User login
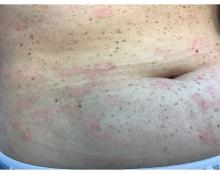
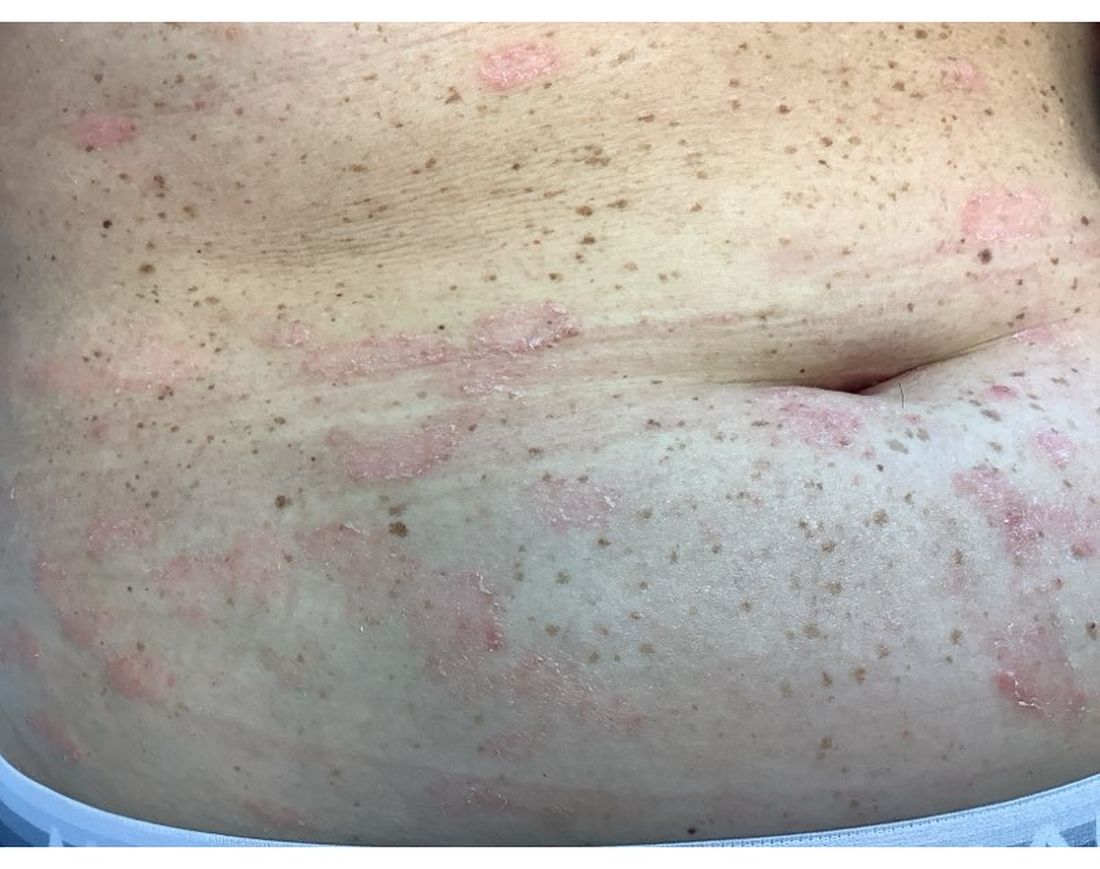
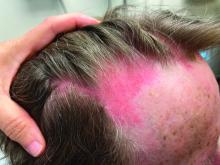
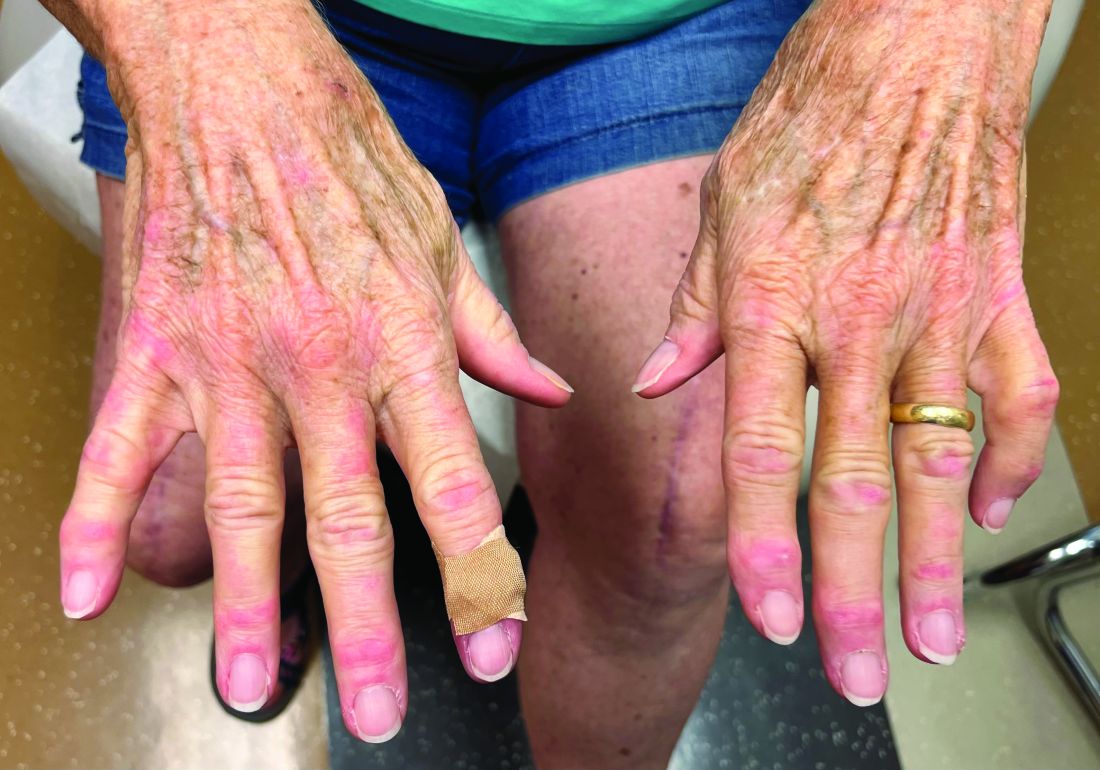
A 30-Year-Old White Female Presented With a 4-Month History of Scaly, Erythematous Patches and Plaques on Her Trunk and Extremities
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibitors are used to treat a variety of autoimmune conditions including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Interestingly, they have also been observed to cause paradoxical psoriasis with an incidence between 0.6%-5.3%, most commonly occurring in patients with underlying Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Infliximab is the most common TNF inhibitor associated with this condition (52.6%-62.6% of cases) followed by etanercept (12%-29%). .
Psoriasis is traditionally divided into two types. Patients with type I psoriasis have a family history, develop symptoms before the age of 40 and are often positive for HLA-Cw6. Type II psoriasis is not related to HLA-Cw6, lacks a family history, and typically manifests after age 40. Psoriatic lesions are well-defined, erythematous plaques with silvery scales most commonly appearing on extensor surfaces and the scalp. Variants include nail psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and guttate psoriasis.
Although psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis, histologic examination may be used to differentiate from other dermatoses if necessary. The lesions of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis characteristically display patterns similar to primary psoriasis, including parakeratosis, microabscesses, and rete ridges. Eosinophilic hypersensitivity reactions and features overlapping with eczematous hypersensitivity (psoriasiform dermatitis) may also be present.
The pathogenesis of this condition is not well understood, but theories include a variety of immune processes including interferon overproduction, interleukin and T-cell activation, and the presence of an infectious nidus. Classical psoriasis is related to type 1 interferon release, so theoretically, immunosuppression caused by TNF inhibitor treatment may permit uncontrolled production of interferons, resulting in psoriatic lesions. Another theory is that interleukin (IL)-23, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, promotes activation of T-helper 17 (Th17) cells. Th17 cells are part of the pathogenesis of primary psoriasis and other inflammatory conditions, such as RA and inflammatory bowel disease. Of note, individuals with gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases are already known to be at a greater risk for developing psoriasis. Immunosuppression caused by a TNF inhibitor may leave patients more susceptible to other infections, which may induce psoriatic plaques.
There are multiple approaches to treatment depending on the severity of the disease. If the psoriatic eruption is mild, the medication may be continued. This “treat-through” method is often considered when stopping the current immunotherapy would cause the patient significant issues. Moderate to severe cases of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis may warrant switching TNF inhibitor therapy or completely changing the drug class used in the treatment of the underlying autoimmune condition. Additional treatments include topical and oral steroids, UV therapy, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Leon S. Maratchi, MD, Gastro Health, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Li SJ et al. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80. doi: 10.1177/2475530318810851.
2. Lu J and Lu Y. J Transl Autoimmun. 2023 Sep 6:7:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100211.
3. Nair PA and Badri T. Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Apr 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibitors are used to treat a variety of autoimmune conditions including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Interestingly, they have also been observed to cause paradoxical psoriasis with an incidence between 0.6%-5.3%, most commonly occurring in patients with underlying Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Infliximab is the most common TNF inhibitor associated with this condition (52.6%-62.6% of cases) followed by etanercept (12%-29%). .
Psoriasis is traditionally divided into two types. Patients with type I psoriasis have a family history, develop symptoms before the age of 40 and are often positive for HLA-Cw6. Type II psoriasis is not related to HLA-Cw6, lacks a family history, and typically manifests after age 40. Psoriatic lesions are well-defined, erythematous plaques with silvery scales most commonly appearing on extensor surfaces and the scalp. Variants include nail psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and guttate psoriasis.
Although psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis, histologic examination may be used to differentiate from other dermatoses if necessary. The lesions of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis characteristically display patterns similar to primary psoriasis, including parakeratosis, microabscesses, and rete ridges. Eosinophilic hypersensitivity reactions and features overlapping with eczematous hypersensitivity (psoriasiform dermatitis) may also be present.
The pathogenesis of this condition is not well understood, but theories include a variety of immune processes including interferon overproduction, interleukin and T-cell activation, and the presence of an infectious nidus. Classical psoriasis is related to type 1 interferon release, so theoretically, immunosuppression caused by TNF inhibitor treatment may permit uncontrolled production of interferons, resulting in psoriatic lesions. Another theory is that interleukin (IL)-23, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, promotes activation of T-helper 17 (Th17) cells. Th17 cells are part of the pathogenesis of primary psoriasis and other inflammatory conditions, such as RA and inflammatory bowel disease. Of note, individuals with gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases are already known to be at a greater risk for developing psoriasis. Immunosuppression caused by a TNF inhibitor may leave patients more susceptible to other infections, which may induce psoriatic plaques.
There are multiple approaches to treatment depending on the severity of the disease. If the psoriatic eruption is mild, the medication may be continued. This “treat-through” method is often considered when stopping the current immunotherapy would cause the patient significant issues. Moderate to severe cases of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis may warrant switching TNF inhibitor therapy or completely changing the drug class used in the treatment of the underlying autoimmune condition. Additional treatments include topical and oral steroids, UV therapy, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Leon S. Maratchi, MD, Gastro Health, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Li SJ et al. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80. doi: 10.1177/2475530318810851.
2. Lu J and Lu Y. J Transl Autoimmun. 2023 Sep 6:7:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100211.
3. Nair PA and Badri T. Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Apr 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibitors are used to treat a variety of autoimmune conditions including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Interestingly, they have also been observed to cause paradoxical psoriasis with an incidence between 0.6%-5.3%, most commonly occurring in patients with underlying Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Infliximab is the most common TNF inhibitor associated with this condition (52.6%-62.6% of cases) followed by etanercept (12%-29%). .
Psoriasis is traditionally divided into two types. Patients with type I psoriasis have a family history, develop symptoms before the age of 40 and are often positive for HLA-Cw6. Type II psoriasis is not related to HLA-Cw6, lacks a family history, and typically manifests after age 40. Psoriatic lesions are well-defined, erythematous plaques with silvery scales most commonly appearing on extensor surfaces and the scalp. Variants include nail psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and guttate psoriasis.
Although psoriasis is typically a clinical diagnosis, histologic examination may be used to differentiate from other dermatoses if necessary. The lesions of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis characteristically display patterns similar to primary psoriasis, including parakeratosis, microabscesses, and rete ridges. Eosinophilic hypersensitivity reactions and features overlapping with eczematous hypersensitivity (psoriasiform dermatitis) may also be present.
The pathogenesis of this condition is not well understood, but theories include a variety of immune processes including interferon overproduction, interleukin and T-cell activation, and the presence of an infectious nidus. Classical psoriasis is related to type 1 interferon release, so theoretically, immunosuppression caused by TNF inhibitor treatment may permit uncontrolled production of interferons, resulting in psoriatic lesions. Another theory is that interleukin (IL)-23, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, promotes activation of T-helper 17 (Th17) cells. Th17 cells are part of the pathogenesis of primary psoriasis and other inflammatory conditions, such as RA and inflammatory bowel disease. Of note, individuals with gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases are already known to be at a greater risk for developing psoriasis. Immunosuppression caused by a TNF inhibitor may leave patients more susceptible to other infections, which may induce psoriatic plaques.
There are multiple approaches to treatment depending on the severity of the disease. If the psoriatic eruption is mild, the medication may be continued. This “treat-through” method is often considered when stopping the current immunotherapy would cause the patient significant issues. Moderate to severe cases of TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis may warrant switching TNF inhibitor therapy or completely changing the drug class used in the treatment of the underlying autoimmune condition. Additional treatments include topical and oral steroids, UV therapy, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Leon S. Maratchi, MD, Gastro Health, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Li SJ et al. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80. doi: 10.1177/2475530318810851.
2. Lu J and Lu Y. J Transl Autoimmun. 2023 Sep 6:7:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100211.
3. Nair PA and Badri T. Psoriasis. [Updated 2023 Apr 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/
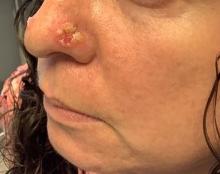
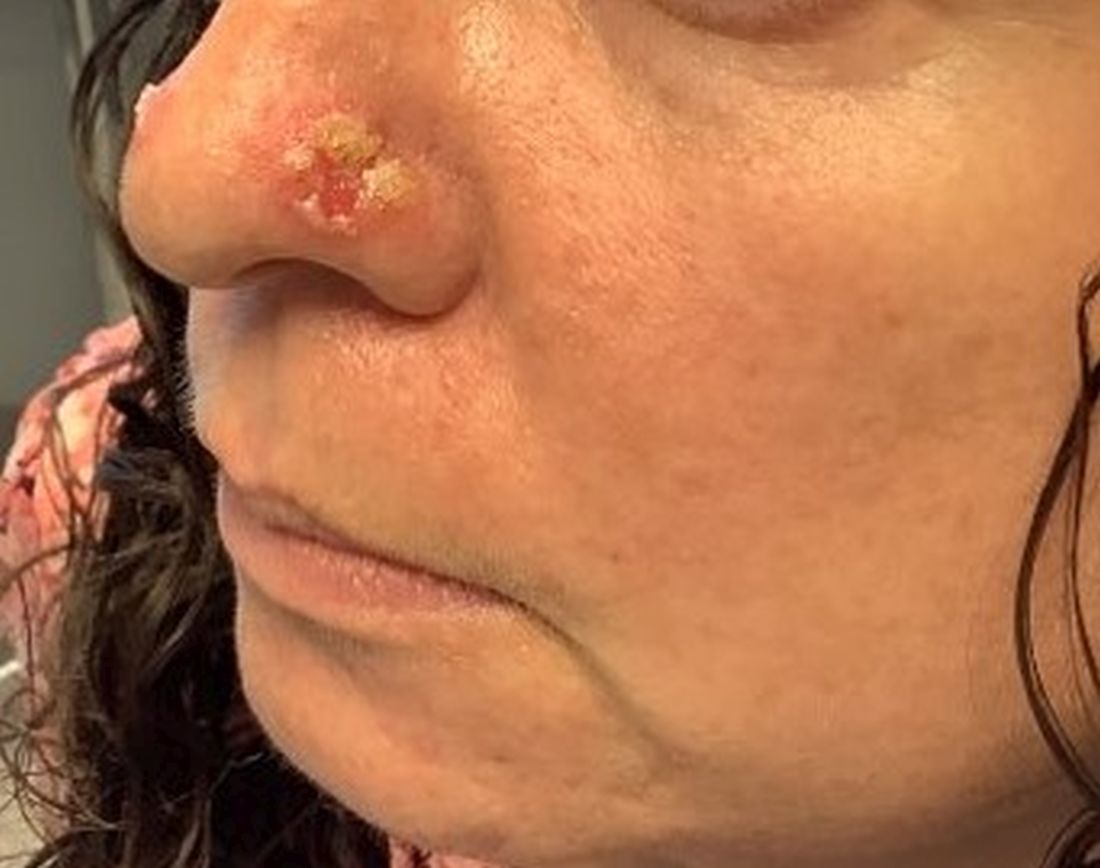
A 35-year-old female presented with a 1-day history of eroded papules and vesicles distributed periorally
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
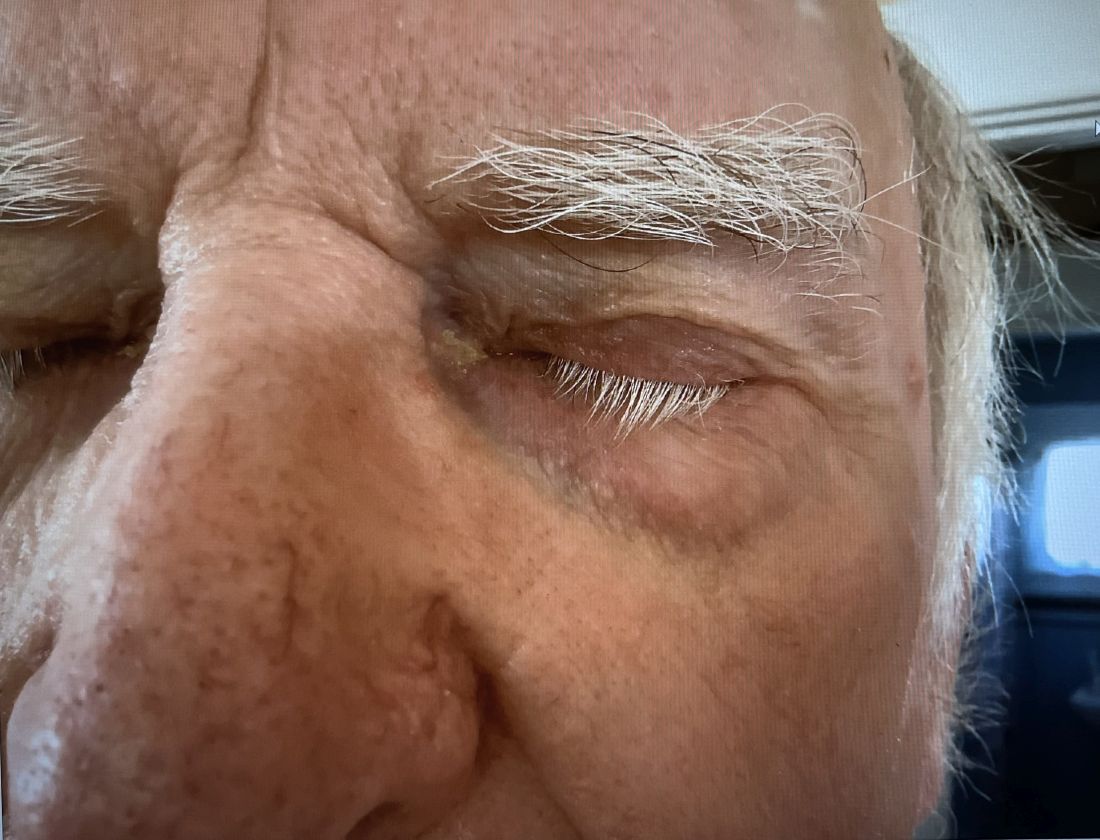
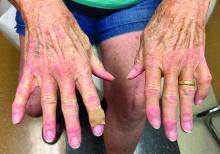
A 74-year-old White male presented with a 1-year history of depigmented patches on the hands, arms, and face, as well as white eyelashes and eyebrows
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
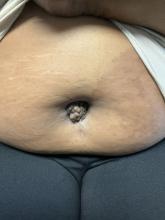
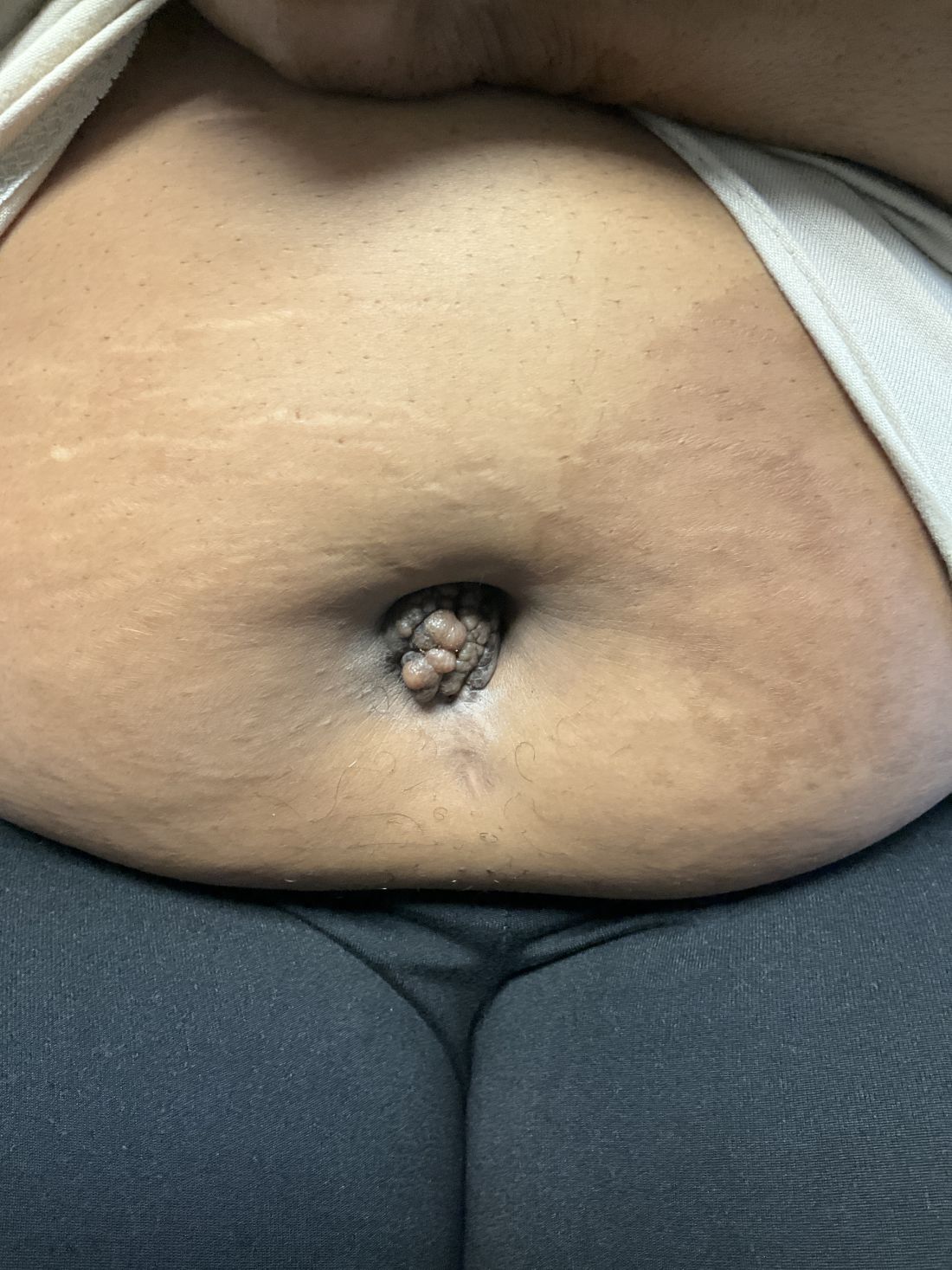
A 27-year-old Haitian woman presented with a painful umbilical mass which had been growing in size for 5 months
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
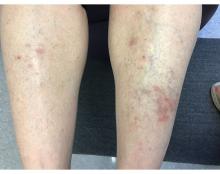
A 55-year-old female presented a with few years' history of pruritic plaques on her shins and wrists
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
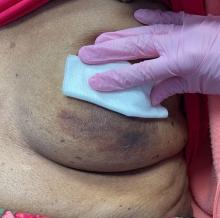
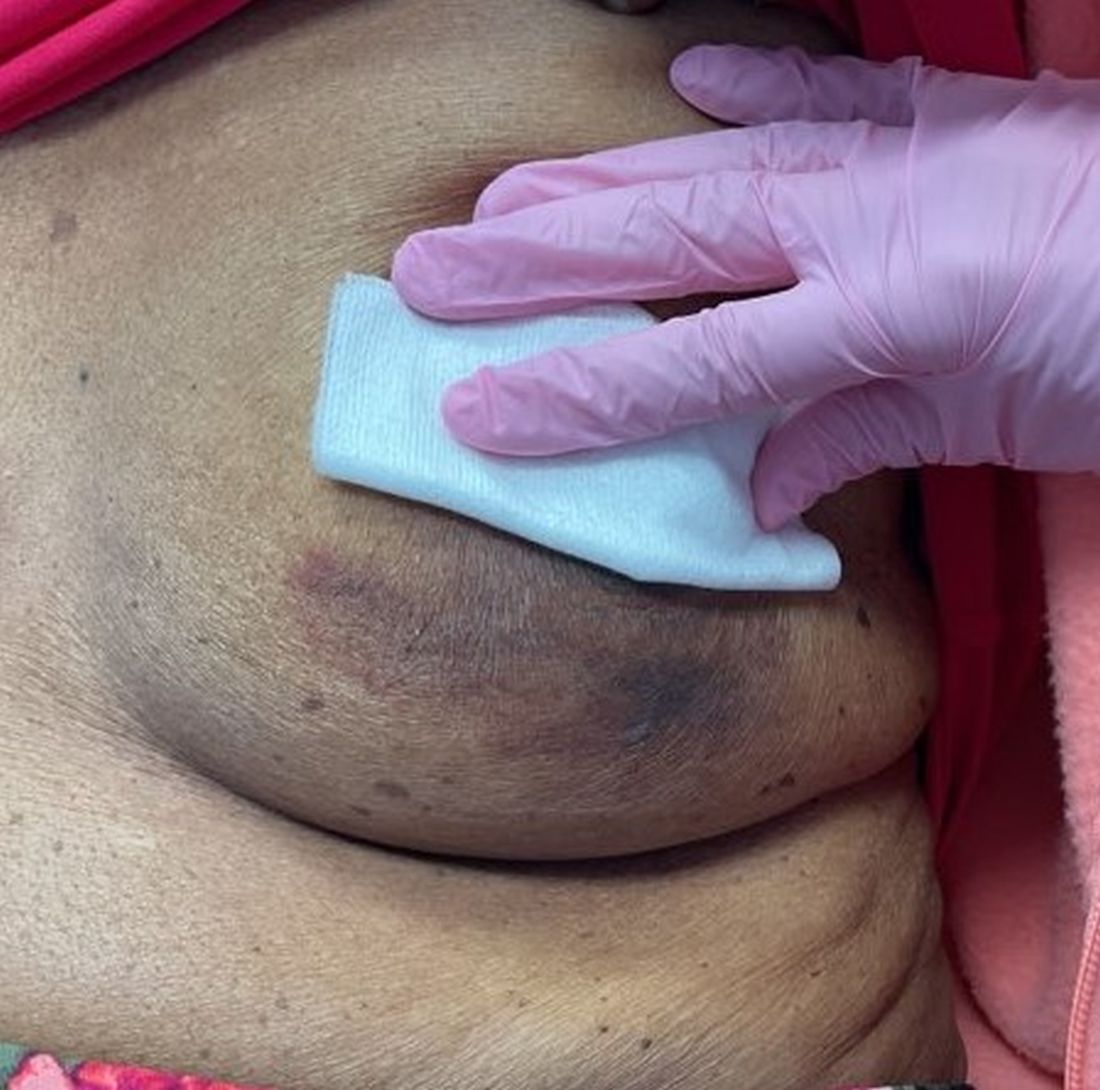
An 88-year-old Black woman presented with 3 months duration of asymptomatic, violaceous patches on the left breast
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
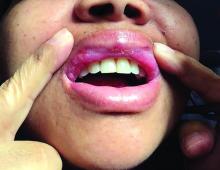
A 42-year-old woman presented with a few days of erosions on her buccal mucosa, tongue, and soft palate
in which lesions present in the same location upon repeated intake of the offending drug. The lesions typically present within 30 minutes to 8 hours of administration of the drug. These reactions can be considered allergic or pseudo-allergic, in which case, there is no notable adaptive immune response. CD8+ T cells appear to play a role in the epidermal injury via release of interferons and interactions with other inflammatory cells.
There are numerous drugs that can precipitate these findings. NSAIDs; antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides; and phenytoin are common offenders. In the case of our patient, naproxen was the offending medication.
The classic presentation of FDE features annular, erythematous to violaceous macules on the skin or mucosa that can be asymptomatic or can produce burning, pain, or pruritus. The most common locations include the trunk and extremities, but the palms, soles, face, scalp, and mucosa can also be impacted. The oral mucosa seems to be the most common mucosal location. Intravenous administration of a drug is associated with more severe symptoms. Systemic symptoms are typically absent, and the eruption may initially be in one location, but may appear elsewhere upon repeated exposure to the offending medication.
The differential diagnosis includes arthropod bite reactions, urticaria, and erythema multiforme. Although FDEs are typically a clinical diagnosis, the histopathology will commonly show a vacuolar interface dermatitis. Furthermore, a variety of immune cells can be found, including neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and lymphocytic infiltrate. A combination of two or more histological patterns often favors the diagnosis of FDE.
Steroid creams can be prescribed to decrease the inflammatory reaction and improve symptoms; however, the definitive treatment of this condition is cessation of the offending agent. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common symptom after resolution of the condition, and it may take months to fade away. Further darkening can be prevented by practicing sun safety measures such as wearing sunblock, covering the affected areas, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Igor Chaplik, DO, Aesthetix Dermatology, Fort Lauderdale. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Shaker G et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 23;14(8):e28299.
Srivastava R et al. Indian J Dent. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):103-6.
Weyers W, Metze D. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011 Jan 31;1(1):33-47.
in which lesions present in the same location upon repeated intake of the offending drug. The lesions typically present within 30 minutes to 8 hours of administration of the drug. These reactions can be considered allergic or pseudo-allergic, in which case, there is no notable adaptive immune response. CD8+ T cells appear to play a role in the epidermal injury via release of interferons and interactions with other inflammatory cells.
There are numerous drugs that can precipitate these findings. NSAIDs; antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides; and phenytoin are common offenders. In the case of our patient, naproxen was the offending medication.
The classic presentation of FDE features annular, erythematous to violaceous macules on the skin or mucosa that can be asymptomatic or can produce burning, pain, or pruritus. The most common locations include the trunk and extremities, but the palms, soles, face, scalp, and mucosa can also be impacted. The oral mucosa seems to be the most common mucosal location. Intravenous administration of a drug is associated with more severe symptoms. Systemic symptoms are typically absent, and the eruption may initially be in one location, but may appear elsewhere upon repeated exposure to the offending medication.
The differential diagnosis includes arthropod bite reactions, urticaria, and erythema multiforme. Although FDEs are typically a clinical diagnosis, the histopathology will commonly show a vacuolar interface dermatitis. Furthermore, a variety of immune cells can be found, including neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and lymphocytic infiltrate. A combination of two or more histological patterns often favors the diagnosis of FDE.
Steroid creams can be prescribed to decrease the inflammatory reaction and improve symptoms; however, the definitive treatment of this condition is cessation of the offending agent. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common symptom after resolution of the condition, and it may take months to fade away. Further darkening can be prevented by practicing sun safety measures such as wearing sunblock, covering the affected areas, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Igor Chaplik, DO, Aesthetix Dermatology, Fort Lauderdale. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Shaker G et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 23;14(8):e28299.
Srivastava R et al. Indian J Dent. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):103-6.
Weyers W, Metze D. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011 Jan 31;1(1):33-47.
in which lesions present in the same location upon repeated intake of the offending drug. The lesions typically present within 30 minutes to 8 hours of administration of the drug. These reactions can be considered allergic or pseudo-allergic, in which case, there is no notable adaptive immune response. CD8+ T cells appear to play a role in the epidermal injury via release of interferons and interactions with other inflammatory cells.
There are numerous drugs that can precipitate these findings. NSAIDs; antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides; and phenytoin are common offenders. In the case of our patient, naproxen was the offending medication.
The classic presentation of FDE features annular, erythematous to violaceous macules on the skin or mucosa that can be asymptomatic or can produce burning, pain, or pruritus. The most common locations include the trunk and extremities, but the palms, soles, face, scalp, and mucosa can also be impacted. The oral mucosa seems to be the most common mucosal location. Intravenous administration of a drug is associated with more severe symptoms. Systemic symptoms are typically absent, and the eruption may initially be in one location, but may appear elsewhere upon repeated exposure to the offending medication.
The differential diagnosis includes arthropod bite reactions, urticaria, and erythema multiforme. Although FDEs are typically a clinical diagnosis, the histopathology will commonly show a vacuolar interface dermatitis. Furthermore, a variety of immune cells can be found, including neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and lymphocytic infiltrate. A combination of two or more histological patterns often favors the diagnosis of FDE.
Steroid creams can be prescribed to decrease the inflammatory reaction and improve symptoms; however, the definitive treatment of this condition is cessation of the offending agent. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common symptom after resolution of the condition, and it may take months to fade away. Further darkening can be prevented by practicing sun safety measures such as wearing sunblock, covering the affected areas, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Igor Chaplik, DO, Aesthetix Dermatology, Fort Lauderdale. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Shaker G et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 23;14(8):e28299.
Srivastava R et al. Indian J Dent. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):103-6.
Weyers W, Metze D. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011 Jan 31;1(1):33-47.
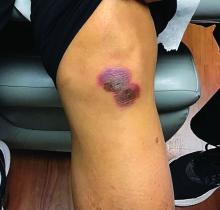
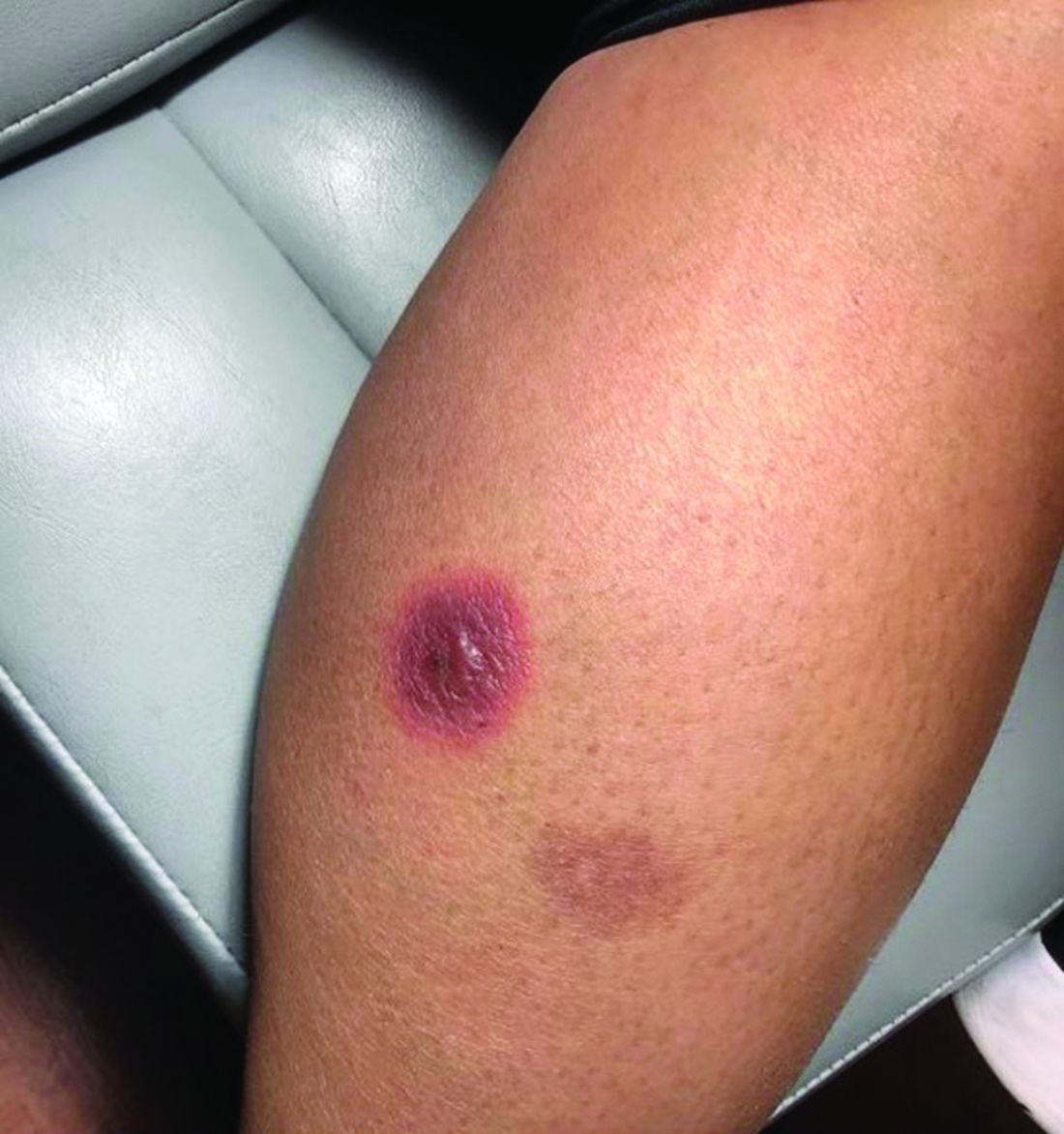
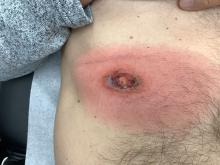
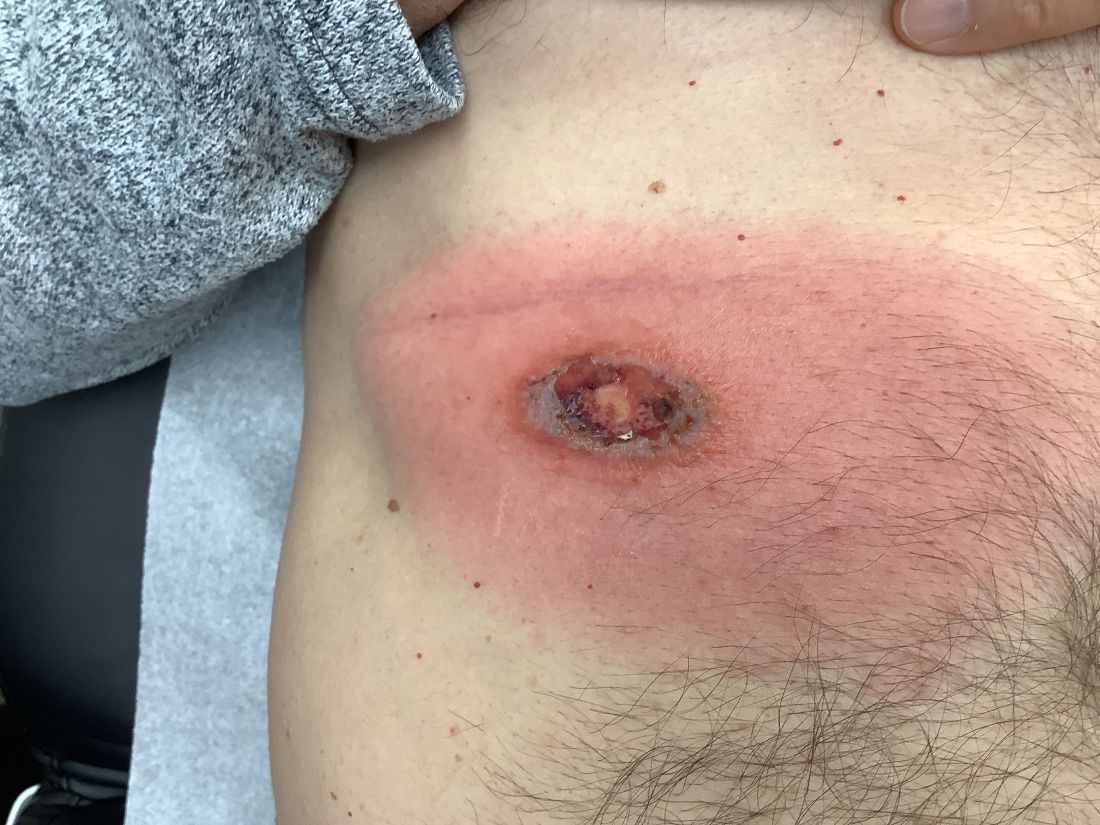
A White male presented with a purulent erythematous edematous plaque with central necrosis and ulceration on his right flank
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
A 75-year-old White woman presented with diffuse erythema, scale, and pruritus on her scalp
The classical presentation includes symmetric proximal muscle weakness and underlying malignancy and is very common in adult patients. The etiology is unknown, however.
Some studies suggest people with certain HLA subtypes are at higher risk, and various infectious and pharmacological triggers are suspected to play a role in the pathogenesis of dermatomyositis. Infectious causes include Coxsackie B, enterovirus, and parvovirus. Drugs such as antineoplastic agents, antibiotics, and NSAIDs have been found to be triggers.
The pathogenesis of dermatomyositis involves immune-mediated damage to muscle capillaries and the endothelium of arterioles. In the typical humoral immune response, complement activation occurs. One mechanism of damage in dermatomyositis occurs when the membrane attack complex formed at the end of the complement process deposits in blood vessels, causing inflammation. B cells, autoantibodies, and interferon overexpression may also play a role in damaging the vasculature and muscle fibers. Hypoxia leads to muscular atrophy, resulting in degeneration and death of the fibers. On muscle biopsy, a perivascular and perimysial inflammatory infiltrate, perifascicular atrophy, and microangiopathy may be present. Skin histology reveals vacuolar changes in the basal layer, a lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin production in the dermis.
On clinical examination, patients will have proximal muscle weakness and a skin rash that may include Gottron’s papules, heliotrope erythema, V-sign, shawl sign, holster sign, scalp erythema, midfacial erythema, and photosensitivity. Scalp erythema in dermatomyositis is highly linked to pruritus, alopecia, and telogen effluvium. Patients may experience small fiber neuropathy in dermatomyositis.
Serologies for this patient, who had previously been diagnosed and treated for dermatomyositis, were significant for a positive ANA 1:2560. Anti-Jo-1 antibody was negative. Her liver function tests, aldolase, creatinine kinase, sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and serum protein electrophoresis were normal. Imaging revealed mild chronic interstitial lung disease. A malignancy workup was negative.
Treatment of dermatomyositis involves lifestyle changes and pharmacologic therapy. Because of the intense photosensitivity, patients should be diligent with their sun protection. Methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil are considered first-line therapies for dermatomyositis. Therapies such as cyclophosphamide, rituximab, IVIg, and plasmapheresis may also be indicated in severe or refractory cases. Additionally, patients with pulmonary involvement should be given systemic steroids. The side effects of these drugs must be considered in the context of the patient’s demographics, comorbidities and lifestyle.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center, Riverside, Calif. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Qudsiya Z and Waseem M. Dermatomyositis, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2023 Jan.
2. Kamperman RG et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 13;23(8):4301.
3. Kassamali B et al. Int J WomensDermatol. 2021 Sep 24;7(5Part A):576-82.
4. Vázquez-Herrera NE et al. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Aug;4(3):187-99.
The classical presentation includes symmetric proximal muscle weakness and underlying malignancy and is very common in adult patients. The etiology is unknown, however.
Some studies suggest people with certain HLA subtypes are at higher risk, and various infectious and pharmacological triggers are suspected to play a role in the pathogenesis of dermatomyositis. Infectious causes include Coxsackie B, enterovirus, and parvovirus. Drugs such as antineoplastic agents, antibiotics, and NSAIDs have been found to be triggers.
The pathogenesis of dermatomyositis involves immune-mediated damage to muscle capillaries and the endothelium of arterioles. In the typical humoral immune response, complement activation occurs. One mechanism of damage in dermatomyositis occurs when the membrane attack complex formed at the end of the complement process deposits in blood vessels, causing inflammation. B cells, autoantibodies, and interferon overexpression may also play a role in damaging the vasculature and muscle fibers. Hypoxia leads to muscular atrophy, resulting in degeneration and death of the fibers. On muscle biopsy, a perivascular and perimysial inflammatory infiltrate, perifascicular atrophy, and microangiopathy may be present. Skin histology reveals vacuolar changes in the basal layer, a lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin production in the dermis.
On clinical examination, patients will have proximal muscle weakness and a skin rash that may include Gottron’s papules, heliotrope erythema, V-sign, shawl sign, holster sign, scalp erythema, midfacial erythema, and photosensitivity. Scalp erythema in dermatomyositis is highly linked to pruritus, alopecia, and telogen effluvium. Patients may experience small fiber neuropathy in dermatomyositis.
Serologies for this patient, who had previously been diagnosed and treated for dermatomyositis, were significant for a positive ANA 1:2560. Anti-Jo-1 antibody was negative. Her liver function tests, aldolase, creatinine kinase, sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and serum protein electrophoresis were normal. Imaging revealed mild chronic interstitial lung disease. A malignancy workup was negative.
Treatment of dermatomyositis involves lifestyle changes and pharmacologic therapy. Because of the intense photosensitivity, patients should be diligent with their sun protection. Methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil are considered first-line therapies for dermatomyositis. Therapies such as cyclophosphamide, rituximab, IVIg, and plasmapheresis may also be indicated in severe or refractory cases. Additionally, patients with pulmonary involvement should be given systemic steroids. The side effects of these drugs must be considered in the context of the patient’s demographics, comorbidities and lifestyle.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center, Riverside, Calif. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Qudsiya Z and Waseem M. Dermatomyositis, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2023 Jan.
2. Kamperman RG et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 13;23(8):4301.
3. Kassamali B et al. Int J WomensDermatol. 2021 Sep 24;7(5Part A):576-82.
4. Vázquez-Herrera NE et al. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Aug;4(3):187-99.
The classical presentation includes symmetric proximal muscle weakness and underlying malignancy and is very common in adult patients. The etiology is unknown, however.
Some studies suggest people with certain HLA subtypes are at higher risk, and various infectious and pharmacological triggers are suspected to play a role in the pathogenesis of dermatomyositis. Infectious causes include Coxsackie B, enterovirus, and parvovirus. Drugs such as antineoplastic agents, antibiotics, and NSAIDs have been found to be triggers.
The pathogenesis of dermatomyositis involves immune-mediated damage to muscle capillaries and the endothelium of arterioles. In the typical humoral immune response, complement activation occurs. One mechanism of damage in dermatomyositis occurs when the membrane attack complex formed at the end of the complement process deposits in blood vessels, causing inflammation. B cells, autoantibodies, and interferon overexpression may also play a role in damaging the vasculature and muscle fibers. Hypoxia leads to muscular atrophy, resulting in degeneration and death of the fibers. On muscle biopsy, a perivascular and perimysial inflammatory infiltrate, perifascicular atrophy, and microangiopathy may be present. Skin histology reveals vacuolar changes in the basal layer, a lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin production in the dermis.
On clinical examination, patients will have proximal muscle weakness and a skin rash that may include Gottron’s papules, heliotrope erythema, V-sign, shawl sign, holster sign, scalp erythema, midfacial erythema, and photosensitivity. Scalp erythema in dermatomyositis is highly linked to pruritus, alopecia, and telogen effluvium. Patients may experience small fiber neuropathy in dermatomyositis.
Serologies for this patient, who had previously been diagnosed and treated for dermatomyositis, were significant for a positive ANA 1:2560. Anti-Jo-1 antibody was negative. Her liver function tests, aldolase, creatinine kinase, sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and serum protein electrophoresis were normal. Imaging revealed mild chronic interstitial lung disease. A malignancy workup was negative.
Treatment of dermatomyositis involves lifestyle changes and pharmacologic therapy. Because of the intense photosensitivity, patients should be diligent with their sun protection. Methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil are considered first-line therapies for dermatomyositis. Therapies such as cyclophosphamide, rituximab, IVIg, and plasmapheresis may also be indicated in severe or refractory cases. Additionally, patients with pulmonary involvement should be given systemic steroids. The side effects of these drugs must be considered in the context of the patient’s demographics, comorbidities and lifestyle.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center, Riverside, Calif. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Qudsiya Z and Waseem M. Dermatomyositis, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2023 Jan.
2. Kamperman RG et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 13;23(8):4301.
3. Kassamali B et al. Int J WomensDermatol. 2021 Sep 24;7(5Part A):576-82.
4. Vázquez-Herrera NE et al. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Aug;4(3):187-99.
A 45-year-old White woman with no significant medical history presented with a 1-month history of lesions on the nose and right cheek
Cultures for bacteria, varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and mpox virus were all negative. A biopsy revealed suprabasilar acantholysis with follicular involvement in association with blister formation and inflammation. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for suprabasilar IgG and C3 deposition, consistent with pemphigus vulgaris (PV).
. There is likely a genetic predisposition. Medications that may induce pemphigus include penicillamine, nifedipine, or captopril.
Clinically, flaccid blistering lesions are present that may be cutaneous and/or mucosal. Bullae can progress to erosions and crusting, which then heal with pigment alteration but not scarring. The most commonly affected sites are the mouth, intertriginous areas, face, and neck. Mucosal lesions may involve the lips, esophagus, conjunctiva, and genitals.
Biopsy for histology and direct immunofluorescence is important in distinguishing between PV and other blistering disorders. Up to 75% of patients with active disease also have a positive indirect immunofluorescence with circulating IgG.
Treatment is generally immunosuppressive. Systemic therapy usually begins with prednisone and then is transitioned to a steroid-sparing agent such as mycophenolate mofetil. Other steroid-sparing agents include azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and intravenous immunoglobulin. Secondary infections are possible and should be treated. Topical therapies aimed at reducing pain, especially in mucosal lesions, can be beneficial.
This case and the photos are from Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Cultures for bacteria, varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and mpox virus were all negative. A biopsy revealed suprabasilar acantholysis with follicular involvement in association with blister formation and inflammation. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for suprabasilar IgG and C3 deposition, consistent with pemphigus vulgaris (PV).
. There is likely a genetic predisposition. Medications that may induce pemphigus include penicillamine, nifedipine, or captopril.
Clinically, flaccid blistering lesions are present that may be cutaneous and/or mucosal. Bullae can progress to erosions and crusting, which then heal with pigment alteration but not scarring. The most commonly affected sites are the mouth, intertriginous areas, face, and neck. Mucosal lesions may involve the lips, esophagus, conjunctiva, and genitals.
Biopsy for histology and direct immunofluorescence is important in distinguishing between PV and other blistering disorders. Up to 75% of patients with active disease also have a positive indirect immunofluorescence with circulating IgG.
Treatment is generally immunosuppressive. Systemic therapy usually begins with prednisone and then is transitioned to a steroid-sparing agent such as mycophenolate mofetil. Other steroid-sparing agents include azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and intravenous immunoglobulin. Secondary infections are possible and should be treated. Topical therapies aimed at reducing pain, especially in mucosal lesions, can be beneficial.
This case and the photos are from Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Cultures for bacteria, varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and mpox virus were all negative. A biopsy revealed suprabasilar acantholysis with follicular involvement in association with blister formation and inflammation. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for suprabasilar IgG and C3 deposition, consistent with pemphigus vulgaris (PV).
. There is likely a genetic predisposition. Medications that may induce pemphigus include penicillamine, nifedipine, or captopril.
Clinically, flaccid blistering lesions are present that may be cutaneous and/or mucosal. Bullae can progress to erosions and crusting, which then heal with pigment alteration but not scarring. The most commonly affected sites are the mouth, intertriginous areas, face, and neck. Mucosal lesions may involve the lips, esophagus, conjunctiva, and genitals.
Biopsy for histology and direct immunofluorescence is important in distinguishing between PV and other blistering disorders. Up to 75% of patients with active disease also have a positive indirect immunofluorescence with circulating IgG.
Treatment is generally immunosuppressive. Systemic therapy usually begins with prednisone and then is transitioned to a steroid-sparing agent such as mycophenolate mofetil. Other steroid-sparing agents include azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and intravenous immunoglobulin. Secondary infections are possible and should be treated. Topical therapies aimed at reducing pain, especially in mucosal lesions, can be beneficial.
This case and the photos are from Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].