User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
COVID-19: Putting distance between projection and reality
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.
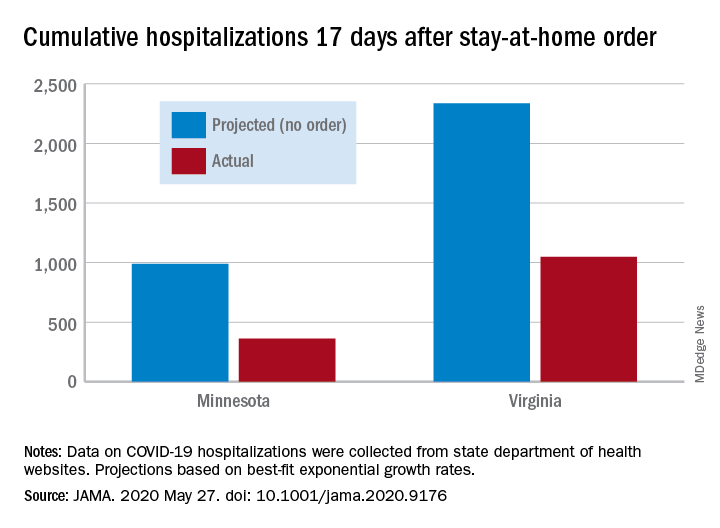
Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.

Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.
Today’s top news highlights: Coping with addiction during COVID, lung rehab part of recovery
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Long road to recovery includes lung rehab
For seriously ill COVID-19 patients, there may a long recovery period even after leaving the intensive care unit. Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, is one of those patients. For 28 days, he was on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab. “The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University. READ MORE.
Detox unit keeps running during COVID-19
Substance use disorder doesn’t take a break for a pandemic. In fact, the stressors from the current COVID-19 situation have increased substance use. In a commentary published on MDedge, Keji Fagbemi, MD, a hospitalist at the BronxCare Health System, shared how his hospital kept its inpatient detoxification unit running, despite the challenges presented by COVID-19. “At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service,” he wrote. “In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.” READ MORE.
Air pollution linked to MS risk
Air pollution may be another environmental risk factor for developing multiple sclerosis, suggests new research released as part of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2020. The findings, which are based on a large cohort study of nearly 550,000 individuals in Italy, appear to confirm the relationship between exposure to air pollutants and risk for MS that has been shown in prior studies. “Countermeasures that cut air pollution can be important for public health, not only to reduce deaths related to cardiac and pulmonary diseases but also the risk of chronic autoimmune diseases such as MS,” said Roberto Bergamaschi, MD, PhD, director of the Multiple Sclerosis Center, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy. READ MORE.
Trials produce conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease
High-dose aducanumab, a human monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly reduced clinical decline in people with early disease in one randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. But there was no statistically significant change in outcomes in an identical study. “We believe that the difference between the results was largely due to patients’ greater exposure to the high dose of aducanumab,” said Samantha Budd Haeberlein, PhD, one of the study investigators and senior vice president and head of the neurodegeneration development unit at Biogen, which is developing the drug. READ MORE.
Pregnant patients have asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
The rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16% among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, according to recent study results. “If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” researchers wrote in Obstetrics & Gynecology. READ MORE.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Nonpharmacologic ankylosing spondylitis recommendations not followed
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
FROM SPARTAN 2020
New York City inpatient detox unit keeps running: Here’s how
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Substance use disorder and its daily consequences take no breaks even during a pandemic. The stressors created by COVID-19, including deaths of loved ones and the disruptions to normal life from policies aimed at flattening the curve, seem to have increased substance use.
I practice as a hospitalist with an internal medicine background and specialty in addiction medicine at BronxCare Health System’s inpatient detoxification unit, a 24/7, 20-bed medically-supervised unit in South Bronx in New York City. It is one of the comprehensive services provided by the BronxCare’s life recovery center and addiction services, which also includes an outpatient clinic, opioid treatment program, inpatient rehab, and a half-way house. Inpatient detoxification units like ours are designed to treat serious addictions and chemical dependency and prevent and treat life-threatening withdrawal symptoms and signs or complications. Our patients come from all over the city and its adjoining suburbs, including from emergency room referrals, referral clinics, courts and the justice system, walk-ins, and self-referrals.
At a time when many inpatient detoxification units within the city were temporarily closed due to fear of inpatient spread of the virus or to provide extra COVID beds in anticipation for the peak surge, we have been able to provide a needed service. In fact, several other inpatient detoxification programs within the city have been able to refer their patients to our facility.
Individuals with substance use disorder have historically been a vulnerable and underserved population and possess high risk for multiple health problems as well as preexisting conditions. Many have limited life options financially, educationally, and with housing, and encounter barriers to accessing primary health care services, including preventive services. The introduction of the COVID-19 pandemic into these patients’ precarious health situations only made things worse as many of the limited resources for patients with substance use disorder were diverted to battling the pandemic. Numerous inpatient and outpatient addiction services, for example, were temporarily shut down. This has led to an increase in domestic violence, and psychiatric decompensation, including psychosis, suicidal attempts, and worsening of medical comorbidities in these patients.
Our wake-up call came when the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in New York in early March. Within a short period of time the state became the epicenter for COVID-19. With the projection of millions of cases being positive and the number of new cases doubling every third day at the onset in New York City, we knew we had a battle brewing and needed to radically transform our mode of operation fast.
Our first task was to ensure the safety of our patients and the dedicated health workers attending to them. We streamlined the patient point of entry through one screening site, while also brushing up on our history-taking to intently screen for COVID-19. This included not just focusing on travels from China, but from Europe and other parts of the world.
Yes, we did ask patients about cough, fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling fatigued, severe body ache, and possible contact with someone who is sick or has traveled overseas. But we were also attuned to the increased rate of community spread and the presentation of other symptoms, such as loss of taste and smell, early in the process. Hence we were able to triage patients with suspected cases to the appropriate sections of the hospital for further screening, testing, and evaluation, instead of having those patients admitted to the detox unit.
Early in the process a huddle team was instituted with daily briefing of staff lasting 30 minutes or less. This team consists of physicians, nurses, a physician assistant, a social worker, and a counselor. In addition to discussing treatment plans for the patient, they deliberate on the public health information from the hospital’s COVID-19 command center, New York State Department of Health, the Office of Mental Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the latest evidence-based information. These discussions have helped us modify our policies and practices.
We instituted a no visiting rule during a short hospital stay of 5-7 days, and this was initiated weeks in advance of many institutions, including nursing homes with vulnerable populations. Our admitting criteria was reviewed to allow for admission of only those patients who absolutely needed inpatient substance use disorder treatment, including patients with severe withdrawal symptoms and signs, comorbidities, or neuropsychiatric manifestations that made them unsafe for outpatient or home detoxification. Others were triaged to the outpatient services which was amply supported with telemedicine. Rooms and designated areas of the building were earmarked as places for isolation/quarantine if suspected COVID-19 cases were identified pending testing. To assess patients’ risk of COVID-19, we do point-of-care nasopharyngeal swab testing with polymerase chain reaction.
Regarding face masks, patients and staff were fitted with ones early in the process. Additionally, staff were trained on the importance of face mask use and how to ensure you have a tight seal around the mouth and nose and were provided with other appropriate personal protective equipment. Concerning social distancing, we reduced the patient population capacity for the unit down to 50% and offered only single room admissions. Social distancing was encouraged in the unit, including in the television and recreation room and dining room, and during small treatment groups of less than six individuals. Daily temperature checks with noncontact handheld thermometers were enforced for staff and anyone coming into the life recovery center.
Patients are continuously being educated on the presentations of COVID-19 and encouraged to report any symptoms. Any staff feeling sick or having symptoms are encouraged to stay home. Rigorous and continuous cleaning of surfaces, especially of areas subjected to common use, is done frequently by the hospital housekeeping and environmental crew and is the order of the day.
Dr. Fagbemi is a hospitalist at BronxCare Health System, a not-for-profit health and teaching hospital system serving South and Central Bronx in New York. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Placental injury reported in women with COVID-19
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Neonates appear healthy so far
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
SARS-CoV-2 infection rate 16% in asymptomatic pregnant women at delivery
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
Among women with a planned delivery in a New York City health system during the first half of April, the rate of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Among the patients’ designated support persons, the asymptomatic carrier rate was 10%.
“If universal testing of pregnant patients in a high prevalence area is not performed, health care workers will be inadvertently exposed to COVID-19, unless universal precautions with personal protective equipment are taken,” wrote the researchers affiliated with the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Angela Bianco, MD, and colleagues conducted an observational study of women who were scheduled for a planned delivery within the Mount Sinai Health System between April 4 and April 15, 2020. Patients and their designated support person completed a telephone screen and underwent COVID-19 testing the day before a scheduled delivery. If support persons screened positive during the telephone interview about COVID-19 symptoms, they could not attend the birth, and patients could contact a different support person to be screened and tested. “All patients and their support persons were informed of their SARS-CoV-2 test results before admission,” the investigators wrote. “Those who tested positive were counseled regarding symptomatology that should prompt medical attention.”
In all, researchers screened 158 patients with a planned delivery, and 155 agreed to undergo COVID-19 testing. Of the 155 women tested, 24 (16%) tested positive for SARS CoV-2 infection. Among 146 support persons who had a negative interview screen and underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing, 14 (10%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Test results were substantially concordant among patient and support person pairs. “Among patients who tested positive for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, 11 of 19 (58%) support persons also tested positive for COVID-19 infection,” the authors reported. “Among patients who tested negative for COVID-19 infection and had a support person present, only 3 of 127 (2.4%) support persons tested positive for COVID-19 infection.”
Telephone screening did not identify any of the COVID-19–positive cases. Of the 24 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of their newborns tested positive at birth.
“Universal testing ... provides a mechanism for more accurate counseling of patients regarding issues such as newborn skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding,” noted Dr. Bianco and colleagues. At their institution, parents with COVID-19 are instructed to wear a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when caring for their newborns.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, said in an interview that the study by Bianco et al. underscores the high rate of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic COVID-19 infections detected with universal screening in a hospital at the U.S. epicenter of the pandemic. “Each state and hospital will need to evaluate their own data to determine the value of universal screening for their patient population. In rural parts of America that have yet to see cases, universal screening may not make sense, but these areas are likely to be few and far between. The rest of America will need to quickly get on board with universal screening to protect their labor and delivery staff.”
Testing the partner was a strength of the study. “It is reassuring that when a pregnant woman tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the rate was very, very low (2.4%) that her partner would test positive. However, it was disconcerting that telephone screening for common symptoms associated with COVID-19 was not very helpful in identifying cases,” said Dr. Waldorf, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. She was not involved in the study by Bianco et al.
One study author receives payment from the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology for serving as a board examiner, receives payment from UpToDate, and serves as an expert witness in malpractice and products liability cases. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bianco A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003985.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Whether to test laboring women for SARS-CoV-2 may hinge on regional prevalence
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Unacceptable RA pain may drop with TNFi treatment but still lingers in many patients
according to findings from 21 months of follow-up in a post hoc analysis of data from the randomized, controlled Swedish Farmacotherapy (SWEFOT) trial.
Although RA patients who took biologic combination therapy had 32% lower risk for unacceptable pain (rated at >40 mm on a 0- to 100-mm visual analog scale) at 21 months, they still had no difference from patients taking triple therapy in the rate of pain described as refractory, or unacceptable despite inflammation control (C-reactive protein <10 mg/L).
While these results lend “some support to a better effect on long-term pain for the biological treatment, compared with triple therapy ... our findings are also in line with insufficient effects of current treatment strategies to prevent development of inflammation-independent pain components, warranting early alternative treatment approaches in affected patients,” Tor Olofsson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care & Research.
The pain outcomes analyzed in this post hoc study were all secondary outcomes of the original open-label SWEFOT trial, which during 2002-2005 enrolled 258 RA patients with less than a year of symptoms who did not reach low disease activity (28-joint Disease Activity Score ≤3.2) after 3 months of methotrexate and randomized them to an addition of either infliximab (3 mg/kg rounded up to nearest 100-mg increment) or sulfasalazine 1,000 mg twice daily plus hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily.
Overall, 90 of 128 patients in the infliximab group and 74 of 130 in the triple-therapy group continued the protocol until the 21-month follow-up. Patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower area under the curve for visual analog scale for pain, most of which was accounted for during months 9-21. The percentage of patients in the infliximab group with unacceptable pain also dropped significantly from 57% at randomization to 32% at 21 months, while no difference was seen for triple therapy patients, of whom 45% had unacceptable pain at 21 months.
While patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower risk of unacceptable pain without inflammatory control at 21 months, neither treatment arm showed a within-group difference in refractory pain from randomization to the 21-month follow-up.
Nearly one-third of patients overall still reported unacceptable pain 21 months after addition of either infliximab or sulfasalazine plus hydroxychloroquine. And at that time point, refractory pain constituted 82% of all unacceptable pain. “Notably, this pattern – with a domination of refractory pain – was evident already 3 months after starting combination therapy,” Dr. Olofsson and colleagues wrote.
The original SWEFOT study was supported in part by a grant from the Swedish Rheumatism Association, and in part by an annual unrestricted grant from Schering-Plough Sweden (now Merck Sharp & Dohme). The post hoc analysis was supported by Lund University and the Kockska Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, and the Stockholm County Council. Two authors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Olofsson T et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1002/acr.24264.
according to findings from 21 months of follow-up in a post hoc analysis of data from the randomized, controlled Swedish Farmacotherapy (SWEFOT) trial.
Although RA patients who took biologic combination therapy had 32% lower risk for unacceptable pain (rated at >40 mm on a 0- to 100-mm visual analog scale) at 21 months, they still had no difference from patients taking triple therapy in the rate of pain described as refractory, or unacceptable despite inflammation control (C-reactive protein <10 mg/L).
While these results lend “some support to a better effect on long-term pain for the biological treatment, compared with triple therapy ... our findings are also in line with insufficient effects of current treatment strategies to prevent development of inflammation-independent pain components, warranting early alternative treatment approaches in affected patients,” Tor Olofsson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care & Research.
The pain outcomes analyzed in this post hoc study were all secondary outcomes of the original open-label SWEFOT trial, which during 2002-2005 enrolled 258 RA patients with less than a year of symptoms who did not reach low disease activity (28-joint Disease Activity Score ≤3.2) after 3 months of methotrexate and randomized them to an addition of either infliximab (3 mg/kg rounded up to nearest 100-mg increment) or sulfasalazine 1,000 mg twice daily plus hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily.
Overall, 90 of 128 patients in the infliximab group and 74 of 130 in the triple-therapy group continued the protocol until the 21-month follow-up. Patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower area under the curve for visual analog scale for pain, most of which was accounted for during months 9-21. The percentage of patients in the infliximab group with unacceptable pain also dropped significantly from 57% at randomization to 32% at 21 months, while no difference was seen for triple therapy patients, of whom 45% had unacceptable pain at 21 months.
While patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower risk of unacceptable pain without inflammatory control at 21 months, neither treatment arm showed a within-group difference in refractory pain from randomization to the 21-month follow-up.
Nearly one-third of patients overall still reported unacceptable pain 21 months after addition of either infliximab or sulfasalazine plus hydroxychloroquine. And at that time point, refractory pain constituted 82% of all unacceptable pain. “Notably, this pattern – with a domination of refractory pain – was evident already 3 months after starting combination therapy,” Dr. Olofsson and colleagues wrote.
The original SWEFOT study was supported in part by a grant from the Swedish Rheumatism Association, and in part by an annual unrestricted grant from Schering-Plough Sweden (now Merck Sharp & Dohme). The post hoc analysis was supported by Lund University and the Kockska Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, and the Stockholm County Council. Two authors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Olofsson T et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1002/acr.24264.
according to findings from 21 months of follow-up in a post hoc analysis of data from the randomized, controlled Swedish Farmacotherapy (SWEFOT) trial.
Although RA patients who took biologic combination therapy had 32% lower risk for unacceptable pain (rated at >40 mm on a 0- to 100-mm visual analog scale) at 21 months, they still had no difference from patients taking triple therapy in the rate of pain described as refractory, or unacceptable despite inflammation control (C-reactive protein <10 mg/L).
While these results lend “some support to a better effect on long-term pain for the biological treatment, compared with triple therapy ... our findings are also in line with insufficient effects of current treatment strategies to prevent development of inflammation-independent pain components, warranting early alternative treatment approaches in affected patients,” Tor Olofsson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care & Research.
The pain outcomes analyzed in this post hoc study were all secondary outcomes of the original open-label SWEFOT trial, which during 2002-2005 enrolled 258 RA patients with less than a year of symptoms who did not reach low disease activity (28-joint Disease Activity Score ≤3.2) after 3 months of methotrexate and randomized them to an addition of either infliximab (3 mg/kg rounded up to nearest 100-mg increment) or sulfasalazine 1,000 mg twice daily plus hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily.
Overall, 90 of 128 patients in the infliximab group and 74 of 130 in the triple-therapy group continued the protocol until the 21-month follow-up. Patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower area under the curve for visual analog scale for pain, most of which was accounted for during months 9-21. The percentage of patients in the infliximab group with unacceptable pain also dropped significantly from 57% at randomization to 32% at 21 months, while no difference was seen for triple therapy patients, of whom 45% had unacceptable pain at 21 months.
While patients in the infliximab group had a significantly lower risk of unacceptable pain without inflammatory control at 21 months, neither treatment arm showed a within-group difference in refractory pain from randomization to the 21-month follow-up.
Nearly one-third of patients overall still reported unacceptable pain 21 months after addition of either infliximab or sulfasalazine plus hydroxychloroquine. And at that time point, refractory pain constituted 82% of all unacceptable pain. “Notably, this pattern – with a domination of refractory pain – was evident already 3 months after starting combination therapy,” Dr. Olofsson and colleagues wrote.
The original SWEFOT study was supported in part by a grant from the Swedish Rheumatism Association, and in part by an annual unrestricted grant from Schering-Plough Sweden (now Merck Sharp & Dohme). The post hoc analysis was supported by Lund University and the Kockska Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, and the Stockholm County Council. Two authors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Olofsson T et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 May 20. doi: 10.1002/acr.24264.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
A long road to recovery: Lung rehab needed after COVID-19
If one word describes Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, it’s “tenacious.” For 28 days, he clung to life on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab, determined to regain function.
“We were not sure if he was going to make it through his first night in the hospital, and for a while after that. We were really prepared that he would not survive his ventilator time,” his daughter, Maria Braganza, said in an interview just 5 days after her father had been transferred to inpatient rehab.
In many ways, Mr. Braganza’s experience is typical of seriously ill COVID-19 patients. Many go from walking and talking to being on a ventilator within 10 hours or less. Mr. Braganza was admitted to the hospital on March 21 and was intubated that day. To keep him on the ventilator, he was heavily sedated and unconscious at times. In the ICU, he experienced bouts of low blood pressure, a pattern of shock that occurs in COVID-19 patients and that does not always respond to fluids.
Doctors have quickly learned to treat these patients aggressively. Many patients in the ICU with COVID-19 develop an inflamed, atypical form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), in which the lung’s compliance, or stiffness, does not match the severity of hypoxia. These patients require high levels of oxygen and high ventilator settings. Many develop pneumothorax, or collapsed lungs, because of the high pressures needed to deliver oxygen and the prolonged time on ventilation.
“The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University.
After about 2 weeks, some of these patients can come off the ventilator, or they may undergo a tracheostomy, a hole in the neck through which a tube is placed to deliver oxygen. By this time, many have developed ICU-acquired weakness and muscle wasting. Some may be so debilitated that they cannot walk. Even the respiratory muscles that help them breathe may have weakened as a result of the ventilator doing the work for them.
These patients “get sick very fast, and it takes a long time for them to heal. What’s not really well appreciated is how much rehab and how much recovery time these patients are going to need,” said David Chong, MD. He is medical director of the ICU at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, and he has been on the front lines during the COVID-19 surge in New York City.
The road to recovery
Regardless of the cause, many people who have a prolonged stint in the ICU face an even longer convalescence. Still-unanswered questions concern whether recovery time will be longer for those with COVID-19, compared with other illnesses, and whether some of the damage may be permanent. A number of small studies in Hong Kong and China, as well as studies of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients’ recoveries, have promoted speculation about possible long-lasting damage to lungs and other organs from COVID-19.
Yet some of these reports have left out important details about ARDS in COVID-19 patients who also may be most at risk for long-lasting damage. To clear up some of the confusion, the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation said on April 6 that some but not all of COVID-19 patients who develop ARDS may go on to develop lung fibrosis – scarring of the lungs – which may be permanent.
“Post-ARDS fibrosis typically is not progressive, but nonetheless can be severe and limiting. The recovery period for post-ARDS fibrosis is approximately 1 year and the residual deficits persist, but generally do not progress,” the foundation noted.
Emerging research on lung damage in COVID-19
Because the pandemic is only a few months in, it’s unclear as yet what the long-term consequences of severe COVID-19 may be. But emerging data are enabling researchers to venture an educated guess about what may happen in the months and years ahead.
The key to understanding the data is knowing that ARDS is a syndrome – the end product of a variety of diseases or insults to the lung. Under the microscope, lung damage from ARDS associated with COVID-19 is indistinguishable from lung damage resulting from other causes, such as vaping, sepsis, or shock caused by a motor vehicle accident, said Sanjay Mukhopadhyay, MD, director of pulmonary pathology at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Mukhopadhyay, who specializes in lung pathology, performed one of the first complete autopsies of a COVID-19 patient in the United States. In most autopsy series published to date, he said, the most common lung finding in patients who have died from COVID-19 is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), a pattern of lung injury seen in ARDS from many other causes.
In DAD, the walls of the alveoli – thinly lined air sacs that facilitate gas exchange in the lung – develop a pink, hyaline membrane composed of damaged cells and plasma proteins that leak from capillaries in the wall of the alveolus. This hyaline membrane gets plastered against the wall of the alveolus and interferes with diffusion of oxygen into the body.
“We know what happens in ARDS from other causes. If you follow people who have been on a ventilator long term, some of their respiratory function goes back to normal,” Dr. Mukhopadhyay said. “But there are other people in whom some degree of respiratory impairment lingers. In these patients, we think the DAD progresses to an organizing stage.”
Organizing pneumonia refers to a family of diseases in which fibroblasts (cells involved in wound healing) arrive and form scar tissue that forms hyaline membranes and fibrin balls (tough proteins) that fill up the alveoli, making gas exchange very difficult.
Also called BOOP (bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia), this condition is sensitive to steroids. Early aggressive steroid treatment can prevent long-term lung damage. Without steroids, damage can become permanent. A variant of this condition is termed acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia (AFOP), which is also sensitive to steroids. A report from France demonstrates AFOP in some patients who have died from COVID-19.
The trick is identifying who is developing BOOP and who is not, and beyond that, who might be most amenable to treatment. Use of steroids for patients with certain other problems, such as a bacterial infection on top of COVID-19, could be harmful. David H. Chong, MD, and colleagues at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, are investigating this to determine which COVID-19 patients may benefit from early steroid therapy.
“It’s not clear if there is a predominant histologic type or if we are catching people at different phases of their disease, and therefore we’re seeing different lung pathology,” Dr. Chong said.
He thinks that many patients with severe COVID-19 probably will not develop this pattern of lung scarring. “We’re speculating that lung damage from severe COVID-19 is probably going to behave more like lung damage from regular ARDS, which is often reversible. We think the vast majority of these patients probably have DAD that is similar to most patients with ARDS from other etiologies,” Dr. Chong said.
That would be consistent with information from China. In an April interview with Chinese domestic media, Zhong Nanshan, MD, a pulmonologist at the head of China’s COVID-19 task force, stated that he expects that the lungs in most patients with COVID-19 will gradually recover. He was responding to a widely publicized small study that found evidence of residual lung abnormalities at hospital discharge in most patients (94%, 66/70) who suffered from COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, from January to February 2020.
Tough research conditions
Experts say that follow-up in this Chinese study and others to date has not been nearly long enough to allow predictions about lasting lung damage in COVID-19.
They also highlight the tough conditions in which researchers are working. Few autopsies have been performed so far – autopsies take time, extra precautions must be taken to avoid spread of COVID-19, and many patients and families do not consent to an autopsy. Furthermore, autopsy data from patients who died of COVID-19 may not extrapolate to survivors.
“I would not hang my hat on any of the limited data I have seen on autopsies,” said Lina Miyakawa, MD, a critical care and pulmonary medicine specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City.
“Even though we have answers about how the lungs are damaged at the end stage, this does not elucidate any answers about the earlier lung damage from this disease,” she continued. “It would be informative to have pathological data from the early or transitional phase, to see if that may translate into a treatment modality for COVID-19 patients.”
The problem is that these patients often experience a large amount of sloughing of airway cells, along with mucous plugging (collections of mucous that can block airflow and collapse alveoli). Bronchoscopy, which is used to view the inside of the lungs and sometimes to retrieve biopsy specimens for microscopic evaluation, is too risky for many COVID-19 patients.
In addition, few CT data exist for severely ill COVID-19 patients, who can be so unstable that to transport them to undergo a CT scan can be dangerous, not to mention the concern regarding infection control.
Even if sufficient data did exist, findings from chest x-rays, CTs, pathology studies, and lung function tests do not always match up. A patient who has lung abnormalities on CT may not necessarily have clinically impaired lung function or abnormal pathologic findings, according to Ali Gholamrezanezhad, MD, an emergency radiologist who is with the department of clinical radiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Together with colleagues at USC, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad has started a long-term study of patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19. The researchers will follow patients for at least 1 year and will use chest x-ray, chest CT, and exercise testing to evaluate lung recovery over time.
“In the acute phase, we have acute inflammation called ground glass opacities, which usually happen bilaterally in COVID-19. That is totally reversible damage that can return to normal with no scarring,” Dr. Gholamrezanezhad said.
On the basis of data from survivors of other severe pneumonias, such as Middle East respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV-1 infection, and H1N1 influenza, Gholamrezanezhad thinks that most survivors of COVID-19 will be able to return to work and normal life, although some may show residual lung dysfunction. Age, underlying medical conditions, smoking, length of hospital stay, severity of illness, and quality of treatment may all play a role in how well these people recover.
The lung has a remarkable capacity to recover, he added. Critical illness can destroy type one pneumocytes — the cells that line the alveoli in the lung — but over time, these cells grow back and reline the lungs. When they do, they can also help repair the lungs.
On top of that, the lung has a large functional reserve, and when one section becomes damaged, the rest of the lung can compensate.
However, for some people, total maximum exercise capacity may be affected, he commented.
Mukhopadhyay said: “My feeling is you will get reversal to normal in some patients and you will get long-term fibrosis from ARDS in some survivors. The question is, how many will have complete resolution and how many will have fibrosis? To know the answer, we will need a lot more data than we have now.”
Convalescence of COVID-19 Patients
Like many who become seriously ill with COVID-19, Braganza had underlying medical problems. Before becoming ill, he had had a heart attack and stroke. He walked with a walker and had some age-related memory problems.
Five days after transfer to inpatient rehab, Braganza was walking up and down the hallway using a walker. He was still shaking off the effects of being heavily sedated for so long, and he experienced periods of confusion. When he first came off the ventilator, he mixed up days and nights. Sometimes he did not remember being so sick. A former software engineer, Braganza usually had no problem using technology, but he has had to relearn how to use his phone and connect his iPad to Wi-Fi.
“He is still struggling quite a bit with remembering how to do basic things,” Maria Braganza said. “He has times of being really depressed because he feels like he’s not making progress.”
Doctors are taking note and starting to think about what lies ahead for ICU survivors of COVID-19. They worry about the potential for disease recurrence as well as readmission for other problems, such as other infections and hip fractures.
“As COVID-19 survivors begin to recover, there will be a large burden of chronic critical illness. We expect a significant need for rehabilitation in most ICU survivors of COVID-19,” said Steve Lubinsky, MD, medical director of respiratory care at New York University Langone Tisch Hospital.
Thinking about her father, Maria Braganza brings an extra dimension to these concerns. She thinks about depression, loneliness, and social isolation among older survivors of COVID-19. These problems existed long before the pandemic, but COVID-19 has magnified them.
The rehab staff estimates that Mr. Braganza will spend 10-14 days in their program, but discharge home creates a conundrum. Before becoming ill, Mr. Braganza lived in an independent senior living facility. Now, because of social distancing, he will no longer be able to hang out and have meals with his friends.
“Dad’s already feeling really lonely in the hospital. If we stay on a semipermanent lockdown, will he be able to see the people he loves?” Maria Braganza said. “Even though somebody is older, they have a lot to give and a lot of experience. They just need a little extra to be able to have that life.”
Dr. Nolan, Dr. Chong, Dr. Mukhopadhyay, Dr. Miyakawa, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad, and Dr. Lubinsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If one word describes Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, it’s “tenacious.” For 28 days, he clung to life on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab, determined to regain function.
“We were not sure if he was going to make it through his first night in the hospital, and for a while after that. We were really prepared that he would not survive his ventilator time,” his daughter, Maria Braganza, said in an interview just 5 days after her father had been transferred to inpatient rehab.
In many ways, Mr. Braganza’s experience is typical of seriously ill COVID-19 patients. Many go from walking and talking to being on a ventilator within 10 hours or less. Mr. Braganza was admitted to the hospital on March 21 and was intubated that day. To keep him on the ventilator, he was heavily sedated and unconscious at times. In the ICU, he experienced bouts of low blood pressure, a pattern of shock that occurs in COVID-19 patients and that does not always respond to fluids.
Doctors have quickly learned to treat these patients aggressively. Many patients in the ICU with COVID-19 develop an inflamed, atypical form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), in which the lung’s compliance, or stiffness, does not match the severity of hypoxia. These patients require high levels of oxygen and high ventilator settings. Many develop pneumothorax, or collapsed lungs, because of the high pressures needed to deliver oxygen and the prolonged time on ventilation.
“The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University.
After about 2 weeks, some of these patients can come off the ventilator, or they may undergo a tracheostomy, a hole in the neck through which a tube is placed to deliver oxygen. By this time, many have developed ICU-acquired weakness and muscle wasting. Some may be so debilitated that they cannot walk. Even the respiratory muscles that help them breathe may have weakened as a result of the ventilator doing the work for them.
These patients “get sick very fast, and it takes a long time for them to heal. What’s not really well appreciated is how much rehab and how much recovery time these patients are going to need,” said David Chong, MD. He is medical director of the ICU at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, and he has been on the front lines during the COVID-19 surge in New York City.
The road to recovery
Regardless of the cause, many people who have a prolonged stint in the ICU face an even longer convalescence. Still-unanswered questions concern whether recovery time will be longer for those with COVID-19, compared with other illnesses, and whether some of the damage may be permanent. A number of small studies in Hong Kong and China, as well as studies of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients’ recoveries, have promoted speculation about possible long-lasting damage to lungs and other organs from COVID-19.
Yet some of these reports have left out important details about ARDS in COVID-19 patients who also may be most at risk for long-lasting damage. To clear up some of the confusion, the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation said on April 6 that some but not all of COVID-19 patients who develop ARDS may go on to develop lung fibrosis – scarring of the lungs – which may be permanent.
“Post-ARDS fibrosis typically is not progressive, but nonetheless can be severe and limiting. The recovery period for post-ARDS fibrosis is approximately 1 year and the residual deficits persist, but generally do not progress,” the foundation noted.
Emerging research on lung damage in COVID-19
Because the pandemic is only a few months in, it’s unclear as yet what the long-term consequences of severe COVID-19 may be. But emerging data are enabling researchers to venture an educated guess about what may happen in the months and years ahead.
The key to understanding the data is knowing that ARDS is a syndrome – the end product of a variety of diseases or insults to the lung. Under the microscope, lung damage from ARDS associated with COVID-19 is indistinguishable from lung damage resulting from other causes, such as vaping, sepsis, or shock caused by a motor vehicle accident, said Sanjay Mukhopadhyay, MD, director of pulmonary pathology at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Mukhopadhyay, who specializes in lung pathology, performed one of the first complete autopsies of a COVID-19 patient in the United States. In most autopsy series published to date, he said, the most common lung finding in patients who have died from COVID-19 is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), a pattern of lung injury seen in ARDS from many other causes.
In DAD, the walls of the alveoli – thinly lined air sacs that facilitate gas exchange in the lung – develop a pink, hyaline membrane composed of damaged cells and plasma proteins that leak from capillaries in the wall of the alveolus. This hyaline membrane gets plastered against the wall of the alveolus and interferes with diffusion of oxygen into the body.
“We know what happens in ARDS from other causes. If you follow people who have been on a ventilator long term, some of their respiratory function goes back to normal,” Dr. Mukhopadhyay said. “But there are other people in whom some degree of respiratory impairment lingers. In these patients, we think the DAD progresses to an organizing stage.”
Organizing pneumonia refers to a family of diseases in which fibroblasts (cells involved in wound healing) arrive and form scar tissue that forms hyaline membranes and fibrin balls (tough proteins) that fill up the alveoli, making gas exchange very difficult.
Also called BOOP (bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia), this condition is sensitive to steroids. Early aggressive steroid treatment can prevent long-term lung damage. Without steroids, damage can become permanent. A variant of this condition is termed acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia (AFOP), which is also sensitive to steroids. A report from France demonstrates AFOP in some patients who have died from COVID-19.
The trick is identifying who is developing BOOP and who is not, and beyond that, who might be most amenable to treatment. Use of steroids for patients with certain other problems, such as a bacterial infection on top of COVID-19, could be harmful. David H. Chong, MD, and colleagues at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, are investigating this to determine which COVID-19 patients may benefit from early steroid therapy.
“It’s not clear if there is a predominant histologic type or if we are catching people at different phases of their disease, and therefore we’re seeing different lung pathology,” Dr. Chong said.
He thinks that many patients with severe COVID-19 probably will not develop this pattern of lung scarring. “We’re speculating that lung damage from severe COVID-19 is probably going to behave more like lung damage from regular ARDS, which is often reversible. We think the vast majority of these patients probably have DAD that is similar to most patients with ARDS from other etiologies,” Dr. Chong said.
That would be consistent with information from China. In an April interview with Chinese domestic media, Zhong Nanshan, MD, a pulmonologist at the head of China’s COVID-19 task force, stated that he expects that the lungs in most patients with COVID-19 will gradually recover. He was responding to a widely publicized small study that found evidence of residual lung abnormalities at hospital discharge in most patients (94%, 66/70) who suffered from COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, from January to February 2020.
Tough research conditions
Experts say that follow-up in this Chinese study and others to date has not been nearly long enough to allow predictions about lasting lung damage in COVID-19.
They also highlight the tough conditions in which researchers are working. Few autopsies have been performed so far – autopsies take time, extra precautions must be taken to avoid spread of COVID-19, and many patients and families do not consent to an autopsy. Furthermore, autopsy data from patients who died of COVID-19 may not extrapolate to survivors.
“I would not hang my hat on any of the limited data I have seen on autopsies,” said Lina Miyakawa, MD, a critical care and pulmonary medicine specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City.
“Even though we have answers about how the lungs are damaged at the end stage, this does not elucidate any answers about the earlier lung damage from this disease,” she continued. “It would be informative to have pathological data from the early or transitional phase, to see if that may translate into a treatment modality for COVID-19 patients.”
The problem is that these patients often experience a large amount of sloughing of airway cells, along with mucous plugging (collections of mucous that can block airflow and collapse alveoli). Bronchoscopy, which is used to view the inside of the lungs and sometimes to retrieve biopsy specimens for microscopic evaluation, is too risky for many COVID-19 patients.
In addition, few CT data exist for severely ill COVID-19 patients, who can be so unstable that to transport them to undergo a CT scan can be dangerous, not to mention the concern regarding infection control.
Even if sufficient data did exist, findings from chest x-rays, CTs, pathology studies, and lung function tests do not always match up. A patient who has lung abnormalities on CT may not necessarily have clinically impaired lung function or abnormal pathologic findings, according to Ali Gholamrezanezhad, MD, an emergency radiologist who is with the department of clinical radiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Together with colleagues at USC, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad has started a long-term study of patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19. The researchers will follow patients for at least 1 year and will use chest x-ray, chest CT, and exercise testing to evaluate lung recovery over time.
“In the acute phase, we have acute inflammation called ground glass opacities, which usually happen bilaterally in COVID-19. That is totally reversible damage that can return to normal with no scarring,” Dr. Gholamrezanezhad said.
On the basis of data from survivors of other severe pneumonias, such as Middle East respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV-1 infection, and H1N1 influenza, Gholamrezanezhad thinks that most survivors of COVID-19 will be able to return to work and normal life, although some may show residual lung dysfunction. Age, underlying medical conditions, smoking, length of hospital stay, severity of illness, and quality of treatment may all play a role in how well these people recover.
The lung has a remarkable capacity to recover, he added. Critical illness can destroy type one pneumocytes — the cells that line the alveoli in the lung — but over time, these cells grow back and reline the lungs. When they do, they can also help repair the lungs.
On top of that, the lung has a large functional reserve, and when one section becomes damaged, the rest of the lung can compensate.
However, for some people, total maximum exercise capacity may be affected, he commented.
Mukhopadhyay said: “My feeling is you will get reversal to normal in some patients and you will get long-term fibrosis from ARDS in some survivors. The question is, how many will have complete resolution and how many will have fibrosis? To know the answer, we will need a lot more data than we have now.”
Convalescence of COVID-19 Patients
Like many who become seriously ill with COVID-19, Braganza had underlying medical problems. Before becoming ill, he had had a heart attack and stroke. He walked with a walker and had some age-related memory problems.
Five days after transfer to inpatient rehab, Braganza was walking up and down the hallway using a walker. He was still shaking off the effects of being heavily sedated for so long, and he experienced periods of confusion. When he first came off the ventilator, he mixed up days and nights. Sometimes he did not remember being so sick. A former software engineer, Braganza usually had no problem using technology, but he has had to relearn how to use his phone and connect his iPad to Wi-Fi.
“He is still struggling quite a bit with remembering how to do basic things,” Maria Braganza said. “He has times of being really depressed because he feels like he’s not making progress.”
Doctors are taking note and starting to think about what lies ahead for ICU survivors of COVID-19. They worry about the potential for disease recurrence as well as readmission for other problems, such as other infections and hip fractures.
“As COVID-19 survivors begin to recover, there will be a large burden of chronic critical illness. We expect a significant need for rehabilitation in most ICU survivors of COVID-19,” said Steve Lubinsky, MD, medical director of respiratory care at New York University Langone Tisch Hospital.
Thinking about her father, Maria Braganza brings an extra dimension to these concerns. She thinks about depression, loneliness, and social isolation among older survivors of COVID-19. These problems existed long before the pandemic, but COVID-19 has magnified them.
The rehab staff estimates that Mr. Braganza will spend 10-14 days in their program, but discharge home creates a conundrum. Before becoming ill, Mr. Braganza lived in an independent senior living facility. Now, because of social distancing, he will no longer be able to hang out and have meals with his friends.
“Dad’s already feeling really lonely in the hospital. If we stay on a semipermanent lockdown, will he be able to see the people he loves?” Maria Braganza said. “Even though somebody is older, they have a lot to give and a lot of experience. They just need a little extra to be able to have that life.”
Dr. Nolan, Dr. Chong, Dr. Mukhopadhyay, Dr. Miyakawa, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad, and Dr. Lubinsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If one word describes Eladio (“Lad”) Braganza, age 77, it’s “tenacious.” For 28 days, he clung to life on a ventilator in a Seattle ICU. Now – after a 46-day hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection – he’s making progress in inpatient rehab, determined to regain function.
“We were not sure if he was going to make it through his first night in the hospital, and for a while after that. We were really prepared that he would not survive his ventilator time,” his daughter, Maria Braganza, said in an interview just 5 days after her father had been transferred to inpatient rehab.
In many ways, Mr. Braganza’s experience is typical of seriously ill COVID-19 patients. Many go from walking and talking to being on a ventilator within 10 hours or less. Mr. Braganza was admitted to the hospital on March 21 and was intubated that day. To keep him on the ventilator, he was heavily sedated and unconscious at times. In the ICU, he experienced bouts of low blood pressure, a pattern of shock that occurs in COVID-19 patients and that does not always respond to fluids.
Doctors have quickly learned to treat these patients aggressively. Many patients in the ICU with COVID-19 develop an inflamed, atypical form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), in which the lung’s compliance, or stiffness, does not match the severity of hypoxia. These patients require high levels of oxygen and high ventilator settings. Many develop pneumothorax, or collapsed lungs, because of the high pressures needed to deliver oxygen and the prolonged time on ventilation.
“The vast majority of COVID patients in the ICU have lung disease that is quite severe, much more severe than I have seen in my 20 years of doing this,” said critical care specialist Anna Nolan, MD, of the department of medicine at New York University.
After about 2 weeks, some of these patients can come off the ventilator, or they may undergo a tracheostomy, a hole in the neck through which a tube is placed to deliver oxygen. By this time, many have developed ICU-acquired weakness and muscle wasting. Some may be so debilitated that they cannot walk. Even the respiratory muscles that help them breathe may have weakened as a result of the ventilator doing the work for them.
These patients “get sick very fast, and it takes a long time for them to heal. What’s not really well appreciated is how much rehab and how much recovery time these patients are going to need,” said David Chong, MD. He is medical director of the ICU at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, and he has been on the front lines during the COVID-19 surge in New York City.
The road to recovery
Regardless of the cause, many people who have a prolonged stint in the ICU face an even longer convalescence. Still-unanswered questions concern whether recovery time will be longer for those with COVID-19, compared with other illnesses, and whether some of the damage may be permanent. A number of small studies in Hong Kong and China, as well as studies of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients’ recoveries, have promoted speculation about possible long-lasting damage to lungs and other organs from COVID-19.
Yet some of these reports have left out important details about ARDS in COVID-19 patients who also may be most at risk for long-lasting damage. To clear up some of the confusion, the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation said on April 6 that some but not all of COVID-19 patients who develop ARDS may go on to develop lung fibrosis – scarring of the lungs – which may be permanent.
“Post-ARDS fibrosis typically is not progressive, but nonetheless can be severe and limiting. The recovery period for post-ARDS fibrosis is approximately 1 year and the residual deficits persist, but generally do not progress,” the foundation noted.
Emerging research on lung damage in COVID-19
Because the pandemic is only a few months in, it’s unclear as yet what the long-term consequences of severe COVID-19 may be. But emerging data are enabling researchers to venture an educated guess about what may happen in the months and years ahead.
The key to understanding the data is knowing that ARDS is a syndrome – the end product of a variety of diseases or insults to the lung. Under the microscope, lung damage from ARDS associated with COVID-19 is indistinguishable from lung damage resulting from other causes, such as vaping, sepsis, or shock caused by a motor vehicle accident, said Sanjay Mukhopadhyay, MD, director of pulmonary pathology at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Mukhopadhyay, who specializes in lung pathology, performed one of the first complete autopsies of a COVID-19 patient in the United States. In most autopsy series published to date, he said, the most common lung finding in patients who have died from COVID-19 is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), a pattern of lung injury seen in ARDS from many other causes.
In DAD, the walls of the alveoli – thinly lined air sacs that facilitate gas exchange in the lung – develop a pink, hyaline membrane composed of damaged cells and plasma proteins that leak from capillaries in the wall of the alveolus. This hyaline membrane gets plastered against the wall of the alveolus and interferes with diffusion of oxygen into the body.
“We know what happens in ARDS from other causes. If you follow people who have been on a ventilator long term, some of their respiratory function goes back to normal,” Dr. Mukhopadhyay said. “But there are other people in whom some degree of respiratory impairment lingers. In these patients, we think the DAD progresses to an organizing stage.”
Organizing pneumonia refers to a family of diseases in which fibroblasts (cells involved in wound healing) arrive and form scar tissue that forms hyaline membranes and fibrin balls (tough proteins) that fill up the alveoli, making gas exchange very difficult.
Also called BOOP (bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia), this condition is sensitive to steroids. Early aggressive steroid treatment can prevent long-term lung damage. Without steroids, damage can become permanent. A variant of this condition is termed acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia (AFOP), which is also sensitive to steroids. A report from France demonstrates AFOP in some patients who have died from COVID-19.
The trick is identifying who is developing BOOP and who is not, and beyond that, who might be most amenable to treatment. Use of steroids for patients with certain other problems, such as a bacterial infection on top of COVID-19, could be harmful. David H. Chong, MD, and colleagues at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, are investigating this to determine which COVID-19 patients may benefit from early steroid therapy.
“It’s not clear if there is a predominant histologic type or if we are catching people at different phases of their disease, and therefore we’re seeing different lung pathology,” Dr. Chong said.
He thinks that many patients with severe COVID-19 probably will not develop this pattern of lung scarring. “We’re speculating that lung damage from severe COVID-19 is probably going to behave more like lung damage from regular ARDS, which is often reversible. We think the vast majority of these patients probably have DAD that is similar to most patients with ARDS from other etiologies,” Dr. Chong said.
That would be consistent with information from China. In an April interview with Chinese domestic media, Zhong Nanshan, MD, a pulmonologist at the head of China’s COVID-19 task force, stated that he expects that the lungs in most patients with COVID-19 will gradually recover. He was responding to a widely publicized small study that found evidence of residual lung abnormalities at hospital discharge in most patients (94%, 66/70) who suffered from COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, from January to February 2020.
Tough research conditions
Experts say that follow-up in this Chinese study and others to date has not been nearly long enough to allow predictions about lasting lung damage in COVID-19.
They also highlight the tough conditions in which researchers are working. Few autopsies have been performed so far – autopsies take time, extra precautions must be taken to avoid spread of COVID-19, and many patients and families do not consent to an autopsy. Furthermore, autopsy data from patients who died of COVID-19 may not extrapolate to survivors.
“I would not hang my hat on any of the limited data I have seen on autopsies,” said Lina Miyakawa, MD, a critical care and pulmonary medicine specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City.
“Even though we have answers about how the lungs are damaged at the end stage, this does not elucidate any answers about the earlier lung damage from this disease,” she continued. “It would be informative to have pathological data from the early or transitional phase, to see if that may translate into a treatment modality for COVID-19 patients.”
The problem is that these patients often experience a large amount of sloughing of airway cells, along with mucous plugging (collections of mucous that can block airflow and collapse alveoli). Bronchoscopy, which is used to view the inside of the lungs and sometimes to retrieve biopsy specimens for microscopic evaluation, is too risky for many COVID-19 patients.
In addition, few CT data exist for severely ill COVID-19 patients, who can be so unstable that to transport them to undergo a CT scan can be dangerous, not to mention the concern regarding infection control.
Even if sufficient data did exist, findings from chest x-rays, CTs, pathology studies, and lung function tests do not always match up. A patient who has lung abnormalities on CT may not necessarily have clinically impaired lung function or abnormal pathologic findings, according to Ali Gholamrezanezhad, MD, an emergency radiologist who is with the department of clinical radiology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Together with colleagues at USC, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad has started a long-term study of patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19. The researchers will follow patients for at least 1 year and will use chest x-ray, chest CT, and exercise testing to evaluate lung recovery over time.
“In the acute phase, we have acute inflammation called ground glass opacities, which usually happen bilaterally in COVID-19. That is totally reversible damage that can return to normal with no scarring,” Dr. Gholamrezanezhad said.
On the basis of data from survivors of other severe pneumonias, such as Middle East respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV-1 infection, and H1N1 influenza, Gholamrezanezhad thinks that most survivors of COVID-19 will be able to return to work and normal life, although some may show residual lung dysfunction. Age, underlying medical conditions, smoking, length of hospital stay, severity of illness, and quality of treatment may all play a role in how well these people recover.
The lung has a remarkable capacity to recover, he added. Critical illness can destroy type one pneumocytes — the cells that line the alveoli in the lung — but over time, these cells grow back and reline the lungs. When they do, they can also help repair the lungs.
On top of that, the lung has a large functional reserve, and when one section becomes damaged, the rest of the lung can compensate.
However, for some people, total maximum exercise capacity may be affected, he commented.
Mukhopadhyay said: “My feeling is you will get reversal to normal in some patients and you will get long-term fibrosis from ARDS in some survivors. The question is, how many will have complete resolution and how many will have fibrosis? To know the answer, we will need a lot more data than we have now.”
Convalescence of COVID-19 Patients
Like many who become seriously ill with COVID-19, Braganza had underlying medical problems. Before becoming ill, he had had a heart attack and stroke. He walked with a walker and had some age-related memory problems.
Five days after transfer to inpatient rehab, Braganza was walking up and down the hallway using a walker. He was still shaking off the effects of being heavily sedated for so long, and he experienced periods of confusion. When he first came off the ventilator, he mixed up days and nights. Sometimes he did not remember being so sick. A former software engineer, Braganza usually had no problem using technology, but he has had to relearn how to use his phone and connect his iPad to Wi-Fi.
“He is still struggling quite a bit with remembering how to do basic things,” Maria Braganza said. “He has times of being really depressed because he feels like he’s not making progress.”
Doctors are taking note and starting to think about what lies ahead for ICU survivors of COVID-19. They worry about the potential for disease recurrence as well as readmission for other problems, such as other infections and hip fractures.
“As COVID-19 survivors begin to recover, there will be a large burden of chronic critical illness. We expect a significant need for rehabilitation in most ICU survivors of COVID-19,” said Steve Lubinsky, MD, medical director of respiratory care at New York University Langone Tisch Hospital.
Thinking about her father, Maria Braganza brings an extra dimension to these concerns. She thinks about depression, loneliness, and social isolation among older survivors of COVID-19. These problems existed long before the pandemic, but COVID-19 has magnified them.
The rehab staff estimates that Mr. Braganza will spend 10-14 days in their program, but discharge home creates a conundrum. Before becoming ill, Mr. Braganza lived in an independent senior living facility. Now, because of social distancing, he will no longer be able to hang out and have meals with his friends.
“Dad’s already feeling really lonely in the hospital. If we stay on a semipermanent lockdown, will he be able to see the people he loves?” Maria Braganza said. “Even though somebody is older, they have a lot to give and a lot of experience. They just need a little extra to be able to have that life.”
Dr. Nolan, Dr. Chong, Dr. Mukhopadhyay, Dr. Miyakawa, Dr. Gholamrezanezhad, and Dr. Lubinsky report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘The story unfolding is worrisome’ for diabetes and COVID-19
The American Diabetes Association has dedicated a whole section of its journal, Diabetes Care, to the topic of “Diabetes and COVID-19,” publishing a range of articles with new data to help guide physicians in caring for patients.
“Certain groups are more vulnerable to COVID-19, notably older people and those with underlying medical conditions. Because diabetes is one of the conditions associated with high risk, the diabetes community urgently needs to know more about COVID-19 and its effects on people with diabetes,” an introductory commentary noted.
Entitled “COVID-19 in people with diabetes: Urgently needed lessons from early reports,” the commentary is penned by the journal’s editor-in-chief, Matthew Riddle, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues.
Also writing in the same issue, William T. Cefalu, MD, and colleagues from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) noted it is known that the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor. The ACE-2 receptor is known to be in the lungs and upper respiratory tract, “but we also know that it is expressed in other tissues such as heart, small and large intestines, and pancreas,” they wrote, and also “in the kidney.”
Hence, there are emerging reports of acute kidney injury resulting from COVID-19, as well as the impact on many other endocrine/metabolic and gastrointestinal outcomes.
“Pilot clinical studies (observational and interventional) are needed that will support the understanding or treatment of COVID-19–related diseases within the mission of the NIDDK,” they stated.
Although rapidly collected, data “offer important clues”
Some of the new ground covered in the journal articles includes an analysis of COVID-19 outcomes by type of glucose-lowering medication; remote glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with COVID-19; a suggested approach to cardiovascular risk management in the COVID-19 era, as already reported by Medscape Medical News; and the diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes during the pandemic.
Other articles provide new data for previously reported phenomena, including obesity as a risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcomes and the role of inpatient glycemic control on COVID-19 outcomes.
“The data reported in these articles were rapidly collected and analyzed, in most cases under urgent and stressful conditions,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues cautioned. “Thus, some of the analyses are understandably limited due to missing data, incomplete follow-up, and inability to identify infected but asymptomatic patients.”
Even so, they wrote, some points are clear. “The consistency of findings in these rapidly published reports is reassuring in terms of scientific validity, but the story unfolding is worrisome.”
Specifically, while diabetes does not appear to increase the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection, progression to severe illness is more likely in people with diabetes and COVID-19: They are two to three times as likely to require intensive care, and to die, compared with those infected but without diabetes.
“Neither the mechanisms underlying the increased risk nor the best interventions to limit it have yet been defined, but the studies in this collection of articles offer important clues,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote.
Existing insulin use linked to COVID-19 death risk
One of the articles is a retrospective study of 904 hospitalized COVID-19 patients by Yuchen Chen, MD, of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
Among the 136 patients with diabetes, risk factors for mortality included older age (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09 per year increase; P = .001) elevated C-reactive protein (aOR, 1.12; P = .043), and insulin use (aOR, 3.58; P = .009).
“Attention needs to be paid to patients with diabetes and COVID-19 who use insulin,” the Chinese authors wrote. “Whether this was due to effects of insulin itself or to characteristics of the patients for whom it was prescribed is not clear,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues noted.
Dr. Chen and colleagues also found no difference in clinical outcomes between those diabetes patients with COVID-19 who were taking an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II type I receptor blocker, compared with those who did not, which supports existing recommendations to continue use of this type of medication.
Remote glucose monitoring a novel tool for COVID-19 isolation
Another publication, by Gilat Shehav-Zaltzman of Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel, and colleagues, describes the use of remote continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in two hospitalized COVID-19 patients who were in isolation – one with type 1 diabetes and the other with type 2 diabetes – treated with basal-bolus insulin.
Using Medtronic CGM systems, the hospital staff was able to view patients’ real-time data uploaded to the Web from computer terminals in virus-free areas outside the patients’ rooms. The hospital’s endocrinology team had trained the intensive care staff on how to replace the sensors weekly and calibrate them twice daily.
“Converting a personal CGM system originally designed for diabetes self-management to team-based, real-time remote glucose monitoring offers a novel tool for inpatient diabetes control in COVID-19 isolation facilities,” the authors wrote.
“Such a solution in addition to ongoing remotely monitored clinical parameters (such as pulse rate, electrocardiogram, and oxygen saturation) adds to quality of diabetes care while minimizing risk of staff exposure and burden,” they observed.
Dr. Riddle and colleagues concurred: “Newer methods of remotely monitoring glucose patterns could be uniquely helpful.”
Key question: Does glycemic management make a difference?
With regard to the important issue of in-hospital control of glucose, Celestino Sardu, MD, PhD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues reported on 59 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and moderately severe pneumonia.
They were categorized as normoglycemic (n = 34) or hyperglycemic (n = 25), as well as with or without diabetes, on the basis of a diagnosis preceding the current illness. Of the 25 patients with hyperglycemia, 15 patients were treated with insulin infusion and 10 patients were not.
In a risk-adjusted analysis, both patients with hyperglycemia and patients with diabetes had a higher risk of severe disease than did those without diabetes and with normoglycemia. Patients with hyperglycemia treated with insulin infusion had a lower risk of severe disease than did patients who didn’t receive an insulin infusion.
And although they noted limitations, the authors wrote, “Our data evidenced that optimal glucose control in the immediate postadmission period for almost 18 days was associated with a significant reduction of inflammatory cytokines and procoagulative status.”
Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote that the findings of this unrandomized comparison were interpreted “as suggesting that insulin infusion may improve outcomes.”
“If the benefits of seeking excellent glycemic control by this means are confirmed, close monitoring of glucose levels will be essential.”
More on obesity and COVID-19, this time from China
Because it has become increasingly clear that obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, new data from China – where this was less apparent initially – support observations in Europe and the United States.
An article by Qingxian Cai, PhD, of Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China, and colleagues looks at this. They found that, among 383 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, the 41 patients with obesity (defined as a body mass index ≥ 28 kg/m2) were significantly more likely to progress to severe disease compared with the 203 patients classified as having normal weight (BMI, 18.5-23.9), with an odds ratio of 3.4.
A similar finding comes from Feng Gao, MD, PhD, of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues, who studied 75 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and obesity (defined as a BMI > 25 in this Asian population) to 75 patients without obesity matched by age and sex. After adjustment for clinical characteristics including the presence of diabetes, those with obesity had a threefold greater risk of progression to severe or critical COVID-19 status, with a nearly linear relationship.
Emerging from the crisis: Protect the vulnerable, increase knowledge base
As the research community emerges from the crisis, “there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research ... aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how ... the current COVID-19 threat” affects “both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” Dr. Cefalu and colleagues concluded in their commentary.
Dr. Riddle and coauthors agreed: “We will enter a longer interval in which we must continue to support the most vulnerable populations – especially older people, those with diabetes or obesity, and those who lack the resources to limit day-to-day exposure to infection. We hope a growing sense of community will help in this task.”
Dr. Riddle has reported receiving research grant support through Oregon Health & Science University from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk, and honoraria for consulting from Adocia, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Theracos. Dr. Cefalu has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Diabetes Association has dedicated a whole section of its journal, Diabetes Care, to the topic of “Diabetes and COVID-19,” publishing a range of articles with new data to help guide physicians in caring for patients.
“Certain groups are more vulnerable to COVID-19, notably older people and those with underlying medical conditions. Because diabetes is one of the conditions associated with high risk, the diabetes community urgently needs to know more about COVID-19 and its effects on people with diabetes,” an introductory commentary noted.
Entitled “COVID-19 in people with diabetes: Urgently needed lessons from early reports,” the commentary is penned by the journal’s editor-in-chief, Matthew Riddle, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues.
Also writing in the same issue, William T. Cefalu, MD, and colleagues from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) noted it is known that the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor. The ACE-2 receptor is known to be in the lungs and upper respiratory tract, “but we also know that it is expressed in other tissues such as heart, small and large intestines, and pancreas,” they wrote, and also “in the kidney.”
Hence, there are emerging reports of acute kidney injury resulting from COVID-19, as well as the impact on many other endocrine/metabolic and gastrointestinal outcomes.
“Pilot clinical studies (observational and interventional) are needed that will support the understanding or treatment of COVID-19–related diseases within the mission of the NIDDK,” they stated.
Although rapidly collected, data “offer important clues”
Some of the new ground covered in the journal articles includes an analysis of COVID-19 outcomes by type of glucose-lowering medication; remote glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with COVID-19; a suggested approach to cardiovascular risk management in the COVID-19 era, as already reported by Medscape Medical News; and the diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes during the pandemic.
Other articles provide new data for previously reported phenomena, including obesity as a risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcomes and the role of inpatient glycemic control on COVID-19 outcomes.
“The data reported in these articles were rapidly collected and analyzed, in most cases under urgent and stressful conditions,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues cautioned. “Thus, some of the analyses are understandably limited due to missing data, incomplete follow-up, and inability to identify infected but asymptomatic patients.”
Even so, they wrote, some points are clear. “The consistency of findings in these rapidly published reports is reassuring in terms of scientific validity, but the story unfolding is worrisome.”
Specifically, while diabetes does not appear to increase the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection, progression to severe illness is more likely in people with diabetes and COVID-19: They are two to three times as likely to require intensive care, and to die, compared with those infected but without diabetes.
“Neither the mechanisms underlying the increased risk nor the best interventions to limit it have yet been defined, but the studies in this collection of articles offer important clues,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote.
Existing insulin use linked to COVID-19 death risk
One of the articles is a retrospective study of 904 hospitalized COVID-19 patients by Yuchen Chen, MD, of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
Among the 136 patients with diabetes, risk factors for mortality included older age (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09 per year increase; P = .001) elevated C-reactive protein (aOR, 1.12; P = .043), and insulin use (aOR, 3.58; P = .009).
“Attention needs to be paid to patients with diabetes and COVID-19 who use insulin,” the Chinese authors wrote. “Whether this was due to effects of insulin itself or to characteristics of the patients for whom it was prescribed is not clear,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues noted.
Dr. Chen and colleagues also found no difference in clinical outcomes between those diabetes patients with COVID-19 who were taking an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II type I receptor blocker, compared with those who did not, which supports existing recommendations to continue use of this type of medication.
Remote glucose monitoring a novel tool for COVID-19 isolation
Another publication, by Gilat Shehav-Zaltzman of Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel, and colleagues, describes the use of remote continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in two hospitalized COVID-19 patients who were in isolation – one with type 1 diabetes and the other with type 2 diabetes – treated with basal-bolus insulin.
Using Medtronic CGM systems, the hospital staff was able to view patients’ real-time data uploaded to the Web from computer terminals in virus-free areas outside the patients’ rooms. The hospital’s endocrinology team had trained the intensive care staff on how to replace the sensors weekly and calibrate them twice daily.
“Converting a personal CGM system originally designed for diabetes self-management to team-based, real-time remote glucose monitoring offers a novel tool for inpatient diabetes control in COVID-19 isolation facilities,” the authors wrote.
“Such a solution in addition to ongoing remotely monitored clinical parameters (such as pulse rate, electrocardiogram, and oxygen saturation) adds to quality of diabetes care while minimizing risk of staff exposure and burden,” they observed.
Dr. Riddle and colleagues concurred: “Newer methods of remotely monitoring glucose patterns could be uniquely helpful.”
Key question: Does glycemic management make a difference?
With regard to the important issue of in-hospital control of glucose, Celestino Sardu, MD, PhD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues reported on 59 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and moderately severe pneumonia.
They were categorized as normoglycemic (n = 34) or hyperglycemic (n = 25), as well as with or without diabetes, on the basis of a diagnosis preceding the current illness. Of the 25 patients with hyperglycemia, 15 patients were treated with insulin infusion and 10 patients were not.
In a risk-adjusted analysis, both patients with hyperglycemia and patients with diabetes had a higher risk of severe disease than did those without diabetes and with normoglycemia. Patients with hyperglycemia treated with insulin infusion had a lower risk of severe disease than did patients who didn’t receive an insulin infusion.
And although they noted limitations, the authors wrote, “Our data evidenced that optimal glucose control in the immediate postadmission period for almost 18 days was associated with a significant reduction of inflammatory cytokines and procoagulative status.”
Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote that the findings of this unrandomized comparison were interpreted “as suggesting that insulin infusion may improve outcomes.”
“If the benefits of seeking excellent glycemic control by this means are confirmed, close monitoring of glucose levels will be essential.”
More on obesity and COVID-19, this time from China
Because it has become increasingly clear that obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, new data from China – where this was less apparent initially – support observations in Europe and the United States.
An article by Qingxian Cai, PhD, of Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China, and colleagues looks at this. They found that, among 383 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, the 41 patients with obesity (defined as a body mass index ≥ 28 kg/m2) were significantly more likely to progress to severe disease compared with the 203 patients classified as having normal weight (BMI, 18.5-23.9), with an odds ratio of 3.4.
A similar finding comes from Feng Gao, MD, PhD, of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues, who studied 75 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and obesity (defined as a BMI > 25 in this Asian population) to 75 patients without obesity matched by age and sex. After adjustment for clinical characteristics including the presence of diabetes, those with obesity had a threefold greater risk of progression to severe or critical COVID-19 status, with a nearly linear relationship.
Emerging from the crisis: Protect the vulnerable, increase knowledge base
As the research community emerges from the crisis, “there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research ... aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how ... the current COVID-19 threat” affects “both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” Dr. Cefalu and colleagues concluded in their commentary.
Dr. Riddle and coauthors agreed: “We will enter a longer interval in which we must continue to support the most vulnerable populations – especially older people, those with diabetes or obesity, and those who lack the resources to limit day-to-day exposure to infection. We hope a growing sense of community will help in this task.”
Dr. Riddle has reported receiving research grant support through Oregon Health & Science University from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk, and honoraria for consulting from Adocia, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Theracos. Dr. Cefalu has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Diabetes Association has dedicated a whole section of its journal, Diabetes Care, to the topic of “Diabetes and COVID-19,” publishing a range of articles with new data to help guide physicians in caring for patients.
“Certain groups are more vulnerable to COVID-19, notably older people and those with underlying medical conditions. Because diabetes is one of the conditions associated with high risk, the diabetes community urgently needs to know more about COVID-19 and its effects on people with diabetes,” an introductory commentary noted.
Entitled “COVID-19 in people with diabetes: Urgently needed lessons from early reports,” the commentary is penned by the journal’s editor-in-chief, Matthew Riddle, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues.
Also writing in the same issue, William T. Cefalu, MD, and colleagues from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) noted it is known that the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor. The ACE-2 receptor is known to be in the lungs and upper respiratory tract, “but we also know that it is expressed in other tissues such as heart, small and large intestines, and pancreas,” they wrote, and also “in the kidney.”
Hence, there are emerging reports of acute kidney injury resulting from COVID-19, as well as the impact on many other endocrine/metabolic and gastrointestinal outcomes.
“Pilot clinical studies (observational and interventional) are needed that will support the understanding or treatment of COVID-19–related diseases within the mission of the NIDDK,” they stated.
Although rapidly collected, data “offer important clues”
Some of the new ground covered in the journal articles includes an analysis of COVID-19 outcomes by type of glucose-lowering medication; remote glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with COVID-19; a suggested approach to cardiovascular risk management in the COVID-19 era, as already reported by Medscape Medical News; and the diagnosis and management of gestational diabetes during the pandemic.
Other articles provide new data for previously reported phenomena, including obesity as a risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcomes and the role of inpatient glycemic control on COVID-19 outcomes.
“The data reported in these articles were rapidly collected and analyzed, in most cases under urgent and stressful conditions,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues cautioned. “Thus, some of the analyses are understandably limited due to missing data, incomplete follow-up, and inability to identify infected but asymptomatic patients.”
Even so, they wrote, some points are clear. “The consistency of findings in these rapidly published reports is reassuring in terms of scientific validity, but the story unfolding is worrisome.”
Specifically, while diabetes does not appear to increase the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection, progression to severe illness is more likely in people with diabetes and COVID-19: They are two to three times as likely to require intensive care, and to die, compared with those infected but without diabetes.
“Neither the mechanisms underlying the increased risk nor the best interventions to limit it have yet been defined, but the studies in this collection of articles offer important clues,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote.
Existing insulin use linked to COVID-19 death risk
One of the articles is a retrospective study of 904 hospitalized COVID-19 patients by Yuchen Chen, MD, of the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
Among the 136 patients with diabetes, risk factors for mortality included older age (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09 per year increase; P = .001) elevated C-reactive protein (aOR, 1.12; P = .043), and insulin use (aOR, 3.58; P = .009).
“Attention needs to be paid to patients with diabetes and COVID-19 who use insulin,” the Chinese authors wrote. “Whether this was due to effects of insulin itself or to characteristics of the patients for whom it was prescribed is not clear,” Dr. Riddle and colleagues noted.
Dr. Chen and colleagues also found no difference in clinical outcomes between those diabetes patients with COVID-19 who were taking an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II type I receptor blocker, compared with those who did not, which supports existing recommendations to continue use of this type of medication.
Remote glucose monitoring a novel tool for COVID-19 isolation
Another publication, by Gilat Shehav-Zaltzman of Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel, and colleagues, describes the use of remote continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in two hospitalized COVID-19 patients who were in isolation – one with type 1 diabetes and the other with type 2 diabetes – treated with basal-bolus insulin.
Using Medtronic CGM systems, the hospital staff was able to view patients’ real-time data uploaded to the Web from computer terminals in virus-free areas outside the patients’ rooms. The hospital’s endocrinology team had trained the intensive care staff on how to replace the sensors weekly and calibrate them twice daily.
“Converting a personal CGM system originally designed for diabetes self-management to team-based, real-time remote glucose monitoring offers a novel tool for inpatient diabetes control in COVID-19 isolation facilities,” the authors wrote.
“Such a solution in addition to ongoing remotely monitored clinical parameters (such as pulse rate, electrocardiogram, and oxygen saturation) adds to quality of diabetes care while minimizing risk of staff exposure and burden,” they observed.
Dr. Riddle and colleagues concurred: “Newer methods of remotely monitoring glucose patterns could be uniquely helpful.”
Key question: Does glycemic management make a difference?
With regard to the important issue of in-hospital control of glucose, Celestino Sardu, MD, PhD, of the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues reported on 59 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and moderately severe pneumonia.
They were categorized as normoglycemic (n = 34) or hyperglycemic (n = 25), as well as with or without diabetes, on the basis of a diagnosis preceding the current illness. Of the 25 patients with hyperglycemia, 15 patients were treated with insulin infusion and 10 patients were not.
In a risk-adjusted analysis, both patients with hyperglycemia and patients with diabetes had a higher risk of severe disease than did those without diabetes and with normoglycemia. Patients with hyperglycemia treated with insulin infusion had a lower risk of severe disease than did patients who didn’t receive an insulin infusion.
And although they noted limitations, the authors wrote, “Our data evidenced that optimal glucose control in the immediate postadmission period for almost 18 days was associated with a significant reduction of inflammatory cytokines and procoagulative status.”
Dr. Riddle and colleagues wrote that the findings of this unrandomized comparison were interpreted “as suggesting that insulin infusion may improve outcomes.”
“If the benefits of seeking excellent glycemic control by this means are confirmed, close monitoring of glucose levels will be essential.”
More on obesity and COVID-19, this time from China
Because it has become increasingly clear that obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, new data from China – where this was less apparent initially – support observations in Europe and the United States.
An article by Qingxian Cai, PhD, of Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China, and colleagues looks at this. They found that, among 383 hospitalized patients with COVID-19, the 41 patients with obesity (defined as a body mass index ≥ 28 kg/m2) were significantly more likely to progress to severe disease compared with the 203 patients classified as having normal weight (BMI, 18.5-23.9), with an odds ratio of 3.4.
A similar finding comes from Feng Gao, MD, PhD, of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues, who studied 75 patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and obesity (defined as a BMI > 25 in this Asian population) to 75 patients without obesity matched by age and sex. After adjustment for clinical characteristics including the presence of diabetes, those with obesity had a threefold greater risk of progression to severe or critical COVID-19 status, with a nearly linear relationship.
Emerging from the crisis: Protect the vulnerable, increase knowledge base
As the research community emerges from the crisis, “there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research ... aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how ... the current COVID-19 threat” affects “both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” Dr. Cefalu and colleagues concluded in their commentary.
Dr. Riddle and coauthors agreed: “We will enter a longer interval in which we must continue to support the most vulnerable populations – especially older people, those with diabetes or obesity, and those who lack the resources to limit day-to-day exposure to infection. We hope a growing sense of community will help in this task.”
Dr. Riddle has reported receiving research grant support through Oregon Health & Science University from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk, and honoraria for consulting from Adocia, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Theracos. Dr. Cefalu has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.