plummeting rate of infections in the United States also means that it may be more difficult for the FDA to justify allowing a vaccine on the market for emergency use for children under age 12.
In its recent advisory committee meeting, the agency asked the panel whether it should consider COVID vaccines for children under an EUA or a biologics license application (BLA), aka full approval.
A BLA typically means the agency considers a year or two of data on a new product, rather than just 2 months’ worth. Emergency use also allows products on the market under a looser standard – they “may be” safe and effective, instead of has been proven to be safe and effective.
Several committee members said they didn’t feel the United States was still in an emergency with COVID and couldn’t see the FDA allowing a vaccine to be used in kids that wasn’t given the agency’s highest level of scrutiny, particularly with reports of adverse events like myocarditis coming to light.
“I just want to be sure the price we pay for vaccinating millions of children justifies the side effects, and I don’t think we know that yet,” Dr. Meissner said.
Others acknowledged that there was little risk to kids now with infections on the decline but said that picture could change as variants spread, schools reopen, and colder temperatures force people indoors.
The FDA must decide whether to act based on where we are now or where we could be in a few months.
“I think it’s the million-dollar question right now,” said Hannah Kirking, MD, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention who presented new and unpublished data on COVID’s impact in children to the FDA’s advisory committee.
She said prospective studies tracking the way COVID moves through a household with weekly testing from New York City and Utah had found that children catch and transmit COVID almost as readily as adults. But they don’t usually get as sick as adults do, so their cases are easy to miss.
She also presented the results of blood tests from samples around the country looking for evidence of past infection. In these seroprevalence studies, about 27% of children under age 17 had antibodies to COVID – the most of any age group. So more than 1 in 4 kids already has some natural immunity.
That means the main benefit of vaccinating children might be the protection of others, while they still bear the risks – however tiny.
Some experts felt that wasn’t enough reason to justify mass distribution of the vaccines to kids, and from a regulatory standpoint, it might not be permissible.
“FDA can only approve a medical product in a population if the benefits outweigh the risks in that population,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, assistant professor of pharmaceutical health services research in the University of Maryland’s school of pharmacy, Baltimore.
“If benefits don’t outweigh risks in children, it can’t be indicated for children. Full stop,” said Dr. Doshi, who is also an editor at the BMJ.
He said there’s another way to give children access to vaccines, through an expanded access or compassionate use program. Because most COVID deaths have been in children with underlying health conditions, Dr. Doshi and others said it might make sense to allow expanded access – which would get vaccines to children at high risk for complications – without turning them loose on millions before they are more thoroughly studied.
“It’s not a particularly attractive option for industry, because there’s no money to be made. Your medicine can’t be commercialized under expanded access. The most you can reap is manufacturing cost, which is not a lot,” he said.
Art Caplan, a professor of bioethics at New York University’s Langone medical center, said the argument for vaccinating children for flu falls along the same lines. The benefit-to-risk ratio is finely balanced in children. The main value of protecting them is to protect others.
“Flu rarely kills young folks. But you’re really trying to protect old folks and that’s the classic example,” he said.
What’s more, he said the idea that children would take on some risk with a vaccine for little personal benefit is oversimplified.
“Yes, you might get vaccinated to prevent harm to others, but those others are providing benefits to you. It’s not a one-way street. I think that’s a little morally distorted,” Mr. Caplan said. “Being able to keep society open benefits kids and adults alike.”
Other committee members felt like it was too early to sound the all-clear on COVID and said the FDA should authorize vaccines for children as quickly as it had for other age groups.
“We are still, I believe, in an emergency situation. I think that when this virus goes into our children, which is what it’s going to do, that will give it an incubator to change,” said Oveta Fuller, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Fuller said that for the good of the world, Americans needed to vaccinate children to prevent the virus from mutating and creating new and potentially more dangerous variants.
Weighing risk over safety
Beth Thielen, MD, PhD, pediatric infectious disease specialist and virologist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said she had not followed the committee’s discussions, but about once a month she treats kids who are very sick because of the virus – either because of a COVID infection or because of multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C), an inflammatory reaction that strikes after infection.
She’s worried about how the virus has already changed. She said the kind of disease she’s seeing in kids now is different than what she saw in the early months of the pandemic.
“In the last couple of months, I’ve actually seen a few cases of severe pulmonary disease, more similar to adult disease in children,” Dr. Thielen said. “I see on the horizon that we could start seeing more significant disease in young people, and then the risks of being unvaccinated go up substantially.”
But she also knows nobody has a crystal ball, and right now, everything seems to be trending in the right direction with COVID. That makes the risk-to-benefit consideration murkier.
“The question in my mind is, what is the risk of side effects from the vaccine?” she said. “I think we really need to know what the safety profile of vaccine looks like in children because we do have a decent understanding now what risk from disease looks like, because it’s small, but we are seeing it.”
Dr. Thielen said she’ll be keeping an eye on the next meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for more answers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
By the numbers: Children and COVID-19 prevention
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
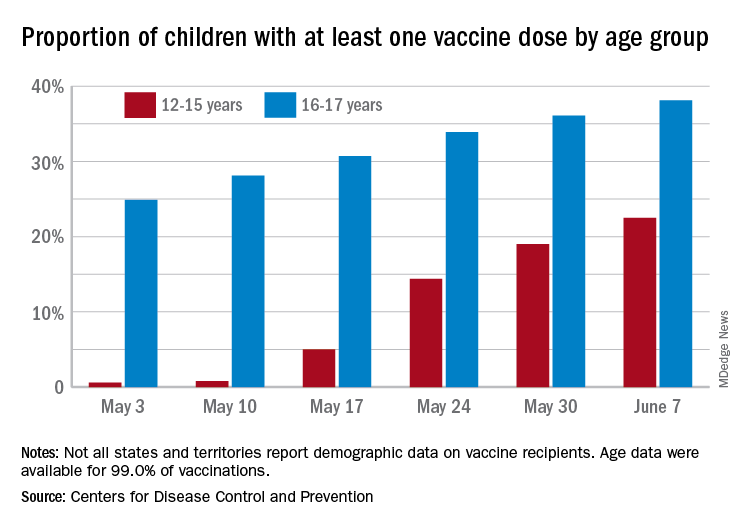
The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”
Over 6.3 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine have been administered to children aged 12-17 years as of June 7, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The latest results from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker show that , with the corresponding figures for vaccine completion coming in at 4.1% and 26.4%. Compared with a week earlier, those numbers are up by 15.4% (one dose) and 486% (completion) for the younger group and by 4.7% and 8.6%, respectively, for the older children.
Children aged 12-15 represented 17.9% of all persons who initiated vaccination in the last 14 days up to June 7, while children aged 16-17 made up 4.8% of vaccine initiation over that period. The 25- to 39-year-olds, at 23.7% of all vaccine initiators, were the only group ahead of those aged 12-15, and the 50- to 64-year-olds were just behind at 17.7%, the CDC data show.
Both groups of children were on the low side, however, when it came to vaccine completion in the last 14 days, with those aged 12-15 at 6.7% of the total and those aged 16-17 years at 4.3%. The only age groups lower than that were ≥75 at 3.5% and <12 at 0.2%, and the highest share of vaccine completion was 26.0% for those aged 25-39, which also happens to be the group with the largest share of the U.S. population (20.5%), the CDC said.
People considered fully vaccinated are those who have received the second dose of a two-dose series or one dose of a single-shot vaccine, but children under age 18 years are eligible only for the Pfizer-BioNTech version, the CDC noted.
Meanwhile, back on the incidence side of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of new cases in U.S. children for the week ending June 3 was at its lowest point (16,281) since mid-June of 2020, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Cases among children now total 3.99 million, which represents 14.1% of cases among all ages, a proportion that hasn’t increased since mid-May, which hasn’t happened since the two groups started keeping track in mid-April of 2020 in the 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam that report such data by age.
Less encouraging was the CDC’s report that “COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates among adolescents ages 12-17 years increased during March and April, following declines in January and February 2021.”
Children have been experiencing much lower rates of severe disease than those of adults throughout the pandemic, the CDC pointed out, but “recent increases in COVID-19-associated hospitalization rates and the potential for severe disease in adolescents reinforce the importance of continued prevention strategies, including vaccination and the correct and consistent use of masks in those who are not yet fully vaccinated.”
CDC director cites rise in hospitalizations in urging teen vaccinations
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
Children aged 12-15 years continue to close COVID-19 vaccination gap
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
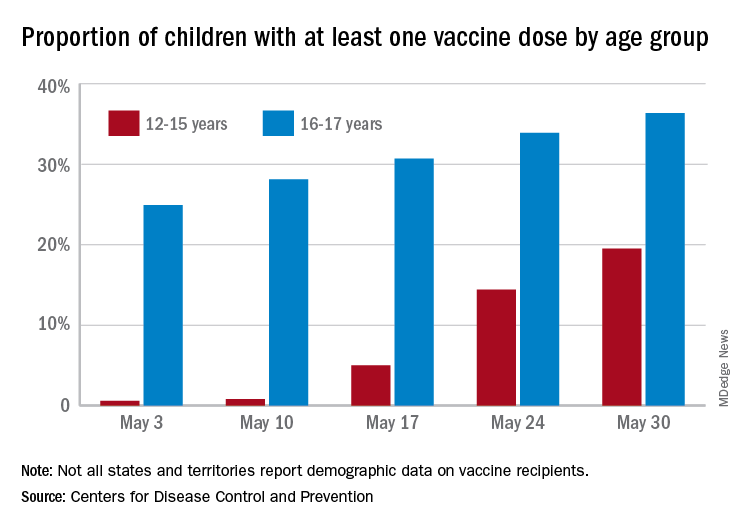
with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
First drug for lung cancer with KRAS mutation gains FDA approval
The first drug to target KRAS mutations in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
KRAS mutations are the most common mutations to occur in NSCLC tumors, accounting for about 25% of them, but for a long time they appeared to be resistant to drug therapy.
The new drug, sotorasib (Lumakras), specifically targets the KRAS G12C mutation, which accounts for about 13% of NSCLC mutations.
It is considered to be something of a breakthrough in cancer research. When clinical data on the new drug (from 126 patients) were presented last year at the World Conference on Lung Cancer, lung cancer experts greeted the results enthusiastically, as reported by Medscape Medical News at the time.
“This is a historic milestone in lung cancer therapy. After four decades of scientific efforts in targeting KRAS, sotorasib has potential to be the first targeted treatment option for this patient population with a high unmet need,” Bob T. Li, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the time.
Now, in a press release from the manufacturer, Amgen, he said: “Sotorasib represents a major advancement in oncology and changes the treatment paradigm for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated non–small cell lung cancer.
“Patients with non–small cell lung cancer who have progressed beyond first-line treatment face a poor prognosis and have limited treatment options available to them. Sotorasib delivers a new option for these patients, and it is the first KRAS-targeted therapy to be approved after nearly four decades of research,” he added.
Details of clinical data
This is an accelerated approval based on response rate data.
The FDA notes that the clinical data come from a study of 124 patients with locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC with disease progression after receiving an immune checkpoint inhibitor and/or platinum-based chemotherapy.
The major outcome measured was overall response rate (ORR), which was 36%. Of the patients who responded, 58% had a duration of response of 6 months or longer.
Sotorasib was approved at a dose of 960 mg, and this dose was based on available clinical data as well as pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling, the FDA noted. As part of the evaluation for this accelerated approval, the agency is requiring a postmarketing trial to investigate whether a lower dose will have a similar clinical effect.
The most common side effects include diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, fatigue, liver damage, and cough. Sotorasib should not be used if patients develop symptoms of interstitial lung disease, and should be permanently discontinued if interstitial lung disease is confirmed.
Patients on sotorasib should have liver function tests prior to starting and while taking the drug; if liver damage develops, the drug should be stopped or the dose reduced. Patients should avoid taking acid-reducing agents, drugs that induce or are substrates for certain enzymes in the liver, and drugs that are substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
Companion diagnostic tests also approved
Along with the new drug, the FDA approved two companion diagnostic tests – the QIAGEN therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR kit (approval granted to QIAGEN GmbH) for analyzing tumor tissue and the Guardant360 CDx (approval granted to Guardant Health) for analyzing plasma specimens to determine if the KRAS G12C mutation is present. The agency notes that if the plasma test comes back negative, the patient’s tumor tissue should be tested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first drug to target KRAS mutations in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
KRAS mutations are the most common mutations to occur in NSCLC tumors, accounting for about 25% of them, but for a long time they appeared to be resistant to drug therapy.
The new drug, sotorasib (Lumakras), specifically targets the KRAS G12C mutation, which accounts for about 13% of NSCLC mutations.
It is considered to be something of a breakthrough in cancer research. When clinical data on the new drug (from 126 patients) were presented last year at the World Conference on Lung Cancer, lung cancer experts greeted the results enthusiastically, as reported by Medscape Medical News at the time.
“This is a historic milestone in lung cancer therapy. After four decades of scientific efforts in targeting KRAS, sotorasib has potential to be the first targeted treatment option for this patient population with a high unmet need,” Bob T. Li, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the time.
Now, in a press release from the manufacturer, Amgen, he said: “Sotorasib represents a major advancement in oncology and changes the treatment paradigm for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated non–small cell lung cancer.
“Patients with non–small cell lung cancer who have progressed beyond first-line treatment face a poor prognosis and have limited treatment options available to them. Sotorasib delivers a new option for these patients, and it is the first KRAS-targeted therapy to be approved after nearly four decades of research,” he added.
Details of clinical data
This is an accelerated approval based on response rate data.
The FDA notes that the clinical data come from a study of 124 patients with locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC with disease progression after receiving an immune checkpoint inhibitor and/or platinum-based chemotherapy.
The major outcome measured was overall response rate (ORR), which was 36%. Of the patients who responded, 58% had a duration of response of 6 months or longer.
Sotorasib was approved at a dose of 960 mg, and this dose was based on available clinical data as well as pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling, the FDA noted. As part of the evaluation for this accelerated approval, the agency is requiring a postmarketing trial to investigate whether a lower dose will have a similar clinical effect.
The most common side effects include diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, fatigue, liver damage, and cough. Sotorasib should not be used if patients develop symptoms of interstitial lung disease, and should be permanently discontinued if interstitial lung disease is confirmed.
Patients on sotorasib should have liver function tests prior to starting and while taking the drug; if liver damage develops, the drug should be stopped or the dose reduced. Patients should avoid taking acid-reducing agents, drugs that induce or are substrates for certain enzymes in the liver, and drugs that are substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
Companion diagnostic tests also approved
Along with the new drug, the FDA approved two companion diagnostic tests – the QIAGEN therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR kit (approval granted to QIAGEN GmbH) for analyzing tumor tissue and the Guardant360 CDx (approval granted to Guardant Health) for analyzing plasma specimens to determine if the KRAS G12C mutation is present. The agency notes that if the plasma test comes back negative, the patient’s tumor tissue should be tested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first drug to target KRAS mutations in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
KRAS mutations are the most common mutations to occur in NSCLC tumors, accounting for about 25% of them, but for a long time they appeared to be resistant to drug therapy.
The new drug, sotorasib (Lumakras), specifically targets the KRAS G12C mutation, which accounts for about 13% of NSCLC mutations.
It is considered to be something of a breakthrough in cancer research. When clinical data on the new drug (from 126 patients) were presented last year at the World Conference on Lung Cancer, lung cancer experts greeted the results enthusiastically, as reported by Medscape Medical News at the time.
“This is a historic milestone in lung cancer therapy. After four decades of scientific efforts in targeting KRAS, sotorasib has potential to be the first targeted treatment option for this patient population with a high unmet need,” Bob T. Li, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said at the time.
Now, in a press release from the manufacturer, Amgen, he said: “Sotorasib represents a major advancement in oncology and changes the treatment paradigm for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated non–small cell lung cancer.
“Patients with non–small cell lung cancer who have progressed beyond first-line treatment face a poor prognosis and have limited treatment options available to them. Sotorasib delivers a new option for these patients, and it is the first KRAS-targeted therapy to be approved after nearly four decades of research,” he added.
Details of clinical data
This is an accelerated approval based on response rate data.
The FDA notes that the clinical data come from a study of 124 patients with locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC with disease progression after receiving an immune checkpoint inhibitor and/or platinum-based chemotherapy.
The major outcome measured was overall response rate (ORR), which was 36%. Of the patients who responded, 58% had a duration of response of 6 months or longer.
Sotorasib was approved at a dose of 960 mg, and this dose was based on available clinical data as well as pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling, the FDA noted. As part of the evaluation for this accelerated approval, the agency is requiring a postmarketing trial to investigate whether a lower dose will have a similar clinical effect.
The most common side effects include diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, fatigue, liver damage, and cough. Sotorasib should not be used if patients develop symptoms of interstitial lung disease, and should be permanently discontinued if interstitial lung disease is confirmed.
Patients on sotorasib should have liver function tests prior to starting and while taking the drug; if liver damage develops, the drug should be stopped or the dose reduced. Patients should avoid taking acid-reducing agents, drugs that induce or are substrates for certain enzymes in the liver, and drugs that are substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
Companion diagnostic tests also approved
Along with the new drug, the FDA approved two companion diagnostic tests – the QIAGEN therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR kit (approval granted to QIAGEN GmbH) for analyzing tumor tissue and the Guardant360 CDx (approval granted to Guardant Health) for analyzing plasma specimens to determine if the KRAS G12C mutation is present. The agency notes that if the plasma test comes back negative, the patient’s tumor tissue should be tested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA reassures myocarditis rare after COVID vaccination, benefits overwhelm risks
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cell phone, smart watch magnets can affect medical devices, FDA says
The Food and Drug Administration is recommending patients and caregivers keep cell phones and smart watches at least 6 inches away from implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
The warning, published on May 13, comes on the heels of recent research reporting that high–field strength magnets in newer smartphones may cause some implanted medical devices to switch to “magnet mode” and suspend normal lifesaving operations until the magnet is moved away.
This, for example, may cause a cardiac defibrillator to be unable to detect tachycardia events, the agency noted. The magnets may also change the operational mode such as turning on asynchronous mode in a pacemaker.
“The FDA is aware of published articles which describe the effect that sufficiently strong magnetic fields can turn on the magnetic safe mode when in close contact,” it said. “The FDA also conducted its own testing on some products that use the high–field strength magnet feature and have confirmed the magnetic field is both consistent with the publications and strong enough to turn on the magnetic safety mode of the medical devices in question.”
The FDA said it believes the risk to patients is low and is not aware of any adverse events associated with this issue at this time.
The American Heart Association has also cautioned that magnetic fields can inhibit the pulse generators for implantable cardioverter defibrillators and pacemakers.
The FDA offered the following simple precautions for individuals with implanted medical devices:
- Keep the consumer electronics, such as certain cell phones and smart watches, 6 inches away from implanted medical devices.
- Do not carry consumer electronics in a pocket over the medical device.
- Check your device using your home monitoring system, if you have one.
- Talk to your health care provider if you are experiencing any symptoms or have questions regarding magnets in consumer electronics and implanted medical devices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration is recommending patients and caregivers keep cell phones and smart watches at least 6 inches away from implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
The warning, published on May 13, comes on the heels of recent research reporting that high–field strength magnets in newer smartphones may cause some implanted medical devices to switch to “magnet mode” and suspend normal lifesaving operations until the magnet is moved away.
This, for example, may cause a cardiac defibrillator to be unable to detect tachycardia events, the agency noted. The magnets may also change the operational mode such as turning on asynchronous mode in a pacemaker.
“The FDA is aware of published articles which describe the effect that sufficiently strong magnetic fields can turn on the magnetic safe mode when in close contact,” it said. “The FDA also conducted its own testing on some products that use the high–field strength magnet feature and have confirmed the magnetic field is both consistent with the publications and strong enough to turn on the magnetic safety mode of the medical devices in question.”
The FDA said it believes the risk to patients is low and is not aware of any adverse events associated with this issue at this time.
The American Heart Association has also cautioned that magnetic fields can inhibit the pulse generators for implantable cardioverter defibrillators and pacemakers.
The FDA offered the following simple precautions for individuals with implanted medical devices:
- Keep the consumer electronics, such as certain cell phones and smart watches, 6 inches away from implanted medical devices.
- Do not carry consumer electronics in a pocket over the medical device.
- Check your device using your home monitoring system, if you have one.
- Talk to your health care provider if you are experiencing any symptoms or have questions regarding magnets in consumer electronics and implanted medical devices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration is recommending patients and caregivers keep cell phones and smart watches at least 6 inches away from implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
The warning, published on May 13, comes on the heels of recent research reporting that high–field strength magnets in newer smartphones may cause some implanted medical devices to switch to “magnet mode” and suspend normal lifesaving operations until the magnet is moved away.
This, for example, may cause a cardiac defibrillator to be unable to detect tachycardia events, the agency noted. The magnets may also change the operational mode such as turning on asynchronous mode in a pacemaker.
“The FDA is aware of published articles which describe the effect that sufficiently strong magnetic fields can turn on the magnetic safe mode when in close contact,” it said. “The FDA also conducted its own testing on some products that use the high–field strength magnet feature and have confirmed the magnetic field is both consistent with the publications and strong enough to turn on the magnetic safety mode of the medical devices in question.”
The FDA said it believes the risk to patients is low and is not aware of any adverse events associated with this issue at this time.
The American Heart Association has also cautioned that magnetic fields can inhibit the pulse generators for implantable cardioverter defibrillators and pacemakers.
The FDA offered the following simple precautions for individuals with implanted medical devices:
- Keep the consumer electronics, such as certain cell phones and smart watches, 6 inches away from implanted medical devices.
- Do not carry consumer electronics in a pocket over the medical device.
- Check your device using your home monitoring system, if you have one.
- Talk to your health care provider if you are experiencing any symptoms or have questions regarding magnets in consumer electronics and implanted medical devices.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC: Vaccinated? You don’t need a mask indoors
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes Pfizer COVID vaccine for teens 12-15
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel narrowly backs avacopan approval
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.




