User login
When your patients are your neighbors
“We’ll have one strawberry sugar cone, two chocolate swirls, and a mocha almond.”
“Dr. Wilkoff, I haven’t seen you in ... must be 5 years. You look great! How’s retirement going?”
“You look great too, Kim. The neighborhood has needed an ice cream parlor like yours for a long time. How’s the family?”
Alerted by the commotion of our catching up, Kim’s husband came outside to see what was going on. Looking at my wife, he said, “You know he saved our daughter’s life?”
Well, not exactly. A timely referral to a psychologist I knew was good with eating disorders had started the slow process of returning their anorectic daughter to health. I thanked him and tried to put a more historically correct spin on his story.
Most of my encounters with former patients and their parents aren’t as dramatic as this one at Kim’s Ice Cream Shack, but they always leave me with a warm, positive feeling that stays with me all day. Every now and then they include a compliment or a thank you, but most of the time the conversations are dominated by questions about how the other are doing and what our families are up to.
One of the perks of living in the town where you practice is that your patients also are your neighbors. Not every physician views this proximity as a positive, but for me, it was a gift that has kept on giving after I retired.
Our house phone number was always listed in the phone book, and I can count on the fingers of two hands how many times in 40 years that I received what I would consider an inappropriate or invasive call. Our office offered evening and weekend hours and a generous schedule of phone-in call times. But I’m convinced that it was the neighbor-to-neighbor relationship that kept the work/home balance intact. Even though I may have helped a plumber and his wife with their sick children, that professional arrangement didn’t include a free pass to call him after hours if I knew my leaking faucet could wait until the weekend was over.
By the same token, when a patient or a customer is also your neighbor there is an unspoken ethic that the service you provide must be your best effort. That’s not an admission that I was in the habit of offering substandard care to “folks from away,” but there is special motivation when your work is being scrutinized by people you’re likely to see next week at the grocery store checkout.
Office visits with neighbors often tended to take longer because there was a tendency to drift off topic and ask about a sibling’s baseball game I had read about in the paper or how the lobster catch was running that season. On the other hand, I must admit that I did my share of reporting (really it was bragging) on my own children’s accomplishments.
But now I’m reaping the benefits of those extra minutes invested in the office, because I suspect former patients and their families are more likely to want to reminisce when we meet in a restaurant or at the farmers’ market.
If you are a young physician and worrying about finding a good work/life balance, I urge you to consider living and working and then staying on in a place in which your patients also will be your neighbors. It will enrich your work experience and repay you many times over when it’s time to retire.
If you can’t find that place, at least treat your patients as though they were your neighbors.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
“We’ll have one strawberry sugar cone, two chocolate swirls, and a mocha almond.”
“Dr. Wilkoff, I haven’t seen you in ... must be 5 years. You look great! How’s retirement going?”
“You look great too, Kim. The neighborhood has needed an ice cream parlor like yours for a long time. How’s the family?”
Alerted by the commotion of our catching up, Kim’s husband came outside to see what was going on. Looking at my wife, he said, “You know he saved our daughter’s life?”
Well, not exactly. A timely referral to a psychologist I knew was good with eating disorders had started the slow process of returning their anorectic daughter to health. I thanked him and tried to put a more historically correct spin on his story.
Most of my encounters with former patients and their parents aren’t as dramatic as this one at Kim’s Ice Cream Shack, but they always leave me with a warm, positive feeling that stays with me all day. Every now and then they include a compliment or a thank you, but most of the time the conversations are dominated by questions about how the other are doing and what our families are up to.
One of the perks of living in the town where you practice is that your patients also are your neighbors. Not every physician views this proximity as a positive, but for me, it was a gift that has kept on giving after I retired.
Our house phone number was always listed in the phone book, and I can count on the fingers of two hands how many times in 40 years that I received what I would consider an inappropriate or invasive call. Our office offered evening and weekend hours and a generous schedule of phone-in call times. But I’m convinced that it was the neighbor-to-neighbor relationship that kept the work/home balance intact. Even though I may have helped a plumber and his wife with their sick children, that professional arrangement didn’t include a free pass to call him after hours if I knew my leaking faucet could wait until the weekend was over.
By the same token, when a patient or a customer is also your neighbor there is an unspoken ethic that the service you provide must be your best effort. That’s not an admission that I was in the habit of offering substandard care to “folks from away,” but there is special motivation when your work is being scrutinized by people you’re likely to see next week at the grocery store checkout.
Office visits with neighbors often tended to take longer because there was a tendency to drift off topic and ask about a sibling’s baseball game I had read about in the paper or how the lobster catch was running that season. On the other hand, I must admit that I did my share of reporting (really it was bragging) on my own children’s accomplishments.
But now I’m reaping the benefits of those extra minutes invested in the office, because I suspect former patients and their families are more likely to want to reminisce when we meet in a restaurant or at the farmers’ market.
If you are a young physician and worrying about finding a good work/life balance, I urge you to consider living and working and then staying on in a place in which your patients also will be your neighbors. It will enrich your work experience and repay you many times over when it’s time to retire.
If you can’t find that place, at least treat your patients as though they were your neighbors.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
“We’ll have one strawberry sugar cone, two chocolate swirls, and a mocha almond.”
“Dr. Wilkoff, I haven’t seen you in ... must be 5 years. You look great! How’s retirement going?”
“You look great too, Kim. The neighborhood has needed an ice cream parlor like yours for a long time. How’s the family?”
Alerted by the commotion of our catching up, Kim’s husband came outside to see what was going on. Looking at my wife, he said, “You know he saved our daughter’s life?”
Well, not exactly. A timely referral to a psychologist I knew was good with eating disorders had started the slow process of returning their anorectic daughter to health. I thanked him and tried to put a more historically correct spin on his story.
Most of my encounters with former patients and their parents aren’t as dramatic as this one at Kim’s Ice Cream Shack, but they always leave me with a warm, positive feeling that stays with me all day. Every now and then they include a compliment or a thank you, but most of the time the conversations are dominated by questions about how the other are doing and what our families are up to.
One of the perks of living in the town where you practice is that your patients also are your neighbors. Not every physician views this proximity as a positive, but for me, it was a gift that has kept on giving after I retired.
Our house phone number was always listed in the phone book, and I can count on the fingers of two hands how many times in 40 years that I received what I would consider an inappropriate or invasive call. Our office offered evening and weekend hours and a generous schedule of phone-in call times. But I’m convinced that it was the neighbor-to-neighbor relationship that kept the work/home balance intact. Even though I may have helped a plumber and his wife with their sick children, that professional arrangement didn’t include a free pass to call him after hours if I knew my leaking faucet could wait until the weekend was over.
By the same token, when a patient or a customer is also your neighbor there is an unspoken ethic that the service you provide must be your best effort. That’s not an admission that I was in the habit of offering substandard care to “folks from away,” but there is special motivation when your work is being scrutinized by people you’re likely to see next week at the grocery store checkout.
Office visits with neighbors often tended to take longer because there was a tendency to drift off topic and ask about a sibling’s baseball game I had read about in the paper or how the lobster catch was running that season. On the other hand, I must admit that I did my share of reporting (really it was bragging) on my own children’s accomplishments.
But now I’m reaping the benefits of those extra minutes invested in the office, because I suspect former patients and their families are more likely to want to reminisce when we meet in a restaurant or at the farmers’ market.
If you are a young physician and worrying about finding a good work/life balance, I urge you to consider living and working and then staying on in a place in which your patients also will be your neighbors. It will enrich your work experience and repay you many times over when it’s time to retire.
If you can’t find that place, at least treat your patients as though they were your neighbors.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
A beautiful diagnosis
Defensive medicine exists. The question is how often it happens and how large a role it plays in making medical care in the United States so costly. When Dr. Tom Price was a congressman, he was quoted as saying that defensive medicine is responsible for more than 25% of every dollar this country spends on health care. (“A Fear of Lawsuits Really Does Seem to Result in Extra Medical Tests” Margot Sanger-Katz, New York Times, July 23, 2018). Neither I nor anyone else had any data to support or refute Dr. Price’s claim in 2010, but based on 50 years of practicing and observing medicine, I don’t find his claim completely unreasonable.
Defensive medicine has been going on for so many generations of physicians that most doctors practicing today don’t realize they are doing it. A physician may order a full battery of chemistries on a patient presenting with mild anemia when only a CBC is necessary because that’s the way he was trained.
However, the evidence to support my suspicion that defensive medicine is a significant financial drain on our economy has been difficult to tease out of the tangled web of confounders that is woven into our patchwork health care system. A recent study by two economists provides a glimpse into the role of defensive medicine in the cost of health care (“Defensive Medicine: Evidence from Military Immunity” Michael D. Frakes and Jonathan Gruber, National Bureau of Economic Research, July 2018). Using the unusual combination of circumstances in which military personnel and their dependents can or cannot sue depending on where they are receiving care, the investigators found that “liability immunity reduces inpatient spending by 5% with no measurable negative effect on patient outcomes.” While that may not be as high as Dr. Price or I think it may be, 5% of three trillion dollars is serious money.
The bigger problem is that defensive medicine is ugly, artless, and intellectually unsatisfying. While the patient may not view your diagnosis of his chronic debilitating or terminal illness as a work of art, there are such things as beautiful diagnoses. One may be beautiful in its simplicity and its ability to unify a variety of previously unexplained symptoms. Another diagnosis may be the intellectually stimulating result of a carefully thought out branching decision tree to solve a puzzling array of complaints using a minimum of costly studies.
Defensive medicine decisions are made primarily to avoid mistakes and omissions. Physicians often behave as though we believe our errors will always be fatal. That may be somewhat true for surgeons, but for the rest of us errors can be an important part of learning. The unfortunate outcome of an error, particularly one of omission, can usually be avoided by following the patient closely, remaining available ... and continuing to exude an aura of caring.
With close and thoughtful follow-up, you are going to discover pretty quickly when you have missed the target. Patients understand that we aren’t going to get the correct diagnosis or prescribe the best treatment on the first try every time. What patients don’t understand and what may prompt them to sue is feeling that they are being ignored.
While practicing defensive medicine isn’t usually listed as one of the cardinal symptoms of physician burnout, it probably deserves more attention. With some introspection and a bit of courage, How many of your decisions are being made to avoid an error? Wouldn’t it be more fun to be making beautiful diagnoses you can be proud of?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Defensive medicine exists. The question is how often it happens and how large a role it plays in making medical care in the United States so costly. When Dr. Tom Price was a congressman, he was quoted as saying that defensive medicine is responsible for more than 25% of every dollar this country spends on health care. (“A Fear of Lawsuits Really Does Seem to Result in Extra Medical Tests” Margot Sanger-Katz, New York Times, July 23, 2018). Neither I nor anyone else had any data to support or refute Dr. Price’s claim in 2010, but based on 50 years of practicing and observing medicine, I don’t find his claim completely unreasonable.
Defensive medicine has been going on for so many generations of physicians that most doctors practicing today don’t realize they are doing it. A physician may order a full battery of chemistries on a patient presenting with mild anemia when only a CBC is necessary because that’s the way he was trained.
However, the evidence to support my suspicion that defensive medicine is a significant financial drain on our economy has been difficult to tease out of the tangled web of confounders that is woven into our patchwork health care system. A recent study by two economists provides a glimpse into the role of defensive medicine in the cost of health care (“Defensive Medicine: Evidence from Military Immunity” Michael D. Frakes and Jonathan Gruber, National Bureau of Economic Research, July 2018). Using the unusual combination of circumstances in which military personnel and their dependents can or cannot sue depending on where they are receiving care, the investigators found that “liability immunity reduces inpatient spending by 5% with no measurable negative effect on patient outcomes.” While that may not be as high as Dr. Price or I think it may be, 5% of three trillion dollars is serious money.
The bigger problem is that defensive medicine is ugly, artless, and intellectually unsatisfying. While the patient may not view your diagnosis of his chronic debilitating or terminal illness as a work of art, there are such things as beautiful diagnoses. One may be beautiful in its simplicity and its ability to unify a variety of previously unexplained symptoms. Another diagnosis may be the intellectually stimulating result of a carefully thought out branching decision tree to solve a puzzling array of complaints using a minimum of costly studies.
Defensive medicine decisions are made primarily to avoid mistakes and omissions. Physicians often behave as though we believe our errors will always be fatal. That may be somewhat true for surgeons, but for the rest of us errors can be an important part of learning. The unfortunate outcome of an error, particularly one of omission, can usually be avoided by following the patient closely, remaining available ... and continuing to exude an aura of caring.
With close and thoughtful follow-up, you are going to discover pretty quickly when you have missed the target. Patients understand that we aren’t going to get the correct diagnosis or prescribe the best treatment on the first try every time. What patients don’t understand and what may prompt them to sue is feeling that they are being ignored.
While practicing defensive medicine isn’t usually listed as one of the cardinal symptoms of physician burnout, it probably deserves more attention. With some introspection and a bit of courage, How many of your decisions are being made to avoid an error? Wouldn’t it be more fun to be making beautiful diagnoses you can be proud of?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Defensive medicine exists. The question is how often it happens and how large a role it plays in making medical care in the United States so costly. When Dr. Tom Price was a congressman, he was quoted as saying that defensive medicine is responsible for more than 25% of every dollar this country spends on health care. (“A Fear of Lawsuits Really Does Seem to Result in Extra Medical Tests” Margot Sanger-Katz, New York Times, July 23, 2018). Neither I nor anyone else had any data to support or refute Dr. Price’s claim in 2010, but based on 50 years of practicing and observing medicine, I don’t find his claim completely unreasonable.
Defensive medicine has been going on for so many generations of physicians that most doctors practicing today don’t realize they are doing it. A physician may order a full battery of chemistries on a patient presenting with mild anemia when only a CBC is necessary because that’s the way he was trained.
However, the evidence to support my suspicion that defensive medicine is a significant financial drain on our economy has been difficult to tease out of the tangled web of confounders that is woven into our patchwork health care system. A recent study by two economists provides a glimpse into the role of defensive medicine in the cost of health care (“Defensive Medicine: Evidence from Military Immunity” Michael D. Frakes and Jonathan Gruber, National Bureau of Economic Research, July 2018). Using the unusual combination of circumstances in which military personnel and their dependents can or cannot sue depending on where they are receiving care, the investigators found that “liability immunity reduces inpatient spending by 5% with no measurable negative effect on patient outcomes.” While that may not be as high as Dr. Price or I think it may be, 5% of three trillion dollars is serious money.
The bigger problem is that defensive medicine is ugly, artless, and intellectually unsatisfying. While the patient may not view your diagnosis of his chronic debilitating or terminal illness as a work of art, there are such things as beautiful diagnoses. One may be beautiful in its simplicity and its ability to unify a variety of previously unexplained symptoms. Another diagnosis may be the intellectually stimulating result of a carefully thought out branching decision tree to solve a puzzling array of complaints using a minimum of costly studies.
Defensive medicine decisions are made primarily to avoid mistakes and omissions. Physicians often behave as though we believe our errors will always be fatal. That may be somewhat true for surgeons, but for the rest of us errors can be an important part of learning. The unfortunate outcome of an error, particularly one of omission, can usually be avoided by following the patient closely, remaining available ... and continuing to exude an aura of caring.
With close and thoughtful follow-up, you are going to discover pretty quickly when you have missed the target. Patients understand that we aren’t going to get the correct diagnosis or prescribe the best treatment on the first try every time. What patients don’t understand and what may prompt them to sue is feeling that they are being ignored.
While practicing defensive medicine isn’t usually listed as one of the cardinal symptoms of physician burnout, it probably deserves more attention. With some introspection and a bit of courage, How many of your decisions are being made to avoid an error? Wouldn’t it be more fun to be making beautiful diagnoses you can be proud of?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Pediatricians doing good globally
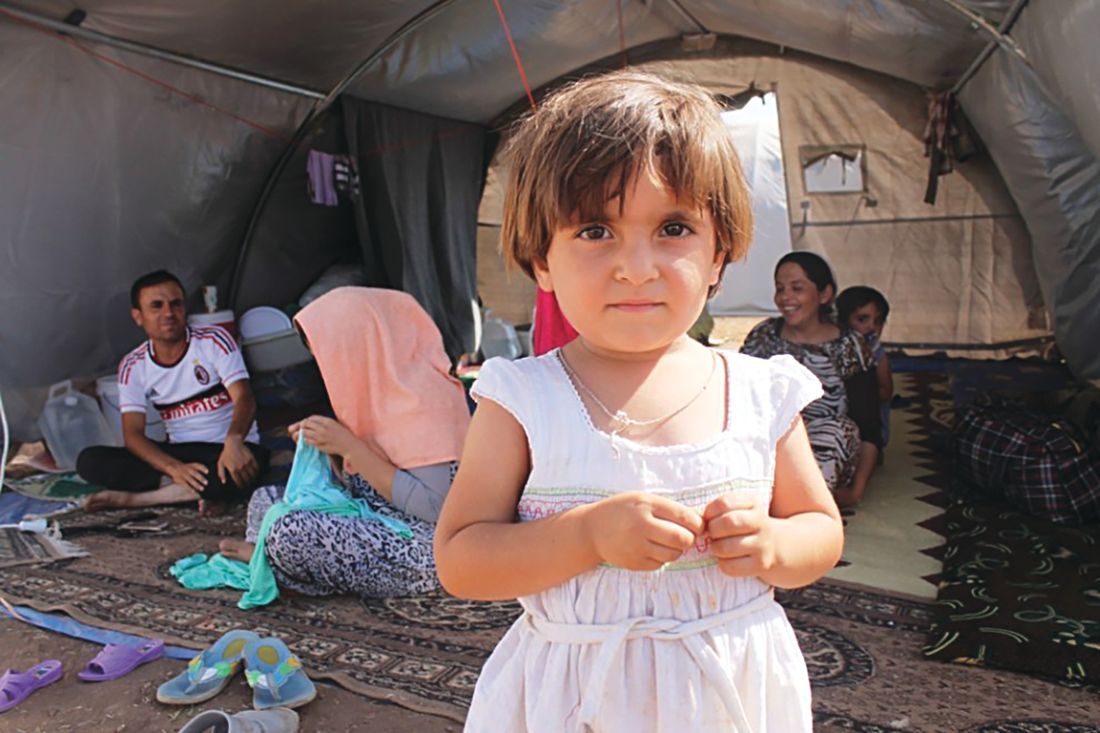
Do the images of Syrian refugee children kindle a desire to leave the privileged suburban-dwelling patients in your practice for just a few weeks and donate your clinical skills to help the victims of political conflict? Or, are you looking for a way to give your post-retirement life some meaning by volunteering on a typhoon-ravaged island in Southeast Asia?
Before you ask your partners for a 1-month leave of absence or try to convince your spouse that camping out in a refugee camp would be a better way to spend this year’s travel budget, I urge you to read Pediatricians and Global Health: Opportunities and Considerations for Meaningful Engagement, published in Pediatrics. This lengthy and thorough report by the American Board of Pediatrics Global Health Task Force will give you pause and should serve as an important reality check before you run off to buy the plane tickets for your personal mission of mercy.
Gitanjli Arora, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, and her coauthors point out that, just because there appears to be a need for people with clinical expertise does not mean that your little black bag of skills honed in the privileged bubble of a first-world country is going to be of much help. This question is one I have pondered on several occasions when I have been offered what might be called “medical voluntourism” opportunities.
If I have distinguished myself as a clinician, that skill has been based on my ability to listen and communicate. Dropped into a community where I have little or no language facility and cultural awareness, I would need to rely on my observational skills. While I pride myself on my ability to make a visual diagnosis, the truth is that my diagnostic successes based solely on observation are almost exclusively dermatologic ones. And, let me add, my familiarity with tropical skin rashes is severely limited. I’m sure I could learn but not in a stay as short as a month.
Taking a history and communicating a treatment plan would force me to rely on the skills of a translator. In settings dominated by upheaval, many of the presenting complaints are going to be the result of, or at least heavily colored by, the chaos induced by anxiety. The ability to sort out where the mind and body connect is difficult enough in a community in which I have spent 40 years and speak the language. Regardless of how much sympathy I feel for the victims of tragic events, my clinical skills would have little value in the short term. Even worse, I would probably just be in the way. As the Task Force points out, my presence could also be squandering local resources as on-site providers worked to get me up to speed.
The authors also explore the numerous other complicating factors that must be considered by those of us who feel the pull to help the victims of global strife and natural disaster. While the authors discourage physicians like you and me from “dropping in” to help, they offer an abundance of suggestions on how we can act globally and stay locally.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Do the images of Syrian refugee children kindle a desire to leave the privileged suburban-dwelling patients in your practice for just a few weeks and donate your clinical skills to help the victims of political conflict? Or, are you looking for a way to give your post-retirement life some meaning by volunteering on a typhoon-ravaged island in Southeast Asia?
Before you ask your partners for a 1-month leave of absence or try to convince your spouse that camping out in a refugee camp would be a better way to spend this year’s travel budget, I urge you to read Pediatricians and Global Health: Opportunities and Considerations for Meaningful Engagement, published in Pediatrics. This lengthy and thorough report by the American Board of Pediatrics Global Health Task Force will give you pause and should serve as an important reality check before you run off to buy the plane tickets for your personal mission of mercy.
Gitanjli Arora, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, and her coauthors point out that, just because there appears to be a need for people with clinical expertise does not mean that your little black bag of skills honed in the privileged bubble of a first-world country is going to be of much help. This question is one I have pondered on several occasions when I have been offered what might be called “medical voluntourism” opportunities.
If I have distinguished myself as a clinician, that skill has been based on my ability to listen and communicate. Dropped into a community where I have little or no language facility and cultural awareness, I would need to rely on my observational skills. While I pride myself on my ability to make a visual diagnosis, the truth is that my diagnostic successes based solely on observation are almost exclusively dermatologic ones. And, let me add, my familiarity with tropical skin rashes is severely limited. I’m sure I could learn but not in a stay as short as a month.
Taking a history and communicating a treatment plan would force me to rely on the skills of a translator. In settings dominated by upheaval, many of the presenting complaints are going to be the result of, or at least heavily colored by, the chaos induced by anxiety. The ability to sort out where the mind and body connect is difficult enough in a community in which I have spent 40 years and speak the language. Regardless of how much sympathy I feel for the victims of tragic events, my clinical skills would have little value in the short term. Even worse, I would probably just be in the way. As the Task Force points out, my presence could also be squandering local resources as on-site providers worked to get me up to speed.
The authors also explore the numerous other complicating factors that must be considered by those of us who feel the pull to help the victims of global strife and natural disaster. While the authors discourage physicians like you and me from “dropping in” to help, they offer an abundance of suggestions on how we can act globally and stay locally.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Do the images of Syrian refugee children kindle a desire to leave the privileged suburban-dwelling patients in your practice for just a few weeks and donate your clinical skills to help the victims of political conflict? Or, are you looking for a way to give your post-retirement life some meaning by volunteering on a typhoon-ravaged island in Southeast Asia?
Before you ask your partners for a 1-month leave of absence or try to convince your spouse that camping out in a refugee camp would be a better way to spend this year’s travel budget, I urge you to read Pediatricians and Global Health: Opportunities and Considerations for Meaningful Engagement, published in Pediatrics. This lengthy and thorough report by the American Board of Pediatrics Global Health Task Force will give you pause and should serve as an important reality check before you run off to buy the plane tickets for your personal mission of mercy.
Gitanjli Arora, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, and her coauthors point out that, just because there appears to be a need for people with clinical expertise does not mean that your little black bag of skills honed in the privileged bubble of a first-world country is going to be of much help. This question is one I have pondered on several occasions when I have been offered what might be called “medical voluntourism” opportunities.
If I have distinguished myself as a clinician, that skill has been based on my ability to listen and communicate. Dropped into a community where I have little or no language facility and cultural awareness, I would need to rely on my observational skills. While I pride myself on my ability to make a visual diagnosis, the truth is that my diagnostic successes based solely on observation are almost exclusively dermatologic ones. And, let me add, my familiarity with tropical skin rashes is severely limited. I’m sure I could learn but not in a stay as short as a month.
Taking a history and communicating a treatment plan would force me to rely on the skills of a translator. In settings dominated by upheaval, many of the presenting complaints are going to be the result of, or at least heavily colored by, the chaos induced by anxiety. The ability to sort out where the mind and body connect is difficult enough in a community in which I have spent 40 years and speak the language. Regardless of how much sympathy I feel for the victims of tragic events, my clinical skills would have little value in the short term. Even worse, I would probably just be in the way. As the Task Force points out, my presence could also be squandering local resources as on-site providers worked to get me up to speed.
The authors also explore the numerous other complicating factors that must be considered by those of us who feel the pull to help the victims of global strife and natural disaster. While the authors discourage physicians like you and me from “dropping in” to help, they offer an abundance of suggestions on how we can act globally and stay locally.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Behavioral sleep interventions can work – if done
Sleep has begun to emerge from the shadows to gain its rightful place in the health pantheon. With this emergence has come a motley group of physicians and self-proclaimed experts (myself included) eager to share their anecdotal evidence and opinions on how new parents can shorten the inevitable and often painfully slow process of settling in.
A study in the May 2018 Journal of Pediatrics is an attempt to provide some data-driven guidance for sleep-deprived parents and their physician-advisors (“Real-World Implementation of Infant Behavioral Sleep Interventions: Results of a Parental Survey”). Using the responses from 652 parents who participated in a Facebook peer support group, the investigators created four categories of behavior sleep intervention for the parents of infants a mean age of 6 months: Modified extinction in which parents left the room and returned to briefly reassure the infant at intervals ranging from 5 to 25 minutes; unmodified extinction in which the parents let the infant cry it out; parental presence with support in which the parents remained in the room and interacted with the child; and parental presence without support. Extinction, both modified and unmodified (50% and 35%), was far and away the most frequently used method.
There was little difference in the effectiveness of the four strategies. By 2 weeks, 79% of the parents reported success, and the interventions were successfully discontinued in a mean and mode of 7 days. Not surprisingly, with success came reduced parental stress, as well as more consistent bedtime routines and smoother transitions to sleep.
When choosing a behavioral sleep intervention to suggest, I have tried to consider what I have learned about each family’s personality in the few months I have gotten to know them. But I have always been a big fan of extinction. And I suspect that my bias is simply a reflection of my no-nonsense, let’s-get-it-done-now personality. The results of this new study suggests that my poorly disguised pessimism about parental presence strategies may have discouraged some parents from trying an intervention that might have been successful for them.
The good news is that all four strategies can be successful. The problem is helping parents find the time and energy required to make any intervention successful. In the short term, extinction or parental presence is likely to mean less sleep for the parents. If work schedules and other family stressors already have drained a family’s energy reserves, it may not be the right time to try an intervention. When it becomes clear that there is never going to be right time, it is time for a frank discussion with the family about rearranging their priorities.
Behavioral sleep interventions require consistency and a family must be prepared to commit at least a week of uninterrupted evenings to get the job done. Business trips, visitors, and social engagements must take a back seat.
Extinction strategies are going to involve some crying, and while as pediatricians, we have developed the ability to buffer ourselves from crying (ignore really isn’t the right word), we must accept that listening to one’s child is too painful for some parents. When only one parent can’t tolerate the crying, the solution may be having that parent leave the home on the intervention evenings. When both parents share the vulnerability, the better answer is a parental presence strategy.
Although this study was small with a self-selected group of parents, the good news is that behavioral sleep intervention can work. We need to share the news with young families and encourage them to just do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Sleep has begun to emerge from the shadows to gain its rightful place in the health pantheon. With this emergence has come a motley group of physicians and self-proclaimed experts (myself included) eager to share their anecdotal evidence and opinions on how new parents can shorten the inevitable and often painfully slow process of settling in.
A study in the May 2018 Journal of Pediatrics is an attempt to provide some data-driven guidance for sleep-deprived parents and their physician-advisors (“Real-World Implementation of Infant Behavioral Sleep Interventions: Results of a Parental Survey”). Using the responses from 652 parents who participated in a Facebook peer support group, the investigators created four categories of behavior sleep intervention for the parents of infants a mean age of 6 months: Modified extinction in which parents left the room and returned to briefly reassure the infant at intervals ranging from 5 to 25 minutes; unmodified extinction in which the parents let the infant cry it out; parental presence with support in which the parents remained in the room and interacted with the child; and parental presence without support. Extinction, both modified and unmodified (50% and 35%), was far and away the most frequently used method.
There was little difference in the effectiveness of the four strategies. By 2 weeks, 79% of the parents reported success, and the interventions were successfully discontinued in a mean and mode of 7 days. Not surprisingly, with success came reduced parental stress, as well as more consistent bedtime routines and smoother transitions to sleep.
When choosing a behavioral sleep intervention to suggest, I have tried to consider what I have learned about each family’s personality in the few months I have gotten to know them. But I have always been a big fan of extinction. And I suspect that my bias is simply a reflection of my no-nonsense, let’s-get-it-done-now personality. The results of this new study suggests that my poorly disguised pessimism about parental presence strategies may have discouraged some parents from trying an intervention that might have been successful for them.
The good news is that all four strategies can be successful. The problem is helping parents find the time and energy required to make any intervention successful. In the short term, extinction or parental presence is likely to mean less sleep for the parents. If work schedules and other family stressors already have drained a family’s energy reserves, it may not be the right time to try an intervention. When it becomes clear that there is never going to be right time, it is time for a frank discussion with the family about rearranging their priorities.
Behavioral sleep interventions require consistency and a family must be prepared to commit at least a week of uninterrupted evenings to get the job done. Business trips, visitors, and social engagements must take a back seat.
Extinction strategies are going to involve some crying, and while as pediatricians, we have developed the ability to buffer ourselves from crying (ignore really isn’t the right word), we must accept that listening to one’s child is too painful for some parents. When only one parent can’t tolerate the crying, the solution may be having that parent leave the home on the intervention evenings. When both parents share the vulnerability, the better answer is a parental presence strategy.
Although this study was small with a self-selected group of parents, the good news is that behavioral sleep intervention can work. We need to share the news with young families and encourage them to just do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Sleep has begun to emerge from the shadows to gain its rightful place in the health pantheon. With this emergence has come a motley group of physicians and self-proclaimed experts (myself included) eager to share their anecdotal evidence and opinions on how new parents can shorten the inevitable and often painfully slow process of settling in.
A study in the May 2018 Journal of Pediatrics is an attempt to provide some data-driven guidance for sleep-deprived parents and their physician-advisors (“Real-World Implementation of Infant Behavioral Sleep Interventions: Results of a Parental Survey”). Using the responses from 652 parents who participated in a Facebook peer support group, the investigators created four categories of behavior sleep intervention for the parents of infants a mean age of 6 months: Modified extinction in which parents left the room and returned to briefly reassure the infant at intervals ranging from 5 to 25 minutes; unmodified extinction in which the parents let the infant cry it out; parental presence with support in which the parents remained in the room and interacted with the child; and parental presence without support. Extinction, both modified and unmodified (50% and 35%), was far and away the most frequently used method.
There was little difference in the effectiveness of the four strategies. By 2 weeks, 79% of the parents reported success, and the interventions were successfully discontinued in a mean and mode of 7 days. Not surprisingly, with success came reduced parental stress, as well as more consistent bedtime routines and smoother transitions to sleep.
When choosing a behavioral sleep intervention to suggest, I have tried to consider what I have learned about each family’s personality in the few months I have gotten to know them. But I have always been a big fan of extinction. And I suspect that my bias is simply a reflection of my no-nonsense, let’s-get-it-done-now personality. The results of this new study suggests that my poorly disguised pessimism about parental presence strategies may have discouraged some parents from trying an intervention that might have been successful for them.
The good news is that all four strategies can be successful. The problem is helping parents find the time and energy required to make any intervention successful. In the short term, extinction or parental presence is likely to mean less sleep for the parents. If work schedules and other family stressors already have drained a family’s energy reserves, it may not be the right time to try an intervention. When it becomes clear that there is never going to be right time, it is time for a frank discussion with the family about rearranging their priorities.
Behavioral sleep interventions require consistency and a family must be prepared to commit at least a week of uninterrupted evenings to get the job done. Business trips, visitors, and social engagements must take a back seat.
Extinction strategies are going to involve some crying, and while as pediatricians, we have developed the ability to buffer ourselves from crying (ignore really isn’t the right word), we must accept that listening to one’s child is too painful for some parents. When only one parent can’t tolerate the crying, the solution may be having that parent leave the home on the intervention evenings. When both parents share the vulnerability, the better answer is a parental presence strategy.
Although this study was small with a self-selected group of parents, the good news is that behavioral sleep intervention can work. We need to share the news with young families and encourage them to just do it.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Is My Child Overtired?: The Sleep Solution for Raising Happier, Healthier Children.” Email him at [email protected].
Maternal lifestyle affects child obesity
A study published in the British Medical Journal found that women who practiced five healthy habits had children who when they reached adolescence were 75% less likely to be overweight, compared with women who practiced none of the those healthy habits.
The healthy habits were maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and consuming no more than a moderate amount of alcohol (BMJ 2018;362:k2486). I suspect you aren’t surprised by the core finding of this study of 16,945 female nurses and their 24,289 children. You’ve seen it scores of times. Mothers who lead unhealthy lifestyles seem to have children who are more likely to be obese. Now you have some numbers to support your decades of anecdotal observations. But the question is, what are we supposed to do with this new data? When and with whom should we share this unfortunate truth?
Evidence from previous studies makes it clear that by the time a child enters grade school the die is cast. Baby fat is neither cute nor temporary. This means that our target audience must be mothers-to-be and women whose children are infants and toddlers. On the other hand, telling the mother of an overweight teenager that her own unhealthy habits have probably contributed to her child’s weight problem is cruel and a waste of time. The mother already may have suspected her culpability. She also may feel that it is too late to do anything about it. While there have been some studies looking for an association between paternal body mass index and offspring BMI, I was unable to find any addressing paternal lifestyle and adolescent obesity.
This new study doesn’t address the unusual situation in which a mother of a teenager sheds all five of her unhealthy habits. I guess there may be examples in which a mother’s positive lifestyle change has helped reverse her adolescent child’s path to obesity. But I suspect these cases are rare.
So on one hand but on the other we must be careful to avoid playing the blame game and giving other mothers a one-way ticket on the guilt train. This is just one more example of the tightrope that we have been walking for generations. Every day in our offices we see children whose health is endangered by their parents’ behaviors and lifestyles. In cases in which the parental behavior is creating a serious short-term risk, such as failing to use an appropriate motor vehicle safety restraint system, we have no qualms about speaking out. We aren’t afraid to do a little shaming in hopes of sparing a family a serious guilt trip. When the threat to the child is more abstract and less dramatic – such as vaccine refusal – shaming and education don’t seem to be effective in changing parental behavior.
Obesity presents its own collection of complexities. It is like a car wreck seen in slow motion as the plots on the growth chart accumulate pound by pound. Unfortunately, parents often are among the last to notice or accept the reality. This new study doesn’t tell us whether we can make a difference. But it does suggest that when we first see the warning signs on the growth chart that we should engage the parents in a discussion of their lifestyle and its possible association with the child’s weight gain. The challenge, of course, is how one can cast the discussion without sounding judgmental.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
A study published in the British Medical Journal found that women who practiced five healthy habits had children who when they reached adolescence were 75% less likely to be overweight, compared with women who practiced none of the those healthy habits.
The healthy habits were maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and consuming no more than a moderate amount of alcohol (BMJ 2018;362:k2486). I suspect you aren’t surprised by the core finding of this study of 16,945 female nurses and their 24,289 children. You’ve seen it scores of times. Mothers who lead unhealthy lifestyles seem to have children who are more likely to be obese. Now you have some numbers to support your decades of anecdotal observations. But the question is, what are we supposed to do with this new data? When and with whom should we share this unfortunate truth?
Evidence from previous studies makes it clear that by the time a child enters grade school the die is cast. Baby fat is neither cute nor temporary. This means that our target audience must be mothers-to-be and women whose children are infants and toddlers. On the other hand, telling the mother of an overweight teenager that her own unhealthy habits have probably contributed to her child’s weight problem is cruel and a waste of time. The mother already may have suspected her culpability. She also may feel that it is too late to do anything about it. While there have been some studies looking for an association between paternal body mass index and offspring BMI, I was unable to find any addressing paternal lifestyle and adolescent obesity.
This new study doesn’t address the unusual situation in which a mother of a teenager sheds all five of her unhealthy habits. I guess there may be examples in which a mother’s positive lifestyle change has helped reverse her adolescent child’s path to obesity. But I suspect these cases are rare.
So on one hand but on the other we must be careful to avoid playing the blame game and giving other mothers a one-way ticket on the guilt train. This is just one more example of the tightrope that we have been walking for generations. Every day in our offices we see children whose health is endangered by their parents’ behaviors and lifestyles. In cases in which the parental behavior is creating a serious short-term risk, such as failing to use an appropriate motor vehicle safety restraint system, we have no qualms about speaking out. We aren’t afraid to do a little shaming in hopes of sparing a family a serious guilt trip. When the threat to the child is more abstract and less dramatic – such as vaccine refusal – shaming and education don’t seem to be effective in changing parental behavior.
Obesity presents its own collection of complexities. It is like a car wreck seen in slow motion as the plots on the growth chart accumulate pound by pound. Unfortunately, parents often are among the last to notice or accept the reality. This new study doesn’t tell us whether we can make a difference. But it does suggest that when we first see the warning signs on the growth chart that we should engage the parents in a discussion of their lifestyle and its possible association with the child’s weight gain. The challenge, of course, is how one can cast the discussion without sounding judgmental.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
A study published in the British Medical Journal found that women who practiced five healthy habits had children who when they reached adolescence were 75% less likely to be overweight, compared with women who practiced none of the those healthy habits.
The healthy habits were maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and consuming no more than a moderate amount of alcohol (BMJ 2018;362:k2486). I suspect you aren’t surprised by the core finding of this study of 16,945 female nurses and their 24,289 children. You’ve seen it scores of times. Mothers who lead unhealthy lifestyles seem to have children who are more likely to be obese. Now you have some numbers to support your decades of anecdotal observations. But the question is, what are we supposed to do with this new data? When and with whom should we share this unfortunate truth?
Evidence from previous studies makes it clear that by the time a child enters grade school the die is cast. Baby fat is neither cute nor temporary. This means that our target audience must be mothers-to-be and women whose children are infants and toddlers. On the other hand, telling the mother of an overweight teenager that her own unhealthy habits have probably contributed to her child’s weight problem is cruel and a waste of time. The mother already may have suspected her culpability. She also may feel that it is too late to do anything about it. While there have been some studies looking for an association between paternal body mass index and offspring BMI, I was unable to find any addressing paternal lifestyle and adolescent obesity.
This new study doesn’t address the unusual situation in which a mother of a teenager sheds all five of her unhealthy habits. I guess there may be examples in which a mother’s positive lifestyle change has helped reverse her adolescent child’s path to obesity. But I suspect these cases are rare.
So on one hand but on the other we must be careful to avoid playing the blame game and giving other mothers a one-way ticket on the guilt train. This is just one more example of the tightrope that we have been walking for generations. Every day in our offices we see children whose health is endangered by their parents’ behaviors and lifestyles. In cases in which the parental behavior is creating a serious short-term risk, such as failing to use an appropriate motor vehicle safety restraint system, we have no qualms about speaking out. We aren’t afraid to do a little shaming in hopes of sparing a family a serious guilt trip. When the threat to the child is more abstract and less dramatic – such as vaccine refusal – shaming and education don’t seem to be effective in changing parental behavior.
Obesity presents its own collection of complexities. It is like a car wreck seen in slow motion as the plots on the growth chart accumulate pound by pound. Unfortunately, parents often are among the last to notice or accept the reality. This new study doesn’t tell us whether we can make a difference. But it does suggest that when we first see the warning signs on the growth chart that we should engage the parents in a discussion of their lifestyle and its possible association with the child’s weight gain. The challenge, of course, is how one can cast the discussion without sounding judgmental.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Looking at study results with a critical eye
As a physician you are the embodiment of delayed gratification. You spent more than 20 years in school before you earned a degree that then allowed you spend another 3-plus years in training before anyone would consider you a “real” doctor. Somewhere along that long and shallow trajectory someone may have said, “You must have done really well on the marshmallow test.”
That is, until this year, when an attempt to replicate the initial study by Shoda et al. failed to find that the associations between delayed gratification and adolescent achievement were anywhere near as significant as those reported in the 1990 study (Psychol Sci. 2018 May. doi: 10.1177/0956797618761661). Watts et al. suggest that the discrepancy may be explained in part by a failure to adequately control for family background, home environment, and early cognitive ability in the initial experimental design.
Is there a message here? Should we stop wasting our time reading papers from the developmental psychology literature? Not just yet. There are more papers coming out in which the authors attempt to replicate other landmark studies, often without success (“Undergrads Can Improve Psychology,” by Russel T. Warne and Jordan Wagge, The Wall Street Journal, June 20, 2018). Let’s wait and see how much more debunking there is going to be before we throw the baby out with the bath water.
regardless of how prestigious the institution of origin and regardless of how much it appeals to our common sense. Our intuition can be a powerful tool when we are looking for answers, but it can lead us astray if we take it too seriously.
It is often said that a good experiment is one that raises more questions than it answers. You don’t have to remember all that stuff you learned when you studied statistics to be able to question the results of a study you read in a peer-reviewed journal. I find that in many of the papers I read I have serious concerns about how well the authors have controlled for the not-so-obvious variables.
So where does this failed attempt at replicating the original marshmallow test study leave us? It is still very likely given your aptitude for delayed gratification that had you been given the test as a preschooler you would not have even touched the marshmallow until the experimenter re-entered the room to end the test and then ... you probably would have offered to share it with her.
But these new results suggest that your ability to delay gratification was not some skill with which you were born. You may have been born smarter than the average child, but your skill at delaying gratification may have been one you learned from your parents and assimilated from the home environment in which your grew up. This may be one of those nature-or-nurture skirmishes in which nurture wins. And, it may be another good example of the importance of the first 3 or 4 years in a child’s emotional and psychological development.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
As a physician you are the embodiment of delayed gratification. You spent more than 20 years in school before you earned a degree that then allowed you spend another 3-plus years in training before anyone would consider you a “real” doctor. Somewhere along that long and shallow trajectory someone may have said, “You must have done really well on the marshmallow test.”
That is, until this year, when an attempt to replicate the initial study by Shoda et al. failed to find that the associations between delayed gratification and adolescent achievement were anywhere near as significant as those reported in the 1990 study (Psychol Sci. 2018 May. doi: 10.1177/0956797618761661). Watts et al. suggest that the discrepancy may be explained in part by a failure to adequately control for family background, home environment, and early cognitive ability in the initial experimental design.
Is there a message here? Should we stop wasting our time reading papers from the developmental psychology literature? Not just yet. There are more papers coming out in which the authors attempt to replicate other landmark studies, often without success (“Undergrads Can Improve Psychology,” by Russel T. Warne and Jordan Wagge, The Wall Street Journal, June 20, 2018). Let’s wait and see how much more debunking there is going to be before we throw the baby out with the bath water.
regardless of how prestigious the institution of origin and regardless of how much it appeals to our common sense. Our intuition can be a powerful tool when we are looking for answers, but it can lead us astray if we take it too seriously.
It is often said that a good experiment is one that raises more questions than it answers. You don’t have to remember all that stuff you learned when you studied statistics to be able to question the results of a study you read in a peer-reviewed journal. I find that in many of the papers I read I have serious concerns about how well the authors have controlled for the not-so-obvious variables.
So where does this failed attempt at replicating the original marshmallow test study leave us? It is still very likely given your aptitude for delayed gratification that had you been given the test as a preschooler you would not have even touched the marshmallow until the experimenter re-entered the room to end the test and then ... you probably would have offered to share it with her.
But these new results suggest that your ability to delay gratification was not some skill with which you were born. You may have been born smarter than the average child, but your skill at delaying gratification may have been one you learned from your parents and assimilated from the home environment in which your grew up. This may be one of those nature-or-nurture skirmishes in which nurture wins. And, it may be another good example of the importance of the first 3 or 4 years in a child’s emotional and psychological development.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
As a physician you are the embodiment of delayed gratification. You spent more than 20 years in school before you earned a degree that then allowed you spend another 3-plus years in training before anyone would consider you a “real” doctor. Somewhere along that long and shallow trajectory someone may have said, “You must have done really well on the marshmallow test.”
That is, until this year, when an attempt to replicate the initial study by Shoda et al. failed to find that the associations between delayed gratification and adolescent achievement were anywhere near as significant as those reported in the 1990 study (Psychol Sci. 2018 May. doi: 10.1177/0956797618761661). Watts et al. suggest that the discrepancy may be explained in part by a failure to adequately control for family background, home environment, and early cognitive ability in the initial experimental design.
Is there a message here? Should we stop wasting our time reading papers from the developmental psychology literature? Not just yet. There are more papers coming out in which the authors attempt to replicate other landmark studies, often without success (“Undergrads Can Improve Psychology,” by Russel T. Warne and Jordan Wagge, The Wall Street Journal, June 20, 2018). Let’s wait and see how much more debunking there is going to be before we throw the baby out with the bath water.
regardless of how prestigious the institution of origin and regardless of how much it appeals to our common sense. Our intuition can be a powerful tool when we are looking for answers, but it can lead us astray if we take it too seriously.
It is often said that a good experiment is one that raises more questions than it answers. You don’t have to remember all that stuff you learned when you studied statistics to be able to question the results of a study you read in a peer-reviewed journal. I find that in many of the papers I read I have serious concerns about how well the authors have controlled for the not-so-obvious variables.
So where does this failed attempt at replicating the original marshmallow test study leave us? It is still very likely given your aptitude for delayed gratification that had you been given the test as a preschooler you would not have even touched the marshmallow until the experimenter re-entered the room to end the test and then ... you probably would have offered to share it with her.
But these new results suggest that your ability to delay gratification was not some skill with which you were born. You may have been born smarter than the average child, but your skill at delaying gratification may have been one you learned from your parents and assimilated from the home environment in which your grew up. This may be one of those nature-or-nurture skirmishes in which nurture wins. And, it may be another good example of the importance of the first 3 or 4 years in a child’s emotional and psychological development.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Should you be worried about the declining birth rate?
The number of births in the United States has fallen for the second year in a row. Births in 2017 were down 2% from 2016, bringing the birth rate to a 30-year low at 60 births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years. This decline spanned nearly all maternal age groups, including teenagers (Hamilton et al. NVSS Vital Statistics Rapid Release Report No 004, May 2018).
In the crudest terms, babies represent the raw material of pediatrics. Without children, we pediatricians would have to begin treating those whining adults. Most of us chose pediatrics because we enjoy being around children, and many of us were motivated to study medicine by a desire to help sick children. Is this decline in the supply stream of patients something we should be worrying about?
Before we start looking for other less appealing employment opportunities, let’s look a little closer at the reasons for this declining birth rate. A traditional explanation cites an association between the number of births and the health of the economy. However, this recent decline has occurred in the face of an obviously improving economy.
In an attempt to find a more nuanced explanation, the New York Times asked a nationally representative sample of 1,858 young adults aged 20-45 years how they felt about having children (“Americans Are Having Fewer Babies. They Told Us Why.” by Claire Cain Miller, July 5, 2018). The results were interesting and not necessarily surprising. When the respondents were asked why they had or were expecting to have fewer children than they considered ideal, six of their first eight reasons were linked to their finances, with “Child care is too expensive” leading all answers at 64%. The second highest response was “Want more time for the children I have” (54%) and the sixth was “Want more leisure time”(42%).
When the young adults were asked why they aren’t having children, “Want more leisure time” moved to No. 1 (32%) and “Can’t afford day care” fell to third place (31%) just ahead of “No desire for children” (30%).
Embedded in this data from the National Vital Statistic System (NVSS) and the New York Times poll are the seeds of reassurance. The observation that the young adults’ second reason for not wanting to have more children was that they wanted to have more time with the children they have suggests what pediatricians already have observed for a generation or two. Modern adults appear to be taking their role as parents more seriously. They worry that they aren’t doing a good job and look to us as one of their, if not their most, trusted advisers.
This epidemic of parental anxiety does not appear to be abating with the declining birth rate. It continues to generate a large percentage of phone calls and office visits. Over the course of my career, it became clear that although there were fewer children being born in our community, pediatricians remained busy, but with a broader spectrum of complaints that tilted toward behavioral issues.
In the current NVSS data, the cesarean section rate rose again and is now 32%, and the preterm birth rate increased for the third year in a row to 10%. The birth rate for low-birth-weight infants climbed to 8%, the highest since 2006. So while the number of births has fallen to a 30-year low, there appear to be more high-risk babies being born.
You can worry about job security if you like, but in a quirky kind of way pediatrics is following along its own rules of supply and demand. And, you should rest easy ... that is until the next panicked call from a parent wakes you in the middle of the night.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The number of births in the United States has fallen for the second year in a row. Births in 2017 were down 2% from 2016, bringing the birth rate to a 30-year low at 60 births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years. This decline spanned nearly all maternal age groups, including teenagers (Hamilton et al. NVSS Vital Statistics Rapid Release Report No 004, May 2018).
In the crudest terms, babies represent the raw material of pediatrics. Without children, we pediatricians would have to begin treating those whining adults. Most of us chose pediatrics because we enjoy being around children, and many of us were motivated to study medicine by a desire to help sick children. Is this decline in the supply stream of patients something we should be worrying about?
Before we start looking for other less appealing employment opportunities, let’s look a little closer at the reasons for this declining birth rate. A traditional explanation cites an association between the number of births and the health of the economy. However, this recent decline has occurred in the face of an obviously improving economy.
In an attempt to find a more nuanced explanation, the New York Times asked a nationally representative sample of 1,858 young adults aged 20-45 years how they felt about having children (“Americans Are Having Fewer Babies. They Told Us Why.” by Claire Cain Miller, July 5, 2018). The results were interesting and not necessarily surprising. When the respondents were asked why they had or were expecting to have fewer children than they considered ideal, six of their first eight reasons were linked to their finances, with “Child care is too expensive” leading all answers at 64%. The second highest response was “Want more time for the children I have” (54%) and the sixth was “Want more leisure time”(42%).
When the young adults were asked why they aren’t having children, “Want more leisure time” moved to No. 1 (32%) and “Can’t afford day care” fell to third place (31%) just ahead of “No desire for children” (30%).
Embedded in this data from the National Vital Statistic System (NVSS) and the New York Times poll are the seeds of reassurance. The observation that the young adults’ second reason for not wanting to have more children was that they wanted to have more time with the children they have suggests what pediatricians already have observed for a generation or two. Modern adults appear to be taking their role as parents more seriously. They worry that they aren’t doing a good job and look to us as one of their, if not their most, trusted advisers.
This epidemic of parental anxiety does not appear to be abating with the declining birth rate. It continues to generate a large percentage of phone calls and office visits. Over the course of my career, it became clear that although there were fewer children being born in our community, pediatricians remained busy, but with a broader spectrum of complaints that tilted toward behavioral issues.
In the current NVSS data, the cesarean section rate rose again and is now 32%, and the preterm birth rate increased for the third year in a row to 10%. The birth rate for low-birth-weight infants climbed to 8%, the highest since 2006. So while the number of births has fallen to a 30-year low, there appear to be more high-risk babies being born.
You can worry about job security if you like, but in a quirky kind of way pediatrics is following along its own rules of supply and demand. And, you should rest easy ... that is until the next panicked call from a parent wakes you in the middle of the night.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The number of births in the United States has fallen for the second year in a row. Births in 2017 were down 2% from 2016, bringing the birth rate to a 30-year low at 60 births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years. This decline spanned nearly all maternal age groups, including teenagers (Hamilton et al. NVSS Vital Statistics Rapid Release Report No 004, May 2018).
In the crudest terms, babies represent the raw material of pediatrics. Without children, we pediatricians would have to begin treating those whining adults. Most of us chose pediatrics because we enjoy being around children, and many of us were motivated to study medicine by a desire to help sick children. Is this decline in the supply stream of patients something we should be worrying about?
Before we start looking for other less appealing employment opportunities, let’s look a little closer at the reasons for this declining birth rate. A traditional explanation cites an association between the number of births and the health of the economy. However, this recent decline has occurred in the face of an obviously improving economy.
In an attempt to find a more nuanced explanation, the New York Times asked a nationally representative sample of 1,858 young adults aged 20-45 years how they felt about having children (“Americans Are Having Fewer Babies. They Told Us Why.” by Claire Cain Miller, July 5, 2018). The results were interesting and not necessarily surprising. When the respondents were asked why they had or were expecting to have fewer children than they considered ideal, six of their first eight reasons were linked to their finances, with “Child care is too expensive” leading all answers at 64%. The second highest response was “Want more time for the children I have” (54%) and the sixth was “Want more leisure time”(42%).
When the young adults were asked why they aren’t having children, “Want more leisure time” moved to No. 1 (32%) and “Can’t afford day care” fell to third place (31%) just ahead of “No desire for children” (30%).
Embedded in this data from the National Vital Statistic System (NVSS) and the New York Times poll are the seeds of reassurance. The observation that the young adults’ second reason for not wanting to have more children was that they wanted to have more time with the children they have suggests what pediatricians already have observed for a generation or two. Modern adults appear to be taking their role as parents more seriously. They worry that they aren’t doing a good job and look to us as one of their, if not their most, trusted advisers.
This epidemic of parental anxiety does not appear to be abating with the declining birth rate. It continues to generate a large percentage of phone calls and office visits. Over the course of my career, it became clear that although there were fewer children being born in our community, pediatricians remained busy, but with a broader spectrum of complaints that tilted toward behavioral issues.
In the current NVSS data, the cesarean section rate rose again and is now 32%, and the preterm birth rate increased for the third year in a row to 10%. The birth rate for low-birth-weight infants climbed to 8%, the highest since 2006. So while the number of births has fallen to a 30-year low, there appear to be more high-risk babies being born.
You can worry about job security if you like, but in a quirky kind of way pediatrics is following along its own rules of supply and demand. And, you should rest easy ... that is until the next panicked call from a parent wakes you in the middle of the night.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Is the rise of suicide a medical or societal issue?
It’s hard to ignore the recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention revealing suicide rates went up by more than 30% in half of states since 1999 (“Suicide rates rising across the U.S.,” CDC Newsroom, June 7, 2018). My professional experience with suicide is limited to one former patient who died several years after aging out of my practice. His death was not a total surprise. The cornerstones of the situation he felt he couldn’t escape were well in place when he was a freshman in high school. I’m sure there was more I could have tried to do at that early stage. Although he was anxious and mildly depressed he never admitted to being suicidal.
Just as in Ms. Roberts’ family, the CDC report has elicited a fresh round of finger pointing and introspection in our country at a time when it is already struggling to find a sense of its own identity. Is it too many guns? Or too few mental health professionals? Or a broken health delivery system?
Dr. Richard A. Friedman, a psychiatrist at Weill Cornell Medical College, writes in the New York Times that “suicide is a medical problem” and that we should declare war on it “as we’ve done with other public health threats like HIV and heart disease” (“Suicide Rates Are Rising. What Should We Do About It?” June 11, 2018). Although it may be contagious with outbreaks and clusters, particularly in the wake of celebrity suicides (“The Science Behind Suicide Contagion,” by Margot Sanger-Katz, The New York Times, Aug 13, 2014), I’m not so sure that suicide is a medical problem. Certainly, it can be spread by a vector, in this case the ubiquitous news media. With more exposure, suicide has become if not the norm, at least in certain subgroups a socially acceptable management option for an unhappy life. But while there are other features of suicide that tempt us to retreat into our comfort zone of the medical model, we need to face the more realistic and unsettling explanation that the increase in the suicide rate is the symptom of a sick society.
We already are making a mistake by interpreting the apparent rise in distractible behavior as a disease that requires medication. Let’s spread a broader net as we search for answers to the alarming suicide death statistics.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
It’s hard to ignore the recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention revealing suicide rates went up by more than 30% in half of states since 1999 (“Suicide rates rising across the U.S.,” CDC Newsroom, June 7, 2018). My professional experience with suicide is limited to one former patient who died several years after aging out of my practice. His death was not a total surprise. The cornerstones of the situation he felt he couldn’t escape were well in place when he was a freshman in high school. I’m sure there was more I could have tried to do at that early stage. Although he was anxious and mildly depressed he never admitted to being suicidal.
Just as in Ms. Roberts’ family, the CDC report has elicited a fresh round of finger pointing and introspection in our country at a time when it is already struggling to find a sense of its own identity. Is it too many guns? Or too few mental health professionals? Or a broken health delivery system?
Dr. Richard A. Friedman, a psychiatrist at Weill Cornell Medical College, writes in the New York Times that “suicide is a medical problem” and that we should declare war on it “as we’ve done with other public health threats like HIV and heart disease” (“Suicide Rates Are Rising. What Should We Do About It?” June 11, 2018). Although it may be contagious with outbreaks and clusters, particularly in the wake of celebrity suicides (“The Science Behind Suicide Contagion,” by Margot Sanger-Katz, The New York Times, Aug 13, 2014), I’m not so sure that suicide is a medical problem. Certainly, it can be spread by a vector, in this case the ubiquitous news media. With more exposure, suicide has become if not the norm, at least in certain subgroups a socially acceptable management option for an unhappy life. But while there are other features of suicide that tempt us to retreat into our comfort zone of the medical model, we need to face the more realistic and unsettling explanation that the increase in the suicide rate is the symptom of a sick society.
We already are making a mistake by interpreting the apparent rise in distractible behavior as a disease that requires medication. Let’s spread a broader net as we search for answers to the alarming suicide death statistics.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
It’s hard to ignore the recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention revealing suicide rates went up by more than 30% in half of states since 1999 (“Suicide rates rising across the U.S.,” CDC Newsroom, June 7, 2018). My professional experience with suicide is limited to one former patient who died several years after aging out of my practice. His death was not a total surprise. The cornerstones of the situation he felt he couldn’t escape were well in place when he was a freshman in high school. I’m sure there was more I could have tried to do at that early stage. Although he was anxious and mildly depressed he never admitted to being suicidal.
Just as in Ms. Roberts’ family, the CDC report has elicited a fresh round of finger pointing and introspection in our country at a time when it is already struggling to find a sense of its own identity. Is it too many guns? Or too few mental health professionals? Or a broken health delivery system?
Dr. Richard A. Friedman, a psychiatrist at Weill Cornell Medical College, writes in the New York Times that “suicide is a medical problem” and that we should declare war on it “as we’ve done with other public health threats like HIV and heart disease” (“Suicide Rates Are Rising. What Should We Do About It?” June 11, 2018). Although it may be contagious with outbreaks and clusters, particularly in the wake of celebrity suicides (“The Science Behind Suicide Contagion,” by Margot Sanger-Katz, The New York Times, Aug 13, 2014), I’m not so sure that suicide is a medical problem. Certainly, it can be spread by a vector, in this case the ubiquitous news media. With more exposure, suicide has become if not the norm, at least in certain subgroups a socially acceptable management option for an unhappy life. But while there are other features of suicide that tempt us to retreat into our comfort zone of the medical model, we need to face the more realistic and unsettling explanation that the increase in the suicide rate is the symptom of a sick society.
We already are making a mistake by interpreting the apparent rise in distractible behavior as a disease that requires medication. Let’s spread a broader net as we search for answers to the alarming suicide death statistics.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Marijuana use is affecting the job market
I have a friend who owns a large paving and excavating company. He currently is turning away large contracts because he can’t find employees to drive his dump trucks and operate his heavy machinery. The situation is so dire that he has begun to explore the possibility of recruiting employees out of the corrections system.
Like much of the country, Maine is experiencing a low level of unemployment that few of us over the age of 50 years can recall. Coupled with a confused and unwelcoming immigration policy at the federal level many small and large companies are struggling to find employees. The employment opportunities my friend’s company is offering are well above minimum wage, paying in the $30,000-$70,000 range with benefits. While the jobs require some special skills, his company is large enough that it can provide in-house training.
Maine residents recently have voted to decriminalize the possession of small amounts of marijuana. It is unclear exactly how this change in the official position of the state government will translate into a distribution network and a system of local codes. However, it does reflect a more tolerant attitude toward marijuana use. It also suggests that job seekers who are avoiding positions that require drug testing are not worried about the stigma of being identified as a user. They understand enough pharmacology to know that marijuana is detectable days and even weeks after it was last ingested or inhaled. Even the recreational users realize that the chances of being able to pass a drug test before employment and at any subsequent random testing are slim.
The problem is that these good-paying jobs are going unfilled because of the pharmacologic properties of a drug, and our current inability to devise a test that can accurately and consistently correlate a person’s blood level and his or her ability to safely operate a motor vehicle or piece of heavy equipment (“Establishing legal limit for driving under the influence of marijuana,” Inj Epidemiol. 2014 Dec.;1[1]: 26). There is some correlation between blood levels and whether a person is a heavy or infrequent user. Laws that rely on a zero tolerance philosophy are not bringing us any closer to a solution. And it is probably unrealistic to hope that in the near future scientists will develop a single, simply administered test that can provide a clear yes or no to the issue of impairment in the workplace.
I can envision a two-tier system in which all employees are blood or urine tested on a 3-month schedule. Those with a positive test must then take a 10-minute test on a laptop computer simulator with a joy stick each morning that they arrive on the job to demonstrate that, despite a history of marijuana use, they are not impaired.
Even if such a test is developed, we still owe our patients the reminder that, despite its decriminalization, marijuana is a drug and like any drug has side effects. One of them is that it can put limits on your employment opportunities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I have a friend who owns a large paving and excavating company. He currently is turning away large contracts because he can’t find employees to drive his dump trucks and operate his heavy machinery. The situation is so dire that he has begun to explore the possibility of recruiting employees out of the corrections system.
Like much of the country, Maine is experiencing a low level of unemployment that few of us over the age of 50 years can recall. Coupled with a confused and unwelcoming immigration policy at the federal level many small and large companies are struggling to find employees. The employment opportunities my friend’s company is offering are well above minimum wage, paying in the $30,000-$70,000 range with benefits. While the jobs require some special skills, his company is large enough that it can provide in-house training.
Maine residents recently have voted to decriminalize the possession of small amounts of marijuana. It is unclear exactly how this change in the official position of the state government will translate into a distribution network and a system of local codes. However, it does reflect a more tolerant attitude toward marijuana use. It also suggests that job seekers who are avoiding positions that require drug testing are not worried about the stigma of being identified as a user. They understand enough pharmacology to know that marijuana is detectable days and even weeks after it was last ingested or inhaled. Even the recreational users realize that the chances of being able to pass a drug test before employment and at any subsequent random testing are slim.
The problem is that these good-paying jobs are going unfilled because of the pharmacologic properties of a drug, and our current inability to devise a test that can accurately and consistently correlate a person’s blood level and his or her ability to safely operate a motor vehicle or piece of heavy equipment (“Establishing legal limit for driving under the influence of marijuana,” Inj Epidemiol. 2014 Dec.;1[1]: 26). There is some correlation between blood levels and whether a person is a heavy or infrequent user. Laws that rely on a zero tolerance philosophy are not bringing us any closer to a solution. And it is probably unrealistic to hope that in the near future scientists will develop a single, simply administered test that can provide a clear yes or no to the issue of impairment in the workplace.
I can envision a two-tier system in which all employees are blood or urine tested on a 3-month schedule. Those with a positive test must then take a 10-minute test on a laptop computer simulator with a joy stick each morning that they arrive on the job to demonstrate that, despite a history of marijuana use, they are not impaired.
Even if such a test is developed, we still owe our patients the reminder that, despite its decriminalization, marijuana is a drug and like any drug has side effects. One of them is that it can put limits on your employment opportunities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I have a friend who owns a large paving and excavating company. He currently is turning away large contracts because he can’t find employees to drive his dump trucks and operate his heavy machinery. The situation is so dire that he has begun to explore the possibility of recruiting employees out of the corrections system.
Like much of the country, Maine is experiencing a low level of unemployment that few of us over the age of 50 years can recall. Coupled with a confused and unwelcoming immigration policy at the federal level many small and large companies are struggling to find employees. The employment opportunities my friend’s company is offering are well above minimum wage, paying in the $30,000-$70,000 range with benefits. While the jobs require some special skills, his company is large enough that it can provide in-house training.
Maine residents recently have voted to decriminalize the possession of small amounts of marijuana. It is unclear exactly how this change in the official position of the state government will translate into a distribution network and a system of local codes. However, it does reflect a more tolerant attitude toward marijuana use. It also suggests that job seekers who are avoiding positions that require drug testing are not worried about the stigma of being identified as a user. They understand enough pharmacology to know that marijuana is detectable days and even weeks after it was last ingested or inhaled. Even the recreational users realize that the chances of being able to pass a drug test before employment and at any subsequent random testing are slim.
The problem is that these good-paying jobs are going unfilled because of the pharmacologic properties of a drug, and our current inability to devise a test that can accurately and consistently correlate a person’s blood level and his or her ability to safely operate a motor vehicle or piece of heavy equipment (“Establishing legal limit for driving under the influence of marijuana,” Inj Epidemiol. 2014 Dec.;1[1]: 26). There is some correlation between blood levels and whether a person is a heavy or infrequent user. Laws that rely on a zero tolerance philosophy are not bringing us any closer to a solution. And it is probably unrealistic to hope that in the near future scientists will develop a single, simply administered test that can provide a clear yes or no to the issue of impairment in the workplace.
I can envision a two-tier system in which all employees are blood or urine tested on a 3-month schedule. Those with a positive test must then take a 10-minute test on a laptop computer simulator with a joy stick each morning that they arrive on the job to demonstrate that, despite a history of marijuana use, they are not impaired.
Even if such a test is developed, we still owe our patients the reminder that, despite its decriminalization, marijuana is a drug and like any drug has side effects. One of them is that it can put limits on your employment opportunities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The demise of family dinners may play role in picky eating
My wife and I have dinner together almost every evening. There is a candle on the table regardless of the menu. And the meal begins with a toast, usually “To this chance to be together.” I can hear you muttering to yourself, “They must be one of those sappy, sweet hand-holding couples that appear to be joined at the hip.” Far from it, we lead very busy, active, but separate lives that only rarely intersect. But we make it a priority that one of those intersections occurs at a meal. For us, an evening dinner works best.
Listening to our friends, we have learned that an increasing number of them have drifted away from sharing a meal together. This phenomenon is surprising because most of them are retired, and time is not an issue. Of course, it is no secret that, for young overscheduled families, sitting down for a shared dining experience is becoming increasingly less frequent. Like some of you, I would like to claim that a return to family meal times would solve all of society’s ills. But some of the literature supporting this claim suggests shared family experiences in general, not particularly those associated with eating, may be just as important in supporting emotional health. But because everyone needs to eat, meals seem to me to be the easy target, low-hanging fruit if you will.
It is interesting that parents’ reports of their children’s eating patterns were validated by the behaviors videotaped by the researchers. But what is really interesting is that children who grew up in households where mealtimes followed a routine were more likely to be in the low–picky eating group. Routines included things like having a specific place times for eating, a habitual way of serving food, and other rituals such as saying grace.
Unfortunately, because this Michigan study began at age 4 years it doesn’t tell us if the worst picky eaters were that way from the beginning. I suspect that some were. But my hunch is that picky eaters who are managed in a home environment that includes mealtime rituals and puts dining together as a high priority are more likely to outgrow their pickiness.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Coping with a Picky Eater: A Guide for the Perplexed Parent.” Email him at [email protected].
My wife and I have dinner together almost every evening. There is a candle on the table regardless of the menu. And the meal begins with a toast, usually “To this chance to be together.” I can hear you muttering to yourself, “They must be one of those sappy, sweet hand-holding couples that appear to be joined at the hip.” Far from it, we lead very busy, active, but separate lives that only rarely intersect. But we make it a priority that one of those intersections occurs at a meal. For us, an evening dinner works best.
Listening to our friends, we have learned that an increasing number of them have drifted away from sharing a meal together. This phenomenon is surprising because most of them are retired, and time is not an issue. Of course, it is no secret that, for young overscheduled families, sitting down for a shared dining experience is becoming increasingly less frequent. Like some of you, I would like to claim that a return to family meal times would solve all of society’s ills. But some of the literature supporting this claim suggests shared family experiences in general, not particularly those associated with eating, may be just as important in supporting emotional health. But because everyone needs to eat, meals seem to me to be the easy target, low-hanging fruit if you will.
It is interesting that parents’ reports of their children’s eating patterns were validated by the behaviors videotaped by the researchers. But what is really interesting is that children who grew up in households where mealtimes followed a routine were more likely to be in the low–picky eating group. Routines included things like having a specific place times for eating, a habitual way of serving food, and other rituals such as saying grace.
Unfortunately, because this Michigan study began at age 4 years it doesn’t tell us if the worst picky eaters were that way from the beginning. I suspect that some were. But my hunch is that picky eaters who are managed in a home environment that includes mealtime rituals and puts dining together as a high priority are more likely to outgrow their pickiness.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Coping with a Picky Eater: A Guide for the Perplexed Parent.” Email him at [email protected].
My wife and I have dinner together almost every evening. There is a candle on the table regardless of the menu. And the meal begins with a toast, usually “To this chance to be together.” I can hear you muttering to yourself, “They must be one of those sappy, sweet hand-holding couples that appear to be joined at the hip.” Far from it, we lead very busy, active, but separate lives that only rarely intersect. But we make it a priority that one of those intersections occurs at a meal. For us, an evening dinner works best.
Listening to our friends, we have learned that an increasing number of them have drifted away from sharing a meal together. This phenomenon is surprising because most of them are retired, and time is not an issue. Of course, it is no secret that, for young overscheduled families, sitting down for a shared dining experience is becoming increasingly less frequent. Like some of you, I would like to claim that a return to family meal times would solve all of society’s ills. But some of the literature supporting this claim suggests shared family experiences in general, not particularly those associated with eating, may be just as important in supporting emotional health. But because everyone needs to eat, meals seem to me to be the easy target, low-hanging fruit if you will.
It is interesting that parents’ reports of their children’s eating patterns were validated by the behaviors videotaped by the researchers. But what is really interesting is that children who grew up in households where mealtimes followed a routine were more likely to be in the low–picky eating group. Routines included things like having a specific place times for eating, a habitual way of serving food, and other rituals such as saying grace.
Unfortunately, because this Michigan study began at age 4 years it doesn’t tell us if the worst picky eaters were that way from the beginning. I suspect that some were. But my hunch is that picky eaters who are managed in a home environment that includes mealtime rituals and puts dining together as a high priority are more likely to outgrow their pickiness.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “Coping with a Picky Eater: A Guide for the Perplexed Parent.” Email him at [email protected].