User login
Introduction: Health Professions Education Evaluation and Research (HPEER) Advanced Fellowship Abstracts
The original four HPEER Advanced Fellowship sites were established by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Academic Affiliation in 2014, and expanded in 2020 to include 8 sites and a national coordinating center with leadership shared between VA facilities in Houston and White River Junction. The VA invests heavily in training the nation’s healthcare professionals. The mission of HPEER is to develop leaders who can educate, evaluate, and innovate in Health Professions Education for the VA and the nation. All HPEER sites take part in a nationally coordinated curriculum covering topics in curriculum design, learner assessment, leadership, interprofessional education, as well as scholarship and educational research.
As part of the national HPEER curriculum covering scholarship and educational research, and in concert with Wednesday, May 14, 2025 VA Research Week 2025, HPEER organized a joint conference with the Center for Health Professions Education at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS). This interagency online event included poster sessions and oral presentations from HPEER fellows and students in USUHS certificate and graduate degree programs.
Education scholarship is broad, ranging from descriptions of curricular innovations and works in progress to advanced research using techniques drawn from psychology, sociology, anthropology, economics, and other scientific disciplines. The abstracts presented here summarize some of the work being done by HPEER fellows. Dougherty et al (Boston) described a project to create a primer outlining methodology for conducting and interpreting cost-effectiveness evaluations in the context of proposed HPE innovations. Cohen et al (Cleveland) found reduction in potentially problematic orders in the context of life-sustaining treatment following a multifaceted intervention program. Sorenson (Dublin, Georgia) reported an expanded Tai Chi program that included modifications allowing seated positions for veterans with mobility limitations. Young et al (Dublin) described an interprofessional curriculum to strengthen communication between nurses and social workers in their conversations with women veterans living in rural settings. Misedah-Robinson et al (Houston) showed that a new training program strengthened coordinators’ self-reports of preparedness and confidence in their ability to support veterans who have experienced human trafficking. Tovar et al (Salt Lake City) describe a methodology for using data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse to optimize schedules of HPE students assigned to VA clinical rotations. Yanez et al (San Francisco) presented initial observations of learner-centered outcomes following participation in a new multidisciplinary integrative health elective. Resto et al (West Haven) reported that implementation of self-serve kiosks increased distribution of substance use harm reduction resources beyond usual clinical care.
A second joint conference between VA HPEER and USUHS is planned for VA Research Week 2026; we look forward to the abstracts that will be produced by this new cohort of fellows, as well as to the future scholarship and contributions to the field that will be made by alumni of the HPEER Advanced Fellowship.
The original four HPEER Advanced Fellowship sites were established by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Academic Affiliation in 2014, and expanded in 2020 to include 8 sites and a national coordinating center with leadership shared between VA facilities in Houston and White River Junction. The VA invests heavily in training the nation’s healthcare professionals. The mission of HPEER is to develop leaders who can educate, evaluate, and innovate in Health Professions Education for the VA and the nation. All HPEER sites take part in a nationally coordinated curriculum covering topics in curriculum design, learner assessment, leadership, interprofessional education, as well as scholarship and educational research.
As part of the national HPEER curriculum covering scholarship and educational research, and in concert with Wednesday, May 14, 2025 VA Research Week 2025, HPEER organized a joint conference with the Center for Health Professions Education at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS). This interagency online event included poster sessions and oral presentations from HPEER fellows and students in USUHS certificate and graduate degree programs.
Education scholarship is broad, ranging from descriptions of curricular innovations and works in progress to advanced research using techniques drawn from psychology, sociology, anthropology, economics, and other scientific disciplines. The abstracts presented here summarize some of the work being done by HPEER fellows. Dougherty et al (Boston) described a project to create a primer outlining methodology for conducting and interpreting cost-effectiveness evaluations in the context of proposed HPE innovations. Cohen et al (Cleveland) found reduction in potentially problematic orders in the context of life-sustaining treatment following a multifaceted intervention program. Sorenson (Dublin, Georgia) reported an expanded Tai Chi program that included modifications allowing seated positions for veterans with mobility limitations. Young et al (Dublin) described an interprofessional curriculum to strengthen communication between nurses and social workers in their conversations with women veterans living in rural settings. Misedah-Robinson et al (Houston) showed that a new training program strengthened coordinators’ self-reports of preparedness and confidence in their ability to support veterans who have experienced human trafficking. Tovar et al (Salt Lake City) describe a methodology for using data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse to optimize schedules of HPE students assigned to VA clinical rotations. Yanez et al (San Francisco) presented initial observations of learner-centered outcomes following participation in a new multidisciplinary integrative health elective. Resto et al (West Haven) reported that implementation of self-serve kiosks increased distribution of substance use harm reduction resources beyond usual clinical care.
A second joint conference between VA HPEER and USUHS is planned for VA Research Week 2026; we look forward to the abstracts that will be produced by this new cohort of fellows, as well as to the future scholarship and contributions to the field that will be made by alumni of the HPEER Advanced Fellowship.
The original four HPEER Advanced Fellowship sites were established by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Academic Affiliation in 2014, and expanded in 2020 to include 8 sites and a national coordinating center with leadership shared between VA facilities in Houston and White River Junction. The VA invests heavily in training the nation’s healthcare professionals. The mission of HPEER is to develop leaders who can educate, evaluate, and innovate in Health Professions Education for the VA and the nation. All HPEER sites take part in a nationally coordinated curriculum covering topics in curriculum design, learner assessment, leadership, interprofessional education, as well as scholarship and educational research.
As part of the national HPEER curriculum covering scholarship and educational research, and in concert with Wednesday, May 14, 2025 VA Research Week 2025, HPEER organized a joint conference with the Center for Health Professions Education at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS). This interagency online event included poster sessions and oral presentations from HPEER fellows and students in USUHS certificate and graduate degree programs.
Education scholarship is broad, ranging from descriptions of curricular innovations and works in progress to advanced research using techniques drawn from psychology, sociology, anthropology, economics, and other scientific disciplines. The abstracts presented here summarize some of the work being done by HPEER fellows. Dougherty et al (Boston) described a project to create a primer outlining methodology for conducting and interpreting cost-effectiveness evaluations in the context of proposed HPE innovations. Cohen et al (Cleveland) found reduction in potentially problematic orders in the context of life-sustaining treatment following a multifaceted intervention program. Sorenson (Dublin, Georgia) reported an expanded Tai Chi program that included modifications allowing seated positions for veterans with mobility limitations. Young et al (Dublin) described an interprofessional curriculum to strengthen communication between nurses and social workers in their conversations with women veterans living in rural settings. Misedah-Robinson et al (Houston) showed that a new training program strengthened coordinators’ self-reports of preparedness and confidence in their ability to support veterans who have experienced human trafficking. Tovar et al (Salt Lake City) describe a methodology for using data from the VHA Corporate Data Warehouse to optimize schedules of HPE students assigned to VA clinical rotations. Yanez et al (San Francisco) presented initial observations of learner-centered outcomes following participation in a new multidisciplinary integrative health elective. Resto et al (West Haven) reported that implementation of self-serve kiosks increased distribution of substance use harm reduction resources beyond usual clinical care.
A second joint conference between VA HPEER and USUHS is planned for VA Research Week 2026; we look forward to the abstracts that will be produced by this new cohort of fellows, as well as to the future scholarship and contributions to the field that will be made by alumni of the HPEER Advanced Fellowship.
Interview Tips for Dermatology Applicants From Dr. Scott Worswick
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
Path of Least Resistance: Guidance for Antibiotic Stewardship in Acne
Path of Least Resistance: Guidance for Antibiotic Stewardship in Acne
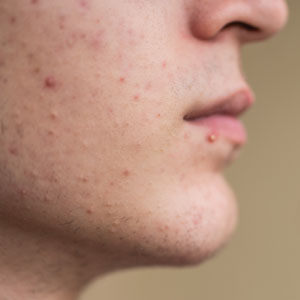
Dermatologists have long relied on oral antibiotics to manage moderate to severe acne1-4; however, it is critical to reassess how these medications are used in clinical practice as concerns about antibiotic resistance grow.5 The question is not whether antibiotics are effective for acne treatment—we know they are—but how to optimize their use to balance clinical benefit with responsible prescribing. Resistance in Cutibacterium acnes has been well documented in laboratory settings, but clinical treatment failure due to resistance remains rare and difficult to quantify.6,7 Still, minimizing unnecessary exposure is good clinical practice. Whether antibiotic resistance ultimately proves to drive clinical failure or remains largely theoretical, stewardship safeguards future treatment options.
In this article, we present a practical, expert-based framework aligned with American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) guidelines to support responsible antibiotic use in acne management. Seven prescribing principles are outlined to help clinicians maintain efficacy while minimizing resistance risk. Mechanisms of resistance in C acnes and broader microbiome impacts also are discussed.
MECHANISMS OF RESISTANCE IN ACNE THERAPY
Antibiotic resistance in acne primarily involves C acnes and arises through selective pressure from prolonged or subtherapeutic antibiotic exposure. Resistance mechanisms include point mutations in ribosomal binding sites, leading to decreased binding affinity for tetracyclines and macrolides as well as efflux pump activation and biofilm formation.8,9 Over time, resistant strains may proliferate and outcompete susceptible populations, potentially contributing to reduced clinical efficacy. Importantly, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may disrupt the skin and gut microbiota, promoting resistance among nontarget organisms.5 These concerns underscore the importance of limiting antibiotic use to appropriate indications, combining antibiotics with adjunctive nonantibiotic therapies, and avoiding monotherapy.
PRESCRIBING PRINCIPLES FOR RESPONSIBLE ORAL ANTIBIOTIC USE IN ACNE
The following principles are derived from our clinical experience and are aligned with AAD guidelines on acne treatment.10 This practical framework supports safe, effective, and streamlined prescribing.
Reserve Oral Antibiotics for Appropriate Cases
Oral antibiotics should be considered for patients with moderate to severe inflammatory acne when rapid anti-inflammatory control is needed. They are not indicated for comedonal or mild papulopustular acne. Before initiating treatment, clinicians should weigh the potential benefits against the risks associated with antibiotic exposure, including resistance and microbiome disruption.
Combine Oral Antibiotics With Topical Retinoids
Oral antibiotics should not be used as monotherapy. Topical retinoids should be initiated concurrently with oral antibiotics to maximize anti-inflammatory benefit, support transition to maintenance therapy, and reduce risk for resistance.
Consider Adding an Adjunctive Topical Antimicrobial Agent
Adjunctive topical antimicrobials can help reduce bacterial load. Benzoyl peroxide remains a first-line option due to its bactericidal activity and lack of resistance induction; however, recent product recalls involving benzene contamination may have raised safety concerns among some clinicians and patients.11,12 While no definitive harm has been established, alternative topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (eg, azelaic acid) may be used based on shared decision-making, tolerability, cost, access, and patient preference. Use of topical antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, erythromycin) as monotherapy is discouraged due to their higher resistance potential, which is consistent with AAD guidance.
Limit Treatment Duration to 12 Weeks or Less
Antibiotic use should be time limited, with discontinuation ideally within 8 to 12 weeks as clinical improvement is demonstrated. Repeated or prolonged courses should be avoided to minimize risk for resistance.
Simplify Treatment Regimens to Enhance Adherence
Regimen simplicity improves adherence, especially in adolescents. A two-agent regimen of an oral antibiotic and a topical retinoid typically is sufficient during the induction phase.13,14
Select Narrower-Spectrum Antibiotics When Feasible
Using a narrower-spectrum antibiotic may help minimize disruption to nontarget microbiota.15,16 Sarecycline has shown narrower in vitro activity within the tetracycline class,17,18 though clinical decisions should be informed by access, availability, and cost. Regardless of the agent used (eg, doxycycline, minocycline, or sarecycline), all antibiotics should be used judiciously and for the shortest effective duration.
Use Systemic Nonantibiotic Therapies When Appropriate
If there is inadequate response to oral antibiotic therapy, consider switching to systemic nonantibiotic options. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for select female patients. Oral isotretinoin should be considered for patients with severe, recalcitrant, or scarring acne. Cycling between antibiotic classes without clear benefit is discouraged.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Oral antibiotics remain a foundational component in the management of moderate to severe acne; however, their use must be intentional, time limited, and guided by best practices to minimize the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. By adhering to the prescribing principles we have outlined here, which are rooted in clinical expertise and consistent with AAD guidelines, dermatologists can preserve antibiotic efficacy, optimize patient outcomes, and reduce long-term microbiologic risks. Stewardship is not about withholding treatment; it is about optimizing care today to protect treatment options for tomorrow.
- Bhate K, Williams H. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:474-485.
- Barbieri JS, Bhate K, Hartnett KP, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic prescription in dermatology, 2008 to 2016. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:290-297.
- Grada A, Armstrong A, Bunick C, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic use for acne treatment: a retrospective, population-based study in the United States, 2014 to 2016. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:265-270.
- Perche PO, Peck GM, Robinson L, et al. Prescribing trends for acne vulgaris visits in the United States. Antibiotics. 2023;12:269.
- Karadag A, Aslan Kayıran M, Wu CY, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: changes, consequences and concerns. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:73-78.
- Eady AE, Cove JH, Layton AM. Is antibiotic resistance in cutaneous propionibacteria clinically relevant? implications of resistance for acne patients and prescribers. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:813-831.
- Eady EA, Cove J, Holland K, et al. Erythromycin resistant propionibacteria in antibiotic treated acne patients: association with therapeutic failure. Br J Dermatol. 1989;121:51-57.
- Grossman TH. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a025387.
- Kayiran M AS, Karadag AS, Al-Khuzaei S, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: mechanisms, complications and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:813-819.
- Reynolds RV, Yeung H, Cheng CE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1006-1035.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Benzoyl peroxide drug products form benzene. Environ Health Perspect. 2024;132:037702.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Evaluation of benzene presence and formation in benzoyl peroxide drug products. J Invest Dermatol. 2025;145:1147-1154.E11.
- Grada A, Perche P, Feldman S. Adherence and persistence to acne medications: a population-based claims database analysis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:758-764.<.li>
- Anderson KL, Dothard EH, Huang KE, et al. Frequency of primary nonadherence to acne treatment. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:623-626.
- Grada A, Bunick CG. Spectrum of antibiotic activity and its relevance to the microbiome. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:E215357-E215357.
- Francino M. Antibiotics and the human gut microbiome: dysbioses and accumulation of resistances. Front Microbiol. 2016;6:164577.
- Moura IB, Grada A, Spittal W, et al. Profiling the effects of systemic antibiotics for acne, including the narrow-spectrum antibiotic sarecycline, on the human gut microbiota. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:901911.
- Zhanel G, Critchley I, Lin L-Y, et al. Microbiological profile of sarecycline, a novel targeted spectrum tetracycline for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:1297-1318.
Dermatologists have long relied on oral antibiotics to manage moderate to severe acne1-4; however, it is critical to reassess how these medications are used in clinical practice as concerns about antibiotic resistance grow.5 The question is not whether antibiotics are effective for acne treatment—we know they are—but how to optimize their use to balance clinical benefit with responsible prescribing. Resistance in Cutibacterium acnes has been well documented in laboratory settings, but clinical treatment failure due to resistance remains rare and difficult to quantify.6,7 Still, minimizing unnecessary exposure is good clinical practice. Whether antibiotic resistance ultimately proves to drive clinical failure or remains largely theoretical, stewardship safeguards future treatment options.
In this article, we present a practical, expert-based framework aligned with American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) guidelines to support responsible antibiotic use in acne management. Seven prescribing principles are outlined to help clinicians maintain efficacy while minimizing resistance risk. Mechanisms of resistance in C acnes and broader microbiome impacts also are discussed.
MECHANISMS OF RESISTANCE IN ACNE THERAPY
Antibiotic resistance in acne primarily involves C acnes and arises through selective pressure from prolonged or subtherapeutic antibiotic exposure. Resistance mechanisms include point mutations in ribosomal binding sites, leading to decreased binding affinity for tetracyclines and macrolides as well as efflux pump activation and biofilm formation.8,9 Over time, resistant strains may proliferate and outcompete susceptible populations, potentially contributing to reduced clinical efficacy. Importantly, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may disrupt the skin and gut microbiota, promoting resistance among nontarget organisms.5 These concerns underscore the importance of limiting antibiotic use to appropriate indications, combining antibiotics with adjunctive nonantibiotic therapies, and avoiding monotherapy.
PRESCRIBING PRINCIPLES FOR RESPONSIBLE ORAL ANTIBIOTIC USE IN ACNE
The following principles are derived from our clinical experience and are aligned with AAD guidelines on acne treatment.10 This practical framework supports safe, effective, and streamlined prescribing.
Reserve Oral Antibiotics for Appropriate Cases
Oral antibiotics should be considered for patients with moderate to severe inflammatory acne when rapid anti-inflammatory control is needed. They are not indicated for comedonal or mild papulopustular acne. Before initiating treatment, clinicians should weigh the potential benefits against the risks associated with antibiotic exposure, including resistance and microbiome disruption.
Combine Oral Antibiotics With Topical Retinoids
Oral antibiotics should not be used as monotherapy. Topical retinoids should be initiated concurrently with oral antibiotics to maximize anti-inflammatory benefit, support transition to maintenance therapy, and reduce risk for resistance.
Consider Adding an Adjunctive Topical Antimicrobial Agent
Adjunctive topical antimicrobials can help reduce bacterial load. Benzoyl peroxide remains a first-line option due to its bactericidal activity and lack of resistance induction; however, recent product recalls involving benzene contamination may have raised safety concerns among some clinicians and patients.11,12 While no definitive harm has been established, alternative topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (eg, azelaic acid) may be used based on shared decision-making, tolerability, cost, access, and patient preference. Use of topical antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, erythromycin) as monotherapy is discouraged due to their higher resistance potential, which is consistent with AAD guidance.
Limit Treatment Duration to 12 Weeks or Less
Antibiotic use should be time limited, with discontinuation ideally within 8 to 12 weeks as clinical improvement is demonstrated. Repeated or prolonged courses should be avoided to minimize risk for resistance.
Simplify Treatment Regimens to Enhance Adherence
Regimen simplicity improves adherence, especially in adolescents. A two-agent regimen of an oral antibiotic and a topical retinoid typically is sufficient during the induction phase.13,14
Select Narrower-Spectrum Antibiotics When Feasible
Using a narrower-spectrum antibiotic may help minimize disruption to nontarget microbiota.15,16 Sarecycline has shown narrower in vitro activity within the tetracycline class,17,18 though clinical decisions should be informed by access, availability, and cost. Regardless of the agent used (eg, doxycycline, minocycline, or sarecycline), all antibiotics should be used judiciously and for the shortest effective duration.
Use Systemic Nonantibiotic Therapies When Appropriate
If there is inadequate response to oral antibiotic therapy, consider switching to systemic nonantibiotic options. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for select female patients. Oral isotretinoin should be considered for patients with severe, recalcitrant, or scarring acne. Cycling between antibiotic classes without clear benefit is discouraged.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Oral antibiotics remain a foundational component in the management of moderate to severe acne; however, their use must be intentional, time limited, and guided by best practices to minimize the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. By adhering to the prescribing principles we have outlined here, which are rooted in clinical expertise and consistent with AAD guidelines, dermatologists can preserve antibiotic efficacy, optimize patient outcomes, and reduce long-term microbiologic risks. Stewardship is not about withholding treatment; it is about optimizing care today to protect treatment options for tomorrow.
Dermatologists have long relied on oral antibiotics to manage moderate to severe acne1-4; however, it is critical to reassess how these medications are used in clinical practice as concerns about antibiotic resistance grow.5 The question is not whether antibiotics are effective for acne treatment—we know they are—but how to optimize their use to balance clinical benefit with responsible prescribing. Resistance in Cutibacterium acnes has been well documented in laboratory settings, but clinical treatment failure due to resistance remains rare and difficult to quantify.6,7 Still, minimizing unnecessary exposure is good clinical practice. Whether antibiotic resistance ultimately proves to drive clinical failure or remains largely theoretical, stewardship safeguards future treatment options.
In this article, we present a practical, expert-based framework aligned with American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) guidelines to support responsible antibiotic use in acne management. Seven prescribing principles are outlined to help clinicians maintain efficacy while minimizing resistance risk. Mechanisms of resistance in C acnes and broader microbiome impacts also are discussed.
MECHANISMS OF RESISTANCE IN ACNE THERAPY
Antibiotic resistance in acne primarily involves C acnes and arises through selective pressure from prolonged or subtherapeutic antibiotic exposure. Resistance mechanisms include point mutations in ribosomal binding sites, leading to decreased binding affinity for tetracyclines and macrolides as well as efflux pump activation and biofilm formation.8,9 Over time, resistant strains may proliferate and outcompete susceptible populations, potentially contributing to reduced clinical efficacy. Importantly, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may disrupt the skin and gut microbiota, promoting resistance among nontarget organisms.5 These concerns underscore the importance of limiting antibiotic use to appropriate indications, combining antibiotics with adjunctive nonantibiotic therapies, and avoiding monotherapy.
PRESCRIBING PRINCIPLES FOR RESPONSIBLE ORAL ANTIBIOTIC USE IN ACNE
The following principles are derived from our clinical experience and are aligned with AAD guidelines on acne treatment.10 This practical framework supports safe, effective, and streamlined prescribing.
Reserve Oral Antibiotics for Appropriate Cases
Oral antibiotics should be considered for patients with moderate to severe inflammatory acne when rapid anti-inflammatory control is needed. They are not indicated for comedonal or mild papulopustular acne. Before initiating treatment, clinicians should weigh the potential benefits against the risks associated with antibiotic exposure, including resistance and microbiome disruption.
Combine Oral Antibiotics With Topical Retinoids
Oral antibiotics should not be used as monotherapy. Topical retinoids should be initiated concurrently with oral antibiotics to maximize anti-inflammatory benefit, support transition to maintenance therapy, and reduce risk for resistance.
Consider Adding an Adjunctive Topical Antimicrobial Agent
Adjunctive topical antimicrobials can help reduce bacterial load. Benzoyl peroxide remains a first-line option due to its bactericidal activity and lack of resistance induction; however, recent product recalls involving benzene contamination may have raised safety concerns among some clinicians and patients.11,12 While no definitive harm has been established, alternative topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (eg, azelaic acid) may be used based on shared decision-making, tolerability, cost, access, and patient preference. Use of topical antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, erythromycin) as monotherapy is discouraged due to their higher resistance potential, which is consistent with AAD guidance.
Limit Treatment Duration to 12 Weeks or Less
Antibiotic use should be time limited, with discontinuation ideally within 8 to 12 weeks as clinical improvement is demonstrated. Repeated or prolonged courses should be avoided to minimize risk for resistance.
Simplify Treatment Regimens to Enhance Adherence
Regimen simplicity improves adherence, especially in adolescents. A two-agent regimen of an oral antibiotic and a topical retinoid typically is sufficient during the induction phase.13,14
Select Narrower-Spectrum Antibiotics When Feasible
Using a narrower-spectrum antibiotic may help minimize disruption to nontarget microbiota.15,16 Sarecycline has shown narrower in vitro activity within the tetracycline class,17,18 though clinical decisions should be informed by access, availability, and cost. Regardless of the agent used (eg, doxycycline, minocycline, or sarecycline), all antibiotics should be used judiciously and for the shortest effective duration.
Use Systemic Nonantibiotic Therapies When Appropriate
If there is inadequate response to oral antibiotic therapy, consider switching to systemic nonantibiotic options. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for select female patients. Oral isotretinoin should be considered for patients with severe, recalcitrant, or scarring acne. Cycling between antibiotic classes without clear benefit is discouraged.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Oral antibiotics remain a foundational component in the management of moderate to severe acne; however, their use must be intentional, time limited, and guided by best practices to minimize the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. By adhering to the prescribing principles we have outlined here, which are rooted in clinical expertise and consistent with AAD guidelines, dermatologists can preserve antibiotic efficacy, optimize patient outcomes, and reduce long-term microbiologic risks. Stewardship is not about withholding treatment; it is about optimizing care today to protect treatment options for tomorrow.
- Bhate K, Williams H. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:474-485.
- Barbieri JS, Bhate K, Hartnett KP, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic prescription in dermatology, 2008 to 2016. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:290-297.
- Grada A, Armstrong A, Bunick C, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic use for acne treatment: a retrospective, population-based study in the United States, 2014 to 2016. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:265-270.
- Perche PO, Peck GM, Robinson L, et al. Prescribing trends for acne vulgaris visits in the United States. Antibiotics. 2023;12:269.
- Karadag A, Aslan Kayıran M, Wu CY, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: changes, consequences and concerns. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:73-78.
- Eady AE, Cove JH, Layton AM. Is antibiotic resistance in cutaneous propionibacteria clinically relevant? implications of resistance for acne patients and prescribers. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:813-831.
- Eady EA, Cove J, Holland K, et al. Erythromycin resistant propionibacteria in antibiotic treated acne patients: association with therapeutic failure. Br J Dermatol. 1989;121:51-57.
- Grossman TH. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a025387.
- Kayiran M AS, Karadag AS, Al-Khuzaei S, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: mechanisms, complications and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:813-819.
- Reynolds RV, Yeung H, Cheng CE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1006-1035.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Benzoyl peroxide drug products form benzene. Environ Health Perspect. 2024;132:037702.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Evaluation of benzene presence and formation in benzoyl peroxide drug products. J Invest Dermatol. 2025;145:1147-1154.E11.
- Grada A, Perche P, Feldman S. Adherence and persistence to acne medications: a population-based claims database analysis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:758-764.<.li>
- Anderson KL, Dothard EH, Huang KE, et al. Frequency of primary nonadherence to acne treatment. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:623-626.
- Grada A, Bunick CG. Spectrum of antibiotic activity and its relevance to the microbiome. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:E215357-E215357.
- Francino M. Antibiotics and the human gut microbiome: dysbioses and accumulation of resistances. Front Microbiol. 2016;6:164577.
- Moura IB, Grada A, Spittal W, et al. Profiling the effects of systemic antibiotics for acne, including the narrow-spectrum antibiotic sarecycline, on the human gut microbiota. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:901911.
- Zhanel G, Critchley I, Lin L-Y, et al. Microbiological profile of sarecycline, a novel targeted spectrum tetracycline for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:1297-1318.
- Bhate K, Williams H. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:474-485.
- Barbieri JS, Bhate K, Hartnett KP, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic prescription in dermatology, 2008 to 2016. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:290-297.
- Grada A, Armstrong A, Bunick C, et al. Trends in oral antibiotic use for acne treatment: a retrospective, population-based study in the United States, 2014 to 2016. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22:265-270.
- Perche PO, Peck GM, Robinson L, et al. Prescribing trends for acne vulgaris visits in the United States. Antibiotics. 2023;12:269.
- Karadag A, Aslan Kayıran M, Wu CY, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: changes, consequences and concerns. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:73-78.
- Eady AE, Cove JH, Layton AM. Is antibiotic resistance in cutaneous propionibacteria clinically relevant? implications of resistance for acne patients and prescribers. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4:813-831.
- Eady EA, Cove J, Holland K, et al. Erythromycin resistant propionibacteria in antibiotic treated acne patients: association with therapeutic failure. Br J Dermatol. 1989;121:51-57.
- Grossman TH. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a025387.
- Kayiran M AS, Karadag AS, Al-Khuzaei S, et al. Antibiotic resistance in acne: mechanisms, complications and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:813-819.
- Reynolds RV, Yeung H, Cheng CE, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:1006-1035.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Benzoyl peroxide drug products form benzene. Environ Health Perspect. 2024;132:037702.
- Kucera K, Zenzola N, Hudspeth A, et al. Evaluation of benzene presence and formation in benzoyl peroxide drug products. J Invest Dermatol. 2025;145:1147-1154.E11.
- Grada A, Perche P, Feldman S. Adherence and persistence to acne medications: a population-based claims database analysis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:758-764.<.li>
- Anderson KL, Dothard EH, Huang KE, et al. Frequency of primary nonadherence to acne treatment. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:623-626.
- Grada A, Bunick CG. Spectrum of antibiotic activity and its relevance to the microbiome. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:E215357-E215357.
- Francino M. Antibiotics and the human gut microbiome: dysbioses and accumulation of resistances. Front Microbiol. 2016;6:164577.
- Moura IB, Grada A, Spittal W, et al. Profiling the effects of systemic antibiotics for acne, including the narrow-spectrum antibiotic sarecycline, on the human gut microbiota. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:901911.
- Zhanel G, Critchley I, Lin L-Y, et al. Microbiological profile of sarecycline, a novel targeted spectrum tetracycline for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:1297-1318.
Path of Least Resistance: Guidance for Antibiotic Stewardship in Acne
Path of Least Resistance: Guidance for Antibiotic Stewardship in Acne
Practice Point
- Oral antibiotics remain a cornerstone in the treatment of moderate to severe acne, but growing concerns about antibiotic resistance necessitate more intentional prescribing.
Therapeutic Approaches for Alopecia Areata in Children Aged 6 to 11 Years
Therapeutic Approaches for Alopecia Areata in Children Aged 6 to 11 Years
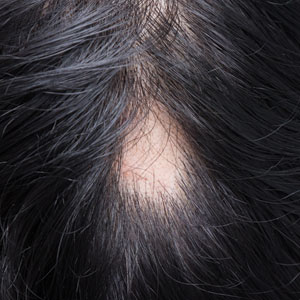
Pediatric alopecia areata (AA) is a chronic autoimmune disease of the hair follicles characterized by nonscarring hair loss. Its incidence in children in the United States ranges from 13.6 to 33.5 per 100,000 person-years, with a prevalence of 0.04% to 0.11%.1 Alopecia areata has important effects on quality of life, particularly in children. Hair loss at an early age can decrease participation in school, sports, and extracurricular activities2 and is associated with increased rates of comorbid anxiety and depression.3 Families also experience psychosocial stress, often comparable to other chronic pediatric illnesses.4 Thus, management requires not only medical therapy but also psychosocial support and school-based accommodations.
Systemic therapies for treatment of AA in adolescents and adults are increasingly available, including US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors such as baricitinib, deuruxolitinib (for adults), and ritlecitinib (for adolescents and adults); however, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA for children younger than 12 years. The therapeutic gap is most acute for those aged 6 to 11 years, for whom the psychosocial burden is high but treatment options are limited.3
This article highlights options and strategies for managing AA in children aged 6 to 11 years, emphasizing supportive and psychosocial care (including camouflage techniques), topical therapies, and off-label systemic approaches.
Supportive and Psychosocial Care
Treatment of AA in children extends beyond the affected child to include parents, caregivers, and even school staff (eg, teachers, principals, nurses).4 Disease-specific organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (naaf.org) and the Children’s Alopecia Project (childrensalopeciaproject.org) provide education, support groups, and advocacy resources. These organizations assist families in navigating school accommodations, including Section 504 plans that may allow children with AA to wear hats in school to mitigate stigma. Additional resources include handouts for teachers and school nurses developed by the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.5
Psychological support for these patients is critical. Many children benefit from seeing a psychologist, particularly if anxiety, depression, and/or bullying is present.3 In clinics without embedded psychology services, dermatologists should maintain referral lists or encourage families to seek guidance from their pediatrician.
Camouflage techniques can help children cope with visible hair loss. Wigs and hairpieces are available free of charge through charitable organizations for patients younger than 17; however, young children often find adhesives uncomfortable, and they will not wear nonadherent wigs for long periods of time. Alternatives include soft hats, bonnets, scarves, and beanies. For partial hair loss, root concealers, scalp powders, or hair mascara can be useful. Temporary eyebrow tattoos are a good cosmetic approach, whereas microblading generally is not advised in children younger than 12 due to procedural risks including pain.
Topical Therapies
Topical agents remain the mainstay of treatment for AA in children aged 6 to 11 years. Potent class 1 or class 2 topical corticosteroids commonly are used, sometimes in combination with calcineurin inhibitors or topical minoxidil. Off-label compounded topical JAK inhibitors also have been tried in this population and may be helpful for eyebrow hair loss,6 though data on their efficacy for scalp AA are mixed.7 Intralesional corticosteroid injections, effective in adolescents and adults, generally are poorly tolerated by younger children and may cause considerable distress. Contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or anthralin can be considered, but these agents are designed to elicit irritation, which may be intolerable for young children.8 Shared decision-making with families is essential to balance efficacy, tolerability, and treatment burden.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapy generally is reserved for children with extensive or refractory AA. Low-dose oral minoxidil is emerging as an off-label option. One systematic review reported that low-dose oral minoxidil was well tolerated in pediatric patients with minimal adverse effects.9 Doses of 0.01 to 0.02 mg/kg/d are reasonable starting points, achieved by cutting tablets or compounding oral solutions.10
In children with AA and concurrent atopic dermatitis, dupilumab may offer dual benefit. A real-world observational study demonstrated hair regrowth in pediatric patients with AA treated with dupilumab.11 Immunosuppressive options such as low-dose methotrexate or pulse corticosteroids (dexamethasone or prednisolone) also may be considered, although use of these agents requires careful monitoring due to increased risk for infection, clinically significant blood count and liver enzyme changes, and metabolic adverse effects related to long-term use of corticosteroids.
Clinical trials of JAK inhibitors in children aged 6 to 11 years are anticipated to begin in late 2025. Until then, off-label use of ritlecitinib, baricitinib, tofacitinib, or other JAK inhibitors may be considered in select cases with considerable disease burden and quality-of-life impairment following thorough discussion with the patient and their caregivers. Currently available pediatric data show few serious adverse events in children—the most common included upper respiratory infections (nasopharyngitis), acne, and headaches—but long-term risks remain unknown. Dosing challenges also exist for children who cannot swallow pills; currently ritlecitinib is available only as a capsule that cannot be opened while other JAK inhibitors are available in more accessible forms (baricitinib can be crushed and dissolved, and tofacitinib is available in liquid formulation for other pediatric indications). Insurance coverage is a major barrier, as these therapies are not FDA approved for AA in this age group.
Final Thoughts
Alopecia areata in children aged 6 to 11 years presents unique therapeutic challenges. While highly effective systemic therapies exist for older patients, younger children have limited options. For the 6-to-11 age group, management strategies should prioritize psychosocial support, topical therapy, and low-burden systemic alternatives such as low-dose oral minoxidil. Family education, school-based accommodations, and access to camouflage techniques are integral to holistic care. The commencement of pediatric clinical trials for JAK inhibitors offers hope for more robust treatment strategies in the near future. In the meantime, clinicians must engage in shared decision-making, tailoring therapy to the child’s disease severity, emotional well-being, and family priorities.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42(suppl 1):12-23. doi:10.1111/pde.15803
- Paller AS, Rangel SM, Chamlin SL, et al; Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. Stigmatization and mental health impact of chronic pediatric skin disorders. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:621-630.
- van Dalen M, Muller KS, Kasperkovitz-Oosterloo JM, et al. Anxiety, depression, and quality of life in children and adults with alopecia areata: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:1054898.
- Yücesoy SN, Uzunçakmak TK, Selçukog?lu Ö, et al. Evaluation of quality of life scores and family impact scales in pediatric patients with alopecia areata: a cross-sectional cohort study. Int J Dermatol. 2024;63:1414-1420.
- Alopecia areata. Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Accessed November 17, 2025. https://pedsderm.net/site/assets/files/18580/spd_school_handout_1_alopecia.pdf
- Liu LY, King BA. Response to tofacitinib therapy of eyebrows and eyelashes in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1778-1779.
- Bokhari L, Sinclair R. Treatment of alopecia universalis with topical Janus kinase inhibitors—a double blind, placebo, and active controlled pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1464-1470.
- Hill ND, Bunata K, Hebert AA. Treatment of alopecia areata with squaric acid dibutylester. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:300-304.
- Williams KN, Olukoga CTY, Tosti A. Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of oral minoxidil in children: a systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:1709-1727.
- Lemes LR, Melo DF, de Oliveira DS, et al. Topical and oral minoxidil for hair disorders in pediatric patients: what do we know so far? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13950.
- David E, Shokrian N, Del Duca E, et al. Dupilumab induces hair regrowth in pediatric alopecia areata: a real-world, single-center observational study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024;316:487.
Pediatric alopecia areata (AA) is a chronic autoimmune disease of the hair follicles characterized by nonscarring hair loss. Its incidence in children in the United States ranges from 13.6 to 33.5 per 100,000 person-years, with a prevalence of 0.04% to 0.11%.1 Alopecia areata has important effects on quality of life, particularly in children. Hair loss at an early age can decrease participation in school, sports, and extracurricular activities2 and is associated with increased rates of comorbid anxiety and depression.3 Families also experience psychosocial stress, often comparable to other chronic pediatric illnesses.4 Thus, management requires not only medical therapy but also psychosocial support and school-based accommodations.
Systemic therapies for treatment of AA in adolescents and adults are increasingly available, including US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors such as baricitinib, deuruxolitinib (for adults), and ritlecitinib (for adolescents and adults); however, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA for children younger than 12 years. The therapeutic gap is most acute for those aged 6 to 11 years, for whom the psychosocial burden is high but treatment options are limited.3
This article highlights options and strategies for managing AA in children aged 6 to 11 years, emphasizing supportive and psychosocial care (including camouflage techniques), topical therapies, and off-label systemic approaches.
Supportive and Psychosocial Care
Treatment of AA in children extends beyond the affected child to include parents, caregivers, and even school staff (eg, teachers, principals, nurses).4 Disease-specific organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (naaf.org) and the Children’s Alopecia Project (childrensalopeciaproject.org) provide education, support groups, and advocacy resources. These organizations assist families in navigating school accommodations, including Section 504 plans that may allow children with AA to wear hats in school to mitigate stigma. Additional resources include handouts for teachers and school nurses developed by the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.5
Psychological support for these patients is critical. Many children benefit from seeing a psychologist, particularly if anxiety, depression, and/or bullying is present.3 In clinics without embedded psychology services, dermatologists should maintain referral lists or encourage families to seek guidance from their pediatrician.
Camouflage techniques can help children cope with visible hair loss. Wigs and hairpieces are available free of charge through charitable organizations for patients younger than 17; however, young children often find adhesives uncomfortable, and they will not wear nonadherent wigs for long periods of time. Alternatives include soft hats, bonnets, scarves, and beanies. For partial hair loss, root concealers, scalp powders, or hair mascara can be useful. Temporary eyebrow tattoos are a good cosmetic approach, whereas microblading generally is not advised in children younger than 12 due to procedural risks including pain.
Topical Therapies
Topical agents remain the mainstay of treatment for AA in children aged 6 to 11 years. Potent class 1 or class 2 topical corticosteroids commonly are used, sometimes in combination with calcineurin inhibitors or topical minoxidil. Off-label compounded topical JAK inhibitors also have been tried in this population and may be helpful for eyebrow hair loss,6 though data on their efficacy for scalp AA are mixed.7 Intralesional corticosteroid injections, effective in adolescents and adults, generally are poorly tolerated by younger children and may cause considerable distress. Contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or anthralin can be considered, but these agents are designed to elicit irritation, which may be intolerable for young children.8 Shared decision-making with families is essential to balance efficacy, tolerability, and treatment burden.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapy generally is reserved for children with extensive or refractory AA. Low-dose oral minoxidil is emerging as an off-label option. One systematic review reported that low-dose oral minoxidil was well tolerated in pediatric patients with minimal adverse effects.9 Doses of 0.01 to 0.02 mg/kg/d are reasonable starting points, achieved by cutting tablets or compounding oral solutions.10
In children with AA and concurrent atopic dermatitis, dupilumab may offer dual benefit. A real-world observational study demonstrated hair regrowth in pediatric patients with AA treated with dupilumab.11 Immunosuppressive options such as low-dose methotrexate or pulse corticosteroids (dexamethasone or prednisolone) also may be considered, although use of these agents requires careful monitoring due to increased risk for infection, clinically significant blood count and liver enzyme changes, and metabolic adverse effects related to long-term use of corticosteroids.
Clinical trials of JAK inhibitors in children aged 6 to 11 years are anticipated to begin in late 2025. Until then, off-label use of ritlecitinib, baricitinib, tofacitinib, or other JAK inhibitors may be considered in select cases with considerable disease burden and quality-of-life impairment following thorough discussion with the patient and their caregivers. Currently available pediatric data show few serious adverse events in children—the most common included upper respiratory infections (nasopharyngitis), acne, and headaches—but long-term risks remain unknown. Dosing challenges also exist for children who cannot swallow pills; currently ritlecitinib is available only as a capsule that cannot be opened while other JAK inhibitors are available in more accessible forms (baricitinib can be crushed and dissolved, and tofacitinib is available in liquid formulation for other pediatric indications). Insurance coverage is a major barrier, as these therapies are not FDA approved for AA in this age group.
Final Thoughts
Alopecia areata in children aged 6 to 11 years presents unique therapeutic challenges. While highly effective systemic therapies exist for older patients, younger children have limited options. For the 6-to-11 age group, management strategies should prioritize psychosocial support, topical therapy, and low-burden systemic alternatives such as low-dose oral minoxidil. Family education, school-based accommodations, and access to camouflage techniques are integral to holistic care. The commencement of pediatric clinical trials for JAK inhibitors offers hope for more robust treatment strategies in the near future. In the meantime, clinicians must engage in shared decision-making, tailoring therapy to the child’s disease severity, emotional well-being, and family priorities.
Pediatric alopecia areata (AA) is a chronic autoimmune disease of the hair follicles characterized by nonscarring hair loss. Its incidence in children in the United States ranges from 13.6 to 33.5 per 100,000 person-years, with a prevalence of 0.04% to 0.11%.1 Alopecia areata has important effects on quality of life, particularly in children. Hair loss at an early age can decrease participation in school, sports, and extracurricular activities2 and is associated with increased rates of comorbid anxiety and depression.3 Families also experience psychosocial stress, often comparable to other chronic pediatric illnesses.4 Thus, management requires not only medical therapy but also psychosocial support and school-based accommodations.
Systemic therapies for treatment of AA in adolescents and adults are increasingly available, including US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors such as baricitinib, deuruxolitinib (for adults), and ritlecitinib (for adolescents and adults); however, no systemic therapies have been approved by the FDA for children younger than 12 years. The therapeutic gap is most acute for those aged 6 to 11 years, for whom the psychosocial burden is high but treatment options are limited.3
This article highlights options and strategies for managing AA in children aged 6 to 11 years, emphasizing supportive and psychosocial care (including camouflage techniques), topical therapies, and off-label systemic approaches.
Supportive and Psychosocial Care
Treatment of AA in children extends beyond the affected child to include parents, caregivers, and even school staff (eg, teachers, principals, nurses).4 Disease-specific organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (naaf.org) and the Children’s Alopecia Project (childrensalopeciaproject.org) provide education, support groups, and advocacy resources. These organizations assist families in navigating school accommodations, including Section 504 plans that may allow children with AA to wear hats in school to mitigate stigma. Additional resources include handouts for teachers and school nurses developed by the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.5
Psychological support for these patients is critical. Many children benefit from seeing a psychologist, particularly if anxiety, depression, and/or bullying is present.3 In clinics without embedded psychology services, dermatologists should maintain referral lists or encourage families to seek guidance from their pediatrician.
Camouflage techniques can help children cope with visible hair loss. Wigs and hairpieces are available free of charge through charitable organizations for patients younger than 17; however, young children often find adhesives uncomfortable, and they will not wear nonadherent wigs for long periods of time. Alternatives include soft hats, bonnets, scarves, and beanies. For partial hair loss, root concealers, scalp powders, or hair mascara can be useful. Temporary eyebrow tattoos are a good cosmetic approach, whereas microblading generally is not advised in children younger than 12 due to procedural risks including pain.
Topical Therapies
Topical agents remain the mainstay of treatment for AA in children aged 6 to 11 years. Potent class 1 or class 2 topical corticosteroids commonly are used, sometimes in combination with calcineurin inhibitors or topical minoxidil. Off-label compounded topical JAK inhibitors also have been tried in this population and may be helpful for eyebrow hair loss,6 though data on their efficacy for scalp AA are mixed.7 Intralesional corticosteroid injections, effective in adolescents and adults, generally are poorly tolerated by younger children and may cause considerable distress. Contact immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutyl ester or anthralin can be considered, but these agents are designed to elicit irritation, which may be intolerable for young children.8 Shared decision-making with families is essential to balance efficacy, tolerability, and treatment burden.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapy generally is reserved for children with extensive or refractory AA. Low-dose oral minoxidil is emerging as an off-label option. One systematic review reported that low-dose oral minoxidil was well tolerated in pediatric patients with minimal adverse effects.9 Doses of 0.01 to 0.02 mg/kg/d are reasonable starting points, achieved by cutting tablets or compounding oral solutions.10
In children with AA and concurrent atopic dermatitis, dupilumab may offer dual benefit. A real-world observational study demonstrated hair regrowth in pediatric patients with AA treated with dupilumab.11 Immunosuppressive options such as low-dose methotrexate or pulse corticosteroids (dexamethasone or prednisolone) also may be considered, although use of these agents requires careful monitoring due to increased risk for infection, clinically significant blood count and liver enzyme changes, and metabolic adverse effects related to long-term use of corticosteroids.
Clinical trials of JAK inhibitors in children aged 6 to 11 years are anticipated to begin in late 2025. Until then, off-label use of ritlecitinib, baricitinib, tofacitinib, or other JAK inhibitors may be considered in select cases with considerable disease burden and quality-of-life impairment following thorough discussion with the patient and their caregivers. Currently available pediatric data show few serious adverse events in children—the most common included upper respiratory infections (nasopharyngitis), acne, and headaches—but long-term risks remain unknown. Dosing challenges also exist for children who cannot swallow pills; currently ritlecitinib is available only as a capsule that cannot be opened while other JAK inhibitors are available in more accessible forms (baricitinib can be crushed and dissolved, and tofacitinib is available in liquid formulation for other pediatric indications). Insurance coverage is a major barrier, as these therapies are not FDA approved for AA in this age group.
Final Thoughts
Alopecia areata in children aged 6 to 11 years presents unique therapeutic challenges. While highly effective systemic therapies exist for older patients, younger children have limited options. For the 6-to-11 age group, management strategies should prioritize psychosocial support, topical therapy, and low-burden systemic alternatives such as low-dose oral minoxidil. Family education, school-based accommodations, and access to camouflage techniques are integral to holistic care. The commencement of pediatric clinical trials for JAK inhibitors offers hope for more robust treatment strategies in the near future. In the meantime, clinicians must engage in shared decision-making, tailoring therapy to the child’s disease severity, emotional well-being, and family priorities.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42(suppl 1):12-23. doi:10.1111/pde.15803
- Paller AS, Rangel SM, Chamlin SL, et al; Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. Stigmatization and mental health impact of chronic pediatric skin disorders. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:621-630.
- van Dalen M, Muller KS, Kasperkovitz-Oosterloo JM, et al. Anxiety, depression, and quality of life in children and adults with alopecia areata: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:1054898.
- Yücesoy SN, Uzunçakmak TK, Selçukog?lu Ö, et al. Evaluation of quality of life scores and family impact scales in pediatric patients with alopecia areata: a cross-sectional cohort study. Int J Dermatol. 2024;63:1414-1420.
- Alopecia areata. Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Accessed November 17, 2025. https://pedsderm.net/site/assets/files/18580/spd_school_handout_1_alopecia.pdf
- Liu LY, King BA. Response to tofacitinib therapy of eyebrows and eyelashes in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1778-1779.
- Bokhari L, Sinclair R. Treatment of alopecia universalis with topical Janus kinase inhibitors—a double blind, placebo, and active controlled pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1464-1470.
- Hill ND, Bunata K, Hebert AA. Treatment of alopecia areata with squaric acid dibutylester. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:300-304.
- Williams KN, Olukoga CTY, Tosti A. Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of oral minoxidil in children: a systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:1709-1727.
- Lemes LR, Melo DF, de Oliveira DS, et al. Topical and oral minoxidil for hair disorders in pediatric patients: what do we know so far? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13950.
- David E, Shokrian N, Del Duca E, et al. Dupilumab induces hair regrowth in pediatric alopecia areata: a real-world, single-center observational study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024;316:487.
- Adhanom R, Ansbro B, Castelo-Soccio L. Epidemiology of pediatric alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025;42(suppl 1):12-23. doi:10.1111/pde.15803
- Paller AS, Rangel SM, Chamlin SL, et al; Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. Stigmatization and mental health impact of chronic pediatric skin disorders. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:621-630.
- van Dalen M, Muller KS, Kasperkovitz-Oosterloo JM, et al. Anxiety, depression, and quality of life in children and adults with alopecia areata: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:1054898.
- Yücesoy SN, Uzunçakmak TK, Selçukog?lu Ö, et al. Evaluation of quality of life scores and family impact scales in pediatric patients with alopecia areata: a cross-sectional cohort study. Int J Dermatol. 2024;63:1414-1420.
- Alopecia areata. Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Accessed November 17, 2025. https://pedsderm.net/site/assets/files/18580/spd_school_handout_1_alopecia.pdf
- Liu LY, King BA. Response to tofacitinib therapy of eyebrows and eyelashes in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1778-1779.
- Bokhari L, Sinclair R. Treatment of alopecia universalis with topical Janus kinase inhibitors—a double blind, placebo, and active controlled pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1464-1470.
- Hill ND, Bunata K, Hebert AA. Treatment of alopecia areata with squaric acid dibutylester. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:300-304.
- Williams KN, Olukoga CTY, Tosti A. Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of oral minoxidil in children: a systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:1709-1727.
- Lemes LR, Melo DF, de Oliveira DS, et al. Topical and oral minoxidil for hair disorders in pediatric patients: what do we know so far? Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13950.
- David E, Shokrian N, Del Duca E, et al. Dupilumab induces hair regrowth in pediatric alopecia areata: a real-world, single-center observational study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024;316:487.
Therapeutic Approaches for Alopecia Areata in Children Aged 6 to 11 Years
Therapeutic Approaches for Alopecia Areata in Children Aged 6 to 11 Years
Finding Your Voice in Advocacy
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Does This Bacterial Toxin Drive Early CRC Risk?
Recent studies have cited an alarming increase in early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) rates, raising concern among gastroenterologists, public health experts, and patients alike. Approximately 10% of CRC cases now occur in those under age 50, and that proportion continues to grow. Between 2000 and 2016, colon cancer rose by 13% and rectal cancer by 16% among those aged 40–49.
According to recently published data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, between 2019 and 2022, CRC incidence among patients aged 45–49 rose by approximately 12% per year.
A Potential Bacterial Connection
What accounts for this disturbing spike? A research group from the University of California, San Diego, may have uncovered part of the answer.
In their study of 981 CRC genomes, most carried mutations suggestive of prior exposure to colibactin, a toxin produced by certain Escherichia coli (E coli) strains. Patients with extremely early-onset CRC (aged < 40 years) were 3 times more likely to have colibactin-suggestive mutations than patients older than 70. Crucially, colonic exposure to colibactin was linked to an adenomatous polyposis coli driver mutation.
These findings suggest that colibactin-induced injury in the gut microbiome may accelerate cancer development in some individuals. Environmental factors may contribute to the rise in early-onset CRC as well, such as consuming red meats, carcinogens from grilling, and processed meats and other highly processed foods; low fiber intake; lack of fruits and vegetables; drinking alcohol; lack of exercise; obesity; and colibactin exposure.
In this video, we will take a closer look at how E coli and colibactin may increase CRC risk.
Bacteria’s Cancer-Causing Properties
The idea that bacteria has cancer-causing properties isn’t new. In the 1970s, researchers linked Streptococcus bovis type 1 (now called Streptococcus gallolyticus) to CRC in a subset of patients with bacterial endocarditis stemming from right-sided colon cancer. Similarly, Helicobacter pylori infection has long been associated with increased gastric cancer risk.
Today, E coli infection is emerging as another possible contributor to CRC, especially via certain pathogenic strains containing the polyketide synthase (pks) genomic island, which encodes the colibactin and is sometimes present in the colon mucosa of patients with CRC.
Colibactin and DNA Damage
Colibactin-producing pks+ E coli strains can cause DNA double-strand breaks, one pathway to carcinogenesis. In animal studies, pks+ E coli strains have been linked to both increased risk for CRC and CRC progression.
In an important study published in Nature, Pleguezuelos-Manzano and colleagues repeatedly exposed intestinal organoids to pks+ E coli over 5 months and then performed whole genome sequencing. The result was a concerning potential for short insertions and deletions and single–base substitutions.
The authors concluded that their “study describes the distinct mutational signature in colorectal cancer and implies that the underlying mutational process results directly from past exposure to bacteria carrying the colibactin-producing pks pathogenicity island.”
Other E coli virulence factors may also contribute. For example, alpha-hemolysin may downregulate DNA mismatch repair proteins. In other words, E coli is probably just a contributing factor for the development of CRC, not the sole cause.
Biofilms and Inflammation
Previous studies have associated dense bacterial biofilms, particularly antibiotic-resistant strains, with CRC. This raises the possibility that widespread antibiotic overuse could predispose certain individuals to CRC development.
Biofilms normally separate the colon mucosal epithelium from bacteria and are essential for protecting against inflammation. In a 2018 study in Science, Dejea and colleagues concluded that “tumor-prone mice colonized with E coli (expressing colibactin), and enterotoxigenic B fragilis showed increased interleukin-17 in the colon and DNA damage in colonic epithelium with faster tumor onset and greater mortality, compared to mice with either bacteria strain alone. These data suggest an unexpected link between early neoplasia of the colon and tumorigenic bacteria.”
Additional research revealed that E coli can create a pro-carcinogenic environment by stimulating mucosal inflammation, hindering DNA and mismatch repair mechanisms, and altering immune responses.
Dysbiosis and Diet
Colibactin can also drive dysbiosis and imbalance in bacteria in the colon, which fuels inflammation and disrupts mucosal barrier integrity. This creates a vicious cycle in which chronic inflammation can further drive additional mucus deterioration and dysbiosis.
In mouse models where the colon mucosal barrier is damaged with dextrin sulfate sodium (DSS), pks+ E coli gains better access to colon epithelium, causes injury, and can even lead to chronic colitis. Colibactin can also hinder epithelial recovery after DSS treatment.
Diet plays a central role in this process. Low fiber consumption can disrupt the barrier between the colon mucus layer and the colon’s exterior layer where bacteria live. A traditional Western diet may bolster bacteria that degrade the mucus layer when the bacteria consume the glycosylated portion as an energy source.
Fortunately, diet is modifiable. High–fiber diets (ideally 25-30 g/d) boost short–chain fatty acids in the colon. This is important because short-chain fatty acids can decrease intercellular pH and impede Enterobacteriaceae replication, yet another reason why we should encourage patients to eat a diet high in vegetables, fruits, and [green] salads.
Two Types of Bacterial Drivers
There appear to be two broad types of bacteria associated with CRC development. It’s been hypothesized that there are “driver” bacteria that might initiate the development of CRC, possibly by creating oxidative stress and causing DNA breaks. Several potential pathogenic bacteria have been identified, including E coli, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bacteroides fragilis. Unfortunately, there are also bacteria such as Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus with the potential to alter intestinal permeability, resulting in downstream effects that can allow colon cancers to expand. Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus have the potential to cause DNA double–strand breaks in the intestine, which can produce chromosomal precariousness.
These secondary bacteria can also lead to DNA epigenetic changes and gene mutations. However, it should be emphasized that “the direct causation of imprinted DNA changes resulting from a direct interaction between bacteria and host cells is not so far established.”
E coli produces compounds called cyclomodulins, which can cause DNA breaks and potentially trigger cell cycle arrest and even cell death through activation of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway. The DNA damage checkpoint pathway is a cellular signaling network that helps detect DNA lesions and allows for genetic stability by stopping growth to allow for repair and simulating cell survival or apoptosis. A key cyclomodulin that E coli makes is colibactin, produced by the pks locus. Other cyclomodulins include cytolethal distending toxin, cytotoxic necrotizing factor, and cycle-inhibiting factor.
Previous research has shown that E coli is the only culturable bacteria found near CRC. A groundbreaking 1998 study employing PCR technology found E coli in 60% of colon polyp adenomas and an alarming 77% of CRC biopsies.
E coli’s capability to downregulate essential DNA mismatch repair proteins has been implicated in colorectal carcinogenesis. Interestingly, when the genetic region responsible for producing colibactin is deleted in animals, the bacteria aren’t able to promote cancer.
Mechanistically, colibactin causes double-stranded DNA breaks, eukaryotic cell cycle arrest, and chromosome abnormalities. It also alkylates DNA. This occurs when the cyclopropane ring of colibactin interacts with the N3 position of adenine in DNA, forming a covalent bond and creating a DNA adduct. DNA adducts occur when a chemical moiety from an environmental or dietary source binds to DNA base. Colibactin can cause DNA interstrand cross-links to form via alkalization of adenine residues on opposing DNA strands, a crucial step in DNA damage. DNA adducts can occur through carcinogens in N-nitroso compounds, such as in processed meats and in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in cigarette smoke. Colibactin-induced damage may also stimulate the senescence–associated secretory phenotype pathway, increasing proinflammatory cytokines.
E coli and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
E coli, the primary colibactin producer in the human intestinal microbiome, is found at higher bacterial percentages in the microbiomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In a study by Dubinsky and colleagues, “the medium relative levels of colibactin–encoding E. coli were about threefold higher in IBD.”
Researchers have also postulated that antibiotics and microbiome dysbiosis may create conditions that allow colibactin–producing bacteria to overpopulate.
Future Directions
Not every patient with CRC carries a colorectal mutational signature, but these findings underscore the need for continued vigilance and prevention.
From a public health standpoint, our advice remains consistent: Promote high-fiber diets with more vegetables and less red meat; avoid highly processed foods; avoid alcohol; encourage exercise; and address overweight and obesity. Our goal is to create the best possible colon environment to prevent DNA damage from bacterial and environmental carcinogens.
In the future, we need more research to clarify exactly how E coli and colibactin increase early–onset CRC risk and whether antibiotics and dysbiosis facilitate their ability to damage the DNA of colon mucosa. It’s still unclear why younger patients are at greater risk. In time, we may be able to screen for colibactin–producing bacteria such as E coli and manipulate the fecal microbiome to prevent damage.
A recent mouse study in Nature by Jans and colleagues suggests it might be possible to block bacterial adhesion and hopefully mitigate damage caused by colibactin. With continued work, colibactin–targeted strategies could become a part of CRC prevention.
Benjamin H. Levy III, MD, is a gastroenterologist at the University of Chicago. In 2017, Levy, a previous Fulbright Fellow in France, also started a gastroenterology clinic for refugees resettling in Chicago. His clinical projects focus on the development of colorectal cancer screening campaigns. Levy, who gave a TEDx Talk about building health education campaigns using music and concerts, organizes "Tune It Up: A Concert To Raise Colorectal Cancer Awareness" with the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG). He frequently publishes on a variety of gastroenterology topics and serves on ACG’s Public Relations Committee and FDA-Related Matters Committee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent studies have cited an alarming increase in early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) rates, raising concern among gastroenterologists, public health experts, and patients alike. Approximately 10% of CRC cases now occur in those under age 50, and that proportion continues to grow. Between 2000 and 2016, colon cancer rose by 13% and rectal cancer by 16% among those aged 40–49.
According to recently published data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, between 2019 and 2022, CRC incidence among patients aged 45–49 rose by approximately 12% per year.
A Potential Bacterial Connection
What accounts for this disturbing spike? A research group from the University of California, San Diego, may have uncovered part of the answer.
In their study of 981 CRC genomes, most carried mutations suggestive of prior exposure to colibactin, a toxin produced by certain Escherichia coli (E coli) strains. Patients with extremely early-onset CRC (aged < 40 years) were 3 times more likely to have colibactin-suggestive mutations than patients older than 70. Crucially, colonic exposure to colibactin was linked to an adenomatous polyposis coli driver mutation.
These findings suggest that colibactin-induced injury in the gut microbiome may accelerate cancer development in some individuals. Environmental factors may contribute to the rise in early-onset CRC as well, such as consuming red meats, carcinogens from grilling, and processed meats and other highly processed foods; low fiber intake; lack of fruits and vegetables; drinking alcohol; lack of exercise; obesity; and colibactin exposure.
In this video, we will take a closer look at how E coli and colibactin may increase CRC risk.
Bacteria’s Cancer-Causing Properties
The idea that bacteria has cancer-causing properties isn’t new. In the 1970s, researchers linked Streptococcus bovis type 1 (now called Streptococcus gallolyticus) to CRC in a subset of patients with bacterial endocarditis stemming from right-sided colon cancer. Similarly, Helicobacter pylori infection has long been associated with increased gastric cancer risk.
Today, E coli infection is emerging as another possible contributor to CRC, especially via certain pathogenic strains containing the polyketide synthase (pks) genomic island, which encodes the colibactin and is sometimes present in the colon mucosa of patients with CRC.
Colibactin and DNA Damage
Colibactin-producing pks+ E coli strains can cause DNA double-strand breaks, one pathway to carcinogenesis. In animal studies, pks+ E coli strains have been linked to both increased risk for CRC and CRC progression.
In an important study published in Nature, Pleguezuelos-Manzano and colleagues repeatedly exposed intestinal organoids to pks+ E coli over 5 months and then performed whole genome sequencing. The result was a concerning potential for short insertions and deletions and single–base substitutions.
The authors concluded that their “study describes the distinct mutational signature in colorectal cancer and implies that the underlying mutational process results directly from past exposure to bacteria carrying the colibactin-producing pks pathogenicity island.”
Other E coli virulence factors may also contribute. For example, alpha-hemolysin may downregulate DNA mismatch repair proteins. In other words, E coli is probably just a contributing factor for the development of CRC, not the sole cause.
Biofilms and Inflammation
Previous studies have associated dense bacterial biofilms, particularly antibiotic-resistant strains, with CRC. This raises the possibility that widespread antibiotic overuse could predispose certain individuals to CRC development.
Biofilms normally separate the colon mucosal epithelium from bacteria and are essential for protecting against inflammation. In a 2018 study in Science, Dejea and colleagues concluded that “tumor-prone mice colonized with E coli (expressing colibactin), and enterotoxigenic B fragilis showed increased interleukin-17 in the colon and DNA damage in colonic epithelium with faster tumor onset and greater mortality, compared to mice with either bacteria strain alone. These data suggest an unexpected link between early neoplasia of the colon and tumorigenic bacteria.”
Additional research revealed that E coli can create a pro-carcinogenic environment by stimulating mucosal inflammation, hindering DNA and mismatch repair mechanisms, and altering immune responses.
Dysbiosis and Diet
Colibactin can also drive dysbiosis and imbalance in bacteria in the colon, which fuels inflammation and disrupts mucosal barrier integrity. This creates a vicious cycle in which chronic inflammation can further drive additional mucus deterioration and dysbiosis.
In mouse models where the colon mucosal barrier is damaged with dextrin sulfate sodium (DSS), pks+ E coli gains better access to colon epithelium, causes injury, and can even lead to chronic colitis. Colibactin can also hinder epithelial recovery after DSS treatment.
Diet plays a central role in this process. Low fiber consumption can disrupt the barrier between the colon mucus layer and the colon’s exterior layer where bacteria live. A traditional Western diet may bolster bacteria that degrade the mucus layer when the bacteria consume the glycosylated portion as an energy source.
Fortunately, diet is modifiable. High–fiber diets (ideally 25-30 g/d) boost short–chain fatty acids in the colon. This is important because short-chain fatty acids can decrease intercellular pH and impede Enterobacteriaceae replication, yet another reason why we should encourage patients to eat a diet high in vegetables, fruits, and [green] salads.
Two Types of Bacterial Drivers
There appear to be two broad types of bacteria associated with CRC development. It’s been hypothesized that there are “driver” bacteria that might initiate the development of CRC, possibly by creating oxidative stress and causing DNA breaks. Several potential pathogenic bacteria have been identified, including E coli, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bacteroides fragilis. Unfortunately, there are also bacteria such as Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus with the potential to alter intestinal permeability, resulting in downstream effects that can allow colon cancers to expand. Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus have the potential to cause DNA double–strand breaks in the intestine, which can produce chromosomal precariousness.
These secondary bacteria can also lead to DNA epigenetic changes and gene mutations. However, it should be emphasized that “the direct causation of imprinted DNA changes resulting from a direct interaction between bacteria and host cells is not so far established.”
E coli produces compounds called cyclomodulins, which can cause DNA breaks and potentially trigger cell cycle arrest and even cell death through activation of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway. The DNA damage checkpoint pathway is a cellular signaling network that helps detect DNA lesions and allows for genetic stability by stopping growth to allow for repair and simulating cell survival or apoptosis. A key cyclomodulin that E coli makes is colibactin, produced by the pks locus. Other cyclomodulins include cytolethal distending toxin, cytotoxic necrotizing factor, and cycle-inhibiting factor.
Previous research has shown that E coli is the only culturable bacteria found near CRC. A groundbreaking 1998 study employing PCR technology found E coli in 60% of colon polyp adenomas and an alarming 77% of CRC biopsies.
E coli’s capability to downregulate essential DNA mismatch repair proteins has been implicated in colorectal carcinogenesis. Interestingly, when the genetic region responsible for producing colibactin is deleted in animals, the bacteria aren’t able to promote cancer.
Mechanistically, colibactin causes double-stranded DNA breaks, eukaryotic cell cycle arrest, and chromosome abnormalities. It also alkylates DNA. This occurs when the cyclopropane ring of colibactin interacts with the N3 position of adenine in DNA, forming a covalent bond and creating a DNA adduct. DNA adducts occur when a chemical moiety from an environmental or dietary source binds to DNA base. Colibactin can cause DNA interstrand cross-links to form via alkalization of adenine residues on opposing DNA strands, a crucial step in DNA damage. DNA adducts can occur through carcinogens in N-nitroso compounds, such as in processed meats and in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in cigarette smoke. Colibactin-induced damage may also stimulate the senescence–associated secretory phenotype pathway, increasing proinflammatory cytokines.
E coli and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
E coli, the primary colibactin producer in the human intestinal microbiome, is found at higher bacterial percentages in the microbiomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In a study by Dubinsky and colleagues, “the medium relative levels of colibactin–encoding E. coli were about threefold higher in IBD.”
Researchers have also postulated that antibiotics and microbiome dysbiosis may create conditions that allow colibactin–producing bacteria to overpopulate.
Future Directions
Not every patient with CRC carries a colorectal mutational signature, but these findings underscore the need for continued vigilance and prevention.
From a public health standpoint, our advice remains consistent: Promote high-fiber diets with more vegetables and less red meat; avoid highly processed foods; avoid alcohol; encourage exercise; and address overweight and obesity. Our goal is to create the best possible colon environment to prevent DNA damage from bacterial and environmental carcinogens.
In the future, we need more research to clarify exactly how E coli and colibactin increase early–onset CRC risk and whether antibiotics and dysbiosis facilitate their ability to damage the DNA of colon mucosa. It’s still unclear why younger patients are at greater risk. In time, we may be able to screen for colibactin–producing bacteria such as E coli and manipulate the fecal microbiome to prevent damage.
A recent mouse study in Nature by Jans and colleagues suggests it might be possible to block bacterial adhesion and hopefully mitigate damage caused by colibactin. With continued work, colibactin–targeted strategies could become a part of CRC prevention.
Benjamin H. Levy III, MD, is a gastroenterologist at the University of Chicago. In 2017, Levy, a previous Fulbright Fellow in France, also started a gastroenterology clinic for refugees resettling in Chicago. His clinical projects focus on the development of colorectal cancer screening campaigns. Levy, who gave a TEDx Talk about building health education campaigns using music and concerts, organizes "Tune It Up: A Concert To Raise Colorectal Cancer Awareness" with the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG). He frequently publishes on a variety of gastroenterology topics and serves on ACG’s Public Relations Committee and FDA-Related Matters Committee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent studies have cited an alarming increase in early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) rates, raising concern among gastroenterologists, public health experts, and patients alike. Approximately 10% of CRC cases now occur in those under age 50, and that proportion continues to grow. Between 2000 and 2016, colon cancer rose by 13% and rectal cancer by 16% among those aged 40–49.
According to recently published data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, between 2019 and 2022, CRC incidence among patients aged 45–49 rose by approximately 12% per year.
A Potential Bacterial Connection
What accounts for this disturbing spike? A research group from the University of California, San Diego, may have uncovered part of the answer.
In their study of 981 CRC genomes, most carried mutations suggestive of prior exposure to colibactin, a toxin produced by certain Escherichia coli (E coli) strains. Patients with extremely early-onset CRC (aged < 40 years) were 3 times more likely to have colibactin-suggestive mutations than patients older than 70. Crucially, colonic exposure to colibactin was linked to an adenomatous polyposis coli driver mutation.
These findings suggest that colibactin-induced injury in the gut microbiome may accelerate cancer development in some individuals. Environmental factors may contribute to the rise in early-onset CRC as well, such as consuming red meats, carcinogens from grilling, and processed meats and other highly processed foods; low fiber intake; lack of fruits and vegetables; drinking alcohol; lack of exercise; obesity; and colibactin exposure.
In this video, we will take a closer look at how E coli and colibactin may increase CRC risk.
Bacteria’s Cancer-Causing Properties
The idea that bacteria has cancer-causing properties isn’t new. In the 1970s, researchers linked Streptococcus bovis type 1 (now called Streptococcus gallolyticus) to CRC in a subset of patients with bacterial endocarditis stemming from right-sided colon cancer. Similarly, Helicobacter pylori infection has long been associated with increased gastric cancer risk.
Today, E coli infection is emerging as another possible contributor to CRC, especially via certain pathogenic strains containing the polyketide synthase (pks) genomic island, which encodes the colibactin and is sometimes present in the colon mucosa of patients with CRC.
Colibactin and DNA Damage
Colibactin-producing pks+ E coli strains can cause DNA double-strand breaks, one pathway to carcinogenesis. In animal studies, pks+ E coli strains have been linked to both increased risk for CRC and CRC progression.
In an important study published in Nature, Pleguezuelos-Manzano and colleagues repeatedly exposed intestinal organoids to pks+ E coli over 5 months and then performed whole genome sequencing. The result was a concerning potential for short insertions and deletions and single–base substitutions.
The authors concluded that their “study describes the distinct mutational signature in colorectal cancer and implies that the underlying mutational process results directly from past exposure to bacteria carrying the colibactin-producing pks pathogenicity island.”
Other E coli virulence factors may also contribute. For example, alpha-hemolysin may downregulate DNA mismatch repair proteins. In other words, E coli is probably just a contributing factor for the development of CRC, not the sole cause.
Biofilms and Inflammation
Previous studies have associated dense bacterial biofilms, particularly antibiotic-resistant strains, with CRC. This raises the possibility that widespread antibiotic overuse could predispose certain individuals to CRC development.
Biofilms normally separate the colon mucosal epithelium from bacteria and are essential for protecting against inflammation. In a 2018 study in Science, Dejea and colleagues concluded that “tumor-prone mice colonized with E coli (expressing colibactin), and enterotoxigenic B fragilis showed increased interleukin-17 in the colon and DNA damage in colonic epithelium with faster tumor onset and greater mortality, compared to mice with either bacteria strain alone. These data suggest an unexpected link between early neoplasia of the colon and tumorigenic bacteria.”
Additional research revealed that E coli can create a pro-carcinogenic environment by stimulating mucosal inflammation, hindering DNA and mismatch repair mechanisms, and altering immune responses.
Dysbiosis and Diet
Colibactin can also drive dysbiosis and imbalance in bacteria in the colon, which fuels inflammation and disrupts mucosal barrier integrity. This creates a vicious cycle in which chronic inflammation can further drive additional mucus deterioration and dysbiosis.
In mouse models where the colon mucosal barrier is damaged with dextrin sulfate sodium (DSS), pks+ E coli gains better access to colon epithelium, causes injury, and can even lead to chronic colitis. Colibactin can also hinder epithelial recovery after DSS treatment.
Diet plays a central role in this process. Low fiber consumption can disrupt the barrier between the colon mucus layer and the colon’s exterior layer where bacteria live. A traditional Western diet may bolster bacteria that degrade the mucus layer when the bacteria consume the glycosylated portion as an energy source.
Fortunately, diet is modifiable. High–fiber diets (ideally 25-30 g/d) boost short–chain fatty acids in the colon. This is important because short-chain fatty acids can decrease intercellular pH and impede Enterobacteriaceae replication, yet another reason why we should encourage patients to eat a diet high in vegetables, fruits, and [green] salads.
Two Types of Bacterial Drivers
There appear to be two broad types of bacteria associated with CRC development. It’s been hypothesized that there are “driver” bacteria that might initiate the development of CRC, possibly by creating oxidative stress and causing DNA breaks. Several potential pathogenic bacteria have been identified, including E coli, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bacteroides fragilis. Unfortunately, there are also bacteria such as Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus with the potential to alter intestinal permeability, resulting in downstream effects that can allow colon cancers to expand. Fusobacterium species and Streptococcus gallolyticus have the potential to cause DNA double–strand breaks in the intestine, which can produce chromosomal precariousness.
These secondary bacteria can also lead to DNA epigenetic changes and gene mutations. However, it should be emphasized that “the direct causation of imprinted DNA changes resulting from a direct interaction between bacteria and host cells is not so far established.”
E coli produces compounds called cyclomodulins, which can cause DNA breaks and potentially trigger cell cycle arrest and even cell death through activation of the DNA damage checkpoint pathway. The DNA damage checkpoint pathway is a cellular signaling network that helps detect DNA lesions and allows for genetic stability by stopping growth to allow for repair and simulating cell survival or apoptosis. A key cyclomodulin that E coli makes is colibactin, produced by the pks locus. Other cyclomodulins include cytolethal distending toxin, cytotoxic necrotizing factor, and cycle-inhibiting factor.
Previous research has shown that E coli is the only culturable bacteria found near CRC. A groundbreaking 1998 study employing PCR technology found E coli in 60% of colon polyp adenomas and an alarming 77% of CRC biopsies.
E coli’s capability to downregulate essential DNA mismatch repair proteins has been implicated in colorectal carcinogenesis. Interestingly, when the genetic region responsible for producing colibactin is deleted in animals, the bacteria aren’t able to promote cancer.
Mechanistically, colibactin causes double-stranded DNA breaks, eukaryotic cell cycle arrest, and chromosome abnormalities. It also alkylates DNA. This occurs when the cyclopropane ring of colibactin interacts with the N3 position of adenine in DNA, forming a covalent bond and creating a DNA adduct. DNA adducts occur when a chemical moiety from an environmental or dietary source binds to DNA base. Colibactin can cause DNA interstrand cross-links to form via alkalization of adenine residues on opposing DNA strands, a crucial step in DNA damage. DNA adducts can occur through carcinogens in N-nitroso compounds, such as in processed meats and in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in cigarette smoke. Colibactin-induced damage may also stimulate the senescence–associated secretory phenotype pathway, increasing proinflammatory cytokines.
E coli and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
E coli, the primary colibactin producer in the human intestinal microbiome, is found at higher bacterial percentages in the microbiomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In a study by Dubinsky and colleagues, “the medium relative levels of colibactin–encoding E. coli were about threefold higher in IBD.”
Researchers have also postulated that antibiotics and microbiome dysbiosis may create conditions that allow colibactin–producing bacteria to overpopulate.
Future Directions
Not every patient with CRC carries a colorectal mutational signature, but these findings underscore the need for continued vigilance and prevention.
From a public health standpoint, our advice remains consistent: Promote high-fiber diets with more vegetables and less red meat; avoid highly processed foods; avoid alcohol; encourage exercise; and address overweight and obesity. Our goal is to create the best possible colon environment to prevent DNA damage from bacterial and environmental carcinogens.
In the future, we need more research to clarify exactly how E coli and colibactin increase early–onset CRC risk and whether antibiotics and dysbiosis facilitate their ability to damage the DNA of colon mucosa. It’s still unclear why younger patients are at greater risk. In time, we may be able to screen for colibactin–producing bacteria such as E coli and manipulate the fecal microbiome to prevent damage.
A recent mouse study in Nature by Jans and colleagues suggests it might be possible to block bacterial adhesion and hopefully mitigate damage caused by colibactin. With continued work, colibactin–targeted strategies could become a part of CRC prevention.
Benjamin H. Levy III, MD, is a gastroenterologist at the University of Chicago. In 2017, Levy, a previous Fulbright Fellow in France, also started a gastroenterology clinic for refugees resettling in Chicago. His clinical projects focus on the development of colorectal cancer screening campaigns. Levy, who gave a TEDx Talk about building health education campaigns using music and concerts, organizes "Tune It Up: A Concert To Raise Colorectal Cancer Awareness" with the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG). He frequently publishes on a variety of gastroenterology topics and serves on ACG’s Public Relations Committee and FDA-Related Matters Committee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Is AI a Cure for Clinician Burnout?
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
The practice of medicine is evolving rapidly, with clinicians facing enhanced pressure to maximize productivity while managing increasingly complex patients and related clinical documentation. Indeed, clinicians are spending less time seeing patients, and more time in front of a computer screen.
Despite the many rewards of clinical medicine, rates of clinical practice attrition have increased among physicians in all specialties since 2013 with enhanced administrative burdens identified as a prominent driver. Among its many applications, artificial intelligence (AI) has immense potential to reduce the administrative and cognitive burdens that contribute to clinician burnout and attrition through tools such as AI scribes – these technologies have been rapidly adopted across healthcare systems and are already in use by ~30% of physician practices. The hope is that AI scribes will significantly reduce documentation time, leading to improvements in clinician wellbeing and expanding capacity for patient care. Indeed, some studies have shown up to a 20-30% improvement in documentation efficiency.
So, is AI a cure for physician burnout? The answer depends on what is done with these efficiency gains. If healthcare organizations respond to this enhanced efficiency by increasing patient volume expectations rather than allowing clinicians to recapture some of this time for meaningful work and professional wellbeing, it could create a so-called “workload paradox” where modest time savings are offset by greater productivity demands and the cognitive burden of reviewing AI-generated errors. that prioritizes clinician well-being and patient safety in addition to productivity.
In our final issue of 2025, we highlight a recent RCT from Annals of Internal Medicine finding that fecal microbiota transplantation is at least as effective as vancomycin in treating primary C. difficile infection. In this month’s Member Spotlight, we feature Andrew Ofosu, MD, MPH (University of Cincinnati Health), who stresses the importance of transparency and compassion in communicating effectively with patients, particularly around complex diagnoses. We hope you enjoy this and all the exciting content in our December issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Managing Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Agonists: Practical Insights From Dr. Bridget E. Shields
Managing Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Agonists: Practical Insights From Dr. Bridget E. Shields
Are you seeing any increase or trends in cutaneous adverse effects related to the use of GLP-1 agonists in your practice?
DR. SHIELDS: The use of GLP-1 agonists is increasing substantially across numerous populations. Patients are using these medications not only for weight management and diabetes control but also for blood pressure modulation and cardiovascular risk reduction. The market size is expected to grow at a rate of about 6% until 2027. While severe cutaneous adverse effects still are considered relatively rare with GLP-1 agonist use, mild adverse effects are quite common. Dermatologists should be familiar with these effects and how to manage them. Rare but serious cutaneous reactions include morbilliform drug eruptions, dermal hypersensitivity reactions, panniculitis, and bullous pemphigoid. It is thought that some GLP-1 agonists may cause more skin reactions than others; for example, exenatide extended-release has been associated with cutaneous adverse events more frequently than other GLP-1 agonists in a recent comprehensive literature review.
Do you see a role for dermatologists in monitoring or managing the downstream dermatologic effects of GLP-1 agonists over the next few years?
DR. SHIELDS: Absolutely. When patients develop a drug eruption, bullous pemphigoid, or eosinophilic panniculitis, dermatologists are going to be the ones to diagnose and manage therapy. Awareness of these adverse effects is crucial to timely and thoughtful discussions surrounding medication discontinuation vs a “treat through” approach.
Do you recommend coordinating with endocrinologists or obesity medicine specialists when managing shared patients on GLP-1s (particularly if skin concerns arise)?
DR. SHIELDS: Yes. This is crucial to patient success. Co-management can provide clarity around the indication for therapy and allow for a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion with the patient, primary care physician, endocrinologist, cardiologist, etc. In my practice, I have found that many patients do not want to stop therapy even when they develop cutaneous adverse effects. There are options to transition therapy or treat through in some cases, but having a comprehensive monitoring and therapy plan is critical.
Have you encountered cases in which rapid weight loss from GLP-1s worsened conditions such as loose skin, cellulite, or facial lipoatrophy, leading to new aesthetic concerns? How would you recommend counseling and/or treating affected patients?
DR. SHIELDS: Accelerated facial aging is a noticeable adverse effect in patients who undergo treatment with GLP-1 agonists, especially when used off-label for weight loss. Localized loss of facial fat can result in altered facial proportions and excess skin. There are multiple additional mechanisms that may underlie accelerated facial aging in patients on GLP-1s, and really we are just beginning to scratch the surface of why and how this happens. Understanding these mechanisms will open the door to downstream preventive and therapeutic options. If patients experience new aesthetic concerns, I currently work with them to adjust their medication to slow weight loss, recommend improved nutrition and hydration, encourage exercise and weight training to maintain muscle mass, and engage my cosmetic dermatology colleagues to discuss procedures such as dermal fillers.
All patients starting GLP-1 agonists should be thoroughly counseled on risks and adverse effects of their medication. These are well reported and should be considered carefully. Starting with lower medication dosing in conjunction with slow escalation and careful monitoring can be helpful in combatting these adverse effects.
Are you seeing any increase or trends in cutaneous adverse effects related to the use of GLP-1 agonists in your practice?
DR. SHIELDS: The use of GLP-1 agonists is increasing substantially across numerous populations. Patients are using these medications not only for weight management and diabetes control but also for blood pressure modulation and cardiovascular risk reduction. The market size is expected to grow at a rate of about 6% until 2027. While severe cutaneous adverse effects still are considered relatively rare with GLP-1 agonist use, mild adverse effects are quite common. Dermatologists should be familiar with these effects and how to manage them. Rare but serious cutaneous reactions include morbilliform drug eruptions, dermal hypersensitivity reactions, panniculitis, and bullous pemphigoid. It is thought that some GLP-1 agonists may cause more skin reactions than others; for example, exenatide extended-release has been associated with cutaneous adverse events more frequently than other GLP-1 agonists in a recent comprehensive literature review.
Do you see a role for dermatologists in monitoring or managing the downstream dermatologic effects of GLP-1 agonists over the next few years?
DR. SHIELDS: Absolutely. When patients develop a drug eruption, bullous pemphigoid, or eosinophilic panniculitis, dermatologists are going to be the ones to diagnose and manage therapy. Awareness of these adverse effects is crucial to timely and thoughtful discussions surrounding medication discontinuation vs a “treat through” approach.
Do you recommend coordinating with endocrinologists or obesity medicine specialists when managing shared patients on GLP-1s (particularly if skin concerns arise)?
DR. SHIELDS: Yes. This is crucial to patient success. Co-management can provide clarity around the indication for therapy and allow for a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion with the patient, primary care physician, endocrinologist, cardiologist, etc. In my practice, I have found that many patients do not want to stop therapy even when they develop cutaneous adverse effects. There are options to transition therapy or treat through in some cases, but having a comprehensive monitoring and therapy plan is critical.
Have you encountered cases in which rapid weight loss from GLP-1s worsened conditions such as loose skin, cellulite, or facial lipoatrophy, leading to new aesthetic concerns? How would you recommend counseling and/or treating affected patients?
DR. SHIELDS: Accelerated facial aging is a noticeable adverse effect in patients who undergo treatment with GLP-1 agonists, especially when used off-label for weight loss. Localized loss of facial fat can result in altered facial proportions and excess skin. There are multiple additional mechanisms that may underlie accelerated facial aging in patients on GLP-1s, and really we are just beginning to scratch the surface of why and how this happens. Understanding these mechanisms will open the door to downstream preventive and therapeutic options. If patients experience new aesthetic concerns, I currently work with them to adjust their medication to slow weight loss, recommend improved nutrition and hydration, encourage exercise and weight training to maintain muscle mass, and engage my cosmetic dermatology colleagues to discuss procedures such as dermal fillers.
All patients starting GLP-1 agonists should be thoroughly counseled on risks and adverse effects of their medication. These are well reported and should be considered carefully. Starting with lower medication dosing in conjunction with slow escalation and careful monitoring can be helpful in combatting these adverse effects.
Are you seeing any increase or trends in cutaneous adverse effects related to the use of GLP-1 agonists in your practice?
DR. SHIELDS: The use of GLP-1 agonists is increasing substantially across numerous populations. Patients are using these medications not only for weight management and diabetes control but also for blood pressure modulation and cardiovascular risk reduction. The market size is expected to grow at a rate of about 6% until 2027. While severe cutaneous adverse effects still are considered relatively rare with GLP-1 agonist use, mild adverse effects are quite common. Dermatologists should be familiar with these effects and how to manage them. Rare but serious cutaneous reactions include morbilliform drug eruptions, dermal hypersensitivity reactions, panniculitis, and bullous pemphigoid. It is thought that some GLP-1 agonists may cause more skin reactions than others; for example, exenatide extended-release has been associated with cutaneous adverse events more frequently than other GLP-1 agonists in a recent comprehensive literature review.
Do you see a role for dermatologists in monitoring or managing the downstream dermatologic effects of GLP-1 agonists over the next few years?
DR. SHIELDS: Absolutely. When patients develop a drug eruption, bullous pemphigoid, or eosinophilic panniculitis, dermatologists are going to be the ones to diagnose and manage therapy. Awareness of these adverse effects is crucial to timely and thoughtful discussions surrounding medication discontinuation vs a “treat through” approach.
Do you recommend coordinating with endocrinologists or obesity medicine specialists when managing shared patients on GLP-1s (particularly if skin concerns arise)?
DR. SHIELDS: Yes. This is crucial to patient success. Co-management can provide clarity around the indication for therapy and allow for a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion with the patient, primary care physician, endocrinologist, cardiologist, etc. In my practice, I have found that many patients do not want to stop therapy even when they develop cutaneous adverse effects. There are options to transition therapy or treat through in some cases, but having a comprehensive monitoring and therapy plan is critical.
Have you encountered cases in which rapid weight loss from GLP-1s worsened conditions such as loose skin, cellulite, or facial lipoatrophy, leading to new aesthetic concerns? How would you recommend counseling and/or treating affected patients?
DR. SHIELDS: Accelerated facial aging is a noticeable adverse effect in patients who undergo treatment with GLP-1 agonists, especially when used off-label for weight loss. Localized loss of facial fat can result in altered facial proportions and excess skin. There are multiple additional mechanisms that may underlie accelerated facial aging in patients on GLP-1s, and really we are just beginning to scratch the surface of why and how this happens. Understanding these mechanisms will open the door to downstream preventive and therapeutic options. If patients experience new aesthetic concerns, I currently work with them to adjust their medication to slow weight loss, recommend improved nutrition and hydration, encourage exercise and weight training to maintain muscle mass, and engage my cosmetic dermatology colleagues to discuss procedures such as dermal fillers.
All patients starting GLP-1 agonists should be thoroughly counseled on risks and adverse effects of their medication. These are well reported and should be considered carefully. Starting with lower medication dosing in conjunction with slow escalation and careful monitoring can be helpful in combatting these adverse effects.
Managing Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Agonists: Practical Insights From Dr. Bridget E. Shields
Managing Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Agonists: Practical Insights From Dr. Bridget E. Shields
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children